- 96259-21993 ,
- 93132-18122

Tourism in India
Whatsapp 96259-93995 For Details
Development of Tourism in India UPSC CSE

Get Free IAS Booklet
Summary of Tourism in India
India's tourism industry plays a significant role in the country's economy, contributing around 10% to its GDP . With diverse attractions ranging from adventure and cultural experiences to wildlife encounters, India attracts both domestic and international travellers.
However, the industry faces several challenges, including infrastructure issues, safety concerns, and the impact of seasonal fluctuations. To address these challenges, the Indian government has introduced initiatives like the Swadesh Darshan Scheme and the PRASHAD Scheme , aimed at improving tourism infrastructure and promoting heritage destinations.
In recent years, India has taken proactive steps to boost its tourism sector. Hosting global tourism summits, launching campaigns like Visit India Year 2023 , and promoting sustainable tourism through the Draft National Tourism Policy 2022 are among these initiatives. These efforts are geared towards enhancing infrastructure, ensuring safety measures, and attracting foreign investments to further develop the tourism sector.
What is tourism?
Tourism involves travelling for pleasure or business, exploring different destinations, and experiencing new cultures and activities.
What measures has India taken to attract international tourists?
India has organised events like the Global Tourism Investors Summit and International Tourism Mart, launched campaigns like Visit India Year 2023, and implemented policies to enhance tourism infrastructure and sustainability.
What are the challenges faced by the Indian tourism industry?
Challenges include infrastructure issues, safety concerns, shortage of skilled manpower, lack of basic amenities, and seasonality in tourism.
Background of Tourism in India
India's tourism potential reflects its rich diversity, encompassing historical monuments, geographical variations, climate diversity, and natural wonders. This array of attractions has made India a sought-after destination for travellers worldwide.
Historical texts such as the 'Arthashastra' emphasise the importance of travel infrastructure for the state, underscoring the enduring significance of tourism. Post-Independence, tourism continued to occupy a central position in India's development agenda, evident in its inclusion in successive Five-Year Plans. The introduction of various forms of tourism, including Business, Health, and Wildlife tourism, following the seventh Five Year Plan, demonstrates the government's efforts to diversify and enhance the tourism sector's offerings.
Tourism acts as an economic multiplier, gaining prominence as India aims for rapid economic expansion and job creation. Throughout history, India has drawn travellers from afar, with figures like Hieun-tsang , a Chinese Buddhist, visiting the country due to its legendary wealth. Pilgrim travel also saw a surge, with Emperors Ashoka and Harsha facilitating the construction of rest houses for pilgrims.
It serves as a crucial driver for employment generation, revenue growth, and bolstering foreign exchange reserves. Notably, India's tourism and hotel industry ranks as the third-largest contributor to foreign exchange earnings.
Introduction of Tourism in India
Tourism involves travel for pleasure or business, including activities such as attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists. According to the UN World Tourism Organization, an international tourist is someone travelling outside their country of residence.
India, one of the oldest civilizations, offers a diverse range of experiences. From the snowy Himalayas to the lush rainforests of the south, it covers a vast area of over 3 million square kilometres. Surrounded by the Great Himalayas in the north and bordered by the Indian Ocean in the south, India has a unique geographical identity.
Travelling across India exposes visitors to a variety of cuisines, religions, arts, crafts, music, landscapes, tribes, history, and adventure sports. The country seamlessly blends the old with the new, with bustling markets alongside modern shopping malls, and ancient monuments coexisting with luxury hotels.
Whether you prefer mountain retreats, beach getaways, or desert expeditions , India offers a wide range of options for every traveller.
Types of Tourism Supported in India
- Adventure Tourism :
- Involves exploring remote areas and engaging in various activities like trekking, skiing, and whitewater rafting.
- Popular destinations include Ladakh, Sikkim, Himalayas, Himachal Pradesh, and Jammu and Kashmir.
- Beach Tourism :
- India's vast coastline and islands offer opportunities for leisure activities.
- Kerala, Goa, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, and Lakshadweep attract tourists with their beaches.
- Cultural Tourism :
- Tourists come to experience India's rich cultural heritage and attend various fairs and festivals.
- Sites such as Ajanta & Ellora caves, Mahabalipuram, Hampi, Taj Mahal, and Hawa Mahal are popular destinations.
- Eco Tourism :
- Focuses on sustainable preservation of natural areas or regions.
- Tourists visit places like Kaziranga National Park, Gir National Park, and Kanha National Park for ecotourism.
- Medical Tourism :
- Offers cost-effective but quality healthcare to foreign tourists.
- Chennai attracts a significant number of medical tourists from foreign countries.
- Wildlife Tourism :
- India's rich forest cover and exotic wildlife species attract tourists.
- Sariska Wildlife Sanctuary, Keoladeo Ghana National Park, and Corbett National Park are popular destinations for wildlife tourism.
Global Tourism Industry
- Economic Contribution: Directly contributes approximately 3.6% to the world's GDP and indirectly about 10.3%. Represents about 12% of total world exports.
- Employment: Employs nearly 77 million people globally, accounting for around 3% of total global employment.
- Market Size and Growth: The global tourism sector's market size grew by nearly 14% in 2023 compared to the previous year, and revenue surpassed pre-pandemic levels, reaching approximately 2.29 trillion U.S. dollars.
- Continuing world prosperity.
- Growing recognition of tourism's contribution to employment and economic growth.
- Availability of better infrastructure.
- Focused marketing and promotion efforts.
- Liberalisation of air transport.
- Growing intra regional cooperation.
- Increasing number of Public-Private-Partnerships (PPPs).
Indian Tourism Industry
- Contribution to GDP: In 2015, the travel and tourism industry contributed $124.8 billion to India's GDP, accounting for about 10% of the total GDP in 2020.
- Growth Trends: India was identified as one of the fastest-growing tourism destinations globally in a 2014 study. Expected annual growth rate of 6.4% between 2014 and 2024. It is anticipated to be the third fastest-growing tourism destination with a 7.9% annual average growth rate till 2023.
- Employment: Tourism in India provides 40 million job s, with over 7.7% of Indian employees working in the industry. In 2019, the sector accounted for 39 million jobs, which was 8.0% of total employment, expected to increase to about 53 million jobs by 2029.
- Visitor Statistics: The US is the largest source marke t for visitors to India, followed by Bangladesh and the UK. Outbound travel from India was forecasted to reach 1.41 million in 2020. Foreign tourist arrivals in March 2022 showed significant growth, indicating a post-pandemic revival.
- World Rankings: India ranks 54th out of 117 countries overall in the World Economic Forum’s Travel and Tourism Development Index 2021. Ranked 10th in terms of contribution to World GDP in the World Travel and Tourism Council’s report in 2019.
- Heritage Sites: India currently has 42 sites listed under the 'World Heritage List', ranking 6th globally.
- Financial Impact: In 2019, the contribution of travel and tourism to India's GDP was 6.8%, amounting to approximately Rs. 13,68,100 crore (USD 194.30 billion).
Significance of Tourism
- Boost to Service Sector: Tourism drives growth in the service sector, including airlines, hotels, and transportation businesses.
- Foreign Exchange Revenue: Foreign travellers contribute to India's foreign exchange earnings, supporting the economy.
- Preservation of National Heritage: Tourism highlights the importance of preserving national heritage sites and the environment.
- Cultural Pride Renewal: Recognition of tourist spots globally instills a sense of pride among Indian residents.
- Infrastructural Development: Investments in infrastructure ensure smooth travel experiences and enhance tourist destinations.
- Global Recognition: Tourism places India on the global map, earning appreciation and fostering cultural exchange.
- Promotion of Cultural Diplomacy: Tourism promotes cultural diplomacy, fostering friendship and cooperation between India and other countries.
- Regional Development: Tourism stimulates regional development by bringing in revenue and encouraging inclusive growth.
- Social Equality: It promotes social equality by directing investment towards areas lacking growth-promoting industries.
- Job Creation: The tourism industry creates jobs in tour operations and hospitality, benefiting local economies.
- Support for Infrastructure: Growth in tourism necessitates infrastructure development, supporting sectors like transportation and real estate.
- Opportunities for Small Businesses: Small businesses in tourist areas benefit from the influx of tourists and opportunities for growth.
- Contribution to Soft Power: Tourism enhances India's soft power by showcasing its attractions and fostering global connections.
- Funding for Monument Preservation: Tourism provides funds for the preservation and restoration of monuments and wildlife areas.
- Promotion of Biodiversity: It showcases India's biodiversity, raising awareness and support for conservation efforts.
Challenges to the Growth of Tourism in India
- Lacking Infrastructure: Inadequate roads, water, sewer systems, hotels, and telecommunication facilities pose challenges for tourists in India.
- Safety and Security Concerns: Ensuring the safety and security of tourists, particularly foreign visitors, remains a significant hurdle. Attacks on foreigners raise doubts about India's ability to host tourists from distant countries.
- Shortage of Skilled Manpower: The tourism industry faces a shortage of skilled personnel, impacting its ability to deliver quality services and experiences.
- Absence of Basic Amenities: Basic facilities such as drinking water, well-maintained toilets, first aid services, and cafeterias are often lacking at tourist destinations.
- Seasonality Issues: Tourism experiences seasonality, with the peak season limited to six months from October to March, resulting in heavy crowds particularly in November and December.
- Non-acceptance of International Cards: Small outlets in India often do not accept international cards, posing inconvenience to foreign tourists and hindering seamless transactions.
- Ecological Carrying Capacity (In case of tourism and infrastructure development): Ecological carrying capacity refers to the maximum number of visitors or level of development an area can sustain without causing significant harm to its natural environment. In the context of geography, tourism, and infrastructure expansion, it's crucial to recognize this limit to ensure the preservation of ecosystems and prevent ecological degradation. This concept considers factors like biodiversity, water and air quality, soil stability, and the resilience of local habitats. Ignoring ecological carrying capacity can lead to environmental degradation, loss of biodiversity, and disruptions to ecosystems, ultimately impacting both the natural environment and the tourism industry. Therefore, responsible planning and management that prioritise sustainability and conservation are essential to maintain the delicate balance between human activities and the environment.
Measures Taken by India to Attract International Tourists
- Global Tourism Investors Summit: Organised to showcase investible projects and opportunities in India's tourism and hospitality sector to both domestic and international investors. Held in conjunction with India's G20 Presidency, highlighting the nation's commitment to tourism development.
- Visit India Year 2023: A collective initiative inviting global travellers to explore India throughout the year 2023.
- PRASHAD Scheme: Focuses on rejuvenating pilgrimage sites and enhancing heritage destinations by undertaking infrastructure developments.
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: Aims at integrated development of theme-based tourist circuits, encouraging private sector investment in tourism infrastructure.
- International Tourism Mart: Dedicated to promoting tourism in the North Eastern region of India, showcasing its unique attractions.
- Utsav Portal: Showcases festivals, events, and live darshans across India to promote various regions as popular tourist destinations worldwide.
- Draft National Tourism Policy 2022: Aims to elevate India as one of the top 5 destinations for sustainable and responsible tourism. Includes provisions for a National Green Tourism Mission to ensure sustainability in tourism development.
- Swachh Bharat Movement: Significant cleaning campaign initiated to preserve the sanctity of national historic monuments, contributing to a cleaner and more attractive tourist environment.
- All India Permit Rules 2021: Allows online application for an All India Tourist Authorization/Permit, simplifying the process for tourist vehicle operators.
- Infrastructure Development: Projects under schemes like Swadesh Darshan, PRASHAD, and Assistance to Central Agencies for Tourism Infrastructure Development focus on enhancing tourism-related infrastructure.
- Swadesh Darshan 2.0 (SD2.0): Revamped scheme aimed at developing sustainable and responsible tourist destinations with a tourist-centric approach.
- Financial Assistance for Events: State Governments and Union Territories receive financial aid for organising fairs, festivals, and tourism-related events under the Domestic Promotion & Publicity including Hospitality (DPPH) Scheme.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative: Launched to encourage domestic travel among citizens, promoting exploration within the country.
- Promotion of Thematic Tourism: Vigorous promotion of thematic tourism such as wellness, culinary, rural, and eco-tourism to diversify tourism offerings.
- E-Visa Facility: Facility extended to nationals of 167 countries across seven sub-categories, making visa procurement easier and more accessible.
- GST Reduction on Hotel Rooms: Reduction in GST rates for hotel rooms with tariffs ranging from ₹1,001 to ₹7,500/night to 12%, enhancing India's competitiveness as a tourism destination.
- Improving Air Connectivity: Collaboration with the Ministry of Civil Aviation under RCS-UDAN Scheme to operationalize 53 tourism routes , enhancing air connectivity to tourist destinations.
- Incredible India Tourist Facilitator (IITF) Certification Program: Digital initiative aimed at creating a pool of well-trained tourist facilitators through an online learning platform, generating employment opportunities at the local level.
- Capacity Building for Service Providers: Programmes conducted under the CBSP Scheme to train and upgrade manpower, ensuring better service standards in the tourism sector.
- National Integrated Database of Hospitality Industry (NIDHI+): Technology-driven system promoting digitalization and ease of doing business for hospitality and tourism sectors, facilitating inclusivity across various segments.
Conclusion for Tourism in India
To propel the growth of India's tourism sector, several key actions must be taken:
- Establish a body, like the National Tourism Authority (NTA) or National Tourism Advisory Board (NTAB), to provide guidance and operationalize initiatives.
- Foster synergy between government and private sectors to streamline tourism development efforts.
- Implement a quality tourism framework for certification of products and services.
- Enhance existing luxury tourism products and increase their numbers while rationalising haulage charges.
- Leverage the reach and connectivity of Indian Railways to promote tourism through more tourist trains.
- Initially, the focus should be on popular tourist destinations instead of spreading resources thinly across numerous circuits or centres.
Mains PYQS Of is Development of Tourism in India
For offline/online admission call: 93132-18122.
Book your Free Class

Free IAS/UPSC Study Material By Chahal Academy:

Tourism Sector in India – Explained, pointwise
ForumIAS announcing GS Foundation Program for UPSC CSE 2025-26 from 19 April. Click Here for more information.
ForumIAS Answer Writing Focus Group (AWFG) for Mains 2024 commencing from 24th June 2024. The Entrance Test for the program will be held on 28th April 2024 at 9 AM. To know more about the program visit: https://forumias.com/blog/awfg2024
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is the current status of Tourism Sector in India?
- 3 What are the driving factors of Tourism Sector in India?
- 4 What are the challenges faced by the Tourism Sector in India?
- 5 What steps have been taken for the development of Tourism Sector in India?
- 6 What more steps can be taken going ahead?
- 7 Conclusion
Introduction
A three-day National Conference of Tourism Ministers of States was held for the first time in Dharmsala (Himachal Pradesh) recently. The purpose of the Conference was to discuss, debate, and deliberate on modes and mechanisms to develop tourism sector in India. The meeting came up with ‘ Dharamshala Declaration ‘. The Dharamshala Declaration aims to recognise India’s role in contributing towards global tourism as well as focus on recovery by also promoting domestic tourism, which has been overlooked for long. India is a vast country with huge geographical, climatic, landscape, wildlife, heritage and cultural diversity. As such India has huge tourism potential. Yet this potential has remained under-utilized. In this context, the Ministry of Tourism has undertaken several initiatives to boost tourism in India.
What is the current status of Tourism Sector in India?
Before the onset of the pandemic, the contribution of tourism sector to India’s GDP had reached ~US$ 250 billion in 2018. However, the contribution had fallen to US$ 122 billion in 2020 due to pandemic. The share of Tourism to GDP has hovered around ~5-6%. With post-pandemic recovery, the tourism industry is expected to reach US$ 512 billion by 2028.

Source: IBEF
Tourism Sector is the third-largest foreign exchange earner for the country in 2019. The foreign exchange earnings between 2016 and 2019 increased at a CAGR of 7%, but dipped in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. By 2028, Indian tourism and hospitality is expected to earn US$ 50.9 billion as visitor exports compared with US$ 28.9 billion in 2018. Foreign Tourist arrivals had reached 10.9 million in 2019, before falling to 2.7 million in 2020 due to the pandemic.
India was ranked 34th in the Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019 published by the World Economic Forum. The Economic Impact 2019 Report published by the World Tourism and Travel Council (WTTC) has noted that between 2014-19, India witnessed the strongest growth in the number of jobs created (6.36 million), followed by China (5.47 million) and the Philippines (2.53 million).
In 2020, the Indian tourism sector accounted for 39 million jobs, which was 8% of the total employment in the country. By 2029, it is expected to account for about 53 million jobs. Tourism sector provides diverse opportunities for jobs like in hospitality/hotels/accommodation, transportation, tour guides, travel operations etc.

Source: IBEF. Components of Tourism Sector
What are the driving factors of Tourism Sector in India?
The Tourism Sector in India is driven by various factors like diverse attractions, robust demand (like for medical tourism) and attractive opportunities.

In addition to the above, rapidly expanding India economy is providing huge opportunities for business tourism. According to the World Bank, India has overtaken Japan to become the world‟s third largest economy in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). India holds a 6.4% share of global GDP on a PPP basis. Because of the economic growth, foreign players are interested to establish their operational facilities in the country. Domestic investors have also made huge investments to expand their business. Tourism industry gets benefited from the growing economic environment and investment made by both domestic and foreign investors. The country‟s growing economic environment acts as one of the major influential driver for tourism growth and development of the country.
What are the challenges faced by the Tourism Sector in India?
Awareness : Despite promotional campaigns by the Government, the awareness regarding India as a tourist destination remains low. Even among domestic tourists, the choice is limited to few popular destinations which remain overcrowded, while many other potential places receive low footfalls of tourists. The information portals and centres are poorly managed. There is lack of promotional campaigns in foreign countries. The absence of online branding campaigns fail to provide information to attract tourists.
Infrastructure and Safety : Many popular destinations lack air connectivity, especially in the hilly regions. Moreover, there is lack of proper hygienic facilities in may places. Lack of cleanliness is off-putting to many tourists. In addition there are safety concerns especially among foreign visitors because of few cases of harassment. Poor experience of some tourists leads to bad word-of-mouth information impacting perception of potential tourists.
Communication : Many tourists face communication problem while in India. This makes them dependent on tourist guides or travel operators to curate their travel in India.
Lack of Skilled Manpower : There is dearth of skilled manpower especially multi-lingual tour guides or hotel staff. The sector is dominated by small unorganized players who can’t spend on skilling their employees or sensitising them to cultural values of the foreign tourists. This impacts tourist experience.
Visa Process : The Government had started the e-visa process (online) which has led to increase in foreign tourists. However, the visa-on-arrival facility is limited to very few countries, limiting foreign tourists.
Currency Fluctuations : Another issue is the fluctuations in the currency exchange rates. The inability to know the value of a currency means that long-range tourism prices are especially hard to predict and the fallout from this monetary instability is already impacting multiple tourism support systems.
Although the coronavirus crisis has short-term destructive effects on the tourism industry, it is challenging the practices of the tourism industry and is drawing attention to a succession of issues like poor risk management in the travel industry, viral globalization, and travel of diseases with tourists to cross borders.
What steps have been taken for the development of Tourism Sector in India?
Infrastructure : The Government has been increasing investments in strengthening of the country’s road and rail networks and promoting port development is a significant driver for the growth of the Tourism sector. The Adarsh Station Scheme is helping modernize railway stations, while the Regional Connectivity Scheme – UDAN ( Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik ), is helping make air travel more economical and widespread to hitherto unserved routes. The Swadesh Darshan and PRASHAD schemes aim to stimulate growth in niche tourism segments such as religious, heritage, wellness, medical, adventure, MICE, wildlife etc. Under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme, the Government has launched several theme based circuits like Buddhist circuit which covers destinations associated with the life of Lord Buddha.
Promotional Campaign : Promotional activities such as the Incredible India 2.0 campaign focuses on niche tourism products including yoga, wellness, luxury, cuisine wildlife among others. “ Find the Incredible You ” Campaign focuses on the promotion of niche tourism products of the Country on digital and social media.
Information Helpline : The government has introduced the concept of e-tourist and e-medical visas which has helped increase inbound tourists to the country. Additional initiatives such as Atithi Devo Bhava , a 24×7 multi-lingual Tourist Helpline, among others have helped improve the safety and security of tourists. On a pilot basis, an ‘ Incredible India Helpline ’ has been set up to guide the tourists.
Safety : The Ministry of Tourism has adopted a code of conduct for safe tourism, which contains a set of guidelines to encourage tourism activities to be undertaken with respect to basic rights like dignity, and safety of both tourists and local residents, in particular women and children.
Investment : The government allows 100% Foreign Direct Investment in the Travel and Tourism sector through the automatic route to increase investments across the sector. More recently, the GST rate cut on hotel room tariffs across the board has been a positive move for the industry and is expected to boost the sector’s competitiveness globally.
Cleanliness and Hygiene : Major cleanliness campaign has been launched under the Swachh Bharat movement for protecting and preserving the sanctity of monuments of national heritage . The Ministry of Tourism has also launched awareness campaign to ensure cleanliness of surroundings and help create a Swachh Bharat, Swachh Smarak .
Assistance to States : Financial assistance to states, including places of religious importance, for various tourism projects in consultation with them subject to availability of funds, inter-se priority, liquidation of pending utilisation certificates and adherence to the scheme guidelines.
Digital Database : In September 2021, the Government launched NIDHI 2.0 (National Integrated Database of Hospitality Industry), a scheme which will maintain a hospitality database comprising accommodation units, travel agents, tour operators and others. NIDHI 2.0 will facilitate digitalisation of the tourism sector by encouraging hotels to register themselves on the platform.
Skilling : The Ministry of Tourism has introduced the Incredible India Tourist Facilitator (IITF) and Incredible India Tourist Guide (IITG) Certification Programme to create an online learning platform of well-trained tourist facilitators and guides across the country.
The Ministry of Tourism had launched an initiative called SAATHI (System for Assessment, Awareness & Training for Hospitality Industry) by partnering with the Quality Council of India (QCI) in October 2020. The initiative was focused on effective implementation of guidelines/SOPs issued with reference to COVID-19 for safe operations of hotels, restaurants, and other units.
What more steps can be taken going ahead?
First , The government should continue to promote India’s diversity and rich heritage to re-establish its position as a tourist paradise. The promotional campaigns should target both domestic and foreign tourists. Similarly, the extent of theme-based tourist circuits can be expanded.
Second , the skilling initiatives should be scaled-up . Tourism sector has a potential to provide lot of livelihood opportunities in smaller cities/towns (below tier-2 level). It can help address the issue of jobless growth.
Third , there is need to balance the promotion of tourism with safeguarding the physical, social, and cultural environment in the destination areas. The government should also promote green and sustainable tourism to tackle issues relating to water crisis, pollution, waste management, etc.
Fourth , the Government should further reform the tourist visa norms and processes to facilitate tourism. The Government should also explore the possibility of expanding the visa-on-arrival facility.
Fifth , the focus should also be on supporting and promoting the emerging segments of tourism.

Source: IBEF. Emerging Segments of Tourism.
The tourism sector in India is gradually recovering from the impact of the pandemic. Even during the pandemic, the sector had shown resilience by adapting its operations to ensure safe practices and social distancing. The sector has huge untapped potential in India. The multiplier effect associated with the tourism sector can help raise the income levels and ensure inclusive growth. A burgeoning tourism industry can prove to be vital in ensuring India’s transition to a high income economy.
Syllabus : GS III, Indian Economy and issues related to growth.
Source : The Hindu , Hindustan Times , IBEF

Type your email…
Search Articles
Latest articles.
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 25 April, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 25 April, 2024
- “Material resources of the community” under Article 39(b)
- On UK’s Rwanda Bill: Why it’s a solution that doesn’t work
- What challenges does the NCAP face: On the National Clean Air Programme
- Sri Lanka’s efforts to improve its economy:
- Universal Basic Income
- Issues with Swacch Bharat Mission
- Safety of Indian Seafarer
- [Download] Prelims Marathon Weekly Compilation – April, 2024 – 3rd week
Prelims 2024 Current Affairs
- Art and Culture
- Indian Economy
- Science and Technology
- Environment & Ecology
- International Relations
- Polity & Nation
- Important Bills and Acts
- International Organizations
- Index, Reports and Summits
- Government Schemes and Programs
- Miscellaneous
- Species in news
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Ecotourism: A Scenic Journey
Last updated on December 28, 2023 by ClearIAS Team

A team of educationists and government officials visited the Dongrim-Mandur area to explore the possibility of developing a pilot eco-tourism project.
Do you think ecotourism should be promoted in India? Learn its role in the sustainable development of the state.
Also, read about the Buddhist tourism circuit.
Table of Contents
What is Ecotourism?
Ecotourism is an entirely new approach to tourism. It is the preservation of trips to natural areas to appreciate the natural and cultural history of the area while taking care not to disturb the ecosystem’s integrity. This will generate economic opportunities that benefit the local population by promoting the conservation and protection of natural resources.
It is also defined as, tourism that includes exploring natural areas such as national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves to take in the scenic beauty of a wide variety of flora and animals.
According to experts, the promotion of ecotourism is essential to spreading a better understanding of nature and bolstering conservation efforts. It significantly contributes to the empowerment of local communities by giving them alternate means of support.
Purpose of Ecotourism
- Educate the traveller.
- Raise public awareness of the need to protect forests.
- To provide funds for ecological conservation.
- Aid and prosper neighborhood communities and raise their standard of existence.
- To foster respect for different cultures and human rights.
Guiding Principles for Ecotourism
- Ecotourism places a paramount emphasis on preserving natural habitats, biodiversity, and ecosystems.
- Responsible tour operators and travelers aim to leave minimal environmental impact during their visits.
- Local communities are integral to ecotourism initiatives, benefiting economically and socially from tourism activities.
- Empowering communities to participate in decision-making fosters a sense of ownership and ensures the long-term success of ecotourism projects.
- Ecotourism emphasizes the importance of respecting and preserving local cultures and traditions.
- Tourists are encouraged to engage in cultural exchange while minimizing any negative impact on indigenous communities.
- Ecotourism seeks to educate visitors about the natural and cultural significance of the destinations they visit.
- Interpretation centers, guided tours, and informational materials contribute to raising awareness and fostering a deeper understanding of the environment.
- Sustainable tourism practices, such as energy conservation, waste reduction, and responsible water usage, are core tenets of ecotourism.
- Accommodations and facilities are designed to operate in harmony with the environment.
The positive impact of Eco-tourism
- An opportunity to preserve ecosystems and biological diversity.
- It is environment-friendly.
- It generates public interest in and awareness of India’s native flora and fauna. It serves as a platform to inform and support conservation activities.
- Increases the revenue derived from tourism: It boosts economic development in areas surrounding reserves through sustainable development.
- Creation of employment opportunities for the locals: In a rural area, it might generate employment. By imparting to the visitor their knowledge of the local geography and environment, it gives the locals a chance to escape poverty.
- Preservation of local culture: neighborhood residents to participate in conserving and defending their local area.
- Ecotourism-related businesses can improve the long-term economic prospects of a town.
- Protected areas and nature conservation provide many benefits to society.
Ecotourism in India
- India, a country with a diverse landscape, has several tourist attractions that can both relieve tension and revitalize you.
- There are several ways to enjoy Mother Nature in the most pristine way.
- A selected few locations, like the Himalayan region, Kerala, Northeast India, the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, and the Lakshadweep Islands, allow you to take advantage of Mother Nature’s priceless bounty. The first planned ecotourism destination in India was Thenmala , which was established to serve eco-tourists and lovers of the outdoors.
- The geography of India is home to a wide variety of plants and animals. India’s surroundings are home to a large number of rare and endangered species.
- The expansion of the wildlife resource, which was once constrained by the hunting of many kings, has been aided by the creation of numerous wildlife areas and national parks.
- Community-led eco-tourism initiatives have been launched in several Indian states and union territories, including Jammu and Kashmir, Nagaland, Kerala, Sikkim, and West Bengal.
- Several communities in Ladakh have started homestay programs for hikers and other tourists, with money raised going toward village development and conservation.
- The Maharana Kumbha Common Interest Group established the “Green Village Project” in Khonoma village, close to Kohima, which includes nine BPL communities. The young people received visitor management training. The camp includes hiking, folk dances, camel and horseback riding, and more.
Challenges associated with Ecotourism
- Striking a balance between allowing access for visitors and protecting delicate ecosystems can be challenging.
- Overcrowding can lead to environmental degradation and disrupt the very ecosystems ecotourism aims to preserve.
- Some businesses may falsely label their operations as ecotourism to attract environmentally conscious consumers.
- Proper certification and transparent communication are crucial to combat greenwashing .
- Developing infrastructure to support ecotourism without negatively impacting the environment poses a challenge.
- Roads, accommodations, and facilities must be designed and constructed with sustainability in mind.
- Unmanaged tourism can lead to cultural commodification and a loss of authenticity in local traditions.
- Balancing cultural preservation with tourism demands requires thoughtful planning.
- Climate change poses a threat to many ecotourism destinations, impacting ecosystems and wildlife.
- Adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change is a growing concern for the sustainability of ecotourism.
India, a country with diverse terrain, offers many tourist destinations that not only help people unwind but also revitalize them. There are numerous methods to take in Mother Nature in the purest form.
There are only a few sites where you may appreciate the priceless bounty of Mother Nature, like the Himalayan region, Kerala, North-East India, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and the Lakshadweep Islands.
Also read: Ecocide
Article Written by: Remya

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2025 (Online)
₹95000 ₹59000

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2026 (Online)
₹115000 ₹69000


Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2027 (Online)
₹125000 ₹79000

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
Tourism Sector in India – Explained ( UPSC Notes)

Government Initiatives
- Heritage cities
- 100% centrally funded
- Religous cities
- Gaya in both
- Theme based tourism circuits
- Ramayana circuit, Krishna, Buddhist, Himalayas Wildlife
- Advantage Health Care India – International Summit
- The duration has been extended to 60 days
- Visa on Arrival , PIO card
Types of Tourism
- Sight Seeing Tourism – India Gate
- Eco Tourism ( also includes Wildlife tourism )
- Business Tourism
- Religious Tourism – Most prominent in India
Medical Tourism
- Educational Tourism
- Rural Tourism
- Slum Tourism 😛
- The number of foreign tourist arrivals in 2014 is 8 million (up from 5 mm in 2009-10),
- World average 10%
- employment.
- Finally, compared to other modern sectors, a higher proportion of tourism benefits (jobs, petty trade opportunities) accrue to women . Internationally 7 0% jobs in tourism to women
- 20 billion dollars
- 2nd Largest
- India moves up 12 places at 40th
- Largest leap by any country in top 50
- Reasons – Schengen, Temperature, Infra, Safety
- Government would need to adopt a ‘ pro-poor tourism ’ approach aimed at increasing the net benefits that flow to the poor from tourism. It includes expansion of local employment through commitment to creation of local jobs and training of locals for employment; expansion of business opportunities for small and micro businesses
- The implementation of these strategies will involve d eveloping formal and informal links between all stakeholders and coordination across all levels of Government.
- Infrastructure – Roads, Hotels, Parks
- Human Resources – Guides, Female Guides
- Security – Scarlet Keening
- Environment – Manali, Climate Change
- Extremism – Darjeeling
- Lack of Awareness – Shortage of ICT connectivity , Inadequate focus on Spiti Valley in Himachal or Tribal tourism of Jharkahand
- Health and Hygiene
- IT connectivity
- Prioritisation of Tourism
STEPS REQUIRED
- Single national level smart cards for all tolls
- Extension of E- Tourist window to 150 days instead of 60 currently ( Eco Survey )
- National Cruise Strategy
- Sustainable Tourism
- Taking Locals into cohgnisance
- Hotels, Roads
- Internet and Awareness
- And all the steps for above issues
- To obtain healthcare
- From Afghanistan, Ban in particular
- But, also from Advanced west like US, UK due to cheap cost
- Ayurveda tourism in Kerala
- Driven mainly by private sector
- 3 billion $
- 2 lakh people every year
E-tourist VISA
- Open to 150 countries now
- Is Tourist Visa on Arrival Facility (TVoA) enabled by Electronic Authorisation
- At 16 Indian airports
- Progress- 3.5 lakh last year, largest from UK, then USA
- Bottomline – Environment , People, Tourists
- Manali – NGT Ban
- Floods – Uttarakhand
- Taj Mahal – Pollution
- Kasaul – Drug Tourism
- Sex Tourism
- Revenue should stay with the tourists
- Basic Infra
- Points on Skill, Awareness,
- Ministry of Tousim – Sustainable tourism Criteria of India
National Tourism Policy (Draft), 2011
Features
- B y 2017, to host 1% of global tourists (current 0.7%). This would require additional 400k hotel rooms and would create 25 mm jobs.
- To target 12 per cent annual growth in this sector in the Twelfth Five Year Plan.
Cruise Shipping Policy, 2008
Potential of Cruise Shipping
- Cruise Shipping refers to leisurely passenger shipping. It beneficial not only in tourism terms but also in promoting the handicrafts industry.
Features
- It provides for better fiscal regime, better port and connectivity facilities and liberal immigration regime.
- A Steering Committee formed in 2010 envisaged developing 5 ports of Goa, Mumbai, Cochin, Chennai and Mangalore and including inland river cruising as LTC for government employees .
Tourism Initiatives for North East
- Incentives are given to Central Government Employees to travel to NE.
- 10% of Planned Tourism Expenditure reserved for NE.
- NE fairs and exhibitions will get 100% central finance assistance.
You might also like:

- Recent Posts
Quick Links
IASBIO Website
Mobile Numbers +918987187161 | +918987187153 +917091958453 | +919576180734
Email Address [email protected]
Home About US
Privacy policy
Terms & Condition
Copyright © 2024 IAS Bio

- UPSC IAS Topper’s Biography
- Ancient History
- Schemes for UPSC
- Constitutional Bodies
- International Relations Notes for UPSC
- Fiscal Policy

civilspedia.com
All you need to crack Civil Services
Tourism (UPSC Notes)
Last Updated: May 2023 (Tourism (UPSC Notes))
Table of Contents
This article deals with ‘ Tourism (UPSC Notes). ’ This is part of our series on ‘Economics’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here .
Introduction
- India is ranked 10th in terms of t tourism’s total contribution to GDP, contributing 4.7% to total GDP.
- It is a labor-intensive sector, accounting for 39 million jobs (2020) and significantly impacts trade, investment, social inclusion, etc.
- But India has not been able to exploit the potential of tourism to full capacity (corroborated by India vs. USA)
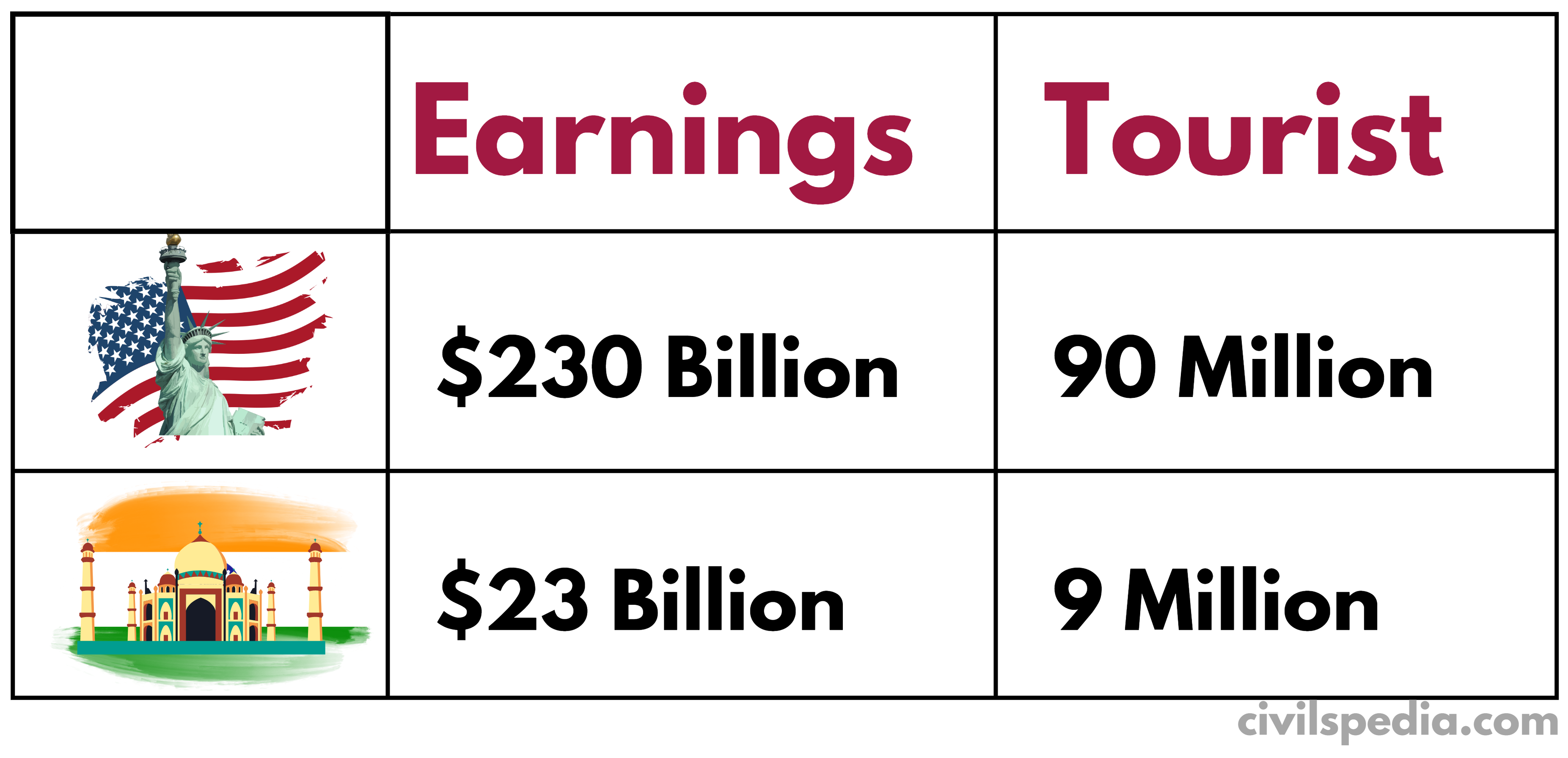
Hence, India has vast untapped potential in the tourism sector
Potential of Tourism in India
- Large Diversity in Landscape: India’s landscape can cater to almost every type of traveller, whether they are seeking adventure, wellness, culture and heritage or cuisines.
- Ancient Civilisation: India is an ancient civilization, and a number of historical places and buildings have tremendous potential to draw tourists. E.g., Hampi, Khajuraho, Agra, Delhi, Madurai etc.
- Religious Tourism: India is home to a large number of religions. Hinduism, Sikhism and Buddhism took birth here.
- Huge Labour Available: The availability of a huge labour force, both skilled and unskilled, can act as a catalyst.
- Medical Tourism: India can provide specialized treatments at the cost of 1/4th that of developed countries. Target countries include Central Asia, Neighbours like Bangladesh, Sri Lanka etc.
- MICE (Meeting, Incentive, Conferences & Exhibitions): It is a specialized niche of business tourism. Indian MICE Tourism potential is pegged at 25,000 crore due to Places like Pragati Maidan Delhi (for exhibition) and institutes like IITs, AIIMS, IIMs etc., for International Conferences.
Reasons for untapped Tourism Potential
- The tourism industry is closely integrated with several other industries like the hotel industry, accommodation, aviation, railway, roadways, healthcare, entertainment etc. The combined weaknesses of all the sectors make Indian Tourism more vulnerable.
- Negative perceptions, such as India being unsafe for female foreign tourists and lack of hygiene, negatively impact Indian tourism.
- Government is unable to make schemes to attract tourists like Buddhist Tourists who have cultural ties with India.
- No advertisement campaigns like Malaysian and Singapore Tourism are run in foreign countries.
- Lack of automated immigration procedures like Visa on Arrival.
- Limited professionalism in people involved in the tourism sector, like tourist guides
- Insurgency in potential Tourist Spots : Tourist places like Kashmir and North East are hit by insurgency, impacting tourism potential.
Schemes to Promote Tourism in India
In the last two years, the Ministry of Tourism has taken many steps to make India an attractive destination.
- PRASAD Scheme : To develop tourism infrastructure in and around famous religious and pilgrimage cities. (12 cities Ajmer , Amritsar , Amravati, Dwarka, Gaya, Kamakhaya, Kancheepuram, Kedarnath, Mathura, Patna, Puri, Varanasi and Velankanni)
- HRIDAY : For holistic development of Heritage cities (12 identified Cities, namely, Ajmer , Amaravati, Amritsar , Badami, Dwarka, Gaya, Kanchipuram, Mathura, Puri, Varanasi, Velankanni and Warangal.)
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme : It aims to develop a theme-based tourist circuit . These circuits include North-East India Circuit, Buddhist Circuit , Himalayan Circuit, Coastal Circuit, Krishna Circuit , Desert Circuit , Tribal Circuit, Eco Circuit, Wildlife Circuit, Rural Circuit, Spiritual Circuit, Ramayana Circuit and Heritage Circuit.
- Adopt a Heritage : Corporate Houses will adopt a Heritage and develop their infrastructure . E.g., Dalmia Group adopted Red Fort for ₹ 25 Crore, and they will provide basic amenities and develop infrastructure.
- E-visa process simplified: Nationals of 161 countries have been allowed visits for business and medical treatment. Additionally, a special visa category called ‘ Medical Visa’ & ‘Medical Attendant Visa ‘ has been created to ease the entry of medical tourists into India
- The government is building a large number of museums to showcase Indian heritage and promote tourism.
- Incredible India Tourist Helpline : Multilingual helpline has been launched to provide assistance and information to tourists in 12 languages of the world, including Hindi & English
- 100 % FDI allowed in hotels, resorts & recreational activities
- Revamped schemes like Hunar se Ruzgar to give training to travel guides and Institutes of Hotel Management have been opened.
- Rajasthan has passed a bill under which misbehaviour with tourists has been made a cognizable offence. It is to prevent the touts from forcing tourists to buy things at exorbitant prices or fraudulating the tourists, as it impacts tourism negatively.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Civilsdaily
No. 1 UPSC IAS Platform for preparation
Tourism Sector
Sustainable tourism in india.
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: tourism as economic driver
- Ministry of Tourism identified Tourism Industry’s potential as a Sunrise Industry.
- There is a need for tourism analysts to hold tourism planners accountable.
What is tourism?
- Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours.
Types of tourism
- Domestic tourism : Refers to activities of a visitor within their country of residence and outside of their home (e.g. a Indian visiting other parts of India)
- Inbound tourism : Refers to the activities of a visitor from outside of country of residence (e.g. a Spaniard visiting Britain).
- Outbound tourism : Refers to the activities of a resident visitor outside of their country of residence (e.g. an Indian visiting an overseas country).
What does sustainable tourism mean?
- Sustainable tourism is defined by the UN Environment Program and UN World Tourism Organization as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities.”
What is the main importance of tourism?
- Tourism boosts the revenue of the economy, creates thousands of jobs, develops the infrastructures of a country, and plants a sense of cultural exchange between foreigners and citizens.
Why tourism is needed?
- Tourism is not a fad. It is a compulsion driven by the urge to discover new places. Because we have this compulsion to venture into the unknown, we need each other. When humans travel, meet and exchange ideas, civilisation flourishes.
What should be done to promote tourism?
- National Tourism Authority : A separate National Tourism Authority (NTA) should be established for executing and operationalizing various tourism related initiatives. Simple, flexible and elegant processes will be laid down to allow for nimbleness.
- National Tourism Advisory Board : A National Tourism Advisory Board (NTAB) should be set up to provide overall vision, guidance and direction to the Development of Tourism Sector in the country.
- Creating Synergy in Tourism Eco System : In order to ensure synergy at various levels of Government and with the Private Sector, it is important to have a well-defined framework in place.
- Quality Tourism Framework : A robust framework for quality certification of products and services across all segments like accommodation providers, tour operators, adventure tour operators, service providers like spa and wellness, guides, restaurants etc. should be laid down.
- Enhancing the existing luxury tourism products: The existing tourism products such as Nilgiri Mountain Railway, Palace on Wheels etc. should be enhanced and their numbers will also be increased. Haulage charges will be rationalised to make luxury trains viable.
- Railways can be a game changer: For tourism Railways have presence in most parts of the country. Most of the tourist destinations in the country are connected by rail. Railways is also in the process of connecting more places especially the strategic locations that also are tourist places with limited connectivity at present. Indian Railways is working towards promoting tourism in the country by operating more trains connecting tourists’ destinations and also by providing an array of products starting from luxury tourist trains to budget catering tourist trains
What is MICE tourism of Gujarat?
- The acronym “MICE” stands for “Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Exhibitions”, and is essentially a version of business tourism that draws domestic and international tourists to a destination.
- The policy aims to make Gujarat one of the top five MICE tourism destinations in the country.
Way forward
- Enhance the contribution of tourism in Indian economy by increasing the visitation, stay and spend
- Create jobs and entrepreneurial opportunities in tourism sector and ensure supply of skilled work force
- Enhance the competitiveness of tourism sector and attract private sector investment
- Preserve and enhance the cultural and natural resources of the country
- To ensure sustainable, responsible and inclusive development of tourism in the country
- We know that India has the highest tourism potential of any country. That is because we have every terrain and climate zone, and a range of customs, traditions, cuisines, crafts, art forms and festivals unmatched by any other nation. We should monetize our potential through putting comprehensive National tourism policy in place.
Mains question Q. What should be done to transform our tourist destinations to provide world class visitor experience making India one of the topmost destinations for sustainable and responsible tourism?
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

Traveling to India is becoming more and more popular. And this is not surprising because this is a country with rich traditions and culture. I also plan to visit there. And of course, I will definitely use the services of a company that provides assistance in flights. Last year used such services for business class flights to Luanda, Angola in Africa. The flight from the USA was quite expensive. But thanks to this company, I saved about 40% on air tickets.

JOIN THE COMMUNITY
Join us across social media platforms., your better version awaits you.

Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

Sansad TV: Perspective- Promoting Tourism

Introduction:
Tourism sector in India is a significant economic multiplier and is becoming increasingly important as the country strives for rapid economic growth and employment creation. Despite the tourism sector being severely affected by COVID, India witnessed a jump in Foreign Tourist Arrivals in 2022. The Draft National Tourism Policy formulated by the Ministry of Tourism is a holistic framework for sustainable and responsible growth of the tourism sector in the country. The Policy aims at improving framework conditions for tourism development in the country and supporting tourism industries. India is observing ‘Visit India Year 2023’ on in order to develop tourism in mission mode and to accelerate India’s rise towards world leadership in tourism sector. The Ministry of Tourism is also organizing 1st Global Tourism Investors’ Summit in May this year to showcase investible projects and opportunities in tourism and hospitality sector in India to domestic and international investors.
Measures needed: Tourist Police Scheme
- As many as 29 foreigners were murdered in the last three years. While 14 foreigners fell victim to rape last year, 16 were raped in 2020 and 12 in 2019.
- As many as 15 cases of assault to outraging modesty of foreign women were registered last year across the country, apart from 14 complaints of cheating.
- Booklet on the tourist police scheme and tourist police stations: The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD) has brought out a booklet on the tourist police scheme detailing the mode of setting up of tourist police stations and control rooms, outposts, uniforms, recruitment, qualifications, training and logistics requirements for tourist police stations.
- Identified tourist spots : As many as 25 popular tourist spots have been identified in the country where the tourist police necessarily need to be deployed to help foreigners. As an incentive, 30% deputation allowance has been recommended for the police personnel who joins the tourist police on deputation.
- Identified Criminals in and around tourists’ spots need to be kept on constant surveillance
- Fast track courts should be set immediately to try cases of crimes against tourists
- States that have tourist police: Though the concept of ‘tourist police’ has been in vogue for the past few years, it has not been given the kind of attention it deserves. The States that have tourist police are Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Delhi, Goa, Rajasthan and Kerala.
- Delhi a neglected state is gearing up for tourist police wing: In view of the forthcoming G20 Summit, the Delhi police is gearing up its tourist police wing, which was hitherto in a neglected state and so are other States which will see a huge influx of foreigners.
Potential and prospects :-
- Tourism in India has emerged as an instrument of income and employment generation, poverty alleviation and sustainable human development. It contributes 6.23% to the national GDP and 8.78% of the total employment in India. Almost 20 million people are now working in the India’s tourism industry.
- Tourism is an important source of foreign exchange earnings in India. This has favourable impact on the balance of payment of the country. The tourism industry in India generated about US$100 billion in 2008 and that is expected to increase to US$275.5 billion by 2018 at a 9.4% annual growth rate.
- The sector also has the potential to create micro-entrepreneurs who in turn can employ more people. The multiplier effect it delivers is high.
- In fact, tourism helped Spain which receives over 68 million international tourists annually fight its recent economic downturn.
- According to the World Tourism Organisation, the sector provides for 10 per cent of the world’s GDP, 7 per cent of the global trade and creates one in every 11 jobs worldwide.
- Travel and tourism sector in India has the potential to grow much faster and support 46 million jobs by 2025, provided the right investments and policies continue to be implemented
- Tourism in a place will put the local culture, handicraft sector in the limelight and increase the standard of living of these people.
- It can help develop rural areas which are tourist spots providing better facilities there itself and can lead to less migration which will further reduce pressure on cities.
- Indian Tourism offers a potpourri of different cultures, traditions, festivals, and places of interest. There are a lot of options for the tourists. India is a country with rich cultural and traditional diversity. This aspect is even reflected in its tourism. The different parts of the country offer wide variety of interesting places to visit.
- With optimistic predictions of about 13.34 million foreign tourists arriving by 2024, there is a pressing need to upgrade our security systems specially to provide a flawless security blanket cover to foreign tourists.
- Safety assumes utmost importance to draw tourists in hordes.
- If the goal of positioning of India as one of the world’s best tourism destinations by 2047 , there is need to integrate various schemes of different ministries.

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

- भाषा : हिंदी
- Classroom Courses
- Our Selections
- Student Login
- About NEXT IAS
- Director’s Desk
- Advisory Panel
- Faculty Panel
- General Studies Courses
- Optional Courses
- Interview Guidance Program
- Postal Courses
- Test Series
- Current Affairs
- Student Portal

Recently ,The National Conference of State Tourism Ministers ended with the adoption of the “Dharamshala Declaration” which affirms commitment toward developing “sustainable and responsible tourism” and positions India as a “global leader in the tourism sector by 2047”.
Potential of Tourism Sector In India
- Tourism and Hospitality sector is one of the largest employment g enerating sectors in India and has been contributing towards generating a major chunk of Foreign Exchange Earning (FEE).
- India is an experiential destination with its kaleidoscope of ancient culture and heritage, ancient systems of healing like Ayurveda, Unani, Siddha, Naturopathy , natural beauty including 70% of the Himalayas and over 7500 km long coastline, rich flora and fauna, world class medical facilities a nd many other aspects make India the favoured destination for the discerning traveller.
- The percentage of Foreign Tourist Arrivals visiting India for Medical Treatment has been increasing over the years and growing rapidly.
- Over the past few months, all the major tourism indices such as domestic air passenger traffic, hotel occupancy and tourist footfalls have shown signs of recovery and are going back to pre-pandemic levels.
- By 2030, India is estimated to grow at 7%-9% compounded annual growth rate and we expect the enabling policy framework to bring in $250 billion in GDP contribution from tourism, 140 million jobs in the tourism sector and $56 billion in foreign exchange earnings with more than 25 million foreign arrivals.
Challenges
- Lack of Infrastructure – It is a major challenge for the Indian tourism sector. This includes hotels, connectivity with other cities, health facilities, and transportation etc.
- Attacks on foreign tourists, especially on women tourists have raised this question.
- COVID-19 pandemic: The Indian tourism and hospitality sector were adversely affected by the COVID-19 pandemic and saw substantial job loss.
- Business Hurdles, Lack of Hygiene and Comfortable accommodation
- Lack of integrated tourism promotion
Governments Initiatives
- Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme: The Government of India’s Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme was recently enhanced by ?50,000 crore, from ?4.5 lakh crore to ?5 lakh crore to benefit enterprises in hospitality and related sectors such as hotels and restaurants, marriage halls, travel agents, tour operators, adventure and heritage facilities.
- The guiding principles include promoting sustainable, responsible and inclusive tourism in line with our civilisational ethos.
- The policy also aims to give impetus to digitalisation, innovation and technology through the National Digital Tourism Mission and skilling through the Tourism and Hospitality Sector Skill Mission
- Theme based schemes for the integrated development of circuits for improvement of infrastructure in the country have been launched by the Ministry of Tourism to enable tourists to experience the destination fully.
- The Ministry has also been working with the Ministry of External Affairs to identify 20 Indian missions abroad with the highest tourist footfalls to India and build country-specific strategies to attract foreign tourists.
- Central Sector Scheme
- Aim: Integrated development of theme-based tourist circuits in the country.
- Focus on identifying and developing pilgrim sites across the country to promote religious tourism.
- Organises webinars, quiz, pledge, discussions to keep people connected with the stakeholders and to encourage citizens to travel within the country.
- It envisages the development and maintenance of tourist amenities at heritage sites and making them tourist-friendly.
- The event highlights various potentials like eco-tourism, culture, heritage and business of the North East Region.
- Gati Shakti Master Plan: It is a project for developing ‘holistic infrastructure’.
- It will incorporate the infrastructure schemes of various Ministries and State Governments like Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, dry/land ports, UDAN etc.
What Lies Ahead ?
- Tourism creates jobs and provides jobs in the tertiary sector. It is now high time for us to work for the betterment of this sector so that from the upcoming years the number of foreign tourists may increase, and more people will be able to know about our culture.
- The Startup India initiative has boosted entrepreneurship. However, the travel and tourism startups need a bigger push. Innovative startups should be encouraged. Support from the government for ideation and access to finance are required.
- The growth in this sector has multiplier effects on income generation as it is employment-intensive with less capital investment
- There is a need to highlight the significance of public-private partnership to improve infrastructure and tackle the problem of end connectivity, which negatively affects the experiences of international travellers.
- India’s age-old dictum of ‘Atithi Devo Bhava’ will come to the fore as it welcomes delegates from the 20 countries/European Union.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
India’s role in global shipping industry, restoring earth’s right to ‘good health’, challenges of renewable energy, daily current affairs 25-04-2024.
UNWTO and India
India became a member of the UNWTO in 1975. The nodal agency in India that works with the UNWTO is the Ministry of Tourism.
The UNWTO leads the World Tourism Day celebrations every year on 27 September. In 2019, New Delhi, India was selected as the host for the celebrations. The theme for the 2019 World Tourism Day was “Tourism and Jobs: A Better Future for All”.
United Nations World Tourism Organization – World Tourism Rankings
The United World Tourism Organization publishes the World Tourism Rankings 3 times in a year. The rankings are assigned by taking into account various indicators like the number of international visitor arrivals, expenditures incurred by outbound travellers, revenue generated through inbound tourism. The countries ranked in the top 10 of World Tourism Rankings as per 2018 are listed below.
- United States
- United Kingdom
Get a list of important reports by international organizations at the linked article.
Tourism in India
The tourism sector in India is an important component of India’s growth and economy. Some of the important facts concerning tourism in India are listed below.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) in India stood at 10.89 million in 2019.
- Tourism in India generated revenue worth $ 240 billion in 2018.
- The share of tourism in the Indian GDP was at 9.2% in 2018.
- Tourism supported more than 42 million jobs.
- The tourism sector generated 8.1% of India’s total employment.
- By 2028, some studies have indicated that tourism in India is expected to grow by approximately 7% and it is expected to be a $ 450 billion industry.
- As per a report by Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report, India is ranked at the 34th position among its member countries.
- Under the Swadesh Darshan scheme, 77 projects have been sanctioned. Read more on the Swadesh Darshan scheme in PIB dated 24 Dec 2019 .
Also read UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritages in India.
The Top 5 states/UTs that received the highest number of Foreign Tourists as per 2017 are listed below.
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
The Top 5 states that received the highest number of Domestic Tourists as per 2017 are listed below.
- Andhra Pradesh
The Ministry of Tourism is working on improving tourism in the following niche areas:
- Medical Tourism
- Eco-tourism
- Rural Tourism
As per 2018, the highest number of foreign tourists visiting India are from the following countries.
Candidates should go through the relevant links provided below to do preparation for UPSC exam even better-
Get the list of International Organizations and their Headquarters on the given link.
Aspirants can find complete information about upcoming Government Exams through the linked article. UPSC exam-related preparation materials will be found through the links given below:

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
India's Tourism is ranked at 7 th position in terms of its contribution to World GDP in World Travel and Tourism Council's report in 2017. India as of now in 2018 has 37 sites listed under 'World Heritage List', 6 th most highest (29 cultural, 7 natural and 1 mixed site) in the world. Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai ...
The tourism sector contributes around 9% of the country's GDP. It has its share in employment, revenue, and forex reserves. India's third-largest source of foreign exchange is the tourism and hotel industry. India's tourism industry is a significant economic multiplier and is getting more crucial as the nation aims for rapid economic ...
The tourism industry in India generated about 100 US$ billion in 2008 and that is expected to increase to US$275.5 billion by 2018 at a 6.9% annual growth rate. According to World Tourism Organization estimates, India will lead in South Asia with 8.9 million arrivals by 2020.
Present scenario of the tourism sector in India. With 1.52 million foreign visitors anticipated in 2021, India is one of the top tourism destinations in the globe. India's foreign exchange revenues increased by roughly $8.8 billion as a result of this. There were also about 680 million domestic travellers.
Expected annual growth rate of 6.4% between 2014 and 2024. It is anticipated to be the third fastest-growing tourism destination with a 7.9% annual average growth rate till 2023. Employment: Tourism in India provides 40 million job s, with over 7.7% of Indian employees working in the industry.
Tourism Sector is the third-largest foreign exchange earner for the country in 2019. The foreign exchange earnings between 2016 and 2019 increased at a CAGR of 7%, but dipped in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. By 2028, Indian tourism and hospitality is expected to earn US$ 50.9 billion as visitor exports compared with US$ 28.9 billion in 2018.
Ecotourism is an entirely new approach to tourism. It is the preservation of trips to natural areas to appreciate the natural and cultural history of the area while taking care not to disturb the ecosystem's integrity. This will generate economic opportunities that benefit the local population by promoting the conservation and protection of ...
The number of foreign tourist arrivals in 2014 is 8 million (up from 5 mm in 2009-10), 7 % to GDP. World average 10%. 10%. employment. Finally, compared to other modern sectors, a higher proportion of tourism benefits (jobs, petty trade opportunities) accrue to women. Internationally 7 0% jobs in tourism to women.
The UPSC aspirants can take the help of Testbook's UPSC CSE Coaching. This can help boost their UPSC Exam preparation! ... Ecotourism is a type of tourism that promotes responsible travel and conservation of natural environments. It is all about exploring nature's beauty while minimizing negative impacts on the environment and respecting local ...
India is ranked 10th in terms of t tourism's total contribution to GDP, contributing 4.7% to total GDP. It is a labor-intensive sector, accounting for 39 million jobs (2020) and significantly impacts trade, investment, social inclusion, etc. But India has not been able to exploit the potential of tourism to full capacity (corroborated by ...
Ecotourism. Ecotourism is a type of tourism to conserve and improve natural, rural areas. So this is quite different from a typical tour to a place. Instead, this type of tourism includes a keen focus on learning and developing that area and the people residing there. Around 1980, the concept of ecotourism took place officially in the Oxford ...
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important : Prelims level: NA. Mains level: tourism as economic driver. ... Types of tourism. Domestic tourism: Refers to activities of a visitor within their country of residence and outside of their home (e.g. a Indian visiting other parts of India)
The tourism industry in India generated about US$100 billion in 2008 and that is expected to increase to US$275.5 billion by 2018 at a 9.4% annual growth rate. The sector also has the potential to create micro-entrepreneurs who in turn can employ more people. The multiplier effect it delivers is high.
Potential of Tourism Sector In India. Tourism and Hospitality sector is one of the largest employment generating sectors in India and has been contributing towards generating a major chunk of Foreign Exchange Earning (FEE). India is an experiential destination with its kaleidoscope of ancient culture and heritage, ancient systems of healing ...
Tourism Industry In India. This article is based on "For tourism, here is an Incredible India 2.0 plan" which was published in The Hindustan Times on 17/06/2020. It talks about underlying challenges and steps to be taken for the promotion of India's Tourism sector. The economy runs on the four wheels of demand, supply, capital and labour.
India's Tourism is ranked at 10th position in terms of its contribution to World GDP (Gross Domestic Product) in the World Travel and Tourism Council's report in 2019. During 2019, contribution of travel & tourism to GDP was 6.8% of the total economy, ~ Rs. 13,68,100 crore (USD 194.30 billion). India as of now in 2021 has 40 sites listed ...
National Tourism Policy Objectives. The Policy's primary strategic goals are: To make India a year-round travel destination and to increase visitors, spending, and time spent there in order to boost the contribution of tourism to the Indian economy. To create jobs and entrepreneurial opportunities in the tourism sector and ensure the supply ...
About: Rural tourism in India is a form of tourism that focuses on exploring and experiencing the rural lifestyle and culture. It involves traveling to rural areas and participating in various activities such as farming, handicrafts, and village walks, to gain a deeper understanding of the local culture and way of life.
The share of tourism in the Indian GDP was at 9.2% in 2018. Tourism supported more than 42 million jobs. The tourism sector generated 8.1% of India's total employment. By 2028, some studies have indicated that tourism in India is expected to grow by approximately 7% and it is expected to be a $ 450 billion industry.