NASA's Voyager probes have been traveling through space for nearly 46 years. Here are 18 groundbreaking photos from their incredible mission.
- Nearly 46 years after their launch, Voyager 1 and 2 will likely soon reach the end of their scientific mission .
- NASA recently lost contact with Voyager 2 after sending it a bad command by mistake.
- Here are 18 pictures the probes took over the course of their forty-plus-year journey.

The Voyager probes are pioneers of science, making it farther into space than any other manufactured object. But now, they face a terminal problem: their power is running out.
The twin probes were originally sent on a four-year mission to tour the solar system, but they exceeded all expectations and are still going nearly 46 years later. That makes them NASA's longest-lived mission.
Scientists are now doing their best to keep the probes going for as long as possible. They recently found a clever hack to extend Voyager 2's life for another three years and plan to do the same with Voyager 1.
But these are old machines and NASA is constantly scrambling to fix mistakes. Last year, Voyager 1 started sending garbled data from the outside of the solar system. NASA ultimately figured out one of its computers had gone dead.
Voyager 2 is now in limbo , as the agency revealed Friday it had lost contact with the probe when someone sent a wrong command. It could be the end of Voyager 2's mission if NASA can't fix the mistake, which the agency probably won't be able to do before October.
As the probes are nearing the end of their scientific mission, here are 18 images from Voyager that changed science.

The Voyager probes were designed to visit Jupiter and Saturn.
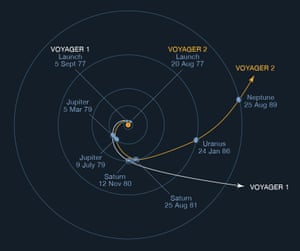
The Voyager mission included two probes — Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 — which NASA launched in 1977 within a few months of each other.
NASA took advantage of a rare planet alignment to turbocharge their journeys into space.
NASA originally built the probes to last five years, but they have exceeded that lifespan many times .
As of August 20 and September 5, 2023, Voyager 2 and Voyager 1 will have been traveling for 46 years, respectively.
This is what Voyager 1 saw on its approach to Jupiter.
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 reached Jupiter in 1979.
As they flew by the planet, they took about 50,000 pictures of Jupiter. These blew away scientists, as the quality of the pictures was much better than those taken from Earth, according to NASA.
These snaps taught scientists important facts about the planet's atmosphere, magnetic forces, and geology that would have been difficult to decipher otherwise.
The probes discovered two new moons orbiting Jupiter: Thebe and Metis.
They also spotted a thin ring around Jupiter.
The probe captured this picture as it was looking back at the planet backlit by the Sun.
Voyager 1 discovered volcanoes at the surface of Io, one of Jupiter's moons.
Next stop: Saturn.
In 1980 and 1981, the probes reached Saturn . The flyby gave scientists unprecedented insight into the planet's ring structure, atmosphere, and moons.
Voyager snapped Saturn's rings in more detail than ever before.
And showed every secret that Enceladus, Saturn's moon, had to offer.
Saturn, snapped as the probe flew away, was shown in a new light.
By 1986, Voyager 2 had made it to Uranus.
By 1986, Voyager 1 has finished its grand tour of the solar system, and few out towards space. But Voyager 2 kept on its exploring our nearest planets, passing 50,600 miles away from Uranus in January 1986.
Voyager 2 discovered two extra rings around Uranus , revealing the planet had at least 11, not 9.
Voyager 2 also spotted 11 previously unseen moons around Uranus.
Here is a picture of Miranda, Uranus's sixth-biggest moon.
Voyager 2 was the first spacecraft to observe Neptune from a close distance.
In 1989, 12 years after its launch, Voyager 2 passed within 3,000 miles of Neptune.
Here's Nepture taken by Voyager 2, in all its blue glory.
Voyager 2 took this unflattering pic of Triton's rough face.
It captured Triton, Neptune's moon in unprecedented detail.
And snapped Triton's southern hemisphere.
As it flew by, Voyager 2 uncovered Neptune's rings.
As its parting gift, Voyager 2 took this beautiful picture of light grazing Neptune's south pole.
This is Voyager 2's last picture. Since it wouldn't come across another planet on its ongoing journey, NASA switched off its cameras after its flyby of Neptune to conserve energy for other instruments.
Voyager 1 had one last trick up its sleeve.
As its last photographic hurrah in 1990, Voyager 1 took 60 images of the solar system from 4 billion miles away.
It gave us the Earth's longest selfie, dubbed the "pale blue dot."
This remains the longest-range selfie: a portrait of the Earth taken by a human-made probe from 4 billion miles away.
After this picture, NASA switched off Voyager 1's cameras to save energy. NASA could switch the probes' cameras back on , but it is not a priority for the mission.
Beyond the solar system
Though the probes are no longer sending pictures, they haven't stopped sending crucial information about space.
In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first human-made instrument to cross into interstellar space by crossing the boundary between our solar system and the rest of the universe, called the heliopause.
Voyager 2 was second, crossing that threshold in 2018 . The probe revealed that there was yet another layer outside of our heliosphere.
The probes keep sending back measurements from interstellar space, like weird hums likely coming from vibrations made by neighboring stars.
Even after their instruments are switched off, the probes' mission continues.
NASA is planning to switch more of the probes' instruments in the hope of extending their life to the 2030s.
But even after all their instruments become quiet, their mission will carry on. As they drift off, they will still be carrying a golden record that carries crucial information about humanity. If intelligent extraterrestrial life exists, they could use that information to reach out to us.
This article was originally published on June 6, 2022, and is being updated with the latest developments about Voyager 1 and 2.
- Main content

Voyager 2: the story of its mission so far – in pictures
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share via Email
Since launching in 1977 , the Nasa probe has captured never-before-seen images of the solar system
- Nasa’s Voyager 2 sends back its first message from interstellar space
Mon 4 Nov 2019 17.10 GMT Last modified on Mon 4 Nov 2019 23.12 GMT
Photograph: JPL-Caltech/Nasa
Photograph: Nasa

Photograph: JPL/Nasa

Photograph: JPL-Caltech/NASA

Photograph: JPL/NASA

Photograph: Corbis/Getty Images

Photograph: Roger Ressmeyer/Corbis Getty Images

Photograph: Nasa Photo/Alamy

More galleries
Most popular.

- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
Watch videos and view images of Voyager 1 and 2 as they passed by Saturn, Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune and get a glimpse into the images relating to the Golden Record.
Voyager Videos

Posters and Infographics

- Become A Member
- Gift Membership
- Kids Membership
- Other Ways to Give
- Explore Worlds
- Defend Earth
How We Work
- Education & Public Outreach
- Space Policy & Advocacy
- Science & Technology
- Global Collaboration
Our Results
Learn how our members and community are changing the worlds.
Our citizen-funded spacecraft successfully demonstrated solar sailing for CubeSats.
Space Topics
- Planets & Other Worlds
- Space Missions
- Space Policy
- Planetary Radio
- Space Images
The Planetary Report
The eclipse issue.
Science and splendor under the shadow.
Get Involved
Membership programs for explorers of all ages.
Get updates and weekly tools to learn, share, and advocate for space exploration.
Volunteer as a space advocate.
Support Our Mission
- Renew Membership
- Society Projects
The Planetary Fund
Accelerate progress in our three core enterprises — Explore Worlds, Find Life, and Defend Earth. You can support the entire fund, or designate a core enterprise of your choice.
- Strategic Framework
- News & Press
The Planetary Society
Know the cosmos and our place within it.
Our Mission
Empowering the world's citizens to advance space science and exploration.
- Explore Space
- Take Action
- Member Community
- Account Center
- “Exploration is in our nature.” - Carl Sagan
Rae Paoletta • Mar 03, 2022
The best space pictures from the Voyager 1 and 2 missions
Launched in 1977, NASA’s Voyager 1 and 2 missions provided an unprecedented glimpse into the outer solar system — a liminal space once left largely to the imagination. The spacecraft provided views of worlds we’d never seen before, and in some cases, haven’t seen much of since.
The Voyager probes were launched about two weeks apart and had different trajectories, like two tour guides at the same museum. Only Voyager 2 visited the ice giants — Uranus and Neptune — for example.
The Voyagers hold a unique position in the pantheon of space history because they’re still making it; even right now, Voyagers 1 and 2 are the only functioning spacecraft in interstellar space. Both hold a Golden Record that contains sights and sounds of Earth in case alien life were to find one of the spacecraft.
As the Voyager missions voyage on, it’s good to look back at how they captured our solar system before leaving it.
This content is hosted by a third party (youtube.com), which uses marketing cookies. Please accept marketing cookies to watch this video.
Let’s Go Beyond The Horizon
Every success in space exploration is the result of the community of space enthusiasts, like you, who believe it is important. You can help usher in the next great era of space exploration with your gift today.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Here are instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
Advertisement
Neptune - Voyager's last picture show: The spacecraft Voyager 2 is leaving the Solar System 12 years after its launch - Its last close encounter showed us clouds on blue and stormy Neptune, and surprises on Triton, the moon with an icecap of methane, vol
By Nigel Henbest
9 September 1989
AS SEEN from Earth through a telescope, it’s a mere speck of light, orbited by two even fainter specks. But now we know Neptune almost as well as we understand the nearer planets – thanks to the doughty spacecraft Voyager 2. On the morning of 25 August, Voyager swept a mere 4900 kilometres from the planet’s cloud tops, its closest encounter with a planet since leaving the Earth in 1977.
Voyager’s last port of call was, ironically, highly reminiscent of its home world – another Blue Planet. Neptune’s deep blue atmosphere is tinted partly by scattering of light and partly because its methane gas absorbs red light.
At about 20 Degree south on Neptune there is a large dark oval, almost the size of planet Earth, and resembling the Great Red Spot on Jupiter. Around the edge of Neptune’s ‘Great Dark Spot’, and stretching away like bright banners, hang wispy white cirrus clouds of methane ice. Near the south pole is a smaller dark spot, with a small patch of cirrus in its centre. Between the two is a small irregularly shaped white patch that the Voyager scientists call ‘the Scooter’ because it shoots around the planet much faster than the other clouds.
All these cloud motions are relative, however, and meteorologists need to know how fast the planet’s core rotates. At other planets, the Voyager scientists have measured the rotation of the planet’s core by detecting bursts of radio waves. These come from Neptune’s magnetic field, which is generated well within the planet.
At Neptune, too, Voyager picked up regular radio bursts, which indicate that the core turns once every 16…
Sign up to our weekly newsletter
Receive a weekly dose of discovery in your inbox! We'll also keep you up to date with New Scientist events and special offers.
To continue reading, subscribe today with our introductory offers
No commitment, cancel anytime*
Offer ends 2nd of July 2024.
*Cancel anytime within 14 days of payment to receive a refund on unserved issues.
Inclusive of applicable taxes (VAT)
Existing subscribers
More from New Scientist
Explore the latest news, articles and features
Environment
Corals that recover from bleaching still struggle to breed.
Subscriber-only
Joel Edgerton must escape the multiverse in a gripping sci-fi series
We now know exactly how thick the boundary between water and air is, gps jamming traced to russia after flights over europe suspended, popular articles.
Trending New Scientist articles

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z

Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.
NASA/JAXA’s XRISM Mission Captures Unmatched Data With Just 36 Pixels

NASA Scientists Gear Up for Solar Storms at Mars

NASA Uses Small Engine to Enhance Sustainable Jet Research
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Two Small NASA Satellites Will Measure Soil Moisture, Volcanic Gases

NASA Balloons Head North of Arctic Circle for Long-Duration Flights
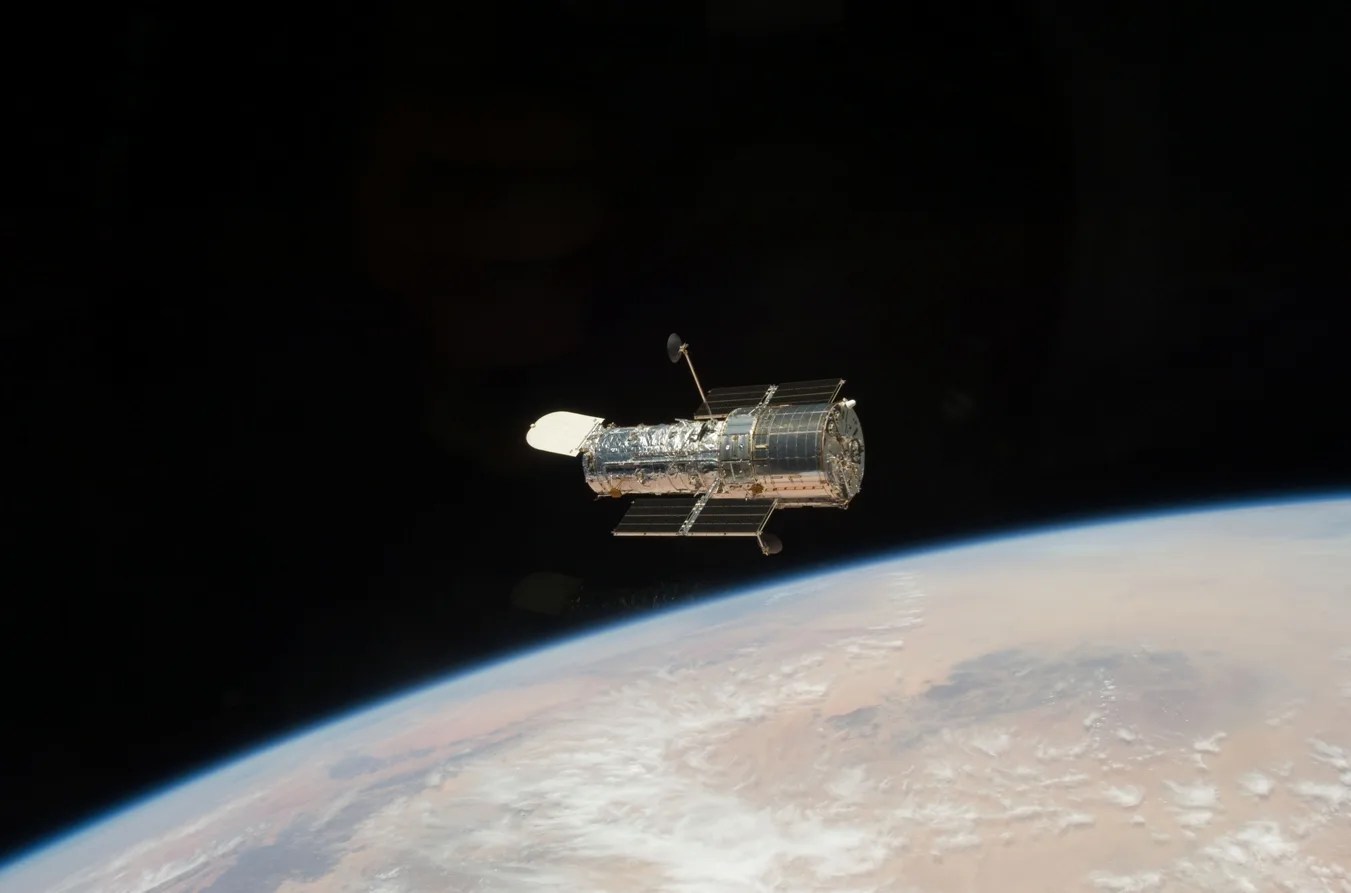

NASA’s Hubble Pauses Science Due to Gyro Issue
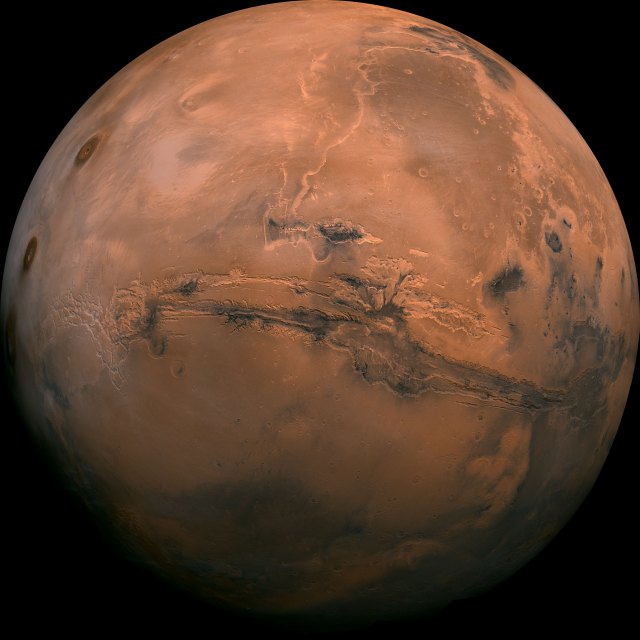

NASA Selects Commercial Service Studies to Enable Mars Robotic Science

NASA’s Commercial Partners Deliver Cargo, Crew for Station Science

NASA Shares Lessons of Human Systems Integration with Industry
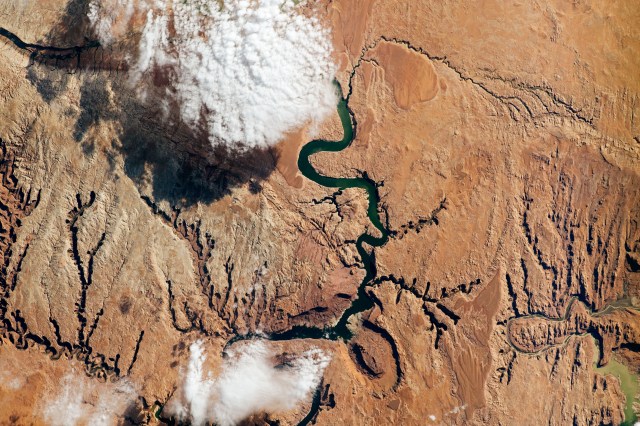

NASA-Led Study Provides New Global Accounting of Earth’s Rivers

NASA’s ORCA, AirHARP Projects Paved Way for PACE to Reach Space

What’s Up: May 2024 Skywatching Tips from NASA
May’s Night Sky Notes: Stargazing for Beginners
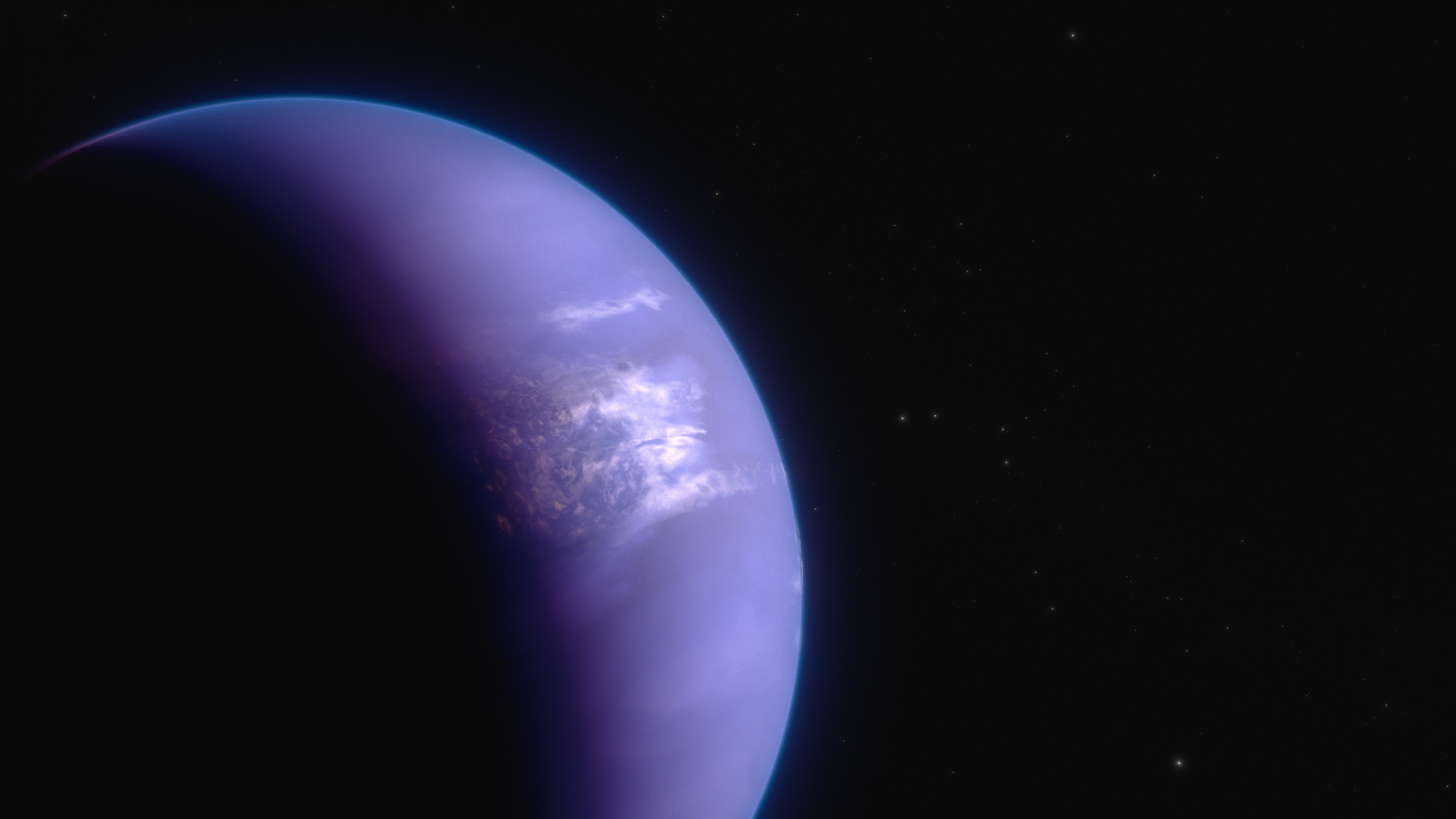
NASA’s Webb Maps Weather on Planet 280 Light-Years Away

Webb Captures Top of Iconic Horsehead Nebula in Unprecedented Detail

NASA Photographer Honored for Thrilling Inverted In-Flight Image

NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter Team Says Goodbye … for Now

Big Science Drives Wallops’ Upgrades for NASA Suborbital Missions

Tech Today: Stay Safe with Battery Testing for Space

NASA Grant Brings Students at Underserved Institutions to the Stars

Washington State High Schooler Wins 2024 NASA Student Art Contest

NASA STEM Artemis Moon Trees

NASA’s Commitment to Safety Starts with its Culture

NASA Challenge Gives Space Thruster Commercial Boost

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
45 years ago: voyager 2 begins its epic journey to the outer planets and beyond, johnson space center.
Forty-five years ago, the Voyager 2 spacecraft left Earth to begin an epic journey that continues to this day. The first of a pair of spacecraft, Voyager 2 lifted off on Aug. 20, 1977. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, manages the spacecraft on their missions to explore the outer planets and beyond. Taking advantage of a rare planetary alignment to use the gravity of one planet to redirect the spacecraft to the next, the Voyagers initially targeted only Jupiter and Saturn, but Voyager 2 went on to explore Uranus and Neptune as well. The Voyagers carried sophisticated instruments to conduct their in-depth explorations of the outer planets. Both spacecraft continue to return data as they make their way out of our solar system and enter interstellar space.
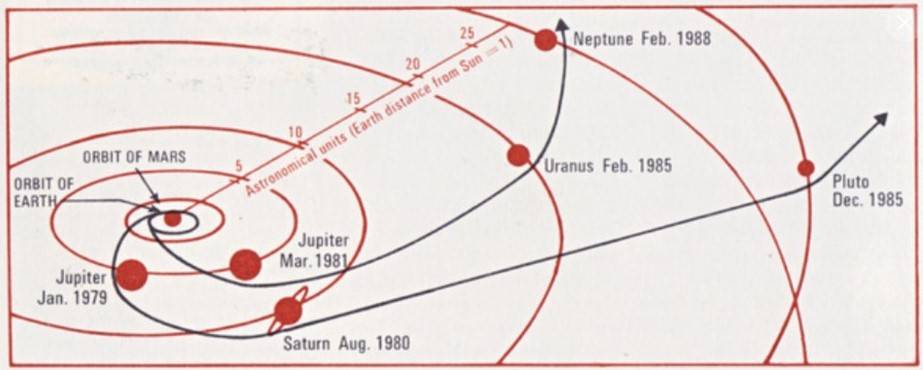
In the 1960s, mission designers at JPL noted that the next alignment of the outer planets that occurs only every 175 years would happen in the late 1970s. Technology had advanced sufficiently that spacecraft could take advantage of this rare alignment to flyby Jupiter and use its gravity to bend their trajectories to visit Saturn, and repeat the process to also visit Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Launching several missions to visit each planet individually would take much longer and cost much more. The original plan to send two pairs of Thermoelectric Outer Planet Spacecraft on these Grand Tours proved too costly leading to its cancellation in 1971. The next year, NASA approved a scaled-down version of the project to launch a pair of Mariner-class spacecraft in 1977 to explore just Jupiter and Saturn. On March 7, 1977, NASA Administrator James C. Fletcher announced the renaming of these Mariner Jupiter/Saturn 1977 spacecraft as Voyager 1 and 2. Scientists held out hope that one of them could ultimately visit Uranus and Neptune, thereby fulfilling most of the original Grand Tour’s objectives – Pluto would have to wait many more years for its first visit.
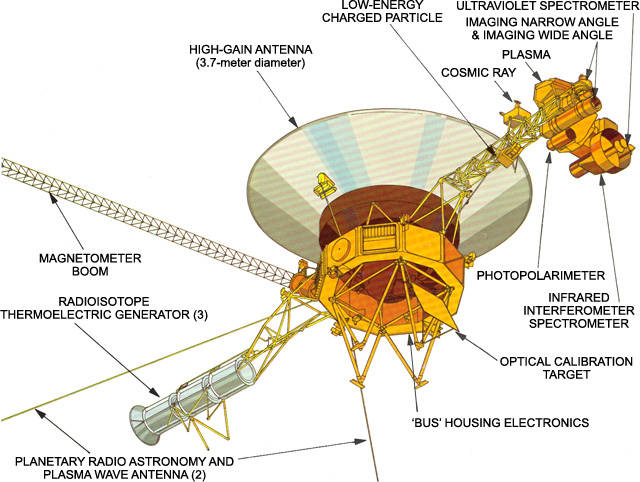
Each Voyager carried a suite of 11 instruments to study the planets during each encounter and to learn more about interplanetary space in the outer reaches of the solar system, including:
- An imaging science system consisting of narrow-angle and wide-angle cameras to photograph the planet and its satellites.
- A radio science system to determine the planet’s physical properties.
- An infrared interferometer spectrometer to investigate local and global energy balance and atmospheric composition.
- An ultraviolet spectrometer to measure atmospheric properties.
- A magnetometer to analyze the planet’s magnetic field and interaction with the solar wind.
- A plasma spectrometer to investigate microscopic properties of plasma ions.
- A low energy charged particle device to measure fluxes and distributions of ions.
- A cosmic ray detection system to determine the origin and behavior of cosmic radiation.
- A planetary radio astronomy investigation to study radio emissions from Jupiter.
- A photopolarimeter to measure the planet’s surface composition.
- A plasma wave system to study the planet’s magnetosphere.
Voyager 2 left Earth first, lifting off on Aug. 20, 1977, atop a Titan IIIE-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, now Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, in Florida. Although its twin launched two weeks later, it traveled on a faster trajectory and arrived at Jupiter four months earlier. Voyager 2 successfully crossed the asteroid belt between Dec. 10, 1977, and Oct. 21, 1978. In April 1978, its primary radio receiver failed, and it has been operating on its backup receiver ever since.
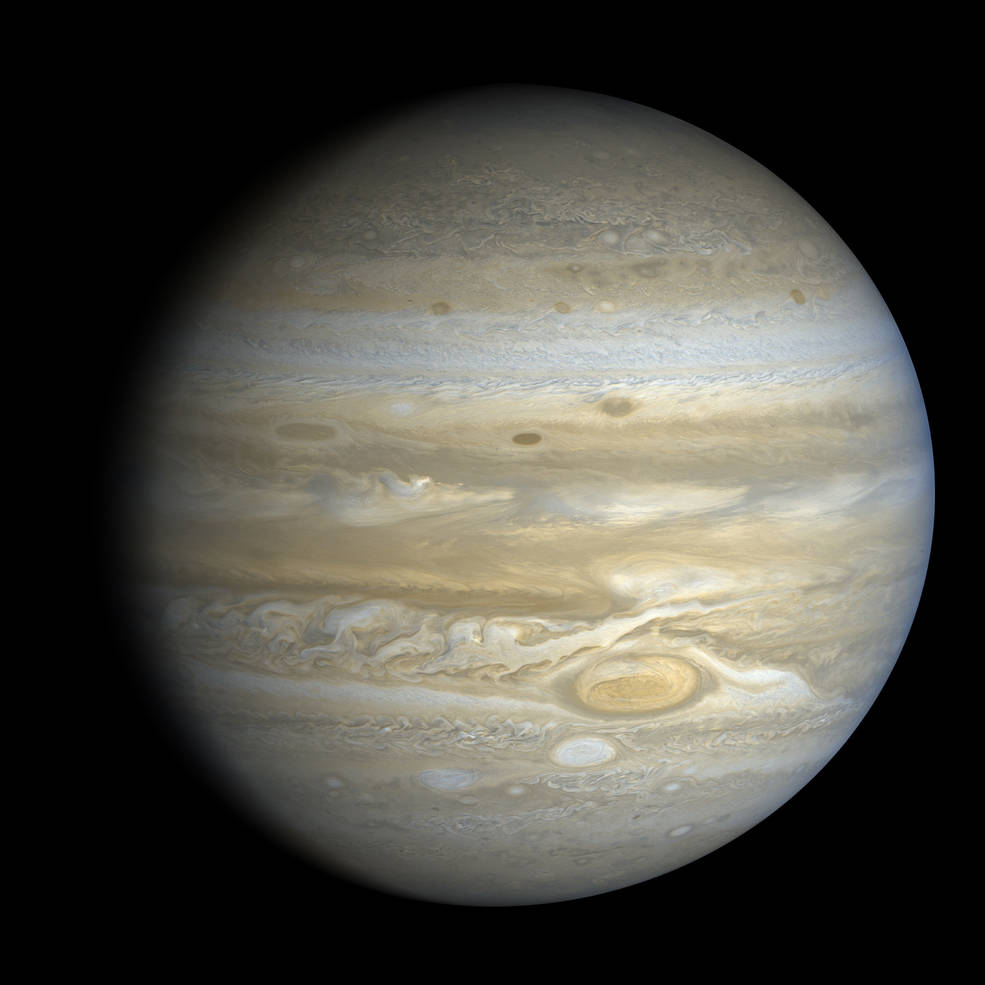

Voyager 2 conducted its observations of Jupiter between April 24 and Aug. 5, 1979, making its closest approach of 350,000 miles above the planet’s cloud tops on July 9. The spacecraft returned 17,000 images of Jupiter, many of its satellites, and confirmed Voyager 1’s discovery of a thin ring encircling the planet. Its other instruments returned information about Jupiter’s atmosphere and magnetic field. Jupiter’s massive gravity field bent the spacecraft’s trajectory, accelerating it toward Saturn. Voyager 2 began its long-range observations of the ringed planet on June 5, 1981, passed within 26,000 miles of the planet’s cloud tops on Aug. 26, and concluded its studies on Sept. 4. The spacecraft captured 16,000 photographs of the planet, its rings, and many of its known satellites. It discovered several new ones, while its instruments returned data about Saturn’s atmosphere. Saturn’s gravity sent Voyager 2 on to Uranus.
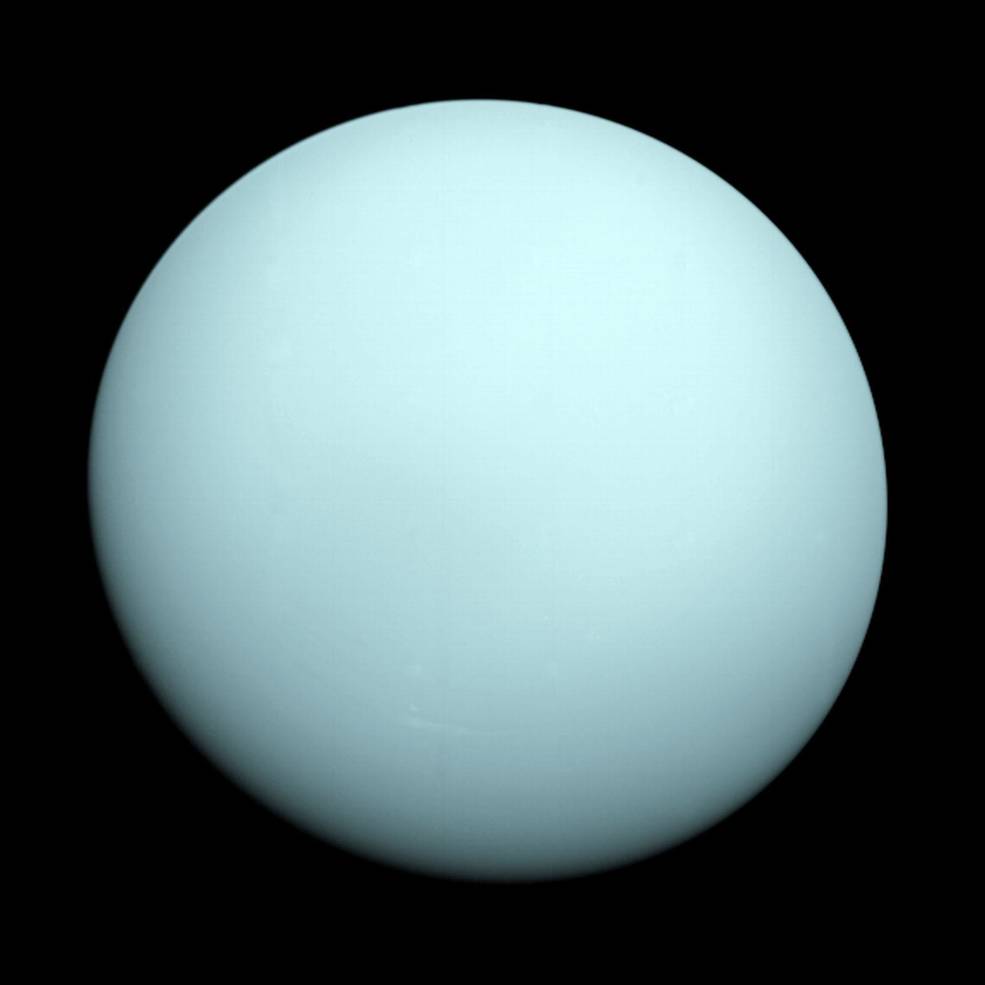

Voyager 2 carried out the first close-up observations of Uranus between Nov. 4, 1985, and Feb. 25, 1986, making its closest approach of 50,700 miles above the planet’s cloud tops on Jan. 24. It returned more than 7,000 photographs of the planet, its rings and moons, discovering two new rings and 11 new moons. The spacecraft’s instruments returned data about the planet’s atmosphere and its unusual magnetic field, tilted by 59 degrees compared to its rotational axis and offset from the planet’s center by about one-third of the planet’s radius. Voyager 2 took advantage of Uranus’ gravity to send it on to its last planetary destination, Neptune. The spacecraft conducted the first close-up observations of the eighth planet between June 5 and Oct. 2, 1989, making its flyby just 3,408 miles above its north pole on Aug. 25, its closest approach to any planet since leaving Earth in 1977. This trajectory allowed Voyager 2 to observe Neptune’s large moon Triton, the last solid object it explored. During the encounter, it returned more than 9,000 images of the planet, its atmosphere, dark rings, and moons, discovering six new moons. Like Uranus, Voyager 2’s instruments revealed that Neptune has an unusual magnetic field, not only tilted 47 degrees from the planet’s axis but also significantly offset from the planet’s center.
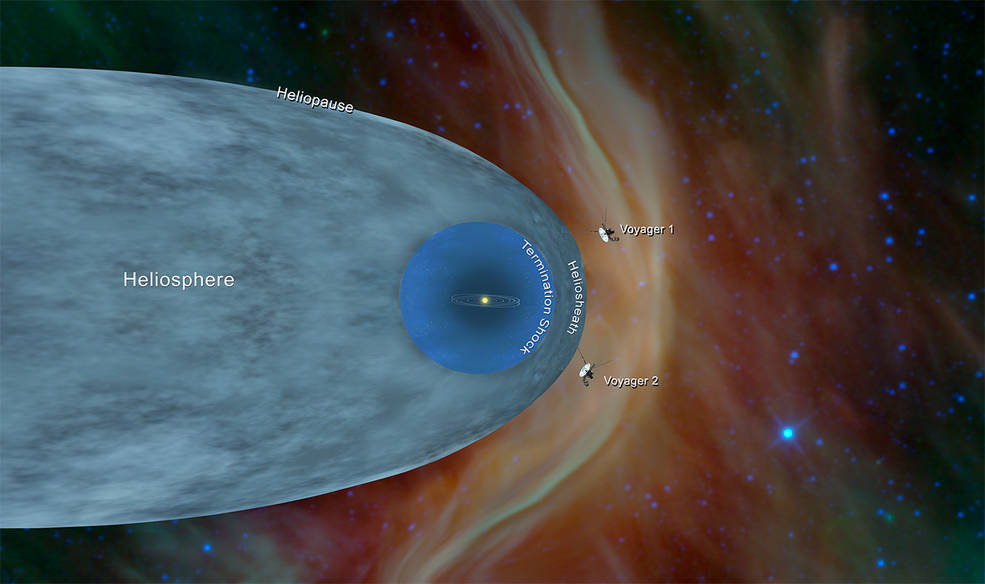
Following its reconnaissance of Neptune, Voyager 2 began its Interstellar Mission extension that continues to this day. Over the years, several of the spacecraft’s instruments have been turned off to conserve power, beginning with the imaging system in 1998, but it continues to return data about cosmic rays and the solar wind. On Nov. 5, 2018, six years after its twin, Voyager 2 crossed the heliopause, the boundary between the heliosphere – the bubble-like region of space created by the Sun – and the interstellar medium. Currently, Voyager 2 continues its mission, more than 12 billion miles from Earth, so distant that a signal from the spacecraft takes 18 hours to reach Earth, and just as long for a return signal to reach the craft. Engineers expect that Voyager 2 will continue to return data until about 2025. And just in case an alien intelligence finds it one day, Voyager 2 like its twin carries a gold-plated record that contains information about its home planet, including recordings of terrestrial sounds, music, and greetings in 55 languages. Engineers at NASA thoughtfully included Instructions on how to play the record.

For more on Voyagers 1 and 2, NASA’s longest-lived missions, please visit here , with thanks to our colleagues at JPL.
The voyage continues…
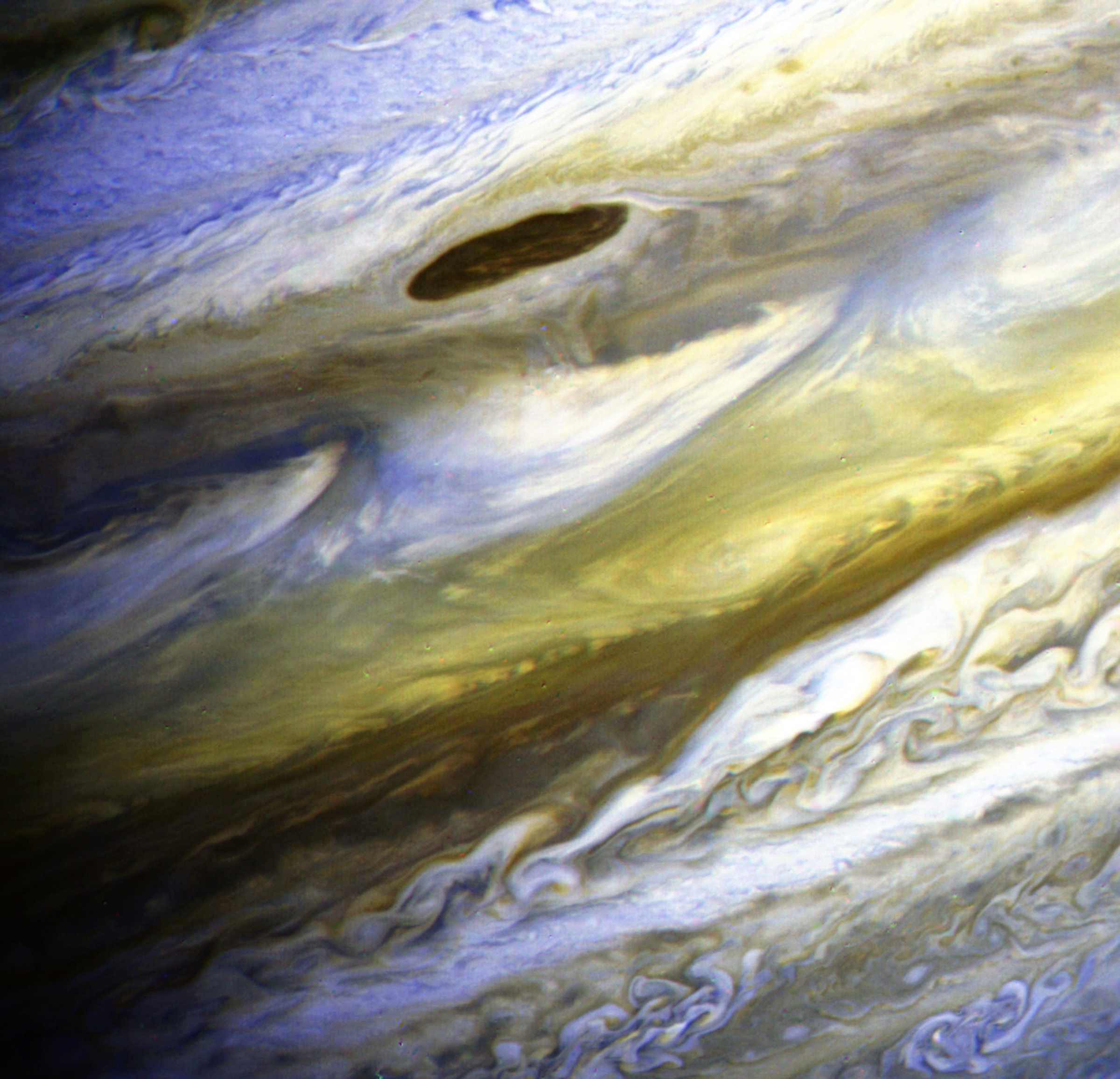
See the 10 Best Photos Taken by Voyager 2

More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Why Your Breakfast Should Start with a Vegetable
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
NASA’s Voyager 1 Resumes Sending Engineering Updates to Earth

NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is depicted in this artist’s concept traveling through interstellar space, or the space between stars, which it entered in 2012.
After some inventive sleuthing, the mission team can — for the first time in five months — check the health and status of the most distant human-made object in existence.
For the first time since November , NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems. The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth.

After receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in five months, members of the Voyager flight team celebrate in a conference room at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on April 20.
The team discovered that a single chip responsible for storing a portion of the FDS memory — including some of the FDS computer’s software code — isn’t working. The loss of that code rendered the science and engineering data unusable. Unable to repair the chip, the team decided to place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. But no single location is large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
So they devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS. To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole. Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated as well.
The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft’s engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22 ½ hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22 ½ hours for a signal to come back to Earth. When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.
Get the Latest News from the Final Frontier
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago , the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history. Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA.
News Media Contact
Calla Cofield
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469
NASA Hears From Voyager 1, the Most Distant Spacecraft From Earth, After Months of Quiet
NASA has finally heard back from Voyager 1 in a way that makes sense

This illustration provided by NASA depicts Voyager 1. The most distant spacecraft from Earth stopped sending back understandable data in November 2023. Flight controllers traced the blank communication to a bad computer chip and rearranged the spacecraft’s coding to work around the trouble. In mid-April 2024, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory declared success after receiving good engineering updates. The team is still working to restore transmission of the science data. (NASA via AP)
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — NASA has finally heard back from Voyager 1 again in a way that makes sense.
The most distant spacecraft from Earth stopped sending back understandable data last November. Flight controllers traced the blank communication to a bad computer chip and rearranged the spacecraft’s coding to work around the trouble.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California declared success after receiving good engineering updates late last week. The team is still working to restore transmission of the science data.
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space. The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.
Contact was never lost, rather it was like making a phone call where you can’t hear the person on the other end, a JPL spokeswoman said Tuesday.
Launched in 1977 to study Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 1 has been exploring interstellar space — the space between star systems — since 2012. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 12.6 billion miles (20 billion kilometers) away and still working fine.
Photos You Should See - April 2024

The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press . All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Join the Conversation
Tags: Associated Press , science
America 2024

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

Fed: High Inflation Stalls Rate Cut
Tim Smart May 1, 2024

Congress Comes Down on Campus Protests
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 1, 2024

University Leaders in Their Own Words
Laura Mannweiler May 1, 2024

April Job Gains Above Forecasts

Nationwide Campus Protests Escalate
Laura Mannweiler April 30, 2024

What to Know: Trump Gag Order Violations
Lauren Camera April 30, 2024


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Photography of Jupiter began in January 1979, when images of the brightly banded planet already exceeded the best taken from Earth. Voyager 1 completed its Jupiter encounter in early April, after taking almost 19,000 pictures and many other scientific measurements. Voyager 2 picked up the baton in late April and its encounter continued into August.
Embark on a captivating exploration of the Voyager spacecraft's epic odyssey through the cosmos, spanning more than four decades and unveiling mind-boggling ...
Here are 18 groundbreaking photos from their incredible mission. This montage shows examples of striking images of the solar system Voyager 1 and 2 took on their missions. NASA/JPL/Insider. Nearly ...
This picture of Neptune was produced from the last whole planet images taken through the green and orange filters on Voyager 2's narrow-angle camera. ... taken in 1989 by Voyager 2 during its ...
Voyager 2's Last Image of Uranus NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft took this haunting final image of Uranus on January 25, 1986, as it left the planet to explore Neptune. NASA/JPL. Most NASA images are in the public domain. Reuse of this image is governed by NASA's image use policy. Explore related images: Bruce Murray Space Image Library, Outer ...
Acknowledgements: Amanda Barnett, Phil Davis and Preston Dyches contributed to this story. Some of the information in this article came from the account of the solar system family portrait detailed in Kosm ann, Hansen and Sagan, "The Family Portrait of the Solar System: The last set of images taken by Voyager 1 and the fascinating story of how they came to be," 70th International Astronautical ...
Each Voyager space probe carries a gold-plated audio-visual disc in the event that the spacecraft is ever found by intelligent life forms from other planetary systems. Examine the images and sounds of planet earth. Images Voyager Took The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft explored Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune before starting their journey ...
Image: NASA / JPL / Ted Stryk. Saturn as seen by Voyager 1 The last picture from Voyager 1's approach to Saturn in which the entire planet and ring system can be seen in a single frame. Image: NASA/JPL/Björn Jónsson. Voyager 2's best view of Enceladus This was the Voyager mission's best view of Enceladus, captured by Voyager 2 on August 26 ...
Voyager 2: Hello Interstellar Space, Goodbye Heliosphere Full Resolution: TIFF (8.947 MB) JPEG (633.8 kB) 2018-12-10: Voyager Interstellar Mission: 1920x1080x3 ... Ganymede - Close Up Photos Full Resolution: TIFF (1.036 MB) JPEG (232.3 kB) 2002-05-10: Ganymede: Galileo Voyager: VG Imaging Science Subsystem VG ...
Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken on February 14, 1990, by the Voyager 1 space probe from an unprecedented distance of approximately 6 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles, 40.5 AU), as part of that day's Family Portrait series of images of the Solar System.. In the photograph, Earth's apparent size is less than a pixel; the planet appears as a tiny dot against the vastness of ...
But now we know Neptune almost as well as we understand the nearer planets - thanks to the doughty spacecraft Voyager 2. On the morning of 25 August, Voyager swept a mere 4900 kilometres from the ...
Voyager 2 took advantage of Uranus' gravity to send it on to its last planetary destination, Neptune. The spacecraft conducted the first close-up observations of the eighth planet between June 5 and Oct. 2, 1989, making its flyby just 3,408 miles above its north pole on Aug. 25, its closest approach to any planet since leaving Earth in 1977.
An enhanced color image of Saturn's rings taken from the Voyager 2 spacecraft on Aug. 1981. Space Frontiers/Getty Images. View of volcanic eruptions of Pele on Jupiter's moon Io taken from the ...
The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars). Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally.
Voyager 1 got to the heliopause in 2012 and Voyager 2 in 2018. The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA's Voyager 1 at a distance of ... [+] 3.7 billion miles (6 ...
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space. The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.