

10 Economic impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
There are many economic impacts of tourism, and it is important that we understand what they are and how we can maximise the positive economic impacts of tourism and minimise the negative economic impacts of tourism.
Many argue that the tourism industry is the largest industry in the world. While its actual value is difficult to accurately determine, the economic potential of the tourism industry is indisputable. In fact, it is because of the positive economic impacts that most destinations embark on their tourism journey.
There is, however, more than meets the eye in most cases. The positive economic impacts of tourism are often not as significant as anticipated. Furthermore, tourism activity tends to bring with it unwanted and often unexpected negative economic impacts of tourism.
In this article I will discuss the importance of understanding the economic impacts of tourism and what the economic impacts of tourism might be. A range of positive and negative impacts are discussed and case studies are provided.
At the end of the post I have provided some additional reading on the economic impacts of tourism for tourism stakeholders , students and those who are interested in learning more.
Foreign exchange earnings
Contribution to government revenues, employment generation, contribution to local economies, development of the private sector, infrastructure cost, increase in prices, economic dependence of the local community on tourism, foreign ownership and management, economic impacts of tourism: conclusion, further reading on the economic impacts of tourism, the economic impacts of tourism: why governments invest.
Tourism brings with it huge economic potential for a destination that wishes to develop their tourism industry. Employment, currency exchange, imports and taxes are just a few of the ways that tourism can bring money into a destination.
In recent years, tourism numbers have increased globally at exponential rates, as shown in the World Tourism Organisation data below.
There are a number of reasons for this growth including improvements in technology, increases in disposable income, the growth of budget airlines and consumer desires to travel further, to new destinations and more often.

Here are a few facts about the economic importance of the tourism industry globally:
- The tourism economy represents 5 percent of world GDP
- Tourism contributes to 6-7 percent of total employment
- International tourism ranks fourth (after fuels, chemicals and automotive products) in global exports
- The tourism industry is valued at US$1trillion a year
- Tourism accounts for 30 percent of the world’s exports of commercial services
- Tourism accounts for 6 percent of total exports
- 1.4billion international tourists were recorded in 2018 (UNWTO)
- In over 150 countries, tourism is one of five top export earners
- Tourism is the main source of foreign exchange for one-third of developing countries and one-half of less economically developed countries (LEDCs)
There is a wealth of data about the economic value of tourism worldwide, with lots of handy graphs and charts in the United Nations Economic Impact Report .
In short, tourism is an example of an economic policy pursued by governments because:
- it brings in foreign exchange
- it generates employment
- it creates economic activity
Building and developing a tourism industry, however, involves a lot of initial and ongoing expenditure. The airport may need expanding. The beaches need to be regularly cleaned. New roads may need to be built. All of this takes money, which is usually a financial outlay required by the Government.
For governments, decisions have to be made regarding their expenditure. They must ask questions such as:
How much money should be spent on the provision of social services such as health, education, housing?
How much should be spent on building new tourism facilities or maintaining existing ones?
If financial investment and resources are provided for tourism, the issue of opportunity costs arises.
By opportunity costs, I mean that by spending money on tourism, money will not be spent somewhere else. Think of it like this- we all have a specified amount of money and when it runs out, it runs out. If we decide to buy the new shoes instead of going out for dinner than we might look great, but have nowhere to go…!
In tourism, this means that the money and resources that are used for one purpose may not then be available to be used for other purposes. Some destinations have been known to spend more money on tourism than on providing education or healthcare for the people who live there, for example.
This can be said for other stakeholders of the tourism industry too.
There are a number of independent, franchised or multinational investors who play an important role in the industry. They may own hotels, roads or land amongst other aspects that are important players in the overall success of the tourism industry. Many businesses and individuals will take out loans to help fund their initial ventures.
So investing in tourism is big business, that much is clear. What what are the positive and negative impacts of this?

Positive economic impacts of tourism
So what are the positive economic impacts of tourism? As I explained, most destinations choose to invest their time and money into tourism because of the positive economic impacts that they hope to achieve. There are a range of possible positive economic impacts. I will explain the most common economic benefits of tourism below.

One of the biggest benefits of tourism is the ability to make money through foreign exchange earnings.
Tourism expenditures generate income to the host economy. The money that the country makes from tourism can then be reinvested in the economy. How a destination manages their finances differs around the world; some destinations may spend this money on growing their tourism industry further, some may spend this money on public services such as education or healthcare and some destinations suffer extreme corruption so nobody really knows where the money ends up!
Some currencies are worth more than others and so some countries will target tourists from particular areas. I remember when I visited Goa and somebody helped to carry my luggage at the airport. I wanted to give them a small tip and handed them some Rupees only to be told that the young man would prefer a British Pound!
Currencies that are strong are generally the most desirable currencies. This typically includes the British Pound, American, Australian and Singapore Dollar and the Euro .
Tourism is one of the top five export categories for as many as 83% of countries and is a main source of foreign exchange earnings for at least 38% of countries.
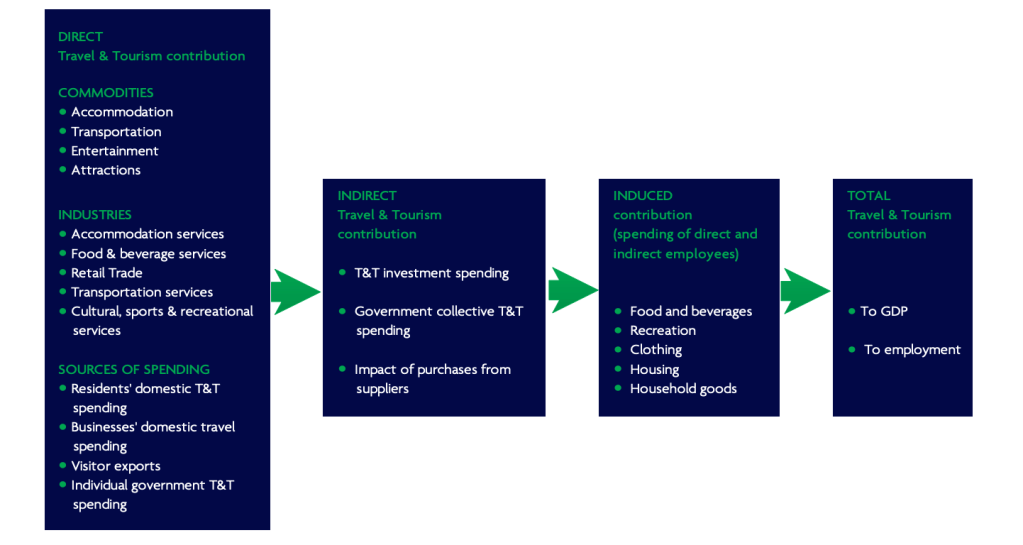
Tourism can help to raise money that it then invested elsewhere by the Government. There are two main ways that this money is accumulated.
Direct contributions are generated by taxes on incomes from tourism employment and tourism businesses and things such as departure taxes.
Taxes differ considerably between destinations. I will never forget the first time that I was asked to pay a departure tax (I had never heard of it before then), because I was on my way home from a six month backpacking trip and I was almost out of money!
Japan is known for its high departure taxes. Here is a video by a travel blogger explaining how it works.
According to the World Tourism Organisation, the direct contribution of Travel & Tourism to GDP in 2018 was $2,750.7billion (3.2% of GDP). This is forecast to rise by 3.6% to $2,849.2billion in 2019.
Indirect contributions come from goods and services supplied to tourists which are not directly related to the tourism industry.
Take food, for example. A tourist may buy food at a local supermarket. The supermarket is not directly associated with tourism, but if it wasn’t for tourism its revenues wouldn’t be as high because the tourists would not shop there.
There is also the income that is generated through induced contributions . This accounts for money spent by the people who are employed in the tourism industry. This might include costs for housing, food, clothing and leisure Activities amongst others. This will all contribute to an increase in economic activity in the area where tourism is being developed.
The rapid expansion of international tourism has led to significant employment creation. From hotel managers to theme park operatives to cleaners, tourism creates many employment opportunities. Tourism supports some 7% of the world’s workers.
There are two types of employment in the tourism industry: direct and indirect.
Direct employment includes jobs that are immediately associated with the tourism industry. This might include hotel staff, restaurant staff or taxi drivers, to name a few.
Indirect employment includes jobs which are not technically based in the tourism industry, but are related to the tourism industry. Take a fisherman, for example. He does not have any contact of dealings with tourists. BUT he does sell his fish to the hotel which serves tourists. So he is indirectly employed by the tourism industry, because without the tourists he would not be supplying the fish to the hotel.
It is because of these indirect relationships, that it is very difficult to accurately measure the economic value of tourism.
It is also difficult to say how many people are employed, directly and indirectly, within the tourism industry.
Furthermore, many informal employments may not be officially accounted for. Think tut tut driver in Cambodia or street seller in The Gambia – these people are not likely to be registered by the state and therefore their earnings are not declared.
It is for this reason that some suggest that the actual economic benefits of tourism may be as high as double that of the recorded figures!
All of the money raised, whether through formal or informal means, has the potential to contribute to the local economy.
If sustainable tourism is demonstrated, money will be directed to areas that will benefit the local community most.
There may be pro-poor tourism initiatives (tourism which is intended to help the poor) or volunteer tourism projects.
The government may reinvest money towards public services and money earned by tourism employees will be spent in the local community. This is known as the multiplier effect.
The multiplier effect relates to spending in one place creating economic benefits elsewhere. Tourism can do wonders for a destination in areas that may seem to be completely unrelated to tourism, but which are actually connected somewhere in the economic system.

Let me give you an example.
A tourist buys an omelet and a glass of orange juice for their breakfast in the restaurant of their hotel. This simple transaction actually has a significant multiplier effect. Below I have listed just a few of the effects of the tourist buying this breakfast.
The waiter is paid a salary- he spends his salary on schooling for his kids- the school has more money to spend on equipment- the standard of education at the school increases- the kids graduate with better qualifications- as adults, they secure better paying jobs- they can then spend more money in the local community…
The restaurant purchases eggs from a local farmer- the farmer uses that money to buy some more chickens- the chicken breeder uses that money to improve the standards of their cages, meaning that the chickens are healthier, live longer and lay more eggs- they can now sell the chickens for a higher price- the increased money made means that they can hire an extra employee- the employee spends his income in the local community…
The restaurant purchase the oranges from a local supplier- the supplier uses this money to pay the lorry driver who transports the oranges- the lorry driver pays road tax- the Government uses said road tax income to fix pot holes in the road- the improved roads make journeys quicker for the local community…
So as you can see, that breakfast that the tourist probably gave not another thought to after taking his last mouthful of egg, actually had the potential to have a significant economic impact on the local community!

The private sector has continuously developed within the tourism industry and owning a business within the private sector can be extremely profitable; making this a positive economic impact of tourism.
Whilst many businesses that you will come across are multinational, internationally-owned organisations (which contribute towards economic leakage ).
Many are also owned by the local community. This is the case even more so in recent years due to the rise in the popularity of the sharing economy and the likes of Airbnb and Uber, which encourage the growth of businesses within the local community.
Every destination is different with regards to how they manage the development of the private sector in tourism.
Some destinations do not allow multinational organisations for fear that they will steal business and thus profits away from local people. I have seen this myself in Italy when I was in search of a Starbucks mug for my collection , only to find that Italy has not allowed the company to open up any shops in their country because they are very proud of their individually-owned coffee shops.
Negative economic impacts of tourism
Unfortunately, the tourism industry doesn’t always smell of roses and there are also several negative economic impacts of tourism.
There are many hidden costs to tourism, which can have unfavourable economic effects on the host community.
Whilst such negative impacts are well documented in the tourism literature, many tourists are unaware of the negative effects that their actions may cause. Likewise, many destinations who are inexperienced or uneducated in tourism and economics may not be aware of the problems that can occur if tourism is not management properly.
Below, I will outline the most prominent negative economic impacts of tourism.

Economic leakage in tourism is one of the major negative economic impacts of tourism. This is when money spent does not remain in the country but ends up elsewhere; therefore limiting the economic benefits of tourism to the host destination.
The biggest culprits of economic leakage are multinational and internationally-owned corporations, all-inclusive holidays and enclave tourism.
I have written a detailed post on the concept of economic leakage in tourism, you can take a look here- Economic leakage in tourism explained .

Another one of the negative economic impacts of tourism is the cost of infrastructure. Tourism development can cost the local government and local taxpayers a great deal of money.
Tourism may require the government to improve the airport, roads and other infrastructure, which are costly. The development of the third runway at London Heathrow, for example, is estimated to cost £18.6billion!
Money spent in these areas may reduce government money needed in other critical areas such as education and health, as I outlined previously in my discussion on opportunity costs.

One of the most obvious economic impacts of tourism is that the very presence of tourism increases prices in the local area.
Have you ever tried to buy a can of Coke in the supermarket in your hotel? Or the bar on the beachfront? Walk five minutes down the road and try buying that same can in a local shop- I promise you, in the majority of cases you will see a BIG difference In cost! (For more travel hacks like this subscribe to my newsletter – I send out lots of tips, tricks and coupons!)
Increasing demand for basic services and goods from tourists will often cause price hikes that negatively impact local residents whose income does not increase proportionately.
Tourism development and the related rise in real estate demand may dramatically increase building costs and land values. This often means that local people will be forced to move away from the area that tourism is located, known as gentrification.
Taking measures to ensure that tourism is managed sustainably can help to mitigate this negative economic impact of tourism. Techniques such as employing only local people, limiting the number of all-inclusive hotels and encouraging the purchasing of local products and services can all help.
Another one of the major economic impacts of tourism is dependency. Many countries run the risk of becoming too dependant on tourism. The country sees $ signs and places all of its efforts in tourism. Whilst this can work out well, it is also risky business!
If for some reason tourism begins to lack in a destination, then it is important that the destination has alternative methods of making money. If they don’t, then they run the risk of being in severe financial difficulty if there is a decline in their tourism industry.
In The Gambia, for instance, 30% of the workforce depends directly or indirectly on tourism. In small island developing states, percentages can range from 83% in the Maldives to 21% in the Seychelles and 34% in Jamaica.
There are a number of reasons that tourism could decline in a destination.
The Gambia has experienced this just recently when they had a double hit on their tourism industry. The first hit was due to political instability in the country, which has put many tourists off visiting, and the second was when airline Monarch went bust, as they had a large market share in flights to The Gambia.
Other issues that could result in a decline in tourism includes economic recession, natural disasters and changing tourism patterns. Over-reliance on tourism carries risks to tourism-dependent economies, which can have devastating consequences.

The last of the negative economic impacts of tourism that I will discuss is that of foreign ownership and management.
As enterprise in the developed world becomes increasingly expensive, many businesses choose to go abroad. Whilst this may save the business money, it is usually not so beneficial for the economy of the host destination.
Foreign companies often bring with them their own staff, thus limiting the economic impact of increased employment. They will usually also export a large proportion of their income to the country where they are based. You can read more on this in my post on economic leakage in tourism .
As I have demonstrated in this post, tourism is a significant economic driver the world over. However, not all economic impacts of tourism are positive. In order to ensure that the economic impacts of tourism are maximised, careful management of the tourism industry is required.
If you enjoyed this article on the economic impacts of tourism I am sure that you will love these too-
- Environmental impacts of tourism
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
- 23 Types of Water Transport To Keep You Afloat
Liked this article? Click to share!
- Open access
- Published: 05 January 2021
The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: a panel cointegration analysis
- Haroon Rasool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0083-4553 1 ,
- Shafat Maqbool 2 &
- Md. Tarique 1
Future Business Journal volume 7 , Article number: 1 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
121k Accesses
91 Citations
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Tourism has become the world’s third-largest export industry after fuels and chemicals, and ahead of food and automotive products. From last few years, there has been a great surge in international tourism, culminates to 7% share of World’s total exports in 2016. To this end, the study attempts to examine the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth by using the panel data over the period 1995–2015 for five BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) countries. The results of panel ARDL cointegration test indicate that tourism, financial development and economic growth are cointegrated in the long run. Further, the Granger causality analysis demonstrates that the causality between inbound tourism and economic growth is bi-directional, thus validates the ‘feedback-hypothesis’ in BRICS countries. The study suggests that BRICS countries should promote favorable tourism policies to push up the economic growth and in turn economic growth will positively contribute to international tourism.
Introduction
World Tourism Day 2015 was celebrated around the theme ‘One Billion Tourists; One Billion Opportunities’ highlighting the transformative potential of one billion tourists. With more than one billion tourists traveling to an international destination every year, tourism has become a leading economic sector, contributing 9.8% of global GDP and represents 7% of the world’s total exports [ 59 ]. According to the World Tourism Organization, the year 2013 saw more than 1.087 billion Foreign Tourist Arrivals and US $1075 billion foreign tourism receipts. The contribution of travel and tourism to gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to reach 10.8% at the end of 2026 [ 61 ]. Representing more than just economic strength, these figures exemplify the vast potential of tourism, to address some of the world´s most pressing challenges, including socio-economic growth and inclusive development.
Developing countries are emerging as the important players, and increasingly aware of their economic potential. Once essentially excluded from the tourism industry, the developing world has now become its major growth area. These countries majorly rely on tourism for their foreign exchange reserves. For the world’s forty poorest countries, tourism is the second-most important source of foreign exchange after oil [ 37 ].
The BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) countries have emerged as a potential bloc in the developing countries which caters the major tourists from developed countries. Tourism becomes major focus at BRICS Xiamen Summit 2017 held in China. These countries have robust growth rate, and are focal destinations for global tourists. During 1990 to 2014, these countries stride from 11% of the world’s GDP to almost 30% [ 17 ]. Among BRICS countries, China is ranked as an important destination followed by Brazil, Russia, India and South Africa [ 60 ].
The importance of inbound tourism has grown exponentially, because of its growing contribution to the economic growth in the long run. It enhances economic growth by augmenting the foreign exchange reserves [ 38 ], stimulating investments in new infrastructure, human capital and increases competition [ 9 ], promoting industrial development [ 34 ], creates jobs and hence to increase income [ 34 ], inbound tourism also generates positive externalities [ 1 , 14 ] and finally, as economy grows, one can argue that growth in GDP could lead to further increase in international tourism [ 11 ].
The tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) proposed by Balaguer and Cantavella-Jorda [ 3 ], states that expansion of international tourism activities exerts economic growth, hence offering a theoretical and empirical link between inbound tourism and economic growth. Theoretically, the TLGH was directly derived from the export-led growth hypothesis (ELGH) that postulates that economic growth can be generated not only by increasing the amount of labor and capital within the economy, but also by expanding exports.
The ‘new growth theory,’ developed by Balassa [ 4 ], suggests that export expansion can trigger economic growth, because it promotes specialization and raises factors productivity by increasing competition, creating positive externalities by advancing the dispersal of specialized information and abilities. Exports also enhance economic growth by increasing the level of investment. International tourism is considered as a non-standard type of export, as it indicates a source of receipts and consumption in situ. Given the difficulties in measuring tourism activity, the economic literature tends to focus on primary and manufactured product exports, hence neglecting this economic sector. Analogous to the ELGH, the TLGH analyses the possible temporal relationship between tourism and economic growth, both in the short and long run. The question is whether tourism activity leads to economic growth or, alternatively, economic expansion drives tourism growth, or indeed a bi-directional relationship exists between the two variables.
To further substantiate the nexus, the study will investigate the plausible linkages between economic growth and international tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. Financial markets are considered a key factor in producing strong economic growth, because they contribute to economic efficiency by diverting financial funds from unproductive to productive uses. The origin of this role of financial development may is traced back to the seminal work of Schumpeter [ 50 ]. In his study, Schumpeter points out that the banking system is the crucial factor for economic growth due to its role in the allocation of savings, the encouragement of innovation, and the funding of productive investments. Early works, such as Goldsmith [ 18 ], McKinnon [ 39 ] and Shaw [ 51 ] put forward considerable evidence that financial development enhances growth performance of countries. The importance of financial development in BRICS economies is reflected by the establishment of the ‘New Development Bank’ aimed at financing infrastructure and sustainable development projects in these and other developing countries. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no attempt has been made so far to investigate the long-run relationship Footnote 1 between tourism, financial development and economic growth in case of BRICS countries. Hence, the present study is an attempt to fill the gap in the existing literature.
Review of past studies
From last few decades there has been a surge in the research related to tourism-growth nexus. The importance of growth and development and its determinants has been studied extensively both in developed and developing countries. Extant literature has recognized tourism as an important determinant of economic growth. The importance of tourism has grown exponentially, courtesy to its manifold advantages in form of employment, foreign exchange production household income and government revenues through multiplier effects, improvements in the balance of payments and growth in the number of tourism-promoted government policies [ 21 , 41 , 53 ]. Empirical findings on tourism and economic development have produced mixed finding and sometimes conflicting results despite the common choice of time series techniques as a research methodology. On empirical grounds, four hypotheses have been explored to determine the link between tourism and economic growth [ 12 ]. The first two hypotheses present an account on the unidirectional causality between the two variables, either from tourism to economic growth (Tourism-led economic growth hypothesis-TLGH) or its reserve (economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis-EDTH). The other two hypotheses support the existence of bi-directional hypothesis, (bi-directional causality hypothesis-BC) or that there is no relationship at all (no causality hypothesis-NC), respectively. According to TLEG hypothesis, tourism creates an array of benefits which spillover though multiple routes to promote the economic growth [ 55 ]. In particular, it is believed that tourism (1) increases foreign exchange earnings, which in turn can be used to finance imports [ 38 ], (2) it encourages investment and drives local firms toward greater efficiency due to the increased competition [ 3 , 31 ], (3) it alleviates unemployment, since tourism activities are heavily based on human capital [ 10 ] and (4) it leads to positive economies of scale thus, decreasing production costs for local businesses [ 1 , 14 ]. Other recent studies which find evidence in favor of the TLGH hypothesis include [ 44 , 52 ]. Even though literature is dominated by TLGH, few studies produce a result in support of EDTH [ 40 , 41 , 45 ]. Payne and Mervar [ 45 ] posit that tourism growth of a country is mobilized by the stability of well-designed economic policies, governance structures and investments in both physical and human capital. This positive and vibrant environment creates a series of development activities which proliferate and flourish the tourism. Pertaining to the readily available information, bi-directional causality could also exist between tourism income and economic growth [ 34 , 49 ]. From a policy view, a reciprocal tourism–economic growth relationship implies that government agendas should cater for promoting both areas simultaneously. Finally, there are some studies that do not offer support to any of the aforementioned hypotheses, suggesting that the impact between tourism and economic growth is insignificant [ 25 , 47 , 57 ]. There is a vast literature examining the relationship between tourism and growth as a result, only a selective literature review will be presented here.
Banday and Ismail [ 5 ] used ARDL cointegration model to test the relationship between tourism revenue and economic growth in BRICS countries from the time period of (1995–2013). The study validates the tourism-led growth hypothesis for BRICS countries, which evinces that tourism has positive influence on economic growth.
Savaş et al. [ 54 ] evaluated the tourism-led growth hypothesis in the context of Turkey. The study employed gross domestic product, real exchange rate, real total expenditure and international tourism arrivals to sketch out the causality among variables. The result reveals a unidirectional relationship between tourism and real exchange rate. The findings suggest that tourism is the driving force for economic growth, which in turn helps turkey to culminate its current account deficit.
Dhungel [ 15 ] made an effort to investigate causality between tourism and economic growth, In Nepal for the period of (1974–2012), by using Johansen’s cointegration and Error correction model. The result states that unidirectional causality exists in the long run, while in short run no causality exists between two constructs. The study emphasized that strategies should be devised to attain causality running from tourism to economic growth.
Mallick et al. [ 36 ] analyzed the nexus between economic growth and tourism in 23 Indian states over a period of 14 years (1997–2011). Using panel autoregressive distributed lag model based on three alternative estimators such as mean group estimator, pooled mean group and dynamic fixed effects, Research found that tourism exerts positive influence on economic growth in the long run.
Belloumi [ 8 ] examines the causal relationship between international tourism receipts and economic growth in Tunisia by using annual time series data for the period 1970–2007. The study uses the Johansen’s cointegration methodology to analyze the long-run relationship among the concerned variables. Granger causality based Vector error correction mechanism approach indicates that the revenues generated from tourism have a positive impact on economic growth of Tunisia. Thus, the study supports the hypothesis of tourism-driven economic growth, which is specific to developing countries that base their foreign exchange earnings on the existence of a comparative advantage in certain sectors of the economy.
Tang et al. [ 58 ] explored the dynamic Inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India for the period 1971–2012. The study employed Bounds testing approach to cointegration and generalized variance decomposition methods to analyze the relationship. The bounds testing and the Gregory-Hansen test for cointegration with structural breaks consistently reveals that energy consumption, tourism and economic growth in India are cointegrated. The study demonstrated that tourism and economic growth have positive impact on energy consumption, while tourism and economic growth are interrelated; with tourism exert significant influence on economic growth. Consequently, this study validates the tourism-led growth hypothesis in the Indian context.
Kadir and Karim [ 24 ]) examined the causal nexus between tourism and economic growth in Malaysia by applying panel time series approach for the period 1998–2005. By applying Padroni’s panel cointegration test and panel Granger causality test, the result indicated both short and long-run relationship. Further, the panel causality shows unidirectional causality directing from tourism receipts to economic growth. The result provides evidence of the significant contribution of tourism industry to Malaysia’s economic growth, thereby justifying the necessity of public intervention in providing tourism infrastructure and facilities.
Antonakakis et al. [ 2 ] test the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe by using a newly introduced spillover index approach. Based on monthly data for 10 European countries over the period 1995–2012, the findings suggested that the tourism–economic growth relationship is not stable over time in terms of both magnitude and direction, indicating that the tourism-led economic growth (TLEG) and the economic-driven tourism growth (EDTG) hypotheses are time-dependent. Thus, the findings of the study suggest that the same country can experience tourism-led economic growth or economic-driven tourism growth at different economic events.
Oh [ 41 ] verifies the contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy by applying Engle and Granger two-stage approach and a bivariate Vector Autoregression model. He claimed that economic expansion lures tourists in the short run only, while there is no such long-run stable relationship between international tourism and economic development in Korea.
Empirical studies have pronouncedly focused on the literature that tourism promotes economic growth. To further substantiate the nexus, the study will investigate the plausible linkages between economic growth and international tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. The inclusion of financial development in the examination of tourism-growth nexus is a unique feature of this study, which have an influencing role in economic growth as financial development has been theoretically and empirically recognized as source of comparative advantage [ 22 ].
This study employs panel ARDL cointegration approach to verify the existence of long-run association among the variables. Further, study estimated the long-run and short-run coefficients of the ARDL model. Subsequently, Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] panel Granger causality test has been employed to check the direction of causality between tourism, financial development and economic growth among BRICS countries.
Database and methodology
Data and variables.
The study is analytical and empirical in nature, which intends to establish the relationship between economic growth and inbound tourism in BRICS countries. For the BRICS countries, limited studies have been conducted depicting the present scenario. Therefore, present study tries to verify the relevance of tourism in economic growth to further enhance the understanding of economic dynamics in BRICS countries. The data used in the study are annual figures for the period stretching from 1995 to 2015, consisting of one endogenous variable (GDP per capita, a proxy for economic growth) and two exogenous variables (international tourism receipts per capita and financial development). The variables employed in the study are based on the economic growth theory, proposed by Balassa [ 4 ], which states that export expansion has a relevant contribution in economic growth. Further, this study incorporates financial development in the model to reduce model misspecification as it is considered to have an influencing role in economic growth both theoretically and empirically [ 22 , 33 ].
The annual data for all the variables have been collected from the World Development Indicators (WDI, 2016) database. The variables used in the study includes gross domestic product per capita (GDP) in constant ($US2010) used as a proxy for economic growth (EG), international tourism receipts per capita (TR) in current US$ as it is widely accepted that the most adequate proxy of inbound tourism in a country is tourism expenditure normally expressed in terms of tourism receipts [ 32 ] and financial development (FD). In line with a recent study on the relationship between financial development and economic growth by Hassan et al. [ 19 ], financial development is surrogated by the ratio of the broad money (M3) to real GDP for all BRICS countries. Here we use the broadest definition of money (M3) as a proportion of GDP– to measure the liquid liabilities of the banking system in the economy. We use M3 as a financial depth indicator, because monetary aggregates, such as M2 or M1, may be a poor proxy in economies with underdeveloped financial systems, because they ‘are more related to the ability of the financial system to provide transaction services than to the ability to channel funds from savers to borrowers’ [ 26 ]. A higher liquidity ratio means higher intensity in the banking system. The assumption here is that the size of the financial sector is positively associated with financial services [ 29 ]. All the variables have been taken into log form.
Unit root test
To verify the long-run relationship between tourism and economic growth through Bounds testing approach, it is necessary to test for stationarity of the variables. The stationarity of all the variables can be assessed by different unit root tests. The study utilizes panel unit root test proposed by Levin et al. [ 35 ] henceforth LLC and Im et al. [ 23 ] henceforth IPS based on traditional augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) test. The LLC allows for heterogeneity of the intercepts across members of the panel under the null hypothesis of presence of unit root, while IPS allows for heterogeneity in intercepts as well as in the slope coefficients [ 48 ].
Panel ARDL approach to Cointegration
After checking the stationarity of the variables the study employs panel ARDL technique for Cointegration developed by Pesaran et al. [ 23 ]. Pesaran et al. [ 23 ] have introduced the pooled mean group (PMG) approach in the panel ARDL framework. According to Pesaran et al. [ 23 ], the homogeneity in the long-run relationship can be attributed to several factors such as arbitration condition, common technologies, or the institutional development which was covered by all groups. The panel ARDL bounds test [ 46 ] is more appropriate by comparing other cointegration techniques, because it is flexible regarding unit root properties of variables. This technique is more suitable when variables are integrated at different orders but not I (2). Haug [ 20 ] has argued that panel ARDL approach to cointegration provides better results for small sample data set such as in our case. The ARDL approach to cointegration estimates both long and short-run parameters and can be applied independently of variable order integration (independent of whether repressors are purely I (0), purely I(1) or combination of both. The ARDL bounds test approach used in this study is specified as follows:
where Δ is the first-difference operator, \(\alpha_{0}\) stands for constant, t is time element, \(\omega_{1} , \omega_{2} \;\;{\text{and}}\;\; \omega_{3}\) represent the short-run parameters of the model, \(\emptyset_{1} , \emptyset_{2} ,and \emptyset_{3}\) are long-run coefficients, while \(V_{it}\) is white noise error term and lastly, it represents country at a particular time period. In the ARDL model, the bounds test is applied to determine whether the variables are cointegrated or not.
This test is based on the joint significance of F -statistic and the χ 2 statistic of the Wald test. The null hypothesis of no cointegration among the variables under study is examined by testing the joint significance of the F -statistic of \(\omega_{1} , \omega_{2} ,\omega_{3}\) .
In case series variables are cointegrated, an error correction mechanism (ECM) can be developed as Eq. ( 2 ), to assess the short-run influence of international tourism and financial development on economic growth.
where ECT is the error correction term, and \(\varPhi\) is its coefficient which shows how fast the variables attain long-term equilibrium if there is any deviation in the short run. The error correction term further confirms the existence of a stable long-run relationship among the variables.
Panel granger causality test
To examine the direction of causality Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] test is employed. Instead of pooled causality, Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] proposed a causality based on the individual Wald statistic of Granger non-causality averaged across the cross section units. Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] assert that traditional test allows for homogeneous analysis across all panel sets, thereby neglecting the specific causality across different units.
This approach allows heterogeneity in coefficients across cross section panels. The two statistics Wbar-statistics and Zbar-statistics provides standardized version of the statistics and is easier to compute. Wbar-statistic, takes an average of the test statistics, while the Zbar-statistic shows a standard (asymptotic) normal distribution.
They proposed an average Wald statistic that tests the null hypothesis of no causality in a panel subgroup against an alternative hypothesis of causality in at least one panel. Following equations will be used to check the direction of causality between the variables.
Estimation, results and Discussion
Descriptive statistics.
Table 1 presents descriptive statistics of variables selected for the period 1995–2015. The variable set includes GDP, FD and TR for all BRICS countries. Brazil tops the list with GDP per capita of 4.18, while India lagging behind all BRICS nations. In the recent economic survey by International Monetary Fund (IMF report 2016), India was ranked 126 for its per capita GDP. India’s GDP per capita went up to $7170 against all other BRICS countries which were placed in the above $10,000 bracket. China has the highest tourism receipts in comparison to other BRICS countries. China is a very popular country for foreign tourists, which ranks third after France and USA. In 2014, China invested $136.8 billion into its tourist infrastructure, a figure second only to the United States ($144.3 billion). Tourism, based on direct, indirect, and induced impact, accounted for near 10% in the GDP of China (WTTC report 2017).
Stationarity results
Primarily, we employed LLC and IPS unit root test to assess the integrated properties of the series. The results of IPS and PP tests are presented in Table 2 . Panel unit root test result evinces that FD and TR are stationary at level, while GDP per capita is integrated variable of order 1. The result exemplifies that GDP per capita, Tourism receipts and Financial Development are integrated at 1(0) and 1(1). Consequently, the panel ARDL approach to cointegration can be applied.
Cointegration test results
In view of the above results with a mixture of order integration, the panel ARDL approach to cointegration is the most appropriate technique to investigate whether there exists a long-run relationship among the variables [ 42 ]. Table 3 illustrates that the estimated value of F-statistics, which is higher than the lower and upper limit of the bound value, when InEG is used as a dependent variable. Hence, we reject the null hypothesis of no cointegration \(H_{0 } : \emptyset_{1} = \emptyset_{2} = \emptyset_{3} = 0\) of Eq. ( 1 ). Therefore, the result asserts that international tourism, financial development and economic growth are significantly cointegrated over the period (1995–2015).
Subsequently, the study investigates the long-run and short-run impact of international tourism and financial development on economic growth. Lag length is selected on the principle of minimum Bayesian information criterion (SBC) value, which is 2 in our case. The long-run coefficients of financial development and tourism receipts with respect to economic growth in Table 4 indicate that tourism growth and financial development exerts positive influence on economic growth in the long run. In other words, an increase in volume of tourism receipts per capita and financial depth spurs economic growth and both the coefficients are statistically significant in case of BRICS nations in the long run. The results are interpreted in detail as below:
The elasticity coefficient of economic growth with respect to tourism shows that 1% rise in international tourism receipts per capita would imply an estimated increase of almost 0.31% domestic real income in the long run, all else remaining the same. Thus, the earnings in the form of foreign exchange from international tourism affect growth performance of BRICS nations positively. This finding of our study is in consonance with the empirical results of Kreishan for Jordan [ 30 ], Balaguer and Cantavella-Jordá [ 3 ] for Spain and Ohlan [ 43 ] for India.
Further our finding lend support to the wide applicability of the new growth theory proposed by Balassa which states that export expansion promote growth performance of nations. Thus, validates TLGH coined by Balaguer and Cantavell-Jorda [ 3 ] which states that inbound tourism acts a long-run economic growth factor. The so called tourism-led growth hypothesis suggests that the development of a country’s tourism industry will eventually lead to higher economic growth and, by extension, further economic development via spillovers and other multiplier effects.
Likewise, financial development as expected is found to be positively associated with economic growth. The coefficient of financial development states that 1% improvement in financial development will push up economic growth by 0.22% in the long run, keeping all other variables constant. The empirical results are consistent with the finding of Hassan et al. [ 19 ] for a panel of South Asian countries. Well-regulated and properly functioning financial development enhances domestic production through savings, borrowings & investment activities and boosts economic growth. Further, it promotes economic growth by increasing efficiency [ 7 ]. Levine [ 33 ] believes that financial intermediaries enhance economic efficiency, and ultimately growth, by helping allocation of capital to its best use. Modern growth theory identifies two specific channels through which the financial sector might affect long-run growth; through its impact on capital accumulation and through its impact on the rate of technological progress. The sub-prime crisis which depressed the economic growth worldwide in 2007 further substantiates the growth-financial development nexus.
In the third and final step of the bounds testing procedure, we estimate short-run dynamics of variables by estimating an error correction model associated with long-run estimates. The empirical finding indicates that the coefficient of error correction term (ECT) with one period lag is negative as well as statistically significant. This finding further substantiates the earlier cointegration results between tourism, financial development and economic growth, and indicates the speed of adjustment from the short-run toward long-run equilibrium path. The coefficient of ECT reveals that the short-run divergences in economic growth from long-run equilibrium are adjusted by 43% every year following a short-run shock.
The short-run parameters in Table 5 demonstrates that tourism and financial development acts as an engine of economic growth in the short run as well. The coefficient of both tourism receipts per capita and financial development with one period lag is also found to be progressive and significant in the short run. These results highlight the role of earnings from international tourism and financial stability as an important driving force of economic growth in BRICS nations in the short run as well.
Further, a comparison between short-run and long-run elasticity coefficients evince that long-run responsiveness of economic growth with respect to tourism and financial development is higher than that of short run. It exemplifies that over time higher international tourism receipts and well-regulated financial system in BRICS nations give more boost to economic growth.
Analysis of causality
At this stage, we investigate the causality between tourism, financial development and economic growth presented in Table 6 . The result shows bi-directional causal relationship between tourism and economic growth, thereby validates ‘feedback hypothesis’ and consequently supported both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) and its reciprocal, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis (EDTH). The bi-directional causality between inbound tourism and GDP, which directs the level of economic activity and tourism growth, mutually influences each other in that a high volume of tourism growth leads to a high level of economic development and reverse also holds true. These results replicate the findings of Banday and Ismail [ 5 ] in the context of BRICS countries, Yazdi et al. [ 27 ] for Iran and Kim et al. [ 28 ] for Taiwan. One of the channels through which tourism spurs economic growth is through the use of receipts earned in the form of foreign currency. Thus, growth in foreign earnings may allow the import of technologically advances goods that will favor economic growth and vice versa. Thus, results demonstrate that international tourism promotes growth and in turn economic expansion is necessary for tourism development in case of BRICS countries. With respect to policy context, this finding suggests that the BRICS nations should focus on economic policies to promote tourism as a potential source of economic growth which in turn will further promote tourism growth.
Similarly, in case of economic growth and financial development, the findings demonstrate the presence of bi-directional causality between two constructs. The findings validate thus both ‘demand following’ and supply leading’ hypothesis. The findings suggests that indeed financial development plays a crucial role in promoting economic activity and thus generating economic growth for these countries and reverse also holds. Our findings are in line with Pradhan [ 48 ] in case of BRICS countries and Hassan et al. [ 19 ] for low and middle-income countries. This suggests that finance development can be used as a policy variable to foster economic growth in the five BRICS countries and vice versa. The study emphasizes that the current economic policies should recognize the finance-growth nexus in BRICS in order to maintain sustainable economic development in the economy. The empirical results in this paper are in line with expectations, confirming that the emerging economies of the BRICS are benefiting from their finance sectors.
Finally, two-sided causal relationship is found between tourism receipts and financial development. That is, tourism might contribute to financial development and, in return, financial development may positively contribute to tourism. This means that financial depth and tourism in BRICS have a reinforcing interaction. The positive impact of tourism on financial development can be attributed to the fact that inflows of foreign exchange via international tourism not only increases income levels but also leads to rise in official reserves of central banks. This in turn enables central banks to adapt expansionary monetary policy. The positive contribution of financial sector to tourism is further characterized by supply leading hypothesis. Further, better financial and market conditions will attract tourism entrepreneurship, because firms will be able to use more capital instead of being forced to use leveraging [ 13 ]. Hence, any shocks in money supply could adversely affect tourism industry in these countries. Song and Lin [ 56 ] found that global financial crisis had a negative impact on both inbound and outbound tourism in Asia. This result is in consistent with Başarir and Çakir [ 6 ] for Turkey and four European countries.
Stability tests
In addition, to test the stability of parameters estimated and any structural break in the model CUSUM and CUSUMSQ tests are employed. Figs. 1 and 2 show blue line does not transcend red lines in both the tests, thus provides strong evidence that our estimated model is fit and valid policy implications can be drawn from the results.
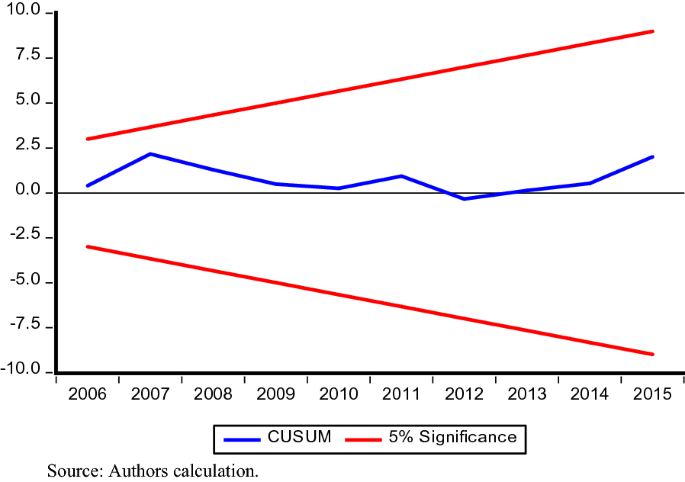
Plot of CUSUM
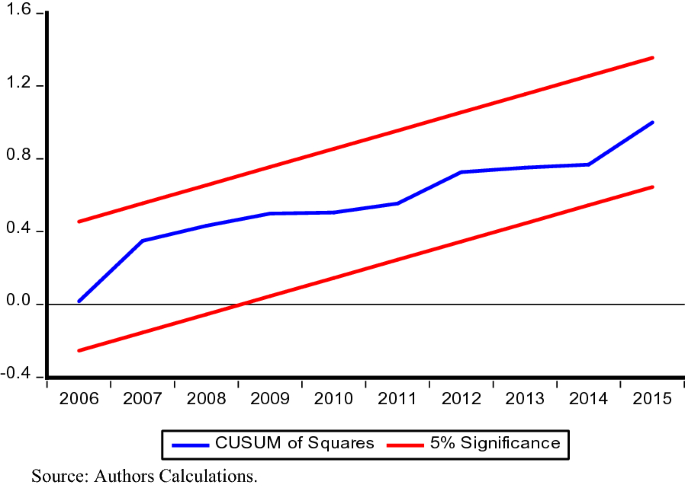
Plot of CUSUMQ
Summary and concluding remarks
A rigorous study of the relationship between tourism and economic growth, through the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) perspective has remained a debatable issue in the economic growth literature. This study aims to empirically investigate the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth in BRICS countries by utilizing the panel data over the period 1995–2015. The study employs the panel ARDL approach to cointegration and Dumitrescu-Hurlin panel Granger causality test to detect the direction of causation.
To the best of authors’ knowledge, this is the first study which explored the relationship between economic growth and tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. The empirical results of ARDL model posits that in BRICS countries inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth are significantly cointegrated, i.e., variables have stable long-run relationship. This methodology has allowed obtaining elasticities of economic growth with respect to tourism and financial development both in the long run and short run. The result reveals that international tourism growth and financial development positively affects economic growth both in the long run and short run. The coefficient of tourism indicates that with a 1% rise in tourism receipts per capita, GDP per capita of BRICS economies will go up by 0.31% in the long run. This finding lends support to TLGH coined by Balaguer and Cantavell-Jorda [ 3 ] which states that inbound tourism acts a long-run economic growth factor. The so called tourism-led growth hypothesis suggests that the development of a country’s tourism industry will eventually lead to higher economic growth and, by extension, further economic development via spillovers and other multiplier effects.
Likewise, 1% improvement in financial development, on average, will increase economic growth in BRICS countries by 0.22% in the long run. The result seems logical as modern growth theory identifies two channels through which the financial sector might affect long-run growth: first, through its impact on capital accumulation and secondly, through its impact on the rate of technological progress. The sub-prime crisis which hit the economic growth Worldwide in 2007 further substantiates the growth-financial development nexus.
The negative and statistically significant coefficient of lagged error correction term (ECT) further substantiates the long-run equilibrium relationship among variables. The negative coefficient of ECT also shows the speed of adjustment toward long-run equilibrium is 43% per annum if there is any short-run deviation. The estimates of parameters are found to be stable by applying CUSUM and CUSUMQ for the time period under consideration. Therefore, inbound tourism earnings and financial institutions can be used as a channel to increase economic growth in BRICS economies.
Further, Granger causality test result indicates the bi-directional causation in all cases. Hence, the causal relationship between international tourism and economic growth is bi-directional. And, consequently this empirical finding lends support to both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) and its reciprocal, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis (EDTH). This means that tourism is not only an engine for economic growth, but the economic outcome on itself can play an important role in providing growth potential to tourism sector.
The Granger causality findings provide useful information to governments to examine their economic policy, to adjust priorities regarding economic investment, and boost their economic growth with the given limited resources. Thus, it is suggested that more resources should be allocated to tourism industry and tourism-related industries if the tourism-led growth hypothesis holds true. On the other side, if economic-driven tourism growth is supported then more resources should be diverted to leading industries rather than the travel and tourism sector, and the tourism industry will in turn benefit from the resulting overall economic growth. And, when bi-directional causality is detected, a balanced allocation of economic resources for the travel and tourism sector and other industries is important and necessary. The policy implication is that resource allocation supporting both the tourism and tourism-related industries could benefit both tourism development and economic growth.
To sum up, the major finding of this study lends support to wide applicability of the tourism-led growth hypothesis in case of BRICS countries. Thus, in the Policy context, significant impact of tourism on BRICS economy rationalizes the need of encouraging tourism. Tourism can spur economic prosperity in these countries and for this reason; policymakers should give serious consideration toward encouraging tourism industry or inbound tourism. BRICS countries should focus more on tourism infrastructure, such as, convenient transportation, alluring destinations, suitable tax incentives, viable hostels and proper security arrangements to attract the potential tourists. Most of these countries are devoid of rich facilities and popular tourist incentives, to get promoted as important destination and in the long-run promotes economic growth. Further, they need a staunch support from all sections of authorities, non-government organizations (NGOs), and private and allied industries, in the endeavor to attain sustainable growth in tourism. Both state and non-state actors must recognize this growing industry and its positive implication on economy.
For future research, we suggest that researchers should consider the nonlinear factor in the dynamic relationship of tourism and economic growth in case of BRICS countries. Further one can go for comparative study to examine the TLGH in BRICS countries.
Availability of data and materials
Data used in the study can be provided by the corresponding author on request.
There are no fixed definitions of short, medium and long run and generally in macroeconomics, short run can be viewed as 1 to 2 or 3 years, medium up to 5 years and long run from 5 years to 20 or 25 years.
Abbreviations
autoregressive distributed lag model
Brazil, Russia, India, China and South-Africa
United Nations World Tourism Organization
World Travel & Tourism Council
gross domestic product
world development indicators
tourism-led growth hypothesis
export-led growth hypothesis
economic-driven tourism hypothesis
augmented Dickey–Fuller test
error correction model
error correction term
Andriotis K (2002) Scale of hospitality firms and local economic development—evidence from Crete. Tourism Manag 23(4):333–341
Google Scholar
Antonakakis N, Dragouni M, Filis G (2015) How strong is the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe? Econ Modell 44:142–155
Balaguer J, Cantavella-Jorda M (2002) Tourism as a long-run economic growth factor: the Spanish case. Appl Econ 34(7):877–884
Balassa B (1978) Exports and economic growth: further evidence. J Dev Econ 5(2):181–189
Banday UJ, Ismail S (2017) Does tourism development lead positive or negative impact on economic growth and environment in BRICS countries? A panel data analysis. Econ Bull 37(1):553–567
Basarir C, Çakir YN (2015) Causal interactions between CO 2 emissions, financial development, energy and tourism. Asian Econ Financ Rev 5(11):1227
Bell C, Rousseau PL (2001) Post-independence India: a case of finance-led industrialization? J Dev Econ 65(1):153–175
Belloumi M (2010) The relationship between tourism receipts, real effective exchange rate and economic growth in Tunisia. Int J Tour Res 12(5):550–560
Blake A, Sinclair MT, Soria JAC (2006) Tourism productivity: evidence from the United Kingdom. Ann Tourism Res 33(4):1099–1120
Brida JG, Pulina M (2010) A literature review on the tourism-led-growth hypothesis. Working paper CRENoS201017. Centre for North South Economic Research, Sardinia
Brida JG, Cortes-Jimenez I, Pulina M (2016) Has the tourism-led growth hypothesis been validated? A literature review. Curr Issues Tourism 19(5):394–430
Chatziantoniou I, Filis G, Eeckels B, Apostolakis A (2013) Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: a structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Manag 36:331–341
Chen M-H (2010) The economy, tourism growth and corporate performance in the Taiwanese hotel industry. Tourism Manag 31:665–675
Croes R (2006) A paradigm shift to a new strategy for small island economies: embracing demand side economics for value enhancement and long term economic stability. Tourism Manag 27:453–465
Dhungel KR (2015) An econometric analysis on the relationship between tourism and economic growth: empirical evidence from Nepal. Int J Econ Financ Manag 3(2):84–90
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Modell 29(4):1450–1460
Daniel Mminele (2016) The role of BRICS in the global economy. Speech at the Bundesbank Regional Office in North Rhine-Westphalia, Düsseldorf, Germany. https://www.bis.org/review/r160720c.pdf
Goldsmith RW (1969) Financial structure and development (No. HG174 G57)
Hassan MK, Sanchez B, Yu JS (2011) Financial development and economic growth: new evidence from panel data. Quart Rev Econ Financ 51(1):88–104
Haug AA (2002) Temporal aggregation and the power of cointegration tests: A Monte Carlo study. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 64:399–412
Henry EW, Deane B (1997) The contribution of tourism to the economy of Ireland in 1990 and 1995. Tourism Manag 18(8):535–553
Hur J, Raj M, Riyanto YE (2006) Finance and trade: a cross-country empirical analysis on the impact of financial development and asset tangibility on international trade. World Dev 34(10):1728–1741
Im KS, Pesaran MH, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econ 115(1):53–74
Kadir N, Karim MZA (2012) Tourism and economic growth in Malaysia: evidence from tourist arrivals from Asean-S countries. Econ Res Ekonomska istraživanja 25(4):1089–1100
Katircioglu S (2009) Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis: the case of Malta. Acta Oeconomica 59(3):331–343
Khan M, Senhadji A (2003) Financial development and economic growth: a review and new evidence. J Afr Econ 12:89–110
Khoshnevis Yazdi S, Homa Salehi K, Soheilzad M (2017) The relationship between tourism, foreign direct investment and economic growth: evidence from Iran. Curr Issues Tourism 20(1):15–26
Kim HJ, Chen MH (2006) Tourism expansion and economic development: the case of Taiwan. Tourism Manag 27(5):925–933
King R, Levine R (1993) Finance, entrepreneurship, and growth: theory and evidence. J Monet Econ 32:513–542
Kreishan FM (2010) Tourism and economic growth: the case of Jordan. Eur J Soc Sci 15:229–234
Krueger A (1980) Trade policy as an input to development. Am Econ Rev 70:188–292
Kumar RR (2014) Exploring the role of technology, tourism and financial development: an empirical study of Vietnam. Qual Quant 48(5):2881–2898
Levine R (1997) Financial development and economic growth: views and agenda. J Econ Lit 35(2):688–726
Lee CC, Chang CP (2008) Tourism development and economic growth: a closer look at panels. Tourism Manag 29(1):180–192
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CSJ (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econ 108(1):1–24
Mallick L, Mallesh U, Behera J (2016) Does tourism affect economic growth in Indian states? Evidence from panel ARDL model. Theor Appl Econ 23(1):183–194
Mastny L (2001) Treading lightly: new paths for international tourism. In: Peterson JA (ed) World Watch Paper 159. World Watch Institute
McKinnon RI (1964) Foreign exchange constraints in economic development and efficient aid allocation. Econ J 74(294):388–409
McKinnon RI (1973) Money and capital in economic development. The Brookings Institution, Washington
Narayan PK (2004) Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Econ 10(4):419–433
Oh CO (2005) The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Manag 26(1):39–44
Ohlan R (2015) The impact of population density, energy consumption, economic growth and trade openness on CO 2 emissions in India. Nat Hazards 79(2):1409–1428
Ohlan R (2017) The relationship between tourism, financial development and economic growth in India. Future Bus J 3(1):9–22
Parrilla JC, Font AR, Nadal JR (2007) Tourism and long-term growth a Spanish perspective. Ann Tourism Res 34(3):709–726
Payne JE, Mervar A (2010) Research note: the tourism-growth nexus in Croatia. Tourism Econ 16(4):1089–1094
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Po WC, Huang BN (2008) Tourism development and economic growth—a nonlinear approach. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 387(22):5535–5542
Pradhan RP, Dasgupta P, Bele S (2013) Finance, development and economic growth in BRICS: a panel data analysis. J Quant Econ 11(1–2):308–322
Ridderstaat J, Oduber M, Croes R, Nijkamp P, Martens P (2014) Impacts of seasonal patterns of climate on recurrent fluctuations in tourism demand: evidence from Aruba. Tourism Manag 41:245–256
Schumpeter JA (1911) The theory of economic development: an inquiry into profits, capital, credit, interest, and the business cycle. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, p 1934
Shaw ES (1973) Financial deepening in economic development. Oxford University Press, London
Sugiyarto G, Blake A, Sinclair MT (2003) Tourism and globalization: economic impact in Indonesia. Ann Tourism Res 30(3):683–701
Szivas E, Riley M (1999) Tourism employment during economic transition. Ann Tourism Res 26(4):747–771
Savaş B, Beşkaya A, Şamiloğlu F (2010) Analyzing the impact of international tourism on economic growth in Turkey. Uluslararası Yönetim İktisat ve İşletme Dergisi 6(12):121–136
Schubert SF, Brida JG, Risso WA (2011) The impacts of international tourism demand on economic growth of small economies dependent on tourism. Tourism Manag 32(2):377–385
Song H, Lin S (2010) Impacts of the financial and economic crisis on tourism in Asia. J Travel Res 49(1):16–30
Tang CF (2013) Temporal Granger causality and the dynamics relationship between real tourism receipts, real income and real exchange rates in Malaysia. Int J Tourism Res 15(3):272–284
Tang CF, Tiwari AK, Shahbaz M (2016) Dynamic inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India. Geosyst Eng 19(4):158–169
United Nations World Tourism Report (2014) Annual report 2014
World Travel & Tourism Council (2012) Travel & Tourism Economic Impact. World, London: World Travel & Tourism Council.
World Travel and Tourism Council (2016) Global travel and tourism economic impact update August 2016
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research has received no specific funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Haroon Rasool & Md. Tarique
Department of Commerce, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Shafat Maqbool
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HR has written introduction, research methodology and results and discussion part. Review of literature and data analysis was done by SM. Conclusion was written jointly by HR and SM. MT has provided useful inputs and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Haroon Rasool .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rasool, H., Maqbool, S. & Tarique, M. The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: a panel cointegration analysis. Futur Bus J 7 , 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00048-3
Download citation
Received : 02 August 2019
Accepted : 30 November 2020
Published : 05 January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00048-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Economic growth
- Inbound tourism
- Financial development
- Cointegration
- Panel granger causality
JEL Classification
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UN report Underscores Importance of Tourism for Economic Recovery in 2022
- All Regions
- 13 Jan 2022
The important role that tourism will play in the recovery of national economies and global trade has been highlighted in the 2022 edition of the World Economic Situation and Prospects (WESP) report by the United Nations. Drawing on data from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), WESP underlines the sector’s importance for the world economy and particularly for developing economies, including Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
After a global contraction of 3.4% in 2020 and a rebound of 5.5% in 2021, the world economy is projected to grow by 4% in 2022 and then 3.5% in 2023. Given its importance as a major export category (prior to the pandemic tourism was the third largest in the world, after fuels and chemicals), and recognizing its role as a source of employment and economic development , the sector’s recovery is expected to drive growth in every world region.
UNWTO Secretary-General Zurab Pololikashvili said: “The sudden halt in international tourism caused by the pandemic has emphasized the sector’s importance to both national economies and individual livelihoods. The flagship UN report makes use of UNWTO data and analysis to assess the cost of declining tourism and illustrates just how important restarting tourism will be in 2022 and beyond.”
Jobs, economic growth and equality all hit
The sudden halt in international tourism caused by the pandemic has emphasized the sector’s importance to both national economies and individual livelihoods
The latest edition of the UN World Economic Situation and Prospects report uses key UNWTO data on international tourist arrivals and tourism receipts to illustrate how the pandemic’s impact has been felt beyond the sector itself . International tourist arrivals plunged by 73% in 2020, dropping to levels not seen for 30 years. And while tourism did record a modest improvement in the third quarter of 2021, international arrivals between January-September 2021 were still 20% below 2020 levels and 76% below 2019 levels (full year 2021 results to be released by UNWTO on 18 January).
The crisis has had a devastating impact on employment, including in hospitality, travel services and retail trade. It has disproportionately affected vulnerable groups, including youth and migrant workers, as well as workers with lower educational attainment and skills. Exacerbation of the gender divide is evident, especially in developing countries, with women seeing greater declines in employment and labour force participation than men.
Diversification for recovery
Further analysing the sector’s role in economic recovery, the UN report notes that many destinations, in particular tourism-dependent countries, will need to diversify their tourism throughout 2022 and beyond. Again drawing on UNWTO analysis , the publication shows how many destinations are developing domestic and rural tourism to help local economies in rural and depressed areas to boost job creation and protect natural resources and cultural heritage , while at the same time empowering women, youth and indigenous peoples. Additionally, the report notes how Small Island Developing States can take steps to ensure local businesses and workers retain more of the economic benefits that international tourism brings, noting for example that that “tourism leakage” amounts to an estimated 80% of all money spent by tourists in the Caribbean region.
Related links
- Download the news release in PDF
- UNWTO Market Intelligence
- UNWTO Tourism Data Dashboard
- Rural Tourism
- World Economic Situation and Prospects 2022
Related Content
The fulani kitchen foundation culinary heritage village..., amadeus & un tourism joint report reveals tourism in th..., djibouti, a veritable natural aquarium, can of hospitality: tourism in all its splendor.

- Press Releases
- Press Enquiries
- Travel Hub / Blog
- Brand Resources
- Newsletter Sign Up
- Global Summit
- Hosting a Summit
- Upcoming Events
- Previous Events
- Event Photography
- Event Enquiries
- Our Members
- Our Associates Community
- Membership Benefits
- Enquire About Membership
- Sponsors & Partners
- Insights & Publications
- WTTC Research Hub
- Economic Impact
- Knowledge Partners
- Data Enquiries
- Hotel Sustainability Basics
- Community Conscious Travel
- SafeTravels Stamp Application
- SafeTravels: Global Protocols & Stamp
- Security & Travel Facilitation
- Sustainable Growth
- Women Empowerment
- Destination Spotlight - SLO CAL
- Vision For Nature Positive Travel and Tourism
- Governments
- Consumer Travel Blog
- ONEin330Million Campaign
- Reunite Campaign

Economic Impact Research
- In 2023, the Travel & Tourism sector contributed 9.1% to the global GDP; an increase of 23.2% from 2022 and only 4.1% below the 2019 level.
- In 2023, there were 27 million new jobs, representing a 9.1% increase compared to 2022, and only 1.4% below the 2019 level.
- Domestic visitor spending rose by 18.1% in 2023, surpassing the 2019 level.
- International visitor spending registered a 33.1% jump in 2023 but remained 14.4% below the 2019 total.
Click here for links to the different economy/country and regional reports
Why conduct research?
From the outset, our Members realised that hard economic facts were needed to help governments and policymakers truly understand the potential of Travel & Tourism. Measuring the size and growth of Travel & Tourism and its contribution to society, therefore, plays a vital part in underpinning WTTC’s work.
What research does WTTC carry out?
Each year, WTTC and Oxford Economics produce reports covering the economic contribution of our sector in 185 countries, for 26 economic and geographic regions, and for more than 70 cities. We also benchmark Travel & Tourism against other economic sectors and analyse the impact of government policies affecting the sector such as jobs and visa facilitation.
Visit our Research Hub via the button below to find all our Economic Impact Reports, as well as other reports on Travel and Tourism.

Tourism: Benefits and Costs Essay
Executive summary, introduction, benefits of tourism, costs of tourism, sustainable tourism, works cited.
Tourism is a phenomenon which was extensively developed during the 20 th century when people became able to afford a vacation once a year. This paper thoroughly examines all the positive and negative consequences of the development of tourism.
First off, it concludes that tourism can improve the economy. Tourism, in the first, place creates jobs, and reduces unemployment. It also generates huge amounts of revenue that the government can collect through taxes.
In addition, all the other branches of the economy can be developed as consequences of a growing tourist industry. Environment and culture can also benefit from this industry because it provides a solid economic reason for preservation of customs and landscapes.
As far as costs of tourism are concerned, it can be said that they are numerous, and that in every domain where it can be useful, tourism can also be devastating if it is not conducted properly.
Therefore, in the economy, it can cause a country to become dependent on the capital generated in the industry. Furthermore, jobs in tourism are often insecure and poorly paid, and the money earned is often taken away from the country in which it is generated.
Costs are also felt in the domain of environment and culture. Huge amounts of waste generated by hotels, restaurants and entertainment complexes destroy the environment. Finally, culture is being viewed as one big show rather than an integral component of the local people’s lifestyle.
In the end, accomplishments and challenges of the newly emerging field of sustainable tourism are discussed. It is concluded that comprehensive theoretical models are lacking in this field, and that it demands long and expensive projects to be carried out before observable changes could take place.
Despite the unsolved issues, it seems that sustainable tourism is the only way to go if we are to prevent the industry from destroying itself.
One distinguished scholar in the field of tourism, Allen Beaver, defined tourism in the following terms: “Tourism is the temporary, short-term movement of people to destination outside the places where they normally live and work and their activities during the stay at each destination.
It includes movements for all purposes (Beaver 313). This phenomenon has a long history since rich people have always wanted to see different places and experience different cultures.
Since the industrial revolution, the number of people who are able to afford such a luxury has been increasing constantly to the point where spending a vacation at some tourist center is no longer considered a luxury (Singh 189).
This increase in popularity of tourism has had a huge impact on the world economy, and tourism plays one of the most significant roles in some of the strongest economies in the world.
It is easy to conclude that tourism can have incredibly positive impact on human society; however, significant changes that the 21 st century has brought are starting to reveal many problems related to tourism.
It is, therefore, essential to reevaluate the role of tourism in the 21 st century, and reshape in the light of the ideas of sustainability.
Economic benefits of tourism
It is widely accepted that countries can benefits tremendously from tourism in economic terms. This is because it is an industry that does not demand huge investments, like for example metallurgy, but can pay off just the same.
In modern market economies, tourism is for the most part run in the private sector, and governments earn large amounts of revenue through taxation.
Furthermore, large tourist complexes employ thousands of people whose existence is dependent upon tourism. Owners, on the other hand, can accumulate large amounts of capital which is then invested in other sectors of the economy.
Taxation of tourism
Even though in politics, it is a constantly debated question as to how much of the income generated through tourism belongs to the government, one thing is certain – the state can earn a lot of revenue from it.
In a recent study by Gooroochurn (2004), it has been confirmed that taxation in tourism is much more effective than taxation in any other domain of the economy.
The author studied the case of Mauritius, an otherwise underdeveloped state, and concluded that in poor countries that have such potentials, it is a good idea to attract investments in tourism, and earn revenue through taxation (Gooroochurn 2004).
Among the countries that earn a huge portion of their revenue from tourism are: Greece, Portugal, Spain, Egypt, Tunisia, etc.
Employment in tourism
Providing goods and services for thousands of tourists every day demands a huge labor force. Ever since the beginning of tourism, people saw the employment potential that it has. According to the national statistical data, 16.5 % of all the labor force or around 700 000 people in Greece are employed in tourism.
Furthermore, many people who do not have large amounts of capital, but live near tourist centers have great opportunities for self-employment. Most of those people run small cafes, trinket or souvenir shops or simply sell local food and drinks to the visitors.
International Labor Organization predicts that in the following decade the number of jobs in tourism is to increase significantly, and claims that it is one sector in which the greatest potential is seen after the crisis (Employment in Tourism Industry).
Secondary economic benefits
Since all parts of the economic structure are interconnected, an economic boom in one of the component parts automatically overflows into all other parts. The income generated by the entrepreneurs is injected into other parts of the economy according to their ideas for further investment since every entrepreneur knows that money has to be invested further.
It has been noticed that one of the most common domains where money earned from tourism is invested is infrastructure. Investors are aware that improving the infrastructure, roads, water and electricity supply, railways, etc. can increase the number of visitors to their tourist complexes.
Furthermore, the government also recognizes the potential in tourism, and is often willing to subsidize the improvement of infrastructure (Karim 2011).
Apart from the infrastructure, other domains of the economy which are often developed as a result of a country’ success in tourism industry are food and drink industry, agriculture, etc.
Noneconomic benefits of tourism
One can argue that in a capitalist society all the positive phenomena can be described in terms of the economy. That might very well be the case; however, all the positive changes that occur in a country as a result of the development of tourism, and which are not directly related to the economy can be discussed under the label non-economic benefits.
Cultural benefits
Since the industrial revolution, together with the development of tourism, there has been an increase in the number of educated people. Their fascination with the historical heritage and cultural diversity of the world made way for the development of the so called cultural tourism.
On the other hand, under the pressure of economic forces, local people are adopting the new ways of life, and because of the lack of time and resources, they are slowly losing their cultural heritage. The fact that there is little to be gained financially from being involved in the traditional customs causes many people to lose interest in them.
For that reason, Weiner (2010) argues that cultural tourism is, in fact, the force that helps to preserve local customs and traditions. The interest of foreigners in local culture, according to Weiner, is what gives the economic value to the culture.
He uses the example of Turkish baths in which he enjoyed while on vacation and concludes that the custom would have been extinct if it had not been for the tourists who were willing to pay to experience it. However, anthropologists argue that this way of preserving culture is deflationary and imperialistic (Menkedick 2010).

Environmental benefits
As in the case of culture, tourism has huge impact on the environment. There are both positive and negative environmental consequences of tourism; however, in this section only the positive ones are discussed.
When a country is industrially underdeveloped, it usually possesses locations with well-preserved environment. In the course of the development of a country, it can be decided that those locations should be used for industrial development, and then polluters like mines and factories are built.
Obviously, this has tremendous environmental consequences. Of course, it can be decided that the location be preserved in the original state which entails opportunity costs, but this seldom happens. Finally, it seems that the best solution is to build tourist complexes, and develop that branch of the economy.
This course of action provides economic motivation for maintaining parks, funding research in resource management, improving environmental education and introducing strong legal framework for environment preservation (Sawkar et al. 8).
Other benefits of tourism
It is certain that benefits of tourism cannot just be reduced to economic, cultural and environmental ones. Surely, there are many other positive phenomena that occur as consequences of the development of tourism. First off, tourism helps in cherishing positive attitudes towards different cultures and customs.
Secondly, it is a very good way of destroying negative attitudes towards foreigners, and rejecting xenophobia, stereotypes and prejudices about others. Thirdly, it affords immense psychological satisfaction which stems from the interaction with others (Ritchie & Goeldner 373-383).
Tourism can also benefit individuals who have some health problems, and various resorts offer extensive treatment programs employing leading experts in therapeutic procedures.
Many people are inclined to think that tourism is a socio-economic phenomenon with only positive consequences; however, in reality the global economic system and the nature of tourism as a branch of the economy lead to some difficult economic problems.
Furthermore, huge seasonal changes in the population which are caused by travel and tourism pose serious cultural and social challenges for the local communities.
Finally, despite the fact that tourism can have positive effects on the environment and culture, if conducted improperly, it can have a devastating environmental and cultural impact.
Economic costs of tourism
Seasonal jobs.
As we saw, the development of tourism has the potential to create a large number of jobs. However, the downside of this fact is that in most centers, these jobs are seasonal and not very well paid. This has some obvious negative consequences.
First off, many people who work in the industry are dependent upon it for their existence. For that reason they are virtually employed for only 5-6 months per year due to the seasonal nature of their employment. This causes them to face severe financial problems during the period of the year in which they have no employment and income.
Secondly, well-developed tourist destinations are very often located in very poor countries such as Maldives, Jamaica, Dominican Republic etc. In these places, unemployment is incredibly high and the average income is very low.
Consequently, employers are in a position to give very low wages, and avoid hiring employees to work in their complexes on a regular basis. For that reason, the turnover of the labor force is immense, and it is very difficult to protect labor rights in that context.
Economic dependence
The fact that profits in the tourism industry can be so high can cause the entire economy of a country or a region to steer towards that industry. This can be very dangerous for several reasons. It is well-known that tourism is not a firm basis for an economy because it is not a productive industry, and it is located in the domain of services.
This has some very important consequences. First off, in case of a crisis, people usually sacrifice the expenses that they regard as luxuries, and their annual vacation is very often one of the first items on the list. Such events as crises can push a country into a severe depression if it is extremely dependent on tourism.
For example, the recent financial crisis of 2008 significantly damaged the economy of Hawaii, which is extremely dependent on tourism because more than one third of the country’s revenue comes from tourism.
Because of the financial crisis that hit the Western world, the tax revenue of Hawaii was reduced by more than 10 per cent, and the country lost 4.9 billion dollars in foreign spending (Woo).
Furthermore, an economy which is extremely dependent on tourism runs not only the risk of economic crises, but also natural disasters. Many of the world’s most famous tourist centers are located in the areas which have the highest risk of natural disasters like earthquakes, volcanoes, tornados, tsunamis, etc.
Such events can not only destroy tourist seasons, but also devastate the infrastructure and buildings of great importance, thereby deleting the region from the world’s tourist map. One recent example is the earthquake in Haiti.
Just as Haiti was recovering from a long history of social and economic problems by developing tourist centers, an earthquake of 7.0 Mw destroyed most of the hotels and buildings leaving the country in ruins (Curley 8).
Other Economic Issues
The economy consists of such a complex set of relations between humans that one should not be surprised to discover that the effects of one phenomenon can have so many economic consequences, both positive and negative ones.
One additional economic cost of tourism is the fact that the structure of the capital within the industry can be such that very small percentage of the total revenue remains in the country where all the tourist complexes are located.
Globalized economy, such as the one we have at the beginning of the 21 st century, allows the rich people and corporations from the Western world to build huge tourist complexes in Kenya or Nigeria, for example.
If that happens, they usually attract Western tourists who are interested in buying Western food such as McDonald’s or clothes, such as Nike. All of that creates a seasonal Western market in Africa.
An unfortunate fact for the local population is that all of those companies, at the end of the season, take their revenue back to the Western countries, and they are left with very little money that they could earn competing with those Western giants (Sunyer 2010).
Environmental costs
It is quite a paradox that while thousands of people visit a location with intact nature and beautiful landscapes, by doing so they are slowly destroying that very same landscape. To make things even worse the more interesting and beautiful the landscape is, the more people it attracts, and the quicker it is destroyed.
From building hotels, restaurants and entertainment centers to the basic elements of infrastructure like heating, water supply and roads, tourism causes significant reshaping of the original landscape, and the environment suffers a lot.
Moreover, supporting thousands of people during the season demands immense amounts of food, fresh water and fuel. All of that creates large quantities of waste. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully plan and construct landfills and sewage systems.
Both of these basic constituents of an urbanized location have to cause some amount of pollution; however, it is essential that this pollution be kept at the minimum.
It has been confirmed that leaving all of these concerns to the market will not do the job because meeting all the necessary requirements costs a lot, and in unregulated circumstances those who are careful to meet them simply cannot remain competitive.
In this way locations which were originally attractive to tourists, within few years, become more polluted than some industrial centers.
Therefore, it is absolutely essential to construct environmentally sound regulations to prevent the self-destruction of tourism in a country (Buckley 401).
Cultural costs
The final danger which comes with the development of tourism is that it can have devastating consequences for the local culture.
By now it is noticeable that economy, environment and culture are the three domains that can benefit the most from the development of tourism, but at the same time it in these three domains that tourism can have the most devastating consequences.
Moreover, it seems that culture is the one domain in which there is no way to establish control and make tourism fully sustainable. This is, for the most part, because of the fact that culture is constantly changing, and it is very difficult to control the direction of that change.
While cultural heritage like, for example, the summer festivals of Scotland is preserved precisely because tourists come from all over the world to experience it, it is absolutely certain that it is not the same in all cases.
From the anthropological point of view, it is questionable whether this way of preserving culture deserves praise at all. Some scholars, like Anthony Smith, would claim that it is not:
“Tourism places the whole of the visited culture on sale, distorting its imagery and symbolism, turning its emotions loose, transforming a way of life into an industry…A culture…is turned from subject to object, from independent to dependent, from audience-in-its-own-right to spectacle” (quoted in Sunyer 2010)
The argument is that culture is not really culture if it is not lived. The anthropologists would claim that this way of viewing the culture robs it of its essence.
For them, the claim that reducing the culture to a mere spectacle helps in preserving it is similar to the claim that we have the culture of the 18 th century France alive and existing when we are watching a play about Napoleon.
Sadly, it is difficult to see any way in which sustainable tourism can account for this problem. After all, reducing the local culture to a mere spectacle is an integral part of cultural tourism, and there is nothing that can be done in that aspect, legally or otherwise.
As it has been explained so far, it is very difficult to imagine tourism disappearing as a social category at this point in history. In fact, given all the beneficial aspect that it has, mirrored mostly in economics, very few people would want it to disappear.
Nonetheless, it is obvious that tourism implies some very difficult problems, in particular, its devastating impact on the environment and its imperialistic view of culture.
Scientists and scholars have recognized this as a problem, and have been trying to find a solution for several decades now in the field called sustainable tourism.
Sustainable tourism is based on the assumption that it is possible to have all the beneficial effects of tourism, while at the same time making as little detrimental impact on the local environment and culture.
It is an interdisciplinary approach to constructing policies that will account for all the relevant factors in order to maximize the positive economic aspects, and minimize the negative cultural and environmental ones.
Sustainable tourism should also be viewed as a global movement that tries to educate people on the benefits of what they call Responsible tourism. Responsible tourism is something very similar to a tourist’s ethical codex.
Its principles oblige tourists to be sensitive towards local cultures, and perform their environmental duties while on vacation. Some of these duties are: producing as little waste as possible, recycling, etc.
However, this whole notion of responsible tourism implies that the visitors are informed about the harms they can potentially make, and the ways in which they can prevent those harm from taking place. Moreover, sustainable tourism is not a strictly defined set of strategies applicable to all contexts.
It demands an analysis of all the relevant factors, and constant awareness of one’s actions from every visitor. As we can see sustainable tourism is a long term mission, which demands a lot of state intervention, education and responsibility. The real question at this point is whether there is time for such a long project.
Some of the results of this global effort are quite obvious. For example, there are more and more customers coming to tourist agencies, and asking for locations that promote sustainable tourism.
On the other hand, what is very disappointing is that there is very little consensus among the experts as to which indicators should be used in order to evaluate whether a resort is practicing sustainable tourism.
Moreover, some of the experts are not even sure where to draw the line between sustainable and unsustainable tourism (Miller 10).
In conclusion, tourism is a widespread and very popular social phenomenon, and people enjoy it for multiple reasons such as: health, education, sport, recreation, religion, or even pure hedonism.
Furthermore, there is a strong economic motivation for the existence of tourism: jobs are created, states and entrepreneurs collect huge amounts of revenue and infrastructure is developed.
Preservation of environment and culture also gets its economic basis in tourism. However, tourism causes some very deep social, cultural and economic issues. History has taught us that many countries, after a certain period, tend to become economically dependent on it, which has its consequences in very deep recessions, seasonal unemployment, etc.
Environment and culture also suffer because of the unplanned and irresponsible practice of tourism. Huge amounts of waste are being generated and culture is being viewed as one big show.
Such practices have been referred to as unsustainable tourism because after a certain period such locations lose their attractiveness to visitors because the hotels are no longer solvent or environment and culture are no longer authentic and intact.
Therefore, the only solution is the introduction of sustainable tourism which is a field in which many experts are trying to define ways to make tourism viable for future generations. It is certain that there are many reasons which make tourism worth struggling for.
Beaver, Allan. A dictionary of travel and tourism terminology . 2nd ed. Wallingford, UK: CABI Publ., 2005. Print.
Buckley, Ralf. “Tourism and Environment.” Annual Review of Environment and Resources 36 (2011): 397-416. Print.
Curley, Robert. “The Tourism Impact of the Haiti Earthquake.” Caribbean Travel, Vacation and Holiday Guide – Guide to Caribbean Travel, Vacations, Trips and Holidays . 2010. Web.
“ Employment in tourism industry to grow significantly over the coming decade, says ILO report. ” International Labour Organization . Web.
Gooroochurn, Nishaal. “Tourism and Taxation: A Theoretical and Empirical Investigation.” Input-Output and General Equilibrium: Data, Modeling and Policy Analysis. ECOMOD. Input-Output and General Equilibrium: Data, Modeling and Policy Analysis, Brussels. 2004. Lecture.
Karim, Iqbal. “Standard Digital News : Magazines : Infrastructure is key to boosting tourism.” Standard Digital News : Home, Breaking News, Business, Jobs, Football, Travel, Tourism, Elections, National, Kenya, Nairobi, County, East Africa, Kibaki, Raila . N.p., 2011. Web.
Menkedick, Sarah. “ Tourism And The “Preservation” Of Culture: A Rebuttal | Matador Network. ” Matador Network | travel culture worldwide . N.p. 2010. Web.
Miller, Graham. The Development of Indicators for Sustainable Tourism: Results of a Delphi Survey of Tourism Researchers . London: University of Westminster, 2000. Print.
Ritchie, J. R. Brent, and Charles R. Goeldner. Travel, tourism, and hospitality research: a handbook for managers and researchers . 2nd ed. New York: J. Wiley, 1994. Print.
Sawkar, K, L Noronha, A Mascarenhas, O Chauhan, and S Saeed. Tourism and the Environment Case Studies on Goa, India, and the Maldives . Washington: The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank, 1998. Print.
Singh, L. Fundamental Of Tourism And Travel . Delhi: ISHA Books, 2008. Print.
Sunyer, Pi. “ The Cultural Costs of Tourism | Cultural Survival. ” Cultural Survival | Partnering with Indigenous Peoples to Defend their Lands, Languages, and Cultures . N.p. 2010. Web.
Weiner, Eric. “ Why Tourism is Not a Four-Letter Word – Features – World Hum. ” The Best Travel Stories on the Internet – Travel Writing – World Hum . N.p., 2010. Web.
Woo, Stu. “ Heavy Reliance on Tourism Has Hawaii’s Economy Hurting – WSJ.com. ” Business News & Financial News – The Wall Street Journal – Wsj.com . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 6). Tourism: Benefits and Costs. https://ivypanda.com/essays/tourism-benefits-and-costs/
"Tourism: Benefits and Costs." IvyPanda , 6 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/tourism-benefits-and-costs/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Tourism: Benefits and Costs'. 6 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Tourism: Benefits and Costs." February 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/tourism-benefits-and-costs/.
1. IvyPanda . "Tourism: Benefits and Costs." February 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/tourism-benefits-and-costs/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Tourism: Benefits and Costs." February 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/tourism-benefits-and-costs/.
- Protein-Protein Complexes Through to Interactomics
- Crossover Complexes of Iron Coordination Compounds
- Advertisement in Beauty Sphere: Psychological Complexes
- Application of N-Hydrocyclyc Carbenes in Antitumor Metallodrugs
- Seasonal Trend of Fertility in Pigs
- Seasonal Demand: Suppliers, Retailers and Clients Views
- Seasonal Changes in Mood and Behavior
- Tourism and Environment
- Tourism Planning and Tourist Agencies
- Tourism as Tool for Sustainable Rural Development
- Tourism for different people in Italy
- Tourism Industry and what way to travel is better
- Factors that have led to the Development of the Tourism Industry
- Adventure tourism and development: Conservation or exploitation
- Tourism Growth in Developing Countries

Essay on Economic Impact Of Tourism
Students are often asked to write an essay on Economic Impact Of Tourism in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Economic Impact Of Tourism
Introduction.
Tourism is a major source of income for many countries. It involves people traveling to different places for various reasons like sightseeing, relaxation, or learning about different cultures. This essay talks about how tourism affects a country’s economy.
Job Creation
Tourism creates jobs. When tourists visit, they need services like hotels, restaurants, and transport. These services need workers, so more jobs are created. This helps to reduce unemployment and poverty in a country, improving the overall economy.
Source of Revenue
Tourism brings in money. Tourists pay for accommodation, food, and other services. They also buy local products as souvenirs. This money helps to boost the country’s economy as it increases the country’s income.
Infrastructure Development
Tourism encourages better infrastructure. To attract more tourists, countries improve their roads, airports, and other facilities. This not only helps the tourists but also benefits the local people, contributing to economic growth.
In conclusion, tourism has a positive impact on a country’s economy. It creates jobs, brings in money, and encourages better infrastructure. Therefore, countries should promote tourism to boost their economy.
250 Words Essay on Economic Impact Of Tourism
What is tourism.
Tourism is the act of people traveling to places outside their usual environment for leisure, business, or other purposes. It’s an activity that can take place domestically or internationally.
Economic Benefits of Tourism
Tourism can bring a lot of money into a local economy. This happens when tourists spend money on hotels, restaurants, shopping, and attractions. This spending supports local businesses and can lead to job creation. For example, if more tourists visit a city, there might be a need for more hotels. This could lead to new jobs for people who work in the hotel industry.
Tourism and Local Economy
Tourism can also help to boost the local economy in other ways. For instance, taxes paid by businesses in the tourism industry can be used by the government to improve infrastructure, like roads and public services. This can make life better for local residents.
Challenges of Tourism
While tourism can bring many benefits, it can also create challenges. For example, if a location becomes too popular, it can lead to overcrowding and strain on local resources. This can make life difficult for local residents and can harm the environment.
In conclusion, tourism can have a big impact on a local economy. It can bring in money, support local businesses, and even help to improve infrastructure. But it’s also important to manage tourism carefully to avoid problems like overcrowding and strain on resources.
500 Words Essay on Economic Impact Of Tourism
Tourism is an important part of many economies around the world. It involves people visiting different places for fun, adventure, or learning. This activity can have a big impact on a country’s economy. It can help to make money, create jobs, and support local businesses.
Money from Tourists
Tourists spend money when they travel. They pay for things like hotels, food, and souvenirs. This money goes into the local economy. It helps to boost businesses and can even lead to more investment in the area. For example, if a lot of tourists visit a place, a new hotel might be built. This can lead to even more tourists visiting in the future.
Tourism can also lead to more jobs. These jobs can be directly related to tourism, like working in a hotel or a restaurant. But they can also be indirect jobs. For example, a local farmer might sell more produce because there are more restaurants serving tourists. Or a local artist might sell more paintings because there are more tourists buying souvenirs.
Support for Local Businesses
Tourism can also help to support local businesses. These businesses might sell things that tourists want to buy, like local crafts or food. Or they might provide services that tourists need, like tours or transportation. These businesses can grow and thrive thanks to the money spent by tourists.
While tourism can bring many benefits, it can also bring challenges. For example, too many tourists can put pressure on local resources like water or energy. It can also lead to higher prices for locals. And in some cases, it can harm the environment.
In conclusion, tourism can have a big impact on a country’s economy. It can bring in money, create jobs, and support local businesses. But it can also bring challenges. It’s important for countries to manage tourism in a way that brings the most benefits and the fewest problems. This way, tourism can be a force for good in the economy.
This essay is a simple explanation of how tourism can impact an economy. It shows that tourism can be both good and bad. But with good management, the benefits can outweigh the challenges.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Break Up
- Essay on Economic Globalization
- Essay on Bread
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Tourism Essay for Students and Children

500+ Words Essay on Tourism
Tourism Essay – Tourism is a major economic activity that has developed significantly over the years. It’s an activity that can be recognized in both developed and developing nations. In general terms, tourism is the movement of a person from one place to another to visit and mesmerize the beauty of that place or to have fun. Moreover, the concept of traveling is considered a luxury and only people with higher income can afford this luxury.

The Growth of Tourism
Earlier our ancestors used to travel by sea routes as it was a convenient and most affordable medium but it was time taking. Due to, technological advancement we can now easily travel to any place without wasting time we can travel thousands of miles within a few hours. Technological advancement has shrunk the earth into a global village. Besides, the modern modes are much safer than the modes that our predecessors used.
Effect of Tourism on a Country
For any country, tourism generates a lot of money especially a country like India. Due to the Taj Mahal (one of the seven wonders of the world) every year the government raise a huge sum of revenue. Also, because of tourism other industries also bloom. Such industries include transportation, wildlife, arts and entertainment, accommodation, etc.
Moreover, this ultimately leads to the creation of job and other opportunities in the area. But there are some drawbacks too which can affect the lifestyle and cultural value of the country.
Importance of Tourism
Traveling is a tiring and difficult thing and not everyone is able to travel. But at the same time, it’s a fun activity that takes your tiredness away. Travelling adds flavor to life as you travel to different places that have a different culture and lifestyle. Also, it’s an easy way to learn about the culture and tradition of a place. Besides, for many areas, tourism is their main source of income.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
India- A Tourist Attraction
The Taj Mahal is not the only destination in India that attract tourist. Likewise, there are hundreds of tourist destination that is spread over the Indian plateau. India has a large variety of Flora and Fauna. Besides, the equator divides the geographical land of India into almost two equal halves that make India a country where six seasons occurs.
Moreover, in almost every city of India, there is a historical monument made by the rulers in their time period.
Benefits of Tourism
Tourism not only benefits the government but also the people that live in the local area. It also creates a business as well as employment opportunities for the local people which ultimately help the government to earn income.
Benefits Due to Tourism
As we know that tourism contributes a lot to the revenue of the country. Also, the government uses this income for the growth and development of the country. Likewise, they construct dams, wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, Dharamshala and many more.
In conclusion, we can say that tourism is a very productive activity both for the tourist and the government. As they support each other simultaneously. Also, the government should consider improving the conditions of the country as more and more number of tourist visit their country.
Above all, tourism is one of the fastest-growing industry in the world that has changed the scenario of the world.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

HYPOTHESIS AND THEORY article
This article is part of the research topic.
"Affiliative nomads" in the age of mobilities
Affiliative nomads in Japan: Potential sustainable tourism stakeholders in depopulated rural areas Provisionally Accepted

- 1 Hannan University, Japan
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
In Japan, the overall population is declining. Depopulation is severe, resulting in various negative consequences, particularly in rural areas. Rural communities could benefit by collaborating with people from other places, mainly urban areas. Typical examples of visitors or tourists from urban areas in these cases are referred to as "kankei jinko." The more fundamental issue, however, is that many rural residents have lost confidence in their ability to live in areas with declining and aging populations. It is important to note the potential for highly mobile people from urban areas to increase the civic pride of rural residents. This raises questions about who these nomadic people, or "affiliative nomads," are and how they interact with residents. To answer these questions, we analyzed cases of affiliative nomads in previous studies. The nomadic people showed respect for the rural areas to the residents; as a result, they were perceived by the residents as being in a stage of growth. When the nomads and residents interact, they create common values such as nature conservation and economic and community revitalization. Thus, the nomads cultivate civic pride among the residents and could be regarded as affiliative nomads. Furthermore, some coordinators bridge residents and nomads to expand their relationships with other people. Affiliative nomads may be sustainable tourism stakeholders and contribute to solving the problems of depopulated areas in Japan and other developed or emerging countries.
Keywords: Nomads, Affiliative, Shared Values, indebtedness, Coordinators, Revitalization, Depopulation, social inclusion
Received: 30 Oct 2023; Accepted: 29 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Horiuchi and Morishige. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Mx. Shiro Horiuchi, Hannan University, Matsubara, Japan
People also looked at
Destroyed by cyclones, impacted by climate change and neglected by foreign owners – these abandoned island resorts are now an eyesore
A pool lined with green sludge, rotting roofs and termite infested buildings – this derelict island resort has become a sad tourist attraction for all the wrong reasons, and it's not an isolated case.
At least half a dozen resorts along the Queensland coast have fallen to a similar fate.
In the heart of tropical Far North Queensland, the picturesque Double Island was once a thriving hub for holiday-makers including former Hollywood power couple Brad Pitt and Jennifer Aniston.
The island resort, 30 minutes north of Cairns, even built a gym for actor Keanu Reeves, so frequent were his stays.
But the resort has long been in a state of disrepair, with rotting roofs punctured by falling coconuts and green sludge lining the bottom of the once sparkling pool.
Brad Madgwick offers guided kayaking tours to the island, and recently incorporated the island's decay into his regular marine-life spotting adventures.
"We've always walked the shorelines looking for wildlife, but in the last few years, we have been given permission to go through the resort," Mr Madgwick said.
"The coconuts have taken a toll and the termites are having a good feed, it's sad really because it used to be a very glamorous resort back in the day."
The derelict state of the resort — safari-style tents covered in mould are dotted throughout — is shaping up to be one of the biggest legal battles ever held over an island in Australia.
The Queensland Government's Department of Resources will attempt to strip Hong Kong based billionaire Benny Wu of the island's lease in the Land Court in Cairns within weeks.
Mr Wu's Fortune Island Holding's is accused of non-compliance for failing to bring the facilities up to scratch and open the island to the public.
The day can't come soon enough for some local Palm Cove business owners, although opinions vary about what should happen with the island, if the state government is successful in its proceedings.
"When it was taken over in 2012, it was a thriving business," said local businessman Tony Richards, who would like to see a resort rebuilt.
"Nothing has been done to it since then. It's a complete bulldoze job."
The ABC has contacted Mr Wu for comment.
Paradise lost
Across the Great Barrier Reef, cyclones and neglect have left half a dozen island resorts shuttered and abandoned, with ruined infrastructure and damaged environments.
Brampton Island Resort, off Mackay, was a jewel in Queensland's tourism crown until it was bought by United Petroleum in 2010 for $5.9 million, its ocean side pool now filled with sand.
Lindeman Island in the Whitsundays, once famed for being the first Club Med in Australia, has sat in ruins since it was pummelled by Cyclone Yasi in 2011.
The Singaporean company, Well Start, has since bought the island and pledged to restore it.
Resorts on South Molle and Hook Island have also been closed for years.
The 1980s party paradise, Great Keppel (Woppa) Island off the central Queensland coast, has been laying in ruin for 15 years, with the Queensland government recently announcing a $30 million master plan including provisions for an eco-resort , new sewage system and conservation areas.
Meanwhile, the beleaguered Dunk Island resort off the coast of Far North Queensland, was also destroyed by Cyclone Yasi in 2011.
There are plans to open "glamping" style accommodation on the island within months, following billionaire Annie Cannon-Brook's purchase in 2022.
Professor Daniel Gschwind, from Griffith University's Institute for Tourism, said abandoned and closed resorts not only had an impact on the Great Barrier Reef's reputation, but Australia's broader tourism brand.
"Globally, the Great Barrier Reef is recognised as an outstanding asset, it's World Heritage listed, which in itself draws a lot of attention," Professor Gshwind said.
"The way Australia manages that asset and presents the asset to visitors is absolutely, critically important for our global reputation."
He said island resorts helped to bring in billions of tourism dollars each year and there needed to be an "expectation that lease holders fulfil their obligations".
However, he said the high cost of maintaining as well as accessing the resorts by plane or barge was impacting on owners to turn a profit, as well as skyrocketing insurance premiums.
"So there are great obstacles to overcome, but the benefit and the value of those islands as a tourism destination really can't be overstated."
Parliamentary inquiry into Queensland islands
Queensland's Transport and Resources Committee held a parliamentary inquiry examining the economic and regulatory frameworks for Queensland's island resorts, tabling a report just over a year ago.
Eighteen recommendations were made to the state government, including cancelling the leases of developers who let the resorts fall to rack and ruin.
Several of the submissions raised concerns about foreign ownership, as well as the impact of climate change, including intense cyclones, on resort infrastructure.
Professor Tim Harcourt, chief economist at the Institute for Public Policy and Governance at the University of Technology Sydney said buying up tropical islands could be seen by some international companies as an attractive proposition.
"They've got to get their money out and they're going to put it somewhere, and buying land is the easiest thing to do," Professor Harcourt said.
He also noted the longevity and success stories of the Hamilton and Hayman Island resorts in the Whitsundays.
The Andrew Forrest-owned Lizard Island, off Cooktown in Far North Queensland has been rebuilt twice due to successive cyclones, and is enjoying strong occupancy numbers.
Orpheus Island and Pelorus Island north of Townsville have also undergone extensive renovations.
Back on Double Island, Mr Madgwick said he would like to see the island returned to its natural splendour.
"I would love to see the island turned into a national park, with a communal kitchen, maybe a caretaker on the island, and to open it up to camping," Mr Madgwick said.
"It's a beautiful island and it should belong to the people."
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Former party paradise great keppel island a step closer to new 'glory' with plans for eco-resort and glamping.
- Brampton Island
- Climate Change
- Dunk Island
- Great Keppel Island
- Lindeman Island
- South Molle
- Travel Health and Safety
- Travel and Tourism (Lifestyle and Leisure)
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition
Why has the yen fallen to a decade’s low and what does it mean for Japan’s economy?
The accelerating slide in the value of Japan’s currency could ultimately be bad news for people in Japan who are heavily reliant on imports
The value of Japan’s currency has tumbled so much, that its value is back to where it was in 1990, shortly after Japan’s famous “bubble economy” burst. For a moment on Monday it was trading at 160 yen to US$1. A few years ago, it was closer to 100 yen to US$1.
The yen’s accelerating slide could ultimately be bad news for people in Japan. A weaker yen squeezes households by increasing import costs. Japan is heavily reliant on imports for both energy supplies and food, meaning inflation could rise.
A weaker yen is however a boon for Japanese exporters’ profits – and for tourists visiting Japan who find their currencies going further.
Why has the yen fallen so far?
The yen has been steadily sliding for more than three years, losing more than a third of its value since the start of 2021.
One factor behind its fall is momentum: the yen falls because investors are selling it – and investors continue to sell it because it is falling. In such instances, the market enters a self-fulfilling loop.
As a result of the falling currency, exporters are discouraged from converting foreign proceeds into yen, further decreasing demand.
However there are also major policy reasons for the currency’s sharp decline.
For years, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) has kept interest rates extraordinarily low to encourage more inflation in its economy, as well as to boost bank lending and spur demand.
In February, in the face of widespread labour shortages and a weakening yen, Japan was overtaken by Germany as the world’s third-biggest economy and slipped into recession .
With low interest rates seen as a key factor in the rapid decline of the yen, last month the BOJ ended its policy of keeping its benchmark interest rate below zero, lifting its short-term policy rate from -0.1% to between zero and 0.1%.
After that decision, markets were then focused on the pace of further rate rises. On Friday, the BOJ announced it would hold interest rates steady, signalling that further increases weren’t imminent. This precipitated another round of selloffs in the yen, putting more pressure on the currency.
It was this wave of selloffs that drove the currency down to 160 yen to the dollar for the first time since 1990.
What effect is it having?
The decades-low value of the yen means tourist dollars are going further than they have for generations, leading to a boom in the industry. As well as the US dollar, the yen has also hit multi-year lows against the euro, the Australian dollar and the Chinese yuan – all strong tourism markets for Japan.
In February, Japan recorded 2.79 million visitors – a record for the month.
Domestic consumption, however, remains a major weak spot. Households tend to be net importers and are facing higher prices due to the weak yen.
The weakening yen is also a factor in the decision by big Japanese investors’ to keep their cash abroad, where it can earn better returns. This trend is exacerbated by an unusually strong US dollar which has meant that American investments and assets offer far better returns for major financial institutions.
What are Japanese authorities doing?
In recent years, Japanese authorities have intervened to prop up the value of the currency , because a weak yen complicates its objective of achieving sustainable inflation, and strengthening it could help increase domestic consumption and local investment.
Japan intervened in the currency market three times in 2022, selling US dollars it holds in reserve in order to buy yen. Tokyo is estimated to have spent around $60bn defending the currency at that time.
On Monday, after briefly hitting its multi-decade low, the yen rose sharply, leading traders to suspect that after weeks of threatening to intervene, Japan had stepped in to support its currency.
Japan’s top currency diplomat, Masato Kanda, declined to comment when asked if authorities in Tokyo had intervened.
“Today’s move, if it represents intervention by the authorities, is unlikely to be a one-and-done move,” said Nicholas Chia, Asia macro strategist at Standard Chartered Bank in Singapore.
“We can likely expect more follow through from [Japan’s Ministry of Finance] if the dollar/yen pair travels to 160 again. In a sense, the 160-level represents the pain threshold, or new line in the sand for the authorities.”
Reuters contributed to this report
Most viewed
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
However, tourism could also have a negative effect on the economy. Its boom may lead to a deindustrialization in other sectors (Copeland, 1991); this phenomenon is often called 'Dutch Disease effect'.Despite contractions of the manufacturing sector are not found in the long-run period, the authors warn that the danger of this effect could still be valid in either short or medium run (Song ...
Development of the Private Sector. Negative economic impacts of tourism. Leakage. Infrastructure cost. Increase in prices. Economic dependence of the local community on tourism. Foreign Ownership and Management. Economic impacts of tourism: Conclusion. Further reading on the economic impacts of tourism.
Tourism has become the world's third-largest export industry after fuels and chemicals, and ahead of food and automotive products. From last few years, there has been a great surge in international tourism, culminates to 7% share of World's total exports in 2016. To this end, the study attempts to examine the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth ...
According to the World Economic Outlook (WEO) Report, the global economy will grow an estimated 3.0% in 2023 and 2.9% in 2024. While this is higher than previous forecasts, it is nevertheless below the 3.5% rate of growth recorded in 2022, pointing to the continued impacts of the pandemic and Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and from the cost-of ...
This paper aims to systematically review and analyze the current research on tourism impacts on destinations during 2016-2020. The Scopus database was used to search for tourism impact studies ...
Tourism is one of the sectors most affected by the Covid-19 pandemic, impacting economies, livelihoods, public services and opportunities on all continents. All parts of its vast value-chain have been affected. Export revenues from tourism could fall by $910 billion to $1.2 trillion in 2020. This will have a wider impact and could reduce global ...
After a global contraction of 3.4% in 2020 and a rebound of 5.5% in 2021, the world economy is projected to grow by 4% in 2022 and then 3.5% in 2023. Given its importance as a major export category (prior to the pandemic tourism was the third largest in the world, after fuels and chemicals), and recognizing its role as a source of employment ...
Table 1 presents a summary of selected tourism economic impact studies. The pioneering study in this field was published by Sadler and Archer in Annals of Tourism Research in 1975, with a further 420 full-length articles published on this subject between 1975 and 2020. On average, fewer than 12 articles were published each year in 20 SSCI or ABS journals, indicating that the research topic has ...
University Carlo Cattaneo, Italy. Abstract. Topics such as the relationship between tourism and economic impact, its potential benefits and negative externalities are characterized by both vastness and heterogeneity of contents. There-fore, it can be complex to pinpoint the seminal works of each area of study.
Throughout time, the global tourism industry and economy have been significantly affected by disasters and crises. At present, COVID-19 represents one of these disasters as it has been causing a serious economic downturn with huge implications in tourism. In this review paper, we have analysed more than 100 papers regarding the effect and consequences of a pandemic on tourism and related ...
In 2023, the Travel & Tourism sector contributed 9.1% to the global GDP; an increase of 23.2% from 2022 and only 4.1% below the 2019 level. In 2023, there were 27 million new jobs, representing a 9.1% increase compared to 2022, and only 1.4% below the 2019 level. Domestic visitor spending rose by 18.1% in 2023, surpassing the 2019 level.
Negative impacts are the increase in process and goods and service, increase in price of land and housing, increase in cost of living, job may pay low wages and many more. (Kreag, 2001) Tourism involves a large range of retail and services. As such, tourism has variety of economic impacts as tourist contributed many to sales, profits, tax ...
Tripoli, Lebanon. We undertake a systematic literature review that looks at the economic ef fects of tourism at subnational. levels. This review, the first of its kind to our knowledge, is timely ...
Abstract. The paper looks at the relationship between tourism and economic development through a holistic lens. It was found that tourism leads to economic development in host nations through job creation, the multiplier effect, infrastructure development and improvement of business conditions. We will write a custom essay on your topic.
Issue Paper Series - The Economic Impact of Tourism: Overview and Examples of Macroeconomic Analysis . Published: 2013 Pages: 26. eISBN: 978-92-844-1562-5. Complete Book PDF (3.64MB) | View Chapters.
The seventh economic factor of tourism is the foreign exchange rates at the destination. Foreign exchange and bank interest rates are in most cases determined by demand and supply of foreign exchange in an economy (Greene& William 2000). This aspect has a direct effect to the cost of tourism in a destination.
This increase in popularity of tourism has had a huge impact on the world economy, and tourism plays one of the most significant roles in some of the strongest economies in the world. It is easy to conclude that tourism can have incredibly positive impact on human society; however, significant changes that the 21 st century has brought are ...
500 Words Essay on Economic Impact Of Tourism Introduction. Tourism is an important part of many economies around the world. It involves people visiting different places for fun, adventure, or learning. This activity can have a big impact on a country's economy. It can help to make money, create jobs, and support local businesses.
Tourism is vital to the success of many economies worldwide and has been a widely researched area for many years. Unfortunately, an insufficient number of studies have been conducted on this subject in the context of Saudi Arabia. Therefore, this research investigates the role of tourism in promoting economic growth in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia by using annual time series data from 2003 to 2019.
This research paper investigates the growth of tourism and its profound impact on the economy in Goa, India. As tourism continues to play a vital role in national GDP growth globally, this study aims to understand the intricate relationship between tourism and economic development. Despite extensive empirical research, there remains ...
Economic Impact Of Tourism Essay. 1419 Words6 Pages. Tourism has been identified for its important participation in the economy in different small islands. Tourism serves to encourage the growth of basic infrastructure, participates in the development of businesses, attracts foreign investment and supports the transfer of information and ...
500+ Words Essay on Tourism. Tourism Essay - Tourism is a major economic activity that has developed significantly over the years. It's an activity that can be recognized in both developed and developing nations. In general terms, tourism is the movement of a person from one place to another to visit and mesmerize the beauty of that place ...
Economic impacts of tourism: Tourism is important to the economy of both the rich and the poor countries. Tourism does not only benefit the economy by handing out employment but also through the expenditure of the tourist (tourismintheunitedkingdom.weebly.com). Tourist destinations can also assist in the improvements and development of ...
In Japan, the overall population is declining. Depopulation is severe, resulting in various negative consequences, particularly in rural areas. Rural communities could benefit by collaborating with people from other places, mainly urban areas. Typical examples of visitors or tourists from urban areas in these cases are referred to as "kankei jinko." The more fundamental issue, however, is that ...
Brampton Island Resort, off Mackay, was a jewel in Queensland's tourism crown until it was bought by United Petroleum in 2010 for $5.9 million, its ocean side pool now filled with sand. The ...
The value of Japan's currency has tumbled so much, that its value is back to where it was in 1990, shortly after Japan's famous "bubble economy" burst. For a moment on Monday it was ...
Germany's economic prospects are looking up after two grueling years of near-zero growth. The consumer-led revival, though, papers over enduring industrial weakness for which there's no quick fix.