
1300 577 017
✉️ Get a Free Quote
📞 1300 577 017


Power Tripped? Common Causes and What to do
by Peter Cardamone | Oct 2, 2020 | Domestic Electrical , Emergency Electrical | 0 comments
Having something trip the power in your home can be an extremely frustrating occurrence – especially if you’re in the middle of a task, and particularly if you don’t know what has caused it. Often, the problem may be simpler than you think. There are a few reasons why your power might have tripped. Even better, there are simple steps to follow to fix the problem quickly and easily, allowing you to get on with your day.
Causes of a Power Trip
Essentially, a power trip occurs when the electrical system in your home is compromised in some way. The trip is a safety mechanism, meaning your circuit breakers will ‘trip the switch’ and automatically shut down power to one or several systems, making sure the problem cannot become anything more serious. This can happen for a number of reasons.
Overloaded Circuit
The most simple cause of a power trip is an overloaded circuit. If you have too many devices or appliances running simultaneously, the circuit can end up drawing more electrical load than it is equipped to handle. It heats up, the circuit breaker senses this, and the power trips before the circuit can heat to a dangerous level.
Short Circuit
A short circuit can be caused by a wiring problem in a device or an appliance when it is connected to your main system. It can also happen if two opposing wires accidentally touch, causing an unexpected surge of electricity that will cause the circuit breaker to trip the system.
Earth Leakage Fault
An earth leakage fault is a type of short circuit, and it will happen when the current flowing through the electrical system finds an alternative path other than the active or neutral conductors. These are slightly more dangerous, particularly if they occur in places such as the bathroom or kitchen where moisture could carry the electricity and cause shocks. Once again, the increase in electricity will cause the circuit to heat up, and the circuit breaker will therefore initiate a power trip to prevent further damage.
What to Do About a Power Trip
In the case of a short circuit or a ground fault, it is advisable to promptly seek professional advice in order to resolve the problem safely. If you live in the south-east, you may want to call your electrician in Brighton and get a specialist to take a look at the problem. However, in the case of an overloaded circuit, you can often fix the problem yourself in a few simple steps.
Before any fault occurs, it’s useful to ensure you know where your electrical board is located, and you have a handheld torch to help you navigate in case of a blackout.
Turn Appliances Off
Make sure to turn any appliances off that are connected to the affected system.
Master Switch
At the power board, your first move should be to turn off the master switch. This will ensure you cannot get hurt whilst fixing the problem.
Safety Switch
Make sure you have an RCD safety switch installed , and use it to check the safety of your appliances.
Once you have flipped the relevant switch back to the ‘on’ position, test that the circuit is working again. If it is not, or if it immediately trips again, it may be that the problem is more severe than an overloaded circuit, and it’s time to call in the professionals.
- Join Insider
Follow This Old House online:
Site search, why do circuit breakers trip.
Master electrician Heath Eastman shows host Kevin O’Connor everything he needs to know about why and how breakers trip.
Heath Eastman talks about circuit breakers. Heath shows Kevin O’Connor that while resetting these breakers is simple, these are complex devices that monitor and protect circuits. First, the two talk about the different sizes of breakers before moving on to the different types. Finally, Heath shows Kevin how to test certain breakers to ensure they’re working properly.
Circuit breakers exist to protect people, appliances, and homes from dangerous electrical current. However, few people understand why the trip and how they operate. Master electrician Heath Eastman shows host Kevin O’Connor why this happens, and even explains a few different types of breakers.
All About Electrical Systems
Breakers protect circuits.
When electricity comes into the house, it flows through the electrical service panel. From there, the electricity flows out through different branches in the house, each controlled by a circuit breaker. Should a branch begin to overload and overheat, the breaker will trip to prevent damage.
Breaker Sizes
There are two main sizes of breakers in a house: 15 amp and 20 amp. The amp rating explains how much current the breaker can handle before it will trip, and each requires a certain size of wire. Fifteen-amp breakers require a 14-gauge wire, while 20-amp breakers require a 12-gauge wire.
How They Work
A 15-amp breaker won’t necessarily trip the moment it experiences a spike above 15 amps. Many devices draw more amps upon start-up, and these breakers allow those temporary spikes. However, should the breaker sense elevated amperage for longer than is typical, it will trip to prevent the circuit from overheating.
GFCIs and AFCIs
Beyond circuit overload protection, there are other types of breakers that offer additional coverage. These include GFCI breakers and relatively-new AFCI breakers .
GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) breakers need to experience the same amount of current going out as coming back through the circuit. If the breaker experiences a drop in returning current, it assumes that the circuit is leaking, whether it be through a water source or a person. When this imbalance occurs, the GFCI trips immediately.
AFCI (arc fault circuit interrupter) breakers sense when the circuit, a device, or an appliance is arcing (the current is jumping from the circuit and onto something else or someone). When the breaker recognizes the arc signature, it trips immediately. These breakers are relatively new and look similar to GFCI breakers, but they’re becoming a code requirement in most locations.
How to Test Breakers
Homeowners, electricians, and inspectors can test their breakers. There are devices that users can plug into an outlet and replicate an error. These devices, known as AFCI/GFCI testers, can trip the breaker altogether or replicate a ground or arc fault, triggering the breaker. This is one of the best ways to ensure that a breaker is working properly.
When to Call a Professional
If a circuit is continuously tripping, or you know that it should be tripping and isn’t, be sure to call in a professional. An electrician will be able to determine the cause of the issue and make sure your circuit breakers and electrical system are safe.
Heath explains what a circuit breaker is, why they trip and how it protects a home. A circuit breaker is a device, installed in the electrical panel, that controls whether power can be sent from the panel through a circuit. Heath explains this ability is controlled by a switch that can be operated either manually—like when a person wants to interrupt power for service—or automatically, like a breaker trip.
He says power overloads, current “leaks”, and arcs are the three reasons that would cause a breaker to trip. A Power overload happens when a device is calling for more power than a receptacle , or a circuit is designed to provide. Current “leaks” are caused when current strays from the circuit for whatever reason, though it happens most commonly when moisture is present. Arcs can happen when the wire breaks down over time (due to overloads but also due to other factors, like animals chewing the wire and other decay) but what Heath sees the most is human error.
If a specific receptacle is consistently tripping the breaker, Heath advises to have a licensed electrician identify the problem to ensure the work is done safely.
Next Up In Electrical
- How to Label a Circuit Breaker
- Simple Guide for Selecting a Home Generator
- All About Portable Power Stations
- Simple Guide to Installing a Generator Hook-Up
- How to Build a Utility Cover
- Understanding Smoke and Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Sign up for the Newsletter
Get the latest This Old House news, trusted tips, tricks, and DIY Smarts projects from our experts–straight to your inbox.
WhatsApp Our Local Electrician To Get a Fast Response & Quote For Your Electrical Needs.

What Causes Circuit Breakers To Trip?
- April 2, 2024
If your circuit breakers keep tripping, there’s no need to stress. This is a typical situation. Below, you’ll find details on the reasons behind this and tips for avoiding it going forward. Get a handle on your circuit breaker issues!
Table of Contents
Understanding Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers are protection devices for electrical circuits. When too much current passes, the breaker trips, stopping the flow of electricity and preventing damage. This can be caused by faulty wiring, too many appliances on one circuit, or a ground fault.
Overloading can cause tripping. This happens when too many devices are connected to a single circuit. Heat builds up in the wires, which can start fires or cause damage. To prevent this, distribute loads across multiple circuits and don’t connect too many appliances to one outlet.
Short circuits also lead to tripping. This happens when two wires with opposite charges come in contact or when a wire touches something grounded. This causes an immediate surge in current that triggers the breaker. Check for exposed wires or insulation damage, and call an electrician if you spot any signs of trouble.
Ground faults can also cause tripping. This happens when there’s an unintentional connection between a live wire and a conductive surface. Install GFCIs to avoid this.
In short, know what causes circuit breakers to trip. Identify potential hazards like overloading, short circuits, and ground faults. Take steps to prevent accidents and ensure your electrical equipment is safe. If you’re unsure how to handle electrical problems, call a licensed electrician.
Overloading Causes
Circuit breakers trip to stop overheating, electrical fires, and damage to electrical parts. Plugging in too many devices can cause the circuit to become overloaded, so the breaker trips to cut off the power.
Short circuits are like a blind date gone wrong. They can be explosive, and often end in disaster. This happens when a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral or insulation/water. This throws off the electric balance, causing danger and tripping.
Short Circuit Causes
A short circuit happens when a low-resistance path appears between two points in the circuit that aren’t usually connected. This can cause too much current to flow, making a circuit breaker trip. Insulation or wiring damage, faulty appliances, and circuit overload are the most common reasons for a short circuit. It’s critical to identify and fix the root cause quickly to avoid electrical fires and other dangers .
When too much power passes through a circuit, the circuit breaker will automatically turn off. It’s designed to protect wiring and guard against electrical accidents . But if the breaker trips regularly, there may be underlying issues that need investigation and repair. Often times, this means upgrading or replacing components.
Sometimes short circuits are caused by human error or wear and tear. But they may also come from design or installation problems. Planning and upkeep from local electricians can keep electrical systems running safely and appropriately for a long time. If your circuit breaker is tripping a lot, get an experienced technician to review your system and suggest solutions that match your needs and budget .
Overheating Causes
Circuit breakers are essential safety features. They stop electrical fires and protect your appliances. When overloaded, too much current flows, producing heat. This causes the breaker to trip!
Other factors can cause overheating. Damaged insulation on wires increases resistance. Loose connections add resistance and heat. High temperatures and poor ventilation worsen the situation.
It’s important to maintain and service the electrical system. Checks of all components will make sure they work efficiently. To avoid tripping, prevent overheating. This will reduce energy consumption and safeguard equipment. So, let’s learn about circuit breakers and how they deal with overloads!
Circuit Breaker Types
Circuit breakers are essential for any electrical system. They prevent overloaded and faulted circuits . There are different types of circuit breakers suitable for specific electrical loads.
See the table below for the different types of circuit breakers and their functions:
It is crucial to select the right type of breaker. Each one has its own advantages in specific situations. For instance, thermal circuit breakers are perfect for small appliances like hair dryers or irons . Meanwhile, magnetic circuit breakers are great for bigger loads such as air conditioners or refrigerators .
Remember, circuit breakers are like Beyoncé – they can handle a lot, but have their limits.
Circuit Breaker Ratings and Specifications
Circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads. To ensure that circuits and appliances are safe, the ratings and specifications of circuit breakers need to be understood.
If a circuit breaker trips often, it may mean there’s an issue. It’s best to get professional help in these cases. Time to go on a hunt for your electrical wiring!
Troubleshooting Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers can flip out for multiple reasons, like overloads , short circuits , and ground faults .
Overloads happen when too much electricity passes through the circuit, creating too much heat and tripping the breaker. Short circuits are when two or more wires touch, resulting in extra current. Ground faults occur when the power takes an unexpected route, like through a person’s body.
To figure out why your circuit breaker is tripping, it’s important to figure out what is going on and act accordingly. Inspections and maintenance can also help avoid future tripping.
Stop your circuit breaker from misbehaving with these prevention tips!
Preventing Circuit Breaker Tripping
A circuit breaker tripping can be prevented with understanding. When circuits are overloaded, breakers trip to avoid overheating and potential fires. Here are 3 steps that can help you prevent circuit breakers tripping:
- Know the electrical load – work out how many appliances & devices are connected to one circuit. Don’t overload them by spreading high-energy equipment across multiple circuits .
- Look after your appliances – ensure all your appliances & devices are in good condition, with no damaged cords or frayed wires.
- Upgrade your system – if you’re tripping breakers often you may need to upgrade the electrical system with higher capacity breakers or more circuits.
Plus, investing in surge protectors can also assist in preventing circuit overload and subsequent tripping of breakers. By following these steps you can make sure your home’s electricity runs safely and without interruption due to circuit breakers tripping.
Remember: these precautions will keep you from tripping more than just your circuit breakers!
Safety Precautions
Safety must be taken seriously when dealing with circuit breakers . Always switch off the main power supply before beginning work. Wear protective gear such as insulated gloves and boots to stay safe from electrocution. Never touch wires or components inside the box without proper training. Keep the area around the breaker box free from any flammable substances. Inspect breakers for damage or wear regularly .
Label each circuit breaker correctly . Test them frequently for functionality. This will help identify circuits quickly in case of an emergency. These precautions and practices ensure safety while dealing with circuit breakers. When in doubt, blame it on the circuit breaker – it’s always a good scapegoat for electrical woes!
Circuit breakers are essential components of any electrical system. They stop too much current flowing and thus, protect against potential fires . The most common cause for tripping is overload. But, other causes like short circuits and ground faults can also cause the breaker to trip. When it trips, there is something wrong that needs to be fixed right away.
Short circuits occur when two wires touch each other. This creates a low resistance path which allows a lot of current to flow with no load. Ground faults occur when the hot wire touches something incorrectly wired or with a damaged cord.
To prevent tripping, regular maintenance of the electrical system is needed. Keeping appliances in good condition, replacing worn-out cords and fixtures, and periodically checking for loose wires all help reduce the chances of tripping. In summary, understanding why the breaker trips and taking precautionary measures will keep you safe and save you repair costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what causes a circuit breaker to trip.
There are several possible causes, including overheating due to circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, and age-related wear and tear.
2. How can I prevent my circuit breaker from tripping?
You can avoid overloading your circuit by keeping the number of electrical appliances used on one circuit to a minimum, regularly checking wires for signs of wear and tear, and not using too many extension cords.
3. What should I do if my circuit breaker keeps tripping?
If your circuit breaker is constantly tripping, it is important to identify and fix the underlying issue. Contact an electrician to inspect and repair any faulty wiring or electrical devices.
4. Can a circuit breaker trip without an overload?
Yes, a circuit breaker can trip due to a short circuit or a ground fault, which may occur without an overload.
5. How do I reset a tripped circuit breaker?
To reset a tripped circuit breaker, turn it off and then back on again. Make sure to identify and correct the underlying issue that caused the trip before restoring power.
6. What is the lifespan of a circuit breaker?
The lifespan of a circuit breaker can vary depending on usage and other factors. However, most circuit breakers last between 10 and 30 years.
Related posts:
- Moving Offices? Here’s How a Commercial Electrician Can Help
- Possible Causes of a Blown Fuse and What to Do
- How to Make an Electrical Plan for a New Home in Puchong
- How to Prepare Your Business in Kuala Lumpur for Power Outage Impacts

1335 Martin Luther King Jr Ave
Dunedin, fl 34698, (727) 648-6101.

1335 Martin Luther King Jr Ave, Dunedin, FL 34698
CALL US: (727) 648-6101

What Does a Circuit Breaker Tripping Mean?
when there's a circuit breaker tripping, it can indicate that the circuit breaker detects an electrical issue, and it shouldn't be ignored..

The pandemic-induced surge in home electricity use is real. Consider that, according to the National Bureau of Economic Research, American spending on home power consump tion skyrocketed by $6 billion!
With more usage comes more problems, and circuit breaker issues are among the most common. When there's a circuit breaker tripping, it can indicate that the circuit breaker detects an electrical issue, and it shouldn't be ignored.
Circuit Breaker Tripping 101
Most circuit breaker issues center around circuit overload. Circuit breakers are a vital part of your home's electrical system since they are designed to prevent costly and damaging surges in electrical current.
The breaker, working in tandem with a fuse, serves as an electrical unit's internal sensing mechanism. At the slightest sense of excess current, the circuit breaker will "trip," triggering a cease in all electrical activity within the circuit.
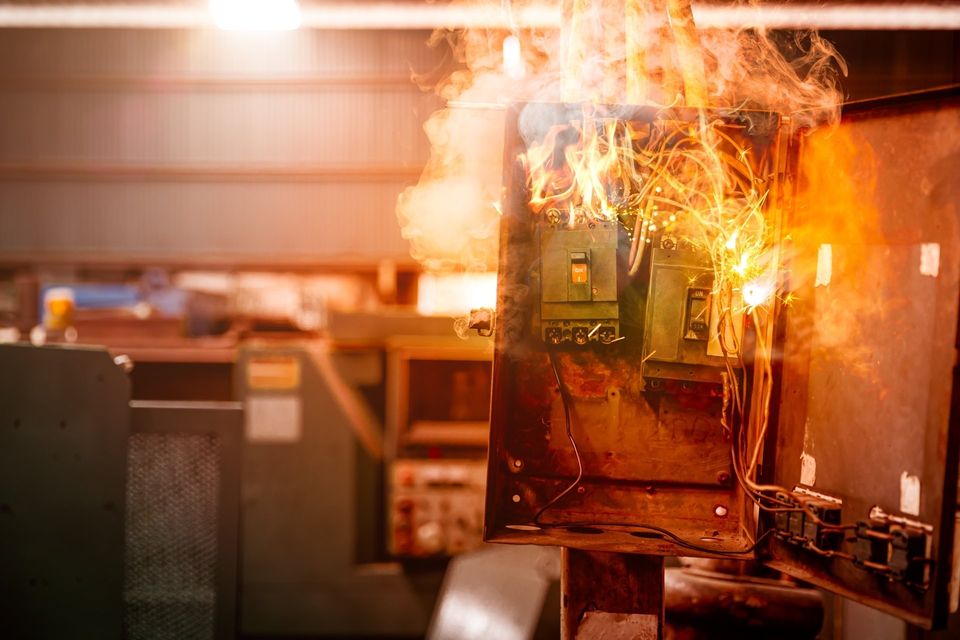
Not only can such a smart mechanism help with preventing damage to wires and other electrical components, but circuit breakers can also save lives by preventing electrical fires. According to the National Fire Protection Association, electrical failures were the second leading cause of home fires between 2012-2016.
So why do circuit breakers trip? Here are the three most common reasons for circuit breaker tripping and how you can go about fixing a circuit breaker.
1) Circuit Overload
By far, the m ost common reason a circuit trips is because it's overloaded. Even running a circuit at its electrical capacity can cause home appliances to burn out or a circuit to trip. Ideally, you want to run a circuit below its capacity to keep it from tripping and to prevent any damage from occurring.
The most familiar example of circuit overload is an over-stuffed power outlet. When you have a dozen gadgets all demanding electrical current to work, eventually that single outlet's capacity will experience overload, and the circuit will trip.
Knowing what each electrical outlet in your house can handle is key to preventing circuit overload. Even a single high-current appliance like a washing machine cannot plug into just any outlet. Understanding your power outlets is critical for a safer home.
Before you head to your circuit breaker box or call your electrician, notice what was plugged in at the outlet where the tripped circuit occurred. You may have overloaded it.
2) Short Circuit
Similar to an overload, when a circuit "shorts," it responds to more current than it can bear. But a short circuit is far more dangerous.
A short circuit occurs when a "hot" or active wire comes into contact with either another active wire or a neutral wire. The touching wires cause a spike in current that can likewise trip your circuit breaker. Most often, the causes for short circuits are mechanical issues like:
- Loose Connections
- Improper Wiring
- Damaged Wires
Faulty components, like switches, plugs, cords, appliances, or lighting fixtures, are often culprits of short circuits. Short circuits can occur if you screw or nail into drywall and penetrate an electrical wire.
Remember that short circuits may involve faulty circuit wiring, but the device you're plugging in can cause the problem as well. Keep this in mind, especially if you're using older devices or gadgets that have been out of commission for years, as these can be more prone to short circuits, independent of what's going on in the outlet.
Due to their volatile nature, short circuits are some of the biggest causes of electrical fires, so be extra attentive and don't hesitate to call a professional. As a general rule, most people should never DIY electrical issues in their homes.
3) Ground Fault Surge
Ground fault surges are similar to short circuits because they involve a sudden spike in current, creating an overload. Ground faults occur when an active wire comes into contact with the ground wire. The contact can come directly or indirectly via the metal housing that connects to the ground wire.
Copper grounding wires are especially prone to ground fault surges. Copper is the most conductive material in everyday use when it comes to home electrical systems. When a hot wire touches the ground wire's copper coating, it results in superconductivity that overwhelms the circuit. A similar result can come from an active wire touching a ground's metal outlet box.
Understanding and Fixing Circuit Breaker Issues
So how should you go about troubleshooting a circuit breaker issue? Even though you should leave anything remotely technical to a professional, there are a few things you can do to investigate circuit breaker trip meaning.
First thing's first. Make sure you and your family are safe. Check for signs of excess heat or burning—smell for what could be smoke from an electrical fire. If you sense any signs of a fire, evacuate and call 911.
Check for any discoloration around an outlet. Also, make a note of any sparks or popping noises coming from the outlet. Any of these could be a sign of a ground fault surge or a short, in which case simply flipping the circuit breaker switch won't help. And remember, the older the outlet, the more likely it is to experience problems.
Look for any signs of damage to your devices. Remember that the problem could be coming, not from your home's outlet, but from what you plugged in.
If there are no signs of a blown circuit, try going to your circuit breaker service panel. You may be familiar with this metal box, often located in a garage or utility room. Flip the switch of the house area that tripped, and see if that "resets" the circuit.
Fixing a Circuit Breaker
If a simple flipping of the switch doesn't work, it's time to call a professional electrician. The seasoned team at Buell Electric can assess the problem and fix a circuit breaker, which may involve repairs or upgrades.
Circuit breaker tripping may be as innocent as overloading an outlet, but it can point to more serious problems as well. The best way to know for sure is to contact us today.
Newer Post >
Buell Electric's Blog

Shedding Light on Your Home: Finding the Right Electrician in Tampa

How Electricians Keep Up with Changing Technology in the Industry

The Importance of Regular Electrical Maintenance For Your Business

Marine Electrical Standards and Regulations You Need to Know

The Benefits of Installing a Smart Home System

Understanding the Different Types of Electrical Wiring in Your Home

How to Prepare Your Home for an Electrical Emergency

5 Reasons Your Ceiling Fan Installation Should be Left to the Pros

5 Tips for Hiring Residential Electrical Services

8 Common Outdoor Lighting Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
[email protected]
Mon-fri 9:00 am - 5:00 pm sat-sun 10:00 am - 5:00 pm privacy page, connect with us:.

Mon-Fri 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM Sat-Sun 10:00 AM - 5:00 PM
All Rights Reserved | Buell Electric, Inc.


Breaker Keeps Tripping: Understanding the Common Causes and Solutions
When a circuit breaker trips, it protects your device and circuit; it’s just doing its job unless it is damaged.
Do you notice that sometimes the lights of a residential place go off due to circuit breaker tripping, or sometimes the fuse blows up? It is due to some faults in the electrical network. I see these faults too much because I work as an electrical maintenance engineer.
I will discuss different reasons that cause circuit breaker tripping. I won’t rely only on my long work experience as an engineer, which is now about 15 years, but also I will provide you with the results of deep searching about circuit breaker tripping.
Table of Contents
How To Find The Reason Behind Tripping My Circuit Breaker?
Tripping of a circuit breaker can occur due to various reasons, such as overloading, short circuits, ground faults, or issues with the electrical appliances or wiring. Here are some steps to help you identify the reason behind the tripping:
Identify the Circuit: Determine which circuit breaker has tripped and which area of the house or building is affected. This can help narrow down the potential causes.
Unplug Appliances: If the tripping occurs when a specific appliance is used, unplug that appliance and try resetting the circuit breaker. If the breaker does not trip, the appliance might be faulty and cause an overload.
Check for Overloading: Assess whether the circuit is overloaded by connecting too many high-powered devices to the same circuit. Try redistributing the load by connecting devices to different circuits.
Inspect for Short Circuits: Examine the electrical outlets, switches, and wiring for signs of damage or exposed wires that could be causing a short circuit. If you notice any issues, consult a qualified electrician to repair or replace the affected components.
Look for Ground Faults: Ground faults occur when a hot wire comes into contact with a ground wire or a metal wall box. Use a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) tester to identify any potential ground fault issues and address them accordingly.
Check for Wet Conditions: If the circuit is in a damp or wet area, it could lead to a ground fault. Ensure that all electrical components in such areas are moisture-resistant and properly grounded.
Inspect the Breaker Itself: Examine the circuit breaker for any signs of damage, corrosion, or overheating. If you notice any issues, consider replacing the circuit breaker with a new one.
Consult a Professional Electrician: If you are unable to identify the cause of the tripping or if you suspect a more complex electrical issue, it is advisable to consult a licensed electrician. They can conduct a comprehensive inspection of the electrical system and troubleshoot any underlying problems.
It is crucial to prioritize safety when dealing with electrical issues. If you are unsure about how to proceed or are not comfortable handling electrical components, it is best to seek professional assistance to ensure a safe and effective resolution to the problem.
What would cause a circuit breaker to keep tripping?
Now, after this quick discussion for non-technical persons. let’s move to the electrical engineering discussion.
Overloaded Circuit:
One of the main reasons for circuit breaker tripping is the overloaded circuit in the electrical system. When many loads are connected to the circuit, the circuit attempts to draw a greater electrical load than its rated value. Due to this, the circuit breaker heats up, and the breaker tripping occurs.

Electrical Short Circuit:
Another reason for the breaker tripping is the electrical short circuit. A short circuit occurs due to low insulation resistance .
When the positive and negative (live and neutral) terminal connects with each other in the absence of any resistance. This causes an unimpeded flow of electricity. A large amount of current flows through a breaker that causes tripping.
It is worth mentioning here how to decide whether the tripping occurs due to a short circuit . The answer is clear and simple. If a circuit breaker trips instantly again and again after you reset it, the tripping occurs due to a short circuit.
How Do I Know That I Have a Short Circuit at the House? If you find fuses being blown regularly or a circuit breaker tripping frequently, it might be a symptom of a short circuit.
A fuse will usually explode, or a circuit breaker will trip instantly. If a new fuse with the proper rating also blows, you’ve got a short circuit.
If a circuit breaker is reset and it trips again instantly, as you connect it, you have a short circuit or a broken circuit breaker. Read my detailed article about Electrical short circuits, why is it dangerous?
Ground Fault:
Another reason that causes the circuit breaker tripping is the ground fault. A ground fault is a type of short circuit when a hot wire comes in contact with the ground or any other type of metal.
The ground fault causes an increase in the flow of current. It causes the circuit breaker to heat up and as a result, circuit breaker tripping occurs.
Some ground faults are not detectable by normal MCB. So it’s recommended to use GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) This is better for human safety as this breaker can detect small milli-amperes and trips before a shock happens. Read my article on my other site: Surge Protectors and GFCI Outlets: Can They Safely Coexist?
When fluctuation or sparking occurs between two-wire connections at a point. Arc faults occur.
Sometimes the screws at a point become loose, In this case, AFCI (arc fault circuit interrupter) is recommended.
While the circuit breaker is an Arc fault interpreter (AFCI ). It detects the early wiring problem and trips in advance to stop the flow of a large amount of current.
Bad Circuit Breaker:
Sometimes the circuit and loads are all OK and in good condition. But the breaker keeps tripping randomly.
This is a sign that the circuit breaker is bad. Like any device, breakers have a lifetime, and then breakers go bad . And it’s time to replace it.
The circuit breaker keeps tripping immediately
If your circuit breaker keeps tripping immediately after resetting it, this indicates a severe electrical issue that requires prompt attention. Here are some steps to follow to address the problem:
Identify the Problem Circuit: Determine which specific circuit is causing the repeated tripping. This can help pinpoint the area of concern and focus your troubleshooting efforts.
Disconnect All Appliances: Unplug or disconnect all devices and appliances from the circuit that keeps tripping the breaker. If the breaker doesn’t trip after disconnection, the issue may be related to one of the appliances or devices.
Check for Short Circuits or Ground Faults: Inspect the wiring, outlets, and switches for signs of damage, exposed wires, or any moisture intrusion. Focus on the affected circuit and look for any visible signs that might indicate a short circuit or ground fault.
Examine the Breaker Itself: Check the circuit breaker for any signs of damage, overheating, or wear. A faulty breaker could be the root cause of the repeated tripping. Consider replacing the circuit breaker with a new one if it appears damaged.
Consult a Professional Electrician: If you are unable to identify the cause of the immediate tripping, or if the issue persists despite your troubleshooting efforts, it is essential to seek assistance from a qualified electrician. They can perform a comprehensive inspection of the electrical system and troubleshoot the problem effectively.
It is crucial to prioritize safety when dealing with electrical issues. If you are uncertain about how to proceed or are uncomfortable handling electrical components, it is best to seek professional help.
Electrical problems can be complex and potentially dangerous, so it is important to have them addressed by a licensed electrician to ensure the safety of your property and its occupants.
Can a circuit breaker trip for no reason?
A breaker will trip for no reason if it malfunctions . A breaker will trip when a short circuit occurs on an electrical circuit, causing sparks, popping sounds, or smoke to be produced.
A loose connection, slipping wire, or even damage from animals chewing on cables could cause this.
If you didn’t find any faults like a short circuit , overload, or lost connection, your circuit breaker might be old and unable to carry current anymore.
In other words, it has become bad. It would be best if you replaced it for the circuit to continue operating.
Why is the circuit breaker tripping without load?
If your circuit breaker trips without loads, a wire with damaged insulation somewhere in the electrical panel or in power outlets can be the cause of breaker tripping and will continue to do so until you fix it .
A general wiring issue can potentially be the reason why a circuit breaker trips. You can have obsolete wiring if your home is older.
The issue with older electrical systems is that new technology and appliances frequently demand more power than previous systems can safely handle.
The older wiring can’t keep up with the increasing demands as our daily energy needs increase. This may be the problem if several breakers are often tripping without a load. Otherwise, there can be a problem with the breaker panel itself.
When your breaker trips without any load being present, you should take into consideration the following three wiring problems:
Current Leakage: One possibility is that one or more of the input wires have current leakage, which causes the circuit breaker to trip even when there isn’t a load attached to it. If so, your annoying issue is taking place for your own benefit. tripping is a precaution for the safety of your all-electrical devices.
Damaged Wires : Not simply the input cables might be damaged; it could happen everywhere. They could have been accessed by pests or insects that, only by gnawing, caused significant harm. This kind of issue may be sufficient to trigger a breaker trip even with no loads.
A Loose Wire in an Outlet : This loose wiring issue may be pretty frustrating. In other words, a loose wire in one of your outlets will keep your breaker continuously tripping. If you have a GFCI outlet, this is a very typical issue (Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter).
Why shouldn’t you reset a tripped circuit breaker immediately?
The straightforward answer is that you shouldn’t reset a circuit breaker unless you are sure of the reason for the fault and that it poses no danger.
Note that if you reset it immediately it may trip again in case it is still hot, even if the fault is cleared.
Circuit breakers are there to safeguard your family, your house, and yourself. When a circuit breaker trips, it indicates that a current greater than the trip current is passing through it.
In case of a faulty circuit or wires, or a short circuit, the circuit breaker will trip again immediately if you reset it.
The short circuit current makes the circuit breaker get hot and trip, it should be cooled before you reset it.
Can a tripped breaker stop a fire?
Yes, if tripping happen before the fire catch wires or panel. But it won’t if tripping happens after the fire catch wires or panel .
There can be two scenarios, 1 st one is before the wiring or breaker panel catches fire.
And 2 nd is the role of the circuit breaker after catching fire let’s explore both scenarios in detail below:
Role of circuit breaker before Catch Fire :
Tripped circuit breakers can prevent fire and protect electrical systems against overloads and short circuits, circuit breakers assure electrical safety in homes, offices, and other buildings as well as for industrial uses.
The circuit breaker instantly shuts off the electrical circuit when a problem is found, protecting the wires and reducing the chance of catching fire.
Role of circuit breaker after catching fire:
Tripped circuit breakers didn’t play any role and could not provide safety to the system after catching fire.
If the circuit breaker is not tripped due to any reason or sometimes the fault current is too much bigger than the rating of the cable, then the circuit breaker wiring or panel box catches fire.
Can tripping circuit breaker damage your devices?
Tripping circuit breakers themselves do not typically cause direct damage to your electrical devices.
In fact, the primary purpose of a circuit breaker is to protect your devices and electrical system from potential damage due to electrical overloads or short circuits.
When a circuit is overloaded or a short circuit occurs, the circuit breaker is designed to trip and cut off the flow of electricity, preventing excessive current from damaging your devices and wiring.
However, frequent or repetitive tripping of circuit breakers may indicate underlying issues within the electrical system that could potentially affect connected devices. Repeated tripping may point to problems such as overloading, short circuits, ground faults, or other electrical faults that could impact the functionality and safety of your devices.
Indirectly, sudden loss of power due to a tripped circuit breaker can cause data loss or corruption in electronic devices like computers, especially if they are not connected to an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). Additionally, frequent power fluctuations resulting from faulty electrical systems can gradually wear down sensitive electronic components, reducing the lifespan of your devices over time.
To prevent potential damage to your devices, it’s important to address any electrical issues promptly. If you notice persistent circuit breaker trips, it’s advisable to consult a qualified electrician to identify the underlying cause and ensure that your electrical system is functioning safely and efficiently. Taking proactive steps to maintain your electrical system can help prevent potential damage to your devices and ensure the safety of your property.
Why is the Main circuit breaker tripping?
The main breaker can trip for a variety of reasons. Whether it be a lightning strike, a power surge from the utility company, or an overload to the electrical panel, the main breaker can be tripped due to any of these factors.
Furthermore, the main circuit breakers can trip simply because they’re worn out . There might be a situation when a branch circuit breaker fails and is no longer capable of tripping as designed, which may result in the main breaker tripping to provide secondary safety shutoffs in the event that the individual circuit breaker fails.
Furthermore, If the total load demand becomes too much or if there is any significant issue with the electrical system, the main breaker cuts off electricity to the entire house.
These issues often entail brief power spikes, although it may be necessary to detect system issues occasionally.
The main circuit breaker “tripping” is somewhat uncommon since often, individual circuit breakers trip long before the main breaker has to shut down.
Does weather affect the circuit breaker?
Yes, weather affects the circuit breakers . In response to the heat generated by the circuit breaker, the bimetallic strip inside the breaker flexes and trips the breaker.
The hot weather also can cause a breaker to trip, it all depends on the thermal effect of heat that causes the bimetallic strip inside the breaker to flex and trip it.
On the other hand, as compared to hot weather, cold weather didn’t affect the circuit breaker as much as lead to tripping, but if there is a foggy season and too much moisture in the environment, that can cause tripping the breaker.
A breaker’s components can also be adversely affected by the ambient heat in the air surrounding the breaker. A circuit breaker should typically not be heated over 140°F. If it happens, it indicates a potential trip of the circuit breaker.
If you can’t keep your finger on the plastic portion of the circuit breaker without being burnt, it’s too hot, according to a reliable “rule of thumb.”
Why do my breakers trip when it rains?
The main cause of a breaker’s trip after the storm is a short circuit brought on by water .
Due to heavy rain, the electrical wire isolation may deteriorate after water exposure, causing a short circuit. Improper panel box installation might be another reason your circuit breaker tripped during the storm.
Rainwater may get into your circuit in a number of ways if the main line is not installed properly.
Water may enter your wiring conduits through the wire leading to the meter and electrical circuit. It’s also conceivable that the conduit or hose you used to install your main line will let water through.
Because of this, if the breaker box is in the basement, water may wet your circuit. The worst possible scenario for your house is a wet circuit breaker.
A wet circuit is dangerous because you might get electrocuted in addition to the electrical problems it can create.
Can you reset a breaker in the rain?
It is generally not recommended to reset a circuit breaker while it is raining or in wet conditions . Water can significantly increase the risk of electrical hazards, potentially leading to electric shocks or other safety risks.
Resetting a circuit breaker in the rain could expose you to electrical currents and pose a danger to your safety.
To ensure your safety when dealing with electrical components, including circuit breakers, it’s crucial to follow these guidelines:
- Safety First: Prioritize your safety at all times. Do not attempt to handle electrical components in wet conditions or when you are standing on a wet surface.
- Turn Off the Main Power: If you need to access the circuit breaker panel during wet conditions, make sure to turn off the main power to the house or the affected circuit before attempting any reset.
- Wait for Dry Conditions: If the circuit breaker trips during the rain, it is advisable to wait until the weather improves and the area is dry before attempting to reset it.
- Take Precautionary Measures: If you must work on electrical components in damp conditions, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as rubber gloves, rubber-soled shoes, and other safety gear to minimize the risk of electrical shock.
If you are unsure about how to safely handle a circuit breaker or if you are uncomfortable with electrical work, it is best to seek assistance from a qualified electrician.
Professional electricians have the necessary expertise and equipment to handle electrical components safely, even in adverse weather conditions.
Prioritizing safety is essential to prevent accidents and ensure the protection of both you and your property.
Can a storm and lightning cause a CB to trip?
Yes, storms and lightning can potentially cause a circuit breaker to trip. Lightning strikes can induce power surges in electrical systems, leading to a sudden increase in electrical current that exceeds the circuit breaker’s capacity.
In response to the excessive current, the circuit breaker will trip, cutting off the power supply to the affected circuit or the entire house to prevent electrical damage or fire hazards.
Additionally, storms can cause power fluctuations and electrical disturbances, which might impact the stability of the electrical supply. These fluctuations can result in overloading or short circuits within the electrical system, leading to the tripping of the circuit breakers.
To protect your electrical system during storms and lightning, consider taking the following precautions:
- Install Surge Protectors: Use surge protectors to safeguard sensitive electronic devices from power surges caused by lightning strikes or other electrical disturbances.
- Unplug Electronic Devices: Unplug sensitive electronic devices during thunderstorms to prevent potential damage from power surges or lightning strikes.
- Invest in Lightning Protection Systems: Consider installing lightning protection systems, such as lightning rods and surge arresters, to divert lightning strikes away from your property and protect your electrical system.
- Maintain the Electrical System: Regularly inspect and maintain your electrical system to ensure that it is in good condition and capable of withstanding electrical disturbances caused by storms and lightning.
If you experience frequent circuit breaker trips during storms or if you suspect damage to your electrical system as a result of a lightning strike, it is advisable to seek the assistance of a licensed electrician.
A professional electrician can assess the condition of your electrical system, identify any potential issues, and implement necessary measures to safeguard your property from electrical hazards.
Will a breaker trip if wires touch each other?
Yes, a circuit breaker can trip if wires touch each other, especially if the wires create a short circuit.
When wires make direct contact or create a path with low resistance between the hot and neutral wires or between the hot wire and the ground, a short circuit occurs.
This causes a sudden increase in electrical current, exceeding the circuit breaker’s capacity and triggering it to trip.
The purpose of a circuit breaker is to protect the electrical system and connected devices from potential damage caused by overcurrent situations like short circuits. When the circuit breaker trips due to a short circuit, it interrupts the flow of electricity and prevents further damage to the wiring, appliances, and other electrical components.
To prevent wires from touching and causing a short circuit, it’s essential to follow proper wiring practices, including:
- Using appropriate wire connectors and junction boxes to secure and protect wire connections.
- Insulating exposed wires to prevent contact with other wires or conductive materials.
- Maintaining proper wire spacing and organization to minimize the risk of accidental contact.
If you suspect that wires are touching or if you experience frequent circuit breaker trips, it’s essential to consult a licensed electrician to inspect your electrical system.
A professional electrician can identify any potential wiring issues, troubleshoot the cause of the tripping, and ensure the safety and functionality of your electrical system.
Can the circuit breaker trip if you hold it?
The circuit breaker standard UL489 requires circuit breakers to be “trip free”. A trip-free circuit breaker will still trip if you hold it in the ON position.
Yes, you can hold the toggle up, but that does not stop the breaker from tripping under an over-current condition.
A circuit breaker cannot be forced if it trips repeatedly; it will keep opening and burn out.
It is usually not harmful to have a momentary connection, as it will only last for a short time.
You will need to resolve the problem causing the trip and then you will need to replace the circuit breaker if it went bad.
Why is the circuit breaker not tripping?
The circuit breaker may not trip if it malfunctions due to (an entirely mechanical problem, or sustains partial or total damage ) Occasionally, a circuit breaker will not trip in circumstances of fault like a short circuit, or overload, indicating it is bad and must be replaced.
It is also possible for the cause of the problem to be entirely mechanical, which means there may be a physical switch that is stuck in the “on” position.
The circuit breaker may also malfunction without tripping if it sustains partial or total damage. On occasion, a power failure occurs as internal components melt. To ensure appropriate operation, examine the circuit breaker and replace the broken one.
Signs of damaged/ faulty circuit
- Inspect the circuit breakers for any burning odors.
- If the panel feels hot to the touch, the circuit is either broken or overloaded.
- If the circuit is beyond its prime or is too old, replace it with a new one.
- Parts become melted or scorched due to heat.
- The item is defective if it trips off more frequently while gadgets draw more power.
What happens if a breaker doesn’t trip in faults condition?
If a circuit breaker fails to trip during a fault condition, it can lead to various hazardous situations, including:
- Overheating and Fire Risk: When a circuit experiences an overload or short circuit, excessive current flows through the wires, leading to overheating. If the circuit breaker does not trip to interrupt the flow of current, the wires, insulation, or other electrical components can overheat and potentially ignite a fire.
- Equipment Damage: The excessive current in the circuit can damage connected electrical devices, appliances, and other equipment. Without the protection of the circuit breaker, the electrical components can sustain irreparable damage, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
- Electrocution and Safety Hazards: In the absence of circuit protection, the risk of electric shock or electrocution increases, especially if someone comes into contact with live wires or faulty electrical equipment.
- Damage to the Electrical System: Continual overloading or short circuits without interruption from the circuit breaker can cause significant damage to the overall electrical system, including the wiring, panels, and other connected components. This can lead to extensive repairs and pose a safety risk to the property.
To mitigate the risks associated with a circuit breaker failing to trip during a fault condition, it is crucial to regularly inspect and maintain the electrical system. Consider the following measures:
- Schedule Regular Inspections: Arrange for periodic inspections of the electrical system by a qualified electrician to ensure that the circuit breakers are functioning correctly.
- Test the Circuit Breakers: Conduct routine tests on the circuit breakers to verify that they trip appropriately during overload or short circuit situations.
- Upgrade to Advanced Protection: Consider installing advanced protection devices, such as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) and arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs), to enhance the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
Prioritizing regular maintenance and promptly addressing any issues with the circuit breakers or the electrical system can help prevent hazardous situations and ensure the safety and functionality of your property.
Is the circuit breaker tripping a good or bad thing?
Yes, circuit breaker tripping is good from the perspective of the safety of your home and home appliances .
It also provides protection against dangerous electrical fire hazards due to short circuits and overloading as long as it is not a bad CB .
But sometimes, apparently, you didn’t see any issue, but your circuit breaker keeps tripping and can get you in trouble.
It can be due to wiring issues like too much old wiring, damaged cables, or loose cable connection, which is difficult to troubleshoot because you have to check all the outlet’s wiring connected to the breaker.
That can be time-consuming, but it’s necessary to troubleshoot the fault and rectify it as soon as possible to avoid any bigger damage or loss.
Install my Free Android App on Google Play :
Electrical Cables Most Common Tables “Electrical Cables Tables”
And, my Electrical Calculations App “ Fast Electrical Calculator ”
Discover more great content by subscribing to My channel
Looking to stay ahead of the game in the world of electrical engineering? Subscribe to my YouTube channel and gain access to exclusive content you won’t find anywhere else!
The staff I recommend
(Amazon Affiliate Links to products I believe are high quality):
- Economy 120 Volt/60Hz AC Power Source – Step-Down Voltage & Frequency Converters 1800W
- UNI-T Digital Multimeter Tester UT139C
- 50-Amp Extension Cord for RV “100ft”
- Voltage Stabilizer 110/220v
- Hair Dryer “best selling “
- TOSHIBA EM131A5C-BS Countertop Microwave Ovens
Disclaimer : This contains affiliate links to Amazon products. I may earn a commission for purchases made through these links.
You Might Also Like
Prevent electrical fires with gfcis: here’s how they work, gfci vs circuit breaker: understanding the differences.

Bad Breaker, Signs, Causes And Repair

Circuit Breaker: 18 Answers You Should Know
When breakers go bad: the top symptoms and solutions.


Understanding Trip Circuit: Breakers, Overloads, and Solutions for Short Circuits
Understanding circuit breakers and how to deal with constant tripping.
When the circuit breaker in your home trips, it’s important to reset it in the fusebox to restore power. This may require a trip under the stairs or down to the garage, depending on where your circuit breaker is located. Circuit breakers are designed to interrupt the electrical current when the switch is tripped, ensuring the safety of your electrical system.
While circuit breakers are essential safety devices, constant tripping and repeated resetting can be frustrating. However, if you can identify the cause of the frequent trips, you can take steps to address the issue.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
Every home and business premises have electrical circuits controlled and protected by a switching device located in a consumer unit or fuse panel. Modern systems typically use circuit breakers for control and protection, while older systems might still rely on fuses that blow when overloaded. The main purpose of a circuit breaker is to cut off the flow of electricity to prevent circuits from overheating, which can cause damage and even lead to electrical fires.
How Does a Circuit Breaker Work?
A circuit breaker is a switching device that can be operated manually or automatically. It trips and disconnects the circuit to cut off the electricity supply if there’s an excessive current flow or an overload that the switch can’t handle. The circuit breaker is designed to protect your electrical power system and any devices connected to it.
Why Does a Circuit Breaker Trip?
A circuit breaker will trip when there is an electrical fault that could damage the circuit. This fault typically falls into three categories:
- Overloads: The most common reason for circuit breakers to trip is overloading. This occurs when you draw more electrical power from a circuit than it can handle. For example, running multiple appliances simultaneously or exceeding the circuit’s capacity. When a circuit overheats due to an overload, it puts all connected appliances at risk. The circuit breaker ensures the wires don’t excessively heat up and protects against fire hazards.
- Power Surges: Power surges can also cause circuit breakers to trip. These surges happen when there is a sudden increase in electrical voltage, often caused by lightning strikes or faulty wiring in the electrical system. Circuit breakers act as a defense mechanism against power surges by cutting off the excessive flow of electricity.
- Faulty Components: Another reason for circuit breakers to trip is faulty components within the electrical system. This can include damaged wires, short circuits, or defective appliances. When these faults occur, the circuit breaker detects the problem and interrupts the current flow to prevent damage.
Dealing with Constant Tripping
If your circuit breaker is frequently tripping, it indicates that you are demanding too much power from the circuit. To resolve this issue:
- Redistribute Appliances: Distribute your appliances and devices onto different circuits. Avoid overloading a single circuit by spreading the load across multiple ones. This ensures that each circuit operates within its designed capacity.
- Upgrade Your Electrical System: If your system doesn’t have enough circuits to meet modern demands, consider upgrading your electrical system. This may involve installing additional circuits or replacing outdated wiring and panels. A professional electrician can assess your needs and recommend the best solution.
By understanding how circuit breakers work and taking appropriate measures, you can prevent constant tripping, protect your electrical system, and ensure the safety of your home or business.
Understanding Circuit Breaker Tripping: Short Circuits and Ground Fault Surges
Have you ever experienced a sudden power outage in your home or office? Chances are, it was due to a circuit breaker tripping. Understanding the causes of circuit breaker tripping, such as short circuits and ground fault surges, is crucial for ensuring the safety of your electrical system. Let’s explore these common issues in more detail:
1. Short Circuits
Short circuits are a common reason for circuit breaker tripping and should be taken seriously due to their potential danger. A short circuit occurs when a live wire comes into contact with a neutral wire, resulting in an abnormal electrical connection. This can happen in electrical outlets or due to faulty wiring in appliances or plugs.
When a short circuit occurs, the normal electrical resistance is overridden, causing an excessive flow of current through the circuit. This generates excessive heat, which can lead to fires. If you notice a burning smell or dark discoloration around the circuit breaker, it is an indication of a short circuit.
2. Ground Fault Surges
Similar to short circuits, ground fault surges involve a live wire touching a bare copper ground wire or a part of a metal outlet box connected to the ground wire. When this happens, an excess flow of electricity occurs, triggering the circuit breaker to trip. Discoloration around the outlet is also a visible sign of a ground fault surge.
Both short circuits and ground fault surges are not only inconvenient but also pose serious risks to your safety. If your circuit breakers frequently trip, it is crucial to seek professional assistance to identify and resolve the underlying electrical issues. Attempting to solve electrical problems on your own can lead to further complications and put your premises at risk.
Remember, the safety of your electrical system should be entrusted to trained professionals. Don’t hesitate to call for professional help to ensure the proper functioning and safety of your electrical circuits.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Galvin Power is reader-supported. When you buy via our links, we may earn a commission at no cost to you. Learn more
Why Do Circuit Breakers Trip? 6 Reasons You May Want to Know!
Written by Edwin Jones / Fact checked by Andrew Wright

Circuit breakers are integral electrical components in our homes. They do a multitude of electricity-related tasks that facilitate the function of our house’s circuitry. Circuit breakers are known for tripping when they register electrical currents higher than the circuit’s capable of handling.
In this regard, we homeowners must be aware as to why do circuit breakers trip, so that we know which electrical problems we have.
For the sake of brevity, each of the following reasons trips a breaker: short circuitry, grounding faults, arc faults , an overloaded circuit, and a corroded circuit.
For more information about what causes a circuit breaker to trip, head on and read more below!
Table of Contents
How Circuit Breakers Work
1. overloaded circuit, 2. short circuits, 3. ground fault surges, 4. arc fault, 5. older circuit breaker, 6. loose or corroded connections, what to do when your breaker trips constantly.
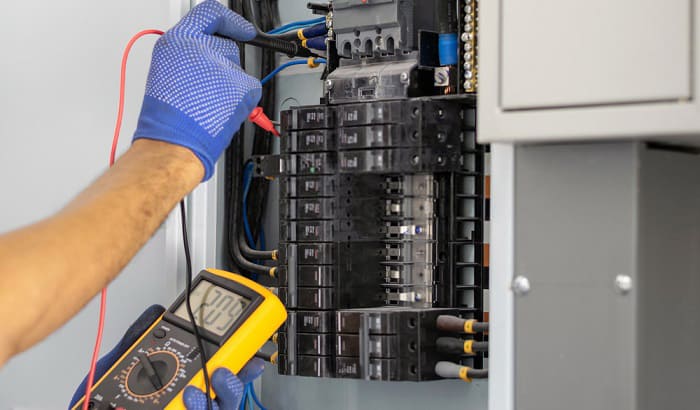

Circuit breakers are specifically installed to prevent any sort of electrical mishap from happening within lines. With this particular task in mind, circuit breakers are designed to detect any electrical qualities that are deemed “out-of-place” for certain electric circuits.
Simply speaking, circuit breakers work by cutting off the electrical connection of circuits when abnormalities are detected to prevent electrical accidents from transpiring and causing damage.
Breakers do this through the use of an internal spring mechanism, deactivating the circuit by force. Hence, the reason for the loud noise made by a circuit breaker trip.
However, to further discuss the intricacies of circuit breakers, you must first understand electricity and its components.
Mainly, electricity is composed of three distinct qualities that dictate how it flows through a circuit line. These qualities are voltage, resistance, and current.
To explain in a simple and more understandable manner, the electrical voltage can be akin to the pressure which moves electric charge. Electrical current, meanwhile, can be understood as the flow rate of electric charge in a circuit. Finally, electric resistance is simply the interaction of the conductor material against the electric charge flowing through it.
With this in mind, the sudden reduction of electrical resistance results in excessively high voltage and current, causing the breaker to trip.
What Causes Breaker to Trip
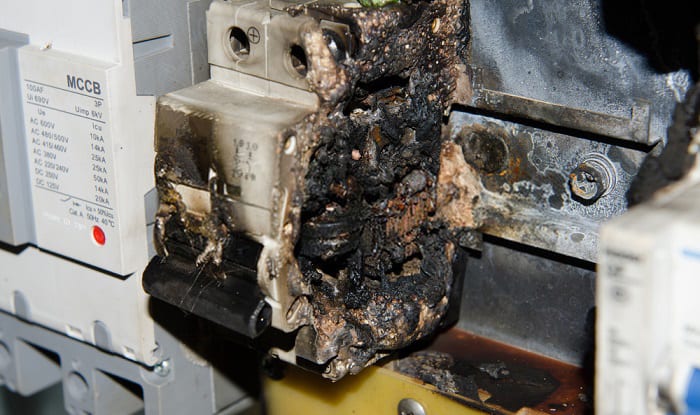

Consequently, there are a multitude of reasons why circuit breakers trip. They can range from circuitry integrity issues to accidental fault surges. For easier reading, I had decided to list the common reasons for circuit breaker tripping.

Circuits being accidentally overloaded is among the common reasons why breakers trip. To explain, an overloaded circuit happens when a lower-rated electric line draws an electrical load that is greater than its intended rating.
This specifically happens when a circuit is being utilized by multiple appliances, causing the line to draw on more electrical load to facilitate the operation of connected electrical devices.
When this happens, the overloaded circuit tends to heat up, triggering the breaker to trip as it senses electric loads greater than the intended capacity of the line it is monitoring.
To prevent an overloaded circuit, ensure that your home’s lines and circuitry are appropriate for the electrical load consumption of your connected appliances and light fixtures.

Yet another leading cause of circuit breaker tripping. Short circuits are regarded to be more hazardous than overloaded circuits. The reason is that short circuits are caused by a “hot” wire coming into contact with a “neutral” wire, resulting in a large flow of electric current overcharging a line.
When this happens, intense heat is produced by the circuit. When this happens, your circuit breaker will trip, effectively preventing further damage to your line.
However, if a shorted circuit remains unchecked by your breaker, then you risk an electric fire from happening in your home.
To prevent short circuits from happening, you can perform circuit inspections for faulty and loose connections. Symptoms of a shorted circuit include a burning smell emanating from outlets or the breaker itself. Discolorations from the circuit line itself could also be a manifestation of shorted circuits.
- Related: Detailed guide on fixing short circuits
Ground fault surges are quite similar to short circuits, with the only difference being that the “hot” wire makes contact with the ground wire of a circuit or the breaker box . When this happens, electrical flow is immensely increased, overloading lower-rated circuits.
An arc fault happens when current flows through an unintended path, creating an arc. Arcs, in an electrical sense, are current discharges from the conductor to the grounding material.
This results in sparking between the contact points of a connection. When this happens, high-intensity heat is produced by arcing, which could burn the insulation of the circuitry.
Due to the unique properties of electrical arcing, neither common breakers nor fuses offer any protection against it. In this regard, the National Electrical Code recommends the installation of arc-fault circuit interrupters, a special type of breaker that senses power fluctuations produced by arcing accidents.
An aged circuit breaker is more sensitive to current. In this sense, older breakers can trip even though an electric line is not overloaded with amperage. Breakers that are of old age are among the leading causes of constant tripping.

Loose or corroded connections may be why a circuit breaker tripped. As extra heat is produced due to the degradation of connections, breakers are immediately triggered, resulting in a tripped line.
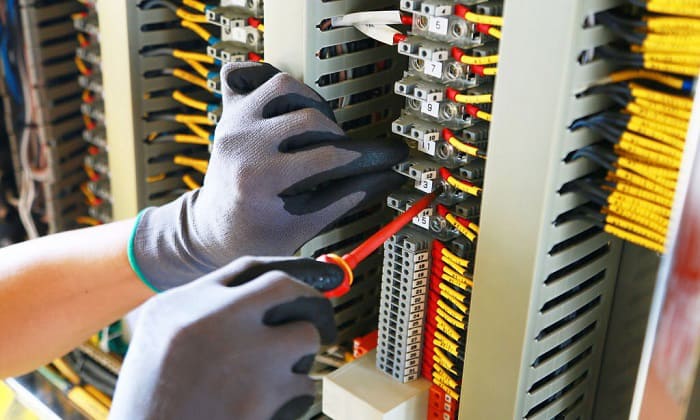

Do you have a breaker that constantly trips? If you have, then I’m sure that repeatedly switching the tripped breaker is a headache and unpleasant to deal with. Look, I understand your pain, as I myself have experienced this in my home in the past.
To deal with this problem, examine your appliances to see if any of the above causes apply to your situation. Another possible reason is that your circuit breaker might be failing, or that it isn’t optimized to adequately handle the current flowing through it.
Additionally, the symptoms of a bad circuit breaker are the following:
- A non-resetting breaker
- Damage is apparent on the breaker box
- Lights that flicker or burn out quickly
To ensure your home’s safety, I recommend that you obtain the services of expert electricians so that they can accurately help you with your breaker problem.
Knowing exactly why do circuit breakers trip is highly important for homeowners. However, lack of prior electrical knowledge can prove the task of determining the reason for tripping breakers difficult.
Taking this into consideration, I decided to write this guide so that you may know why breakers trip. I can only hope that I clearly explained everything outlined in this article.
If you have any questions, then ask away in the comment section below. Thanks for reading!
Other articles you may also like:
- The Most Common Reasons Why Your Circuit Breaker Trip Whenever It Rains.

I am Edwin Jones, in charge of designing content for Galvinpower. I aspire to use my experiences in marketing to create reliable and necessary information to help our readers. It has been fun to work with Andrew and apply his incredible knowledge to our content.
Daylight Electrician Singapore Articles / Blog
- Power Failure
Power Trip At Home? 3 Reasons Why Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping And How To Fix It

- Author : daylightadmin4
Electrical Issues? Whatsapp Us for Help! WhatsApp Us For Enquiry!
In Singapore, power trips are a frequent electrical emergency faced by homeowners. This occurs when the current in a circuit breaker exceeds the prescribed amount, thereby cutting off the electric supply.
Although a power trip prevents damage to the wiring and other appliances, it can also result in a blackout. So to prevent it, here are some reasons why a power trip may occur in your circuit breaker and how you can resolve it.
3 Reasons Why Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping
Overloaded Electric Circuit

One main reason why a power trip happens is because of the electrical circuit getting overloaded beyond the prescribed limit. When the current exceeds the rated capacity of the wiring, it can get damaged or create a fire hazard. In order to prevent an actual fire from taking place, a circuit trip occurs.
Connecting multiple electrical appliances to a power supply may also cause the power supply to trip. Malfunctioning appliances in particular may use up more power, increasing the total current supply and causing the circuit breaker to trip.
Short Circuit

A short circuit can also cause an HDB circuit breaker trip . One way to identify this is by checking for burning smells. Usually, a Short circuit occurs when the hot wire (black) touches a neutral wire (white). A surge in current supply can also happen when electrical wiring with damaged insulation come into contact with each other. Damaged appliances or lighting components with wiring problems can also cause a short circuit when plugged into an outlet.
Ground Fault
Besides short circuits, a power trip can also happen because of a ground fault. . When the circuit breaker’s hot wire comes into contact with the ground, the resistance is lowered and causes increased current. A hot wire (black) which makes contact with a metallic object can also cause a circuit breaker trip to occur.
Ground faults can also happen when homeowners ignore general electricity safety tips . Furthermore, this can cause a highly dangerous accident such as an electrical shock from switches or sockets .
How to Fix a Power Trip
Overloaded Electric Circuit
- Firstly, switch off all electronic appliances, gadgets, and light installations in the house.
- Next, switch on all low power consumption electrical devices.
- Now turn on your high power consumption appliances gradually until an electric trip occurs. Note down which high power consumption devices were connected when the trip happened.
- Whichever appliance has caused an increase in the power supply is likely to be the cause of your power trip.
- After determining the cause of your power trip, you can Connect the high power consumption electric appliance to another electric circuit to avoid another electric trip.
- Alternatively, you can upgrade your electrical wiring and hardware to carry the additional power load. While waiting for the wiring to be upgraded, you should minimize the use of appliances that consume more power as much as possible. You can also switch off all other appliances when only one is being used.
Compared to a power trip caused by overloading, fixing one which results from a short circuit is usually more difficult.
Usually, in the case of a short circuit, there is a massive spike in current which results in burning (causing a bad smell and discoloration). In that case, the electrical outlets should be switched off, and each of the power points and sockets should be inspected for any discoloration or smell. The insulation of the wiring should be checked as well. Furthermore, all the appliances should also be inspected for damage or odor. Usually the appliance with a short circuit will stop working and will have to be replaced or repaired.
Since most homes and offices have concealed wiring , it is not easy to inspect the wiring for damage or short circuit. Moreover, it is not easy to find out the exact condition of the wiring to detect any damage which has occurred.
During monsoon seasons, an increase in the moisture levels or wet walls may cause a short circuit. Unfortunately, most property owners do not have the tools and experience to detect the damage to the concealed wiring. Hence it is advisable to hire the services of a licensed and experienced electrician who can accurately detect the short circuit and conduct an electrical wiring repair or replacement.
- Switch off all appliances and unplug them from the electric circuit.
- Switch on the circuit breaker .
- If there is no electric trip, each of the appliances should be connected to the circuit. Once the defective appliance is connected, the circuit breaker will trip.
- The faulty appliance should be repaired or replaced to prevent another ground fault.
If the circuit breaker continues to trip, it’s p o ssible that you might have electric wiring mistakes present. In that case, you should contact a reliable electrician to check the wiring and fix it if needed.
Depending on the cause of the electric trip, the property owner can either fix it himself or hire the services of a well-trained licensed electrician in Singapore. If you opt for the latter, you can contact someone from Daylight Electrician Singapore with many years of experience in providing all kinds of electrical services .
Daylight Electrician Singapore provides complete electrical services including emergency electrician service in Singapore. Our network of electrical workers and EMA licensed electricians are specially trained to execute all kinds of electrical repairs and works including electrical installation such as light installation , ceiling fan installation , power failure recovery as well as electrical wiring and rewiring , power socket , electrical switches , light switches and DB Box replacement . We have over 10 years of electrician experience and have done thousands of electrical works for both residential (Landed, condo and HDB electrician) and commercial electrician. We are the highly recommended electrician in Singapore with many happy customers and positive reviews over the years both on Google and Facebook . WhatsApp us at +65 8241 0032 for transparent quotation and honest pricing for all your electrical needs or Call us at +65 6909 9921 . We offer a fast and efficient service to serve any of your electrical needs!

#1 Recommended Electrician in Singapore. WhatsApp us now at +65 8241 0032
Recent Posts
- Why Your Light Switch Is Not Working and How To Fix It?
- Should I Choose Zigbee or Z-Wave Smart Switch Communication Protocol?
- A Guide To Buying The Right Smart Switch For Your Home
- Myths About Home Smart Switch Installation
- Factors Which Should Be Considered Before Installing A Doorbell
- 24/7 Electrician Services
- Electrical Installation
- Electrical Maintenance
- Electrical Wiring
- Electrical Works
- Electrician Singapore
- EMA licensed Electrician Singapore
- Find a reliable Electrician Singapore
- Light Installation
- Uncategorized

© 2022 Daylight Electrician Singapore• All Rights Reserved. Terms of Service • Privacy Policy

Why Does My Power Outlet Keep Tripping?

There’s nothing more frustrating than a power outlet that keeps tripping, interrupting your daily activities, and potentially damaging your electrical devices. If you’ve been wondering, “Why does my power outlet keep tripping?” you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the top reasons for this common issue and provide practical solutions to keep your electrical system running smoothly.
Your power outlet may keep tripping due to several reasons such as ground-fault occurrences, moisture in the receptacle box, an overloaded circuit, electrical faults, or a faulty GFCI outlet. It’s a safety mechanism designed to protect from potential hazards like fire or electrocution. If the problem persists, it’s advisable to consult a professional electrician.
Ground-Fault Occurrences
One of the most common causes of a tripping power outlet is a ground-fault occurrence. This happens when the hot wire or live wire comes into contact with the ground wire or the grounded area of an appliance. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets are designed to detect these occurrences and trip to prevent electrocution or fire hazards.
Moisture in the Receptacle Box
Water or moisture in the outlet can cause the GFCI to trip. This is common in areas prone to moisture, such as kitchens and bathrooms. Regularly checking these areas and ensuring they are dry can prevent unnecessary tripping.
Overloaded Circuit
An overloaded circuit occurs when too many devices are plugged into one circuit, drawing more current than the circuit is designed to handle. This can cause the circuit breaker to trip to protect the electrical system from damage. To avoid this, limit the number of devices plugged into a single circuit and distribute high-power devices across multiple circuits.
Electrical Fault
Short circuits or wiring issues can cause the breaker to trip. This can happen if wires are loose, damaged, or incorrectly connected. Regularly inspecting and maintaining your electrical system can help prevent these issues.
Faulty GFCI Outlet
A malfunctioning GFCI outlet can cause it to trip repeatedly, even when there is no apparent issue. In such cases, the outlet may need to be replaced.
The Dangers of a Tripping Power Outlet
A constantly tripping power outlet can pose several potential dangers, including overheating and fire risk, arcing, electrocution, and damage to appliances and electronics. Therefore, addressing the issue promptly is essential for safety and to prevent costly damage.
How to Correctly Reset a Tripped Power Outlet
Resetting a tripped power outlet involves unplugging all devices, pressing the “RESET” button on a GFCI outlet, or resetting the circuit breaker at the electrical panel. Always ensure the outlet is operational again by plugging a device back into it.
When to Call a Professional Electrician
If the outlet is constantly tripping, the walls, switches, or outlets feel hot, burn marks are located on or near outlets, or your appliances or electronics are not performing well, it’s time to call a professional electrician.
Understanding why your power outlet keeps tripping is the first step in resolving the issue. Regular inspections, proper use, and maintenance of your electrical system can prevent unnecessary trips and prolong the lifespan of your appliances. Always consult a professional electrician when in doubt to ensure safety and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a gfci outlet.
A Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlet is a special type of electrical outlet designed to protect against electrical shock. It monitors the imbalance of current between the hot and neutral wires and trips the circuit if it detects an imbalance, indicating a ground fault.
How can I identify a GFCI outlet?
A GFCI outlet can be easily identified by the “TEST” and “RESET” buttons located on its face. Standard outlets do not have these buttons.
How often should I inspect my electrical system?
It’s recommended to inspect your electrical system at least once a year. However, if you notice any signs of electrical problems, such as frequent tripping, flickering lights, or burning smells, you should inspect it immediately.
Can I replace a faulty GFCI outlet myself?
While it’s possible to replace a GFCI outlet yourself, it’s recommended to hire a professional electrician, especially if you’re not experienced with electrical work. Incorrect installation can lead to electrical hazards.
How many devices can I plug into one circuit?
The number of devices you can plug into a single circuit depends on the total electrical load of the devices and the capacity of the circuit. As a general rule, a circuit should not be loaded to more than 80% of its capacity to prevent overloading.
Related Posts

Why Are Some Electrical Outlets Red?

How To Stop an AC Unit from Leaking

Who Can Hook Up a Gas Dryer?

How To Clean a GE Deep Fill Washing Machine

Do Microwaves Shut Down When They Get Too Hot?

Where Is the Microwave Filter?
About the author, trevor ritter, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Trevor is an appliance repair technician with years of experience fixing all sorts of appliances. He enjoys sharing his knowledge so that others can avoid common mistakes when repairing appliances.

Why Should You Cover an Air Conditioner?

How To Use Liquid Detergent in Washing Machine

How Long Does a Water Heater Last in Florida?

How To Set Auto Mode in LG AC

Where Is the Charcoal Filter on a GE Microwave?

How To Disable the Child Lock on a Samsung Dishwasher
- Our Promise
- Certifications
- NICEIC Domestic
- NICEIC Contractors
- Meet The Team
- Testimonials
- Air conditioning
- Audio & visual
- Consumer units / fuse boards
- Electric storage heaters
- Emergency electrician
- EV chargers
- Home appliances
- Immersion heaters
- NICEIC domestic installers
- Security alarms
- Services for landlords
- Smart home installations
- Smoke alarms
- Domestic FAQs
- Electrical Installation Condition Reports (EICR)
- Electrical testing
- Commercial electricians
- Door entry systems
- Emergency lighting
- Fire alarms
- NICEIC approved contractors
- Outdoor lighting
- Services for Landlords
- Car park lights
- PAT testing
- Data and telephone
- Commercial maintenance
- Commercial floodlights
- Commercial FAQs
- LED lighting
- Electrical inspections & testing
- Domestic Solar Panels
- Commercial Solar Panels
- Battery Storage
- 03301 757 529
- [email protected]

Why does my electric keep tripping?
- Damien Heath
- 10th April 2023
Over the past few years, we have all relied on our home electricity supply more than ever. Whether you have been working from home since lockdown, or you spend your weekends in front of the TV, much of our day revolves around the use of electricity. However, with the increase in reliance, we have seen a significant rise in the number of clients contacting us and asking, ‘Why does my electric keep tripping?’.
If your power keeps tripping, then there are ways that you can resolve the issue without an electrician, and we have put together an easy-to-follow guide on how to perform this simple routine.
Why does my electric keep tripping? Causes, solutions & preventions
There are many reasons why you may be experiencing power trips, such as an overloaded socket or problems with the circuit; however, in most cases, the issue can easily be rectified without the need to contact an electrician. Nevertheless, as with any electrical-related problem, if you are worried about your electrical circuits and would prefer professional guidance before carrying out any tests, our team of electrical contractors in Milton Keynes will happily answer any questions you have. They can assess the issue over the phone and recommend the next steps you should take. In the meantime, here is our top advice on the following topics.
Why do my electrics keep tripping?
How to resolve an electric trip, how to stop power tripping.

Electrical circuits can trip for a variety of reasons, and we know better than anyone how frustrating it can be when it keeps happening. One common cause is an overloaded circuit, which occurs when too many appliances or devices are connected to a single circuit or socket, exceeding its capacity. This can cause the circuit breaker to trip or the fuse to blow, resulting in power loss and potential damage to your electrical system – this is common in a business setting due to the many appliances plugged into the sockets.
To prevent overloaded circuits, ensure that your electrical appliances are distributed across multiple sockets and are compatible with their capacity. Additionally, it is best to avoid using extension cables as a permanent solution for powering multiple devices, as it can create a fire hazard. If you’re unsure about the capacity of the electrical system in your office or are experiencing persistent tripping issues, our talented team of commercial electricians in Milton Keynes will be more than happy to help.
Another common cause of electrical circuit tripping is a short circuit, which can happen when wires within the circuit come into contact with each other or when an appliance has a fault. This results in a sudden surge of electricity, causing the circuit breaker to trip as a safety measure.
Another cause of tripping electrics occurs when a live wire comes into contact with a grounded surface, such as a metal fixture or water pipe causing a ground fault. Identifying the underlying cause of the tripping is essential to prevent potential safety hazards and avoid further damage to your electrical system. It’s always best to consult a qualified electrician if you’re experiencing persistent tripping issues.
Before contacting our team, we would always recommend completing the following steps; this will help you to determine whether the cause of the power trips is an appliance that needs replacing or an issue with the circuit itself. Follow the steps below or take a look at our “how-to” video for full instructions.
1. Find your consumer unit
The first step is to track down your consumer unit. In most properties, this is either in the cupboard under the stairs or in the garage.
Most homeowners have a dual RCD consumer unit, which means that there are two RCDs. If you are unsure what type you have, we recommend taking a look at our consumer unit page , which, if you scroll down on, you will find three examples of the most common options. Alternatively, we also have a full guide on what consumer units are and how they operate .
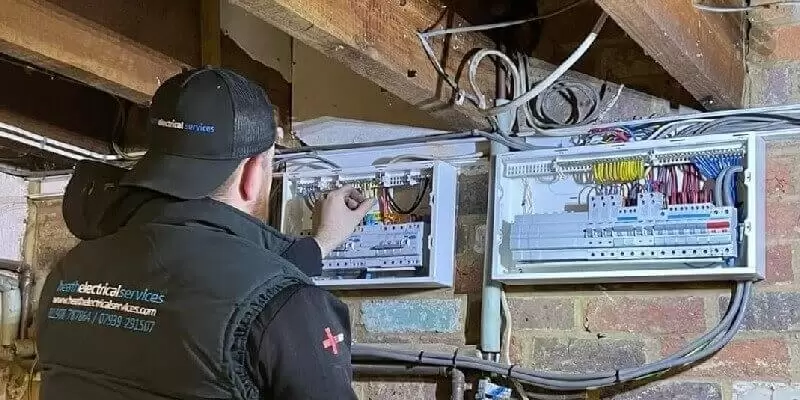

2. Checking the RCDs
The RCDs are the most likely component of your consumer unit to trip out, so you want to start by turning the RCD back on. If the power trips again after this, then you have a problem with your circuit.
In this instance, you will need to turn off all of the circuit breakers that relate to the RCD. The circuit breakers can be on the left or right side of the RCD, depending on what consumer unit you have.
Next, reset the RCD with the circuits off. If it does not reset, there may be an issue with the RCD itself. If so, contact one of our electricians if the RCD stays on.

3. Finding the circuit problem
To determine whether you have an issue with something plugged in, begin by taking a look at the switches on your consumer unit. You will see that each switch is labelled with what component it relates to, i.e. the cooker or sockets. The easiest route is to try the sockets.
Before testing the sockets, go around the house, switch off the plugs, and unplug everything connected to the circuit. In some cases, you may know exactly what circuit the switch relates to, so you will only need to do this on the sockets that connect.
Once sockets are off and appliances are unplugged, go back to the consumer unit – you should now be able to reset the RCD. If the RCD does not reset, contact an electrician to investigate the fault further. We have a reputable team of experienced electricians in Milton Keynes who are able to visit your home to rectify any circuit issues. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you require assistance.
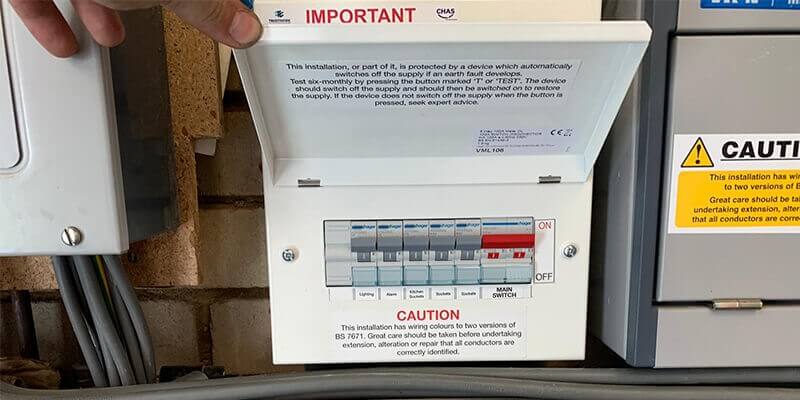
4. Dealing with faulty appliances
If the RCD has reset, then this is an indication that the power trip may be caused by one of your electrical appliances. Begin by attempting to reset the RCD and following the steps above.
If resetting a particular circuit breaker causes the RCD to trip, the fault is most likely linked to this circuit. Leave the circuit breaker off and disconnect appliances or switch off connected equipment (i.e., unplug appliances) if the fault is socket related. Switch off light switches if it is lighting-related.
If you notice that when you plug any of the appliances on, it causes the power to trip, then it means that this is what is causing the issue. We would highly recommend replacing this appliance to prevent future tripping.

For those who have recently replaced their circuits or have good condition circuits but are still experiencing power trips, there are a number of ways that you can minimise the likelihood of losing power. These tips are straightforward lifestyle changes that you can make to prevent your power supply from overworking and include the following.
- Unplug any electrical appliances that are not in use; this will also help you to prevent wasted power and, therefore, save money on your energy bills.
- Consider how many appliances you have plugged into one socket. If possible, try to spread them across different outlets to avoid overloading the socket.
- Keep an eye out for any damage to appliances, such as frayed cords or scorch marks around the plug. We recommend replacing any damaged items before they have the chance to cause a danger.
- Be wary about using extension cords to power appliances that require a lot of power, such as TVs, as this can also be a culprit for overloading the main socket.
- Spend time understanding your amp usage, as this will help you to pair appliances with a socket that can withstand the electrical current they require.

Preventing power trips is as easy as that!
At Heath Electrical Services, we are dedicated to ensuring that our clients can enjoy long-lasting, reliable electrical installations by minimising the likelihood of an issue. We take an honest approach which means that if we feel that you can rectify the problem without our assistance, we will always share our knowledge on the steps to take. Finding and resolving the cause of regular power trips is one of the most straightforward electrical-related tasks that you can complete yourself, and we hope that we have been able to guide you in the right direction. However, if you suspect you have a more serious issue or feel more comfortable leaving it to our experts, our engineers are always just a phone call away !
Share this Article
Similar articles, how are solar panels installed.
February 20, 2024
Fun fact: did you know that the amount of sunlight that hits the earth...
Installing your EV charger with Heath Electrical Services
January 8, 2024
With electric vehicles becoming increasingly popular in the UK, more a...
What is an EICR?
December 21, 2023
Whether you are a business owner or landlord, investing in a property...
Did you know we offer bespoke commercial maintenance packages?
November 9, 2023
At Heath Electrical Services, we work closely with business owners, la...

Sign up to our newsletter
Search our site, view all our client & customer testimonial.


Common Electrical Problems At Home

Do You Need Electrician To Replace A Light Switch?
What causes a power trip.

What Causes A Power Trip? A power trip happens when there is an overload of the circuit, causing the electric breaker to trip. However, a power trip can occur when there is a short circuit or ground fault.
What is a trip to electricity?

A trip to electricity is when a circuit attempts to draw a higher electrical load than it can carry in its system. Therefore, the breaker trips before the circuit system heat up to unsafe levels. When the trip occurs, the electricity flow shuts off completely.
How do you stop a power trip?

Ensure that you unplug all electrical devices that are not in use. It is essential to unplug because electrical current flows to the appliances even if it’s not in use but is off.
Make sure that your appliance cables have no damages.
Avoid overloading your socket with many devices. In this case, ensure that devices with high voltage run one at a time.
Ensure that you spread out electrical appliances that consume a lot of energy in your home.
Why does lighting cause a power trip?

Lighting causes a power trip when an electrical surge enters your house via an electric power line. The surge voltage increases to cause high voltage spikes in the wiring and electrical appliances hence result in a power trip .
Why does my circuit breaker trip whenever it rains?

During heavy rains, water makes contact into the cords, causing the circuit breaker to trip. It is essential to fix this problem as soon as possible since it becomes risky when water mixes with electricity.
Will a power surge trip a breaker?

A power surge occurs when there is an interruption in the flow of electricity. Therefore, a power surge can trip a breaker when the electrical current is high. In this case, the breaker trips to prevent electrical appliances from blowing up, which may also cause fires.
What are the three warning signs of an overloaded electrical circuit?

- Electrical shorts. An electrical short occurs when the circuit is highly overloaded since the power draw, on the other hand, is higher for the cable to contain. You will observe the breaker keeps on tripping.
- Discolored sockets. Accumulation of heat between the plug and it makes it hot hence it discolors the device. Note that you should not use discolored outlets. However, it would help if you had the sockets checked by electricians to examine and prevent further damages.
- Odors. Overloaded sockets produce an electrical burning smell. The smell is a result of heat emitted from the internal metal wires, which gets hot enough to melt the protective case. On detecting the odor, one should trace the source circuit that might be burning. You should take caution on this sign as the outer case can melt and generate fire.
How do you fix an overloaded circuit?

Upon identifying the circuit, ensure that you unplug the appliances plugged in and turn off any lights. Plug the electrical devices one by one.
This step will help you in identifying the machines that cause a trip. When you plug in everything without the circuit breaker tripping, then you have a potential overload.
Related posts

Essential Safety Inspections for Homes

Understanding the Importance of Electrical Safety in Your Home

Top Handyman Services to Request Before CNY
- Home Improvement
- Skills & Specialties
Electrical Wiring, Circuitry, and Safety
Explore more electrical.

Explainer: power station ‘trips’ are normal, but blackouts are not
Honorary Associate Professor, Centre for Climate Economics and Policy, Australian National University
Disclosure statement
Hugh Saddler writes a monthly newsletter on electricity policy issues, published by the Australia Institute
Australian National University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Tens of thousands of Victorians were left without power over the long weekend as the distribution network struggled with blistering temperatures, reigniting fears about the stability of our energy system.
It comes on the heels of a summer of “trips” , when power stations temporarily shut down for a variety of reasons. This variability has also been used to attack renewable energy such as wind and solar, which naturally fluctuate depending on weather conditions.
The reality is that blackouts, trips and intermittency are three very different issues, which should not be conflated. As most of Australia returns to school and work in February, and summer temperatures continue to rise, the risk of further blackouts make it essential to understand the cause of the blackouts, what a power station “trip” really is, and how intermittent renewable energy can be integrated into a national system.
Read more: A month in, Tesla's SA battery is surpassing expectations
Initial reports indicate recent blackouts in Victoria were caused by multiple small failures in the electricity distribution system across the state, affecting all but one of the five separately owned and managed systems that supply Victorians.
Across the whole of mainland Australia, very hot weather causes peak levels of electricity consumption. Unfortunately, for reasons of basic physics, electricity distribution systems do not work well when it is very hot, so the combination of extreme heat and high demand is very challenging. It appears that significant parts of the Victorian electricity distribution system were unable to meet the challenge, leading to uncontrolled blackouts.
Parenthetically, electricity distribution systems are vulnerable to other types of uncontrollable extreme environmental events, including high winds, lightning, and bushfires. Sometimes blackouts last only a few seconds, sometimes for days, depending on the nature and extent of the damage to the system.
Read more: What caused South Australia's state-wide blackout?
These blackouts are very different from those caused by power station “trips”, although they have the same effect on consumers. When electricity is insufficient to meet demand, certain sections of the grid have to be startegically blacked out to restore the balance (this is known as “load shedding”).
It is the possibility of blackouts of this second type which has excited so much commentary in recent months, and has been linked to power station “trips”.
What is a ‘trip’ and how significant is it?
“Trip” simply means disconnect; it is used to describe the ultra-fast operation of the circuit breakers used as switching devices in high-voltage electricity transmission systems. When a generator trips, it means that it is suddenly, and usually unexpectedly, disconnected from the transmission network, and thus stops supplying electricity to consumers.
The key words here are suddenly and unexpectedly . Consider what happened in Victoria on January 18 this year. It was a very hot day and all three brown coal power stations in the state were generating at near full capacity, supplying in total about 4,200 megawatts towards the end of the afternoon, as total state demand climbed rapidly past 8,000MW (excluding rooftop solar generation).
Suddenly, at 4:35pm, one of the two 500MW units at Loy Yang B, Victoria’s newest (or, more precisely, least old) coal-fired power station tripped. At the time this unit was supplying 490MW, equal to about 6% of total state demand.
The system, under the operational control of the Australia Energy Market Operator (AEMO), responded just as it was meant to. There was considerable spare gas generation capacity, some of which was immediately made available, as was some of the more limited spare hydro capacity. There was also a large increase in imports from New South Wales, and a smaller reduction in net exports to South Australia.
By the time Loy Yang B Unit 1 was fully back on line, three hours later, Victoria had passed its highest daily peak demand for nearly two years. There was no load shedding: all electricity consumers were supplied with as much electricity as they required. However, spot wholesale prices for electricity reached very high levels during the three hours, and it appears that some large consumers, whose supply contracts exposed them to wholesale prices, made short-term reductions in discretionary demand.
Read more: A high price for policy failure: the ten-year story of spiralling electricity bills
This (relatively) happy outcome on January 18 was made possible by the application of the system reliability rules and procedures, specified in the National Electricity Rules.
These require AEMO to ensure that at all times, in each of the five state regions of the NEM, available spare generation capacity exceeds the combined capacity of the two largest units operating at any time.
In other words, spare capacity must be sufficient to allow demand to continue to be reliably supplied if both of the two largest units generating should suddenly disconnect.
Forecasting
AEMO forecasts energy demand, and issues market notices alerting generators about reliability, demand and potential supply issues. On a busy day, like January 18, market notices may be issued at a rate of several per hour.
These forecasts allowed generators to respond to the loss of Loy Yang B without causing regional blackouts.
What is not publicly known, and may never be known, is why Loy Yang Unit B1 tripped. AEMO examines and reports in detail on what are called “ unusual power system events ”, which in practice means major disruptions, such as blackouts. There are usually only a few of these each year, whereas generator trips that don’t cause blackouts are much more frequent (as are similar transmission line trips).
It has been widely speculated that, as Australia’s coal fired generators age, they are becoming less reliable, but that could only be confirmed by a systematic and detailed examination of all such events.
Managing variable generation
Finally, and most importantly, the events described above bear almost no relationship to the challenges to reliable system operation presented by the growth of wind and solar generation.
With traditional thermal generation, the problems are caused by unpredictability of sudden failures, and the large unit size, especially of coal generators, which means that a single failure can challenge total system reliability. Individual wind generators may fail unpredictably, but each machine is so small that the loss of one or two has a negligible effect on reliability.
The challenge with wind and solar is not reliability but the variability of their output, caused by variations in weather. This challenge is being addressed by continuous improvement of short term wind forecasting. As day-ahead and hour-ahead forecasts get better, the market advice AEMO provides will give a more accurate estimate of how much other generation will be needed to meet demand at all times.
Read more: 100% renewable by 2050: the technology already exists to make it happen
Of course, AEMO, and the generation industry, do still get caught out by sudden and unexpected drops in wind speed, but even the fastest drop in wind speed takes much longer than the milliseconds needed for a circuit breaker in a power station switchyard to trip out.
At the same time, as the share of variable renewable generation grows, the complementary need for a greater share of fast response generators and energy storage technologies will also grow, while the value to the system of large, inflexible coal-fired generators will shrink.
- Renewable energy
- Solar power
- Energy policy
- National Electricity Market
- South Australia blackout

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Project Offier - Diversity & Inclusion

Senior Lecturer - Earth System Science

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Social Media Producer

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you suspect a short circuit, unplug your appliances and check the wires for melted coverings. You might also notice a burning smell coming from the outlet. Call in a professional electrician to find the source of the problem. 3. Circuit Overload. Circuit overloads are the most common reason that a breaker trips.
Overloaded Circuit. The most simple cause of a power trip is an overloaded circuit. If you have too many devices or appliances running simultaneously, the circuit can end up drawing more electrical load than it is equipped to handle. It heats up, the circuit breaker senses this, and the power trips before the circuit can heat to a dangerous level.
Devices charging slowly. Electrical outlets not working. Flickering lights. Scorch marks on outlets and light switches. If a circuit breaker keeps tripping in one room, homeowners can test for ...
He says power overloads, current "leaks", and arcs are the three reasons that would cause a breaker to trip. A Power overload happens when a device is calling for more power than a receptacle, or a circuit is designed to provide. Current "leaks" are caused when current strays from the circuit for whatever reason, though it happens most ...
Circuit breakers trip to stop overheating, electrical fires, and damage to electrical parts. Plugging in too many devices can cause the circuit to become overloaded, so the breaker trips to cut off the power. Short circuits are like a blind date gone wrong. They can be explosive, and often end in disaster.
Find out the cost to replace an electrical panel. On every breaker, there will be an "On" and "Off" position. On a tripped breaker, the handle will be in the middle, neither On nor Off. To reset, flip the handle to Off first, then to On. Stand to the side of the panel and turn your face away when flipping breakers.
The breaker, working in tandem with a fuse, serves as an electrical unit's internal sensing mechanism. At the slightest sense of excess current, the circuit breaker will "trip," triggering a cease in all electrical activity within the circuit. Not only can such a smart mechanism help with preventing damage to wires and other electrical ...
Electrical Short Circuit: Another reason for the breaker tripping is the electrical short circuit. A short circuit occurs due to low insulation resistance. When the positive and negative (live and neutral) terminal connects with each other in the absence of any resistance. This causes an unimpeded flow of electricity.
They're usually black or off-white with a number printed on the end of the switch that indicates the number of amps the circuit breaker can handle. One side of the breaker has an "on" label and the other has an "off" label. If you have subpanels, you may have more than one electrical box. Check all of your boxes for the tripped breaker.
Power Surges: Power surges can also cause circuit breakers to trip. These surges happen when there is a sudden increase in electrical voltage, often caused by lightning strikes or faulty wiring in the electrical system. Circuit breakers act as a defense mechanism against power surges by cutting off the excessive flow of electricity.
Your appliances could be tripping the circuit breaker for a number of reasons, such as a circuit overload or a faulty appliance. Run through these steps to determine the root of the problem. 1. Test for a Circuit Overload. Circuit breakers in your house are critical safety mechanisms that keep wires from overheating.
5. Older Circuit Breaker. An aged circuit breaker is more sensitive to current. In this sense, older breakers can trip even though an electric line is not overloaded with amperage. Breakers that are of old age are among the leading causes of constant tripping. 6. Loose or Corroded Connections.
Short-time pickup is adjustable from 1.5 to 10 times the trip unit ampere setting (Ir). For example, a 1000 ampere frame can be adjusted to trip anywhere from 1500 to 10,000 amps. The switch also has an "OFF" position to eliminate short-time pickup and short-time delay. Short-time pickup used for selective tripping.
The Electrical grid is the fundamental requirement of modern-day society. Ideally, power system reliability needs to be preserved for power system operations, ensuring continued power supply to the customers at all times and costs. One of the major events that affect the reliability of a power system is nuisance tripping of circuit breakers.
So to prevent it, here are some reasons why a power trip may occur in your circuit breaker and how you can resolve it. 3 Reasons Why Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping. Overloaded Electric Circuit. One main reason why a power trip happens is because of the electrical circuit getting overloaded beyond the prescribed limit. When the current exceeds ...
A circuit breaker will usually trip when there is an electrical fault that could cause damage to the circuit. This is usually an excess of current, a power surge or a faulty component. These events fall into three broad categories: Overloads. Short circuits.
Your power outlet may keep tripping due to several reasons such as ground-fault occurrences, moisture in the receptacle box, an overloaded circuit, electrical faults, or a faulty GFCI outlet. It's a safety mechanism designed to protect from potential hazards like fire or electrocution. If the problem persists, it's advisable to consult a ...
The thermomagnetic trip unit consists of two parts: The thermal trip unit - Made up by a bimetal thermal device which actuates the opening of a circuit breaker with a delay depending on the overcurrent value. This trip unit is intended for the protection against overloads. The magnetic trip unit - Made up by an electromagnetic device, with ...
The most obvious sign of an electrical circuit overload is a breaker tripping and shutting off all the power. Other signs can be less noticeable: Dimming lights, especially if lights dim when you turn on appliances or more lights. Buzzing outlets or switches. Outlet or switch covers that are warm to the touch.
2. Checking the RCDs. The RCDs are the most likely component of your consumer unit to trip out, so you want to start by turning the RCD back on. If the power trips again after this, then you have a problem with your circuit. In this instance, you will need to turn off all of the circuit breakers that relate to the RCD.
An electrical short occurs when the circuit is highly overloaded since the power draw, on the other hand, is higher for the cable to contain. You will observe the breaker keeps on tripping. Discolored sockets. Accumulation of heat between the plug and it makes it hot hence it discolors the device. Note that you should not use discolored outlets.
Electrical Wiring, Circuitry, and Safety. Wires and circuits are the base of your electrical system. Learn about different types of wiring, cords, switches, and outlets and more circuitry basics. How to Hang a Ceiling Light Easily in 10 Steps. How to Wire a 3-Way Switch for Added Convenience at Home.
"Trip" simply means disconnect; it is used to describe the ultra-fast operation of the circuit breakers used as switching devices in high-voltage electricity transmission systems.