Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base

Action Verbs | Definition, List & Examples
Published on September 18, 2023 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou .
An action verb (also called a dynamic verb ) describes the action that the subject of the sentence performs (e.g., “I run”).
Action verbs differ from stative verbs, which describe a state of being (e.g., “believe,” “want”).
My grandfather walks with a stick.
The train arrived on time.
You can download our list of common action verbs in the format of your choice below.
Download PDF list Download Google Docs list
Table of contents
What is an action verb, how to use action verbs, action verbs vs. stative verbs, action verbs vs. linking verbs, worksheet: action verbs, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
An action verb is a type of verb that describes the action that the subject of a sentence is performing. Action verbs can refer to both physical and mental actions (i.e., internal processes and actions related to thinking, perceiving, or feeling).
Whitney analyzed the data to find patterns.
He played football in high school.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Action verbs can be transitive or intransitive. Transitive verbs require a direct object , such as a noun or pronoun , that receives the action. Without a direct object, sentences with a transitive verb are vague or incomplete.
In contrast, intransitive verbs do not require a direct object that receives the action of the verb. However, other information may come after the verb, such as an adverb .
Some action verbs can act as both transitive and intransitive verbs.
He grows tomatoes on his balcony. My niece is growing quickly. Note Because action verbs make your writing more vivid, they can be effectively used for resume writing. Unlike generic phrases like “responsible for,” “tasked with,” or “experienced in,” action verbs are attention-grabbing and help emphasize our abilities and accomplishments.
- I was responsible for social media accounts across various platforms.
- I managed social media accounts across various platforms.
Action or dynamic verbs are often contrasted with stative verbs . While action verbs communicate action, stative verbs describe a state of being or perception (e.g., “it tasted,” “he is,” “she heard”). Due to this, they are typically used to provide more information about the subject, rather than express an action that the subject did. For example, the sentence “Tom loves spending time with friends” uses a stative verb “love” to give us more information about Tom’s personality.
However, some verbs can be used as either dynamic or stative verbs depending on the meaning of the sentence. For example, the verb “think” can denote someone’s opinion ( stative verb ) or the internal process of considering something ( action verb ).
One way to tell action verbs from stative verbs is to look at the verb tenses . Because stative verbs usually describe a state of being that is unchanging, they can’t be used in the continuous (or progressive) tenses. Action verbs, on the other hand, can be used in continuous tenses.
- I am wanting some food.
- I want some food.
Another way is to look at the meaning of the sentence and ask yourself if the verb shows what someone does or how someone feels or is. If the verb describes what someone does, it is an action verb. Otherwise, it is probably a stative verb.
Action verbs should not be confused with linking verbs , like “be,” “become,” and “seem.” Linking verbs connect the subject of a sentence with a subject complement (i.e., a noun or adjective that describes it).
Unlike action verbs, linking verbs do not describe an action, but add more details about the subject, such as how it looks or tastes.
For example, the sentence “The children seem happy” uses the linking verb “seem” to link the subject (“the children”) with the adjective (“happy”).
Some verbs can be either linking verbs or action verbs . If you are unsure, try replacing the linking verb with a conjugated form of the verb “be.” If the sentence still makes sense, then it is a linking verb.
To test your understanding of action verbs, try the worksheet below. Choose the correct answer for each question.
- Practice questions
- Answers and explanations
- Are you baking cookies? They_______[smell/are smelling] delicious!
- Understand is not an action verb, but a stative verb because we can’t use it in a continuous tense. For example, “I’m not understanding you at all” is incorrect.
- Kick is an action verb, while “believe” and “agree” are both stative verbs.
- Smell is correct because it is a stative verb and cannot be used in the present continuous.
If you want to know more about commonly confused words, definitions, common mistakes, and differences between US and UK spellings, make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Sentence structure
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
There are many ways to categorize verbs into various types. A verb can fall into one or more of these categories depending on how it is used.
Some of the main types of verbs are:
- Regular verbs
- Irregular verbs
- Transitive verbs
- Intransitive verbs
- Dynamic verbs
- Stative verbs
- Linking verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
- Modal verbs
If you are unsure whether a word is an action verb , consider whether it is describing an action (e.g., “run”) or a state of being (e.g., “understand”). If the word describes an action, then it’s an action verb.
The function of an action verb is to describe what the subject of the sentence is doing. For example, in the sentence “You have been working since 7 o’clock this morning,” the action verb “work” shows us what the subject (“you”) has been doing.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Nikolopoulou, K. (2023, September 18). Action Verbs | Definition, List & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/action-verb/
Is this article helpful?

Kassiani Nikolopoulou
Other students also liked, what is a transitive verb | examples, definition & quiz, what is an intransitive verb | examples, definition & quiz, what is a linking verb | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Action Verbs: Definition, Examples, & Exercises
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022

Verbs are an essential part of any sentence. Without verbs, you cannot express a complete thought.
The Merriam Webster dictionary defines a verb as “a word that expresses an action, an occurrence, or a state of being”. These three different functions fall into three different types of verbs: action verbs, linking or “to be” verbs , and auxiliary verbs .
In this blog post, we will focus on learning how to recognize and use action verbs , but you can learn more about the other types of verbs in Albert’s Grammar Course .
When you’re ready, test yourself with a quiz and practice with our high-quality, standards-aligned questions here .
What We Review
The Basics of Action Verbs
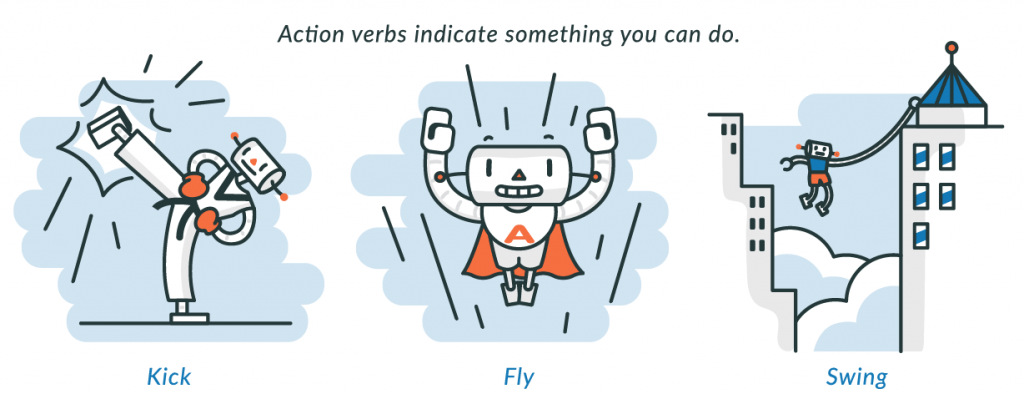
What is an action verb?
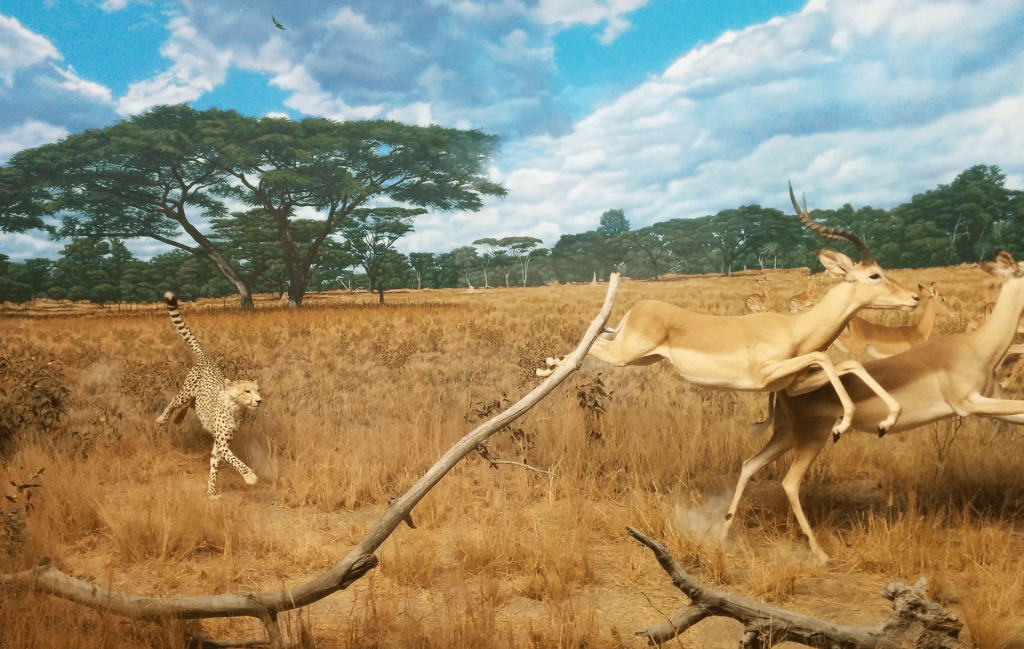
An action verb describes an action that a person , animal, object, or process in nature can do. For example, a cheetah chases gazelles across a plain, and the gazelles sprint away, hearing the tall grass rustle underneath the lion’s paws.
In the sentence above, there are several verbs that describe action; the cheetah chases the gazelles, and the gazelles hear the grass rustle and sprint away.

How are action verbs different from auxiliary verbs?
While action verbs are typically the main verb of the sentence and express the action being done by the subject, auxiliary verbs “help” the main action verb by expressing tense, mood, or voice.
For example, if the gazelles were no longer being chased by the cheetah, the sentence would read: The gazelles were chased by the cheetah and would have been caught if the cheetah would not have stubbed his toe on a rock.

Let’s take this sentence apart, because there is a lot going on!
In the sentence above, there are three action verbs: chased, caught, and stubbed .
However, there are also several auxiliary verbs that add meaning to both the action verbs and the overall sentence. These auxiliary verbs are: were, would, have, and been . Were , have , and been are auxiliary verbs that express tense, or when the cheetah chased the gazelles.
The auxiliary verb would expresses possibility. It was very possible that the gazelles would have been the cheetah’s breakfast if the cheetah had not stubbed his toe.
If you want to read more about auxiliary verbs, check out this post on Albert.
How are action verbs different from linking verbs?
Action verbs and linking verbs are alike in that they can both be the main verb of a sentence. However, they are different in that linking verbs cannot show action. Ever. Linking verbs can only show a state of being or condition.
For example, Kevin was tired of asking Joe for his Netflix password, so he finally bought his own subscription.
In this sentence, the linking verb was is the main verb of the first clause. This linking verb “links” or connects the subject, Kevin , to his current state of being, which is tired . There is also an action verb in the second independent clause of this sentence. Because Kevin was tired of bugging his friend, he took action when he bought a Netflix subscription.

What is the relationship between these different types of verbs?
To recap what we learned above, actions verbs and linking verbs can stand on their own in sentences as the main verb, even though they have very different functions. Sentences can have both action and linking verbs in the same sentence, but they have to be in separate clauses.
Here is what it might look like:
When Carlos and Suzanne rode the Haunted Mansion ride at Disney World, Carlos thought he might be scared, but Suzanne assured him that the ride was more silly than scary.
In the sentence above, rode, thought, and assured are all action verbs . Each of these action verbs are connected to a subject. Both was and be are linking verbs . Each of these linking verbs are also connected to their own subjects.
Conversely, action verbs can exist without auxiliary verbs , but auxiliary verbs must be connected to a main verb, whether it is an action or linking verb, to make sense.
Let’s look at the sentence above one more time:
If you look closely, you’ll see that there is an auxiliary verb attached to a linking verb. The auxiliary verb, might, is attached to the linking verb, be .
Two things are going on here: while the linking verb, be, expresses a state of being (Carlos is scared!), the auxiliary verb, might, helps the reader understand that Carlos is not actually scared right now, but there is a possibility that he could be scared later.

How do you use action verbs?
Simply put, writers use action verbs in sentences to express an action done by a person, an animal, an object, or nature.
For example, a postal worker delivering mail, a cat meowing , a ball rolling , or a flower blooming are all action verbs.

Return to the Table of Contents
3 Tips for Understanding Action Verbs
Here are some important tips to help you understand action verbs:

Tip #1. Action verbs must describe an action–not a state of being
- For example, the sentence, “the sun scorched the parched desert sand” uses an action verb to describe an action done by the hot sun.
- You would NOT use an action verb to say that “the sun is hot” because the verb, is , is a linking verb that describes a state of being

Tip #2. Action verbs and linking verbs can be used together, but they must be in separate clauses
- For example, Marcus played Fortnite until 2 in the morning last night, so he was too tired to get up for school the next morning.
- In this sentence, played is an action verb describing an action done by Marcus in the first clause. Then, in the second clause, a linking verb is used to show Marcus’ state of being: Marcus was tired.

Tip #3. Action verbs can be paired with auxiliary verbs to express tense, mood, or voice
- For example, Laura Jean should tell Will that she has feelings for him, but she is too nervous.
- In this sentence, the auxiliary verb, should , shows the reader that Laura Jean has not told Will how she feels about him, but the writer believes that she should.

Applying the Basics: Action Verb Review & Practice
Now that you understand how action verbs are used, review the anchor chart below and complete the review to test your knowledge of these verbs.
The Ultimate List of Action, Linking, and Auxiliary Verb Examples
Refer to the graphic below to learn the difference between these three types of verbs:

This list, obviously, does not include all action, linking, and auxiliary verbs; however, it is meant to be used as a guide while identifying these types of verbs.
Action Verb Exercises and Review
Now that you know some common action verbs, test your ability to accurately identify these verbs.
Select the action verb(s) in the sentences below. Remember, these verbs must describe action and not a state of being.
1. Esperanza could not wait to celebrate her upcoming quinceanera with her family and closest friends.
- In this sentence, wait is the only action verb . While there are other verbs in this sentence, this is the only one that describes action.

2. The crowd exploded with cheers as the hockey puck slid through the goalie’s legs and into the goal.
- In this sentence , exploded and slid are both examples of action verbs . Exploded describes the loud cheers of the crowd of people, and slid describes how the hockey puck narrowly made it into the goal.
3. Alexis stared gloomily out of her bedroom window as the rain poured down unceasingly.
- In this sentence, both stared and poured are action verbs. Stared describes an action done by Alexis, while poured describes an action performed by the rain.
4. The cat reared its back and hissed through its teeth even though the excited lab only wanted to play.
- In this sentence , reared, hissed, and wanted are all examples of action verbs. Reared and hissed are actions performed by the cat, while wanted expresses an action done by the dog.
5. As the runners approached the final mile, they ignored their screaming legs and pushed themselves even harder.
- In this sentence, approached, ignored, and pushed are all action verbs that describe the runners.

Pro tip : When evaluating whether a verb is an action verb, ask yourself, is this verb describing an action that can be performed by a person, an animal, an object, or nature? If it is not describing an action but rather a state of being, then it is NOT an action verb.
For additional practice, check out Action Verb content on Albert.
Try for Yourself: Action Verbs Quiz

Feeling confident in your understanding of action verbs?
Take this short six-question quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Does an action verb have to include an auxiliary or helping verb in order to make sense?
- Answer: No
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! An action verb can stand on its own without an auxiliary verb. Auxiliary verbs are only added if the writer wants to express tense, mood, or voice.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, an action verb can stand on its own as the main verb of a sentence. While auxiliary verbs can be used with action verbs, they are not required.
2. Can an action verb be used in the same sentence as a linking verb as long as these verbs are in different clauses?
- Answer: Yes
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Action and linking verbs can be used together in the same sentence, but they must be in separate clauses.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, both action verbs and linking verbs can both function as the main verb of the sentence. This means that if you have a sentence with multiple independent clauses, you can have more than one main verb.
3. In this sentence, are the underlined words action or linking verbs ?
As she spoke , her lips moved but no sound came out, then suddenly, her hands formed words in sign language as quickly as she mouthed them.
- Answer: Action
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verbs spoke, moved, came, formed, and mouthed are all examples of action verbs because they describe actions done by the girl.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, an action verb must express action while linking verbs must express a state of being.
4. In this sentence, are the underlined words action or linking verbs ?
When he was first rescued, the Pit Bull puppy was scared and trembling, but as soon as he knew he was safe and had a loving home, he was happy.
- Answer: Linking
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verbs was and had are linking verbs that connect the subject, the Pit Bull puppy, to his changing state of being.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, a linking verb connects the subject to a state of being.
5. In this sentence, are the underlined words action or auxiliary verbs ?
The caterpillar burst out of his chrysalis as a radiant butterfly.
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verb burst is an example of an action verb because it describes an action done by the caterpillar.
6. In this sentence, are the underlined words action or auxiliary verbs ?
You may go to bed late, but you may not eat five cartons of ice cream.
- Answer: Auxiliary
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verb may “helps” the action verbs express permission and is an auxiliary verb .
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, an auxiliary verb must connect to an action or linking verb to make sense, and auxiliary verbs exist to “help” verbs express tense, voice, or mood.
For additional practice with action verbs, check out our practice on Albert: Action Verbs .
Teacher’s Corner for Action Verbs
While it’s true that understanding the difference between these three types of verbs is a foundational grammar skill, the Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart shows that even elementary-level skills require regular practice in the upper grades.
The Common Core State Standards site is a great resource that lists specific standards addressing action verbs.
Albert’s action verb practice can easily be implemented in the classroom for various grade levels. These short practice assignments are great for homework, bell work, mini-lessons, and exit tickets.
We also provide full-fledged assessments to evaluate student understanding of these grammatical concepts, but if you prefer, you can select different concepts to craft your own assessments to best fit your students’ needs.
Summary for Action Verbs
Action Verbs describe an action that can be done by a person, an animal, an object, or nature.
Linking Verbs describe a state of being.
Auxiliary Verbs help action and linking verbs by adding tense, mood, or voice to these verbs.
Be sure to check out our grammar course for more action verb practice.
You can also access over 3,400 high-quality questions that address nearly every grammatical concept.
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.
Interested in a school license?
Popular posts.

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
Interested in a school license?

Bring Albert to your school and empower all teachers with the world's best question bank for: ➜ SAT® & ACT® ➜ AP® ➜ ELA, Math, Science, & Social Studies aligned to state standards ➜ State assessments Options for teachers, schools, and districts.
- Clerc Center | PK-12 & Outreach
- KDES | PK-8th Grade School (D.C. Metro Area)
- MSSD | 9th-12th Grade School (Nationwide)
- Gallaudet University Regional Centers
- Parent Advocacy App
- K-12 ASL Content Standards
- National Resources
- Youth Programs
- Academic Bowl
- Battle Of The Books
- National Literary Competition
- Youth Debate Bowl
- Bison Sports Camp
- Discover College and Careers (DC²)
- Financial Wizards
- Immerse Into ASL
- Alumni Relations
- Alumni Association
- Homecoming Weekend
- Class Giving
- Get Tickets / BisonPass
- Sport Calendars
- Cross Country
- Swimming & Diving
- Track & Field
- Indoor Track & Field
- Cheerleading
- Winter Cheerleading
- Human Resources
- Plan a Visit
- Request Info

- Areas of Study
- Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- American Sign Language
- Art and Media Design
- Communication Studies
- Data Science
- Deaf Studies
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Programs
- Educational Neuroscience
- Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Information Technology
- International Development
- Interpretation and Translation
- Linguistics
- Mathematics
- Philosophy and Religion
- Physical Education & Recreation
- Public Affairs
- Public Health
- Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Theatre and Dance
- World Languages and Cultures
- B.A. in American Sign Language
- B.A. in Art and Media Design
- B.A. in Biology
- B.A. in Communication Studies
- B.A. in Communication Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Deaf Studies
- B.A. in Deaf Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Early Childhood Education
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Elementary Education
- B.A. in English
- B.A. in Government
- B.A. in Government with a Specialization in Law
- B.A. in History
- B.A. in Interdisciplinary Spanish
- B.A. in International Studies
- B.A. in Interpretation
- B.A. in Mathematics
- B.A. in Philosophy
- B.A. in Psychology
- B.A. in Psychology for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Social Work (BSW)
- B.A. in Sociology
- B.A. in Sociology with a concentration in Criminology
- B.A. in Theatre Arts: Production/Performance
- B.A. or B.S. in Education with a Specialization in Secondary Education: Science, English, Mathematics or Social Studies
- B.S in Risk Management and Insurance
- B.S. in Accounting
- B.S. in Biology
- B.S. in Business Administration
- B.S. in Information Technology
- B.S. in Mathematics
- B.S. in Physical Education and Recreation
- B.S. In Public Health
- General Education
- Honors Program
- Peace Corps Prep program
- Self-Directed Major
- M.A. in Counseling: Clinical Mental Health Counseling
- M.A. in Counseling: School Counseling
- M.A. in Deaf Education
- M.A. in Deaf Education Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Cultural Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Language and Human Rights
- M.A. in Early Childhood Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Early Intervention Studies
- M.A. in Elementary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in International Development
- M.A. in Interpretation: Combined Interpreting Practice and Research
- M.A. in Interpretation: Interpreting Research
- M.A. in Linguistics
- M.A. in Secondary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Sign Language Education
- M.S. in Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- M.S. in Speech-Language Pathology
- Master of Social Work (MSW)
- Au.D. in Audiology
- Ed.D. in Transformational Leadership and Administration in Deaf Education
- Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology
- Ph.D. in Critical Studies in the Education of Deaf Learners
- Ph.D. in Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Ph.D. in Linguistics
- Ph.D. in Translation and Interpreting Studies
- Ph.D. Program in Educational Neuroscience (PEN)
- Individual Courses and Training
- Certificates
- Certificate in Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Educating Deaf Students with Disabilities (online, post-bachelor’s)
- American Sign Language and English Bilingual Early Childhood Deaf Education: Birth to 5 (online, post-bachelor’s)
- Peer Mentor Training (low-residency/hybrid, post-bachelor’s)
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Certificate
- Online Degree Programs
- ODCP Minor in Communication Studies
- ODCP Minor in Deaf Studies
- ODCP Minor in Psychology
- ODCP Minor in Writing
- Online Degree Program General Education Curriculum
- University Capstone Honors for Online Degree Completion Program
Quick Links
- PK-12 & Outreach
- NSO Schedule

Action Verbs and Linking Verbs
202.448-7036
Action Verbs
An action verb describes an action, such as:
The sentence pattern will be:
SUBJECT → ACTION VERB → THE REST OF THE SENTENCE
(noun, pronoun, or noun phrase) → (verb) → (adjective, adverb, noun, prepositional phrase, etc.)
Examples of action verbs in sentences:
Greg is kicking the ball now.
The action verb is Kicking. It describes what Greg is doing.
The wind blows constantly in Chicago.
The action verb is Blows. It describes what the wind does.
He accepted my apology.
The action verb is Accepted. It describes what he did.
Linking Verbs
A linking verb links (connects) the subject of the sentence to information about that subject. Linking verbs do not describe action.
The sentence structure will be:
SUBJECT → LINKING VERB → INFORMATION ABOUT THE SUBJECT
(noun, pronoun, or noun phrase) → (verb) → (adjective, noun, or complement)
Some verbs are always linking verbs because they never describe an action. Others can be linking verbs in some sentences and action verbs in different sentences. (See below for examples.)
The following are always linking verbs:
- To be: (is, am, are, was, were, has been, have been, had been, is being, are being, was being, will have been, etc.)
- To become: (become, becomes, became, has become, have become, had become, will become, will have become, etc.)
- To seem: (seemed, seeming, seems, has seemed, have seemed, had seemed, is seeming, are seeming, was seeming, were seeming, will seem)
Here are some examples of linking verbs that are ALWAYS linking verbs in sentences:
The ball is red.
” Is” links the subject “ball” to information about that subject (that it is red).
The children are smart.
“Are” connects the subject “children” to information about that subject (that they are smart).
The child will be tall five years from now.
“Will be” links “child” to the information that she will be “tall five years from now.”
The cat seems fine.
“Seems” links “cat” with information about the cat (that it is fine).
The dog became thin after his surgery.
“Became” links “dog” with information about it (that he became thin).
Words that can be action verbs and linking verbs
There are verbs that, in some sentences, are linking verbs but, in other sentences, are action verbs. These include:
One way to determine whether the verb is functioning as an action verb or a linking verb is to substitute the word “Is” for the verb in question. If the sentence still makes sense, then it is probably a linking verb. If the sentence would not make sense with the word “Is,” then it is probably serving as an action verb.
Jane appeared uninjured after the accident.
You could substitute the word “is” for the word Appeared, and the sentence would still make sense: “Jane is uninjured after the accident.” This lets you know that Appeared is a linking verb here.
Before I could leave, Jane appeared.
In this sentence, Appeared is not linking anything. It is telling the action that Jane did. She appeared, or showed up.
The cake smells good!
This sentence describes the cake. Smells is a linking verb in this sentence. It connects the subject “cake” with information about that subject (that it smells good).
Ellen smells the cake.
The word Smells is not linking anything. If you replaced Smells with “Is,” the sentence would not make sense. That means Smells must be an action verb in this sentence. Ellen performed the action of smelling the cake.
The woman grew silent.
This sentence may seem confusing. Remember that Grow has more than one meaning! In this sentence, Grew means became. The woman became silent.
The gardener grew some flowers.
The word Grew is not linking two things together here. If you tried to replace Grew with “Is,” the sentence would not make sense. This means that Grew must be an action verb. The gardener performed the action of growing some flowers.
Grammar and Vocabulary
202-448-7036
At a Glance
- Quick Facts
- University Leadership
- History & Traditions
- Accreditation
- Consumer Information
- Our 10-Year Vision: The Gallaudet Promise
- Annual Report of Achievements (ARA)
- The Signing Ecosystem
- Not Your Average University
Our Community
- Library & Archives
- Technology Support
- Interpreting Requests
- Ombuds Support
- Health and Wellness Programs
- Profile & Web Edits
Visit Gallaudet
- Explore Our Campus
- Virtual Tour
- Maps & Directions
- Shuttle Bus Schedule
- Kellogg Conference Hotel
- Welcome Center
- National Deaf Life Museum
- Apple Guide Maps
Engage Today
- Work at Gallaudet / Clerc Center
- Social Media Channels
- University Wide Events
- Sponsorship Requests
- Data Requests
- Media Inquiries
- Gallaudet Today Magazine
- Giving at Gallaudet
- Financial Aid
- Registrar’s Office
- Residence Life & Housing
- Safety & Security
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- University Communications
- Clerc Center

Gallaudet University, chartered in 1864, is a private university for deaf and hard of hearing students.
Copyright © 2024 Gallaudet University. All rights reserved.
- Accessibility
- Cookie Consent Notice
- Privacy Policy
- File a Report
800 Florida Avenue NE, Washington, D.C. 20002

What is an Action Verb? Definition, Examples of Action Verbs in English
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is an Action Verb? Definition, Examples of Action Verbs in English
Action verb definition: An action verb is a verb that a subject can complete.
What is an Action Verb?
What does action verb mean? An action verb is type of verb . An action verb is a verb that the subject can do.
If a subject can DO the action, it is an action verb.
Action verbs can be in any verb tense .
Action Verb Examples in Sentences
- We responded
- I thought about my response.
Common Action Verbs

In all of these example action verbs, the subject can do them.
Transitive, Intransitive Verbs are Action Verbs

Transitive verbs “transfer” the action to an object . That is, the subject does something to someone or something else through a transitive verb. Transitive verbs will answer the question “to what?” or “to whom?”
Examples of Transitive Verbs:
- Fred hit Ginger. (Fred hit whom ? Ginger.)
- Sarah answered the question. (Sarah answered what ? The question.)
Intransitive verbs do not transfer action and will not have direct objects. Intransitive verbs will not answer the question “to what?” or “to whom?”
Examples of Intransitive Verbs:
- “At the airport” does not answer “what?” or “whom?”.
- “landed” is an intransitive verb.
- “in the pool” does not answer “what?” or “whom?”.
- “swam” is an intransitive verb.
Both transitive and intransitive verbs are action verbs, however. In each example sentence above, the subject is DOING something.
Action vs. Non-action Verbs

Common Non-action Verbs Include:
- sensory verbs: to look, to smell, to taste, to sound
- to consider
Examples in Sentences:
- I own the house.
- She considers her answer.
- We need a new car.
As you can see, there is not action taking place in these sentences. Rather, they are more descriptions of reality, a state of being, a preference, etc.
Action Verbs and Progressive Tenses

Non-action verbs cannot be used in the progressive tense. This is because the progressive tense itself is used for ongoing action. Only an action verb can be used in the progressive tense.
- Incorrect: He is wanting dinner.
- Incorrect: They are seeming friendly.
- Incorrect: She is needing a new phone.
Rather, non-action verbs use the simple present tense.
- Correct: He wants dinner.
- Correct: They seem friendly.
- Correct: She needs a new phone.
Summary: What are Action Verbs?
Define action verb: The definition of action verb is a verb that expresses the action of the subject; a verb that does something and the subject can complete.
In summary,
- Action verbs are any verb that a subject can do.
- Action verbs can be transitive or intransitive verbs.
- Additionally, only action verbs (not non-action verbs) can be used in the progressive tenses.

Paraphrasing Tool
AI Paraphraser
Action Verbs: What They Are and How to Use Them
February 19, 2024
Andrew Dinu
Verbs are the backbone of sentences, and action verbs, in particular, add movement and dynamism to our language. In this blog post, we’ll break down what action verbs are, provide examples to illustrate their use, and discuss how they differ from stative and linking verbs.
What are Action Verbs?
Action verbs are the type of verb , these are words that express physical or mental actions. These verbs describe what a subject does, bringing a sense of activity and motion to our sentences.
Examples of Action Verbs:
Let’s take a look at some straightforward examples of action verbs:
These examples show how action verbs (run, jump, write, eat) can depict various activities in different tenses.
What are the Types of Action Verbs?
Action verbs can be categorized into several types based on the kind of action they describe. Here are some common types of action verbs:
Physical Action Verbs:
- These verbs describe actions that involve physical movement or activity.
- Examples: run, jump, walk, swim, dance, climb, lift, kick.
Mental Action Verbs:
- These verbs describe actions related to mental processes, such as thinking, learning, or understanding.
- Examples: think, learn, understand, analyze, imagine, remember.
Communication Action Verbs:
- Verbs that involve the exchange of information or communication.
- Examples: talk, speak, write, read, listen, discuss.
Creation Action Verbs:
- Verbs that describe the act of creating or producing something.
- Examples: create, build, design, compose, craft, paint.
Emotional Action Verbs:
- Verbs that express emotions or reactions.
- Examples: smile, laugh, cry, cheer, sigh, frown.
Consumption Action Verbs:
- Verbs related to consuming or using something.
- Examples: eat, drink, taste, consume, use.
Motion Action Verbs:
- Verbs that describe various types of movement.
- Examples: move, travel, navigate, drive, fly.
Manipulation Action Verbs:
- Verbs related to handling or manipulating objects.
- Examples: handle, manipulate, lift, carry, push, pull.
Social Action Verbs:
- Verbs related to social interactions and relationships.
- Examples: meet, greet, socialize, collaborate, connect.
Performance Action Verbs:
- Verbs related to performing activities or tasks.
- Examples: perform, execute, accomplish, complete, achieve.
List of Action Verbs:
Here’s a list of action verbs to help you express various activities and movements:
Action Verbs vs. Stative Verbs:
Action verbs describe actions, while stative verbs convey static states or conditions. Let’s compare some examples:
Action Verbs Examples:
- The cat chases the mouse.
- She creates beautiful paintings.
- We play soccer every weekend.
Stative Verbs Examples:
- He knows the answer.
- She owns a lovely house.
- They understand the concept.
As seen in these examples, action verbs represent dynamic activities, while stative verbs express unchanging states or conditions.
Linking Verbs vs. Action Verbs:
Linking verbs , unlike action verbs, connect the subject to a complement but don’t express action. Here’s a quick comparison:
- The flowers bloomed beautifully.
- He solved the puzzle.
- They laughed at the joke.
Linking Verbs Examples:
- The flowers are beautiful.
- He seemed confused.
- They became friends.
Linking verbs (are, seemed, became) link the subject to the complement without indicating action.
Q: What are action verbs?
Action verbs, or dynamic verbs, express physical or mental actions, adding vitality to sentences. Examples include run, jump, and eat.
Q: What types of action verbs exist?
Action verbs categorize into physical (run), mental (think), communication (talk), creation (create), emotional (smile), consumption (eat), motion (move), manipulation (handle), social (meet), and performance (perform) verbs.
Q: How do action verbs differ from stative verbs?
Action verbs depict dynamic activities (e.g., play soccer), while stative verbs convey unchanging states or conditions (e.g., know the answer).
Q: How are linking verbs distinct from action verbs?
Linking verbs (e.g., are, seemed) connect subjects to complements without indicating action, unlike action verbs that express dynamic activities.

Conclusion:
Understanding action verbs enhances your ability to communicate effectively. By discerning action verbs from stative and linking verbs, you can craft clearer and more engaging sentences. So, the next time you want your writing to pack a punch, consider the impact of action verbs!
Related posts:
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs: What’s the difference?
Linking Verbs: Definition and Examples
- Phrasal Verbs: Everything you need to know
- Infinitive Verbs: what are they and how to use them?
- Regular verb vs. irregular verb

Paraphraser.co - The Best and Free AI Paraphraser
Address: New York, United States
Get To Know Us
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
©2024 Paraphraser.co
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Grammar Tips: Action Verbs and Stative Verbs
4-minute read
- 20th May 2020
Most people think of verbs as “action words.” But they actually come in two kinds: action verbs and stative verbs . Here, we will look at the difference between the two so you can use them with confidence in your writing .
What Are Action Verbs?
An action verb (or dynamic verb ) describes an action performed (physically or mentally) by a person, animal or object. For example:
The ballerinas leap gracefully across the stage.
We learned about cacti at school today.
These are action verbs because they describe a dynamic action (e.g., leaping) or process (e.g., learning). They also have duration, meaning they take place over a period of time (i.e., they describe actions that start and finish).
Dynamic verbs can be used in the continuous tenses . This means they have “-ing” forms (e.g., leaping or learning) that we can use to describe ongoing actions. For instance, we could adapt the examples above as follows:
The ballerinas are leaping gracefully across the stage.
We were learning about cacti at school yesterday.
This is much less common with stative verbs, as we will see below.
What Are Stative Verbs?
A stative verb (or state verb ) describes a state of being . This is usually something that does not change or that does not occur over a period of time in the same way as an active verb does.
Stative verbs can refer to various states, including thoughts, emotions, perceptions, relations, and qualities:
Timmy still believes in Santa.
I love grammar.
She smells of cheese.
The box contains many chocolates.
This elephant weighs a ton.
The common factor is that they describe a state of being or the way something is, not an action a person or object is performing in the present. As a result, we cannot usually use the continuous tenses with stative verbs:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Simple present: You seem tired. ✓
Simple continuous: You are seeming tired. ✗
Simple past: Harry liked to have nap after lunch. ✓
Past continuous: Harry was liking to have a nap after lunch. ✗
One potential point of confusion is that some verbs can be either active or stative. We will look at how this works below.
Verbs That Work Both Ways
Some verbs can be either active or stative depending on the context.
Take “smell,” for example. In the example above, we used “smell” as a stative verb in the simple present tense to describe somebody’s odor:
But “smell” can also describe the act of smelling something:
She smelled the flower.
And since this describes a subject performing a dynamic action with a duration, “smell” here is an active verb. The rule about not using continuous tenses with stative verbs still applies when a word can be either active or stative. Using “smell” again, for instance, we can see the difference below:
She is smelling the flower. ✓
She is smelling of cheese. ✗
This is the difference between a state of being (e.g., someone’s personal odor) and an action (e.g., using the sense of smell to experience an odor).
Summary: Action Verbs and Stative Verbs
Essentially, the differences between stative and action verbs are:
- Action verbs actions performed (physically or mentally) by a person, animal or object. The “-ing” forms of active verb can be used in the continuous tenses to describe an ongoing action.
- Stative verbs describe a state of being, such as what something is, feels, or possesses. They cannot typically be used with the continuous tenses.
We hope this clarifies the difference between stative and dynamic verbs. But if you’d like any more help with your grammar, why not enlist one of our professional proofreaders to make sure your writing is always error free?
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
active verb (action verb)
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Active verb is a term in traditional English grammar for a verb used primarily to indicate an action, process, or sensation as opposed to a state of being. Also called dynamic verb , action verb , activity verb , or event verb . Contrast with stative verb and linking verb .
In addition, the term active verb may refer to any verb used in a sentence in the active voice . Contrast with passive verb .
See Examples and Observations below. Also see:
- Active Voice and Passive Voice
- Habitual Present
- Lexical Verbs
- Ten Quick Questions and Answers About Verbs and Verbals
- Ten Types of Verbs
- Transitive Verbs and Intransitive Verbs
Examples and Observations
- "Graham laughed giddily and skipped off down a hallway." (John Green, The Fault in Our Stars . Dutton, 2012)
- " I often sing, hum and whistle but I would not do any of those things in the company of other people." (Lyn Overall, Supporting Children's Learning . SAGE, 2007)
- " Fighters using kung fu twirled, kicked, jumped , and punched with grace and skill through every life-threatening challenge, including dragons, sorcerers, assassins, and armies." (Gark Zukav, Soul to Soul: Communications From the Heart . Free Press, 2007)
- Birth of the Action Verb "When our forbears were grunting all those nouns that named people, animals, and things, they also noticed that people did things . . .. They noticed activity. They perceived action. So they grunted some words to describe all the activity around them: The baby crawled , the cow mooed , the wheel rolled , the fire blazed , the spear snagged the fish, and, of course, John hit the ball. "The action verb was born." (C. Edward Good, A Grammar Book for You and I--Oops, Me!: All the Grammar You Need to Succeed in Life . Capital Books, 2002)
- Active Verbs in Chapter Summaries "Chapter summaries may be written in complete sentences or in fragments that begin with an active verb . For instance, some active verbs I used in my chapter summaries include: explains, suggests, defines, shows, ends with, discusses, introduces, lists, offers, details, features, draws, gives, presents , and advises ." (Elizabeth Lyon, Nonfiction Book Proposals Anybody Can Write , rev. ed. Perigee, 2000)
- Action Verbs in Résumés " Action verbs are the verbs that precede the detailed description in your résumé and help explain what you have done. Action verbs should be written in the correct tense -- past or present . Alternatives to action verbs include such phrases as 'duties included' and 'was responsible for,' but these are long, take up valuable space on the résumé, and do little to add to the descriptions of your activities. (Francine Fabricant, Jennifer Miller, and Debra Stark, Creating Career Success: A Flexible Plan for the World of Work . Wadsworth, 2014)
- Temporal Meaning: Stative Verbs and Active Verbs "[C]onsider sentences such as those in (17): (17a) Mary know -s the answer. (17b) Mary sing -s . When the simple present affix -s is attached to a stative verb as in (17a), the speaker is asserting that the proposition that the sentence expresses is true 'at the moment of speech'--Mary knows the answer 'right now.' However, when this -s is attached to an active verb , this isn't so--Mary isn't necessarily singing right now. Instead, it means something like 'Mary is in the habit of singing' or 'Mary sings frequently' ('present' time and 'frequentative' aspect ). To express the idea that the action is happening 'now,' active verbs require instead the present progressive verb form be V -ing , as in (18b), a form that stative verbs disallow or allow only rarely, as seen in (18a). (18a) *Mary is (=be -s) know -ing the answer. (18b) Mary is (=be -s) singing . . . . [T]he verb form in (18b) also indicates that the action is 'continuing' ('present' time and progressive/continuative ' aspect)." (Nicholas Sobin, Syntactic Analysis: The Basics . Wiley-Blackwell, 2010)
- Active Verbs in Scientific Articles "When we use an active verb , the grammatical subject of the verb (the answer to who or what in front of the verb) actually does the action indicated by the verb. For example: The dog [subject] + bit [active verb] + the man [object]. With a passive verb, the grammatical subject does not do the action of the verb (the biting, in this case). For example: The man [subject] + was bitten [passive verb] + by the dog [object]. The agent is often omitted in passive sentences, which is why this form is popular when the action is more important than the actor, as in many experimental procedures. . . . "If authors of research articles are comfortable with using active voice sentences with 'we' as the subject, . . . then it is relatively easy to avoid the passive voice , even in Methods sections. However, many authors are not comfortable with this usage , or do not like the repetitive sound of many 'we' sentences together, and many passive verbs can still be found in science writing ." (Margaret Cargill and Patrick O'Connor, Writing Scientific Research Articles: Strategy and Steps , 2nd ed. Wiley & Blackwell, 2013)
- Parts of Speech: What Are Verbs?
- Learn How to Use the Present Continuous Tense
- Definition and Examples of Dynamic Verbs
- What Is a Verb of Being?
- Active Voice in Grammar
- A Quick Introduction to Mood and Voice in Spanish Verbs
- Understanding the Types of Verbs in English Grammar
- Using ‘Se’ for the Equivalent of the English Passive Voice
- Grammar Definitions: What is Passive Voice?
- How to Avoid the Passive Voice in Spanish
- 100 Key Terms Used in the Study of Grammar
- Agents in English Grammar
- Changing Verbs From Passive to Active
- Passive Voice Usage and Examples for ESL/EFL
- Definition and Examples of Voice in Grammar
- Differences between Action and Stative Verbs
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Action Verbs | Definition, List & Examples
Published on 18 September 2023 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou .
An action verb (also called a dynamic verb ) describes the action that the subject of the sentence performs (e.g., “I run”).
Action verbs differ from stative verbs, which describe a state of being (e.g., “believe”, “want”).
My grandfather walks with a stick.
The train arrived on time.
You can download our list of common action verbs in the format of your choice below.
Download PDF list Download Google Docs list
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What is an action verb, how to use action verbs, action verbs vs. stative verbs, action verbs vs. linking verbs, worksheet: action verbs, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
An action verb is a type of verb that describes the action that the subject of a sentence is performing. Action verbs can refer to both physical and mental actions (i.e., internal processes and actions related to thinking, perceiving, or feeling).
Whitney analysed the data to find patterns.
He played football in high school.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Action verbs can be transitive or intransitive. Transitive verbs require a direct object , such as a noun or pronoun , that receives the action. Without a direct object, sentences with a transitive verb are vague or incomplete.
In contrast, intransitive verbs do not require a direct object that receives the action of the verb. However, other information may come after the verb, such as an adverb .
Some action verbs can act as both transitive and intransitive verbs.
He grows tomatoes on his balcony. My niece is growing quickly. Note Because action verbs make your writing more vivid, they can be effectively used for resume writing. Unlike generic phrases like “responsible for”, “tasked with”, or “experienced in”, action verbs are attention-grabbing and help emphasise our abilities and accomplishments.
- I was responsible for social media accounts across various platforms.
- I managed social media accounts across various platforms.
Action or dynamic verbs are often contrasted with stative verbs . While action verbs communicate action, stative verbs describe a state of being or perception (e.g., “it tasted”, “he is”, “she heard”). Due to this, they are typically used to provide more information about the subject, rather than express an action that the subject did. For example, the sentence “Tom loves spending time with friends” uses a stative verb “love” to give us more information about Tom’s personality.
However, some verbs can be used as either dynamic or stative verbs depending on the meaning of the sentence. For example, the verb “think” can denote someone’s opinion ( stative verb ) or the internal process of considering something ( action verb ).
One way to tell action verbs from stative verbs is to look at the verb tenses . Because stative verbs usually describe a state of being that is unchanging, they can’t be used in the continuous (or progressive) tenses. Action verbs, on the other hand, can be used in continuous tenses.
- I am wanting some food.
- I want some food.
Another way is to look at the meaning of the sentence and ask yourself if the verb shows what someone does or how someone feels or is. If the verb describes what someone does, it is an action verb. Otherwise, it is probably a stative verb.
Action verbs should not be confused with linking verbs , like “be”, “become”, and “seem”. Linking verbs connect the subject of a sentence with a subject complement (i.e., a noun or adjective that describes it).
Unlike action verbs, linking verbs do not describe an action, but add more details about the subject, such as how it looks or tastes.
For example, the sentence “The children seem happy” uses the linking verb “seem” to link the subject (“the children”) with the adjective (“happy”).
Some verbs can be either linking verbs or action verbs . If you are unsure, try replacing the linking verb with a conjugated form of the verb “be”. If the sentence still makes sense, then it is a linking verb.
To test your understanding of action verbs, try the worksheet below. Choose the correct answer for each question.
- Practice questions
- Answers and explanations
- Are you baking cookies? They_______[smell/are smelling] delicious!
- Understand is not an action verb, but a stative verb because we can’t use it in a continuous tense. For example, “I’m not understanding you at all” is incorrect.
- Kick is an action verb, while “believe” and “agree” are both stative verbs.
- Smell is correct because it is a stative verb and cannot be used in the present continuous.
If you want to know more about commonly confused words, definitions, common mistakes, and differences between US and UK spellings, make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Sentence structure
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
There are many ways to categorize verbs into various types. A verb can fall into one or more of these categories depending on how it is used.
Some of the main types of verbs are:
- Regular verbs
- Irregular verbs
- Transitive verbs
- Intransitive verbs
- Dynamic verbs
- Stative verbs
- Linking verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
- Modal verbs
If you are unsure whether a word is an action verb , consider whether it is describing an action (e.g., “run”) or a state of being (e.g., “understand”). If the word describes an action, then it’s an action verb.
The function of an action verb is to describe what the subject of the sentence is doing. For example, in the sentence “You have been working since 7 o’clock this morning,” the action verb “work” shows us what the subject (“you”) has been doing.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Nikolopoulou, K. (2023, September 18). Action Verbs | Definition, List & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/verb/action-verbs/
Is this article helpful?

Kassiani Nikolopoulou
Other students also liked, what is a transitive verb | examples, definition & quiz, what is an intransitive verb | examples, definition & quiz, what is a linking verb | definition & examples.
What Are Action Verbs? List And Examples
- What Is An Action Verb?
- Action Verbs In Grammar vs. Resumes
- Rules And Best Practices
- Try Grammar Coach!
Lights, camera, action ! It takes a lot of hard work to make a movie. Directors tell everyone what to do. Actors memorize all of their lines. The crew makes all the scenery and props. Camera operators film all the exciting scenes and dramatic moments. Stunt people perform dangerous antics. The producer manages the entire project. Everybody has a job that they must do.
Don’t worry, we aren’t making a movie. Instead, we are going to learn a bit more about all the exciting words that we used to describe the work that goes on behind the scenes. All of these words are verbs , which are used to express actions or states of beings. While there are many types of verbs that we use in sentences and clauses, we are going to shine the spotlight on the verbs that really want to be action stars: action verbs.

What is an action verb ?
An action verb is a verb that expresses something that a person, animal, object, or process in nature (such as a storm) can do rather than expressing a state of being. What exactly does this mean? Let’s look at this example:
- Andre plays rugby.
In this sentence, the verb plays expresses an action that Andre does: Andre physically plays the sport of rugby. That is why plays is an action verb.
Action verbs are often contrasted and should not be confused with two other types of verbs: stative verbs and linking verbs . Unlike action verbs, stative verbs express states of being or conditions. Stative verbs are typically used to provide more information about the subject rather than say what the subject does. For example, the sentence The skunks smells really bad uses the stative verb smells to say what kind of odor the skunk has and the sentence Paula hates pineapple on pizza expresses an opinion that Paula has. These sentences both use stative verbs to provide more information about the subject rather than express an action that the subject did.
Grammatically, linking verbs are used differently than both stative and action verbs. A linking verb “serves as a connecting link or establishes an identity between subject and complement.” For example, the sentence The blanket is green uses the linking verb is to link the subject the blanket with the adjective green that provides information about the subject. The following sentences show the difference between action and linking verbs:
- The children happily opened their gifts. (In this sentence, opened is an action verb.)
- Tomorrow is Thursday. (In this sentence, is is a linking verb. The verb is linking the subject with a subject complement rather than expressing an action.)
Study the differences between action and linking verbs (and more) in our guide on the types of verbs.
It is possible for some verbs to be used as either action or stative verbs depending on meaning or context. For example, the following two sentences use the verb think as an action and stative verb:
- Nicole thinks that Freddy is a hard worker.
- Albert is thinking of funny jokes to tell his nieces.
In the first sentence, thinks is a stative verb that expresses an opinion that Nicole has. In the second sentence, the verb thinking is expressing a mental action that Albert is doing. Lots of verbs have multiple meanings, which means it is a good idea to stop and think—like Albert—for a little bit about what the verb is actually referring to in order to determine if it is an action or stative verb.
List of action verbs
There are many examples of action verbs. Action verbs come in two main types: verbs that refer to physical actions and verbs that refer to mental actions.
Physical action verbs
Generally speaking, we say that an action verb describes a physical action if it refers to an action that requires movement of bodies or objects. Here are examples of action verbs that refer to physical actions:
- ask, bend, climb, drive, eat, frolic, go, hang, inch, jiggle, kick, leap, mumble, nod, open, pull, quake, run, swim, tumble, unlock, vibrate, walk, yell, zip
Mental action verbs
Action verbs that refer to mental actions are a bit trickier. At first glance, many of these verbs may not seem like action verbs at all. However, all of these verbs can still refer to things that a person can do. Rather than physical activities, these verbs refer to actions that you can use your brain to do. It may not surprise you to learn that many of these verbs can also be used as stative verbs to express states of being or conditions:
- consider, dream, imagine, ponder, think, remember, forget, memorize, learn, doubt, condemn, analyze, review, dread, worry, fear, fantasize, appreciate, evaluate
Action verb examples
Let’s look at sentences that use action verbs. Remember, an action verb expresses something that a person or thing can do, either physically or mentally. As you read each example, consider if each action verb is referring to a physical or mental action.
- I ride my bicycle to work.
- The teacher asked Zach for the answer, but he forgot what it was.
- Our grandparents will visit us next week, so we are preparing the guest room.
- The art collector has spent millions of dollars on fabulous masterpieces.
- The cunning thieves formulated a plan to steal the diamonds.
- The angry queen exiled the corrupt minister from the country.
- Brianna was smiling because the university accepted her application.
- Lord Horatio passionately argued that the government should lower taxes, but Duchess Cecilia fiercely rebutted his position.
Action verbs in grammar vs. résumés
Now you know what an action verb means when we’re speaking about grammar. But the phrase action verbs is also used in the process of writing and editing résumés, and it refers to writing that is vivid and effective. A résumé filled with action verbs uses verbs that are powerful enough to convey not only what an applicant did on the job, but also how they excelled at tasks and on-the-job challenges. The verbs are both effective and specific. To learn more about writing a résumé take a look at our comprehensive list of the most effective action verbs to include .
Action verb rules & best practices
Now back to grammar: by now you’ve realized we use many different action verbs when we speak or write sentences. An action verb is a specific type of verb, but it follows other general rules of verbs. For example, action verbs can be used in the active or passive voice and can be used in all 12 of the verb tenses .
Let’s put your understanding of action verbs to the test. Carefully read each of the following sentences and see if you can tell if the bolded verb is or is not an action verb. (Check your answers below!)
- The busy squirrels quickly climbed the tree.
- That idea sounds foolish.
- Romeo loves Juliet.
- Tabitha remembered the right answer.
- My mom remembers every bad decision I make.
Take action with Grammar Coach™
Confused about verb tenses? Not sure if you’re using action and stative verbs correctly? Check your writing on Thesaurus.com’s Grammar Coach ™. This writing tool uses machine learning technology uniquely designed to catch grammar and spelling errors. Its Synonym Swap will find the best nouns, adjectives, and more to help say what you really mean, guiding you toward clearer, stronger, writing.
Answers: 1. Action verb 2. Not an action verb (linking verb) 3. Not an action verb (stative verb) 4. Action verb (Remembered is an action verb because it refers to a mental action that Tabitha did.) 5. Not an action verb (Remembers is a stative verb that is referring to the mom’s ability to retain information for future use.)
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Do you know what transitive verbs are? Take a look at them here.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day
English Grammar Here
Action verbs: list of common action verbs, definition and examples.
English Vocabulary; Action Verbs: List of Common Action Verbs, Definition and Examples

ACTION VERBS
Sentences established with verbs of action should include an action physically or mentally. The action verbs what is done in the sentence, what is the movement or the subject. Action verbs are also called dynamic verbs. There are many actions used in English, the action verbs, unlike the others, indicate the work done in the sentence, the reader gives information about the actions performed, specifies specifically what the subject in the sentence does.
Some of the Action Verbs :
( +250 Action Verbs List )
Example Sentences with Action Verbs
- Every morning I comb my daughter ‘s hair.
- I paid my debts with all the money I made this month.
- I feed six cats and three dogs in my garden.
- We grub up almost all over the field to find gold.
- I wash my car and wipe the windows every weekend.
- An elderly aunt was coming from the market and I carried her bags to help her.
- My friends go on vacation every summer, until the evening we swim in the sea.
- I’ve been waiting for hours at the bank for me to come.
- When spring comes , I ride bikes on the beach every morning.
(Here is Commonly Used Verbs List )
TYPES OF ACTION VERBS
Transitive Verbs : Transitive verbs take the object. To find the object, we can ask verb ‘what’, ‘whom’. In these verbs, the action is performed by an object. The verb action must be included in the sentence.
- Today is my girlfriend’s birthday, so I bought her these red roses.
- Yesterday while walking around the market, I met an old friend.
- I have a graduation this summer. I have to buy myself a nice dress already.
- Can I get your book to study for the exam?
- I saw him last night at the mall.
- We forgot to take bread with us on our way to the picnic.
- Every day I regularly water the lawns in the garden.
Note: If there is no object in the sentence, there is still the possibility of receiving the object. If there is no object in the sentence, if there is a situation that can bring the object we want, this sentence is considered transitive. In short, every transitive sentences clause does not contain an object. The important thing here is that the action can take the object.
- We live in England for many years.
- The killer was on the run, so the police took action.
- Everyone in her establishment was very upset when she became this.
- My father fell asleep in front of the television.
- We didn’t leave the house today because we were so tired yesterday.
- He was standing in the store where he worked all day.
- Tomorrow we will gather the whole class and go to the museum.
- We’ve been going very slowly for a while since he just learned to drive.
- I’m very worried that he’s going away for business.
Related Posts

Milk V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Milk

Wax V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Wax

Strew V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Strew
About the author.
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of tour verb from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- tour something He toured America with his one-man show.
- She toured the country promoting her book.
- (+ adv./prep.) We spent four weeks touring around Europe.
- He's toured across Europe, the UK and North America.
- She is currently touring with her new band.
- He no longer tours.
- The band toured the UK last year.
- The town makes an ideal base for touring the Highlands.
- I was on my own as I toured round.
- We plan to tour all over the country.
- She has toured extensively in the US.
- The Beatles stopped touring years before.
- extensively
- internationally
Definitions on the go
Look up any word in the dictionary offline, anytime, anywhere with the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app.

'tour' conjugation table in English
Past participle, present participle, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All ENGLISH words that begin with 'T'
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of tour in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- break-journey
- circumnavigation
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
- She spent three months touring her empire .
- The prime minister toured the flooded regions .
- I spent a month touring round Europe .
- around Robin Hood's barn idiom
- communication
- public transport
- super-commuting
- transoceanic
- well travelled
Related word
Tour | american dictionary, tour | business english, examples of tour, collocations with tour.
These are words often used in combination with tour .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of tour
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
a type of singing in which four, usually male, voices in close combination perform popular romantic songs, especially from the 1920s and 1930s

Alike and analogous (Talking about similarities, Part 1)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun Verb
- American Noun Verb
- Business Noun Verb
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
Add tour to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
action verb
Definition of action verb
Examples of action verb in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'action verb.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Articles Related to action verb

8 More Grammar Terms You Used to Know:...
8 More Grammar Terms You Used to Know: Special Verb Edition
These grammarians are going places
Dictionary Entries Near action verb
action time
actio stricti juris
Cite this Entry
“Action verb.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/action%20verb. Accessed 11 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of action verb.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 5, 12 bird names that sound like compliments, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, games & quizzes.


COMMENTS
An action verb is a type of verb that describes the action that the subject of a sentence is performing. Action verbs can refer to both physical and mental actions (i.e., internal processes and actions related to thinking, perceiving, or feeling). Examples: Physical and mental action verbs. We climbed to the highest peak.
What is an action verb? An action verb describes an action that a person, animal, object, or process in nature can do.For example, a cheetah chases gazelles across a plain, and the gazelles sprint away, hearing the tall grass rustle underneath the lion's paws.. In the sentence above, there are several verbs that describe action; the cheetah chases the gazelles, and the gazelles hear the ...
An action verb is different from an active verb. The latter term is used to indicate that the subject of a sentence is the one performing an action. In all the examples above, the primary verb is both an action verb and active verb. Active verbs refer to the structure of a sentence as opposed to the verb itself. The following examples may clarify.
When used as the main verb, "have" can either be an action verb or a stative verb depending on the context.. Usually, "have" is a stative verb, as it describes the state of the subject—what it possesses, includes, or contains (e.g., "the car has a scratch on the door," "I have a degree").. However, there are some cases where "have" describes an action.
Action Verbs. An action verb describes an action, such as: The sentence pattern will be: SUBJECT → ACTION VERB → THE REST OF THE SENTENCE. (noun, pronoun, or noun phrase) → (verb) → (adjective, adverb, noun, prepositional phrase, etc.) Examples of action verbs in sentences: Greg is kicking the ball now. The action verb is Kicking.
Define action verb: The definition of action verb is a verb that expresses the action of the subject; a verb that does something and the subject can complete. In summary, Action verbs are any verb that a subject can do. Action verbs can be transitive or intransitive verbs. Additionally, only action verbs (not non-action verbs) can be used in ...
Action verbs have the power to transform a sentence. Improve your writing by learning more about them including the difference between action and linking verbs.
Verbs are the backbone of sentences, and action verbs, in particular, add movement and dynamism to our language. In this blog post, we'll break down what action verbs are, provide examples to illustrate their use, and discuss how they differ from stative and linking verbs.
Action verbs are essential to speaking and writing. These key verb examples show physical or mental action. This list shows how exciting verbs can be!
Action verbs actions performed (physically or mentally) by a person, animal or object. The "-ing" forms of active verb can be used in the continuous tenses to describe an ongoing action. Stative verbs describe a state of being, such as what something is, feels, or possesses. They cannot typically be used with the continuous tenses.
Definition. Active verb is a term in traditional English grammar for a verb used primarily to indicate an action, process, or sensation as opposed to a state of being. Also called dynamic verb, action verb, activity verb, or event verb. Contrast with stative verb and linking verb . In addition, the term active verb may refer to any verb used in ...
Pin. Related: A big list of verbs in English and action verbs in English grammar.. List of Common Action Verbs with Pictures and Examples Ride "Ride" is a verb that means to travel on or in a vehicle or animal. Example: I love to ride my bike to the park on sunny days.
Action verbs are the verbs you can probably identify as verbs quickly and easily. These are the words that show action, words like jump, run, and eat.. There are two main classes of action verbs: transitive and intransitive, and there aren't separate lists for each class.Action verbs can be both transitive and intransitive because it all depends on the structure of the sentence.
An action verb is a type of verb that describes the action that the subject of a sentence is performing. Action verbs can refer to both physical and mental actions (i.e., internal processes and actions related to thinking, perceiving, or feeling). Examples: Physical and mental action verbs. We climbed to the highest peak.
Action verbs are words that describe what a person or thing in a sentence does. Learn more about transitive verbs with our lists and examples!
Action verbs are also called dynamic verbs. There are many actions used in English, the action verbs, unlike the others, indicate the work done in the sentence, the reader gives information about the actions performed, specifies specifically what the subject in the sentence does. Some of the Action Verbs: eat. catch. sleep.
Definition of tour verb in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.
Future Perfect Continuous. I will have been touring you will have been touring he/she/it will have been touring we will have been touring you will have been touring they will have been touring. New from Collins.
The verb "live" in your example means "reside", and hence is dynamic not stative. There's a lot of idioms with the verb "live", I'd be unsurprised if some were dynamic and others were stative. 'Live a little.'. @StuartF True, but I think the question is about the sense used in the example, and idioms in general create exceptions to rules.
TOUR definition: 1. a visit to a place or area, especially one during which you look around the place or area and…. Learn more.
tour: [noun] a series of professional tournaments (as in golf or tennis). a brief turn : round.
The meaning of ACTION VERB is a verb that expresses action. How to use action verb in a sentence.
what is said about the subject or what the subject does. c. the form of a verb used to show when an action happened. d. a verb quality that tells if its subject performs or receives action. ... During the scenic tour of the national park, the cascading waterfall was photographed repeatedly. Which grammatical structure is used in this sentence? a.