Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University website
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State


Magellan’s Circumnavigation of the Earth
- Dani Anthony
On September 20, 1519, five ships carrying about 270 men left the Spanish port of Sanlúcar de Barrameda sailing west — and kept going. Led by explorer Ferdinand Magellan, the armada’s goal was to reach the Spice Islands of Maluku (in the Indonesian archipelago) and open a new trading route for Spain.

Thus began the first recorded trip around the globe. An almost unimaginably difficult and perilous journey for the crew, Magellan’s voyage was the opening chapter in the rise of global trade and globalization that defines our world today. It also generated important scientific knowledge, including more information about the earth’s circumference and new understandings of global time.
Establishing this new western sailing route was vital to Spain’s future as an international power. In 1494, after Christopher Columbus returned from the West Indies, the Spanish and Portuguese governments signed a deal known as the Treaty of Tordesillas in which the world was divided into two halves: Portugal could colonize and develop trade with Africa, Asia, and the East Indies, while Spain controlled the Americas. By 1515, then, the only way for Spain to access the luxury goods available in the Spice Islands and elsewhere in Asia was via a westward route.
A map showing the demarcation line between Spanish (green) and Portuguese (blue) claims, as resolved in the Treaty of Tordesillas.
It was at this crucial moment that Ferdinand Magellan (Fernão Magalhães) arrived in Spain. A minor Portuguese noble, Magellan possessed an extensive knowledge of mapmaking and sailing, and already had years of experience sailing the Indian Ocean.
In 1513, Spanish explorer Vasco Nuñez de Balboa had marched across the Isthmus of Panama and confirmed that Asia and the Americas were separated by an ocean. Magellan was convinced he could sail around those continents and easily reach this ocean, accessing the Spice Islands beyond.
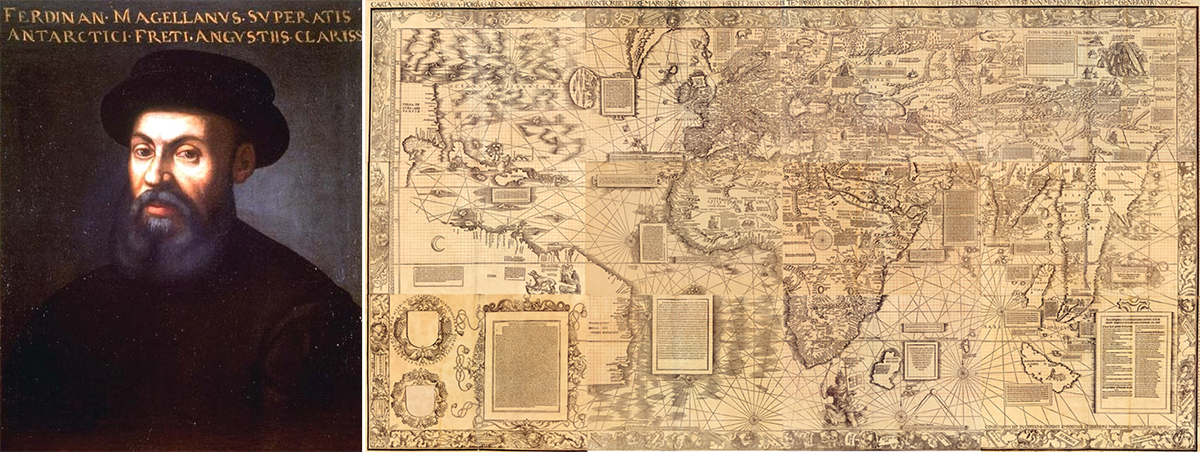
A posthumous portrait of Ferdinand Magellan, painted c. 16th or 17th century (left) ; a 1516 map of the known world at the time of Magellan's voyage (right).
Unable to convince the Portuguese of the importance of finding a route to the west, Magellan then turned to the new king of Spain, Charles I. If Magellan’s expedition was successful, Spain would have access to the goods of the East again.
Like most Spanish-funded endeavors, the people who sailed on this voyage were a diverse group, including German, Greek, French, and Afro-descended crewmembers. Besides Magellan’s Portuguese close friends and family, Spaniards and other Europeans with sailing experiences were brought in, some of them to work off debts. Magellan’s second-in-command was the Spanish overseer and accountant, Juan de Cartagena, and the chronicler was the Venetian Antonio Pigafetta.
Magellan and João Serrão were the only Portuguese captains, with Magellan in charge of the largest ship, the Trinidad , and Serrão at the helm of the Santiago . Spaniards captained the other three ships ( San Antonio , Concepción , and Victoria ), and constant Spanish scheming against the Portuguese would have grave consequences for the voyage.
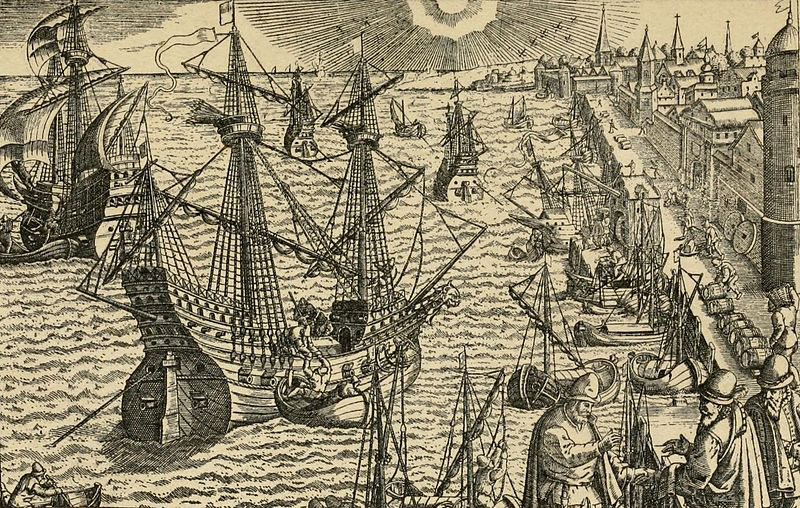

A 19th-century illustration of Magellan's armada preparing to set sail in 1519.
Magellan did nothing to promote Spanish trust, keeping the route a tight secret until the ships were at sea. His plan relied on Portuguese sailing routes, which were well known to him but unfamiliar to many of his crew.
As the armada crossed the Atlantic, morale declined precipitously. By the time the ships arrived on the coast of what is now Brazil to wait out the Southern Hemisphere winter, many aboard were suffering from scurvy, and the Spanish captains were in open rebellion against Magellan. Mutiny was in the air, with Juan de Cartagena, who resented Magellan’s secrecy, leading the effort.
Brazil, as depicted in a 1519 atlas.
In the cold of their wintering grounds and with reduced rations, the mutineers made their move. Although they managed to take over as many as three of the five ships, they were eventually captured and Magellan exiled Cartagena to an uninhabited island off the coast.
The winter of 1520 also saw the destruction of the Santiago, which ran aground while on a scouting mission to the south. Although the ship’s crew survived, the loss of the Santiago put more pressure on an already pinched crew.
An 1885 drawing of the Strait of Magellan.
By late spring, surviving on seal and penguin meat, the armada entered what is now known as the Strait of Magellan, the narrow body of water separating mainland South America from the Tierra del Fuego. The armada lost another ship during the passage through the Strait: the San Antonio , which became separated from the rest of the armada, and turned around and returned to Spain.

An engraving (c. 1580–1618) of Magellan crossing the Strait that would bear his name.
Once the three remaining ships reached the other side of the Strait of Magellan, the sea they found was calm and placid. Magellan christened it the Pacific Ocean. Crossing the Pacific, the crew of the remaining ships suffered terribly. Twenty-nine sailors died during the four-month voyage.
In April 1521, the group put into an island in the Pacific: Cebu, in what is now the Philippines . As the first Europeans to see these islands, Magellan’s crew would lay the groundwork for the long Spanish colonization of the archipelago, which lasted until 1898. Magellan befriended the local ruler, Raja Humabon, and became embroiled in local politics, which would be his downfall.
On April 27, 1521, Magellan went to war against the ruler Lapu Lapu on Mactan Island, who refused to bring tribute for Raja Humabon and the King of Spain. Fighting in the shallow waters off the shore, Magellan and 49 of his men squared off against over 1,000 Mactanese warriors. Facing such poor odds, Magellan was killed, as well as seven of his men, and his ships returned to Cebu.

A 19th-century illustration of the death of Magellan (left) ; a plaque in Cebu commemorating the site of Magellan's death, Philippines (right).
Raja Humabon, displeased at the newcomer’s loss, hosted a feast where he poisoned a group of some of the highest-ranking members of the expedition, leaving less than half of the original crew. The rest of the members set sail, fleeing to the safety of the sea. On May 2, 1521, those sailors who remained scuttled the Concepción and divided the crew among the remaining two ships, the Trinidad and the Victoria.
For the next six months the ships engaged in piracy as they made their way to the Spice Islands. Finally, in November, they arrived at the island of Tidore, part of the Malukus, and filled their holds with cloves. The Trinidad, which was taking on water, could not be repaired, and it was abandoned along with its crew.

Detail of a 1590 map showing the Victoria , the only ship from the armada to successfully circumnavigate the earth.
The Spaniard Juan Sebastián Elcano was elected captain of the remaining ship Victoria, which set sail west to the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa. This voyage took over six months, during which the crew subsisted on rice alone.
On September 6, 1522, the Victoria at last reached harbor in Spain, nearly three years after first setting out. Of the original 270-strong crew, only eighteen had survived.
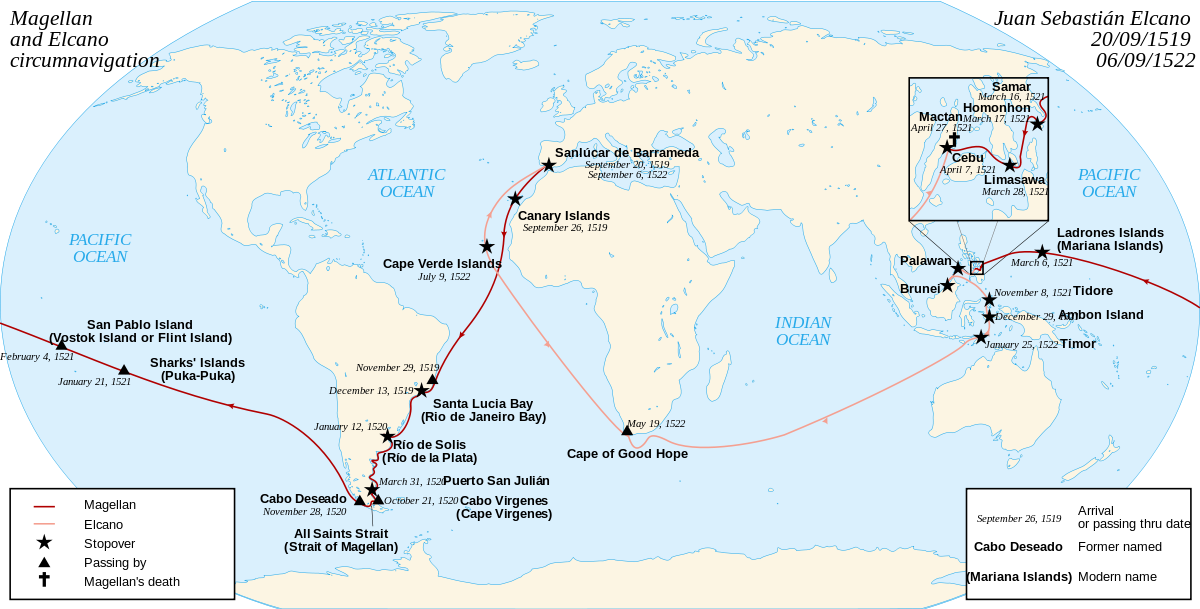
Map showing the route and chronology of the circumnavigation voyage from 1519 to 1522.
Although Magellan is remembered today for circumnavigating the globe, his reputation in the expedition’s immediate aftermath took a battering from those who had survived the expedition. Both the sailors of the Victoria , as well as the crew of the San Antonio who had turned back from the Strait of Magellan in 1520, disparaged him.
Juan Elcano, on the other hand, was given a hero’s welcome, even though he had joined the voyage only to receive a royal pardon. He was elevated to the peerage and added a globe and the words “first to circumnavigate me” to his coat of arms. In Spain, the circumnavigation is known as the Magellan-Elcano expedition.

Engraving of Juan Elcano, 1791 (left) ; Juan Elcano's coat of arms, bearing the phrase, "Primus circumdedisti me" ("First to circumnavigate me") (right).
The first recorded circumnavigation had important political, economic, and scientific consequences.
Spain calculated the total circumference of the globe for the first time, and determined that the Pacific was much wider than previously guessed, meaning that they owned some of the Pacific islands as demarcated by the Treaty of Tordesillas. Spain took control of the Philippines, and began exploration of the East Pacific.
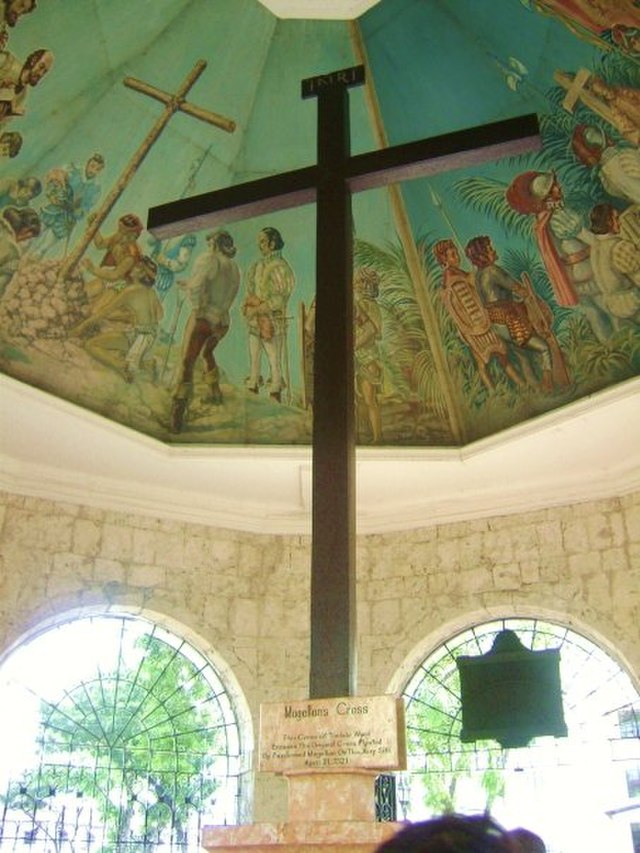

Cross erected by Magellan's crew on the island of Cebu.
Magellan’s voyage also opened the door for trade. By the 1600s, Spanish territories produced most of the world’s silver, and around a third of it ended up in China through trade. This would have lasting effects on global strategy and economies, and propel Spain to the height of European power.
Perhaps just as important for us today, however, is the establishment of the International Date Line. Upon return to Spain, the sailors of the Victoria learned that they were a day behind in their reckoning. As they sailed against the Earth’s rotation, they lost hours. Many mysteries of the globe were revealed.
Search Icon
Events See all →
Earth week 2024.

This is a campuswide week of events, lectures, and volunteer opportunities designed to educate and inspire action related to environmental justice, climate, and nature-based solutions. This year’s theme is Restore & Regenerate.
Various locations
Excellence in Graduate Teaching Reception

5:00 p.m. - 6:30 p.m.
Penn Graduate Student Center, 3615 Locust Walk

1:00 p.m. - 4:00 p.m.
College Green
Maggie Nelson

6:30 p.m. - 10:00 a.m.
Kelly Writers House, 3805 Locust Walk
Arts, Humanities, & Social Sciences
Around the world in 1,082 days
A q&a with historian antonio feros reflecting on the 500th anniversary of ferdinand magellan’s circumnavigation of the globe, and how the voyage shaped both the 16th century and today..

On Sept. 20, 1519, Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, with five ships and a crew of 270 men, set sail from Sanlucar de Barrameda in southern Spain, on what would become the first circumnavigation of the world. Magellan himself died during the tumultuous three year voyage, with Spaniard Juan Sebastian Elcano completing the journey from the Phillipines back to Spain with a final crew of only 18 men. Despite Magellan’s tragic end, his legacy has become synonymous with exploration and geography—including the Strait in South America that still bears his name.
To reflect on the 500 th anniversary of the Magellan-Elcano circumnavigation, Penn Today sat down with Antonio Feros , who specializes in the history of early modern Spain. Feros shares his insights on the state of the world in 1519, the political and economic factors that motivated this challenging journey, and what Magellan’s legacy looks like today.
What was Spain, and Europe as a whole, like in the year 1519?
In 1519, Spain was, in many ways, the political superpower in Europe. Its ruling king, Charles I, was also the Holy Roman Emperor, under the name of Charles V. Charles was the head of the pan-European Habsburg dynasty, and by 1519, the Spanish monarchy under Charles I, was also acquiring and conquering enormous overseas territories in the Americas. In 1519, Hernán Cortés also initiated his voyages that will end with the defeat of the Mexica empire in 1521.
But this was also a period of profound divisions and competitions. By 1519, the religious split provoked by Martin Luther’s challenges to the Pope’s authority were already provoking political and religious divisions in every European polity, with the exception of Portugal and Spain. This was also a time when the powerful Ottoman empire challenged the European polities, and the Hapsburgs’ attempts to extend their power and influence to the Mediterranean and Northern Africa.
Because of profound religious and political crises, almost no European country had the ability to enter the process of political expansion. Only Spain and Portugal were involved in a sustained process of overseas expansions, which started already in the early fifteenth century.
Magellan was Portuguese, but Spain ended up supporting his circumnavigation. Why did that happen?
Magellan did a lot of voyages to many of the settlements that the Portuguese were creating around India. When he came back to Portugal after a grueling few years sailing and fighting in Asia, he felt that the Portuguese crown did not give the honors and respect he believed he truly deserved. It was in this context that he offered his service to the Spanish king, his knowledge of the Asian powers, trading networks, and maritime routes. His action was not something unique in the period. Europe was dominated by dynasties and monarchies and they attracted the personal loyalty of many individuals from many regional origins. Maybe to the Portuguese king and part of the aristocracy Magellan was a traitor, but for the Spaniards he was simply serving a new king, a new master.
What did Spain hope to gain from Magellan’s voyage?
There was strong competition between Spain and Portugal to dominate different parts of the world, and Magellan’s voyage has quite a lot to do with this competition, not so much with scientific or geographic knowledge.
By the Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in 1494, and other pacts, Portugal and Spain agreed on the need to regulate the various spheres of geopolitical influence. Spain got the monopoly of expeditions and control over all territories they encountered going west—towards the land we now know as America. Portugal in turn received a monopoly over trading routes and territories in the south and east. In many ways, both polities decided to divide the entire world into two areas of influence: one controlled by the Portuguese, including Africa and Asia; the other controlled by the Spanish monarchy, encompassing almost the entire American continent, and some areas in the Pacific and Asia.
There were, however, some points of contention among both monarchies. One was Brazil, where Spaniards and Portuguese would disagree for centuries about the extension of their power. More important were the disagreements on the other side of the world, in Asia, the rich land of trading. The disagreements resulted from the inability to clearly delimit the areas of influence assigned by the Treaty of Tordesillas. The Portuguese believed they had a monopoly over trade and settlement in all important trading centers, and the Spaniards believed some of these areas belonged to their king according to the treaty.
It is in this context that Magellan offered a plan that, respecting the agreement, would give Spain the right to trade and settlement in areas that, until that moment, were controlled by the Portuguese. His proposal was simply to cross the Americas and get to Asia through the back door. The Spanish ruler was evidently happy to hear this, because it would allow his subjects, merchants, and sailors to become players in the wealthiest economic center of the world.
What made this three-year journey particularly challenging?
They already knew that there was a continent between Europe and Asia—the New World, or how Spaniards liked to call it, the Indies. But they didn’t know exactly the extension of this continent, in the north or the south, or whether or not there was a clear passage that would allow sailors to cross to the Pacific. In many senses, they had no idea where they were going, the distance between America and Asia, what were the challenges, and the dangers, or how long it would take them. Compared to the Magellan’s voyage, the Portuguese navigation through the south and east passage, was relatively simple. It was dangerous, it took a long time and many lives, but it was relatively known and predictable.
Magellan’s enterprise was of a different quality—open oceans, difficult passages, difficult weather, diseases, discontent, and rebellions within his tripulation. At least one ship and many men were already lost before crossing the passage that lead them to the Pacific. Once in the Pacific, they encountered new challenges, new dangers, more diseases, more deaths, and conflicts with local powers. They were pioneers in traveling regions and areas unknown to Europeans until then, and they did this with relatively primitive tools.
How did the completion of the circumnavigation shape the rest of the 16th century?
Magellan’s voyage definitively demonstrated that the globe was round, and in reflecting about this voyage, some geographers started to better understand the globe, the various regions of the world. The ‘Universal Map’ drawn by Diogo Ribero in 1529 is clear proof of this.
But these were the unintended consequences of Magellan’s voyage. His was not a scientific expedition, it was a commercial and political expedition, an intent by the Spanish monarchy to enter into the wealthy Asian trade, dominated until then by the Portuguese. Magellan was a sailor, a man serving a king, not a geographer or a scholar. He wanted to discover a route that gave the Spanish monarchy economic power and political influence, but he was not interested in the advancement of geography, or science. He never wrote any treatise about the geography, or the world—mapmakers did that. He was thinking and acting as a man of state.
The real consequences of his voyage were economic and commercial: It allowed the Spanish to establish commercial routes between its colonies in the Americas and the territories they ended controlling in Asia—like the commercial route between the Philippines and Acapulco in Mexico, ‘the Manila Galleons,’ which lasted for more than two centuries. It also accelerated the connections between the various regions of the world.
By the mid-1500s, as a consequence of Magellan’s voyage and many others after him, Europeans became aware that Spanish and Portuguese explorations had ushered in the first period of globalization in the history of humanity. As the French writer Louis Le Roy wrote in 1577, thanks to these voyages and expeditions ‘all humans can now exchange commodities with one another and provide for each other’s dearth, like residents of one city and one republic of the world.’
Now, with 500 years to reflect, what does Magellan’s legacy look like today? Do Spain and Portugal see him differently?
Magellan was, for the Portuguese, unimportant compared to other explorers, but in Spain Magellan-Elcano’s circumnavigation is celebrated as a moment in discovery and in the history of Spain and the world. There is no doubt that his experience allowed people to think about geography, about global trade, and about human diversity in ways that were impossible before.
But one has the feeling that the commemorations around Magellan’s voyage go beyond the celebration of the man and his real accomplishments. What is being celebrated seem to me is not the man but a country, Spain. Magellan’s voyage did not have important effects during his time, but for Spain, it seems to represent that at some point in history the country was the world’s pioneer in scientific and geographic exploration, and that for long periods of time, they were interested not only on conquering and economic exploitation, but also in the promotion and funding of scientific progress.
For more insights on the circumnavigation, read the journal of Antonio Pigafetta , a detailed description of the circumnavigation and the crew’s perspectives on the world they saw.
Antonio Feros is the Rose Family Endowed Term Professor and chair of the Department of History in the School of Arts and Sciences .
Picturing artistic pursuits

Campus & Community
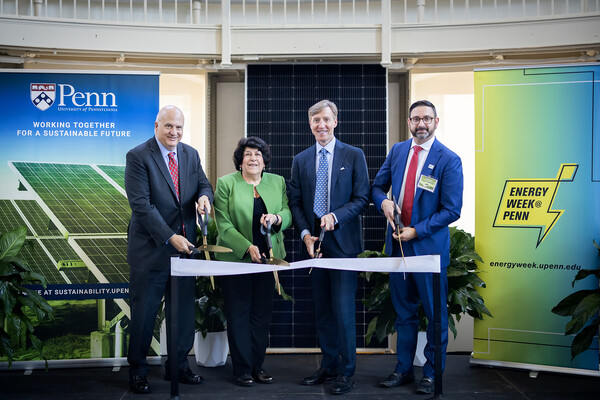
Penn celebrates operation and benefits of largest solar power project in Pennsylvania
Solar production has begun at the Great Cove I and II facilities in central Pennsylvania, the equivalent of powering 70% of the electricity demand from Penn’s academic campus and health system in the Philadelphia area.

Education, Business, & Law
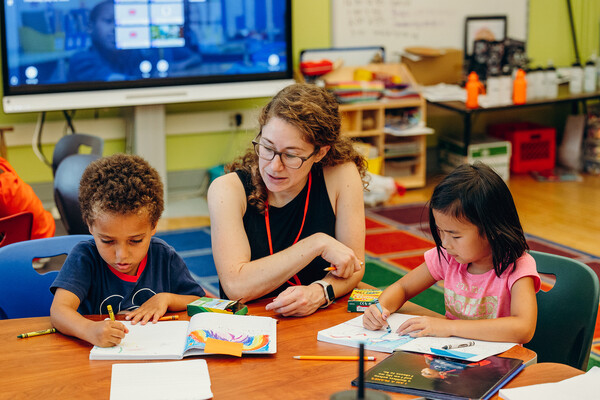
Investing in future teachers and educational leaders
The Empowerment Through Education Scholarship Program at Penn’s Graduate School of Education is helping to prepare and retain teachers and educational leaders.
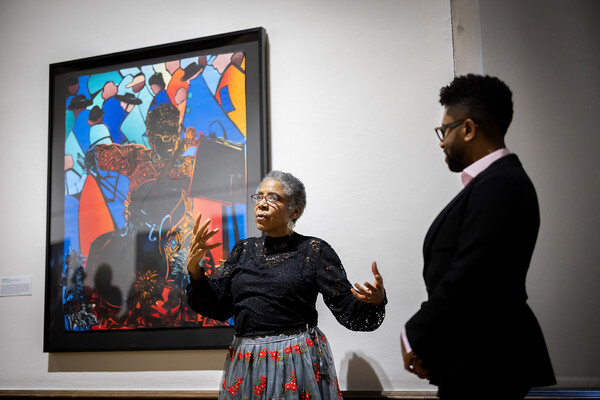

‘The Illuminated Body’ fuses color, light, and sound
A new Arthur Ross Gallery exhibition of work by artist Barbara Earl Thomas features cut-paper portraits reminiscent of stained glass and an immersive installation constructed with intricately cut material lit from behind.

25 years of ‘LOVE’
The iconic sculpture by pop artist Robert Indiana arrived on campus in 1999 and soon became a natural place to come together.
Magellan, Elcano and Their Voyage Around the World
Discover the details of the first circumnavigation of the globe..
By Naval Museum
Museo Naval
We Were The First: Magellan, Elcano, and the Voyage Around the World Naval Museum
The Voyage Around the World In 2019, Spain celebrated 500 years since 5 ships set sail from Seville, heading west in search of a new route to the spices of the east. Around 250 men from at least 9 different countries began the journey, which was funded by the Spanish monarch King Charles I. It was a journey that would end 3 years later with the arrival of just 1 ship carrying 18 men, having completed the first circumnavigation of the world.
Chart of Juan de la Cosa (1500) by Juan de la Cosa Original Source: Museo Naval Madrid.
The World of Magellan and Elcano
Finding a maritime route to the east was a constant preoccupation in the Middle Ages and Early Modern Period. The decline of the overland trade route called the Silk Road forced European powers to look for new ways to the east. Portugal began crossing the Atlantic and Spain's Catholic Monarchs, Ferdinand II and Isabella I, financed Christopher Columbus' voyage in search of a new route.
Ptolemy's Mappamundi (1472) by Claudio Ptolomeo Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
When Columbus set sail for the Indies in 1492, sea voyages were an adventure into the unknown. The discovery of new lands helped improve cartography, which was essential for navigation. Claudius Ptolemy's Geography, an ancient Roman atlas, was hugely influential in this, as it was the first example of using a systematic method to map the world.
The first map to depict the Americas was produced in 1500 by Juan de la Cosa. It represents the limits of European knowledge of this new world by the time Ferdinand Magellan's expedition set sail in 1519.
The Cantino planisphere. The original is in the Biblioteca Estense Universitaria library in Modena (1502-1505) by Anonimuos Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
In the east, accounts from merchants and travelers alluded to rich and fertile lands. To the south, Portuguese explorers had provided more specific details of the outline of the African coast. Looking west, the tales of Spanish conquistadors described the recently discovered Americas as a new land full of natural riches.
In 1502, Alberto Cantino's Planisphere, or world map, was the first to depict the meridian designated by the Treaty of Tordesillas. Signed in 1494, the treaty divided the rights to sail to and conquer new lands in the Atlantic Ocean and the New World between the Spanish monarchy and Portugal.
Model of the Victoria (2019) by Francisco Fernández González, Luis Fariña Filgueira, Fernando Sagra Sanz, José Antonio Álvarez Manzanares Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. All rights reserved.
Inspiration and Preparation for the Voyage
By that time, Europe had begun to realize that the Americas were a new continent rather than part of Asia, and so continued to send expeditions there. During one of these, Vasco Núñez de Balboa discovered the South Sea (now known as the Pacific Ocean) in 1513. This created new opportunities for navigation on the other side of Panama.
Ratification of the Treaty of Tordesillas (1494) Original Source: Archivo del Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
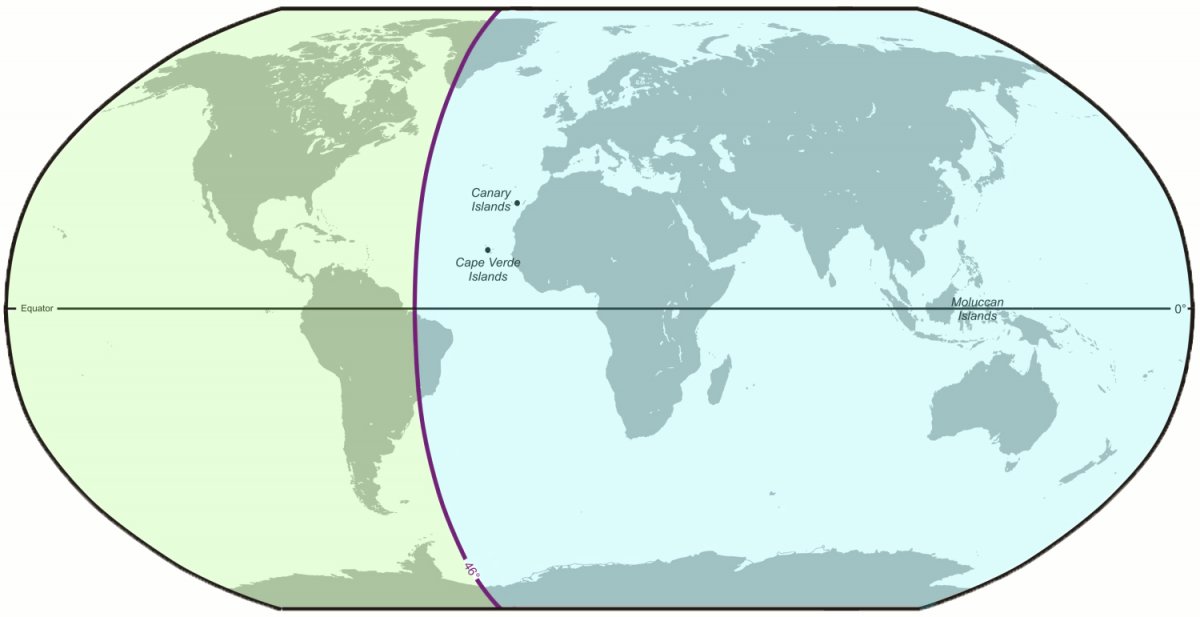
Spain and Portugal began searching for a passage to this ocean to reach the Indies, while adhering to the boundaries established in the Treaty of Tordesillas. Signed in 1494, this treaty comprised a series of agreements between King Ferdinand II of Aragon and Queen Isabella I of Castile on the one hand, and King John II of Portugal on the other. These established a new line of demarcation between their kingdoms from pole to pole, 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde Islands.
Portrait of Ferdinand Magellan (19th Century) by Spanish anonimous Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese-born sailor who knew the Portuguese route to Africa and Asia, having sailed in the service of King Manuel I of Portugal for over 20 years. He wanted to begin a journey that would take a new route to the Moluccas (Spice Islands), but the idea did not get far at the Portuguese court. That is how he ended up in Spain, where he was welcomed by the young monarch Charles I, grandchild of Ferdinand and Isabella.
Model of the Victoria (2019) by Francisco Fernández González, Luis Fariña Filgueira, Fernando Sagra Sanz, José Antonio Álvarez Manzanares. Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
In 1518, an agreement (the Capitulaciones de Valladolid) was signed between Magellan, his cosmographer Rui Faleiro, and the Spanish monarch to find a new western route to the Spice Islands that avoided the areas under Portuguese control. They had five ships with which to make the journey (the "Trinidad", "San Antonio", "Concepción", "Victoria", and "Santiago"), which the Casa de la Contratación (House of Commerce) supplied with provisions for a planned two-year voyage.
The Voyage (1519–22)
The expedition left Seville on August 10, 1519, arriving in Sanlucár de Barrameda 10 days later to collect the final provisions and equipment. From there, they set sail into the unknown, on a journey that would take three years.
Map of South America (1630) by Gerardis Mercatoris Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
The Familiar: From Seville to Río de Solís Leaving Seville, they journeyed south and, at the beginning of October, they headed southwest across the Atlantic Ocean, which was already familiar to the experienced sailors. On December 13, they dropped anchor in Santa Lucia Bay (now Rio de Janeiro), where they picked up food supplies. In January 1520, they reached the mouth of Río de Solís (now Río de la Plata).
Map of America (Siglo XVI) by Diego Gutierrez Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid.
The Unknown: From the Río de Solís to The South Sea Due to the weather, they decided to stop in Port St. Julian. The "Santiago" was lost on a reconnaissance mission, although the crew and cargo were saved. Discontent was starting to grow among the crew due to the rationing of supplies and not knowing which route to follow. Juan de Cartagena, led a mutiny with the support of the "Victoria" and the "Concepción". Magellan quelled the uprising, killing the captain of the "Victoria" (Luis de Mendoza) and the captain of the "Concepción" (Gaspar de Quesada), and abandoning Juan de Cartagena on an island in Patagonia.
Tierra del Fuego (18th century) by Anónimo Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid.
On August 24, the expedition set off again, but with one less ship after the "Santiago" crashed into a sandbank. “On the 21st of the said month [October 1520] … we saw an opening like a bay … within this bay we found a strait … and passing this strait we found another small bay, and then we found another strait …” (Francisco Albo). They had finally found the passage. What is now known as the Strait of Magellan allowed them access to a new ocean that they called the Pacific.
Penguin Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid.
The accounts of Antonio Pigafetta describe the never-before-seen animals they discovered there, such as the penguin, now known as the Magellanic penguin. During this discovery, the "San Antonio" deserted the expedition and turned east, back to Spain.
Model of a rowboat (rocking boat) (19th Century) by Spanish anonimous Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
The seas gradually became more difficult to navigate. They crossed open waters that were unknown to them, leading to a shortage in supplies and illness among the crew. The expedition landed on islands such as San Pablo, Guam, and the Caroline Islands, signing treaties of loyalty to the king of Spain and spreading Christianity along the way. Finally, in 1521, they reached the Archipelago of San Lazaro, now the Philippines.
Kris with wavy blade (c. 1840) by Philippine anonimous Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
Magellan's Death The commander of the expedition established good relations with the king of Cebu, Rajah Humabon, arousing suspicion in the other local kings. Quarrels broke out, with some in favor of the Spanish and others against, creating a hostile environment. Finally, in 1521, Magellan and 60 men confronted Lapu-Lapu, the king of Mactan. The island's reefs stopped the Spanish artillery boats from landing and they were attacked by 1,500 islanders. Magellan died in the battle.
Primus Circumdedisti Me (2019) by Augusto Ferrer Dalmau Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid.
Elcano and the Arrival at the Moluccas The early departure from the Philippines led to a reorganization of the remaining crew. They set fire to the "Concepción", which was in poor condition, and the crew were split between the two remaining ships. The "Trinidad" was commanded by Gonzalo Gómez de Espinosa, and Juan Sebastián Elcano became captain of the "Victoria". At last, on November 8, 1521, they caught sight of the Moluccas, landing on Tidore.
Juan Sebastián Elcano (1854) by J. Donon Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
After arriving at these islands, they discovered the "Trinidad" was no longer seaworthy. Gómez de Espinosa stayed for a few months to repair the ship and wait for more favorable winds to help them sail east and return via the Americas. Meanwhile, Elcano began the return journey across the Indian Ocean towards Africa, setting course for the Cape of Good Hope, which was under Portuguese control.
The Return of the Victoria from the Moluccas to Seville Following more storms and illnesses, the "Victoria" landed in Cape Verde, in Portuguese territory, in May 1522 to carry out repairs and take on supplies. When the Portuguese discovered their cargo and the origin of the crew, they were forced to abandon the island suddenly, leaving some of the crew on land.
Juan Sebastián Elcano returning to Seville in 1522 (Ca. 1944-45) by Elías Salaverría Inchaurrandieta Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
“On the 4th of the said month [September 1522], in the morning, we saw land, and it was Cape St. Vincent, and it was to the northeast of us, and so we changed our course to the southeast …” (Francisco Albo). They had finally returned home. The "Victoria" reached Seville with 18 survivors, 4 days after catching sight of Cape St. Vincent. They had made it possible to carry out commercial trade around the world. They were the first to circumnavigate the globe.
Charles V welcoming back Elcano (1854) by Carlos Mugica y Pérez Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
The king summoned Juan Sebastián Elcano to Valladolid, where he gave him a personal report on the mission and requested the rescue of the crew members held prisoner in Cape Verde. The monarch granted him a lifetime income of 500 gold ducats a year—which he never paid him—and a coat of arms featuring a world globe with the inscription, "Primus circumdedisti me (You were the first to circumnavigate me)."
Model of the barquentine Juan Sebastián de Elcano, a training ship for the Royal Spanish Navy (1927–active service) (1982-1987) by José Francisco Arregui Arambarri Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
Elcano died four years later, during a new mission to the Moluccas led by García Jofre de Loaísa. The current Spanish navy training ship bears his name in his honor.
Descriptio Maris Pacifici (1589) by Abraham Ortelius Original Source: Museo Naval. Madrid. Todos los derechos reservados.
Legacy: A New World
The importance of the Magellan-Elcano voyage far exceeded the original plans for the expedition.
Universal Chart (1866) by Diego Ribero Original Source: Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana (Vatican City)
What began as a mission to find a way to the Spice Islands, far from the Portuguese routes, became a successful enterprise for two other reasons: it helped prove the shape of the Earth and showed that the Americas were not part of the Indies, but in fact a whole new continent. It generated numerous economic, geographic, and political changes, and led to the beginnings of globalization.
Organized by the Naval Museum, Madrid Curators: Enrique Martínez Ruiz, Susana García Ramírez, José María Moreno Martín Online adaptation: Blanca Sazatornil, Alicia Suárez. Outreach Department, Naval Museum, Madrid. This exhibition is part of the First Voyage Around the World project.
Chart of Juan de la Cosa: The First Known Map of America
Naval museum, elcano's return (el regreso de elcano), navigational instruments and equipment in the 16th century, scale model ships, masters of the sea, lords of the world, midshipmen: the arrival of science in spain, isaac peral and the invention of the first electric submarine, blas de lezo, the last voyage of the mercedes, la batalla de lepanto.
Ferdinand Magellan and the first Trip around the World
Ferdinand Magellan (1480 – 1521)
On 10 August 1519, five ships under Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan ‘s command left Seville and descended the Guadalquivir River to Sanlúcar de Barrameda, at the mouth of the river. After further preparation 5 weeks later the ships set sail for the very first circumnavigation of the earth.
Growing up in Lisbon
Magellan was born Fernão de Magalhães (or Magalhãens) to an impoverished noble family in the northern Portuguese province of Trás-os-Montes . His father, Rui de Magalhães, was mayor of his home village Sabrosa . His mother was Alda de Mesquita. When he was ten years old, Magellan lost his parents. In 1492, like his brother before him, he went to the royal court of King John II of Portugal and Queen Eleonora as a page. Here, in Lisbon, together with his cousin Francisco Serrão, he enjoyed a comprehensive education, possibly by Martin Behaim , and was raised to the rank of squire in 1496.
Expeditions to India and Malacca
In 1505 he participated in the India expedition of the viceroy Francisco de Almeida , where he distinguished himself as a lifesaver and prevented a mutiny. Under Afonso de Albuquerque he took part in the conquest of the important port of Malacca , now Malaysia, in 1511 and played an important role in the storming of the city on 10 August. In December 1511, an expedition of three ships under the command of António de Abreu sailed on to the Spice Islands . According to a source, Magellan was among the 100-man crew and was appointed captain during the expedition. A short time later, however, Magellan lost his captain’s post again because he had sneaked away from the fleet with his ship and sailed further east.
Fighting in Morocco , Disgrace in Portugal, Service for Spain
On his return he was sent to Morocco in 1513, where he fought in the Battle of Azamor and was wounded at the knee. Because of illegal trade with the Moors, he fell out of favour with King Manuel I and was released from Portuguese civil service on 15 May 1514. Thereupon he went to Spain and offered his services in 1517 to the Spanish King Charles I (from 1519 as Charles V Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire).
In Search for the Spice Islands
Magellan had probably found a secret map in the Portuguese Maritime Archives which indicated that a paso , a passage to the Pacific Ocean, existed in South America. It is possible that the large estuary delta of the Río de la Plata had been misconstrued as a strait. He decided to be the first to use this path to the west to reach the Spice Islands (today’s Moluccas). They were a strategically important starting point for the lucrative spice trade. Moreover, Magellan was convinced that, according to the Treaty of Tordesillas of 1494, the Spice Islands were located on the world half promised by Pope Spain.[4] On 22 March 1518 he signed a contract in Valladolid with Charles I of Spain, who provided Magellan with five ships with which he was to find the Spice Islands.
Starting for a Trip around the World
The provided fleet consisted of five ships of which the flagship Trinidad sailed under Ferdinand Magellan’s command. The crew consisted of 270 men across the continent and took off on August 10, 1519. The ships sailed from Seville down the Guadalquivir, at its mouth near Sanlúcar de Barrameda, where the Spanish authorities tried to prevent the Portuguese admiral from travelling for more than five weeks. It was not until September 20, 1519 that the fleet set sail from here. On his flagship, the Trinidad, Magellan had a torch installed at night so that the other ships could maintain visual contact. Magellan sailed first to the Canary Islands, where he took up supplies in Tenerife on 26 September, and then to the Cape Verde Islands (3 October), where he set course for Brazil. On November 20th, his fleet crossed the equator. On December 6, the fleet reached the South American coast, where it anchored on December 13 in a bay named by Magellan as Bahia de Santa Lucía (now Guanabara Bay) – after the day saint Santa Lucia. The Portuguese later gave it the name of St. Januarius . It is today’s bay of Rio de Janeiro .
Magellan’s ship Victoria , detail from a world map by Abraham Ortelius, 1590
Reaching the South Sea
On March 30, the fleet reached a bay called Puerto San Julián. As the southern winter was approaching, Magellan decided to hibernate. Because of running out of supplies, he had his food rations cut. Already on April 1, the poor supply situation led to a mutiny. Due to hunger, disease and exhaustion, some crew members demanded their return to Spain. In October 1520 the four ships left Puerto San Julián after seven months of winter quarters. Again all bays and estuaries were searched in detail for the paso. On October 21, 1520, Magellan reached a cape he called Cabo Vírgenes. The Concepción and the San Antonio were sent on a reconnaissance trip south of the cape and discovered the entrance to the long sought-after passage. Before the passage, Magellan asked the captains of the other ships whether they favoured a continuation of the voyage or a return. No one except the pilot of the San Antonio dared to recommend a change. Since the passage is divided several times, a boat and two ships were sent out for exploration. From the crew of the boat came the message that the road had an exit to the northwest: The South Sea was reached.
The Island of Thieves
The fleet continued and in early 1521 they reached the equator and later Guam . The cities they traveled to were named by Magellan according to the features he observed. For instance he renamed the island to the ‘ Island of Thieves ‘ since his small boats on board of the Trinidad were stolen.
The Magellan–Elcano voyage. Victoria, one of the original five ships, circumnavigated the globe, finishing 16 months after Magellan’s death.
The Philippines and a Poisoned Arrow
After taking up much-needed supplies, Magellan’s fleet sailed on to the Philippines . At that time, 150 sailors were still alive. With the help of his interpreter Enrique Melaka, Ferdinand Magellan was able to exchange gifts with the Prince of Limasawa, Raja Kolambu, who led the Spaniards to the island of Cebu , where they succeeded in converting the prince of Cebu, Rajah Humabon, and many of his subjects to Christianity. The chief Lapu-Lapu on the neighbouring island of Mactan , however, rejected the idea of supremacy and missionary work. As a result, Magellan tried to take possession of the island by force for his ally and thus for Spain and Christianity. The military action on Mactan on 27 April 1521 failed: despite their firearms, the Spaniards were pushed back on the shore by the locals and had to mourn several casualties. Magellan was killed in that battle. According to the reports of his chronicler Pigafetta , he was one of the last to fight in the water to cover the retreat of his people. A poisoned arrow had pierced his thigh; shortly thereafter he had been struck down by two lance shots, one wounding him in the face, the other under his right arm. Soon after the failed attack on Mactan, the prince of Cebu renounced Christianity and lured the Europeans into a trap. 35 sailors were killed.
Elcano Finishing the Journey
The Spaniards barely escaped, but they were now so few that they sank the Concepción themselves and distributed the survivors to Trinidad and Victoria. Juan Sebastián Elcano captained the Victoria and Gonzalo Gómez de Espinosa the Trinidad . Elcano had been chosen captain, although he had only been a simple bosun at the beginning of the voyage. They began their journey home with the flagship and the Victoria, arriving in September, 1522. Through interviewing some of the survivors, Europe learned about the first circumnavigation of the globe. Also during this journey, the crew observed numerous animals that were completely new to Europeans. Afterwards, several straits and locations were named after Ferdinand Magellan and even craters on the Moon and Mars have been named after him.
Since the 19th century, Ferdinand Magellan’s name has been associated primarily with the first historically documented circumnavigation of the Earth. However, Magellan neither circumnavigated the earth himself, nor did he ever plan to do so – even if his companion and admirer Antonio Pigafetta claimed he did. But Pigafetta’s statements about Magellan are clearly written with apologetic intent, that is, he wanted to defend the reputation of his late boss against his enemies and critics. In the documents from the planning phase of the expedition, there is not a single indication that Magellan or anyone else had planned a circumnavigation of the earth at that time. In the end, this came about only out of necessity, because Juan Sebastián Elcano , the last captain of the Victoria , and his crew hoped to bring their worn-out ship with its valuable spice cargo back to Spain this way – which they eventually succeeded in doing. Consequently, Elcano and his crew first reaped the glory of being the first humans to circumnavigate the earth. Since every educated contemporary at the time knew that the earth was a sphere, the voyage of the Victoria was seen not so much as proof of the spherical shape as of the superiority of their own time, in which they lived, over antiquity. Before the 19th century, little of this fame fell on Magellan. While his Spanish patrons did not hold him in particularly high esteem either during his lifetime or afterwards, his Portuguese compatriots reviled him as a traitor. However, his seafaring and military achievements were certainly recognized – especially the discovery and passage of the strait between South America and Tierra del Fuego, known as the “ Estrecho de Magallanes ” ( Strait of Magellan ) from around the middle of the 16th century.
However, subsequent expeditions – notably that of García Jofre de Loaísa in 1525, in which Elcano also participated – showed that the practical value of the sea route to the Pacific and on to Asia found by Magellan was very small. The passage of the Strait of Magellan was a gamble, and the Pacific Ocean was not only immensely large, but made it impossible to establish lasting trade and dominion relations as long as it could only be crossed from east to west. The opposite direction was not achieved until 1565, when Andrés de Urdaneta succeeded in making his way back from the Visayas to Mexico by sailing far out into the North Pacific and taking advantage of the prevailing westerly winds there. Only now were the Spaniards able to colonize the Philippines (soon to be called the Philippines).
References and Further Reading
- [1] Magellan at Britannica
- [2] Stefan Zweig (2007), Conqueror of the Seas – The Story of Magellan
- [3] The Voyage of Ferdinand Magellan
- [4] How the Pope divided the New World among Spain and the Rest of the World , SciHi Blog
- [5] Juan Sebastián Elcano and the First Circumnavigation of the Earth , SciHi Blog
- [6] Dr. Gallup-Diaz, Great Voyages: Ferdinand Magellan, ‘Our One True Guide’: The First Circumnavigation of the Globe , Penn Museum @ youtube
- [7] Primera vuelta al mundo Magallanes-Elcano – V Centenario , official Spanish website for the 500th anniversary of the first circumnavigation of the earth
- [8] Antonio Pigafetta : Magellan’s voyage around the world. 3 vol. Ed. by James Alexander Robertson, Cleveland (Ohio), 1906.
- [9] Antonio de Herrera y Tordesillas : Historia general de los hechos de los castellanos en las islas y tierra firme del mar océano. Madrid 1601.
- [10] Ferdinand Magellan at Wikidata
- [11] Timeline of 16th Century Explorers via DBpedia and Wikidata
Tabea Tietz
Related posts, henry the navigator and the age of discoveries, baltasar gracian and the art of wisdom, antónio egas moniz and the cerebral angiography, michael servetus and the pulmonary circulation.
Pingback: Whewell’s Gazette: Year 2, Vol: #38 | Whewell's Ghost
Pingback: Whewell’s Gazette: Year 03, Vol. #52 | Whewell's Ghost
Though Magellan is often credited with the first circumnavigation on the globe, he did so on a technicality: He first made a trip from Europe to the Spice Islands, eastward via the Indian Ocean, and then later made his famous westward voyage that brought him to the Philippines. So he did cover the entire terrain, but it was not a strict point A to point A, round-the-world trip, and it was made in two different directions. His slave, Enrique, however, was born in either Cebu or Mallaca and came to Europe with Magellan by ship. Ten years later, he then returned to both Cebu (with Magellan) and Mallaca (after Magellan died) by ship on the armada s westward route. So Enrique was the first person to circumnavigate the world in one direction, from point A to point A.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Further Projects
- February (28)
- January (30)
- December (30)
- November (29)
- October (31)
- September (30)
- August (30)
- January (31)
- December (31)
- November (30)
- August (31)
- February (29)
- February (19)
- January (18)
- October (29)
- September (29)
- February (5)
- January (5)
- December (14)
- November (9)
- October (13)
- September (6)
- August (13)
- December (3)
- November (5)
- October (1)
- September (3)
- November (2)
- September (2)
- Entries RSS
- Comments RSS
- WordPress.org
Legal Notice
- Privacy Statement
- Corrections
Ferdinand Magellan & The First Voyage Around the World
During the Age of Exploration, one task was particularly noteworthy: the circumnavigation of Earth. Discover the life of Ferdinand Magellan and the first voyage around the world.

The Age of Exploration saw the achievement of incredible feats with the voyages of European expeditions. Perhaps the most famous of them all is the arrival of Christopher Columbus to the Americas, but many other expeditions are equally groundbreaking. Besides making contact with a “new continent,” the circumnavigation of the Earth was seen as an enormous feat. With Columbus’ travels and following expeditions by other explorers, the circumnavigation of the world was believed possible, but who would be first? Europe’s major powers put their efforts into completing the task, but one expedition, led by Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese explorer serving the Spanish crown, would ultimately be successful: the Magellan expedition.
Magellan’s Early Life & First Travels

Magellan was born in the north of Portugal in 1480. His family was of noble origin and enjoyed a minor presence yet sufficient status among the higher classes of the Kingdom of Portugal. His father, Rui Magellan, was the mayor of a small town. Ferdinand served as a page to Queen Eleanor, consort of John II of the Portuguese crown. After the death of John, Magellan served under Manuel I. When Magellan was 25, he joined a Portuguese expedition to India, where they would establish Francisco de Almeida as the first viceroy of Portuguese India. Magellan stayed in India for almost a decade; then, he traveled to Malacca, where, in 1511, the Portuguese conquered the city under the governor Alfonso de Albuquerque.
Magellan received great riches and promotions from his participation in the conquest of Malacca. He received a slave, baptized under the name Enrique of Malacca, who would join Magellan through many of his travels and endeavors. Magellan’s behavior became increasingly rebellious and not in tune with the Portuguese authorities’ expectations. He took leave without permission, was accused of illegally trading in Morocco, and even quarreled with the Portuguese King Manuel I.
Magellan dedicated himself to studying the most recent nautical charts available to him. He investigated, alongside cosmographer Rui Faleiro, the possibility of reaching the Moluccas through a gateway from the Atlantic to the South Pacific in the Americas. While in Malacca, Magellan befriended the navigator Francisco Serrao, who reached and stayed in the Spice Islands (the Moluccas). His letters to Magellan would prove very useful for his consequent travels to the Islands.
Magellan the Spanish Explorer: Pledging Loyalty to the Opposing Crown

Get the latest articles delivered to your inbox
Please check your inbox to activate your subscription.
When Magellan fell out of favor with the Portuguese King, he turned to the Spanish crown. Magellan had been refused time and time again an expedition made possible by the Portuguese crown. King Manuel I disapproved of Magellan’s planned expedition. Thus, Magellan renounced his Portuguese nationality and proposed his travel expedition to King Charles I of Spain (Charles V as Holy Roman Emperor ).
At the time of Magellan’s proposed expedition, Spain was at the start of its expansion into other continents, mainly the Americas, which would be decisive for the Spanish to consolidate their empire.
Portugal had a similar situation. The Portuguese Empire had explored most of the coasts of Africa, reached the Indies through said passage, and established colonies all throughout Africa and Asia.
However, both Iberian empires had become rivals whose differences were often solved only through external intervention. The Treaty of Tordesillas of 1494 established a division of lands outside of Europe between Spain and Portugal. The treaty was largely left unsettled, but in 1529, the Treaty of Zaragoza clarified and formalized the divisions. Before its formalization, however, Magellan and his fleet would achieve the first circumnavigation of the Earth, arguably abusing the agreement set in the Tordesillas treaty.
Magellan convinced the Spanish king that his expedition would not be opposed to the agreement between Spain and Portugal; thus, he was allowed to sail. King Manuel I was greatly insulted by Magellan’s expedition and work under the Spanish crown. The preparations of the Spanish fleet were disrupted by the Portuguese, and a fleet was sent after Magellan, though it failed to capture him.
Expedition through the Atlantic & Reaching the Americas

Magellan and his fleet left Spain from the port of Seville in 1519. The fleet traveled through the Guadalquivir River until they reached the Atlantic through the port of Sanlucar de Barrameda. The fleet remained in place for weeks, going back and forth from Seville to solve unforeseen difficulties. More than a month later, they departed. The fleet reached the Canary Islands, then passed next to Cape Verde and the coasts of Sierra Leone. Four months went by before the fleet reached the coasts of the Americas.
In December 1519, Magellan and his fleet touched land in what is now Rio de Janeiro. They traveled through the estuary of the Rio de la Plata River, then reached and named the region of Patagonia . In Patagonia, the Spaniards met local Indigenous people for the first time. After making contact and trading with them, the Spanish kidnapped some to bring them back for the king. Unfortunately, the kidnapped Indigenous people didn’t survive.
In March 1520, the fleet found itself in harsh conditions. They took refuge in the port of San Julian, but after considering the expedition had failed, some of the crew attempted to overthrow Magellan as their leader. The insurrection ultimately failed; the leaders of the unsatisfied crew were killed or banished, and Magellan forgave the rest as he needed them to continue. Later, the crew of one of the five ships, San Antonio , once again rose against Magellan and turned back for Spain.
The Strait of Magellan & the Voyage in the Pacific

After facing difficulties finding a passage to the Pacific Ocean (known to them as Mar del Sur ), the fleet reached the Strait of Magellan. Magellan originally named it the Strait of All Saints ( estrecho de Todos los Santos ), but the strait gained its name in honor of Magellan and his expedition, having been the first European explorer to find the strait.
Known to be a harsh place, the Strait of Magellan was challenging to pass through. The Spaniards saw bonfires lit by the natives and thus named the territory “ Tierra del Fuego ” (Land of Fire). Indigenous people lived or had reached as far down as Antarctica . The ocean known to them as Mar del Sur was then baptized the Pacific Ocean for its tranquil waters. For three months, after passing through the strait, the fleet was unable to reach land and disembark. The conditions aboard were challenging, to say the least.
The difficulties during the voyage in the Pacific decreased once the fleet reached the Mariana Islands . The state of the fleet was in tatters, having barely survived over three months without touching land. They then reached the Philippines, becoming the first Europeans to do so. Magellan and his fleet carried out the conversion of the local islanders to Catholicism. Magellan won over the locals by proving his strength and urging them to convert so that they could become like them. Thus, the fleet remained in the region before continuing to the Moluccas.
The Battle of Mactan, Magellan’s Death, & the First Circumnavigation of the World

In the Philippines, the locals were manipulated into converting to Catholicism, but when attempting to form an alliance with one chieftain, Magellan proposed to battle an opposing leader to win over his potential ally. Magellan and his fleet went to the Island of Mactan to fight, convert, and make the chieftain Lapulapu submit to the Spanish crown. The battle was a decisive defeat for the Spanish, who were unprepared and outnumbered. Magellan himself was killed during combat. After Magellan’s death, the expedition under his command had to choose a new leader.
The expedition chose Magellan’s brother-in-law and Juan Serrano as co-commanders, but their leadership would be short-lived. On the first of May, the Spanish disembarked to join the Cebuanos for a feast, yet once the meal was finished, they were surprised and murdered by the Cebuanos. The Spaniards had been betrayed by Magellan’s slave Enrique, who was supposed to be freed after his master’s death but was forced to continue working as an interpreter for them. Enrique made a deal with the island’s leader, Humabon, in order to regain his freedom.

With both co-commanders murdered, Juan Lopez de Carvalho was named captain. The fleet chose to continue with just two ships: Trinidad and Victoria . Carvalho was deemed unable to command, and Gonzalo Gomez de Espinosa was chosen as the new captain, leading the ship Trinidad . Meanwhile, Juan Sebastian Elcano was to captain the ship Victoria . When the fleet reached the Moluccas, it was decided that they should leave for Spain at once, yet the Trinidad was in no shape for that sort of travel, so only the Victoria would continue, and the Trinidad would follow later. Elcano and his ship circumnavigated the African continent for their return, and in September 1522, they reached Spain, completing the first circumnavigation of the world .

5 Things Marco Polo Discovered on His Travels

By Francisco Perpuli BA History (in progress) Francisco is completing a History degree at the University of Guadalajara. He has a keen interest in the study of culture and the arts. In his spare time, he tries to explore and develop other interests while saving up to travel the world.

Frequently Read Together

The Holy Roman Empire in 3 Key Leaders

Modern Argentina: A Struggle for Independence from Spanish Colonization

Polynesians in Antarctica: Were They the First?

The Ages of Exploration
Magellan’s voyage.
Quick Facts:
Magellan’s Voyage Around the World

Map of Ferdinand Magellan’s voyage around the world.
- Original "EXPLORATION through the AGES" site
- The Mariners' Educational Programs

- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Why the Magellan Expedition Was So Treacherous
By: Patrick J. Kiger
Updated: July 24, 2023 | Original: July 20, 2023

In September 20, 1519, a fleet of five ships and 260 sailors set sail from the Spanish port of Sanlúcar de Barrameda, under the command of Ferdinand Magellan , a Portuguese mariner who had shifted his allegiance to Spain.
Magellan sought to find a westward route by water to the Spice Islands, a small archipelago in Indonesia that was the source of the nutmeg, cloves and other spices that Europeans coveted as flavorings and medicines. In accomplishing that, the expedition would circumnavigate the planet for the first time in human history.
It was an audacious plan, one that involved sailing through thousands of miles of uncharted waters and finding a previously undiscovered passage through the Americas from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific. But Magellan, who believed that it was God’s will for him to succeed, was confident of success.
The mariner was “an unparalleled example of navigational smarts, personal courage and indifference to hardship,” says Laurence Bergreen , author of the 2003 book Over the Edge of the World: Magellan’s Terrifying Circumnavigation of the Globe.
In the end, Magellan’s quest would cost him his life, and lead to the loss of all but one of his ships and most of his crew through death or desertion.
Here are some of the hazards that made Magellan’s expedition so treacherous, and how the explorer and his crew overcame some, but not all, of those obstacles.
Magellan didn't really know how to get to his destination.
Magellan initially tried to get Portugal’s King Manuel to authorize a voyage to discover a water route to the Spice Islands, according to Bergreen, but the king, who didn’t like him, nixed the idea. In frustration, he got permission from Manuel to pitch his plan elsewhere, and in 1517, he moved to Spain, where he lobbied officials on his idea.
As a selling point, Magellan proclaimed his belief that the Spice Islands were located inside the Spanish realm delineated by the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas , in which Spain and Portugal agreed to divide the non-Christian world between them. Magellan may actually have believed this, because he had a friend, Portuguese mariner Francisco Serrão, who had settled in the Spice Islands and wrote Magellan letters in which he placed the islands far to the east of where they actually were.
Not only was Magellan mistaken about his destination, but he was even shakier about the route he would take to get there.
Magellan told Spanish officials that his plan was to sail along the eastern coast of South America until the land ended, and even showed them a globe to illustrate the route. Though he didn’t know the actual distance, he estimated that the round trip from the Spice Islands would take no more than two years.
But Magellan was vague about how he would get past the Americas. According to historian Jerry Brotton’s A History of the World in 12 Maps , a priest and author named Bartolome de las Casas, who witnessed the presentation, asked Magellan, “What will you do if you find no strait to pass into the other sea?” Magellan dodged the question.
When Magellan finally crossed the Atlantic and got to South America, finding the passageway turned out to be a lot harder than he had expected. One of his ships, the Santiago, was wrecked in a storm during the search and had to be abandoned.
Magellan had to defeat a mutiny by some of his crew.
“The greatest danger that he encountered as a masterful navigator wasn’t the physical threats, the storms, or the natural hazards of sailing across a vast ocean,” Bergreen explains. “It was the often-rebellious group that he led, who came from many different countries and spoke different languages, and were often dead set against him and each other.”
“The captains who accompanied him hated him exceedingly,” wrote Antonio Pigafetta, a diplomat who kept a detailed diary of the expedition, which he later published as a book, Magellan’s Voyage Around the World. “I know not why, unless because he was a Portuguese, and they Spaniards.”
After a rough voyage across the Atlantic to Brazil, in which the fleet was battered by storms, the tensions increased when an officer on the Victoria, Antonio Salamón, was tried and executed by strangulation in December 1519 for sexually assaulting an apprentice seaman. The rumblings got worse. One of the captains, Juan de Cartagena, accused Magellan of being a Portuguese double-agent and sabotaging the mission.
Cartagena and others hatched a plot to stage a mutiny and kill Magellan in April 1520. But according to an account by Portuguese historian Gaspar Correa, Magellan anticipated their treachery. When they tried to strike, an officer loyal to him pulled a dagger and cut the throat of mutineer Luis de Mendoza, whose corpse was then hung by his feet, “so they might see him from the other ships.”
Magellan captured the other conspirators, and their punishment was brutal. After one captain was beheaded, his body was drawn and quartered as an example of the price for disloyalty. Cartagena, who had tried to hatch a second plot, was left to starve on a small island off the coast.
Magellan’s severity might seem shocking today, but Bergreen says it wasn’t that unusual in his time. “Captains had life-and-death powers over their sailors, and they sometimes used it,” the historian explains.
But that didn’t quell all the dissent. The officers and crew of one ship, the San Antonio , managed to skip away in November 1520 and return to Spain.
The Pacific turned out to be a lot bigger than Magellan imagined.
In November 1520, Magellan finally discovered the Strait of Magellan , a natural channel that passes between the continent’s southern tip and the island of Tierra Del Fuego, he and his three remaining ships finally were able to sail into the ocean that he named the Pacific, because it seemed so serene.
“He thought it would be a hop, skip and jump to circumnavigate the world and get to the Spice Islands, and then he would go home in triumph,” Bergreen says. “Of course, it didn’t turn out that way.”
Once the coast of South America disappeared, Magellan found himself out in the middle of an ocean that was vastly larger than he had imagined.
“He's crossing the Pacific, he's expecting to find land any day, not realizing that he’s crossing the largest body of water on the planet,” Bergreen explains.
As the voyage stretched on, the ships’ crews had to subsist on a severely sparse diet and ration their water. The predicament even took its toll upon Magellan. “At one point, he got irritable, maybe because of the shortage of food, and started to become less reasonable,” Bergreen explains. The explorer realized that the maps he had been using were hopelessly inaccurate. Magellan abruptly threw them overboard.
Magellan’s men were horrified. “They thought they were doomed without the maps,” Bergreen says. On the contrary, they actually were liberated. Without the charts, Magellan was forced to navigate by reading the signs in the ocean environment. He discovered the trade winds that blew across the Pacific, and his skill as a sailor—combined with the agility and maneuverability of his ships’ design—enabled him to speed his way across the Pacific before he and his men died of hunger and thirst.
Magellan's own overconfidence proved fatal.
When Magellan reached the Philippines in March 1521, he saw an opportunity to convert the indigenous people to Catholicism and place them under the authority of the Spanish King, according to Australian Catholic University scholars Kate Fullagar and Kristie Patricia Flannery.
Some local rulers, who saw advantages in an alliance with the Spanish, went along with Magellan. But Lapu Lapu, chief of the island of Mactan, refused. Magellan, who had experience as a soldier, decided to attack. On April 27, 1521, he and a small Spanish force of 60 armed men and 20 to 30 native allies attempted an amphibious invasion at dawn.
As Bergreen notes, Magellan assumed that his superior technology—muskets and armor—would overcome the indigenous people armed with wooden spears. That proved to be a fatal miscalculation.
In Pigafetta’s account, the invasion force’s boats couldn’t get too close to shore because of rocks in the water, which forced Magellan’s men to jump into the water and try to wade to land. More than 1,500 warriors awaited them. Magellan’s musketeers and crossbow archers fired on the defenders, but in the chaos, they weren’t able to hit them.
“So many were the spears and stones that they hurled at us, that we could offer no resistance,” Pigafetta wrote. Magellan himself was shot through the leg with a poisoned arrow and had his helmet knocked off by attackers. He fought hard to survive, until a warrior slashed him in the leg with a cutlass, and he fell, allowing others to swarm over Magellan and hack and stab him to death.
Only one of Magellan's ships and 18 sailors made it back.
The Spanish suffered so many casualties that they had to abandon another of their ships, the Concepción, because they didn’t have enough men left to sail it. The two remaining vessels eventually made it to the Spice Islands in November 1521.
One of the two remaining ships, the Trinidad, was in disrepair and stayed behind for an overhaul. It was later captured by the Portuguese and eventually sank in a storm. That left only the Victoria to sail around Africa’s Cape Horn and head back along the west coast of Africa toward Europe.
On September 6, 1522, the Victoria reached the same Spanish harbor from which it had departed three years before. As Bergreen describes in his book. The Victoria’s tattered sails and battered, sun-bleached hull were evidence of the ordeal it had survived. Just 18 sailors out of the original 260 were left, and they were so weak from malnutrition and exposure that they had trouble walking or speaking.
The survivors did manage to bring back a load of spices, it was obvious that Magellan’s notion of establishing a westward route to Asia was too slow, costly and downright dangerous to be practical.
How Magellan's expedition influenced history
Though the expedition might have seemed at the time like a failure, Magellan’s quest changed the world in critical ways.
By circumnavigating the globe, the expedition had extinguished any remaining doubts that the world was round , and it also showed that North and South America were separate continents from Asia and that our planet’s surface was mostly covered with water.
It would take another half a century before English navigator, pirate and slave trader Sir Francis Drake matched the Magellan expedition’s feat by circumnavigating the globe in 1577-1580.

HISTORY Vault: Columbus the Lost Voyage
Ten years after his 1492 voyage, Columbus, awaiting the gallows on criminal charges in a Caribbean prison, plotted a treacherous final voyage to restore his reputation.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
share this!
August 5, 2019
500 years on, how Magellan's voyage changed the world
Ferdinand Magellan set off from Spain 500 years ago on an epoch-making voyage to sail all the way around the globe for the first time.
The Portuguese explorer was killed by islanders in the Philippines two years into the adventure, leaving Spaniard Juan Sebastian Elcano to complete the three-year trip. But it is Magellan's name that is forever associated with the voyage.
"Magellan is still an inspiration 500 years on," said Fabien Cousteau, a French filmmaker and underwater explorer like his grandfather Jacques-Yves Cousteau.
"He was a pioneer at a time when explorers who went off into the unknown had a strong habit of not coming back."
Here are five ways in which Magellan's voyage marked human history and continues to inspire scientists and explorers today.
Some of them spoke to AFP at a conference in Lisbon to mark the August 10 fifth centenary.
Magellan's voyage was a turning point in history, as unique as the first manned journey into outer space and the later moon landings, said NASA scientist Alan Stern, leader of its New Horizons interplanetary space probe.
"When the first one circled the planet, (that) sort of meant that we now had our arms around the planet for the first time," he said.
"That just transformed humanity in my view. I would call it the first planetary event, in the same way that Yuri Gagarin was the first off-planetary event" when the Soviet cosmonaut went into outer space.
Geographical
Magellan's voyage rewrote the maps and geography books. He was the first to discover the strait, which now bears his name, linking the Atlantic and Pacific oceans at the tip of South America.
"Perhaps his greatest feat, and still considered today one of the greatest feats of the history of navigation, was negotiating this strait, of which there were no maps and whose existence was vaguely rumoured," said US historian Laurence Bergreen, author of a biography of Magellan.
Philosophical
The voyage transformed humans' own conception of their place in the world.
"It wasn't just geography and anthropology, it showed something philosophical: that it's all one world," said Bergreen.
"Before Magellan people didn't really know that. They didn't know how the world was connected or how big it was."
Astronomical
The voyage contributed to Europeans' knowledge of the universe and has marked the worlds of space exploration and astronomy to this day.
While crossing the Magellan Strait, the explorer and his crew observed two galaxies visible to the naked eye from the southern hemisphere, now known as the Magellanic Clouds.
Some recently-designated areas of the surface of Mars have been given the same names that Magellan gave to parts of South America, with Bergreen's help. A giant telescope being developed in Chile will also bear the explorer's name.
Inspirational
Magellan's achievement was a landmark in the history of exploration still hailed by his modern-day successors.
"In the space program, to prepare for these long duration missions, we say 'the lessons for the future are written in the past'," said Dafydd Williams, a former NASA astronaut, now 65, who went on two space missions.
"So many in the space program have read about Magellan."
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Managing meandering waterways in a changing world
12 hours ago


New dataset sheds light on relationship of far-red sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence to canopy-level photosynthesis

How much trust do people have in different types of scientists?
14 hours ago

Scientists say voluntary corporate emissions targets not enough to create real climate action

Barley plants fine-tune their root microbial communities through sugary secretions

A shortcut for drug discovery: Novel method predicts on a large scale how small molecules interact with proteins

Yeast study offers possible answer to why some species are generalists and others specialists

Cichlid fishes' curiosity promotes biodiversity: How exploratory behavior aids in ecological adaptation

Climate change could become the main driver of biodiversity decline by mid-century, analysis suggests

First-of-its-kind study shows that conservation actions are effective at halting and reversing biodiversity loss
Relevant physicsforums posts, favorite mashups - all your favorites in one place.
2 hours ago
Cover songs versus the original track, which ones are better?
11 hours ago
Interesting anecdotes in the history of physics?
Apr 24, 2024
Great Rhythm Sections in the 21st Century
Biographies, history, personal accounts.
Apr 23, 2024
History of Railroad Safety - Spotlight on current derailments
Apr 21, 2024
More from Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
Related Stories
Researcher finds el nino may have been factor in magellan's pacific voyage.
May 15, 2008

Blind children in Chile get solar eclipse experience
Jun 26, 2019
Giant Magellan Telescope's third mirror unveiled
Dec 4, 2013

Chile breaks ground on world's largest telescope
Nov 11, 2015
Giant Magellan telescope site selected
Oct 4, 2007
Giant telescope will keep an eye on planets in other solar systems
Dec 29, 2004
Recommended for you

Saturday Citations: Irrationality modeled; genetic basis for PTSD; Tasmanian devils still endangered
Apr 20, 2024
Saturday Citations: Listening to bird dreams, securing qubits, imagining impossible billiards
Apr 13, 2024

Saturday Citations: AI and the prisoner's dilemma; stellar cannibalism; evidence that EVs reduce atmospheric CO₂
Apr 6, 2024
Saturday Citations: 100-year-old milk, hot qubits and another banger from the Event Horizon Telescope project
Mar 30, 2024
Saturday Citations: An anemic galaxy and a black hole with no influence. Also: A really cute bug
Mar 23, 2024

Saturday Citations: The volcanoes of Mars; Starship launched; 'Try our new menu item,' say Australian researchers
Mar 16, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Voyages of Ferdinand Magellan
First voyage, king charles i finances the voyage, rio de janeiro, strait of magellan, philippines, death in battle, rounding the cape, voyage home.

The Magellan expedition, also known as the Magellan–Elcano expedition, was the first voyage around the world. It was a 16th century Spanish expedition initially led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan to the Moluccas, which departed from Spain in 1519, and completed in 1522 by Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, after crossing the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans, culminating in the first circumnavigation of the world.
The expedition accomplished its primary goal – to find a western route to the Moluccas (Spice Islands). The fleet left Spain on 20 September 1519, sailed across the Atlantic ocean and down the eastern coast of South America, eventually discovering the Strait of Magellan, allowing them to pass through to the Pacific Ocean (which Magellan named). The fleet completed the first Pacific crossing, stopping in the Philippines , and eventually reached the Moluccas after two years. A much-depleted crew led by Juan Sebastián Elcano finally returned to Spain on 6 September 1522, having sailed west across the great Indian Ocean, then around the Cape of Good Hope through waters controlled by the Portuguese and north along the Western African coast to eventually arrive in Spain.
The fleet initially consisted of five ships and about 270 men. The expedition faced numerous hardships including Portuguese sabotage attempts, mutinies, starvation, scurvy, storms, and hostile encounters with indigenous people. Only 30 men and one ship (the Victoria) completed the return trip to Spain. Magellan himself died in battle in the Philippines, and was succeeded as captain-general by a series of officers, with Elcano eventually leading the Victoria's return trip.
The expedition was funded mostly by King Charles I of Spain, with the hope that it would discover a profitable western route to the Moluccas, as the eastern route was controlled by Portugal under the Treaty of Tordesillas. Though the expedition did find a route, it was much longer and more arduous than expected, and was therefore not commercially useful. Nevertheless, the expedition is regarded as one of the greatest achievements in seamanship, and had a significant impact on the European understanding of the world.

In March 1505 at the age of 25, Magellan enlisted in the fleet of 22 ships sent to host Francisco de Almeida as the first viceroy of Portuguese India . Although his name does not appear in the chronicles, it is known that he remained there eight years, in Goa, Cochin and Quilon. He participated in several battles, including the battle of Cannanore in 1506, where he was wounded. In 1509 he fought in the battle of Diu.

After having his proposed expeditions to the Spice Islands repeatedly rejected by King Manuel of Portugal, Magellan turned to Charles I, the young King of Spain (and future Holy Roman Emperor). Under the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas, Portugal controlled the eastern routes to Asia that went around Africa. Magellan instead proposed reaching the Spice Islands by a western route, a feat which had never been accomplished. Hoping that this would yield a commercially useful trade route for Spain , Charles approved the expedition, and provided most of the funding.

On 10 August 1519, the five ships under Magellan's command left Seville and descended the Guadalquivir River to Sanlúcar de Barrameda, at the mouth of the river. There they remained more than five weeks. The fleet left Spain on 20 September 1519, sailing west across the Atlantic toward South America. Magellan's fleet consisted of five ships, carrying supplies for two years of travel. The crew consisted of about 270 men. Most were Spanish, but around 40 were Portuguese.

On 13 December, the fleet reached Rio de Janeiro, Brazil . Though nominally Portuguese territory, they maintained no permanent settlement there at the time. Seeing no Portuguese ships in the harbour, Magellan knew it would be safe to stop.
The fleet spent 13 days in Rio, during which they repaired their ships, stocked up on water and food (such as yam, cassava, and pineapple), and interacted with the locals. The expedition had brought with them a great quantity of trinkets intended for trade, such as mirrors, combs, knives and bells. The locals readily exchanged food and local goods (such as parrot feathers) for such items. The crew also found they could purchase sexual favours from the local women. Historian Ian Cameron described the crew's time in Rio as "a saturnalia of feasting and lovemaking".
On 27 December, the fleet left Rio de Janeiro. Pigafetta wrote that the natives were disappointed to see them leave, and that some followed them in canoes trying to entice them to stay.

After three months of searching (including a false start in the estuary of Río de la Plata), weather conditions forced the fleet to stop their search to wait out the winter. They found a sheltered natural harbor at the port of Saint Julian, and remained there for five months. Shortly after landing at St. Julian, there was a mutiny attempt led by the Spanish captains Juan de Cartagena, Gaspar de Quesada and Luis de Mendoza. Magellan barely managed to quell the mutiny, despite at one point losing control of three of his five ships to the mutineers. Mendoza was killed during the conflict, and Magellan sentenced Quesada and Cartagena to being beheaded and marooned, respectively. Lower-level conspirators were made to do hard labor in chains over the winter, but later freed.

During the winter, one of the fleet's ships, the Santiago, was lost in a storm while surveying nearby waters, though no men were killed. Following the winter, the fleet resumed their search for a passage to the Pacific in October 1520. Three days later, they found a bay which eventually led them to a strait, now known as the Strait of Magellan, which allowed them passage through to the Pacific. While exploring the strait, one of the remaining four ships, the San Antonio, deserted the fleet, returning east to Spain. The fleet reached the Pacific by the end of November 1520. Based on the incomplete understanding of world geography at the time, Magellan expected a short journey to Asia, perhaps taking as little as three or four days. In fact, the Pacific crossing took three months and twenty days. The long journey exhausted their supply of food and water, and around 30 men died, mostly of scurvy. Magellan himself remained healthy, perhaps because of his personal supply of preserved quince.

On 6 March 1521, the exhausted fleet made landfall at the island of Guam and were met by native Chamorro people who came aboard the ships and took items such as rigging, knives, and a ship's boat. The Chamorro people may have thought they were participating in a trade exchange (as they had already given the fleet some supplies), but the crew interpreted their actions as theft. Magellan sent a raiding party ashore to retaliate, killing several Chamorro men, burning their houses, and recovering the 'stolen' goods

On 16 March, the fleet reached the Philippines , where they would remain for a month and a half. Magellan befriended local leaders on the island of Limasawa, and on 31 March, held the first Mass in the Philippines, planting a cross on the island's highest hill. Magellan set about converting the locals to Christianity . Most accepted the new religion readily, but the island of Mactan resisted.

On 27 April, Magellan and members of his crew attempted to subdue the Mactan natives by force, but in the ensuing battle, the Europeans were overpowered and Magellan was killed by Lapulapu, a native chieftain in Mactan.

Following his death, Magellan was initially succeeded by co-commanders Juan Serrano and Duarte Barbosa (with a series of other officers later leading). The fleet left the Philippines (following a bloody betrayal by former ally Rajah Humabon) and eventually made their way to the Moluccas in November 1521. Laden with spices, they attempted to set sail for Spain in December, but found that only one of their remaining two ships, the Victoria, was seaworthy.

The Victoria set sail via the Indian Ocean route home on 21 December 1521, commanded by Juan Sebastián Elcano. By 6 May 1522 the Victoria rounded the Cape of Good Hope, with only rice for rations.

Twenty crewmen died of starvation by 9 July 1522, when Elcano put into Portuguese Cape Verde for provisions. The crew was surprised to learn that the date was actually 10 July 1522, as they had recorded every day of the three-year journey without omission. They had no trouble making purchases at first, using the cover story that they were returning to Spain from the Americas. However, the Portuguese detained 13 crew members after discovering that Victoria was carrying spices from the East Indies. The Victoria managed to escape with its cargo of 26 tons of spices (cloves and cinnamon).

On 6 September 1522, Elcano and the remaining crew of Magellan's voyage arrived in Sanlúcar de Barrameda in Spain aboard Victoria, almost exactly three years after they departed. They then sailed upriver to Seville, and from there overland to Valladolid, where they appeared before the Emperor. When Victoria, the one surviving ship and the smallest carrack in the fleet, returned to the harbour of departure after completing the first circumnavigation of the Earth, only 18 men out of the original 270 men were on board. In addition to the returning Europeans, the Victoria had aboard three Moluccans who came aboard at Tidore.
Magellan has come to be renowned for his navigational skill and tenacity. The first circumnavigation has been called "the greatest sea voyage in the Age of Discovery", and even "the most important maritime voyage ever undertaken". Appreciation of Magellan's accomplishments may have been enhanced over time by the failure of subsequent expeditions which attempted to retrace his route, beginning with the Loaísa expedition in 1525 (which featured Juan Sebastián Elcano as second-in-command). The next expedition to successfully complete a circumnavigation, led by Francis Drake, would not occur until 1580, 58 years after the return of the Victoria.
Magellan named the Pacific Ocean (which was also often called the Sea of Magellan in his honor until the eighteenth century), and lends his name to the Strait of Magellan.
Even though Magellan did not survive the trip, he has received more recognition for the expedition than Elcano has, since Magellan was the one who started it, Portugal wanted to recognize a Portuguese explorer, and Spain feared Basque nationalism.
How Did the Caravel Change the World?
Technology of the age of exploration.

Holy Roman Emperor

Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese Explorer

Juan Sebastián Elcano
Castilian Explorer

Juan de Cartagena
Spanish Explorer

Francisco de Almeida

Mactan Datu
- The First Voyage Round the World, by Magellan, full text, English translation by Lord Stanley of Alderley, London: Hakluyt, [1874] – six contemporary accounts of his voyage
- Guillemard, Francis Henry Hill (1890), The life of Ferdinand Magellan, and the first circumnavigation of the globe, 1480–1521, G. Philip, retrieved 8 April 2009
- Zweig, Stefan (2007), Conqueror of the Seas – The Story of Magellan, Read Books, ISBN 978-1-4067-6006-4
Premium Content

- HISTORY MAGAZINE
240 men started Magellan's voyage around the world. Only 18 finished it.
The explorer died on a Philippines beach in April 1521, joining the scores who perished in Spain's quest to circumnavigate the globe.
As it moored under Seville’s imposing skyline on September 8, 1522, the Victoria may not have stood out as anything exceptional among the bustle of Spanish ships arriving from the Americas. When 18 men stepped off board, “leaner than old, worn-out nags,” as one of them later recalled, they stepped into the history books as the first people to have sailed entirely around the world.
It had been a brutal voyage, led by the brilliant, if ruthless, Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan. When they set out from Seville, three years before in summer 1519, they were a crew of 240 manning five ships. A series of blows—including starvation, illness, mutiny, executions, and the death of their leader—decimated their numbers and their fleet before returning to Spain.
These men had, however, completed their global journey, despite the violence and greed that marred it from the outset. The venture would be remembered for the skill and endurance of many of its members. As the first Europeans to enter the eastern Pacific, the expedition radically altered Europe’s understanding of the world, while posterity would lionize Magellan for an accomplishment that he never lived to see.
Despite the aura of heroism that has formed around Magellan, his voyage was not driven by geographic curiosity, but by trade and Spain’s struggle to surpass Portugal. Following Christopher Columbus’s voyages of the 1490s and the discovery of a landmass to the west, the two premier naval powers competed to control the new vistas opening before them. In 1493 Pope Alexander VI drew a line from north to south down the Atlantic, decreeing that Spain could exploit the new continent to the west. The papal bull did not specify, however, that Portugal could exploit the territory to the east of the line.
Portugal cried foul, pointing out that the pope, a Borgia of Spanish descent, was not an impartial arbiter. To avoid a war, direct talks opened between Portugal and Spain and the line was moved farther west in the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas. This allowed Portugal more room to maneuver down the eastern coastline of Africa. Happily for the Portuguese, Pedro Álvares Cabral’s 1500 discovery of the eastern coastline of South America fell on Portugal’s side of the 1494 line.
Portugal had already bested Spain in the exploration race, when in 1497 Vasco de Gama was the first European to discover a sea route to India around Africa. While this period of global exploration is often associated with the Americas, both powers were also seeking riches in the Asia-Pacific. It was there that Magellan gained experience vital to his later expedition. ( Was Magellan the first to sail around the world? Think again. )
A sea change
Born Fernão de Magalhães in northern Portugal in 1480, Magellan grew up in a noble family. At age 10 he was sent to Lisbon to train as a page in the court of Queen Leonora. He came of age as Europe began shaking off its medieval sensibilities and looking outward. The few sources on his early life suggest he became fascinated with maps and charts, an interest that may have coincided with the news, at age 13, of the Spanish expedition under Columbus that had made landfall in the Americas.
Portuguese eastward expansion began to move rapidly after Vasco de Gama rounded the Cape of Good Hope in 1497. By 1505 the 25-year-old Magellan was with the Portuguese fleet heading around the Cape, and up the other side, to East Africa. The aim of King Manuel of Portugal was to wrest control of the entire Indian Ocean from the Arabs so as to control trade with India.
In 1507 Magellan participated in a naval battle that consolidated Portuguese power over the Indian Ocean. More Portuguese victories followed in Goa (western India), and in 1511 the Portuguese seized Malacca on the Malay Peninsula. The city overlooks the strait through which the spices from modern-day Indonesia were funneled westward. By controlling Malacca, Portugal could exert control over the spice trade.
An older relative (and possible cousin) of Magellan, Francisco Serrão, had also forged a dramatic career as a sailor and took part in the seizure of Malacca before going on an expedition to the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, in 1512. His venture would later inspire Magellan’s own goal to reach them by sailing west from Europe.
Magellan took part in the battle for Malacca and honed his navigational skills during Portugal’s eastern victories. After returning to Europe, in 1514 he entered into a bitter dispute with King Manuel over the king’s refusal to reward him. Having used up all his appeals, Magellan rejected his native land and traveled to the Spanish court at Valladolid in 1517 to offer his services to the Spanish king Charles I (who would become Holy Roman Emperor Charles V in June 1519). From that day, Fernão de Magalhães would be known by his Spanish name, Fernando de Magallanes.
By offering his services to Spain, Magellan was not engaging in any truly scandalous behavior. Seafaring expertise often crossed borders, and crews were drawn from different nations. Columbus too, a Genoan from northern Italy, had offered himself to the Spanish crown after initially working for the Portuguese. Magellan’s plan was strikingly similar to Columbus’s from nearly 30 years earlier: to sail west to bring back spices from the Moluccas, the Spice Islands of Indonesia. ( Discover the secrets hidden in a 500-year-old map used by Columbus. )
Citing the theories of other navigators at the time, Magellan postulated that a strait cut through the Americas to a sea whose eastern shore was first glimpsed by Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa in 1513. If he could find it, this passage would allow Spain a kind of “back-door” access to the Moluccas, bypassing Portugal’s Cape route. Magellan’s reputation as a sailor and his knowledge of the east convinced Charles, and the expedition received royal assent.
Not all were happy that this Portuguese interloper had gained such favor with the king. The nobility and the Casa de Contratación (the state body that controlled such expeditions) took every opportunity to obstruct Magellan’s preparations. Under two-thirds of the crew were Spaniards; of the foreigners, 24 were Portuguese and 27 were Italian.
Marvels and mutiny
Among the crew was a young Venetian nobleman named Antonio Pigafetta, a student of astronomy and geography. Pigafetta’s lively journal became history’s principal written source for detailed information on the entire voyage.
“On Monday, August 10, St. Lawrence’s day, the fleet, having been supplied with all the things necessary for the sea, made ready to leave the harbor of Seville,” Pigafetta recorded in his log. Five ships in total—the San Antonio, the Concepción, the Victoria, the Santiago , and the flagship, the Trinidad —struck out west from Spain via the Canary Islands. Pigafetta’s observations were not solely nautical. He took a lively interest in geography and zoology and science, noting different kinds of birds and wildlife.
While Pigafetta wrote his log, Magellan was deeply concerned about his authority. He was officially the supreme commander, but prior to departure, pressure from the Spanish authorities had forced him to accept a nobleman, Juan de Cartagena, as the voyage’s second-in-command. This decision led to violent power struggles during the voyage. Early on, Magellan was forced to arrest and demote Cartagena for insubordination. As a royal appointee, he was otherwise untouchable, but his resentful presence would prove nearly catastrophic for Magellan later.
The coast of modern-day Brazil, which Europeans had only been aware of for 20 years, was a source of wonder. But it was its inhabitants that captured Pigafetta’s attention most. He recorded in his journal that some of the people of “Verdin” (as he called it)
live a hundred, or a hundred and twenty, or a hundred and forty years, and more; they go naked, both men and women. Their dwellings are houses that are rather long . . . [and] in each of these houses . . . there dwells a family of a hundred persons, who make a great noise. In this place they have boats, which are made of a tree, all in one piece, which they call “canoo.” These are not made with iron instruments, for they have not got any . . . Into these thirty or forty men enter.
Pigafetta’s writings revealed a condescending attitude toward the indigenous peoples. His descriptions of the peoples he meets in Patagonia, the Pacific Islands, and lands in Asia are centered on the amount of clothing worn, physical traits including skin color, height, and build, and whether they could be converted to Christianity. He recorded certain words from their languages, many of which related to commodities that could be of use to colonial Spain. ( See a shipwreck from explorer Vasco da Gama's fleet. )
The small armada sailed south, scanning for any strait or opening in the great landmass to starboard. A great inlet in early 1520 aroused much excitement. Once it had been ascertained it was not the longed-for strait, but a river mouth (the Río de la Plata), the fleet continued south to San Julián, where, in April, surrounded on all sides by the frozen expanse of Patagonia, a full-scale mutiny was launched against Magellan by the captains of the four other ships.
Played out across five vessels, the scenes were chaotic and confusing, but Magellan prevailed. In the ensuing skirmishes, the rebellious captains of the Victoria and the Concepción were arrested and executed. One of the leaders of the revolt was the demoted and resentful Juan de Cartagena. Magellan opted to maroon him on an island, thus avoiding shedding the blood of a powerful nobleman, while also ridding himself of an incompetent troublemaker. Cartagena’s fate is unknown, but other mutineers were pardoned, including one of the officers, Juan Sebastián Elcano.
You May Also Like

Magellan got the credit, but this man was first to sail around the world

Has Amelia Earhart’s plane really been found? 6 key things to know

This legendary Polynesian canoe will sail 43,000 miles, from Alaska to Tahiti
Shortly after the failed mutiny, as resentments still simmered, Magellan lost the Santiago in a storm. Unbowed, the reduced fleet continued south until glacial conditions forced a halt for two months to provision; then it set out once more. Finally, as Pigafetta records on “the day of the feast of the eleven thousand virgins,” St. Ursula’s Day which falls on October 21, they sighted a strait “surrounded by lofty mountains laden with snow... Had it not been for the captain-general, we would not have found that strait, for we all thought that it was closed on all sides.”
For over a month, buffeted by storms and currents, the fleet ventured down the strait that Charles V would later name for Magellan. The commander named an archipelago they saw on the south side Tierra del Fuego (“land of fire”) in reference to the many bonfires lit there by its indigenous hunter-gatherer peoples, who had occupied this tip of South America for millennia.
In the course of this passage, another ship disappeared: the San Antonio . Pigafetta records it had been believed lost; in fact, it had deserted and was returning to Spain. Equipped now with only three vessels, Magellan and his men “on Wednesday, November 28, 1520, . . . debouched from that strait, engulfing . . . in the Pacific Sea.” They were the first Europeans to enter that vast ocean from its eastern shore.
Hard crossing
After being borne northward along what is today the Chilean coast, Magellan’s fleet finally struck out northwest in search of land beyond. Magellan knew that the Malay archipelago he had visited years before must lie somewhere to the west. To find it, the limping expedition had to sail through rough seas for over three months.
Hunger and disease stalked the crossing. Pigafetta records how he and his crewmates ate sawdust, ox hides, and “biscuit, which was no longer biscuit, but powder of biscuits swarming with worms, and which stank strongly of the urine of rats.” General privation, the lack of food, and illness greatly reduced their numbers. Perhaps the most devastating was scurvy, the distinctive symptoms of which Pigafetta captured: “[I]t was that the upper and lower gums of most of our men grew so much that they could not eat, and in this way so many suffered, that nineteen died.” ( Scurvy killed more people than the American Civil War. )
Savaged by scurvy
While crossing the Pacific, Pigafetta recorded how many of Magellan’s crew seemed to waste away from a horrific illness: Their gums bled, their limbs ulcerated, and delirium addled their minds. Scurvy and its symptoms, which are caused by a lack of vitamin C, would ravage many European expeditions. The captain who completed the Magellan expedition, Juan Sebastián Elcano, succumbed to scurvy on a later voyage, and it killed an estimated two million sailors between the 15th and 18th centuries. The medical properties of vitamin C were not discovered until the 1920s, but it became common wisdom in the 1700s that citrus fruit could be a preventative, a remedy that was resisted by some in the British Navy. It was not until the 1790s that fruit was distributed routinely among crews.
On March 6, 1521, after 100 days in Pacific waters, the exhausted armada finally was able to make landfall in the Mariana Islands where they restocked the ships and then continued west. Days later, they reached an archipelago (later christened the Philippines by another Spanish explorer) of many inhabited islands that Magellan would attempt to claim for Spain. The crew celebrated mass on the island of Limasawa in late March and then converted the rulers of Cebu Island to Christianity.
Magellan heard that rivals of the Becu who lived on the nearby island of Mactan refused to convert and submit to Spain. Magellan tried to claim their land for Spain and their souls for the church, but the occupants of Mactan Island, led by the chieftain known traditionally as Lapulapu, stood firm in the face of Spanish guns and swords. On April 27, 1521, Magellan led 60 men to the island with an ultimatum to surrender. The islanders refused, and a fierce battle ensued, which Pigafetta recounted:
When we reached land we found the islanders fifteen hundred in number . . . they came down upon us with terrible shouts . . . seeing that the shots of our guns did them little or no harm [they] would not retire, but shouted more loudly, and . . . at the same time drew nearer to us, throwing arrows, javelins, spears hardened in fire, stones, and even mud, so that we could hardly defend ourselves.
Pigafetta reported that Magellan was killed by Lapulapu and his warriors on the shore. Despite Spanish firepower, the islanders quickly overcame the invaders with their numbers and bravery and drove them back. The Europeans retreated, leaving their commander to die on the beach; Magellan’s body was never recovered. Later, the king of Cebu would turn against the Europeans, too, and kill 26 of them. The remaining Europeans soon departed.
Their numbers dwindling, the surviving crew, under the command of Juan Sebastián Elcano, did finally reach the Moluccas in November 1521. They were able to stock up the ships with spices and goods to bring back to Spain. Having been forced to abandon two of their three remaining ships, the crew would return to Spain in a fleet of one—the Victoria . Ten months later, the ship and its bedraggled crew of 18, including Pigafetta, entered Seville’s harbor. ( Who really discovered Antarctica? )
Final frontier
The first continuous circumnavigation of the world was complete. It took almost exactly three years and, surprisingly, turned a profit. The 381 sacks of cloves brought back by the Victoria were worth more than all five ships that had set out on the voyage. Despite the hopes and funds invested, it did not translate into immediate meaningful economic benefits for Spain. The treacherous course around the tip of South America was never a practical route for trade with the Moluccas.
Despite the death and destruction brought on by the voyage, many historians believe Magellan’s expedition was a worthy accomplishment. The careful records kept by Pigafetta and others dramatically expanded Europe’s knowledge of the world beyond the Atlantic, giving cartographers a firm sense of the world’s actual size and future navigators intelligence on the conditions and currents of the Pacific Ocean. Europeans had known of the eastern shore of the Pacific since 1513, but Magellan revealed its sheer size and power, knowledge that transformed Europeans’ understanding of the extent of the globe.
Related Topics
- CIRCUMNAVIGATION
- IMPERIALISM
- AGE OF DISCOVERY

Mass grave found in Fiji sparks a mystery: cannibalism or contagion?

Who gets to claim the ‘world’s richest shipwreck’?

Queen Elizabeth I's favorite pirate was an English hero, but his career has a dark side

Was Napoleon Bonaparte an enlightened leader or tyrant?

See scenes from classic fairy tales—with a Nigerian twist
- Environment
- Perpetual Planet
- History & Culture
History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In search of fame and fortune, Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan (c. 1480-1521) set out from Spain in 1519 with a fleet of five ships to discover a western sea route to the Spice Islands.
The Magellan expedition, sometimes called the Magellan-Elcano expedition, was an early 16th-century Spanish expedition planned and led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan with the objective of crossing the Atlantic and Pacific oceans in order to open a trade route with the Moluccas ("Spice islands"). The expedition departed from Spain in 1519 and returned there in 1522, completed by the ...
Ferdinand Magellan (born 1480, Sabrosa or Porto?, Portugal—died April 27, 1521, Mactan, Philippines) was a Portuguese navigator and explorer who sailed under the flags of both Portugal (1505-13) and Spain (1519-21). From Spain, he sailed around South America, discovering the Strait of Magellan, and across the Pacific.Though he was killed in the Philippines, one of his ships continued ...
Ferdinand Magellan (/ m ə ˈ ɡ ɛ l ə n / mə-GHEL-ən or / m ə ˈ dʒ ɛ l ə n / mə-JEL-ən; Portuguese: Fernão de Magalhães, IPA: [fɨɾˈnɐ̃w̃ dɨ mɐɡɐˈʎɐ̃j̃ʃ]; Spanish: Fernando de Magallanes, IPA: [feɾˈnando ðe maɣaˈjanes]; c. 1480 - 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East Indies ...
The route of the Victoria, which completed the world's first recorded circumnavigation over about 3 years.. The Magellan expedition (10 August or 20 September 1519 - 6 September 1522) was the first voyage around the world in human history. It was a Spanish expedition that sailed from Seville in 1519 under the initial command of Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese sailor, and completed in 1522 ...
Definition. Ferdinand Magellan, or Fernão de Magalhães (c. 1480-1521), was a Portuguese mariner whose expedition was the first to circumnavigate the globe in 1519-22 in the service of Spain. Magellan was killed on the voyage in what is today the Philippines, and only 22 of the original 270 crew members made it back to Europe.
Voyages of Ferdinand Magellan (1519-22) and Francis Drake (1577-80) across the Atlantic Ocean and around the globe. After Magellan's death only two of the ships, the Trinidad and the Victoria, reached the Moluccas. Gonzalo Gómez de Espinosa, Magellan's master-at-arms, attempted to return to Spain on the Trinidad, but it soon became ...
Magellan was convinced he could sail around those continents and easily reach this ocean, accessing the Spice Islands beyond. A posthumous portrait of Ferdinand Magellan, painted c. 16th or 17th century ; a 1516 map of the known world at the time of Magellan's voyage (right).
On Sept. 20, 1519, Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, with five ships and a crew of 270 men, set sail from Sanlucar de Barrameda in southern Spain, on what would become the first circumnavigation of the world. Magellan himself died during the tumultuous three year voyage, with Spaniard Juan Sebastian Elcano completing the journey from the ...
The Voyage Around the World In 2019, Spain celebrated 500 years since 5 ships set sail from Seville, heading west in search of a new route to the spices of the east. Around 250 men from at least 9 different countries began the journey, which was funded by the Spanish monarch King Charles I. ... Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese-born sailor ...
Half-length portrait of Ferdinand Magellan (circa 1580-1521), first European to circle the globe. The Mariners Museum 1949.0619.000001. Introduction. Ferdinand Magellan is known for circumnavigating - sailing around - the world. From Spain he sailed around South America, discovering the Strait of Magellan, and across the Pacific.
Starting for a Trip around the World. The provided fleet consisted of five ships of which the flagship Trinidad sailed under Ferdinand Magellan's command. The crew consisted of 270 men across the continent and took off on August 10, 1519. The ships sailed from Seville down the Guadalquivir, at its mouth near Sanlúcar de Barrameda, where the ...
One of Ferdinand Magellan's five ships—the Victoria—arrives at Sanlúcar de Barrameda in Spain, thus completing the first circumnavigation of the world. The Victoria was commanded by Basque ...
Ferdinand Magellan set off from Spain 500 years ago on an epoch-making voyage to sail all the way around the globe for the first time. The Portuguese explorer was killed by islanders in the ...
Discover the life of Ferdinand Magellan and the first voyage around the world. The Age of Exploration saw the achievement of incredible feats with the voyages of European expeditions. Perhaps the most famous of them all is the arrival of Christopher Columbus to the Americas, but many other expeditions are equally groundbreaking.
Ferdinand Magellan, or Fernão de Magalhães (c. 1480-1521), was a Portuguese mariner whose expedition was the first to circumnavigate the globe in 1519-22 in the service of Spain. Magellan was killed on the voyage in what is today the Philippines, and only 22 of the original 270 crew members made it back to Europe. More about: Ferdinand Magellan.
Quick Facts: Magellan's Voyage Around the World. Map of Ferdinand Magellan's voyage around the world. More. Vocabulary; Original "EXPLORATION through the AGES" site
In 1519, Ferdinand Magellan set off on an audacious journey around the globe. Find out what made the expedition so dangerous—and why its leader did not survive. By: Patrick J. Kiger
Around the World. In 1519, Ferdinand Magellan set sail from Spain with five ships to find a western route to the Moluccas. Battling storms, mutinies, and the unknown, Magellan died before reaching ...
500 years on, how Magellan's voyage changed the world. Ferdinand Magellan set off from Spain 500 years ago on an epoch-making voyage to sail all the way around the globe for the first time. The ...
The Magellan expedition, also known as the Magellan-Elcano expedition, was the first voyage around the world. It was a 16th century Spanish expedition initially led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan to the Moluccas, which departed from Spain in 1519, and completed in 1522 by Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, after crossing the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans, culminating ...
HISTORY MAGAZINE. 240 men started Magellan's voyage around the world. Only 18 finished it. The explorer died on a Philippines beach in April 1521, joining the scores who perished in Spain's quest ...
Illustration. by Sémhur & Uxbona. published on 14 June 2021. Download Full Size Image. A map of the 1519-22 circumnavigation - the first in history - made by the expedition led by the Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan (c. 1480-1521). Remove Ads.