
How frequently can I visit the United States as a visitor (B1/B2) and how long can I stay for each visit?


- Immigration
Tourist Visa Duration: How Long Can I Stay in the U.S.?
If you are visiting the u.s. on a tourist visa, you can stay for a maximum of six months. however, the actual length of stay is determined by the u.s. customs and border protection officer at the port of entry. it's important to adhere to the authorized duration to avoid any immigration issues..

Quick Glance:
- Understanding the B-2 tourist visa : Stay in the U.S. for up to six months, determined by CBP officer.
- Extension of stay possible with proof of temporary visit, intention to leave, and financial means.
- Overstaying can lead to deportation or difficulty obtaining future U.S. visas; consult USCIS for emergencies. Have you ever dreamed of exploring the vast landscapes of the United States, delving into its rich culture, or perhaps visiting its iconic landmarks? Well, if a holiday or a short visit is on your mind, obtaining a tourist visa might be your first step to making that dream a reality. But once you have that visa in hand, an important question arises: How long can you actually stay in the U.S. with it?
Understanding Your Tourist Visa Duration
The tourist visa , technically known as the B-2 visa, is what non-U.S. citizens need for vacationing or for certain non-business activities in the U.S. While the excitement of getting the visa is quite understandable, it’s crucial to know the rules and limits to avoid any hiccups in your travel plans.
A standard piece of advice given to tourists is, “Your stay should align with the purpose of your visit.” But let’s make it more clear. Under a tourist visa, you can generally stay in the United States for up to six months. However, the exact length of stay is determined by the Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer at your point of entry.
When you arrive, the CBP officer will record your arrival, and, crucially, the allowed duration of your stay on a form called the I-94. The I-94 form serves as evidence of your legal visitor status in the country. You should keep track of this date because overstaying can lead to some serious consequences.
Extension of Stay
So what happens if you find yourself wanting to bask in the U.S. sights for a bit longer? Good news! You can apply for an extension of stay. But remember, this extension is not guaranteed. You must show that:
- The extended visit is temporary
- You intend to leave at the end of the extended period
- You have the financial means to support your extended stay

Also of Interest:
H-1b amended petitions: top 20 faqs, get your aos approval explained: what it means for you.
For this process, use Form I-539, Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status before your authorized stay expires.
Overstaying Is a No-No
Now, let’s talk about overstaying your welcome. It’s a serious issue that can affect your ability to return to the United States in the future. If you stay beyond the period authorized by the CBP officer, you could be deported, or find it difficult to obtain a U.S. visa down the line.
But life is unpredictable, right? If there is an emergency or unexpected reason that requires you to overstay, reach out to the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) immediately for guidance.
Pro Tips for a Stress-Free Visit
Here are a few handy tips to keep your tourist experience smooth and enjoyable:
- Know your permitted stay: always check the departure date on your I-94 form.
- Plan for extensions: if you think you might want to extend your trip, apply well in advance of your I-94 expiration date.
- Maintain good records: keep all your travel, support, and immigration documents organized and handy.
For additional information or any assistance, you should consult the U.S. Department of State website or reach out to the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate.
Discovering the United States can be the adventure of a lifetime. Whether you’re awe-struck by the glittering lights of New York City, the majestic Grand Canyon, or the sunny beaches of California, understanding the conditions of your tourist visa can help ensure your visit is as carefree as possible. So, remember the guidelines, adhere to the rules, and most importantly, enjoy your travels across the U.S.
Don’t forget: The key to a perfect trip is good planning and following the rules – your passport to creating lasting memories. Safe travels!
There you have it, my fellow travel enthusiasts! Now you know the ins and outs of staying in the United States with a tourist visa. Just remember to check your I-94 departure date, plan for extensions in advance, and keep those immigration documents organized. And if you want even more handy tips and advice, head over to visaverge.com. Bon voyage, my friends!
FAQ’s to know:
FAQ 1: How long can I stay in the United States with a tourist visa (B-2 visa)?
Answer: With a tourist visa (B-2 visa), you can generally stay in the United States for up to six months. The exact length of stay is determined by the Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer at your point of entry. They will record the allowed duration of your stay on the I-94 form, which serves as evidence of your legal visitor status. It’s crucial to keep track of this date to avoid overstaying and potential consequences.
FAQ 2: Can I extend my stay in the United States with a tourist visa?
Answer: Yes, it is possible to apply for an extension of stay if you want to stay in the United States a bit longer. However, this extension is not guaranteed and must meet certain criteria. You must show that the extended visit is temporary, that you intend to leave at the end of the extended period, and that you have the financial means to support your stay. To apply for an extension, you need to use Form I-539, Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status before your authorized stay expires.
FAQ 3: What are the consequences of overstaying a tourist visa in the United States?
Answer: Overstaying your welcome on a tourist visa in the United States is a serious issue with potential consequences for future visits. If you stay beyond the period authorized by the CBP officer, you could be deported and face difficulties obtaining a U.S. visa in the future. It’s essential to adhere to the authorized duration of your stay and reach out to the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) immediately in case of emergency or unexpected reasons that require you to overstay for guidance.
What did you learn? Answer below to know:
- How long can you stay in the United States with a tourist visa? a) Up to one year b) Up to six months c) Indefinitely d) As long as you want
- What form is used to record the allowed duration of your stay on a tourist visa? a) I-130 b) I-539 c) I-94 d) I-20
- What are the consequences of overstaying your authorized stay in the United States? a) Deportation b) Difficulty obtaining future U.S. visas c) Both a) and b) d) No consequence
Did you Know?
Did you know.
- Did you know that the United States has the highest number of immigrants in the world? As of 2021, there are approximately 44.9 million immigrants living in the U.S., accounting for about 13.7% of the total population.
- Did you know that the United States has a long history of immigration? Between 1820 and 2019, over 100 million immigrants arrived in the U.S. This massive influx of people from different parts of the world has shaped and diversified American society and culture.
- Did you know that the majority of international migrants move to high-income countries? According to the United Nations, around two-thirds of all international migrants reside in high-income countries, with the United States, Germany, and Saudi Arabia being popular destinations.
- Did you know that India has the highest number of emigrants? As of 2020, India tops the list of countries with the most emigrants, with over 18 million Indian-born individuals residing in other countries.
- Did you know that immigrants make significant contributions to the U.S. economy ? According to the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, immigrants contribute more in taxes and social contributions than they receive in benefits, playing a vital role in sustaining economic growth and innovation.
- Did you know that many Fortune 500 companies were founded by immigrants or their children? Brands like Google, Apple, Amazon, and Tesla were established by immigrants or their descendants, showcasing the entrepreneurial spirit and economic impact of immigrants in the United States.
- Did you know that the United States has historically been a top destination for refugees? In the fiscal year 2020, the U.S. resettled over 11,800 refugees, providing a safe haven to individuals fleeing persecution and violence in their home countries.
- Did you know that seeking asylum is a legal right protected by international law? The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights recognizes the right to seek asylum from persecution. People seeking asylum often undergo complex legal processes to establish their eligibility for protection.
- Did you know that the United States has a Diversity Visa Lottery program? Each year, the U.S. government randomly selects approximately 55,000 individuals from countries with low immigration rates to receive permanent residency in the U.S. This program aims to promote diversity and provide opportunities for individuals from underrepresented regions.
- Did you know that the chances of winning the Diversity Visa Lottery are slim? With millions of applicants each year, the odds of being selected are less than 1%. However, for the lucky winners, it can be a life-changing opportunity to start a new chapter in the United States.
There is so much more to learn about immigration and its impact on societies worldwide. These fascinating facts shed light on the diverse nature of immigration and its significance in shaping the countries we live in today. Let’s continue exploring the intricacies of immigration and celebrate the contributions and stories of individuals who have embarked on extraordinary journeys in search of a better future.
Learn Today: Key Terms Explained
Glossary or Definitions:
- B-2 Visa: Also known as the tourist visa, it is a non-immigrant visa that allows non-U.S. citizens to visit the United States for tourism or certain non-business activities.
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP): The agency within the Department of Homeland Security responsible for managing the security and control of the U.S. borders, including the inspection of travelers at ports of entry.
I-94 Form: A form issued by CBP to non-U.S. citizens upon arrival in the United States. It records the individual’s arrival and departure dates, as well as the authorized duration of their stay. It serves as evidence of their legal visitor status in the country.
Extension of Stay: The process by which individuals on certain non-immigrant visas, such as the B-2 visa, can apply to extend their authorized period of stay in the United States.
Form I-539: An application form used to request an extension of stay or a change in non-immigrant status. It is commonly used by individuals on B-2 visas to apply for an extension of stay.
Overstaying: The act of staying in the United States beyond the period authorized by the CBP officer. Overstaying can have serious consequences, including deportation and difficulties obtaining future U.S. visas.
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS): The agency within the Department of Homeland Security responsible for administering immigration benefits and services, including processing of applications for extensions of stay and changes in non-immigrant status.
U.S. Department of State: The federal executive department responsible for implementing U.S. foreign policy and managing diplomatic relations with other countries. It provides information and guidance on U.S. visas and immigration-related matters.
U.S. Embassy or Consulate: A U.S. government facility located in foreign countries that represents the United States and provides various consular services, including visa processing and assistance to U.S. citizens abroad.
I-130 Form: A form used for family-based immigrant visa petitions. It is not directly related to the tourist visa and not applicable to temporary visits.
I-20 Form: A form used for student visa applications ( F-1 visa ). It is not directly related to the B-2 visa for tourist visits.
Acronyms: CBP (Customs and Border Protection), USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services)
Jargon: Non-immigrant visa, Legal visitor status, Non-immigrant status
Still Got Questions? Read Below to Know More
I came to the u.s on a tourist visa and found a short course that i’d like to take, which extends a bit beyond my allowed stay. is it possible to extend my b-2 visa for educational purposes, or do i need a different type of visa for that.
If you entered the U.S. on a B-2 tourist visa and found a short course you want to take, it is important to understand the limitations and requirements of your visa status. In general, the B-2 visa is intended for tourism, pleasure, or medical treatment, and enrolling in a course of study is not typically permissible if it’s a full-time program that leads to an academic or vocational degree. However, for a recreational or vocational short course that does not provide a degree or academic credit, you might be able to attend while on a B-2 visa as long as the course is less than 18 hours a week.
If the course you intend to take extends beyond your allowed stay, you would need to apply for an extension of your B-2 visa by filing Form I-539, “Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status,” with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). You need to apply before your authorized stay expires, and you should include in your application the reasons for your request and evidence of your financial support during the extended stay (such as bank statements or a letter of support from friends or relatives).
If the course does not fit the criteria for incidental study on a B-2 visa, or you’re looking to enroll in a longer program or one that grants academic credit, you might require a different type of visa, such as the F-1 student visa. In that case, you would need to apply to and be accepted by a U.S. Student and Exchange Visitor Program (SEVP)-certified school, receive a Form I-20, and then apply for a change in visa status. For more information on changing your nonimmigrant status and the specific requirements for student visas, you can visit the official USCIS website:
- Change My Nonimmigrant Status
- Study in the States
My aunt on a tourist visa wants to undergo a medical treatment in the U.S. that may take longer than six months. How can she ensure that she stays legally throughout her medical treatment
Your aunt can ensure she stays legally in the U.S. for her medical treatment by applying for a B-2 visa extension. The B-2 visa is designed for tourists, and medical treatment is an allowable purpose for visiting. Here’s a step-by-step process she can follow:
- Before her visa expires , she should file Form I-539, Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status, with USCIS . This form can be found on the official USCIS website: Form I-539 .
- A letter from a medical professional or institution detailing the nature of the treatment, expected duration, and why it’s necessary for her to remain in the U.S.
- Proof that she has the financial means to pay for the treatment and support herself during her stay.
- A statement explaining her intent to return to her home country after the treatment.
It’s important to apply for the extension well in advance because if her visa expires while her application is pending, she generally may stay in the U.S. for up to 240 days while awaiting a decision or until the date on her I-94 expires, whichever is shorter. However, it is advisable not to wait until the last minute.
“USCIS must receive the Form I-539 application before your authorized stay expires,” as stated on the USCIS website.
Remember that approval is not automatic, and the decision is at the discretion of USCIS. In case her situation changes or unexpected delays occur, keeping USCIS updated and maintaining valid legal status is crucial. If her application is denied, she must prepare to leave the United States immediately to avoid accruing unlawful presence.
For additional guidance, it’s often helpful to consult with an immigration attorney or a legal aid organization that can provide personalized advice based on her specific situation. This external resource from USCIS offers further information on extending your stay: Extend Your Stay .
I want to visit my grandchildren for their graduation and summer break, which is about 7 months total. Can I apply for a B-2 visa extension before I travel to cover the entire period, or must I wait until I’m in the U.S. to do so
If you plan to visit your grandchildren in the United States for their graduation and summer break, which totals around 7 months, you would typically enter the country on a B-2 tourist visa. A B-2 visa is generally granted for short-term stays for purposes such as tourism, visiting family, and receiving medical treatment.
Initially, when you apply for a B-2 visa, you cannot apply for an extension before your travel. Your authorized period of stay would be determined by the Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer when you arrive at a U.S. port of entry . Most visitors are admitted for 6 months, although the CBP officer has the discretion to grant a shorter or longer period of stay up to 1 year.
If you find that the duration of your approved stay is not sufficient, you can request an extension of your B-2 status by filing Form I-539, Application To Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status, before your authorized stay expires. You must submit this form to U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) with all required documentation and the applicable fee. It’s important to file for the extension before your current authorization ends to avoid violating immigration laws. For more information on B-2 visa extensions, visit the official USCIS website: USCIS – Extend Your Stay .
- The decision to grant an extension is not guaranteed and is at the discretion of USCIS.
- You should have a valid reason for requesting an extension and provide evidence to support your request.
- Filing for an extension doesn’t allow you to stay beyond the expiration date of your original authorized stay until a decision is made. If your request is denied, you may be required to leave the United States immediately.
If my flight back home gets canceled due to sudden travel bans and my B-2 visa expires soon, what are my options to avoid overstaying in the U.S. legally
If you find yourself in a situation where your flight back home gets canceled due to sudden travel bans and your B-2 visa is about to expire, it is important to take timely action to avoid overstaying in the U.S. Here are your options:
“USCIS must receive your I-539 application before your current authorized stay expires. However, we recommend that you file as soon as you determine that you need to extend your stay.” – U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services
Keep Evidence of Canceled Flights and Travel Restrictions : If you apply for an extension, it’s important to keep records of any canceled flights and official notices about travel bans affecting your return. This documentation can support your case for needing an extension.
Consider Other Legal Avenues : In extreme cases, if you cannot leave because of extraordinary circumstances beyond your control and if your visa is about to expire, consider looking into humanitarian or significant public benefit parole, although these options are rare and used in exceptional circumstances.
For the most up-to-date information and steps to take, visit the official U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) website or contact their support directly: – For information on how to file the Form I-539, visit the USCIS page at Extend Your Stay . – For further advice or exceptional cases, consult the USCIS Contact Center at USCIS Contact Center .
Remember to act promptly and keep all your communications and filings with USCIS well-documented to protect your immigration status.
I am in the U.S. on a B-2 visa and have met someone I want to marry who is a U.S. citizen. Can I change my status to a fiance visa while I’m here, or do I need to return to my home country and apply from there
If you are currently in the U.S. on a B-2 visa and have decided to marry a U.S. citizen, it is generally not necessary for you to change to a fiancé(e) visa, formally known as a K-1 visa. Instead, you have the option to get married and directly apply for an adjustment of status to become a lawful permanent resident (i.e. get a Green Card).
Here are the basic steps you would need to follow:
- Get married to your U.S. citizen partner : You must have a legally valid marriage in the state where you got married.
- File Form I-485 : Your partner, as a U.S. citizen, can file a Form I-130 (Petition for Alien Relative) concurrently with your Form I-485 (Application to Register Permanent Residence or Adjust Status). You can find the forms and instructions on the USCIS website .
- Attend the interview and await approval : After filing your paperwork, you will need to go through a biometrics appointment and an interview with United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). If approved, you’ll be granted a Green Card.
It’s important to comply with all USCIS guidelines and ensure that you did not misrepresent your intentions upon entering the U.S. with a B-2 visa, as this could affect your eligibility. The USCIS policy states:
“An individual who comes to the U.S. as a visitor and then decides to get married and remain in the U.S. will generally not be accused of visa fraud. However, if the U.S. government believes that the individual misrepresented their intentions, there could be serious consequences.”
Make sure you stay well-informed about the latest immigration procedures and policies by regularly checking the official USCIS website .
If you are unsure about your situation or require further assistance, it is advisable to consult with an immigration attorney who can provide guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Verging Today

The Dark Side of Desi Consultancies in the USA

How to Check Your H-1B Lottery Results: Step-by-Step Guide

Traveling to Canada from the US as a Green Card Holder: Do I Need a Visa?

H-1B 2025: Will There Be a Second Lottery?

U.S. Visa Invitation Letter Guide with Sample Letters
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Winter is here! Check out the winter wonderlands at these 5 amazing winter destinations in Montana
- Travel Destinations
- United States
How Long Can I Stay In The US On A Tourist Visa?
Published: November 7, 2023
Modified: December 28, 2023
by Melba Merryman
- Plan Your Trip
Introduction
Welcome to the United States, a country renowned for its diverse landscapes, vibrant cities, and rich cultural heritage. If you’re planning a visit to this mesmerizing country, one of the first things you’ll need to consider is your travel documentation. For many tourists, a visitor or tourist visa is the key to exploring the wonders of the United States.
A tourist visa allows individuals from foreign countries to enter the United States temporarily for the purpose of tourism, pleasure, or visiting friends and family. It grants visitors the opportunity to experience the iconic landmarks, indulge in the culinary delights, and immerse themselves in the unique traditions that define this nation.
In this article, we will delve into the details of how long you can stay in the United States on a tourist visa. From the duration of stay to the visa waiver program, we will explore various aspects that will help you plan your trip effectively and stay within the bounds of the law.
Before we embark on this journey, it’s important to note that immigration regulations can change over time, so it’s always wise to consult the official U.S. Department of State website or seek advice from an immigration attorney to ensure you have up-to-date and accurate information.
So, let’s dive in and uncover how long you can stay in the U.S. on a tourist visa!
What is a tourist visa?
A tourist visa is a type of non-immigrant visa that allows individuals from foreign countries to enter the United States for a temporary period of time for tourism, pleasure, or to visit friends and family. It is typically issued for a specific duration, allowing visitors to explore the country and engage in various recreational activities.
Obtaining a tourist visa requires applicants to demonstrate their intent to return to their home country after their visit and that they have sufficient funds to support themselves during their stay. The application process involves submitting the necessary documentation, such as a valid passport, visa application forms, and any supporting documents required by the U.S. embassy or consulate.
It’s important to note that a tourist visa does not grant individuals the right to work or study in the United States. If you intend to engage in activities that go beyond the scope of tourism, such as attending conferences or pursuing educational opportunities, you may need to apply for a different type of visa that suits your specific purpose.
The validity of a tourist visa varies and is determined by the U.S. embassy or consulate. Generally, tourist visas are valid for multiple entries within a set period, often ranging from three months to ten years. However, the duration of stay allowed on each entry is typically limited to a specific time frame, as determined by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer at the port of entry.
Understanding the limitations and regulations surrounding a tourist visa is crucial to ensure a smooth and enjoyable visit to the United States. Next, let’s explore the duration of stay allowed on a tourist visa.
Duration of stay on a tourist visa
The duration of stay on a tourist visa in the United States varies depending on several factors. When you arrive in the country, a U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer will determine how long you can stay by stamping your passport with an admission stamp. This stamp will indicate the date until which you are allowed to stay in the United States.
Typically, visitors on a tourist visa are granted a maximum initial period of stay of 6 months. However, the CBP officer has the discretion to grant a shorter period based on their evaluation of your circumstances. It’s essential to comply with the authorized duration of stay to avoid any legal issues or complications with future visits to the United States.
If you wish to extend your stay beyond the initial authorized period, you must apply for an extension with the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) before your authorized stay expires. The extension request must be supported by valid reasons, such as medical treatment, unforeseen emergencies, or exceptional circumstances. It’s crucial to file the extension request well in advance to allow sufficient processing time.
It’s important to note that even if you have a valid tourist visa, the CBP officer at the port of entry has the final authority to determine the duration of stay. They may grant a shorter period if they deem it necessary, and it’s essential to respect their decision and comply with the authorized stay.
If you overstay the authorized duration of stay on a tourist visa, you may be subject to penalties and future immigration difficulties. It is crucial to understand the consequences of overstaying, which we will explore in the next section.
Now that we understand the general duration of stay on a tourist visa, let’s explore the Visa Waiver Program, an alternative option for certain eligible travelers.
Visa Waiver Program
The Visa Waiver Program (VWP) is an alternative option for travelers from specific countries who wish to visit the United States for tourism or business purposes for a short duration. The VWP allows eligible individuals to enter the United States without obtaining a traditional visa, making the travel process more convenient and streamlined.
Currently, citizens or nationals of 39 countries, including the United Kingdom, Germany, Japan, Australia, and many others, are eligible to participate in the VWP. To qualify for the program, travelers must meet certain requirements, such as possessing a valid electronic passport, having a return or onward ticket, and obtaining authorization through the Electronic System for Travel Authorization (ESTA) prior to travel.
Under the VWP, visitors are typically granted a maximum stay of 90 days for tourism or business purposes. It’s important to note that this duration is non-extendable, and individuals must depart the United States within the specified timeframe to comply with the program’s regulations.
While the VWP offers a convenient way to travel to the United States without a visa, it’s crucial to be aware of the limitations and requirements of the program. Overstaying the allowed 90-day period or engaging in unauthorized activities can lead to serious consequences, including future travel restrictions and difficulties obtaining visas in the future.
If you are a citizen or national of a participating country in the VWP, it’s advisable to review the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the U.S. Department of State to ensure a smooth and hassle-free visit to the United States.
Next, let’s explore the options available for extensions and change of status for individuals who need to extend their stay beyond the authorized period on a tourist visa or under the VWP.
Extensions and Change of Status
If you find yourself needing to extend your stay in the United States beyond the authorized period on a tourist visa or under the Visa Waiver Program (VWP), there are certain options available to you.
For visitors on a tourist visa, you have the option to apply for an extension of stay with the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). This process involves filing Form I-539, Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status, along with the required supporting documents and applicable fees. It’s crucial to submit the extension request before your authorized stay expires to avoid any legal complications.
The USCIS will review your extension request and consider the specific circumstances presented. Valid reasons for an extension may include medical treatment, unforeseen emergencies, or exceptional situations that necessitate a longer stay. The decision to grant an extension is determined on a case-by-case basis, and it’s important to provide compelling evidence and explanations to support your request.
Similarly, if you are in the United States under the Visa Waiver Program (VWP) and wish to extend your stay, you must apply for a change of status. This process involves submitting Form I-539 to the USCIS and providing the necessary documentation and fees. It’s important to note that the VWP does not allow for extensions, so you must transition to a different nonimmigrant status if you wish to stay longer.
It’s crucial to consult the official USCIS website or seek guidance from an immigration attorney to ensure you follow the correct procedures and meet all requirements when applying for an extension or change of status. Failing to do so may result in a denial of your request or even potential legal consequences.
Remember, it’s always better to plan your trip and anticipate your length of stay beforehand to avoid the need for extensions or changes in status. However, unforeseen circumstances can arise, and knowing the correct procedures will help you navigate through them smoothly.
Now, let’s explore the potential consequences of overstaying a tourist visa or the authorized period under the Visa Waiver Program.
Overstaying a Tourist Visa
Overstaying a tourist visa in the United States occurs when an individual remains in the country beyond the authorized period granted by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer at the port of entry. While it may seem like a minor offense, overstaying a visa can have serious consequences and impact future travel plans.
When you overstay a tourist visa, you violate the terms and conditions of your entry into the United States. The length of the overstay can vary, ranging from a few days to several months or even years. Regardless of the duration, it is important to address the situation promptly and take appropriate action.
Overstaying a visa can result in several negative consequences. Firstly, it can lead to a violation of U.S. immigration laws, potentially affecting your eligibility for future visas or entry into the United States. Overstays can result in a ban on re-entry, making it difficult or even impossible to visit the United States in the future.
Additionally, overstaying can have financial implications. For each day you overstay, you may be subject to fines and penalties. These fines can accumulate quickly and become a substantial financial burden. In some cases, individuals who overstay their visa may face deportation proceedings, which can further complicate matters and result in additional expenses.
Overstaying a visa can also impact your ability to change or adjust your immigration status while in the United States. If you overstay your authorized period, you may become ineligible for certain immigration benefits or pathways, making it harder to pursue opportunities such as working, studying, or obtaining a different type of visa.
It’s crucial to address any visa overstays promptly. If you realize that you have overstayed, it is advisable to consult with an immigration attorney or contact the appropriate immigration authority to discuss your options. They can provide guidance and assistance on how to rectify the situation and resolve any potential immigration issues.
Understanding the consequences of overstaying a tourist visa is essential to ensure compliance with U.S. immigration laws and to protect your future travel and immigration opportunities. Let’s now conclude this article by summarizing the key points discussed.
Consequences of Overstaying
Overstaying a tourist visa in the United States can result in various consequences, some of which can have long-lasting effects on your immigration status and future travel plans. It’s important to understand and be aware of the potential ramifications of overstaying to avoid any unnecessary difficulties or legal issues.
One major consequence of overstaying is the potential impact on future travel to the United States. When you overstay your authorized period, you violate U.S. immigration laws, which can result in a ban on re-entry. Depending on the duration of the overstay, you may be subjected to a three or ten-year bar from entering the country. This can significantly hinder your ability to visit the U.S. for tourism, business, or any other purposes.
In addition to travel restrictions, overstaying a visa can also have financial implications. For each day you exceed your authorized stay, you may be subjected to fines and penalties. These fines can accumulate quickly, resulting in a significant financial burden. Moreover, if you accrue a significant period of unlawful presence, you may be deemed inadmissible in the future, making it even more challenging to obtain a new visa or change your immigration status.
Overstaying can also impact your eligibility for certain immigration benefits and opportunities. If you overstay your visa, you may become ineligible for certain adjustment of status processes or other immigration benefits. This can limit your ability to pursue employment opportunities, attend educational programs, or apply for different visas in the future.
In some cases, overstaying can even lead to removal proceedings and deportation. If you are caught overstaying your visa, you may be subject to detention and removal from the United States. This can be an emotionally traumatizing experience and can have severe consequences on your future immigration endeavors.
It’s crucial to address any visa overstay issues promptly. If you have overstayed, it is advisable to consult with an immigration attorney or contact the appropriate immigration authority to discuss your options. They can provide guidance and assistance on how to rectify the situation and resolve any potential immigration issues.
Understanding the consequences of overstaying a tourist visa is paramount to ensure compliance with U.S. immigration laws and protect your immigration status in the future. It’s important to respect the authorized period on your visa or the Visa Waiver Program and take appropriate action within the designated time frame.
Now, let’s summarize the key points discussed in this article.
In conclusion, understanding the duration of stay on a tourist visa is essential for a smooth and enjoyable visit to the United States. Whether you are traveling on a traditional visa or under the Visa Waiver Program (VWP), it’s important to familiarize yourself with the regulations and limitations to ensure compliance with U.S. immigration laws.
A tourist visa grants individuals the opportunity to explore the wonders of the United States for a temporary period, typically up to six months. The duration of stay is determined by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer at the port of entry. It’s important to respect the authorized period and seek an extension if needed.
The Visa Waiver Program (VWP) provides an alternative option for eligible individuals from specific countries to visit the U.S. for up to 90 days without obtaining a traditional visa. However, it’s crucial to adhere to the 90-day limit and avoid overstaying to avoid any legal consequences or future travel restrictions.
If you find yourself needing to extend your stay or change your status, it is possible to apply for an extension or a change of status with the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). It’s important to understand the requirements and follow the correct procedures to ensure a valid and legal stay in the United States.
Overstaying a tourist visa or the authorized period under the Visa Waiver Program can have serious consequences, including travel restrictions, financial penalties, and potential inadmissibility in the future. It is crucial to address any visa overstays promptly and consult with an immigration attorney or the appropriate immigration authority for guidance and assistance.
By understanding the rules and regulations surrounding the duration of stay on a tourist visa, you can ensure a memorable and lawful visit to the United States. Remember to plan your trip accordingly, respect the authorized period, and seek appropriate extensions or changes of status as needed to enjoy your time in the U.S. without any legal complications.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Immigration help for your business
- News & Reports
- Guides: Individual immigration
B-1/B-2 Visitor Visa, Explained
Understanding the b visas for u.s. business and tourism, in this guide.
- How long does it take to get a B-1/B-2 visa?
- How many times can you visit the U.S. with a B-1/B-2 Visa?
- B-1/B-2 Visa Cost
- Can you change status from B1/B2?
- Required documents for a travel visa
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Boundless guides
- B-1/B-2 Visas
What is a B-1/B-2 visa?
A B-1/B-2 visa is a non-immigrant , visa that allows foreign nationals to travel to the United States temporarily for business (B-1), tourism (B-2), or a mix of both (B1/B2). This visa category is widely used for brief visits to the U.S. B visas are typically valid for up to 10 years from the issue date, and travelers to the U.S. can stay up to 180 days, with the option to return to the U.S. again after that time.
Take our 5-minute quiz to check your eligibility.
Learn how to increase your chance of travel visa approval, and get unlimited, live application support from start to finish.
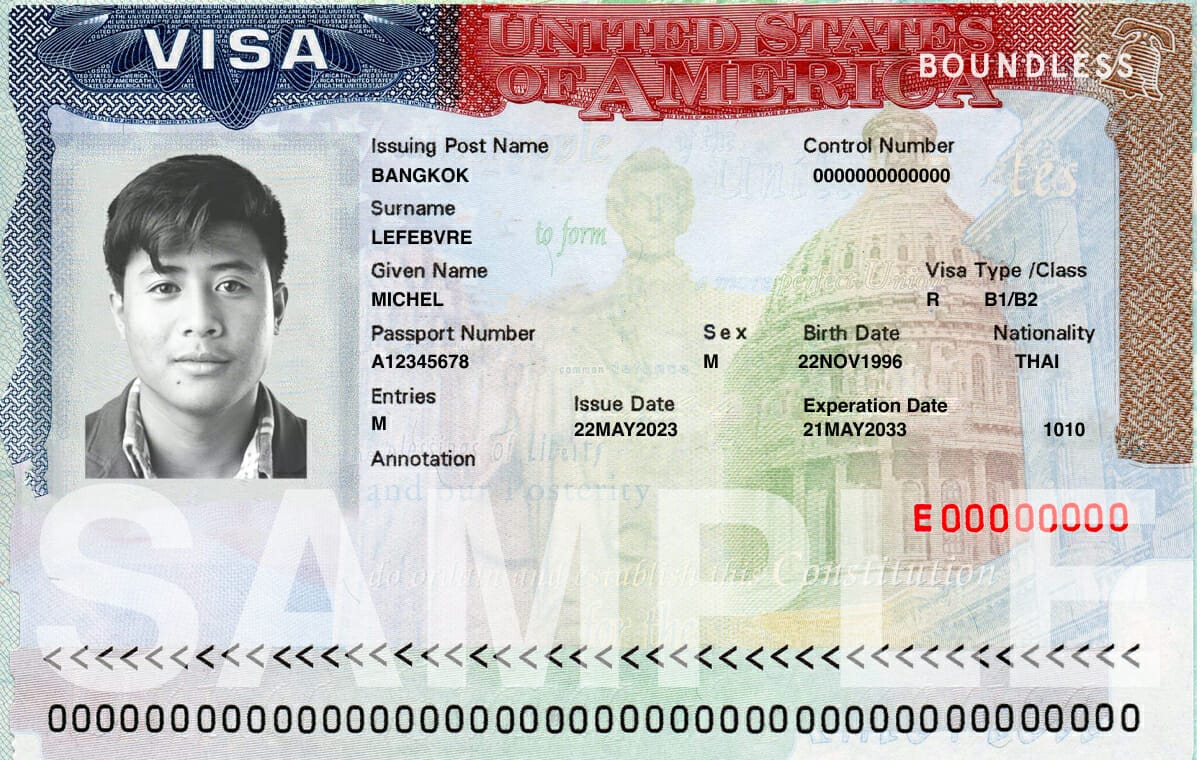
How long does it take to get a B-1/B-2 visa?
As of December 2023, the average wait time (processing time) for most B1/B2 visa interview appointments is between 2 months (Brazil) to 2+ years (Canada). To check the wait time for your specific embassy or consulate, enter your city in this handy State Department tool under the section “Appointment Wait Time.” Note that if you are applying for an interview in a country other than your home country, wait times may be longer.
How long can you stay in the USA on a B-1/B-2 Visa?
A maximum of 6 months may be obtained for any B-1/B-2 entry, with the possibility for extensions within the U.S. in qualifying cases. The exact duration varies per visa holder, but you can typically stay in the U.S. for up to six months. The B1/B2 visa is a multiple-entry visa, which means you can use it to enter the U.S. more than once. There’s no set limit to the number of times you can visit the U.S. in a year, and it depends on the specific circumstances and discretion of the CBP officers who review your case each time you enter.
It’s important to remember that the B1/B2 visa is intended for temporary, occasional visits for business, tourism, or medical treatment. It’s not meant to be used for living long-term in the U.S. or spending the majority of your time in the country.
What’s the difference between a B1 visa and a B2 visa?
The B1 is used for short business trips (conferences, meetings, contract negotiations, etc). Those with B1 visas cannot work in the U.S. in the traditional sense, as of March 2023, B1 or B2 visa holders can apply for jobs in the U.S. and attend interviews.
The B2 (tourist visa) is for tourism, vacation, or visiting friends and family. It also covers certain medical treatments and participation in social events or contests, like music or sports, without receiving pay. In most cases, a B1/B2 visa is issued together, allowing the holder to travel for both business and pleasure.
How many times can you visit the U.S. with a B-1/B-2 Visa?
Depending on the context, the number of times you can visit the U.S. with a B visa varies. B1B2 visas are multiple-entry, meaning they can be used to enter the U.S. more than once. There’s no set limit to the number of times you can visit the U.S. in a year, and it depends on the specific circumstances and discretion of the CBP officers who review your case each time you enter.
If officers think you’re trying to live in the U.S. through frequent or extended visits, or if you’re not maintaining significant ties to your home country, they may suspect you’re misusing the visa, which could lead to denial of entry or future visa issues.
While there’s no official limit, it’s vital to respect the purpose and restrictions of your visa to avoid any problems. If you need guidance on your specific situation, it’s a good idea to consult with an immigration expert.
Currently, the government filing fee for a B visa is $185, which does not include the cost of gathering documents and evidence and acquiring passport photos.
Boundless has helped more than 100,000 people navigate the visa application process, and we’ll help you make a travel visa plan based on your unique situation. Get started today!
B visa requirements
A B1/B2 visitor visa is for many types of trips to the U.S., including business and non-business activities like tourism. If you want to apply for a B1 or B2 visa, you need to prove that your trip to the U.S. is only for a short time.
You must also show proof that you plan to return to your home country after your visit, and that you have a place to live outside the U.S. that you will not leave for good. These points help show that you will follow the rules of the B1/B2 visa.
Reasons for travel under a B1 visitor visa include:
- Business consultations : This might include meetings, negotiations, or discussions with business associates in the U.S.
- Attending conferences or seminars : This can cover professional, educational, scientific, or business conventions.
- Settling an estate : If someone inherits property or assets in the U.S., a B1 visa can allow them to handle these matters legally.
- Contract negotiations : If a person needs to sign or negotiate a contract with a U.S. company, a B1 visa is often the correct choice.
- Professional examination and licensing : Some professionals must be in the U.S. to take exams or get licenses only available there.
Reasons for travel under a B2 tourist visa include:
- Tourism : This could be sightseeing, visiting famous landmarks, exploring cities, or simply enjoying the country’s culture and atmosphere.
- Visiting family or friends : Many people use a B2 visa to visit their loved ones living in the U.S.
- Medical treatment : If someone requires medical treatment or a procedure that’s available in the U.S., they might apply for a B2 visa.
- Social events : Attending events like concerts, cooking classes, conventions, festivals, or other social gatherings can be another reason for using a B2 visa.
- Participation in events or contests : If the event doesn’t involve professional participation (like amateur tournaments or contests), a B2 visa could be suitable.
- Short courses of study : If the course duration is less than 18 hours per week, this falls under B2 visa regulations.
You cannot travel under this visa to engage any of the following:
- Long-term employment by a U.S. firm
- Paid performances, or any professional performance before a paying audience
- Arrival as a crewmember on a ship or aircraft
- Work as foreign press, in radio, film, print journalism, or other information media
- Permanent residence in the United States
Boundless has helped more than 100,000 people with their immigration and U.S. travel plans. We’ll be your partner from beginning to end. Get started today!
Boundless tip
The Visa Waiver Program allows nationals from certain countries to travel to the United States without a visa for business, tourism, or while in transit for up to 90 days. The program currently covers 38 countries and territories, including most countries in the European Union.
Canadian nationals also typically do not need a visa to enter the US for tourism purposes. Canadian nationals will need the appropriate visa if they have specific plans to study, work, or move permanently to the U.S.
Different entry requirements also apply to Canadian nationals, depending on whether they plan to work, study, invest, or immigrate. The maximum length of stay can vary, depending on circumstances, between 6 months and 1 year.
The B1 visa and B2 visa do not grant permanent resident status — they are temporary visas – but you can adjust your status from a B1/B2 visa to another type of visa while you are in the U.S., as long as you meet certain requirements. This process involves submitting a change of status application to U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
Here are a few key points to consider:
Key points to consider if you want to change status from B1/B2
- Purpose of stay : Your reason for wanting to stay in the U.S. should match the new visa type. For example, if you wish to study, you may apply to change to a student visa (F-1). If you find an employer willing to sponsor you, you could apply to change to a work visa (like H-1B).
- Timing : You should apply before your current status expires, typically indicated on the I-94 Arrival/Departure Record. USCIS recommends applying at least 45 days before your current status expires.
- Eligibility : Not everyone can change their status. For example, you cannot change your status if you entered the U.S. under the Visa Waiver Program unless it is due to marriage to a U.S. citizen.
- Status violation : If you’ve violated the terms of your current status (for instance, if you’ve started working while on a B1/B2 visa without authorization), you usually can’t change your status.
- Approval : Even if you meet all conditions and file an application, the final decision is up to USCIS.
If you’ve just married someone who’s a U.S. citizen or a permanent resident (they have a green card), you can also apply for a marriage green card. This lets you stay in the U.S. and live with your spouse. You can either apply for a green card while you’re still in the country in a process is called “adjustment of status” (AOS), or you can apply from your home country through what’s called consular processing. To find out if you’re eligible for a B1B2 visa or to change your status from a B1B2 visa, take our eligibility quiz. Get started today!
Documents needed to apply for a B1/B2 visa include:
- A passport valid for six months past the date of return
- A recent digital photograph that meets government requirements
- Documentation of the past five previous trips to the United States, if applicable
- Proof of funds to cover the entire cost of the trip, including travel, accommodation, and living expenses
- Proof of binding ties to the applicant’s home country, such as a job, property, or family

B1/B2 visa application process
Applications are processed by the United States Embassy or consulate in your country.
You will need to attend an interview before your visa is approved. You can attend an interview at an embassy or consulate in a third country, but you will likely wait longer for a visa appointment.
Steps to getting a B Visa
- First, you must complete the Online Non-Immigrant Application, Form DS-160. File the form online and print the confirmation page as you will need it for your interview.
- Upload your digital photo
- Attend the visa interview
As part of the process, ink-free, digital fingerprint scans are taken, typically at the interview. After the interview, the consular officer may request additional documents or information to make a decision about your case.
Boundless’ Travel Visa Service makes applying a breeze with online filing, 1:1 interview coaching, interview scheduling, and support if your visa is denied. Take our approval odds quiz to check your eligibility.
B-1 visas are issued for short business trips, while B-2 visas are issued for tourism purposes, such as vacations or visiting family.
If you’re looking to temporarily visit the U.S. for either holiday or work purposes, for example, attending a conference, touring a place or visiting relatives, then you can apply for a B-1/B-2 visa. You may need to show proof that you have ties to your home country, and that you plan on leaving the U.S..
When you enter the U.S., a customs officer will give you authorization to stay in the the country for up to six months . If you’d like to stay for longer, you may be able to apply to extend this for up to one year.
If you are nearing the end of your permitted stay in the U.S., then you may wish to extend it, especially since there can be future consequences if you stay in the U.S. longer than you were allowed to.
If you’re on a B-1 visa or a B-2 visa, you can request to extend your stay up to one year. To do this, you will need to file Form I-539 to extend or change your status. It’s recommended that you apply to extend your status at least 45 days before your authorized stay expires, so make sure you’re thinking ahead.
No. While you can enter the U.S. for business purposes, you cannot work or be employed by a U.S. employer. If you’re interested in working in the U.S. for a U.S. employer, you may be interested in other visa categories, such as the H-1B visa .
How can I renew my B1 visa or B2 visa?
If you would like to renew your B-1/B-2 visa, then you will need to go through the original process. Depending on the U.S. embassy or consulate where you apply, you may be able to complete your visa renewal without the need for an interview.
Should I apply for a B-1/B-2 visa or an ESTA?
If you are a citizen of one of the 38 countries that are part of the Visa Waiver Program , then you have the option of applying for an ESTA instead of a B1 visa or B2 visa.
Both allow you to enter the U.S. for the same reasons of tourism or business, but you can apply for the ESTA online. Entering the U.S. this way only permits you to stay for up to 90 days, however, so if you would like to stay in the U.S. for travel or business purposes for longer, the B-1/B-2 visitor visa may be an option for you.
Do Canadian citizens need a B-1/B-2 visa?
For casual business or tourism travel, most Canadian citizens don’t need a visa and will automatically be admitted on a B-1 visa or B-2 visa category.
Is the B-1/B-2 visa an immigrant or non-immigrant visa?
The B-1/B-2 visa is a non-immigrant visa, but if your circumstances change, for example, you marry a U.S. citizen or permanent resident, there are several paths from a visitor visa to a green card . Learn more to see how Boundless can help you avoid major headaches and make the process easier.
Do I need a certain amount of money in my bank account to be approved for a travel visa?
No. A common misconception about the travel visa process is that in order be approved, you must provide proof of a certain amount of funds in your bank account. Although financial considerations are one aspect of the B-1/B-2 process, and the consular officer may check to see if you are able to support yourself financially during your time in the U.S., there is no minimum required amount of funds that needs to be met. Evaluation of finances will vary from applicant to applicant, depending on a variety of other factors. Learn more common myths about the travel visa process in Boundless’ blog post .
Not sure how to get started? Boundless + RapidVisa can help.
Not sure how to get started? Boundless can help.
Article Contents
Apply for your visa with boundless., unlimited live support. lawyer review. money-back guarantee., which service.
Looks like you were working on a application just now. Applicants typically only require one service at a time.
You unlocked a $50 discount!
Congrats! Because your friend referred you, your application with Boundless is discounted. Start the application with Boundless within the next 14 days, and you'll save $50.
Featured on

- What is a visa?
- Electronic Visa (eVisa)
- Visa on Arrival
- Appointment Required Visa
- Invitation Letter
- Arrival Card
- Passport Renewal
- Project Kosmos: Meet the man with the world's most challenging travel schedule
- Australia Visa and ETA Requirements for US Citizens Explained
- Brazil eVisa for US Citizens
- India Tourist Visa for UK Citizens
- Possible B1/B2 Visa Questions During the Interview
Select Your Language
- Nederlandse
- 中文 (Zhōngwén), 汉语, 漢語
Select Your Currency
- AED United Arab Emirates Dirham
- AFN Afghan Afghani
- ALL Albanian Lek
- AMD Armenian Dram
- ANG Netherlands Antillean Guilder
- AOA Angolan Kwanza
- ARS Argentine Peso
- AUD Australian Dollar
- AWG Aruban Florin
- AZN Azerbaijani Manat
- BAM Bosnia-Herzegovina Convertible Mark
- BBD Barbadian Dollar
- BDT Bangladeshi Taka
- BGN Bulgarian Lev
- BIF Burundian Franc
- BMD Bermudan Dollar
- BND Brunei Dollar
- BOB Bolivian Boliviano
- BRL Brazilian Real
- BSD Bahamian Dollar
- BWP Botswanan Pula
- BZD Belize Dollar
- CAD Canadian Dollar
- CDF Congolese Franc
- CHF Swiss Franc
- CLP Chilean Peso
- CNY Chinese Yuan
- COP Colombian Peso
- CRC Costa Rican Colón
- CVE Cape Verdean Escudo
- CZK Czech Republic Koruna
- DJF Djiboutian Franc
- DKK Danish Krone
- DOP Dominican Peso
- DZD Algerian Dinar
- EGP Egyptian Pound
- ETB Ethiopian Birr
- FJD Fijian Dollar
- FKP Falkland Islands Pound
- GBP British Pound Sterling
- GEL Georgian Lari
- GIP Gibraltar Pound
- GMD Gambian Dalasi
- GNF Guinean Franc
- GTQ Guatemalan Quetzal
- GYD Guyanaese Dollar
- HKD Hong Kong Dollar
- HNL Honduran Lempira
- HTG Haitian Gourde
- HUF Hungarian Forint
- IDR Indonesian Rupiah
- ILS Israeli New Sheqel
- INR Indian Rupee
- ISK Icelandic Króna
- JMD Jamaican Dollar
- JPY Japanese Yen
- KES Kenyan Shilling
- KGS Kyrgystani Som
- KHR Cambodian Riel
- KMF Comorian Franc
- KRW South Korean Won
- KYD Cayman Islands Dollar
- KZT Kazakhstani Tenge
- LAK Laotian Kip
- LBP Lebanese Pound
- LKR Sri Lankan Rupee
- LRD Liberian Dollar
- LSL Lesotho Loti
- MAD Moroccan Dirham
- MDL Moldovan Leu
- MGA Malagasy Ariary
- MKD Macedonian Denar
- MNT Mongolian Tugrik
- MOP Macanese Pataca
- MUR Mauritian Rupee
- MVR Maldivian Rufiyaa
- MWK Malawian Kwacha
- MXN Mexican Peso
- MYR Malaysian Ringgit
- MZN Mozambican Metical
- NAD Namibian Dollar
- NGN Nigerian Naira
- NIO Nicaraguan Córdoba
- NOK Norwegian Krone
- NPR Nepalese Rupee
- NZD New Zealand Dollar
- OMR Omani Rial
- PAB Panamanian Balboa
- PEN Peruvian Nuevo Sol
- PGK Papua New Guinean Kina
- PHP Philippine Peso
- PKR Pakistani Rupee
- PLN Polish Zloty
- PYG Paraguayan Guarani
- QAR Qatari Rial
- RON Romanian Leu
- RSD Serbian Dinar
- RUB Russian Ruble
- RWF Rwandan Franc
- SAR Saudi Riyal
- SBD Solomon Islands Dollar
- SCR Seychellois Rupee
- SEK Swedish Krona
- SGD Singapore Dollar
- SHP Saint Helena Pound
- SLL Sierra Leonean Leone
- SOS Somali Shilling
- SRD Surinamese Dollar
- SVC Salvadoran Colón
- SZL Swazi Lilangeni
- THB Thai Baht
- TJS Tajikistani Somoni
- TOP Tongan Pa anga
- TRY Turkish Lira
- TTD Trinidad and Tobago Dollar
- TWD New Taiwan Dollar
- TZS Tanzanian Shilling
- UAH Ukrainian Hryvnia
- UGX Ugandan Shilling
- USD United States Dollar
- UYU Uruguayan Peso
- UZS Uzbekistan Som
- VND Vietnamese Dong
- VUV Vanuatu Vatu
- WST Samoan Tala
- XAF CFA Franc BEAC
- XCD East Caribbean Dollar
- XOF CFA Franc BCEAO
- XPF CFP Franc
- YER Yemeni Rial
- ZAR South African Rand
- ZMW Zambian Kwacha
We've updated our app!
Download it now
What is the US Tourist visa duration?
Please note that as of June 2022 the CDC no longer requires travelers to present a negative COVID-19 test or documentation of recovery from COVID pre arrival to the US
The US Tourist visa duration refers to the amount of time you may stay in the US with your tourist visa . It is also called the maximum stay. One of the most popular tourist visas is the US B1/B2 visa , which allows for a maximum stay of 180 days Per Entry . However, the amount of time you can spend in the US is at the discretion of the consular officer who interviews you at the US embassy.
So, what is the US Tourist Visa duration then? This question has not a specific answer for everyone, but we can help you with that and with other questions related to the US Tourist Visa, including how to apply for it.
An in-person interview is a required aspect of applying for a US Tourist visa , but you don’t have to do all the application process by yourself, you can get help from the excellent service of iVisa , an online company that helps you get your visa without filling complicated forms or making long lines at the embassy.
Learn more about this process by reading the information below.
Safe time and effort. Apply with iVisa here.

WHAT DO I NEED TO APPLY FOR A B1/B2 VISA?
Getting a B1/B2 visa is a lot simpler than you think if you take advantage of iVisa and you consider the following list of items:
A valid passport , which is the most important. It needs to be valid for at least six months beyond your period of stay in the United States.
A passport-style photograph . You can take it yourself following the guidelines.
An email address . You will need this because iVisa will deliver the B1/B2 visa renewal by email.
Payment method . You can use a credit or debit card to pay the corresponding fees.
Copies of any past visas (if you are renewing your actual visa). We remind you that if your last B1/B2 visa expired within the last 24 months, no embassy interview will be needed to finish the B1/B2 visa renewal . If you are applying for the first time, an interview will be obligatory.
Supporting documents . This could be anything, for example, travel insurance and proof of funds. Applicants using iVisa , will be notified by their support team if other supporting documents are needed during the application process.
We recommend you to start the B1/B2 visa process on the iVisa page now.
WHERE CAN I APPLY FOR THE B1/B2 VISA?
In case you want to avoid delays with your B1/B2 visa process , then apply for your visa with iVisa . They have a 24/7-available customer service team that has already assisted more than 110,722 travelers to enter the United States.
Apply for your B1/B2 visa with iVisa now.
See more information about this topic “What is the US Tourist visa duration” below.
HOW DO I APPLY FOR MY US TOURIST VISA WITH IVISA?
You don’t need to do a lot of things to get the process started. With iVisa, you only have to follow these steps:
The first step is to fill in our simplified form with your general information. In this part, you have to be very careful with all the information you offer to avoid mistakes.
The second step will ask you to check all the information given in step one.
The last step consists of fee payment, so be ready to use your debit or credit card.
How long does the visa process usually take?
The processing time for this visa is very difficult to predict because it has a lot of bureaucracy behind it. Fortunately, that’s not something you have to stress about but keep in mind that the entire process could take anywhere between two to six weeks.
What you should know is that iVisa team of experts checks every single application for the smallest error so that you have no issues in the end. We value your time so we offer you a really fast service compared to the standard ones.
WHAT IS THE US TOURIST VISA DURATION?
This visa (The B1/B2 Visa) is valid for 10 years after issued , but it allows you to stay within 180 days Per Entry in the U.S. for each entry.
Where can I read more about the B1/B2 visa renewal process?
For a faster resolution click here and start chatting with one of our customer service agents. You are free to see more information on our website as well.
Be ready to apply for your visa with iVisa.
Related Articles

UNITED STATES 14 DAY QUARANTINE REQUIREMENT


DS-160 Sample PDF Doc U.S. Visa Info and Application

U.S. 10 Year Multiple Entry Visa rules and requirements
- iVisa is NOT affiliated with any government agency. This site does not provide legal advice and we are not a law firm. None of our customer service representatives are lawyers and they also do not provide legal advice. We are a private, internet-based travel and immigration consultancy provider dedicated to helping individuals travel around the world. You may apply by yourself directly on the various government websites. The source of information: https://www.uscis.gov/
How long can we stay in USA with tourist visa

- Post author: Curbelo Law
- Post published: January 30, 2022
- Post category: Immigration
In this article we will respond to a question that we usually get in the office: “How long can we stay in the USA with a tourist visa” and the legal immigration consequences that this could bring.
The B2 tourist visa is one of the most requested US visas , as it allows travel to the US for the purpose of visiting friends or family, tourism or pleasure. However, immigrants often take advantage of its use and stay illegally in the country. Our mmigration law firm in New Jersey can help you stay in the country legally. Call us today to find out more.
Table of Contents
So, how long can we really stay in the USA with a tourist visa in 2024?
It is something that thousands of immigrants in the same situation ask themselves.
Foreigners who remain in the US with a tourist visa for more time that the one allowed will be considered undocumented since they will not have a valid document that authorizes them to maintain a legal presence in the country.
The B-2 temporary tourist visa is a temporary visa, so staying longer than authorized will make your presence illegal. If you remain in excess, you will be considered inadmissible to enter the US again for a period of 3 or 10 years.
Under immigration law, you cannot overstay your visa by more than 180 days. Therefore, if the deadline approaches, you must leave the US.

On our website you can also read about the business B-1 visa for those who wish to travel to the US for business purposes.
Consequences Of Staying In The US For More Time Than the Allowed
There are different consequences for all those who misuse the tourist visa by staying illegally:
- Illegal presence.
- Risk of deportation if they come into contact with an immigration authority.
- Inadmissibility from 3 to 10 years or permanently.
- Cancellation or removal of your tourist visa.
- Immigration detention.
In general, foreigners do not usually go to prison for misusing their tourist visa. In these cases, deportation is the punishment used for offenders.
It is possible for an alien to end up in immigration detention, especially if they commit an act that involves crimmigration . Paying an immigration bond could free the offender to later be expelled from the country.
What Is Unlawful Presence In The US?
Unlawful presence is the period in which an alien is in the United States without being admitted or possessing any document or permit to do so.
Those who entered the US illegally will not be able to adjust their immigration status. Even if they are eligible for a Green Card, they would have to apply through consular processing .
It is possible to apply for a waiver before leaving the country using Form I-601 . However, you must show that there are other grounds for inadmissibility.

How Long Does It Take To Re-Enter The United States With A Tourist Visa?
The period of time a foreign national has to re-enter the US on a tourist visa depends on how long they stayed in the country.
- If their presence was 90 days or less, they will be able to return to the country again after leaving the US up to a maximum of 180 continuous days per year.
- If their presence was more than 180 days but less than a year, they will have to wait 3 years to re-enter the country on a tourist visa.
- Having been present illegally for more than a year, they will have to wait 10 years to re-enter the country on a tourist visa.
In these cases, requesting an immigration waiver could allow them to re-enter the country without having to wait years for it.
How Long Can I Stay In The United States On A Tourist Visa?
Aliens can only stay on a tourist visa in the United States for a maximum period of up to 180 days or 6 months. Note that:
- In some cases, the United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer will establish a specific time of stay in the country, so it can be a period shorter than 6 months.
- However, if you are granted a stay of up to 6 months, you can enjoy your stay in the country even if in the interview with the embassy or consulate you have clarified that you would be for a few weeks.
It is always advisable not to exceed the date indicated with the stamp of your passport.
For overland travel, Form I-94, Arrival/Departure Record , indicates the day of entry into the country and the deadline for leaving the U.S. This form must be completed by individuals traveling overland to more than 40 km from the border or who remain in the US for more than 30 days.
Can I Enter The United States Multiple Times With One Visa?
You can enter the US several times with a single visa, as long as it is used for the indicated use. For example, if your visa is for tourism, your purpose in the US must be tourism.
In general, the visa is a permit for multiple entries as long as it does not exceed the established limit. This visa can be granted with a validity of up to 10 years, so you can use it as many times as necessary without the need to renew it.
How To Stay In The United States With A Tourist Visa?
Legally, it is not possible to stay in the US on a tourist visa. This is because the B2 tourist visa is designed to be a temporary visa.
If you intend to stay longer in the US, you must apply for or be eligible for a non-tourist visa. However, it is possible to change your tourist status for another through:

Only immigrants who marry a US citizen or if they have a US citizen child over 21 years of age, can apply for adjustment of status in the USA and thus legalize their situation.
Fiancées of an American may be eligible to apply for a K-1 visa and travel to the US without the need to apply for a B-2 tourist visa.
However, it is sometimes possible to adjust status if you arrived in the USA on a tourist visa and you are the fiancé(e) of an American citizen.

Of course, you must show that your marriage is bona fide and not fraudulent. To do this, you will be asked some essential questions to obtain permanent residence by marriage .
If you came to the United States as a tourist and have been the victim of violence or battery by a permanent resident or a US citizen, you may be eligible to apply for a VAWA visa .
Victims of Human Trafficking, migrant Smuggling or other crimes
If you came to the country on a tourist visa or illegally and have been a victim of certain crimes, you may be eligible for a U visa or a T visa .
Special Immigrant Juvenile Status allows young immigrants who have been homeless, abandoned, or abused to remain in the country legally.
Keep in mind that children or minors require a B-2 tourist visa to travel to the USA, so if they came to the country as a tourist and were denied entry, they may be eligible for SIJS.
If a foreign national entered the United States as a tourist and was presented with the opportunity to study legally, it is possible to adjust their status to obtain an F-1 or M-1 student visa .
Students can stay in the country longer than a tourist. It all depends on the duration of their studies.
Other Options
There are other ways to change your tourist status and stay longer in the US:
- J-1 visa for exchange visitors.
- H-1B for professionals with college degrees.
- H-2A and H-2B visa for temporary workers.
- O visa for individuals with extraordinary abilities.
You can change your status as long as you legally maintain your initial status, in this case, the tourist visa.
Can A Tourist Stay More Than 6 Months In The United States?
A tourist may be able to stay in the United States for more than 6 months on a B-2 tourist visa, but is required to complete Form I-539, Application to Extend or Change Nonimmigrant Status to extend the stay.
If you do not respect the extension time of the tourist visa or do not apply for the extension and stay longer in the US, you will be breaking immigration law.
What Is A Tourist Visa Extension?
Tourists who wish to extend their stay in the United States beyond the time granted can apply for a tourist visa extension. To do this, they must file the application with USCIS .
Who Qualifies For A Tourist Visa Extension Of Stay?
The extension of a tourist visa stay must be for temporary purposes. For example:
- Medical matters.
- A recovery.
- Not being able to fly or return to their country of origin.
- Family mishaps.
- Circumstances where you will return but require more time to meet an unforeseen event.
How To Apply For A Tourist Visa Extension?
To apply for an extension of your tourist visa, you will need to meet the following requirements:
- Your nonimmigrant status is currently valid.
- You have not committed any crime.
- The authorities legally admit you with your nonimmigrant status.
- Your passport is valid.
- There are no reasons forcing you to leave the US.
- By mail to the corresponding filing addresses .
- Electronically through an online form.
Check the status of your extension request. The time to process an extension request varies.
- You can enter your case number to find out your application status.
- You can receive notifications about your request if you subscribe.
What Is A Visa Waiver?
The Visa Waiver Program (VWP) is a US government program that authorizes entry to the United States to citizens of other countries that are part of the Visa Waiver Program .
A visa waiver gives long-term stayers in the United States the ability to exempt themselves from the 3- to 10-year unlawful presence bars. However, this type of process can be difficult to obtain.
Who May Be Eligible For A Visa Waiver?
Nonimmigrants eligible for a visa waiver are those who have received protection through humanitarian programs authorized by Congress, such as:
- Refugees or asylees .
- Temporary Protected Status (TPS) .
- Victims of crimes applying for the U Visa.
- Victims of human trafficking and smuggling who apply for the T visa.
- Victims of domestic violence applying for the VAWA visa.
Is It Possible To Get Permanent Residence If I Stay Longer Than Allowed?

Immigration laws dictate that there are some ways to obtain a Green Card even if the person who entered stayed longer than allowed. This is achieved thanks to a family reunification in the United States .
To be eligible for a family petition, the immigrant must have a:
- US citizen spouse petitioning in their name.
- US citizen son or daughter over 21 years of age petitioning in their name.
Keep in mind that if you want to obtain a permanent residence or Green Card and you entered the country as a tourist, the worst mistake you can make is to apply for an extension of your tourist visa.
When you apply for an extension to apply for residency, you will be making it clear that your purpose of traveling to the USA on a tourist visa is to stay. Most people recommend the extension to avoid unlawful presence, however, you will be committing immigration fraud at the same time.
What Are The Requirements To Renew The Visa?
To renew the tourist visa in the USA, you must submit the following requirements:
- The visa you are trying to renew must be current or have expired within the last 48 months.
- You have a valid passport.
- Also a valid email address.
- You have a credit or debit card.
- The renewal must be processed from the same country.
- Applicants must renew the same type of visa that they hold.
Once you meet the corresponding requirements, you will need to follow the next steps:
- Complete DS-160 Form .
- Make the application payment.
- Send the documentation to the American consulate or embassy.
- Pick up the visa and passport to travel to the USA.
How Long Can I Stay In The US As A Visitor?
As we have mentioned throughout the article, visitors cannot legally stay in the USA beyond what is allowed by their tourist visa. By law, it is for a maximum period of 6 months.
Generally, a passport stamp without a written date means that the holder has been granted a stay of 6 months in the country.
Visa extensions can provide a much longer stay to the visitor who requests it, this allows them to stay in the country for a longer time than authorized. Applications usually require a good explanation of why you need to stay longer.
Although these types of requests are usually approved, it is advisable to hire a lawyer to help you during the process and thus avoid having to leave the country if you have just cause to stay longer than allowed.
What To Do If I Have Already Exceeded The Length Of Stay?
If you have already exceeded the legal physical presence time in the United States, we recommend that you check the following steps:
- Contact our immigration attorney immediately.
- Determine eligibility for an extension period on your visa.
- Comply with all immigration laws.
- Be patient.
What Can Our Immigration Attorney Do For You?
This article seeks to be informative and useful regarding: How long can we stay in USA with tourist visa? Now, to give you precise answers, it is important to know your case in detail. All legal matters can be stressful, complicated and difficult, especially if you want to manage them on your own.
At the law firm of Curbelo Law, attorney Carolina T. Curbelo and her team can help you address your legal needs, streamline the entire process, and represent you in court. Our offices are located in Ridgewood and Newark, New Jersey although we can assist you online and immigration experts are available to assist you in any situation you face.
You Might Also Like

What is adjustment of status

What happens at a bond hearing

What is TPS status
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Tourism & Visit
Study & Exchange
Other Visa Categories
U.S. Visa: Reciprocity and Civil Documents by Country
Visa Information & Resources
Share this page:
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Japanese
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Turkish
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Hebrew
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Albanian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Tagalog
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Russian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Polish
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Ukranian
Visa Wizard
Visa Denials
Fraud Warning
What the Visa Expiration Date Means
Automatic Revalidation
Lost and Stolen Passports, Visas, and Arrival/Departure Records (Form I-94)
Directory of Visa Categories
Straight Facts on U.S. Visas
Customer Service Statement
Photo Requirements
Photo Examples
Digital Image Requirements
Photo Frequently Asked Questions
Photo Composition Template
Online Immigrant Visa Forms
DS-260 Immigrant Visa Electronic Application - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
DS-160: Online Nonimmigrant Visa Application
DS-160: Frequently Asked Questions
Administrative Processing Information
Visa Appointment Wait Times
Nonimmigrants in the United States–Applying for Visas in Canada or Mexico
Frequently Asked Questions
Visa Applicants - State Sponsors of Terrorism Countries
What is a U.S. Visa?
About Visas - The Basics
Rights and Protections for Foreign-Citizen Fiancé(e)s and Spouses of U.S. Citizens and Spouses of Lawful Permanent Residents
Your Rights and Protections
Ineligibilities and Waivers: Laws
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers
Advisory Opinions
Fees for Visa Services
Treaty Countries
Fees and Reciprocity Tables
Temporary Reciprocity Schedule
Country Acronyms
Reciprocity: What's New? 2019 Archive
Reciprocity: What's New? 2022 Archive
Reciprocity: What's New? 2020 Archive
Reciprocity: What's New? 2021 Archive
Reciprocity: What's New?
Reciprocity: What's New? 2023 Archive
Safety & Security of U.S. Borders: Biometrics
National Visa Center Customer Service Pledge
Americans Traveling Abroad
The United States and China Agree to Extending Visas for Short-term Business Travelers, Tourists, and Students
Special Visa Processing Procedures Pursuant to Section 306
Capitalizing on Visa Demand to Spur Economic Growth in the United States
Congressional Testimony
Cuban Family Reunification Parole (CRFP) Program Appointments
List of U.S. Embassies and Consulates - K1-K3 Visas
U.S. Government Fact Sheet on Female Genital Mutilation or Cutting (FGM/C)
Skill List by Country
Presidential Proclamation 9645 and the January 2020 Presidential Proclamation
Public Inquiry Form
List of U.S. Embassies and Consulates
Affidavit of Support Fee Refund
Immigrant Visa Prioritization
USCIS Extends Suspension of Premium Processing Service for Religious Workers (R-1) Nonimmigrant Visa Classification
Record Numbers of U.S. Students Are Studying Abroad
U.S. Student Visas Reach Record Numbers in 2007
U.S. security officials will begin scanning all 10 fingerprints of most non-Americans traveling to the United States
Electronic Submission of Diversity Visa Lottery Applications
USCIS Centralizes Filing for H-2A Petitions
USCIS Field Office Adopts Teletech Call Appointment System For Filing Waiver of Inadmissibility Applications
Application Fees for Non-Immigrant Visas to Increase on January 1, 2008
Senior Advisors to Brief Press on the Latest Developments in Iraqi Refugee and Special Immigrant Visa Issues
Briefing on Developments in the Iraqi Refugee and Special Immigrant Visa (SIV) Admissions Programs
DHS Proposes Changes to Improve H-2A Temporary Agricultural Worker Program
Testimony of Stephen A. “Tony” Edson on U.S. House of Representatives, Committee on Science and Technology Subcommittee on Research and Science Education, House Committee on Science and Technology
Update: Biometric Changes for Re-entry Permits and Refugee Travel Documents
With All the Talk about Illegal Immigration, a Look at the Legal Kind
Latvia, Estonia Sign Deals with US on Visa-Free Travel
Fact Sheet: Changes to the FY2009 H-1B Program
USCIS Announces Interim Rule on H-1B Visas
USCIS Releases Preliminary Number of FY 2009 H-1B Cap Filings
USCIS Extends Comment Period for Proposed Change to H-2A Program
USCIS Runs Random Selection Process for H-1B Petitions
17-Month Extension of Optional Practical Training for Certain Highly Skilled Foreign Students
DHS Begins Collecting 10 Fingerprints from International Visitors at Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport
Hague Convention on Intercountry Adoption Enters into Force
USCIS to Accept H-1B Petitions Sent to California or Vermont Service Centers Temporary Accommodation Made for FY 09 Cap-Subject H-1B Petitions
USCIS Revises Filing Instructions for Petition for Alien Relative
USCIS Announces Update for Processing Petitions for Nonimmigrant Victims of Criminal Activity
USCIS to Allow F-1 Students Opportunity to Request Change of Status
Immigration Tops Agenda at North American Summit
USCIS Issues Guidance for Approved Violence against Women Act (VAWA) Self-Petitioners
USCIS Modifies Application for Employment Authorization Previous Versions of Form I-765 Accepted until July 8, 2008
Overseas Education More Attainable for Chinese Students
New York Business Group Seeks Fewer Restrictions on Foreign Worker Visas
Admission to the United States and your Duration of Stay
Extension of stay, what if i decide to stay longer and am out-of-status with the department of homeland security.
Sometimes understanding the difference between the visa expiration date and the length of time you have permission to remain in the United States can be confusing. These are very different terms. Also review our “ What is a U.S. Visa ?” webpage.
- A U.S. visa in his/her passport gives a foreign citizen permission to apply to enter the United States. A visa by itself doesn’t authorize entry to the U.S. A visa simply indicates that your application has been reviewed by a consular officer at a U.S. Embassy or Consulate, and that the officer determined you’re eligible to travel to a U.S. port-of-entry for a specific purpose. The port-of-entry can be an airport, a seaport or a land border crossing.
- At the port-of-entry, a U.S. immigration officer of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) decides whether to allow you to enter and how long you can stay for any particular visit, as part of the Admission process. Only the U.S. immigration officer has the authority to permit you to enter the United States.
The visa expiration date is shown on the visa along with the visa issuance date. The time between visa issuance and expiration date is called your visa validity. The visa validity is the length of time you are permitted to travel to a port-of-entry in the United States.
Depending on your nationality, visas can be issued from a single entry (application) up to multiple/unlimited entries.
- A visa issued for a single entry (denoted on the visa under “Entries” with the number 1) is valid, or can be used from the date it is issued until the date it expires to travel to a U.S. port-of-entry one time.
- Applying for a new visa is not necessary if your visa has not expired and you have not exceeded the number of entries permitted on your visa.
- Multiple uses of a visa must be for the same purpose of travel allowable on the type of visa you have.
Please be aware, a visa does not guarantee entry to the United States. Additionally, the visa expiration date shown on your visa does not reflect how long you are authorized to stay within the United States. Entry and the length of authorized stay within the United States are determined by the Customs and Border Protection (CBP) Officer at the port-of-entry each time you travel.
It is important to note that there are circumstances which can serve to void or cancel the period of visa validity. If you overstay the end date of your authorized stay, as provided by the CBP officer at a port-of-entry, or United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), your visa will automatically void or cancel unless;
- You have filed an application in a timely manner for an extension of stay or a change of status;
- That application is pending and not frivolous;
If you have applied for adjustment of status to become a permanent resident (LPR, also called green card holder), you should contact USCIS regarding obtaining Advance Parole before leaving the United States.
Upon arriving at a port of entry, the CBP official will determine the length of your visit.
On the admission stamp or paper Form I-94, the U.S. immigration inspector records either an admitted-until date or "D/S" (duration of status). If your admission stamp or paper Form I-94 contains a specific date, then that is the date by which you must leave the United States. If you have D/S on your admission stamp or paper Form I-94, you may remain in the United States as long as you continue your course of studies, remain in your exchange program, or qualifying employment. The admitted-until date or D/S notation, shown on your admission stamp or paper Form I-94 is the official record of your authorized length of stay in the United States. You cannot use the visa expiration date in determining or referring to your permitted length of stay in the United States.
Carefully review information about international visitor admission on the CBP Website.
If you came to the United States on a nonimmigrant visa and you want to extend your stay you must apply with USCIS before your authorized stay, denoted on your admission stamp or paper Form I-94, expires. It is recommended you apply well in advance of your expiration date. To learn more select USCIS, How Do I Extend My Stay ?.
Important Note: Providing permission to enter and/or remain in the United States. to persons holding a nonimmigrant visa is not the responsibility of the Department of State, and therefore Visa Services is unable assist you in this regard. All inquiries must be directed to USCIS.
- You should carefully consider the dates of your authorized stay and make sure you are following the procedures. Failure to do so will cause you to be out-of-status.
- Staying beyond the period of time authorized, by the Department of Homeland Security, and out-of-status in the United States, is a violation of U.S. immigration laws, and may cause you to be ineligible for a visa in the future for return travel to the United States. If you overstay the end date of your authorized stay, as provided by the CBP officer at a port-of-entry, or United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), your visa will generally be automatically be voided or cancelled, as explained above. Select Classes of Aliens Ineligible to Receive Visas to learn more.
More Information
A-Z Index Latest News What is a U.S. Visa? Diversity Visa Program Visa Waiver Program Fraud Warning Find a U.S. Embassy or Consulate Straight Fact on U.S. Visas
Immigrant Visa Interview-Ready Backlog Report
Global Visa Wait Times
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - English
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - French
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Spanish
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Portuguese
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Mandarin
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Arabic
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Italian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - German
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Vietnamese
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Romanian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Korean
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Armenian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Bulgarian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Czech
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Hungarian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Indonesian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Lithuanian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Serbian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Thai
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Mongolian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Kurdish
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Fourth time's the charm: House passes controversial spying bill after bitter infighting

WASHINGTON – The fourth time (yes, the fourth) was the charm for House Republicans when the lower chamber of Congress on a bipartisan basis voted to renew a controversial spying law, not without plenty of hiccups along the way.
The House approved reauthorization of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act , or FISA, by a vote of 273-147, on Friday, with most of the bill’s dissenters coming from the body’s civil-liberty minded ultraconservative and progressive factions.
The law’s strongest advocates come from the intelligence committee, who say FISA's warrantless surveillance provisions are essential to protecting national security.
The final product wasn’t enough to completely satisfy most of the conservative hardliners that have long been a thorn in House Speaker Mike Johnson’s side. But they ultimately settled on a change to the program’s regular expiration date to two years from five years. They did that with the hope of enacting significant reforms later down the line should Donald Trump win back the White House in 2024 and be positioned through his administration to shape the contours of the next version of legislation.
Among the major sticking points that created headaches for Johnson and his fellow GOP leaders was a portion of the law called Section 702, which allows U.S. authorities to surveil communications of foreigners outside the United States.
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
That surveillance is later collected into a database for authorities to search without a warrant. But because those foreigners often contact Americans, domestic data is also swept up in collection as well.
Section 702’s opponents heavily pushed for a warrant requirement, claiming it was necessary for American’s privacy rights. The law’s supporters, though, pointed to other reforms made to FISA to prevent abuses and argued a warrant requirement would neuter the program.
“The constitutional liberties of Americans have to come first, we don’t suspend the constitution for anything,” Rep. Bob Good, R-Va., chair of the House Freedom Caucus, said on the steps of the Capitol on Wednesday, flanked by his like-minded colleagues. “That has to be the premium, protecting American’s constitutional liberties.”
Against conservative opposition, Johnson defended Section 702 at a weekly news conference, saying “it’s a critically important piece of our intelligence and law enforcement.” Before becoming speaker last October, Johnson was also a conservative critic of the law but said that classified briefings on the law have given him a “different perspective.”
House Republicans were trying to lead on FISA renewal for months, but the issue revealed deep divisions within the GOP conference and forced Johnson to pull consideration of FISA from the House two times a few months prior due to infighting. The disagreements prompted Congress to temporarily extend the program until April 19.
The House returned this week expecting to reauthorize FISA earlier but it became apparent that right-wingers were heavily opposed to the legislation, accusing leadership of manipulating the process to sidestep them.
It certainly didn’t help that Trump essentially gave the hard-right his blessing, posting on Truth Social telling Republicans to “KILL FISA.”
In retaliation against leadership, 19 of those conservative lawmakers shot down a traditionally procedural “rule” vote for the bill on Wednesday, bringing the House to a standstill and highlighting the ugly divides between House Republicans once again.
Related: Fentanyl kills thousands of Americans. Could plugging a gap in U.S. intelligence save lives?
The new bill Republicans presented isn’t far off from what conservatives tanked earlier this week, with the only major change being the shortened two-year expiration date, but that modification was enough to satiate hardliners to allow the legislation to pass in hopes of Republicans taking full control of Washington in the 2024 elections to drastically change the law later on.
Conservatives were also able to pressure leadership to allow a vote on an amendment from Rep. Andy Biggs, R-Ariz., that would have included a warrant requirement under Section 702, but the amendment failed in a nail-biter vote of 212-212 where the issue divided both sides of the aisle.
The House isn't necessarily done yet though. In a bid to stop the bill from going to the Senate, Rep. Anna Paulina Luna, R-Fla., filed a procedural motion just before lawmakers left Washington for the weekend that if it's adopted would force the House to vote again on the measure.
House Intelligence Committee Chairman Mike Turner, R-Ohio, moved to dismiss Luna's effort, and the chamber is now slated to once again vote on the issue when members return next Monday.
Without the warrant requirement, the bill is expected to easily clear the Democratic-controlled Senate and the White House has expressed support for the renewal of the law as well.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

How to extend your stay in the U.S.
You may be able to extend your stay in the U.S. Learn if you qualify and how to file for an extension.
You may apply to extend your stay while you are in the U.S. However, you must do so before your visa expires. Not all visa categories are eligible for an extension. See the list of situations when you can and cannot extend your stay in the U.S.
Learn how to extend your stay in the U.S.
- Find out how to file for an extension online or by mail.
- Use the fee calculator to see how much you will have to pay. Select Form I-539 and then select your current nonimmigrant status.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Create Account
When to File Your Adjustment of Status Application for Family-Sponsored or Employment-Based Preference Visas: May 2024
Are you seeking to adjust your status and become a U.S. permanent resident under a family-sponsored or employment-based preference immigrant visa? If you have not yet had a relative or employer file an immigrant visa petition on your behalf, please learn more about the Adjustment of Status Filing Process . If you already have a petition filed or approved on your behalf, you may have to wait for an available visa in your category (if applicable) before you can file your Form I-485, Application to Register Permanent Residence or Adjust Status . This page will help you determine when to file your adjustment of status application.
When to File
Use the Visa Bulletin charts below to determine when to file your adjustment of status application.
To use the charts:
- Find your visa type in the first column (on the left) of the appropriate chart (Family-sponsored or Employment-based).
- Stay in that row and move directly to the right to find the corresponding date under the country of your birth (as listed in the boldface columns across the top).
- If the date on the chart is current (“C”), or your priority date is earlier than the date on the chart, you may file your adjustment of status application, if otherwise eligible to do so.
- “U” means unauthorized; for example, numbers are not authorized for issuance.
Your priority date is generally the date when your relative or employer properly filed the immigrant visa petition on your behalf with USCIS. If a labor certification is required to be filed with your immigrant visa petition, the priority date is the date the labor certification application was accepted for processing by the Department of Labor.
About the Visa Bulletin
DOS publishes current immigrant visa availability information in a monthly Visa Bulletin . The Visa Bulletin indicates when statutorily limited visas are available for issuance to prospective immigrants based on their individual priority date.
On Nov. 20, 2014, the Secretary of Homeland Security directed USCIS to work with DOS to:
- Ensure that all immigrant visas authorized by Congress are issued to eligible individuals when there is sufficient demand for such visas, and
- Improve the Visa Bulletin system for determining when immigrant visas are available to applicants during the fiscal year.
Additionally, in July 2015, the Administration issued its report on Modernizing and Streamlining Our Legal Immigration System for the 21st Century (PDF) . This report included detailed recommendations to revise and update the monthly Visa Bulletin to better estimate immigrant visa availability and provide needed predictability to nonimmigrant workers seeking permanent residency.
USCIS, in coordination with DOS, revised the procedures for determining visa availability for applicants waiting to file for adjustment of status. The revised process will better align with procedures DOS uses for noncitizens who seek to become U.S. permanent residents by applying for immigrant visas at U.S. consulates and embassies abroad.
This revised process will enhance DOS’s ability to more accurately predict overall immigrant visa demand in determining the cut-off dates for the Visa Bulletin. This will help ensure that the maximum number of immigrant visas are issued annually as intended by Congress, and minimize month-to-month fluctuations in Visa Bulletin final action dates. Additional goals are outlined in the White House report, Modernizing and Streamlining Our Legal Immigration System for the 21st Century (PDF) .
New Visa Bulletin Charts
The Visa Bulletin will now have two different charts because of the revised procedures. DOS will post two charts per visa preference category in the DOS Visa Bulletin. The charts are:
- Application Final Action Dates (dates when visas may finally be issued); and
- Dates for Filing Applications (earliest dates when applicants may be able to apply).
When USCIS determines there are immigrant visas available for the filing of additional adjustment of status applications, the Dates for Filing Applications chart may be used to determine when to file an adjustment of status application with USCIS. Otherwise, the Application Final Action Dates chart must be used to determine when to file an adjustment of status application with USCIS.
In coordination with the DOS, USCIS will monitor visa numbers each month and post the relevant chart on this page under When to File.
Determining Visa Availability
USCIS considers several factors to determine if there is a greater supply of visas than the demand for those visas. To determine visa availability, USCIS will compare the number of visas available for the remainder of the fiscal year with:
- Documentarily qualified visa applications reported by DOS;
- Pending adjustment of status applications reported by USCIS; and
- Historical drop off rate of applicants for adjustment of status (for example, denials, withdrawals and abandonments)
Watch CBS News
U.S. issues travel warning for Israel with Iran attack believed to be imminent and fear Gaza war could spread
By Debora Patta , Tucker Reals
Updated on: April 13, 2024 / 5:25 PM EDT / CBS News
Update: Iran launched drone attacks against Israel on Saturday. Read CBS News' latest coverage here .
Tel Aviv — Israel is bracing for a worst-case scenario that U.S. officials believe could materialize within just hours — the possibility of a direct attack on Israeli soil by Iran in retaliation for a strike almost two weeks ago that killed seven Iranian military officers. Iran has vowed to take revenge for Israel killing its commanders, who were hit by an April 1 strike on the Iranian embassy in Syria's capital.
Two U.S. officials told CBS News that a major Iranian attack against Israel was expected as soon as Friday, possibly to include more than 100 drones and dozens of missiles aimed at military targets inside the country. Sources have told CBS News the retaliation could include attacks carried out both by Iranian forces, and proxy groups around the region that it has been funneling additional arms to for weeks.
The officials said it would be challenging for the Israelis to defend against an attack of that magnitude, and while they held out the possibility that the Iranians could opt for a smaller-scale attack to avoid a dramatic escalation, their retaliation was believed to be imminent.
Asked Friday how imminent he believes an attack is, President Biden responded, "I don't want to get into secure information, but my expectation is sooner than later." The president urged Iran not to move forward, saying his message to Tehran was: "Don't."
Tehran has not indicated publicly how or when it will return fire, so it's unclear how far Iran's leaders will go. If they decide to carry out a direct attack on Israel, there's fear it could blow Israel's ongoing war against Iranian ally Hamas up into a much wider regional conflict.
With the Iranian retaliation expected at any time, the U.S. State Department on Thursday warned Americans in Israel not to travel outside major cities, which are better protected from incoming rocket fire by the country's Iron Dome missile defense system. The latest guidance noted that travel by U.S. government employees in Israel could be further restricted with little notice as things develop in the tinderbox region.
"Whoever harms us, we will harm them," Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu vowed Thursday as he visited troops at an Israel Defense Forces airbase. "We are prepared … both defensively and offensively."

On Saturday, all U.S. embassies in the Middle East were put on high alert and required to hold emergency action committee meetings. Diplomats in Lebanon and Israel were specifically told not to travel to certain areas within those countries.
Sima Shine, a security expert and former official with Israel's national intelligence agency Mossad, told CBS News it was a dangerous moment for the region, and the "most worried" she has been. She said anxiety over an all-out war was likely just as high "on both sides, in Israel and in Iran."
If Iran does choose to strike Israel directly, it could involve a complex missile and drone attack similar to the one Iranian forces launched against a Saudi oil facility in 2019 .
"They will try to do it on the military or some military asset," Shine predicted. "But the question will be the damage. If there would be many injured people, killed or injured … I think it has the potential for a huge escalation."

Shine stressed, however, that she still believes neither side actually wants a regional conflict.
U.S. "really trying to avoid war"
The U.S. sent a senior general to Israel this week to coordinate with the close American ally on any response it might make to an Iranian attack. Speaking Friday on "CBS Mornings," America's top military officer said, "we're really trying to avoid war."
"This is part of the dialogue that I have with my counterparts within the region, to include the Israeli chief of defense, who I talked to yesterday," said Joint Chiefs chairman Gen. Charles Q. Brown, Jr., adding that the U.S. military was "doing things not only to prevent a war, but at the same time, one of my primary things is to make sure all the forces in the region are protected."
"My role, as the chairman of the Joint Chiefs, is to plan and prepare," Brown said. "That's one thing we do very well."
Brown's Israeli counterpart, Chief of the General Staff Lt. Gen. Herzi Halevi, "completed a comprehensive situational assessment on the readiness of the IDF for all scenarios," Israel's military said Friday.
"The IDF is very strongly prepared, both offensively and defensively, against any threat," Halevi was quoted as saying in the statement. "The IDF continues to monitor closely what is happening in Iran and different arenas, constantly preparing to deal with existing and potential threats in coordination with the United States Armed Forces."
The IDF said the visiting U.S. general, Central Command chief Gen. Michael Erik Kurilla, was taking part in the IDF's situational assessment.
The dilemma for Iran, said Israeli expert Shine, is to figure out how to deliver its promised response to Israel's attack in Syria, but in a way that does not lead to further escalation. Likewise, Shine said Israel could choose to show restraint when it responds to whatever Iran eventually does.
If either side gets the balance wrong, the consequences for the region, and even the world, could be dire.
Weijia Jiang, David Martin, Margaret Brennan and Olivia Gazis contributed reporting.
- Middle East
- Benjamin Netanyahu
Debora Patta is a CBS News foreign correspondent based in Johannesburg. Since joining CBS News in 2013, she has reported on major stories across Africa, the Middle East and Europe. Edward R. Murrow and Scripps Howard awards are among the many accolades Patta has received for her work.
More from CBS News

Rising numbers say Biden should encourage Israel to stop Gaza actions

Trump allies encourage visits with foreign leaders at Mar-a-Lago before election

Teen suspect held over stabbing attack inside Australian church

Johnson faces growing pressure over Ukraine, Israel aid
More From Forbes
More than 1 million indians waiting for highly skilled immigrant visas.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
People are reflected in the window of the Nasdaq MarketSite in Times Square in New York City. U.S. ... [+] government data has confirmed that more than one million Indians now wait in employment-based immigration backlogs, highlighting problems in the U.S. immigration system. Many work for technology companies in the United States. (Photo by Spencer Platt/Getty Images)
U.S. government data confirm that more than one million Indians now wait in employment-based immigration backlogs, highlighting problems in the U.S. immigration system. The data from U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services indicate many highly skilled professionals from India face potentially decades-long waits to gain permanent residence (a green card) due to a per-country limit and the low annual quota. The waits create personal turmoil for individuals and families, affecting America’s ability to attract and retain talent .
Analysis Of USCIS Data
Over 1.2 million Indians, including dependents, are waiting in the first, second and third employment-based green card categories, according to a National Foundation for American Policy analysis of USCIS data . The data reflect approved I-140 immigrant petitions as of November 2, 2023.
NFAP analyzed the data and calculated the dependents to arrive at an estimated backlog in the top three employment-based immigration categories (excluding “other workers”).
First Preference: According to USCIS, 51,249 principals are in the employment-based first preference, also known as EB-1. NFAP estimates an additional 92,248 dependents for a total of 143,497 Indians in the first preference backlog. EB-1 includes workers with extraordinary ability, outstanding professors and researchers and multinational executives or managers.
Second Preference: According to USCIS, as of November 2, 2023, there were 419,392 principals in the employment-based second preference, also known as EB-2. NFAP estimates an additional 419,392 dependents for a total of 838,784 Indians in the second preference backlog. EB-2 includes professionals holding an advanced degree and persons with exceptional ability in the sciences, arts or business.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
USCIS data from 2020 suggest that the Indian backlog in the EB-2 category rose by more than 240,000 or 40% in approximately three years.
Third Preference: According to USCIS, 138,581 principals are in the employment-based third preference, also known as EB-3. NFAP estimates an additional 138,581 dependents for a total of 277,162 Indians in the third preference backlog. EB-3 includes skilled workers and “members of the professions whose jobs require at least a baccalaureate degree.” (Unskilled or “Other Workers” in the third preference are not included in the analysis.)
According to the National Foundation for American Policy’s analysis of USCIS data, there are 1,259,443 Indians in the top three employment-based immigration categories as of November 2, 2023.
USCIS says the agency’s data does not “identify or exclude multiple petitions by the same petitioner or beneficiary.” However, NFAP based its estimates of dependents on the ratio of employment visa principals to dependents in FY 2021 and FY 2022 for all countries of origin. That would underestimate dependents for Indians because their long waits in the backlog mean they would be older than other employment-based immigrants and more likely to have spouses and multiple children.
Without Congressional action, the backlog will continue to increase. In 2020, the Congressional Research Service (CRS) estimated the backlog for Indians in the top three employment-based green card categories would reach 2,195,795 individuals by FY 2030 and take 195 years to eliminate the backlog.
The Visa Bulletin And Chinese Immigrants
The per-country limit (discussed below) also affects would-be employment-based immigrants from China and the Philippines. NFAP estimates that nearly 148,000 Chinese professionals and their dependents are waiting in the employment-based green card backlog, with approximately 83,000 in the second preference and 41,000 in the third preference.
According to the May 2024 Visa Bulletin , Indians can receive their green card in the employment-based second preference only if their application was filed before May 15, 2012. While that provides a general sense of an applicant’s wait time, for Indians, the dates in the Visa Bulletin often do not advance monthly and sometimes may regress. For Chinese, the date in the May 2024 Visa Bulletin is June 1, 2020. For comparison, for the rest of the world, the application filing date to be eligible to receive a green card in the second preference is last year—February 15, 2023. (See here for background on interpreting the Visa Bulletin.)
“Applicants for immigrant visas who have a priority date earlier than the application date in the [Visa Bulletin] chart may assemble and submit required documents to the Department of State’s National Visa Center,” according to the State Department .
The Reasons For The Long Green Card Wait Times
Two parts of U.S. law created the long wait times for employment-based immigrants. In 1990, Congress set the annual limit for employment-based green cards at 140,000, including dependents, a level far from high enough since the demand for technical talent has exploded in recent decades due to the internet, smartphones, AI, e-commerce and other innovations. At the same time, lawmakers retained a per-country limit of 7%. The per-country limit has most harmed highly skilled professionals from India, China and the Philippines due to larger populations.
Indians have suffered the brunt of the law’s impact. Due to the per-country limit, only 7,820 Indian immigrants received employment-based green cards in the EB-2 category in FY 2015, even though employers submitted tens of thousands of green card applications for Indians years earlier than individuals from other countries who received green cards that year.
In 2022, Senator Charles Grassley (R-IA), supported by Senate Republican Leader Mitch McConnell, blocked a reform that would have ended the long waits for many employment-based immigrants. Analysts say Grassley’s blocking of the exemption for highly educated immigrants caused potentially irreparable harm to America’s ability to attract and retain foreign-born scientists and engineers in the United States.
When the House of Representatives passed the America COMPETES (CHIPS) Act, it included an exemption from annual green card limits and backlogs for foreign nationals with a Ph.D. in STEM fields and those with a master’s degree “in a critical industry.” During the House-Senate conference committee on the bill, the Biden administration, Rep. Zoe Lofgren (D-CA), businesses and universities argued for keeping the provisions. However, Grassley, the ranking Republican on the Senate Judiciary Committee, blocked the immigration measures from becoming law.
The Impact Of Long Green Card Wait Times
In July 2023, a Forbes article reported on Canada’s program to entice H-1B visa holders. The number of applications was so overwhelming that the 10,000 limit was reached in less than 48 hours. “The response is likely a warning sign to U.S. policymakers that many highly sought foreign-born scientists and engineers in the United States are dissatisfied with the U.S. immigration system and seeking other options.”
Beyond the hit to U.S. competitiveness and companies’ ability to retain talent in the United States, the long waits for employment-based green cards exact a human toll.
Emily Neumann, a managing partner at Reddy Neumann Brown PC, noted a recent application for a client who has needed to renew his H-1B five times while waiting for his green card priority date. “He’s been with the company for 16 years. Still no green card solely because he was born in India.” An H-1B denial, layoff or economic downturn could force him to leave the country.
Roshan Taroll’s story illustrates the impact of the employment-based green card problem. It shows the immigration system creates fear and uncertainty that sways the course of people’s lives, including the children of highly skilled immigrants.
Roshan was born in India and came to America as a 10-year-old with his parents in 2008. His mother worked in H-1B status for a U.S. technology company, which sponsored her for an employment-based green card in 2010. Eight years later, in 2018, Roshan’s mother died before she was granted her green card. The low annual employment-based immigrant visa limit and the per-country limit affecting Indians caused the long wait and prevented her from becoming a permanent resident.
Family members can use the employment-based visa petition of a deceased principal to gain permanent residence. However, Roshan turned 21 and “aged out” of being included on his mother’s application before the “priority date” arrived. (See this interview and the website of Improve The Dream , which focuses on “child dependents of long-term visa holders.”)
Even though Roshan grew up in Boston, he needed to obtain F-1 international student status to attend Boston College. After graduating, he has worked for a company on Optional Practical Training for three years.
Roshan has experience in a high-demand field—semiconductor manufacturing—but due to the low annual limit on H-1B petitions, his company could not secure an H-1B visa for him despite attempts in three separate H-1B lotteries. (According to analysts, the yearly limit of 85,000 new H-1B petitions for companies is reached annually because it is inadequate for a technology-based economy with a labor force of more than 160 million people.)
As a result, even though he has lived in America since he was 10 years old, Roshan will soon have to leave the United States. He appreciates the company’s efforts to find a location where he can use his education and training to work for the corporation in another country.
“It's been challenging,” said Roshan. “With my mother's passing, she moved us to this country to give us a better life and ensure that we were educated and did well. Now that I have to leave, I won’t be able to fulfill her wishes of living my life in the United States.”

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
EPA imposes first national limits on 'forever chemicals' in drinking water
For the first time, the Environmental Protection Agency has established national limits for six types of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in drinking water.
The substances, known by the initialism PFAS, are nicknamed "forever chemicals" because they barely degrade and are nearly impossible to destroy , so they can linger permanently in air, water and soil.
As a class of chemicals, PFAS have been associated with a higher risk of certain cancers, heart disease, high cholesterol, thyroid disease , low birth weight and reproductive issues, including decreased fertility.
Most people in the U.S. have PFAS in their blood , according to the Department of Health and Human Services.

The EPA announced Wednesday that levels of PFOA and PFOS — two types of PFAS commonly used in nonstick or stain-resistant products such as food packaging and firefighting foam — can’t exceed 4 parts per trillion in public drinking water.
Three additional PFAS chemicals will be restricted to 10 parts per trillion. They are PFNA and PFHxS — older versions of PFAS — and GenX chemicals, a newer generation of chemicals created as a replacement for PFOA.
PFOA and PFOS are the most widely used and studied types of PFAS, according to the EPA. Companies started making them in the 1940s, but the substances were largely phased out of U.S. chemical and product manufacturing in the mid-2000s. However, they persist in the environment and have mostly been replaced by newer types of chemicals within the same class.
The EPA’s new limit reflects the lowest levels of PFOA and PFOS that laboratories can reasonably detect and public water systems can effectively treat. But, according to the agency, water systems should aim to eliminate the chemicals, because there is no safe level of exposure.
Eleven states already have regulatory standards for PFAS in drinking water. The EPA estimated that 6% to 10% of the country’s public water systems — 4,100 to 6,700 systems in total — will need to make changes to meet the new federal limits.
“One hundred million people will be healthier and safer because of this action,” EPA Administrator Michael Regan said Tuesday on a media call, referring to the number of people served by the water systems that will need upgrades.
As of Wednesday, public water systems that don’t monitor for PFAS have three years to start. If they detect PFAS at levels above the EPA limits, they will have two more years to purchase and install new technologies to reduce PFAS in their drinking water.
The EPA estimates that the new limits will prevent thousands of deaths and tens of thousands of serious illnesses.
One of the biggest health concerns associated with PFOA is an increased risk of kidney cancer . Exposure to high levels of PFOS has also been associated with an increased risk of liver cancer .
GenX chemicals have been shown in animal studies to damage the liver, kidneys and immune system, as well as liver and pancreatic tumors. According to studies in rodents, PFNA exposure could lead to developmental issues and PFHxS may disrupt the thyroid system.
The EPA also set a limit Wednesday for mixtures of at least two of the following chemicals: PFNA, PFHxS, PFBS and GenX. Public water systems can use an equation provided by the EPA to determine whether the cumulative concentrations of the chemicals exceed the agency’s threshold.
The EPA proposed limits to PFAS in drinking water last year. After it reviewed public comments, it made the limits official Wednesday.
“This is a huge, historic public health win,” said Scott Faber, senior vice president of government affairs for the Environmental Working Group, an activist group that advocates for stricter regulations of drinking water pollutants.
Faber called the new EPA limits “the most important step we’ve taken to improve the safety of our tap water in a generation” and “the single most important step we’ve taken to address PFAS ever.”
Jamie DeWitt, director of the Environmental Health Sciences Center at Oregon State University, said that although the new limits don’t end the problem of PFAS in drinking water, they represent significant progress.
“This is going to give people in contaminated communities at least a sense that the federal government cares about them and cares about their exposure, because I think many people living in PFAS-impacted communities have not felt heard,” she said.
The EPA said Wednesday that $1 billion in funding is newly available to help states and territories implement PFAS testing and treatment at public water systems and to help owners of private wells do the same. The funding comes from the federal infrastructure law passed in 2021, which set aside $9 billion to address PFAS and other contaminants in water. The money will be distributed as grants.
Some public water systems have also sued companies that manufacture or previously manufactured PFAS, aiming to hold them accountable for the costs of testing and filtering for PFAS. One such lawsuit resulted in a $1.18 billion settlement last year for 300 drinking water providers nationwide. Another lawsuit awarded $10.5 billion to $12.5 billion , depending on the level of contamination found, to public water systems across the country through 2036.
The most common way to remove PFAS from water is through an activated carbon filter, which traps the chemicals as water passes through. Other options include reverse osmosis or ion exchange resins, which act like tiny magnets that attract PFAS chemicals.
But even once water is treated for PFAS, it can take a while to see positive impacts, said Anna Reade, director of PFAS advocacy at the National Resources Defense Council, a nonprofit environmental advocacy group.
“For most of these six chemicals, it’s between two to eight years for the amount in our bodies to decrease by half. So we’re looking at years before we see some substantial decreases in our exposure over time,” she said.
The EPA’s new drinking water limits apply to only a small fraction of the more than 12,000 types of PFAS , so activists are still concerned about overall exposure.
“This is not the final step,” Reade said. “We still have a lot of other PFAS to worry about.”
Aria Bendix is the breaking health reporter for NBC News Digital.
Brazil again extends visa exemptions for US, Canada and Australia, this time until 2025
Brazil’s government has extended exemptions to tourist visa requirements for citizens of the U.S., Australia and Canada until April 2025, extending a program aimed at boosting tourism that had been scheduled to end Wednesday
RIO DE JANEIRO -- Brazil’s government extended exemptions to tourist visa requirements for citizens of the U.S., Australia and Canada until April 2025, extending a program aimed at boosting tourism that had been scheduled to end Wednesday.
The decision, issued by Brazilian presidency and the Ministry of Foreign Relations late Tuesday, marks the third time Brazil has delayed the visa requirement since President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva took office in 2023.
His predecessor, Jair Bolsonaro, exempted the countries from visas as a means to boost tourism — although all three countries continued to demand visas from Brazilians.
That went against the South American country’s tradition of requiring visas from travelers based on the principle of reciprocity and equal treatment, and prompted Lula’s Foreign Ministry to say it would scrap the exemptions.
“Brazil does not grant unilateral exemption from visiting visas, without reciprocity, to other countries,” the ministry said at the time, while noting that the government stood ready to negotiate visa waiver agreements on a reciprocal basis. It did reach a deal with Japan to ease travel provisions.
The decision to maintain exemptions for the three countries is important for boosting tourism in Brazil, notably from the U.S., Brazil’s official tourism board Embratur said in a statement Tuesday.
Official data shows that nearly 670,000 Americans visited Brazil in 2023, making the U.S. the second largest country of origin after neighboring Argentina.
The government initially postponed the reinstatement of the visa requirement in October, then again in January. At the time, the government said it was still finalizing a new visa system and wanted to avoid implementing it close to the high season, mainly during the New Year’s celebrations and Carnival festivities in February, which attract tens of thousands of tourists.
Top Stories

Dad runs Boston Marathon in memory of 3 slain children
- Apr 16, 2:14 PM

Dubai sees severe flooding after getting 2 years' worth of rain in 24 hours
- 2 hours ago

Kansas women identified as 2 dead bodies discovered in Oklahoma: Medical Examiner

Theresa Nist of 'Golden Bachelor' shares message following divorce from Gerry Turner
- Apr 15, 1:52 PM

Why is Trump's Truth Social stock plummeting?
- Apr 16, 12:25 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
Advertisement
Supported by
Arizona Reinstates 160-Year-Old Abortion Ban
The state’s highest court said the law, moribund for decades under Roe v. Wade, was now enforceable, but it put its decision on hold for a lower court to hear other challenges to the law.
- Share full article

By Jack Healy and Kellen Browning
Jack Healy reported from Phoenix and Kellen Browning from San Francisco.
Arizona’s highest court on Tuesday upheld an 1864 law that bans nearly all abortions, a decision that could have far-reaching consequences for women’s health care and election-year politics in a critical battleground state.
“Physicians are now on notice that all abortions, except those necessary to save a woman’s life, are illegal,” the court said in a 4-to-2 decision.
But the court, whose justices are all Republican appointees, also put its ruling on hold for the moment and sent the matter back to a lower court for additional arguments about the law’s constitutionality. Abortion providers said they expected to continue performing abortions through May as their lawyers and Democratic lawmakers searched for new legal arguments and additional tactics to delay the ruling.
The ruling immediately set off a political earthquake. Democrats condemned it as a “stain” on Arizona that would put women’s lives at risk. Several Republicans, sensing political peril, also criticized the ruling and called for the Republican-controlled Legislature to repeal it.

Read the Arizona Supreme Court’s Abortion Ruling
The state’s highest court on Tuesday upheld an 1864 law that bans nearly all abortions.
The decision from the Arizona Supreme Court concerned a law that was on the books long before Arizona achieved statehood. It outlaws abortion from the moment of conception, except when necessary to save the life of the mother, and it makes no exceptions for rape or incest. Doctors prosecuted under the law could face fines and prison terms of two to five years.
Planned Parenthood Arizona, the plaintiff, and other abortion-rights supporters argued that the 1864 ban, which had sat dormant for decades, had essentially been overtaken by years of subsequent Arizona laws regulating and limiting abortion — primarily, a 2022 law banning abortion after the 15th week of pregnancy.
But the territorial-era ban was never repealed. And the Arizona Supreme Court said Arizona’s Legislature had not created a right to abortion when it passed the 15-week ban. Because the federal right to abortion in Roe v. Wade had now been overturned, nothing in federal or state law prevented Arizona from enforcing the near-total ban, the court wrote.
“Because the federal constitutional right to abortion that overrode § 13-3603 no longer exists, the statute is now enforceable,” the court’s four-person majority wrote, using the statutory number of the 1864 ban.
Justice Bill Montgomery recused himself from the case after the publication of news reports that he had written a Facebook post saying that Planned Parenthood had participated in “the greatest generational genocide known to man.”
The court’s ruling was a stinging loss for abortion-rights supporters, who said it would put doctors in legal jeopardy, prompt clinics in Arizona to stop providing abortions and force women to travel to nearby states like California, New Mexico or Colorado to end their pregnancies.
At a news conference on Tuesday, Dr. Atsuko Koyama, an abortion provider in Phoenix, said she had recently provided abortions to one woman trying to flee an abusive partner and another whose pregnancy had endangered her health. She said that the court’s ruling would end that kind of care and that it “criminalizes me.”
President Biden called the ban “cruel,” and said that it was a result of “the extreme agenda of Republican elected officials who are committed to ripping away women’s freedom.”
“Millions of Arizonans will soon live under an even more extreme and dangerous abortion ban, which fails to protect women even when their health is at risk or in tragic cases of rape or incest,” he said in a statement.
Arizona’s attorney general, Kris Mayes, a Democrat, called the ruling “unconscionable and an affront to freedom.” She promised to mount a legal effort to fight off implementation of the law and said she would not prosecute doctors for providing abortions.
It is unclear whether other Arizona prosecutors will follow suit.
Gov. Katie Hobbs, a Democrat, issued an executive order putting authority to prosecute abortion-related cases under the attorney general. Ms. Mayes said on Tuesday that she would refuse to allow Arizona’s elected county attorneys to bring cases under the 1864 ban, potentially opening a new legal fight with Republican prosecutors and abortion opponents.
Jake Warner, a senior counsel for the Alliance Defending Freedom, a conservative Christian advocacy group that argued to reinstate the near-total ban, said at a news conference that he believed county prosecutors had the authority “to enforce the law as written, and so protect unborn life here in Arizona.”
At a news conference on Tuesday, Ms. Hobbs and other Democratic politicians decried the decision as “a stain on our state” that would energize abortion-rights supporters to vote in November’s elections.
Anti-abortion groups cheered the ruling.
“Life is a human right, and today’s decision allows the state to respect that right and fully protect life again — just as the Legislature intended,” Mr. Warner said. “We celebrate the Arizona Supreme Court’s decision that allows the state’s pro-life law to again protect the lives of countless, innocent, unborn children.”
Republicans control both chambers of the Legislature. The governor, Ms. Hobbs, is a first-term Democrat who campaigned on supporting abortion rights.
State Senator T.J. Shope, a Republican who represents a suburban and rural area south of Phoenix, said he would work to repeal the 1864 ban but leave in place a 15-week prohibition on abortions that was passed two years ago and signed into law by the previous governor, Doug Ducey, a Republican.
The stakes could also be significant for races up and down the ballot in Arizona this fall, after former President Donald J. Trump said this week that he thought abortion rights should be left up to the states to decide.
Political scientists in Arizona said the court’s abortion ruling was far out of step with public opinion. Only 7 percent of Arizona voters said they supported an outright abortion ban with no exceptions, according to a poll conducted last month by YouGov and Samara Klar, a political science professor at the University of Arizona.
Democrats, who seized on abortion to win campaigns for governor and attorney general in midterm elections two years ago, said it would galvanize their supporters , who were already pushing for a state constitutional right to abortion as a ballot initiative in November. In other states where abortion has been at risk of being curtailed, voters have turned out in force to protect it.
Representative Ruben Gallego, running unopposed in the Democratic primary for Senate, criticized the ruling and tied it to his opponent, Kari Lake, who called the near-total ban a “great law” when she was running for governor in 2022.
“Yet again, extremist politicians like Kari Lake are forcing themselves into doctors’ offices and ripping away the right for women to make their own health care decisions,” Mr. Gallego said, adding that he would do “whatever it takes to protect abortion rights at the federal level.”
Ms. Lake has been emblematic of a Republican shift on abortion . She came out against a federal ban last year while still backing the 15-week restriction that was in effect in Arizona, and she said on Tuesday that it was “abundantly clear that the pre-statehood law is out of step with Arizonans.” Ms. Lake called on the Legislature and Ms. Hobbs, her 2022 opponent in the governor’s race, to “come up with an immediate common sense solution.”
Representatives Juan Ciscomani and David Schweikert, two Republicans facing re-election challenges in closely divided districts, also criticized the ruling and urged state lawmakers to address it.

Tracking Abortion Bans Across the Country
The New York Times is tracking the status of abortion laws in each state following the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
For nearly two years, supporters and opponents of abortion rights in Arizona have been fighting in court over whether the 1864 law could still be enforced, or whether it had been effectively overtaken and neutered by decades of other state laws that regulate and restrict abortion but stop short of banning it entirely.
The 1864 ban had sat mothballed for decades, one of several sweeping state abortion-ban laws that were moribund while Roe v. Wade was in effect but became the focus of intense political and legal action after Roe fell.
Abortions in Wisconsin were largely halted because of an 1849 ban, but resumed last September after a judge said the law did not make abortions illegal. In Michigan, Gov. Gretchen Whitmer, a Democrat, signed a repeal of a 1931 ban on abortion last spring after voters added abortion-rights protections to the state constitution.
Elizabeth Dias contributed reporting.
Jack Healy is a Phoenix-based national correspondent who focuses on the fast-changing politics and climate of the Southwest. He has worked in Iraq and Afghanistan and is a graduate of the University of Missouri’s journalism school. More about Jack Healy
Kellen Browning is a Times reporter covering the 2024 election, with a focus on the swing states of Nevada and Arizona. More about Kellen Browning

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Generally, a citizen of a foreign country who wishes to enter the United States must first obtain a visa, either a nonimmigrant visa for a temporary stay, or an immigrant visa for permanent residence. Visitor visas are nonimmigrant visas for persons who want to enter the United States temporarily for business (visa category B-1), for tourism (visa category B-2), or for a combination of both ...
It is risky to accumulate a travel record that shows that a visitor has stayed many months in the United States, left for only a short time, and re-entered the United States to stay for another several months. This is because it can give the visa officer reason to suspect that you are actually a "de facto" resident of the U.S.
Under a tourist visa, you can generally stay in the United States for up to six months. However, the exact length of stay is determined by the Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer at your point of entry. When you arrive, the CBP officer will record your arrival, and, crucially, the allowed duration of your stay on a form called the I-94.
The Visa Waiver Program allows citizens of participating countries to travel to the U.S. for tourism or business for up to 90 days without a visa. How to apply for or renew a U.S. tourist visa If you visit the U.S. for tourism or business, you may need a visitor visa, also known as a tourist visa.
A visa must be valid at the time a traveler seeks admission to the United States, but the expiration date of the visa (validity period/length of time the visa can be used) has no relation to the length of time a temporary visitor may be authorized by the Department of Homeland Security to remain in the United States.
The process to renew a visitor visa is the same as getting one for the first time. Follow the process to apply for a visitor visa from the Department of State. Find the contact information for your nearest U.S. embassy or consulate and contact them for visa renewal information. LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023.
Visitors from Europe are limited in the length of time they can stay in the USA to 90 days. getty. For travellers from almost all the countries of the European Union, but as well for travellers ...
However, in their case, they are limited at the border to a maximum 183 days per year of physical presence in the USA. All travellers must be careful with U.S. stays beyond 183 days since that can ...
How to apply for or renew a U.S. tourist visa. If you visit the U.S. for tourism or business, you may need a visitor visa, also known as a tourist visa. Learn how to get and renew this type of nonimmigrant visa.
A citizen of a foreign country who seeks to enter the United States generally must first obtain a U.S. visa, which is placed in the traveler's passport, a travel document issued by the traveler's country of citizenship. Certain international travelers may be eligible to travel to the United States without a visa if they meet the ...
A tourist visa is a type of non-immigrant visa that allows individuals from foreign countries to enter the United States for a temporary period of time for tourism, pleasure, or to visit friends and family. It is typically issued for a specific duration, allowing visitors to explore the country and engage in various recreational activities.
What is a B-1/B-2 visa? A B-1/B-2 visa is a non-immigrant, visa that allows foreign nationals to travel to the United States temporarily for business (B-1), tourism (B-2), or a mix of both (B1/B2). This visa category is widely used for brief visits to the U.S. B visas are typically valid for up to 10 years from the issue date, and travelers to ...
L-1 visa holders can enter the U.S. up to 10 days before their intended period of employment begins and remain up to 10 days after their employment ends. M vocational students: Length of the vocational program as shown on the SEVIS Form I-20, up to a maximum of one year, plus a 30-day grace period in order to prepare to depart the United States ...
The B2 visitor's visa allows Canadians to stay in the US for up to six months (182 days) in any 12-month period, so long as you have the resources to support yourself, you do not work while in ...
The US Tourist visa duration refers to the amount of time you may stay in the US with your tourist visa. It is also called the maximum stay. One of the most popular tourist visas is the US B1/B2 visa, which allows for a maximum stay of 180 days Per Entry. However, the amount of time you can spend in the US is at the discretion of the consular ...
November 17, 2022. The Department of State is committed to facilitating legitimate travel to the United States while safeguarding national security. Many applicants for U.S. visas are required by U.S. law to appear in person. However, local pandemic-era restrictions on public places like our overseas consular sections curbed our ability to see ...
A tourist may be able to stay in the United States for more than 6 months on a B-2 tourist visa, but is required to complete Form I-539, Application to Extend or Change Nonimmigrant Status to extend the stay. If you do not respect the extension time of the tourist visa or do not apply for the extension and stay longer in the US, you will be ...
The B1/B2 Visa has a 10-year validity from its issuance, offering the liberty to visit the U.S. every now and then. However, for each individual visit to the United States, you're permitted a maximum stay of 180 days or 6 months. Applicants are advised to use this time judiciously in order to avoid the trouble of overstaying your visa.
The visa expiration date is shown on the visa along with the visa issuance date. The time between visa issuance and expiration date is called your visa validity. The visa validity is the length of time you are permitted to travel to a port-of-entry in the United States. Depending on your nationality, visas can be issued from a single entry ...
Most travel bans have been lifted and with an exception of some travelers, everyone can enter the United States on a valid B2 visitor visa. It is important to ensure that your passport has at least 6-months validity before starting your journey from your home country. If traveling for personal reasons, you are eligible to get a B2 visitor visa.
Section 702's opponents heavily pushed for a warrant requirement, claiming it was necessary for American's privacy rights. The law's supporters, though, pointed to other reforms made to FISA ...
From April 10, 2025, citizens from Australia, Canada and the US will need a visa to enter the country. On the plus side, those traveling for tourism or cruise travel can apply for an evisa online ...
See the list of situations when you can and cannot extend your stay in the U.S. Learn how to extend your stay in the U.S. Find out how to file for an extension online or by mail. Use the fee calculator to see how much you will have to pay. Select Form I-539 and then select your current nonimmigrant status. LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023.
This revised process will enhance DOS's ability to more accurately predict overall immigrant visa demand in determining the cut-off dates for the Visa Bulletin. This will help ensure that the maximum number of immigrant visas are issued annually as intended by Congress, and minimize month-to-month fluctuations in Visa Bulletin final action dates.
Americans in Israel have been warned to limit their travel as U.S. officials say Iran is expected to launch an attack on the country as soon as Friday.
At the same time, lawmakers retained a per-country limit of 7%. The per-country limit has most harmed highly skilled professionals from India, China and the Philippines due to larger populations.
The EPA's new drinking water limits apply to only a small fraction of the more than 12,000 types of PFAS, so activists are still concerned about overall exposure. "This is not the final step ...
Brazil again extends visa exemptions for US, Canada and Australia, this time until 2025. Brazil's government has extended exemptions to tourist visa requirements for citizens of the U.S ...
April 9, 2024. Arizona's highest court on Tuesday upheld an 1864 law that bans nearly all abortions, a decision that could have far-reaching consequences for women's health care and election ...