
KATHERINE TURNER, MD
Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(6):347-353
Related letter: Well-Child Visits Provide Physicians Opportunity to Deliver Interconception Care to Mothers
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
The well-child visit allows for comprehensive assessment of a child and the opportunity for further evaluation if abnormalities are detected. A complete history during the well-child visit includes information about birth history; prior screenings; diet; sleep; dental care; and medical, surgical, family, and social histories. A head-to-toe examination should be performed, including a review of growth. Immunizations should be reviewed and updated as appropriate. Screening for postpartum depression in mothers of infants up to six months of age is recommended. Based on expert opinion, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends developmental surveillance at each visit, with formal developmental screening at nine, 18, and 30 months and autism-specific screening at 18 and 24 months; the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found insufficient evidence to make a recommendation. Well-child visits provide the opportunity to answer parents' or caregivers' questions and to provide age-appropriate guidance. Car seats should remain rear facing until two years of age or until the height or weight limit for the seat is reached. Fluoride use, limiting or avoiding juice, and weaning to a cup by 12 months of age may improve dental health. A one-time vision screening between three and five years of age is recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force to detect amblyopia. The American Academy of Pediatrics guideline based on expert opinion recommends that screen time be avoided, with the exception of video chatting, in children younger than 18 months and limited to one hour per day for children two to five years of age. Cessation of breastfeeding before six months and transition to solid foods before six months are associated with childhood obesity. Juice and sugar-sweetened beverages should be avoided before one year of age and provided only in limited quantities for children older than one year.
Well-child visits for infants and young children (up to five years) provide opportunities for physicians to screen for medical problems (including psychosocial concerns), to provide anticipatory guidance, and to promote good health. The visits also allow the family physician to establish a relationship with the parents or caregivers. This article reviews the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines for screenings and recommendations for infants and young children. Family physicians should prioritize interventions with the strongest evidence for patient-oriented outcomes, such as immunizations, postpartum depression screening, and vision screening.

Clinical Examination
The history should include a brief review of birth history; prematurity can be associated with complex medical conditions. 1 Evaluate breastfed infants for any feeding problems, 2 and assess formula-fed infants for type and quantity of iron-fortified formula being given. 3 For children eating solid foods, feeding history should include everything the child eats and drinks. Sleep, urination, defecation, nutrition, dental care, and child safety should be reviewed. Medical, surgical, family, and social histories should be reviewed and updated. For newborns, review the results of all newborn screening tests ( Table 1 4 – 7 ) and schedule follow-up visits as necessary. 2
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
A comprehensive head-to-toe examination should be completed at each well-child visit. Interval growth should be reviewed by using appropriate age, sex, and gestational age growth charts for height, weight, head circumference, and body mass index if 24 months or older. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-recommended growth charts can be found at https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/who_charts.htm#The%20WHO%20Growth%20Charts . Percentiles and observations of changes along the chart's curve should be assessed at every visit. Include assessment of parent/caregiver-child interactions and potential signs of abuse such as bruises on uncommonly injured areas, burns, human bite marks, bruises on nonmobile infants, or multiple injuries at different healing stages. 8
The USPSTF and AAP screening recommendations are outlined in Table 2 . 3 , 9 – 27 A summary of AAP recommendations can be found at https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule.pdf . The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) generally adheres to USPSTF recommendations. 28
MATERNAL DEPRESSION
Prevalence of postpartum depression is around 12%, 22 and its presence can impair infant development. The USPSTF and AAP recommend using the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (available at https://www.aafp.org/afp/2010/1015/p926.html#afp20101015p926-f1 ) or the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (available at https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0115/p139.html#afp20120115p139-t3 ) to screen for maternal depression. The USPSTF does not specify a screening schedule; however, based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends screening mothers at the one-, two-, four-, and six-month well-child visits, with further evaluation for positive results. 23 There are no recommendations to screen other caregivers if the mother is not present at the well-child visit.
PSYCHOSOCIAL
With nearly one-half of children in the United States living at or near the poverty level, assessing home safety, food security, and access to safe drinking water can improve awareness of psychosocial problems, with referrals to appropriate agencies for those with positive results. 29 The prevalence of mental health disorders (i.e., primarily anxiety, depression, behavioral disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) in preschool-aged children is around 6%. 30 Risk factors for these disorders include having a lower socioeconomic status, being a member of an ethnic minority, and having a non–English-speaking parent or primary caregiver. 25 The USPSTF found insufficient evidence regarding screening for depression in children up to 11 years of age. 24 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends that physicians consider screening, although screening in young children has not been validated or standardized. 25
DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE
Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends early identification of developmental delays 14 and autism 10 ; however, the USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend formal developmental screening 13 or autism-specific screening 9 if the parents/caregivers or physician have no concerns. If physicians choose to screen, developmental surveillance of language, communication, gross and fine movements, social/emotional development, and cognitive/problem-solving skills should occur at each visit by eliciting parental or caregiver concerns, obtaining interval developmental history, and observing the child. Any area of concern should be evaluated with a formal developmental screening tool, such as Ages and Stages Questionnaire, Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status, Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status-Developmental Milestones, or Survey of Well-Being of Young Children. These tools can be found at https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/Screening/Pages/Screening-Tools.aspx . If results are abnormal, consider intervention or referral to early intervention services. The AAP recommends completing the previously mentioned formal screening tools at nine-, 18-, and 30-month well-child visits. 14
The AAP also recommends autism-specific screening at 18 and 24 months. 10 The USPSTF recommends using the two-step Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) screening tool (available at https://m-chat.org/ ) if a physician chooses to screen a patient for autism. 10 The M-CHAT can be incorporated into the electronic medical record, with the possibility of the parent or caregiver completing the questionnaire through the patient portal before the office visit.
IRON DEFICIENCY
Multiple reports have associated iron deficiency with impaired neurodevelopment. Therefore, it is essential to ensure adequate iron intake. Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends supplements for preterm infants beginning at one month of age and exclusively breastfed term infants at six months of age. 3 The USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend screening for iron deficiency in infants. 19 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends measuring a child's hemoglobin level at 12 months of age. 3
Lead poisoning and elevated lead blood levels are prevalent in young children. The AAP and CDC recommend a targeted screening approach. The AAP recommends screening for serum lead levels between six months and six years in high-risk children; high-risk children are identified by location-specific risk recommendations, enrollment in Medicaid, being foreign born, or personal screening. 21 The USPSTF does not recommend screening for lead poisoning in children at average risk who are asymptomatic. 20
The USPSTF recommends at least one vision screening to detect amblyopia between three and five years of age. Testing options include visual acuity, ocular alignment test, stereoacuity test, photoscreening, and autorefractors. The USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend screening before three years of age. 26 The AAP, American Academy of Ophthalmology, and the American Academy of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus recommend the use of an instrument-based screening (photoscreening or autorefractors) between 12 months and three years of age and annual visual acuity screening beginning at four years of age. 31
IMMUNIZATIONS
The AAFP recommends that all children be immunized. 32 Recommended vaccination schedules, endorsed by the AAP, the AAFP, and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, are found at https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/child-adolescent.html . Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season. Additional vaccinations may be necessary based on medical history. 33 Immunization history should be reviewed at each wellness visit.
Anticipatory Guidance
Injuries remain the leading cause of death among children, 34 and the AAP has made several recommendations to decrease the risk of injuries. 35 – 42 Appropriate use of child restraints minimizes morbidity and mortality associated with motor vehicle collisions. Infants need a rear-facing car safety seat until two years of age or until they reach the height or weight limit for the specific car seat. Children should then switch to a forward-facing car seat for as long as the seat allows, usually 65 to 80 lb (30 to 36 kg). 35 Children should never be unsupervised around cars, driveways, and streets. Young children should wear bicycle helmets while riding tricycles or bicycles. 37
Having functioning smoke detectors and an escape plan decreases the risk of fire- and smoke-related deaths. 36 Water heaters should be set to a maximum of 120°F (49°C) to prevent scald burns. 37 Infants and young children should be watched closely around any body of water, including water in bathtubs and toilets, to prevent drowning. Swimming pools and spas should be completely fenced with a self-closing, self-latching gate. 38
Infants should not be left alone on any high surface, and stairs should be secured by gates. 43 Infant walkers should be discouraged because they provide no benefit and they increase falls down stairs, even if stair gates are installed. 39 Window locks, screens, or limited-opening windows decrease injury and death from falling. 40 Parents or caregivers should also anchor furniture to a wall to prevent heavy pieces from toppling over. Firearms should be kept unloaded and locked. 41
Young children should be closely supervised at all times. Small objects are a choking hazard, especially for children younger than three years. Latex balloons, round objects, and food can cause life-threatening airway obstruction. 42 Long strings and cords can strangle children. 37
DENTAL CARE
Infants should never have a bottle in bed, and babies should be weaned to a cup by 12 months of age. 44 Juices should be avoided in infants younger than 12 months. 45 Fluoride use inhibits tooth demineralization and bacterial enzymes and also enhances remineralization. 11 The AAP and USPSTF recommend fluoride supplementation and the application of fluoride varnish for teeth if the water supply is insufficient. 11 , 12 Begin brushing teeth at tooth eruption with parents or caregivers supervising brushing until mastery. Children should visit a dentist regularly, and an assessment of dental health should occur at well-child visits. 44
SCREEN TIME
Hands-on exploration of their environment is essential to development in children younger than two years. Video chatting is acceptable for children younger than 18 months; otherwise digital media should be avoided. Parents and caregivers may use educational programs and applications with children 18 to 24 months of age. If screen time is used for children two to five years of age, the AAP recommends a maximum of one hour per day that occurs at least one hour before bedtime. Longer usage can cause sleep problems and increases the risk of obesity and social-emotional delays. 46
To decrease the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), the AAP recommends that infants sleep on their backs on a firm mattress for the first year of life with no blankets or other soft objects in the crib. 45 Breastfeeding, pacifier use, and room sharing without bed sharing protect against SIDS; infant exposure to tobacco, alcohol, drugs, and sleeping in bed with parents or caregivers increases the risk of SIDS. 47
DIET AND ACTIVITY
The USPSTF, AAFP, and AAP all recommend breastfeeding until at least six months of age and ideally for the first 12 months. 48 Vitamin D 400 IU supplementation for the first year of life in exclusively breastfed infants is recommended to prevent vitamin D deficiency and rickets. 49 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends the introduction of certain foods at specific ages. Early transition to solid foods before six months is associated with higher consumption of fatty and sugary foods 50 and an increased risk of atopic disease. 51 Delayed transition to cow's milk until 12 months of age decreases the incidence of iron deficiency. 52 Introduction of highly allergenic foods, such as peanut-based foods and eggs, before one year decreases the likelihood that a child will develop food allergies. 53
With approximately 17% of children being obese, many strategies for obesity prevention have been proposed. 54 The USPSTF does not have a recommendation for screening or interventions to prevent obesity in children younger than six years. 54 The AAP has made several recommendations based on expert opinion to prevent obesity. Cessation of breastfeeding before six months and introduction of solid foods before six months are associated with childhood obesity and are not recommended. 55 Drinking juice should be avoided before one year of age, and, if given to older children, only 100% fruit juice should be provided in limited quantities: 4 ounces per day from one to three years of age and 4 to 6 ounces per day from four to six years of age. Intake of other sugar-sweetened beverages should be discouraged to help prevent obesity. 45 The AAFP and AAP recommend that children participate in at least 60 minutes of active free play per day. 55 , 56
Data Sources: Literature search was performed using the USPSTF published recommendations ( https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/BrowseRec/Index/browse-recommendations ) and the AAP Periodicity table ( https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule.pdf ). PubMed searches were completed using the key terms pediatric, obesity prevention, and allergy prevention with search limits of infant less than 23 months or pediatric less than 18 years. The searches included systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, and position statements. Essential Evidence Plus was also reviewed. Search dates: May through October 2017.
Gauer RL, Burket J, Horowitz E. Common questions about outpatient care of premature infants. Am Fam Physician. 2014;90(4):244-251.
American Academy of Pediatrics; Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Hospital stay for healthy term newborns. Pediatrics. 2010;125(2):405-409.
Baker RD, Greer FR Committee on Nutrition, American Academy of Pediatrics. Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children (0–3 years of age). Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):1040-1050.
Mahle WT, Martin GR, Beekman RH, Morrow WR Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery Executive Committee. Endorsement of Health and Human Services recommendation for pulse oximetry screening for critical congenital heart disease. Pediatrics. 2012;129(1):190-192.
American Academy of Pediatrics Newborn Screening Authoring Committee. Newborn screening expands: recommendations for pediatricians and medical homes—implications for the system. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):192-217.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):898-921.
Maisels MJ, Bhutani VK, Bogen D, Newman TB, Stark AR, Watchko JF. Hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant > or = 35 weeks' gestation: an update with clarifications. Pediatrics. 2009;124(4):1193-1198.
Christian CW Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect, American Academy of Pediatrics. The evaluation of suspected child physical abuse [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2015;136(3):583]. Pediatrics. 2015;135(5):e1337-e1354.
Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for autism spectrum disorder in young children: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;315(7):691-696.
Johnson CP, Myers SM American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Children with Disabilities. Identification and evaluation of children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics. 2007;120(5):1183-1215.
Moyer VA. Prevention of dental caries in children from birth through age 5 years: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1102-1111.
Clark MB, Slayton RL American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Oral Health. Fluoride use in caries prevention in the primary care setting. Pediatrics. 2014;134(3):626-633.
Siu AL. Screening for speech and language delay and disorders in children aged 5 years and younger: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2015;136(2):e474-e481.
Council on Children with Disabilities, Section on Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics, Bright Futures Steering Committee, Medical Home Initiatives for Children with Special Needs Project Advisory Committee. Identifying infants and young children with developmental disorders in the medical home: an algorithm for developmental surveillance and screening [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2006;118(4):1808–1809]. Pediatrics. 2006;118(1):405-420.
Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ, et al. Screening for lipid disorders in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;316(6):625-633.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents. October 2012. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/peds_guidelines_full.pdf . Accessed May 9, 2018.
Moyer VA. Screening for primary hypertension in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(9):613-619.
Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, et al. Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2017;140(6):e20173035]. Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e20171904.
Siu AL. Screening for iron deficiency anemia in young children: USPSTF recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2015;136(4):746-752.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for elevated blood lead levels in children and pregnant women. Pediatrics. 2006;118(6):2514-2518.
Screening Young Children for Lead Poisoning: Guidance for State and Local Public Health Officials . Atlanta, Ga.: U.S. Public Health Service; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; National Center for Environmental Health; 1997.
O'Connor E, Rossom RC, Henninger M, Groom HC, Burda BU. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and post-partum women: evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(4):388-406.
Earls MF Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health, American Academy of Pediatrics. Incorporating recognition and management of perinatal and postpartum depression into pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):1032-1039.
Siu AL. Screening for depression in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(5):360-366.
Weitzman C, Wegner L American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Council on Early Childhood; Society for Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; American Academy of Pediatrics. Promoting optimal development: screening for behavioral and emotional problems [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2015;135(5):946]. Pediatrics. 2015;135(2):384-395.
Grossman DC, Curry SJ, Owens DK, et al. Vision screening in children aged 6 months to 5 years: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;318(9):836-844.
Donahue SP, Nixon CN Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on Ophthalmology, American Academy of Pediatrics; American Association of Certified Orthoptists, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Visual system assessment in infants, children, and young adults by pediatricians. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1):28-30.
Lin KW. What to do at well-child visits: the AAFP's perspective. Am Fam Physician. 2015;91(6):362-364.
American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Community Pediatrics. Poverty and child health in the United States. Pediatrics. 2016;137(4):e20160339.
Lavigne JV, Lebailly SA, Hopkins J, Gouze KR, Binns HJ. The prevalence of ADHD, ODD, depression, and anxiety in a community sample of 4-year-olds. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2009;38(3):315-328.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on Ophthalmology, American Association of Certified Orthoptists, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Visual system assessment of infants, children, and young adults by pediatricians. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1):28-30.
American Academy of Family Physicians. Clinical preventive service recommendation. Immunizations. http://www.aafp.org/patient-care/clinical-recommendations/all/immunizations.html . Accessed October 5, 2017.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents aged 18 years or younger, United States, 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/child-adolescent.html . Accessed May 9, 2018.
National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. 10 leading causes of death by age group, United States—2015. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/images/lc-charts/leading_causes_of_death_age_group_2015_1050w740h.gif . Accessed April 24, 2017.
Durbin DR American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Child passenger safety. Pediatrics. 2011;127(4):788-793.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Reducing the number of deaths and injuries from residential fires. Pediatrics. 2000;105(6):1355-1357.
Gardner HG American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Office-based counseling for unintentional injury prevention. Pediatrics. 2007;119(1):202-206.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Prevention of drowning in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2003;112(2):437-439.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Injuries associated with infant walkers. Pediatrics. 2001;108(3):790-792.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Falls from heights: windows, roofs, and balconies. Pediatrics. 2001;107(5):1188-1191.
Dowd MD, Sege RD Council on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention Executive Committee; American Academy of Pediatrics. Firearm-related injuries affecting the pediatric population. Pediatrics. 2012;130(5):e1416-e1423.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Prevention of choking among children. Pediatrics. 2010;125(3):601-607.
Kendrick D, Young B, Mason-Jones AJ, et al. Home safety education and provision of safety equipment for injury prevention (review). Evid Based Child Health. 2013;8(3):761-939.
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Oral Health. Maintaining and improving the oral health of young children. Pediatrics. 2014;134(6):1224-1229.
Heyman MB, Abrams SA American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. Fruit juice in infants, children, and adolescents: current recommendations. Pediatrics. 2017;139(6):e20170967.
Council on Communications and Media. Media and young minds. Pediatrics. 2016;138(5):e20162591.
Moon RY Task Force on Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths: evidence base for 2016 updated recommendations for a safe infant sleeping environment. Pediatrics. 2016;138(5):e20162940.
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841.
Wagner CL, Greer FR American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding; Committee on Nutrition. Prevention of rickets and vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2009;123(1):197]. Pediatrics. 2008;122(5):1142-1152.
Huh SY, Rifas-Shiman SL, Taveras EM, Oken E, Gillman MW. Timing of solid food introduction and risk of obesity in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics. 2011;127(3):e544-e551.
Greer FR, Sicherer SH, Burks AW American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition; Section on Allergy and Immunology. Effects of early nutritional interventions on the development of atopic disease in infants and children: the role of maternal dietary restriction, breastfeeding, timing of introduction of complementary foods, and hydrolyzed formulas. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):183-191.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. The use of whole cow's milk in infancy. Pediatrics. 1992;89(6 pt 1):1105-1109.
Fleischer DM, Spergel JM, Assa'ad AH, Pongracic JA. Primary prevention of allergic disease through nutritional interventions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2013;1(1):29-36.
Grossman DC, Bibbins-Domingo K, Curry SJ, et al. Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;317(23):2417-2426.
Daniels SR, Hassink SG Committee on Nutrition. The role of the pediatrician in primary prevention of obesity. Pediatrics. 2015;136(1):e275-e292.
American Academy of Family Physicians. Physical activity in children. https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/physical-activity.html . Accessed January 1, 2018.
Continue Reading

More in AFP
More in pubmed.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. See permissions for copyright questions and/or permission requests.
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved.
Your Child’s Well Visit: What Parents Need to Know

In the world of pediatric care, a well visit is the equivalent of what used to be called a check-up or a physical. Once a year, parents typically make an appointment for a well visit with their family physician or pediatrician to make sure all’s well with their child and to voice any concerns. For children 3 and under, though, visits are as frequent as every few weeks in the newborn period to every 2 to 6 months. Well visits are a must for infants, toddlers, school-age children and teens alike.
Understandably, parents tend to have plenty of questions about what’s involved in a well visit : how to prepare for it, what to bring and what to expect once you get called into the doctor’s office. Let’s review all your FAQs in detail with Weill Cornell Medicine pediatrician Dr. Corey Wasserman as your guide.
What is generally included in a well visit?
Depending on your child’s age, a well visit may include immunizations, a complete physical examination, a review of your child’s medical history and a conversation regarding any concerns. The visit will typically take from 15 to 30 minutes.
“We can actually accomplish a great deal during that 15 minutes, Dr. Wasserman says. “Mainly, the idea is to check on your child’s vital signs and developmental milestones, and to listen to any concerns you may have. Most of the time, your children are indeed well, not sick, so we start out with that assumption. And if there is reason for concern, you can follow up with a separate appointment to investigate what may be happening with your child’s health.”
How should I prepare for my child’s well visit?
First, check in via Connect up to 5 days before your child’s visit to make sure we have your most up-to-date information, including your pharmacy and insurance , along with a list of your child’s medications , if any . Y ou can also review and update your responses to your health questionnaire.
When it comes to blood work and other medical r ecords, instead of uploading them to Connect , it may be preferable to email them to the Medical Records Department at [email protected] .
On the day of your appointment, please arrive 10 minutes before your scheduled time, which will allow you t o complete and submit any additional forms beforehand.
As a matter of policy, we require at least one parent or guardian to be present for the duration of the well visit. That will facilitate the best possible communication between provider and parent and allow us to secure your permission for any necessary immunizations.
If you can’t be present, you’ll need to reschedule the appointment.
What should I bring?
Please b ring :
- Your insurance card and ID
- School or camp forms as needed
- Records of medical visits elsewhere (with a different provider or institution), if you weren’t able to submit these electronically
“ Keep in mind that your doctor may not be able to fill out school or camp forms on the day of your appointment . If they have the time to complete the form during your visit, they will do so. But it’s just as likely that the information from your child’s well visit will be entered afterwards and sent to you at a later date ,” Dr. Wasserman says.
What, exactly, will take place during the visit?
Your doctor will:
- Review your child’s height, weight, and BMI (body mass index).
- Check your child’s blood pressure, heart rate and breathing.
- Perform a head-to-toe physical exam.
- Administer any needed immunizations.
- Address your concerns and offer advice regarding your child’s growth and development.
Additionally, your doctor will assess your child based on their age.
At an infant well visit, your doctor will:
- Look for developmental milestones.
- Measure your baby’s weight, length and head circumference.
- Look at her ears, eyes, mouth and skin.
- Press on his belly to detect any problems.
- Inspect your baby’s genitals for tenderness, lumps or other signs of infection.
If your child is a toddler , your doctor will also:
- Conduct a vision and hearing check.
- Ask questions to get a sense of your child’s mental, emotional and social development.
During a school-age well check , your doctor will ask questions about the following:
- Behavioral changes, if any
- Physical activity
- Sleeping habits
- Motor, language and problem-solving skills
During a teen well visit , your doctor— optimally, someone your teenager feels comfortable with—will :
- Look for indications of alcohol, tobacco or drug use, as well as anxiety or depression.
- Discuss your teenager’s sexual health and provide guidance on birth control, the risk of contracting an STI (sexually transmitted infection) and other pertinent issues.
What if I need to ask the doctor about a specific medical issue?
Specific issues are considered part of a follow up or “sick” visit. These will be billed to your insurance, and you may be responsible for copayments, coinsurance or deductible payments, based on the terms of your policy.
If you’d like to address non-routine concerns during your child’s annual well visit, let your doctor ’s office know about these issues when you schedule your appointment. Depending on their complexity, your doctor may need to deal with them at a later time.
What does a follow-up or “sick” visit entail?
- Any new problems or complaints
- Your child’s need for new medications or tests
- Referrals to a specialist
- Additional treatment options for an already-existing condition
Can I combine my child’s well visit with a non-routine or sick office visit?
Combining your child’s well visit with a non-routine office visit will save you time by eliminating an extra appointment, but doing so may affect your costs. Your doctor will bill your visit based on the reason you originally gave for scheduling the appointment, plus the specific issues you raised during the appointment. Anything more than a check-up may result in unplanned out-of-pocket costs to you. For these reasons, we recommend that you schedule your child’s annual well visit and any follow-up or sick office visits separately.
The most i mportant points to remember
- When scheduling your child’s well visit, clearly state the purpose of the visit.
- A parent or guardian must accompany all patients under 18 to their well visit.
- Arrive 10 minutes before your appointment time.
- Bring all relevant information and documentation, including any forms you need filled out.
- The well visit will take 15 minutes.
- Review your insurance plan’s summary of benefits to clarify what will and won’t be covered during your child’s well visit.
To make an appointment with a pediatrician at Weill Cornell Medicine, go to https://weillcornell.org/services/pediatrics
Related Links
Back to News
In This Article
Clinical service.
Internet Explorer Alert
It appears you are using Internet Explorer as your web browser. Please note, Internet Explorer is no longer up-to-date and can cause problems in how this website functions This site functions best using the latest versions of any of the following browsers: Edge, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, or Safari . You can find the latest versions of these browsers at https://browsehappy.com
- Publications
- HealthyChildren.org
Shopping cart
Order Subtotal
Your cart is empty.
Looks like you haven't added anything to your cart.
- Career Resources
- Philanthropy
- About the AAP
- The Role of the Pediatrician in the Promotion of Healthy, Active Living
- How Can You Support Patients in Healthy, Active Living? Check Out Updated Report
- Helping Kids Build Healthy Active Lives: AAP Policy Explained
- Climate Change & Children’s Health: AAP Policy Explained
- News Releases
- Policy Collections
- The State of Children in 2020
- Healthy Children
- Secure Families
- Strong Communities
- A Leading Nation for Youth
- Transition Plan: Advancing Child Health in the Biden-Harris Administration
- Health Care Access & Coverage
- Immigrant Child Health
- Gun Violence Prevention
- Tobacco & E-Cigarettes
- Child Nutrition
- Assault Weapons Bans
- Childhood Immunizations
- E-Cigarette and Tobacco Products
- Children’s Health Care Coverage Fact Sheets
- Opioid Fact Sheets
- Advocacy Training Modules
- Subspecialty Advocacy Report
- AAP Washington Office Internship
- Online Courses
- Live and Virtual Activities
- National Conference and Exhibition
- Prep®- Pediatric Review and Education Programs
- Journals and Publications
- NRP LMS Login
- Patient Care
- Practice Management
- AAP Committees
- AAP Councils
- AAP Sections
- Volunteer Network
- Join a Chapter
- Chapter Websites
- Chapter Executive Directors
- District Map
- Create Account

- Materials & Tools
- Clinical Practice
- States & Communities
- Quality Improvement
- Implementation Stories
Well-Child Visits: Parent and Patient Education
The Bright Futures Parent and Patient Educational Handouts help guide anticipatory guidance and reinforce key messages (organized around the 5 priorities in each visit) for the family. Each educational handout is written in plain language to ensure the information is clear, concise, relevant, and easy to understand. Each educational handout is available in English and Spanish (in HTML and PDF format). Beginning at the 7 year visit , there is both a Parent and Patient education handout (in English and Spanish).
For the Bright Futures Parent Handouts for well-child visits up to 2 years of age , translations of 12 additional languages (PDF format) are made possible thanks to the generous support of members, staff, and businesses who donate to the AAP Friends of Children Fund . The 12 additional languages are Arabic, Bengali, Chinese, French, Haitian Creole, Hmong, Korean, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Somali, and Vietnamese.
Reminder for Health Care Professionals: The Bright Futures Tool and Resource Kit, 2nd Edition is available as an online access product. For more detailed information about the Toolkit, visit shop.aap.org . To license the Toolkit to use the forms in practice and/or incorporate them into an Electronic Medical Record System, please contact AAP Sales .
Parent Educational Handouts
Infancy visits.

3 to 5 Day Visit

1 Month Visit

2 Month Visit
4 Month Visit

6 Month Visit

9 Month Visit
Early childhood visits.

12 Month Visit

15 Month Visit
18 Month Visit

2 Year Visit

2.5 Year Visit

3 Year Visit

4 Year Visit
Parent and patient educational handouts, middle childhood visits.

5-6 Year Visit

7-8 Year Visit

7-8 Year Visit - For Patients

9-10 Year Visit

9-10 Year Visit - For Patients
Adolescent visits.

11-14 Year Visit

11-14 Year Visit - For Patients

15-17 Year Visit

15-17 Year Visit - For Patients

18-21 Year Visit - For Patients
Last updated.
American Academy of Pediatrics
Skip to content
Why Well-Child Visits Matter
Published on May 02, 2023
Primary Care Locations
Don't fall behind on your child's routine care — a minor issue today could become a major problem tomorrow.

Well-child visits allow your pediatrician to examine your child holistically, assess their physical and emotional needs, support their growth and development, and intervene quickly if any issues arise.
What are the risks of skipping well-child visits?
If your child is healthy, it can be easy to let well visits fall by the wayside. While those annual checkups may seem like just another thing to fit into your family’s hectic schedule, they play a crucial role in preventing future problems.
Find a CHOP Pediatrician
CHOP Primary Care practices, located throughout southeastern Pennsylvania and Southern New Jersey, provide convenient access to primary health and wellness services for children close to home.
Well visits are essential to ensure your child gets the required vaccinations to attend school, go to daycare and participate in sports. Visiting the pediatrician when your child is well also provides you with an opportunity to ask questions – and get expert answers – about your child’s health, development and well-being. Delaying these visits can put your child at greater risk of illness or delay needed interventions. For example, many common developmental delays are discovered during routine checkups with pediatricians – early intervention makes a big difference in getting your child the support they need before something small turns into a bigger issue.
What to expect at a well-child visit
During an annual wellness visit, your child's pediatrician will:
- Determine if your child is meeting growth and developmental milestones for their age.
- Evaluate your child's vision and hearing for anything out of the ordinary – it's important to catch these issues early.
- Ask about sudden changes in your child's usual activities, mood and overall health.
- Assess your child's mental health, and ask questions about how they are coping with school, friends, family and any other outside influences.
- Provide immunizations for childhood diseases and common conditions that affect children or young adults, such as measles and HPV.
- Give sports physicals to children who want to want to participate in competitive sports at school or in the community.
- Get to know your child: their diet, sleeping patterns, nutrition, social interactions, behavior and stress levels
- Help your child establish healthy habits and provide tips for families to reinforce these at home.
- Provide age- and behavior-based counseling for teens on topics such as driver safety, depression and drug or alcohol use.
- Check in on how your family is doing and identify any supportive resources or advice related to navigating daily life.
What are the ages for well-child visits?
A standard well-child visit schedule spans from infancy through adolescence, and includes checkups at the following ages:
- In your baby’s first year: Newborn visit (3-5 days after birth), at 1 month old, 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 9 months, and at 12 months
- 11-14 years
- 15-17 years
- 18-21 years
Your pediatrician can be a trusted partner at every age and stage of your child’s development.
Contributed by: Lisa Biggs, MD
Stay in Touch
Are you looking for advice to keep your child healthy and happy? Do you have questions about common childhood illnesses and injuries? Subscribe to our Health Tips newsletter to receive health and wellness tips from the pediatric experts at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, straight to your inbox. Read some recent tips .

With our patient portal you can schedule appointments, access records, see test results, ask your care provider questions, and more.

Subscribe to Health Tips
Subscribe to our Health Tips enewsletter to receive health and wellness tips from the pediatric experts at CHOP.
You Might Also Like

A Dose of Prevention
Learn why vaccinations are important for kids and the community, and what to do if you missed a vaccine and need to get back on track.
Preparing for an Annual Well Visit
Being properly prepared for annual well visits is a great way to get the most out of each appointment with your pediatrician.
How to Have a Productive Video Visit
If your child is scheduled for an online doctor’s appointment, read these tips to get the most out of your visit.
- Family Resources
- Provider Info

Welcome to the Well Visit Planner ®
Your child, your well visit.
A quick and free pre-visit planning tool to focus care on your unique needs and goals.
Get started now: Covers all 15 age-specific well visits from your child’s first week of life to age 6
Learn more about creating a family account
Take about 10 minutes to get a personalized Well Visit Guide. Get the best care focused on your child and family’s unique goals and needs.
Do you want to use the WVP with the children and families you serve?
Learn more here!
What is a Well Visit?: Well visits are regular check-ups with your child’s personal doctor, nurse, or other child health professional. At least 15 visits are recommended in the first six years of life when children are growing rapidly. Be sure to stay on track with well visits to help your child and family thrive.
What families like about using the Well Visit Planner (WVP):
- Saves time filling out forms during visits
- Gives you a personalized Well Visit Guide with results specific to your child and family
- Provides easy to read resources on your needs and priorities
- Helps you and your child’s providers focus care on your goals and needs
- Builds confidence that your child’s care meets expert guidelines
- You choose what sections to complete and share.
Three Easy Steps for Using the Well Visit Planner
The Well Visit Planner was created to be used in partnership with your provider. If you have a unique code from your provider, enter it here now:
Enter provider ID code
If you do not have a provider ID code, please continue:
If you already have a family account, login here.
Plan ahead for well visits for all your children up to age 6
Store, save and send your personalized Well Visit Guides at any time
Pause and return to complete WVP sessions within one week
Access and review educational resources specific to your priorities, needs and goals
Please note that using the Well Visit Planner as a guest and without a “provider ID code” means you must download, save and share your Well Visit Guide each time you use the WVP . Your data and Well Visit Guides will NOT be saved for future review.
Important Note: Without a provider ID code you need to share your Well Visit Guide with your child’s provider(s) yourself.
Your personalized Well Visit Guide summarizes your priorities and needs based on the information you shared in the Well Visit Planner. The guide provides resources about your priorities and gives you example questions to help you discuss your priorities with your child’s provider. Consider these four ways to share your Well Visit Guide with your child’s provider(s).

Save & print

Save to your phone or mobile device

Upload your Well Visit Guide to your Patient Portal

Email your Well Visit Guide to your child's provider
- Sign up for a free family account HERE to save, access, review and share your Well Visit Guides at any time.
- Do you want your Well Visit Guide to be automatically shared with your child's provider(s)? Learn more HERE .
Your Data: The Well Visit Planner is operated on a fully secure platform and your data is not shared with anyone except you and, if you agree, your child’s provider or care team.
What our families are saying!
“It’s helpful to know ahead of time what areas my provider will be checking. It also helps you to get an understanding of the milestones that you want to look out for in your child’s development. The idea that my provider can see what my concerns are before my visit is nice. Best case scenario, they would use the information to bring resources to the start of the visit rather than having to gather them during or after the visit.” (Parent)
“I would recommend the WVP, since it a tool that helps organize and prioritize the medical needs of our children. We can share concerns and our provider can get to know them beforehand. The WVP is a good medical attention guide.” [Parent, translated from Spanish]
“As a mother, I would recommend the use of the Well Visit Planner since it is a tool that can help us be organized with everything we'd like to discuss with the doctors. Also, it gives an overview of the visit.” [Parent, translated from Spanish]
“I really like the WVP, and I believe that it is a really resourceful tool to provide more communication between the provider and families. It is also a great tool to have important information to reference that is specific to the child’s growth and development.” (Parent)

Well Visit Planner: Before Getting Started
Please review and scroll to the bottom before agreeing to the voluntary consent.
VOLUNTARY CONSENT FORM
The purpose of the tool, the Well Visit Planner (WVP), is to enable parents to optimize visit time by focusing on priorities, concerns, and other issues specific to the child and family. The WVP asks parents about their child and family and the kind of topics they want to discuss at their child’s well-child visit. The health care provider can use this information to customize the visit to the needs of the parent and child. Additionally, the tool provides educational information about potential discussion topics based on national recommendations for health care providers.
To use this tool, complete the online Well Visit Planner which should take you about 10 minutes. You will be asked to do the following:
- Agree to the WVP Terms and Conditions.
- You will be asked to voluntarily consent to allow the Child and Adolescent Health Measurement Initiative to mine the de-identified information that you provide in order to analyze and improve the WVP tool.
- Provide basic information about your child who has the upcoming well-child visit.
- Answer a series of questions about your child and family that will help you and your child's health care provider know what they may need to focus on during the visit.
- Pick the topics that you want your child's doctor to address and give you information about at the upcoming visit.
- Receive a "Visit Guide" that you may use at your child's well-visit. This guide highlights the topics you may want to discuss and should be brought to the visit.
- You have the option of creating your own account on the WVP. You can use your account to plan future visits, complete unfinished WVP visits, add other eligible children, and review previous Visit Guides and educational information.
Although we have made every effort to protect your identity, there is a minimal risk of loss of confidentiality. Additionally, you may find that some questions or topics cause you emotional discomfort. You may choose not to answer some of the questions. The choice is up to you.
You may or may not benefit from using the online Well Visit Planner. However, by completing the online tool, you may improve your child's well-visit and you may receive useful information in partnering with your child's health care provider. Additionally, the answers you provide may help your child's health care provider understand your child and family health so that they can better provide well-child care for you. Finally, your participation may help us learn how to benefit parents and children in the future by providing information to health care providers that will help them improve well-child visits.
Confidentiality
We implement a variety of security measures to maintain the safety of your personal information when you enter or submit answers. We offer the use of a secure server. All supplied sensitive information is housed in our database which is protected through a secure dedicated port which only allows data entry from the tool to our database. The database is protected by having a closed-off port for the SQL Server installation. Only authorized personnel with special access rights to our systems are given access to the data. We are required to keep the information confidential.
The WVP does not collect protected health information or information that can lead to the identification of you or your child. You are asked to provide only two pieces of personally identifiable information: child’s first name (optional) and date of birth. These are not stored in our database. The child’s first name is displayed on the Visit Guide. The date of birth is used to calculate the appropriate upcoming well-visit and present the age-specific questions. That visit (e.g. 4 month or 6 month) is stored in our database rather than the date of birth. If you choose to create an account on the WVP, you have the option to add your child’s first name or nickname to appear on the family dashboard and Visit Guide. This name will be saved on our secure servers.
The email address that you use for registering an account will not be shared with any third parties, nor will your email address be sold or used for purposes other than sharing educational resources or sending updates about the Well Visit Planner. You can unsubscribe if you wish to stop receiving emails from us by sending us an email on [email protected] .
In addition, identifying information connected to your computer (IP address) will not be recorded by the CAHMI at any time. If you choose to download or print your Visit Guide, CAHMI will not be liable for any actions related to your choice to disseminate, distribute or copy the Visit Guide with the name(s) of your child(ren) or any other information contained in the guide.
The Well Visit Planner will store the de-identified information that you provide about your child's health, development, and home environment; along with the priorities you select on a secure server. It will not be possible to link this anonymous information to you or your child. We will use this anonymous information to understand parents' concerns and priorities for their well-child visits. This information may also be combined with other parents’ responses and shared with your child’s provider to help them learn more about families they provide care to and improve well-child care for children and their families.
Access and use the Well Visit Planner is free.
You do not have to use the Well Visit Planner. If you do elect to use the Well Visit Planner, and later change your mind, you may discontinue use at any time. If you do not complete the WVP, there will be no penalty or loss of any benefits to which you are otherwise entitled.
If you have any questions, you may contact us at [email protected]
Your provider ID code
If your child’s provider has invited you to use their tailored Well Visit Planner, you can enter their ID code below. This ID code is also the text included after “/” in the WVP URL that your child’s provider shared (i.e. www.wellvisitplanner.org/ providerIDcode ).
Your Customized Well Visit Planner
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Phasellus ut urna ultricies, eleifend tortor ac, sollicitudin tortor. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia curae; Nunc convallis mi sed consequat tempor. Praesent rhoncus nibh tellus, in sodales neque pellentesque eu
Well Visit Planner: Voluntary Consent
Your privacy is important to us. Please review our terms and conditions , and consent form , check each box below and click the Continue button below.
Session Warning!
Session expired.

Personalize Your Experience
Log in or create an account for a personalized experience based on your selected interests.
Already have an account? Log In
Free standard shipping is valid on orders of $45 or more (after promotions and discounts are applied, regular shipping rates do not qualify as part of the $45 or more) shipped to US addresses only. Not valid on previous purchases or when combined with any other promotional offers.
Register for an enhanced, personalized experience.
Receive free access to exclusive content, a personalized homepage based on your interests, and a weekly newsletter with topics of your choice.
Home / Parenting, Kids & Teens / Quick guide to your infant’s first pediatrician visits
Quick guide to your infant’s first pediatrician visits
Please login to bookmark.

Frequent checkups with a health care provider are an important part of your baby’s first few years. These checkups — often called well-child visits — are a way for you and your child’s health care provider to keep tabs on your child’s health and development, as well as spot any potential problems. Well-child visits also give you a chance to discuss any questions or concerns you might have and get advice from a trusted source on how to provide the best possible care for your child.
The benefit of seeing your child’s provider regularly is that each visit adds critical information to your child’s health history. Over time, you and the provider will get a good idea of your child’s overall health and development.
In general, the provider will be more attentive to your child’s pattern of growth over time, rather than to specific one-time measurements. Typically what you’ll see is a smooth curve that arcs upward as the years go by. Regularly reviewing your child’s growth chart can also alert you and the provider to unexpected delays in growth or changes in weight that may suggest the need for additional monitoring.
Each health care provider does things a bit differently, but here’s what will generally be on the agenda during your first well-child exams.
Body measurements
Checkups usually begin with measurements. During first-year visits, a nurse or your baby’s health care provider will measure and record your baby’s length, head circumference and weight.
Your child’s measurements will be plotted on his or her growth chart. This will help you and the provider see how your child’s size compares with that of other children the same age. Try not to fixate on the percentages too much, though. All kids grow and develop at different rates. In addition, babies who take breast milk gain weight at a different rate than do babies who are formula-fed.
Keep in mind that a child who’s in the 95th percentile for height and weight isn’t necessarily healthier than a child who’s in the fifth percentile. What’s most important is steady growth from one visit to the next. If you have questions or concerns about your child’s growth rate, discuss them with your child’s provider.
Physical exam
Your child’s health care provider will give your child a thorough physical exam and check his or her reflexes and muscle tone. Be sure to mention any concerns you have or specific areas you want the doctor to check out.
Here are the basics of what providers commonly check for during an exam:
- Head — In the beginning, your child’s health care provider will likely check the soft spots (fontanels) on your baby’s head. These gaps between the skull bones give your baby’s brain plenty of room to grow in the coming months. They’re safe to touch and typically disappear within two years, when the skull bones fuse together. The health care provider may also check baby’s head for flat spots. A baby’s skull is soft and made up of several movable plates. If his or her head is left in the same position for long periods of time, the skull plates might move in a way that creates a flat spot.
- Ears — Using an instrument called an otoscope, the health care provider can see in your child’s ears to check for fluid or infection in the ears. The provider may observe your child’s response to various sounds, including your voice. Be sure to tell the provider if you have any concerns about your son’s or daughter’s ability to hear or if there’s a history of childhood deafness in your family. Unless there’s cause for concern, a formal hearing evaluation isn’t usually needed at a well-child exam.
- Eyes — Your child’s health care provider may use a flashlight to catch your child’s attention and then track his or her eye movements. The provider may also check for blocked tear ducts and eye discharge and look inside your child’s eyes with a lighted instrument called an ophthalmoscope. Be sure to tell the provider if you’ve noticed that your child is having any unusual eye movements, especially if they continue beyond the first few months of life.
- Mouth — A look inside your baby’s mouth may reveal signs of oral thrush, a common, and easily treated, yeast infection. The health care provider might also check your baby’s mouth for signs of tongue-tie (ankyloglossia), a condition that affects the tongue’s range of motion and can interfere with a baby’s oral development as well as his or her ability to breast-feed.
- Skin — Various skin conditions may be identified during the exam, including birthmarks, rashes, and jaundice, a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes. Mild jaundice that develops soon after birth often disappears on its own within a week or two. Cases that are more severe may need treatment.
- Heart and lungs — Using a stethoscope, your child’s health care provider can listen to your child’s heart and lungs to check for abnormal heart sounds or rhythms or breathing difficulties.
- Abdomen, hips and legs — By gently pressing a child’s abdomen, a health care provider can detect tenderness, enlarged organs, or an umbilical hernia, which occurs when a bit of intestine or fatty tissue near the navel breaks through the muscular wall of the abdomen. Most umbilical hernias heal by the toddler years without intervention. The provider may also move your child’s legs to check for dislocation or other problems with the hip joints, such as dysplasia of the hip joint.
- Genitalia — Your child’s care provider will likely inspect your son’s or daughter’s genitalia for tenderness, lumps or other signs of infection. The provider may also check for an inguinal hernia, which results from a weakness in the abdominal wall.
For girls, the doctor may ask about vaginal discharge. For boys, the provider will make sure a circumcised penis is healing well during early visits. The provider may also check to see that both testes have descended into the scrotum and that there’s no fluid-filled sac around the testes, a condition called hydrocele.
Your child’s provider will likely ask you about your child’s eating habits. If you’re breastfeeding, the provider may want to know how often you’re feeding your baby during the day and night and whether you’re having any problems. If you’re pumping, the provider may offer suggestions for managing pumping frequency and storing breast milk. If you’re formula-feeding, the provider will likely want to know how often you feed and how many ounces of formula your baby takes at each feeding. In addition, the provider may discuss with you your baby’s need for vitamin D and iron supplements.
Bowel and bladder function
In the first few visits, your child’s health care provider will likely also ask how many wet diapers and bowel movements your baby produces a day. This information offers clues as to whether your baby is getting enough to eat.
Sleeping status
Your child’s health care provider may ask you questions about your child’s sleep habits, such as your regular bedtime routine and how many hours your child is sleeping during the day and night. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns you may have about your child’s sleep, such as getting your baby to sleep through the night. Your child’s provider may also help you figure out how to find rest for yourself, especially in the early baby months.
Development
Your child’s development is important, too. The health care provider will monitor your child’s development in the following five main areas.
- Gross motor skills — These skills, such as sitting, walking and climbing, involve the movement of large muscles. Your child’s health care provider may ask you how well your baby can control his or her head. Is your baby attempting to roll over? Is your baby trying to sit on his or her own? Is your child starting to walk or throw a ball? Can your toddler walk up and down steps?
- Fine motor skills — These skills involve the use of small muscles in the hand. Does your baby reach for objects and bring them to his or her mouth? Is your baby using individual fingers to pick up small objects?
- Personal and social skills — These skills enable a child to interact and respond to his or her surroundings. Your child’s health care provider may ask if your baby is smiling. Does your baby relate to you with joy and enthusiasm? Does he or she play peekaboo?
- Language skills — These skills include hearing, understanding and use of language. The health care provider may ask if your baby turns his or her head toward voices or other sounds. Does your baby laugh? Is he or she responding to his or her name?
- Cognitive skills — These skills allow a child to think, reason, solve problems and understand his or her surroundings. Your child’s provider might ask if your baby can bang together two cubes or search for a toy after seeing you hide it.
Vaccinations
Your baby will need a number of scheduled vaccinations during his or her first years. The health care provider or a nurse will explain to you how to hold your baby as he or she is given each shot. Be prepared for possible tears. Keep in mind, however, that the pain caused by a shot is typically short-lived but the benefits are long lasting.
Your child’s provider may talk to you about safety issues, such as the importance of placing your baby to sleep on his or her back and using a rear-facing infant car seat as long as possible.
Questions and concerns
During your son’s or daughter’s checkups, it’s likely that you’ll have questions, too. Ask away! Nothing is too trivial when it comes to caring for your baby. Write down questions as they arise between appointments so that you’ll be less likely to forget them when you’re at your child’s checkup.
Also, don’t forget your own health. If you’re feeling depressed, stressed-out, run-down or overwhelmed, describe what’s happening. Your child’s provider is there to help you, too.
Before you leave the health care provider’s office, make sure you know when to schedule your child’s next appointment. If possible, set the next appointment before you leave the provider’s office. If you don’t already know, ask how to reach your child’s provider in between appointments. You might also ask if the provider has a 24-hour nurse information service. Knowing that help is available when you need it can offer peace of mind.

Relevant reading
Health Heroes Bundle
Meet the health heroes who work every day to keep our community safe and healthy. From doctors to hospital custodians, health heroes make sure the needs of the patient come first. Learn more about these community helpers and how they do their important work. Meet real health heroes from Mayo…

Medical Artificial Intelligence Breakthroughs
From machine learning to virtual surgery practice, this exploration of scientific inquiry celebrates the greatest developments to date in medical artificial intelligence. Get to know the physicians, scientists, and other researchers responsible for these breakthroughs in medicine, and explore the ups, the downs, and the eureka moments that are science…

Discover more Parenting, Kids & Teens content from articles, podcasts, to videos.
Want more children’s health and parenting information? Sign up for free to our email list.
Children’s health information and parenting tips to your inbox.
Sign-up to get Mayo Clinic’s trusted health content sent to your email. Receive a bonus guide on ways to manage your child’s health just for subscribing.
You May Also Enjoy

Privacy Policy
We've made some updates to our Privacy Policy. Please take a moment to review.

Catch Up on Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations

Many children missed check-ups and recommended childhood vaccinations over the past few years. CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommend children catch up on routine childhood vaccinations and get back on track for school, childcare, and beyond.

Making sure that your child sees their doctor for well-child visits and recommended vaccines is one of the best things you can do to protect your child and community from serious diseases that are easily spread.
Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations Are Essential

Well-child visits and recommended vaccinations are essential and help make sure children stay healthy. Children who are not protected by vaccines are more likely to get diseases like measles and whooping cough . These diseases are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children. In recent years, there have been outbreaks of these diseases, especially in communities with low vaccination rates.
Well-child visits are essential for many reasons , including:
- Tracking growth and developmental milestones
- Discussing any concerns about your child’s health
- Getting scheduled vaccinations to prevent illnesses like measles and whooping cough (pertussis) and other serious diseases

It’s particularly important for parents to work with their child’s doctor or nurse to make sure they get caught up on missed well-child visits and recommended vaccines.
Routinely Recommended Vaccines for Children and Adolescents
Getting children and adolescents caught up with recommended vaccinations is the best way to protect them from a variety of vaccine-preventable diseases . The schedules below outline the vaccines recommended for each age group.
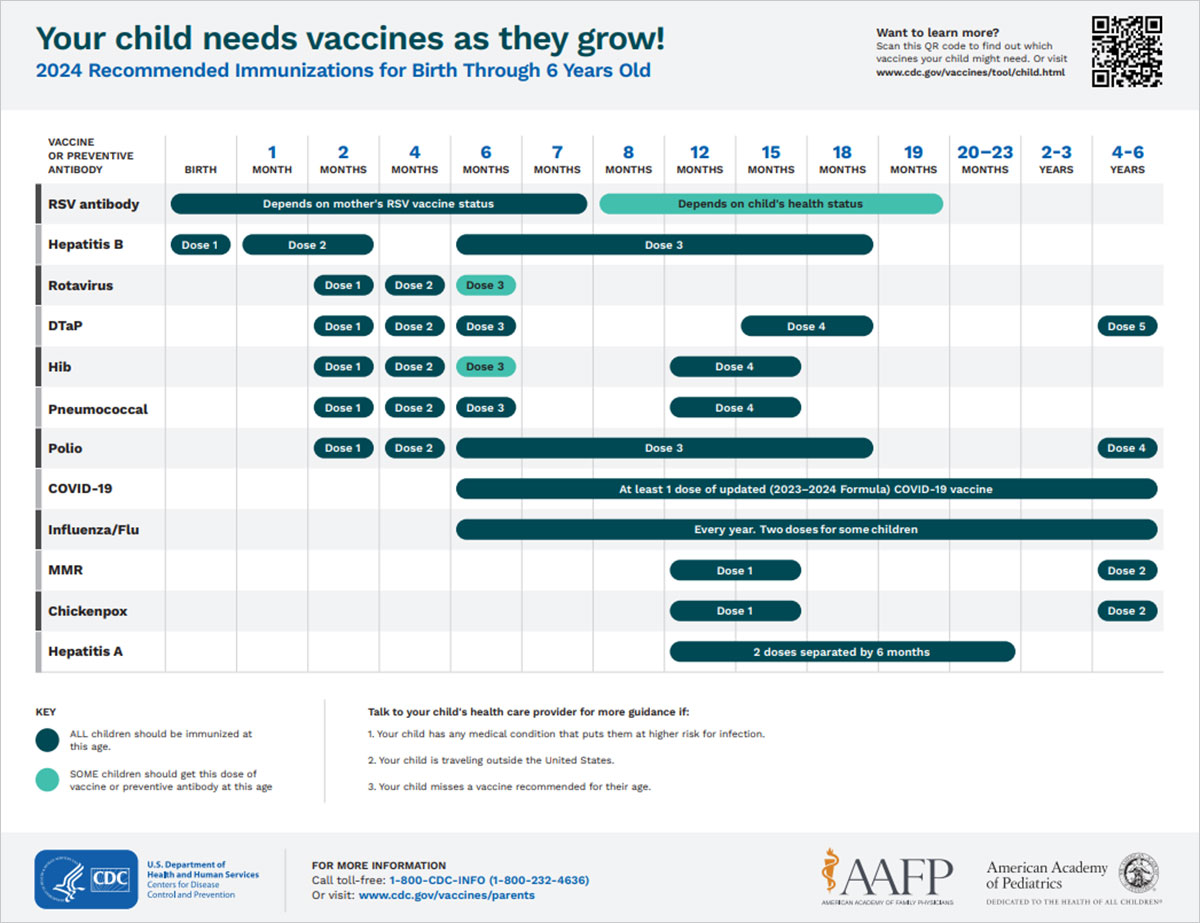
See which vaccines your child needs from birth through age 6 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
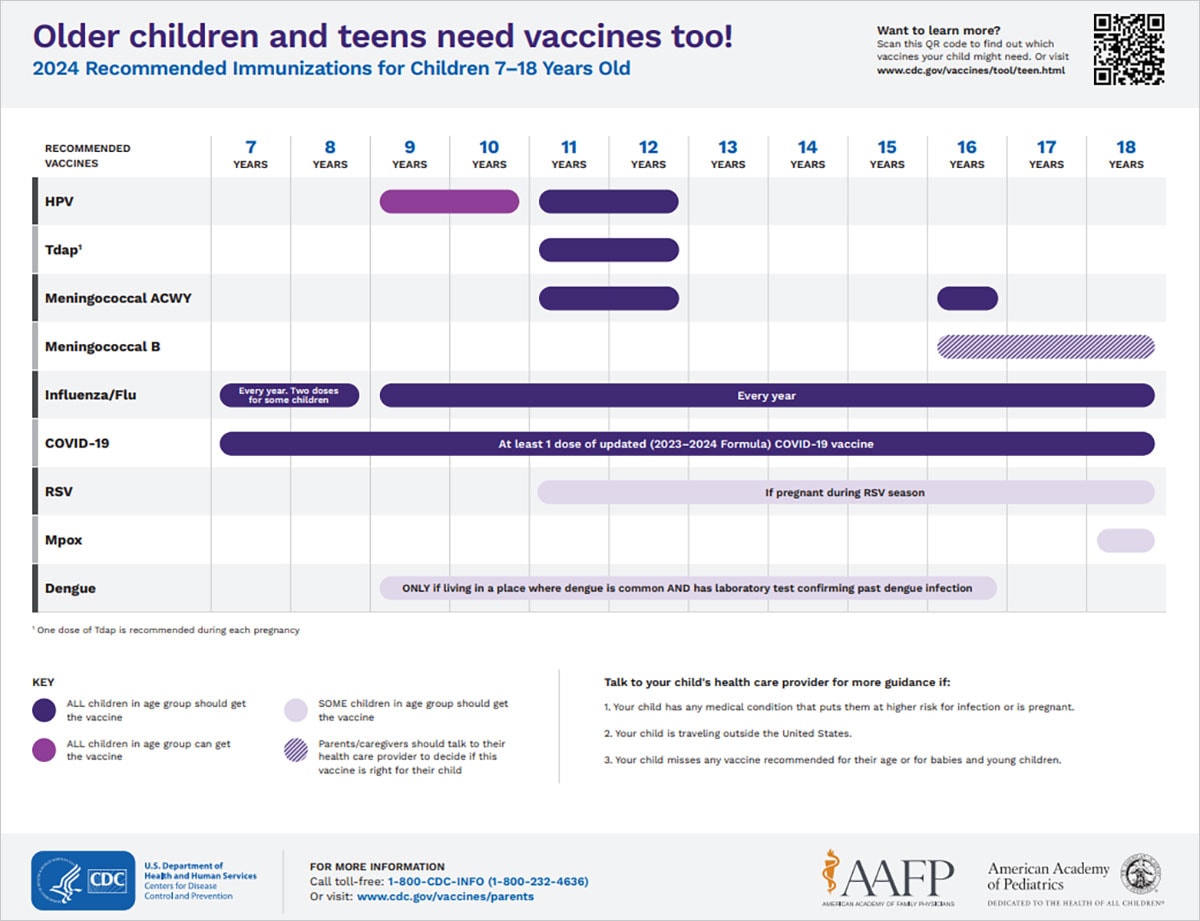
See which vaccines your child needs from ages 7 through 18 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program’s requirements and talk to your child’s doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider. You can also find a VFC provider by calling your state or local health department or seeing if your state has a VFC website.
COVID-19 Vaccines for Children and Teens
Everyone aged 6 months and older can get an updated COVID-19 vaccine to help protect against severe illness, hospitalization and death. Learn more about making sure your child stays up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- For Parents
- For Educators
- Sitio para padres
- Parents Home
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Diseases & Conditions
- Pregnancy & Baby
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Emotions & Behavior
- School & Family Life
- First Aid & Safety
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Expert Answers (Q&A)
- All Categories
- All Wellness Centers

- Sitio para niños
- How the Body Works
- Puberty & Growing Up
- Staying Healthy
- Staying Safe
- Health Problems
- Illnesses & Injuries
- Relax & Unwind
- People, Places & Things That Help

- Sitio para adolescentes
- Sexual Health
- Food & Fitness
- Drugs & Alcohol
- School & Jobs

Well-Child Visit: 10 Years
- Listen Play Stop Volume mp3 Settings Close Player
- Larger text size Large text size Regular text size
What to Expect During This Visit
Your doctor and/or nurse will probably:
1. Check your child's weight and height, calculate body mass index (BMI) , and plot the measurements on a growth chart .
2. Check your child's blood pressure, vision , and hearing using standard testing equipment.
3. Ask questions, address concerns, and offer advice about your child's:
Eating. Schedule 3 meals and 1–2 nutritious snacks a day. Serve your child a balanced diet that includes lean protein, whole grains, fruits and vegetables, and low-fat dairy. Kids this age should get 3 cups (720 ml) of low-fat milk daily (or other low-fat dairy products or fortified soy milk). Aim for 5 servings of fruits and vegetables per day. Limit foods and drinks that are high is sugar, salt, and fat. Don't give than 8 ounces (240 ml) of 100% juice per day. Teach your child to pay attention to feelings of hunger and fullness.
Sleeping. Kids this age need about 9–12 hours of sleep per night. Lack of sleep can make it hard to pay attention at school. Set a bedtime that allows for enough sleep and encourage your child to follow a relaxing bedtime routine. Keep TVs and electronic devices out of your child's bedroom.
Physical activity. Kids this age should get at least 60 minutes of physical activity per day. Set limits on screen time , including TV, video games, smartphones, tablets, and computers.
Growth and development. By 10 years, it's common for many kids to:
- show more independence from family and begin to prefer being with friends
- have friends of the same gender
- read to learn about a topic of interest
- accomplish increasingly difficult tasks in school, like gathering and organizing information into a book report
- begin to take on chores at home and handle more homework
- begin to show the signs of puberty ( oily skin , acne, body odor). Girls may start breast development and grow hair in the armpit and pubic area. Boys may develop body hair and have testicle and penis enlargement.
4. Do an exam . This will include listening to the heart and lungs, checking the back for any curvature of the spine , and checking for the signs of puberty. A parent, caregiver, or chaperone should be present during this part of the exam. Siblings should stay in the waiting room to give your child privacy.
5. Update immunizations. Immunizations can protect kids from serious childhood illnesses, so it's important that your child get them on time. Immunization schedules can vary from office to office, so talk to your doctor about what to expect.
6. Order tests. Your doctor may check for anemia , high cholesterol , and tuberculosis and order tests, if needed.
Looking Ahead
Here are some things to keep in mind until your child's next checkup at 11 years :
- Encourage your child to participate in a variety of activities , including music, arts and crafts, sports , after-school clubs, and other activities of interest. But try to avoid overscheduling and allow for some downtime.
- Praise accomplishments and provide support in areas where your child struggles.
- Provide a quiet place to do homework . Minimize distractions, such as TV and electronic devices.
- As schoolwork gets harder, your child may struggle . If this happens, work with the school staff to find the cause, such a learning or attention problem, bullying , or other stressors.
- Talk to your child about the dangers of smoking , vaping , alcohol , and drugs .
- Teach your child to use technology wisely . A general rule: Don't text, post, or send pictures online that you couldn't share with a grandparent.
- Spend time with your child every day. Share mealtimes , be active together, and talk about things that are important to your child.
- Set rules and explain your expectations. Have fair consequences for rule-breaking. Praise good choices.
- Be prepared to answer questions about puberty and the feelings associated with those changes. Encourage your child to bring questions or concerns to you. Girls usually get their first period about 2 years after breast development. Boys may have wet dreams and their voices may begin to deepen and crack.
- Encourage your child to bathe or shower daily . If body odor is a concern, have your child use a deodorant.
- Remind your child know that it's never OK for an adult to ask them to keep a secret from you. No one should look at or touch your child's private parts, or ask them to look at or touch theirs.
- Make sure your child brushes their teeth twice daily, flosses once a day, and sees a dentist once every 6 months.
- Your child should continue to ride in the back seat of the car and use a belt-positioning booster seat until they're 4 feet 9 inches (150 cm) tall. Kids usually reach this height when they're 8–12 years old.
- Make sure your child wears a helmet while riding a bike , skateboard, or scooter. Your child should wear the right protective equipment, like mouth guards and pads, when playing sports.
- Teach your child to swim but do not allow swimming unless an adult is watching.
- Apply sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher at least 15 minutes before your child goes outside and reapply about every 2 hours.
- Protect your child from secondhand smoke .
- Monitor your child's Internet use . Keep the family computer in a place where you can watch what your child is doing. Install safety filters and check the browser history to see what websites your child visits. Teach your child not to give out personal information.
- Protect your child from gun injuries by not keeping a gun in the home. If you do have a gun, keep it unloaded and locked away. Ammunition should be locked up separately. Make sure kids can't get to the keys.
- Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about your living situation . Do you have the things that you need to take care of your child? Do you have enough food , a safe place to live, and health insurance ? Your doctor can tell you about community resources or refer you to a social worker.
These checkup sheets are consistent with the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)/Bright Futures guidelines.
Doctor Visits
Make the Most of Your Child’s Visit to the Doctor (Ages 11 to 14 Years)

Take Action
Kids ages 11 to 14 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a “well-child visit” once a year.
A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they’re healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury.
At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any problems early, when they may be easier to treat.
Learn what to expect so you can make the most of each visit.
Child Development
How do i know if my child is growing and developing on schedule.
Your child’s doctor or nurse can help you identify “developmental milestones,” or signs to look for that show your child is developing normally. This is an important part of the well-child visit.
Some developmental milestones are related to your child’s behavior and learning, and others are about physical changes in your child’s body.
Check out these resources to learn more about developmental milestones:
- Developmental Milestones (Ages 9 to 11 years)
- Developmental Milestones (Ages 12 to 14 years)
Behavior Changes
What are some changes i might see in my child’s feelings, relationships, and behavior.
Developmental milestones for kids ages 11 to 14 years include:
- Wanting more independence and privacy
- Having mood swings (going quickly from happy to sad or sad to happy)
- Showing more concern about what their friends and classmates think
- Developing stronger problem-solving skills
- Developing a clearer sense of right and wrong
- Challenging rules and resisting advice from parents
This is also a time when some kids may start showing signs of depression or eating disorders. Bullying and social media use may also become issues at this age. It’s important to:
- Make sure the doctor screens your child for depression
- Have your child screened for anxiety
- Know the signs of eating disorders
- Teach your kids to use social media safely
- Watch for signs of bullying
Physical Changes
What physical changes will my child go through.
Many kids ages 11 to 14 years are going through puberty. Puberty is when a child’s body develops into an adult’s body.
- For girls, puberty usually starts between ages 9 and 13 years. Get more information about puberty to share with your daughter .
- For boys, it usually starts between ages 10 and 13 years. Get more information about puberty to share with your son .
You can help by giving your child information about what changes to expect during puberty. You can also encourage your child to talk about puberty with the doctor or another trusted adult, like a teacher or school nurse.
Puberty can be a difficult time for gender-diverse children — kids who feel that they’re a different gender than the sex that’s listed on their birth certificate. Encourage your child to talk with you or their doctor if they have questions about their gender. Find tips for parenting a gender-diverse child .
Behavior and Emotions
The doctor or nurse will pay special attention to signs of certain issues. .
The doctor or nurse will offer additional help if your child may:
- Be depressed
- Have anxiety
- Struggle with an eating disorder
- Use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs
- Experience any kind of violence
And if your child may be having sex, the doctor or nurse will talk to your child about preventing STIs (sexually transmitted infections) — also called STDs (sexually transmitted diseases) — and pregnancy. Learn how to talk with your child about preventing STIs .
The doctor or nurse will make sure you and your child have the resources you need.
This may include telling you and your child about:
- Websites or apps that have helpful health information
- Organizations in your community where you can go for help
If needed, the doctor or nurse may also refer your child to a specialist.
Take these steps to help you and your child get the most out of well-child visits.
Gather important information.
Take any medical records you have to the appointment, including a record of vaccines (shots) your child has received.
Make a list of any important changes in your child’s life since the last visit, like a:
- New brother or sister
- Separation or divorce — or a parent spending time in jail or prison
- New school or a move to a new neighborhood
- Serious illness or death of a friend or family member
Use this tool to keep track of your child’s family health history .
Help your child get more involved in visits to the doctor.
Once your child starts puberty, the doctor will usually ask you to leave the room for a few minutes so your child can ask questions about their health. This lets your child develop a relationship with the doctor or nurse, and it's an important step in helping your child learn about their health care.
Your child can also:
- Call to schedule appointments (if the doctor’s office allows it)
- Help you fill out medical forms
- Write down questions for the doctor or nurse
For more ideas, check out these tips to help your child take charge of their health care . You can also share this list of questions for the doctor with your child .
What about cost?
Under the Affordable Care Act, insurance plans must cover well-child visits. Depending on your insurance plan, you may be able to get well-child visits at no cost to you. Check with your insurance company to find out more.
Your child may also qualify for free or low-cost health insurance through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). Learn about coverage options for your family.
If you don’t have insurance, you may still be able to get free or low-cost well-child visits. Find a health center near you and ask about well-child visits.
To learn more, check out these resources:
- Free preventive care for children covered by the Affordable Care Act
- How the Affordable Care Act protects you and your family
- Understanding your health insurance and how to use it [PDF - 698 KB]
Ask Questions
Make a list of questions you want to ask the doctor..
Before the well-child visit, write down 3 to 5 questions you have — and ask your child if they have any questions to add. This visit is a great time to ask the doctor or nurse any questions about:
- A health condition your child has (like an allergy, asthma, or acne)
- Changes in behavior or mood
- Loss of interest in favorite activities
- Problems at school (like learning challenges or not wanting to go to school)
Here are some questions you may want to ask:
- How can I make sure my child is getting enough physical activity?
- How can I help my child eat healthy?
- Is my child at a healthy weight?
- Is my child's body developing normally?
- Is my child up to date on vaccines?
- How can I help my child succeed at school?
You may also want to ask:
- How can I talk with my child about sex?
- How can I talk with my child about tobacco, alcohol, and drugs?
- How can I teach my child to use the internet safely?
- How can I talk with my child about bullying?
Take a notepad, smartphone, or tablet and write down the answers so you can remember them later.
Get tips to help you:
- Talk with your child about sex
- Talk with your child about tobacco, alcohol, and drugs
- Talk with your child about bullying
Find more tips to talk to your child about a range of tricky topics .
Ask what to do if your child gets sick.
Make sure you know how to get in touch with a doctor or nurse when the office is closed. Ask how to get hold of the doctor on call, or if there's a nurse information service you can call at night or on the weekend.
What to Expect
Know what to expect..
During each well-child visit, the doctor or nurse will ask you questions, do a physical exam, and update your child’s medical history. You'll also be able to ask your questions and discuss any problems.
The doctor or nurse will ask you and your child questions.
The doctor or nurse may ask about:
- Behavior — Does your child have trouble following directions at home or at school?
- Health — Does your child often complain of headaches or other pain? How much sleep does your child get? When was their last visit to the dentist?
- Safety — Does anyone in your home have a gun? If so, is it unloaded and locked in a place where your child can’t get it?
- School and activities — Does your child look forward to going to school? What does your child like to do outside of school?
- Eating habits — What does your child eat on a normal day?
- Family and friends — Have there been any recent changes in your family? How many close friends does your child have? Has your child been bullied at school or online?
- Emotions — Does your child often seem sad, stressed, or bored? Do they seem scared or worried a lot? Does your child have someone to talk to about problems?
- Sexuality — Have you talked with your child about puberty? Is your child dating?
The answers to questions like these will help the doctor or nurse make sure your child is healthy, safe, and developing normally.
Physical Exam
The doctor or nurse will also check your child’s body..
To check your child’s body, the doctor or nurse will:
- Measure height and weight and figure out your child's body mass index (BMI)
- Check your child’s blood pressure
- Check your child’s vision and hearing
- Check your child’s body parts (this is called a physical exam)
- Decide if your child needs any lab tests, like a blood test
- Give your child shots they need
Learn more about your child’s health care:
- Find out how to get your child’s shots on schedule
- Learn about getting your child’s vision checked
Content last updated February 16, 2024
Reviewer Information
This information on well-child visits was adapted from materials from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health.
Reviewed by: Sara Kinsman, M.D., Ph.D. Director, Division of Child, Adolescent, and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
Bethany Miller, M.S.W. Chief, Adolescent Health Branch Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
Diane Pilkey, R.N., M.P.H. Nursing Consultant, Division of Child, Adolescent, and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
October 2021
You may also be interested in:

Talk to Your Kids About Tobacco, Alcohol, and Drugs

Get Your Pre‑teen’s Vaccines on Schedule

Help Your Child Stay at a Healthy Weight
The office of disease prevention and health promotion (odphp) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website..
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by ODPHP or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.

Ages & Stages
1st week checkup checklist: 3 to 5 days old.
Congratulations on the birth of your new baby! For many parents, the first visit to the pediatrician is also their newborn's first trip away from home. Don't worry—we've got you covered with what questions to ask, what paperwork to remember, and what to expect at your baby's first checkup.
✅ What to bring
Hospital paperwork—including information about your baby's discharge weight or complications during pregnancy or birth.
✅ Immunizations
Your baby will receive the Hepatitis B (HBV) vaccine if they did not receive it in the hospital. (The AAP recommends newborns receive their first dose of vaccine within the first 24 hours of birth.)
✅ Screenings
Your pediatrician will review the results of two screenings that all babies receive in the hospital for hearing and blood . Based on the results, your pediatrician may rescreen or recommend a referral to a specialist.
✅Development & feeding
Your doctor will measure and weigh your baby to make sure their growth is on track, observe their development and behavior, and perform a physical exam.
Questions your pediatrician may ask
Does your baby receive breast milk , iron-fortified formula, or a combination of the two?
If breastfeeding, do you have support from a lactation consultant? The first few weeks of breastfeeding can be an adjustment, but try to stick with it ! (The AAP recommends breastfeeding as the sole source of nutrition for your baby for about 6 months. When you add solid foods to your baby's diet, continue to breastfeed as long as you and your baby desire, for 2 years or beyond.
Is your breastfed baby getting a vitamin D supplement ? (The AAP recommends 400 IU of supplemental vitamin D daily, beginning in the first few days of life.)
Questions you may have
How many diapers should I be changing?
How long is formula good after making it?
How long is breast milk good after pumping it?
How well can my baby see ?
❓ Did you know
Your baby can see you best if you are face-to-face about 6 to 10 inches away. Learn more about newborn eyesight.
How are you feeling? If you are having postpartum issues with breastfeeding, anxiety, or sadness , or anything else, please feel free to discuss it with your baby's pediatrician.
Where does your baby sleep? Here are great tips from the AAP on keeping your sleeping baby safe .
Are my baby's umbilical cord and/or circumcision healing as expected?
Am I preparing bottles safely?
When is it safe to bathe my baby?
What should I do if my baby has a fever ? Can you show me how to safely use a rectal thermometer to take my baby's temperature?
✅ Communication
Never hesitate to call your pediatrician's office with any questions or concerns—even if you know the office is closed. If your pediatrician is unable to see you but believes your baby should be examined, they will advise you on the most appropriate place for your baby to receive care and how quickly your baby should be seen.
More information
AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits
Your Baby's First Week: How to Prepare & What to Expect
Depression Before or After Pregnancy: You Are Not Alone
AAP Bright Futures Previsit Questionnaire: First Week Visit (3 to 5 Days)
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.15(9); 2023 Sep
- PMC10576162

Analyzing Best Practices for Pediatric Well-Child Clinic Visits in the United States for Children Aged Three to Five Years: A Review
Okelue e okobi.
1 Family Medicine, Larkin Community Hospital Palm Springs Campus, Miami, USA
2 Family Medicine, Medficient Health Systems, Laurel, USA
3 Family Medicine, Lakeside Medical Center, Belle Glade, USA
Patience F Akahara
4 Family Medicine, Inglewood Medical Centre, Edmonton, CAN
Onyinyechukwu B Nwachukwu
5 Neurosciences and Psychology, California Institute of Behavioral Neurosciences & Psychology, Fairfield, USA
6 Family Medicine, American International School of Medicine Georgetown, Guyana, USA
Thelma O Egbuchua
7 Pediatrics and Neonatology, Delta State University Teaching Hospital, Oghara, NGA
Olamide O Ajayi
8 Internal Medicine, Obafemi Awolowo College of Health Sciences, Olabisi Onabanjo University, Sagamu, NGA
Kelechukwu P Oranu
9 Obstetrics and Gynecology, Kenechukwu Specialist Hospital and Maternity Enugu, Enugu, NGA
Ifreke U Ibanga
10 Pediatrics, Thompson General Hospital, Manitoba, CAN
Inadequate routine healthcare check-up visits for children aged three to five years impose substantial economic and social burdens due to morbidity and mortality. The absence of regular well-child visits and vaccinations leads to avoidable diseases, underscoring the need for a renewed emphasis on childhood immunizations and check-ups. Out of 160 articles initially screened after removing duplicates, 45 were chosen for full-text review following initial title and abstract screening by two independent reviewers. Afterward, 20 studies met the predefined inclusion criteria during the final assessment of full-text articles, and data were systematically extracted from these selected studies using standardized forms to ensure accuracy and consistency. Well-child visits promote holistic development, health, and well-being in children aged three to five years. Following established guidelines and evidence-based practices, healthcare professionals provide assessments, vaccinations, and guidance for a healthy future. Despite challenges, well-child visits are vital for preventive care, empowering informed decisions for children's growth and development. The benefits of well-child visits encompass growth monitoring, anticipatory guidance, and preventive measures, crucial for children with chronic illnesses. Key components include comprehensive assessments, developmental screenings, vision and hearing evaluations, immunizations, health education, and counseling. In the case of juvenile diabetes, parental education is paramount. Parents need to understand the intricacies of insulin administration, including proper dosage calculation based on glucose measurements, meal planning, and the importance of timing insulin injections. Implementing guidelines and principles by organizations such as Bright Futures and the American Academy of Pediatrics ensures holistic care, parent involvement, and evidence-based practices. This review explores best practices and guidelines for such visits, emphasizing their role in monitoring and promoting children's development.
Introduction and background
Pediatric-associated morbidity and mortality resulting from inadequate routine healthcare check-up visits impose a considerable national economic and social burden worldwide, including in the United States. The data collected from medical check-up records from January 2019 to December 2020 revealed that the risk of disease-related adverse outcomes in a population is higher if routine non-healthcare check-up visits are ignored [ 1 - 4 ]. For example, missed vaccinations have been identified as a significant contributor to the rise of pediatric vaccine-preventable illnesses in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), millions of children in the United States are under-vaccinated or unvaccinated against preventable diseases [ 1 - 5 ]. The CDC website provides a recommended immunization schedule for children from birth through 18 years of age, and parents can check with their child's healthcare provider to ensure that their child is up to date on vaccinations [ 1 - 3 ]. However, missed well-child visits (WCVs) have resulted in significant declines in vaccination coverage in children at all milestone ages [ 1 ]. The decline in vaccination coverage has markedly increased the risk of vaccine-preventable diseases in children, including measles, polio, and pertussis [ 1 , 2 ]. Re-prioritizing childhood immunizations and well-visits can prevent the re-emergence of vaccine-preventable diseases, and it is essential that parents and care providers prioritize children's well-child schedule to prevent the rise of pediatric-preventable illnesses in the United States. In addition to that, re-prioritizing childhood immunizations has a far-reaching impact beyond the prevention of vaccine-preventable diseases. This, in turn, can help prevent non-vaccine-preventable diseases by alleviating the burden on healthcare systems, reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections, and improving overall population health [ 1 - 5 ].
Also, these absences of regular and full body healthcare check-ups for children aged three to five years can lead to undetected health issues, delayed interventions, and potentially fatal consequences [ 2 - 6 ]. This translates into increased medical costs, reduced productivity, and an emotional toll on families. The economic impact encompasses direct medical expenses for treating preventable illnesses, emergency care, and hospitalization, often straining healthcare resources. Moreover, the long-term consequences of inadequate health supervision during these critical developmental years can lead to reduced educational attainment, hindered workforce participation, and a perpetuated cycle of health disparities [ 5 - 8 ]. As a result, investing in and promoting routine healthcare check-up visits for pediatric populations is essential not only for safeguarding the well-being of the younger generation but also for alleviating the economic and social ramifications that arise from preventable disease burdens and loss of life [ 1 - 9 ].
Pediatric WCVs are marked by significant changes in speech and language proficiency, as well as the refinement of fine and gross motor skills. Their burgeoning social interactions and cognitive abilities further underscore the importance of this developmental phase. Regular WCVs during this stage assume a vital role in assessing a child's progress, offering a valuable chance to identify any potential deviations from the expected trajectory and intervene promptly if necessary [ 8 - 10 ].
Moreover, the preschool years witness the emergence of emotional and behavioral skills in children, a domain equally crucial to their holistic development. Within this context, WCVs serve as a platform for healthcare providers to engage with parents, addressing concerns related to behavior, furnishing strategies for managing behavioral obstacles, and discerning subtle signs of emotional or psychological challenges that might warrant attention. Adding to the array of advantages inherent in these WCVs, it is noteworthy that this age range coincides with a critical juncture for immunizations. The routine check-ups between three and five years of age routinely encompass pivotal immunizations that bolster a child's immunity, safeguarding them against a spectrum of severe diseases, and forging a shield of protection that will serve them well into the future [ 3 - 6 , 11 - 14 ].
This comprehensive review analyzes the best practices and guidelines for pediatric WCVs in children aged three to five years. We will explore the importance and benefits of these visits and the components that make up a successful visit. Additionally, we will examine the best practices and potential challenges associated with implementing them and review the guidelines and principles that should be followed during these visits. By doing so, we hope to provide a thorough understanding of the importance of these visits and the relationship between continuity, quality of care, and long-term health outcomes that can guide healthcare providers in delivering the most effective care to pediatric patients, ultimately leading to improved health and well-being in the years to come.
Methods and Materials, and Literature Search
For the present systematic review, an in-depth and comprehensive literature search was conducted on various online databases, including PubMed, Science Direct, Google Scholar, Embase, and Cochrane Library, for peer-reviewed and English-language articles published between 2000 and 2023. The search used various combinations of MeSh terms: “Well child visit,” “well child clinic,” “pediatric healthcare check-up visit,” and “well-baby care,” “preventive care,” and “primary care,” and Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) and parentheses to specify various combinations of operations in PubMed, Science Direct, Google Scholar, Embase, Cochrane Library, and HINARI: (1) PubMed (All terms with OR): (“Well child visit” OR “well child clinic” OR “pediatric healthcare check-up visit” OR “well-baby care”) AND (“preventive care” OR “primary care”); (2) Science Direct (Well-child visit and preventive care): (“Well-child visit” OR “pediatric healthcare check-up visit” OR “well-baby care”) AND “preventive care”; (3) Google Scholar (primary care and well-child visit): (Well child visit” OR “pediatric healthcare check-up visit” OR “well-baby care”) AND “primary care”; (4) Embase (Well-child visit and NOT primary care): (“Well child visit” OR “pediatric healthcare check-up visit” OR “well-baby care”) NOT “primary care”; (5) Cochrane Library (Well-child visit OR well-child clinic): (“Well child visit” OR “well-child clinic”) AND (“preventive care” OR “primary care”). We also used exact phrase search, and these combinations allowed us to specify different search criteria related to child healthcare visits, preventive care, and primary care. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA; Figure Figure1) 1 ) was then used as the preferred guideline for consistency. To locate the articles, we employed keywords that included “well child clinic,” “pediatric healthcare check-up visit,” and “well-baby care,” alongside MeSH terms “preventive care” and “primary care.” The references of the included studies were searched to identify additional articles. The articles sought for were mainly those that analyzed the best practices related to well-child clinic visits, those that explored the significance of such clinical visits, and those that reviewed the components making up successful and effective well-child clinic visit, as well as the best practices and challenges linked to execution of best practices guidelines and principles. The present systematic review has focused on the best practices and guidelines for well-child clinic visit for children aged three to five years. To attain the objectives, the interventions are to be practice-based and applicable to well-child clinic care delivery.

PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
For the current systematic review, we excluded studies that had focused on the evaluation of the process of quality improvement in best practices in well-child clinic visits without acknowledging specific practice changes to child care delivery; articles that focused on one topic in well-child care as opposed to tackling the different aspects of well-child clinic practices more generally; articles that were published before 2010 and those that were published in languages other than English, and studies that focused on tackling changes in well-child clinic without tackling the issue of changes in service delivery.
A total of 160 articles were screened for primary screening (title and abstract review) after removing duplicates. Two independent reviewers conducted the initial screening of titles and abstracts to identify potentially relevant articles. After the initial screening, a total of 45 studies were included for secondary screening or full-text review. Full-text articles were obtained for studies that met the initial screening criteria or where there was uncertainty. The full-text articles were then assessed for final inclusion based on the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, and, finally, 20 studies were included in this review for data extraction. Data were systematically extracted from the selected studies and assessed using standardized forms to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Consequently, the studies included in this review (Table (Table1) 1 ) were observational studies, randomized controlled trials, and systematic reviews, which included child participants aged zero to five years (with focus on three to five years), and whose findings are directly related to delivery and reception of well-child clinic services, care quality, and child health and development outcomes. We also independently screened the studies and titles with the objective of excluding articles that were duplicated and were irrelevant to the study objectives. The abstracts of studies were also screened using a brief and structured screening tool with the objective of establishing if the selected article satisfied the inclusion criteria, including the topic being studied, the study design, target population, sample size, and study location. We also reviewed the abstract screening outcomes, even as disagreements were solved through general consensus. For the accepted abstracts, retrieval of full texts was conducted, even as a structured form was employed in the extraction of data pertaining to the study design, methodology, results, and findings.
EPDS, Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale; PPD, postpartum depression; PRO, patient-reported outcome; RCT, randomized controlled trial; WCC, well-child clinic; WCV, well-child visit
Quality assessment
The assessment of the included studies’ quality was evaluated using the Joanna Briggs Institute quality assessment tool. The tool scores every publication using the frequency scales that were accorded yes, no, unclear, and not applicable responses. The overall quality score of every study was aptly calculated based on the total amount of positive scores received.
An overview of the importance of pediatric well-child visits for children aged three to five years
The importance of a pediatric WCV for children aged three to five years should not be underestimated. These visits provide an opportunity for the physician to screen for medical issues, provide anticipatory guidance, and promote good health for the child [ 6 ]. They also allow primary care physicians to establish a bond with the parents or caregivers and to prioritize interventions with the strongest evidence for good patient-oriented outcomes, such as family social-economic dynamics, assessment and support, and other health-related goals [ 6 ]. Following the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines, immunizations should be updated if necessary, and a one-time vision screening should be carried out between three and five years of age [ 6 ]. Additionally, a head-to-toe examination should be performed, including a review of growth [ 6 ]. During the visit, the physician can answer any questions the parents or caregivers might have and provide age-appropriate guidance [ 6 ]. Furthermore, if any abnormalities are detected, the visit offers the opportunity for further evaluation [ 6 ]. Pediatricians are often parents' main formal counseling source for their children's development and education. Their anticipatory guidance can help improve outcomes in various areas such as infant vocal behavior, parenting skills, infant sleep patterns, parental use of discipline, language development, prevention of falls, home accidents, and auto-passenger injuries [ 7 ]. The WCV is also a chance to use the CDC-recommended growth charts for assessment and to review parent/caregiver-child interactions [ 6 ]. Furthermore, potential signs of abuse should be assessed, and interval growth should be reviewed using appropriate growth charts for height, weight, head circumference, and body mass index [ 6 - 7 ]. Moreover, primary care providers are well-positioned to engage parents and provide referrals to community services during WCVs [ 8 ]. Table Table2 2 shows an overview of the main components of a WCV.
Benefits of a well-child visit for young children
The benefits of WCVs for young children are numerous [ 8 , 9 ]. WCVs enable pediatricians to review a patient's health history, track a child's growth and development, and provide guidance for parents around topics such as nutrition, sleep, and behavioral development [ 10 , 11 ]. Furthermore, studies have shown that the length of a WCV is linked to the amount of unmet needs experienced by a family [ 12 , 13 ]. This is especially pertinent for children with chronic illnesses or special healthcare needs [ 12 ], as pediatric visits are more likely to result in hospital admission than adults [ 14 ]. Additionally, WCVs provide an opportunity to discuss prevention, as in the case of childhood obesity [ 15 ]. To ensure that WCVs are valuable, there should be an agreement between parents and medical professionals about the visit's goals [ 7 ]. Furthermore, physicians should discuss topics such as when to introduce solid foods [ 6 ], as this has implications for a child's long-term health. As a result, WCVs can be incredibly beneficial to young children and their families.
Components of a well-child visit for children aged three to five years
This analysis also provided details of the topics discussed during the visits. These topics were classified into seven categories: secondary prevention, primary prevention, health promotion, development, education, and those focused on the parents and family relationship [ 7 ]. The study was based on 49 visits to five pediatricians for children aged three to five years [ 7 ]. The results showed that the major topics discussed during the visits were illness prevention and education, followed by physical examination and development. Other topics such as health promotion, safety, nutrition, and emotional and mental health were also discussed but in lesser amounts. These results suggest that pediatric providers focus on the primary aspects of a child's physical and mental health, although other topics are often included in the visit. However, this study did not provide specific information about the components of a WCV for children aged three to five years [ 7 ]. This means that it is still necessary to understand the specific topics discussed during a WCV to effectively assess a child's health. Therefore, further studies are needed to provide more information about the components of a WCV for children aged three to five years.
Best practices for pediatric well-child visits
A recent study assessed the effectiveness of the Improved Care for Moms and Babies (ICC) model on maternal depression screening and other health behaviors discussed during pediatric WCVs. The study gathered information from mothers who had accompanied their children to WCVs at ages 12 and 24 months [ 15 ]. The survey included questions about health history, behaviors, and whether the physician discussed maternal depression, tobacco use, family planning, and folic acid supplementation [ 16 ]. The results of the study showed that the ICC model had improved the way maternal depression was being addressed during WCVs. However, best practices for screening, referral processes, and documentation related to PPD screening during WCVs still require further study [ 17 ]. This is especially important, as screening for postpartum depression in mothers is recommended during WCVs for young children [ 17 ].
Best practices implemented in a well-child visit
Best practices for WCVs are those that provide the most patient-oriented outcomes, such as immunizations, postpartum depression screening, and vision screening [ 18 ]. The American Academy of Pediatrics has created guidelines for WCVs, known as the periodicity schedule, and they recommend scheduled WCVs [ 19 ]. A study was conducted to determine the impact of the intervention on illness visits between WCVs [ 10 ]. The results showed that there were few differences between the two study arms, but a chart review showed that intervention children had fewer illness visits [ 10 ]. Pediatric WCVs also provide an opportunity to address psychosocial issues and developmental assessments [ 20 , 21 ], and there is wide variation in practice patterns regarding screening [ 22 ]. As far as the duration of WCVs, they are usually short; therefore, strategies for addressing the time devoted to WCVs must be considered [ 23 ]. Finally, it is important to understand the best practice of screening, education, and referral processes for addressing psychosocial issues during WCVs [ 16 ], as they are a significant part of pediatric office visits [ 24 ].
Potential challenges to implementing these best practices in a well-child visit
Additionally, the potential challenges to implementing best practices in a WCV must be acknowledged [ 18 ]. For instance, the lack of evidence-based practices can lead to uncertainty about how best to use the limited time available [ 23 ]. Furthermore, the Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine of the American Academy of Pediatrics has offered a periodicity schedule to recommend scheduled WCVs [ 19 ]. In a study to assess the differences between the interventions and the control arms, it was found that children in the intervention group had fewer illness visits between WCVs than control children [ 10 ]. This points to the importance of further understanding best practices for screening, education, and referral during the WCVs [ 16 ]. In this regard, research has revealed that 11.6% of the 483 WCVs were with children between 18 and 36 months of age [ 24 ]. Moreover, wide variations in practice patterns have been observed with some using a parent questionnaire for all WCVs and some using formal screens only at specific ages [ 22 ]. In addition, there is growing interest in understanding the practices of pediatric well-child care internationally [ 21 ] and exploring promising strategies for screening during WCVs [ 17 ]. Finally, there is a need to consider the ethical and legal dimensions of the boundaries of pediatric care [ 20 ].
Guidelines and principles for pediatric well-child visits
The subject of pediatric WCVs has been studied, and a number of guidelines have been developed to ensure that young children receive the best care. Studies have looked into adherence to pediatric WCV recommendations [ 25 ], and the standards and principles of Bright Futures [ 26 ]. In addition, similarities in approach to child health with periodic visits and anticipatory guidance have been seen abroad [ 21 ]. Guidelines recommend scheduled WCVs, detailing the schedule and content of care [ 19 ]. This includes preventive care such as guidance directed by a physician [ 27 ], and screening tests such as hearing screening [ 28 ]. However, further work is needed to optimize well child care [ 29 ], and a study found that a schedule with fewer visits had no detrimental effect on child health [ 30 ]. Pediatric WCVs are essential for the health and well-being of children, and research has been conducted to ensure that these visits are up-to-date and provide the best possible care.
Implementing guidelines and principles in a well-child visit
Therefore, the implementation of established guidelines and principles for WCVs is necessary [ 25 ]. The standards and principles of Bright Futures and the American Academy of Pediatrics [ 26 ] are similar in their approach of providing periodic visits and anticipatory guidance [ 21 ]. These guidelines and principles are used to define the schedule and content of well-child care [ 19 ], which includes guidance directed by a physician and preventive issues [ 17 ]. For example, screening tests for children who cannot fully participate are recommended [ 28 ]. Furthermore, research has shown that a schedule with fewer visits has no detrimental effect on child health [ 30 ]. Even though these articles provide a proof of principle, additional work is necessary to optimize well-child care [ 20 ]. Table Table3 3 shows an overview of the basic principles fostering a WCV.
Potential challenges to implementing these guidelines and principles in a well-child visit
Challenges to implementing effective WCV guidelines and principles arise from multiple areas [ 25 ]. For instance, the adherence rate of WCV recommendations may be lower for certain children [ 26 ]. Various countries have a similar approach to child health, focusing on periodic visits and anticipatory guidance [ 21 ]. The principles of prevention that shape WCV can vary depending on the country [ 19 ]. WCV is the most common type of physician visit for children, and it typically involves guidance from a physician [ 27 ]. For example, some children may have difficulty participating in screening tests [ 28 ]. In addition, further work is needed to optimize WCV, and research has suggested that a schedule with fewer visits may not have a detrimental effect on child health [ 29 ]. While there are suggested approaches for WCV programs, these are intended to be illustrative principles rather than specific programs [ 30 ]. As such, there are multiple potential challenges to implementing WCV guidelines and principles that must be carefully considered.
Study strengths and limitations
The research conducted in this study possesses several strengths. Firstly, the systematic review follows the PRISMA guidelines, ensuring a rigorous and transparent approach to study selection, data extraction, and synthesis. The search strategy utilized a range of global databases, including Web of Science, EMBASE, PubMed, Cochrane Library, HINARI, and Google Scholar, as well as reference list searches, minimizing the risk of missing relevant studies and enhancing the comprehensiveness of the review. The use of Boolean operators and specific keywords contributes to the thoroughness of the search process; however, the debate surrounding the replication of search results using mesh terms, Boolean combinations, and parentheses for precise literature retrieval stems from concerns about sensitivity and specificity. This debate continues due to factors such as the publication rate, retractions in online scholarly articles, and limitations in search algorithms. Additionally, the focus on studies published within a specific timeframe (2000-2023) enables the inclusion of recent and up-to-date evidence, relevant to the current landscape of acute gout treatment. The evolution and progression of best practices in pediatric well-child clinic visits from 2000 to 2023 have been influenced by advancements in healthcare, changes in technology, evolving clinical guidelines, and a growing understanding of child development and preventive care. The systematic approach to data extraction and quality assessment, including the use of the Joanna Briggs Institute quality assessment tool, enhances the credibility of the findings and the overall reliability of the review. Moreover, the analysis of both monotherapy and combination therapy approaches provides a comprehensive understanding of their respective impacts on serum urate levels, gout symptoms, and overall management. By evaluating various outcomes such as serum urate levels, tophi, gout flare rates, and urinary uric acid, the study contributes a holistic perspective on the effectiveness of the different treatment strategies. Overall, these methodological strengths support the reliability and validity of the conclusions drawn from the research.
However, there are some limitations. Firstly, the scope of included studies is limited to those published between 2000 and 2023, potentially excluding relevant earlier studies that could contribute valuable insights to the topic. Moreover, the inclusion criteria focus on observational studies with specific designs and geographic restrictions, which might omit relevant experimental or international studies that could provide a more comprehensive perspective on the subject matter. Secondly, the diversity in methodologies, patient populations, and study quality across the included studies introduces heterogeneity, which can lead to inconsistencies in findings and complicate direct comparisons between the studies. Despite the use of the Joanna Briggs Institute quality assessment tool, variations in study quality could influence the reliability and robustness of the conclusions drawn from the review. Finally, the search for studies was confined to a selection of global databases and conducted exclusively in English. This approach may introduce publication bias; favoring studies with significant findings and excluding studies published in other languages may limit the representation of findings from non-English-speaking regions, ultimately affecting the generalizability of the conclusions derived from the research.
Conclusions
Pediatric WCV for children aged three to five years is a vital part of preventive healthcare, addressing physical, emotional, cognitive, and social development. Evidence-based practices ensure comprehensive assessments, vaccinations, developmental screenings, and guidance, thus nurturing a healthy future. These visits benefit immediate and long-term well-being, enhancing individual and community health.
This review emphasizes the importance of WCVs in screening for medical issues, providing guidance, and promoting health. It underlines bonding between physicians, parents, and caregivers, prioritizing evidence-based interventions. Immunizations and socio-dynamic support are highlighted, emphasizing their relevance in WCVs. These visits also offer opportunities for answering parental questions and giving age-appropriate advice. However, challenges exist in implementing guidelines, especially for children with chronic conditions. Primary care providers are essential in engaging parents and linking them to community services, improving outcomes in areas such as vocal behavior, parenting, and language development.
Further research is required to assess individual components' effectiveness in these visits and address implementation challenges, especially for children aged three to five years. In conclusion, policy changes are crucial to underscore the significance of WCVs and ensure that best practices are consistently followed. These changes can lead to better health outcomes, increased vaccination coverage, improved parental education, and reduced healthcare disparities, ultimately benefiting children and communities as a whole.
Acknowledgments
O.E.O. contributed to the conceptualization of this project and the acquisition of the pieces of literature, played several roles in analyzing the collated works of literature, carefully reviewed them for the correctness of the intellectual content, agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the integrity of the work, and approved the final version. P.F.A. contributed to the design of this work, played a role in the interpretation of the collated literature and writing parts such as the introduction, discussion, and other parts, reviewed it for intellectual accuracy, agreed to be accountable for its integrity and will answer any question that may arise, and provided final approval of the final draft. O.B.N. played a role in creating the manuscript design, collating the works of literature used, analyzing the kinds of literature used, drafting parts of the body and conclusion, agreeing to be responsible for the intellectual accuracy and validity of the work, answering the ensuing questions, and authorizing the final version. T.O.E. substantially contributed to this study concept, was involved in analyzing the collated literature that was reviewed, reviewed its scientific content for correctness, drafted part of the abstract and body, agreed to be accountable for its integrity and to resolve any unfolding issues, and then approved its final version. O.O.A. significantly contributed to the creation of this manuscript by playing a role in the conceptualization, ensuring it was critically reviewed for intellectual content and accuracy, agreeing to resolve any unfolding queries about the work and its integrity, and finally approving the final draft. KPO: played a role in conceptualizing this study; reviewed, analyzed, and drafted parts of the body of the work; ensured its intellectual content is worthy of publication; agreed to be accountable for its integrity and to resolve any queries that may arise; and finally approved the final version. IUI: In addition to conceptualizing and designing the manuscript, this author played a role in synthesizing the works of literature, analyzing the content, creating parts of the original drafts, reviewing subsequent drafts for their intellectual validity and content, agreeing to be accountable for all aspects of the work, and finally approving its final version.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.

Why Are Well-Baby Visits So Important?

Table Of Contents
- Introduction
Immunizations: Protecting Against Preventable Illnesses
Tracking growth and development milestones, age-appropriate advice for every stage.
- Building Trust and Open Communication With a Doctor-Parent Relationship
The Importance of Finding the Right Pediatrician
The journey of parenthood is filled with a whirlwind of emotions – excitement, joy, perhaps a touch of worry. It’s natural to want the absolute best for your little one, and that includes safeguarding their health and well-being. While there will be bumps and sniffles along the way, regular well-baby visits with your pediatrician lay a strong foundation for your child’s overall health.
These checkups are much more than just weigh-ins and vaccinations. They offer a chance to track growth, catch potential issues early, and build a trusting relationship with your child’s doctor. These are some of the reasons why well-baby visits are so important:
One of the most critical aspects of well-baby visits is ensuring your child stays up-to-date on their immunizations. Vaccines are a safe and remarkably effective way to protect children from a wide range of serious, and sometimes life-threatening, illnesses. Here’s how they work:
- Training the Immune System: Vaccines introduce a weakened or inactive form of a virus or bacteria, tricking your child’s immune system into thinking it’s under attack. This triggers the body to produce antibodies – proteins that fight off specific infections.
- Building Immunity: If your child is later exposed to the real disease, their immune system already knows how to fight it, significantly reducing the risk of getting sick or preventing the illness altogether.
Key Immunizations
Your pediatrician will follow the recommended immunization schedule from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This schedule includes vaccines protecting against diseases like:
- Measles, Mumps, and Rubella: Highly contagious diseases that can have serious complications.
- Polio: A potentially disabling and life-threatening disease caused by a virus.
- Whooping Cough (Pertussis): A severe respiratory infection that can be especially dangerous for infants.
- Hepatitis A and B: Viruses that infect the liver.
- Chickenpox (Varicella): A contagious illness causing an itchy rash and fever.
- Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis: A combination vaccine for three serious bacterial diseases.
Beyond the Basics
There are also vaccines that protect against other diseases, such as:
- Rotavirus: Causes severe diarrhea, vomiting, and dehydration, primarily in infants.
- Pneumococcal disease: Causes various illnesses, including pneumonia, meningitis, and ear infections.
- Haemophilus Influenzae type B: A bacteria that causes serious infections, particularly in young children.
- Meningococcal disease: Can lead to meningitis (infection of the brain lining) and bloodstream infections.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Protects against cancers caused by HPV, including cervical cancer.
Discussing Vaccines with Your Pediatrician
Well-baby visits are the perfect opportunity to discuss vaccinations with your pediatrician. They can address any concerns you have, explain the benefits and risks, and provide reassurance about vaccine safety.
Well-baby visits aren’t just about shots and checkmarks. They’re vital for monitoring your child’s physical growth and developmental progress. Well-baby visits make sure your little one is growing and developing along the anticipated timeline. Your pediatrician will carefully track several key metrics:
- Growth: Measuring your child’s height, weight, and head circumference helps ensure they are growing at a healthy rate. Your pediatrician will plot these measurements on growth charts, comparing them to other children of the same age and sex. This helps identify potential growth concerns or areas where extra nutritional support might be needed.
- Gross Motor Skills: Large movements like sitting, crawling, standing, and walking.
- Fine Motor Skills: Smaller, precise movements like grasping objects, drawing, and using utensils.
- Language and Communication: Babbling, understanding simple words, forming sentences, and engaging in conversations.
- Social and Emotional Development: Making eye contact, smiling, forming attachments, and learning how to express emotions.
The Benefits of Early Detection
Tracking growth and development is more than just satisfying curiosity. It allows your pediatrician to identify any potential delays, differences, or concerns early on. Early detection is crucial because interventions and therapies can be most effective when started at a young age. Addressing potential issues early can help your child reach their full potential.
Beyond the Checkboxes
Well-baby visits offer more than just measurements and assessments. They’re a chance for you to discuss your child’s growth and development with their doctor. Share your observations, any questions you have, and celebrate those exciting new milestones together! These visits foster a strong partnership between you, your child, and their pediatrician, laying a foundation for open communication and support as your child grows.
Well-baby visits are your chance to tap into your pediatrician’s extensive knowledge about child health and development. A key part of these visits is what’s called anticipatory guidance – advice tailored to your child’s current age and upcoming stages.
What to Expect
Anticipatory guidance covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Nutrition and Feeding: Guidance on breastfeeding, introducing solid foods, establishing healthy eating habits, and addressing picky eating or food allergies.
- Sleep: Advice on establishing sleep routines, managing nighttime wakings, and addressing sleep issues at different ages.
- Safety: Tips on preventing accidents in the home, car seat safety, water safety, and age-appropriate discussions about stranger danger.
- Development and Behavior: Insights into typical behaviors for different age groups, positive discipline strategies, managing tantrums, and promoting healthy emotional development.
- Preparing for Change: Guidance on helping your child navigate transitions like starting daycare or preschool, welcoming a new sibling, or moving to a new home.
The Power of Prevention
Anticipatory guidance is about preventing problems before they start. By providing you with proactive advice and support, your pediatrician empowers you to make informed decisions for your child’s well-being. This knowledge can also give you greater confidence as a parent, knowing you’re equipped to handle the challenges and joys of each new stage.
Tailored to Your Child
The beauty of anticipatory guidance is that it’s personalized. Your pediatrician will consider your child’s individual temperament, family dynamics, and specific needs. It’s also an opportunity for you to raise any concerns and get the targeted advice you need to support your child’s unique journey.
Building Trust and Open Communication With a Doctor-Parent Relationship
Well-baby visits offer a valuable opportunity to build a strong and trusting relationship between you, your child, and your pediatrician. This relationship is especially important during the early years when your child’s health is rapidly evolving. Your pediatrician becomes a partner in your child’s care, offering medical expertise and ongoing support and reassurance.
You should feel comfortable discussing any questions, concerns, or observations about your child’s health and development. Your pediatrician, in turn, should listen attentively, provide clear explanations, and involve you in decision-making.
Regular well-baby visits allow your pediatrician to get to know your child as an individual. This familiarity helps create a comfortable environment for your child–and you–during checkups and through the subsequent years of growth and development.
Well-baby visits provide a foundation for your child’s lifelong health and well-being. By prioritizing these checkups, you’re taking proactive steps to ensure your child thrives. However, the benefits of well-baby visits extend far beyond the exam room. Choosing the right pediatrician is essential for a positive and supportive healthcare experience for both you and your child.
If you’re looking for a dedicated Anchorage pediatrician to partner with on your parenting journey, we invite you to consider LaTouche Pediatrics. Our experienced pediatricians are committed to providing compassionate, personalized care for children of all ages. We offer convenient locations in Anchorage and Eagle River to serve families throughout the region.
Schedule your child’s well-visit today and discover the peace of mind that comes from knowing your little one is in the best hands.
Key Takeaways
- Well-baby visits are essential for every child’s health and development. They go far beyond basic checkups.
- Immunizations offer life-saving protection. Vaccines are safe and effective in preventing serious illnesses. Discuss any vaccine concerns with your pediatrician.
- Monitoring growth and development is crucial. Well-baby visits help catch potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions to support your child’s progress.
- Your pediatrician is your parenting partner. They provide anticipatory guidance on nutrition, sleep, safety, development, and more.
- A strong doctor-parent relationship fosters trust. Open communication with your pediatrician is vital for your child’s well-being.
- Choosing the right pediatrician makes all the difference. Look for a provider who listens, offers personalized care, and makes you and your child feel comfortable.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
You may use these <abbr title="HyperText Markup Language">HTML</abbr> tags and attributes: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Your Guide to Well-Baby Visits
Medical review policy, latest update:, what are well-baby visits and why are they so important, when will my child's well-baby visits happen, read this next, what you can expect at well-baby visits, tips on making the most of well-baby visits, time it right, make a checklist, write down your questions, have some answers, too, dress baby for success.
What to Expect the First Year , 3rd edition, Heidi Murkoff. WhatToExpect.com, Your Baby's Vaccine Schedule: What Shots Should Your Child Get When? , January 2021. American Academy of Pediatrics, AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits , September 2021. American Academy of Pediatrics, Checkup Checklist: 1 Month Old , September 2021. KidsHealth From Nemours, Your Child's Checkup: 1 Month , April 2021.
Go to Your Baby's Age
Trending on what to expect, the covid-19 vaccine for infants, toddlers and young children, how to create a night shift system when you have a newborn, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., when do babies start laughing, baby-led weaning, what happens in the ‘4th trimester’ (and is it a real thing).
Pediatrician well visits
You May Also Like
Planning visitors during hospital stay, you’re pregnant how these moms reacted, jump to your week of pregnancy, trending on what to expect, moms share home remedies for pregnancy morning sickness, 8 expensive products moms say are worth the money, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., 14 moms on what labor really feels like, what are your go-to healthy snacks, things they don't tell you about: mom edition, pregnancy brain moments let's have a laugh, help keep our community safe, to create a safe place, please, on our end, we will.
https://www.high-endrolex.com/8

Best Places to visit in Moscow
Moscow is the capital city, as well as one of the, most visited tourist places in Russia . The city has a fascinating history and colorful, awe-inspiring architecture in the form of stunning cathedrals, churches, and palaces. The intricate detailing and complex architectural designs of the bygone era will surely keep anyone tranquilized. Red Square, St. Basil’s Cathedral, and Moscow’s Kremlin are the most prominent historical places to visit in Moscow. Besides, the city is also home to several museums where you can learn about Russia’s fantastic literary heritage, such as the Pushkin Memorial Museum, the Tolstoy House Museum, the Dostoevsky House Museum, and the Mayakovsky Museum. These places to see in Moscow are not just interesting but are beyond magical. Explore here, our list of best places to visit as part of Moscow Tour Packages .

Red Square or Krasnaya Ploshchad is one of the largest and most impressive squares situated at the heart of the city of Moscow. Built-in the 1490s, the 73,000 square meters Red Square is separating the royal citadel of the Kremlin from the ancient merchant quarter of Kitai-gorod. It served as a gathering tourist place in Moscow, a marketplace, and a festival ground during the Soviet era. It is one of the most popular places to visit in Moscow due to its wealth of historical sights and cultural landmarks such as the Kremlin, St. Basil’s Cathedral, Lenin’s Mausoleum, and the State Historical Museum. Moscow’s Red Square along with the Kremlin was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 1990. Besides, wandering around the massive square is a humbling experience and undoubtedly one of the highlights the city has to offer as part of the Russia tour packages .
Bolshoi Theatre

The Bolshoi Theatre is a historic theatre of ballet and opera situated at the Theatre Square in Moscow. With more than 200 dancers, it is one of the second-largest ballet and opera companies in Europe, and the main theater in Russia. This historic theatre was founded back in 1776, but the present magnificent building was built in 1825. Designed by architect Joseph Bove in classical Russian architectural style, the building is all in white with 8 columns, intricate detailing on the facade, and the ‘quadriga’ adorned at the entrance. The six-tier auditorium is lavishly decorated and is a perfect setting for the world-class performances that take place on its stage. The performances here are mostly of Russian origins, with a few foreign performances also taking place. Spending a night watching a performance at the glittering Bolshoi Theatre is sure to be a memorable experience.
The Moscow Kremlin

The Moscow Kremlin is a fortified complex located in the center of Moscow. Founded by the Rurik dynasty in the 15th century, it was once the home of the Tsar family and is now the official residence of the president of the Russian Federation. Constructed beautifully and with a great eye for detail, the Moscow Kremlin complex covers an area of 275,000 square meters with 20 towers, 15 buildings, and more than 1.5 miles of walls that are made up to 21 feet thick. The intricate decor inside the Grand Kremlin Palace reflects the pure charm of the Revival architecture in Russian that blends perfectly with the architectural style of Byzantine Revival. The Cathedral Square is considered to be the center of the Kremlin complex and has three cathedrals of magnificent architecture. The complex is also home to several palaces and also the Ivan the Great Bell Tower. In the south is the Armoury building, a museum holding everything from the royal crown and imperial carriages to the ivory throne of Ivan the Terrible and Faberge eggs. Designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1990, it is undoubtedly one of the best Moscow tourist places.
St. Basil’s Cathedral

A trip to Moscow is incomplete without visiting this unique and impressive cathedral. Located in the impressive Red Square, St. Basil’s Cathedral is one of the top places to visit in Moscow and a popular cultural symbol of Russia. Also called ‘Pokrovsky Cathedral’, it was built in 1555 – 1561 by the order of Tsar Ivan the Terrible to celebrate his victory over the Khanate of Kazan. Built-in unique architecture inspired by Byzantine and Asian design, it is a magnificent work with 8 distinctive candy-colored onion domes. There are nine individual chapels inside the church, all decorated with colorful mural art. Today, St. Basil’s Cathedral serves as a museum, allowing visitors to see the simply breathtaking interiors and the intricacy of the work that was put into its construction.
The State Tretyakov Gallery

The State Tretyakov Gallery is one of the most important and greatest art museums in Russia as well as in the world. Named after Pavel Tretyakov, a Moscow industrialist, and patron of art, the museum boasts the largest collection of Russian art in the world. A trip to this art gallery helps you to get a peek into the history of Russia and its evolution. The museum hosts an incredible collection that includes more than 190,000 paintings, icons, and sculptures of various eras and art traditions. The Tretyakov museum has two main buildings – one is on Lavrushinsky lane, where you can see the collections of Russian art from the 11th to 20th centuries, including famous masterpieces of Rublev, Repin, Serov, Vasnetsov, Surikov, Aivazovsky while the other building is on Krymsky Val which exhibits the collection of avant-garde, social realism, and other art trends of the 20th and 21st centuries.
State Historical Museum

The State Historical Museum, located on the opposite end of Red Square, is one of the largest museums in Russia, and among the must-visit Moscow tourist places. This amazing museum was constructed in 1872 by the orders of Emperor Alexander II to commemorate national history and educate the masses about the long past of the country. This imposing Russian Revivalism style building houses an enormous collection of objects reaching the 5 million figure. Ranging from the days of the pre-historic tribes of the region to the Russia of today, the collection includes several relics, artifacts, paintings, thrones, etc.
The Moscow Planetarium

The Moscow planetarium is one of the oldest planetariums in Russia and among the best places to visit in Moscow. It is one of the favorite places for recreation, with all kinds of interactive exhibits, educational programs, entertainment, high-tech gadgetry, and scientific components. Inaugurated in 1929, it was built by the architects Mikhail Barsh, Mikhail Sinyavsky, and engineer Georgy Zunblat. The main highlight of the museum is the Large Star Hall which boasts Europe’s largest star projection dome with its 25-silver dome roof that features glowing northern lights, floating clouds, August meteor showers, flickering stars, flying comets, and solar eclipses. Attracting thousands of visitors, it is one of the biggest destinations on the Moscow Museum circuit.
Ostankino Television Tower

Ostankino Television Tower is the most famous television and radio tower located in Moscow. Designed by Nikolai Nikitin. it was built in 1967 to mark the 50th anniversary of the October Revolution, and named after the Ostankino district of Moscow. Towering 1,772 feet, it is the eleventh high-rising structure in the world and the only free-standing structure in the whole of Europe. Also, don’t miss to visit the glass-floored observation deck located at a height of 1,105 feet (337 feet) from where one can get incredible views of Moscow city.
Museum of Cosmonautics

Located in the northeast of Moscow city, the museum of Cosmonautics is one of the best museums in Russia dedicated to space exploration. This museum is a must-visit place for those who want to know everything about space adventure as the Museum of Cosmonautics traces the history of astronautics from the 1920s to the present day. The museum consists of more than 98,000 artifacts including historical documents, spacesuits, an authentic spacecraft, personal belongings of astronauts, and even the replica of the space station “Mir”. Furthermore, it is also known for its rich collection and brilliant architecture.
The Pushkin State Museum of Fine Arts

Located in the center of Moscow, the Pushkin Museum is one of the most famous museums in Russia. The museum was opened in 1912 amid Emperor Alexander III’s rule and was renamed the Pushkin Museum in 1937, in honor of the celebrated Russian writer, Alexander Pushkin. The museum houses the largest collections of foreign art in Russia, showcasing global artistic developments from ancient times to the present day. Currently, the museum houses around 700,000 paintings, sculptures, drawings, applied works, photographs, and archaeological and animalistic objects. Some of the exhibits date back to Ancient Egypt and antiquity while others are modern demonstrating the more recent artistic and cultural trends. The museum houses the second-largest collection of world art in Russia after the Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg. One of the greatest masterpieces of the museum is the actual main building itself which reflects the architectural traditions of the antique Greek temples.
Grand Kremlin Palace

Built-in 1849 atop Borovitsky Hill, the Grand Kremlin is a lavishly decorated palace that is closely associated with the wealth and splendor of the Russian emperors who lived here a long time ago. Designed by Konstantin Thon, the palace reflects the pure charm of Russian architecture that stands 125 meters long, 47 meters high, and total area of around 25,000 sq. m. Made of gold, marble and intricate designs, the main highlight of the palace is the Holy Vestibule, the nine churches, Palace of Facets for celebrations and glimpses of majestic imperial thrones, Tsarina’s Golden Chamber, the place of Russian Queen, five grand reception halls and over 700 rooms and apartments. The Grand Kremlin Palace was once home to the Tsar family and is now the official residence of the president of the Russian Federation, although most heads of state choose to reside elsewhere.
Arbat Street

Surrounded by historical buildings, the Arbat Street is one of the oldest streets in Moscow and among the best Moscow tourist places. With 1.25 km long, this 15th century lively street was once a popular place to live for the novelty families, merchants, poets, artists, and academics. The street has been decorated with distinctively beautiful street lantern on weekends and evenings that add more charm to this place. Today, the street is filled with several restaurants, cafes, shops, as well as many statues and monuments. Besides, it is also one of the best places for shopping in Moscow that attracts huge number of tourists as part of Moscow Tour Packages.
Featured Source
- Find a hospital Results See all results Balashikha 1 hospitals Barnaul 2 hospitals Ivanovo 2 hospitals Kaliningrad 2 hospitals Kazan 2 hospitals Kislovodsk 1 hospitals Korolev 1 hospitals Kovrov 1 hospitals Krasnodar 3 hospitals Krasnogorsk 1 hospitals Moscow 41 hospitals Nizhny Novgorod 3 hospitals Novokuibyshevsk 1 hospitals Novokuznetsk 1 hospitals Novosibirsk 4 hospitals Obninsk 1 hospitals Orenburg 1 hospitals Penza 1 hospitals Saint Petersburg 8 hospitals Samara 3 hospitals Surgut 1 hospitals Tomsk 1 hospitals Tyumen 1 hospitals Ulan-Ude 1 hospitals Ulyanovsk 2 hospitals Vladivostok 1 hospitals Volgograd 1 hospitals Vologda 1 hospitals Yalta 1 hospitals Yekaterinburg 2 hospitals All hospitals
- Find a sanatorium Results See all results Altai region 4 sanatoriums Buryatia 1 sanatoriums Crimea 4 sanatoriums Ingushetia 1 sanatoriums Karelia 1 sanatoriums Kislovodsk 1 sanatoriums Krasnodar region 2 sanatoriums Moscow region 5 sanatoriums Nizhny Novgorod Region 1 sanatoriums Saint Petersburg region 1 sanatoriums All sanatoriums
- Check the prices Allergology 29 hospitals Andrology 35 hospitals Bariatric surgery 15 hospitals Cardiology 42 hospitals Cosmetology 21 hospitals Dentistry 25 hospitals Dermatology 37 hospitals Dietetics 15 hospitals Endocrinology 42 hospitals Gastroenterology 38 hospitals Genetics 4 hospitals Gynecology 54 hospitals Hematology 17 hospitals IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) 14 hospitals Mammalogy 33 hospitals Maxillofacial Surgery 9 hospitals Narcology 3 hospitals Neurology 51 hospitals Neurosurgery 16 hospitals Obstetrics 14 hospitals Oncology 42 hospitals Ophthalmology 36 hospitals Orthopedics and traumatology 32 hospitals Otolaryngology (ENT) 39 hospitals Pediatrics 29 hospitals Phlebology 29 hospitals Plastic surgery 22 hospitals Proctology 27 hospitals Psychiatry 13 hospitals Pulmonology 24 hospitals Rehabilitation 17 hospitals Rheumatology 26 hospitals Speech therapy 6 hospitals Surgery 37 hospitals Urology 47 hospitals Venereology 21 hospitals
- List of diseases Aesthetic problems 24 hospitals Allergic diseases 31 hospitals Blood diseases 17 hospitals Cardiovascular diseases 44 hospitals Childhood diseases 27 hospitals Colon diseases 27 hospitals Diseases of the digestive system 42 hospitals Diseases of the mammary glands 34 hospitals Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and injuries 37 hospitals Diseases of veins and lymph nodes 32 hospitals Endocrine diseases 46 hospitals ENT (eye, nose, throat) diseases 40 hospitals Eye diseases 39 hospitals Female diseases 56 hospitals Genetic diseases 6 hospitals Infectious diseases 25 hospitals Male diseases 39 hospitals Mental disorders and phenomena 13 hospitals Narcological problems 6 hospitals Nervous diseases 50 hospitals Oncological diseases 43 hospitals Respiratory diseases 25 hospitals Rheumatic diseases 27 hospitals Skin diseases 37 hospitals Speech disorders 7 hospitals Teeth Diseases 26 hospitals Urological diseases 50 hospitals Venereal diseases 24 hospitals
- Our contacts
Morozovskaya Children's City Clinical Hospital
Tap to book

About clinic
The largest children's hospital in Russia and Europe. More than a third of the total number of hospitalized children in Moscow falls on the Morozovskaya hospital. Located on nine hectares in the historical center of the capital, it resembles a small town in its spirit.
The bed capacity is 1205 beds. Morozovskaya Children's Hospital is a multidisciplinary (31 profiles) clinical hospital and has 48 departments, including 34 clinical ones.
The Morozov hospital employs:
- 10 out of 24 children's Chief freelance specialists of the Moscow City Health Department are a neonatologist, geneticist, rheumatologist, endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, pulmonologist, gastroenterologist, oncologist, hematologist, cardiovascular surgeon.
- more than 700 doctors,
- more than 900 nursing staff.
13 unique Centers
On the basis of the Morozov hospital, 13 unique Centers of city specialized medical care for children and adolescents have been formed and are constantly operating:
- Center for the treatment of cerebrovascular pathology in children and adolescents (the only one in Russia)
- Center for Pediatric Rheumatology (the only one in the city health care system)
- Center for Pediatric Oncology and Hematology
- Center for Orphan and Other Rare Diseases
- Center for the treatment of children with von Willebrand disease
- Reference center for congenital hereditary diseases, genetic abnormalities, orphan and other rare diseases
- Center for Reproductive Health of Children and Adolescents
- Center for Pediatric Endocrinology
- Center for Pediatric Gastroenterology
- Neonatal Screening Center
- Center for the Prevention of Chronic Noncommunicable Diseases
- Respiratory Medicine Center
- Consultative and Diagnostic Center of Neurology and Family Psychotherapy
Medical equipment
More than 3 thousand units of unique and advanced medical equipment have been installed in the Morozov hospital, including integrated equipment in operating rooms for microsurgical, endovascular and endoscopic operations, pain stress monitors, equipment for artificial lung ventilation of newborns and incubators for nursing children with extremely low body weight, computer and magnetic resonance tomographs (including 3.0 TL), digital X-ray diagnostic and X-ray surgical devices, ultrasound diagnostic systems, high-tech equipment for laboratory, including genetic research, etc.
The figures for the effectiveness of treatment are comparable, and in some cases even exceed the indicators of the world's leading children's clinics.
A team of specialist doctors works seven days a week at the hospital, which allows to provide emergency multidisciplinary medical care (pediatricians, pediatric surgeons, orthopedic traumatologists, maxillofacial surgeons, anesthesiologists-resuscitators, neonatologists, otorhinolaryngologists, hematologist, neurologists, doctors of radiation, ultrasound and clinical laboratory diagnostics, etc.). There is no similar one-step round-the-clock work of a multidisciplinary team of medical specialists in any children's hospital in Russia and Europe.
Today, the medical care that patients receive at the Morozov hospital is no different from that which they could receive in any other country in the world.
Since 2015, the Morozovskaya Children's Hospital has received a license for the implementation of educational detail and became the Center for Postgraduate Pediatric Education. The Morozovskaya hospital is a clinical base for 15 departments of three medical universities in Moscow.
Since 1903, the Morozovskaya hospital has not interrupted its work for a single day, remaining faithful to the motto "Mercy and professionalism", laid down when the hospital was founded.
Specialization
What diseases are treated, additional services and facilities, patients also choose.


COMMENTS
The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the "periodicity schedule." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence. Schedule of well-child visits. The first week visit (3 to 5 ...
Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season ...
In the world of pediatric care, a well visit is the equivalent of what used to be called a check-up or a physical. Once a year, parents typically make an appointment for a well visit with their family physician or pediatrician to make sure all's well with their child and to voice any concerns. For children 3 and under, though, visits are as frequent as every few weeks in the
Take blood pressure. Measure oxygen levels. Listen to your child's lungs. Look at your child's eyes, ears, and throat. Press on your child's tummy to feel organs. Move your child's hips ...
While you already have a lot on your plate, well-child visits are critical to keeping your kids, family and the community healthy. Keep reading to explore common questions to ask a pediatrician about your newborn, toddler, grade-schooler, pre-teen or teenager during well-child visits. Preparing for a well-child visit
Most pediatricians follow the American Academy of Pediatrics recommended schedule: 1st year: newborn, 2-4 weeks, two months, four months, six months, nine months. 2nd year: 12 months, 15 months, 18 months. 3rd year: 24 months, 30 months (2-1/2 years) Then every 12 months starting at their third birthday. While we often call this a "well visit ...
Your Check-up Checklist: Preparing for an Annual Well Visit. Your child's pediatrician plays a key role in keeping your child both physically and mentally healthy. At first, when your child is an infant, you see the doctor every few months. As kids get older, though, you may only see the pediatrician once every year during an annual well visit.
Beginning at the 7 year visit, there is both a Parent and Patient education handout (in English and Spanish). For the Bright Futures Parent Handouts for well-child visits up to 2 years of age, translations of 12 additional languages (PDF format) are made possible thanks to the generous support of members, staff, and businesses who donate to the ...
Visiting the pediatrician when your child is well also provides you with an opportunity to ask questions - and get expert answers - about your child's health, development and well-being. Delaying these visits can put your child at greater risk of illness or delay needed interventions. For example, many common developmental delays are ...
What Happens During a Well-Child Visit? The pediatrician will review weight and height and calculate body mass index (BMI) to determine if your child is growing normally. Blood pressure, heart rate and breathing will be checked. A head-to-toe physical exam will be done.
Children ages 5 to 10 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a "well-child visit" once a year. A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any ...
Welcome to the Well Visit Planner ® Your Child, Your Well Visit. A quick and free pre-visit planning tool to focus care on your unique needs and goals. Get started now: Covers all 15 age-specific well visits from your child's first week of life to age 6. Enter provider ID code Continue without code. Learn more about creating a family account
Checkups usually begin with measurements. During first-year visits, a nurse or your baby's health care provider will measure and record your baby's length, head circumference and weight. Your child's measurements will be plotted on his or her growth chart. This will help you and the provider see how your child's size compares with that ...
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program's requirements and talk to your child's doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider.
1. Check your child's weight and height, calculate body mass index (BMI), and plot the measurements on a growth chart. 2. Check your child's blood pressure, vision, and hearing using standard testing equipment. 3. Ask questions, address concerns, and offer advice about your child's: Eating. Schedule 3 meals and 1-2 nutritious snacks a day.
Overview. Kids ages 11 to 14 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a "well-child visit" once a year. A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch ...
1st Week Checkup Checklist: 3 to 5 days old. Congratulations on the birth of your new baby! For many parents, the first visit to the pediatrician is also their newborn's first trip away from home. Don't worry—we've got you covered with what questions to ask, what paperwork to remember, and what to expect at your baby's first checkup.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria. For the current systematic review, we excluded studies that had focused on the evaluation of the process of quality improvement in best practices in well-child clinic visits without acknowledging specific practice changes to child care delivery; articles that focused on one topic in well-child care as opposed to tackling the different aspects of well-child ...
Well-baby visits help catch potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions to support your child's progress. Your pediatrician is your parenting partner. They provide anticipatory guidance on nutrition, sleep, safety, development, and more. A strong doctor-parent relationship fosters trust.
Your baby's first official checkup (and first immunization) will take place at the hospital. After that, well-baby visits are scheduled throughout the first two years at: The first week (usually a couple of days after you're discharged from the hospital) 1 month. 2 months.
Pediatrician well visits. L. Liz224. Apr 12, 2024 at 8:26 PM. What schedule does your pediatrician have your baby come in for well checks/vaccinations. I saw my baby's DR when my baby was a few days old & then at 2 weeks. They said I don't have to go again until my baby is 2mos old. That seems like a long stretch to me for a newborn.
If you dont own a place in Moscow City region or live in some iconic place then you are also safe from UAV/drone. Even if the UAV does hit your flat, it only shatters windows, so make sure not to sleep near the window. Right now, Its the best time to hit on russian girls since a lot of men gone to the front or abroad.
It served as a gathering tourist place in Moscow, a marketplace, and a festival ground during the Soviet era. It is one of the most popular places to visit in Moscow due to its wealth of historical sights and cultural landmarks such as the Kremlin, St. Basil's Cathedral, Lenin's Mausoleum, and the State Historical Museum. Moscow's Red ...
The largest children's hospital in Russia and Europe. More than a third of the total number of hospitalized children in Moscow falls on the Morozovskaya hospital. Located on nine hectares in the historical center of the capital, it resembles a small town in its spirit. It is a multidisciplinary (31 profiles) clinical hospital and has 48 departments, including 34 clinical ones.