The Geography of Transport Systems
The spatial organization of transportation and mobility

B.7 – Tourism and Transport
Author: dr. jean-paul rodrigue.
Tourism, as an economic activity, relies on transportation to bring tourists to destinations, and transportation can be part of the touristic experience.
1. The Emergence of the Tourism Industry
Since the 1970s where tourism became increasingly affordable, the number of international tourists has more than doubled . The expansion of international tourism has a large impact on the discipline of transport geography since it links traffic generation, interactions at different scales (from the local to the global), and the related transportation modes and terminals. As of 2016, 1.2 billion international tourist receipts were accounted for, representing more than 10% of the global population. The industry is also a large employer accounting for 10% of all the global employment; 30 tourist visits are usually associated with one job. 30% of the global trade of services is accounted for by tourism. Tourism dominantly takes place in Europe and North America , but geographical diversification is taking place.
Traveling has always been an important feature, but its function has substantially evolved. Historically, travelers were explorers and merchants looking to learn about regions, potential markets and to find goods and resources. The risks and exoticism associated also attracted the elite that could afford the large expenses and the time required to travel to other remote destinations. Many wrote realistic and even imaginary travel accounts. As time moved on and as transportation became more reliable, traveling became a more mundane activity taking place in an organized environment; tourism. In the modern world, traveling is more centered around annual holidays and can be reasonably well predicted.
As an economic activity, tourism is characterized by a high demand level of elasticity. As transport costs are significant for international transportation, cost fluctuations strongly influence demand. Therefore, transport is a key element in the tourism industry. The demand in international and even national transport infrastructures implies a large number of people to be transported in an efficient, fast, and inexpensive manner. It requires heavy investments and complex organization. Well-organized terminals and planned schedules are essential in promoting adequate transportation facilities for tourists, notably since the industry is growing at a fast rate.
Transport is the cause and the effect of the growth of tourism. First, the improved facilities have incited tourism , and the expansion of tourism has prompted the development of transport infrastructure. Accessibility is the main function behind the basics of tourism transport. In order to access sought-after destinations, tourists have a range of transportation modes that are often used in a sequence. Air transport is the primary mode for international tourism, which usually entails travel over long distances. Growth rates of international air traffic are pegged to growth rates of international tourism.
Transport policies and national regulations can influence destinations available to tourists. One dimension concerns the openness to tourism through travel visa restrictions , which vary substantially depending on the countries of origin of tourists. Unsurprisingly, travelers from developed countries, particularly Europe, face the least restrictions, while travelers from developing countries face a much more stringent array of restrictions. Another dimension concerns the provision of infrastructure. If the public sector does not cope with the demand in terms of transport infrastructures, the tourist industry might be impaired in its development. However, land transport networks in various countries are designed to meet the needs of commercial movements that tourism requires.

Tourism usually contributes enough to the local economy that governments are more than willing to improve road networks or airport facilities, especially in locations with limited economic opportunities other than tourism. There are, however, significant differences in the amount of spending per type of mode, namely between cruise and air transport tourism. Cruise shipping tourism provides much less revenue than a tourist brought by air travel. A significant reason is that cruise lines are capturing as much tourism expenses within their ships as possible (food, beverages, entertainment, shopping) and have short port calls, often less than a day. Tourists arriving by air transport usually stay several days at the same location and use local amenities.
2. Means and Modes
Tourism uses all the standard transportation modes since travelers rely on existing passenger transport systems, from local transit systems to global air transportation.
- Car traveling is usually an independent transport conveyance where the traveler decides the route and the length of the trip. It is usually cheaper since road fees are not directly paid and provided as a public. It is the only transportation mode that does not require transfers, in the sense that the whole journey, from door to door can be achieved. Along major highway corridors, service activities such as restaurants, gas stations, and hotels have agglomerated to service the traffic, many of which touristic. Car transport is the dominant mode in world tourism (77% of all journeys), notably because of advantages such as flexibility, price, and independence. Tourists will often rent cars to journey within their destinations, which has triggered an active clustering of car rental companies adjacent to main transport terminals (airports, train stations) and touristic venues.
- Coach traveling uses the same road network as cars. Coaches are well suited for local mass tourism but can be perceived as a nuisance if in too large numbers since they require a large amount of parking space. They can be used for short duration local tours (hours) but also can be set for multi-days journeys where the coach is the conveyance moving tourists from one resort to another.
- Rail travel was the dominant form of passenger transport before the age of the automobile. The railway network usually reflects more the commercial needs of the national economy then holiday tourist flows which can make it a less preferred choice as a traveling mode. The railway systems of several countries, notably in Europe, have seen massive investments for long-distance routes and high-speed services. Due to the scenery or the amenities provided, rail transportation can also be a tourist destination in itself. Several short rail lines that no longer had commercial potential have been converted for tourism.
- Air transport is by far the most effective transport mode. Notably because of prices, only 12.5% of the tourists travel by plane, but for international travel, this share is around 40%. Air transport has revolutionized the geographical aspect of distances; the most remote areas can now be reached any journey around the world can be measured in terms of hours of traveling. Business travelers are among the biggest users of airline facilities, but low-cost air carriers have attracted a significant market segment mainly used for tourism.
- Cruises are mainly providing short sea journeys of about a week. Cruising has become a significant tourist industry. Cruise ships act as floating resorts where guests can enjoy amenities and entertainment while being transported along a chain of port calls. The international market for cruising was about 22.2 million tourists in 2015, which involves an annual growth rate above 7% since 1990. The main cruise markets are the Caribbean and the Mediterranean, with Alaska and Northern Europe fjords also popular during the summer season. This industry is characterized by a high level of market concentration with a few companies, such as Carnival Corporation and Royal Caribbean Cruises who account for about 70% of the market. The impacts of cruising on the local economy are mitigated as the strategy of cruising companies is to retain as much income as possible. This implies that tourists spend most of their money on the cruise ship itself (gift shops, entertainment, casinos, bars, etc.) or on-island facilities owned by cruise shipping companies.

3. Mass Tourism and Mass Transportation
Tourism transport can be divided into two categories:
- Independent means of travel ; controlled by individual tourists who book them on their own. This mainly involves the private automobile, but also mass conveyances that are booked to travel on an individual basis such as regularly scheduled flights, rail connections, ferries, and even cruises.
- Mass travel ; where tourists travel in organized groups. The most common form involves chartered buses and flights used for this single purpose.
When tourism was mainly for the elite, independent means of travel prevailed. However, the emergence of mass tourism and the significant revenue it provides for local economies required the setting of mass transportation systems and specialized firms such as travel agencies organizing travel on behalf of their customers. These firms were able to take advantage of their pricing power being able to negotiate large volumes of passengers for carriers and hotels. Some were even able to become air carriers, such as Thomas Cook Airlines and Air Transat, which are major charterers in their respective markets. Paradoxically, the growth of online travel booking services has favored the re-emergence of independent means of travel since an individual is able to book complex travel services, including transport and hotel accommodations. Thus, the segmentation of the travel industry is linked with the segmentation of the supporting transport systems.

The seasonality of tourism has an important impact on the use and allocation of transportation assets.
- Air transport has a notable seasonality where tourism results in variations in demand, summer being the peak season. Because of this seasonality and the high cost of acquiring additional assets to accommodate peak demand, the airline industry has pricing power during peak touristic demand. This also leads the seasonal charter services to pick up the potential unmet demand. During the winter, charterers focus on subtropical destinations (e.g. Caribbean, Mexico), while during the summer there is more a focus on the European market.
- Cruises also have a seasonality where many cruise lines are repositionning their assets according to variations in the destination preferences. During winter months, the Caribbean is an important destination market, while during the summer, destinations like the Mediterranean, Alaska, and Norway are more prevalent.
4. Covid-19 and its Impacts
Related topics.
- Air Transport
- Airport Terminals
- Transportation and Economic Development
- The Cruise Industry
Bibliography
- Graham, A. and F. Dobruszkes (eds) (2019) Air Transport – A Tourism Perspective, Amsterdam: Elsevier.
- World Economic Forum (2017) The travel & tourism competitiveness report 2017, World Economic Forum.
Share this:
Tourism Transportation
The transport industry has gained a vital place in the global network system and is one of the most important components of the tourism infrastructure. It now becomes easier for people to travel from one place to another because of the various modes of transportation available.
The earliest forms of transportation in the ancient times were animals on land and sails on the sea. Travel development from the need to survive, to expand and develop trade to far off countries, and the hunger to capture new lands and territories. This was followed by the use of steams and electricity in the nineteenth century followed by internal combustion engines.
Aircraft with the jet engines were introduced in the 1950s . With the development of technology, travel became faster and more and people could travel around the globe.
Since tourism involves the movement of people from their places of residence to the places of tourist attractions, every tourist has to travel to reach the places of interest. Transport is, thus, one of the major components of the tourism industry. To develop any place of tourist attraction there have to be proper, efficient, and safe modes of transportation.
Transportation is vital to tourism. Studies have shown that tourists spend almost 30 to 40 percent of their total holiday expenditure on transportation and the remaining on food, accommodation, and other activities. This aspect once again highlights the importance of transportation.
A tourist can travel by a variety of means. The tourism professional, as well as tourist, should be aware of the various modes of transport available to reach the destination and at the destination.
The various mode of transport can be broadly divided into the following three categories :
- Air transport
- Land transport
- Water transport
Air Transport
Due to the growth of air transport in recent years, long-distance travel has become much simpler and affordable. Distance is now measured in hours and not in kilometers. The world has indeed shrunk and becomes a small village.
The development of air transport mostly occurred after World War I and II. Commercial airlines were created for travelers. Because of increasing air traffic, the commercial sector grows rapidly. Before the World War II, Swissair already was carrying around 14-16 passenger between Zurich to London.
The first commercial service was introduced by KLM, the Dutch Airlines, in 1920 between Amsterdam and London. Commercial air travel grew mostly after World War II. More facilities were introduced and there was more comfort in travel.
Jet flights were inaugurated by Great Britain in the year 1952. In the year 1958 Pan American introduced the Boeing 707 services between Paris and New York. Due to the introduction of jet flights, the year 1959 onward saw a tremendous increase in air traffic. The concept of chartered flights was also introduced during this year.
Jumbo jets have revolutionized travel. A large number of people travel by air because of the speed, comfort, and economy in terms of time saved.
The modern era, thus, is the era of mass air travel. After road transport, air travel is the most popular mode of travel, particularly for international travel. For the business travelers, air transport is more convenient as it saves their precious time and offers a luxurious and hassle-free travel. Many airlines nowadays offer special facilities to the business tourist such as Internet on board.
There two types of airlines . These are following as:
Scheduled airlines operate as regular schedules. Chartered airlines or the non-scheduled airlines operate only when there is a demand, mainly during the tourist seasons. The chartered flights work out cheaper than the scheduled carriers as they are operated only when there is a high load factor. Chartered flights provide cheaper packages to the destination such as Portugal and Spain.
India receives more than 400 chartered flights, especially to Goa. Goa has a maximum number of chartered flights coming in during the months of December to January.
The International Air Transport Association (IATA) regulates international air travel. IATA has more than 105 major airlines of the world as its members. IATA regulates the price of tickets on different sectors of travel in the world. The concerned government decides the domestic fares.
The airfares are normally determined on the volume and the air travel demand in an area.
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) is an intergovernmental organization established in the year 1945. Only the government of the country can become a member. The government has to enter into a bilateral agreement for the frequency of flights for operating commercial airlines between them.
Airlines are classified into two broad categories namely small carrier and large carrier . The small carrier also known as commuter airlines have less than 30 seats . The larger carriers, also known as major airlines fly direct routes between the major cities and seat and seat 100 to 800 passengers .
The recent boom in the aviation technology has certainly bought some new development to airlines industry. There has been a major change in the size of the aircraft.
Every year there are a growing number of new airlines being introduced. Because of the growing number of new private airlines, there is stiff competition among them. This has resulted in a considerable reduction in air fairs and has boosted the growth of air traffic. To woo and attract customers, many airlines offer cheaper promotional fares such as excursion fares, group fares, and apex fares.
Million of tonnes of cargo and mail are also handled by the air transport industry.
Road Transport
Humans travel place to place in search of food in the primitive era. They tamed animals such as the dog, ox, horse, camel, reindeer, elephants, etc. for carrying the load and traveling. After the discovery of the wheel, humans developed the cart, the chariot, and the carriage.
Until the seventeenth century, horses were used for traveling. Later on better roads were constructed and some of these roads developed into trade routes, which linked many countries. One of them is the Silk Route which was used for transporting silk from China to Persia and the Blue Gem road from Iran to Afghanistan and India.
Today, the most popular and widely used mode of road travel is the automobile or the car. Road transport is dominated by the automobile, which provides views of the landscape and the freedom to travel. Tourist often travels with their entire family for holidays.
To promote tourism , the vehicle required are coaches and tourist cars. Tourist coaches or buses are preferred for large tourist groups traveling together on a specified tour itinerary. Many tourists prefer to travel in comfort and privacy and hire cars. Cars of various makes and standards are available on a rental basis.
Tourist also uses their own motorcar when holidaying. Cars and coaches carried long distance by train facility is also available in some countries.
The car rental segment of the tourism industry is in a very advanced stage in foreign countries. The client can book a car, himself or through agents, and make it wait at the desired place at the destination. The client can then drive the car himself /herself on reaching the destination.
Rail Transport
The railway is the most economical, convenient, and popular mode of travel especially for long distance travel all over the world. The railroad was invented in the seventeenth century in Germany with wooden tracks. The first steel rail was developed in the USA during the early 1800s . The railways revolutionized transportation and mass movement of people seen in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries.
The broad gauge lines account for more than 55 percent of the total network and carry 85 percent of total traffic. The steam engines have been replaced by diesel and electric engines which have helped in increasing the speed. Railways have promoted tourism by introducing a special tourist train.
In Europe, the railway systems of six European countries have been clubbed to make rail travel easier for the people of Europe. A rail passenger can buy a ticket in any one country of Europe and travel through six countries. For the foreign tourists, Eurail Passes offer unlimited discounts travel in express trains for periods ranging from a week to three months. In the USA, AMTRAK operates trains.
Water Transport
Humans have been traveling through water since time immemorial and carried good and people from one place to another. The boats progressed from the simple raft with some modifications and improvement and were first used around 6000 BC.
Travel by ship was the only means for traveling overseas until the middle of the twentieth century. The Cunard Steamship Company was formed in 1838 with regular steamship services operating on the North Atlantic. During the World War I, in 1914 the operations of the steamship company had to be suspended. After the World War I, the steamship luxury liners were back to business till World War II.
After the World War II, the large luxury liners again started their operations all over the world and carried passengers and holidaymakers. Some of the linear were very large accommodating up to 1000 passengers and had facilities like swimming pools, cinema halls, shops, casino, etc.
The cruise lines are the new attraction among the tourist. The cruises are booked several months in advance for trips into the tropical and sub-tropical waters of the Hawaii, Caribbean, Mediterranean, etc. Water transport today plays two main roles in travel and tourism namely ferrying and cruising .
Modern vessels such as the wave -piercing, the hydrofoil and the hovercraft are the over the water transport and used for short distance routes.
Water transportation is also used in riverboat travel. The Mississippi River has been a popular tourist river since the first settlers came to the USA. Today, tourists enjoy two or three-day luxury trips along the river. In Europe, the Rhine, winding through the grapes growing areas of Germany, offers similar leisure tourist trips.
Motorized ferries and launches are used over rivers to transport tourists and locals, to transport vehicles, and offer facilities such as car parking, restaurants, viewing decks, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Modes of Transport
Tourist has a wide variety of transport options available today. There are several advantages and disadvantages of all the model of transport. These are following as:
Direct root, high speed, quick service, social and political significance, luxurious travel are the advantages of air transportation.
High cost, jet lag, unsuitable for heavy bulk cargo, accidents always fatal, international rule to be observed are the disadvantages of air transportation.
Flexibility, reliable, door to door service, economical, supplements other modes of transport, quick transit for short distances are the advantages of road transport.
Slow speed, carrying capacity limited, accidents, none- AC coaches not so comfortable, comfort depends upon the conditions of roads are the disadvantages of road transport.
Long distance travel cheaper, carrying capacity large, dependable service, quicker than road transportation, ability to view scenery en route is the advantage of railways.
Inflexible, unfit to hilly regions, difficulties in rural areas, dining car facilities not always available are the disadvantage of railways.
Economical, carrying capacity enormously, develops international and coastal trades are the advantages of water transport.
Transportation As An Attraction
To attract customers as well as take them around an attraction, destination developers have used many forms of transport to move people around. These novel modes of transport ensure that major exhibits are viewed in a certain sequence and ensure that the crowd moves through at a reliable pace.
Overcrowding should be avoided at all costs to prevent untoward incidents and to maintain the beauty of the place. Tourist can cover the entire park in a shorter duration with the help of these modes of transport.
Transportation is the most crucial component of the tourism infrastructure. It is required not only for reaching the destination but also visiting the site and moving about at the destination. Variety in modes of transportation adds color to the overall tourism experience.
Unusual forms of transportation are also an attraction such as the cable cars in hilly terrain, the funicular railway, or jet boating. The choice of mode of transport is vast and tourists can choose a mode to suit their budget. They can opt for scheduled or non-scheduled transport such as the hiring of vehicles, boats, coaches or trains so that they can travel with their group.

50 types of transport from around the world
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
There are so many weird and wonderful types of transport around the world. From traditional types of transport such as cars, planes and trains through to unusual types of transport such as camels, dune buggies or cable cars, there is plenty of variety to choose from in the world that we live in today. Read on to find out about the top 50 types of transport around the world….
U.S. Department of Commerce
- Fact Sheets
Was this page helpful?
Fact sheet: 2022 national travel and tourism strategy, office of public affairs.
The 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy was released on June 6, 2022, by U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina M. Raimondo on behalf of the Tourism Policy Council (TPC). The new strategy focuses the full efforts of the federal government to promote the United States as a premier destination grounded in the breadth and diversity of our communities, and to foster a sector that drives economic growth, creates good jobs, and bolsters conservation and sustainability. Drawing on engagement and capabilities from across the federal government, the strategy aims to support broad-based economic growth in travel and tourism across the United States, its territories, and the District of Columbia.
The federal government will work to implement the strategy under the leadership of the TPC and in partnership with the private sector, aiming toward an ambitious five-year goal of increasing American jobs by attracting and welcoming 90 million international visitors, who we estimate will spend $279 billion, annually by 2027.
The new National Travel and Tourism Strategy supports growth and competitiveness for an industry that, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, generated $1.9 trillion in economic output and supported 9.5 million American jobs. Also, in 2019, nearly 80 million international travelers visited the United States and contributed nearly $240 billion to the U.S. economy, making the United States the global leader in revenue from international travel and tourism. As the top services export for the United States that year, travel and tourism generated a $53.4 billion trade surplus and supported 1 million jobs in the United States.
The strategy follows a four-point approach:
- Promoting the United States as a Travel Destination Goal : Leverage existing programs and assets to promote the United States to international visitors and broaden marketing efforts to encourage visitation to underserved communities.
- Facilitating Travel to and Within the United States Goal : Reduce barriers to trade in travel services and make it safer and more efficient for visitors to enter and travel within the United States.
- Ensuring Diverse, Inclusive, and Accessible Tourism Experiences Goal : Extend the benefits of travel and tourism by supporting the development of diverse tourism products, focusing on under-served communities and populations. Address the financial and workplace needs of travel and tourism businesses, supporting destination communities as they grow their tourism economies. Deliver world-class experiences and customer service at federal lands and waters that showcase the nation’s assets while protecting them for future generations.
- Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Travel and Tourism Goal : Reduce travel and tourism’s contributions to climate change and build a travel and tourism sector that is resilient to natural disasters, public health threats, and the impacts of climate change. Build a sustainable sector that integrates protecting natural resources, supporting the tourism economy, and ensuring equitable development.
Travel and Tourism Fast Facts
- The travel and tourism industry supported 9.5 million American jobs through $1.9 trillion of economic activity in 2019. In fact, 1 in every 20 jobs in the United States was either directly or indirectly supported by travel and tourism. These jobs can be found in industries like lodging, food services, arts, entertainment, recreation, transportation, and education.
- Travel and tourism was the top services export for the United States in 2019, generating a $53.4 billion trade surplus.
- The travel and tourism industry was one of the U.S. business sectors hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent health and travel restrictions, with travel exports decreasing nearly 65% from 2019 to 2020.
- The decline in travel and tourism contributed heavily to unemployment; leisure and hospitality lost 8.2 million jobs between February and April 2020 alone, accounting for 37% of the decline in overall nonfarm employment during that time.
- By 2021, the rollout of vaccines and lifting of international and domestic restrictions allowed travel and tourism to begin its recovery. International arrivals to the United States grew to 22.1 million in 2021, up from 19.2 million in 2020. Spending by international visitors also grew, reaching $81.0 billion, or 34 percent of 2019’s total.
More about the Tourism Policy Council and the 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy
Created by Congress and chaired by Secretary Raimondo, the Tourism Policy Council (TPC) is the interagency council charged with coordinating national policies and programs relating to travel and tourism. At the direction of Secretary Raimondo, the TPC created a new five-year strategy to focus U.S. government efforts in support of the travel and tourism sector which has been deeply and disproportionately affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read the full strategy here
If you build it, they will come: Why infrastructure is crucial to tourism growth and competitiveness

Tourism is expanding globally, but can infrastructure keep up?
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Maksim Soshkin
.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Infrastructure is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, infrastructure.
With international tourist arrivals reaching 1.4 billion in 2018— two years ahead of initial projections —the travel and tourism industry will continue to drive global connectivity. The World Economic Forum’s 2019 Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report shows this growth is backed by improving global travel and tourism competitiveness, which stems, in part, from growing aviation capacity, increased international openness, and declining travel costs.
However, the report also shows the need for developing infrastructure, which may not be able to keep up with the additional 400 million arrivals forecasted by 2030 . While infrastructure challenges differ for various regions and levels of economic development, failure to address these challenges may reduce competitiveness, hurting the travel and tourism industry.
Infrastructure—including air, ground, port, and tourism services like hotel rooms and car rental services—plays a vital role in travel and tourism competitiveness, serving as the arteries of the industry. And from a global perspective, infrastructure continues to improve.

Since 2017 , air transport infrastructure is one of the most improved components in the index, with strong growth in scores across most regions, subregions and economic development levels. However, much of this performance has come from growing route capacity and the number of carriers operating. Perceptions of the quality of air transport infrastructure, while better since 2017, have grown more slowly, while most recent airport density figures indicate slightly reduced airport access than before. These results potentially indicate that travel demand and airline growth may eventually outstrip hard-infrastructure capacity. By 2037, the International Air Transport Association projects the number of air passengers could double to 8.2 billion.
The report also shows that global perspectives on the quality and efficiency of ground transport infrastructure and services have remained, on average, near stagnant. Given the projected growth in travel as well as the need for infrastructure to accommodate more tourism-related needs, significant work will be required to bridge multi-trillion dollar investment deficits for airports, ports, rail and roads.

The results could be used to assess the infrastructure readiness of economies by looking at their scores for infrastructure and tourist arrival trends. The figure above compares country subregion and income-level groupings against their growth in international tourist arrivals from 2013 to 2017. It is clear tourism is growing in most subregions and among all income groups, with many above the global rate of growth.
Most of the regions on the right side of the figure above are relatively advanced countries with well-developed infrastructure. As a result, they may have more capacity to handle tourism growth. Moreover, it is also apparent that, despite market maturity, such countries are still welcoming more and more tourists each year. As the figure shows, high-income economies had the largest increase in arrivals, growing faster than the global rate. But while these economies have strong infrastructure, their share of arrivals and growth rates reveals the pressure on their infrastructure.
High-income economies analysed accounted for nearly 65% of arrivals in 2017 and 74.3% of growth in arrivals between 2013 and 2017. Subregions like Southern Europe and Eastern Asia-Pacific have seen rapid growth in arrivals, putting pressure on their more developed infrastructure. Arrivals in Western European countries, which on average, have the best infrastructure in the ranking, might seem to be below the global rate of growth but accounted for nearly one-fifth of global arrivals in 2017, and nearly 14% of the increase globally since 2013.
Northern Europe has experienced some of the fastest growth in arrivals in recent years and had the third-largest improvement in scores for air transport infrastructure since 2017. But its well-developed infrastructure may still come under strain, with this year’s report showing the region’s growth in ground, port and tourist infrastructure was below the global average.
South-East Asia has also experienced strong growth in tourism in recent years, but its near-average infrastructure scores indicate it might lack the capacity to continue accepting tourists. Countries like Vietnam, Indonesia and the Philippines have recently seen a surge in tourism, but, despite improvement in scores, all rank below average for infrastructure.
The regions on the left side of the figure mostly consist of lower-income countries. While these economies do not account for the same volume of arrivals as the more developed regions and countries, they still face capacity issues because their infrastructure is less developed. Nevertheless, due to higher price competitiveness, economic growth and declining travel barriers, many of these countries have also seen some of the biggest percentage increases in arrivals.
Countries in subregions on the upper left-hand quadrant may be at greatest risk of strain due to rapid visitor growth and underdeveloped infrastructure. In particular, this is an issue for South Asia, Western Africa, South America and the Balkans and Eastern Europe. On the other hand, nations on the bottom left-hand quadrant have less tourism growth, though this might be due to their limited infrastructure capacity, among other factors.
How countries deal with their infrastructure will be a crucial factor in their long-term travel and tourism competitiveness. Even nations with developed airports and roads may face strain under growing utilization, which may lead to issues related to quality.
Have you read?
These islands are using tourists to help offset the effects of tourism, why china will soon be the world's top destination for tourists, in the age of the tourism backlash, we need 'destination stewards', tourism is damaging the ocean. here’s what we can do to protect it.
However, it is also important to note competitiveness relies on far more than just infrastructure. Emerging economies also have more work to do when it comes to improving business environments, addressing safety and security concerns and reducing travel barriers. Natural assets, which attract a significant number of visitors internationally, also need to be better protected. For example, South America and South-East Asia outscore the global average for natural resources by about 27% and 11%, respectively, but score below average for environmental sustainability. Consequently, many countries in these subregions may be at risk of damaging the very assets that make great travel destinations.
In some cases, improvements in one area of competitiveness without progress elsewhere can also lead to issues. For instance, Iceland’s improvement in air connectivity and surging visitor volumes was not matched by price competitiveness and overall tourism capacity, potentially explaining its recent slowdown .
Handling all these issues cannot be the purview of only travel and tourism stakeholders. Improving competitiveness, especially as it relates to travel and tourism, requires a holistic, multistakeholder approach.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Industries in Depth .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Industry government collaboration on agritech can empower global agriculture
Abhay Pareek and Drishti Kumar
April 23, 2024

Nearly 15% of the seafood we produce each year is wasted. Here’s what needs to happen
Charlotte Edmond
April 11, 2024

How Paris 2024 aims to become the first-ever gender-equal Olympics
Victoria Masterson
April 5, 2024

5 ways CRISPR gene editing is shaping the future of food and health
Douglas Broom
April 3, 2024

How Japan is attracting digital nomads to shape local economies and innovation
Naoko Tochibayashi and Naoko Kutty
March 28, 2024

The Paris Olympics aims to be the greenest Games in history. Here's how
Sustainable Transport and Tourism Destinations: Volume 13

Table of contents
Introduction.
The relationship between transport and tourism is very complex to analyze due to mutual causality. Nonetheless, it is worthwhile investigating it, especially paying attention to sustainable mobility, due to the need to minimize the externalities of transport, which can otherwise reduce the attractiveness of a tourism destination. To this aim, after a brief overview of different analytical frameworks, this chapter focuses on transport at destination and sustainable mobility options, such as local public transport (PT) and active modes (walking and cycling). In particular, it provides some insights from the literature about both tourists’ mobility patterns — by taking into account both psychological aspects of tourism experience and the localization of the amenities — and specific modal choices, more focused on the impact of transport on the environment. It then concludes by presenting short summaries of each chapter of the book, in order to provide an overview of the investigated topics, which are dealing with both geographical (islands, coastal areas, natural areas) and management/administration (technical solutions, PT provision, transport demand) issues.
Changes of Transport in Cross-Border Tourist Regions in the Polish–Slovak Borderland: An (Un)Sustainable Development?
The Polish–Slovak borderland is a mountainous area with extraordinary natural conditions for tourism development. The main aim of this chapter is to analyze theoretical aspects of a relationship between transport and tourism and to assess selected changes in cross-border transport that have influenced tourism in Polish–Slovak tourism regions. We have tried to answer the questions on changes in transport infrastructure (based on the analysis of the cross-border projects) and public transport (based on the analysis of timetables of the cross-border public transport connections) in the borderland during the last 30 years and to answer the question whether these changes are in accordance with the sustainable development goals. The Polish–Slovak border is seen as a barrier to transport. The increasing cross-border movement of people and goods through Polish–Slovak border after 1989 required the opening of new border crossings and the construction of new cross-border transport infrastructure. Investments to the road infrastructure have led to using of individual automobile transport. Public transport is currently of marginal importance in cross-border transport. The three cross-border rail lines are in poor technical condition, and plans for their modernization are uncertain. Bus transport has been limited on two tourist-oriented lines in the central part of the borderland. In terms of the structure of the use of means of transport, therefore, no change in trends should be expected and most of the incoming people will continue to cross the Polish–Slovak border by their own means of communication. What is worrying, in the future, in the absence of modernization of the railway infrastructure and no organizational measures, there will be a further decline in the importance of public transport in relation to individual road transport.
Tourist Sustainable Mobility at the Destination. A Case Study of a Polish Conurbation
Much attention has of late been paid to the issue of tourist sustainable mobility at the destination. This issue takes on particular significance in big cities, which, prior to the outbreak of the pandemic, saw considerable increases in visitor numbers. The aim of this chapter, which draws on the case study method, is to explore the question of how foreign tourists move around in a Polish conurbation, known as Tri-city. Made up of three cities – Gdansk, Sopot, and Gdynia – it is one of Poland’s most popular tourist destinations. Crucially, in Tri-city all major tourist attractions and facilities are dispersed over a wide area, which makes it particularly well suited to researching visitor mobility patterns. The case study that forms the core of this chapter relies mainly on a paper-and-pencil questionnaire survey conducted among foreign tourists visiting Tri-city in January 2020 as well as on direct observation of reality. It turned out that walking was a preferred way of moving around Tri-city for most foreigners. The findings indicate, too, that young female visitors used public transport more often than older women and all men regardless of age. Furthermore, tourists with a university education more often opted for public transport than those without a degree, and visitors who lived in urban areas used public transport more often than those living in the countryside. The chapter concludes by summarizing the argument and drawing practical lessons for municipal authorities interested in facilitating tourist sustainability in their cities.
Walking and Sustainable Tourism: “Streetsadvisor.” A Stated Preference GIS-Based Methodology for Estimating Tourist Walking Satisfaction in Rome
This chapter proposes a methodology to develop a tool aimed at helping tourists moving sustainably in Rome, focusing on the “last mile” of their transport experience, that is, walking trips. The methodology consists of the development of a stated preference survey, where tourists’ preferences are elicited with respect to alternative configurations of walking paths. This is performed by taking into consideration path accessibility, interference with other modes of transport, and thermal comfort aspects. Besides, georeferenced data are collected and systematized with the overall aim to create a geographical information system of the first municipality of Rome with useful information to evaluate the status of the walking network. The results of the analysis help to understand the relevant factors affecting tourists’ walking behavior. Additionally, the chapter provides the preliminary considerations needed for the definition of a “tourist walking satisfaction indicator” related to their walking experience with two aims: first, it provides useful information for policy-makers on how to design and manage walking networks; second, it provides a framework for a tourist traveler information system (a “StreetsAdvisor”) that can guide them in the city on the base of their heterogeneous preferences.
Environmental Sustainability of City Sightseeing Cruises: A Case Study on Battery-Powered Electric Boats in Berlin, Germany
With continued growth in tourism, demand for guided local excursions, sightseeing, and entertainment has increased rapidly, particularly in European tourist destinations cities. Many touristic sights can often be viewed best from the water. Operators offer a variety of sightseeing cruises on motor barges along rivers, canals, lakefronts, or ports. In many tourist destination cities and around urban heritage sites, however, increasing boat traffic and the associated air pollution from diesel-powered engines have become a local environmental concern. Based on complaints from residents and visitors, several cities have already announced plans for (mandatory) tourist boat emission reductions. Today, electric mobility offers alternative options for safely and conveniently powering commercial tourist boats, that may contribute to mutually beneficial solutions for local operators, tourist visitors, and residents alike. However, the technology is still expensive and new businesses may also face considerable challenges when entering established local competitive tourism markets. Focusing on the local waterways of the city of Berlin, Germany, the authors have conducted a local case study, including interviews with several operators of (electric) tour boats, as well as an initial empirical survey of their tourist customers. The authors point out the viewpoints of the various stakeholders, identify opportunities, discuss constraints, and offer policy recommendations with a view to enhance the sustainability of waterborne transport in tourist destination cities.
Sustainable Tourism Mobility in Malta: Encouraging a Shift in Tourist Travel Behavior Through an Innovative Smartphone App for Trip Planning
Malta has long been a tourist destination with visitors totaling 2.6 million in 2018. A 2013 survey by the Malta Tourism Authority found that 22% of tourists opted for a rental car during their stay, whereas 76% chose public transport to meet their travel needs. In recent years, the modernization of the bus fleet, improved information provision, and the introduction of a ferry service in the Valletta harbors, have contributed to the increased appeal of public transport. However, the increase in independent tourists might give rise to an increase in the rentals of individual cars. This is a concern given Malta’s high car ownership, and its ever-increasing congestion problem. As part of the CIVITAS DESTINATIONS Project, focused on tourist sustainable mobility, the University of Malta developed a Tourist Mobility smartphone application: MyMaltaPlan. The app enables tourists to plan trips and schedule itineraries between touristic sites. The app, which was launched in the summer of 2019, aims to encourage a shift toward greener travel behavior. A survey was conducted with tourists to understand current tourist travel behavior, and tourists’ use of smartphone or web applications for trip planning. The vast majority of visitors own a smartphone and use it on holiday to plan, access, or book transport. To test the app’s functionalities, a focus group was held with a group of volunteers who shared their experiences in a group discussion. Participants appreciated the automatically created itinerary but noted that to truly promote sustainable mobility, the app should be able to provide the full picture of available alternatives.
Tourists, Residents, and Sustainable Mobility in Islands: The Case of Ischia (Italy)
While tourism is mostly considered a crucial driver for local development, its impact in terms of sustainability and attractiveness of local destinations must also be taken into account. This is especially true for small islands, where tourism may determine detrimental effects in the long term to the limited space and resources. The “sustainable tourism” approach considers this phenomenon and proposes possible solutions to problems such as the loss of public space, waste management, energy and water over-consumption, traffic congestion, air, water, and visual pollution. This chapter presents and discusses the results of a survey that has been carried out in Ischia, a small Mediterranean island located in the Gulf of Naples in order to explore the propensity toward sustainable mobility of both tourists and residents. In particular, the mobility patterns of the respondents have been deeply investigated both at home (domestic behavior) and on holiday (tourist behavior). The results suggest that the promotion of a higher level of cooperation among different stakeholders and local governments is of paramount importance in order to achieve sustainable tourism on islands. This may also generate important effects in terms of destination attractiveness.
Sources of Data to Tackle the Challenges of Public Transport Provision in Seasonal Tourist Destinations
Tourism reconfigures the metropolitan dynamics and the patterns of use of the urban systems. The seasonal nature of tourism produces an impact on the urban hierarchies, since it affects the labor, residential, and recreational markets. As a result, people move to and in the destination and it challenges the supply of sustainable modes of transport such as public transport. This research is set within the context of three demanding challenges that tourist destinations need to face-up: to increase environmental sustainability, to enhance destination competitiveness, and finally to assure quality and comfort of public transport services for the local resident population. Camp de Tarragona region, where Costa Daurada (one of the most important Spanish tourist brands) is located, is analyzed to illustrate how different data sources can aid to confront the aforementioned challenges. Given that seasonality is a dynamic phenomenon, suitable data should be flexible in terms of its time framework. To this end data from smart travel cards provided by the consortium that manages the public transport system in the region has been analyzed. Data unveiled the impact of seasonality on the evolution of demand throughout the year, the type of transport tickets used, or changes occurred in the geographical distribution of the mobility Alternative data sources such as surveys and passive mobile positioning data have also been examined, and their pros and cons have been addressed.
Validity of Repeated Applications of TDM Measures Toward Sustainable Development in Tourism Destinations: A Case Study on Managing Peak Hourly Congested Traffic After the Formula 1 World Championship Japanese Grand Prix at Suzuka
The Formula 1 World Championship Japanese Grand Prix (denoted SUZUKA F1) has been held in Suzuka city in the Mie Prefecture of Japan every year since 2009. This event gathers a large number of motor racing fans around the circuit. The total number of attendees over three days amounts to more than 200,000. Reducing the traffic congestion around expressway interchanges (ICs) and decreasing the departure times of return traffic during peak hours are of critical importance not only for short-term transportation demand management (TDM) measures but also for sustainable development management in Suzuka city as a tourism destination. The chapter starts a brief review of previous studies on the TDM measures to identify the current trends in both their methodological and problem-oriented approaches and then introduces our approach called the area marketing and management approach (AMMA) relating to an issue on how we can pursue the sustainable development in tourism destinations. Based on the concept of the AMMA, a set of the Smart TDM measures are proposed involving the development of the application software that will be used as an interactive communication tool. The validity of the repeated applications of the Smart TDM measures is empirically examined by assessing the most recent experiences at the SUZUKA F1 until 2017. The limitations to what the current Smart TDM measures can do are finally discussed to improve the smartness of these TDM measures to contribute to the sustainable area development.
Cycle Tourism as a Driver for a Sustainable Local Development. The Case of a Natural Tourist Destination in a North-Western Area of Italy
Cycle tourism is considered as a trendy opportunity of local development that should be taken into consideration by several destinations to (further) increase tourism according to the sustainable development approach. It is a broad and complex phenomenon that involves various social and economic actors. Cycle tourists are looking for new and deep experiences to better benefit from the local identities and the uniqueness of the landscape of a territory. Cycle tourism gives sustainable access to environmental and cultural resources of territories often neglected. Despite its evident potentialities, the lack of studies represents a drawback that could compromise the local development. The aim of this chapter is first to describe the characteristics of this form of tourism both in terms of its contribution to the sustainable development and of demand and supply features. Second, the study focuses on an Italian area that is strongly investing in the development of this form of mobility: an area called “Insubria,” which is located in the Lombardy region, near the Swiss border and includes, as main cities, Varese and Como. The work explores whether the supply of the tourism product in this area is aligned with the current and future demand trends of cycling and tourism. The analysis ends with some suggestions about possible improvements in the area and for the long-term industry competitiveness.
Proposals for Sustainable Transport in Natural Areas: A Case Study of Teide National Park
The exponential growth in the number of visitors and the mass-tourism mobility patterns in natural areas are causing serious issues such as traffic congestion, crowding in car parks, pollution, high noise levels, and traffic accidents. In order to redress this situation, demand management policies that propose more sustainable transportation systems are crucial. In this chapter, the authors summarize extensive research carried out in Teide National Park (Canary Islands, Spain), the most visited national park in Spain, one of the most visited in the world, and a clear example of a natural area under pressure from mass tourism. The authors present the current situation of the natural site and three scientific contributions based on a survey combining revealed and stated preferences that analyzes visitor preferences with regard to the use of sustainable transportation systems. The first study analyzes visitors’ preferences regarding the implementation of a public bicycle-sharing system. The second study explores visitors’ willingness to pay to reduce the environmental impact of their visit and the potential implementation of a shuttle-bus service. The third study investigates the recreational economic value of the site. The chapter provides useful information for decision-makers who need to address problems associated with the unsustainable visitor mobility and reports results that can be extrapolated to other natural parks with similar characteristics and high inflow of tourists.
Conclusions
This concluding chapter is explicitly comparative in orientation. It analytically draws the similarities and the heterogeneities of the themes, frameworks, and policies introduced and discussed in the previous chapters. It also highlights the new contributions that emerge from the chapters for both scholars and practitioners. The main issues that a conjoint perusal of the various contributions to the book allow to highlight are: (a) the role played by public policies in fostering solutions that aim at increasing the sustainability of transport in tourist destinations; (b) the role of collaboration among stakeholders and of networks for the implementation of sustainable transport policies and strategies; (c) the importance of the availability of information both on the supply side and on the demand side of the tourist market; and (d) the importance of considering the trends of transport demand of tourists.
- Luca Zamparini
We’re listening — tell us what you think
Something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Sweepstakes
- Travel Tips
What Travel Looked Like Through the Decades
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/maya-kachroo-levine-author-pic-1-2000-1209fcfd315444719a7906644a920183.jpg)
Getting from point A to point B has not always been as easy as online booking, Global Entry , and Uber. It was a surprisingly recent event when the average American traded in the old horse-and-carriage look for a car, plane, or even private jet .
What was it like to travel at the turn of the century? If you were heading out for a trans-Atlantic trip at the very beginning of the 20th century, there was one option: boat. Travelers planning a cross-country trip had something akin to options: carriage, car (for those who could afford one), rail, or electric trolley lines — especially as people moved from rural areas to cities.
At the beginning of the 1900s, leisure travel in general was something experienced exclusively by the wealthy and elite population. In the early-to-mid-20th century, trains were steadily a popular way to get around, as were cars. The debut regional airlines welcomed their first passengers in the 1920s, but the airline business didn't see its boom until several decades later. During the '50s, a huge portion of the American population purchased a set of wheels, giving them the opportunity to hit the open road and live the American dream.
Come 1960, airports had expanded globally to provide both international and domestic flights to passengers. Air travel became a luxury industry, and a transcontinental trip soon became nothing but a short journey.
So, what's next? The leisure travel industry has quite a legacy to fulfill — fancy a trip up to Mars , anyone? Here, we've outlined how travel (and specifically, transportation) has evolved over every decade of the 20th and 21st centuries.
The 1900s was all about that horse-and-carriage travel life. Horse-drawn carriages were the most popular mode of transport, as it was before cars came onto the scene. In fact, roadways were not plentiful in the 1900s, so most travelers would follow the waterways (primarily rivers) to reach their destinations. The 1900s is the last decade before the canals, roads, and railway plans really took hold in the U.S., and as such, it represents a much slower and antiquated form of travel than the traditions we associate with the rest of the 20th century.
Cross-continental travel became more prevalent in the 1910s as ocean liners surged in popularity. In the '10s, sailing via steam ship was the only way to get to Europe. The most famous ocean liner of this decade, of course, was the Titanic. The largest ship in service at the time of its 1912 sailing, the Titanic departed Southampton, England on April 10 (for its maiden voyage) and was due to arrive in New York City on April 17. At 11:40 p.m. on the evening of April 14, it collided with an iceberg and sank beneath the North Atlantic three hours later. Still, when the Titanic was constructed, it was the largest human-made moving object on the planet and the pinnacle of '10s travel.
The roaring '20s really opened our eyes up to the romance and excitement of travel. Railroads in the U.S. were expanded in World War II, and travelers were encouraged to hop on the train to visit out-of-state resorts. It was also a decade of prosperity and economic growth, and the first time middle-class families could afford one of the most crucial travel luxuries: a car. In Europe, luxury trains were having a '20s moment coming off the design glamour of La Belle Epoque, even though high-end train travel dates back to the mid-1800s when George Pullman introduced the concept of private train cars.
Finally, ocean liners bounced back after the challenges of 1912 with such popularity that the Suez Canal had to be expanded. Most notably, travelers would cruise to destinations like Jamaica and the Bahamas.
Cue "Jet Airliner" because we've made it to the '30s, which is when planes showed up on the mainstream travel scene. While the airplane was invented in 1903 by the Wright brothers, and commercial air travel was possible in the '20s, flying was quite a cramped, turbulent experience, and reserved only for the richest members of society. Flying in the 1930s (while still only for elite, business travelers) was slightly more comfortable. Flight cabins got bigger — and seats were plush, sometimes resembling living room furniture.
In 1935, the invention of the Douglas DC-3 changed the game — it was a commercial airliner that was larger, more comfortable, and faster than anything travelers had seen previously. Use of the Douglas DC-3 was picked up by Delta, TWA, American, and United. The '30s was also the first decade that saw trans-Atlantic flights. Pan American Airways led the charge on flying passengers across the Atlantic, beginning commercial flights across the pond in 1939.
1940s & 1950s
Road trip heyday was in full swing in the '40s, as cars got better and better. From convertibles to well-made family station wagons, cars were getting bigger, higher-tech, and more luxurious. Increased comfort in the car allowed for longer road trips, so it was only fitting that the 1950s brought a major expansion in U.S. highway opportunities.
The 1950s brought the Interstate system, introduced by President Eisenhower. Prior to the origination of the "I" routes, road trippers could take only the Lincoln Highway across the country (it ran all the way from NYC to San Francisco). But the Lincoln Highway wasn't exactly a smooth ride — parts of it were unpaved — and that's one of the reasons the Interstate system came to be. President Eisenhower felt great pressure from his constituents to improve the roadways, and he obliged in the '50s, paving the way for smoother road trips and commutes.
The '60s is the Concorde plane era. Enthusiasm for supersonic flight surged in the '60s when France and Britain banded together and announced that they would attempt to make the first supersonic aircraft, which they called Concorde. The Concorde was iconic because of what it represented, forging a path into the future of aviation with supersonic capabilities. France and Britain began building a supersonic jetliner in 1962, it was presented to the public in 1967, and it took its maiden voyage in 1969. However, because of noise complaints from the public, enthusiasm for the Concorde was quickly curbed. Only 20 were made, and only 14 were used for commercial airline purposes on Air France and British Airways. While they were retired in 2003, there is still fervent interest in supersonic jets nearly 20 years later.
Amtrak incorporated in 1971 and much of this decade was spent solidifying its brand and its place within American travel. Amtrak initially serviced 43 states (and Washington D.C.) with 21 routes. In the early '70s, Amtrak established railway stations and expanded to Canada. The Amtrak was meant to dissuade car usage, especially when commuting. But it wasn't until 1975, when Amtrak introduced a fleet of Pullman-Standard Company Superliner cars, that it was regarded as a long-distance travel option. The 235 new cars — which cost $313 million — featured overnight cabins, and dining and lounge cars.
The '80s are when long-distance travel via flight unequivocally became the norm. While the '60s and '70s saw the friendly skies become mainstream, to a certain extent, there was still a portion of the population that saw it as a risk or a luxury to be a high-flyer. Jetsetting became commonplace later than you might think, but by the '80s, it was the long-haul go-to mode of transportation.
1990s & 2000s
Plans for getting hybrid vehicles on the road began to take shape in the '90s. The Toyota Prius (a gas-electric hybrid) was introduced to the streets of Japan in 1997 and took hold outside Japan in 2001. Toyota had sold 1 million Priuses around the world by 2007. The hybrid trend that we saw from '97 to '07 paved the way for the success of Teslas, chargeable BMWs, and the electric car adoption we've now seen around the world. It's been impactful not only for the road trippers but for the average American commuter.
If we're still cueing songs up here, let's go ahead and throw on "Lifestyles of the Rich and Famous," because the 2010s are when air travel became positively over-the-top. Qatar Airways rolled out their lavish Qsuites in 2017. Business class-only airlines like La Compagnie (founded in 2013) showed up on the scene. The '10s taught the luxury traveler that private jets weren't the only way to fly in exceptional style.
Of course, we can't really say what the 2020 transportation fixation will be — but the stage has certainly been set for this to be the decade of commercial space travel. With Elon Musk building an elaborate SpaceX rocket ship and making big plans to venture to Mars, and of course, the world's first space hotel set to open in 2027 , it certainly seems like commercialized space travel is where we're headed next.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Ellie-Nan-Storck-00d7064c4ef24a22a8900f0416c31833.jpeg)

©Dmitry Vinogradov/500px
During any season, at any hour of the day, Moscow thrills visitors with its artistry, history and majesty.
Your next trip starts here
Go from dreaming to planning with trip planning options made to help you craft your ideal itinerary.
Attractions
Must-see attractions.

The Armoury dates to 1511, when it was founded under Vasily III to manufacture and store weapons, imperial arms and regalia for the royal court. Later it…
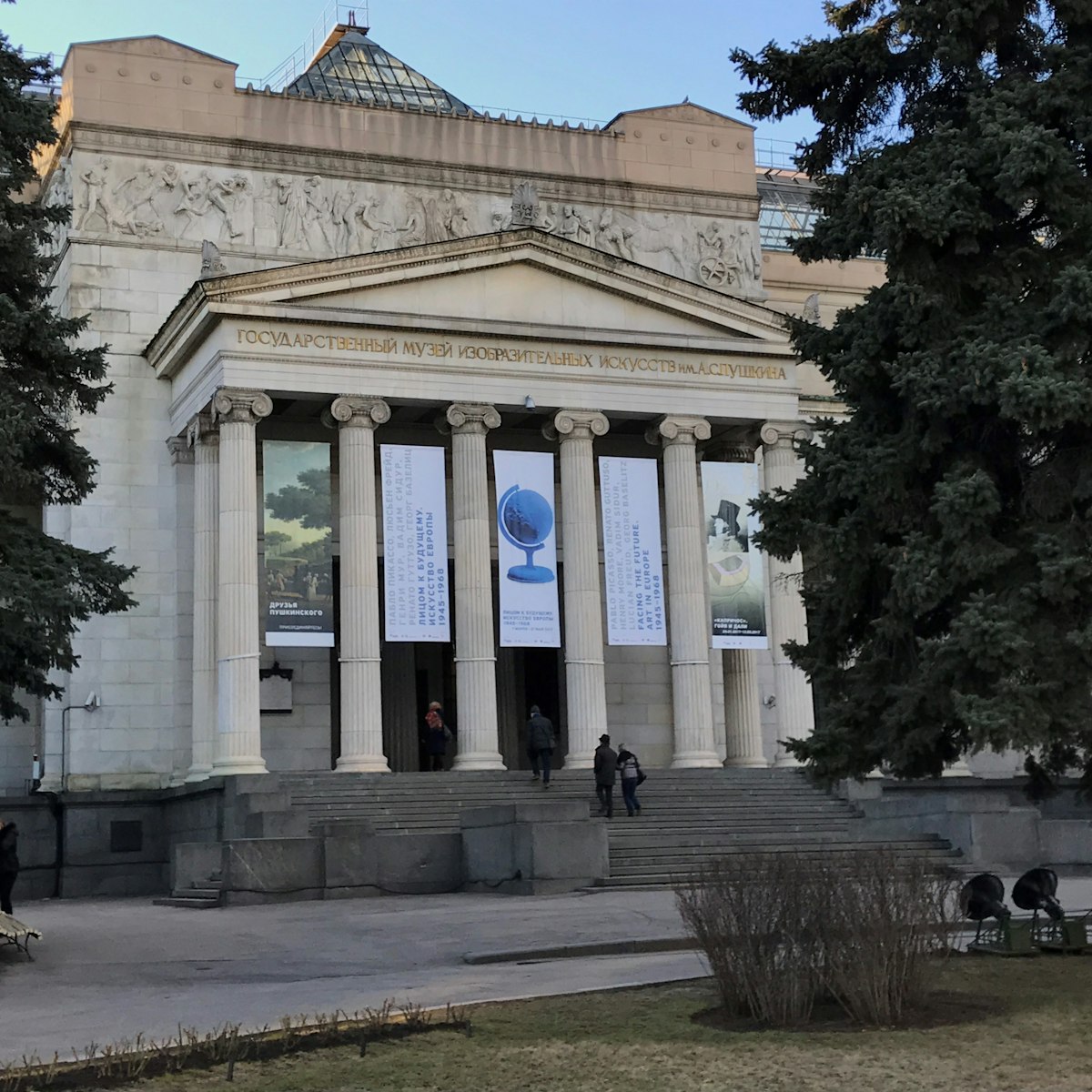

Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts
Arbat & Khamovniki
This is Moscow’s premier foreign-art museum, split over three branches and showing off a broad selection of European works, including masterpieces from…
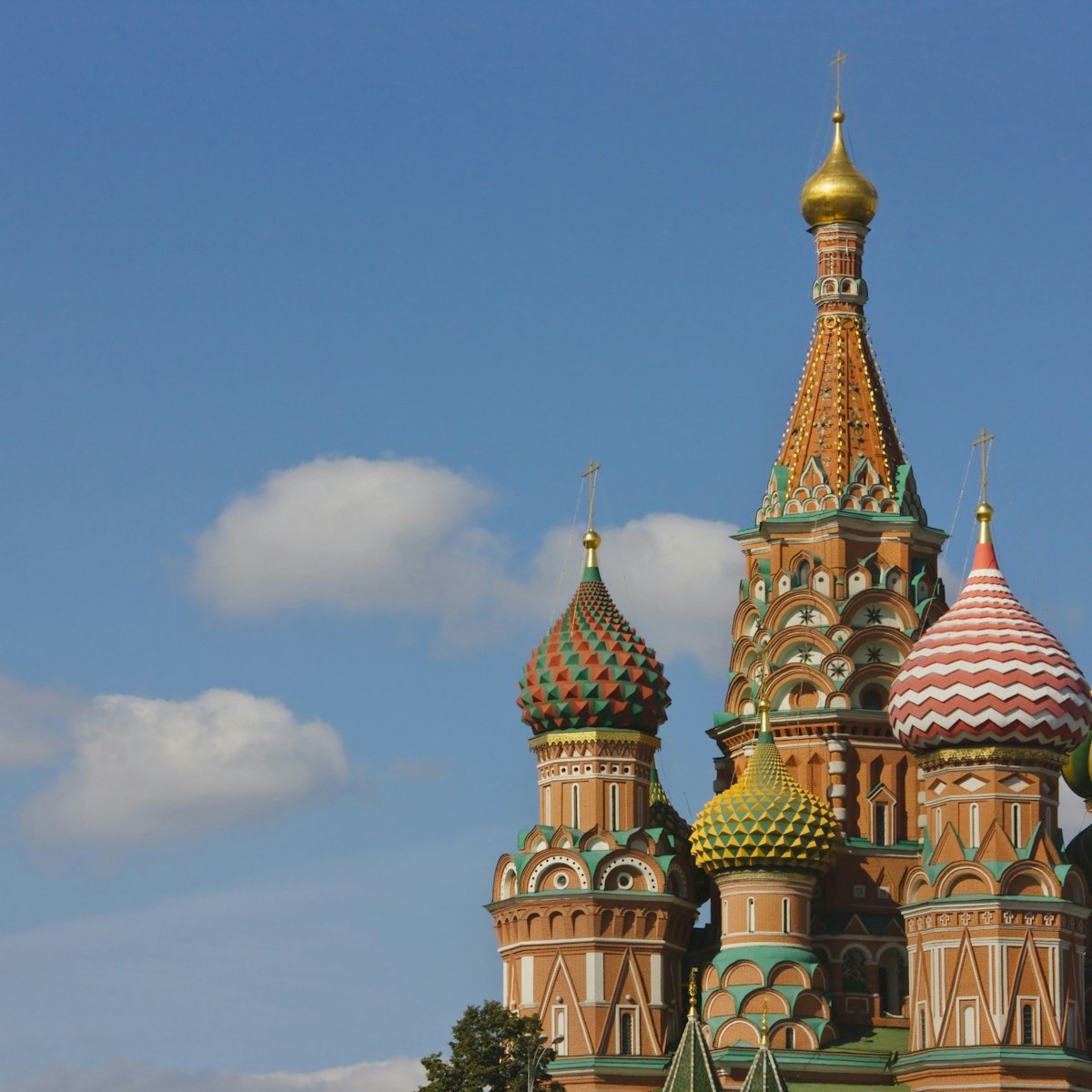

St Basil's Cathedral
At the southern end of Red Square stands the icon of Russia: St Basil’s Cathedral. This crazy confusion of colours, patterns and shapes is the culmination…
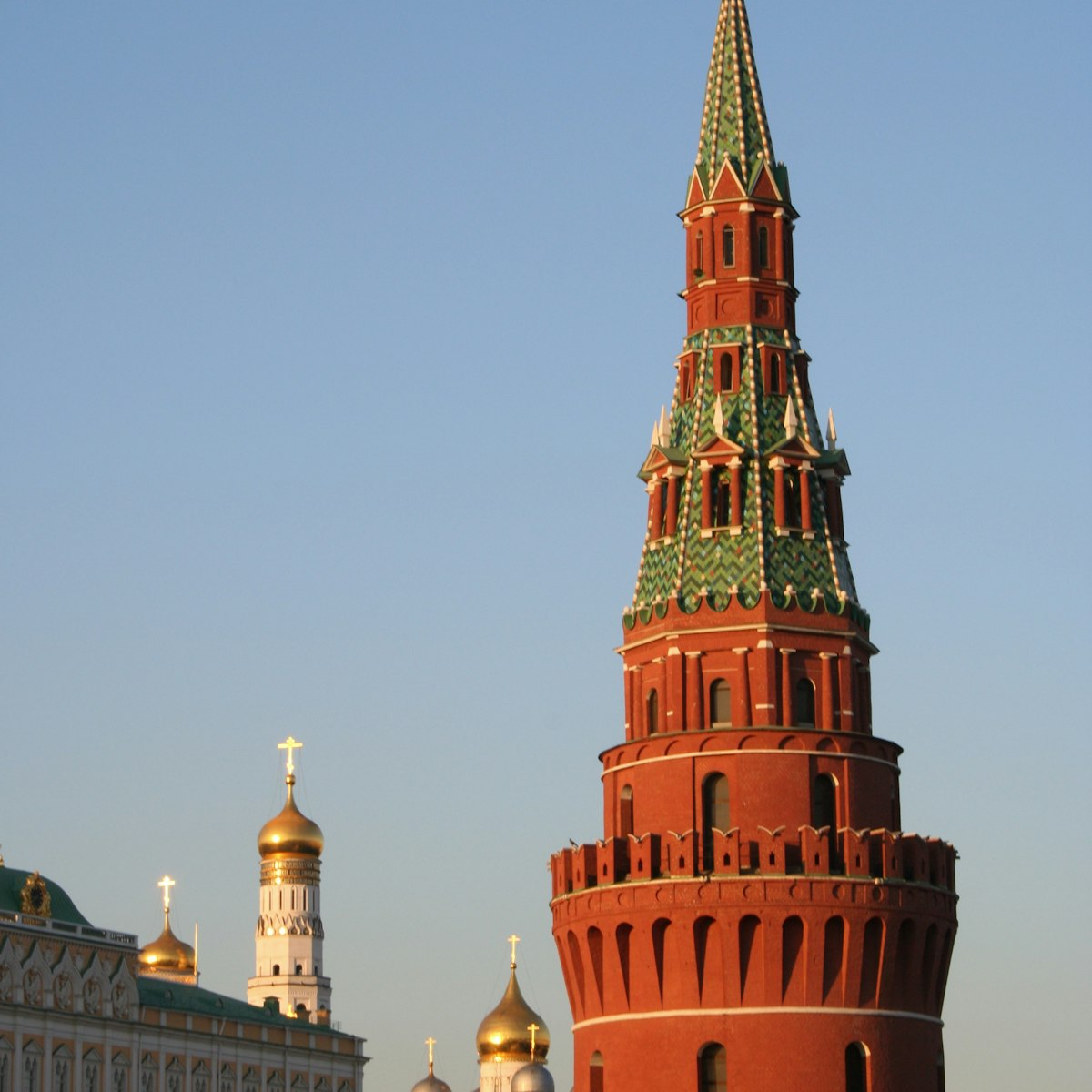

Moscow Kremlin
The apex of Russian political power and once the centre of the Orthodox Church, the Kremlin is the kernel of not only Moscow, but of the whole country…
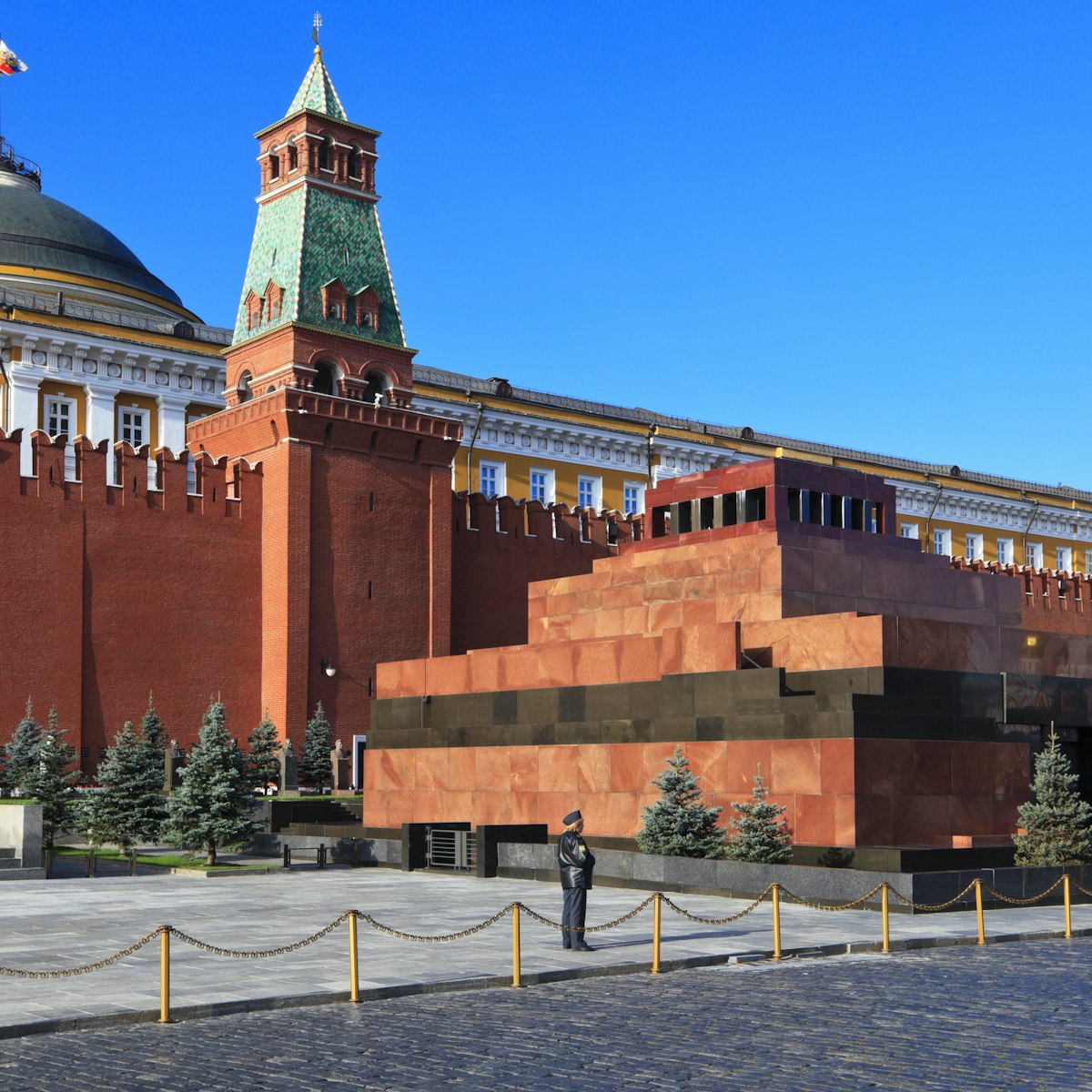

Lenin's Mausoleum
Although Vladimir Ilych requested that he be buried beside his mum in St Petersburg, he still lies in state at the foot of the Kremlin wall, receiving…
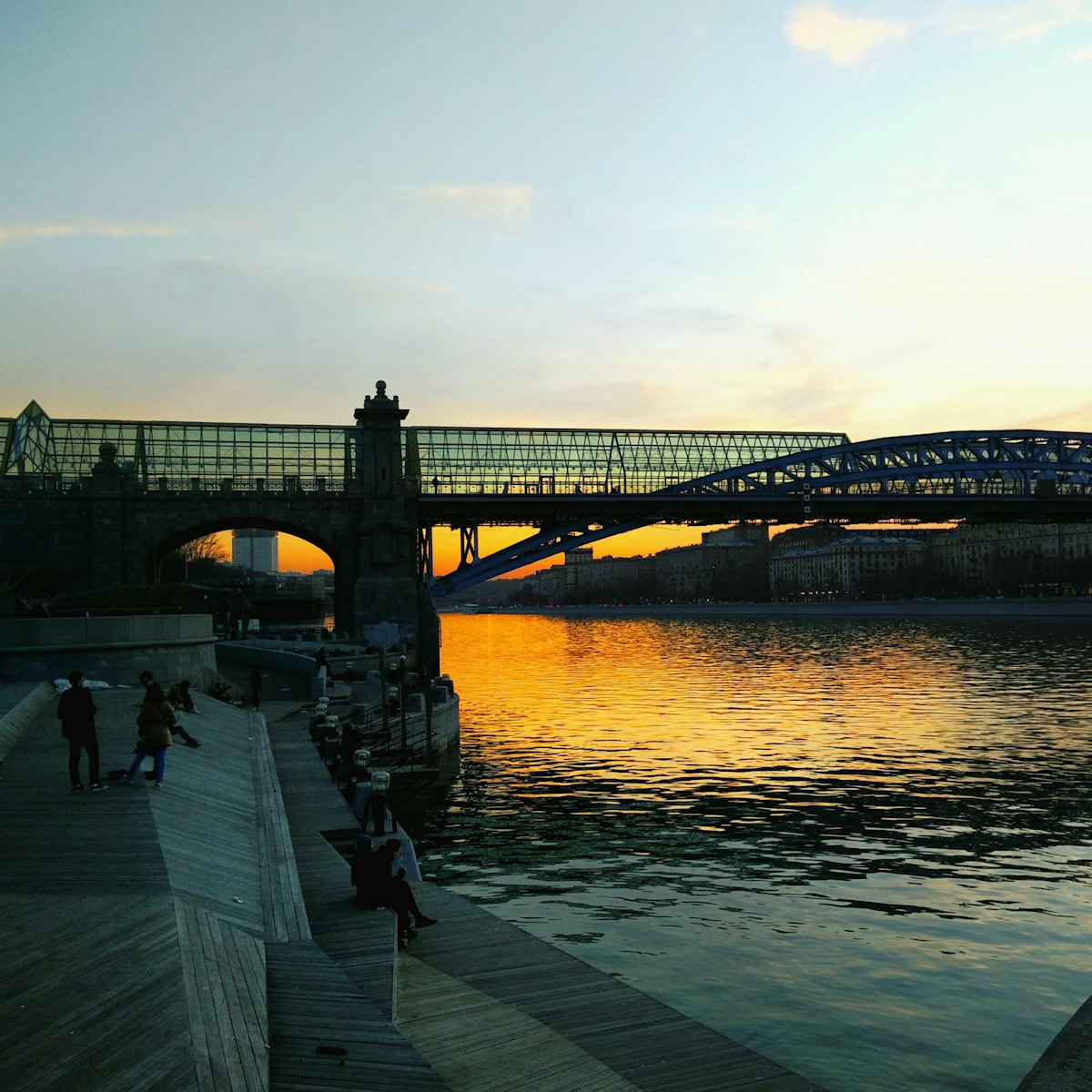

Zamoskvorechie
Moscow's main city escape isn't your conventional expanse of nature preserved inside an urban jungle. It's not a fun fair either, though it used to be one…
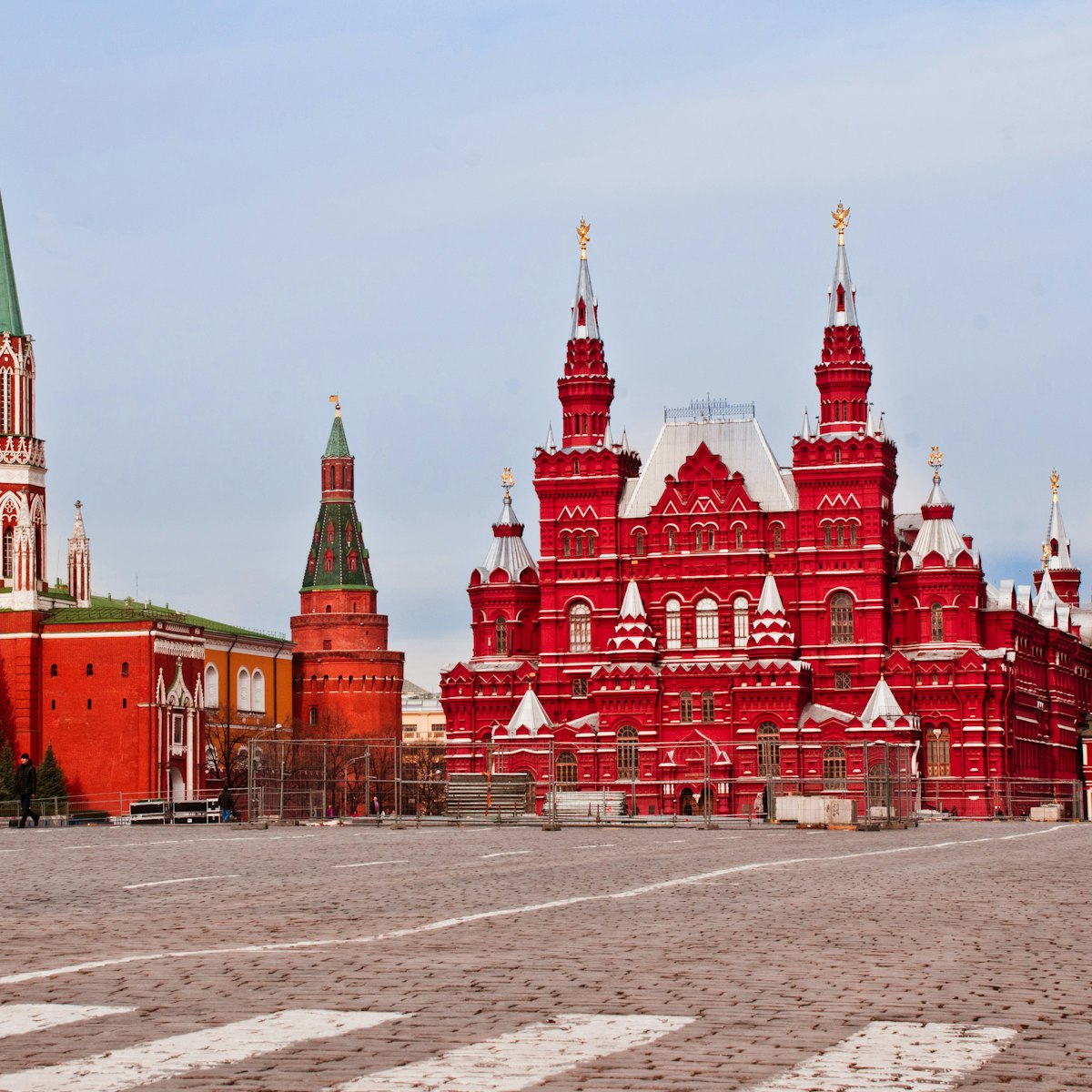

Immediately outside the Kremlin’s northeastern wall is the celebrated Red Square, the 400m-by-150m area of cobblestones that is at the very heart of…
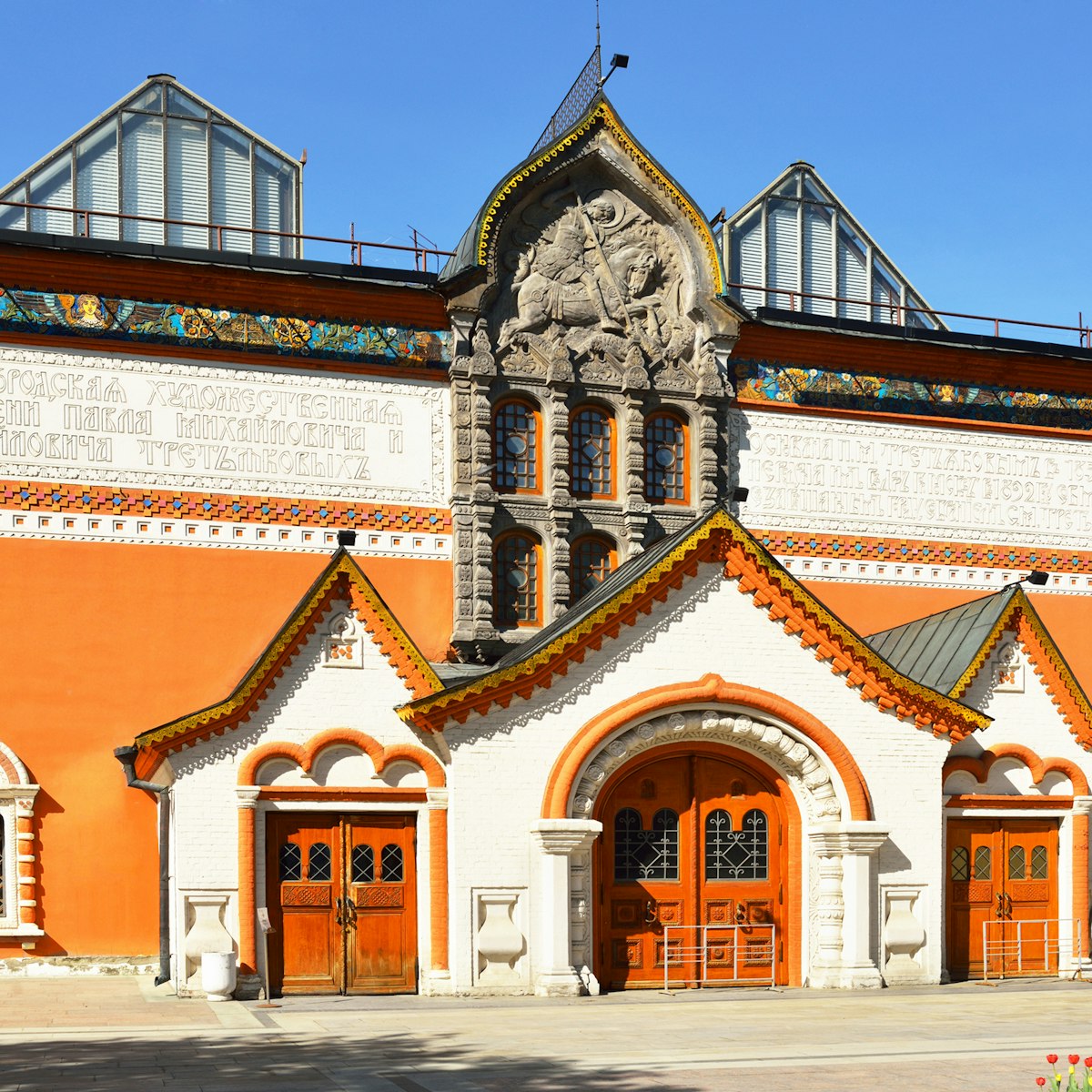

State Tretyakov Gallery Main Branch
The exotic boyar (high-ranking noble) castle on a little lane in Zamoskvorechie contains the main branch of the State Tretyakov Gallery, housing the world…
Latest stories from Moscow
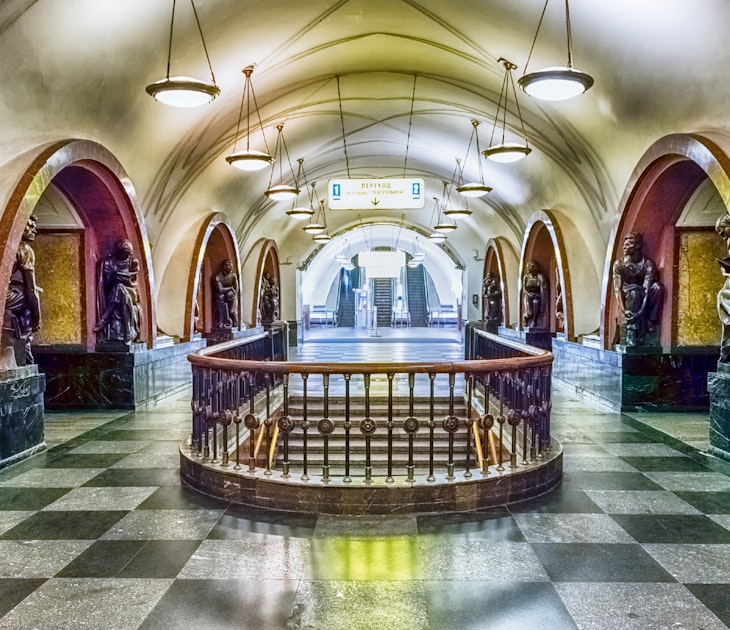

Public Transport
Apr 3, 2020 • 2 min read
You can check out the history and beauty of Moscow Metro's Soviet and modern Russian architecture online.

Mar 31, 2020 • 2 min read

Mar 5, 2020 • 2 min read

Feb 11, 2020 • 5 min read

Jan 23, 2020 • 5 min read

Dec 11, 2019 • 2 min read

Oct 28, 2019 • 5 min read

Sep 25, 2019 • 7 min read

Sep 24, 2019 • 1 min read

Sep 17, 2019 • 5 min read
in partnership with getyourguide
Book popular activities in Moscow
Purchase our award-winning guidebooks.
Get to the heart of Moscow with one of our in-depth, award-winning guidebooks, covering maps, itineraries, and expert guidance.
Moscow and beyond


Plan Your Trip to Moscow: Best of Moscow Tourism

Essential Moscow

Trending in the forums

Moscow Is Great For
Eat & drink.

Art & history

Historic sites

Concerts & shows

- Hotel Metropol Moscow
- Ararat Park Hotel Moscow
- Four Seasons Hotel Moscow
- Lotte Hotel Moscow
- Hotel Baltschug Kempinski Moscow
- Cafe Pushkin
- Sabor de la Vida Restaurant
- Metropol Restaurant
- Restaurant White Rabbit
- Pasta Na Solyanke
- Crocus City Hall
- Nudist Beach in Strogino
- Moscow Metro
- Moscow: Ultimate Dog-sledding Tour in Russian Nature
- A Journey to Christmas in Moscow, Russia
- Snowmobile tours
- Marvellous Moscow Self Guided Audio Walking Tour
- Moscow CityPass
2018 Primetime Emmy & James Beard Award Winner
R&K Insider
Join our newsletter to get exclusives on where our correspondents travel, what they eat, where they stay. Free to sign up.
A History of Moscow in 13 Dishes
Featured city guides.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Automatic Refunds and No More Hidden Fees: D.O.T. Sets New Rules for Airlines
The Transportation Department issued new requirements on refunds when flights are canceled or delayed and on revealing “junk” fees before booking. Here’s what passengers can expect.

By Christine Chung
The Transportation Department on Wednesday announced new rules taking aim at two of the most difficult and annoying issues in air travel: obtaining refunds and encountering surprise fees late in the booking process.
“Passengers deserve to know upfront what costs they are facing and should get their money back when an airline owes them — without having to ask,” said U.S. Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg in a statement, adding that the changes would not only save passengers “time and money,” but also prevent headaches.
The department’s new rules, Mr. Buttigieg said, will hold airlines to clear and consistent standards when they cancel, delay or substantially change flights, and require automatic refunds to be issued within weeks. They will also require them to reveal all fees before a ticket is purchased.
Airlines for America , a trade group representing the country’s largest air carriers, said in a statement that its airlines “abide by and frequently exceed” D.O.T. consumer protection regulations.
Passenger advocates welcomed the new steps.
Tomasz Pawliszyn, the chief executive of AirHelp, a Berlin-based company that assists passengers with airline claims, called it a “massive step forward and huge improvement in consumer rights and protection” that brings the United States closer to global standards in passenger rights.
Here’s what we know about the D.O.T.’s new rules, which will begin to go into effect in October.
There’s now one definition for a “significant” delay.
Until now, airlines have been allowed to set their own definition for a “significant” delay and compensation has varied by carrier . Now, according to the D.O.T., there will be one standard: when departure or arrival is delayed by three hours for domestic flights and six hours for international flights.
Passengers will get prompt refunds for cancellations or significant changes for flights and delayed bags, for any reason.
When things go wrong, getting compensation from an airline has often required establishing a cumbersome paper trail or spending untold hours on the phone. Under the new rules, refunds will be automatic, without passengers having to request them. Refunds will be made in full, excepting the value of any transportation already used. Airlines and ticket agents must provide refunds in the original form of payment, whether by cash, credit card or airline miles. Refunds are due within seven days for credit card purchases and within 20 days for other payments.
Passengers with other flight disruptions, such as being downgraded to a lower service class, are also entitled to refunds.
The list of significant changes for which passengers can get their money back also includes: departure or arrival from an airport different from the one booked; connections at different airports or flights on planes that are less accessible to a person with a disability; an increase in the number of scheduled connections. Also, passengers who pay for services like Wi-Fi or seat selection that are then unavailable will be refunded any fees.
Airlines must give travel vouchers or credits to ticketed passengers unable to fly because of government restrictions or a doctor’s orders.
The vouchers or credits will be transferable and can be used for at least five years after the date they were issued.
Fees for checked baggage and modifying a reservation must be disclosed upfront.
Airlines and ticket agents are now required to display any extra fees for things like checking bags or seat selection clearly and individually before a ticket purchase. They will also need to outline the airline’s policies on baggage, cancellations and changing flights before a customer purchases a ticket.
The rules, which apply to all flights on domestic airlines and flights to and from the United States operated by foreign airlines, have varying start dates.
For example, automatic refunds must be instituted by the airlines within six months. But carriers have a year before they’re required to issue travel vouchers and credits for passengers advised by a medical professional not to fly.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram and sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to get expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places to Go in 2024 .
Christine Chung is a Times reporter covering airlines and consumer travel. More about Christine Chung
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
Mumbai: Spend 36 hours in this fast-changing Indian city by exploring ancient caves, catching a concert in a former textile mill and feasting on mangoes.
Kyoto: The Japanese city’s dry gardens offer spots for quiet contemplation in an increasingly overtouristed destination.
Iceland: The country markets itself as a destination to see the northern lights. But they can be elusive, as one writer recently found .
Texas: Canoeing the Rio Grande near Big Bend National Park can be magical. But as the river dries, it’s getting harder to find where a boat will actually float .
- Partner with AGBI
Moscow courts UAE to bump up inbound tourism
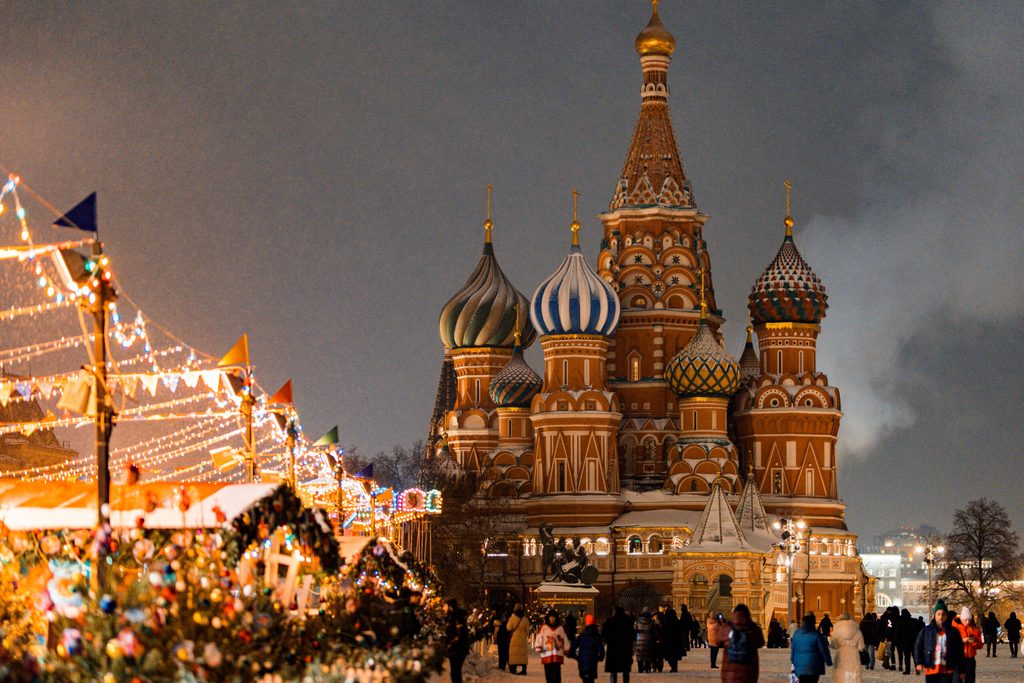

- Moscow targetting UAE tourism
- International visitors 10% of total
- Gulf tourists spend more
Moscow aims to double the number of annual visitors from the UAE this year, to expand its international tourist base amid headwinds such as the war with Ukraine.
Bulat Nurmukhanov, head of the International Cooperation Division at Moscow City Tourism Committee (MCTC), told AGBI that while the Russian capital’s domestic tourism has broadly recovered since the pandemic, international tourism has yet to do so.
Moscow received 24.3 million visitors in 2023, he said, of which 2.3 million were international and the rest were from elsewhere in Russia. In 2019, Moscow recorded 25 million visitors, of which four million were from overseas.
- In Dubai, it looks like the Russians are staying
- Moscow still a key destination for Middle East tourists
- UAE-Russia trade grows as Putin arrives in Gulf
“Despite the challenges Moscow faces today, it has almost recovered its pre-Covid visitor flow of 2019 – our best year for the industry, helped by the effect of hosting the Fifa World Cup in 2018,” Nurmukhanov said.
“But most of these are domestic tourists. We hope that by working with new markets such as the UAE, we can restructure the international tourism base and attract more visitors from the Emirates and wider GCC.”
Moscow has yet to calculate the number of visitors from the UAE last year, but it is a small proportion of the overseas total, according to Nurmukhanov. However, it is an important source market because of its higher-than-average spend per visit.
“They’re helping load Moscow’s five-star hotels”, he said. These are not as popular among domestic tourists and other nationalities as three and four-star hotels.

Last summer, MCTC revealed that tourists from the Middle East accounted for more than 30 percent of Moscow’s total tourist flow from outside the Commonwealth of Independent States in 2022.
“Middle Eastern countries are among the most promising markets for inbound tourism,” the committee noted.
In the UAE, the number of Russian tourists and investors leapt in the year after Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine, as Russian businesses sought a safe haven free of sanctions imposed on them by the West.
Bilateral trade between the two countries has also risen sharply , by 63 percent between January and September 2023 to $9 billion, according to Russia’s government.
Nurmukhanov said: “We’re already receiving a decent amount of tourists from the UAE and want to make sure that now, we adapt our infrastructure and design new hospitality products, entertainment and offerings that will be in their interest.”
The strategy includes enhancing relationships between Moscow and UAE hotels, travel agents and tour operators; improving restaurants’ halal offerings; translating menus and other literature to Arabic, and promoting popular activities such as bear hunting, helicopter trips and horse riding.
Some Moscow hotels even help GCC tourists to purchase warm clothing for their trip, Nurmukhanov said. Gulf visitors can obtain visas on arrival in Russia, and in November a rapid e-visa service was extended to other countries.
Latest articles

- Real Estate
UAE puts up two billion dirhams to pay for flood-damaged homes
The UAE has pledged AED2 billion ($545 million) to help rebuild homes of citizens that were damaged in this month’s floods. Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, the UAE prime minister and ruler of Dubai, said on X (formerly Twitter) that the UAE’s cabinet of ministers had also formed a committee to assess the flood […]

Shareholders to vote on merger to create UAE space giant
Shareholders of two Abu Dhabi technology companies will vote on Thursday on a proposed merger to create a $4 billion space organisation. Bayanat AI and Al Yah Satellite Communications Company, better known as Yahsat, will hold their general assembly meetings simultaneously. The proposed merger will create Space42, an AI-powered space technology champion for the Middle […]

- People & Lifestyle
Cairo has most billionaires in Africa, but wealthy are leaving
Cairo is home to more billionaires than any other African city, but Egypt is facing an exodus of its wealthiest citizens. The international wealth advisory firm Henley & Partners said Cairo is home to four billionaires, and 30 centi-millionaires – those worth $100 million or more. Most reside in affluent parts of Greater Cairo, including […]

- Infrastructure
AD Ports commits $250m to Angola port upgrade
Abu Dhabi Ports Group is investing more than $250 million in a project to upgrade the port terminal at Luanda in Angola. The company said it hd secured a 20-year concession agreement, extendable by another 10 years, with the Luanda Port Authority for operating and modernising the terminal. In agreements with the Angolan logistics companies […]
Download the AGBI app today

Tourism Transportation and Sustainability
- First Online: 01 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- M. R. Dileep 10 &
- Francesca Pagliara ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6332-6313 11
Part of the book series: Advances in Spatial Science ((ADVSPATIAL))
437 Accesses
Transport is integral and inherent in the process of tourism, and the increase in tourism would certainly lead to an increase in transportation. When destinations emerge and turn out to be major tourist centers, demand for transport will also increase by default, which will have a consequent increase in transport infrastructure. This is in addition to the transport need for the people of the place.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Adler, N., Martini, G., & Volta, N. (2013). Measuring the environmental efficiency of the global aviation fleet. Transportation Research Part B , 53(2013), 82–100.
Article Google Scholar
Agrawal, H., Welch, W.A., Henningsen, S., Miller, J.W., & Cocker, D.R. (2010). Emissions from main propulsion engine on container ship at sea. Journal of Geophysical Research , 115, D23205.
Anciaes, P.R. (2015). Visual pollution. In M. Garrett (Ed.), Encyclopedia of transportation: Social science and policy . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, pp. 1709–1711.
Google Scholar
Athanasopoulou, A., Kollarou, V., & Kollaros, G. (2014), Chemicals from different sources, etc. Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Protection and Restoration of the Environment, retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313598720_Soil_pollution_by_transportation_projects_and_operations
Baltrenas, P., & Kliaugiene, E. (2003). Environmental impacts on soils from transport systems in various cities in Lithuania. Transactions on the Built Environment , 64, 373–382.
Banister, D., & Hickman, R. (2013). Transport futures: thinking the unthinkable. Transport Policy , 29, 283–293.
Barr, S., Gilg, A., et al. (2011). ‘Helping people make better Choices’: Exploring the behaviour change agenda for environmental sustainability. Applied Geography , 31(2), 712–720.
Becken, S. (2002). Analyzing international tourist flows to estimate energy use associated with air travel. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 10(2), 114–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669580208667157
Becken, S. (2007). Tourists’ perception of international air travel’s impact on the global climate and potential climate change policies. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15(4), 351–368.
Bows, A., Anderson, K., & Peeters, P. (2009). Air transport climate change and tourism. Tourism and Hospitality Planning & Development , 6(1), 7–20.
Brida, J.G., & Risso, W.A. (2010). Cruise passengers expenditure analysis and probability of repeat visits to Costa Rica: A cross section data analysis. Tourism Analysis , 15, 425–434.
Broaddus, A., Litman, T., & Menon, G. (2009). Transportation Demand Management, Division 44—Water, Energy and Transport Sector Project “Transport Policy Advisory Services”, Deutsche Gesellschaft für- German Technical Cooperation—ESCHBORN, Germany.
Caric, H. (2015). Challenges and prospects of valuation of cruise ship pollution case. Journal of Cleaner Production , 111(B), 487–498.
Caric, H., & Mackelworth, P. (2014). Cruise tourism environmental impacts: The perspective from the Adriatic Sea. Ocean & Coastal Management , 102, 350–363.
Carleton. (2007). The Perils of Parking Lots. https://www.carleton.edu/sustainability/news/the-perils-of-parking-lots/
Castillo-Manzano, J.I., L´opez-Valpuesta, L., & Gonz´alez-Laxe, F. (2011). The effects of the LCC boom on the urban tourism fabric: The viewpoint of tourism managers. Tourism Management , 32, 1085–1095.
Ceron, J.-P., & Dubois, G. (2003, April 9–11). Tourisme et changement climatique. Impacts potentiels du changement climatique en France au XXième siècle. First International Conference on Climate Change and Tourism, Djerba: WTO World Tourism Organisation.
Cheng, Q., Su, B., & Tan, J. (2013). Developing an evaluation index system for low-carbon tourist attractions in China—A case study examining the Xixi wetland. Tourism Management , 36, 314–320.
Chèze, B., Chevallier, J., & Gastineau, P. (2013, January). Will technological progress be sufficient to stabilize CO2 emissions from air transport in the mid-term? Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment , 18, 91–96.
Chilembwe, M.J. (2017). Bycycle transport sustainability opportunnities for tourism development: Case study of Mzuzu City, Malawi. International Journal of Tourism & Hospitality Reviews , 4(1), 01–09.
Cohen, G. (2008). Overview of Cruise Ship Facts, Threats to Environment, Criminal History [online]. Campaign to Safeguard Americas Waters (C-SAW): EarthIsland Institute. www.eii.org/csaw/Gen_Cruise_web_docs/Cruise_Industry_Overview_2008.pdf . Accessed 15 January 2009.
Cohen, S.A., Higham, J.E.S., & Cavaliere, C.T. (2011). Binge flying: Behavioural addiction and climate change. Annals of Tourism Research , 38(3), 1070–1089.
Curtis, C., & Scheurer, J. (2010). Planning for sustainable accessibility: Developing tools to aid discussion and decision-making. Progress in Planning , 74(2), 53–106.
Dube, K., & Nhamo, G. (2019, March). Climate change and the aviation sector: A focus on the Victoria Falls tourism route. Environmental Development , 29, 5–15.
Dubois, G., & Ceron, J.P. (2006). Tourism/leisure greenhouse gas emissions forecasts for 2050: Factors for change in France. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 14(2), 172–191.
EEA. (2017). Road traffic remains biggest source of noise pollution in Europe, retrieved from https://www.eea.europa.eu/highlights/road-traffic-remains-biggest-source
European Conference of Ministers of Transport. (2004). ECMT Annual Report 2004. OECD-ECMT Transport Research Centre, data available online at https://read.oecd-ilibrary.org/transport/ecmt-annual-report-2004_9789282103463-en#page1
Eyring, V., Isaksen, I.S.A., Berntsen, T., Collins, W.J., Corbett, J.J., Endresen, O., Grainger, R.G., Moldanova, J., Schlager, H., & Stevenson, D.S. (2010). Transport impacts on atmosphere and climate: Shipping. Atmospheric Environment , 44, 4735–4771.
Frändberg, L., & Vilhelmson, B. (2003). Personal mobility: A corporeal dimension of transnationalisation. The case of long-distance travel from Sweden. Environment and Planning A , 35, 1751–1768.
Gössling, S., Ceron, J.-P., Dubois, G., & Hall, C.M. (2009). Hypermobile travellers. In Stefan Gössling & Paul Upham (Eds.), Climate Change and Aviation: Issues, Challenges and Solutions . Earthscan: Gateshead-UK, pp. 131–150.
Gössling, S., Hall, M.C., Peeters, P., & Scott, D. (2010). The future of tourism: Can tourism growth and climate policy be reconciled? A Mitigation Perspective, Tourism Recreation Research , 35(2), 119–130.
Greentumble. (2016). Environmental Problems with Parking Lots, greentumble.com, retrieved from https://greentumble.com/environmental-problems-with-parking-lots/
Grossling, S., & Peeters, P. (2007). It Does Not Harm the Environment!’ An Analysis of Industry Discourses on Tourism, Air Travel and the Environment. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (4), 402–417.
Gudmundsson, V.S., & Anger, A. (2012). Global carbon dioxide emissions scenarios for aviation derived from IPCC storylines: A meta-analysis. Transportation Research Part D , 17, 61–65.
Hall, D. (1999). Conceptualising tourism transport: Inequality and externality issues. Journal of Transport Geography , 7(4), 181–188.
Han, X., Liu, A., & Liu, M. (2017), Noise Perception and Its Effects on Tourists’ Satisfaction: A Case Study of Nanluoguxiang Lane in Beijing, INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, InterNoise17, Hong Kong, p. 1-1003, pp. 136–146(11).
Hares, A., Dickinson, J., & Wilkes, K. (2010). Climate change and the air travel decisions of UK tourists. Journal of Transport Geography , 18, 466–473.
Higham, J., Cohen, S.A., Peeters, P., & Gössling, S. (2013). Psychological and behavioural approaches to understanding and governing sustainable mobility. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 21(7), 949–967.
Higham, J. E. S., Cohen, S. A., & Cavaliere, C. T. (2014). Climate Change, Discretionary Air Travel, and the “Flyers’ Dilemma”. Journal of Travel Research , 53(4), 462–475. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287513500393
Higham, J., Cohen, A.S., Cavaliere, T.C., Reis, A., & Finkler, W. (2016, January 16). Climate change, tourist air travel and radical emissions reduction. Journal of Cleaner Production , 111, Part B, 336–347.
Hildebrand, J.A. (2009). Anthropogenic and natural sources of ambient noise in the ocean. Marine Ecology Progress Series , 395, 5–20. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps08353’
Høyer, K.G. (2004). From sustainable mobility to sustainable tourism. In F.D. Pineda, C.A. Brebbia, & M. Mugica (Eds.), Sustainable Tourism . Southampton-UK: WIT Press.
IEA. https://www.iea.org/topics/transport
IPCC. (1999). Aviation and the Global Atmosphere . Cambridge: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change—Cambridge University Press.
Kelly, J., Haider, W., & Williams, W.P. (2007). A behavioral assessment of tourism transportation options for reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gases. Journal of Travel Research , 45(3).
Kenchington, R. (1993). Tourism in coastal and marine environments—A recreational perspective. Ocean & Coastal Management , 19(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/0964-5691(93)90073-8
Khisty, C.J., & Zeitler, U. (2001). Is hypermobility a challenge for transport ethics and systemicity? Systemic Practice and Action Research , 14, 597–613.
Klein, R.A. 2003. Cruising e Out of Control: the Cruise Industry, the Environment, Workers, and the Maritimes. Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives‚ Nova Scotia, Canada.
Klein, R.A. (2011). Responsible cruise tourism: Issues of cruise tourism and sustainability. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management , 18, 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1375/jhtm.18.1.107
Lawson, C.T. (2001). Leisure travel/activity decisions: Time and location differences. Transportation Quarterly , 55(3), 51–61.
Lumsdon, L. (2000). Transport and tourism: Cycle tourism—A model for sustainable development? Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8(5), 361–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669580008667373
Lumsdon, L.M., & Page, S. (2004). Tourism and transport: Issues and agenda for the new millennium . London: Elsevier.
MacNeill, T. (2017). Development as Imperialism: Power and the Perpetuation of Poverty in Afro-Indigenous Communities of Coastal Honduras. Humanity & Society, 41(2), 209–239. https://doi.org/10.1177/0160597615603748
Marsanic, R. (2019). Parking Organization in Urban Areas; Organizacija Parkiranja u Urbanim Podruˇcjima, Naklada Kvarner Novi Vinodolski and University of North Koprivnica, Novi Vinodolski–Koprivnica: Novi Vinodolski, Croatia. ISBN 978-953-7773-98-4.
Maršanic, R., Mrnjavac, E., Pupavac, D., & Krpan, L. (2021). Stationary traffic as a factor of tourist destination quality and sustainability. Sustainability , 2021, 13.
Moriarty, P., & Honnery, D. (2019). Prospects for hydrogen as a transport fuel. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy , 4(4), 16029–16037.
Mowforth, M., & Munt, I. (1998). Tourism and sustainability-new tourism in the this Millennium . London: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Münzel, T., Sørensen, M., & Daiber, A. (2021). Transportation noise pollution and cardiovascular disease. Nature Reviews Cardiology , 18, 619–636. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-021-00532-5
NASA/climate.nasa.gov, retrieved from https://climate.nasa.gov/resources/global-warming-vs-climate-change/
Orsi, F., & Geneletti, D. (2014). Assessing the effects of access policies on travel mode choices in an Alpine tourist destination. Journal of Transport Geography , 39, 21–35.
Peeters, P.M. (2017). Tourism’s impact on climate change and its mitigation challenges. How can tourism become ‘climatically sustainable’? Delft: Delft University of Technology.
Peteers, M.P., & Dings, J. (2007). Climate change, tourism and air transport—Global sustainable tourism requires sustainable air transport. In B. Amelung, K. Blazejczyk, & A. Matzarakis (Eds.), Climate change and tourism—Assessment and copying strategies . Maastricht and Warsaw: Institute of Geography and Spatial Organization, Polish Academy of Sciences.
Peeters, P.M., & Dubois, G. (2010). Tourism travel under climate change mitigation constraints. Journal of Transport Geography , 18, 447–457.
Peeters, P., Egmond, T., & Visser, N. (2004). European tourism, transport and environment, Centre for Sustainability, Tourism and Transport, data available online at https://www.cstt.nl/userdata/documents/appendix_deliverable_1_subject_matter_review_30082004.pdf
Peeters, P., Gössling, S., & Becken, S. (2006). Innovation towards tourism sustainability: climate change and aviation. International Journal of Innovation and Sustainable Development , 1(3), 184–199.
Peeters, P., Higham, J., Cohen, S., Eijgelaar, E., & Gössling, S. (2018). Desirable tourism transport futures. Journal of Sustainable Tourism . https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2018.1477785
Peeters, P., Higham, J., Kutzner, D., Cohen, S., & Gössling, S. (2016). Are technology myths stalling aviation climate policy? Transport Research: Part D Transport Environment , 44, 30–32.
Penner, J.E., Lister, D.H., Griggs, D.J., Dokken, D.J., & McFarland, M. (Eds.). (1999). Aviation and the global atmosphere; a special report of IPCC working groups I and III . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Prideaux, B. (2000). The role of the transport system in destination development. Tourism Management , 21, 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/SO261-5177(99)00079-5
Ritchie, H. (2020). Cars, planes, trains: Where do CO2 emissions from transport come from?, Our World in Data, retrieved from https://ourworldindata.org/co2-emissions-from-transport
Rodrigue, J.-P., Comtois, C., & Slack, B. (2006). The geography of transport systems . Oxon (UK): Routledge.
Saarinen, J. (2018): Beyond growth thinking: The need to revisit sustainable development in tourism. Tourism Geographies , 20(2), 337–340.
Sajida, J.W., Cao, Q., & Kang, W. (2019). Transport sector carbon linkages of EU’s top seven emitters. Transport Policy , 80, 24–38.
Schäfer, A.W., & Waitz, I.A. (2014). Air transportation and the environment. Transport Policy , 34, 1–4.
Scott, D., Hall, C.M., & Gössling, S. (2012). Tourism and climate change: Impacts, adaptation and mitigation . New York: Routledge.
Sheng, L., Li, T., & Wang, J. (2017). Tourism and externalities in an urban context: Theoretical model and empirical evidence. Cities , 70, 40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2017.06.012
Sims, R., Schaeffer, F., Creutzig, X., Cruz-Núñez, M., et al. (2014). Transport. In O.R. Edenhofer, et al. (Eds.), Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . Cambridge, UK and New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, retrieved form https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/ipcc_wg3_ar5_chapter8.pdf
Smith, A., Robbins, D., & Dickinson, J.E. (2018). Defining sustainable transport in rural tourism: Experiences from the New Forest. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 27(2). https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2017.1401633
Speakman, C. (2005). Tourism and transport: Future prospects. Tourism and Hospitality Planning & Development , 2(2), 129–135.
Synáková. (2019). Retrieved from http://tomun.eu/upload/image/Backgrounds/UNESCO/Pollution_effects_on_world_heritage_and_monuments.pdf
Tan, Y.P., & Ismail, N.H. (2020). Reviews on interrelationship between transportation and tourism: Perspective on sustainability of urban tourism development, IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science , 447. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/447/1/012065
Terre d'avenir. (2010). Mediterranean endangered e for a sea free of waste. Expedition M.E.D. e Meditteranee en danger. www.expeditionmed.eu/fr/
Tomej, K., & Liburd, J.J. (2019). Sustainable accessibility in rural destinations: a public transport network approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 28(2), 222–239.
Turner, K. (1988). Environmental management . London: West View Press.
Ubbels, B., Rietveld, P., & Peeters, P. (2002). Environmental effects of a kilometre charge in road transport: An investigation for the Netherlands. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment , 7, 255–264.
Uebersax, M.B. (1996). Indecent proposal: Cruise ship pollution in the Caribbean. http://www.greenbuilder.com/mader/planeta/0896/0896cruise.html
UN-Climate change. https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-climate-change
UNCTAD. (2007). United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, retrieved from https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/ditctncd20065_en.pdf
UNECE. (2015). Air pollution puts cultural heritage at risk, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. https://unece.org/environment/news/air-pollution-puts-cultural-heritage-risk
UNEP. https://www.unep.org/explore-topics/energy/what-we-do/transport
UNWTO-UNEP-WMO. (2008). Climate change and tourism: Responding to global challenges. Madrid. United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and World Meteorological Organization (WMO), UNWTO.
Upham, P., et al. (2003). Towards sustainable aviation . London: Earthscan Publications Ltd.
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). (2008). Cruise Ship Discharge Assessment Report. USEPA Oceans and Coastal Protection Division,Washington. EPA 842-R-07-005.
Vega-Muñoz, A., Arjona-Fuentes, J.M., Ariza-Montesa, A., Han, H., & Law, R. (2010). In search of ‘a research front’ in cruise tourism studies. International Journal of Hospitality Management , 85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2019.102353
WHO. (2022). Road traffic injuries, retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/road-traffic-injuries
WHO, World Health Organization-air pollution, retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/how-air-pollution-is-destroying-our-health
World Health Organization, retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/how-air-pollution-is-destroying-our-health
Zhang, L., Wang, P.Y., Sun, J., & Yu, B. (2016). The sightseeing bus schedule optimization under Park and Ride System in tourist attractions. Annals of Operations Research , 273, 587–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-016-2364-4
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Kerala Institute of Tourism and Travel Studies (KITTS), Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India
M. R. Dileep
Department of Civil, Architectural and Environmental Engineering, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy
Francesca Pagliara
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to M. R. Dileep .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Dileep, M.R., Pagliara, F. (2023). Tourism Transportation and Sustainability. In: Transportation Systems for Tourism. Advances in Spatial Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22127-9_16
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22127-9_16
Published : 01 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-22126-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-22127-9
eBook Packages : Economics and Finance Economics and Finance (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Biden-Harris Administration Announces Final Rule Requiring Automatic Refunds of Airline Tickets and Ancillary Service Fees
Rule makes it easy to get money back for cancelled or significantly changed flights, significantly delayed checked bags, and additional services not provided
WASHINGTON – The Biden-Harris Administration today announced that the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) has issued a final rule that requires airlines to promptly provide passengers with automatic cash refunds when owed. The new rule makes it easy for passengers to obtain refunds when airlines cancel or significantly change their flights, significantly delay their checked bags, or fail to provide the extra services they purchased.
“Passengers deserve to get their money back when an airline owes them - without headaches or haggling,” said U.S. Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg . “Our new rule sets a new standard to require airlines to promptly provide cash refunds to their passengers.”
The final rule creates certainty for consumers by defining the specific circumstances in which airlines must provide refunds. Prior to this rule, airlines were permitted to set their own standards for what kind of flight changes warranted a refund. As a result, refund policies differed from airline to airline, which made it difficult for passengers to know or assert their refund rights. DOT also received complaints of some airlines revising and applying less consumer-friendly refund policies during spikes in flight cancellations and changes.
Under the rule, passengers are entitled to a refund for:
- Canceled or significantly changed flights: Passengers will be entitled to a refund if their flight is canceled or significantly changed, and they do not accept alternative transportation or travel credits offered. For the first time, the rule defines “significant change.” Significant changes to a flight include departure or arrival times that are more than 3 hours domestically and 6 hours internationally; departures or arrivals from a different airport; increases in the number of connections; instances where passengers are downgraded to a lower class of service; or connections at different airports or flights on different planes that are less accessible or accommodating to a person with a disability.
- Significantly delayed baggage return: Passengers who file a mishandled baggage report will be entitled to a refund of their checked bag fee if it is not delivered within 12 hours of their domestic flight arriving at the gate, or 15-30 hours of their international flight arriving at the gate, depending on the length of the flight.
- Extra services not provided: Passengers will be entitled to a refund for the fee they paid for an extra service — such as Wi-Fi, seat selection, or inflight entertainment — if an airline fails to provide this service.
DOT’s final rule also makes it simple and straightforward for passengers to receive the money they are owed. Without this rule, consumers have to navigate a patchwork of cumbersome processes to request and receive a refund — searching through airline websites to figure out how make the request, filling out extra “digital paperwork,” or at times waiting for hours on the phone. In addition, passengers would receive a travel credit or voucher by default from some airlines instead of getting their money back, so they could not use their refund to rebook on another airline when their flight was changed or cancelled without navigating a cumbersome request process.
The final rule improves the passenger experience by requiring refunds to be:
- Automatic: Airlines must automatically issue refunds without passengers having to explicitly request them or jump through hoops.
- Prompt: Airlines and ticket agents must issue refunds within seven business days of refunds becoming due for credit card purchases and 20 calendar days for other payment methods.
- Cash or original form of payment: Airlines and ticket agents must provide refunds in cash or whatever original payment method the individual used to make the purchase, such as credit card or airline miles. Airlines may not substitute vouchers, travel credits, or other forms of compensation unless the passenger affirmatively chooses to accept alternative compensation.
- Full amount: Airlines and ticket agents must provide full refunds of the ticket purchase price, minus the value of any portion of transportation already used. The refunds must include all government-imposed taxes and fees and airline-imposed fees, regardless of whether the taxes or fees are refundable to airlines.
The final rule also requires airlines to provide prompt notifications to consumers affected by a cancelled or significantly changed flight of their right to a refund of the ticket and extra service fees, as well as any related policies.
In addition, in instances where consumers are restricted by a government or advised by a medical professional not to travel to, from, or within the United States due to a serious communicable disease, the final rule requires that airlines must provide travel credits or vouchers. Consumers may be required to provide documentary evidence to support their request. Travel vouchers or credits provided by airlines must be transferrable and valid for at least five years from the date of issuance.
The Department received a significant number of complaints against airlines and ticket agents for refusing to provide a refund or for delaying processing of refunds during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. At the height of the pandemic in 2020, refund complaints peaked at 87 percent of all air travel service complaints received by DOT. Refund problems continue to make up a substantial share of the complaints that DOT receives.
DOT’s Historic Record of Consumer Protection Under the Biden-Harris Administration
Under the Biden-Harris Administration and Secretary Buttigieg, DOT has advanced the largest expansion of airline passenger rights, issued the biggest fines against airlines for failing consumers, and returned more money to passengers in refunds and reimbursements than ever before in the Department’s history.
- Thanks to pressure from Secretary Buttigieg and DOT’s flightrights.gov dashboard, all 10 major U.S. airlines guarantee free rebooking and meals, and nine guarantee hotel accommodations when an airline issue causes a significant delay or cancellation. These are new commitments the airlines added to their customer service plans that DOT can legally ensure they adhere to and are displayed on flightrights.gov .
- Since President Biden took office, DOT has helped return more than $3 billion in refunds and reimbursements owed to airline passengers – including over $600 million to passengers affected by the Southwest Airlines holiday meltdown in 2022.
- Under Secretary Buttigieg, DOT has issued over $164 million in penalties against airlines for consumer protection violations. Between 1996 and 2020, DOT collectively issued less than $71 million in penalties against airlines for consumer protection violations.
- DOT recently launched a new partnership with a bipartisan group of state attorneys general to fast-track the review of consumer complaints, hold airlines accountable, and protect the rights of the traveling public.
- In 2023, the flight cancellation rate in the U.S. was a record low at under 1.2% — the lowest rate of flight cancellations in over 10 years despite a record amount of air travel.
- DOT is undertaking its first ever industry-wide review of airline privacy practices and its first review of airline loyalty programs.
In addition to finalizing the rules to require automatic refunds and protect against surprise fees, DOT is also pursuing rulemakings that would:
- Propose to ban family seating junk fees and guarantee that parents can sit with their children for no extra charge when they fly. Before President Biden and Secretary Buttigieg pressed airlines last year, no airline committed to guaranteeing fee-free family seating. Now, four airlines guarantee fee-free family seating, and the Department is working on its family seating junk fee ban proposal.
- Propose to make passenger compensation and amenities mandatory so that travelers are taken care of when airlines cause flight delays or cancellations.
- Expand the rights for passengers who use wheelchairs and ensure that they can travel safely and with dignity . The comment period on this proposed rule closes on May 13, 2024.
The final rule on refunds can be found at https://www.transportation.gov/airconsumer/latest-news and at regulations.gov , docket number DOT-OST-2022-0089. There are different implementation periods in this final rule ranging from six months for airlines to provide automatic refunds when owed to 12 months for airlines to provide transferable travel vouchers or credits when consumers are unable to travel for reasons related to a serious communicable disease.
Information about airline passenger rights, as well as DOT’s rules, guidance and orders, can be found at https://www.transportation.gov/airconsumer .
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Transportation Department cracks down on airline 'junk fees'
NPR's Leila Fadel talks with Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg about airlines and consumer air travel concerns.
LEILA FADEL, HOST:
Air travel can be a headache with flight cancellations and delays. Well, today, the Department of Transportation may be making that hassle a little more palatable. It's got a new rule out that would compensate travelers whose flights are canceled or are changed in a big way. Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg is with us now to talk about this. Good morning. Thanks for being on the program.
PETE BUTTIGIEG: Good morning. Thank you for having me.
FADEL: So what's the big change here?
BUTTIGIEG: So the big change here has to do with how and when you get your money back. It is already a matter of policy that you're entitled to a cash refund if your flight gets canceled. But right now, you have to know that. You have to go in. You have to fight for it. Now we are making that the default. An airline is required to promptly return payment to the same way that you paid. If it's miles, they give you your miles back. If it's a credit card, the money shows back on your credit card without you having to ask. We're also defining a significant delay. If your flight is delayed more than three hours domestically, more than six hours internationally...
FADEL: Yeah.
BUTTIGIEG: ...Same thing. If you have that delay, you wind up not taking that flight, you get your money back.
FADEL: Now, what prompted this rule change? Like you said, there are ways that customers have been able to get refunds in the past. But what prompted this?
BUTTIGIEG: Well, let me give you an example of something that would often happen. You would have a major delay or have your flight canceled. And the airline would say, we're going to offer you 5,000 miles, which might sound good. But that might be worth 50 bucks when you're actually entitled to 300. And by taking the miles, you give up your right to get the cash. This changes the default so that you get the cash unless you proactively say as a customer that you'll take some other form of compensation.
It also defines what a significant delay is. This is important because sometimes there'd be a scenario where your flight gets delayed by many hours. You book a different ticket on a different airline that's more expensive just to be able to get to where you're going.
BUTTIGIEG: But you never get your money back on the original flight.
FADEL: That's happened to me before.
BUTTIGIEG: You know, we hear so many of these stories because we've been taking in these complaints. Those have informed this rule. There's also a part of the rule that covers fee transparency, requiring airlines to make it very clear upfront what is included in the price of a ticket. Do you have to pay extra for bags? Will you have to pay a change fee if you try to cancel? It finally standardizes that level of transparency and clarifies that if you don't get what you paid for on one of those - like, you pay extra for baggage, but the baggage doesn't get there, or you pay for Wi-Fi, but the Wi-Fi doesn't work - it specifies for the first time that you're entitled to a refund on that as well.
FADEL: And what happens - well, first of all, how do airlines feel about this rule, these rules that are coming into play? And what happens if the airlines don't comply?
BUTTIGIEG: Look, airlines don't love these expansions of passenger rights, but I believe this is to the benefit of the sector as a whole because passengers will have more confidence that it's worth that ticket in the first place and just have more confidence in the aviation sector. So this is really about making sure that we create a better experience for passengers and a stronger aviation sector in the United States.
If an airline is not living up to this rule or any rule, you can let us know at our website, flightrights.gov. Not only is there information about what you can expect and demand, but also a way to file a complaint with us. If the airline's not refunding you promptly or doing what they ought to be doing, let us know. We'll follow up.
FADEL: Secretary of Transportation Pete Buttigieg, thank you for your time.
BUTTIGIEG: Thank you.
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
Airlines must cough up cancellation cash and can no longer hide fees under new federal rule
A federal rule announced Wednesday will require airlines to quickly give cash refunds — without lengthy arguments — to passengers whose flights have been canceled or seriously delayed, the Biden administration said.
“Passengers deserve to get their money back when an airline owes them — without headaches or haggling,” Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg said in a statement.
The rule from the Transportation Department says passengers who decline other reimbursement like travel credits are to get cash refunds.

It applies when a flight is canceled or has a “significant change,” the administration said.
A “significant change” includes when departure or arrival times are three or more hours different from the scheduled times for domestic flights or six hours for international flights, and when the airport is changed or connections are added, it said.
Passengers are also to get refunds when their baggage is 12 hours late in delivery for domestic flights.
The new rule comes after promises to hold airlines accountable after major disruptions that made travel hell for passengers, including the 2022 Southwest Airlines meltdown , which resulted in almost 17,000 significantly delayed or canceled flights and a missing baggage nightmare.
The Transportation Department said that the new rule means refunds are automatic and that "airlines must automatically issue refunds without passengers having to explicitly request them or jump through hoops."
Also announced Wednesday was a rule requiring airlines to more clearly disclose so-called junk fees upfront, such as surprise baggage or other fees, the department said.
It said that rule is expected to save fliers around $500 million a year.
The surprise fees are used so tickets look cheaper than they really are, and then fliers get the unwelcome surprise of fees on checked bags, carry-on bags or reservation changes — or even discounts that are advertised but apply to only part of the ticket price, officials said.
Airlines will also have to tell fliers clearly that their seats are guaranteed and that they don't have to pay extra to ensure they have seats for flights, according to the Transportation Department.
Airlines for America, an industry trade group, said that its member airlines “offer transparency and vast choice to consumers from first search to touchdown” and that they do offer cash refunds.
The 11 largest U.S. airlines returned $10.9 billion in cash refunds last year, an increase over $7.5 billion in 2019 but slightly down from $11.2 billion in 2022, the group said.
“U.S. airlines are providing more options and better services while ticket prices, including ancillary revenues, are at historic lows,” Airlines for America said.
Left out of the federal changes announced Wednesday are those involving "family seating fees," but the Transportation Department said in a statement that "DOT is planning to propose a separate rule that bans airlines from charging these junk fees."
Travelers have complained to the Transportation D epartment that children weren’t seated next to accompanying adults, including in some cases young children, department officials said last year.
Fees on bags specifically have made up an increasing amount of airline revenues, the Transportation Department said Wednesday in announcing the new rules.
A Transportation Department analysis found that airline revenue from baggage fees increased 30% from 2018 to 2022, while operating revenue — which is from the flights themselves — increased by only half that amount, the department said.
Jay Blackman is an NBC News producer covering such areas as transportation, space, medical and consumer issues.
Phil Helsel is a reporter for NBC News.
Enough with airline hidden fees: DOT rules take aim at 'corporate rip-offs'

The Department of Transportation announced new rules on Wednesday to better protect airline passengers against “costly surprise airline fees,” the agency said.
As part of the Biden-Harris Administration’s efforts to crack down on “corporate rip-offs,” two new air travel rules were finalized. The rules mandate airlines to pay full refunds in a timely and straightforward manner and ensure transparency regarding fees associated with air travel.
The new regulations are expected to save consumers over half a billion dollars each year in hidden junk fees, the DOT said.
“Passengers deserve to know upfront what costs they are facing and should get their money back when an airline owes them – without having to ask,” Secretary of Transportation Pete Buttigieg said in a statement.
“Today’s announcements will require airlines to both provide passengers better information about costs before ticket purchase, and promptly provide cash refunds to passengers when they are owed – not only saving passengers time and money, but also preventing headaches.”
Learn more: Best travel insurance
What to know about the newly finalized rules for airline passengers:
What are the new rules from the DOT and how do they impact passengers?
The first new regulation will simplify the process for airline passengers to get what they’re owed by requiring airlines to give automatic cash refunds. Passengers can get these refunds when their flights are “cancelled or significantly changed, their checked bags are significantly delayed, or the ancillary services, like Wi-Fi, they purchased are not provided,” the announcement said.
The second will require airlines and ticket agents to be upfront about any hidden fees, such as checking a bag or changing a flight, to help “consumers avoid unneeded or unexpected charges that can quickly increase and add significant cost to what may, at first, look like a cheap ticket.” Airline fees, increasingly common for airlines to boost their profit, have grown “confusing” for passengers.
Both rules will go into effect in about six months, or around the end of October, the agency said.
Making the skies more accessible: This proposal would help the DOT 'more easily penalize airlines' that damage wheelchairs
How will the new rules make getting refunds from airlines easier?
Getting a refund from airlines is a long-winded and often complicated process. Sometimes, passengers end up getting a travel credit or voucher instead of an actual reimbursement or just a partial refund. Under the new regulation, refunds will be much more straightforward.
Airlines must promptly provide automatic refunds without passengers explicitly requesting them, and the refunds must be issued in the original payment method used to make the purchase.
How fast will the refund get to me?
Airlines will have seven business days to make full refunds for credit card purchases and 20 calendar days for other payment methods.
How else is the DOT cracking down on hidden airline junk fees?
It can be tricky to know exactly how much your final airline ticket will cost due to hidden fees. What may look like a low price at first can quickly add up. Airlines will now have to disclose any baggage, change and cancellation fees and policies before purchases are made – and it has to be clear and upfront, not hidden behind a hyperlink. Airlines will also need to be transparent about weight and dimension limitations. Third-party websites such as Expedia or Booking.com will also be required to display this information.
These days, it’s common for people to pay for seat selection, especially for the lowest price fares, but carriers will now need to inform consumers that seats are guaranteed and it’s unnecessary to pay for one.
The DOT is also banning airlines from using bait-and-switch tactics, in which an airline advertises a discounted fare that doesn’t include mandatory fees that drive the ticket price up.
Kathleen Wong is a travel reporter for USA TODAY based in Hawaii. You can reach her at [email protected] .

Transportation | Spirit Airlines shows improvements, but still…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
Daily e-Edition
Evening e-Edition
- Latest Headlines
- Environment
- Crime and Public Safety
Transportation
Breaking news, transportation | madeline soto: stephan sterns charged with first-degree murder, subscriber only, transportation | spirit airlines shows improvements, but still finishes last in travel industry customer satisfaction study.

Discount carriers Spirit Airlines and Frontier Airlines, once destined to be merger partners, both upped their games in terms of serving their customers, but remained on the bottom of an annual customer satisfaction survey for 2023-24, a national research firm has announced.
Although it registered more improvement points than any airline, South Florida-based Spirit finished last in the annual American Customer Satisfaction Index Travel Study conducted by CFI Group of Ann Arbor, Mich. The study, released Tuesday, assessed the performance of not only the nation’s bigger airlines, but also of hotels, car rental firms, rideshare operators and online travel services.
Overall, all of the industry segments serving travelers showed improvements in the eyes of customers, many of whom are still eager to hit the road despite rising prices and inflation.
For the survey, travelers graded the airlines on multiple service metrics, including baggage handling, boarding process, call centers, cleanliness of airplane cabins and lavatories, food quality (both paid and complimentary). loyalty programs, mobile apps, overhead storage, seat comfort and staff performances at airport gates and ticket counters.
The percentage of people surveyed who said they complained declined year-over-year, with 26% of the business travel respondents saying they filed a complaint in 2024 versus 48% in 2023. Of the leisure travelers surveyed, only 13% said they complained versus 17% last year.
“Airline customer satisfaction has climbed to new heights, reaching scores not seen even before the pandemic disrupted travel,” Forrest Morgeson, associate professor of marketing at Michigan State University and director of research emeritus at the ACSI, said in a statement. “Carriers have bounced back strongly, showing that innovations and service improvements implemented during the last two years have resonated with customers.”
The index was founded at the University of Michigan’s Ross School of Business in partnership with other organizations including CFI, which now conducts the survey. It is no longer affiliated with the university.
Alaska Airlines, which had a door plug blow out of one its planes during a flight over the Pacific Northwest in January, topped the survey for the second straight year, followed by American Airlines.
Discounters register improvements
Among the discount airlines, Allegiant, Frontier and Spirit made the biggest gains in the survey “as they crank up their value propositions,” the organization said in its statement.
Asked for more detail, a CFI spokeswoman said the three airlines “showed improved scores this year on flight experience metrics such as check-in/boarding, in-flight service, travel planning, and staff.”
“Now that the legacy carriers have added so many fees related to seat selection and baggage, customers may perceive a greater value proposition from budget airlines,” she said.
Despite the improvements shown by the discounters, “only Allegiant avoids sitting at the low end of the industry, finishing in third place,” the statement said.
Allegiant, which is based in Las Vegas, was followed in descending order by Southwest Airlines, Delta Air Lines, JetBlue Airways, United Airlines, unidentified carriers in an “All Other” category, then Denver-based Frontier and South Florida-based Spirit.
Spirit, which is moving into a new headquarters complex in Dania Beach, did not immediately respond to an emailed request for comment.
The airline is emerging from a protracted turbulent period highlighted by two failed merger deals and a manufacturers’ engine recall that has left 20 of its 200-plus jetliners grounded.
At a formal opening of its headquarters last week, Ted Christie, the CEO and president, told the South Florida Sun Sentinel the company is eager to start communicating what it wants to do for its customers.
‘We’ve been listening to what our guests have been telling us over the years. We’ve been listening to what the markets have been saying,” he said. “And we haven’t had an opportunity yet to tell our story and to energize what’s going to happen next, and we’re going to take that opportunity.”
Christie didn’t elaborate. But before the breakout of the COVID-19 pandemic, the airline did undertake initiatives to show it wanted better relations with its customers. The airline upgraded its fleet, installed seating with more legroom, and upgraded technology to increase flight schedule reliability.
More recently, the airline has landed in the upper quadrant of the U.S. Department of Transportation’s monthly on-time performance scorecards. For example, the company ranked fourth at 72.5% in January of this year in overall percentage of reported flights arriving on time, according to department data.
More in Transportation

Transportation | Airlines will now be required to give automatic cash refunds for canceled and delayed flights

Rail spikes hammered, bullet train being built from Sin City to the City of Angels

Local News | Orange County Mayor: Sales tax hike is ‘best long-term prospect’ to fund transit

Local News | Orange County abandons proposed transportation sales tax
Emirates is dealing with a 30,000 bag backlog as it grovels to customers about its handling of Dubai floods
- Severe flooding caused by the heaviest rain in 75 years brought travel chaos to Dubai Airport last week.
- The ongoing fallout has prompted Emirates boss Tim Clark to issue an apology to customers.
- 30,000 bags still need to be returned to customers, he said.

Emirates, the Middle East's largest airline, is still trying to return 30,000 leftover bags to customers affected by the torrential rains and flooding that brought Dubai Airport to a standstill last week.
Over the weekend, the airline's president, Tim Clark, acknowledged that Emirates' response to the disruption had been "far from perfect" and apologized to customers.
"I would like to offer our most sincere apologies to every customer who has had their travel plans disrupted during this time," Clark wrote in an open letter posted online on Saturday.
Calling the previous week "one of the toughest for Emirates operationally," he said that the airline had been forced to cancel nearly 400 flights and delay many more after storms brought the region's highest rainfall in 75 years.
"Flooded roads impeded the ability of our customers, pilots, cabin crew, and airport employees to reach the airport, and also the movement of essential supplies like meals and other flight amenities," Clark wrote.
In total, 1,478 flights had been canceled at the world's second busiest airport by Friday morning, according to Reuters.
While planes remained stuck on flooded taxiways, submerged roads surrounding the airport left some passengers stranded in the airport.
Related stories
To accommodate disrupted passengers, Emirates said it had secured 12,000 hotel rooms and issued 250,000 meal vouchers.
Despite the chaos and a government warning telling people to stay at home, Emirates flight attendants in Dubai were also told to report for duty.
However, Clark acknowledged that many passengers had been frustrated by the congestion, lack of information, and confusion at terminals.
In an effort to handle the ongoing fallout, he said that a task force had been created to sort and return 30,000 pieces of left-over luggage to its owners.
The airline officially resumed regular flight operations at Dubai Airport on Saturday, but warned it would still take several days to clear the backlog.
Non-UAE-based carriers were still facing restrictions over the weekend. Foreign airlines with more than two flights in 24 hours were issued with a Notice to Air Missions (NOTAM) instructing them to reduce operations by 50%, Indian news agency PTI reported.
According to FlightRadar 24's data , all arrivals and departures were largely running to schedule again on Monday morning.
The oil-rich United Arab Emirates has become one of the most attractive economic hubs in the Gulf region.
Its efforts to diversify its economy away from oil, centered on Dubai as a tourism hot spot, have helped the country position itself as a major player on the world stage. In a sign of its growing popularity, the number of passengers traveling to Dubai Airport increased by 31.7% in the last year.
Watch: Thousands of bags pile up at US airports after flight cancellations
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Author: Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue. Tourism, as an economic activity, relies on transportation to bring tourists to destinations, and transportation can be part of the touristic experience. 1. The Emergence of the Tourism Industry. Since the 1970s where tourism became increasingly affordable, the number of international tourists has more than doubled.
Air Transport. Direct root, high speed, quick service, social and political significance, luxurious travel are the advantages of air transportation. High cost, jet lag, unsuitable for heavy bulk cargo, accidents always fatal, international rule to be observed are the disadvantages of air transportation.
But transport is a key element in the tourism industry, facilitating and constraining the development of tourism. In other words, transport is the cause and the effect of the growth of tourism at the same time. There is a close connection between mobility and transport. Mobility is commonly defined as the quality of moving freely.
The impacts of transport on tourism. Compared to some of our European competitors such as Switzerland, England has a lack of transport integration and this is compounded by deregulated service provision in areas outside London.This can cause problems for local attractions, accommodations and such like… because if a tourist cannot reach a destination then it I likely to thrive from tourism!
In 2020 alone, the travel and tourism sector lost $4.5 trillion and 62 million jobs globally. But as the world recovers from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, travel and tourism can bounce back as an inclusive, sustainable, and resilient sector. Two experts highlight some of the key transformations in the sector going forward during the ...
A train is one of the most common types of transport around the world. Trains are track-based modes of transport used for both short and long journeys. 24. Airboat. Found in marshy areas like the Everglades, Florida, airboats are used for fishing and also for tourist purposes. 25.
Tourism is based on the physical movement of people, and it is therefore of fundamental importance to have a transport system that is functional and that can facilitate travel to tourist destinations. However, transport is also important in itself because it ensures the freedom of movement for people and reduces social distances, in turn promoting growth and economic development. For this ...
The development of transport infrastructure is a prerequisite and a fundamental factor in tourism sector growth, as without the variety of transport means (i.e. tourist transport by air, by water ...
Tourism supply chains involve many components: accommodation, transport, excursions, bars and restaurants, handicrafts, food production, waste disposal, and the infrastructure that supports tourism within chosen destinations. The importance of one such component, transport, for the efficiency of the tourism supply chain is precisely the topic ...
Transport and Tourism: Global Perspectives investigates the complex relationship between transport provision and tourism, and adopts a global perspective throughout. Maintaining its 4-part structure, this substantially updated third edition addresses all the key issues and new challenges that transport providers, decision-makers, managers and tourists face in the use, operation and management ...
Abstract. Transportation remains one of the most significant elements in the Tourism system and is all-pervasive in the geographical constituents of it. The transportation system forms a network in every site connecting its nook and corner, linking its attractions, industries, gateways, and connecting transportation nodes with one another.
Transport innovation was an essential enabler of tourism's spread and democratization and its ultimate globalization. Beginning in the mid-19th century, the steamship and the railway brought greater comfort and speed and cheaper travel, in part because fewer overnight and intermediate stops were needed.
The 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy was released on June 6, 2022, by U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina M. Raimondo on behalf of the Tourism Policy Council (TPC). ... entertainment, recreation, transportation, and education. Travel and tourism was the top services export for the United States in 2019, generating a $53.4 billion trade ...
Since 2017, air transport infrastructure is one of the most improved components in the index, with strong growth in scores across most regions, subregions and economic development levels.However, much of this performance has come from growing route capacity and the number of carriers operating. Perceptions of the quality of air transport infrastructure, while better since 2017, have grown more ...
The relationship between transport and tourism is very complex to analyze due to mutual causality. Nonetheless, it is worthwhile investigating it, especially paying attention to sustainable mobility, due to the need to minimize the externalities of transport, which can otherwise reduce the attractiveness of a tourism destination.
1900s. The 1900s was all about that horse-and-carriage travel life. Horse-drawn carriages were the most popular mode of transport, as it was before cars came onto the scene. In fact, roadways were ...
National Advisory Committee on Travel and Tourism Infrastructure. On January 19, 2021, the U.S. Department of Transportation released the National Travel and Tourism Infrastructure Strategic Plan (NTTISP). The Department recognizes the importance of tourism to the U.S. economy and the critical need for a comprehensive infrastructure plan that...
Chapter 1 - Progress in Transport and Tourism Research: Reformulating the Transport-Tourism Interface and Future Research Agendas. Les Lumsdon and Stephen J. Page. Pages 1 - 27. View chapter. Select Chapter 2 - Life Cycle, Tourist Motivation and Transport: Some Consequences for the Tourist Experience. Book chapter Full text access.
Public Transport. Take a virtual tour of the fascinating history and architecture of the Moscow Metro. Apr 3, 2020 • 2 min read. You can check out the history and beauty of Moscow Metro's Soviet and modern Russian architecture online. in partnership with getyourguide.
The ancient and modern are juxtaposed side by side in this city of 10 million. Catch a metro from one of the ornate stations to see Red Square, the Kremlin, the nine domes of St. Basil's Cathedral, Lenin's Mausoleum, the KGB Museum and other symbols of Moscow's great and terrible past, then lighten up and shop Boulevard Ring or people watch in ...
1: Off-kilter genius at Delicatessen: Brain pâté with kefir butter and young radishes served mezze-style, and the caviar and tartare pizza. Head for Food City. You might think that calling Food City (Фуд Сити), an agriculture depot on the outskirts of Moscow, a "city" would be some kind of hyperbole. It is not.
April 24, 2024, 9:37 a.m. ET. The Transportation Department on Wednesday announced new rules taking aim at two of the most difficult and annoying issues in air travel: obtaining refunds and ...
Bulat Nurmukhanov of the Moscow City Tourism Committee hopes working with the UAE can 'restructure the international tourism base' Last summer, MCTC revealed that tourists from the Middle East accounted for more than 30 percent of Moscow's total tourist flow from outside the Commonwealth of Independent States in 2022. "Middle Eastern countries are among the most promising markets for ...
16.1 Introduction. Transport is integral and inherent in the process of tourism, and the increase in tourism would certainly lead to an increase in transportation. When destinations emerge and turn out to be major tourist centers, demand for transport will also increase by default, which will have a consequent increase in transport infrastructure.
Media Contact. Press Office. US Department of Transportation 1200 New Jersey Ave, SE Washington, DC 20590 United States. Email: [email protected] Phone: 1 (202) 366-4570 If you are deaf, hard of hearing, or have a speech disability, please dial 7-1-1 to access telecommunications relay services.
LEILA FADEL, HOST: Air travel can be a headache with flight cancellations and delays. Well, today, the Department of Transportation may be making that hassle a little more palatable.
The rule from the Department of Transportation says passengers who decline other reimbursement like travel credits are to get a cash refund. Travelers pass through Salt Lake City International ...
The Department of Transportation announced new rules on Wednesday to better protect airline passengers against "costly surprise airline fees," the agency said. As part of the Biden-Harris ...
The percentage of people surveyed who said they complained declined year-over-year, with 26% of the business travel respondents saying they filed a complaint in 2024 versus 48% in 2023.
Emirates is dealing with a 30,000 bag backlog as it grovels to customers about its handling of Dubai floods. Ground personnel upload luggage and cargo containers onto an Emirates Boeing 777-300 ER ...