How to travel to Yemen (mainland) in 2024
By Joan Torres 11 Comments Last updated on April 12, 2024

Yemen is a country which has been taken from a fairy tale, a destination that overawes each and every visitor who is captivated by the mesmerizing architecture that dots the unexpectedly radiant and fertile valleys that comprise the country.
Local men strolling the streets with their colorful jambiya – traditional dagger – are the cherry on top that make Yemen such a unique country, because there’s nothing like Yemen; not only in terms of sights, but years of isolation have made Yemen an incredibly raw country, where travelers can still experience Yemeni rural life as it used to be centuries ago.
Traditionally grouped in tribes with strong codes of conduct that tend to prevail over the country’s law, their rules dictate that one must protect their guest, with their own life if needed, and treat them like one more member of their family.
The result is a particularly warm and welcoming society whose main aim is always watching over your safety and to feed you with the best honey and Yemeni food.
Yemen is certainly one of the most legendary countries in the world.
In this travel guide to Yemen , you will find the latest, updated info on how to travel to Yemen, including safety, how to get a visa and more.


In this Yemen travel guide, you will find:
Table of Contents
Need to know before traveling to Yemen
- Which regions can you visit?
- Top experiences
- Is it safe to travel?
- How to get a visa
- Travel Insurance
- Best time to visit
- Useful books for traveling
- Independent travel
- How to get to Yemen
- The country, people and culture
- Yemeni food and cuisine
- Solo female traveler
- Money and prices
- Transportation
- Where to stay
- More Information
Yemen is a complicated country which is going through an even more complicated conflict, and it’s important to understand what are you getting into.
There are 2 Yemens, north and south
Before visiting Yemen, you should know that the country is divided into two separate, big regions:
- Yemen Arab Republic, also known as North Yemen
- People’s Democratic Republic of Yemen, also known as South Yemen
By the way, the capital Sanaa is in North Yemen.
In the 19th century, North Yemen was under Ottoman rule, while Britain controlled the South.
When the Ottoman Empire collapsed in 1918, North Yemen became an independent state, but the British ruled over South Yemen until 1967.
After the British withdrawal in 1967, North and South Yemen were two separate UN countries until they unified in 1991, becoming the Yemen Arab Republic.
North Yemen is where most issues are happening
As a traveler, you need to be aware that, despite the unification, this division is still part of every-day Yemen, both politically and culturally.

First of all, all the bad things you hear about Yemen, like famine and aerial bombings – the world’s worst humanitarian crisis according to some sources – are mostly happening in North Yemen, a region today controlled by the Houthis , a militia that belongs to a branch of Shia Islam, who want to take control of the country.
Saudi Arabia is trying to get rid of them.
Update March 2023: Now that Iran and Saudi are in peace , nobody knows what will happen
South Yemen is mostly pro-Saudi, but it’s pretty messy too
South Yemen on the other hand, is controlled by the Yemeni Government, which is extremely pro-Saudi.
However, the members of the Government do not live there anymore; they are all exiled in Saudi Arabia , leaving the country mostly under the control of the Yemeni Army. It’s quite a mess.
To make things even more complicated, part of South Yemen is controlled by the STC (Southern Transitional Council) , a separatist group who want South Yemen to become an independent country.
They are supported by the United Arab Emirates, who fight against Saudi over power, believe it or not.
As a foreign traveler, North Yemen is today off limits. More on that in the following section.

Which region of Yemen mainland can you visit?
Can you visit north yemen.
Today, North Yemen – and that includes the capital Sanaa – is practically impossible to visit.
The area is not under the jurisdiction of the Yemeni Government, hence getting the necessary security clearances and permits for going through all the checkpoints is difficult.
Difficult, not impossible, but, even with all the necessary permits, there is a high chance of getting arrested, like happened to a friend of mine who spent one week traveling in North Yemen, until the Houthis decided to lock him up for a week, giving him a very hard time.
You might bump into a fixer who sells you the yummy, irresistible idea of traveling all the way to Sanaa but in my opinion, this is still a bit sketchy, and my recommendation would be to wait until things calm down a bit more.
I’ll be updating this post as soon as I figure out more about visiting Sanaa.
Fun fact: How many tourists visit Yemen mainland each year? Less than 200 people visit Yemen (mainland) each year.
Can you visit South Yemen?
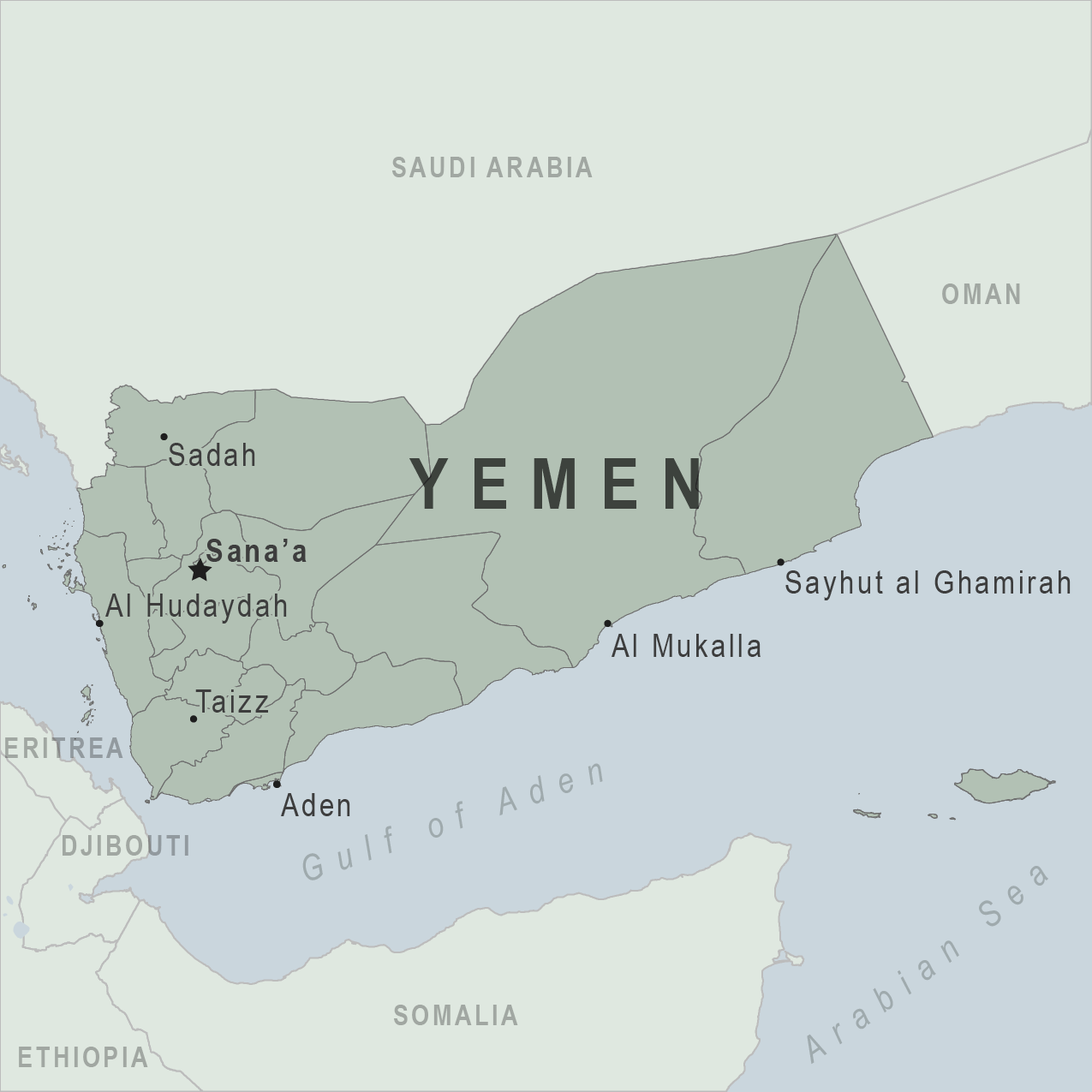
From the western city of Aden all the way to the border with Oman , South Yemen comprises around two thirds of the country, but the only place you can visit is a region named Hadramut, the only stable region in the country.
That’s where I traveled to.
Hadramut is a beautiful, mostly rural region home to jaw-dropping valleys and postcard-like mud-villages often dominated by hypnotic palaces once owned by the local sultans.
Shibam, a city entirely built of 9-story mud-brick buildings in the middle of the desert, is today a UNESCO World Heritage Site and by far, the highlight of Yemen.
Hadramut by itself is certainly worth the trip to mainland Yemen.
Can you visit Socotra?
Socotra is a remote Yemeni island, which has unique geology and flora, as well as being home to a Yemeni society with significant cultural differences due to their isolation from Yemen mainland.
For many years, Socotra has been sort of a hotspot for intrepid travelers looking for some real off the beaten path adventures. The island is used to receiving visitors, so you can find some relatively developed tourism infrastructure run by a few local tour operators.

🛖 Top experiences in Yemen
Visiting the mud-brick towns like shibam.
And I specify towns because this isn’t like the tiny mud villages you may find in Mali or Sudan but they are actual towns built in the past as caravan cities.

Shopping in a khat market
In addition to sparing one day for chewing khat, visiting one of the many khat markets with tens of stalls selling all sorts of types and quality of khat is a real highlight.

Meeting Yemeni people
With their daggers, traditional clothes, smiles and hospitality, meeting Yemenis are an essential part of any trip to Yemen.

Trekking around Wadi Doa’n
This canyon-shaped valley offers plenty of trekking opportunities through unspoiled villages and spectacular views.

Is it safe to travel to Yemen?
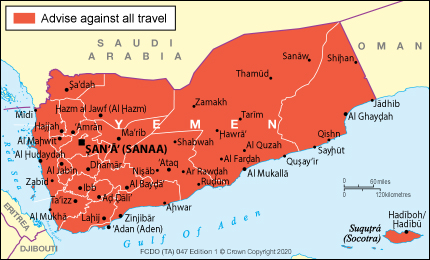
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) advises against all travel to Yemen , including both the Yemeni mainland and Socotra.

I have done safety analysis for several countries – only from a tourist perspective – and my answer to the FCDO advice is always the same: their analysis is extremely biased and based on extremely unlikely scenarios, since they want nothing to do with travelers venturing in those areas if the extremely unlikely happens.
The situation in Hadramut is arguable, yes, but Socotra is an isolated paradise that always stayed at the edge of the conflict, the reason why it keeps receiving thousands of tourists every year.
My personal perspective on safety in Yemen
You have already learnt that, when talking about Yemen, one must be able to differentiate between North Yemen and South Yemen, the first being the apparently dangerous part of the country.
However, I haven’t been in North Yemen, so I can’t really verify whether that region is safe or not.
Actually, nobody does, since you can’t really travel there nowadays.
Similarly, South Yemen is pretty big, but the only place which can be visited is Hadramut, so this section will mainly focus on safety in Hadramut.
Is it safe to travel to Hadramut?
This is a difficult question to answer.
When I was traveling around Hadramut, everything felt very safe indeed, and it shouldn’t be a coincidence that Hadramut is the only area in Yemen which foreigners are allowed to visit.
Hadramut Insurgency
Nonetheless, we can’t deny the fact that from 2016 to 2018, Hadramut had a large presence of Al-Qaeda and ISIS, terrorist groups that were even controlling the regional capital: Mukalla.
For nearly two years, suicide bombings and actual fighting happened nearly every day.
The situation, however, has drastically improved, since the area has been cleared up from terrorists, hence they decided to open it for international tourists.
Still, one must travel to Hadramut with extra caution but at the end of the day, you will certainly do that because:
- Independent travel is not allowed and one must always be with their local guide, who will not allow you to wander around on your own
- You must be accompanied at all times by Yemeni armed escorts during your trip in Hadramut, and you must pay for their service.
- There are endless checkpoints
It’s difficult to say whether Hadramut is safe or not: your trip to Yemen will be rather short, you will always be with armed escorts and an expert fixer who knows where to go and how to deal with complicated situations.
Would it be safe if you traveled to Yemen as an independent backpacker?
We don’t know because nobody has done it.

How to get a visa for Yemen
A visa is strictly required for traveling to Yemen.
Good news is that all nationalities can apply for a tourist visa, an easy, straightforward process – as long as you can afford it.
Bad news is that you can only get it through a local fixer, with whom you must book a full tour – like in Syria – and it’s usually pretty expensive.
Join our Yemen tour and get your visa instantly, with no hassle!
Typically, the visa takes around 1 full month to process, but this is Yemen, and it’s recommended to get in touch with your local fixer/tour operator way before that.
Everything can be arranged on WhatsApp, and all you need to do is send a copy of your passport, a passport photo and a filled-out form.
In addition to the Yemeni visa, your local tour operator/fixer will also apply for a security clearance, something needed for going through all checkpoints.
Your fixer should send you your visa via email and all you have to do is print it out and collect your stamp upon arrival in Yemen.
The visa process for Socotra is pretty similar, but it’s a distinct process that shall be done with Socotra-specific tour operators. A visa for mainland Yemen is not valid for Socotra and viceversa.

🚑 Travel insurance for Yemen
Don’t travel to Yemen without travel insurance. I recommend IATI Insurance because:
- One of the very few that covers travel in Yemen.
- Different plans for all budgets.
- It covers senior citizens too
- Readers of this blog can get a 5% exclusive discount
⛅ Best time to visit Yemen
Like in other Gulf countries, such as Oman or Saudi Arabia , you should avoid traveling in Yemen during the summer months.
I visited Yemen in the month of November. Days were warm but rarely over 30ºC and evenings were pleasant.
📚 Useful books for traveling in Yemen
Yemen travel guide by lonely planet.
Very outdated (1999) but the only available guidebook to the country.

Tribes and Politics in Yemen: A History of the Houthi Conflict
Indispensable book to understand everything related to today’s conflict.

A pictorial guide to Yemen by Sian Pritchard-Jones & Bob Gibbons
My friends and fellow travelers Sian and Bob just published this pictorial guide to Yemen which also contains fresh and actionable advice to the country.

Independent travel in Yemen mainland
Can you travel in Yemen mainland independently?
Unfortunately not.
Today, independent travel in Yemen is strictly forbidden, including within Hadramut.
My fixer in Yemen told me the story of a Japanese traveler who tried to escape while having an after-lunch break at the hotel, time which the tourist took advantage of to buy or rent a motorbike.
He was detained at the first checkpoint and wasn’t allowed to leave until the fixer showed up.
Moreover, traveling in Yemen is so restricted that you can’t even change your itinerary once permits have been issued, because those permits must specify the dates you will be in each area of Yemen.

🗺️ Tours for Yemen
Remember that independent travel in Yemen is not possible nowadays, like no way.
Against the Compass, however tends to always have scheduled group expeditions into Yemen.
Learn more about our Tours for Yemen
🛫 How to get to Yemen
Insurance for traveling to Yemen I strongly recommend IATI Insurance : Yemen coverage + 5% discount BUY IT HERE TO GET YOUR SPECIAL DISCOUNT
How to travel to Yemen by air
Today, the only feasible way to travel to the Yemeni mainland by air is with Yemenia Airways via Cairo to a city named Seiyun.
There are 3 to 4 flights a week and tickets must be purchased via a tour agent based in Cairo , the contact of which should be shared by your Yemeni tour operator.
In my case, I reached out the mentioned tour agent on WhatsApp, who told me to wire her the total cost of the flight ticket to an Egyptian bank account.
The round-trip ticket from Cairo to Seiyun cost 870USD.
After a week, she acknowledged receipt of the money and sent me a copy of my flight ticket, also on WhatsApp.
It was a strange but a pretty simple and legit process.

How to travel to Yemen by land
Yemen shares a border with Oman and Saudi Arabia.
How to travel to Yemen from Oman
The border is fully open because the region of Salalah in Oman leads directly to Hadramut.
Nevertheless, my fixer stopped picking up travelers from the Omani border because as of today, the scenic coastal road that leads to Mukallah is controlled by the STC, therefore it remains closed to foreigners.
Alternatively, you can use the northern road, but that involves driving over 600km (one-way) through an empty desert, and that’s something he doesn’t really want to do anymore, especially because he would have to come all the way from Seiyun and back, a 1200km journey.
How to travel from Saudi to Yemen
With proper clearance, you can use the Al Wadeeah border.
I know a few people who have crossed into Saudi from Yemen using that border, but I don’t know anyone who has actually entered Yemen from there.
Travel reports on that matter are welcome.
Chewing khat in Yemen Khat is a local plant and a drug – similar to coca leaves – typically consumed in Yemen but also in the Horn of Africa , especially in Somalia, southeast Ethiopia , Djibouti and North Kenya . Yemeni men are addicted to it and basically, life stops every day after lunch time for chewing khat. It’s an actual social problem because khat isn’t cheap and there are many Yemeni men who spend their wages on this drug rather than buying food for their families. Still, if you are traveling in Yemen, you must spare one afternoon to chew khat with the locals. If you buy the best quality one, it will give you an extra dose of energy and that night you won’t sleep.

🕌 The country, people, and culture
Yemen is actual Arabia, the place where it is believed the Arabs come from, and the birthplace of the Sabaeans , a group of Ancient South Arabians who founded Sheba, home to worldwide famous Queen of Sheba, all stories that appear in the Quran and the Hebrew Bible.
In terms of GDP per capita, Yemen is among the poorest countries in the world and, along with Afghanistan , Haiti , and North Korea, the only non-African country that makes it to the list.
Despite its location, Yemen is the only country in the peninsula that doesn’t belong to the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) an agreement between the Gulf States – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman , Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates – similar to the EU.
Culture in Yemen
Yemenis are purely Arabs but from a traveling perspective, sometimes I feel they do have a slight South Asian (Pakistani) twist, in the way they eat and behave, different from the rest of the Gulf States.
This shouldn’t be surprising, however, since the coast of Yemen has been benefited from the frankincense trade for centuries, receiving visitors from many parts of the world, specially from South Asia.
Tribal laws in Yemen
They are grouped in tribes and, similarly to Pashtuns in Afghanistan , their tribal laws dictate their daily life.
Like Pashtuns, Yemenis treat their guests even better than family members but at the same time, they are really, really conservative and their acts might be subject to certain rules that may create absolute rejection to international visitors.
For example, without wanting you to fall into a Yemeni stereotype, a woman having extra marital relations is considered one of the most dishonorable things that could happen to a family.
In the city of Seiyun, an unmarried woman was caught in the house hanging out with an unrelated man. They weren’t caught having sex, but they were just sitting together. After doing their own research and investigation, the family decided to murder her by cutting her head off.
Such is the strength and importance of their tribal laws that in these cases, the police decide not to intervene.
By the way, this was an extreme case carried out by an uneducated family. Most Yemenis condemned such an act.

In Yemen, they speak Modern Standard Arabic.
Religion in Yemen
Islam is the state religion, 35% of the population being Shia and 65% Sunni.
Women in Yemen
Yemen is the most conservative country I have ever been to, even more than Afghanistan.
Nonetheless, you need to remember that I only visited the region of Hadramut, a rural and remote area of Yemen, where people are probably more traditional than in the capital Sanaa.
Still, I was particularly shocked by some of the things I experienced.
100% of the women wear niqab
Except for one beggar, we never saw the face of a woman, but all of them were wearing the niqab, which covers everything but the eyes.
You are not allowed to talk to women, not even to look at them
The only female interaction we had was the day we got hissed at by a local woman while we were sitting in the car.
All we did was smile at her, but she reacted by hissing at us.
She basically told you to fuck off – our fixer said.
Saudi women are surprisingly liberal compared to Yemeni
One day, while walking around a village, we heard some young women talking and laughing, something we had not witnessed in that country yet.
They are very liberal – our fixer said. And the reason was that those young girls had been born in Saudi and they came to Yemen to visit their family.
While Saudi women might seem extremely conservative, you are likely to talk with them when you are traveling in Saudi . A Saudi woman wearing a niqab asking for a selfie isn’t rare, plus they work in many supermarkets and shops.
Local women with long hats When traveling around Yemen, you will notice many local women wearing some pretty high hats. They are farmers and they use those hats to protect themselves from the heat. Apparently, that shape helps to keep their heads cool. These woman are among the poorest in Yemen and they despise being photographed.

🍲 Yemeni food and cuisine
Yemeni food is heavy and mostly based on meat and rice, but I believe it is the best food in the peninsula.
In fact, Yemeni mandi is one of the most common dishes in Oman, UAE, and Saudi.
Yemeni restaurants don’t usually to have tables but people gather on a circle on the floor and eat with their hands from the same plate.
Why is Yemeni honey so famous?
For a long time, Yemen was believed to produce some of the best and purest honey in the world, coming from bees that are fed exclusively from the flowers of the Sidr tree, which also has therapeutic properties.
Honey plays a big role in Yemen’s economy and according the UN, more than 100,000 households depend on it for their livelihoods.

Is there alcohol in Yemen?
Yemen is a dry country, you can’t buy alcohol legally.
💃 How to travel in Yemen as a solo female traveler
Yemen might possibly be the most challenging country in the world to travel as a female traveler, way more difficult than in Afghanistan.
In Afghanistan, foreign women don’t need to wear the burqa, but a hijab is enough, like in Iran .
However, in the region of Hadramut, foreign women must wear the niqab in all public spaces, markets and pretty much everywhere, but in the hotel and in the wild.
You may remove your niqab when you are in the car, but not when going through villages and checkpoints.
Is it safe to travel in Yemen as a female traveler?
As long as you are accompanied by men, traveling in Yemen as a woman is safe.
If you removed your niqab, you’d get a lot of attention but if you are wearing it, nobody will dare to tell you a thing.

💰 Money and prices
In Yemen, they use Yemeni Rials (YRI) and approximately:
$1 = 250 YRI
This is the official currency.
Recently, in South Yemen, they have started using a different, unofficial currency also named Yemeni Rials, but with a different value.
With South Yemen Rials,
$1 = around 1000 YRI
I never understood why South Yemen adopted a different currency and how the value was defined but, in any case, if traveling to Hadramut, that’s the only currency you will see.
ATMs and exchanging money
Your debit or credit card will be useless in Yemen, so do bring everything in cash.
The only currency which I recommend bringing is US dollars. They didn’t even want to exchange my Euros, at an acceptable rate at least.
Your US dollars should be brand-new, they are very strict about this.
They actually found a tiny ink stain in one of my bills and they didn’t accept it, even though I received a bunch of dirty Yemeni Rials in exchange.
How much does it cost to travel in Yemen?
A tour to Yemen booked through a local fixer is always all-inclusive, so it’s difficult for me to say what are the actual prices of the most typical things, including hotels and restaurants.
What I can tell you however is that a solo trip to Yemen is expensive, with prices starting at $4,500 for a solo 6-day tour, excluding international flights.
If you want to travel to Yemen for less, I recommend joining a group .
🛺 Transportation: how to move around Yemen
It will be difficult for me to write much in this section since I only moved around in a private car, and you are certainly going to do the same.

🏨 Where to stay in Yemen
I stayed in two different hotels:
Hawta Palace Hotel : a traditional boutique hotel in the city of Seiyun. It has a pleasant garden where many local families hang out in the weekends by paying a fee.
Hayd Aljazeel Resort : a mountain resort in Wadi Doa’n with awesome views to the valley.
Both were pretty amazing and I believe the two best options in the area. Other than that, I don’t recall seeing many hotels besides basic ones.
💻 Internet in Yemen
Can you buy a SIM card in Yemen?
You can, but in the region of Hadramut, 4G barely works.
We did have some decent Wi-Fi in the hotel in Seiyun but that’s all what we got during our trip.
Get a VPN for traveling in Yemen
You should always use a VPN when you travel, especially when you connect to public Wi-Fi networks.
Your connection will be much safer.
Moreover, you will be able to access content which is typically censored in Yemen.
I recommend ExpressVPN – Extremely easy to use, fast and cheap.
If you want to learn more about VPN, check: Why you need a VPN for traveling .
❗ More Information
📢 In my Travel Resources Page you can find the list of all the sites and services I use to book hotels, tours, travel insurance and more.
Travel guides to other countries in the Middle East
- Iran Travel Guide
- Palestine Travel Guide
- Syria Travel Guide
- Travel Guide to Lebanon
- Iraq Travel Guide
- Travel Guide to Saudi Arabia
- Travel Guide to Oman
You might also like our Haiti travel guide .
You will also be interested in: Where in the Middle East is safe? and The most beautiful places in the Middle East .

11 comments
Once I spend one week in Sanaa and around. The moment I stepped out of the plane I regretted it. I was much younger then, I wouldn’t repeat it again. Nobody should support such despicable people, nobody should help with money or otherwise people who are undescribably racist, intolerant, mysogynistic, who don’t respect basic human rights.
Hello Joan,
As I told you before, my grandmother was born in Sana.
That’s why I want to go to Yemen so much.
But I want to see Sana too, so I’ll wait for the conditions to improve a bit.
You can put me first when you organize a tour that includes Sana…
I’m going on a month long trip to Indochina with my wife this Saturday.
Stay healthy.
Fatih UGURLU
Hello Fatih, I hope the situation gets better and you can visit your grandmother’s hometown soon!
Hi Joan, can you please share the contact to the fixer you had for your trip to Hadramaut?
Sorry, I can’t do that, but you are welcome to join our tour: https://expeditions.againstthecompass.com/tours/yemen/
How do you find the fixers?
l was working with a humanitairian organisation for four months in 2023 in northern Yemen. It is a very beautiful country, indeed, with rich culture and kind people. Unfortunately though, it is still a war country, so I think its quite dangerous to travel there. Even if the situation north and south is different, is alltogether dangerous and unpredictable, so personally i would wait till peace comes in order to travel there.
Hey, American living in Russia married to a Russian. Russians almost unanimously agree that North Yemen is a great place to travel to. I’ve heard similarly overblown warnings against Dagestan, and when I traveled there it was totally safe (never mind that I am living in Russia now as an American, and have had absolutely no issues from Russia’s end).
Wondering if there’s some difference between diplomatic recognition by native countries which might influence the experience? For example, Russians seem to go to North Yemen.
Hi Collin, in my opinion, it’s not a matter of safety , it’s just that they aren’t officially issuing visas to travel to North Yemen, so any visit will be sort of sketchy from a legal perspective
Hey, how are you? I have a Jordanian passport and i do not need a visa for all of Yemen, i verified through the embassy. When i asked about permits to travel around the country they said they dont know, do you have any information on how to travel around Yemen independently, for people from visa exempt countries ?
Hi Yahya, we just had one guest from Kuwait (he doesn’t need a visa either) and even then, you’ll need a security clearance and a guide with you
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me when new comments are added.
Join our Expeditions
From Syria to Iraq in Pakistan, Against the Compass is finally running expeditions to the most epic and off-the-beaten-track countries.
We have scheduled expeditions for every month of the year.
Latest posts
- Backpacking Venezuela Travel Guide (2024)
- How to travel to Afghanistan during Taliban rule (2024)
- How to visit Los Llanos in Venezuela
- How to visit Angel Falls and Canaima National Park
- Things to do in Haiti in a 1-week itinerary
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against advice from the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO).
FCDO advises against all travel to Yemen
FCDO advises against all travel to the whole of the Yemen due to the unpredictable security conditions.
If you’re in Yemen, you should leave immediately.
See Safety and security for more information.
Military activity in the region
On 13 April 2024 Iran carried out military action against Israel.
On 19 April, there have been reports of explosions in Iran, and unconfirmed reports of explosions in Syria and Iraq.
Monitor this travel advice and other media as the situation is changing fast. Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also get email notifications when this travel advice is updated.
Read FCDO advice on how to deal with a crisis overseas.
UK government support
Support for British people is severely limited in Yemen. British Embassy services in Sana’a are suspended, and all diplomatic and consular staff have been withdrawn.
The UK government cannot help British nationals leaving Yemen. There are no evacuation procedures in place.
FCDO cannot offer advice on the safety of travelling to any potential departure point. The UK government’s ability to help with onward travel is severely limited and you’ll be expected to cover the cost of visas, accommodation, insurance and onward travel yourself.
If you choose to remain in Yemen, you should minimise movement around the country and within cities and towns, monitor developments in the local security situation and follow other precautions in this travel advice.
If you’re a British national in Yemen and need help from the UK government, you can call FCDO on 020 7008 5000 (24 hours).
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel against FCDO advice, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
About FCDO travel advice
FCDO provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Yemen travel advice
Latest updates: The Health section was updated - travel health information (Public Health Agency of Canada)
Last updated: April 17, 2024 11:58 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, yemen - avoid all travel.
Avoid all travel to Yemen due to ongoing armed conflict, terrorist attacks, and kidnapping. If you’re in Yemen, you should leave the country if it’s safe to do so.
Back to top
Security situation
Despite truce agreements, the security situation in Yemen remains highly unstable and unpredictable due to the ongoing civil war that started in 2014. The state of emergency declared in March 2011 remains in effect.
Armed terrorist and criminal groups are still active in many parts of the country, particularly in the south.
The humanitarian situation remains extremely precarious in the country due to several years of armed clashes between rebels and a coalition led by neighboring countries that conducted airstrikes on territories held by rebels in western and northern Yemen. The conflict led to the displacement of millions of people and significant disruptions to the availability of essential services and goods such as:
- medical supplies
- power distribution
- health care
There is severe damage to critical infrastructure, including hospitals.
The Government of Canada has urged Canadians to leave Yemen since May 2009 and continues to advise against all travel to Yemen. Commercial means to leave the country are extremely limited. If the armed conflict intensifies it could impact your ability to depart the country by commercial means.
Your safety continues to be at risk in Yemen due to war, terrorism, and kidnapping. The Government of Canada’s ability to provide consular assistance and other support in Yemen is extremely limited.
Do not travel to Yemen. If you choose to travel to Yemen, or remain in the country, despite this advisory:
- seek safe shelter and remain there until you can identify safe means to exit
- maintain emergency provisions such as water and food
- exercise extreme caution at all times
- always be aware of your surroundings
- keep in mind that you are responsible for your own safety and that of your family
- ensure that your travel documents are up-to-date
- monitor local and international media to stay informed of the situation
Regional conflicts
Since November 2023, rebels regularly conduct attacks against commercial vessels in the Red Sea with drones and missiles. In response, since January 2024, a US-led coalition has conducted air strikes on rebel-controlled positions in western and northern Yemen, including the cities of Hajjah, Taiz, Hodeidah and Sanaa.
During the civil war between rebels and government forces, armed rebels in Yemen have targeted neighbouring countries, such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, in retaliation for their involvement in the war in Yemen. The April 2022 truce significantly reduced the violence in the country and in the region, but there is still no agreement to end the civil war. There is a continued risk of internal armed conflict and a heightened risk of attacks targeting western interests in Yemen and in the region.
Due to security risks, the Government of Canada cannot provide assistance to citizens trying to leave Yemen by land to Saudi Arabia.
There is a high threat of terrorism. Terrorists have targeted Western interests and Yemeni government buildings. Terrorist groups also target checkpoints manned by the Houthi rebel group in Sanaa and elsewhere in the country, and target Houthis in general.
Terrorist attacks could occur at any time.
Other targets could include:
- government buildings, including schools
- places of worship
- airports and other transportation hubs and networks
- public areas such as tourist attractions, restaurants, bars, coffee shops, shopping centres, markets, hotels and other sites frequented by foreigners
Always be aware of your surroundings when in public places. Exercise extreme caution, particularly in areas known to be frequented by foreigners.
Be particularly vigilant during:
- religious holidays
- public celebrations
- major political events, such as elections
Terrorists may use such occasions to mount attacks.
Exercise extreme caution, particularly in areas known to be frequented by foreigners.
There is a high risk of kidnapping, especially on the highway connecting the cities of Sanaa, Ta’izz and Aden. Foreigners have been targeted. Some hostages have been killed.
- Be extremely vigilant at all times
- Avoid travelling on the Sanaa– Ta’izz –Aden highway
- Use varied and unpredictable travel routes and schedules
Demonstrations and civil unrest
Demonstrations take place frequently due to the ongoing conflict throughout the country.
Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Landmines and unexploded munitions remain a danger in the southern and eastern areas of the country, particularly around Aden, and in the central highlands. Most have been marked and access clearly delimited.
- Exercise caution in these areas
- Look for posted landmine warnings
- Stay on paved roads
- Avoid walking or hiking in these areas
Violent crime
Car bombs and drones have been used in assassinations.
Exercise a high level of personal security awareness at all times.
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs. Although credit cards are rarely accepted, scams may also occur.
Carjacking is a serious concern in Yemen.
- Don’t show signs of affluence
- Avoid travelling at night
- Lock car doors and ensure that windows are closed at all times
- Ensure that personal belongings and passports and other travel documents are secure at all times
Women’s safety
Women travelling alone have been subject to different types of harassment, verbal abuse, or physical assaults.
If you are the victim of a sexual assault, you should report it immediately to the nearest Government of Canada office.
- Avoid travelling alone, especially at night
- Remain particularly vigilant in less populous areas
- Be careful when dealing with strangers or recent acquaintances
Advice for women travellers
There is a shortage of fuel in Yemen. You may have difficulty securing fuel. Fuel and diesel shortages could impact sectors and services such as:
- telecommunication, including internet
- water and waste collection
- shops, cafes and restaurants
Power shortages often occur.
Not all businesses are equipped with a generator. As a result, shortages could affect essential services such as:
- health care services
- food production
- goods distribution
Certain parts of Yemen are experiencing famine. If food is available, it can be expensive because most of the country’s food is imported.
Plan to have adequate water, food and fuel supplies.
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety are poor throughout the country.
Drivers may not respect traffic laws and may often drive on the wrong side of the road. Vehicles are poorly maintained. Roaming animals also pose hazards.
Roadblocks and checkpoints may be set up without warning. Local authorities may close access to certain areas without notice.
If you are involved in an accident resulting in death or injuries, you may be jailed or fined. Compensation has to be paid to the family of any victim.
If you chose to drive in Yemen:
- undertake overland travel in a convoy of four-wheel-drive vehicles and with an experienced guide only
- avoid driving after dark
- leave a travel itinerary with a third party
- be well prepared and equipped with gasoline, water, food and a cell phone
- avoid renting a car and driving it yourself
- call the police if involved in an accident
Public transportation
Public transportation is unsafe and unreliable.
Minibuses service – known as dabaabs – is available in most major cities. However, many bus drivers aren’t experienced and don’t respect traffic laws.
If you want to reach Aden or Seiyun airport, the International Organization for Migration may be able to help by providing ground transportation through a local bus company. You may purchase tickets through their local offices.
Once you arrive at Aden or Seiyun airport, you will need to produce copies of airline tickets at checkpoints.
Contact information - International Organization for Migration in Yemen
Shared taxis are common in Yemen. Private taxis are also available in major cities and at airports.
Motorcycles are often used as taxis. Drivers may often drive on the wrong side of the road and don’t follow traffic laws. Accidents are common.
- Use officially marked taxis only
- Negotiate fares in advance or insist that the driver use the meter
- Avoid taking shared taxis
- Never enter a cab if it already has one or more passengers
- Avoid using ridesharing apps
Ferry services are connecting the various ports in the area, including to Djibouti. Vessels are frequently hijacked or attacked while crossing the Red sea, or in the coastal waters of the Gulf of Aden.
Avoid using ferries.
There are pirate attacks and armed robberies against ships in coastal waters and, in some cases, farther out at sea. Mariners should take appropriate precautions.
Live Piracy Report - International Maritime Bureau
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Yemeni authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
The Government of Canada can't facilitate your entry into or exit from Yemen.
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Yemen.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Student visa: required
Yemeni authorities don’t issue visas at ports of entry. You must obtain your visa well in advance at the closest Yemeni diplomatic mission prior to travelling.
If you intend to stay in Yemen for more than 14 days, you must register your passport with the Yemeni Immigration authorities. You can expect heavy penalties if you overstay the duration of your visa.
Local sponsors
Some local sponsors retain students or employees passports. However, this is not required under Yemeni law.
You could be denied entry into Yemen if your passport bore an Israeli visa, an Israeli border stamp or an Egyptian or Jordanian border stamp issued by an office bordering Israel.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Polio: Advice for travellers - 17 April, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is not required to enter this country.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
* It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Polio (poliomyelitis) is an infectious disease that can be prevented by vaccination. It is caused by poliovirus type 1, 2 or 3. Circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus 2 (cVDPV2) is present in this country. Polio is spread from person to person and through contaminated food and water. Infection with the polio virus can cause paralysis and death in individuals of any age who are not immune.
Recommendations:
- Be sure that your polio vaccinations are up to date before travelling. Polio is part of the routine vaccine schedule for children in Canada.
- One booster dose of the polio vaccine is recommended as an adult .
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Rift Valley fever is a viral disease that can cause severe flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can be fatal. It is spread to humans through contact with infected animal blood or tissues, from the bite of an infected mosquito, or eating or drinking unpasteurized dairy. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from insect bites and avoid animals, particularly livestock, and unpasteurized dairy. There is no vaccine available for Rift Valley fever.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Cases of locally-acquired Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) have been reported in this country.
MERS is a viral respiratory disease caused by the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Some people infected with MERS-CoV experience no symptoms, while others may experience mild flu-like or more severe pneumonia-like symptoms. About one-third of reported cases have result ed in death.
Eat and drink safely , and avoid close contact with animals, especially camels. If you must visit a farm or market, make sure you practise good hygiene and wash your hands before and after contact with animals.
There is currently no licensed vaccine to protect against MERS.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Medical services and facilities
Health care is inadequate throughout the country. Medical facilities and hospitals are very limited, even in major cities. They lack of medical staff and supplies. You will likely need medical evacuation if you are seriously ill or injured.
There are no adequate emergency ambulance services. Cash payment in advance is often required.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
There is a significant shortage of prescription medication.
If you take prescription medication, you’re responsible for determining their legality in Yemen.
- Bring sufficient quantities of your medication with you
- Always keep your medication in the original container
- Pack them in your carry-on luggage
- Carry a copy of your prescriptions
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect heavy fines and lengthy jail sentences.
The consumption of alcohol in public is illegal. Public intoxication is also a criminal offence, no matter where the alcohol was consumed.
Avoid drinking alcohol outside licensed premises.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Yemeni law criminalizes sexual acts and relationships between persons of the same sex.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers could also be discriminated against or detained based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, or sex characteristics.
If you are convicted, you could face corporal punishment, imprisonment or the death penalty.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Yemen.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dress and behaviour
Yemeni customs, laws and regulations adhere closely to traditional and Islamic practices and beliefs. Women should carry a headscarf to cover their head at all times while travelling in Yemen.
To avoid offending local sensitivities:
- dress conservatively
- behave discreetly
- respect religious and social traditions
- seek permission prior to photographing individuals
Religious proselytism
Religious proselytism is illegal.
Avoid engaging in religious activities that contradict or challenge Islamic teachings and values. This includes preaching, possessing, or distributing religious literature or material.
In 2024, the lunar month of Ramadan is expected to begin on or around March 10.
In public, between sunrise and sunset, refrain from:
Common law partnership is illegal in Yemen. Men and women are not permitted to share a home unless they are legally married or are related to one another.
Sexual relations outside of marriage are a criminal offence and may be subject to severe punishment, including the death penalty.
Marriage outside Canada
Yemen family law is different from Canadian family law. Yemen isn't a signatory to The Hague Convention. Decisions are based on Islamic law. It's extremely difficult for woman, even if she is a Muslim, to obtain custody of her children through Yemeni courts. Canadian custody orders may not be recognized in Yemen.
Local authorities may prevent Canadian children or spouse from leaving the country without prior authorization of the Yemeni father, husband or male relative.
To avoid any difficulties in Yemen, consult a Canadian and a Yemeni lawyer before travelling. If you're involved in legal proceedings such as divorce or custody dispute in Yemen, consult a Yemeni lawyer for advice and assistance regarding your own specific situation.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Yemen.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Yemen by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Yemen to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre.
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
Others illegal activities
The following activities are illegal in Yemen and punishable by heavy fines or jail time:
- photographing government buildings, military installations and holy sites
- trafficking or eating pork
- exporting any Yemeni antique
- importing pornographic material
- engaging in prostitution
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Yemen.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Yemen, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
Identification
Local authorities may ask you to show identification at any time.
Depending on the region and the local authority, each town may have an entrance checkpoint where you will have to show your travel documents if you travel by land. You must also obtain permission from the Yemen Tourist Police to travel outside Sanaa.
- Carry identification documents at all times
- Keep a photocopy of your passport and visa in a safe place, in case they are lost or confiscated
You must carry an international driving permit.
International Driving Permit
The country has a zero tolerance policy for drinking and driving.
The currency is the Yemeni rial (YER).
The economy is primarily cash-based. Credit cards are accepted in some major hotels only. ATMs may only be available in major cities.
- Plan accordingly
- Make sure you have access to sufficient local currency while in the country
- Check with your hotel which payment methods will be accepted
Earthquakes
Yemen is located in a seismic and a volcanic zone.
- Earthquakes - What to Do?
Large-scale emergencies abroad
Severe weather
In summer, sandstorms and dust storms occur in some areas. Sand-laden winds can blow at high speeds for days, creating difficult driving conditions. These storms can also cause respiratory problems, which can be fatal in some individuals.
If a dust storm is occurring:
- stay indoors
- keep windows closed
Rainy season
The monsoon season runs from June to September. Seasonal flooding can slow down overland travel and reduce the delivery of essential services.
Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
Drought and flooding
Yemen has been facing drought in recent years, leading to crop failure and severe food shortages. Most of the country’s food is imported.
While infrequent, torrential rains and heavy flooding also occur, which can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
In the event of flooding:
- avoid the affected area
- stay informed of the latest regional weather forecasts
- follow the instructions of local authorities
The mountainous region of Yemen is prone to landslides.
Local services
Dial 199 for emergency assistance.
Consular assistance
Bahrain, Oman, Yemen
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Saudi Arabia, in Riyadh, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Yemen Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Yemen. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 2 Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Global Polio January 05, 2024 Some international destinations have circulating poliovirus. Before any international travel, make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines. Destination List: Afghanistan, Algeria, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Guinea, Indonesia, Israel, including the West Bank and Gaza, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Republic of the Congo, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, including Zanzibar, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Global Measles March 22, 2024 Many international destinations are reporting increased numbers of cases of measles. Destination List: Afghanistan, Angola, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Liberia, Libya, Malaysia, Mauritania, Nepal, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Qatar, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Romania, Russia, Senegal, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Togo, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Yemen, Zambia
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Cholera is presumed to be present in Yemen. Cholera is rare in travelers. Certain factors may increase the risk of getting cholera or having severe disease ( more information ). Avoiding unsafe food and water and washing your hands can also help prevent cholera. Avoiding unsafe food and water and washing your hands can also help prevent cholera.
Vaccination may be considered for children and adults who are traveling to areas of active cholera transmission.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Yemen.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Yemen. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Yemen.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Yemen take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Yemen.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
In Yemen poliovirus has been identified in the past year.
Travelers to Yemen are at increased risk of exposure to poliovirus.
Vaccine recommendations : Adults traveling to Yemen who received a complete polio vaccination series as children may receive a single lifetime booster dose of inactivated polio vaccine; travelers who are unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated should receive a complete polio vaccination series before travel. Children who are not fully vaccinated will be considered for an accelerated vaccination schedule .
Polio - CDC Yellow Book
Polio: For Travelers
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Yemen. If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Yemen, there may be limited or no rabies treatment available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Yemen.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Avoid bug bites.
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
- Avoid animals
Rift Valley Fever
- Touching blood, body fluids, or tissue of infected livestock
Rift Valley fever
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
- Scientists do not fully understand how the MERS virus spreads
- May spread from to others when an infected person coughs or sneezes
- May spread to people from camels.
Middle East Respiratory virus syndrome (MERS)
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Counsel your patients on actions they can take on their trip to stay healthy and safe.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Yemen. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Yemen include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Yemen. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Yemen’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Yemen. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Yemen may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Yemen, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Remind your patients to pack health and safety items. Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Yemen for a list of health-related items they should consider packing.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- 3 Other destinations
- 4.1 History
- 4.2 Climate
- 4.3 Landscape
- 5.1 Entry requirements
- 5.2 By plane
- 5.3 By train
- 5.6 By boat
- 6 Get around
- 10.2 Shopping
- 16 Stay safe
- 17 Stay healthy
- 18.1.1 Politics
- 18.1.2 Religion
- 18.2 Miscellaneous
Yemen ( Arabic : ٱلْيَمَن) is a country in the southern Arabian Peninsula of the Middle East . Although it is rich in history and culture, being part of several civilizations, the country has been in a state of flux since the 1980s. It is one of the least developed and poorest countries in the world.
However, under less extreme circumstances, this vast country has a lot to offer to the adventurous, thrill-seeking traveller, from desert to mountains. Yemen is a difficult country to get around, but the rewards for the persistent visitor are unforgettable.
Yemenis are very friendly and open, and tourists might find themselves being treated as celebrities here; in fact, they might be showered with a lot of hospitality and care, even if they unintentionally make a few cultural blunders.
Regions [ edit ]

Cities [ edit ]
- 15.35 44.2 1 Sana'a – capital
- 12.8 45.033333 2 Aden – seaside former capital of South Yemen.
- 14.802222 42.951111 3 Al Hudayda – a relatively large city on the Red Sea with beautiful beaches
- 14.533333 49.133333 4 Al Mukalla – East Yemen's biggest city and bustling port, the gateway to the historical Hadhramaut region
- 13.966667 44.166667 5 Ibb
- 15.5 43.9 6 Kawkaban
- 15.926944 48.626667 8 Shibam / Seiyun / Tarim – the three famous historical towns of Hadhramaut, perhaps Yemen's most fascinating and exotic destination
- 13.578889 44.021944 9 Ta'izz
Other destinations [ edit ]

- 15.166667 43.75 1 Haraz Mountains
- Hutaib – the most important center of pilgrimage for Yemen's Ismaili population
Understand [ edit ]
History [ edit ].
Yemen has long existed at the crossroads of cultures, linked to some of the oldest centres of civilization in the Near East by virtue of its location in South Arabia. Between the 12th century BCE and the 6th century, it was part of the Minaean, Sabaean, Hadhramaut, Qataban, Ausan and Himyarite kingdoms, which controlled the lucrative spice trade, and later came under Ethiopian and Persian rule. In the 6th century, the Himyarite king Abu-Karib Assad converted to Judaism. In the 7th century, Islamic caliphs began to exert control over the area. After this caliphate broke up, South Arabia came under the control of many dynasties who ruled part, or often all of South Arabia. Imams of Persian origin ruled Yemen intermittently for 160 years, establishing a theocratic political structure that survived until modern times.

Egyptian Sunni caliphs occupied much of Yemen throughout the 11th century. By the 16th century and again in the 19th century, Yemen was part of the Ottoman Empire, and in some periods Imams exerted control over all of Yemen.
The modern history of south Arabia and Yemen began in 1918 when Yemen gained independence from the Ottoman Empire. Between 1918 and 1962, Yemen was a monarchy ruled by the Hamidaddin family. North Yemen then became a republic in 1962, but it was not until 1967 that the British Empire, which had set up a protective area around the South Arabia port of Aden in the 19th century, withdrew from what became South Yemen. In 1970, the southern government adopted a nominally Communist governmental system. The two countries were united as the Republic of Yemen on 22 May 1990.
Unification did not lead to peace, however. The USS Cole, a visiting U.S. Navy ship, was attacked by Al Qaeda in 2000 while on a fuel stop in Aden. Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula has since grown stronger in the country, and the U.S. has responded by striking targets in Yemen repeatedly with drone-fired missiles. The government of longtime dictator, Ali Abdullah Saleh, fell amid dramatic protests associated with the Arab Spring in 2012, but his successor, former Vice President Abd Rabbu Mansour Hadi, hardly rushed to institute the reforms demanded by the demonstrators and was overthrown by the militia of the Shi'a Houthis, who took over the government outright in February 2015. Sunni Arab governments, especially that of Saudi Arabia, were close to Saleh and Hadi and oppose Shi'a rule in this Arabian country. They have supported a coalition of Sunni Islamists called Al-Islah in a civil war against the Houthi forces, and have led a brutal bombing campaign that has damaged the country's infrastructure to the extent that the December 14, 2014 U.S. State Department travel warning states that:
Climate [ edit ]

Mostly desert; hot and humid along west coast; temperate in western mountains affected by seasonal monsoon; extraordinarily hot, dry, harsh desert in east. The weather can be chilly in areas where the elevation is high. Sana'a for example is at an elevation of over 2,195 m (7,200 ft). During the winter months, the temperatures can fall to freezing point during the night.
Landscape [ edit ]
Narrow coastal plain backed by flat-topped hills and rugged mountains; dissected upland desert plains in the centre slope into the desert interior of the Arabian Peninsula. The interior of Yemen is a highland dissected by valleys. Yemen can be divided into five regions:
Coastal Plain: The Tihamah coastal plain is a low-lying flat plain that has areas with very fertile soil from the streams from the mountains emptying into it. Some of the hottest places on Earth are in Tihamah. Most of its towns are coastal because the salty sea air can lessen the effect of the heat.
Western Highlands: The coastal plain ends abruptly at the western mountains, where monsoon rains coming from Africa gain strength across the Red Sea and the clouds coming in get tangled by the jagged peaks of the Western mountains and precipitate all of whatever the clouds hold. Some areas in the western highlands, notably Ibb and Ta'izz, get rainfall similar to rainforests, supporting fertile land great for coffee, qat, wheat and sorghum. Mountains here are known to have lengthy ascents; most mountains pop out of land 600 m (2,000 ft) above sea level to 2,135-3,050 m (7,000-10,000 ft) peaks. Notable peaks include Jabal Sumarah, Jabal Ba'dan, Jabal Sabir, and Jabal Ad Dukayik, all about 3,000 m (10,000 ft) high.
Central Highlands: This is more of a plateau with rolling hills atop it, for the mountains are less jagged and get less precipitation because most of it is released onto the Western Highlands. Some of the highest mountains of the Arabian Peninsula can be found here, including the legendary Jabal an Nabi Shu'ayb near the capital Sana'a, at about 3,660 m (12,000 ft) above sea level. Some areas in the central highlands have extremely fertile soil, like in Dhamar, and temperature in the central highlands are extreme also. Diurnal temperatures are the highest in the world, with daytime highs of around 80°F while during the night they can dip to below freezing. Most of the central highlands, other than the mountains, is above 2,000-2,440 m (7,000-8,000 ft) high.
Central Plateau: As a gradual descent from the central highlands begins, it eventually levels off at a 915-1,525 m (3,000-5,000 ft) plateau that is bisected by valleys and wadis, or streams. This terrain is not as rough as the central or western highlands, but vegetation is only possible in the valleys or near wadis, for they provide a lot of irrigation water from precipitation that only occurs in the remote areas. Flash floods are very common. This extends from Shabwah though Hadhramaut and Al Mahra, continuing into Dhofar in Oman, which also revered by many Yemenis as part of Greater Yemen, not to mention also Najran, Jizan, and Asir in Saudi Arabia.
Desert: Rub Al-Khali, aka the Empty Quarter, the most treacherous desert in the world, and also the largest expanse of sand in the world, is in northeastern Yemen, southeastern Saudi Arabia, and northwestern Oman. It receives no rain at all for periods of years, and little to no vegetation exists. Temperature can reach 61°C (142°F)
People [ edit ]
You might think that Yemen is one of the more ethnically homogeneous countries in the Middle East, if all you knew was that nearly 100% of the population identify themselves as Arab . However, many Yemenis have strong regional, sectarian and tribal identities, and political differences also run deep, giving rise to an often contentious and sometimes violent diversity.
Get in [ edit ]
Entry requirements [ edit ].

Visa regulations change quite regularly, and an embassy should be contacted to make certain that the relevant documentation is obtained (it is recommended also to ask one of the licensed tour operators in Sana'a). Citizens of most countries (with the possible exception of Gulf Co-operation Council members) must obtain visas in advance. Most visas are valid for 30 days from the date of issue (3 months for European Union, but sometimes it depends on the mood of the official dealing with you). If you have a local contact to help you push the paperwork through, this can increase your chance of getting the visa. Another way of getting visa is via one of the licensed tour operators, as they are allowed to prepare pre-visa paper in the Ministry of Foreign affairs for their clients. Such pre-visa paper is valid for 30 days from the day of issue and upon this a real visa is issued at the Sana'a airport.
By plane [ edit ]

As of 2023, most flights to Yemen are suspended. Yemenia runs a skeleton service based in Aden with flights from Amman , Cairo and Riyadh . There are also flights into Say'un as of 2023 from Aden and Cairo. Other airports, including Sanaa, are either closed permanently or operate only infrequently.
By train [ edit ]
There are no trains to or within Yemen.
By car [ edit ]
It is possible to cross the Omani-Yemeni border in a car, although the border posts are often difficult to negotiate. Crossing from Saudi Arabia in a car is substantially more difficult, as regulations for getting a car into Saudi are very intricate.
By bus [ edit ]
Some buses operating throughout the Arabian peninsula connect to Yemen. The buses are mostly air-conditioned and comfortable, although the fleet sometimes contains old buses which may not be very comfortable to be on for several hour trips. Arriving from Oman can be difficult, especially if you're trying to get to Sana'a . There are buses from Salalah to Sayu'n in Wadi Hadramawt and Al Mukalla on the Indian Ocean, but tourists (especially from non-Arab countries) are not allowed to use public transport on roads linking the East and the West of Yemen: Al Mukalla - Aden and Say'un - Sana'a . The tourist have to take a plane in order to come from the west to the eastern part of the country.
By boat [ edit ]
There are passenger ferries from Djibouti. They are pretty cheap, but not very comfortable.
Supposedly, people have hitchhiked on a cement ship to Socotra from Salalah that leaves once a week and takes 4 days. However, it is often delayed.
Get around [ edit ]

Yemen is not an easy country to get around, since foreign nationals need travel permits and, in some regions, independent travel is not possible. There is a lack of road infrastructure in the eastern Mahra region, while all other Yemeni regions have hundreds of kilometres of newly built roads. If you are an intrepid traveller, the local transport (taxis, buses, aircraft) is perfect to get around on the cheap. More expensive, but more efficient travel is to book your tour via one of the registered tour operators, that are found on the Yemen Ministry of Tourism webpage [dead link] . Be aware that there are many non-registered tour operators in Yemen offering lower quality services, providing non-relevant information and many times tourists do not get all the paid services. In case of any problem, the Ministry of tourism will not be able to help you if you choose to travel with a non-registered tour operator or services provider.
For trips outside the capital, many travellers prefer a car (preferably 4WD) and may choose to hire a driver through a local travel agency. More intrepid travellers should certainly take advantage of the local intracity bus service, which is cheap, comfortable, and a wonderful way to see the country. The buses usually take a pit stop every hour or so, making this a slower but much more interesting way to travel for those who are up for an adventure and some friendly conversation. The biggest company in Yemen is Yemitco, their offices can be found in major cities.
Additionally, all travel outside the capital will require a travel permit ( tasriih ) from the tourist police; their station is 30m up the canal from the Arabian Felix Hotel. You need your passport, list of destinations and how long you are going to stay outside the capital. No photos required, however bring a photocopy of your visa and the picture page in your passport, as the photocopier there often doesn't work. This takes about 15 minutes. Office is closed from noon to (let's say) 14:00. Then you take many photocopies of the tasriih which you hand over at military checkpoints along the way. This may seem inconvenient, however it is designed to prevent travellers unwittingly venturing into areas of tribal unrest—and vice versa. Some areas of the country are off-limits to travel without military escorts, and still other areas are totally off-limits to travel. While the concept of staying informed about local conditions in your intended destinations is an overused one, in Yemen it is essential, as failure to do so may result in kidnappings or worse. No tasriih is checked if you fly to main cities in Yemen, like Aden, Al-hudaida etc.
The usual Middle Eastern shared taxi system exists in Yemen. In every city and often in towns there is at least one shared taxi ( bijou , from Peugeot) station, from where cars go to different destinations. Just ask anyone for your destination and they will point you to a car going there. The driver will not depart until all seats are completely full, which means 2 people in the passenger's seat, four in the middle and three in the back in a standard Peugeot almost invariably used for this purpose. If you want to travel in more comfort, you can pay for two seats or for the whole row. If you're a woman travelling alone you might be offered two seats in front for the price of one, but often you'll be asked to pay for both.
Talk [ edit ]
The official language of Yemen is Arabic .
Yemeni Arabic , the local vernacular, is spoken natively by almost everyone. The dialect is perhaps the toughest Arabic dialect to learn; Yemeni Arabic borrows many features from Classical Arabic, i.e., the variant of Arabic used to write the Qu'ran. It is not unusual for a visitor to be told that their Arabic is not "Yemeni" or "Yemeni enough". Don't be discouraged by this; most Yemenis will appreciate your efforts!
If you don't know the local dialect, do not despair; all Yemeni people learn Modern Standard Arabic at school, so you should have no problems communicating in major cities like Aden or Sana'a .
English is gradually becoming more and more popular, but most Yemenis have little to no knowledge of the language, which is why you will most likely be spoken to in Arabic. If you don't know any Arabic, don't panic! Yemenis are open communicators, and you can get your point across by hand-waving, making noises, and using a variety of gestures.
See [ edit ]

Sana'a: Babel Yemen (old city), Wadi Dhar (Dar al-Hadschar Palace—also known as the rock house). Sana'a is at over 2,200 metres (7,200 feet) in elevation. The old city is a mystical and amazing place and also a UNESCO World Heritage site. The streets are alive and bustling around gingerbead-like houses several stories high, one of the oldest cities in the world.
Socotra: Off the south coast of Yemen—an idyllic island untouched by modern man and home to many rare species and plants. The seas are turquoise blue and the sands white and unspoiled. One of the most valuable islands on the planet, often described as the most alien-looking place on Earth. Its beaches resemble those of the Caribbean and its mountains and Yemeni mountains covered in 300 species only found in Socotra. A must-see.
Kawkaban: An old fortress-city northwest of Sana'a 3,000 m (10,000 feet) high, with elegant old buildings an artefacts from the old Himyar civilization 2,000 years ago. Himyaric inscriptions can be seen and so can old Stars of David from the old Jewish roots of Himyar. Below the mountain is a magnificent view of a plain dotted by old towns made of mud-brick.
Sa'dah: The northernmost major town in Yemen, with its old city made entirely out of strong mud that keeps internal temperature warm during the bitter winter. Its surroundings are known for its delicious grapes, raisins, date palms, and other fruits.
Al Mahweet: A northwest town from Sana'a, Al Mahweet is a beautiful and magnificent town atop a mountain where the green scenery and outstanding architectural example of Yemen are at its best. It is part of the western highlands, an area where rain can be extensive and clouds can always be seen below the mountains during the summer.
Bura': A protected area in Yemen in Al Hudaydah governate, this place is a 2,200 m (7,200 foot) mountain covered by a natural forests resembling one of the rainforests of Africa. There are many flora and fauna varieties in Bura' located only in Yemen and its historic boundaries (Najran, Jizan, Asir, Dhofar, & ar Rub' al Khali). It is one of the most beautiful places in Yemen.
Manakhah: A large old town on a peak 2,700 m (9,000 feet) high known for its daring location and beautiful scenery. This town is a good example of life in medieval Yemen.
Ma'rib: The capital of the Sabaean Kingdom, built about 3,000 years ago, with its famous Ma'rib dam, one of the engineering wonders of the world. It was said that thousands of years ago the magnificent dam helped create some of the greenest areas in the world, a notion also supported by historical texts like the Qur'an. The Queen of Sheba is known to have had her kingdom here and artifacts and temples from her reign are still preserved and present.

Ibb: The green heartland of Yemen, with annual rainfall at about 1200 mm per year. It sits in 3300-m high (10,000 foot) mountains. The city of Ibb, however, is in the valley, but waterfalls are known to be present and beautiful. The historic town of Jiblah is near Ibb city. And with the freshest climate on the whole peninsula, there is no wonder why it is referred to as the Green Heart of Yemen.
Al Khawkhah: At one of the hottest places on earth, you need a beach, and at Al Khawkhah, it has one of the best beaches in Yemen. The shore is long and back by fields of palm trees and a small pleasant town. The Red Sea is relatively calm and cool, great for an area where summer temperatures are commonly over 48°C.
Ta'izz: The cultural capital of Yemen, which is the most liberal and the friendliest city in the country. It has been the capital of Yemen when the last Imam was in power and is a medieval city. Towering above Ta'izz is the 3,000 m (10,000 foot) Jabal Sabir, which is known all around Yemen for its dazzling ascent and view from the top. This mountain is very fertile and is home to tens of thousands of people living on and around the mountain.
Shibam: Commonly referred to as the Manhattan of the Desert, this town located in Wadi Hadhramaut has the first skyscrapers of the world. Hundreds of adobe homes ranging from 5-11 storeys high are boxed into a walled area that is simply marvellous. The tops are painted with gypsum, a mineral commonly found in Yemen. Some of the buildings are over 700 years old.
Tarim and Say'un: These nearby towns are made almost entirely of adobe. The towns are well organized and elegant, with famous palaces and mosques in each city.
Al Mukalla: Perhaps the most developed-looking city in Yemen, Al Mukalla is the jewel of the Arabian Sea. Around it around beautiful beaches, however, the best in Yemen is known to be at Bir Ali, which is a lengthy 100 km drive, though well worth it.
Hauf National Park: The only natural forest in the Arabian Peninsula because it is affected by the seasonal monsoon rains that also affects India. Mountains and Hills are layered with a cap of green for mile with wild life similar to one of a rain forests, this forest also extends to the Omani side of the border, from Qishn, Yemen to Salalah, Oman.
Do [ edit ]
Although the accommodation might not be the best, the country holds so many treasures that appeal to any open-minded visitor. The sights are amazing, the people are friendly, their culture is unique, and their food is tasty. Take trips with a personal driver through the mountains to see natural beauty found nowhere else on the planet. See the historical role Yemen played as it survived even during the times of the Sumerians and the Ancient Egyptians, and how no one was able to completely conquer Yemen. And enjoy what the country provides, like gemstones literally littered throughout the mountains, precious beaches, and historical artifacts from this multi-faced nation.
Buy [ edit ]
Money [ edit ].
The currency of the country is the Yemeni rial ( YER or ﷼ ). Banknotes circulate in denominations of 50, 100, 200, 250, 500 and 1000 rials, and you are also likely to come across 10 and 20 coins.
The rial is freely convertible and subject to frequent fluctuations.
Shopping [ edit ]

Almost everywhere you look, you will have the chance to buy the curved dagger (jambiya) worn by local men. This purchase can be simply of the dagger and its accompanying sheath, however handmade belts and silver pouches are also for sale. When purchasing a jambiya, remember that it classed as a weapon for customs purposes. Traditionally, handles were made of animal horn or even ivory. While it is doubtful that the handles sold today as being made from either of these products are the real thing, a wooden or amber handle may be a better option. Cheaper options are pendants and brooches commonly available in the shape of the knife and its sheath.
Necklaces and jewellery are also common souvenirs, and many of these are made of the semi-precious stones the souvenir sellers claim. Nevertheless, a healthy grain of salt taken a necklace is made of lapis lazuli or other precious stone.
Bargaining , even with village children, is expected and worthwhile. If you are with local guides, a common approach is to have them ask for the "Yemeni price", however any bargaining on the part of the tourist will result in discounts.
In tourist sites, there will be souvenir-sellers everywhere you look. In some mountain villages, such as Kawkaban , their technique involves almost trapping the tourists with wheelbarrows full of souvenirs. There is an art form to firmly turning down the goods on offer, even when the seller is a young boy or girl in desperately poor circumstances.
The rial is subject to high inflation. As a result, many prices, particularly those quoted to light-skinned visitors, will be given in euros or US dollars. Any of these three currencies will be accepted by the seller, so ask for the cost in whichever currency you are carrying at the time. Discounts for paying in one currency or the other are not high enough to warrant only paying in local money, but you may be lucky.
Eat [ edit ]
Yemeni cuisine differs markedly from the rest of the Arabian Peninsula, and is a real highlight of any trip to the country—particularly if shared by locals (which is an invitation most visitors will receive more often than they might expect).
The signature dish is salta , a meat-based stew spiced with fenugreek and generally served at the end of the main course. The taste may take newcomers by surprise, but it is a taste well worth acquiring.
Mandi is a popular dish of meat and rice with spices originating in the Hadhramaut region. What distinguishes mandi from other similar dishes in the rest of the Middle East and South Asia is that the meat is cooked in a clay oven and hung over the rice, allowing the juices to drip onto the rice as it is cooked.
Yemeni honey is particularly famous throughout the region, and most desserts will feature a liberal serving of it. Bint al-sahn is a sort of flat dough dish which is drenched in honey. Other sweet foods well worth the trying are Yemeni raisins.
While not a "food" per se, something else to put in one's mouth is the qat leaf. This is the Yemeni social drug and is chewed by almost all of the population from after lunch until roughly dinnertime. The plant is cultivated all over the country, and most Yemenis are more than happy to offer visitors a branch or two. Chewing qat is something of an art, but the general idea is to chew the small, soft leaves, the soft branches (but not hard ones) and to build up a large ball of the stuff in a cheek. The ability to chew ever-increasing balls of qat is something of a mark of pride among Yemenis, and the sight of men and boys walking down the street in the afternoon with bulging cheeks is one the visitor will soon get used to. Qat acts as a mild stimulant, and it also has something of an appetite-suppressant function, which may explain why there are so few overweight Yemenis in spite of the nature of their cuisine. Insomnia is another side effect. Qat is associated with mouth and esophageal cancers, so partake carefully.
Drink [ edit ]
Yemen is officially a dry country; however, non-Muslims are entitled to bring up to two bottles of any alcoholic beverage into the country. These may be drunk only on private property, but venturing outside while under the influence is not a wise decision.
Many juices and soft drinks are readily available, but you should avoid more scruffy-looking juice shops as they might be using tap water as base. Many Yemenis will drink tea (shay) or coffee (qahwa or bun) with their meals. Yemeni coffee is considerably weaker than the strong Turkish coffee found elsewhere in peninsular Arabia.
Tap water should be avoided. This is comparatively easy to do, as bottled water—both chilled and at room temperature—is readily available everywhere.
Sleep [ edit ]

Outside of the capital and the major centres ( Sana'a , Aden and al-Mukalla ), accommodation tends to be rather basic and generally of the mattress-on-the-floor variety, generally with shared shower rooms and WCs. Most larger villages will have at least one funduq , which will provide this sort of accommodation. The places tend to be named the [Name of Village] Tourist Hotel. Electricity supplies tend to be a little erratic, so hot water cannot always be counted on.
Funduq accommodation is not rated on the star scale used in other countries, but rather on the Yemeni "sheet" scale, with "no-sheet" being the most basic and "two-sheet" the top of the line. Some other hotels, mostly in Sana'a, go by the star scale, most notably the Movenpick, Sheraton, and the Hilton. This does not mean that in a "no-sheet" funduq one will not receive a sheet, although in some places it may be worthwhile to bring one! Most funduqs will offer some food, almost invariably local cuisine, and the better ones will serve it in a diwan -style room, where one can eat while reclining on cushions. In some funduqs, dinner will be followed by a "party", featuring performances of traditional music and jambiya dances—sometimes with audience participation.
Learn [ edit ]
Particularly in Sana'a, there are institutes offering instruction in Arabic. The advantages of learning the language in Yemen are that the dialect spoken is often quite close to Classical Arabic, and also that languages other than Arabic are much less commonly spoken than they are in nearby countries. However, the one important exception to this rule is the Old Sana'a dialect, which is difficult to understand even for Arabs from other countries, and becoming completely incomprehensible when combined with a big ball of qat in the speaker's cheek.
Work [ edit ]
Yemen is one of the poorest countries in the world. The main reason for the lack of wealth: Yemen has paltry deposits of oil compared to its oil-rich neighbours.
Most of the following applied before the ongoing civil war:
- Work in Yemen is difficult to obtain as a foreigner. The collections of young men waiting in public areas and by the roadside looking for work does not reflect a lack of jobs. Rather, it reflects that many Yemenis do not have enough education to work in non-manual jobs. As a result, immigrants from sub-Saharan Africa are often seen in service industries (with a popular joke among expats being that "something typically Yemeni" is in fact an Ethiopian maid). Educated westerners do not, however, have it easy as there are many bureaucratic hurdles to working in Yemen. Most westerners who find jobs there tend to be working as expat staff for a western company with interests in the country.
- The only exception is that if you're an English native speaker, a lot of places in big cities, ranging from schools through universities to governmental organisations and companies are desperate for English teachers , and usually don't require any qualifications. Sometimes it is even possible to get a teaching job if English is not your first language.
- Also in Sana'a the local English-language magazines often need proofreaders.
Stay safe [ edit ]
Yemen is at war, under international attack, and is heavily damaged; see the warning at the top of this page. In addition, there have been problems with terrorism and kidnappings of people including foreigners.
Once it is possible to visit Yemen again, the following will again become relevant:
- The public consumption of alcohol is punishable under Islamic law in Yemen. Homosexual acts are also prohibited and may be punishable by death.
- Driving is on the right. While Yemeni drivers have something of a reputation for bad driving, the reality is slightly more nuanced. Risks are taken, particularly in Sana'a, which would not normally be taken in other places, but the locals expect this to happen and compensate accordingly.
- For trips outside Sana'a, however, a 4-wheel-drive is almost mandatory as most roads away from the routes connecting main cities are not paved. Travellers should also give serious consideration to hiring a local driver/guide, as maps tend not to be as useful as they can be in other countries. A city limits border pass is required as only the cities are well protected by the military. It is also worth noting that Yemen has one of the largest populations of armed civilians in the world, so be polite.
Stay healthy [ edit ]

Health care facilities are seriously underdeveloped in Yemen. If you fall seriously ill during your stay, it is advised that you go to neighbouring Oman or Saudi Arabia .
The country in the midst of a cholera outbreak. Wash your hands often, cook food well, and clean up well. For more information on how to stay safe, you may view more information here .
Tap water should be avoided . To stay safe, it is recommended to stick to the bottled variety.
The country is exceptionally dusty . Travelers with breathing difficulties (such as asthma) may encounter problems in more remote destinations.
The dry air (especially from September 'til April) can be bothersome, causing cracked lips and sometimes nosebleeds. Always carry a Vaseline stick with you, available in most pharmacies in Yemen, and a packet of tissues.
Particularly when hiking , remember that much of the country is at altitude. Therefore, as well as taking the usual steps of drinking plenty of water and protection from the sun (which can be very harsh in Yemen), be aware of any dizziness you may be experiencing due to rapid ascents. Many of the more popular hiking routes are covered in loose stones, so be careful of your footing. Some peak ascents can be at a near 70-80 degree angle, so any fall will be devastating. Be prepared with bandages and/or anti-bacterial creams just in case you get a cut, which is normal during hiking.
Malaria is present in low-lying areas along the Red Sea.
Rabid dogs are common in Yemen. If you are bitten by a rabid animal, there is little to no chance that you will be able to receive a rabies vaccination, and you will likely die if you are infected with rabies. Preventative vaccination for rabies prior to arrival is recommended.
Respect [ edit ]
Yemenis, North Africans , and Arabs in the Gulf share a common culture; therefore, what is considered good manners in Arab world is applicable to Yemen.
Things to avoid [ edit ]
There are some things which will be met with disapproval and you should avoid doing the following during your stay in the country.
Politics [ edit ]
- Avoid talking about the United States — many Yemenis feel that the US 'interferes' in the affairs of the country and has done more harm than good.
- Avoid talking about Israel — like their counterparts throughout the Arab world, many Yemenis express negative feelings towards Israel.
Religion [ edit ]
Islam is the state religion of Yemen and it plays an important role in the lives of every Yemeni. As is the case throughout the Arab world, religion is a delicate topic of discussion . Always approach religious discussions with sensitivity and respect.
- When visiting sites of religious importance, behave and dress well. Some mosques may be off-limits to non-Muslims. If in doubt, ask.
- During Ramadan, you should refrain from eating, drinking, smoking, and chewing in public. Not doing so would be seen as incredibly disrespectful.
- Do not criticise or speak badly of Islam; Yemen has some harsh blasphemy laws.
- Do not talk about religion from an agnostic point of view; this will be met with total incomprehension.
- Anything hinting at proselytism will neither be appreciated nor welcomed; apostasy is a crime in Yemen.
Miscellaneous [ edit ]
1. This is a Muslim country. As such, be sensitive about where you point your camera. There are many great photo opportunities around every corner (the question is usually what to leave out of each image), but when photographing people, always ask first. The Arabic phrase "mumkin akhud sura minak?" is very useful indeed. Don't ever, ever try to take pictures of women , even if you're a woman yourself. This is considered a great offense and can even result in more than a few harsh words. Also don't try to take pictures of anything that looks as if it could be of any strategic importance (i.e. has at least one soldier or policeman guarding it). However, if you ask with good manners and the guards are in a good mood, you might be allowed and take a souvenir photo with a military man holding a machine-gun!
2. Despite being close to the richer oil-producing countries, Yemen is one of the poorest states on earth. Living conditions for many locals are very tough. As a tourist, expect local merchants to demand higher prices from you. While being mindful of the poverty level in Yemen, tourists should resist sympathetic urges to pay the merchant's first price. Bargaining is a way of life in much of the world and is expected of all buyers.
3. If an area is off-limits, it is that way for a very good reason. Tempting as it may be to play the intrepid explorer, there is no reason to increase your risk of being kidnapped or worse unless you absolutely have to.
In addition, be prepared to be asked for pens (qalam, galam) for the local schools, and also sweets (bonbon). In the former case, if you have one to spare you may wish to consider it. In the latter, resist the urge to give a handout as it will create an expectation for the next foreigner to arrive. It should go without saying that you shouldn't give money ("fulus!" "bizniz!") to children. Donate to local charities instead.
Connect [ edit ]
- Has custom banner
- Has warning box
- Has map markers
- Articles with dead external links
- Outline countries
- Outline articles
- Country articles
- Has Geo parameter
- Middle East
- All destination articles
- Pages with maps
Navigation menu

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
We continue to advise:
Do not travel to Yemen (including the island of Socotra) due to the dangerous security situation and the threat of armed conflict, kidnapping and terrorism.
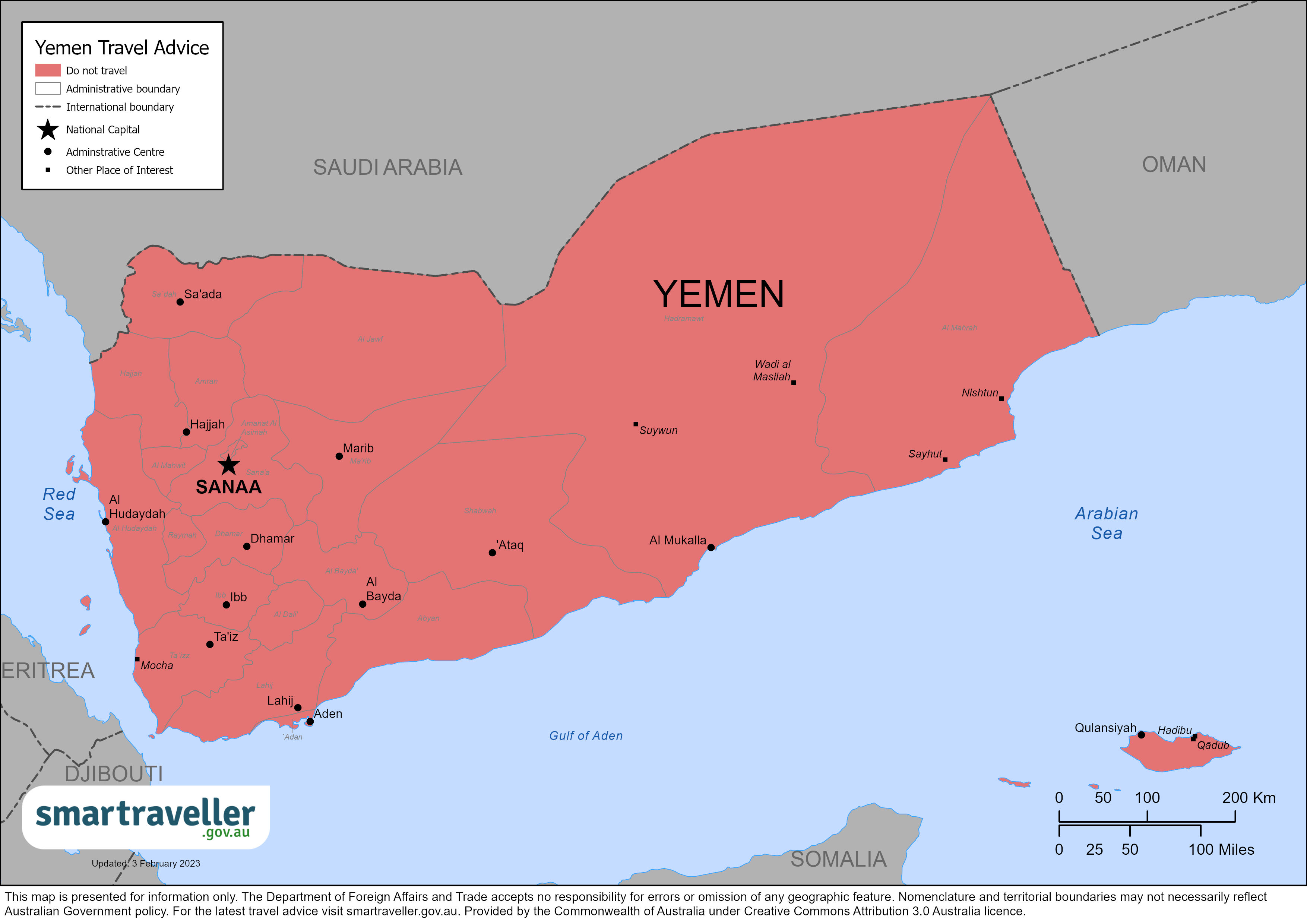
Yemen (PDF 717.25 KB)
The Middle East (PDF 1.45 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies, advice levels.
Do not travel to Yemen (including the island of Socotra).
Do not travel to Yemen (including the island of Socotra) due to the dangerous security situation and the threat of armed conflict, kidnapping and terrorism.
See Safety
- An increased threat of military and terrorist attacks against Israel and Israeli interests across the region and ongoing military action in the Occupied Palestinian Territories could lead to increased tensions in other locations in the Middle East. Demonstration and protest activity may occur, and localised security situations could deteriorate with little notice. Avoid all demonstrations and protests. This may also result in airspace closures, flight cancellations and flight diversions and other travel disruptions.
- Do not travel to Yemen (including the island of Socotra) due to the ongoing civil and international conflict. Military operations continue in Yemen and the Red Sea in response to attacks by Houthi militants on ships transiting the Red Sea and surrounding waters, including the Gulf of Aden.
- Despite truce agreements, the security situation in Yemen remains highly unstable and unpredictable. Airstrikes, other military activities and violent clashes may occur sporadically and without warning. There may be limited government control over parts of the country.
- There's extreme political instability, risk of injury from landmines and unexploded ordinance, and a very high threat of kidnapping and terrorism. You may also be unable to get enough food, water or medical care.
- There's a very high threat of kidnapping and terrorism in urban and rural areas around Yemen, including in the main cities of Sana'a, Aden, Hadhramaut and Ta'izz. If you're in Yemen despite our advice, get professional security advice. Keep a low profile and vary your routines and behaviours. Targets include the Yemeni Government and Houthi interests, foreigners and foreign interests, journalists, international organisations and NGOs. Take extreme care near places that belong to Yemeni authorities.
- Most international airlines no longer fly to Yemen. If you're in Yemen despite our advice, consider leaving if it's safe to. If you can't leave, then shelter in a safe place. Follow the advice of local authorities or trusted security experts before trying to leave by road or other method.
- Australian officials can't currently travel to Yemen to provide consular help. Nearly all countries have suspended embassy operations and withdrawn diplomatic staff. If you enter Yemen or stay despite our advice, work with only reliable, registered and authorised organisations. Don't travel alone or at night.
- Physical, verbal and sexual harassment can occur.
- Important dates and religious or political anniversaries, such as Unity Day on 22 May each year, can cause violence and civil unrest. Avoid public gatherings. Be careful around Friday prayer times.
- Weapons are readily available. Yemenis are often heavily armed. Armed carjacking is common.
- There's a high threat of piracy in Yemeni waters and the Gulf of Aden.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave. Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. You'll probably need a special insurance policy that covers travel to high-risk destinations. Most Australian policies won't cover you for travel to Yemen.
- Cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) have been reported. Avoid contact with camels and products contaminated with camel secretions.
- The Sana'a region is at a high altitude which may cause issues if you have lung, heart or chest problems.
- The standard of medical facilities is basic. It's difficult to access medical services in the current conflict, and medical facilities or services in Sana'a, Aden, and elsewhere in the country may not be readily available or efficient. If you're seriously ill or injured, you'll need medical evacuation, which can be very expensive and difficult to arrange.
Full travel advice: Health
- Get professional legal advice if you're involved in local legal matters, including family and business law.
- Don't use, carry or traffic illegal drugs. Severe penalties include jail terms and the death sentence.
- Many laws in Yemen are different to those in Australia, including for same-sex relationships, adultery and abandoning the Islamic religion or promoting a religion other than Islam. Punishment may include imprisonment and the death penalty. Drinking alcohol in public, slander, and adultery are all punishable by lashing.
- If you're sexually assaulted, you may face criminal prosecution. Authorities may not consider you to be a victim of crime.
- Be careful when taking photos. Photographing government buildings, military personnel and sites, airports, equipment and other sensitive infrastructure is illegal. These may not be clearly marked.
- Yemen doesn't recognise dual nationality. Dual nationals may need to complete national service.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- If, despite our advice you travel to Yemen, including the island of Socotra, you'll require a visa to enter. This can't be issued on arrival. A visa does not guarantee entry to Yemen.
- You may be denied entry to Yemen if your passport has an Israeli visa, an Israeli border stamp or an Egyptian or Jordanian border stamp issued by a border office with Israel.
- If you're trying to leave Yemen, check exit requirements with local immigration authorities before you book your ticket.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. You should contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Yemen for the latest details.
- Land borders, seaports and airports may close with little or no notice. Check with local authorities before travelling to the border.
- The Houthi authorities in northern Yemen have imposed a 'mahram' requirement, which bans women from travelling without a male guardian. In some cases, evidence of a male guardian's written approval may be sufficient.
- A Yemeni husband may legally stop his wife from leaving the country, regardless of her nationality. Children under 18 need their father's permission to leave the country, regardless of who has custody.
- Don't travel by road without expert local advice. You may need permission from local authorities to travel outside Sana'a and some other cities. Unexploded weapons and landmines are a high risk in the central highlands and southern and eastern regions, especially around Aden and Sa'ada province.
- The waters around Yemen have sensitive security issues and territorial disputes. Get advice from authorities before entering Yemeni waters or ports.
- Forced marriage and marriage of girls under the age of 18 is common in Yemen. Sharia (Islamic) courts have jurisdiction over custody cases involving Muslim parents.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what we can and can't do to help you overseas.
- Australia doesn't have an embassy or consulate in Yemen. Our ability to provide consular services in Yemen is extremely limited. For consular advice, contact the Embassy of Australia in Saudi Arabia .
- To stay updated with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Security situation.
Do not travel to Yemen, including the island of Socotra due to the ongoing civil and international conflict. There's extreme political and security instability.
Military operations are taking place in response to attacks by Houthi militants on international shipping in the Red Sea. Houthis continue to target and attack ships transiting the Red Sea and surrounding waters, including the Gulf of Aden. This may change at short notice. There may be limited government control over parts of the country.
Violent jihadist groups have a strong presence in some parts of Yemen. Terrorist groups in Yemen remain a serious threat and continue to plan and conduct attacks.
Terrorists have staged repeated attacks against Yemeni Government interests and civilian targets. Foreign interests continue to be prime terrorist targets.
Locals and foreigners, including UN officials and international aid workers, have been targets of kidnapping, terrorism and assassination.
Despite truce agreements, the security situation in Yemen remains highly unstable and unpredictable.
Tribal fighting over land and other causes is common. Local tribes are heavily armed and may use weapons, including in major cities.
There are landmines in some areas of the country, including Hudaydah city. These have killed civilians.
Some regional countries also have a military presence in Yemen.
Following years of conflict, there's been a breakdown in government and public services, including power and water supplies. It has impacted the supply of goods and services across the country. Medical services and supplies are extremely limited and may not be available in some areas.
Food insecurity and a deteriorating economic situation may worsen due to Houthi attacks in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden.
Truce agreements may be violated or terminated at any moment, which may escalate the security situation and levels of violence.
Transport options to leave Yemen are very limited, and roads may be closed at any time without notice.
Most people in Yemen do not speak English.
Australia does not have an Embassy or Consulate in Yemen. It may be difficult for the Australian Government and the Embassy in Riyadh to provide emergency consular or passport services. The Embassy of Australia in Riyadh is not able to provide assistance with evacuation or repatriation to Australians in Yemen.
Travel disruption
Terrorism and civil unrest have severely disrupted air travel and other means of leaving the country.
Most international flights have been suspended. Commercial flights to and from Yemen have operated out of Aden, Seiyun (Hadhramaut) and Sana'a to different destinations in the region. Flights may be disrupted at any time with little notice.
The conflict has damaged airport infrastructure.
You may not be able to get enough food, water or medical care.
If you're in Yemen despite our advice, you should consider leaving if it's safe to do so.
If you can't leave, take shelter in a safe place. Keep a low profile and explore all available options to leave.
Follow the advice from local authorities or trusted security experts before trying to leave by road.
Electricity outages
Electricity supply throughout Yemen is unreliable, and power outages are common. Power outages can last for hours.
Opportunistic criminal acts can occur during power outages.
Businesses such as petrol stations that are reliant on government-supplied electricity or without backup electricity generators may temporarily suspend operations during power outages.
Consular help
There's no Australian Embassy or Consulate in Yemen, and it may be difficult to provide emergency consular or passport services to Australians in Yemen. Our ability to provide other consular and passport help is extremely limited. In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre in Australia on +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas or 1300 555 135 from Australia.
If you need to renew your passport while in Yemen, contact the Embassy of Australia in Riyadh to check whether you're eligible for a mailed-in application .
Australian officials have been instructed not to travel to Yemen because of security concerns.
The US and UK governments have recalled their diplomatic staff and suspended embassy operations.
If you enter the country or remain despite our advice:
- keep in contact with family and friends
- don't travel alone or at night
- check routes before you travel
- don't put your travel or other plans on social media
- work with only reliable, registered and authorised organisations and travel agencies
- don't carry large amounts of cash.
There's a very high threat of kidnapping throughout Yemen.
Terrorists in Yemen have kidnapped locals and foreigners in recent years, including UN staff, aid workers and journalists. Some foreign hostages have been killed, and some may have been sold to terrorist groups, including Al Qaeda and Daesh (ISIS).
Kidnappings occur in urban and rural settings around Yemen.
Terrorist groups, tribal groups and criminal gangs kidnap foreigners, including Australians. Tribal groups and gangs sell victims to terrorist groups.
Kidnappers often ask for large ransom payments to release captives.
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
If, despite our advice, you decide to travel to an area where there's a threat of kidnapping, you should:
- get professional security advice and consider reliable resources to protect yourself
- arrange personal security measures, including travelling in convoys during daylight hours
- liaise with trusted contacts
- exercise extreme caution and keep a low profile at all times
- avoid displaying expensive jewellery, electronics or other valuables
- monitor local and international media and other resources for up-to-date information on the local situation.
More information
Terrorist attacks
There's a very high threat of terrorism throughout Yemen.
Terrorist targets include:
- Yemeni Government interests, including infrastructure, seaports and airports, security force bases, government Ministries, and surrounding areas
- security patrols and parades
- Houthi interests
- places of worship
- foreign interests
- tourist attractions, embassies, diplomatic vehicles, international businesses and organisations, and hotels other locations where foreigners might be
Foreign officials, business travellers, tourists and foreign residents have also been targets.
Terrorists can launch attacks in all parts of Yemen. Foreigners have been attacked in urban and regional areas.
Terrorists have attacked oil interests and kidnapped oil and international aid workers. They may be planning more attacks on oil infrastructure and organisations, including aid organisations in Yemen.
Houthi militants have conducted attacks targeting oil facilities and terminals in Yemen.
Attacks and assassinations by car bombs, drones and gunfire have occurred. These can occur anywhere in Yemen. If you decide to remain in Yemen despite our advice, you should:
- get professional security advice and liaise with trusted contacts
- adopt strict security procedures and explore reliable resources to protect yourself
- be aware of your surroundings
- be extremely cautious and keep a low profile at all times
- carefully consider the need for any travel
- monitor local and international media for up-to-date information on the local situation
- consider keeping your next of kin informed by your welfare
All Australians are at risk, regardless of occupation, ethnic or religious background, location or length of stay.
Always be alert. Avoid posting your photos and geographical locations on social media while in Yemen. Vary your routines and make sure patterns in your behaviour and movement aren't obvious to anyone watching.
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
More information:
Terrorist threats
Civil unrest and political tension
The security situation in the region remains unpredictable and could deteriorate with little or no warning.
Demonstrations and protests
Demonstrations and protests can take place at any time and place. Even peaceful events can turn violent without warning.
Important dates and political anniversaries can motivate violence and civil unrest.
Significant civil unrest occurs around days related to the reunification of North and South Yemen. This includes Unity Day on 22 May every year.
If you're in Yemen, despite our advice, you should:
- avoid major events because violence could happen
- not go to any demonstrations, protests or political rallies and leave affected areas as soon as it's safe
- stay away from crowds because they can often turn violent
Be careful around Friday prayers, mourning, and religious anniversaries and festivals, and stay indoors.
Carefully monitor local media for safety and security risks, including significant political events that may increase tensions. Follow the advice of local authorities.
Protests and demonstrations may affect your ability to travel by road. During demonstrations, roads, highways, and other routes, including to and from the airport, can be blocked. Security checkpoints can be deployed in or around the areas of demonstrations and protests.
Demonstrations and civil unrest
Weapons are readily available, and tribes are often heavily armed.
Violent crimes and organised crime are widespread in Yemen. Police response times are poor. Local law enforcement's ability or willingness to respond to serious crimes may be limited or non-existent.
Armed carjacking has occurred in many parts of the country. Drive with your doors locked and windows up at all times.
Pickpocketing, bag snatching, and credit card fraud, such as skimming, may happen. Avoid displaying expensive jewellery, electronic items or other valuables.
Don't bring large amounts of cash to Yemen. Exchange currency at official exchange stores only.
To protect yourself against petty theft:
- keep a close eye on your belongings
- leave valuables in a safe place and carry only what you need
- secure your passport and other travel documents
If you're female, take extra care when dealing with strangers or people you've just met. Be especially wary about accepting rides or invitations. Women travelling alone can be harassed and should take care, especially at night.
In Houthi-controlled areas (central and northern Yemen), authorities may seek to detain women participating in community and leadership activities or women travelling without a male guardian.
There's a significant threat of piracy and armed robbery in Yemeni waters, the Gulf of Aden and Indian Ocean.
Pirates have attacked vessels and held foreigners hostage for ransom in the Gulf of Aden.
Somali pirates have attacked vessels more than a thousand nautical miles (1850km) from the coast of Somalia.
Attractive targets for Somali pirates include:
- commercial vessels
- pleasure craft
- luxury cruise liners
You should remain out of the designated High-Risk Area or face the risk of being hijacked and held hostage for ransom. Check with the Maritime Security Centre (Horn of Africa) at www.mschoa.org .
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it does not make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
- Piracy reports issued by the International Maritime Bureau (IMB).
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you’re connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
Cyber security when travelling overseas
Climate and natural disasters
Yemen experiences severe weather .
The monsoon season is from June to September. Flooding can occur.
Sandstorms and dust storms can happen.
Yemen has earthquakes and active volcanoes.
Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
If a natural disaster happens:
- secure your passport in a safe, waterproof place
- monitor local media and other sources, such as the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
- follow the advice of local authorities
- keep in touch with friends and family
- seek local advice before entering affected areas
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including hospital stays and medical evacuation. Be aware that most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept Australian or other health insurance. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs or get involved in any commercial disputes.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
You'll probably need a specialised insurance policy that covers travel to high-risk destinations. Most Australian policies won't cover you for travel to Yemen.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare, or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location .
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Some medicines may not be available in Yemen, and there may be shortages of other medicines.
Some skincare products and e-cigarette refills may contain ingredients that are illegal in Yemen, such as Cannabidiol (CBD) oil. CBD oil or products are illegal in Yemen, even if they're for medical or recreational purposes. It's a serious crime to carry illegal drugs or CBD oil or products in Yemen. Punishment can result in imprisonment and deportation.
For more information or to check if your medication is legal in Yemen, please contact and check with your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Yemen prior to your departure.
Local authorities may detain or deport travellers for:
- carrying medication to treat HIV/AIDS or hepatitis
- testing positive for HIV/AIDS or hepatitis - see Health
Always take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry your medicine in its original packaging and a copy of your prescription or a dated letter from your doctor that states:
- the medicine's brand and scientific (chemical) name
- the prescribed dosage and the duration of treatment, and
- that it's for your personal use.
Health risks
Respiratory system risks.
Cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) have been reported in Middle Eastern countries, including Yemen.
Countries outside the Middle East have also reported cases from returning travellers.
The altitude in the Sana'a region can cause problems, especially for those who suffer from lung, heart or chest problems.
Insect-borne diseases
Malaria is common, except in areas above 2000m. Chloroquine-resistant strains have been reported.
Other insect-borne diseases, such as dengue , filariasis and leishmaniasis are common.
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria
Get medical advice if you have a fever, muscle pain, rash or severe headache.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are common. These include:
- tuberculosis
- bilharzia (schistosomiasis)
- polio (poliomyelitis)
Severe outbreaks sometimes happen. Ensure all your vaccinations are up to date before you travel.
A major cholera outbreak has intensified since late April 2017. Cholera is spread mainly through contaminated drinking water or food. In addition to cholera, other contagious diseases are circulating in the country.
To stay safe:
- avoid drinking tap water. Drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- don't eat ice cubes
- avoid raw or undercooked food, such as salads
Get medical advice if you have a fever or diarrhoea.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The current conflict has made it difficult to access medical services.
The standard of medical facilities and services is generally poor and is of an even lower standard in rural areas. Ambulance and emergency services are inadequate and are often not available or accessible, particularly in rural areas.
You must pay upfront if you're treated in private healthcare facilities. Most hospitals accept cash payments only.
You may need to be medically evacuated for serious illness, an accident, or complex procedures. Medical evacuation can be very expensive and difficult to organise. Check your insurance policy and contact your insurance provider for assistance.
The electricity supply throughout Yemen is unreliable, and power outages are very common. Public and private hospitals that don't have backup power generators sometimes temporarily suspend operations during power outages.
If you're in a rural area and become seriously ill or injured, you'll need to be evacuated to main cities or internationally. Medical evacuation can be very expensive. Keep local emergency numbers and local contacts with you at all times.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
There's no Australian Embassy or Consulate in Yemen. Our ability to provide consular assistance to Australians in Yemen is extremely limited, including if you're arrested or jailed.
Get professional legal advice if you're involved in local legal matters. This includes criminal, business or family law, divorce, child custody and child support.
It's illegal to give birth out of wedlock. Sentences can include imprisonment or the death penalty. Yemen does not recognise children born outside marriage and does not issue birth certificates for children born outside marriage.
Buying or removing Yemeni antiquities is illegal without a permit from the relevant local authorities.
In Yemen, both men and women should dress modestly in public.
Be aware of your rights and responsibilities.
If you wish to marry a Yemeni national, your partner will first need approval from the Government of Yemen. Check current requirements and timeframes directly with the relevant local authorities.
Punishment for possessing, using or trafficking illegal drugs is severe. Penalties include fines, jail or the death penalty.
- Carrying or using drugs
Serious offences
Authorities can detain you without charge if you're suspected of committing an offence.
You may have to wait months for legal help or for a court appearance while authorities investigate.
Trials are held under Islamic law and procedures.
People convicted of serious offences can face:
- long jail sentences
- heavy fines
- deportation
Penalties for some offences are severe and can carry the death penalty. These offences include:
- arson/explosion
- endangering transport and communications
- prostitution
- same-sex relationships
- abandoning the Islamic religion
- promoting religions other than Islam
Some crimes are punishable by lashing and imprisonment. These include drinking alcohol in public, slander and adultery.
Get permission before taking photographs of people, especially women and children.
It's illegal to take photos of:
- government buildings
- military personnel
- military installations
- other sensitive infrastructure
Military sites aren't always clearly marked or defined.
Preaching or promoting a religion other than Islam in public, except in churches, is illegal. Attempting to convert Muslims is illegal.
Preaching non-Islamic religions in Yemen, even to non-Muslims, may be perceived negatively by local people and may raise the attention of radical and extremist groups. Consequences could be severe and could result in assaults or death by such groups or other local religious organisations or individuals.
Restrictions apply to the sale or possession of alcohol, pornography and pork. Customs authorities at border entry points will confiscate these products.
In some cases, authorities have detained travellers at borders because of the smell of alcohol on their breath.
LGBTQIA+ laws
Yemen doesn't recognise or allow same-sex marriages and rights.
Same-sex relationships are illegal, and sentences can include imprisonment or the death penalty.
- Advice for LGBTQIA+ travellers
Australian law
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
Staying within the law and respecting customs
Local customs
The Islamic holy month of Ramadan is observed in Yemen. Respect religious and cultural customs and laws at this time.
During Ramadan, eating, drinking, and smoking may be illegal in public during the day. Avoid dressing inappropriately, eating, drinking or smoking in public or around people who are fasting. Seek local advice to avoid offence.
Explore our Ramadan page to learn more, including dates for Ramadan.
Dress and behaviour standards
There are strict Islamic codes of dress and behaviour. Any disrespect for Islam will cause offence. Be modest in your dress and behaviour. Take care not to offend. If in doubt, get local advice.
Wear a headscarf and cover your arms and legs if you're a woman. Don't wear shorts or unbuttoned shirts if you're a man.
Other local customs
Non-Muslims may not enter mosques.
Public displays of affection may cause offence.
It's generally unacceptable for unmarried couples to live together.
Hotels may not allow couples to stay unless they can prove they are married.
Dual citizenship
Yemen doesn't recognise dual nationality.
If you're a dual citizen and enter Yemen using a non-Australian passport, you can only leave Yemen with the passport you used to enter.
If you're in Yemen, it may be difficult for us to provide you with emergency consular services.
Dual nationals may need to complete national service if they visit Yemen.
If you have any enquiry related to dual nationality, contact the nearest Embassy or Consulate of Yemen before you travel.
Dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
We advise against all travel to Yemen, including the island of Socotra.
Australians are required to obtain a visa before travelling to Yemen.
Some private tourist companies located outside Yemen may be offering tourist visas and flight packages to the Island of Socotra in Yemen. Ensure that you obtain a visa from the legitimate Yemeni Government. Please contact your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Yemen for details.
If you're trying to leave Yemen, check exit requirements with local immigration authorities before you book your ticket.
Contact your airline and/or travel agent for their schedules and how to purchase tickets. You may be charged administrative fees.
Flights could be delayed or cancelled at short notice. Check with your airline before travelling to the airport.
All land borders with countries neighbouring Yemen, seaports and airports may close at short or without prior notice. Check with local authorities before travelling to the border. Check our travel advice for Saudi Arabia and Oman , which share land borders with Yemen.
Regardless of the purpose and duration of stay, persons with known HIV infection are not allowed to enter Yemen.
Local authorities may detain and deport travellers for:
- carrying medication to treat HIV/AIDS or hepatitis
- testing positive for HIV/AIDS or hepatitis
You may be denied entry to Yemen if your passport has an Israeli visa, an Israeli border stamp, or an Egyptian or Jordanian border stamp issued by a border office with Israel.
Check with your airline for the latest information on the airline's own boarding requirements.
Other formalities
Women can be subject to strict family controls and may be stopped from leaving the country.
In Houthi-controlled areas, a decree has been issued that women, including female aid workers, may only travel if accompanied by a male guardian ('Mahram'). This includes women travelling between Houthi-controlled areas and when travelling outside Yemen via Sana’a International Airport. An exemption may be granted in limited circumstances.
A Yemeni husband may legally stop his wife from leaving the country, regardless of her nationality.
Children under 18 must have their father's permission to leave the country. It doesn't matter what the status of their parent's marriage is or who has custody.
Single parents or adults travelling alone with children may need documentation. You may need evidence of parental responsibility before you're allowed to leave the country with children.
Forced marriage and the marriage of girls under the age of eighteen is common in Yemen. Australian girls/women, including dual nationals who travel to Yemen, may become victims of forced marriage. Local authorities may not be in a position to provide protection or support to victims of forced marriage or women suffering from domestic violence and abuse.
Sharia (Islamic) courts have jurisdiction over custody cases involving Muslim parents. When custody disputes arise, and a custody case is before the local court, the local court may impose a travel ban on the child/children. In line with the Consular Services Charter , the Embassy of Australia cannot intervene in court proceedings and private and/or legal matters, including family and custody disputes. Seek advice from a competent local lawyer.
A travel ban can be imposed against individuals even without a court order. In this case, the Embassy of Australia cannot assist, as outlined in the Consular Services Charter .
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Authorities may not let you enter or exit Yemen if:
- you're travelling on an emergency passport
- the name and/or photo in your passport are different from how you present
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by Yemen. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of Yemen before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The local currency is the Yemeni Rial (YER).
Banking facilities are limited.
ATMs are rare outside Sana'a. It's difficult to exchange Australian dollars in Yemen. US dollars in cash is the most easily convertible currency. Exchange currency at official exchange stores only. You may need to use cash for most transactions in Yemen. Most places, including hotels and hospitals, do not accept payment via bank or credit cards.
Yemen has rules about the amount of currency you can bring in and take out. Currency limits can change. Check details with your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Yemen prior to your travel.
Local travel
If you travel to Yemen against our advice, you should regularly assess your security arrangements and carefully plan your movements. Security precautions and arrangements may not remove the security threat in Yemen. Many areas are sensitive from a security or territorial point of view. If you travel against our advice, you should:
- be proactive and remain alert to your surroundings at all times
- not travel alone within and between cities
- not draw attention to yourself and keep a low profile
- secure your belongings, and leave copies of important documents in a safe place or with your family
- carry as little currency as possible
- know who to call in an emergency
- keep your friends and family updated.
You may need permission from local authorities to travel outside Sana'a and some other cities.
Authorities may close access to certain areas without notice.
Petrol and diesel may be limited and unavailable sometimes without prior notice by local authorities.
Unexploded weapons and munitions, including landmines, are a major hazard. They're found in the central highlands and the western, southern and eastern regions, especially around Aden, Lahij, Ad Dali, Al Hudaydah, Al Jawf, Ma'rib, Shabwah and Ta'iz and in Sa'ada province.
Road travel
Travelling by road in conflict areas is dangerous. Don't consider it without expert local advice. Public transportation is insecure and unreliable. Access routes in and out of major cities may be blocked or closed. Roadblocks and checkpoints may be set up without warning. Driving standards are poor, and mountain roads are hazardous. There is a severe shortage of fuel.
Other potential risks may include landmines and unexploded ordnance from previous and ongoing conflicts, including in some rural areas and areas where there is conflict. Landmine locations may not be marked.
Avoid all road travel outside of the main cities at night.
If you plan to drive:
- check your insurance covers you
- learn local traffic rules and behaviour
- know what to do in case of an incident or accident
- follow the speed limits
- do not cross any red traffic lights
- always keep your car windows up and doors locked, even when moving
- stay alert, especially when driving at night
- remain alert as drivers may drive on the wrong side of the road and don’t follow traffic laws
Shared taxis are common in Yemen. Private taxis are also available in major cities and at airports. Negotiate taxi fares in advance. It may not be safe to use local taxis. Seek advice from local authorities and trusted contacts.
Boat travel
Do not travel to Yemen, including the island of Socotra, due to the security situation. There is extreme political and security instability.
Military operations are occurring in Yemen and the Red Sea in response to attacks by Houthi militants on ships transiting the Red Sea and surrounding waters, including the Gulf of Aden. If you travel to Yemen despite our advice, seek guidance from authorities before entering Yemeni waters or ports.
There are reports of sea mines planted in the southern Red Sea near ports and drifting sea mines near the border with Saudi Arabia.
Keep a safe distance from the FSO Safer supertanker, moored approximately 4.8 nautical miles off Yemen’s Red Sea coast near Hodeidah Port, which is at risk of exploding or sinking.
The security situation remains volatile. There's widespread disruption to air travel and other departure options.
The safety record of airlines in Yemen is not available. There is no data about how well local planes are maintained. This lack of transparency raises concerns about airline safety.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Emergencies
Emergency services may not be available or reliable. Don't rely on them.
Check with local authorities for the emergency contact numbers you may need in the city of your stay. Emergency contact operators may not speak English.
Depending on what you need, you should contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
The phone network is unreliable and limited outside of cities and large towns. Internet services are available but are poor and do not cover most areas of the country. Internet services are very unreliable on mobile networks.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
Australia doesn't have an embassy or consulate in Yemen, therefore the Australian government and Embassy in Riyadh are unable to provide emergency services to Australians in Yemen.
The ability of the Australian Government to provide consular help to Australians in Yemen is extremely limited.
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact the Embassy of Australia in Riyadh, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre in Australia on +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas or 1300 555 135 from Australia.
Embassy of Australia, Riyadh
Abdullah Bin Hozafa Al-Shami Avenue
Diplomatic Quarter
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Phone: +966 11 2500 900
Fax: +966 11 2500 902
Email: [email protected]
Website: saudiarabia.embassy.gov.au
X: @AusAmbKSA
Facebook: www.facebook.com/AusEmbKSA
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
The working week is Sunday to Thursday.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Yemen?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.

IMAGES
VIDEO