- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault

Ferdinand Magellan
By: History.com Editors
Updated: October 4, 2023 | Original: October 29, 2009

In search of fame and fortune, Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan (c. 1480-1521) set out from Spain in 1519 with a fleet of five ships to discover a western sea route to the Spice Islands. En route he discovered what is now known as the Strait of Magellan and became the first European to cross the Pacific Ocean. The voyage was long and dangerous, and only one ship returned home three years later. Although it was laden with valuable spices from the East, only 18 of the fleet’s original crew of 270 returned with the ship. Magellan himself was killed in battle on the voyage, but his ambitious expedition proved that the globe could be circled by sea and that the world was much larger than had previously been imagined.
Ferdinand Magellan’s Early Years
Ferdinand Magellan (c. 1480–1521) was born in Sabrosa, Portugal, to a family of minor Portuguese nobility. At age 12 Ferdinand Magellan ( Fernão de Magalhães in Portuguese and Fernando de Magallanes in Spanish) and his brother Diogo traveled to Lisbon to serve as pages at Queen Leonora’s court. While at the court Magellan was exposed to stories of the great Portuguese and Spanish rivalry for sea exploration and dominance over the spice trade in the East Indies, especially the Spice Islands, or Moluccas, in modern Indonesia. Intrigued by the promise of fame and riches, Magellan developed an interest in maritime discovery in those early years.
Did you know? Clove was the most valuable spice in Europe during Magellan's day. It was used to flavor food, but Europeans also believed that its essence could improve vision, its powder could relieve fevers and that it could enhance intercourse when mixed with milk.
In 1505, Magellan and his brother were assigned to a Portuguese fleet headed for India. Over the next seven years, Magellan participated in several expeditions in India, Southeast Asia, and Africa and was wounded in several battles. In 1513 he joined the enormous 500-ship, 15,000-soldier force sent by King Manuel to Morocco to challenge the Moroccan governor who refused to pay its yearly tribute to the Portuguese empire. The Portuguese easily overwhelmed the Moroccan forces, and Magellan stayed on in Morocco. While there he was seriously wounded in a skirmish, which left him with a limp for the rest of his life.
Magellan: From Portugal to Spain
In the 15th century, spices were at the epicenter of the world economy, much like oil is today. Highly valued for flavoring and preserving food as well as masking the taste of meat gone bad, spices like cinnamon, clove, nutmeg and especially black pepper were extremely valuable. Since spices could not be cultivated in cold and arid Europe, no effort was spared to discover the quickest sea route to the Spice Islands. Portugal and Spain led the competition for early control over this critical commodity. Europeans had reached the Spice Islands by sailing east, but none had yet to sail west from Europe to reach the other side of the globe. Magellan was determined to be the first to do so.
By now an experienced seaman, Magellan approached King Manuel of Portugal to seek his support for a westward voyage to the Spice Islands. The king refused his petition repeatedly. In 1517, a frustrated Magellan renounced his Portuguese nationality and relocated to Spain to seek royal support for his venture.
When Magellan arrived in Seville in October 1517, he had no connections and spoke little Spanish. He soon met another transplanted Portuguese named Diogo Barbosa, and within a year he had married Barbosa’s daughter Beatriz, who gave birth to their son Rodrigo a year later. The well-connected Barbosa family introduced Magellan to officers responsible for Spain’s maritime exploration, and soon Magellan secured an appointment to meet the king of Spain.
The grandson of King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, who had funded Christopher Columbus ’s expedition to the New World in 1492, received Magellan’s petition with the same favor shown by his grandparents. Just 18 years old at the time, King Charles I granted his support to Magellan, who in turn promised the young king that his westward sea voyage would bring immeasurable riches to Spain.
Strait of Magellan
On August 10, 1519 Magellan bade farewell to his wife and young son, neither of whom he would ever see again, and the Armada De Moluccas set sail. Magellan commanded the lead ship Trinidad and was accompanied by four other ships: the San Antonio , the Conception , the Victoria and the Santiago . The expedition would prove long and arduous, and only one ship, the Victoria , would return three years later across the Pacific, carrying a mere 18 of the fleet’s original crew of 270.
In September 1519 Magellan’s fleet sailed from Sanlúcar de Barrameda, Spain, and crossed the Atlantic Ocean, which was then known simply as the Ocean Sea. The fleet reached South America a little more than one month later. There the ships sailed southward, hugging the coast in search of the fabled strait that would allow passage through South America. The fleet stopped at Port San Julian where the crew mutinied on Easter Day in 1520. Magellan quickly quelled the uprising, executing one of the captains and leaving another mutinous captain behind. Meanwhile Magellan had sent the Santiago to explore the route ahead, where it was shipwrecked during a terrible storm. The ship’s crew members were rescued and assigned out among the remaining ships. With those disastrous events behind them, the fleet left Port San Julian five months later when fierce seasonal storms abated.
On October 21, 1520 Magellan finally entered the strait that he had been seeking and that came to bear his name. The voyage through the Strait of Magellan was treacherous and cold, and many sailors continued to mistrust their leader and grumble about the dangers of the journey ahead. In the early days of the navigation of the strait, the crew of the San Antonio forced its captain to desert, and the ship turned and fled across the Atlantic Ocean back to Spain. At this point, only three of the original five ships remained in Magellan’s fleet.
The Magellan Expedition: Circumnavigation the Glob e
After more than a month spent traversing the strait, Magellan’s remaining armada emerged in November 1520 to behold a vast ocean before them. They were the first known Europeans to see the great ocean, which Magellan named Mar Pacifico, the Pacific Ocean, for its apparent peacefulness, a stark contrast to the dangerous waters of the strait from which he had just emerged. In fact, extremely rough waters are not uncommon in the Pacific Ocean, where tsunamis, typhoons and hurricanes have done serious damage to the Pacific Islands and Pacific Rim nations throughout history.
Little was known about the geography beyond South America at that time, and Magellan optimistically estimated that the trip across the Pacific would be rapid. In fact, it took three months for the fleet to make its way slowly across the vast Mar Pacifico. The days dragged on as Magellan’s crew anxiously waited to utter the magic words “Land, ho!” At last, the fleet reached the Pacific island of Guam in March 1521, where they finally replenished their food stores.
Magellan’s fleet then sailed on to the Philippine archipelago landing on the island of Cebu, where Magellan befriended the locals and, struck with a sudden religious zeal, sought to convert them to Christianity . Magellan was now closer than ever to reaching the Spice Islands, but when the Cebu asked for his help in fighting their neighbors on the island of Mactan, Magellan agreed. He assumed he would command a swift victory with his superior European weapons, and against the advice of his men, Magellan himself led the attack. The Mactanese fought fiercely, and Magellan fell when he was shot with a poison arrow. Ferdinand Magellan died on April 27, 1521.
Magellan would never make it to the Spice Islands, but after the loss of yet another of his fleet’s vessels, the two remaining ships finally reached the Moluccas on November 5, 1521. In the end, only the Victoria completed the voyage around the world and arrived back in Seville, Spain, in September 1522 with a heavy cargo of spices but with only 18 men from the original crew, including Italian scholar and explorer Antonio Pigafetta. The journal Pigafaetta kept on the voyage is a key record of what the crew encountered on their journey home.
Impact of Ferdinand Magellan
Seeking riches and personal glory, Magellan’s daring and ambitious voyage around the world provided the Europeans with far more than just spices. Although the trip westward from Europe to the east via the Strait of Magellan had been discovered and mapped, the journey was too long and dangerous to become a practical route to the Spice Islands. Nevertheless, European geographic knowledge was expanded immeasurably by Magellan’s expedition. He found not only a massive ocean, hitherto unknown to Europeans, but he also discovered that the earth was much larger than previously thought. Finally, although it was no longer believed that the earth was flat at this stage in history, Magellan’s circumnavigation of the globe empirically discredited the medieval theory conclusively.
Though Magellan is often credited with the first circumnavigation of the globe, he did so on a technicality: He first made a trip from Europe to present-day Malaysia, eastward via the Indian Ocean, and may have continued further east to the Spice Islands. He then later made his famous westward voyage that brought him to the Philippines. So he did cover the entire terrain, but it was not a strict point A to point A, round-the-world trip, and it was made in two different directions. His enslaved servant Enrique was born in the region, possibly near Malacca or Cebu, and had come to Europe with Magellan by ship. Enrique reached Cebu (and possibly Mallaca) on the expedition’s westward voyage, meaning he may have been the first person to circumnavigate the world in one direction to return to the same starting point.

HISTORY Vault: Columbus the Lost Voyage
Ten years after his 1492 voyage, Columbus, awaiting the gallows on criminal charges in a Caribbean prison, plotted a treacherous final voyage to restore his reputation.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Ferdinand Magellan
While in the service of Spain, the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan led the first European voyage of discovery to circumnavigate the globe.

(1480-1521)
Who Was Ferdinand Magellan?
As a boy, Ferdinand Magellan studied mapmaking and navigation. By his mid-20s, he was sailing in large fleets and was engaged in combat. In 1519, with the support of Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, Magellan set out to find a better route to the Spice Islands. He assembled a fleet of ships which, despite huge setbacks and Magellan’s death, circumnavigated the world in a single voyage.
Magellan was born in Portugal, either in the city of Porto or in Sabrosa, circa 1480. His parents were members of the Portuguese nobility and after their deaths, Magellan became a page for the queen, at age 10. He studied at Queen Leonora's School of Pages in Lisbon and spent his days poring over texts on cartography, astronomy, and celestial navigation — subjects that would serve him well in his later pursuits.
Navigator and Explorer
In 1505, when Magellan was in his mid-20s, he joined a Portuguese fleet that was sailing to East Africa. By 1509, he found himself at the Battle of Diu, in which the Portuguese destroyed Egyptian ships in the Arabian Sea. Two years later, he explored Malacca, located in present-day Malaysia, and participated in the conquest of Malacca's port. It was there that he acquired a native servant he named Enrique. It is possible that Magellan sailed as far as the Moluccas, islands in Indonesia, then called the Spice Islands. The Moluccas were the original source of some of the world's most valuable spices, including cloves and nutmeg. The conquest of spice-rich countries was, as a result, a source of much European competition.
While serving in Morocco, in 1513, Magellan was wounded and walked the remainder of his life with a limp. After his injury, he was falsely accused of trading illegally with the Moors, and despite all of his service to Portugal, and his many pleas to the king, any further offers of employment were withheld him.
Final Years and Death
Magellan presented his plan to King Charles I of Spain (soon to become Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire), who gave his blessing. On September 20, 1519, he set out with a fleet of five fully supplied ships, but hardly adequate to sail the distances he proposed. The fleet sailed first to Brazil and then down the coast of South America to Patagonia. There an attempted mutiny took place and one of the ships was wrecked. Despite the setback, the crew continued on with the four remaining vessels.
By October 1520, Magellan and his men had entered what is now called the Strait of Magellan. It took them over a month to pass through the strait, during which time the master of one of the ships deserted and sailed back home. The remaining ships sailed across the Pacific Ocean. In March 1521, the fleet anchored in Guam.
Later in March, 1521, Magellan’ fleet reached Homonhom Island on the edge of the Philippines with less than 150 of the 270 men who started the expedition. Magellan traded with Rajah Humabon, the island king, and a bond was quickly formed. The Spanish crew soon became involved in a war between Humabon and another rival leader and Magellan was killed in battle on April 27, 1521.
The remaining crew escaped the Philippines and continued on towards the Spice Islands, arriving in November 1521. The Spanish commander of the last ship, the Victoria, set sail December and reached Spain on September 8, 1522.
The Controversy Over Who was First
There has been considerable debate around who were the first persons to circumnavigate the globe. The easy answer is Juan Sabastian Elcano and the remaining crew of Magellan’s fleet starting from Spain on September 20, 1519, and returning in September 1522. But there is another candidate who might have gone around the world before them — Magellan’ servant Enrique. In 1511, Magellan was on a voyage for Portugal to the Spice Islands and participated in the conquest of Malacca where he acquired his servant Enrique. Fast forward ten years later, Enrique is with Magellan in the Philippines. After Magellan’s death, it is reported that Enrique was grief-stricken and when he found out he was not going to be freed, contrary to Magellan’s will, he ran away. At this point the record gets murky. Some accounts state Enrique fled into the forest. Official Spanish records list Enrique as one of the men massacred in the attack, but some historians question the records’ credibility or accuracy, citing a bias against Indigenous peoples.
So, it is possible that if Enrique had survived after his escape, he might have made his way back to Malacca where he was originally enslaved by Magellan back in 1511. If true, it would mean Enrique — not Elcano and the surviving members of the crew — was the first person to circumnavigate the globe, albeit not in a single voyage.
QUICK FACTS
- Name: Ferdinand Magellan
- Birth Year: 1480
- Birth City: Sabrosa or Porto
- Birth Country: Portugal
- Gender: Male
- Best Known For: While in the service of Spain, the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan led the first European voyage of discovery to circumnavigate the globe.
- Nationalities
- Death Year: 1521
- Death date: April 27, 1521
- Death City: Mactan
- Death Country: Philippines
We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us !
- The Church says that the Earth is flat, but I know that it is round. For I have seen the shadow of the earth on the moon and I have more faith in the Shadow than in the Church.
- Rebel, this is mutiny! You are my prisoner in the king's name.
- Follow me and ask no questions.
European Explorers

Christopher Columbus

10 Famous Explorers Who Connected the World

Sir Walter Raleigh

Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo

Leif Eriksson

Vasco da Gama

Bartolomeu Dias

Giovanni da Verrazzano

Jacques Marquette

René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle

Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University website
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State

Magellan’s Circumnavigation of the Earth
- Dani Anthony
On September 20, 1519, five ships carrying about 270 men left the Spanish port of Sanlúcar de Barrameda sailing west — and kept going. Led by explorer Ferdinand Magellan, the armada’s goal was to reach the Spice Islands of Maluku (in the Indonesian archipelago) and open a new trading route for Spain.

Thus began the first recorded trip around the globe. An almost unimaginably difficult and perilous journey for the crew, Magellan’s voyage was the opening chapter in the rise of global trade and globalization that defines our world today. It also generated important scientific knowledge, including more information about the earth’s circumference and new understandings of global time.
Establishing this new western sailing route was vital to Spain’s future as an international power. In 1494, after Christopher Columbus returned from the West Indies, the Spanish and Portuguese governments signed a deal known as the Treaty of Tordesillas in which the world was divided into two halves: Portugal could colonize and develop trade with Africa, Asia, and the East Indies, while Spain controlled the Americas. By 1515, then, the only way for Spain to access the luxury goods available in the Spice Islands and elsewhere in Asia was via a westward route.
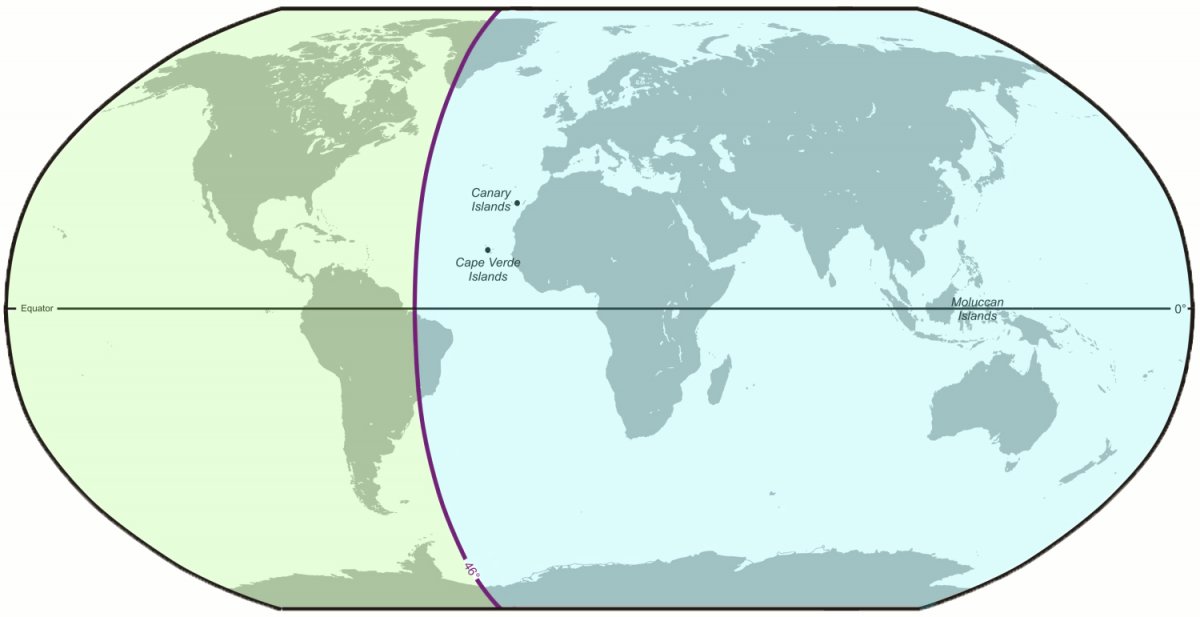
A map showing the demarcation line between Spanish (green) and Portuguese (blue) claims, as resolved in the Treaty of Tordesillas.
It was at this crucial moment that Ferdinand Magellan (Fernão Magalhães) arrived in Spain. A minor Portuguese noble, Magellan possessed an extensive knowledge of mapmaking and sailing, and already had years of experience sailing the Indian Ocean.
In 1513, Spanish explorer Vasco Nuñez de Balboa had marched across the Isthmus of Panama and confirmed that Asia and the Americas were separated by an ocean. Magellan was convinced he could sail around those continents and easily reach this ocean, accessing the Spice Islands beyond.
A posthumous portrait of Ferdinand Magellan, painted c. 16th or 17th century (left) ; a 1516 map of the known world at the time of Magellan's voyage (right).
Unable to convince the Portuguese of the importance of finding a route to the west, Magellan then turned to the new king of Spain, Charles I. If Magellan’s expedition was successful, Spain would have access to the goods of the East again.
Like most Spanish-funded endeavors, the people who sailed on this voyage were a diverse group, including German, Greek, French, and Afro-descended crewmembers. Besides Magellan’s Portuguese close friends and family, Spaniards and other Europeans with sailing experiences were brought in, some of them to work off debts. Magellan’s second-in-command was the Spanish overseer and accountant, Juan de Cartagena, and the chronicler was the Venetian Antonio Pigafetta.
Magellan and João Serrão were the only Portuguese captains, with Magellan in charge of the largest ship, the Trinidad , and Serrão at the helm of the Santiago . Spaniards captained the other three ships ( San Antonio , Concepción , and Victoria ), and constant Spanish scheming against the Portuguese would have grave consequences for the voyage.
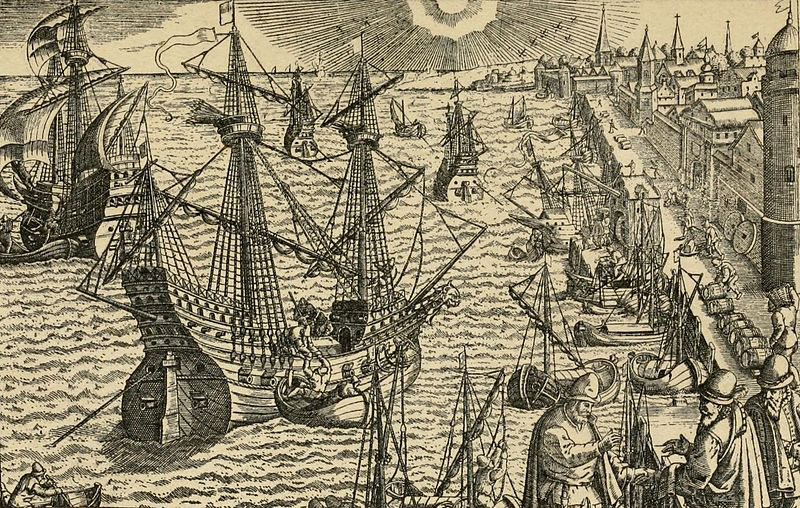

A 19th-century illustration of Magellan's armada preparing to set sail in 1519.
Magellan did nothing to promote Spanish trust, keeping the route a tight secret until the ships were at sea. His plan relied on Portuguese sailing routes, which were well known to him but unfamiliar to many of his crew.
As the armada crossed the Atlantic, morale declined precipitously. By the time the ships arrived on the coast of what is now Brazil to wait out the Southern Hemisphere winter, many aboard were suffering from scurvy, and the Spanish captains were in open rebellion against Magellan. Mutiny was in the air, with Juan de Cartagena, who resented Magellan’s secrecy, leading the effort.
Brazil, as depicted in a 1519 atlas.
In the cold of their wintering grounds and with reduced rations, the mutineers made their move. Although they managed to take over as many as three of the five ships, they were eventually captured and Magellan exiled Cartagena to an uninhabited island off the coast.
The winter of 1520 also saw the destruction of the Santiago, which ran aground while on a scouting mission to the south. Although the ship’s crew survived, the loss of the Santiago put more pressure on an already pinched crew.
An 1885 drawing of the Strait of Magellan.
By late spring, surviving on seal and penguin meat, the armada entered what is now known as the Strait of Magellan, the narrow body of water separating mainland South America from the Tierra del Fuego. The armada lost another ship during the passage through the Strait: the San Antonio , which became separated from the rest of the armada, and turned around and returned to Spain.
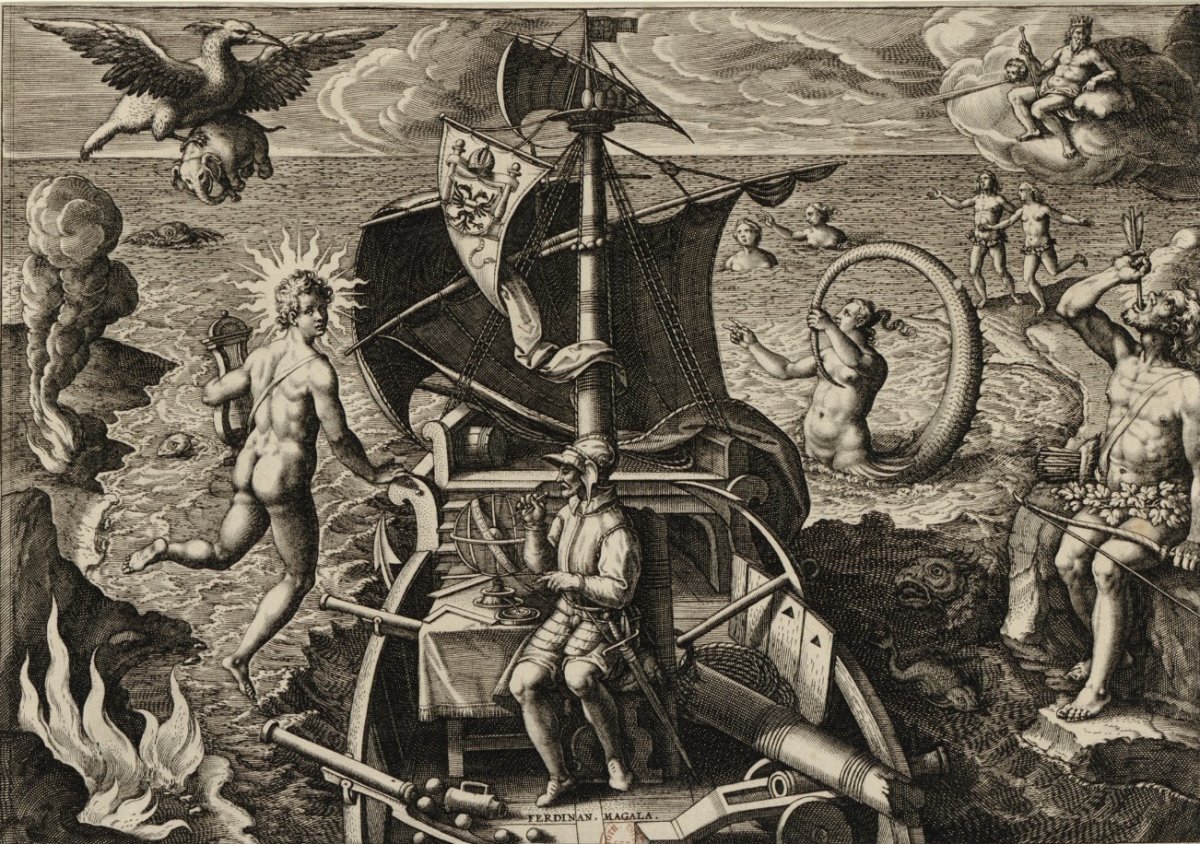

An engraving (c. 1580–1618) of Magellan crossing the Strait that would bear his name.
Once the three remaining ships reached the other side of the Strait of Magellan, the sea they found was calm and placid. Magellan christened it the Pacific Ocean. Crossing the Pacific, the crew of the remaining ships suffered terribly. Twenty-nine sailors died during the four-month voyage.
In April 1521, the group put into an island in the Pacific: Cebu, in what is now the Philippines . As the first Europeans to see these islands, Magellan’s crew would lay the groundwork for the long Spanish colonization of the archipelago, which lasted until 1898. Magellan befriended the local ruler, Raja Humabon, and became embroiled in local politics, which would be his downfall.
On April 27, 1521, Magellan went to war against the ruler Lapu Lapu on Mactan Island, who refused to bring tribute for Raja Humabon and the King of Spain. Fighting in the shallow waters off the shore, Magellan and 49 of his men squared off against over 1,000 Mactanese warriors. Facing such poor odds, Magellan was killed, as well as seven of his men, and his ships returned to Cebu.

A 19th-century illustration of the death of Magellan (left) ; a plaque in Cebu commemorating the site of Magellan's death, Philippines (right).
Raja Humabon, displeased at the newcomer’s loss, hosted a feast where he poisoned a group of some of the highest-ranking members of the expedition, leaving less than half of the original crew. The rest of the members set sail, fleeing to the safety of the sea. On May 2, 1521, those sailors who remained scuttled the Concepción and divided the crew among the remaining two ships, the Trinidad and the Victoria.
For the next six months the ships engaged in piracy as they made their way to the Spice Islands. Finally, in November, they arrived at the island of Tidore, part of the Malukus, and filled their holds with cloves. The Trinidad, which was taking on water, could not be repaired, and it was abandoned along with its crew.

Detail of a 1590 map showing the Victoria , the only ship from the armada to successfully circumnavigate the earth.
The Spaniard Juan Sebastián Elcano was elected captain of the remaining ship Victoria, which set sail west to the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa. This voyage took over six months, during which the crew subsisted on rice alone.
On September 6, 1522, the Victoria at last reached harbor in Spain, nearly three years after first setting out. Of the original 270-strong crew, only eighteen had survived.
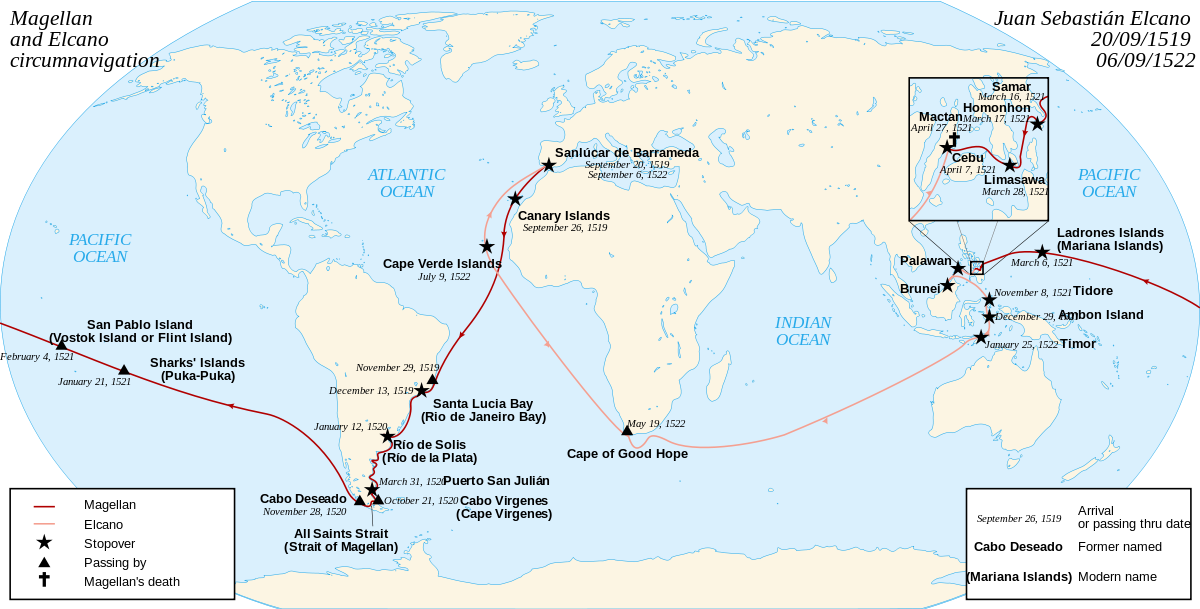
Map showing the route and chronology of the circumnavigation voyage from 1519 to 1522.
Although Magellan is remembered today for circumnavigating the globe, his reputation in the expedition’s immediate aftermath took a battering from those who had survived the expedition. Both the sailors of the Victoria , as well as the crew of the San Antonio who had turned back from the Strait of Magellan in 1520, disparaged him.
Juan Elcano, on the other hand, was given a hero’s welcome, even though he had joined the voyage only to receive a royal pardon. He was elevated to the peerage and added a globe and the words “first to circumnavigate me” to his coat of arms. In Spain, the circumnavigation is known as the Magellan-Elcano expedition.

Engraving of Juan Elcano, 1791 (left) ; Juan Elcano's coat of arms, bearing the phrase, "Primus circumdedisti me" ("First to circumnavigate me") (right).
The first recorded circumnavigation had important political, economic, and scientific consequences.
Spain calculated the total circumference of the globe for the first time, and determined that the Pacific was much wider than previously guessed, meaning that they owned some of the Pacific islands as demarcated by the Treaty of Tordesillas. Spain took control of the Philippines, and began exploration of the East Pacific.
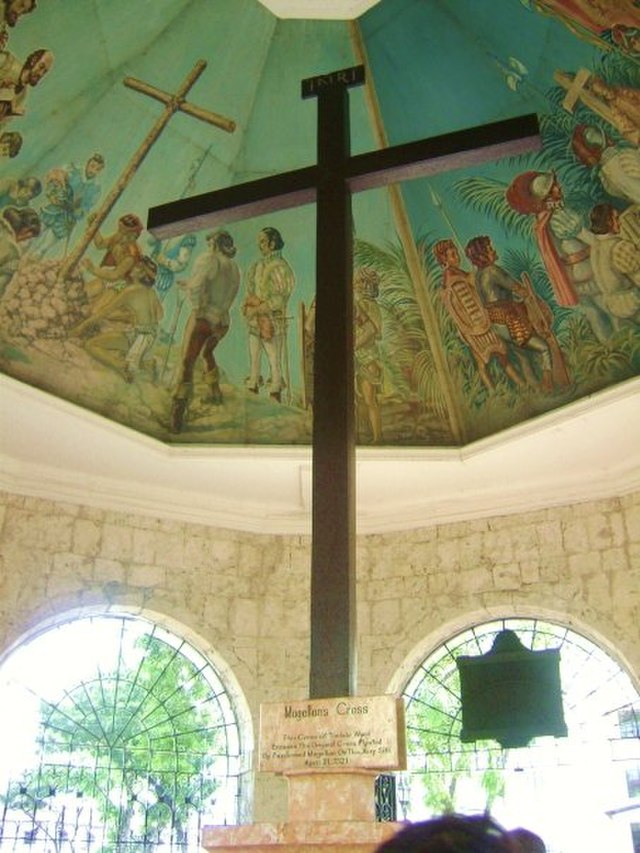

Cross erected by Magellan's crew on the island of Cebu.
Magellan’s voyage also opened the door for trade. By the 1600s, Spanish territories produced most of the world’s silver, and around a third of it ended up in China through trade. This would have lasting effects on global strategy and economies, and propel Spain to the height of European power.
Perhaps just as important for us today, however, is the establishment of the International Date Line. Upon return to Spain, the sailors of the Victoria learned that they were a day behind in their reckoning. As they sailed against the Earth’s rotation, they lost hours. Many mysteries of the globe were revealed.
- Corrections
Ferdinand Magellan & The First Voyage Around the World
During the Age of Exploration, one task was particularly noteworthy: the circumnavigation of Earth. Discover the life of Ferdinand Magellan and the first voyage around the world.

The Age of Exploration saw the achievement of incredible feats with the voyages of European expeditions. Perhaps the most famous of them all is the arrival of Christopher Columbus to the Americas, but many other expeditions are equally groundbreaking. Besides making contact with a “new continent,” the circumnavigation of the Earth was seen as an enormous feat. With Columbus’ travels and following expeditions by other explorers, the circumnavigation of the world was believed possible, but who would be first? Europe’s major powers put their efforts into completing the task, but one expedition, led by Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese explorer serving the Spanish crown, would ultimately be successful: the Magellan expedition.
Magellan’s Early Life & First Travels

Magellan was born in the north of Portugal in 1480. His family was of noble origin and enjoyed a minor presence yet sufficient status among the higher classes of the Kingdom of Portugal. His father, Rui Magellan, was the mayor of a small town. Ferdinand served as a page to Queen Eleanor, consort of John II of the Portuguese crown. After the death of John, Magellan served under Manuel I. When Magellan was 25, he joined a Portuguese expedition to India, where they would establish Francisco de Almeida as the first viceroy of Portuguese India. Magellan stayed in India for almost a decade; then, he traveled to Malacca, where, in 1511, the Portuguese conquered the city under the governor Alfonso de Albuquerque.
Magellan received great riches and promotions from his participation in the conquest of Malacca. He received a slave, baptized under the name Enrique of Malacca, who would join Magellan through many of his travels and endeavors. Magellan’s behavior became increasingly rebellious and not in tune with the Portuguese authorities’ expectations. He took leave without permission, was accused of illegally trading in Morocco, and even quarreled with the Portuguese King Manuel I.
Magellan dedicated himself to studying the most recent nautical charts available to him. He investigated, alongside cosmographer Rui Faleiro, the possibility of reaching the Moluccas through a gateway from the Atlantic to the South Pacific in the Americas. While in Malacca, Magellan befriended the navigator Francisco Serrao, who reached and stayed in the Spice Islands (the Moluccas). His letters to Magellan would prove very useful for his consequent travels to the Islands.
Get the latest articles delivered to your inbox
Please check your inbox to activate your subscription, magellan the spanish explorer: pledging loyalty to the opposing crown.

When Magellan fell out of favor with the Portuguese King, he turned to the Spanish crown. Magellan had been refused time and time again an expedition made possible by the Portuguese crown. King Manuel I disapproved of Magellan’s planned expedition. Thus, Magellan renounced his Portuguese nationality and proposed his travel expedition to King Charles I of Spain (Charles V as Holy Roman Emperor ).
At the time of Magellan’s proposed expedition, Spain was at the start of its expansion into other continents, mainly the Americas, which would be decisive for the Spanish to consolidate their empire.
Portugal had a similar situation. The Portuguese Empire had explored most of the coasts of Africa, reached the Indies through said passage, and established colonies all throughout Africa and Asia.
However, both Iberian empires had become rivals whose differences were often solved only through external intervention. The Treaty of Tordesillas of 1494 established a division of lands outside of Europe between Spain and Portugal. The treaty was largely left unsettled, but in 1529, the Treaty of Zaragoza clarified and formalized the divisions. Before its formalization, however, Magellan and his fleet would achieve the first circumnavigation of the Earth, arguably abusing the agreement set in the Tordesillas treaty.
Magellan convinced the Spanish king that his expedition would not be opposed to the agreement between Spain and Portugal; thus, he was allowed to sail. King Manuel I was greatly insulted by Magellan’s expedition and work under the Spanish crown. The preparations of the Spanish fleet were disrupted by the Portuguese, and a fleet was sent after Magellan, though it failed to capture him.
Expedition through the Atlantic & Reaching the Americas

Magellan and his fleet left Spain from the port of Seville in 1519. The fleet traveled through the Guadalquivir River until they reached the Atlantic through the port of Sanlucar de Barrameda. The fleet remained in place for weeks, going back and forth from Seville to solve unforeseen difficulties. More than a month later, they departed. The fleet reached the Canary Islands, then passed next to Cape Verde and the coasts of Sierra Leone. Four months went by before the fleet reached the coasts of the Americas.
In December 1519, Magellan and his fleet touched land in what is now Rio de Janeiro. They traveled through the estuary of the Rio de la Plata River, then reached and named the region of Patagonia . In Patagonia, the Spaniards met local Indigenous people for the first time. After making contact and trading with them, the Spanish kidnapped some to bring them back for the king. Unfortunately, the kidnapped Indigenous people didn’t survive.
In March 1520, the fleet found itself in harsh conditions. They took refuge in the port of San Julian, but after considering the expedition had failed, some of the crew attempted to overthrow Magellan as their leader. The insurrection ultimately failed; the leaders of the unsatisfied crew were killed or banished, and Magellan forgave the rest as he needed them to continue. Later, the crew of one of the five ships, San Antonio , once again rose against Magellan and turned back for Spain.
The Strait of Magellan & the Voyage in the Pacific

After facing difficulties finding a passage to the Pacific Ocean (known to them as Mar del Sur ), the fleet reached the Strait of Magellan. Magellan originally named it the Strait of All Saints ( estrecho de Todos los Santos ), but the strait gained its name in honor of Magellan and his expedition, having been the first European explorer to find the strait.
Known to be a harsh place, the Strait of Magellan was challenging to pass through. The Spaniards saw bonfires lit by the natives and thus named the territory “ Tierra del Fuego ” (Land of Fire). Indigenous people lived or had reached as far down as Antarctica . The ocean known to them as Mar del Sur was then baptized the Pacific Ocean for its tranquil waters. For three months, after passing through the strait, the fleet was unable to reach land and disembark. The conditions aboard were challenging, to say the least.
The difficulties during the voyage in the Pacific decreased once the fleet reached the Mariana Islands . The state of the fleet was in tatters, having barely survived over three months without touching land. They then reached the Philippines, becoming the first Europeans to do so. Magellan and his fleet carried out the conversion of the local islanders to Catholicism. Magellan won over the locals by proving his strength and urging them to convert so that they could become like them. Thus, the fleet remained in the region before continuing to the Moluccas.
The Battle of Mactan, Magellan’s Death, & the First Circumnavigation of the World

In the Philippines, the locals were manipulated into converting to Catholicism, but when attempting to form an alliance with one chieftain, Magellan proposed to battle an opposing leader to win over his potential ally. Magellan and his fleet went to the Island of Mactan to fight, convert, and make the chieftain Lapulapu submit to the Spanish crown. The battle was a decisive defeat for the Spanish, who were unprepared and outnumbered. Magellan himself was killed during combat. After Magellan’s death, the expedition under his command had to choose a new leader.
The expedition chose Magellan’s brother-in-law and Juan Serrano as co-commanders, but their leadership would be short-lived. On the first of May, the Spanish disembarked to join the Cebuanos for a feast, yet once the meal was finished, they were surprised and murdered by the Cebuanos. The Spaniards had been betrayed by Magellan’s slave Enrique, who was supposed to be freed after his master’s death but was forced to continue working as an interpreter for them. Enrique made a deal with the island’s leader, Humabon, in order to regain his freedom.

With both co-commanders murdered, Juan Lopez de Carvalho was named captain. The fleet chose to continue with just two ships: Trinidad and Victoria . Carvalho was deemed unable to command, and Gonzalo Gomez de Espinosa was chosen as the new captain, leading the ship Trinidad . Meanwhile, Juan Sebastian Elcano was to captain the ship Victoria . When the fleet reached the Moluccas, it was decided that they should leave for Spain at once, yet the Trinidad was in no shape for that sort of travel, so only the Victoria would continue, and the Trinidad would follow later. Elcano and his ship circumnavigated the African continent for their return, and in September 1522, they reached Spain, completing the first circumnavigation of the world .

5 Things Marco Polo Discovered on His Travels

By Francisco Perpuli BA History (in progress) Francisco is completing a History degree at the University of Guadalajara. He has a keen interest in the study of culture and the arts. In his spare time, he tries to explore and develop other interests while saving up to travel the world.

Frequently Read Together

The Holy Roman Empire in 3 Key Leaders

Modern Argentina: A Struggle for Independence from Spanish Colonization

Polynesians in Antarctica: Were They the First?
Voyages of Ferdinand Magellan Timeline
First voyage, king charles i finances the voyage, rio de janeiro, strait of magellan, philippines, death in battle, rounding the cape, voyage home.

Voyages of Ferdinand Magellan
The Magellan expedition, also known as the Magellan–Elcano expedition, was the first voyage around the world. It was a 16th century Spanish expedition initially led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan to the Moluccas, which departed from Spain in 1519, and completed in 1522 by Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, after crossing the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans, culminating in the first circumnavigation of the world.
The expedition accomplished its primary goal – to find a western route to the Moluccas (Spice Islands). The fleet left Spain on 20 September 1519, sailed across the Atlantic ocean and down the eastern coast of South America, eventually discovering the Strait of Magellan, allowing them to pass through to the Pacific Ocean (which Magellan named). The fleet completed the first Pacific crossing, stopping in the Philippines , and eventually reached the Moluccas after two years. A much-depleted crew led by Juan Sebastián Elcano finally returned to Spain on 6 September 1522, having sailed west across the great Indian Ocean, then around the Cape of Good Hope through waters controlled by the Portuguese and north along the Western African coast to eventually arrive in Spain.
The fleet initially consisted of five ships and about 270 men. The expedition faced numerous hardships including Portuguese sabotage attempts, mutinies, starvation, scurvy, storms, and hostile encounters with indigenous people. Only 30 men and one ship (the Victoria) completed the return trip to Spain. Magellan himself died in battle in the Philippines, and was succeeded as captain-general by a series of officers, with Elcano eventually leading the Victoria's return trip.
The expedition was funded mostly by King Charles I of Spain, with the hope that it would discover a profitable western route to the Moluccas, as the eastern route was controlled by Portugal under the Treaty of Tordesillas. Though the expedition did find a route, it was much longer and more arduous than expected, and was therefore not commercially useful. Nevertheless, the expedition is regarded as one of the greatest achievements in seamanship, and had a significant impact on the European understanding of the world.

In March 1505 at the age of 25, Magellan enlisted in the fleet of 22 ships sent to host Francisco de Almeida as the first viceroy of Portuguese India . Although his name does not appear in the chronicles, it is known that he remained there eight years, in Goa, Cochin and Quilon. He participated in several battles, including the battle of Cannanore in 1506, where he was wounded. In 1509 he fought in the battle of Diu.

After having his proposed expeditions to the Spice Islands repeatedly rejected by King Manuel of Portugal, Magellan turned to Charles I, the young King of Spain (and future Holy Roman Emperor). Under the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas, Portugal controlled the eastern routes to Asia that went around Africa. Magellan instead proposed reaching the Spice Islands by a western route, a feat which had never been accomplished. Hoping that this would yield a commercially useful trade route for Spain , Charles approved the expedition, and provided most of the funding.

On 10 August 1519, the five ships under Magellan's command left Seville and descended the Guadalquivir River to Sanlúcar de Barrameda, at the mouth of the river. There they remained more than five weeks. The fleet left Spain on 20 September 1519, sailing west across the Atlantic toward South America. Magellan's fleet consisted of five ships, carrying supplies for two years of travel. The crew consisted of about 270 men. Most were Spanish, but around 40 were Portuguese.

On 13 December, the fleet reached Rio de Janeiro, Brazil . Though nominally Portuguese territory, they maintained no permanent settlement there at the time. Seeing no Portuguese ships in the harbour, Magellan knew it would be safe to stop.
The fleet spent 13 days in Rio, during which they repaired their ships, stocked up on water and food (such as yam, cassava, and pineapple), and interacted with the locals. The expedition had brought with them a great quantity of trinkets intended for trade, such as mirrors, combs, knives and bells. The locals readily exchanged food and local goods (such as parrot feathers) for such items. The crew also found they could purchase sexual favours from the local women. Historian Ian Cameron described the crew's time in Rio as "a saturnalia of feasting and lovemaking".
On 27 December, the fleet left Rio de Janeiro. Pigafetta wrote that the natives were disappointed to see them leave, and that some followed them in canoes trying to entice them to stay.

After three months of searching (including a false start in the estuary of Río de la Plata), weather conditions forced the fleet to stop their search to wait out the winter. They found a sheltered natural harbor at the port of Saint Julian, and remained there for five months. Shortly after landing at St. Julian, there was a mutiny attempt led by the Spanish captains Juan de Cartagena, Gaspar de Quesada and Luis de Mendoza. Magellan barely managed to quell the mutiny, despite at one point losing control of three of his five ships to the mutineers. Mendoza was killed during the conflict, and Magellan sentenced Quesada and Cartagena to being beheaded and marooned, respectively. Lower-level conspirators were made to do hard labor in chains over the winter, but later freed.

During the winter, one of the fleet's ships, the Santiago, was lost in a storm while surveying nearby waters, though no men were killed. Following the winter, the fleet resumed their search for a passage to the Pacific in October 1520. Three days later, they found a bay which eventually led them to a strait, now known as the Strait of Magellan, which allowed them passage through to the Pacific. While exploring the strait, one of the remaining four ships, the San Antonio, deserted the fleet, returning east to Spain. The fleet reached the Pacific by the end of November 1520. Based on the incomplete understanding of world geography at the time, Magellan expected a short journey to Asia, perhaps taking as little as three or four days. In fact, the Pacific crossing took three months and twenty days. The long journey exhausted their supply of food and water, and around 30 men died, mostly of scurvy. Magellan himself remained healthy, perhaps because of his personal supply of preserved quince.

On 6 March 1521, the exhausted fleet made landfall at the island of Guam and were met by native Chamorro people who came aboard the ships and took items such as rigging, knives, and a ship's boat. The Chamorro people may have thought they were participating in a trade exchange (as they had already given the fleet some supplies), but the crew interpreted their actions as theft. Magellan sent a raiding party ashore to retaliate, killing several Chamorro men, burning their houses, and recovering the 'stolen' goods

On 16 March, the fleet reached the Philippines , where they would remain for a month and a half. Magellan befriended local leaders on the island of Limasawa, and on 31 March, held the first Mass in the Philippines, planting a cross on the island's highest hill. Magellan set about converting the locals to Christianity . Most accepted the new religion readily, but the island of Mactan resisted.

On 27 April, Magellan and members of his crew attempted to subdue the Mactan natives by force, but in the ensuing battle, the Europeans were overpowered and Magellan was killed by Lapulapu, a native chieftain in Mactan.

Following his death, Magellan was initially succeeded by co-commanders Juan Serrano and Duarte Barbosa (with a series of other officers later leading). The fleet left the Philippines (following a bloody betrayal by former ally Rajah Humabon) and eventually made their way to the Moluccas in November 1521. Laden with spices, they attempted to set sail for Spain in December, but found that only one of their remaining two ships, the Victoria, was seaworthy.

The Victoria set sail via the Indian Ocean route home on 21 December 1521, commanded by Juan Sebastián Elcano. By 6 May 1522 the Victoria rounded the Cape of Good Hope, with only rice for rations.

Twenty crewmen died of starvation by 9 July 1522, when Elcano put into Portuguese Cape Verde for provisions. The crew was surprised to learn that the date was actually 10 July 1522, as they had recorded every day of the three-year journey without omission. They had no trouble making purchases at first, using the cover story that they were returning to Spain from the Americas. However, the Portuguese detained 13 crew members after discovering that Victoria was carrying spices from the East Indies. The Victoria managed to escape with its cargo of 26 tons of spices (cloves and cinnamon).

On 6 September 1522, Elcano and the remaining crew of Magellan's voyage arrived in Sanlúcar de Barrameda in Spain aboard Victoria, almost exactly three years after they departed. They then sailed upriver to Seville, and from there overland to Valladolid, where they appeared before the Emperor. When Victoria, the one surviving ship and the smallest carrack in the fleet, returned to the harbour of departure after completing the first circumnavigation of the Earth, only 18 men out of the original 270 men were on board. In addition to the returning Europeans, the Victoria had aboard three Moluccans who came aboard at Tidore.
Magellan has come to be renowned for his navigational skill and tenacity. The first circumnavigation has been called "the greatest sea voyage in the Age of Discovery", and even "the most important maritime voyage ever undertaken". Appreciation of Magellan's accomplishments may have been enhanced over time by the failure of subsequent expeditions which attempted to retrace his route, beginning with the Loaísa expedition in 1525 (which featured Juan Sebastián Elcano as second-in-command). The next expedition to successfully complete a circumnavigation, led by Francis Drake, would not occur until 1580, 58 years after the return of the Victoria.
Magellan named the Pacific Ocean (which was also often called the Sea of Magellan in his honor until the eighteenth century), and lends his name to the Strait of Magellan.
Even though Magellan did not survive the trip, he has received more recognition for the expedition than Elcano has, since Magellan was the one who started it, Portugal wanted to recognize a Portuguese explorer, and Spain feared Basque nationalism.
How Did the Caravel Change the World?

Technology of the Age of Exploration

Holy Roman Emperor

Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese Explorer

Juan Sebastián Elcano
Castilian Explorer

Juan de Cartagena
Spanish Explorer

Francisco de Almeida

Mactan Datu
- The First Voyage Round the World, by Magellan, full text, English translation by Lord Stanley of Alderley, London: Hakluyt, [1874] – six contemporary accounts of his voyage
- Guillemard, Francis Henry Hill (1890), The life of Ferdinand Magellan, and the first circumnavigation of the globe, 1480–1521, G. Philip, retrieved 8 April 2009
- Zweig, Stefan (2007), Conqueror of the Seas – The Story of Magellan, Read Books, ISBN 978-1-4067-6006-4

Ferdinand Magellan
How did the Pacific Ocean get its name and what did this Portuguese explorer have to do with it?
Ferdinand Magellan (1480–1521) was a Portuguese explorer who is credited with masterminding the first expedition to circumnavigate the world.
Magellan was sponsored by Spain to travel west across the Atlantic in search of the East Indies. In doing so, his expedition became the first from Europe to cross the Pacific Ocean and circumnavigate the world.
Who was Magellan?
Magellan was born in Portugal and was a successful explorer and navigator. He wanted to reach South-East Asia, where spices grew and gems were to be found, by sailing westwards across the Atlantic Ocean. He hoped to find a passage through South America so that he could sail all the way from the Atlantic to the ocean beyond the Americas (now known as the Pacific). He left Spain in 1519 with five ships and about 260 men.
Did he find a passage through South America?
Magellan found the strait that is now named after him, but only by chance. When two of his ships were driven towards land in a storm, the men feared they would be wrecked on the shore. Then, just in time, they spotted a small opening in the coastline. It was the passage for which they had been searching since they left home.
Where did the name ‘Pacific’ come from?
Magellan named the ocean the Pacific (meaning 'peaceful') because it was calm and pleasant when he entered it.
By now one of his ships had deserted, but the other four started the journey across their new-found sea. To everyone's amazement, the crossing was to take three months and 20 days. Magellan and his men suffered terrible hunger on the voyage. They ran out of fresh food and many died of scurvy.
Did Magellan get home safely?
No: he was killed in a fight with islanders in the Philippines. He died on 27 April 1521 on Mactan Island, Cebu, Philippines.
So although he had masterminded the first expedition to sail around the world, he didn’t complete the voyage. In fact, the first person to sail around the world was a Malaysian, who had come back to Europe with Magellan many years before and then went as an interpreter on his later voyage. The first European to complete the circumnavigation was Magellan's second-in-command, Juan Sebastian de Elcano, who took over after his death.
How many men returned to Spain?
Of all the men who sailed with Magellan, only 18 returned to Spain in 1522. People were amazed when they saw those on board the one remaining ship, Victoria , for they looked starved and filthy.
Did people make use of the trade route Magellan had discovered?
The western sea route to the Spice Islands was not used for many years. Spain was too busy taking land in South America, and it was easier for the Portuguese to get to the East by sailing around the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa.
Shop nautical gifts
Browse our best selling books, or pick up nautical inspired homewares


The Ages of Exploration
Magellan’s voyage.
Quick Facts:
Magellan’s Voyage Around the World

Map of Ferdinand Magellan’s voyage around the world.
- Original "EXPLORATION through the AGES" site
- The Mariners' Educational Programs

Magellan was first to sail around the world, right? Think again.
Five hundred years on, the explorer’s legacy is complicated—and contested.

In September 1519, Magellan set sail from Spain with five ships. Three years later only one ship, the Victoria (depicted on a 1590 map), made it back to Spain after circumnavigating the world.
Five hundred years ago, Ferdinand Magellan began a historic journey to circumnavigate the globe. Simple, right? Not really— the explorer and his voyage are a study in contradiction. Magellan was Portuguese, but sailed on behalf of Spain. He was a formidable captain, but his crew hated him. His expedition was the first to sail around the world, but he didn’t end up circling the globe himself. His name wasn’t even Magellan.

Like Columbus before him, Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan proposed reaching Asia and the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, by sailing west from Europe.
Nonetheless, it’s clear that Ferdinand Magellan’s 1519 expedition changed the world forever. His journey was “the greatest sea voyage ever undertaken, and the most significant,” says historian Laurence Bergreen , author of Over the Edge of the World: Magellan’s Terrifying Circumnavigation of the Globe . “That’s not hyperbole.”
Brutal, bellicose, and brave, Magellan turned a commercial voyage into a hair-raising showdown with a wide world few Europeans could imagine. At the beginning of his journey, his contemporaries suspected it was impossible to sail around the entire globe—and feared that everything from sea monsters to killer fogs awaited anyone foolhardy enough to try. “It sounded suicidal to do this,” says Bergreen.
The Portuguese nobleman was born Fernão de Magalhães around 1480. As a page to queen consort Eleanor and Manuel I, he experienced court life in Lisbon. But the young man had a sense of adventure, and took part in a string of Portuguese voyages designed to discover and seize lucrative spice routes in Africa and India.
At the time, Portugal and Spain were involved in an intense rivalry to see who could find and claim new territory where they could source the spices coveted by European aristocrats. In 1505, Magellan joined the fight, traveling to India, Malaysia, and Indonesia. But his days in service to Portugal were numbered: He was accused of illegal trading and fell out with Manuel I, who turned down his proposal to locate a new spice route.
Magellan was convinced that by sailing west instead of east and going through a rumored strait through South America, he could map a new route to Indonesia and India. So he abandoned his Portuguese loyalty and headed to Spain, where he gained both citizenship and Charles V’s blessing for a five-ship journey westward.
The captain stood to gain great wealth and status from the trip: Charles gave him a decade-long monopoly on any route he might discover, a cut of the profits, and a noble title to boot. But he was in an awkward position when it came to his majority-Spanish crew and his royal mission. “The Castilians resented sailing under a Portuguese commander and the Portuguese considered him a traitor,” writes historian Lincoln Paine.

A 16 th -century engraving depicts Magellan surrounded by mythological characters and fantastic animals and represents European views of the still-mysterious Americas.
After winter weather forced his ships to wait for months in what is now Argentina, Magellan’s crew mutinied. One ship wrecked; another ditched the expedition altogether and headed back to Spain. The captain struggled to regain control of his men, but once he did, the repercussions were swift and harsh. He ordered some of the mutineers beheaded and quartered; others were marooned or forced into hard labor.
The voyage got back on track and Magellan managed to navigate a treacherous passage that’s now named in his honor—the Strait of Magellan. But his troubles weren’t over. As the crew forged across the Pacific Ocean, food spoiled and scurvy and starvation struck . Magellan and his men briefly made landfall in what was likely Guam , where they killed indigenous people and burned their homes in response to the theft of a small boat.
A month later, the expedition reached the Philippines. To the crew’s surprise, Enrique, an enslaved man Magellan had purchased before the journey, could understand and speak the indigenous people’s language. It turned out he was likely raised there before his enslavement—making him, not Magellan, the first person to circumnavigate the globe.
Magellan swiftly claimed the Philippines on Spain’s behalf, but his involvement in what Bergreen calls an “unnecessary war” was his undoing. “He wasn’t defeated by natural forces,” says Bergreen.

In March 1521 the expedition reached the Philippines, where relations with the indigenous people (as depicted in this engraving) went from peacefully trading fruit to engaging in pitched battle. Magellan was killed on Mactan Island on April 27.
Instead, he demanded that local Mactan people convert to Christianity and became embroiled in a rivalry between Humabon and Lapu-Lapu, two local chieftains. On April 27, 1521, Magellan was killed by a poison arrow while attacking Lapu-Lapu’s people.
You May Also Like

Has Amelia Earhart’s plane really been found? 6 key things to know
Who was Mary Magdalene? Historians are still trying to figure that out.

These enigmatic documents have kept their secrets for centuries
They “all at once rushed upon him with lances of iron and of bamboo,” wrote Antonio Pigafetta, an Italian scholar who accompanied the journey, “so that they slew our mirror, our light, our comfort, and our true guide.” The crew left his body behind—an indication, perhaps, of how they truly felt about their relentless leader.
After Magellan’s death, his crew continued in the single ship that remained, captained by Juan Sebastian Elcano, a Basque. They returned to Spain in September 1522. Along the way, they had encountered a new ocean, mapped new routes for European trade, and set the stage for modern globalism. Sixty thousand miles later, and after the death of 80 percent of those involved, the expedition had proven that the globe could be circumnavigated and opened the door to European colonization of the New World in the name of commerce.

A legend was born—and in 1989, one of Magellan’s namesakes even traveled to Venus. During a five-year-long journey, NASA’s Magellan spacecraft made images of the planet before burning up in its atmosphere.
But though Magellan’s name is associated with discovery by some, others shy away from that word. “When I write my textbook I will state that Magellan arrived in the Philippines in 1521,” says historian Ambeth Ocampo , former chairman of the Republic of the Philippines’ national historical commission. “Magellan should not be seen as the beginning of Philippine history but one event [in] a history that still has to be written and rewritten for a new generation.”

A 1545 map traces the route of Magellan's world voyage—a milestone in the centuries-long process of globalization.
For the indigenous people encountered by Magellan and his crew, the explorer’s arrival heralded a new age of conquest, Christianization, and colonization. Lapu-Lapu, the Mactan ruler whose forces killed Magellan, is often credited with slaying the explorer. As a result, notes Ocampo, he has become a national hero in the Philippines.
Though Lapu-Lapu likely did not do the deed, he is widely commemorated as a symbol of Filipino resistance and pride. Now, historians are working toward a more accurate portrayal ahead of the 500th anniversary of Magellan’s arrival in the Philippines. The government’s quincentennial celebrations in 2021 will include replacing a 10-foot statue of Lapu-Lapu in the city that bears his name. A monument that shows the battle itself—and the group effort that brought down an epic explorer—will take its place.
Should Magellan be considered a hero, or what Ocampo calls the Philippines’ “first tourist”? As Guam , the Philippines , Spain and even Portugal celebrate and question the quincentennial, the explorer’s legacy remains as complicated as ever.
Related Topics
- CIRCUMNAVIGATION
- AGE OF DISCOVERY
- INDIGENOUS PEOPLES
- CHRISTIANITY

Gettysburg was no ordinary battle. These maps reveal how Lee lost the fight.

What did childbirth look like when Jesus was born?

The origins of this naked chalk drawing in England are still a mystery

This brilliant philosopher was murdered by a mob. But there's much more to her story.

See how ancient Indigenous artists left their mark on the landscape
- Environment
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Coronavirus Coverage
- Paid Content
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Biography of Ferdinand Magellan, Explorer Circumnavigated the Earth
Though killed en route, his fleet continued on
Corbis via Getty Images / Getty Images
- Key Figures & Milestones
- Physical Geography
- Political Geography
- Country Information
- Urban Geography
- M.A., Geography, California State University - East Bay
- B.A., English and Geography, California State University - Sacramento
Ferdinand Magellan (February 3, 1480–April 27, 1521), a Portuguese explorer, set sail in September 1519 with a fleet of five Spanish ships in an attempt to find the Spice Islands by heading west. Although Magellan died during the journey, he is credited with the first circumnavigation of the Earth.
Fast Facts: Ferdinand Magellan
- Known For : Portuguese explorer credited with circumnavigating the Earth
- Also Known As : Fernando de Magallanes
- Born : February 3, 1480 in Sabrosa, Portugal
- Parents : Magalhaes and Alda de Mesquita (m. 1517–1521)
- Died : April 27, 1521 in the Kingdom of Mactan (now Lapu-Lapu City, Philippines)
- Awards and Honors : The Order of Magellan was established in 1902 to honor those who have circumnavigated the Earth.
- Spouse : María Caldera Beatriz Barbosa
- Children : Rodrigo de Magalhães, Carlos de Magalhães
- Notable Quote : “The church says the earth is flat; but I have seen its shadow on the moon, and I have more confidence even in a shadow than in the church.”
Early Years and Voyages
Ferdinand Magellan was born in 1480 in Sabrosa, Portugal, to Rui de Magalhaes and Alda de Mesquita. Because his family had ties to the royal family, Magellan became a page to the Portuguese queen after his parents' untimely deaths in 1490.
This position as a page allowed Magellan the opportunity to become educated and learn about the various Portuguese exploration expeditions—possibly even those conducted by Christopher Columbus .
Magellan took part in his first sea voyage in 1505 when Portugal sent him to India to help install Francisco de Almeida as the Portuguese viceroy. He also experienced his first battle there in 1509 when one of the local kings rejected the practice of paying tribute to the new viceroy.
From here, however, Magellan lost the viceroy Almeida's support after he took leave without permission and was accused of illegally trading with the Moors. After some of the accusations were proven to be true, Magellan lost all offers of employment from the Portuguese after 1514.
The Spanish and the Spice Islands
Around this same time, the Spanish were engaged in trying to find a new route to the Spice Islands (the East Indies, in present-day Indonesia ) after the Treaty of Tordesillas divided the world in half in 1494.
The dividing line for this treaty went through the Atlantic Ocean and Spain got the lands west of the line, including the Americas. Brazil, however, went to Portugal as did everything east of the line, including India and the eastern half of Africa.
Similar to his predecessor Columbus, Magellan believed that the Spice Islands could be reached by sailing west through the New World. He proposed this idea to Manuel I, the Portuguese king, but was rejected. Looking for support, Magellan moved on to share his plan with the Spanish king.
On March 22, 1518, Charles I was persuaded by Magellan and granted him a large sum of money to find a route to the Spice Islands by sailing west, thereby giving Spain control of the area, since it would in effect be "west" of the dividing line through the Atlantic.
Using these generous funds, Magellan set sail going west toward the Spice Islands in September 1519 with five ships ( the Conception, the San Antonio, the Santiago, the Trinidad, and the Victoria ) and 270 men.
The Early Portion of the Voyage
Since Magellan was a Portuguese explorer in charge of a Spanish fleet, the early part of the voyage to the west was riddled with problems. Several of the Spanish captains on the ships in the expedition plotted to kill him, but none of their plans succeeded. Many of these mutineers were held prisoner and/or executed. In addition, Magellan had to avoid Portuguese territory since he was sailing for Spain.
After months of sailing across the Atlantic Ocean, the fleet anchored at what is today Rio de Janeiro to restock its supplies on December 13, 1519. From there, they moved down the coast of South America looking for a way into the Pacific. As they sailed farther south, however, the weather got worse, so the crew anchored in Patagonia (southern South America) to wait out the winter.
As the weather began to ease in the spring, Magellan sent the Santiago on a mission to look for a way through to the Pacific Ocean. In May, the ship was wrecked and the fleet did not move again until August 1520.
Then, after months of exploring the area, the remaining four ships found a strait in October and sailed through it. This portion of the journey took 38 days, cost them the San Antonio (because its crew decided to abandon the expedition) and a large amount of supplies. Nevertheless, at the end of November, the remaining three ships exited what Magellan named the Strait of All Saints and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Later Voyage and Death
From here, Magellan mistakenly thought it would only take a few days to reach the Spice Islands, when it instead took four months, during which time his crew suffered immensely. They began to starve as their food supplies were depleted, their water turned putrid, and many of the men developed scurvy.
The crew was able to stop at a nearby island in January 1521 to eat fish and seabirds, but their supplies were not adequately restocked until March when they stopped in Guam.
On March 28, they landed in the Philippines and befriended a tribal king, Rajah Humabon of Cebu Island. After spending time with the king, Magellan and his crew were persuaded into helping the tribe kill their enemy Lapu-Lapu on Mactan Island. On April 27, 1521, Magellan took part in the Battle of Mactan and was killed by Lapu-Lapu's army.
After Magellan's death, Sebastian del Cano had the Conception burned (so it could not be used against them by the locals) and took over the two remaining ships and 117 crewmembers. To ensure that one ship would make it back to Spain, the Trinidad headed east while the Victoria continued west.
The Trinidad was seized by the Portuguese on its return journey, but on September 6, 1522, the Victoria and only 18 surviving crew members returned to Spain, completing the first circumnavigation of the Earth.
Though Magellan died before the voyage was completed, he is often credited with the first circumnavigation of the Earth as he initially led the voyage. He also discovered what is now called the Strait of Magellan and named both the Pacific Ocean and South America's Tierra del Fuego.
Magellanic Clouds in space were also named for him, as his crew was the first to view them while sailing in the Southern Hemisphere. Most important to geography though, was Magellan’s realization of the full extent of the Earth—something that significantly aided to the development of later geographic exploration and the resulting knowledge of the world today.
- Editors, History.com. “ Ferdinand Magellan. ” History.com , A&E Television Networks, 29 Oct. 2009.
- “ The Ages of Exploration. ” Exploration.marinersmuseum.org.
- Burgan, Michael. Magellan: Ferdinand Magellan and the First Trip Around the World . Mankato: Capstone Publishers, 2001.
- Biography and Legacy of Ferdinand Magellan
- Biography of Juan Sebastián Elcano, Magellan's Replacement
- Explorers and Discoverers
- Circling the Globe: The Voyage of the Great White Fleet
- A Timeline of North American Exploration: 1492–1585
- Biography of Christopher Columbus, Italian Explorer
- Biography of Christopher Columbus
- Biography of Explorer Cheng Ho
- A Brief History of the Age of Exploration
- Captain James Cook
- The Fourth Voyage of Christopher Columbus
- Major Chokepoints of the World
- Profile of Prince Henry the Navigator
- The Truth About Christopher Columbus
- Biography of Jacques Cartier, Early Explorer of Canada
- Great White Fleet: USS Minnesota (BB-22)
Magellan's Voyage and the Perspective of "Otherness"
Explore other cultural realities through the diary of antonio pigafetta, journalist of this first voyage around the world..
By Museo de América
Museo de América
View of the port of Seville (ca. 1600) Museo de América
The first expedition to voyage around the world, captained by Ferdinand Magellan, set sail on August 20, 1519 from the port of Sanlúcar de Barrameda (Cádiz, Spain). The larger ships could not sail the river Guadalquivir up to the city of Seville due to the sandbanks formed around its mouth.
The nationalities of the expedition's crew, which included the Italian Pigafetta, were extremely diverse. But it was only made up of men, as women were prohibited from joining the crew in order to prevent potential riots.
Cinnamon tree (1789/1794) by José Guio Museo de América
…to seek out and discover spices in the Maluku Islands. The aim of the journey was to reach the Spice Islands, today known as the Maluku Islands. Spices were used to season meat and fish, enhancing flavors or camouflaging those brought about by the conditions of storage. The search for spices continued into subsequent centuries. This image shows a drawing of the Ishpingo or cinnamon tree. This example is an Amazonian variety of cinnamon, of which the flowers—shown here—are used, unlike the Asian variety, of which the bark is used.
Pepper shaker (1600/1622) by MR Museo de América
Some of the most sought after condiments were clove, pepper, nutmeg, and cinnamon, which were used to flavor delicious food and drinks. This silver spice rack was found in the Nuestra Señora de Atocha shipwreck, which sunk off the coast of Florida in 1622. This type of rack is called a turret. It is made up of different elements stacked on top of each other, with this dome-shaped pepper pot placed at the very top of the set.
Scarlet macaw (ca. 1942) Museo de América
Exotic Nature
Knowledge of the natural world and the use of its resources are themes that run throughout the diary of Pigafetta, as the purpose of his voyage was to locate valuable natural produce (spices) for selling.
Tridacna gigas shell Museo de América
The flesh of these two mollusks, respectively, weighed 26 and 44 pounds [more than 11.7 and almost 20 kilos]. Some previously unknown species caused surprise due to their giant size, such as these Pacific shells, which were first used in Spain as basins for holy water at the entrance to churches.
The expeditionaries exchanged various objects for food, live animals, and other products. In Brazil, they were interested in large macaws ( Ara sp.) and a species of golden lion tamarin monkey ( Leontopithecus rosalia ). These kinds of exotic animals became prized pets in Europe, reflecting the status of their owners. There are numerous portraits, particularly of women and children, with these animals, such as Infanta Isabel Clara Eugenia and Magdalena Ruiz, by Alonso Sánchez Coello, in the Prado Museum (Museo Nacional del Prado).
Basket (20th Century) by Kayapó Museo de América
Visions of the Indigenous World
The meeting of societies that had had no previous contact had an enormous impact on the expeditionaries as well as the other cultures.
Population of the Napo River shore (1789/1794) Museo de América
Visions of the Indigenous World in America ...These people paint their entire body and face beautifully with fire and in other ways... The corporal appearance of the Amazonian communities was admired by the Europeans. These societies totally or partially covered their bodies with paint. The designs were not intended to look pretty, but rather were an expression of belonging to a specific group, or a protection against spiritual influences.
Canoe (1862/1865) Museo de América
They have boats carved out of a single piece of wood with stone tools, known as canoes. The tribes that live along the banks of the Amazon basin maintain a close relationship with the river. It is the main route for communication, a fundamental part of their beliefs, and an essential source of economic resources. The most efficient way to move along the river is via canoe. Traditionally, a tree trunk would be hollowed out using fire or hot stones, and the lack of metal meant that stone tools had to be used to carve out the inside.
The women work and carry all the food in wicker backpacks, or in baskets placed upon or tied to their heads. The expeditionaries saw how the Amazonian tribes organized a division of work based on gender and age. Women invested a large part of their day on gathering duties. In order to leave their hands free, they put the food they gathered in vegetable fiber baskets that they could carry on their backs, but tied with a belt around their front.
Bow (1867) by Ona (selk´nam) Museo de América
Within the division of labor by gender, the men of the groups that lived in the region of Patagonia were mainly dedicated to hunting guanaco ( Lama guanicoe ). Apart from the meat, they also used their skin and tendons for tools and clothing. The guanaco was a species previously unknown in Europe, which is why Pigafetta uses comparisons with other animals to describe it: the body and long neck of a camel, the hooves of a deer, and the tail of a horse. According to the author, it also imitates a horse's neigh.
Man from the Guam island (1789/1794) by Juan Ravenet Museo de América
Visions of the Pacific Indigenous Community After 100 days of traveling across the Pacific, and with an urgent need for food, they had a brief encounter with the inhabitants of the island of Guam. They named it the Island of Thieves due to the theft of a skiff from one of their boats. The absence of the concept of private property in these indigenous communities led to an unexpected clash of mindset. The behavior of these skilled navigators was not understood by the expeditionaries, and was met with violence until they were able to recover the valuable part of their vessel.
Peineta (Helu) (1775/1880) by Tonga Museo de América
These combs are one of the few elements of personal adornment that women would wear on their heads in some Polynesian societies such as Tonga. They are delicate pieces made from very thin rods obtained from the central spines of the coconut palm leaf, joined together with braided vegetable fibers, forming geometric designs. Following contact with western societies, some elements of the material culture changed in meaning, going from common use to being considered a symbol of higher social status.
Woman of the aeta group or "negritos" from the Manila mountains (19th Century) by Juan Ravenet Museo de América
Visions of the Asian Indigenous Community Journeying around the myriad islands allowed the expeditionaries to learn about the enormous ethnic diversity of the Philippine archipelago, which was populated by cultural groups with a wide variety of languages, customs, and physical appearances. Some societies, such as the Aeta people, have dark skin and were therefore known as blacks. This female portrait is a delicate study of the particular characteristics of the population of the mountainous region of Manila.
Bracelet (19th Century) by Kalinga Museo de América
In many societies of Oceania and Indonesia, pigs were one of the most prized animals, used as an element of prestige in exchanges. The teeth of the wild boar were especially valued by the men, who would use them to make bracelets, as in this case, but also pendants or even a nose adornment. Among the tribes in the north of the island of Luzon, defending these animals was considered a symbol of affluence and power.
Swords (Kalasag) (19th Century) by Bagobo Museo de América
Different Types of Relationships
Although the preferred relationship was one of commercial exchange, contacts with other populations sometimes led to tension, conflict, and confrontation.
Mirror (18th Century) Museo de América
Commercial Relationships All of our mirrors had broken and the few good ones were wanted by the King [King of Tidore, of the Maluku Islands]. The economic system was based on trade. The expeditionaries offered iron objects, knives, scissors, cloth, combs, bells, glass, and particularly mirrors, which were all considered curios. Obviously exchanges were established based on precisely the difference in the valuation criteria of the items, so that each party thought they were getting a good deal.
Carrier of Manila (1789/1794) by Juan Ravenet Museo de América
Following the arrival of the Spanish, the port of Manila became one of the most important centers of commercial activity in the world. Silver from American mines was exchanged for sought-after Asian products, which would end up in the houses of noblemen and the bourgeoisie across America and Europe. The presence in Manila of numerous Chinese traders, or Sangleys (those that came to trade) was essential to boost economic development and facilitate the necessary flow of merchandise with the Asian powerhouse.
Headdress (Aheto) (ca. 1993) by Karajá Museo de América
The Process of "Othering" They wrap themselves in clothing made from macaw feathers, with large rolls on their backside made with the longest feathers; they look ridiculous. The Amazonian cultures used feathers from various birds to make headdresses, bracelets, and skirts. These elements were used in special ceremonies, though not always understood or valued by western cultures. The feather objects were not held in high regard by the expeditionaries. Societies were categorized based on the complexity of their material culture, which marked the relationship established with them, and was used as a criterion to legitimize their domination.
Sword (19th Century) by Moros de Mindanao Museo de América
Throughout this voyage around the world, the expeditionaries made contact with different populations, and each required different types of relationships and exchange of different goods. In the text, distancing is justified with regard to these groups, marking them as "other" based on their religion (moors, pagans, and gentiles), their clothing, their economy, their way of life, and even their size (giant Patagonians). This sword, made by the moors of the Southern Philippines, and called kalis tulid, is an emblem of power and prestige for the chief, used both in battle and on parades.
Figure (Bulul) (19th Century) by Ifugao Museo de América
The expeditionaries observed the beliefs of the cultures that they came across along their voyage, but most were dismissed as idolism, and their representations burned. These types of anthropomorphic sculptures by the Ifugao culture, made from wood, represent the ancestral spirits, guardians of the granaries and houses, and invoke the protection of harvests, health, and prosperity.
Conflicts and Confrontations Weapons were highly valued objects by the western expeditionaries when they made contact with other cultures. They were used to profile a scale of value between societies, and to estimate the potential relationships that were possible between the parties. Wooden swords similar to these ( kalasag ) could have been used by the indigenous people who clashed with Magellan on the island of Mactán, which ended with the death of the captain. They stuffed hair from their defeated enemies around the edge of the ancient kalasag in order to appropriate their power and courage.
Spear (19th Century) by Malayo-filipino Museo de América
Bows and arrows with poisoned tips were common weapons among the Filipino indigenous communities. It was precisely one of these that caused the death of Ferdinand Magellan. In the Muslim communities of the Southern Philippines, known as moors, lances as well as swords were essential elements for face-to-face confrontations. They would use lances made from a metal sheet shaped into a lance, that could be finished with extended blades, and a handle made from a thick piece of bamboo or wood.
Morion (helmet) (19th Century) by Moros de Mindanao Museo de América
Filipinos had their own collections of arms, but they also started adapting new weapons following the European influx. For example, this bronze helmet is similar to the Hispanic morion, a military helmet typical of the second half of the 16th century. It may be an imitation, but is a version made by the moors of the Philippines. The differences that the expeditionaries found between other populations were an excuse for the violent interaction which took place: attacks, battles, and even kidnapping men and women considered different and "other."
Hammock (1862/1865) Museo de América
Cultural Influences
Contact with different groups led to the adoption, on both sides, of new customs, and the use of previously unknown objects.
Some Amazonian communities with a nomadic or semi-nomadic way of life required light tools that could be easily transported. A hammock is a lightweight netting made from vegetable fiber. It is hung at each end from two strong posts, to allow a person to rest while preventing contact with the floor. The position of the body in the hammock avoids any pressure points, and aids venous return. The relaxation of the soft swinging, and the sensation of weightlessness, led to these items being distributed to other cultures in warm environments, or regions of high humidity.
Cockfight (1789/1794) by Tomás de Suría Museo de América
They have large, domestic roosters, but they do not eat them; rather they worship them, although they also make them fight… Hens are not native to America, and so it is surprising that these domestic birds have been described there from very early dates. The breeding of European chickens spread from the Antilles to many indigenous groups in Brazil. However, another route that these birds took to America was via the Pacific, from Asia and Polynesia, where white-feathered hens were bred for rituals, and in some cases for cock fights; a tradition that made its way to Mexico.
Curation and texts: Beatriz Robledo Sanz, Andrés Gutiérrez Usillos Coordination: Susana Alcalde Amieva Photographs: Joaquin Otero, Gonzalo Cases Museo de América This exhibition is part of the First Voyage Around the World project.
The Asian Influence on American Arts
ENCORE 39. Circumnavigation of the World History of North America
Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan's 1519-22 expedition was the first known circumnavigation of the Earth. His epic voyage opened trade routes connecting much of the world, including the North American continent. Guest podcaster Charles Kimball of the «History of Southeast Asia» shares his views on the daring feats of this celebrated adventurer. Enjoy this Encore Presentation! Check out the YouTube version of this episode at https://youtu.be/SZKSM8ZVxQ4 which has accompanying visuals including maps, charts, timelines, photos, illustrations, and diagrams. Ferdinand Magellan books available at https://amzn.to/3IpV5Vf THANKS for the many wonderful comments, messages, ratings and reviews. All of them are regularly posted for your reading pleasure on https://patreon.com/markvinet where you can also get exclusive access to Bonus episodes, Ad-Free content, Extra materials, and an eBook Welcome Gift when joining our growing community on Patreon or Donate on PayPal at https://bit.ly/3cx9OOL and receive an eBook GIFT. SUPPORT this series by purchasing any product on Amazon using this FREE entry LINK https://amzn.to/3POlrUD (Amazon gives us credit at no extra charge to you). It costs you nothing to shop using this FREE store entry link and by doing so encourages & helps us create more quality content. Thanks! Mark Vinet's HISTORICAL JESUS podcast is available at https://parthenonpodcast.com/historical-jesus Mark's TIMELINE video channel at https://youtube.com/c/TIMELINE_MarkVinet Website: https://markvinet.com/podcast Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/denarynovels Twitter: https://twitter.com/MarkVinet_HNA Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/mark.vinet.9 YouTube Podcast Playlist: https://www.bit.ly/34tBizu Podcast: https://parthenonpodcast.com/history-of-north-america TikTok: https://tiktok.com/@historyofnorthamerica Books: https://amzn.to/3j0dAFH Linktree: https://linktr.ee/WadeOrganization See omnystudio.com/listener for privacy information.
- Episode Website
- More Episodes
Top Podcasts In History

Uncharted: Are Santiago Moncada and The Moncada Foundation Real?
Starring Tom Holland and Mark Wahlberg, ‘ Uncharted ’ is an action-adventure film that focuses on the hunt for the lost treasure of Ferdinand Magellan. Based on the video game series of the same name, the film gives an origin story to Nathan Drake’s character, who is brought into the hunt by Victor “Sully” Sullivan . Drake’s knowledge of history becomes an important aspect of his decoding of the clues left behind by Magellan’s crew, who were in possession of a treasure worth $5 billion.
But he and Sully are not the only ones after the fortune. They have a fierce competitor in a man named Santiago Moncada, who believes that Magellan’s gold is his birthright because it was his family, all those years ago, who funded the voyage that never brought them anything in return. Considering that Magellan is a real character and did take a voyage across the world, one is bound to wonder about the connection between him and Moncada.
The House of Moncada is a Fictional Aspect of Uncharted
There is a real House of Moncada, an aristocratic Catalan house, but it has no connection whatsoever with Magellan’s gold or even his voyage. In fact, the whole story about the House of Moncada funding Magellan’s voyage is entirely fictional and created solely for the purpose of the plot. To add a touch of authenticity to it, the film does give a few real details to the audience. For example, it is true that Magellan went on a voyage that was supposed to bring him around the world but was cut short due to his death. However, the story about him and his crew finding $5 billion worth of gold is made up.

The same goes for the story about his sponsors as well. Magellan’s journey was supposed to find new trade routes that could help European countries establish better trade relations with other countries, their focus being on spice, which was actually much more valuable than gold at the time. It is true that the crown refused to fund his voyage, but it was the Portuguese Crown who did that. Instead, the Spanish Crown funded his voyage and brought in a couple of other rich businessmen when their own funds didn’t meet the mark.
The Crown provided Magellan and his crew with supplies that would allow them to travel for two years without want. However, there were other factors to be considered, and the Crown knew that they couldn’t fund the whole thing by themselves. So, they invited the investors who, at the time, were one of the biggest banking families in Europe: the House of Fugger.
The Fugger were a group of European bankers who were at the top of their game at the time they were approached with the idea of Magellan’s voyage. The House of Medici, who had ruled the banking scene of Europe for a long time, was past its prime, and the Fugger had replaced them to become one of the most influential families. In addition, a Castilian merchant named Cristóbal de Haro was brought on board, and he also provided a great portion of the funding.
With so much money in his pocket, Magellan was ready to take that journey, but as is known, it didn’t turn out to be quite as successful as the investors had hoped. Still, making a journey of that scale back in the day was a huge thing, and for current storytellers, it opens the doors to all kinds of conspiracy theories, which serve as a great premise for films like ‘Uncharted.’
Read More: Is Uncharted’s Nathan Drake Based on a Real Person?
SPONSORED LINKS

- Movie Explainers
- TV Explainers
- About The Cinemaholic

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ferdinand Magellan's Early Years. Ferdinand Magellan (c. 1480-1521) was born in Sabrosa, Portugal, to a family of minor Portuguese nobility. At age 12 Ferdinand Magellan ( Fernão de ...
Ferdinand Magellan (born 1480, Sabrosa or Porto?, Portugal—died April 27, 1521, Mactan, Philippines) was a Portuguese navigator and explorer who sailed under the flags of both Portugal (1505-13) and Spain (1519-21). From Spain, he sailed around South America, discovering the Strait of Magellan, and across the Pacific.Though he was killed in the Philippines, one of his ships continued ...
Ferdinand Magellan, or Fernão de Magalhães (c. 1480-1521), was a Portuguese mariner whose expedition was the first to circumnavigate the globe in 1519-22 in the service of Spain.Magellan was killed on the voyage in what is today the Philippines, and only 22 of the original 270 crew members made it back to Europe.. Discovering what became known as the Straits of Magellan in southern Patagonia ...
The Magellan expedition, sometimes called the Magellan-Elcano expedition, was an early 16th-century Spanish expedition planned and led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan with the objective of crossing the Atlantic and Pacific oceans in order to open a trade route with the Moluccas ("Spice islands"). The expedition departed from Spain in 1519 and returned there in 1522, completed by the ...
Ferdinand Magellan (c. 1480 - 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East Indies across the Pacific Ocean to open a maritime trade route, during which he discovered the interoceanic passage thereafter bearing his name and achieved the first European navigation to Asia via the Pacific.
By his mid-20s, he was sailing in large fleets and was engaged in combat. In 1519, with the support of Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, Magellan set out to find a better route to the Spice Islands ...
Half-length portrait of Ferdinand Magellan (circa 1580-1521), first European to circle the globe. The Mariners Museum 1949.0619.000001. Introduction. Ferdinand Magellan is known for circumnavigating - sailing around - the world. From Spain he sailed around South America, discovering the Strait of Magellan, and across the Pacific.
Voyages of Ferdinand Magellan (1519-22) and Francis Drake (1577-80) across the Atlantic Ocean and around the globe. After Magellan's death only two of the ships, the Trinidad and the Victoria, reached the Moluccas. Gonzalo Gómez de Espinosa, Magellan's master-at-arms, attempted to return to Spain on the Trinidad, but it soon became ...
Magellan's Circumnavigation of the Earth. On September 20, 1519, five ships carrying about 270 men left the Spanish port of Sanlúcar de Barrameda sailing west — and kept going. Led by explorer Ferdinand Magellan, the armada's goal was to reach the Spice Islands of Maluku (in the Indonesian archipelago) and open a new trading route for Spain.
Ferdinand Magellan set off from Spain 500 years ago on an epoch-making voyage to sail all the way around the globe for the first time. The Portuguese explorer was killed by islanders in the ...
Ferdinand Magellan set off from Spain 500 years ago on an epoch-making voyage to sail all the way around the globe for the first time.
Discover the life of Ferdinand Magellan and the first voyage around the world. The Age of Exploration saw the achievement of incredible feats with the voyages of European expeditions. Perhaps the most famous of them all is the arrival of Christopher Columbus to the Americas, but many other expeditions are equally groundbreaking.
Ferdinand Magellan - Explorer, Strait, Voyage: The fleet, carrying about 270 men, predominantly from Spain and Portugal but also from far-flung parts of Europe and North Africa, reached Tenerife in the Canary Islands on September 26, 1519, and set sail on October 3 for Brazil. Becalmed off the Guinea coast of Africa, it met storms before reaching the Equator; by November 29, having crossed the ...
The Magellan expedition, also known as the Magellan-Elcano expedition, was the first voyage around the world. It was a 16th century Spanish expedition initially led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan to the Moluccas, which departed from Spain in 1519, and completed in 1522 by Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, after crossing the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans, culminating ...
Magellan's fleet left Seville on August 10, 1519. After stopovers in the Canary and Cape Verde Islands, they headed for Portuguese Brazil. Here, they anchored near present-day Rio de Janeiro in January of 1520 to take on supplies, trading with locals for food and water. It was at this time that serious troubles began: the Santiago was wrecked and the survivors had to be picked up.
Ferdinand Magellan (1480-1521) was a Portuguese explorer who is credited with masterminding the first expedition to circumnavigate the world. Magellan was sponsored by Spain to travel west across the Atlantic in search of the East Indies. In doing so, his expedition became the first from Europe to cross the Pacific Ocean and circumnavigate ...
Quick Facts: Magellan's Voyage Around the World. Map of Ferdinand Magellan's voyage around the world. More. Vocabulary; Original "EXPLORATION through the AGES" site
In 1519, Ferdinand Magellan set sail from Spain with five ships to find a western route to the Moluccas. Battling storms, mutinies, and the unknown, Magellan died before reaching his destination ...
Updated on July 24, 2019. Ferdinand Magellan (February 3, 1480-April 27, 1521), a Portuguese explorer, set sail in September 1519 with a fleet of five Spanish ships in an attempt to find the Spice Islands by heading west. Although Magellan died during the journey, he is credited with the first circumnavigation of the Earth.
Ferdinand Magellan set off from Spain 500 years ago on an epoch-making voyage to sail all the way around the globe for the first time. The Portuguese explorer was killed by islanders in the ...
Between 1519 and 1522, the Magellan-Elcano expedition completed the first circumnavigation of the world. This contribution offers a new interpretation of the political context leading to the voyage and, in particular, it considers the long history of Portuguese-Castilian rivalry in the Atlantic, reassessing the importance of the Treaty of Alcáçovas (1479).
The first expedition to voyage around the world, captained by Ferdinand Magellan, set sail on August 20, 1519 from the port of Sanlúcar de Barrameda (Cádiz, Spain). The larger ships could not sail the river Guadalquivir up to the city of Seville due to the sandbanks formed around its mouth. ... as the purpose of his voyage was to locate ...
Explore LearningMedia Resources by Subject. Ferdinand Magellan was the first person to reach Asia and the Indian Ocean by sailing a westward route through the Americas and across the Pacific Ocean. Magellan's groundbreaking voyage was the first circumnavigation of earth and gave the first true record of the distribution of oceans and continents.
Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan's 1519-22 expedition was the first known circumnavigation of the Earth. His epic voyage opened trade routes connecting much of the world, including the North American continent. Guest podcaster Charles Kimball of the «History of Southeast Asia» shares his views…
Starring Tom Holland and Mark Wahlberg, 'Uncharted' is an action-adventure film that focuses on the hunt for the lost treasure of Ferdinand Magellan. Based on the video game series of the same name, the film gives an origin story to Nathan Drake's character, who is brought into the hunt by Victor "Sully" Sullivan.Drake's knowledge of history becomes an important aspect of his ...