The Planets

Space Facts: 50 Amazing and Incredible Facts About Space
Space is amazing. The sheer vastness of it, along with the trillions upon trillions of objects in the many billion galaxies of the universe is almost incomprehensible to the human brain.
This page is a continuously updated list of the most incredible, awe-inspiring and unbelievable facts about space. Whether it's for kids looking to learn more about space, or you're looking for incredible facts for an article, or even if you just love space facts for no real reason, this is for you.
Below we have put together a list of 50 of the most ‘out there’ space facts to inspire young minds, and old alike. From the jaw dropping to the awe inspiring, the universe we live in is a magnificent bundle of chaos and majesty. So let’s get started!
50 Incredible Space Facts
1. space is completely silent..

There is no air or atmosphere in space. Since it is a vacuum, sound waves will have no medium to travel to. That means, no one will hear you scream in space, even if you shout the loudest!
While sound waves (mechanical waves) need a medium to travel, radio waves (electromagnetic waves) can travel in the void of space. Astronauts use radios to stay in communication while in space since radio waves can still be sent and received in a vacuum environment.
2. The hottest planet in our solar system is 450° C.
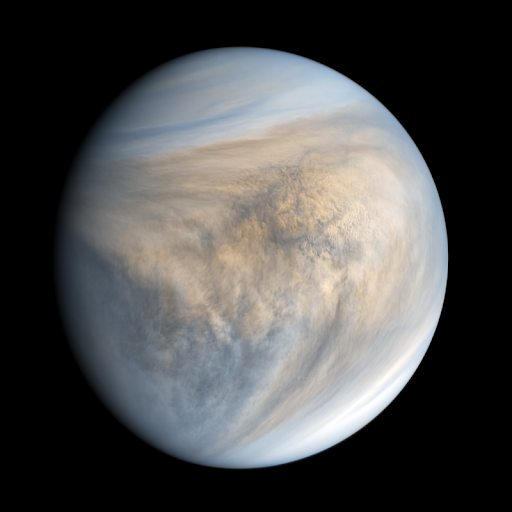
The hottest planet in the solar system is Venus . This scorching planet has an average surface temperature of about 232 °F (450 °C). Interestingly, Venus is not the closest planet to the Sun, Mercury is.
Mercury has no atmosphere to regulate temperature so it has a very large temperature fluctuation. Venus, on the other hand, has the thickest atmosphere among all planets. This atmosphere traps heat, making Venus very hot.
3. There may be life on Mars.
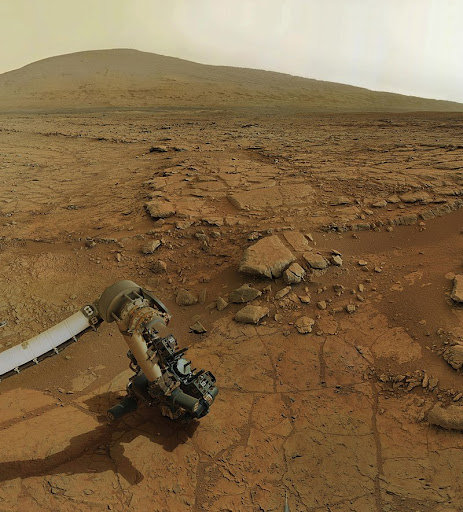

Of all the planets in our solar system (apart from Earth), Mars is the one most likely to be hospitable to life. In 1986, NASA found what they thought may be fossils of microscopic living things in a rock recovered from Mars.
4. Nobody knows how many stars are in space.

The sheer size of space makes it impossible to accurately predict just how many stars we have. Right now, scientists and astronomers use the number of stars only within our galaxy, the Milky Way , to estimate.
That number is between 200-400 billion stars and there are estimated to be billions of galaxies so the stars in space really are completely uncountable.
5. Halleys Comet won’t orbit past Earth again until 2061.

Discovered in 1705 by Edmond Halley, the famous comet was last seen in 1986 and is only seen once every 75 to 76 years.
6. A full NASA space suit costs $12,000,000.
About 70% of the total cost was for the backpack and control module. If we were to convert the total amount to today’s pricing, this would be approximately around $150 million.
Up to now, NASA reuses the spacesuits that were made in 1974. In 2019, the first all-female spacewalk was cancelled because of spacesuit availability.
7. Neutron stars can spin 600 times per second.
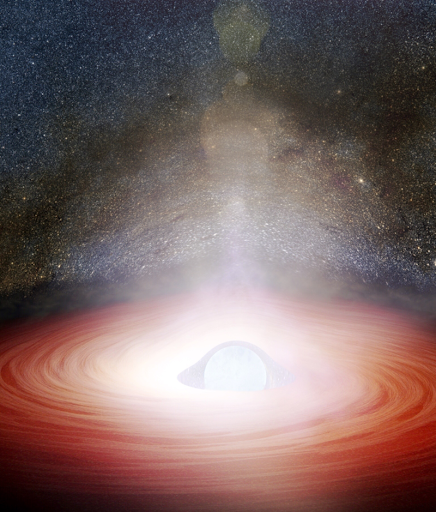

Neutron stars are the densest and tiniest stars in the known universe and although they only have a radius of about 10 km (6 mi), they may have a mass of a few times that of the Sun .
They can rotate up to 60 times per second after they are born from a core-collapse supernova star explosion and have been known to spin as fast as 600-712 times per second because of their physics.
8. There may be a planet made out of diamonds.

As space facts go, this is pretty impressive. Research by Yale University scientists suggests that a rocky planet called 55 Cancri e. It is twice the size of Earth and has a mass eight times greater. It may have a surface made up of graphite and diamond. It’s 40 light-years away but visible to the naked eye in the constellation of Cancer.
9. The footprints on the Moon will be there for 100 million years.
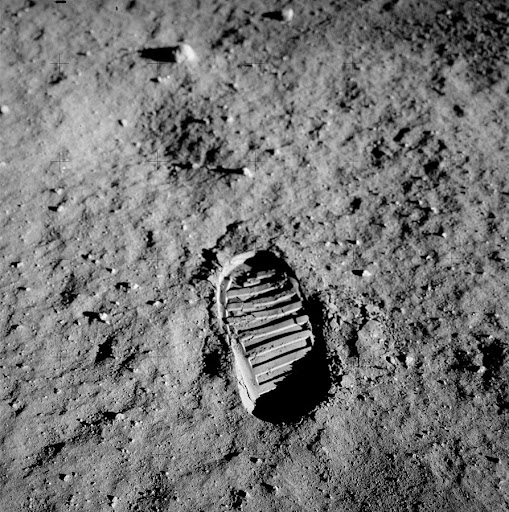

The Moon has no atmosphere, which means there is no wind to erode the surface and no water to wash the footprints away. This means the footprints of the Apollo astronauts, along with spacecraft prints, rover prints, and discarded material, will be there for millions of years.
10. One day on Venus is longer than one year.
Venus has a slow axis rotation which takes 243 Earth days to complete its day. The orbit of Venus around the Sun is 225 Earth days, making a year on Venus 18 days less than a day on Venus.
11. In 3.75 billion years the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies will collide.

The Andromeda Galaxy is approaching the Milky Way–where our solar system is–at a rate of around 110 kilometers per second (68 mi/s) and eventually the two will collide to form a giant elliptical galaxy.
12. If two pieces of the same type of metal touch in space they will permanently bond.

This incredible fact is also known as “cold welding” and it happens because the atoms of two pieces of metal have no way of knowing they are separate. This doesn’t happen on Earth because of the air and water found between the pieces.
13. There is floating water in space.

Astronomers have found a massive water vapor cloud that holds 140 trillion times the mass of water in the Earth’s oceans somewhere around 10 billion light-years away, making it the largest discovery of water ever found.
14. The largest known asteroid is 965 km (600 mi) wide.
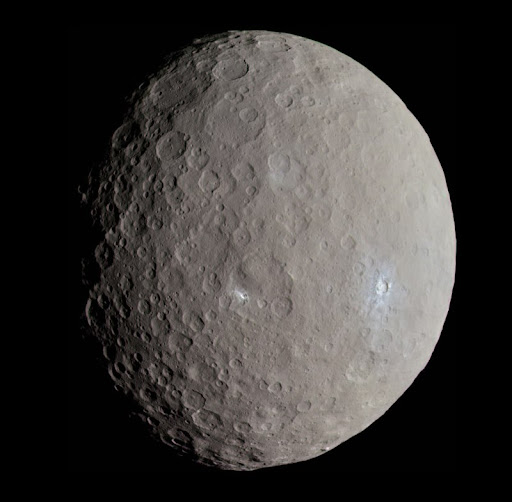

Discovered by Italian astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi in 1801, the dwarf planet Ceres was the first, and largest, object to be considered an asteroid. It is located in the Asteroid Belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter and accounts for 33% of the entire belt’s mass.
15. The Moon was once a piece of the Earth.
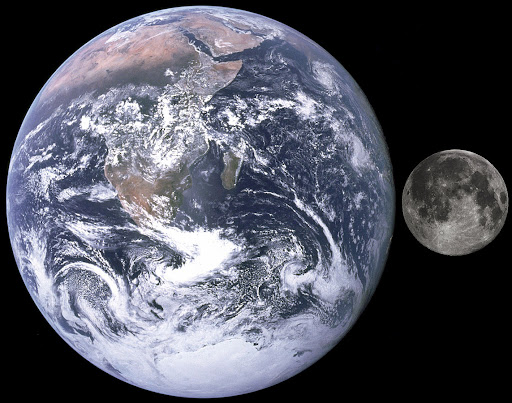

The theory is that when Earth was a relatively young planet, it was struck by a giant object and this collision broke a piece of the Earth away to create the moon . This piece then began to orbit the Earth as a result of its gravitational pull.
16. The Sun’s mass takes up 99.86% of the solar system.

The Sun is made of three-quarters hydrogen and most of its remaining mass is helium. This yellow star is 330,000 times as massive as Earth. It accounts for 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. The gas giant Jupiter accounts for about two-thirds of the remaining mass.
17. There is a volcano on Mars three times the size of Everest.
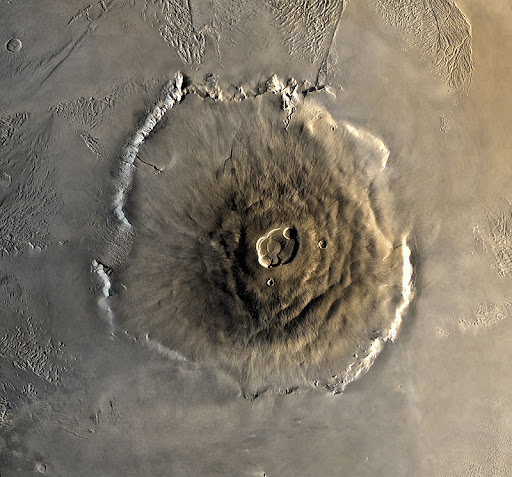
At 600 km wide and 21 km high, Olympus Mons is a volcano on Mars that may still be active, according to scientists. It is the tallest peak of any planet. However, the Rheasilvia central peak on the asteroid Vesta is taller at 22 km.
18. Mercury and Venus are the only planets with no moons.
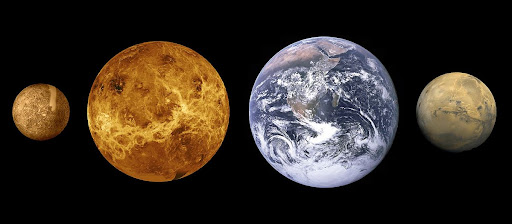
The terrestrial planets Mercury and Venus are not able to hold any moons because of their close distance to the Sun. The Sun’s gravity is much stronger and it will pull any natural satellite orbiting these nearby planets.
19, Saturn has 82 known moons and counting.

Saturn has the most number of moons known in the solar system. Its biggest moon, Titan, is bigger than Mercury. The ringed planet also has some smaller moons called “shepherd moons” that help keep Saturn’s rings in shape.
20. The gas giant Jupiter is a failed star.
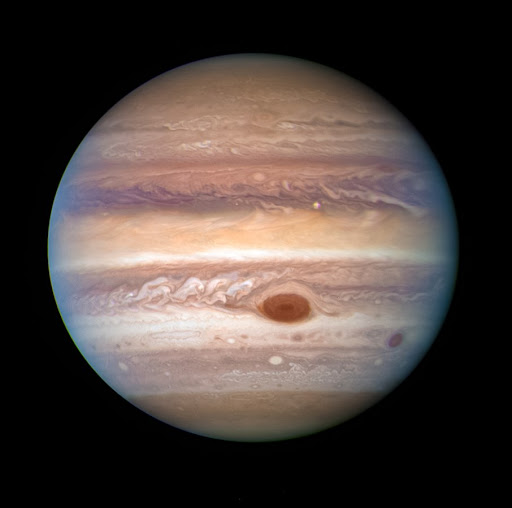

Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system , is composed of hydrogen and helium. These are the same elements that our Sun is made up of. However, Jupiter is not large enough to start nuclear fusion and generate its own energy. If it were around 80 times bigger, it would become a star with low mass.
Another fun fact about Jupiter is that it has a storm called the Great Red Spot . It has been swirling for more than a hundred years.
21. Uranus orbits the Sun on its side.
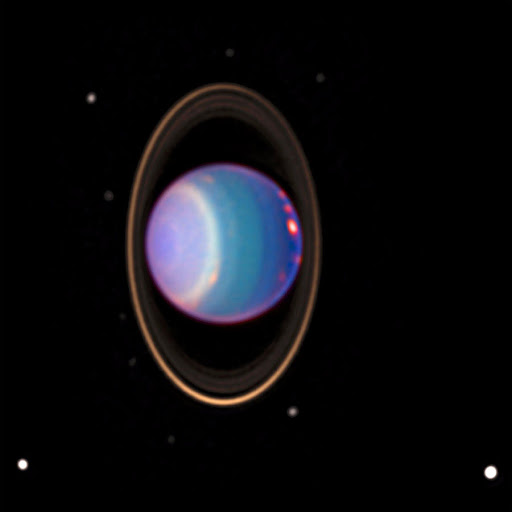

Uranus is often called the “sideways planet” because its orbit is tilted by about 98 degrees. This tilt makes the ice giant planet appear as if it is spinning sideways.
22. Pluto is now classified as a dwarf planet, not a planet.

Many planet-like objects are getting discovered which means the number of planets will keep on changing. Because of this, the International Astronomical Union made a new category called “dwarf planets.”
Dwarf planets are objects like Pluto that are planet-like but do not dominate the neighborhood of their orbit.
23. Pluto and Charon could be a double dwarf planet system.
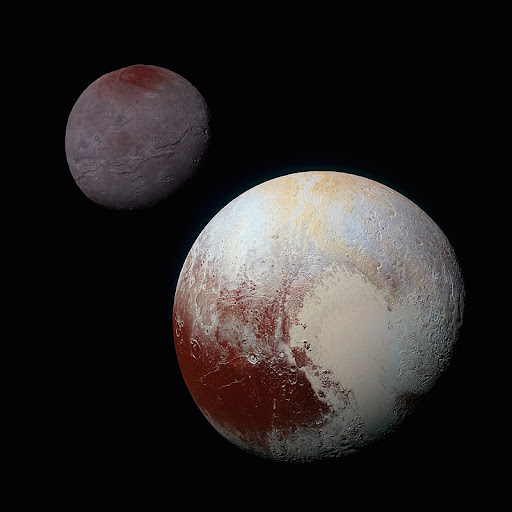

Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, is about half the size of this dwarf planet . This makes it the biggest moon in relative size to its parent body. These two are mutually tidally locked to each other. It means that the same side of Charon faces Pluto and vice versa.
24. There are five officially recognized dwarf planets in the solar system.
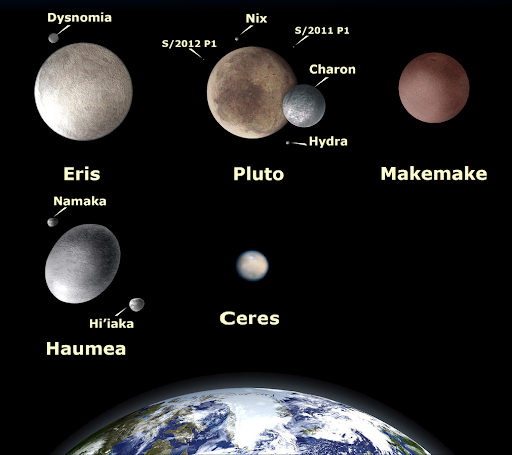

The five dwarf planets are Ceres , Pluto, Haumea , Makemake , and Eris . This number could grow as more objects like these are discovered.
25. Earth’s Moon is the fifth largest moon in the solar system.
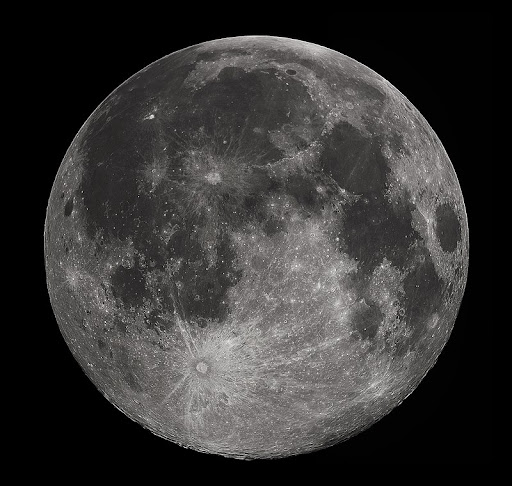

The biggest natural satellite is Ganymede which orbits Jupiter. The second largest is Titan from Saturn. In the third and fourth place are Callisto and Io which are both moons of Jupiter .
26. Enceladus, Saturn’s Moon, is the most reflective body in the solar system.
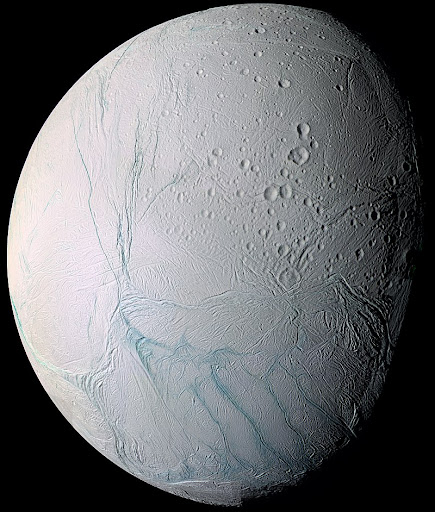

Enceladus has an icy shell that reflects about 100% of the light that reaches it. It does not absorb much sunlight which makes it a very cold world with temperatures around -201 °C (-330 °F).
This icy world spurts water jets which are thought to be from its internal global ocean. This moon is one of the strongest candidates for life outside Earth.
27. The moons of Uranus were named after characters created by Alexander Pope and William Shakespeare.

Uranus has 27 known moons. Some of its most notable moons are Oberon , Titania, Miranda, Ariel, and Umbriel.
28. There are more stars in the universe than all the grains of sand on Earth.

If we combined all the sand on the beaches and deserts in the world, there would still be 10 times more stars in the universe. It is estimated that there are 70 sextillion stars out there. This figure translates to 70 followed by 22 zeros or 70,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 stars!
29. The Sun will engulf Earth 5 billion years from now.
The Sun is still a main-sequence star now. It generates energy by turning hydrogen into helium. As it turns into a red giant , it would become bigger and brighter. When our Sun reaches this stage, its expansion would likely reach the orbit of the red planet Mars.
Though the Sun is not yet a red giant, it is still much bigger than the Earth . In fact, about one million Earths can fit inside the Sun .
30. When you look at a star, what you actually see is how it was in the past.

Light takes time to reach Earth. For instance, sunlight takes about 8.5 minutes to reach the Earth’s surface. The bright star, Sirius , for example, is roughly 8.6 light-years away. That means when you see it in the sky tonight, you are actually seeing Sirius the way it was 8.6 years ago!
31. Massive stars end their lives through supernova explosions.

In the last stages of their stellar lives, stars that are more than 5 times more massive than the Sun would explode into supernovae . Supernova explosions are caused by either a star collapsing into itself or a white dwarf in a binary system. Some of these big blasts leave black holes too.
32. Galaxies are either elliptical, spiral, or irregular.

Galaxy types are usually classified based on their appearance. Our own Milky Way, for example, is a spiral galaxy. As more galaxies are discovered, we have also learned that they come in all shapes. Aside from the main types, there are also lenticular galaxies and weird-looking peculiar galaxies.
33. There are 2,000,000,000,000 galaxies in the observable universe.
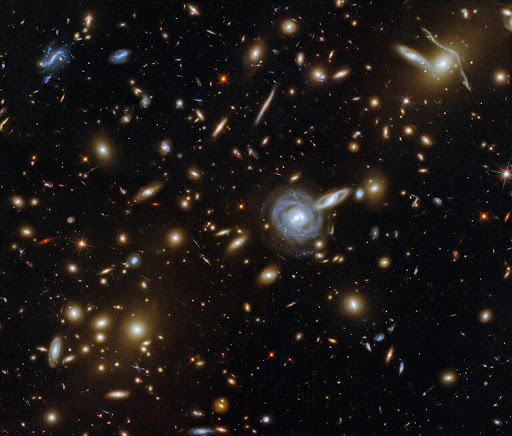

The universe is so big that we would not be able to see its entirety. The only region of space visible to us is called the observable universe. Still, estimates show that there are roughly two trillion or two million million galaxies in the observable universe alone.
34. Most galaxies have a central black hole.
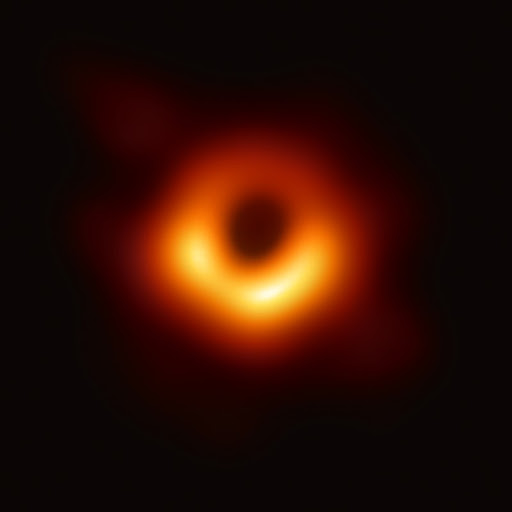

While the nature of black holes is still uncertain, scientists have found out that they are usually around 1/1000th as massive as their home galaxy. The central black hole of the Milky Way, for example, is 4.6 million times the Sun’s mass.
35. All planets in the solar system have been visited by uncrewed spacecraft.
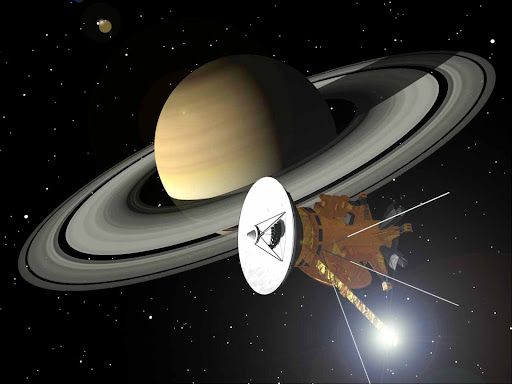
Venus was the first planet to be visited by a spacecraft in 1962. It was also the first where probes have landed. Even the outer planets have had visitors, like the Cassini spacecraft which orbited Saturn for 13 years.
36. Voyager 1 and 2 have been operating for more than 40 years.
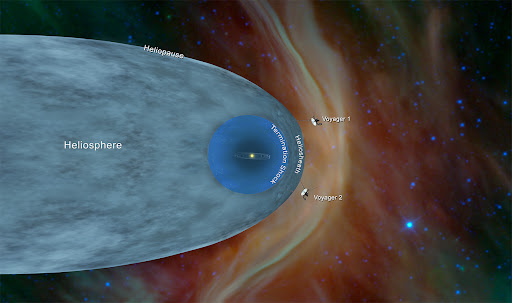
The Voyagers launched in 1977 and are still sending back data to Earth. Voyager 1 entered interstellar space in 2012 and Voyage 2 also reached this region in 2018. These are the farthest and the only spacecraft that have left the heliopause .
37. The boundary of the solar system ends in a spherical cloud known as the Oort cloud.
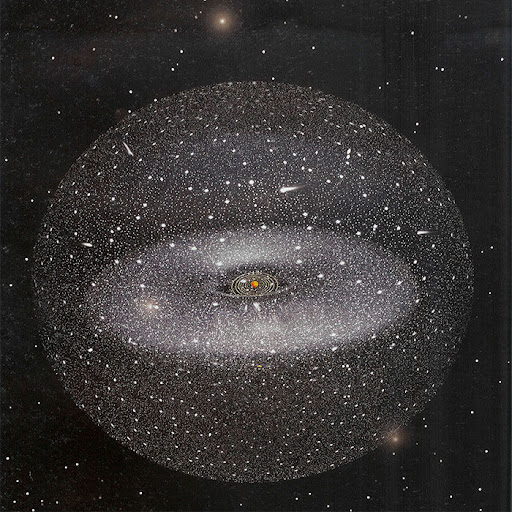

This is a hypothetical sphere composed of icy bodies that surround the solar system . It marks the limit of the Sun’s gravitational influence. This predicted region is believed to be around 2,000 to 100,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun.
Since the Oort cloud is so far from the Sun, it is often influenced by the tidal forces of the Milky Way galaxy and other passing stars. Because of the great distance, scientists have not yet seen any Oort Cloud object.
38. About 1.4 billion years ago, a day on Earth was just 18 hours 41 minutes long.

The Moon is moving away from Earth by around 3.78 centimeters (1.48 inches). This causes changes in the Moon’s tidal effects, which, in turn, slows down Earth’s rotation.
39. The International Space Station (ISS) is about as wide as a soccer field.

The ISS is the largest thing we have flown in space. From end to end, measures around 109 meters or 356 feet. Traveling at 27,700 km/h, it orbits Earth around every 1.5 hours.
40. It is possible to see the International Space Station from your backyard.

This is something that requires timing though. The ISS becomes visible from Earth when it reflects sunlight. However, during the day, it can easily get lost in the Sun’s glare. The best time to see it, even with the naked eye, is before sunrise and after sunset.
41. Mars has a reddish sky but bluish twilights.

Mars is known as the red planet because it is rich in iron. This iron reacts with the elements and rusts, making it red all around. The same fine dust particles scatter light differently when the Sun is close to the horizon.
42. Astronauts grow taller in space.

Astronauts can grow about 5 centimeters (2 inches) during their stay in space. The reason for this is the lack of gravity which expands the disks of their spines, making them taller. This was proven when astronaut Scott Kelly spent 340 days in space. And when he returned to Earth, he became taller than his twin brother.
43. The closest star system to us, Proxima Centauri, is 4.25 light-years away.
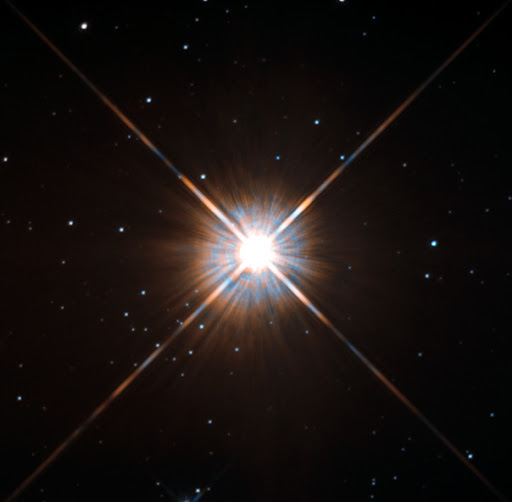

Proxima Centauri is also called Alpha Centauri C. It is part of the Alpha Centauri triple star system. Alpha Centauri A and B form a binary, slightly farther at 4.35 light-years from Earth. Proxima Centauri is host to several exoplanets, like Proxima Centauri b which may have the potential to host life.
44. A rose was brought to space in 1998.

The company International Flavors & Fragrances (IFF) wanted to know if bringing a rose into space would yield new scents. The rose was aboard the Discovery space shuttle . When it came back to Earth, it was sampled and used to produce perfume.
45. There are more than 4,000 known exoplanets, and counting.

“Exoplanets” is short for extrasolar planets. These are planets that are outside the solar system. They come in different sizes and compositions. Extragalactic planets, on the other hand, are planets outside the Milky Way.
46. Other planets, and even a moon, have auroras too.
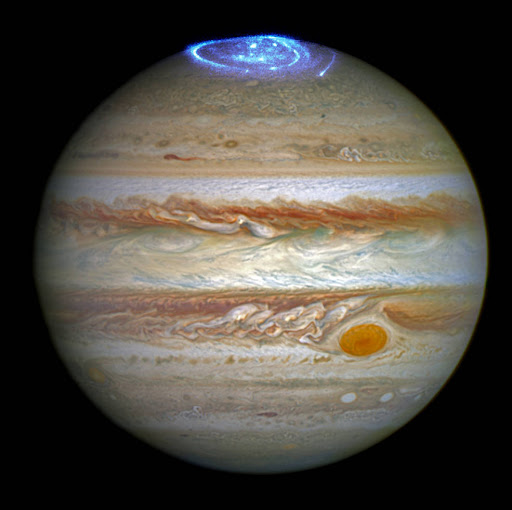

The colorful light shows of auroras happen when solar particles collide with the atmosphere. This event has also been observed on Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune . The largest moon, Ganymede , also has auroral displays.
47. Shooting stars are space debris that burn up when they enter Earth’s atmosphere.

There are lots of space debris in space called meteoroids. These are usually chunks of comets and asteroids . Sometimes, the Earth passes them in its orbit. These objects burn up in our atmosphere looking like shooting stars .
48. We often see astronauts in white spacesuits, but there are orange spacesuits too.

The color of spacesuits depends on the astronauts’ activity. White suits are for Extravehicular Activity (EVA) when they spacewalk. This color helps reflect the Sun’s heat.
The orange Advanced Crew Escape Suits (ACES) are used when astronauts take off or re-enter Earth. The color makes it easier for them to be seen anywhere, especially at sea.
49. As of 2021, more than 600 people have been in space.

Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin was the first man in space on April 12, 1961. American astronaut Alan Shepard followed about a month later on May 5, 1961. Space exploration has skyrocketed from there. In the future, with the booming space tourism, more people will have the opportunity to experience space travel.
50. The outer space is very cold with a temperature of around -454.75 °F (-270.42 °C).

Space is indeed a very cold place. This is close to absolute zero or −459.67 °F (−273.15 °C) which is the lowest temperature ever possible.
Link/cite this page
If you use any of the content on this page in your own work, please use the code below to cite this page as the source of the content.
<a href="https://theplanets.org/space-facts/">Space Facts: 50 Amazing and Incredible Facts About Space</a>
Stewart, Suzy. "Space Facts: 50 Amazing and Incredible Facts About Space". The Planets . Accessed on April 14, 2024. https://theplanets.org/space-facts/.
Stewart, Suzy. "Space Facts: 50 Amazing and Incredible Facts About Space". The Planets , https://theplanets.org/space-facts/. Accessed 14 April, 2024.
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
Everything you need to know about space travel (almost)
We're a long way from home...
Paul Parsons
When did we first start exploring space?
The first human-made object to go into space was a German V2 missile , launched on a test flight in 1942. Although uncrewed, it reached an altitude of 189km (117 miles).
Former Nazi rocket scientists were later recruited by both America and Russia (often at gunpoint in the latter case), where they were instrumental in developing Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) – rockets capable of carrying nuclear weapons from one side of the planet to the other.
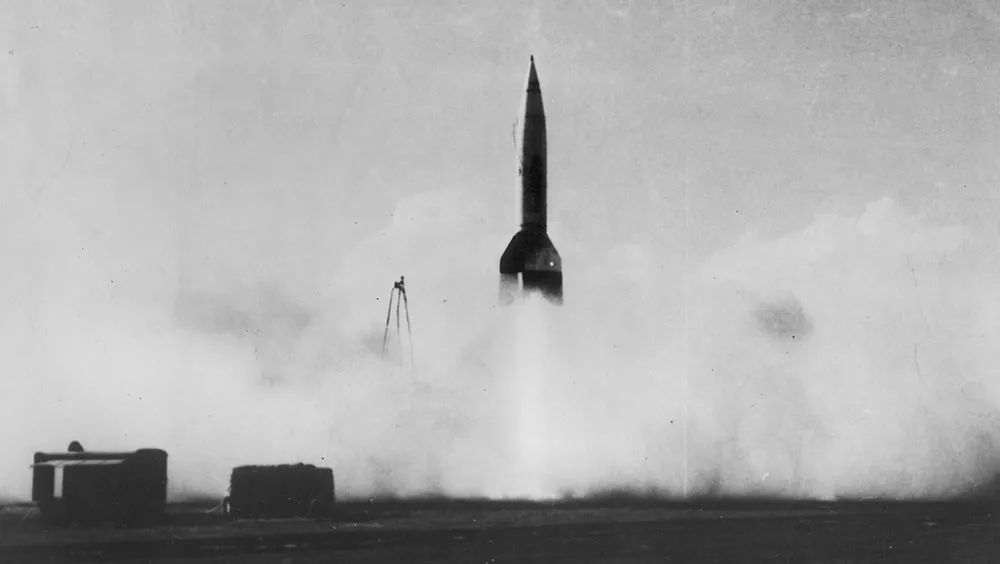

It was these super-missiles that formed the basis for the space programmes of both post-war superpowers. As it happened, Russia was the first to reach Earth orbit, when it launched the uncrewed Sputnik 1 in October 1957, followed a month later by Sputnik 2, carrying the dog Laika – the first live animal in space.
The USA sent its first uncrewed satellite, Explorer 1, into orbit soon after, in January 1958. A slew of robotic spaceflights followed, from both sides of the Atlantic, before Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin piloted Vostok 1 into orbit on 12 April 1961, to become the first human being in space . And from there the space race proper began, culminating in Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin becoming the first people to walk on the Moon as part of NASA's Apollo programme .
Why is space travel important?
Space exploration is the future. It satisfies the human urge to explore and to travel, and in the years and decades to come it could even provide our species with new places to call home – especially relevant now, as Earth becomes increasingly crowded .
Extending our reach into space is also necessary for the advancement of science. Space telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope and probes to the distant worlds of the Solar System are continually updating, and occasionally revolutionising, our understanding of astronomy and physics.
- Subscribe to the Science Focus Podcast on these services: Acast , iTunes , Stitcher , RSS , Overcast
But there are also some very practical reasons, such as mining asteroids for materials that are extremely rare here on Earth.
One example is the huge reserve of the chemical isotope helium-3 thought to be locked away in the soil on the surface of the Moon . This isotope is a potential fuel for future nuclear fusion reactors – power stations that tap into the same source of energy as the Sun. Unlike other fusion fuels, helium-3 gives off no hard-to-contain and deadly neutron radiation.
However, for this to happen the first challenge to overcome is how to build a base on the Moon. In 2019, China's Chang’e 4 mission marked the beginning of a new space race to conquer the Moon, signalling their intent to build a permanent lunar base , while the NASA Artemis mission plans to build a space station, called Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway , providing a platform to ferry astronauts to the Moon's surface.
Could humans travel into interstellar space and how would we get there?
It’s entirely feasible that human explorers will visit the furthest reaches of our Solar System. The stars, however, are another matter. Interstellar space is so vast that it takes light – the fastest thing we know of in the Universe – years, centuries and millennia to traverse it. Faster-than-light travel may be possible one day, but is unlikely to become a reality in our lifetimes.
It’s not impossible that humans might one day cross this cosmic gulf, though it won’t be easy. The combustion-powered rocket engines of today certainly aren’t up to the job – they just don’t use fuel efficiently enough. Instead, interstellar spacecraft may create a rocket-like propulsion jet using electric and magnetic fields. This so-called ‘ ion drive ’ technology has already been tested aboard uncrewed Solar System probes.

Another possibility is to push spacecraft off towards the stars using the light from a high-powered laser . A consortium of scientists calling themselves Breakthrough Starshot is already planning to send a flotilla of tiny robotic probes to our nearest star, Proxima Centauri, using just this method.
Though whether human astronauts could survive such punishing acceleration, or the decades-long journey through deep space, remains to be seen.
How do we benefit from space exploration?
Pushing forward the frontiers of science is the stated goal of many space missions . But even the development of space travel technology itself can lead to unintended yet beneficial ‘spin-off’ technologies with some very down-to-earth applications.
Notable spin-offs from the US space programme, NASA, include memory foam mattresses, artificial hearts, and the lubricant spray WD-40. Doubtless, there are many more to come.
Read more about space exploration:
- The next giant leaps: The UK missions getting us to the Moon
- Move over, Mars: why we should look further afield for future human colonies
- Everything you need to know about the Voyager mission
- 6 out-of-this-world experiments recreating space on Earth
Space exploration also instils a sense of wonder, it reminds us that there are issues beyond our humdrum planet and its petty squabbles, and without doubt it helps to inspire each new generation of young scientists. It’s also an insurance policy. We’re now all too aware that global calamities can and do happen – for instance, climate change and the giant asteroid that smashed into the Earth 65 million years ago, leading to the total extinction of the dinosaurs .
The lesson for the human species is that we keep all our eggs in one basket at our peril. On the other hand, a healthy space programme, and the means to travel to other worlds, gives us an out.
Is space travel dangerous?
In short, yes – very. Reaching orbit means accelerating up to around 28,000kph (17,000mph, or 22 times the speed of sound ). If anything goes wrong at that speed, it’s seldom good news.
Then there’s the growing cloud of space junk to contend with in Earth's orbit – defunct satellites, discarded rocket stages and other detritus – all moving just as fast. A five-gram bolt hitting at orbital speed packs as much energy as a 200kg weight dropped from the top of an 18-storey building.

And getting to space is just the start of the danger. The principal hazard once there is cancer-producing radiation – the typical dose from one day in space is equivalent to what you’d receive over an entire year back on Earth, thanks to the planet’s atmosphere and protective magnetic field.
Add to that the icy cold airless vacuum , the need to bring all your own food and water, plus the effects of long-duration weightlessness on bone density, the brain and muscular condition – including that of the heart – and it soon becomes clear that venturing into space really isn’t for the faint-hearted.
When will space travel be available to everyone?
It’s already happening – that is, assuming your pockets are deep enough. The first self-funded ‘space tourist’ was US businessman Dennis Tito, who in 2001 spent a week aboard the International Space Station (ISS) for the cool sum of $20m (£15m).
Virgin Galactic has long been promising to take customers on short sub-orbital hops into space – where passengers get to experience rocket propulsion and several minutes of weightlessness, before gliding back to a runway landing on Earth, all for $250k (£190k). In late July 2020, the company unveiled the finished cabin in its SpaceShipTwo vehicle, suggesting that commercial spaceflights may begin shortly.
Meanwhile, Elon Musk’s SpaceX , which in May 2020 became the first private company to launch a human crew to Earth orbit aboard the Crew Dragon , plans to offer stays on the ISS for $35k (£27k) per night. SpaceX is now prototyping its huge Starship vehicle , which is designed to take 100 passengers from Earth to as far afield as Mars for around $20k (£15k) per head. Musk stated in January that he hoped to be operating 1,000 Starships by 2050.
10 Short Lessons in Space Travel by Paul Parsons is out now (£9.99, Michael O'Mara)
- Buy now from Amazon UK , Foyles , WH Smith and Wordery
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
The History of Space Exploration
During the time that has passed since the launching of the first artificial satellite in 1957, astronauts have traveled to the moon, probes have explored the solar system, and instruments in space have discovered thousands of planets around other stars.
Earth Science, Astronomy, Social Studies, U.S. History, World History
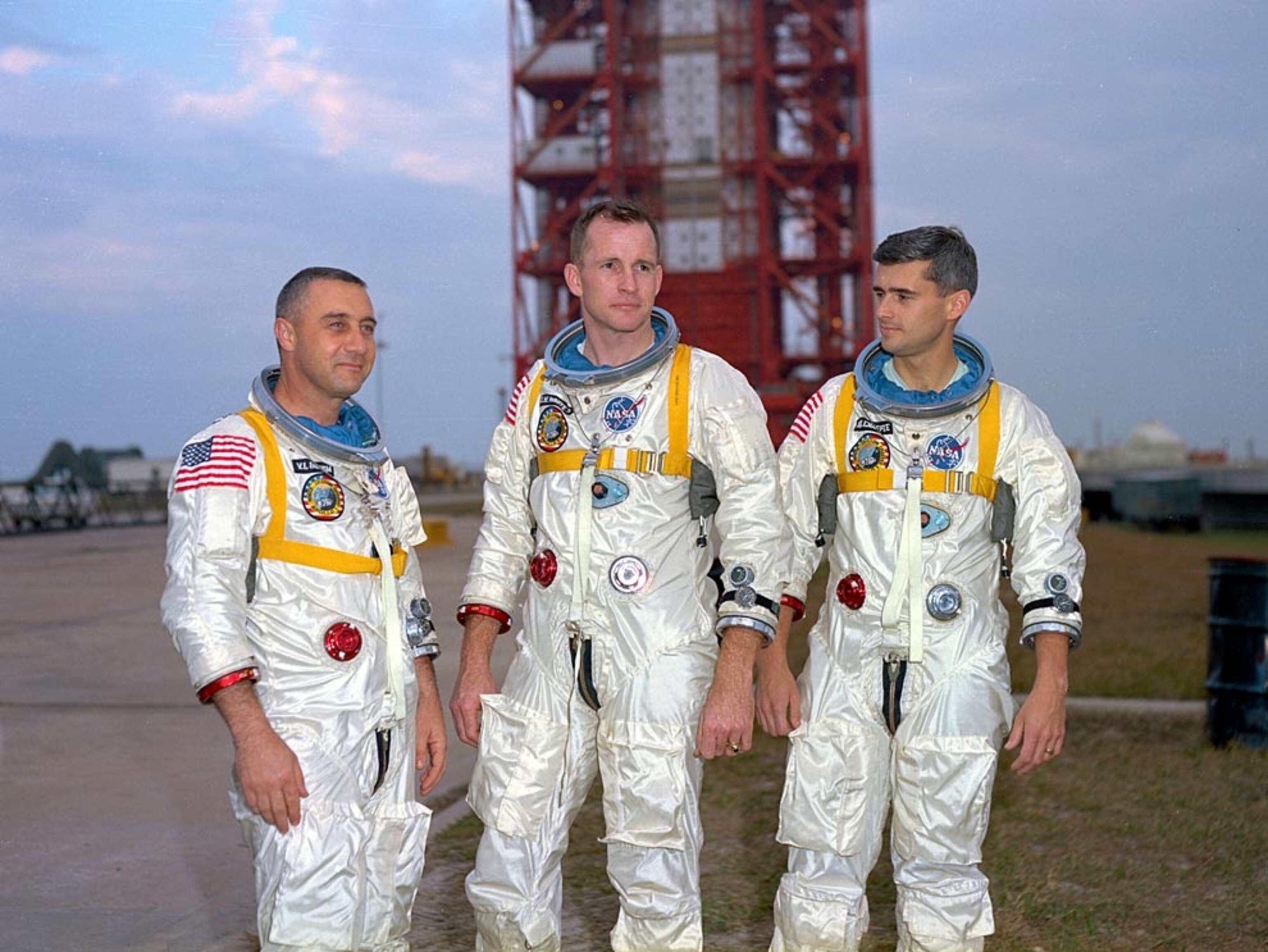
Apollo 11 Astronauts on Moon
A less belligerent, but no less competitive, part of the Cold War was the space race. The Soviet Union bested its rival at nearly every turn, until the U.S. beat them to the finish line by landing astronauts on the moon.
NASA photograph

We human beings have been venturing into space since October 4, 1957, when the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (U.S.S.R.) launched Sputnik, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth. This happened during the period of political hostility between the Soviet Union and the United States known as the Cold War. For several years, the two superpowers had been competing to develop missiles, called intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), to carry nuclear weapons between continents. In the U.S.S.R., the rocket designer Sergei Korolev had developed the first ICBM, a rocket called the R7, which would begin the space race. This competition came to a head with the launch of Sputnik . Carried atop an R7 rocket, the Sputnik satellite was able to send out beeps from a radio transmitter. After reaching space, Sputnik orbited Earth once every 96 minutes. The radio beeps could be detected on the ground as the satellite passed overhead, so people all around the world knew that it was really in orbit. Realizing that the U.S.S.R. had capabilities that exceeded U.S. technologies that could endanger Americans, the United States grew worried. Then, a month later, on November 3, 1957, the Soviets achieved an even more impressive space venture. This was SputnikII, a satellite that carried a living creature, a dog named Laika. Prior to the launch of Sputnik, the United States had been working on its own capability to launch a satellite. The United States made two failed attempts to launch a satellite into space before succeeding with a rocket that carried a satellite called Explorer on January 31, 1958. The team that achieved this first U.S. satellite launch consisted largely of German rocket engineers who had once developed ballistic missiles for Nazi Germany. Working for the U.S. Army at the Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama, the German rocket engineers were led by Wernher von Braun and had developed the German V2 rocket into a more powerful rocket, called the Jupiter C, or Juno. Explorer carried several instruments into space for conducting science experiments. One instrument was a Geiger counter for detecting cosmic rays. This was for an experiment operated by researcher James Van Allen, which, together with measurements from later satellites, proved the existence of what are now called the Van Allen radiation belts around Earth. In 1958, space exploration activities in the United States were consolidated into a new government agency, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). When it began operations in October of 1958, NASA absorbed what had been called the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), and several other research and military facilities, including the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (the Redstone Arsenal) in Huntsville. The first human in space was the Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, who made one orbit around Earth on April 12, 1961, on a flight that lasted 108 minutes. A little more than three weeks later, NASA launched astronaut Alan Shepard into space, not on an orbital flight, but on a suborbital trajectory—a flight that goes into space but does not go all the way around Earth. Shepard’s suborbital flight lasted just over 15 minutes. Three weeks later, on May 25, President John F. Kennedy challenged the United States to an ambitious goal, declaring: “I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before the decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him safely to Earth." In addition to launching the first artificial satellite, the first dog in space, and the first human in space, the Soviet Union achieved other space milestones ahead of the United States. These milestones included Luna 2, which became the first human-made object to hit the Moon in 1959. Soon after that, the U.S.S.R. launched Luna 3 . Less than four months after Gagarin’s flight in 1961, a second Soviet human mission orbited a cosmonaut around Earth for a full day. The U.S.S.R. also achieved the first spacewalk and launched the Vostok 6 mission, which made Valentina Tereshkova the first woman to travel to space. During the 1960s, NASA made progress toward President Kennedy’s goal of landing a human on the moon with a program called Project Gemini, in which astronauts tested technology needed for future flights to the moon, and tested their own ability to endure many days in spaceflight. Project Gemini was followed by Project Apollo, which took astronauts into orbit around the moon and to the lunar surface between 1968 and 1972. In 1969, on Apollo11, the United States sent the first astronauts to the Moon, and Neil Armstrong became the first human to set foot on its surface. During the landed missions, astronauts collected samples of rocks and lunar dust that scientists still study to learn about the moon. During the 1960s and 1970s, NASA also launched a series of space probes called Mariner, which studied Venus, Mars, and Mercury. Space stations marked the next phase of space exploration. The first space station in Earth orbit was the Soviet Salyut 1 station, which was launched in 1971. This was followed by NASA’s Skylab space station, the first orbital laboratory in which astronauts and scientists studied Earth and the effects of spaceflight on the human body. During the 1970s, NASA also carried out Project Viking in which two probes landed on Mars, took numerous photographs, examined the chemistry of the Martian surface environment, and tested the Martian dirt (called regolith ) for the presence of microorganisms . Since the Apollo lunar program ended in 1972, human space exploration has been limited to low-Earth orbit, where many countries participate and conduct research on the International Space Station. However, unpiloted probes have traveled throughout our solar system. In recent years, probes have made a range of discoveries, including that a moon of Jupiter, called Europa, and a moon of Saturn, called Enceladus, have oceans under their surface ice that scientists think may harbor life. Meanwhile, instruments in space, such as the Kepler Space Telescope , and instruments on the ground have discovered thousands of exoplanets , planets orbiting other stars. This era of exoplanet discovery began in 1995, and advanced technology now allows instruments in space to characterize the atmospheres of some of these exoplanets.
Articles & Profiles
Media credits.
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
We have completed maintenance on Astronomy.com and action may be required on your account. Learn More

- Login/Register
- Solar System
- Exotic Objects
- Upcoming Events
- Deep-Sky Objects
- Observing Basics
- Telescopes and Equipment
- Astrophotography
- Space Exploration
- Human Spaceflight
- Robotic Spaceflight
- The Magazine
15 things kids should know about space travel

Professional and amateur astronomers alike love to share facts about our amazing universe: “The brightest star is…,” “A black hole is…,” and lots more. These facts are so incredible that we sometimes overlook our own little corner of the cosmos and how humans have ventured into it. Space exploration, however, goes hand in hand with astronomy. So, I’ve come up with a list of 15 simple facts about spaceflight that you can share with your children — or with your non-astronomer friends.
1. Russia was first
Yep, Russia (then the main country of the Soviet Union) beat the U.S. in spaceflight pretty much every step of the way until NASA landed people on the Moon. The first artificial satellite — Sputnik, launched Oct. 4, 1957 — was Russian. So was the first human in space, Yuri Gagarin, who also became the first person to orbit Earth. That happened April 12, 1961. The first woman in space was also Russian. Valentina Tereshkova orbited Earth 48 times starting June 16, 1963. She’s also the only woman who ever flew a mission to space alone.
2. Space begins above our atmosphere

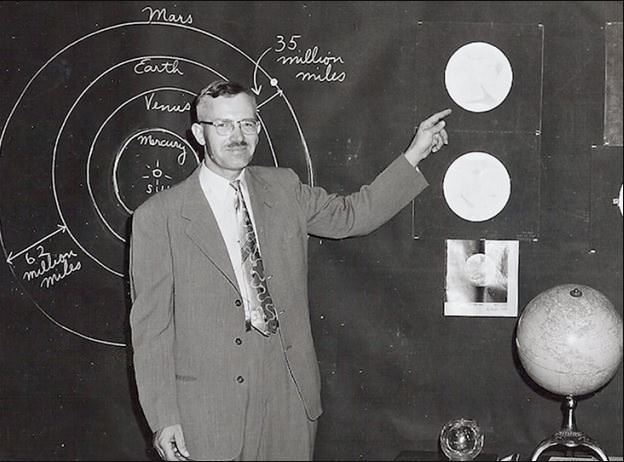
Believe it or not, there is a legal definition for where space begins. That’s because the movements of spacecraft are regulated by different treaties than those of aircraft. Most countries use the Kármán line, which is named for Hungarian-American physicist Theodore von Kármán, the first person to calculate an altitude where space begins. The Kármán line lies 62 miles (100 kilometers) above sea level.
3. rockets were invented long ago

The Chinese invented rockets perhaps as early as the 10th century. Some historians date their first recorded use to 1232. Early Chinese rockets used gunpowder as fuel, so they were a lot like fireworks. Soldiers attached an arrow to each rocket and launched them at their enemies during battles. By the 15th century, militaries around the world had adopted rocket technology.
4. Robert Goddard was a pioneer rocket man

Goddard was an American inventor who built the first liquid-fueled rocket. Historians credit the launch of his first rocket, on March 16, 1926, with starting the modern age of rocketry. Over the next decade, he and his team launched several dozen rockets, which traveled as fast as 550 mph (885 km/h) and as high as 1.6 miles (2.6 km).
5. Sputnik changed everything

If the question is “When did the Space Age start?”, the answer is “When Sputnik was launched.” In the 1950s, the Soviet Union was in a race with the U.S. to be the first country to send a satellite into space. Scientists and engineers on both sides spent years trying to reach this goal. Then, on Oct. 4, 1957, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 1, which became Earth’s first artificial satellite (i.e., one launched by humans). Sputnik had four radio antennas and measured 23 inches (58 centimeters) across. It orbited Earth once every 96 minutes and 12 seconds. The radio transmitter Sputnik carried only sent back beeps. It worked for three weeks until the batteries ran out. And although the message was simple, it seemed to tell every radio operator on Earth who listened to it, “The Soviet Union is in space.”
6. Alan Shepard was first for the U.S.
Shepard was a naval pilot and one of seven people chosen for Project Mercury, NASA’s first space program. On May 5, 1961, he became the first American and the second person in space. In 1971, he became the fifth astronaut — and, at age 47, the oldest — to walk on the Moon.
7. The “Moon race” began with a speech

On Sept. 12, 1962, President John F. Kennedy gave a speech to a crowd of about 40,000 at Rice University Stadium in Houston, Texas. Among other things, Kennedy said, “We choose to go to the Moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard.” However, The line that most historians think started the race to land a person on the Moon didn’t come from this speech. Instead, it came from an address to Congress May 25, 1961, in which Kennedy said, “I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth.” And although Kennedy didn’t live to see it, in July 1969, the U.S. did exactly that.
8. Neil Armstrong was first on the Moon.
This naval pilot entered the astronaut program in 1962. He first flew into space in 1966 aboard Gemini 8. That mission featured the first docking of two spacecraft in orbit. Later, he was named commander of the historic Apollo 11 mission, the first human Moon landing.
9. Spacewalks aren’t really walks

Many astronauts have completed an extravehicular activity (EVA) in space. Astronauts often refer to this as a spacewalk. But usually, that term means going outside a vessel in orbit, attached by a cord.
In 1965, the Soviet cosmonaut Alexei Leonov became the first human to walk in space. The journey, during his Voskhod 2 mission, lasted 12 minutes. The first U.S. spacewalk took place later in 1965, when astronaut Ed White walked in space for 23 minutes during the Gemini 4 mission.
10. That’s a long time in space
Russian cosmonaut Valeri Polyakov spent 437 days and 18 hours on a single trip to space, the longest ever by any human. He launched to the Mir space station Jan. 8, 1994, and returned to Earth March 22, 1995. The longest spaceflight by a woman is 328 days. NASA astronaut Christina Koch launched to the International Space Station March 14, 2019. She returned to Earth Feb. 6, 2020.
11. This crew went the fastest

On May 26, 1969, the crew of NASA’s Apollo 10 mission (Thomas Stafford, John Young, and Eugene Cernan) reached a speed of 24,791 mph (39,897 km/h), or about 32 times faster than the speed of sound on Earth at sea level.
12. Spaceflight is dangerous.
As of this writing, 30 humans have been killed in the pursuit of outer space. Six were Soviet or Russian cosmonauts, one was Israeli, and the rest were U.S. astronauts. Of these, 11 were killed during training or test flights and 19 were killed in actual flight. The latter group includes two seven-person crews aboard the space shuttles Challenger and Columbia , which were destroyed during atmospheric flight. The three-man crew of Soyuz 11 are the only people to have died in space.
13. Spacesuits are important

Space is a harsh environment. It’s extremely cold and there’s no atmosphere. Plus, human beings are pretty fragile creatures. So, exploring space means using special suits that allow astronauts to breathe and stay at the right temperature.
In 1961, cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin wore the first spacesuit; since then, they have come a long way. In the U.S., the Project Mercury spacesuits were just a bit different from the jumpsuits worn by fighter pilots. Each had a bubble-shaped helmet and its own air supply. The Gemini suits were more advanced and there were several types. One was for wearing inside the spacecraft, while others were for spacewalks.
NASA’s spacesuits took a big leap forward with the Apollo missions. These suits were larger and made so astronauts could walk around on the Moon for hours. The suits were fireproof and had a liquid cooling system inside. The outer layer protected astronauts from possible strikes from micrometeoroids, tiny particles of rock that zip through space at high speeds.
Space shuttle astronauts wore partially pressurized suits adapted from the Air Force. And shuttle astronauts on spacewalks used the advanced extravehicular mobility unit, which gave them a lot more protection.
Future spacesuits will be even better. New models are already being used by SpaceX astronauts and will be used by the men and women who journey back to the Moon.

A book your kids will enjoy Check out A Child’s Introduction to Space Exploration: An Explorer’s Guide to Rockets, Astronauts, and Life in Zero Gravity (Black Dog and Leventhal, 2022), written by Astronomy Editor David J. Eicher and Contributing Editor Michael E. Bakich, and illustrated by Chelen Écija. It’s packed with dozens of NASA photos, illustrations, and a pull-out poster, and contains STEM activities that will help kids of all ages better understand the science behind humanity’s greatest adventure. Copies of the book signed by the authors can be ordered at MyScienceShop.com .
14. Astronauts use the bathroom in space.

Bathrooms became very important for Alan Shepard, NASA’s first astronaut. There was no toilet because the flight would last only 15 minutes. Nobody thought that he might have to wait in his capsule for about four hours before the launch. When he asked to go, the command crew first said no, but finally said OK — but he couldn’t leave the capsule. Luckily, the air flowing through his suit dried everything out before the launch. After that, NASA designed equipment to deal with pee.
The first one was connected to a plastic tube, a valve, a clamp, and a collection bag. It wasn’t great because it sometimes leaked. In 1962, John Glenn used one on his five-hour flight.
Because the Gemini flights were a lot longer than earlier ones, NASA finally had to deal with poop in space. The first equipment was pretty simple: a bag that the astronauts taped to their butts. NASA’s first space station, Skylab, needed a toilet because astronauts would be living in space for months. Unfortunately, it was just a hole in the wall with a fan for suction and a bag.
With women as part of the space shuttle crews, NASA needed to rethink their toilet design. It was called the Waste Collection System. The opening was much smaller than a regular toilet hole, so an astronaut’s aim had to be good! Today, astronauts on the International Space Station use a much larger toilet and a vacuum sucks waste away. The waste then goes into a container that its jettisoned and burns up in Earth’s atmosphere. Using the bathroom in space is still a pain, but it’s a lot better than it was.
15. The future looks bright.

The U.S., Russia, China, India, and other nations are all active with big plans for their space programs. And rather than governments being the only players in space, private companies are now joining the effort. SpaceX, Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, and more are getting involved in space travel.
The U.S. and China both have plans to return humans to the Moon. Japan and South Korea are planning their first robotic lunar-landing missions, too. Several countries, space organizations, and companies would also like to send humans to Mars. This would be an extremely expensive, time-consuming, and dangerous endeavor.
Many nations are also actively exploring our solar system via robotic craft, including the United Arab Emirates, which recently sent a probe to Mars for the first time. There are missions from the U.S., Europe, and Japan — both planned and underway — to visit asteroids and comets, and other missions will explore the outer planets and their moons.
NASA’s snake-like EELS robot impresses in early testssssssss

NASA is taking astronaut applications. Here’s how to apply

It’s hard to grow food in space. These sensors can help.

Mariner 10, a mission of firsts, used gravity to bend its way from Venus to Mercury

Remembering Tom Stafford, the Apollo commander who did his part to thaw the Cold War

Dwarf galaxies turned on the lights near the dawn of time, JWST reveals

What are the smallest brown dwarfs? The JWST has a new answer

The upgrades to spacesuits that need to be made sooner rather than later

JWST data show intense bursts of radiation are vaporizing parts of a young star’s disk in the Orion Nebula
History of Space Travel
Learn about the history of humans traveling into space.
The first earthling to orbit our planet was just two years old, plucked from the streets of Moscow barely more than a week before her historic launch. Her name was Laika. She was a terrier mutt and by all accounts a good dog. Her 1957 flight paved the way for space exploration back when scientists didn’t know if spaceflight was lethal for living things.
Humans are explorers. Since before the dawn of civilization, we’ve been lured over the horizon to find food or more space, to make a profit, or just to see what’s beyond those trees or mountains or oceans. Our ability to explore reached new heights—literally—in the last hundred years. Airplanes shortened distances, simplified travel, and showed us Earth from a new perspective. By the middle of the last century, we aimed even higher.
Our first steps into space began as a race between the United States and the former Soviet Union, rivals in a global struggle for power. Laika was followed into orbit four years later by the first human, Soviet Cosmonaut Yuri A. Gagarin. With Earth orbit achieved, we turned our sights on the moon. The United States landed two astronauts on its stark surface in 1969, and five more manned missions followed. The U.S.’s National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched probes to study the solar system. Manned space stations began glittering in the sky. NASA developed reusable spacecraft—space shuttle orbiters—to ferry astronauts and satellites to orbit. Space-travel technology had advanced light-years in just three decades. Gagarin had to parachute from his spaceship after reentry from orbit. The space shuttle leaves orbit at 16,465 miles an hour (26,498 kilometers an hour) and glides to a stop on a runway without using an engine.
Space travel is nothing like in the movies. Getting from A to B requires complex calculations involving inertia and gravity—literally, rocket science—to "slingshot" from planet to planet (or moon) across the solar system. The Voyager mission of the 1970s took advantage of a rare alignment of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune to shave off nearly 20 years of travel time. Space is also dangerous. More than 20 astronauts have died doing their job.
That hasn’t stopped people from signing up and blasting off. NASA’s shuttle program has ended, but private companies are readying their own space programs. A company called Planetary Resources plans to send robot astronauts to the Asteroid Belt to mine for precious metals. Another company named SpaceX is hoping to land civilian astronauts on Mars—the next human step into the solar system—in 20 years. NASA and other civilian companies are planning their own Mars missions. Maybe you’ll be a member of one? Don’t forget to bring your dog.
Space videos
Outer this world, planet earth, calling all earthlings, the milky way, shoot for the stars, what is hubble, how hubble works, read this next, total solar eclipse.
- African American Heroes
Katherine Johnson
- Action and Adventure
Space Explorer
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your California Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell My Info
- National Geographic
- National Geographic Education
- Shop Nat Geo
- Customer Service
- Manage Your Subscription
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

The future of spaceflight—from orbital vacations to humans on Mars
NASA aims to travel to the moon again—and beyond. Here’s a look at the 21st-century race to send humans into space.
Welcome to the 21st-century space race, one that could potentially lead to 10-minute space vacations, orbiting space hotels , and humans on Mars. Now, instead of warring superpowers battling for dominance in orbit, private companies are competing to make space travel easier and more affordable. This year, SpaceX achieved a major milestone— launching humans to the International Space Station (ISS) from the United States —but additional goalposts are on the star-studded horizon.
Private spaceflight
Private spaceflight is not a new concept . In the United States, commercial companies played a role in the aerospace industry right from the start: Since the 1960s, NASA has relied on private contractors to build spacecraft for every major human spaceflight program, starting with Project Mercury and continuing until the present.
Today, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is expanding on the agency’s relationship with private companies. Through it, NASA is relying on SpaceX and Boeing to build spacecraft capable of carrying humans into orbit. Once those vehicles are built, both companies retain ownership and control of the craft, and NASA can send astronauts into space for a fraction of the cost of a seat on Russia’s Soyuz spacecraft.
SpaceX, which established a new paradigm by developing reusable rockets , has been running regular cargo resupply missions to the International Space Station since 2012. And in May 2020, the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft carried NASA astronauts Doug Hurley and Bob Behnken to the ISS , becoming the first crewed mission to launch from the United States in nearly a decade. The mission, called Demo-2, is scheduled to return to Earth in August. Boeing is currently developing its Starliner spacecraft and hopes to begin carrying astronauts to the ISS in 2021.
Other companies, such as Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic , are specializing in sub-orbital space tourism. Test launch video from inside the cabin of Blue Origin’s New Shepard shows off breathtaking views of our planet and a relatively calm journey for its first passenger, a test dummy cleverly dubbed “Mannequin Skywalker.” Virgin Galactic is running test flights on its sub-orbital spaceplane , which will offer paying customers roughly six minutes of weightlessness during its journey through Earth’s atmosphere.
With these and other spacecraft in the pipeline, countless dreams of zero-gravity somersaults could soon become a reality—at least for passengers able to pay the hefty sums for the experience.
Early U.S. Spaceflight

Looking to the moon
Moon missions are essential to the exploration of more distant worlds. After a long hiatus from the lunar neighborhood, NASA is again setting its sights on Earth’s nearest celestial neighbor with an ambitious plan to place a space station in lunar orbit sometime in the next decade. Sooner, though, the agency’s Artemis program , a sister to the Apollo missions of the 1960s and 1970s, is aiming to put the first woman (and the next man) on the lunar surface by 2024.
FREE BONUS ISSUE
Extended lunar stays build the experience and expertise needed for the long-term space missions required to visit other planets. As well, the moon may also be used as a forward base of operations from which humans learn how to replenish essential supplies, such as rocket fuel and oxygen, by creating them from local material.
You May Also Like

In a first, NASA Mars lander feels shockwaves from meteor impacts

SpaceX takes 4 passengers to orbit—a glimpse at private spaceflight’s future

Why go back to the moon? NASA’s Artemis program has even bigger ambitions
Such skills are crucial for the future expansion of human presence into deeper space, which demands more independence from Earth-based resources. And although humans have visited the moon before, the cratered sphere still harbors its own scientific mysteries to be explored—including the presence and extent of water ice near the moon's south pole, which is one of the top target destinations for space exploration .
NASA is also enlisting the private sector to help it reach the moon. It has awarded three contracts to private companies working on developing human-rated lunar landers—including both Blue Origin and SpaceX. But the backbone of the Artemis program relies on a brand new, state-of-the-art spacecraft called Orion .
Archival Photos of Spaceflight

Currently being built and tested, Orion—like Crew Dragon and Starliner—is a space capsule similar to the spacecraft of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo programs, as well as Russia’s Soyuz spacecraft. But the Orion capsule is larger and can accommodate a four-person crew. And even though it has a somewhat retro design, the capsule concept is considered to be safer and more reliable than NASA’s space shuttle—a revolutionary vehicle for its time, but one that couldn’t fly beyond Earth’s orbit and suffered catastrophic failures.
Capsules, on the other hand, offer launch-abort capabilities that can protect astronauts in case of a rocket malfunction. And, their weight and design mean they can also travel beyond Earth’s immediate neighborhood, potentially ferrying humans to the moon, Mars, and beyond.
A new era in spaceflight
By moving into orbit with its Commercial Crew Program and partnering with private companies to reach the lunar surface, NASA hopes to change the economics of spaceflight by increasing competition and driving down costs. If space travel truly does become cheaper and more accessible, it’s possible that private citizens will routinely visit space and gaze upon our blue, watery home world—either from space capsules, space stations, or even space hotels like the inflatable habitats Bigelow Aerospace intends to build .
The United States isn’t the only country with its eyes on the sky. Russia regularly launches humans to the International Space Station aboard its Soyuz spacecraft. China is planning a large, multi-module space station capable of housing three taikonauts, and has already launched two orbiting test vehicles—Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2, both of which safely burned up in the Earth’s atmosphere after several years in space.
Now, more than a dozen countries have the ability to launch rockets into Earth orbit. A half-dozen space agencies have designed spacecraft that shed the shackles of Earth’s gravity and traveled to the moon or Mars. And if all goes well, the United Arab Emirates will join that list in the summer of 2020 when its Hope spacecraft heads to the red planet . While there are no plans yet to send humans to Mars, these missions—and the discoveries that will come out of them—may help pave the way.
Related Topics
- SPACE EXPLORATION
- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
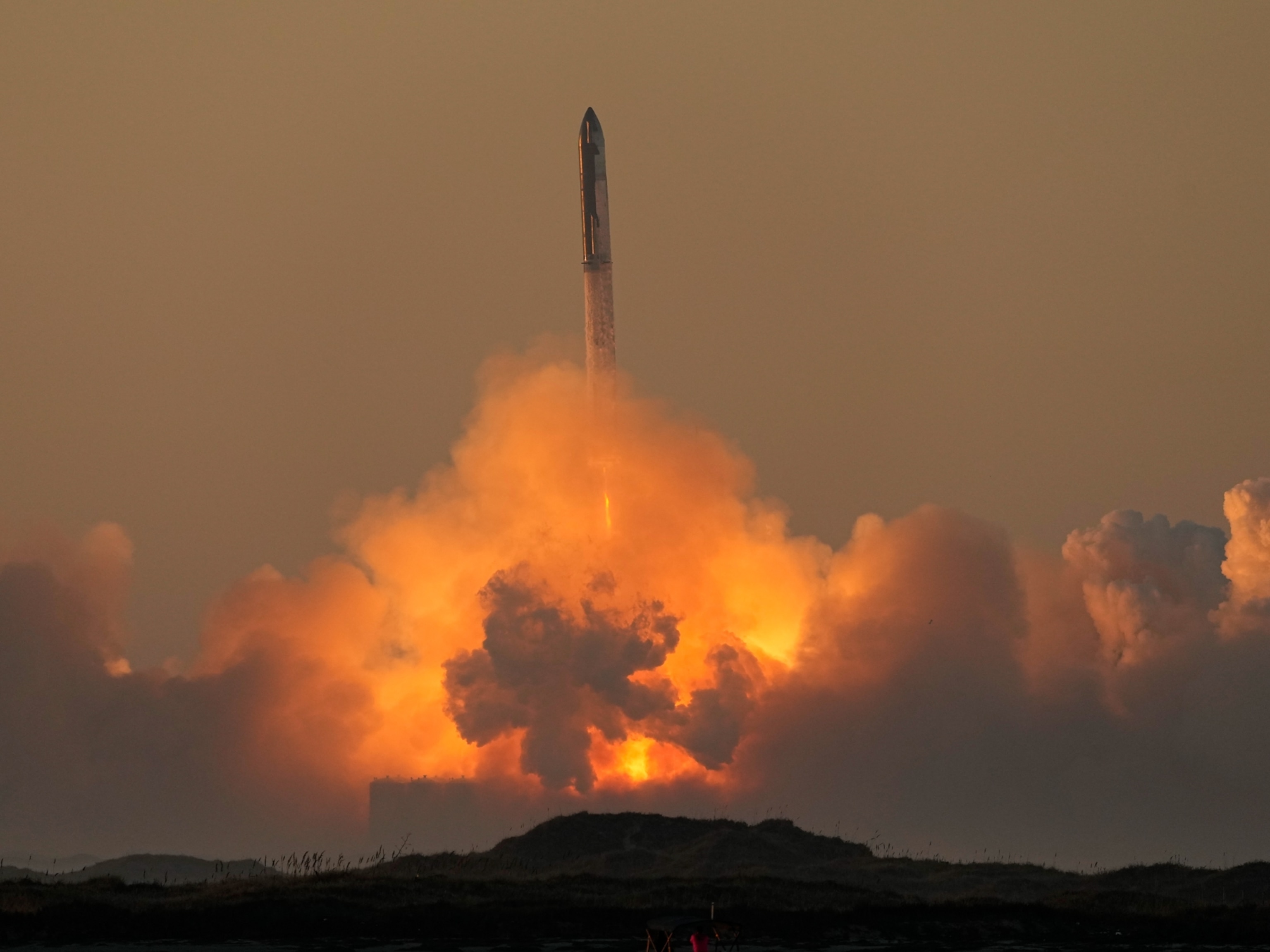

Second SpaceX megarocket launch ends with another explosion. What happens next?

Why did India land near the moon’s south pole?
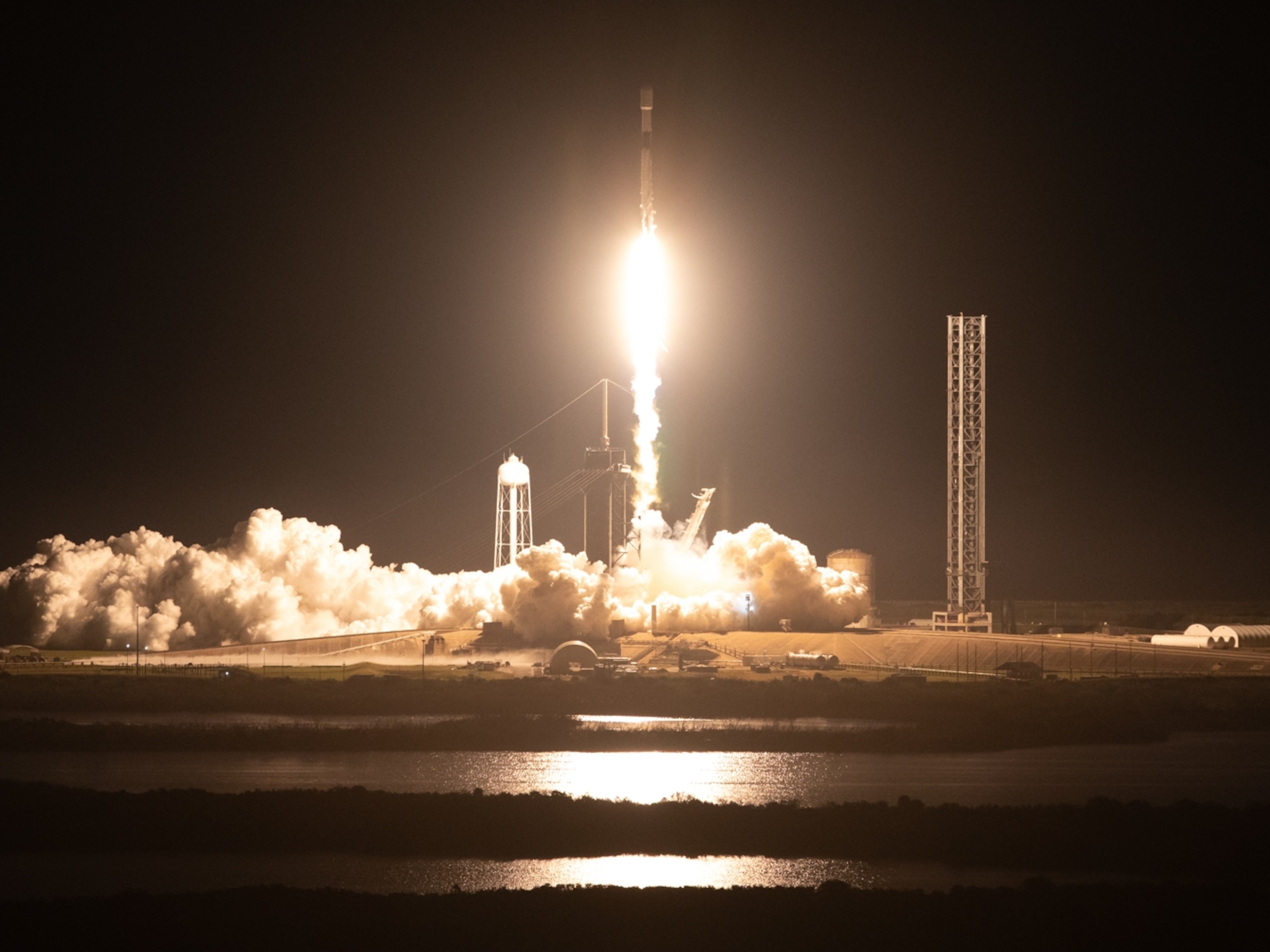

U.S. returns to the moon as NASA's Odysseus successfully touches down
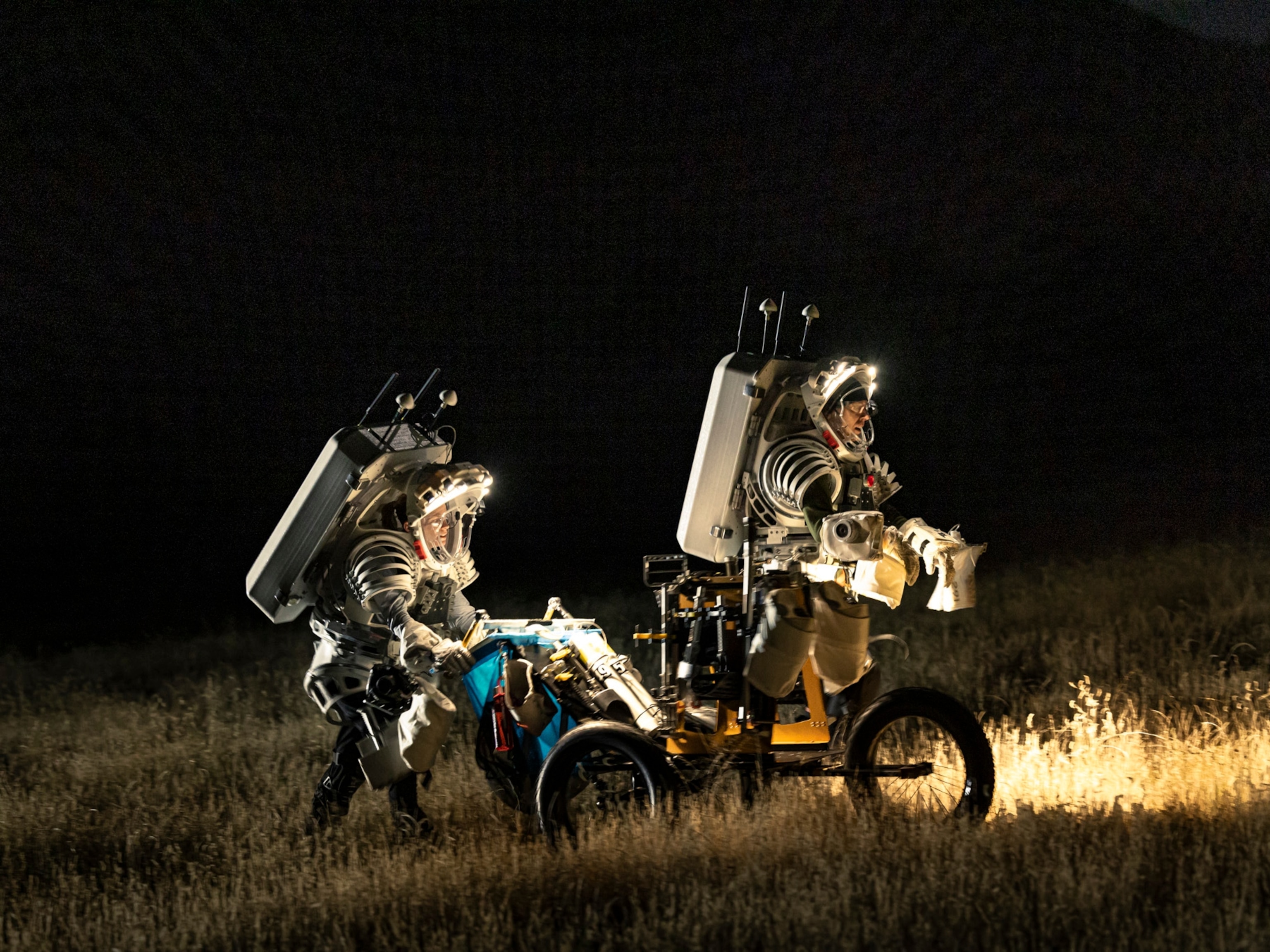

In the Arizona desert, NASA prepares for walking on the moon
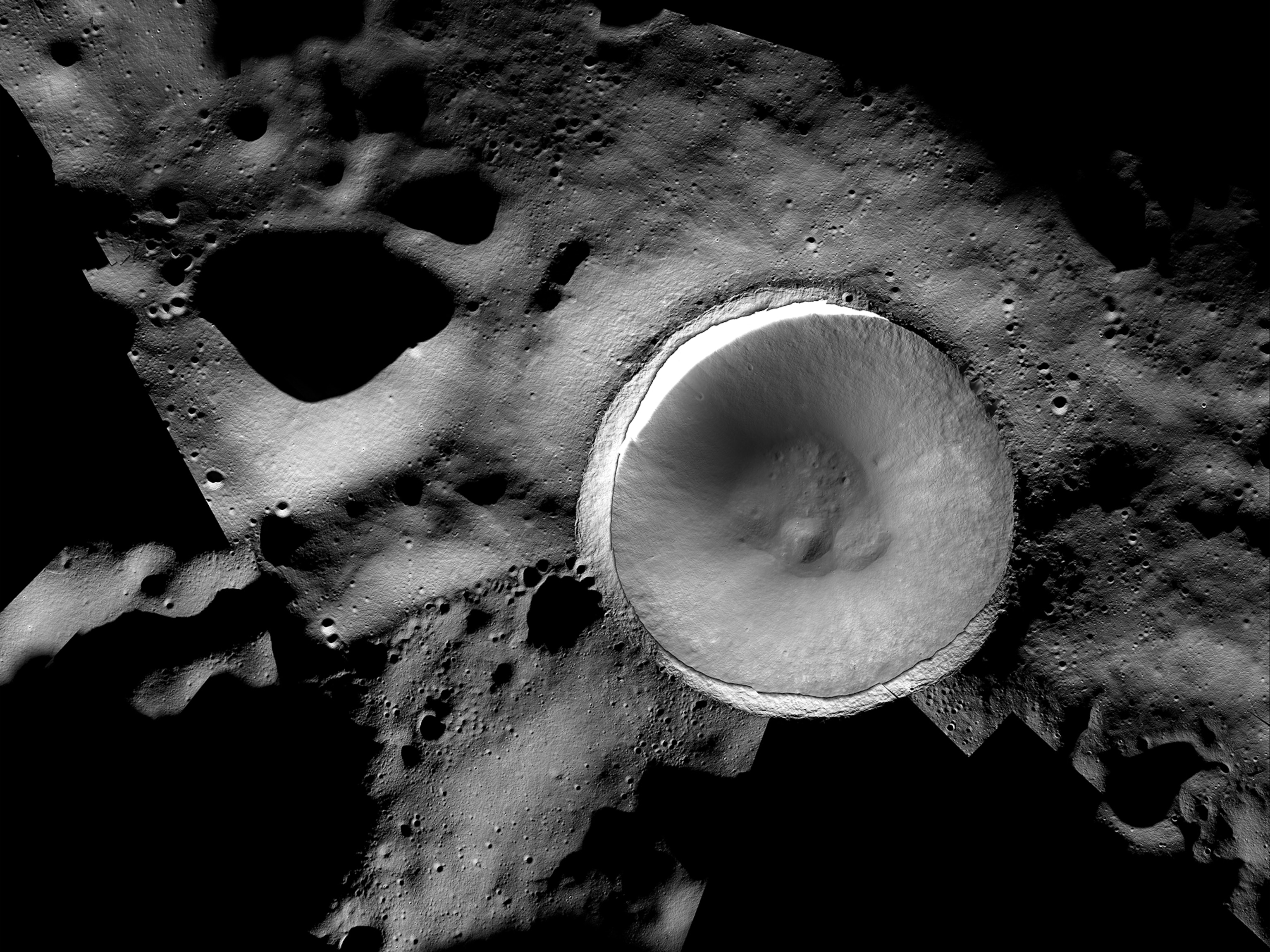

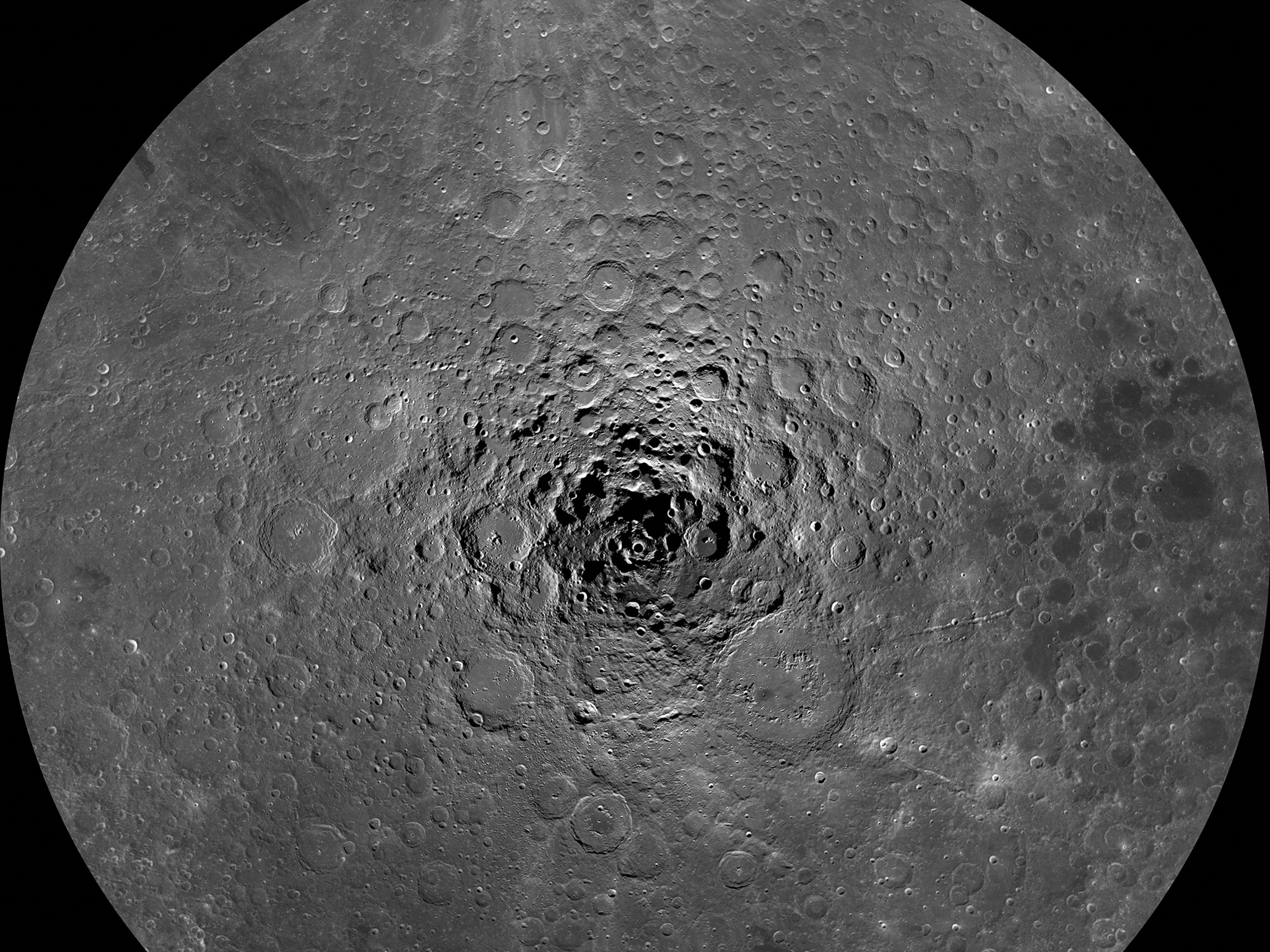
The moon’s darkest corners are a mystery. This image offers a stunning new glimpse.
- Environment
- Paid Content
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Gory Details
- 2023 in Review
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- Privacy Policy
- Write And Get Paid
- Submit A List Post
The Mysterious World
Know The Unknown
Top 10 Amazing Facts about Space Travel
Space travel is the reaching of the universe beyond the atmosphere of the earth. We can use the information gained from these travels to increase cosmos knowledge and benefit humanity. People referred it to the astronomy use and technology in space. The astronomers with telescopes are mainly carried out the journey through space. Here we are listing the top ten amazing facts about space travel.
10 Humans have traveled into space for over 50 years now

The 27-year-old Russian astronaut Yuri Gagarin made the first human journey into space on April 12, 1961, and the spacecraft used for this voyage called Vostok 1. Yuri Gagarin also orbited around the planet before he was parachuting back down to earth safely. The entire flight of this journey took one hour and forty-eight minutes from launch to landing.
Ever since then, people worldwide celebrate ‘Yuri’s Night’ on April 12 to remember the beginning of human space exploration. Following the flight, he became a Soviet Union’s cultural hero. Even today, over six decades after his historic trip, Soviet cosmonaut celebrated widely in Russian space museums. Moreover, the celebration also includes several artifacts, busts, and statues displayed in his honor.
People buried Gagarin’s remains at the Kremlin in Moscow, and part of the spacecraft is on display at the RKK Energiya museum. The U.S and the Soviet Union challenged the space’s technological supremacy, and then his flight came at a time. The first artificial satellite of the Soviet Union, called Sputnik they had already sent it into space in October 1957.
Before Gagarin’s mission, the Soviets sent a test flight into space using the Vostok spacecraft’s prototype. They sent a life-size dummy, known as Ivan Ivanovich, and a dog named Zvezdochka into space during this flight. After this test flight, the Soviets considered the vessel fit to take a person into space. Thus, this is one of the amazing facts about space travel.
9 The first “space tourist” traveled to the International Space Station in 2001

It is one of the amazing facts about space travel. Space tourism is the traveling activity of humans into space for recreational purposes. We can also see lots of different kinds of space tourism, such as orbital, suborbital, and lunar space tourism here. Besides, Dennis Tito, a California millionaire and former NASA engineer paid for his trip to the International Space Station EP-1. So, he became the first paying space tourist in the world when the Russian Federal Space Agency launched two Russian cosmonauts and Dennis aboard a rocket.
He also spent almost eight days in orbit as an ISS EP-1’s crew member in mid- 2001, and this is the mission of visiting the International Space Station. The spacecraft Soyuz TM-32 launched this mission, and Soyuz TM-31 landed it. He circled Earth 128 times when he was a crew member. Dennis Tito is never a regular American tourist, though.
He also studied astronautics and aeronautics in school. Moreover, Dennis went on to work as a NASA in the Jet Propulsion Laboratory’s scientist. Officials said that he paid $20 million of his money to take the trip! Tito announced the intention of him to send a spaceflight of privately financed to Mars in 2018.
He was stating that the technology of travel is already in place. The issues that need to overcome are only the requirements of a 501-day trip rigor on a physical level and psychological for the human crew.

10 Rarest And Amazing Astronomical Events
8 the first person reached on the moon on july 20, 1969.
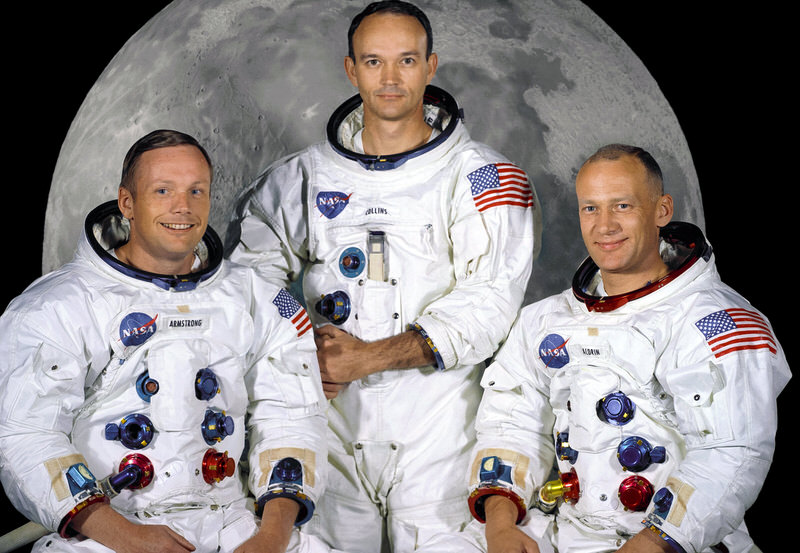

It is also amazing facts about space travel. The American crews, commander Neil Armstrong and lunar module pilot Buzz Aldrin, were the first humans to reach the moon. They also return safely to earth. When these people arrive on the moon, then they went outside of the spacecraft and walked around! The spaceflight, Apollo 11, was first landed the humans on the moon.
On July 20, 1969, the two Americans landed the Apollo Lunar Module Eagle at 20:17 UTC. Neil was the first person to fall onto the lunar surface and took six hours and 39 minutes. Later, Aldrin joined him on July 21 in 19 minutes then. They together spent around two and a quarter-hour of spacecraft outside. They also collected lunar material, about 47.5 pounds, to bring back to earth. The trip was around 402,336 kilometers.
It is like the traveling of the equator of the planet around ten times! A Saturn V rocket launched Apollo ll from Kennedy Space Center on Merritt Island, Florida. The first step of Armstrong onto the lunar surface was broadcast on live television to the audience worldwide.
The lunar module land on the moon’s Sea of Tranquility. It was a sizeable basaltic region. While on the surface, they set up many experiments. They collected lunar soil samples and rocks to bring home. Additionally, the astronauts erected the flag of the United States and took core samples from the crust.
7 Sputnik stunned the world
The Sputnik launch 60 years ago opened a space era. It also became a significant triumph for the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union was showcasing the power of military and technological heroism. So, Sputnik discovery stunned the rest of the world. The Soviet Union’s first artificial satellite launched in October 1957, marking a new space exploration age.
This satellite, named Sputnik, was a beach ball size. It took ninety-eight minutes to complete an earth’s orbit successfully. Moreover, other continents were not expecting the Soviets to launch the satellite of them so soon. America did not start the first satellite until January 1958. Development details and the first artificial satellite launch hidden behind the secrecy veil surrounded the Soviet space program and became known decades later.
Sputnik orbited for three weeks before the batteries of it died. Then it silently circled for two more months before it dropped back into the atmosphere. It was a diameter of 23 inches. It polished metal sphere and four external radio antennas to broadcast radio pulses.
The Russian name of Sputnik is for spouse/traveling companion or satellite when interpreted in the context of an astronomical. It went at around 18,000 mph, taking 96.2 minutes to finish each orbit. Radio operators monitored Sputnik that transmitted on 20.005 and 40.002 MHz. It had a mass of 184 lb.
6 Many monkeys have sent into space
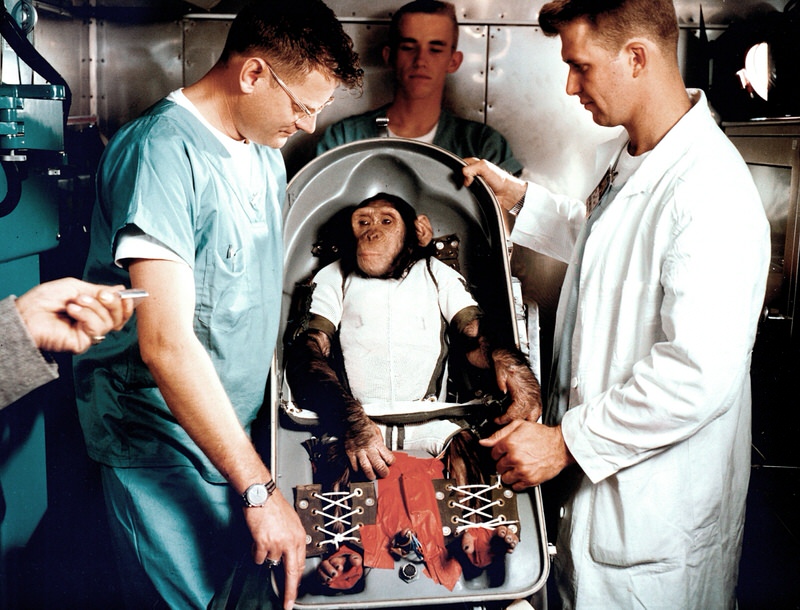

It has the sixth position in the list of amazing facts about space travel. Several brave astronauts participated and given their lives when they travel into space. But before those astronauts, there was a long line of other creatures like fruit flies paved the way for human spaceflight. Officials sent the first monkey on June 11, 1948, into space launched from New Mexico.
Albert, a male rhesus monkey, was aboard a V2 rocket. Also, it reached 39 miles of altitude during his trip. But it suffocated after a technical malfunction. The height of this monkey was 83 miles on June 14, 1949. Albert proceeded to Albert II. The fate of Albert II was not as lucky as that of the fruit flies .
Sadly, a problem in the parachute on the recovery capsule caused Albert II to die from the impact upon landing. His capsule only made it to a height on June 11, 1948. Also, Albert did not last long. He suffocated even before the capsule left the earth. Space officially starts at 100 km above the earth’s surface. People called this height as the Karman Line.
After Albert II made it into space, several other monkeys, such as Albert III, IV, and V, flew aboard rockets. But none of them survived the flight. Dying on impact as well as during the trip can occur. Able and Miss Baker were the two monkeys that survive the flight into space. They flew up to a height of 360 miles aboard a Jupiter rocket. This fantastic space travel facts also hold a position on this list.
5 The first pup to orbit the earth was a stray

It has the fifth position in the list of amazing facts about space travel. Just a month after the Russian satellite Sputnick 1 launch, the Soviets sent the first dog. The Soviets sent this dog named Laika into the space to orbit the Earth in November 1957. The first animal to leave the orbit of the planet, taking off 60 years ago.
The stray mutt was found in Moscow and landed a place in history on November 3. The first canine suffered from overheating just a few hours after the mission’s start and died in space. The officials selected Laika, from Moscow’s streets, as the occupant of the Soviet spacecraft Sputnik 2. People knew little about the spaceflight impact on living creatures at the time of Laika’s mission.
The technology was also not yet developed to de-orbit at that time. Therefore, we never expected the survival of Laika. Some scientists believed human beings would not be able to survive the launch or extreme space conditions. The engineers used animals as a necessary precursor for viewed flights to human missions.
The central R-7 sustainer failure to separate from the payload caused the Laika’s death. The real reason and her death time were not made public until 2002. The media widely reported that she died because the oxygen ran out on day six or, as the Soviet government initially claimed. Then she euthanized before the depletion of oxygen. Laika also appears on the Moscow’s Monument to the Conquerors of space.
4 The ashes of Pluto’s discoverer orbit the dwarf planet
Experts once considered that the Pluto was the ninth and most distant planet from the sun. But now it is the solar system’s most massive known dwarf planet. It is also among the largest known Kuiper Belt members. In 2006, officials reclassified Pluto as a dwarf planet, and they widely thought that the change was a demotion. The question of the planet status of Pluto attracted controversy. Also, it stirred a debate in the scientific community and one of the general public.
A science group proposed a new planethood definition in 2017, based on “round objects in space smaller than stars.” This topic would make the planets’ number in our solar system expand from 8 to 100. In 1930, American astronomer Clyde Tombaugh made the striking Pluto discovery. He requested that, after the death of him, people kindly sent the ashes into space. The end of Tombaugh occurred on January 17, 1997.
The ashes of him were earlier this year sent into space on NASA’s spacecraft, New Horizons. Tombaugh’s remains are the first human remains that officials sent outside the solar system. In a small container attached to the probe’s upper deck that orbited Pluto recently. The ashes of Tombaugh affixed to the spacecraft with an inscription.
3 Unusual Insurance

The early astronauts were not able to get life insurance for such a risky venture. They would autograph their pictures to ensure the officials would take care of their families if they failed to return. Then the authorities auctioned off this autograph if needed. Luckily for heroes like Neil Armstrong, they never were.
While the successful mission of SpaceX, the officials created new space exploration enthusiasm. Global Aerospace companies have been giving space initiative insurance from the time of the first commercial satellites. They also launch vehicles needed financial support to cover the risk.
The insurance coverage contains liability of third party arising from launch activities and surrounding the property value established to space. The traditional market of space insurance ensures and launched the satellite value into orbit around the earth. While governmental and satellites of the military are usually self-insured, commercially owned satellites’ financial backers often wanted insurance to be in place.
People used commercial satellites for communications and television transmissions around the world. People also expanded to include satellite radio (SiriusXM), imaging satellites, and soon 5G networks. We can divide the Space insurance into four types of coverage. Prelaunch, Launch, In-orbit, Launch, plus Life are the leading insurance of space travel.
2 Astronaut food
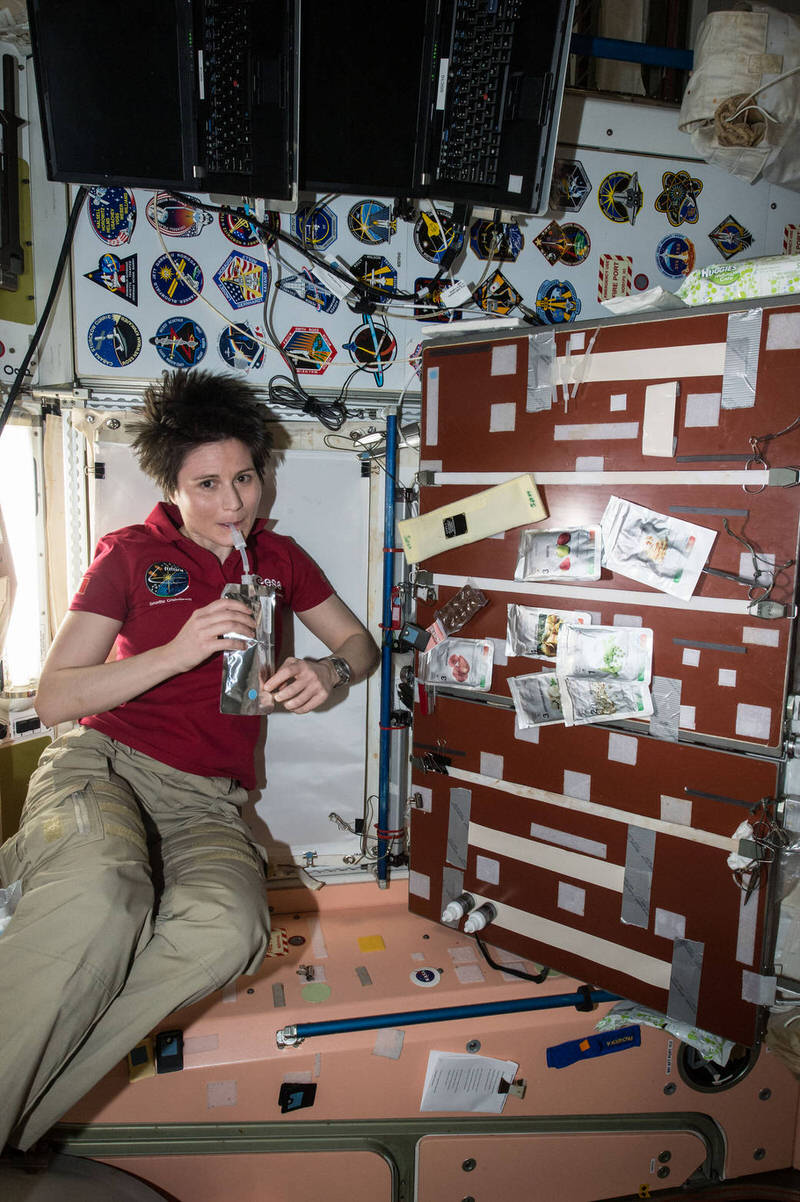

Astronauts can eat the same food as they do on earth. But NASA said astronauts to reduce 40% of sodium content in their diet. They stored all the food in air-tight packaging, known as retort packaging. Officials not allowed cookies or bread on board. All the little crumbs of these foods go into the zero-gravity conditions of spacecraft when they fall.
Additionally, they can get stuck in the tiny space buttons. There is no diet of pre-flight that astronauts require to follow. Stay healthy is most important. Moreover, they may seem like superheroes, but they take only the supplement, Vitamin D. Since they are not getting more sun and are not eating many fresh fruits or vegetables, these people have a stay healthy.
Astronauts’ bones become weaker in space because they do not have to work so hard in zero-gravity. Therefore, every food they eat requires more and more calcium and vitamin D to keep them healthy and happy. One of the unique space foods is Space Ice cream that developed to satisfy an astronaut’s sweet tooth! The people do not need to freeze this ice cream but melt in our mouth just like the real thing.
When the officials first explored the travel through space, the astronauts who went into space had to have every food eaten out of toothpaste-like tubes! An American eaten apple sauce squeezed out of a tube was the first meal. These space travel facts also have all the rights to be on this list.
Related Articles

Top 10 massive things on Earth that can be seen from space

Top 10 Most Spectacular Space Photos From NASA

Top 10 Fastest Man Made Objects Ever
1 the cost of space travel.

It is also one of the amazing facts about space travel. The mission of the Space Shuttle cost too much and provided too little. Traditionally, space travel is an activity of government. So, it has never been cheap. But the stratospheric cost for putting persons and space payloads is finally starting to fall, due to the part to the rise of SpaceX and other private companies of spaceflight.
One of many reasons for the expensive Shuttles were because of some equipment like the external tank. People used it to launch. These non-reusable external tanks must replace with each launch. The machine was so ancient is another reason. People designed it in the 1970s and finished its work in the 1980s. Also, space travel had some modifications over the years.
We could set a ticket anywhere from $250,000 to tens of millions of dollars based on where we are going. We are looking to cross the 62-mile-high Karman line, and it will take us there for $250,000. This line is the boundary between the upper atmosphere and outer space. Before making a lifetime trip, travelers need to pass emotional health and training tests.
If travelers’ journey is a success, it must be the fastest and farthest people have gone into space in 45 years. SpaceX company is hoping to send two travelers into space for a vacation in 2018. Experts estimated that the Apollo 11 mission’s total cost that first put a man on the moon was $25.4 billion. Today this money is around $135 billion.


Turn Your Curiosity Into Discovery
Latest facts.

Approach for Using 5 Tips To Help You Write Your Dissertation

Dmitry Doev Projects as CEO of VIS Group Doev Dmitry Vitalievich
12 astounding facts about space travel.
Written by Garnette Golding
Modified & Updated: 02 Mar 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett
- Physical Sciences
- Astronomy Facts
- Astrophysics Facts
- Black Holes Facts
- Celestial Bodies Facts
- Exoplanets Facts
- Interstellar Travel Facts
- Nasa Missions Facts
- Space Technology Facts
- Space Travel Facts

Space travel has always captivated the imagination of humankind. The idea of exploring the vast expanse beyond our planet is both thrilling and awe-inspiring. Over the years, incredible advancements in technology have made space travel a reality, allowing astronauts to venture beyond the Earth’s atmosphere and push the boundaries of human exploration. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of space travel and uncover 12 astounding facts that will leave you in awe of the cosmos. From the mind-boggling distances covered to the mind-bending effects of zero gravity , these facts will give you a glimpse into the incredible journey of astronauts and the wonders of the universe. So, fasten your seatbelts and join us on this extraordinary adventure through the cosmos.
Key Takeaways:
- Space travel can make astronauts taller and experience 16 sunrises and sunsets in a day, showing the amazing effects of zero gravity and orbiting the Earth.
- Astronauts may experience less time passing than people on Earth due to time dilation, and space tourism is becoming a possibility with private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin.
The First Human to Journey Into Space
Yuri Gagarin, a Soviet cosmonaut, became the first human to travel into space on April 12, His spacecraft, Vostok 1, completed one orbit around the Earth in just under two hours, marking a significant milestone in space exploration.
The Speed of a Spacecraft
Spacecraft can reach extraordinary speeds. The fastest spacecraft ever recorded is the Helios 2, which reached a speed of approximately 157,078 miles per hour (252,792 kilometers per hour) as it approached the sun.
The Length of a Day in Space
While a day on Earth lasts 24 hours, a day in space is slightly different. Astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) experience 16 sunrises and sunsets every day, as the ISS orbits the Earth approximately once every 90 minutes.
The Effect of Gravity on Astronauts
Due to the absence of gravity in space, astronauts experience significant changes in their bodies. They can grow up to two inches taller while in space as the spinal disks expand, and their muscles and bones undergo weakening due to lack of use.
The International Space Station’s Size
The International Space Station (ISS) is an impressive structure, spanning approximately the size of a football field when its solar panels are fully extended. It serves as a crucial research laboratory for scientific experiments and as a platform for international collaboration.
The Weightlessness of Astronauts
Astronauts experience weightlessness in space due to the microgravity environment. Objects and individuals in orbit around the Earth appear to be floating because the gravitational force acting on them is much weaker than on the surface of the planet.
The Farthest Journey from Earth
The farthest journey from Earth by humans was made by the crew of the Apollo 13 mission in They reached a distance of approximately 248,655 miles (400,171 kilometers) from Earth, circumnavigating the Moon during a critical mission that tested the limits of human ingenuity and courage.
The First Woman in Space
Valentina Tereshkova, a Soviet cosmonaut , made history on June 16, 1963, by becoming the first woman to travel into space. She orbited the Earth 48 times during her mission aboard Vostok 6.
The Dangers of Space Radiation
Space radiation poses a significant threat to astronauts. Exposure to high levels of radiation can lead to an increased risk of cancer, damage to the central nervous system, and other long-term health concerns. Protective measures, such as shielding and monitoring, are essential to mitigate these risks.
The Length of a Journey to Mars
A journey from Earth to Mars can take anywhere from six to nine months, depending on the alignment of the planets. This vast distance poses numerous challenges for future manned missions, including fuel requirements, crew wellbeing, and the need for sustainable life-support systems.
Space Travel and Time Dilation
Einstein’s theory of relativity has a fascinating implication for space travel. As a spacecraft approaches the speed of light, time slows down relative to an observer on Earth. This phenomenon, known as time dilation, means that astronauts may experience less time passing than people on Earth.
The Potential for Space Tourism
Advancements in technology and increased interest in space exploration have paved the way for the future of space tourism. Private companies, such as SpaceX and Blue Origin, aim to offer commercial trips to space, allowing individuals to experience the wonders of space firsthand.
In conclusion, space travel is a remarkable feat of human ingenuity, pushing the boundaries of our understanding and exploration of the universe. The 12 astounding facts about space travel demonstrate the incredible achievements and challenges faced by astronauts as they journey beyond our planet’s atmosphere.
In conclusion, space travel is an extraordinary and fascinating field that continues to captivate our imaginations. The facts presented here highlight some of the awe-inspiring aspects of this incredible journey beyond our planet. From the mind-boggling distances involved to the astonishing speeds achieved, space travel pushes the boundaries of human knowledge and exploration.
As we uncover more about the vastness of the universe, the possibilities for space travel and exploration only continue to expand. It is undoubtedly a challenging endeavor, but with each mission, we gain valuable insights and pave the way for future generations to explore further into the cosmos.
Space travel embodies the spirit of human curiosity, resilience, and determination to understand our place in the universe. It offers us a glimpse into the wonders and mysteries that lie beyond our home planet. So let us marvel at the marvels of space travel and remain eager for the discoveries and adventures that await us in the vast expanse of the universe.
Q: How fast do spacecraft travel in space?
A: Spacecraft can travel at incredible speeds, reaching velocities of up to 17,500 miles per hour (28,000 kilometers per hour). This speed allows them to overcome Earth’s gravity and venture into the depths of space.
Q: How do astronauts stay healthy during long-duration space missions?
A: Astronauts undergo rigorous physical training before their missions and follow special exercise routines to counteract muscle and bone loss in microgravity. They also have carefully planned diets and strict medical protocols to maintain their health and well-being.
Q: How long does it take to reach the Moon?
A: It takes approximately three days for a spacecraft to reach the Moon. The actual duration can vary depending on the trajectory and propulsion system used.
Q: Can humans survive on other planets?
A: Currently, humans can only survive on Earth without the aid of special equipment. However, scientists are actively exploring the possibility of establishing colonies on other planets, such as Mars, by developing technologies to create habitable environments.
Q: Can space travel affect the human body?
A: Space travel can have various effects on the human body, including muscle and bone loss, cardiovascular changes, and vision problems. Long-duration missions also pose psychological challenges to astronauts due to isolation and confinement. However, ongoing research aims to mitigate these effects and ensure astronaut well-being during space travel.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
What’s next in space
The moon, private space travel, and the wider solar system will all have major missions over the next 12 months.
- Jonathan O'Callaghan archive page

We’re going back to the moon—again—in 2023. Multiple uncrewed landings are planned for the next 12 months, spurred on by a renewed effort in the US to return humans to the lunar surface later this decade. Both private space companies and national agencies are set to make the 240,000-mile trek to our celestial neighbor, where they will test landing capabilities, look for usable water ice , and more.
Previous years were “all about Mars,” says Jill Stuart, a space policy expert from the London School of Economics in the UK. “Now we’ve shifted back to the moon.”
That is not all 2023 has in store. We’re also likely to see significant strides made in private human spaceflight, including the first-ever commercial spacewalk, compelling missions heading out into—or back from—other solar system destinations, and new rockets set to take flight.
Here’s what the next year has lined up for space.
Moon landings
A lunar lander will already be on its way when 2023 begins. Launched in December on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, the private spacecraft Hakuto-R, developed by Japanese firm ispace , is on a four-month journey to reach the moon , where it will deploy rovers built by the space agencies of Japan and the United Arab Emirates, among other goals. If successful, Hakuto-R could become the first private mission to land on the moon in March.
We say “could” because two private landers from the US—one from the firm Astrobotic and the other from Intuitive Machines, called Peregrine and Nova-C, respectively—are also set to reach the moon around the same time. Both are NASA-backed missions with various instruments on board to study the lunar environment, part of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payloads Services program, which aims to spur commercial interest in the moon ahead of human missions planned for later this decade under its Artemis program.
The first part of that program, Artemis I, saw an uncrewed Orion spacecraft launch to the moon on NASA’s giant new Space Launch System rocket in November 2022. While the next Artemis mission, a crewed flight around the moon, is not planned until 2024, these next 12 months will lay important groundwork for Artemis by studying the moon’s surface and even looking for water ice that could be a potential target for future human missions, among other goals. “The moon is getting a lot more attention than it has done for many years,” says Jon Cowart, a former NASA human spaceflight manager now at the Aerospace Corporation in the US.
Intuitive Machines has a second lunar landing planned in 2023. Also on the books are landings from the space agencies of India and Japan, with Chandrayaan-3 and SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon) , respectively. India hopes to launch in August 2023. It will be the country’s second attempt—the first crash-landed on the moon in 2019. A date for SLIM, which will test precision landing on the moon, has not yet been set. Russia reportedly has plans for the moon in 2023 too with its Luna-25 lander, but the status of the mission is unclear.
Private space travel
Since May 2020, SpaceX has been using its Crew Dragon spacecraft to ferry astronauts to space, some to the International Space Station (ISS) under contract with NASA and others on private missions. But SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn mission , currently slated for March 2023, will be a big new step.
Four commercial astronauts, including billionaire Jared Isaacman, who is paying for the flight and also funded SpaceX’s first all-private human spaceflight in 2021, will target a maximum orbit of 1,200 kilometers, higher than any human spacecraft since the Apollo missions. And in a first for commercial human spaceflight, the crew will don spacesuits and venture outside the spacecraft.
“Polaris Dawn is really exciting,” says Laura Forczyk from the space consulting firm Astralytical. “My understanding is that the entire vehicle will be evacuated. Everybody is going to at least stick their heads out.”
The mission may help NASA decide whether a future Crew Dragon mission could be used to service the Hubble Space Telescope, a capability that the agency has been investigating with SpaceX. “We’ll have some idea whether it’s feasible,” says Forczyk.
Two more private missions using Crew Dragon—Axiom-2 and Axiom-3—are planned to head for the ISS in 2023, as well as two NASA flights using Crew Dragon. A competing vehicle from the US firm Boeing is also set to launch with crew for the first time in April 2023, following multiple delays .
Meanwhile, we wait to see if Jeff Bezos’s company Blue Origin will be allowed to launch with humans again. The company has been grounded following an uncrewed launch failure in September 2022. Another private spaceflight pioneer, Virgin Galactic, has been relatively quiet since it launched its founder Sir Richard Branson into space in July 2021.
All these developments in commercial human spaceflight may be overshadowed by the first orbital flight attempt of SpaceX’s massive and reusable Starship rocket, which was undergoing launchpad tests earlier this month and should launch in 2023, if not by the end of 2022.
If successful, the rocket, which would surpass NASA’s Space Launch System as the largest rocket to make it to orbit, could transform our exploration of space . “The ability to take more mass up opens up new opportunities,” says Uma Bruegman, an expert in space strategies at the Aerospace Corporation. That could include, one day, human missions to Mars—or beyond. But there’s a long way to go yet. “It’s definitely an important year [for Starship],” says Cowart. “They’ve got a lot to do.” One of its nearer-term goals will be preparing for the moon—NASA chose Starship’s upper stage as the initial lunar lander for the Artemis program.
Into the solar system
Moons of the solar system’s biggest planet are also on the agenda next year. April 2023 will see a gripping new mission launch from the European Space Agency (ESA) called JUICE, for “Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer.” Scheduled to arrive in orbit at Jupiter in 2031, the spacecraft will perform detailed studies of the Jovian moons Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa, all of which are thought to harbor oceans that could contain life beneath their icy surfaces.
“It’s the first mission that’s fundamentally focused on the icy moons,” says Mark McCaughrean, senior advisor for science and exploration at ESA. “We now know these icy moons have very deep water oceans, and they could have the conditions for life to have developed.”
JUICE will map these oceans with radar instruments, but McCaughrean says it will also be able to look for possible biosignatures on the surface of Europa’s ice, which could rain down from plumes ejected into space from its subsurface ocean.
Later in 2023, ESA is scheduled to see another major mission launch: its Euclid telescope, which was switched from a Russian rocket to a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. The telescope will probe the “dark universe,” observing billions of galaxies over a third of the sky to better understand dark matter and dark energy in the cosmos.
In October, NASA should launch a significant science mission of its own when Psyche takes flight following a delay from 2022. The spacecraft will head to 16 Psyche, an unusual metal-rich asteroid that has never been seen up close.
A number of other intriguing developments are expected in 2023. NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission is scheduled to return to Earth in September with pieces of an asteroid called Bennu, which could offer new insight into the structure and formation of the solar system. Amazon aims to send up the first satellites for Project Kuiper in early 2023, the start of a 3,000-satellite orbiting communications network it hopes will rival SpaceX’s Starlink constellation. And several new rockets are set to launch, including the United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan Centaur rocket (it will carry Astrobotic’s moon lander and some of Amazon's satellites) and possibly Blue Origin’s large New Glenn rocket. Both are heavy-lift rockets that could take many satellites into space.
“There’s a huge swathe of activity,” says Cowart. “I’m very excited about this year.”
Keep Reading
Most popular, large language models can do jaw-dropping things. but nobody knows exactly why..
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
- Will Douglas Heaven archive page
OpenAI teases an amazing new generative video model called Sora
The firm is sharing Sora with a small group of safety testers but the rest of us will have to wait to learn more.
The problem with plug-in hybrids? Their drivers.
Plug-in hybrids are often sold as a transition to EVs, but new data from Europe shows we’re still underestimating the emissions they produce.
- Casey Crownhart archive page
Google DeepMind’s new generative model makes Super Mario–like games from scratch
Genie learns how to control games by watching hours and hours of video. It could help train next-gen robots too.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.

Space Travel

Please enable JavaScript
A few hundred years ago, traveling over the Earth’s surface was a risky adventure. Early explorers who set out to explore the New World went by boat, enduring fierce storms , disease and hunger, to reach their destinations. Today, astronauts exploring space face similar challenges.

Space travel has become much safer as scientists have overcome potential problems, but it’s still dangerous. It’s also very expensive. In order for a space shuttle to break free of Earth’s gravity , it has to travel at a speed of 15,000 miles per hour. Space shuttles need 1.9 million liters of fuel just to launch into space. That’s enough fuel to fill up 42,000 cars! Combine the high speed, heat and fuel needed for launching and you’ve got a very potentially dangerous situation.

Re-entering the atmosphere is dangerous too. When a space craft re-enters the atmosphere, it is moving very fast. As it moves through the air, friction causes it to heat up to a temperature of 2,691 degrees. The first spacecrafts were destroyed during re-entry. Today’s space shuttles have special ceramic tiles that help absorb some of the heat, keeping the astronauts safe during re-entry.

Fun Facts about Space Travel for Kids
- One space shuttle launch costs $450 million.
- The German V2 was the first rocket to reach space in 1942.
- In 1947, fruit flies were launched into space. Scientists wanted to see how they reacted to space travel. Later, in 1949, Albert II, a Rhesus monkey went to space. In 1957, the Russian space dog , Laika, orbited the Earth. Scientists wanted to make sure space travel was safe for humans . Sending animals first gave them valuable information about how bodies react to being in space.

- In 1959, the Russian space craft, Luna 2, landed on the moon . It crashed at high speed. Fortunately, it was an unmanned craft with no astronauts inside.
- Russian astronaut, Yuri Gagarin , was the first human in space. He orbited the Earth in 1961.

- In 1963, the first woman, Valentina Tereshkova , entered space.
- The first U.S. spacecraft landed on the moon in 1966.
- On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first men to walk on the moon and return home safely – a journey of 250,000 miles.
- In 1970, Apollo 13 was headed to the moon when an explosion on board caused serious problems. The astronauts fixed the problems with materials they had on hand and returned home safely.
- US astronauts returned to the moon three more times in 1971.
- 1981 marked the first space shuttle that could be used again. Six shuttles have been built since then.
- In 1986, Space Shuttle Challenger exploded shortly after launch, killing all seven astronauts onboard, including school teacher, Christa McAuliffe.
- Since 2000, permanent crews have been living and working in space at the International Space Station .
- In 2001, the first private citizen, millionaire Dennis Tito, toured space. He paid $20 million to spend a week in space.

Learn More All About Space Travel
Check out this cool video all about space travel:
A video about the N.E.X.T. mission for space travel by NASA.
Enjoyed the Easy Science for Kids Website all about Space Travel info? Take the FREE & fun all about Space Travel quiz and download FREE Space Travel worksheet for kids . For lengthy info click here .
100 Interesting Space Facts That’ll Blow Your Mind
Neptune's moon, Triton, orbits the planet backwards. It's the only large moon in our solar system that does this.

With new space discoveries happening weekly, it’s no surprise we wanted to write these 100 random & interesting facts about space!
Space facts are always interesting to learn!
As time goes by, technological advancements have seen us learn more facts about space in the past century than in all time before that.
We’ve literally searched the universe for the most amazing space facts, including facts about the planets in our solar system, moons, the Milky Way, and beyond! We’re pretty sure #100 will make you smile!
Without further ado, let’s launch right into these 100 crazy facts about space!
Mercury & Venus are the only 2 planets in our solar system that have no moons.

In total, there are 176 confirmed moons that orbit the planets in our solar system, with some of them being bigger than Mercury itself!
If a star passes too close to a black hole, it can be torn apart.

For 20 years, a team of astronomers observed a star at the center of our galaxy orbiting a black hole .
The star has now got close enough to the black hole for “gravitational redshift” to occur which is where the star’s light loses energy as the black hole’s gravity intensified.
The hottest planet in our solar system is Venus.

Most people think that this would be Mercury, as it is the closest planet to the sun.
However, Venus has a lot of gasses in its atmosphere which creates a “Greenhouse Effect” that causes a constant temperature of 864° Fahrenheit (462° Celsius) everywhere on the plant’s surface.
Our solar system is 4.57 billion years old.

Well, give or take 30 million years(ish). Accurately speaking, it is 4.571 billion years old.
Scientists estimate that in about 5 billion years, our Sun will expand becoming a Red Giant.
In about 7.5 billion years its expanding surface will swallow up and engulf the Earth.
Enceladus, one of Saturn’s smaller moons, reflects 90% of the Sun’s light.
Because Enceladus’ icy surface reflects sunlight rather than absorbing it, temperatures reach as low as -394° Fahrenheit (-201° Celsius).
The highest mountain discovered is the Olympus Mons, which is located on Mars.

Its peak is 16 miles (25 km) high, making it nearly 3 times higher than Mount Everest.
And not only is it tall, but it’s also 374,015 ft² (114,000 m²) wide – that’s an area the size of Arizona !
The Whirlpool Galaxy (M51) was the first celestial object identified as being spiral.

The grand, spiraling arms of the Whirlpool Galaxy are made up of long lanes of stars and gas, sprinkled with lots of space dust.
These arms act as star formation factories, compressing hydrogen gas and creating clusters of new stars.
A light-year is the distance covered by light in a single year.
Light moves at the velocity of about 186,411 miles (300,000 km) a second.
So one light-year equates to roughly 5,903,026,326,255 miles!
The Milky Way galaxy is 105,700 light-years wide.

It would take a modern spacecraft 450,000,000 years to travel to the center of our galaxy!
You can read more unbelievable space facts with this list of Milky Way facts!
The Sun weighs about 330,000 times more than Earth.

It is about 109 times the diameter of Earth and is so large the Earth could fit inside the sun about 1,300,000 times over!
In fact, the sun is so gigantic that it contains 99.85% of all mass in our solar system.
Footprints left on the Moon won’t disappear as there is no wind.

But wait a minute… if there’s no wind to blow them away then why is the flag blowing? Well, it actually wasn’t blowing.
That rippling you see is because of a stubborn telescopic horizontal rod that the astronauts were struggling to remove from the flag’s upper hem.
Still unsure whether we’ve walked on the Moon? Here are 5 common Moon landing myths debunked .
Because of lower gravity, a person who weighs 220 lbs on Earth would weigh 84 lbs on Mars.

When sending droids to the surface of Mars, this is something scientists plan for, being able to load the droid up with more equipment and build it from more robust materials.
There are 79 known moons orbiting Jupiter.

Jupiter is the planet in our solar system with the most moons, and it also has the largest moon in our solar system.
That moon is called Ganymede and is 3,270 miles (5,270 km) in diameter – that’s bigger than Mercury and it is visible with just a pair of binoculars!

The Martian day is 24 hours 39 minutes and 35 seconds long.

So you’d therefore assume there are less days in a year on Mars than Earth, right? Wrong!
Because Mars orbits the sun slower than the Earth, there are actually 687 Martian days in a Martian year!
NASA’s Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) found evidence of water on the Earth’s Moon.

Whilst water cannot exist on the Moon’s surface under its current conditions, scientists believe water ice could survive within the cold, permanently shadowed crates at the Moon’s two poles.
The Sun makes a full rotation once every 25 – 35 days.

So for us on Earth, one full rotation equals one full day. However, our gargantuan sun takes 25 – 35 Earth days to make one full rotation!
Want to learn more space facts? Check out these 40 fiery facts about the Sun !
Earth is the only planet not named after a God.

Nobody knows how the Earth got its name; all we know is that it is derived from an amalgamation of both the Old English and Old Germanic words for “ground”.
Due to the Sun and Moon’s gravitational pull, we have tides.

This is because the Moon’s tidal force causes the Earth – and the water on it – to bulge out on the side closest to the Moon.
These bulges are what cause the world’s high tides.
Pluto is smaller than the United States.
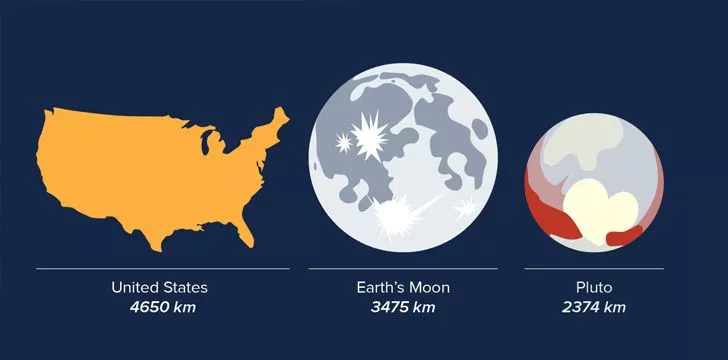
If you were to walk around the equator of Pluto it would be the same distance as walking from London to Denver (well, plus or minus an extra 56 miles).
According to mathematics, white holes are possible, although as of yet we have found none.

A white hole is a hypothetical region of space-time which can’t be entered from the outside, although matter and light can escape from within.
Basically, it’s the reverse of a black hole.
There are more volcanoes on Venus than any other planet in our solar system.

There are more than 1,600 major volcanoes across the surface of Venus, including a 5 mile (8 km) high volcano called Maat Mons.
However, none of these volcanoes are known to be erupting at present and most are probably long extinct.
Uranus’ blue glow is due to the gases in its atmosphere.

Uranus’ atmosphere is made up of hydrogen, helium and methane.
The methane in Uranus’ upper atmosphere filters out all the red light from the Sun but reflects the Sun’s blue light back into space, giving it its blue appearance.
Enjoying our space facts? If you’re interested in learning more, we have more interesting facts about Uranus .
In our solar system that are 4 planets known as gas giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus & Neptune.
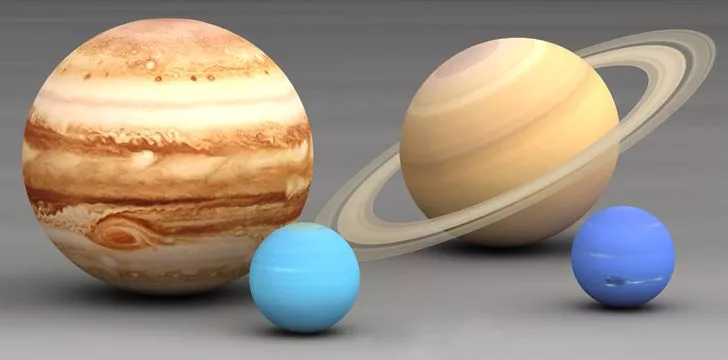
A gas giant is a large planet that is made up mostly of gases like hydrogen and helium and has only a relatively small rocky core.
Uranus has 27 moons that have been discovered so far.

It has 5 large moons and 22 small moons. Titania is the largest of Uranus’ moons and is the eighth largest moon in our solar system with an average diameter of 980.5 miles (1,578 kilometers).
Because of its unique tilt, a season on Uranus is equivalent to 21 Earth years.

Also, the 97.77 degrees tilt on Uranus’ axis means that a day there only last 17 hours, 14 minutes, and 24 seconds.
Neptune’s moon, Triton, orbits the planet in reverse.

Triton is the only large moon of any of the planets that does this.
This is known as a retrograde orbit and astronomers are unsure as to why Triton orbits Neptune this way.
Triton is gradually getting closer to the planet it orbits.

Scientists believe that when Triton eventually gets too close to Neptune, it will be torn apart by the planet’s gravity and could potentially create another ring around Neptune – giving it more rings than Saturn.
There are more stars in space than there are grains of sand in the world.

There are 10 times more stars in the night sky than grains of sand on the Earth, with 70 sextillion stars being visible from Earth through a telescope.
To put that in numbers, 70 sextillion is this: 70,000,000,000,000,000,000,000.
Neptune takes nearly 165 Earth years to make one orbit of the Sun.

That’s equivalent to 60,190 Earth days to orbit the sun once! Neptune has a very slow orbital speed of 3.37 miles per second (5.43 km/s).
This means that since it was discovered in 1846, it has only completed just one orbit!
You may also like these interesting facts about Neptune that are outta this world!
Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, is half the size of Pluto.

The same surfaces of Charon and Pluto always face each other, which is known as mutual tidal locking.
The International Space Station is the largest manned object ever sent into space.

At 119 yards (109 meters) long, the International Space Station (ISS) sits roughly 250 miles (400 km) above the Earth and is the third-brightest object in the night sky.
A day on Pluto is lasts for 153.6 hours long.

This equates to 6 days 9 hours and 36 minutes. A day on Pluto lasts so long because of its slow rotation rate.
Check out these other interesting space facts about the Dwarf Planet, Pluto .
Saturn is the second largest planet in our solar system.

It has a radius of 36,184 miles (58,232 km) – nine times that of Earth.
However, due to its low density it only has a weight roughly one-eighth of Earth.
Any free-moving liquid in outer space will form itself into a sphere.

This is because of something called surface tension, which is an imbalance of intermolecular attractive forces.
This can also occur in low Earth orbit.
Mercury, Venus, Earth & Mars are known as the “Inner Planets”.

They are named the Inner Planets because they orbit closest to the Sun.
An inner planet is classified as a planet located within the asteroid belt.
We know more about Mars and our Moon than we do about our oceans.

We have fully mapped 100% of the surface of Mars and Earth’s Moon, whereas we have only been able to map roughly 5% of the ocean floor.
The Black Arrow is the only British satellite to be launched using a British rocket.

Black Arrow was developed during the 1960’s and was used for four launches between 1969 and 1971.
In 2019 it was retrieved from its crash landing site in the Australian outback and put on a display Penicuik, Scotland.
Only 5% of the universe is visible from Earth.

68% of the universe is dark energy and 27% is dark matter. Both of these are invisible, even with a telescope, which means we are only able to see 5% of the universe.
Light travels from the Sun to the Earth in less than 10 minutes.

The Photons emitted from the Sun’s surface travel across the vacuum of space at the speed of light to reach our eyes in only 8 minutes and 20 seconds.
At any given moment, there are at least 2,000 thunderstorms happening on Earth.

Worldwide, there are an estimated 16 million thunderstorms each year.
Roughly 100,000 of these thunderstorms happen in the U.S. alone.
You can read more strange facts about thunder and lightning here.
The Earth’s rotation is slowing slightly as time goes on.

This means that days were shorter in the past. This is because of the tidal effects the Moon has on the Earth’s rotation.
If you were driving at 75 miles per hour, it would take 258 days to drive around Saturn’s rings.

Saturn’s rings are roughly 175,000 miles long, although they are only about 3,200 feet thick.
You can find out more interesting facts about Saturn’s rings here!
Outer Space is only 62 miles away.

Although there is no official solid boundary for where space begins, the Kármán line sits at 62 miles above sea-level and is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties or for aerospace records keeping.
The International Space Station circles Earth every 92 minutes.

The speed of the ISS as it orbits Earth is roughly 17,150 miles per hour – that equates to 5 miles a second!
Stars twinkle because of the way light is disrupted as it passes through Earth’s atmosphere.

Starlight is affected by the winds in our atmosphere as it enters, as well as being affected by different areas and temperatures.
This causes the light from each star to twinkle as we look at them.
We always see the same side of the Moon, no matter where we stand on Earth.

This is because the Moon rotates on its axis at the same rate that it rotates the Earth. It’s known as synchronous rotation or tidal locking.
There are three main types of galaxies: elliptical, spiral & irregular.

The Milky Way galaxy, the one that our solar system resides in, is classified as a spiral galaxy.
There are approximately 100 thousand million stars in the Milky Way.

That may sound like a lot, but its nothing compared to the galaxy with the most stars in the universe, IC 1101, which has a mind-blowing 100 trillion stars!
Using the naked eye, you can see 3 – 7 different galaxies from Earth.

You can see the Andromeda Galaxy (M-31), both Magellanic Clouds, our own Milky Way galaxy, the Triangulum Galaxy (M-33), the Omega Centauri and the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy.
In 2016, scientists detected a radio signal from a source 5 billion light-years away.

This means that when the signal started its journey, Earth didn’t even exist.
The detected signals were located using the Very Large Array (VLA) of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory in New Mexico.
The closest galaxy to us is the Andromeda Galaxy – it’s estimated at 2.5 million light-years away.

Before the discovery of the Andromeda Galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud was believed to be the closest galaxy to us.
The first Supernovae observed outside of our own galaxy was in 1885.

This supernova was called the S Andromedae, located in the Andromeda galaxy.
This was observed by Ernst Hartwig in Estonia and was only made possible due to recent improvements to telescope designs.
The first-ever black hole photographed is 3 million times the size of Earth.

The photo was released in April 2019 and shows a halo of dust and gas 310 million trillion miles from Earth.
It was captured by the Event Horizon Telescope, a network of eight linked telescopes, and was also captured due to the algorithm of programmer Katie Bouman.
The distance between the Sun & Earth is defined as an Astronomical Unit.
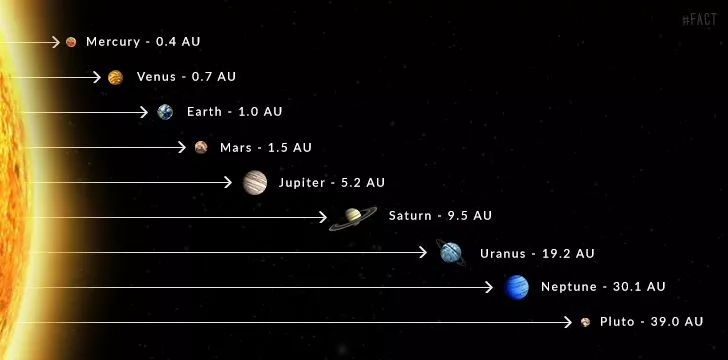
An Astronomical Unit (AU) equates to roughly 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers.
The second man on the moon was Buzz Aldrin. “Moon” was Aldrin’s mother’s maiden name.

She was born Marion Moon and later married Edwin Eugene Aldrin.
Buzz Aldrin’s birth name was Edwin Eugene Aldrin Jr.

He got the nickname “Buzz” from his sister’s mispronunciation of the word “brother”, which became “buzzer”.
In 1988, he legally changed his first name to “Buzz”.
On Venus, it snows metal and rains sulfuric acid.

This is because Venus is a scorching planet choked with sulfuric acid, which causes the planet’s metals to become gas and then liquid in the atmosphere, before raining down to the ground after the freezing temperatures turn it into a solid.
The Mariner 10 was the first spacecraft that visited Mercury in 1974.

It was launched at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in 1973 and flew by Venus 3 months later. It then crossed into Mercury’s orbit managing to photograph 45% of Mercury’s surface.
The second spacecraft to visit Mercury was the “Messenger”, which completed mapping of 100% of Mercury’s surface in 2013.
Space is completely silent.

This is because there is no air in space, and air is needed to carry the sound vibrations.
So if you shouted to someone next to you in space they wouldn’t be able to hear you. How’s that for a fun space fact!?
Coca-Cola was the first commercial soft drink that was ever consumed in space.

The first food ever eaten in space was applesauce and was eaten by John Glenn in space during the Friendship 7 mission in 1962.
Astronauts can grow approximately two inches (5 cm) in height when in space.

This is due to the lack of gravity in space causes the discs between the vertebrae to expand a little.
However, this extra height is lost when re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere and being subjected to the Earth’s gravity again.
The Kuiper Belt is a region of the Solar System beyond the orbit of Neptune.
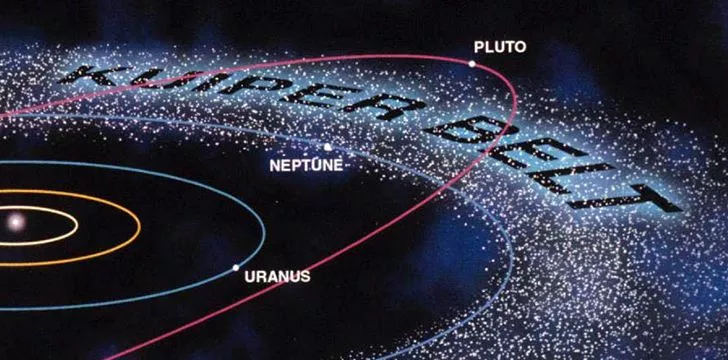
The Kuiper Belt is a ring of icy bodies and is where Pluto is located.
The first woman in space was a Russian called Valentina Tereshkova.

She launched into both history and space during the Vostok 6 mission on June 16 , 1963.
She spent almost three days in space and orbited the Earth 48 times in her space capsule before returning to Earth.
If Saturn’s rings were 3 feet long, they would be 10,000 times thinner than a razor blade.

The rings around Saturn are so thin because they are made up of pieces of dusty water ice ranging in size from dust grains to boulders.
The Hubble Space Telescope is one of the most productive scientific instruments ever built.

Astronomers using Hubble data have published more than 15,000 scientific papers. Those papers have been cited in other papers 738,000 times.
We have more facts about space & The Hubble Space Telescope here!
The first artificial satellite in space was called “Sputnik”.

It was launched by the Soviet Union into an elliptical low Earth orbit on October 4 , 1957.
Exoplanets are planets that orbit around other stars.

All of the planets in our solar system orbit around the Sun. But what about other solar systems?
In 2009, NASA launched a spacecraft called Kepler to look for exoplanets, and has discovered thousands since its launch.
The center of the Milky Way smells like rum & tastes like raspberries.

This was discovered by the IRAM radio telescope zeroed in on a gas cloud called Sagittarius B2 at the center of the our galaxy.
The IRAM detected a chemical called ethyl formate which gives rum its distinct smell and raspberries their distinct flavor.
You can read more about this fascinating space fact here – The Milky Way Smells Like Rum & Tastes Like Raspberries
Our moon is moving away from Earth at a rate of 1.6 inch (4 cm) per year!

Scientists do believe that eventually the Moon will move out of the field of Earth’s gravity; however this won’t happen for billions of years to come.
Pluto is named after the Roman god of the underworld, not the Disney Dog.

The name for the planet was suggested by Venetia Burney, an eleven-year old British schoolgirl, to the planet’s discoverer Clyde Tombaugh.
Spacesuit helmets have a Velcro patch, to help astronauts itch.

This is the Velcro patch’s one and only purpose.
The ISS is visible to more than 90% of the Earth’s population.

When you see the International Space Station (ISS) in the night sky it appears as a fast-moving star crossing from horizon to horizon.
Saturn is the only planet that could float in water.

Although Saturn is the second largest planet in our solar system, it is also the lightest planet.
Saturn could float in water because it is mostly made of gas – although the real fact here is that you would need a giant bath tub!
Asteroids are the byproducts of formations in the solar system, more than 4 billion years ago.

The birth of Jupiter in our solar system prevented any planetary bodies forming between Mars and Jupiter, causing the small objects that were there to collide with each other and fragment into asteroids.
Astronauts can’t burp in space.

This is because the lack of gravity in space means the air in astronaut’s stomach doesn’t separate and rise up from ingested food.
Uranus was originally called “George’s Star”.

This name was in honor of discoverer William Hershel’s new patron, King George III.
The name “Uranus” was proposed in 1782, one year after its discovery, but wasn’t officially used until 1850.
You may like these facts about when the planets in our solar system were discovered .
A sunset on Mars is blue.

Mars has less than 1% of the Earth’s atmosphere.
So the sunsets on Mars appear as blue due to the way the blue light from the Sun is captured within the atmosphere of Mars.
The Earth weighs about 81 times more than the Moon.

The Moon’s gravity, much like other planets, differs depending on where you are on its surface.
The first living mammal to go into space was a dog named “Laika” from Russia.

Laika was a stray mongrel from the streets of Moscow and was launched into space on the Soviet spacecraft Sputnik 2 on November 3 , 1957.
Sadly, Laika died 5-7 hours into the flight due to overheating and stress. Poor doggo.
The word “astronaut” means “star sailor” in its origins.

It is derived from the Greek words “astron”, meaning “star”, and “nautes”, which means “sailor”.
So, the word astronaut literally means “star sailor”.
“NASA” stands for National Aeronautics and Space Administration.

It is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government and was established in 1958.
NASA discovers new facts about space every day, check out these NASA facts if you want to learn more!
Gennady Padalka has spent more time in space than anyone else.

He is an RKA cosmonaut and has spent 879 days in space
He has worked on both Mir and the International Space Station.
Mercury has no atmosphere, which means there is no wind or weather.

Instead of an atmosphere, Mercury possesses a thin exosphere made up of atoms blasted off the surface by the solar wind and striking meteoroids.
In China, the Milky Way is known as the “Silver River”.

In Japan and Korea “Silver River” means galaxies in general, not just the Milky Way.
Red Dwarf stars that are low in mass can burn continually for up to 10 trillion years!

A Red Dwarf is a small and cool star in a later stage of its life and has a surface temperature of less than 7,200k degrees Fahrenheit.
Scientists once believed that the same side of Mercury always faced the Sun.

However, in 1965 astronomers discovered that the planet rotates three times during every two orbits it makes.
Jupiter’s Red Spot is shrinking.

Jupiter’s red spot is a huge swirling hurricane-like storm that used to be three times the size of Earth! However, the storm is shrinking over time, but even as it shrinks it gets taller.
Scientists are still stumped as to what’s causing this although they believe it may be to do with jet streams on Jupiter changing location or direction.
A large percentage of asteroids are pulled in by Jupiter’s gravity.

For this reason, Jupiter is known as the dumping grounds for our solar system.
Many of the asteroids that are potentially harmful to Earth, the long period comets, tend to be sucked into Jupiter’s gravity field.
Thanks Jupiter!
A day on Mercury is equivalent to 58 Earth days.

This is because Mercury rotates on its axis very slowly compared to Earth.
As space has no gravity, pens won’t work.

Normal pens work by gravity pulling the ink towards the pen’s nib (the writing part) – as you hold the pen in your hand writing part facing downwards.
As there’s no gravity in space, the ink doesn’t get pulled to the nib.
However, special pens have been made that work in zero gravity.
On average it takes the light only 1.3 seconds to travel from the Moon to Earth.

The distance between the Earth and the Moon is only 238,855 miles (384,400 kilometers).
There are 88 recognized star constellations in our night sky.

These 88 constellations cover the Earth’s night sky and can be observed from the southern and northern hemispheres.
The center of a comet is called a “nucleus”.

The streams of dust that streak behind comets are known as a “coma” or a “tail”.
Space facts aren’t just about the planets! Here are some cool facts about comets .
As early as 240BC the Chinese began to document the appearance of Halley’s Comet.

After 164BC there was a continuous recording of the comet each time it was visible.
In 2006, the International Astronomical Union reclassified Pluto as a dwarf planet.

This is because Pluto does not gravitationally dominate the neighborhood around its orbit.
There are 5 Dwarf Planets recognized in our Solar System.

The Dwarf Planets are Ceres, Makemake, Haumea, Eris and Pluto.
The dwarf planet Ceres is also the largest asteroid in our solar system, and resides in the asteroid belt, making it the only dwarf planet to not inhabit the outer solar system.
Mars is the most likely planet in our solar system to be hospitable to life.

In 1986, NASA found what they believe may be fossils of microscopic living organisms in a rock recovered from the surface of Mars .
Halley’s Comet will pass over Earth again on July 26, 2061.

This space fact is one for kids to look forward to!
The famous comet was last seen on February 9, 1986 , and only orbits the Earth once every 75 – 76 years.
There is a planet half the radius of the Earth with a surface made up of diamonds.

55 Cancri e has a mass eight times that of Earth’s despite having half the radius, and may very well have a surface made up of graphite and diamonds.
It is only 40 light-years away and visible to the naked eye under the constellation of Cancer.
Buzz Lightyear from Toy Story has actually been to outer space!

Buzz Lightyear spent 15 months onboard the International Space Station and returned to Earth on September 11 , 2009.
To infinity, and beyond!
We told you #100 would make you smile!
Space, for many, is a weird & wonderful thing. The great unknown is something mankind has always observed and tried to learn from – by understanding our galaxy we may be able to understand our place in it, and how this world came to be.
We hope these 100 cool space facts helped the mystery of space to become… well, less mysterious!
If you enjoyed these unusual facts about space, we have plenty more space facts for you to enjoy over at our Space category.
All these fun space facts were accurate at the time of writing, although we’ll update these facts about space regularly – so please let us know if something here is incorrect!
Long Reads , Top 100
Related Posts

The History of Space Travel Timeline

9 Interesting Facts About The James Webb Space Telescope

10 Incredible Facts About The International Space Station

26 Facts About Space Shuttles That Are Outta This World!
About the author.

Jack De Graaf
Jack De Graaf is a BA English Studies graduate and a part-time writer. In his spare time he likes to read and do circus skills. He enjoys writing about video games, television and general knowledge.
Popular Today

April 14: Facts & Historical Events On This Day

22 Facts About The Sinking Of The Titanic

20 Facts About Daisies & Sweet Peas, April’s Birth Flowers

22 Super Facts About Sunday
We have a thorough fact-checking process and a dedicated team verifying our content for accuracy. But occasionally, we may get things wrong, or information becomes outdated. If you believe something to be incorrect, please leave us a message below.
Leave a Comment
Latest facts.

National Pet Day | April 11

31 Fast-Paced Facts About Pickleball

15 Magnificent Facts About the Millennial Generation (1981-1996)

The Fact Site is the number one source for the most interesting & random facts about animals, celebrities, food, films, games & so much more. You will learn something about everything!
Popular Facts Lists
1000 Interesting Facts
100 Random Fun Facts
100 Mind Blowing Facts
100 Strange But True Facts
100 Interesting Space Facts
Popular Pages
Big Questions
Days of the Year
Today In History
World Records
Information
Privacy Policy
The Fact Shop
News | Meet Amanda Nguyen, set to be the first woman…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Investigative Reporting
- Environment
News | Meet Amanda Nguyen, set to be the first woman of Vietnamese descent in space

For Amanda Nguyen, not even the sky is the limit.
Nguyen, 32 years old and a Southern California native, is set to be the first woman of Vietnamese descent in space.
It’s a lifelong dream of hers — traveling to space, becoming an astronaut — but it’s one that was put on hold after she was sexually assaulted in 2013 while studying national security and astrophysics at Harvard University. She discovered then that seeking justice was an arduous and antiquated process, and as she puts it, she had to choose between that justice and her dream.
Justice, making life on earth a better place, won out.
Nguyen got legislation passed in Congress that preserves the rights of sexual assault survivors — mainly through maintaining the preservation of and survivors’ access to rape kits — and in 2014 founded Rise , a nonprofit that works with state legislatures to implement similar rights for survivors. Two members of Congress, including former Rep. Mimi Walters from Orange County, nominated her for the Nobel Peace Prize in 2018 , and she was selected as one of Time’s 2022 Women of the Year .
Now, nearly eight years since Congress passed that “Sexual Assault Survivors’ Bill of Rights” — and unanimously at that — the nonprofit Space for Humanity said it is sponsoring her on an upcoming trip to space on a Blue Origin New Shepard vehicle.

NEW YORK, NEW YORK – SEPTEMBER 14: Amanda Nguyen speaks onstage during Ford Foundation Center for Social Justice on September 14, 2023 at the Ford Foundation Center in New York City. (Photo by Rob Kim/Getty Images)

SINGAPORE, SINGAPORE – SEPTEMBER 17: Amanda Nguyen poses for a photo during the TIME100 Impact Awards on September 17, 2023 in Singapore. (Photo by Matt Jelonek/Getty Images for TIME)

NEW YORK, NEW YORK – SEPTEMBER 13: Amanda Nguyen attends Ford Foundation Center for Social Justice on September 13, 2023 at the Ford Foundation Center in New York City. (Photo by Rob Kim/Getty Images)

Amanda Nguyen, a civil rights activist and founder of Rise, is set to fly to space on a Blue Origin New Shepard. She will be the first Vietnamese Woman to fly to space, according to Space for Humanity, the nonprofit that is sponsoring her trip. (Photo courtesy of Sal Boccia with Blue Origin)
“As somebody whose dreams have always been to go to space but were deferred and delayed — like so many people, so many women, especially, who encounter gender-based violence — for me, learning that I could have this opportunity meant justice in a way,” said Nguyen.
It’s a trip that celebrates her heritage — she’ll be the first Vietnamese woman and first Southeast Asian woman to fly in space — and it honors her survivor status, she said.
“I chose to delay those dreams to fight for these rights, and I’m still able to hold onto that identity of the person who I was before I was hurt,” said said.
Space for Humanity is a group that “sends thoughtfully selected, impact-driven individuals of any walk of life to space to experience the ‘overview effect,’ a cognitive shift brought on by viewing the Earth from space,” according to its website.
The idea for its Citizen Astronaut Program, the group says, is to encourage those it sends on spaceflights to use that unique experience to better the world upon return.
“Amanda’s novel voyage will represent a much-overdue, shining example to countless others,” Space for Humanity executive director Antonio Peronace said in a statement. “As an organization committed to democratizing space and making it accessible to all the world’s citizens, we’re proud that Amanda and her journey represent the strength, passion and brilliance we want to continue to launch to new heights.”
Nguyen was born and raised in Corona, spending all her weekends in Orange County’s Little Saigon, a community that she says is a microcosm of immigrant resilience and determination.
“I wouldn’t be where I am without that,” she said. “I’m just so grateful for the community I was able to grow up in in Southern California. There are clear skies in Southern California and looking up at them is helping me make my way to them to touch the sky.”
Both of her parents are refugees from Vietnam, her mom by fleeing by boat.
“As boat refugees, my family looked to the stars to guide their way to freedom,” Nguyen says in a video announcing her trip .
“Mom, you swam so I can fly. You crossed the ocean so I could touch the sky,” she adds in Vietnamese.
Some details — like who she’ll be traveling with and the date — are not yet public, but Nguyen is preparing by chatting with other female astronauts, dubbed the “space sisters,” and collecting their advice. The preparation is physical, too, training, for example, how to eat lunch in a microgravity environment.
And she’s found her activism and space travel go hand-in-hand.
She taught herself box breathing techniques — hold four, breathe four in, hold four, breathe four out — when she found herself in situations that could be triggering or scary, like testifying before the U.S. Senate. And those techniques have carried over as she trains and tests in a hyperbaric chamber at the International Institute for Astronautical Sciences
“Innovation lies at the edge of different disciplines and being able to combine them in different ways,” Nguyen said.
Nguyen looks up at the sky, knowing it can take up to a few million years for those photons to reach her sight. It’s humbling, she notes, knowing just how short of a time humans are on earth.
But it also instills a sense of gratitude, she says, “that I am able to be conscious and make choices and have the agency to fight for the things I believe in.”
And that’s a message she wants to give to younger girls interested in STEM careers: “Go for it. You don’t have to feel like you are qualified enough to just really go for it. You are already enough, and your dreams really do matter. Even if they seem impossible, just shoot for it.”
- Newsroom Guidelines
- Report an Error
More in News

Crime and Public Safety | Firefighters, animal officers rescue locked-out dog from 4th-floor balcony in Irvine

Crime and Public Safety | CHP recovers $300,000 worth of stolen Legos, arrests 4 people in LA, OC
Us helps israel shoot down ‘nearly all’ iran-launched attack drones as biden vows support.

News | Off-limits and tainted, Santa Susana Field Lab superfund site opens to rare tour
The April 8 solar eclipse will bring weird sights, sounds and feelings
The darkening of the sky on April 8 will bring with it a plethora of strange phenomena.

Bailey's beads appear around the moon
- Diamond ring
- Atmospheric manifestation
- Revealing hidden stars and planets
A horned 'devil' may appear!
- Shadow bands
- Weird colors
- Bending light
- Temperature shift
- Animal behavior
You can watch the total solar eclipse live on Space.com . And keep up with all the actions with our total solar eclipse 2024 live updates blog.
On Monday (April 8), the sky over a swathe of North America will briefly darken as the moon covers the sun completely during a total solar eclipse.
For a maximum of 4 minutes and 28 seconds along a 115-mile-wide (185 kilometers) and 10,000-mile-long (16,000 km) path passing through Mexico, the United States and Canada, the moon will completely cover the sun, and the sky will fall dark. And, outside this path of totality , observers will be treated to a partial solar eclipse, which is still a sight to behold.
It's not surprising that our ancient ancestors viewed total solar eclipses with trepidation and fear. They were often thought to be dire portents from the gods, indicating the deities' displeasure — or observations of the sun being consumed by fearsome creatures like dragons, which needed to be scared away with loud noises.
In our current (mostly) scientifically enlightened times, we have abandoned such supernatural explanations. But rejecting the concept of star-eating dragons doesn't mean that the total solar eclipse isn't capable of throwing up some unusual and phenomena that may leave witnesses scratching their heads.
Related: Total solar eclipse 2024: Everything you need to know
Space.com takes you through a brief list of some of the strange phenomena that may distract you as you attempt to take in the most exciting astronomical event of 2024!
Astronomical occurrences

As the moon makes its final approach to the sun in the sky, light will begin streaming through the valleys, mountains, craters , and rough terrain at the edge of the lunar disk. This creates droplets of light at the very edge of the moon's disk called " Bailey's beads ."
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Bailey's beads are named after English astronomer Francis Bailey, who described the phenomenon in 1836. Ironically, Bailey may not actually be the discoverer of Bailey's beads. Edmond Halley made the first recorded observations of Bailey's beads during a solar eclipse on May 3, 1715, also correctly describing their cause.
On April 8, watch out for Bailey's Beads before the moon completely covers the sun , and again as the lunar disk begins to move away from the solar disk.
The sun gives the moon a diamond ring

The appearance of Bailey's beads at the edge of the moon may be accompanied by another striking phenomenon.
A "diamond ring" happens during a total solar eclipse just moments before the point at which the moon completely covers the sun, known as totality. This is caused by the last sunlight streaming through the rugged terrain at the edge of the lunar disk.
During the 2024 total solar eclipse, skywatchers can attempt to observe a rare "double diamond ring" when two prominent points of sunlight appear at the edge of the moon.
Related: The moon: Everything you need to know about Earth's companion
The sun's atmosphere manifests

Normally, when observing the sun, the atmosphere of our star is "washed out" by light flowing from what can roughly be described as the solar surface, the photosphere.
During a total solar eclipse, however, photons from the photosphere are blocked, and the two elements of the solar atmosphere, the outer layer or corona and the inner layer or chromosphere become more visible.
The corona will appear as waving white streamers surrounding the blacked-out solar disk. The chromosphere will appear as a more subtle, thin halo of color, mostly pink and red, closer to the lunar disk. The eclipse may also reveal solar filaments made of plasma and molded by solar magnetic fields extending out from behind the moon.
Hidden stars and planets are revealed

Some skywatchers may be focused on other solar system bodies or stars farther afield than the sun during the April 8 total solar eclipse.
According to Space.com skywatching columnist Joe Rao , some of the planets that may make an appearance during totality, which would usually be hidden in daylight, will be Venus , around 15 degrees to the west of the sun, and Jupiter , 30 degrees east of the star. Other planets that may be visible are Saturn and Mars , which will be 35 degrees and 36 degrees to the west of the sun, respectively. (Your fist held at arm's length covers about 10 degrees of sky.)
For eclipse watchers on the path of totality outside Mexico and Texas, the brightest star over Earth, Sirius, will be over the horizon and should be visible toward the east-southeast. Among the other fainter stars that should become apparent are the Goat Star Capella , high in the east-northeast, and Rigel , lower in the southeast.

Don't panic! We haven't slipped back into medieval fears and superstition; the "horned devil" we are speaking about in this case is Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks . The comet, which can currently be seen in the night skies of the Northern Hemisphere, has a strange "horned aura" resulting from the outflow of its icy material that has resulted in it being nicknamed the " devil comet ."
This faux-satanic space rock visits the inner solar system around every 71 years and will be at its closest to the sun on April 21, 2024. That means Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks will be fairly close to the sun when the moon will obscure it on April 8, according to EarthSky.org .
If it is visible, the comet should appear between the sun and Jupiter, but closer to the gas giant. Whether it can be seen or not on the day of the eclipse will depend on the ferocity of the explosions of material that burst from it, boosting the size of its halo and the brightness of its glow.
Related: A 'horned' comet may be visible during the 2024 total solar eclipse
Strange light effects
Shadow bands sweeep across earth.

Shadow bands are one of the strangest effects associated with solar eclipses. These alternating light and dark bands can sometimes be seen during these events on the ground and buildings in the path of the eclipse.
First occurring around the time of totality, shadow bands initially seem disordered and chaotic but become increasingly well-ordered and more prominent as totality approaches. These bands are caused by atmospheric turbulence over Earth, which causes refraction of and collimation of sunlight when the solar disk is 99% covered.
Shadow bands are tough to image because they are only briefly visible and don't occur everywhere in the path of totality. The 1-inch to 2-inch-wide (2.5 to 5 centimeters) bands slide across the ground and buildings at a pace of around 10 feet (3 m) per second.
Colors look different
During the solar eclipse, many skywatchers will see colors shifting, giving familiar objects unusual hues. This natural shift in color perception is caused by fluctuating light levels resulting from the darkening of the sun.
Colors the human eye sees as rich and vibrant in bright light, like red and orange, become muted compared with blues and greens, which brighten in dim light. The rapid dimming of the sun during a total solar eclipse heightens this phenomenon, called the " Purkinje shift ," making the eclipse a potentially surreal event in which the most familiar objects look almost alien.
Light gets bent!
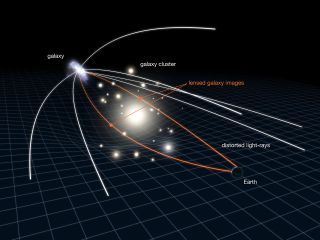
Some scientists will see the total solar eclipse as an opportunity to test one of Albert Einstein 's most revolutionary ideas, general relativity .
This 1915 theory of gravity suggests that massive objects warp the very fabric of space-time . When light passes this warping from a background source, it too is curved, an effect called gravitational lensing . This results in those background sources apparently shifting position in the sky.
When the sun darkens on April 8, scientists have the chance to observe the shift in the position of background stars caused by the mass of our star and its warping effect on space-time.
Eclipses have a long history of being used to verify general relativity. The first experimental verification of the theory, which was not initially widely accepted by the scientific community, came about when two teams of scientists led by Frank Watson Dyson and Arthur Stanley Eddington observed gravitational lensing during the May 1919 total solar eclipse from the African island of Príncipe and the Brazilian town of Sobral.
The natural world shifts
Eclipses are cool.
The sun isn't just a source of light over Earth , it is also our planet's major source of heat. That means that, as the moon covers the sun on April 8, eclipse watchers may suddenly find themselves needing a jacket.
The amount by which the temperature fluctuates during the total solar eclipse will depend strongly on the location from which it is viewed. Temperatures could drop by as little as 5 degrees Fahrenheit (2.8 degrees Celsius) or as much 10 degrees F (5.6 degrees C).
As the moon covers the sun, onlookers may also experience a sudden drop in wind speed. As the moon moves away, winds will pick up again, but they could be blowing in an entirely different direction.
— A 'horned' comet may be visible during the 2024 total solar eclipse
— How photos of the April 8 solar eclipse will help us understand of the sun's atmosphere
— How fast will April's total solar eclipse travel?
Animals act differently

Animal behavior is controlled by many factors, one of which is an internal biological clock that keeps track of a " circadian rhythm ." This rhythm is optimized by light, with diurnal animals prompted to sleep when the sun sets and nocturnal animals prompted to rise at the same time. That means the dimming light of the eclipse and the "false dusk" could prompt the release of hormones related to the sleeping and waking cycle in animals.
Additionally, the drop in temperature could cause a drop in atmospheric pressure that feels like an approaching storm to animals, making them anxious or fearful. Eclipse watchers may also expect to hear a dawn's chorus from birds as the eclipse ends, fooling our feathered friends into believing it is a new day.
During the total solar eclipse, one project that will be attempting to better understand the effect of the eclipse on wildlife is the NASA Soundscapes project. This multisensory approach will see citizen scientists making recordings of the sounds heard as the sky falls dark, and also make written accounts of what is seen, heard, or felt during the event.
Related: Solar eclipse glasses: Where to buy the best, high-quality eyewear
People get emotional

It isn't just animals that will potentially get spooked by the darkening skies of the total solar eclipse eclipse. Humans can also be emotionally affected by these events.
NASA advises that, if skywatchers aren't too busy looking for Bailey's Beads, diamond rings, or shadow bands, they should take a look at the people around them and observe if anyone has a deep emotional response when the sun goes into totality.
Of course, these shifts in emotions are temporary. If you intend to view any eclipse stages, the most important thing to consider is how to safely view it. Looking at the sun without adequate protection at any time is harmful to the eyes, so eclipse watchers should take precautions on April 8.
Sunglasses, regardless of how dark they are, can't protect the eyes from the effects of the sun, so specialized eclipse glasses made from safe solar filter materials will be needed. If skywatchers intend to watch the event with a telescope, special filters will be needed to make this a safe viewing experience.
Our how to observe the sun safely guide tells you everything you need to know about safe solar observations.
Submit your photos! If you capture a photo of the April 8 total solar eclipse or any of these strange effects and would like to share it with Space.com's readers, send photos, videos, comments, and your name, location and content usage permission release to [email protected].
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
'You could feel the energy and wonder': Despite clouds, totality wows crowds during solar eclipse in Syracuse
No, you didn't see a solar flare during the total eclipse — but you may have seen something just as special
This Week In Space podcast: Episode 106 — Space Potpourri!
Most Popular
- 2 Tiny black holes left over from the Big Bang may be prime dark matter suspects
- 3 'You could feel the energy and wonder': Despite clouds, totality wows crowds during solar eclipse in Syracuse
- 4 In a virtual reality universe, upcoming 'JUICE' mission flies by Jupiter's moon Callisto
- 5 Artemis 2 Orion spacecraft starts testing ahead of moon mission with astronauts in 2025 (video)
2044 solar eclipse path: See where in US totality hits in next eclipse
Compared to this year's eclipse, with a path of totality that will cross over 13 states, the 2044 total solar eclipse won't have as quite as broad of a reach. here's what to know:.

Millions of Americans are by now eagerly awaiting the next total solar eclipse , which is only hours away from passing over a large swath of the continent .
But when the celestial event comes and goes, the awe-inspiring impression it leaves on skygazers may leave them with one question: "When can we see that again?"
Unfortunately, we'll have to wait awhile – this sort of spectacular astral phenomenon doesn't happen very often . Here's what we know about the next total solar eclipse that will cross over the contiguous U.S.
Solar eclipse glasses: What to know about glasses, safe viewing before the solar eclipse
When will the next total solar eclipse happen in the U.S?
Only seven years have passed since Americans had the opportunity to view a total solar eclipse, a relatively rare celestial event in which the moon appears to us here on Earth to completely block the sun.
The resulting fleeting moments of darkness can last for minutes or just mere seconds and is known as " totality ," whereby the sun's outermost layer known as the corona makes a rare appearance.
Today's total solar eclipse , the first in North America since 2017, will travel over portions of northern Mexico, thousands of miles of the U.S. and the maritime provinces of Canada, according to NASA . According to astronomers, this eclipse will be brighter, will last longer and will be visible to more people than the last one in North America.
It's also the last one for 20 years in the United States.
After Monday, the next total solar eclipse viewable from the lower 48 states will be on Aug. 23, 2044.
2044 total solar eclipse path of totality
Compared to this year's eclipse, with a path of totality that will cross over 13 states, the 2044 total solar eclipse won't have as quite as broad of a reach .
The Planetary Society, a nonprofit involved in research, public outreach and political space advocacy, says that during the 2044 eclipse, the path of totality will only touch three states.
The eclipse will begin in Greenland, sweep through Canada and end around sunset in Montana, North Dakota and South Dakota.
It's not too early to start thinking about where you want to witness it. According to whenisthenexteclipse.com , Americans may want to make sure their passports up to date.
The place to be will likely be Banff National Park in Alberta and Jasper National Park , with Calgary and Edmonton also within the path of totality.
What to know about the 2033 eclipse in Alaska
Outside of the "lower 48," Alaska is set to experience a total solar eclipse much sooner.
On March 30, 2033, a total solar eclipse will occur in Russia and cross over Alaska, according to nationaleclipse.com . The maximum duration of totality for this eclipse will be 2 minutes and 37 seconds.
Contributing: Mary Walrath-Holdridge and Gabe Hauari
Eric Lagatta covers breaking and trending news for USA TODAY. Reach him at [email protected]

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.
NASA’s PACE Data on Ocean, Atmosphere, Climate Now Available

Altitude Chamber Gets Upgrade for Artemis II, Spacecraft Testing Begins

NASA Next-Generation Solar Sail Boom Technology Ready for Launch
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia
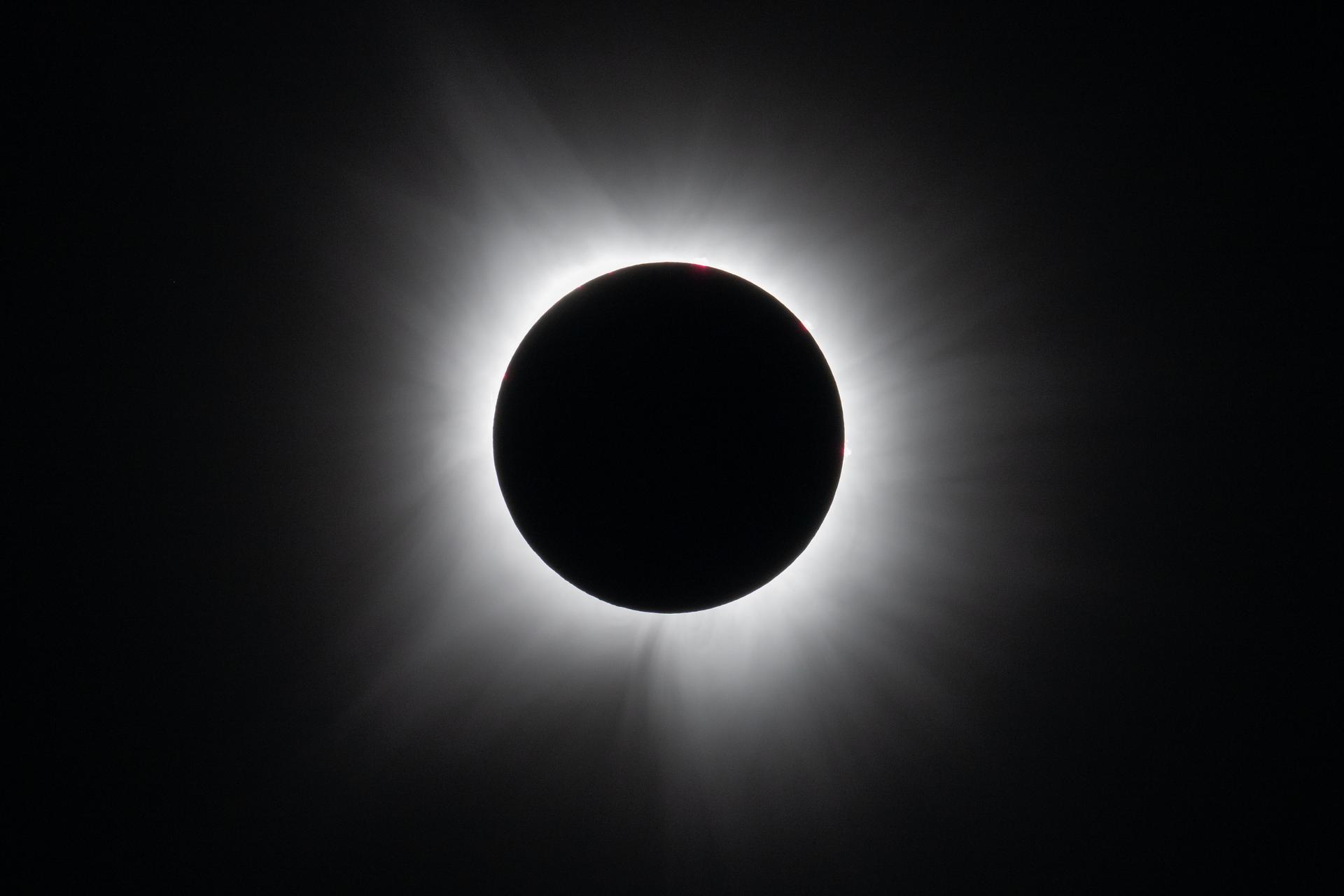

The April 8 Total Solar Eclipse: Through the Eyes of NASA

NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test Mission Overview

Hubble Spots a Galaxy Hidden in a Dark Cloud

NASA Shares Medical Expertise with New Space Station Partners

From NASA’s First Astronaut Class to Artemis II: The Importance of Military Jet Pilot Experience

The Ocean Touches Everything: Celebrate Earth Day with NASA
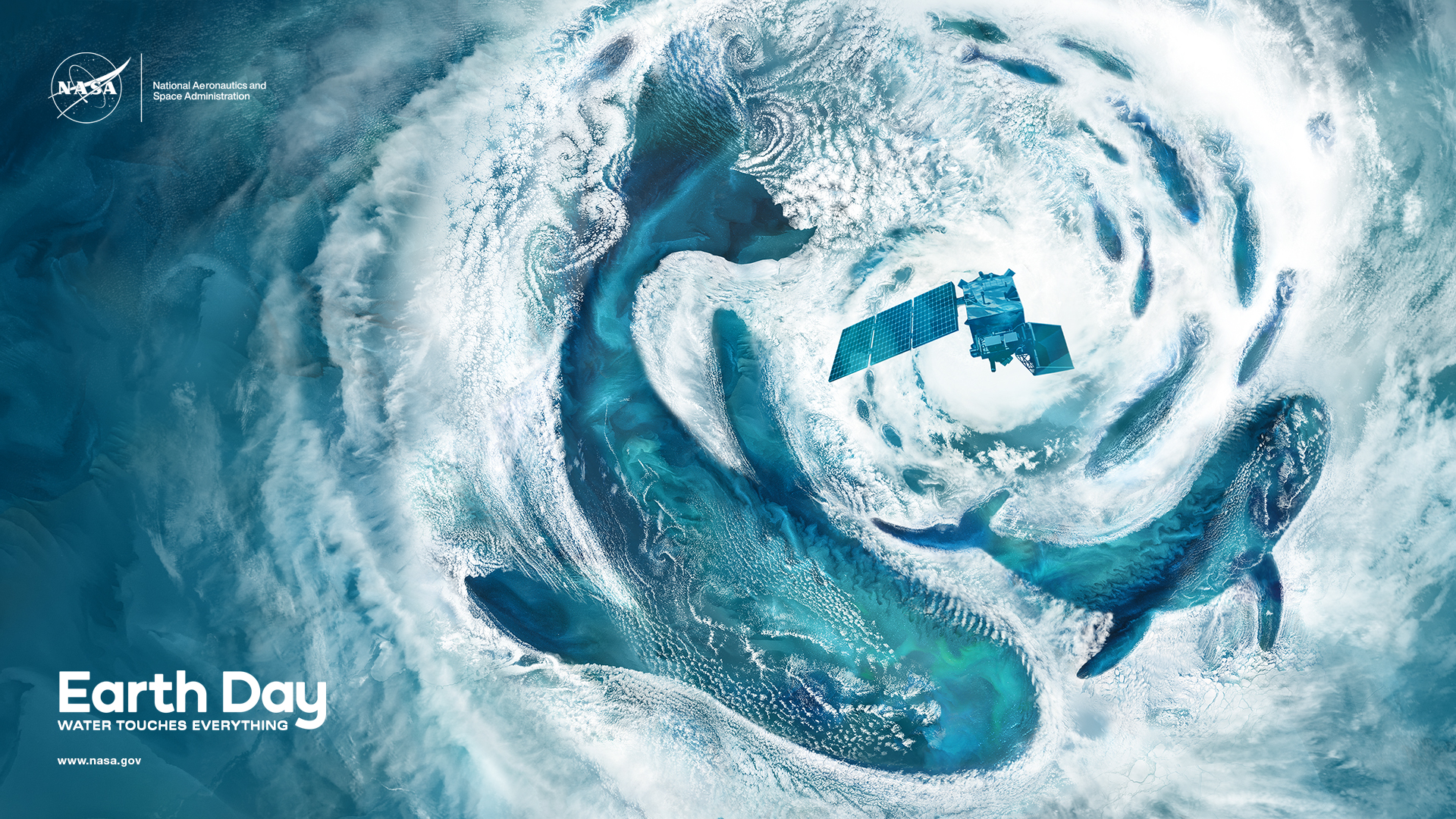

Earth Day Poster 2024

Media Get Close-Up of NASA’s Jupiter-Bound Europa Clipper

More Than 36,000 Volunteers Helped Do NASA Eclipse Science

NASA’s TESS Temporarily Pauses Science Observations

NASA Names Finalists of the Power to Explore Challenge
Earth Day 2024: Posters and Virtual Backgrounds

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles

ARMD Solicitations
NASA Noise Prediction Tool Supports Users in Air Taxi Industry

Tech Today: Folding NASA Experience into an Origami Toolkit
NASA’s SERT II: ‘A Genuine Space Success Story’

NASA Partnerships Bring 2024 Total Solar Eclipse to Everyone

Shawnta M. Ball Turns Obstacles into Opportunities in Goddard’s Education Office
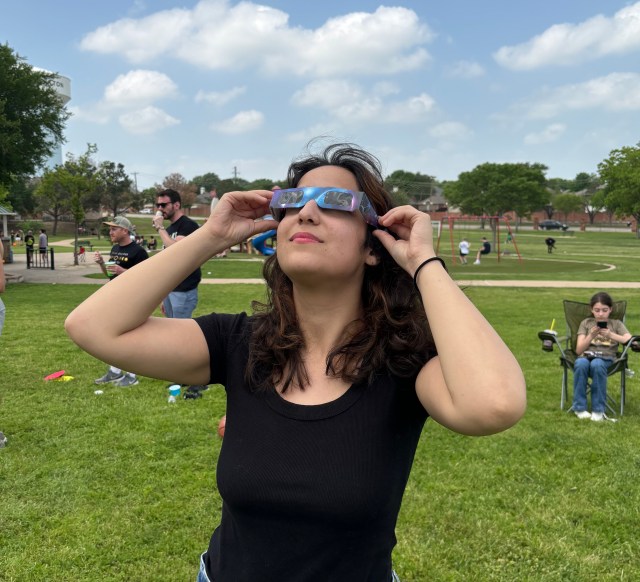

A Langley Intern Traveled 1,340 Miles to View a Total Solar Eclipse. Here’s What She Saw.

La presentación del X-59 de la NASA personifica la tradición aeronáutica
Extreme space facts.

Educators, Students
Grade Levels
Grades K-4, Grades 5-8, Grades 9-12
Space Science, Solar System and Planets
Posters, Read About It
Did you know giant, spinning storms on Neptune are big enough to swallow the whole Earth? Find this and other fun facts about the solar system on this downloadable mini poster. Extreme Space Facts (PDF)
Watch CBS News
Solar eclipse maps show 2024 totality path, peak times and how much of the eclipse people could see across the U.S.
By Aliza Chasan
Updated on: April 9, 2024 / 5:00 AM EDT / CBS News
A total solar eclipse crossed North America Monday with parts of 15 U.S. states within the path of totality. Maps show where and when astronomy fans could see the big event as skies darkened in the middle of the day Monday, April 8.
The total eclipse first appeared along Mexico's Pacific Coast at around 11:07 a.m. PDT, then traveled across a swath of the U.S., from Texas to Maine, and into Canada.
About 31.6 million people live in the path of totality , the area where the moon fully blocked out the sun , according to NASA. The path ranged between 108 and 122 miles wide. An additional 150 million people live within 200 miles of the path of totality.
Solar eclipse path of totality map for 2024

The total solar eclipse started over the Pacific Ocean, and the first location in continental North America that experienced totality was Mexico's Pacific Coast, around 11:07 a.m. PDT, according to NASA. From there, the path continued into Texas, crossing more than a dozen states before the eclipse enters Canada in southern Ontario. The eclipse exited continental North America at around 5:16 p.m. NDT from Newfoundland, Canada.
The path of totality included portions of the following states:
- Pennsylvania
- New Hampshire
Small parts of Tennessee and Michigan also experienced the total solar eclipse.
Several major cities across the U.S. were included in the eclipse's path of totality, while many others saw a partial eclipse. These were some of the best major cities for eclipse viewing — though the weather was a factor :
- San Antonio, Texas (partially under the path)
- Austin, Texas
- Waco, Texas
- Dallas, Texas
- Little Rock, Arkansas
- Indianapolis, Indiana
- Dayton, Ohio
- Cleveland, Ohio
- Buffalo, New York
- Rochester, New York
- Syracuse, New York
- Burlington, Vermont
Map of when the solar eclipse reached totality across its path
The eclipse began in the U.S. as a partial eclipse beginning at 12:06 p.m. CDT near Eagle Pass, Texas, before progressing to totality by about 1:27 p.m. CDT and then moving along its path to the northeast over the following few hours.
NASA shared times for several cities in the path of totality across the U.S. People could have also checked their ZIP code on NASA's map to see when the eclipse was to reach them if they were on, or near, the path of totality — or if they saw a partial eclipse instead.
How much of the eclipse did people see if they live outside the totality path?
While the April 8 eclipse covered a wide swath of the U.S., outside the path of totality observers may have spotted a partial eclipse, where the moon covers some, but not all, of the sun, according to NASA. The closer they were to the path of totality, the larger the portion of the sun that was hidden.
NASA allowed viewers to input a ZIP code and see how much of the sun was to be covered in their locations.
Could there be cloud cover be during the solar eclipse?
Some areas along the path of totality had a higher likelihood of cloud cover that could interfere with viewing the eclipse. Here is a map showing the historical trends in cloud cover this time of year.
You could have checked the latest forecast for your location with our partners at The Weather Channel .

Where did the solar eclipse reach totality for the longest?
Eclipse viewers near Torreón, Mexico, got to experience totality for the longest. Totality there lasted 4 minutes, 28 seconds, according to NASA.
Most places along the centerline of the path of totality saw a totality duration of between 3.5 and 4 minutes, according to NASA. Some places in the U.S. came close to the maximum; Kerrville, Texas, had a totality duration of 4 minutes, 24 seconds.
What is the path of totality for the 2044 solar eclipse?
The next total solar eclipse that will be visible from the contiguous U.S. will be on Aug. 23, 2044.
Astronomy fans in the U.S. will have far fewer opportunities to see the 2044 eclipse they had on April 8. NASA has not yet made maps available for the 2044 eclipse but, according to The Planetary Society , the path of totality will only touch three states.
The 2024 eclipse will start in Greenland, pass over Canada and end as the sun sets in Montana, North Dakota and South Dakota, according to the Planetary Society.

Aliza Chasan is a digital producer at 60 Minutes and CBSNews.com. She has previously written for outlets including PIX11 News, The New York Daily News, Inside Edition and DNAinfo. Aliza covers trending news, often focusing on crime and politics.
More from CBS News

Here's how to get a tax extension from the IRS in 2024

Truck plows into Texas DPS office in "intentional" act, killing 1, officials say

TSA found more than 1,500 guns at airport checkpoints in 1st quarter of 2024

"Sunday Morning" archives: Impressionism at 150

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about the most incredible, awe-inspiring and unbelievable facts about space, from the hottest planet in the solar system to the largest known asteroid. Discover how sound waves, life, stars, comets, planets and more are affected by the vacuum of space.
Learn about the history, definition, and facts of space exploration, the investigation of the universe beyond Earth's atmosphere. Explore the achievements, motivations, and challenges of spaceflight, from Sputnik to the Hubble Space Telescope.
Everything you need to know about space travel (almost) - BBC Science Focus Magazine.
Space Travel. The path to the Moon, Mars, and beyond requires technologies to get us where we need to go quickly, safely and efficiently. Space travel includes launch and in-space propulsion systems, cryogenic fluid management, and thermal management, as well as navigation and landing systems to get our supplies, equipment, and robotic or human ...
In addition to launching the first artificial satellite, the first dog in space, and the first human in space, the Soviet Union achieved other space milestones ahead of the United States. These milestones included Luna 2, which became the first human-made object to hit the Moon in 1959. Soon after that, the U.S.S.R. launched Luna 3.
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is currently carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration is conducted both by uncrewed robotic space probes and human spaceflight.Space exploration, like its classical form astronomy, is one of the main sources for space science.
The large modules and other pieces of the station were delivered on 42 assembly flights, 37 on the U.S. space shuttles and five on Russian Proton/Soyuz rockets. The space station is 356 feet (109 meters) end-to-end, one yard shy of the full length of an American football field including the end zones.
Learn about the oldest and largest water cloud, the shrinking red spot on Jupiter, the two-tone moon Iapetus, and more amazing space facts. Discover how NASA's Perseverance rover landed on Mars and what it will search for there.
Space exploration unites the world to inspire the next generation, make ground-breaking discoveries, and create new opportunities. Technologies and missions we develop for human spaceflight have thousands of applications on Earth, boosting the economy, creating new career paths, and advancing everyday technologies all around us.
Space exploration - History, Technology, Benefits: Since ancient times, people around the world have studied the heavens and used their observations and explanations of astronomical phenomena for both religious and practical purposes. Some dreamed of leaving Earth to explore other worlds. For example, the French satirist Cyrano de Bergerac in the 17th century wrote Histoire comique des états ...
6. Alan Shepard was first for the U.S. Shepard was a naval pilot and one of seven people chosen for Project Mercury, NASA's first space program. On May 5, 1961, he became the first American and ...
Space tourism is recreational space travel, either on established government-owned vehicles or on a growing number of vehicles fielded by private companies. ... You'll find on this page a collection of facts about everything from the size of the universe to the business of space. All of these facts and numbers add up to a vivid portrait of space.
History of Space Travel. Learn about the history of humans traveling into space. The first earthling to orbit our planet was just two years old, plucked from the streets of Moscow barely more than a week before her historic launch. Her name was Laika. She was a terrier mutt and by all accounts a good dog. Her 1957 flight paved the way for space ...
NASA aims to travel to the moon again—and beyond. Here's a look at the 21st-century race to send humans into space. Private spaceflight is not a new concept. In the United States, commercial ...
Learn about the history, achievements, and challenges of space travel from the Soviet Union, the United States, and other countries. Discover the first human in space, the first space tourist, the first person on the moon, and more amazing facts about space exploration.
The History of Space Travel Timeline. Albert II became the first monkey in space on June 14, 1949, in a specially adapted US V2 rocket. To travel into the unknown of space is a dream for so many children and adults alike, although one that very few will ever reach. Throughout time so many countries, and now private companies, across the world ...
The 12 astounding facts about space travel demonstrate the incredible achievements and challenges faced by astronauts as they journey beyond our planet's atmosphere. Conclusion. In conclusion, space travel is an extraordinary and fascinating field that continues to captivate our imaginations. The facts presented here highlight some of the awe ...
NASA One Step Closer to Fueling Space Missions with Plutonium-238. 2 min read. The recent shipment of heat source plutonium-238 from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) Oak Ridge National Laboratory to its…. Article.
Here's what the next year has lined up for space. Moon landings. A lunar lander will already be on its way when 2023 begins. Launched in December on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, the private ...
Today's space shuttles have special ceramic tiles that help absorb some of the heat, keeping the astronauts safe during re-entry. In 1957, the Russian space dog, Laika, orbited the Earth. Fun Facts about Space Travel for Kids. One space shuttle launch costs $450 million. The German V2 was the first rocket to reach space in 1942.
The Milky Way galaxy is 105,700 light-years wide. It would take a modern spacecraft 450,000,000 years to travel to the center of our galaxy! You can read more unbelievable space facts with this list of Milky Way facts! The Sun weighs about 330,000 times more than Earth.
Space travel is a dream for the Corona native who grew up going to Little Saigon; she put it on hold after she was sexually assaulted in college.
The April 8 solar eclipse will bring weird sights, sounds and feelings. The darkening of the sky on April 8 will bring with it a plethora of strange phenomena. A horned 'devil' may appear! You can ...
Travel to the Moon, Mars, and beyond will require new systems to provide medical care far from Earth. Learn more about the changes humans may undergo during spaceflight, as well as the steps NASA takes to keep astronauts healthy and safe. NASA astronaut and Flight Engineer Andrew Morgan flexes his muscles in an airlock of the space station.
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between Earth and the sun, completely blocking the sun's face. Those within the path of totality will see a total solar eclipse. People outside ...
The Planetary Society, a nonprofit involved in research, public outreach and political space advocacy, says that during the 2044 eclipse, the path of totality will only touch three states. The ...
Posters, Read About It. Did you know giant, spinning storms on Neptune are big enough to swallow the whole Earth? Find this and other fun facts about the solar system on this downloadable mini poster. Extreme Space Facts (PDF) Download this mini poster full of fun facts about the solar system.
A total solar eclipse crossed North America Monday with parts of 15 U.S. states within the path of totality. Maps show where and when astronomy fans could see the big event as skies darkened in ...