

Family Life

AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits

Parents know who they should go to when their child is sick. But pediatrician visits are just as important for healthy children.
The Bright Futures /American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the " periodicity schedule ." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence.
Schedule of well-child visits
- The first week visit (3 to 5 days old)
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
- 12 months old
- 15 months old
- 18 months old
- 2 years old (24 months)
- 2 ½ years old (30 months)
- 3 years old
- 4 years old
- 5 years old
- 6 years old
- 7 years old
- 8 years old
- 9 years old
- 10 years old
- 11 years old
- 12 years old
- 13 years old
- 14 years old
- 15 years old
- 16 years old
- 17 years old
- 18 years old
- 19 years old
- 20 years old
- 21 years old
The benefits of well-child visits
Prevention . Your child gets scheduled immunizations to prevent illness. You also can ask your pediatrician about nutrition and safety in the home and at school.
Tracking growth & development . See how much your child has grown in the time since your last visit, and talk with your doctor about your child's development. You can discuss your child's milestones, social behaviors and learning.
Raising any concerns . Make a list of topics you want to talk about with your child's pediatrician such as development, behavior, sleep, eating or getting along with other family members. Bring your top three to five questions or concerns with you to talk with your pediatrician at the start of the visit.
Team approach . Regular visits create strong, trustworthy relationships among pediatrician, parent and child. The AAP recommends well-child visits as a way for pediatricians and parents to serve the needs of children. This team approach helps develop optimal physical, mental and social health of a child.
More information
Back to School, Back to Doctor
Recommended Immunization Schedules
Milestones Matter: 10 to Watch for by Age 5
Your Child's Checkups
- Bright Futures/AAP Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care (periodicity schedule)
Catch Up on Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations

Many children missed check-ups and recommended childhood vaccinations over the past few years. CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommend children catch up on routine childhood vaccinations and get back on track for school, childcare, and beyond.

Making sure that your child sees their doctor for well-child visits and recommended vaccines is one of the best things you can do to protect your child and community from serious diseases that are easily spread.
Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations Are Essential

Well-child visits and recommended vaccinations are essential and help make sure children stay healthy. Children who are not protected by vaccines are more likely to get diseases like measles and whooping cough . These diseases are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children. In recent years, there have been outbreaks of these diseases, especially in communities with low vaccination rates.
Well-child visits are essential for many reasons , including:
- Tracking growth and developmental milestones
- Discussing any concerns about your child’s health
- Getting scheduled vaccinations to prevent illnesses like measles and whooping cough (pertussis) and other serious diseases

It’s particularly important for parents to work with their child’s doctor or nurse to make sure they get caught up on missed well-child visits and recommended vaccines.
Routinely Recommended Vaccines for Children and Adolescents
Getting children and adolescents caught up with recommended vaccinations is the best way to protect them from a variety of vaccine-preventable diseases . The schedules below outline the vaccines recommended for each age group.
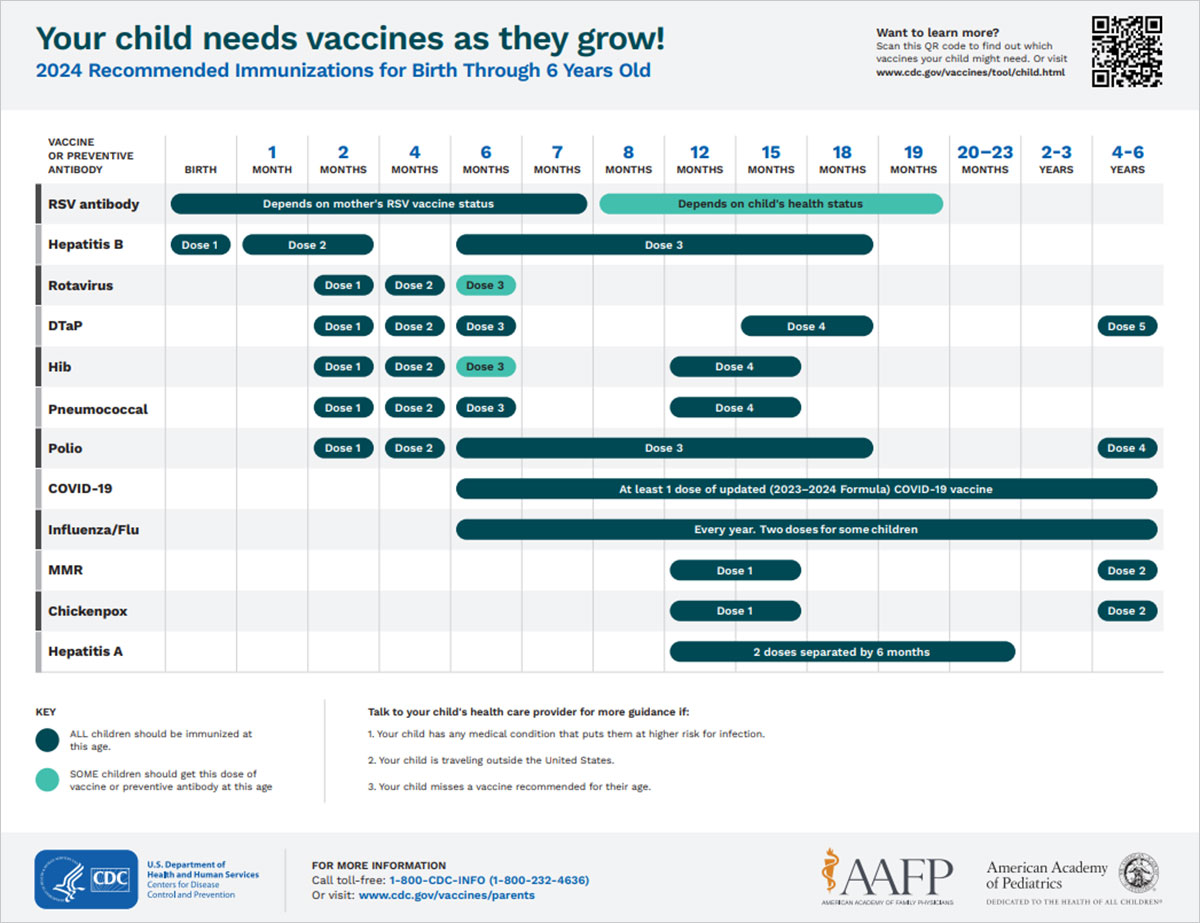
See which vaccines your child needs from birth through age 6 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
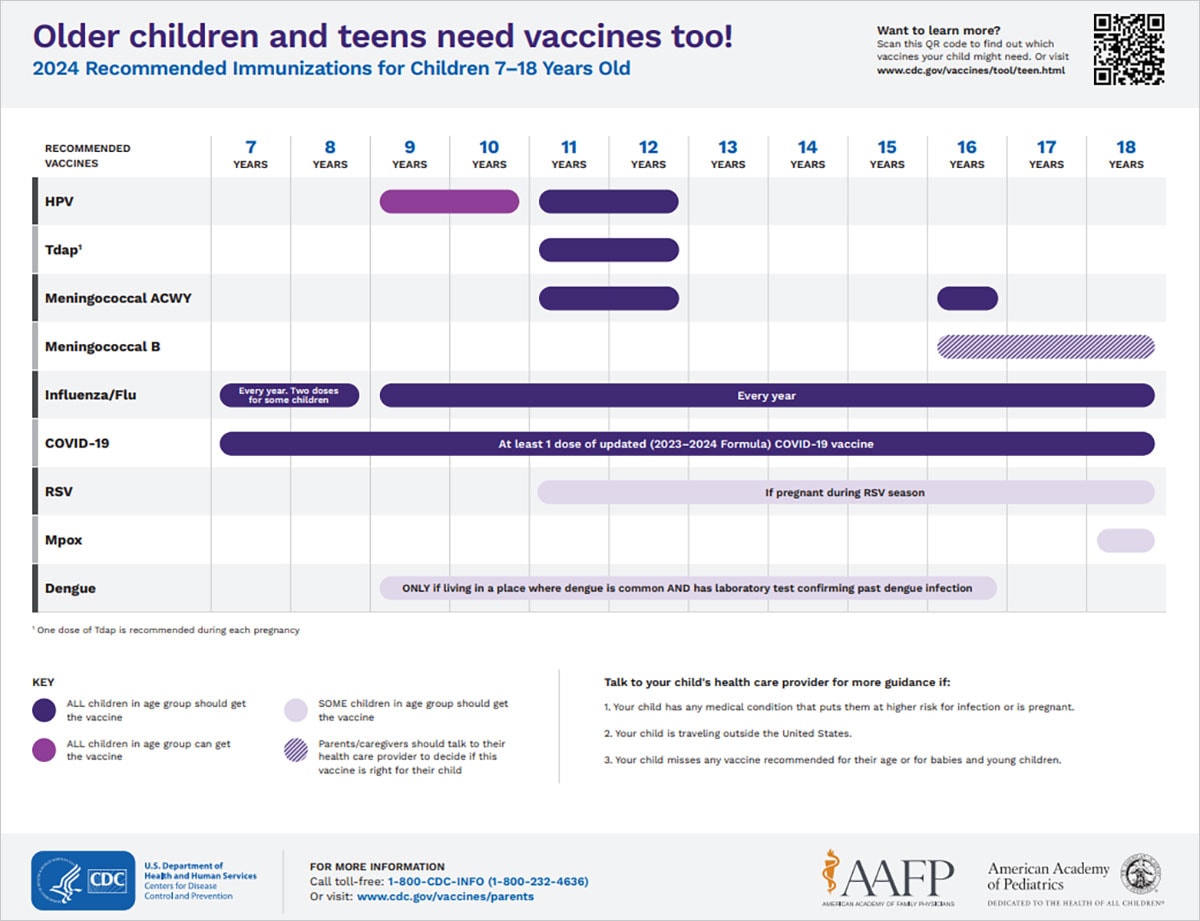
See which vaccines your child needs from ages 7 through 18 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program’s requirements and talk to your child’s doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider. You can also find a VFC provider by calling your state or local health department or seeing if your state has a VFC website.
COVID-19 Vaccines for Children and Teens
Everyone aged 6 months and older can get an updated COVID-19 vaccine to help protect against severe illness, hospitalization and death. Learn more about making sure your child stays up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Preventive Health Care Visits in Infants
Healthy infants should be seen by their doctor often during the first year of life. Preventive health care visits (also called well-child visits) typically take place within a few days after birth or by 2 weeks of age and at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 9 months of age. During these visits, the doctor uses age-specific guidelines to monitor the infant's growth and development and asks the parents questions about various developmental milestones (see table Developmental Milestones From Birth to Age 12 Months ). Tests are sometimes done, and during many visits, the doctor vaccinates the infant against various illnesses (see Childhood Vaccination Schedule ).
Health care visits also allow the doctor to educate the parents about eating, sleeping, behavior, child safety, nutrition, exercise, and good health habits. In addition, the doctor advises the parents what developmental changes to expect in their infant by the next visit.
Examination
The infant's length and height , weight , and head circumference are measured at every visit. The doctor examines the infant for various abnormalities, including signs of hereditary disorders or birth defects .
The eyes are examined, and vision is tested. Infants who were born very prematurely (before the completion of 32 weeks of development in the uterus) usually need more frequent eye examinations by an eye specialist to look for retinopathy of prematurity , which is an eye disease that occurs when infants are born before the blood vessels in their eyes are fully developed and may result in blindness, and for the development of refractive errors , which result in blurring of vision. These disorders are more common among infants who were born very prematurely.
The doctor checks the infant’s hips for signs that the hip joints are loose or dislocated ( developmental dysplasia of the hip ). The doctor checks the infant's teeth , if they are present, for cavities and the mouth for thrush , which is a common yeast infection among infants.
The doctor also examines the heart, lungs, abdomen, arms and legs, and genitals.
Screening tests are done to assess whether infants are at risk of certain disorders.
Blood tests are done to detect anemia , sickle cell disease , and exposure to lead .
Hearing tests are done shortly after birth to determine whether an infant has a hearing disorder or hearing loss (see Newborn Screening Tests ) and are repeated later if new concerns about the infant's hearing develop (see also Hearing Impairment in Children ).
Infants are screened for tuberculosis (TB) risk factors with a questionnaire at all well-child visits, usually beginning in infancy. Risk factors include exposure to TB, being born in or having traveled to areas of the world where TB is common (countries other than the United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand and Western and North European countries), having a family member with TB, and having parents or close contacts who are recent immigrants from an area where TB is common or who have recently been in jail. Those with risk factors usually have tuberculosis screening tests done.
At these visits, the doctor gives parents age-appropriate safety guidelines.
The following safety guidelines apply to infants from birth to age 12 months:
Use a rear-facing car seat and place it in the back seat of the vehicle.
Set the hot water heater to 120° F or less.
Prevent falls from changing tables and around stairs.
Place infants on their back to sleep on a firm, flat mattress for every sleep, do not share a bed, and do not place pillows, bumper pads, nonfitted sheets, stuffed animals or other toys, quilts, comforters, or weighted or loose blankets in the crib. (See also sidebar Safe to Sleep: Reducing the Risk of SIDS .)
Do not give infants foods and objects that can cause choking or be inhaled into the lungs.
Do not use baby walkers.
Place safety latches on cabinets and cover electrical outlets.
Remain alert when watching infants in the bathtub or near a pool or any body of water and when they are learning to walk.
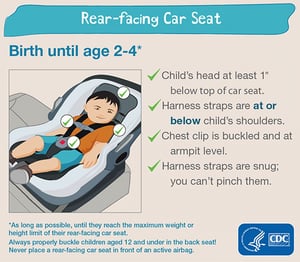
Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), National Center for Injury Prevention and Control ( Transportation Safety Resources ). This guidance from the CDC is for the United States, and regulations may differ in other countries.

Nutrition and exercise
For infants, recommendations for nutrition are based on age. The doctor can help parents weigh the benefits of breastfeeding versus formula-feeding and give guidance regarding solid foods .
Parents should provide infants with a safe environment they can roam in and explore. Outdoor play should be encouraged from infancy.
Screen time (for example, television, video games, cell phones and other handheld devices, and noneducational computer time) may result in inactivity and obesity. Limits on the time a child spends using devices with screens should start at birth and be maintained throughout adolescence.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Skip to content
Why Well-Child Visits Matter
Published on May 02, 2023
Primary Care Locations
Don't fall behind on your child's routine care — a minor issue today could become a major problem tomorrow.

Well-child visits allow your pediatrician to examine your child holistically, assess their physical and emotional needs, support their growth and development, and intervene quickly if any issues arise.
What are the risks of skipping well-child visits?
If your child is healthy, it can be easy to let well visits fall by the wayside. While those annual checkups may seem like just another thing to fit into your family’s hectic schedule, they play a crucial role in preventing future problems.
Find a CHOP Pediatrician
CHOP Primary Care practices, located throughout southeastern Pennsylvania and Southern New Jersey, provide convenient access to primary health and wellness services for children close to home.
Well visits are essential to ensure your child gets the required vaccinations to attend school, go to daycare and participate in sports. Visiting the pediatrician when your child is well also provides you with an opportunity to ask questions – and get expert answers – about your child’s health, development and well-being. Delaying these visits can put your child at greater risk of illness or delay needed interventions. For example, many common developmental delays are discovered during routine checkups with pediatricians – early intervention makes a big difference in getting your child the support they need before something small turns into a bigger issue.
What to expect at a well-child visit
During an annual wellness visit, your child's pediatrician will:
- Determine if your child is meeting growth and developmental milestones for their age.
- Evaluate your child's vision and hearing for anything out of the ordinary – it's important to catch these issues early.
- Ask about sudden changes in your child's usual activities, mood and overall health.
- Assess your child's mental health, and ask questions about how they are coping with school, friends, family and any other outside influences.
- Provide immunizations for childhood diseases and common conditions that affect children or young adults, such as measles and HPV.
- Give sports physicals to children who want to want to participate in competitive sports at school or in the community.
- Get to know your child: their diet, sleeping patterns, nutrition, social interactions, behavior and stress levels
- Help your child establish healthy habits and provide tips for families to reinforce these at home.
- Provide age- and behavior-based counseling for teens on topics such as driver safety, depression and drug or alcohol use.
- Check in on how your family is doing and identify any supportive resources or advice related to navigating daily life.
What are the ages for well-child visits?
A standard well-child visit schedule spans from infancy through adolescence, and includes checkups at the following ages:
- In your baby’s first year: Newborn visit (3-5 days after birth), at 1 month old, 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 9 months, and at 12 months
- 11-14 years
- 15-17 years
- 18-21 years
Your pediatrician can be a trusted partner at every age and stage of your child’s development.
Contributed by: Lisa Biggs, MD
Stay in Touch
Are you looking for advice to keep your child healthy and happy? Do you have questions about common childhood illnesses and injuries? Subscribe to our Health Tips newsletter to receive health and wellness tips from the pediatric experts at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, straight to your inbox. Read some recent tips .

With our patient portal you can schedule appointments, access records, see test results, ask your care provider questions, and more.

Subscribe to Health Tips
Subscribe to our Health Tips enewsletter to receive health and wellness tips from the pediatric experts at CHOP.
You Might Also Like

A Dose of Prevention
Learn why vaccinations are important for kids and the community, and what to do if you missed a vaccine and need to get back on track.
Preparing for an Annual Well Visit
Being properly prepared for annual well visits is a great way to get the most out of each appointment with your pediatrician.
How to Have a Productive Video Visit
If your child is scheduled for an online doctor’s appointment, read these tips to get the most out of your visit.

KATHERINE TURNER, MD
Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(6):347-353
Related letter: Well-Child Visits Provide Physicians Opportunity to Deliver Interconception Care to Mothers
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
The well-child visit allows for comprehensive assessment of a child and the opportunity for further evaluation if abnormalities are detected. A complete history during the well-child visit includes information about birth history; prior screenings; diet; sleep; dental care; and medical, surgical, family, and social histories. A head-to-toe examination should be performed, including a review of growth. Immunizations should be reviewed and updated as appropriate. Screening for postpartum depression in mothers of infants up to six months of age is recommended. Based on expert opinion, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends developmental surveillance at each visit, with formal developmental screening at nine, 18, and 30 months and autism-specific screening at 18 and 24 months; the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found insufficient evidence to make a recommendation. Well-child visits provide the opportunity to answer parents' or caregivers' questions and to provide age-appropriate guidance. Car seats should remain rear facing until two years of age or until the height or weight limit for the seat is reached. Fluoride use, limiting or avoiding juice, and weaning to a cup by 12 months of age may improve dental health. A one-time vision screening between three and five years of age is recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force to detect amblyopia. The American Academy of Pediatrics guideline based on expert opinion recommends that screen time be avoided, with the exception of video chatting, in children younger than 18 months and limited to one hour per day for children two to five years of age. Cessation of breastfeeding before six months and transition to solid foods before six months are associated with childhood obesity. Juice and sugar-sweetened beverages should be avoided before one year of age and provided only in limited quantities for children older than one year.
Well-child visits for infants and young children (up to five years) provide opportunities for physicians to screen for medical problems (including psychosocial concerns), to provide anticipatory guidance, and to promote good health. The visits also allow the family physician to establish a relationship with the parents or caregivers. This article reviews the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines for screenings and recommendations for infants and young children. Family physicians should prioritize interventions with the strongest evidence for patient-oriented outcomes, such as immunizations, postpartum depression screening, and vision screening.
Clinical Examination
The history should include a brief review of birth history; prematurity can be associated with complex medical conditions. 1 Evaluate breastfed infants for any feeding problems, 2 and assess formula-fed infants for type and quantity of iron-fortified formula being given. 3 For children eating solid foods, feeding history should include everything the child eats and drinks. Sleep, urination, defecation, nutrition, dental care, and child safety should be reviewed. Medical, surgical, family, and social histories should be reviewed and updated. For newborns, review the results of all newborn screening tests ( Table 1 4 – 7 ) and schedule follow-up visits as necessary. 2
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
A comprehensive head-to-toe examination should be completed at each well-child visit. Interval growth should be reviewed by using appropriate age, sex, and gestational age growth charts for height, weight, head circumference, and body mass index if 24 months or older. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-recommended growth charts can be found at https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/who_charts.htm#The%20WHO%20Growth%20Charts . Percentiles and observations of changes along the chart's curve should be assessed at every visit. Include assessment of parent/caregiver-child interactions and potential signs of abuse such as bruises on uncommonly injured areas, burns, human bite marks, bruises on nonmobile infants, or multiple injuries at different healing stages. 8
The USPSTF and AAP screening recommendations are outlined in Table 2 . 3 , 9 – 27 A summary of AAP recommendations can be found at https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule.pdf . The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) generally adheres to USPSTF recommendations. 28
MATERNAL DEPRESSION
Prevalence of postpartum depression is around 12%, 22 and its presence can impair infant development. The USPSTF and AAP recommend using the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (available at https://www.aafp.org/afp/2010/1015/p926.html#afp20101015p926-f1 ) or the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (available at https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0115/p139.html#afp20120115p139-t3 ) to screen for maternal depression. The USPSTF does not specify a screening schedule; however, based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends screening mothers at the one-, two-, four-, and six-month well-child visits, with further evaluation for positive results. 23 There are no recommendations to screen other caregivers if the mother is not present at the well-child visit.
PSYCHOSOCIAL
With nearly one-half of children in the United States living at or near the poverty level, assessing home safety, food security, and access to safe drinking water can improve awareness of psychosocial problems, with referrals to appropriate agencies for those with positive results. 29 The prevalence of mental health disorders (i.e., primarily anxiety, depression, behavioral disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) in preschool-aged children is around 6%. 30 Risk factors for these disorders include having a lower socioeconomic status, being a member of an ethnic minority, and having a non–English-speaking parent or primary caregiver. 25 The USPSTF found insufficient evidence regarding screening for depression in children up to 11 years of age. 24 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends that physicians consider screening, although screening in young children has not been validated or standardized. 25
DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE
Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends early identification of developmental delays 14 and autism 10 ; however, the USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend formal developmental screening 13 or autism-specific screening 9 if the parents/caregivers or physician have no concerns. If physicians choose to screen, developmental surveillance of language, communication, gross and fine movements, social/emotional development, and cognitive/problem-solving skills should occur at each visit by eliciting parental or caregiver concerns, obtaining interval developmental history, and observing the child. Any area of concern should be evaluated with a formal developmental screening tool, such as Ages and Stages Questionnaire, Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status, Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status-Developmental Milestones, or Survey of Well-Being of Young Children. These tools can be found at https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/Screening/Pages/Screening-Tools.aspx . If results are abnormal, consider intervention or referral to early intervention services. The AAP recommends completing the previously mentioned formal screening tools at nine-, 18-, and 30-month well-child visits. 14
The AAP also recommends autism-specific screening at 18 and 24 months. 10 The USPSTF recommends using the two-step Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) screening tool (available at https://m-chat.org/ ) if a physician chooses to screen a patient for autism. 10 The M-CHAT can be incorporated into the electronic medical record, with the possibility of the parent or caregiver completing the questionnaire through the patient portal before the office visit.
IRON DEFICIENCY
Multiple reports have associated iron deficiency with impaired neurodevelopment. Therefore, it is essential to ensure adequate iron intake. Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends supplements for preterm infants beginning at one month of age and exclusively breastfed term infants at six months of age. 3 The USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend screening for iron deficiency in infants. 19 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends measuring a child's hemoglobin level at 12 months of age. 3
Lead poisoning and elevated lead blood levels are prevalent in young children. The AAP and CDC recommend a targeted screening approach. The AAP recommends screening for serum lead levels between six months and six years in high-risk children; high-risk children are identified by location-specific risk recommendations, enrollment in Medicaid, being foreign born, or personal screening. 21 The USPSTF does not recommend screening for lead poisoning in children at average risk who are asymptomatic. 20
The USPSTF recommends at least one vision screening to detect amblyopia between three and five years of age. Testing options include visual acuity, ocular alignment test, stereoacuity test, photoscreening, and autorefractors. The USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend screening before three years of age. 26 The AAP, American Academy of Ophthalmology, and the American Academy of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus recommend the use of an instrument-based screening (photoscreening or autorefractors) between 12 months and three years of age and annual visual acuity screening beginning at four years of age. 31
IMMUNIZATIONS
The AAFP recommends that all children be immunized. 32 Recommended vaccination schedules, endorsed by the AAP, the AAFP, and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, are found at https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/child-adolescent.html . Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season. Additional vaccinations may be necessary based on medical history. 33 Immunization history should be reviewed at each wellness visit.
Anticipatory Guidance
Injuries remain the leading cause of death among children, 34 and the AAP has made several recommendations to decrease the risk of injuries. 35 – 42 Appropriate use of child restraints minimizes morbidity and mortality associated with motor vehicle collisions. Infants need a rear-facing car safety seat until two years of age or until they reach the height or weight limit for the specific car seat. Children should then switch to a forward-facing car seat for as long as the seat allows, usually 65 to 80 lb (30 to 36 kg). 35 Children should never be unsupervised around cars, driveways, and streets. Young children should wear bicycle helmets while riding tricycles or bicycles. 37
Having functioning smoke detectors and an escape plan decreases the risk of fire- and smoke-related deaths. 36 Water heaters should be set to a maximum of 120°F (49°C) to prevent scald burns. 37 Infants and young children should be watched closely around any body of water, including water in bathtubs and toilets, to prevent drowning. Swimming pools and spas should be completely fenced with a self-closing, self-latching gate. 38
Infants should not be left alone on any high surface, and stairs should be secured by gates. 43 Infant walkers should be discouraged because they provide no benefit and they increase falls down stairs, even if stair gates are installed. 39 Window locks, screens, or limited-opening windows decrease injury and death from falling. 40 Parents or caregivers should also anchor furniture to a wall to prevent heavy pieces from toppling over. Firearms should be kept unloaded and locked. 41
Young children should be closely supervised at all times. Small objects are a choking hazard, especially for children younger than three years. Latex balloons, round objects, and food can cause life-threatening airway obstruction. 42 Long strings and cords can strangle children. 37
DENTAL CARE
Infants should never have a bottle in bed, and babies should be weaned to a cup by 12 months of age. 44 Juices should be avoided in infants younger than 12 months. 45 Fluoride use inhibits tooth demineralization and bacterial enzymes and also enhances remineralization. 11 The AAP and USPSTF recommend fluoride supplementation and the application of fluoride varnish for teeth if the water supply is insufficient. 11 , 12 Begin brushing teeth at tooth eruption with parents or caregivers supervising brushing until mastery. Children should visit a dentist regularly, and an assessment of dental health should occur at well-child visits. 44
SCREEN TIME
Hands-on exploration of their environment is essential to development in children younger than two years. Video chatting is acceptable for children younger than 18 months; otherwise digital media should be avoided. Parents and caregivers may use educational programs and applications with children 18 to 24 months of age. If screen time is used for children two to five years of age, the AAP recommends a maximum of one hour per day that occurs at least one hour before bedtime. Longer usage can cause sleep problems and increases the risk of obesity and social-emotional delays. 46
To decrease the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), the AAP recommends that infants sleep on their backs on a firm mattress for the first year of life with no blankets or other soft objects in the crib. 45 Breastfeeding, pacifier use, and room sharing without bed sharing protect against SIDS; infant exposure to tobacco, alcohol, drugs, and sleeping in bed with parents or caregivers increases the risk of SIDS. 47
DIET AND ACTIVITY
The USPSTF, AAFP, and AAP all recommend breastfeeding until at least six months of age and ideally for the first 12 months. 48 Vitamin D 400 IU supplementation for the first year of life in exclusively breastfed infants is recommended to prevent vitamin D deficiency and rickets. 49 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends the introduction of certain foods at specific ages. Early transition to solid foods before six months is associated with higher consumption of fatty and sugary foods 50 and an increased risk of atopic disease. 51 Delayed transition to cow's milk until 12 months of age decreases the incidence of iron deficiency. 52 Introduction of highly allergenic foods, such as peanut-based foods and eggs, before one year decreases the likelihood that a child will develop food allergies. 53
With approximately 17% of children being obese, many strategies for obesity prevention have been proposed. 54 The USPSTF does not have a recommendation for screening or interventions to prevent obesity in children younger than six years. 54 The AAP has made several recommendations based on expert opinion to prevent obesity. Cessation of breastfeeding before six months and introduction of solid foods before six months are associated with childhood obesity and are not recommended. 55 Drinking juice should be avoided before one year of age, and, if given to older children, only 100% fruit juice should be provided in limited quantities: 4 ounces per day from one to three years of age and 4 to 6 ounces per day from four to six years of age. Intake of other sugar-sweetened beverages should be discouraged to help prevent obesity. 45 The AAFP and AAP recommend that children participate in at least 60 minutes of active free play per day. 55 , 56
Data Sources: Literature search was performed using the USPSTF published recommendations ( https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/BrowseRec/Index/browse-recommendations ) and the AAP Periodicity table ( https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule.pdf ). PubMed searches were completed using the key terms pediatric, obesity prevention, and allergy prevention with search limits of infant less than 23 months or pediatric less than 18 years. The searches included systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, and position statements. Essential Evidence Plus was also reviewed. Search dates: May through October 2017.
Gauer RL, Burket J, Horowitz E. Common questions about outpatient care of premature infants. Am Fam Physician. 2014;90(4):244-251.
American Academy of Pediatrics; Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Hospital stay for healthy term newborns. Pediatrics. 2010;125(2):405-409.
Baker RD, Greer FR Committee on Nutrition, American Academy of Pediatrics. Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children (0–3 years of age). Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):1040-1050.
Mahle WT, Martin GR, Beekman RH, Morrow WR Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery Executive Committee. Endorsement of Health and Human Services recommendation for pulse oximetry screening for critical congenital heart disease. Pediatrics. 2012;129(1):190-192.
American Academy of Pediatrics Newborn Screening Authoring Committee. Newborn screening expands: recommendations for pediatricians and medical homes—implications for the system. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):192-217.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):898-921.
Maisels MJ, Bhutani VK, Bogen D, Newman TB, Stark AR, Watchko JF. Hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant > or = 35 weeks' gestation: an update with clarifications. Pediatrics. 2009;124(4):1193-1198.
Christian CW Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect, American Academy of Pediatrics. The evaluation of suspected child physical abuse [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2015;136(3):583]. Pediatrics. 2015;135(5):e1337-e1354.
Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for autism spectrum disorder in young children: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;315(7):691-696.
Johnson CP, Myers SM American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Children with Disabilities. Identification and evaluation of children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics. 2007;120(5):1183-1215.
Moyer VA. Prevention of dental caries in children from birth through age 5 years: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1102-1111.
Clark MB, Slayton RL American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Oral Health. Fluoride use in caries prevention in the primary care setting. Pediatrics. 2014;134(3):626-633.
Siu AL. Screening for speech and language delay and disorders in children aged 5 years and younger: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2015;136(2):e474-e481.
Council on Children with Disabilities, Section on Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics, Bright Futures Steering Committee, Medical Home Initiatives for Children with Special Needs Project Advisory Committee. Identifying infants and young children with developmental disorders in the medical home: an algorithm for developmental surveillance and screening [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2006;118(4):1808–1809]. Pediatrics. 2006;118(1):405-420.
Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ, et al. Screening for lipid disorders in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;316(6):625-633.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents. October 2012. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/peds_guidelines_full.pdf . Accessed May 9, 2018.
Moyer VA. Screening for primary hypertension in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(9):613-619.
Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, et al. Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2017;140(6):e20173035]. Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e20171904.
Siu AL. Screening for iron deficiency anemia in young children: USPSTF recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2015;136(4):746-752.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for elevated blood lead levels in children and pregnant women. Pediatrics. 2006;118(6):2514-2518.
Screening Young Children for Lead Poisoning: Guidance for State and Local Public Health Officials . Atlanta, Ga.: U.S. Public Health Service; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; National Center for Environmental Health; 1997.
O'Connor E, Rossom RC, Henninger M, Groom HC, Burda BU. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and post-partum women: evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(4):388-406.
Earls MF Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health, American Academy of Pediatrics. Incorporating recognition and management of perinatal and postpartum depression into pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):1032-1039.
Siu AL. Screening for depression in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(5):360-366.
Weitzman C, Wegner L American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Council on Early Childhood; Society for Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; American Academy of Pediatrics. Promoting optimal development: screening for behavioral and emotional problems [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2015;135(5):946]. Pediatrics. 2015;135(2):384-395.
Grossman DC, Curry SJ, Owens DK, et al. Vision screening in children aged 6 months to 5 years: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;318(9):836-844.
Donahue SP, Nixon CN Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on Ophthalmology, American Academy of Pediatrics; American Association of Certified Orthoptists, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Visual system assessment in infants, children, and young adults by pediatricians. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1):28-30.
Lin KW. What to do at well-child visits: the AAFP's perspective. Am Fam Physician. 2015;91(6):362-364.
American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Community Pediatrics. Poverty and child health in the United States. Pediatrics. 2016;137(4):e20160339.
Lavigne JV, Lebailly SA, Hopkins J, Gouze KR, Binns HJ. The prevalence of ADHD, ODD, depression, and anxiety in a community sample of 4-year-olds. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2009;38(3):315-328.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on Ophthalmology, American Association of Certified Orthoptists, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Visual system assessment of infants, children, and young adults by pediatricians. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1):28-30.
American Academy of Family Physicians. Clinical preventive service recommendation. Immunizations. http://www.aafp.org/patient-care/clinical-recommendations/all/immunizations.html . Accessed October 5, 2017.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents aged 18 years or younger, United States, 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/child-adolescent.html . Accessed May 9, 2018.
National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. 10 leading causes of death by age group, United States—2015. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/images/lc-charts/leading_causes_of_death_age_group_2015_1050w740h.gif . Accessed April 24, 2017.
Durbin DR American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Child passenger safety. Pediatrics. 2011;127(4):788-793.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Reducing the number of deaths and injuries from residential fires. Pediatrics. 2000;105(6):1355-1357.
Gardner HG American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Office-based counseling for unintentional injury prevention. Pediatrics. 2007;119(1):202-206.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Prevention of drowning in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2003;112(2):437-439.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Injuries associated with infant walkers. Pediatrics. 2001;108(3):790-792.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Falls from heights: windows, roofs, and balconies. Pediatrics. 2001;107(5):1188-1191.
Dowd MD, Sege RD Council on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention Executive Committee; American Academy of Pediatrics. Firearm-related injuries affecting the pediatric population. Pediatrics. 2012;130(5):e1416-e1423.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Prevention of choking among children. Pediatrics. 2010;125(3):601-607.
Kendrick D, Young B, Mason-Jones AJ, et al. Home safety education and provision of safety equipment for injury prevention (review). Evid Based Child Health. 2013;8(3):761-939.
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Oral Health. Maintaining and improving the oral health of young children. Pediatrics. 2014;134(6):1224-1229.
Heyman MB, Abrams SA American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. Fruit juice in infants, children, and adolescents: current recommendations. Pediatrics. 2017;139(6):e20170967.
Council on Communications and Media. Media and young minds. Pediatrics. 2016;138(5):e20162591.
Moon RY Task Force on Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths: evidence base for 2016 updated recommendations for a safe infant sleeping environment. Pediatrics. 2016;138(5):e20162940.
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841.
Wagner CL, Greer FR American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding; Committee on Nutrition. Prevention of rickets and vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2009;123(1):197]. Pediatrics. 2008;122(5):1142-1152.
Huh SY, Rifas-Shiman SL, Taveras EM, Oken E, Gillman MW. Timing of solid food introduction and risk of obesity in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics. 2011;127(3):e544-e551.
Greer FR, Sicherer SH, Burks AW American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition; Section on Allergy and Immunology. Effects of early nutritional interventions on the development of atopic disease in infants and children: the role of maternal dietary restriction, breastfeeding, timing of introduction of complementary foods, and hydrolyzed formulas. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):183-191.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. The use of whole cow's milk in infancy. Pediatrics. 1992;89(6 pt 1):1105-1109.
Fleischer DM, Spergel JM, Assa'ad AH, Pongracic JA. Primary prevention of allergic disease through nutritional interventions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2013;1(1):29-36.
Grossman DC, Bibbins-Domingo K, Curry SJ, et al. Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;317(23):2417-2426.
Daniels SR, Hassink SG Committee on Nutrition. The role of the pediatrician in primary prevention of obesity. Pediatrics. 2015;136(1):e275-e292.
American Academy of Family Physicians. Physical activity in children. https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/physical-activity.html . Accessed January 1, 2018.
Continue Reading

More in AFP
More in pubmed.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. See permissions for copyright questions and/or permission requests.
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved.
Doctor Visits
Make the Most of Your Baby’s Visit to the Doctor (Ages 0 to 11 Months)

Take Action
Babies need to go to the doctor or nurse for a “well-baby visit” 6 times before their first birthday.
A well-baby visit is when you take your baby to the doctor to make sure they’re healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury.
At a well-baby visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any problems early, when they may be easier to treat. You’ll also have a chance to ask any questions you have about caring for your baby.
Learn what to expect so you can make the most of each well-baby visit.
Well-Baby Visits
How often do i need to take my baby for well-baby visits.
Babies need to see the doctor or nurse 6 times before their first birthday. Your baby is growing and changing quickly, so regular visits are important.
The first well-baby visit is 2 to 3 days after coming home from the hospital, when the baby is about 3 to 5 days old. After that first visit, babies need to see the doctor or nurse when they’re:
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
If you’re worried about your baby’s health, don’t wait until the next scheduled visit — call the doctor or nurse right away.
Child Development
How do i know if my baby is growing and developing on schedule.
Your baby’s doctor or nurse can help you understand how your baby is developing and learning to do new things — like smile or turn their head to hear your voice. These are sometimes called “developmental milestones.”
At each visit, the doctor or nurse will ask you how you’re doing as a parent and what new things your baby is learning to do.
By age 2 months, most babies:
- Lift their head when lying on their stomach
- Look at your face
- Smile when you talk to them
- React to loud sounds
See a complete list of milestones for kids age 2 months .
By age 4 months, most babies:
- Bring their hands to their mouth
- Make cooing sounds
- Hold toys that you put in their hand
- Turn their head to the sound of your voice
- Make sounds when you talk to them
See a complete list of milestones for kids age 4 months .
By age 6 months, most babies:
- Lean on their hands for support when sitting
- Roll over from their stomach to their back
- Show interest in and reach for objects
- Recognize familiar people
- Like to look at themselves in a mirror
See a complete list of milestones for kids age 6 months .
By age 9 months, most babies:
- Make different sounds like “mamamama” and “bababababa”
- Smile or laugh when you play peek-a-boo
- Look at you when you say their name
- Sit without support
See a complete list of milestones for kids age 9 months .
What if I'm worried about my baby's development?
Remember, every baby develops a little differently. But if you’re concerned about your child’s growth and development, talk to your baby’s doctor or nurse.
Learn more about newborn and infant development .
Take these steps to help you and your baby get the most out of well-baby visits.
Gather important information.
Take any medical records you have to the appointment, including a record of vaccines (shots) your baby has received and results from newborn screenings . Read about newborn screenings .
Make a list of any important changes in your baby’s life since the last doctor’s visit, like:
- Falling or getting injured
- Starting daycare or getting a new caregiver
Use this tool to keep track of your baby’s family health history .
What about cost?
Under the Affordable Care Act, insurance plans must cover well-child visits. Depending on your insurance plan, you may be able to get well-child visits at no cost to you. Check with your insurance company to find out more.
Your child may also qualify for free or low-cost health insurance through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). Learn about coverage options for your family.
If you don’t have insurance, you may still be able to get free or low-cost well-child visits. Find a health center near you and ask about well-child visits.
To learn more, check out these resources:
- Free preventive care for children covered by the Affordable Care Act
- How the Affordable Care Act protects you and your family
- Understanding your health insurance and how to use it [PDF - 698 KB]
Ask Questions
Make a list of questions to ask the doctor..
Before the well-baby visit, write down 3 to 5 questions you have. Each well-baby visit is a great time to ask the doctor or nurse any questions about:
- How your baby is growing and developing
- How your baby is sleeping
- Breastfeeding your baby
- When and how to start giving your baby solid foods
- What changes and behaviors to expect in the coming months
- How to make sure your home is safe for a growing baby
Here are some questions you may want to ask:
- Is my baby up to date on vaccines?
- How can I make sure my baby is getting enough to eat?
- Is my baby at a healthy weight?
- How can I make sure my baby is sleeping safely — and getting enough sleep?
- How can I help my baby develop speech and language skills?
- Is it okay for my baby to have screen time?
- How do I clean my baby's teeth?
Take a notepad, smartphone, or tablet and write down the answers so you can remember them later.
Ask what to do if your baby gets sick.
Make sure you know how to get in touch with a doctor or nurse when the office is closed. Ask how to reach the doctor on call, or if there's a nurse information service you can call at night or on the weekend.
What to Expect
Know what to expect..
During each well-baby visit, the doctor or nurse will ask you about your baby and do a physical exam. The doctor or nurse will then update your baby’s medical history with all of this information.
The doctor or nurse will ask questions about your baby.
The doctor or nurse may ask about:
- Behavior — Does your baby copy your movements and sounds?
- Health — How many diapers does your baby wet each day? Does your baby spend time around people who are smoking or using e-cigarettes (vaping)?
- Safety — If you live in an older home, has it been inspected for lead? Do you have a safe car seat for your baby?
- Activities — Does your baby try to roll over? How often do you read to your baby?
- Eating habits — How often does your baby eat each day? How are you feeding your baby?
- Family — Do you have any worries about being a parent? Who can you count on to help you take care of your baby?
Your answers to questions like these will help the doctor or nurse make sure your baby is healthy, safe, and developing normally.
Physical Exam
The doctor or nurse will also check your baby’s body..
To check your baby’s body, the doctor or nurse will:
- Measure height, weight, and the size of your baby’s head
- Take your baby’s temperature
- Check your baby’s eyes and hearing
- Check your baby’s body parts (this is called a physical exam)
- Give your baby shots they need
Learn more about your baby’s health care:
- Read about what to expect at your baby’s first checkups
- Find out how to get your baby’s shots on schedule
Content last updated March 30, 2023
Reviewer Information
This information on well-baby visits was adapted from materials from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health.
Reviewed by: Sara Kinsman, M.D., Ph.D. Director, Division of Child, Adolescent, and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
Bethany Miller, M.S.W. Chief, Adolescent Health Branch Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
Diane Pilkey, R.N., M.P.H. Nursing Consultant, Division of Child, Adolescent, and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
September 2021
You may also be interested in:

Protect Yourself from Seasonal Flu

Breastfeed Your Baby

Take Care of Your Child's Teeth
The office of disease prevention and health promotion (odphp) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website..
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by ODPHP or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- Pennsylvania
- West Virginia
- Online hoaxes
- Coronavirus
- Health Care
- Immigration
- Environment
- Foreign Policy
- Kamala Harris
- Donald Trump
- Mitch McConnell
- Hakeem Jeffries
- Ron DeSantis
- Tucker Carlson
- Sean Hannity
- Rachel Maddow
- PolitiFact Videos
- 2024 Elections
- Mostly True
- Mostly False
- Pants on Fire
- Biden Promise Tracker
- Trump-O-Meter
- Latest Promises
- Our Process
- Who pays for PolitiFact?
- Advertise with Us
- Suggest a Fact-check
- Corrections and Updates
- Newsletters
Stand up for the facts!
Our only agenda is to publish the truth so you can be an informed participant in democracy. We need your help.
I would like to contribute

- Public Health
- Facebook Fact-checks
- Facebook posts
A pediatrician examines a newborn baby at her practice in Chicago, Aug. 13, 2019. (AP)

Well-baby visits to the doctor are safe, not harmful
If your time is short.
Well-baby and well-child visits are regular check ups with pediatricians that are intended for the purpose of monitoring growth and development in babies and children.
Doctors, health organizations and data stress that well-child visits are incredibly important for a child’s health.
Children are more likely to get sick from outside sources like school or family, not doctor’s offices, experts say.
It’s common practice for parents to bring their healthy children to the doctor for check ups. Often called well-baby or well-child visits, these appointments give pediatricians the opportunity to monitor child growth and development.
But a Facebook post offered parental advice that goes against the grain.
"Want a healthy, happy baby? Skip the Well Baby visits. They make your doctor money and make your baby sick," read a March 30 post .
The post comes from Jennifer Margulis, author of books that explore alternative health approaches for parents and their children while challenging financial interests of those involved in shaping infant health and care.
It was flagged as part of Facebook’s efforts to combat false news and misinformation on its News Feed. (Read more about our partnership with Facebook .)
It’s doctors’ jobs to see patients, and so we aren’t questioning whether they make money doing their jobs, though one expert we spoke to said the field would not be supported if physicians didn’t also regularly care for the sick.
We wondered, however, if the advice to skip these well-child visits aligns with data.
Experts in the field of pediatrics and medicine widely tout well-child visits as key for child health and parent information. Mayo Clinic describes well-baby visits as "an important way to monitor your baby's growth and development and check for serious problems." The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says seeing a doctor regularly for well-child visits and recommended vaccines is "one of the best things you can do to protect your child and community from serious diseases that are easily spread."
While there is a possibility that a child could get sick from a visit to the doctor, experts say the benefits of taking a healthy child to a doctor for these preventative visits outweigh the risk.
Asked about her post, Margulis pointed us to a Science Daily article about a 2014 study out of the University of Iowa . The study examined data from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s Medical Expenditure Panel Survey spanning 1996-2008 and involving 84,595 families. It found that there was a 3.17% increase in the probability of a child under 6 getting sick with a flu-like illness two weeks after their well-child visit.
Contrary to the point of Margulis’ Facebook post, the authors of that study emphasized the importance of well-child visits and instead said the data undergirded the need for strong infection control precautions.
"We believe that attendance at well-child visits is critically important for preventing infections through vaccination and that the benefits far outweigh the risks," the researchers wrote. "Nonetheless, our results stress the importance of improving compliance with current infection control guidelines for ambulatory settings—not just for well-child visits, but for all office visits."
Dr. Philip Polgreen, one of the study’s co-authors, reiterated that point in the Science Daily article and in an interview with NBC’s TODAY Show, calling t he risk of a child getting sick from a well-child visit "actually quite modest."
The study’s authors also noted several limitations in their findings, including that their analysis didn’t consider flu vaccination habits among the families of the children. They also wrote that by relying on medical coding data rather than microbiological evidence, the study might have misclassified some of the cases.
The study also noted that two other, smaller studies examining the question of illness transmission in children found no increased risk of infection.
Featured Fact-check

Dr. Michael Crocetti, associate professor of clinical pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, said the data in the University of Iowa study is also problematic in that it didn’t break down the findings by patient age or school and day care attendance.
"You cannot make a cause and effect conclusion that having a well check two weeks prior to a viral illness is the sole cause," Crocetti said. "In a two-week span, children can have multiple other exposures to viruses."
Crocetti rejected the notion that children are more likely to get sick from well-child visits.
Such visits, he said, enable physicians to provide physical exams for children, monitor their behavior and mental health developments, and administer immunizations in alignment with the CDC’s recommended timeline. They also give parents the chance to ask questions related to a child’s safety, diet, growth and development. The American Academy of Pediatrics also recommends physicians use well-child visits to survey for signs of developmental delay.
Crocetti said that a child is more likely to get sick from being around their family, in a daycare or a school setting than they would going into the doctor’s office. In healthcare settings, he said, medical staff wash their hands often, wear masks when needed and are vaccinated against viruses like COVID-19 and the flu.
"Many offices actually separate out a sick and a well waiting room," he said.
Indeed, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends physicians take specific precautions that include diligent hand hygiene, regular surface cleaning and targeted masking. It recommends separate waiting rooms and precautions for patients who may be contagious and are more vulnerable to infection.
Dr. Joseph F. Hagan, Jr., fellow of the American Academy of Pediatrics and co-editor of the Bright Futures Guidelines for Health Supervision of Infants, Children and Adolescents, said the benefits of well-child visits are in prevention.
"You don’t find many very serious diseases in a well visit, thank God. But sometimes you do," Hagan said. "More importantly though, you spend a lot of time with disease prevention — healthy nutrition being a good example of that, encouraging breastfeeding being an example of that."
Margulis made three other points in response to our inquiry to back up her claim that well-child visits make children sick.
First, she said that pediatricians at well visits "routinely recommend Tylenol," which she said damages the brain, the immune system and can lead to autism. She pointed to a 2017 paper published in the Journal of International Research that called for more research into links between the drug and autism. But Tylenol at the appropriate dose has been found to be safe, and links between acetaminophen, the active ingredient in Tylenol, and autism are in dispute. There is no indication that healthy children attending well-child visits would be urged to take acetaminophen, which is used to treat fevers and minor aches and pains, unless it were recommended to treat short-term side-effects of a vaccination delivered during the visit.
Second, Margulis argued that doctors often "find problems at these well baby checks that don’t exist." She pointed to a study that found that in cases where well-checks involved routine temperature checks of asymptomatic patients, fever was detected 0.2% of the time. In about half those cases, doctors deferred planned vaccinations and in some instances prescribed an antibiotic. But that study didn’t question the need for well-child visits. Rather, it recommended a closer examination of the use of routine temperature checks during well-child visits.
Finally, Margulis said doctors discourage mothers from nursing and instead promote baby formula. But this sweeping claim contradicts data collected by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that show an overall upward trend in breastfeeding, from about 70% in 2000 to nearly 84% in 2018. The American Academy of Pediatrics has published articles and statements that support, not discourage, breastfeeding and, in 2012, it adopted a position that discouraged physicians from handing out formula promotions in clinic settings.
Margulis’ Facebook post advised parents to "skip the well baby visits" if they "want a healthy, happy baby" because they "make your baby sick."
While there is a risk a child could become sick following a visit to a pediatrician’s office, evidence linking these two is not conclusive. A study Margulis cited as evidence did indicate a small increase in the probability of a child under 6 getting sick with a flu-like illness two weeks after their well-child visit. But even the authors of that study emphasized the importance of well-child visits and said the data undergirded the need for strong infection control precautions — not an end to well-child visits.
Regular check-ups for healthy babies and children are recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics, the CDC, the Mayo Clinic and more as a means to monitor growth and development and assist with parent education and communication.
We rate this claim False.
Read About Our Process
The Principles of the Truth-O-Meter
Our Sources
Facebook post , March 30, 2022
The Mayo Clinic, Well-baby exam: What to expect during routine checkups , Feb. 8, 2022
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Catch Up on Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations , April 6, 2022
American Academy of Pediatrics, Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care , accessed April 4, 2022
Science Daily, Well-child visits linked to more than 700,000 subsequent flu-like illnesses , Feb. 12, 2014
JSTOR, Are Well-Child Visits a Risk Factor for Subsequent Influenza-Like Illness Visits? March 2014
TODAY Show, Taking your healthy kids to the doctor may make them sick , Feb. 14, 2014
American Family Physician, Screening for Developmental Delay , Sept. 1, 2011
American Academy of Pediatrics, Infection Prevention and Control in Pediatric Ambulatory Settings , Nov. 1, 2017
ProPublica, Use Only as Directed , Sept. 20, 2013
U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Acetaminophen Information , Nov. 14, 2017
Medical Xpress, Temperature measurement occurs in over half of well-child visits , Dec. 13, 2017
American Academy of Pediatrics, Frequency and Consequences of Routine Temperature Measurement at Well-Child Visits , Dec. 13, 2017
The Christian Science Monitor, NYC breastfeeding: a new-old plan to wean the world off formula , Aug. 6, 2012
Interview with Dr. Michael Crocetti, associate professor of clinical pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, April 1, April 4, 2022
Phone interview with Dr. Joseph F. Hagan, JR., fellow of the American Academy of Pediatrics and co-editor of the Bright Futures Guidelines for Health Supervision of Infants, Children and Adolescents, April 5, 2022

Browse the Truth-O-Meter
More by gabrielle settles.

Support independent fact-checking. Become a member!
Your Guide to Well-Baby Visits
Medical review policy, latest update:, what are well-baby visits and why are they so important, when will my child's well-baby visits happen, read this next, what you can expect at well-baby visits, tips on making the most of well-baby visits, time it right, make a checklist, write down your questions, have some answers, too, dress baby for success.
What to Expect the First Year , 3rd edition, Heidi Murkoff. WhatToExpect.com, Your Baby's Vaccine Schedule: What Shots Should Your Child Get When? , January 2021. American Academy of Pediatrics, AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits , September 2021. American Academy of Pediatrics, Checkup Checklist: 1 Month Old , September 2021. KidsHealth From Nemours, Your Child's Checkup: 1 Month , April 2021.
Go to Your Baby's Age
Trending on what to expect, the covid-19 vaccine for infants, toddlers and young children, how to create a night shift system when you have a newborn, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., when do babies start laughing, baby-led weaning, what happens in the ‘4th trimester’ (and is it a real thing).
All About Your Child’s Well-Baby Visits

From the first few days of life all the way through to age 21, your child will have regular appointments with her healthcare provider. These are often referred to as well-baby visits or well-child checkups. Initially, they will happen every few months or so, but later on they will happen annually. Learn why well-child checkups are important, what the typical schedule is, and how to get the most out of each visit.
Well-Child Checkup Schedule
Well-child checkups are crucial for keeping your little one healthy and safe as she grows and develops. Below you will find the standard schedule of well-child checkups for the first three years, along with a few examples of what may come up during each checkup. Beginning at age 3, most children will have annual well-child visits. Keep in mind that your child’s healthcare provider may recommend additional visits, and you can always schedule an extra visit between appointments if your little one needs medical care.
The First Week
This visit usually happens within 72 hours of your newborn being home—usually when your baby is about 3 to 5 days old. As part of this checkup your child’s skin color may be checked for signs of jaundice . Your child’s provider may also take a peek inside your newborn’s mouth for signs of tongue-tie . If you are breastfeeding, your little one’s provider can answer any questions you have about latch or sore nipples , for example. The provider may also be able to recommend a lactation consultant for additional help and support.
1 Month Old Checkup
During this visit, your child’s healthcare provider may check things like your baby’s reflexes and muscle tone, as well examining the soft spots on your baby’s head called the fontanelles. If there’s something specific you’d like your child’s provider to check, go ahead and mention it. Your baby’s provider may ask you about how feeding is going. For example, you may be asked how much formula you’re offering, or how often you breastfeed your baby. If you’re planning to return to work soon while continuing to breastfeed, your newborn’s provider may give you advice on pumping and storing breast milk. You might also like to use this opportunity to ask how to go about finding good childcare. Use this appointment to ask any questions you have about adjusting to life as a parent. For example, if you suspect you may have postpartum depression or are not recovering as you had hoped after childbirth , bring this up as well. If you’re the dad, you might like to ask about what you can do to bond with your baby.
2 Months Old Checkup
At this visit your baby may receive some vaccines, including the DTaP, Hib, and IPV vaccines. Vaccinations will be given at a number of different well-child checkups, so it’s worth taking a look at the immunization schedule or asking your child’s provider for guidance on which vaccines to expect when. Your baby’s heart and lung health may be checked. Your child’s provider will use a stethoscope to listen to your baby’s heartbeats for signs of irregularity, and to listen to your baby’s lungs for signs of breathing difficulties. If your baby has diaper rash , your child’s healthcare provider can recommend ointments or barrier creams for treatment and prevention. Your child’s provider can also let you know about other common baby rashes to keep an eye out for.
4 Months Old Checkup
At this visit, your baby’s provider may examine your child's eyes and track her eye movements. Your child’s provider may also move your baby’s legs to check that the joints are developing well, and press gently on your baby’s tummy to check whether the organs are forming well. At this point your doctor will ask you about your baby’s sleep, including nap times. To help you keep track of this, and to help make sure your baby’s sleeping well, we suggest downloading the Smart Sleep Coach by Pampers™. Co-developed with pediatricians and backed by science, this easy-to-use app is like having a personal sleep coach, in your pocket! Get started today by taking their free sleep assessment .
6 Months Old Checkup
This month, your child’s healthcare provider may offer pointers on introducing solids and tell you about signs of an allergic reaction to watch for as you introduce new foods one at a time. Your child’s provider can also give you personalized advice on which foods to start with, how to set up healthy eating habits, and how to actually feed your baby solids.
9 Months Old Checkup
As your baby’s teeth start erupting , your child’s healthcare provider may check on their growth and recommend a good pediatric dentist in your area. Your baby’s provider can also show you how to care for those first tiny teeth. Other topics that may come up at this checkup include how to wean your baby off the bottle when the time comes, when to start giving cow’s milk, and when to introduce utensils and a sippy cup.
1 Year Old Checkup
During this visit your child’s healthcare provider may ask about certain fine and gross motor skills , such whether your child can pull up to a standing position, or walk on his own or with his hand held, or use his finger to point at objects he wants. You might like to ask your child’s healthcare provider about when your little one might start walking , if he isn’t already; what baby proofing measures you should take at home now that your child is getting more mobile; and where to go to get shoes fitted for your child.
15 Months Old Checkup
Your child’s healthcare provider may ask about how your toddler’s interpersonal, language, and cognitive skills are coming along. For example, she might ask whether your child is starting to explore more independently, whether he points to common objects when you say their names, and whether he can follow simple instructions like “give the spoon to Daddy.” If you are planning to have another baby soon, you might like to ask the healthcare provider about how to introduce your toddler to the concept of him getting a little brother or sister.
18 Months Old Checkup
As your child gets more active and independent you may like to ask your child’s provider about strategies for keeping your child safe in your home environment. This is also a good time to discuss ways to manage your child's behavior and set up age-appropriate rules and boundaries. If your toddler has certain risk factors, the relevant screening tests may be offered at this checkup. For example, screening tests may be recommended for things like hearing, vision, development delays, or autism. Your provider may also bring up the topic of potty training, and go over some of the signs of readiness for potty training .
2 Years Old Checkup
Before this visit you may have been wondering about the upcoming “terrible twos” and how you should handle temper tantrums and the inevitable meltdowns at the grocery store. This visit is a great chance to bring up your questions and concerns around how your child’s behavior and personality may be evolving. Your child’s provider will explain what is normal during this stage of development and how to support your child’s growing independence. Preschool could be coming up in the next year or two, and your provider can help you find a preschool that's a good fit for your child.
2 ½ Years Old Checkup
Besides the usual checks, one topic that may come up during this visit is potty training. If potty training has begun and isn't going well, or if you're unsure how to get the process started , your provider can offer suggestions. This checkup may also be a great time to talk to your child’s provider about your little one’s temperament and personality. For example, if you have any concerns about how your toddler is interacting with other children, or if your child seems particularly shy, you might like to bring it up to see what advice or reassurance your toddler’s provider can give you.
3 Years Old Checkup
During this session your toddler’s healthcare provider may ask you about anything that’s disturbing your child’s sleep, like nightmares, for example, and how to handle other sleep issues. Screen time may also come up. You may talk about how much screen time a 3-year-old should be getting, and what type of programming is good for a child of this age.
Baby Growth Chart Calculator
Keep an eye on your baby’s average growth by tracking height, weight, and head circumference with our simple tool.
This is a mandatory field.
*Input details of your baby’s last measurements. **Source: World Health Organization
What Happens at a Well-Child Visit?
Each visit may be a little different based on your child’s age and stage of development, any specific needs your child has, and the way your child’s healthcare provider does things. However, here are some of the things that typically happen at a well-child visit in the early years:
Tracking your child’s growth by measuring her length, weight, and head circumference
A physical exam that could include checking your baby’s ears, eyes, mouth, skin, limbs, tummy, and other body parts
An assessment of your child's physical development, including her movement and motor skills
An evaluation of her emotional and cognitive development; for example, checking that your child is reacting and interacting normally for her age, and is learning appropriately for her age
Immunizations may be given
Screening tests or other tests may be recommended if needed
Your child’s provider may give you advice on feeding and nutrition or recommend extra vitamins or supplements, like vitamin D or iron, if they are needed
Your provider may share insights into the next phase of your child’s development. If your child is not developing as expected, the provider will also be able to offer recommendations on treatment or therapies to help your child get back on track.
Your child’s healthcare provider will answer any questions you have about parenting or about your child’s health and well-being. No question is too big or too small. You can ask anything from how much your child should be sleeping during the day to when to switch your car seat from rear facing to front facing.
Your child’s healthcare provider can give your information about resources in your area, and about how to go about certain things like choosing a good babysitter, finding an affordable pediatric dentist, or selecting the right preschool.
Benefits of the Well-Child Visit
Well-child checkups are invaluable for both you and your child. Here are just some of the benefits of the well-child checks:
Spotting issues early. Your child’s healthcare provider will use these visits to keep an eye out for any possible problems so that steps can be taken to get your child back on the right track. As an example, if your little one is gaining too much weight, your provider can give you advice on nutrition so that your child gets back to a healthy weight.
Preventing problems. As an example, ensuring your child is immunized against certain childhood diseases helps prevent your child from getting sick with a preventable disease.
Getting answers. You might have some questions that aren’t pressing enough to warrant a separate doctor’s visit. Knowing that you have a well-child visit coming up gives you a chance to collect all of your questions and have them answered by a medical professional you trust. Remember, there are no “silly questions” when it comes to your child’s health and well-being.
Learning about what’s to come. Your child’s healthcare provider can give you insights and information about the next stage of your child’s development. That means that certain things might be less of surprise when they happen. As an example, your child’s provider might tell you what kind of behavioral changes to expect with the “terrible twos” and how to manage the tantrums that follow.
Creating a strong relationship with your child’s healthcare provider. Seeing your child’s provider regularly gives you the chance to build up a rapport. You’ll get to know her during these well-child visits, and she’ll get to know you and your little one. Having a relationship built on trust ensures that you can work as a team for the best outcomes for your child.
How to Make the Most of the Well-Child Visit
There are a few things you can do to ensure you get the most out of your child’s well-child checkups:
If it’s workable, schedule the visit for a time when you think your child will be well-rested and well-fed, and try to pick a time when you yourself aren’t rushed. Also, consider how busy your child’s healthcare provider will be. It may be easiest if you can get the first appointment of the day, or one that’s not during “rush hour.”
If it’s possible, both parents should be at the first few visits to ensure that you both get to know your child’s healthcare provider and get the same basic information about newborn baby care
Pack everything you’ll need like your insurance information, your child’s medical history, and your diaper bag (filled with extra diapers, snacks, and toys)
Consider keeping a physical or digital record of what was discussed at each well-child visit. Keep copies of your child’s lab results and evidence of immunizations in the same spot or format as well. Having all this information in one place from the start will make it easier to look back and find the information when you need it. When your child enters preschool or school, you may need to provide documentation of certain medical details.
Dress your child in clothes that are easy to remove and put back on. Your little one may be undressed for part of the visit and your child’s healthcare provider may need easy access to give immunizations.
Write down any questions you have and take the list with you so you don’t forget anything important. Having a list of questions also allows you to focus on the answers instead of thinking ahead about what to ask next.
Using the Smart Sleep Coach by Pampers™ to track your baby’s night sleeps and naps can be a huge help when discussing your baby’s health and development with your doctor. By taking a broad view of your baby’s sleep, you can understand and shape your baby’s sleep and give them the rest they need to keep growing and developing well. In fact, if you're experiencing sleep challenges, you can take this free sleep assessment to get helpful guidance and support on how to get sleep back on track!
The bottom line
Well-child checkups are important for your child. They allow the healthcare provider to to track your child’s growth and development, give vaccinations or screening tests that are needed, and identify any problems nice and early. By working together, you and your child’s provider can give your child the best possible start in life.
Plus, each well-child visit is a great opportunity for you to ask any questions you have about your child’s health and parenting in general.
Try not to miss your scheduled well-baby checkups; they can be a wealth of information and an important way to help ensure your child’s happy and healthy development. By taking advantage of these one-on-one sessions with your child’s provider, you may find he becomes less of a “provider” and more of a partner in your parenting journey.
How We Wrote This Article The information in this article is based on the expert advice found in trusted medical and government sources, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. You can find a full list of sources used for this article below. The content on this page should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult medical professionals for full diagnosis and treatment.
- healthychildren.org. “AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits.”
- Kids Health. “Your Child's Checkup: 3 Years.”
- CDC. “Developmental Monitoring and Screening.”
- Kids Health. “Your Child's Checkup: 1.5 Years (18 Months).”
- Kids Health. “Your Child's Checkups.”
Review this article:
Read more about baby.
- Explore Baby Sleep
- Parenting Life
- Development
Join a World of Support
through Pregnancy and Parenthood.

TRACK WITH TOOLS

LEARN WITH EXPERTS

GET REWARDED

Where You Already Belong
Internet Explorer Alert
It appears you are using Internet Explorer as your web browser. Please note, Internet Explorer is no longer up-to-date and can cause problems in how this website functions This site functions best using the latest versions of any of the following browsers: Edge, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, or Safari . You can find the latest versions of these browsers at https://browsehappy.com
- Publications
- HealthyChildren.org
Shopping cart
Order Subtotal
Your cart is empty.
Looks like you haven't added anything to your cart.
- Career Resources
- Philanthropy
- About the AAP
- Confidentiality in the Care of Adolescents: Policy Statement
- Confidentiality in the Care of Adolescents: Technical Report
- AAP Policy Offers Recommendations to Safeguard Teens’ Health Information
- One-on-One Time with the Pediatrician
- American Academy of Pediatrics Releases Guidance on Maintaining Confidentiality in Care of Adolescents
- News Releases
- Policy Collections
- The State of Children in 2020
- Healthy Children
- Secure Families
- Strong Communities
- A Leading Nation for Youth
- Transition Plan: Advancing Child Health in the Biden-Harris Administration
- Health Care Access & Coverage
- Immigrant Child Health
- Gun Violence Prevention
- Tobacco & E-Cigarettes
- Child Nutrition
- Assault Weapons Bans
- Childhood Immunizations
- E-Cigarette and Tobacco Products
- Children’s Health Care Coverage Fact Sheets
- Opioid Fact Sheets
- Advocacy Training Modules
- Subspecialty Advocacy Report
- AAP Washington Office Internship
- Online Courses
- Live and Virtual Activities
- National Conference and Exhibition
- Prep®- Pediatric Review and Education Programs
- Journals and Publications
- NRP LMS Login
- Patient Care
- Practice Management
- AAP Committees
- AAP Councils
- AAP Sections
- Volunteer Network
- Join a Chapter
- Chapter Websites
- Chapter Executive Directors
- District Map
- Create Account
- Early Relational Health
- Early Childhood Health & Development
- Safe Storage of Firearms
- Promoting Firearm Injury Prevention
- Mental Health Education & Training
- Practice Tools & Resources
- Policies on Mental Health
- Mental Health Resources for Families
Well Baby Visits, 1 and 2 Months
Topics to discuss with patients during their well baby visit at 1 and 2 months.
- Babies should gain ½ lb per week
- Infants gain approximately 1 inch per month during this time
- Continuing exclusive breastfeeding or formula without supplemental water or juice
- Ask mothers who are working whether allowances are made in the workplace for breastfeeding support. Federal law requires providing breaks and adequate place for expressing breast milk.
- Breastfed infants continue to require 8 to 12 feedings per day
- Daily formula intake should increase from 24 oz (at 1 month) to 30 to 32 oz (by 4 months)
Consider Referral
- Growth faltering (failure to thrive) [Nutrition Related Illnesses and Concerns/Growth faltering]
- Persistent dysphagia [Optimizing Nutrition for Newborns and Infants/Breastfeeding the Newborn/Feeding Issues]
- Dysphagia of unknown cause
Additional Information
- Gastroesophageal reflux and gastroesophageal reflux disease: Parent FAQs , American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Parent’s Guide to GER (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) and GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- Breastfeeding Your Baby: Getting Started (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- New Mother’s Guide to Breastfeeding, 3rd Edition (book), American Academy of Pediatrics (also available in Spanish)
- Breastfeeding-Baby Questions (handout)
- Preparing Infant Formula: Important Safety Information (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
- Healthy Active Living—Responsive Feeding (handout) American Academy of Pediatrics
- Bottle Feeding (Formula) Questions (handout), American Academy of Pediatrics
Last Updated
American Academy of Pediatrics

An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Well-Child Care
Improving infant well-child visits.
High-quality well-child visits can improve children’s health, support caregivers’ behaviors to promote their children’s health, and prevent injury and harm. The American Academy of Pediatrics and Bright Futures recommend nine well-care visits by the time children turn 15 months of age. These visits should include a family-centered health history, physical examination, immunizations, vision and hearing screening, developmental and behavioral assessment, an oral health risk assessment, a social assessment, maternal depression screening, parenting education on a wide range of topics, and care coordination as needed. i When children receive the recommended number of high-quality visits, they are more likely to be up-to-date on immunizations, have developmental concerns recognized early, and are less likely to visit the emergency department. ii , iii , iv , v , vi , vii However, many infants do not receive the recommended number of infant well-child visits.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) offers quality improvement (QI) technical assistance (TA) to help states increase the attendance and quality of well-child visits for Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) beneficiaries ages 0 to 15 months.
QI TA resources , to help state Medicaid and CHIP staff and their QI partners get started improving the use of infant well-child visits for their beneficiaries
Improving Infant Well-Child Visit learning collaborative resources , to share different approaches to improving well-child visit care and state examples
For more information on these materials and other QI TA, please email [email protected] .
QI TA Resources
These resources can help states get started in developing their own infant well-child QI projects:
Getting Started on Quality Improvement Video . This video provides an overview of how Medicaid and CHIP agencies can start a QI project to improve the use of infant well-child visits. The Model for Improvement begins with small tests of change, enabling state teams to “learn their way” toward strong programs and policies.
Driver Diagram and Change Idea Table . A driver diagram is a visual display of what “drives” or contributes to improvements in infant well-child visits. This example of a driver diagram shows the relationship between the primary drivers (the high-level elements, processes, structures, or norms in the system that must change to use and quality of infant well-child visits) and the secondary drivers (the places, steps in a process, time-bound moments, or norms in which changes are made to spur improvement). The document also includes change idea tables, which contain examples of evidence-based or evidence-informed QI interventions to improve the use of infant well-child care. The change ideas were tailored for Medicaid and CHIP.
Measurement Strategy . This document provides examples of measures that can be used to monitor infant well-child care QI projects.
Improving Infant Well-Child Visits: Learning Collaborative Resources
Beginning in 2021, CMS facilitated the two year Infant Well-Child Visit learning collaborative to support state Medicaid and CHIP agencies’ efforts to improve the use of infant well-child visits from 0-15 months of age. The learning collaborative included a webinar series and an affinity group to support state Medicaid and agencies’ quality improvement efforts. The webinars, listed and linked to below, described approaches that states can use to improve attendance and quality of infant well-child visits.
California, Missouri, North Carolina, South Carolina, Texas and Virginia participated in the action-oriented affinity group where teams designed and implemented an infant well-child quality improvement (QI) project in their state with tailored TA from CMS. Learnings from participating states can be found in the state highlights brief.
Learning Collaborative Webinar Series
State Spotlights Webinar on Improving Infant-Well Child Care ( Video ) ( Transcript ). This 2024 webinar spotlighted several state QI projects from the affinity group, highlighting their strategies, partnerships, and lessons learned.
Using Payment, Policy and Partnerships to Improve Infant Well-Child Care ( Audio )( Transcript ). This August 2021 webinar focused on Medicaid and CHIP payment incentives, managed care contracts, and other strategies that can increase the use and quality of infant well-child visits and advance equity. Speakers from the CMS and Mathematica introduced CMS’ Maternal and Infant Health Initiative and shared the importance of high-quality well-child visits and the opportunities within Medicaid and CHIP to impact infant health. Speakers from Pennsylvania and Texas’ Medicaid and CHIP agencies described their efforts to expand and incentivize participation in infant well-child visits, such as through value-based purchasing, performance improvement projects, CHIP Health Services Initiatives (HSIs), and partnerships with aligned service providers like the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC). State presenters offered insights into ways to incentivize efforts to close gaps in care, engage families, and improve performance on quality measures. During the Q&A session, presenters discussed the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on well-child care, the potential of using telehealth or hybrid visits to increase access, and incentives for managed care entities, and addressing the social determinants of health in value-based payment strategies.
Improving Quality and Utilization of Infant Well-Child Visits ( Audio )( Transcript ). This September 2021 webinar focused on the characteristics of a high-performing system of well-child health care. CMS and Mathematica presenters shared the Maternal and Infant Health Initiative’s Theory of Change. Speakers from Washington and Arkansas Medicaid and CHIP agencies discussed how their states have achieved high rates of participation in infant well-child visits and how they use data to monitor performance and disparities and ensure access to services. Washington shared insights on leveraging collaborative performance improvement projects to identify and address barriers to care. Arkansas discussed the state’s per member per month incentives for performance and minimum performance measures for infant well-child visit rates. During the Q&A session, presenters highlighted efforts to improve health equity, engage parents and providers, and leverage performance measures and quality tools to improve attendance at infant well-child visits.
Models of Care that Drive Improvement in Infant Well-Child Visits ( Audio )( Transcript ). In this September 2021 webinar, three states—Oregon, Michigan, and North Carolina—shared approaches to designing and implementing models of care associated with improved infant well-child visit participation, including patient-centered medical homes (PCMHs) and home visiting. States offered insights on the importance of strategic alignment of policies, processes, and partnerships. Oregon discussed its home visiting program and quality incentive strategy for its coordinated care organizations. The state incentivizes progress on the HEDIS measures and other measures designed by the state’s Pediatric Improvement Partnership, including a measure of social-emotional health service capacity and access for infants and children. Michigan discussed how they requires MCOs to identify and publish disparities in well-child visit rates and how they encourage plans to reduce disparities. The state also uses an algorithm that automatically assigns members to MCOs based on MCOs’ performance and reimburses for maternal-infant health home visiting. North Carolina shared its Keeping Kids Well program, which aims to increase well-child visit and immunization rates and reduce disparities in those rates. The program offers coaches to practices to support their improvements, established an advisory board of key interested parties, and provides customized vaccination notices for practices to distribute to beneficiaries, in partnership with health systems and pharmaceutical companies. The state also used the Healthy Opportunities payment to incentivize the identification and redress of health-related social needs and provided the Health Equity Payment to providers serving areas with high poverty rates.
i 3 Hagan, J.F., J.S. Shaw, and P.M. Duncan (eds.). Bright Futures: Guidelines for Health Supervision of Infants, Children, and Adolescents. 4th ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics, 2017.
ii Gill, J.M., A. Saldarriaga, A.G. Mainous, and D. Unger. “Does Continuity Between Prenatal and Well-Child Care Improve Childhood Immunizations?” Family Medicine, vol. 34, no. 4, April 2002, pp. 274–280.
iii Buchholz, M., and A. Talmi. “What We Talked About at the Pediatrician’s Office: Exploring Differences Between Healthy Steps and Traditional Pediatric Primary Care Visits.” Infant Mental Health Journal, vol. 33, no. 4, 2012, pp. 430–436.
iv DeVoe, J.E., M. Hoopes, C.A. Nelson, et al. “Electronic Health Record Tools to Assist with Children’s Insurance Coverage: A Mixed Methods Study.” BMC Health Services Research, vol.18, no. 1, May 2018, p. 354–360.
v Coker, T.R., S. Chacon, M.N. Elliott, et al. “A Parent Coach Model for Well-Child Care Among Low-Income Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” Pediatrics, vol. 137, no. 3, March 2016, p. e20153013.
vi Flores, G., H. Lin, C. Walker, M. Lee, J. Currie, R. Allgeyer, M. Fierro, M. Henry, A. Portillo, and K. Massey. “Parent Mentoring Program Increases Coverage Rates for Uninsured Latino Children.” Health Affairs, vol. 37, no. 3, 2018, pp. 403–412.
vii Hakim, R.B., and D.S. Ronsaville. “Effect of Compliance with Health Supervision Guidelines Among US Infants on Emergency Department Visits.” Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, vol. 156, no. 10, October 2002, pp. 1015–1020.
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
The Impact of the Pandemic on Well-Child Visits for Children Enrolled in Medicaid and CHIP
Elizabeth Williams , Alice Burns , Robin Rudowitz , and Patrick Drake Published: Mar 18, 2024
In Medicaid, states are required to cover all screening services as well as any services “necessary… to correct or ameliorate” a child’s physical or mental health condition under Medicaid’s Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnostic and Treatment (EPSDT) benefit (see Box 1). Many of these screening services along with immunizations are provided at well-child visits. These visits are a key part of comprehensive preventive health services designed to keep children healthy and to identify and treat health conditions in a timely manner. Various studies have also shown that children who forego their well-child visits have an increased chance of going to the emergency room or being hospitalized. Well-child visits are recommended once a year for children ages three to 21 and multiple times a year for children under age three according to the Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) periodicity schedule .
A recent Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) analysis shows that half of children under age 19 received a Medicaid or CHIP funded well-child visit in 2020. The onset of the pandemic in 2020 had a substantial impact on health and health care service utilization, but research has shown that many Medicaid-covered children were not receiving recommended screenings and services even before the pandemic. This issue brief examines well-child visit rates overall and for selected characteristics before and after the pandemic began and discusses recent state and federal policy changes that could impact children’s preventive care. The analysis uses Medicaid claims data which track the services enrollees use and may differ from survey data. In future years, claims data will be used to monitor adherence to recommended screenings. Key findings include:
- More than half (54%) of children under age 21 enrolled in Medicaid or CHIP received a well-child visit in 2019, but the share fell to 48% in 2020, the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Despite having the highest well-child visit rates compared to other ethnic and racial groups, Hispanic and Asian children enrolled in Medicaid or CHIP saw the largest percentage point declines in well-child visit rates from 2019 to 2020.
- Children over age three enrolled in Medicaid or CHIP have lower rates of well-child visits and experienced larger declines in well-child visits during the pandemic than children under age three.
- Well-child visit rates are lower for Medicaid/CHIP children in rural areas, but rates in urban areas declined more during the pandemic.
How did use of well-child visits change during the pandemic?
More than half (54%) of children under 21 enrolled in Medicaid or CHIP received a well-child visit in 2019, but the share fell to 48% in 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic (Figure 1). Rates examined here use Medicaid claims data which differ substantially from survey data (see Box 2). While the vast majority of children in the analysis (91% in 2019 and 88% in 2020) used a least one Medicaid service, including preventive visits, sick visits, filling prescriptions, or hospital or emergency department visits, well-child visit rates remained low and are substantially below the CMS goal of at least 80%. One recent analysis found that 4 in 10 children enrolled in Medicaid or CHIP experienced at least one challenge when accessing health care. Barriers to Medicaid/CHIP children receiving needed care can include lack of transportation, language barriers, disabilities , and parents having difficulty finding childcare or taking time off for an appointment as well as the availability of and distance to primary care providers. Some states have seen a loss in Medicaid pediatric providers, and one recent story reported that families with Medicaid in California were traveling long distances and experiencing long wait times for primary care appointments. Data have also shown slight declines in the share of kindergarten children up to date on their routine vaccinations since the COVID-19 pandemic, which may, in part, be associated with the decline in well-child visits. The national measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccination rate is below the goal of at least 95%, and some states are now seeing measle outbreaks among children.
Despite having the highest well-child visit rates compared to other ethnic and racial groups, Hispanic and Asian children enrolled in Medicaid or CHIP saw the largest percentage point declines in well-child visit rates from 2019 to 2020 (Figure 2). Prior to the pandemic in 2019, about half or more of children across most racial and ethnic groups had a well-child visit, with rates highest for Hispanic (60%) and Asian (57%) children. The rate for American Indian and Alaska Native (AIAN) children lagged behind at just over one in three (36%), although this may reflect that some services received from Indian Health Service providers not being captured in the analysis (see Methods ). Between 2019 and 2020, the well-child visit rate fell for all racial and ethnic groups. Hispanic and Asian children experienced the largest percentage point declines in well-child rates (9 percentage points for both groups), but they still had higher rates compared to other groups as of 2020. Black, Native Hawaiian, and Other Pacific Islander (NHOPI), and AIAN children also experienced larger percentage point declines in their well-child visit rates compared with White children, and AIAN children had the largest relative decline on account of their lower starting rate. As of 2020, rates remained lowest for NHOPI (42%) and AIAN children (29%). Twenty-two states, including some states that are home to larger shares of AIAN and NHOPI children, were excluded from the race/ethnicity analysis due to data quality issues (see Methods ).
Children ages three and older have lower rates of well-child visits and experienced larger declines in well-child visits during the pandemic than children under age three (Figure 2). Well-child visit rates are highest when children are young because multiple well-child visits are recommended for children under age three. Although children under three have highest rates of a single well-child visit within the year, it is unknown whether the rates of adherence to recommended well-child screenings are higher or lower than that of other groups because this analysis only accounts for one well-child visit in a year. Well-child visit rates steadily decrease as children get older with the exception of the 10-14 age group, where somewhat higher rates may reflect school vaccination requirements .
Well-child visit rates are lower in rural areas than urban ones, but urban areas had larger declines during the first year of the pandemic (Figure 2). The share of Medicaid/CHIP children living in rural areas with a well-child visit declined from 47% in 2019 to 43% in 2020 while the share for urban areas fell from 56% in 2019 to 49% in 2020, narrowing the gap between Medicaid/CHIP well-child visit rates in rural and urban areas. Note that 18% of children in the analysis lived in a rural area, and three states were excluded from the geographic area analysis due to data quality issues (see Methods ). This analysis also examined changes for children by eligibility group, managed care status, sex, and presence of a chronic condition; data are not shown but well-child visit rates for Medicaid/CHIP children declined across all groups from 2019 to 2020.
What to watch?
Well-child visit rates for Medicaid/CHIP children overall fall below the goal rate, with larger gaps for AIAN, Black and NHOPI children as well as older children and children living in rural areas, highlighting the importance of outreach and other targeted initiatives to address disparities. Addressing access barriers and developing community partnerships have been shown to increase well-child visit rates and reduce disparities. It will be important to track, as data become available, the extent to which well-child visit rates as well as vaccination rates (often administered at well-child visits) rebounded during the pandemic recovery and where gaps remain.
Recent state and federal actions could help promote access, quality and coverage for children that could increase well-child visit rates. The Bipartisan Safer Communities Act included a number of Medicaid/CHIP provisions to ensure access to comprehensive health services and strengthen state implementation of the EPSDT benefit. CMS also released an updated school-based services claiming guide , and states have taken action to expand Medicaid coverage of school-based care in recent years. In 2024, it became mandatory for states to report the Child Core Set, a set of physical and mental health quality measures, with the goal of improving health outcomes for children. In addition, as of January 2024, all states are now required to provide 12-month continuous eligibility for Medicaid and CHIP children, which could help stabilize coverage and help children remain connected to care. Three states also recently received approval to extend continuous eligibility for children in Medicaid for multiple years, which could help children maintain coverage beyond one year. In the recently released FY 2025 budget, the Biden Administration proposes establishing the option for states to provide continuous eligibility in Medicaid and CHIP for children from birth to age six or for 36 month periods for children under 19.
Lastly, millions of children are losing Medicaid coverage during the unwinding of the continuous enrollment provision, which could have implications for access. Data up to March 2024 show that children’s net Medicaid enrollment has declined by over 4 million. In some cases, children dropped from Medicaid may have transitioned to other coverage, but they may also become uninsured, despite in many cases remaining eligible for Medicaid or CHIP. While people of color are more likely to be covered by Medicaid , data on disenrollment patterns by race and ethnicity are limited . KFF analysis shows individuals without insurance coverage have lower access to care and are more likely to delay or forgo care due to costs. A loss of coverage or gaps in coverage can be especially problematic for young children who are recommended to receive frequent screenings and check-ups.
- Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
- Access to Care
Also of Interest
- Recent Trends in Children’s Poverty and Health Insurance as Pandemic-Era Programs Expire
- More Children are Losing Medicaid Coverage as Child Poverty Grows
- Medicaid Enrollment and Unwinding Tracker
- Headed Back To School in 2023: A Look at Children’s Routine Vaccination Trends
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Well-baby and well-child visits
New Hampshire’s GOP Is Taking a Stand—Against the Polio Vaccine
The granite state could be the first to ditch polio and measles requirements for child care..

Julia Métraux
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
New Hampshire could soon beat Florida—known for its anti-vaccine Surgeon General —when it comes to loosening vaccine requirements. A first-in-the-nation bill that’s already passed New Hampshire’s state House, sponsored only by Republican legislators, would end the requirement for parents enrolling kids in child care to provide documentation of polio and measles vaccination. New Hampshire would be the only state in the US to have such a law, although many states allow religious exemptions to vaccine requirements.
Currently, Republicans control New Hampshire’s state House, Senate and governor’s office—but that isn’t a guarantee that the bill will be signed into law, with GOP Gov. Chris Sununu seemingly flip-flopping when it comes to disease control. Sununu did sign a bill in 2021 allowing people to use public places and services even if they did not receive the Covid-19 vaccine. But the next year, the governor vetoed a bill that would bar schools from implementing mask mandates.
The polio vaccine, first offered in 1955, and the MMR shot, which treats the highly infectious measles, mumps, and rubella viruses, are two very crucial vaccines both in the US and internationally. Since the year 2000 alone, vaccines against measles are estimated to have saved over 55 million lives around the world.
The CDC recommends that kids get their first dose of MMR vaccine between 12 and 15 months of age, and a first dose of the polio vaccine at around two months old. All states currently require children to have at least started vaccination against measles and polio in order to enroll in child care, according to the nonprofit Immunize.org. A CDC report found that for the 2021-2022 school year, around 93 percent of children had received the MMR and polio vaccines by the time they entered kindergarten. That figure drops to less than 80 percent for both vaccines—the lowest rate in the country—in Alaska, where a measles outbreak could be devastating.
Rises in anti-vaccine sentiments have largely been linked to concerns that vaccines cause health issues, like the debunked claim that the MMR vaccine leads to kids being autistic. What parents may want to keep in mind is that polio and measles themselves are disabling conditions: according to the World Health Organization , 1 in 200 polio infections leads to irreversible paralysis. Children who get measles can experience symptoms including swelling of the brain . Death is always a possibility, too.
“Childhood vaccines have helped protect generations of Americans from potentially devastating vaccine-preventable diseases,” S. Wesley Long, a professor of pathology and genomic medicine at the Houston Methodist medical center, told Mother Jones . “Many of these diseases still exist around the world, and we rely on our collective immunity, often from childhood vaccines, to prevent these diseases from circulating in our population.”
The bill would strike language requiring that immunization records be submitted to child care agencies, but would keep those requirements for students enrolling in kindergarten through 12th grade. As of 2022, according to the nonprofit ChildCare Aware of America , there are some 700 licensed child care centers and homes in New Hampshire (which doesn’t require the Covid-19 vaccine for enrollment in child care, either, despite its efficiency in reducing both death rates and acute symptoms).
Vaccine hesitancy is rising among parents of young children. A 2023 survey from the Pew Research Center found that around half of parents with kids four or younger thought that not all standard childhood vaccines—a list that also includes hepatitis B, rotavirus, DTaP and chickenpox—may be necessary. Anti-vaccine misinformation plays a role in this phenomenon, which began before the Covid-19 pandemic, but has certainly increased since. In a 2019 UK report , about 50 percent of parents of young kids encountered false information about vaccines on social media.
While it’s nice when a beloved celebrity makes a comeback, comebacks of the very infectious measles and polio epidemics are less welcome. As New Hampshire’s state epidemiologist, Dr. Benjamin Chan, said during a state Senate hearing on the bill, “as vaccination levels decrease, this is putting our children and our communities and our childcare agencies at risk.”

The Weird Story of Ohio Senate Candidate Bernie Moreno’s $3.4 Million Car
Abby Vesoulis

How the Right Turned Protest Into A Criminal Enterprise
Nia t. evans
I Read Everything Elon Musk Posted for a Week. Send Help.

Why Are Some Latinos Drifting to the Right?
Isabela Dias
We Recommend

This Anti-Trans, Pro-Life Activist Was Pardoned by Donald Trump. Now She’s Working for RFK Jr.
Kiera Butler

Democratic Lawmakers Blast Fossil Fuel Industry’s “Denial” and “Duplicity”
Dharna Noor

The Governor of Kansas Vetoed Four Anti-Abortion Measures. Republicans Rammed Them Through Anyway.
Julianne McShane

Feds Get a Guilty Plea From Aide to Chinese Mogul Guo Wengui. That’s Bad for Steve Bannon.
Dan Friedman

TikTok’s Raw Milk Influencers Are Going to Give Us All Bird Flu

The NYPD’s “Outside Agitators” Narrative Is an Excuse for Force

Trump Will Likely Face More Fines for Violating Gag Order

Cities Scramble for Trees That Can Adapt to a Changing Climate
Laura Hautala
Sign up for our free newsletter
Subscribe to the Mother Jones Daily to have our top stories delivered directly to your inbox.
By signing up, you agree to our privacy policy and terms of use , and to receive messages from Mother Jones and our partners.
Get our award-winning magazine
Save big on a full year of investigations, ideas, and insights.
Support our journalism
Help Mother Jones ' reporters dig deep with a tax-deductible donation.
Independent. In print. In your mailbox.
Inexpensive, too! Subscribe today and get a full year of Mother Jones for just $14.95.

Bold. Brave. Beautiful.
Award-winning photojournalism. Stunning video. Fearless conversations.
Looking for news you can trust?
We noticed you have an ad blocker on..
Can you pitch in a few bucks to help fund Mother Jones' investigative journalism? We're a nonprofit (so it's tax-deductible), and reader support makes up about two-thirds of our budget.
We noticed you have an ad blocker on. Can you pitch in a few bucks to help fund Mother Jones' investigative journalism?
Don't let an algorithm decide what news you see.
Sign up for the free Mother Jones Daily newsletter and follow the news that matters.
Annual skilled trades competition builds technical and professional skills for Iowa students
- Wednesday, May 1, 2024
- Headline Story

Southeast Polk senior Simon Frohock (R) competed in the cabinet making contest for a second year.
High-quality career and professional skill development took center stage last week as over 600 high school and college students took part in the annual SkillsUSA State Leadership and Skills Conference . Held in Ankeny at the Des Moines Area Community College campus, this two-day competition featured over 50 different leadership and technical competitions for students to test their technical skills and knowledge, explore career pathways and make valuable connections with local industry leaders.

Southeast Polk High School seniors Delvis Kouete and Simon Frohock, both 17, were well-prepared for the competition, which featured timed activities related to industrial technology, carpentry, robotics, automotive repair and job interview techniques, among many others. For this year’s skills competition, Delvis competed in architectural drafting and was a member of the school’s quiz bowl team. Simon, the 2023 state champion in cabinet making, returned for a second year in the cabinet making contest. Both students competed well in their individual competitions, with Delvis placing fifth and Simon serving as this year’s runner-up.
“The skills competition can help you strive for excellence in your work and learning,” Simon said. “Even though it’s a competition and there is pressure to do well, it’s a good, low-risk way to see what an employee in this work has to do every day.”
Both Simon and Delvis noted that the competition not only helps to strengthen a student’s technical skills, but it also engages students in career pathway discovery and professional skill development.
“Being a part of SkillsUSA and competing in the skills competition has helped me learn new skills with my hands and work on teamwork, communication and leadership skills,” Delvis said. “You learn how to work with other people that aren’t like you and get your mind thinking about your future career.”
Along with the individual contests, all competitors at the SkillsUSA State Leadership and Skills Conference were required to submit a resume and take a professional development test that focused on workplace, professional and technical skills as well as overall knowledge of SkillsUSA.
“SkillsUSA helps provide real-world context to the content being taught by classroom educators,” said Kent Storm, state director for SkillsUSA Iowa. “Taking the learning beyond the classroom allows students to grow and learn next to industry partners and gain valuable experience."
As one of Iowa’s career and technical student organizations (CTSO) , SkillsUSA champions the skilled trades industry and provides opportunities for students to apply the skills they have developed in classrooms through conferences, competitions, community service events, worksite visits and other activities.
“Participation in a CTSO like SkillsUSA helps students gain hands-on experience and connect classroom curricula to careers,” said Cale Hutchings, education consultant at the Iowa Department of Education. “Through CTSOs, students can become leaders and strengthen their employability skills, which is valuable as they explore potential next steps in their college and career pathways.”
SkillsUSA boasts a roster of over 400,000 members nationwide. In Iowa, over 1,300 students and advisers in career and technical education programs participate in local SkillsUSA chapters.
At Southeast Polk, 21 student members are a part of their SkillsUSA chapter. Led by industrial technology teachers and chapter advisers Ryan Andersen and Brett Rickabaugh, the students have been involved with several community service projects, employer presentations and opportunities to work closely with instructors.
“Any time a student participates in SkillsUSA, it gives us more time with that student to elaborate on what we’ve learned in class,” Andersen said. “They can connect the idea to the planning, design and completion of a project and how that activity fits into a real career. That’s something we can’t replicate without a CTSO.”
Anderson also stated that students who participate in SkillsUSA and activities like the State Leadership and Skills Conference build confidence through their experiences.
“It really helps students to have the confidence to rely on their skills and what they know,” he said. “The skills competition requires them to use problem-solving skills and build off their knowledge to continue to learn and persevere.”
This year’s first-place winners at the SkillsUSA State Leadership and Skills Conference will move onward to compete with 6,000 other students at the national conference in Atlanta this June.

For Simon and Delvis, the skills competition was another step in building necessary skills and acumen for their futures. Simon, with his penchant for cabinet making, already has a full-time job lined up after graduation with a local cabinet shop. Additionally, Delvis would like to pursue something within the computer science field, perhaps in the coding or software engineering areas, and although he is changing fields, he believes SkillsUSA has helped him feel more prepared for the future.
“It has definitely helped me with skill-building and problem-solving,” he said. “What I’ve learned will be beneficial no matter what I decide to do next.”
Recommended
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to copy URL
Prince William shares rare update on how Kate Middleton is doing amid cancer battle
- View Author Archive
- Follow on Twitter
- Get author RSS feed
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Prince William provided a hopeful update on Kate Middleton’s health amid her ongoing cancer battle .
During his visit to northern England Tuesday, a royal supporter asked the Prince of Wales, 41, how his wife and their three children – Prince George, 10, Princess Charlotte, 8, and Prince Louis, 6 – are doing in light of the news.
“Do you mind if I ask how your wife and children are?” asked one concerned fan, who was draped in the British flag, according to a video circulating online .

William graciously responded, “All doing well, yes, thank you. All doing well,” while kindly patting the woman on the shoulder.
The well-wisher then asked for further clarification on Middleton, 42, adding, “I mean, obviously Catherine?,” to which William reinstated, “Yeah, we’re all doing well.”
The future king engaged in a spontaneous walkabout during a visit to James’ Place Newcastle, a male suicide prevention center in the city of Newcastle-Upon-Tyne.
Nearly two weeks ago, William made his return to public duties for the first time since Middleton’s cancer diagnosis was revealed.

On April 18, the prince went to the food charity Surplus to Supper in Surrey, where he chatted to volunteers and lent a helping hand in the kitchen.
More must-see royals coverage:
- How Prince Harry and Meghan Markle met
- Prince William and Kate Middleton’s relationship timeline
- Royal family tree and line of succession
Royal expert Richard Fitzwilliams told the Sun shortly thereafter that William’s appearance was an indication that the royals were returning to some sense of normalcy.
“Royals realise that every single thing they do sends a message in one way or another,” the royal commentator said on April 20, adding, “If Catherine had been there, it would have been fantastic, but no one is expecting that.”

Middleton shocked fans worldwide on March 22 when she revealed she had cancer – which she discovered after undergoing major abdominal surgery in January.
“We hope that you will understand that, as a family, we now need some time, space and privacy while I complete my treatment,” the Princess of Wales said in an emotional video message at the time.
“My work has always brought me a deep sense of joy and I look forward to being back when I am able, but for now I must focus on making a full recovery.”
Want more celebrity and pop culture news?
Start your day with Page Six Daily.
Thanks for signing up!
Please provide a valid email address.
By clicking above you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Want celebrity news as it breaks? Hooked on Housewives?

As expected, Middleton then skipped out on the royals’ Easter Sunday service as she continued to undergo chemotherapy and treatments for her illness.
She has reportedly also spent some time with her family at a vacation home in Norfolk, England, while she recuperated.
The exact form of cancer Middleton is battling or which stage she is in remains unknown.
Share this article:

Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the "periodicity schedule." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence. Schedule of well-child visits. The first week visit (3 to 5 ...
Are well-baby visits mandatory? While well-baby visits are not required by law, they are considered critical to a child's health and development. Skipping wellness visits and falling behind on your infant's checkup schedule could lead to missing certain health or developmental problems, and delaying needed medical treatment.
Well-child visits and recommended vaccinations are essential and help make sure children stay healthy. Children who are not protected by vaccines are more likely to get diseases like measles and whooping cough. These diseases are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children.
Take blood pressure. Measure oxygen levels. Listen to your child's lungs. Look at your child's eyes, ears, and throat. Press on your child's tummy to feel organs. Move your child's hips ...
Sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention counseling and screening for adolescents at higher risk. Tuberculin testing for children at higher risk of tuberculosis: Age 0 to 11 months , 1 to 4 years , 5 to 10 years , 11 to 14 years , 15 to 17 years. Vision screening for all children. Well-baby and well-child visits.
7-10 years: Annual well-child check. Vision/hearing and TB screenings; any immunizations previously missed. 11-12 years: Annual well-child check. Depression and TB screenings; DTaP, HPV and ...
Children ages 5 to 10 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a "well-child visit" once a year. A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any ...
Beginning at the 7 year visit, there is both a Parent and Patient education handout (in English and Spanish). For the Bright Futures Parent Handouts for well-child visits up to 2 years of age, translations of 12 additional languages (PDF format) are made possible thanks to the generous support of members, staff, and businesses who donate to the ...
Preventive health care visits (also called well-child visits) typically take place within a few days after birth or by 2 weeks of age and at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 9 months of age. During these visits, the doctor uses age-specific guidelines to monitor the infant's growth and development and asks the parents questions about various developmental ...
Well visits are essential to ensure your child gets the required vaccinations to attend school, go to daycare and participate in sports. Visiting the pediatrician when your child is well also provides you with an opportunity to ask questions - and get expert answers - about your child's health, development and well-being.
Your child's doctor will recommend a schedule for well-child visits. One example is for visits at ages: footnote 1. 3 to 5 days old. By 1 month. 2 months. 4 months. 6 months. 9 months. 1 year. 15 months. 18 months. 2 years. 30 months. 3 years. After age 3, well-child visits are usually scheduled yearly through the teen years.
More than two-thirds of practicing family physicians report that they provide care for children, 1 and well-child visits provide the best opportunities to deliver evidence-based preventive ...
Overview. Kids ages 11 to 14 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a "well-child visit" once a year. A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch ...
Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season ...
A well-baby visit is when you take your baby to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-baby visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any problems early, when they may be easier to treat. You'll also have a chance to ask any questions you have ...
Well-baby and well-child visits are regular check ups with pediatricians that are intended for the purpose of monitoring growth and development in babies and children. Doctors, health ...
Your baby's first official checkup (and first immunization) will take place at the hospital. After that, well-baby visits are scheduled throughout the first two years at: The first week (usually a couple of days after you're discharged from the hospital) 1 month. 2 months.
Well-Child Checkup Schedule. Well-child checkups are crucial for keeping your little one healthy and safe as she grows and develops. Below you will find the standard schedule of well-child checkups for the first three years, along with a few examples of what may come up during each checkup. Beginning at age 3, most children will have annual ...
Ask mothers who are working whether allowances are made in the workplace for breastfeeding support. Federal law requires providing breaks and adequate place for expressing breast milk. Breastfed infants continue to require 8 to 12 feedings per day. Daily formula intake should increase from 24 oz (at 1 month) to 30 to 32 oz (by 4 months)
Improving Infant Well-Child VisitsHigh-quality well-child visits can improve children's health, support caregivers' behaviors to promote their children's health, and prevent injury and harm. The American Academy of Pediatrics and Bright Futures recommend nine well-care visits by the time children turn 15 months of age.
More than half (54%) of children under age 21 enrolled in Medicaid or CHIP received a well-child visit in 2019, but the share fell to 48% in 2020, the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite ...
Back to glossary. Well-baby and well-child visits. Routine doctor visits for comprehensive preventive health services that occur when a baby is young and annual visits until a child reaches age 21. Services include physical exam and measurements, vision and hearing screening, and oral health risk assessments. We take your privacy seriously.
Final Rule Brings the Child Welfare System Closer to Better Supporting Youth with Resources and Services that Meet their Needs. Today, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), through the Administration for Children and Families (ACF), finalized a policy that strengthens protections for youth in foster care by clarifying how states must meet their statutory requirements to ...
All states currently require children to have at least started vaccination against measles and polio in order to enroll in child care, according to the nonprofit Immunize.org. A CDC report found ...
High-quality career and professional skill development took center stage last week as over 600 high school and college students took part in the annual SkillsUSA State Leadership and Skills Conference.Held in Ankeny at the Des Moines Area Community College campus, this two-day competition featured over 50 different leadership and technical competitions for students to test their technical ...
00:01. 00:37. Prince William provided a hopeful update on Kate Middleton's health amid her ongoing cancer battle. During his visit to northern England Tuesday, a royal supporter asked the Prince ...