- English (CA)
- Deutsch (DE)
- Deutsch (CH)

8 types of tourism that you need to know
The three tourism categories, domestic tourism, inbound tourism, outbound tourism, the 8 types of tourism according to motivation, business tourism.
- Meet with business partners or prospects
- Attend an event, conference, or trade show
- Visit another office location of the same company
?)
See how to save money on business travel
Leisure tourism, shopping tourism, cultural tourism, sports tourism, rural tourism, mountain tourism, urban tourism, many people travel – but for completely different reasons.
?)
Make business travel simpler. Forever.
- See our platform in action . Trusted by thousands of companies worldwide, TravelPerk makes business travel simpler to manage with more flexibility, full control of spending with easy reporting, and options to offset your carbon footprint.
- Find hundreds of resources on all things business travel, from tips on traveling more sustainably, to advice on setting up a business travel policy, and managing your expenses. Our latest e-books and blog posts have you covered.
- Never miss another update. Stay in touch with us on social for the latest product releases, upcoming events, and articles fresh off the press.
?)
5 inefficient processes affecting your business and how to fix them
?)
Duty of care in the workplace: everything you need to know
?)
CEO Roles and Responsibilities: conquer your role as CEO
- Business Travel Management
- Offset Carbon Footprint
- Flexible travel
- Travelperk Sustainability Policy
- Corporate Travel Resources
- Corporate Travel Glossary
- For Travel Managers
- For Finance Teams
- For Travelers
- Thoughts from TravelPerk
- Careers Hiring
- User Reviews
- Integrations
- Privacy Center
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Modern Slavery Act | Statement
- Supplier Code of Conduct
Exploring the World of Tourism: A Comprehensive Guide to 49 Types of Tourism

Have you ever thought about how many types of tourism there are in the world? From adventure tourism to medical tourism, the tourism industry offers a wide range of experiences for travelers.
Tourism is a rapidly growing industry, contributing greatly to the global economy . With the rise of globalization and advancements in technology, traveling has become more accessible and affordable for people all around the world.
As a result, the tourism industry has diversified and expanded to cater to the different interests and preferences of travelers.
If you are a travel enthusiast, you might be surprised to know that there are over 40 different types of tourism to choose from. Each type of tourism offers a unique experience, ranging from cultural immersion to extreme sports.
In this article, we will explore the different types of tourism in the world, giving you a glimpse into the vast array of options available to you.
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
49 Types of Tourism in the World
The tourism sector is constantly evolving, expanding beyond the basics of domestic, inbound, and outbound tourism.
As travel agencies, it is crucial to stay informed about the diverse range of tourism types to develop effective strategies and fuel the growth of your business. This comprehensive guide presents 62 types of tourism, offering valuable insights and opportunities for your agency to thrive in the dynamic world of travel.
Traditional Forms of Tourism
Leisure tourism.

Leisure tourism encompasses a range of activities that provide relaxation, entertainment, and cultural enrichment to travelers. Let's explore some popular forms of leisure tourism in more detail:
1. Beach Tourism
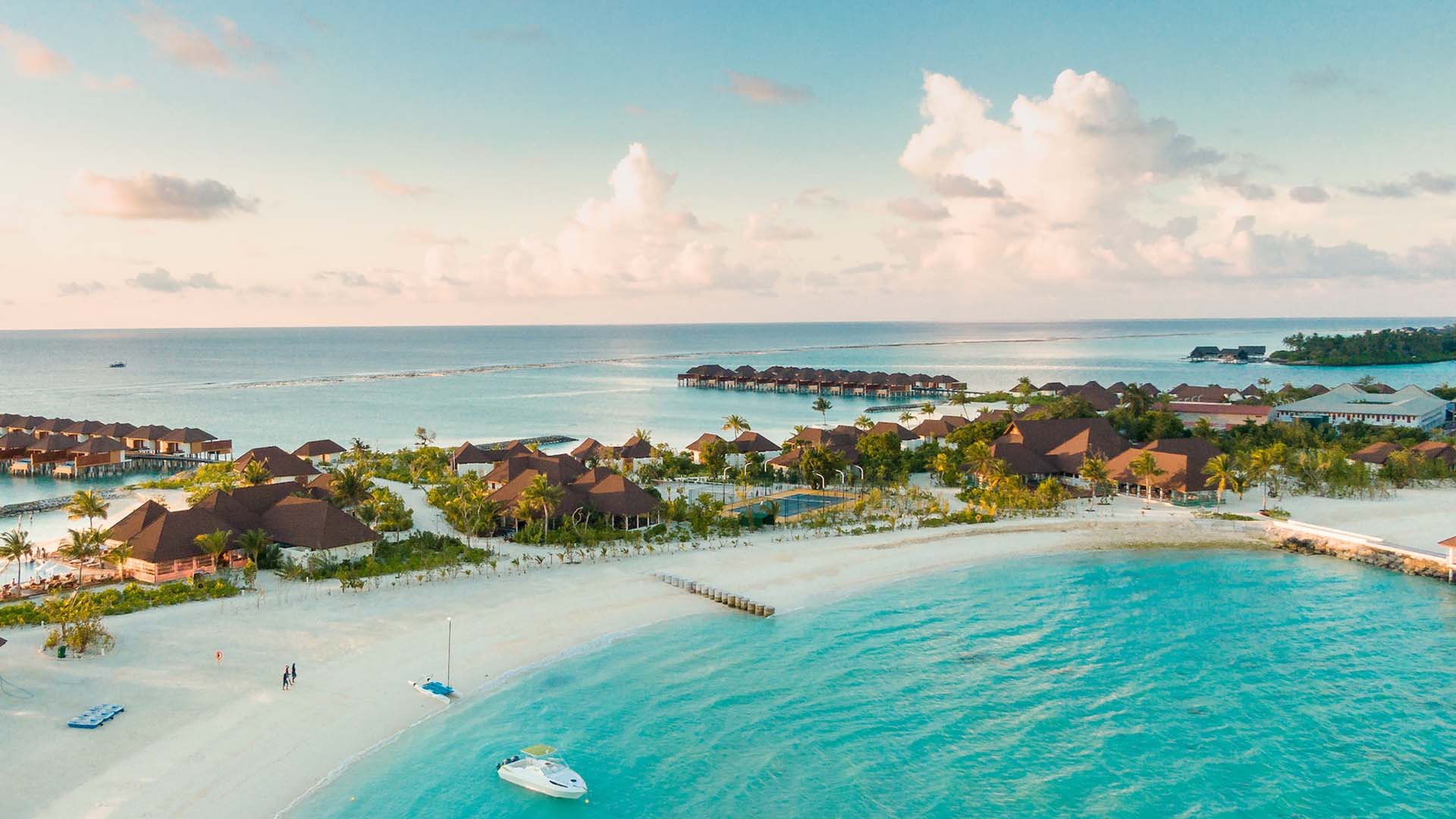
Beach tourism revolves around vacations and holidays spent in coastal areas, offering sun, sand, and various recreational activities such as swimming, sunbathing, beach volleyball, and water sports like snorkeling, surfing, and jet skiing.
Beach destinations around the world, such as Bali, Maldives, and the Caribbean, attract millions of tourists seeking relaxation and enjoyment in idyllic seaside settings.
2. Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism caters to thrill-seeking individuals who seek exciting and adrenaline-pumping experiences. It includes activities like hiking, rock climbing, zip-lining, white-water rafting, paragliding, and bungee jumping in natural and adventurous settings.
Destinations like New Zealand, Costa Rica, and Switzerland offer breathtaking landscapes and thrilling adventure opportunities that attract adventure enthusiasts from across the globe.
3. Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism focuses on exploring the rich heritage, traditions, and artistic expressions of a destination.
It involves visits to museums, historical sites, cultural festivals, and interactions with local communities to gain insight into their customs, rituals, and way of life. Destinations renowned for their cultural attractions include Rome with its ancient ruins, Kyoto with its traditional temples, and Istanbul with its diverse blend of cultures.
4. Wildlife Tourism
Wildlife tourism centers on observing and experiencing a particular region's diverse fauna and flora.
It includes activities such as safaris, birdwatching, nature walks, and visits to national parks and wildlife reserves. Destinations like South Africa's Kruger National Park, the Galapagos Islands in Ecuador, and the Serengeti in Tanzania offer incredible wildlife encounters and opportunities for conservation education.
Business Tourism

Business tourism, also known as MICE tourism (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions), caters to individuals traveling for business-related purposes.
Let's explore some key components of business tourism:
5. Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions (MICE) Tourism
MICE tourism encompasses corporate meetings, conferences, conventions, trade shows, and exhibitions. It provides a platform for professionals to network, exchange knowledge, showcase products and services, and forge business relationships.
Major cities and convention centers worldwide, such as London, Dubai, and Las Vegas, host numerous MICE events, driving economic growth and fostering industry collaboration.
6. Trade Shows and Conventions
Trade shows and conventions are industry-specific events where businesses exhibit their products or services to potential clients, partners, and investors. These events serve as valuable marketing platforms, allowing companies to showcase their latest innovations, generate leads, and gain industry insights.
Trade shows like CES (Consumer Electronics Show) and Hannover Messe attract businesses from diverse sectors, facilitating business-to-business interactions and promoting industry growth.
7. Corporate Retreats and Team-Building Activities
Corporate retreats and team-building activities aim to foster teamwork, boost employee morale, and enhance organizational productivity. These events often take place in scenic locations, away from the usual office environment, and incorporate team-building exercises, workshops, brainstorming sessions, and recreational activities.
Corporate retreats not only strengthen internal relationships but also provide opportunities for strategic planning, innovation, and professional development.
Niche and Special Interest Tourism

Ecotourism promotes responsible travel practices that focus on preserving and conserving natural environments while providing educational and enriching experiences for travelers.
Let's delve into some facets of ecotourism:
8. Rainforest Exploration
Rainforest exploration allows travelers to immerse themselves in the lush biodiversity and unique ecosystems of tropical rainforests. Guided hikes, canopy walks, and wildlife spotting tours provide opportunities to witness rare flora and fauna, learn about sustainable conservation efforts, and contribute to local communities.
Destinations like the Amazon Rainforest in South America, Borneo's rainforests in Southeast Asia, and Costa Rica's Monteverde Cloud Forest offer captivating rainforest experiences.
9. Wildlife Conservation Tours
Wildlife conservation tours allow travelers to actively participate in conservation initiatives, contributing to the protection of endangered species and their habitats. These tours often involve volunteer work, such as monitoring wildlife, assisting in research projects, and habitat restoration efforts.
Popular wildlife conservation destinations include the Galapagos Islands, where visitors can help preserve unique marine and terrestrial ecosystems, and South Africa's game reserves, where wildlife conservation programs support endangered species.
10. Sustainable Travel Practices
Sustainable travel practices promote environmentally friendly behaviors, aiming to minimize negative impacts on natural resources, local communities, and cultures. These practices may include reducing carbon footprint, supporting local businesses, respecting local traditions, and engaging in activities that promote environmental stewardship.
Travelers can choose eco-lodges, and eco-friendly transportation options, and participate in community-based tourism initiatives to ensure their travel has a positive impact on the destination.
Wellness Tourism

Wellness tourism focuses on enhancing and rejuvenating one's well-being through various activities and experiences that prioritize physical, mental, and spiritual health.
Let's explore some aspects of wellness tourism:
11. Spa Retreats
Spa retreats offer a serene environment where travelers can indulge in relaxation, pampering treatments, and wellness therapies. From soothing massages and rejuvenating facials to holistic healing practices like yoga and meditation, spa retreats provide a sanctuary for rejuvenation and stress relief.
Destinations such as Bali, Thailand, and California's Napa Valley are renowned for their luxurious and holistic spa retreats.
12. Yoga and Meditation Retreats
Yoga and meditation retreats provide opportunities for individuals to deepen their mindfulness and spiritual practices in tranquil and picturesque settings. These retreats often combine daily yoga sessions, meditation practices, healthy cuisine, and workshops focused on personal growth and self-awareness.
Destinations like Rishikesh in India, Ubud in Bali, and Sedona in the United States are renowned for their yoga and meditation retreats.
13. Health and Wellness Resorts
Health and wellness resorts offer comprehensive programs designed to improve physical fitness, promote healthy lifestyles, and provide personalized wellness experiences. These resorts may offer fitness classes, nutritional guidance, spa treatments, wellness consultations, and activities like hiking, yoga, and mindfulness workshops.
Wellness-focused destinations such as Switzerland's renowned Swiss Alps resorts, Thailand's wellness retreats, and the wellness resorts in Arizona's Sonoran Desert cater to those seeking a holistic approach to well-being.
Culinary Tourism

Culinary tourism revolves around the exploration and appreciation of a destination's cuisine, culinary traditions, and gastronomic experiences. Let's discover the different aspects of culinary tourism:
14. Food and Wine Tours
Food and wine tours allow travelers to savor the local flavors, taste traditional dishes, and indulge in culinary delights unique to a particular region. These tours often include visits to local markets, food tastings, cooking demonstrations, and wine tastings at vineyards.
Destinations like Italy's Tuscany, France's Bordeaux region, and Japan's Kyoto are renowned for their culinary heritage and offer exceptional food and wine tours.
15. Cooking Classes and Culinary Experiences
Cooking classes and culinary experiences provide hands-on opportunities for travelers to learn about the local cuisine, traditional cooking techniques, and regional specialties. Under the guidance of expert chefs or local home cooks, participants can prepare and savor authentic dishes, gaining insights into the culinary culture of the destination.
Cities like Bangkok, Marrakech, and Barcelona are known for their immersive cooking classes and culinary workshops.
16. Farm-to-Table and Gastronomic Experiences
Farm-to-table experiences involve visits to local farms, orchards, and vineyards to witness the production process of fresh, organic ingredients. Gastronomic experiences encompass fine dining at renowned restaurants, tasting menus curated by celebrity chefs, and exploring local street food scenes.
Destinations like California's Napa Valley, France's Lyon, and Thailand's Chiang Mai provide exceptional farm-to-table and gastronomic experiences.
Adventure and Outdoor Tourism
Mountain tourism.

Mountain tourism attracts adventurous travelers seeking exhilarating experiences in breathtaking alpine landscapes. Here are some popular activities within mountain tourism:
17. Hiking and Trekking
Hiking and trekking adventures take travelers through scenic mountain trails, allowing them to explore the pristine wilderness, enjoy stunning vistas, and challenge themselves physically.
Destinations like the Himalayas in Nepal, the Swiss Alps, and the Rocky Mountains in North America offer a range of hiking and trekking opportunities suitable for different skill levels.
18. Mountaineering and Rock Climbing
Mountaineering and rock climbing appeal to those with a passion for conquering towering peaks and vertical rock formations.
From scaling iconic summits like Mount Everest and Mount Kilimanjaro to rock climbing in Yosemite National Park or the Dolomites, these activities offer a thrilling combination of physical endurance, technical skill, and awe-inspiring natural surroundings.
19. Skiing and Snowboarding
Skiing and snowboarding attract winter sports enthusiasts who enjoy gliding down snow-covered slopes and experiencing the adrenaline rush of downhill descents.
Popular ski destinations include Aspen in the United States, Whistler Blackcomb in Canada, and the Swiss Alps, where skiers and snowboarders can enjoy diverse terrains, world-class facilities, and picturesque mountain landscapes.
Water Tourism

Water tourism encompasses a wide range of activities centered around bodies of water, including oceans, lakes, rivers, and coastal areas. Let's explore some popular water-based tourism experiences:
20. Scuba Diving and Snorkeling
Scuba diving and snorkeling allow travelers to explore vibrant underwater ecosystems, encounter marine life, and marvel at coral reefs.
Destinations like the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, the Maldives, and the Red Sea in Egypt are renowned for their exceptional diving and snorkeling sites, offering opportunities to witness the beauty and biodiversity of the marine world.
21. Surfing and Water Sports
Surfing and water sports, such as paddleboarding, kayaking, and windsurfing, cater to adrenaline seekers looking to ride the waves and engage with the power of the ocean. Destinations like Hawaii's North Shore, Bali's Uluwatu, and California's Huntington Beach are renowned for their world-class surf breaks and water sports scenes.
22. Sailing and Yachting
Sailing and yachting experiences provide a luxurious and leisurely way to explore coastal regions, island hopping, and cruise along scenic coastlines. Chartering a yacht or joining a sailing excursion offers the opportunity to relax, soak in breathtaking seascapes, and visit remote islands and hidden coves.
Destinations like the Greek Islands, the Caribbean, and the French Riviera are popular sailing and yachting destinations.
Wildlife Tourism

Wildlife tourism appeals to nature enthusiasts and animal lovers who seek encounters with diverse wildlife species in their natural habitats.
Here are some popular wildlife tourism experiences:
23. Safari and Wildlife Photography
Safari adventures take travelers into national parks and game reserves, providing opportunities to spot iconic wildlife species like lions, elephants, giraffes, and zebras. Wildlife photography enthusiasts can capture stunning images of animals in their natural environment.
Destinations like Botswana's Okavango Delta, Tanzania's Serengeti National Park, South Africa's Kruger National Park, and India's Ranthambore National Park offer exceptional safari and wildlife photography experiences.
24. Birdwatching and Nature Reserves
Birdwatching enthusiasts flock to nature reserves and sanctuaries known for their rich avian biodiversity. These destinations offer opportunities to observe and identify a wide array of bird species in their natural habitats.
Places like Costa Rica's Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve, Australia's Kakadu National Park, and Ecuador's Galapagos Islands are renowned for their birdwatching opportunities.
25. Whale Watching and Marine Wildlife Tours
Whale-watching tours provide an up-close and personal experience with these magnificent marine creatures. Travelers can observe whales breaching, swimming, and interacting in their natural habitat.
Destinations such as Iceland, Canada's Vancouver Island, and the Azores in Portugal are popular for whale watching and marine wildlife tours.
Cultural and Heritage Tourism
Historical tourism.

Historical tourism appeals to individuals interested in exploring the rich heritage and significant historical sites around the world. It provides insights into past civilizations, events, and cultural traditions.
Here are some key aspects of historical tourism:
26. Archaeological Sites and Ruins
Archaeological sites and ruins offer a glimpse into ancient civilizations and their architectural marvels.
Places like the Colosseum in Rome, Machu Picchu in Peru, and Angkor Wat in Cambodia attract history enthusiasts who are fascinated by the remnants of past civilizations and the stories they hold.
27. UNESCO World Heritage Sites
UNESCO World Heritage Sites are culturally or naturally significant locations recognized for their outstanding universal value. These sites range from iconic landmarks like the Taj Mahal in India to entire historical city centers like Prague in the Czech Republic.
Visiting UNESCO World Heritage Sites allows travelers to appreciate the world's cultural diversity and historical importance.
28. Historical Landmarks and Monuments
Historical landmarks and monuments symbolize key moments in history or commemorate notable figures or events. Examples include the Statue of Liberty in the United States, the Great Wall of China, and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt.
Exploring these landmarks provides a deeper understanding of their historical significance and their impact on society.
Religious Tourism

Religious tourism caters to individuals seeking spiritual experiences, pilgrimages, or a connection with sacred sites. It offers insights into different religious traditions and the architectural wonders associated with them.
Here are some facets of religious tourism:
29. Pilgrimages and Sacred Sites
Pilgrimages involve journeys to sacred destinations associated with specific religions or spiritual beliefs. Places like Mecca for Muslims, Jerusalem for Christians, and Varanasi for Hindus hold immense religious significance and attract millions of pilgrims each year.
30. Spiritual Retreats and Meditation Centers
Spiritual retreats and meditation centers offer tranquil environments for introspection, relaxation, and spiritual growth. These retreats focus on mindfulness, meditation practices, and holistic healing.
Popular destinations for spiritual retreats include Bali in Indonesia, Sedona in the United States, and Rishikesh in India.
31. Religious Festivals and Events
Religious festivals and events provide a vibrant and immersive experience of cultural traditions and religious celebrations. Examples include the Kumbh Mela in India, the Holi festival of colors, and the Christmas celebrations in various parts of the world.
Participating in these festivals offers a unique glimpse into local customs, rituals, and the spirit of the community.
Indigenous Tourism

Indigenous tourism aims to promote understanding, appreciation, and respect for indigenous cultures, traditions, and ways of life. It provides opportunities to engage with indigenous communities and learn about their heritage.
Here are elements of indigenous tourism:
32. Indigenous Cultural Experiences
Indigenous cultural experiences allow travelers to interact with indigenous communities, learn about their traditions, crafts, music, and storytelling. These experiences foster cultural exchange and promote the preservation of indigenous heritage.
Destinations like the Maori culture in New Zealand, the Aboriginal culture in Australia, and the Native American reservations in the United States offer such immersive experiences.
33. Tribal Village Visits
Visiting tribal villages allows travelers to observe and learn about the traditional lifestyles, customs, and rituals of indigenous communities. It provides insights into their sustainable practices, craftsmanship, and deep-rooted connections with nature.
Destinations such as the Amazon rainforest, the Maasai Mara in Kenya, and the Highlands of Papua New Guinea offer opportunities to visit tribal communities.
34. Traditional Arts and Crafts
Indigenous cultures often have a rich tradition of art, crafts, and handicrafts that reflect their unique identity and skills. Exploring indigenous arts and crafts markets, workshops, and galleries allows travelers to appreciate and support the preservation of these traditional artistic practices.
From intricate weaving in Peru to intricate beadwork in South Africa, there is a vast array of indigenous art to discover.
Urban Tourism

City Tourism
City tourism encompasses visits to vibrant urban destinations, exploring their iconic landmarks, cultural attractions, and modern lifestyle. It offers a blend of history, art, entertainment, and culinary experiences.
Key aspects of city tourism include:
35. Sightseeing and Iconic Landmarks
Cities are known for their iconic landmarks, such as the Eiffel Tower in Paris, the Statue of Liberty in New York City, and the Sydney Opera House. Sightseeing allows visitors to capture the essence of a city's character and architectural splendor.
36. Museums and Art Galleries
Cities are often home to renowned museums and art galleries that showcase world-class collections, historical artifacts, and contemporary artworks.
The Louvre Museum in Paris, the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, and the Hermitage Museum in Saint Petersburg are just a few examples of the cultural treasures found in urban areas.
37. Shopping and Entertainment Districts
Urban centers offer diverse shopping experiences, from luxury boutiques to bustling street markets. Additionally, cities provide vibrant entertainment districts with theaters, music venues, and nightlife hotspots.
These districts cater to a variety of interests, ensuring that visitors can indulge in shopping, dining, and entertainment.
Architectural Tourism

Architectural tourism focuses on exploring unique architectural styles, landmarks, and urban design within cities. It allows travelers to appreciate the creativity, innovation, and historical significance of various structures.
Key elements of architectural tourism include:
38. Architectural Marvels and Landmarks
Cities showcase architectural marvels, such as the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the Sydney Opera House, and the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao. These structures captivate visitors with their impressive design, engineering, and cultural impact.
39. Modern and Contemporary Architecture Tours
Urban areas often feature striking modern and contemporary architecture that reflects the city's identity and vision. Walking tours or guided visits to architectural highlights, such as the Shard in London, the Marina Bay Sands in Singapore, or the Dancing House in Prague, offer insights into cutting-edge design and urban development.
40. Urban Design and City Planning
City tourism also encompasses exploring the urban design, layout, and city planning concepts that shape the physical environment. Sustainable urban planning, pedestrian-friendly streets, and green spaces contribute to the livability and attractiveness of cities.
Examples of urban design excellence can be found in cities like Copenhagen, Singapore, and Barcelona.
Emerging Forms of Tour

Dark Tourism
Dark tourism refers to visiting sites that are associated with death, tragedy, or historical atrocities. It offers a unique perspective on the darker aspects of human history. While it may seem unusual, dark tourism has gained popularity in recent years.
Here are some examples of dark tourism:
41. War Memorials and Battlefields
Visiting war memorials and battlefields provides insights into the sacrifices made during significant conflicts. Examples include the Normandy American Cemetery and Memorial in France and the Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park in Japan.
These sites allow visitors to reflect on the consequences of war and honor those who lost their lives.
42. Holocaust and Genocide Sites
Holocaust and genocide sites, such as Auschwitz-Birkenau in Poland and the Killing Fields in Cambodia, serve as reminders of the darkest chapters in human history.
These places educate visitors about the horrors of genocide and the importance of promoting peace and tolerance.
43. Disaster Tourism
Disaster tourism involves visiting locations affected by natural or man-made disasters. Examples include areas hit by hurricanes, volcanic eruptions, or industrial accidents.
While controversial, this form of tourism can raise awareness about the impact of disasters and the resilience of affected communities.
Space Tourism

Space tourism is an emerging frontier in the travel industry, allowing individuals to experience the thrill of space travel and explore the mysteries of the universe. While it is currently limited to a select few, advancements in technology and space exploration are making it more accessible.
Key aspects of space tourism include:
44. Space Travel and Exploration
Space tourism involves journeys beyond the Earth's atmosphere, offering a unique perspective of our planet and the vastness of space. Companies like Virgin Galactic and SpaceX are developing spacecraft to transport civilians into space, opening up new possibilities for adventurous travelers.
45. Astronaut Training Experiences
Before embarking on a space journey, aspiring space tourists can undergo astronaut training experiences. These programs simulate the physical and mental challenges faced by astronauts, including zero-gravity simulations, centrifuge training, and survival skills.
46. Observatories and Space Centers
Visiting observatories and space centers allows enthusiasts to learn about astronomy, space missions, and ongoing research. Places like the Kennedy Space Center in Florida and the European Space Agency's Spaceport in French Guiana offer interactive exhibits, rocket launches, and behind-the-scenes glimpses into space exploration.
Virtual Tourism

Virtual tourism has emerged as a response to the limitations of physical travel, allowing individuals to explore destinations and landmarks virtually. It offers a convenient and immersive way to experience different places from the comfort of one's home. Key aspects of virtual tourism include:
47. Virtual Reality Travel Experiences
Virtual reality (VR) technology allows users to immerse themselves in simulated environments, including famous landmarks, natural wonders, and cultural sites. VR headsets transport users to different locations, providing a realistic and interactive experience.
48. Online Museum and Landmark Tours
Many museums, historical sites, and landmarks offer virtual tours that enable visitors to explore their collections and exhibits online. These tours provide detailed information, multimedia content, and the ability to navigate through the spaces virtually.
49. Virtual Travel Platforms and Apps
Various platforms and apps offer virtual travel experiences, curated itineraries, and interactive content. These platforms leverage technology to create virtual travel communities, where users can connect, share experiences, and plan future trips.
As the travel industry evolves, embracing these emerging forms of tourism can open up new opportunities for businesses and provide unique experiences for travelers.
In conclusion, the tourism industry is a dynamic and ever-evolving sector that encompasses a wide range of experiences and opportunities. By understanding the diverse types of tourism in the world, business professionals can position themselves for success and growth in this competitive landscape.
By recognizing the unique characteristics and preferences of different traveler segments, businesses can tailor their offerings and marketing strategies to meet the specific needs of their target audiences. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also helps in creating a competitive advantage in the market.
Moreover, as the world becomes increasingly interconnected and travelers seek authentic and immersive experiences, businesses must embrace the diversity of tourism segments. By incorporating sustainable practices, respecting local cultures, and promoting responsible tourism, businesses can contribute to the preservation of natural and cultural heritage, while also appealing to environmentally and socially conscious travelers.
Let us embrace the diversity of tourism, foster innovation, and collaborate to shape the future of this exciting industry.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization
- World Travel and Tourism Council
- International Ecotourism Society
- Global Wellness Institute
- International Culinary Tourism Association
- Adventure Travel Trade Association
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre
- The International Dark-Sky Association
- Space Tourism Society
- World Tourism Organization
- National Geographic Travel
- International Association of Antarctica Tour Operators
- World Food Travel Association
- Beach Holidays by Expedia
Tumisang Bogwasi
2X Award-Winning Entrepreneur | Empowering Brands to Generate Leads, Grow Revenue with Business Strategy and Digital Marketing | Founder, CEO of Fine Group
Related Posts

The Importance of Tourism on Economies and Businesses
- April 6, 2023

The Ultimate Guide To Types of Tourism: From Active to Zoological and More
Social Listening in Tourism: A Key Tool for Destination Marketers
Welcome to our ultimate guide to types of tourism! This collection is a comprehensive exploration of the diverse world of travel.
In this guide, we delve into an extensive array of tourism types, each offering unique experiences and perspectives on the world. From thrill-seekers to animal enthusiasts and more, this guide covers a spectrum that caters to every traveler’s preference and style.
Our aim is to enlighten both seasoned and novice tourism professionals and providers about the myriad ways people can explore, learn, and interact with different cultures, environments, and communities.
Join us as we journey through each type of tourism, uncovering the nuances and specialties that make each one distinct and worthwhile.
3 Benefits to Understanding Types of Tourism
3 limitations of tourism typologies, active tourism, adventure tourism, accessible tourism, agritourism, alternative tourism, archaeological tourism, birth tourism, business tourism or mice tourism, bird tourism, coffee tourism, community-based tourism, craft tourism, cruise tourism, culinary tourism or food tourism, cultural tourism, dark tourism, dental tourism, disaster tourism, domestic tourism, drug tourism, educational tourism, enotourism/wine tourism, experiential tourism, extreme tourism, fashion tourism, film tourism, genealogy tourism, halal tourism, health tourism, heritage tourism, honeymoon tourism, industrial tourism, jungle tourism, justice tourism, lgbt tourism, literary tourism, medical tourism, militarism heritage tourism, music tourism, nautical tourism, ocean tourism, photography tourism, political tourism, rail tourism, regenerative tourism, religious tourism, rural tourism, science tourism, senior tourism, sex tourism, slow tourism, slum tourism, snow and ice tourism, space tourism, sports tourism, sustainable tourism, virtual tourism, voluntourism, war tourism, wellness tourism, wildlife tourism, zoological tourism, what other types of tourism are out there, what are the benefits of understanding types of tourism.
As you explore this guide, consider both the benefits and limitations of these tourism types.
Use them as a lens to view the vast, dynamic landscape of travel, keeping in mind that the real essence of tourism often lies in the unique, unclassifiable experiences that transcend these categories.
This guide aims to spark ideas, foster understanding, and offer a structured overview while celebrating the diversity and complexity of travel experiences worldwide.
- Identifying Personal Preferences and Destination Offerings – By exploring the different types of tourism, you can better understand what appeals to you as a traveler or what your destination can uniquely offer. This knowledge helps in tailoring travel experiences to personal tastes or in marketing a destination effectively.
- Competitive Analysis – For travel professionals and destination planners, understanding the breadth of tourism types provides a valuable tool for competitive analysis. By seeing what other destinations are doing, you can identify trends, gaps, and opportunities in the market.
- Learning from Successes and Failures – This guide serves as a repository of diverse tourism practices, allowing you to see what works and what doesn’t in different contexts. Such insights are invaluable for refining strategies and offerings in the tourism industry.
- Academic Orientation – While the categorization of tourism types is insightful, it’s important to recognize that this approach can be somewhat academic. The way these categories are defined and discussed may not always align with the more fluid, real-world experiences of travelers and industry practitioners.
- Tourist Self-Identification – Many tourists may not consciously identify with specific tourism labels like “wellness tourism seekers” or “adventure tourists.” Their motivations and behaviors might overlap across several types of tourism, making it challenging to pigeonhole their experiences into a single category.
- Guidelines, Not Rules – Consequently, it’s crucial to view these categories as flexible guidelines rather than rigid classifications. They offer a framework for understanding the broad spectrum of tourism, but they should be adapted and interpreted in the context of real-world experiences and market dynamics.
Now, I would like to begin expanding our list of types of tourism. I would like to give you 5 at a time. For each type of tourism, please give a 4-5 sentence paragraph explaining generally what this type of tourism consists of. Then give 3 bullets of examples from around the world that classify this type of tourism. Does that sound doable?
64 Types of Tourism (and Counting!)
Active tourism is centered around travel experiences that involve physical activities and outdoor adventures. It’s ideal for those who seek an energetic and health-conscious way to explore new destinations.
This type of tourism includes a range of activities such as hiking tours, cycling tours, and running tours, each offering a unique way to connect with the landscape and culture of a place.
Examples of active tourism :
- Hiking Tours in the Swiss Alps – Trekking through scenic mountain trails and enjoying breathtaking views.
- Cycling Tours in the Loire Valley, France – Exploring picturesque villages and vineyards on bike.
- Run Tours in the Italian Dolomites – Self-guided and guide-led tours through one of the most challenging and dramatic run destinations.
Adventure tourism is characterized by its focus on active, outdoor experiences that often involve an element of risk or physical exertion. It caters to travelers seeking excitement, adrenaline, and exploration in natural or exotic environments.
This type of tourism usually involves activities like trekking, mountain biking, rock climbing, or water sports. It appeals to those who want to step outside their comfort zone and embrace nature’s challenges.
Examples of Adventure Tourism :
- Trekking in the Himalayas, Nepal – Offering some of the world’s most breathtaking treks, including the famous Everest Base Camp trek.
- White-water Rafting in the Grand Canyon, USA – Navigating the rapids of the Colorado River amidst stunning canyon scenery.
- Safari Adventure in Kruger National Park, South Africa – Experiencing wildlife up close on guided safaris and bush walks.
Accessible tourism ensures travel and tourism opportunities are available to all people, regardless of their physical limitations, disabilities, or age.
This form of tourism focuses on creating inclusive environments, from transportation to accommodations and attractions, ensuring accessibility for everyone. It’s about removing barriers to travel and embracing a diverse range of travelers.
Examples of accessible tourism :
- Barrier-Free Travel in Berlin, Germany – Known for its accessible public transportation and facilities.
- Accessible Beaches in Gold Coast, Australia – Featuring beach wheelchairs and accessible walkways.
- Disney World, Florida, USA – Offering extensive accessibility options for visitors with various disabilities.
Agritourism, or agricultural tourism, involves visiting a working farm or any agricultural, horticultural, or agribusiness operation to enjoy, be educated, or be involved in activities.
This type of tourism includes a wide range of activities like fruit picking, farm stays, wine tasting, and learning about rural ways of life. It’s a way for tourists to experience and understand the agricultural landscape and traditions.
Examples of agritourism :
- Wine Tours in Tuscany, Italy – Exploring vineyards and tasting world-class wines.
- Farm Stays in Vermont, USA – Participating in farm activities and enjoying local, farm-to-table meals.
- Tea Plantation Tours in Kerala, India – Witnessing tea production and enjoying scenic plantation walks.
Alternative tourism is an approach that emphasizes travel outside of the conventional mass tourism model. It focuses on smaller groups, less trodden destinations, and experiences that promote environmental sustainability, cultural understanding, and local community engagement.
This type of tourism often involves eco-friendly practices, cultural immersion, and responsible travel ethics.
Examples of alternative tourism:
- Eco-Lodges in the Amazon Rainforest, Brazil – Providing sustainable accommodation and immersive rainforest experiences.
- Community-based Tourism in Chiang Mai, Thailand – Engaging with local hill tribes and participating in their daily activities.
- Responsible Wildlife Tours in Galapagos Islands, Ecuador – Promoting conservation and responsible interaction with unique wildlife.
Archaeological tourism involves traveling to sites of historical and archaeological significance. It appeals to those interested in the ancient history and civilizations of different cultures.
Tourists get to explore ruins, artifacts, and museums, often with the guidance of experts to enrich their understanding of the site’s historical context.
Examples of archaeological tourism :
- Pyramids of Giza, Egypt – Exploring one of the most iconic and ancient wonders of the world.
- Machu Picchu, Peru – Visiting the well-preserved ruins of an Incan city set high in the Andes Mountains.
- Roman Colosseum, Italy – Touring the remains of the ancient Roman amphitheater, rich in historical significance.
Birth tourism refers to the practice of traveling to another country for the purpose of giving birth in that country. The primary motivation is often to obtain certain benefits for the child, such as citizenship or access to superior healthcare.
This type of tourism involves extended stays and often requires considerable planning and understanding of the destination’s legal and medical systems.
Examples of birth tourism :
- Canada and the United States – Popular destinations for birth tourism due to the automatic right to citizenship for children born in these countries.
- Brazil – Known for its high-quality healthcare facilities attracting birth tourists.
- Germany – Offers excellent healthcare and allows children born to foreign parents to apply for citizenship under certain conditions.
Business tourism, also known as corporate or MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions) tourism, involves travel for business-related purposes. This includes attending conferences, meetings, trade shows, and corporate events.
It’s a major sector of the tourism industry, often involving high-level logistics and luxury accommodations.
Examples of business tourism/MICE tourism :
- Dubai, UAE – Frequently hosts international business conferences and exhibitions.
- Las Vegas, USA – Known for its large convention centers and hosting major trade shows.
- Singapore – A hub for corporate meetings and international business events in Asia.
Bird tourism, or birding, is a form of natural tourism where individuals travel specifically to observe and study birds in their natural habitat. This type of tourism is popular among wildlife enthusiasts and nature photographers.
It contributes to conservation efforts and promotes awareness of bird species and their environments.
Examples of bird tourism :
- Costa Rica – Home to a diverse range of bird species, attracting bird watchers from around the world.
- Kruger National Park, South Africa – Offers birding safaris to see African bird species.
- Papua New Guinea – Known for its endemic bird species, including the famous Birds of Paradise.
Coffee tourism centers around visiting coffee plantations, learning about the coffee production process, and tasting various types of coffee. It provides insight into the journey of coffee from bean to cup, including cultivation, harvesting, and roasting.
This type of tourism is especially popular among coffee enthusiasts and those interested in agritourism. It’s also a way to understand the cultural and economic importance of coffee in different regions.
Examples of coffee tourism :
- Coffee Plantations in Colombia – Exploring the renowned coffee-growing regions and experiencing the rich flavor of Colombian coffee.
- Café Tours in Vienna, Austria – Discovering the historic coffee houses and the city’s coffee culture.
- Coffee Farms in Uganda – A special recommendation from Travel Marketing School’s founder, as he conducted a research project in Uganda, delving into the local coffee industry and its impact on communities.
Community-based tourism focuses on local communities and their cultures, traditions, and daily lives. It’s a form of sustainable tourism that aims to benefit local residents directly, often through immersive cultural experiences.
This tourism type encourages respectful and meaningful interactions between tourists and host communities.
Examples of community-based tourism :
- Sapa, Vietnam – Visitors engage with local hill tribes and experience traditional lifestyles.
- Masai Mara, Kenya – Offers cultural experiences with the Maasai people, including village tours and traditional dance performances.
- Oaxaca, Mexico – Known for community-based cultural tours, artisan workshops, and local cuisine.
Craft tourism involves traveling to destinations known for unique local crafts and artisanal products. Tourists get the chance to see artisans at work, learn about traditional crafting techniques, and purchase handmade goods.
This type of tourism supports local artisans and preserves cultural heritage.
Examples of craft tourism :
- Marrakech, Morocco – Famous for its souks with traditional crafts like pottery, leather goods, and textiles.
- Kyoto, Japan – Offers experiences in traditional Japanese crafts such as kimono making and woodworking.
- Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA – Known for Native American and Spanish colonial crafts, including jewelry and pottery.
Cruise tourism involves traveling on cruise ships that offer various on-board amenities and stop at multiple destinations. It’s a unique way to explore different places while enjoying the luxury and entertainment provided on the cruise.
This type of tourism is popular for its convenience, all-inclusive packages, and the ability to visit multiple locations in a single trip.
Examples of cruise tourism :
- Caribbean Cruises – Known for their scenic island stops and vibrant on-board activities.
- Mediterranean Cruises – Offering a journey through historic ports in countries like Italy, Greece, and Spain.
- Alaskan Cruises – Showcasing stunning glacier views, wildlife, and unique shore excursions.
Culinary tourism, also known as food tourism, involves traveling primarily for experiencing the food and culinary traditions of a particular region.
This type of tourism is not just about dining out, but also includes activities like food tours, cooking classes, wine tastings, and visiting farmers’ markets. It appeals to those keen on exploring a destination’s culture through its gastronomy.
Examples of culinary tourism or food tourism :
- Bologna, Italy – Known for its rich food culture, including dishes like Bolognese sauce and Parmigiano Reggiano cheese.
- Bangkok, Thailand – Famous for its street food tours offering a taste of authentic Thai cuisine.
- Oaxaca, Mexico – Offers culinary experiences centered around traditional Mexican cuisine, including mole and mezcal tasting.
Cultural tourism involves traveling to experience the culture, traditions, and lifestyle of a particular area. This includes visiting historical sites, festivals, art galleries, theaters, and experiencing local customs.
Cultural tourists seek to gain an authentic experience and a deeper understanding of the destination’s heritage.
Examples of cultural tourism :
- Kyoto, Japan – Renowned for its temples, traditional tea ceremonies, and Geisha culture.
- Paris, France – Offers a rich cultural experience with its world-famous museums, art galleries, and historical architecture.
- Marrakech, Morocco – Known for its vibrant souks, historic palaces, and Berber culture.
Dark tourism involves visiting sites associated with death, suffering, or tragedy. This controversial form of tourism is often educational and thought-provoking, aiming to commemorate and remember historical events.
It includes visiting war zones, genocide memorials, disaster sites, and prisons.
Examples of dark tourism :
- Auschwitz-Birkenau, Poland – A former Nazi concentration and extermination camp, now a museum and memorial.
- Chernobyl, Ukraine – Tours to the site of the Chernobyl nuclear disaster.
- Ground Zero, New York, USA – The site of the September 11 attacks, now home to a memorial and museum.
Dental tourism involves traveling abroad for affordable dental care, surgery, or procedures that are more expensive in one’s home country. It’s often combined with the opportunity to vacation and relax during the recovery period.
This type of tourism is popular due to the cost savings and quality of care available in certain countries.
Examples of dental tourism :
- Bangkok, Thailand – Known for high-quality dental services at a fraction of the cost compared to Western countries.
- Budapest, Hungary – A popular destination for dental care, offering modern clinics and experienced dentists.
- Costa Rica – Attracts dental tourists with its combination of professional dental care and beautiful vacation spots.
Disaster tourism is the practice of visiting locations that have experienced natural or man-made disasters. It can be controversial, but when managed ethically, it can offer educational value and support for the affected communities through tourism revenue.
This type of tourism includes visiting areas hit by hurricanes, earthquakes, or industrial catastrophes.
Examples of disaster tourism :
- New Orleans, USA – Tours of areas affected by Hurricane Katrina, focusing on the disaster’s impact and recovery efforts.
- Pompeii, Italy – An ancient city preserved in volcanic ash from Mount Vesuvius, offering insights into the life and sudden end of a Roman city.
- Fukushima, Japan – Guided tours in the regions affected by the 2011 tsunami and nuclear disaster, focusing on the impacts and ongoing recovery.
Domestic tourism involves traveling within one’s own country rather than going abroad. This type of tourism allows individuals to explore different regions, cultures, and attractions within their national borders. It’s a way to support local economies and discover the diversity of one’s own country.
Domestic travel can range from weekend getaways to extended tours and can include a variety of activities like city breaks, countryside excursions, or coastal holidays.
Examples of domestic tourism :
- The Lake District, England – Known for its stunning landscapes, hiking trails, and quaint villages.
- Yellowstone National Park, USA – Attracts visitors with its geothermal features and wildlife.
- Great Ocean Road, Australia – A scenic drive famous for its rugged coastline, including the Twelve Apostles.
Drug tourism refers to travel to a region to obtain or use drugs that are illegal in one’s home country. This controversial type of tourism often involves substances that are culturally or legally accepted in the destination.
It’s important to approach this topic with an understanding of the legal and ethical implications involved.
Examples of drug tourism :
- Amsterdam, Netherlands – Known for its coffee shops where certain types of cannabis are legally sold and consumed.
- Ayahuasca Retreats in Peru – Offering spiritual experiences with the traditional Ayahuasca brew, often under the guidance of a shaman.
- Certain States in the USA – Where the recreational use of cannabis is legal, attracting tourists from other states or countries.
Ecotourism focuses on responsible travel to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of local people. It emphasizes minimizing the impact of tourism, promoting environmental awareness, and providing direct financial benefits for conservation and community development.
Ecotourism experiences often include wildlife viewing, nature hikes, and educational activities about local ecosystems.
Examples of ecotourism :
- Costa Rica – A global leader in ecotourism, known for its rainforest tours and conservation efforts.
- The Galapagos Islands, Ecuador – Offers unique wildlife experiences with a strong emphasis on preserving the islands’ delicate ecosystem.
- Kenya – Renowned for its safari experiences in national parks that combine wildlife viewing with conservation efforts.
Educational tourism is travel aimed at acquiring knowledge or learning something new, including student exchanges, study tours, and academic sabbaticals.
This type of tourism can encompass a wide range of subjects, from language learning to cultural studies, and is often facilitated by educational institutions.
Examples of educational tourism :
- Language Schools in Spain – Offering immersive Spanish language learning experiences.
- Historical Tours in Rome, Italy – Focusing on the city’s rich ancient history and architecture.
- Cooking Schools in Thailand – Where tourists learn to cook traditional Thai dishes in a hands-on setting.
Enotourism, or wine tourism, involves visiting vineyards, wineries, wine festivals, and tasting rooms to experience the process of wine production and to taste wines in their natural setting.
This type of tourism often includes learning about viticulture and winemaking processes, and experiencing the culture and cuisine associated with wine regions.
Examples of enotourism or wine tourism :
- Bordeaux, France – Famous for its wine tours and tastings in renowned vineyards.
- Napa Valley, California, USA – Known for its world-class wineries and beautiful landscapes.
- Tuscany, Italy – Offers picturesque vineyards, wine tastings, and tours of historic wineries.
Experiential tourism focuses on creating immersive experiences for travelers, allowing them to actively engage with the history, people, culture, food, and environment of a destination. Instead of being passive observers, tourists are encouraged to participate actively in the local way of life.
This type of tourism often involves authentic, hands-on activities that provide a deeper understanding of the local culture.
Examples of experiential tourism :
- Live Like a Local in Bali, Indonesia – Engaging in traditional Balinese daily activities, from rice farming to temple rituals.
- Culinary Classes in France – Learning to cook regional French dishes with local chefs.
- Maori Cultural Experiences in New Zealand – Immersive experiences in Maori history, art, and traditional ceremonies.
Extreme tourism caters to tourists seeking adrenaline-pumping activities and experiences that involve a high level of risk. This type of tourism is for thrill-seekers who enjoy challenging themselves physically and mentally.
Activities often take place in extreme or unusual environments, from remote wilderness to harsh climates.
Examples of extreme tourism :
- Mount Everest Expeditions, Nepal – Attempting to summit the world’s highest peak.
- Volcano Boarding in Nicaragua – Sliding down the slopes of an active volcano on a specialized board.
- Ice Diving in Antarctica – Exploring underwater environments beneath the ice.
Fashion tourism revolves around traveling to destinations known for their influence in the world of fashion. This includes visiting fashion capitals for events like Fashion Week, exploring famous shopping districts, and attending fashion shows.
It’s a blend of travel and the love of fashion, style, and shopping.
Examples of fashion tourism :
- Milan Fashion Week, Italy – Attending one of the most prestigious events in the fashion world.
- Shopping in Paris, France – Exploring high-end fashion boutiques in areas like the Champs-Élysées.
- Garment District Tour in New York City, USA – Discovering the heart of America’s fashion industry.
Film tourism involves visiting locations where famous movies or TV shows were filmed. This type of tourism allows fans to connect with their favorite media by seeing and experiencing the actual places featured on screen.
It includes guided tours of film sets, themed attractions, and visiting iconic locations from popular films.
Examples of film tourism :
- Hobbiton Movie Set, New Zealand – Exploring the filming location of “The Lord of the Rings” and “The Hobbit” trilogies.
- Game of Thrones Tours in Dubrovnik, Croatia – Visiting key filming locations from the popular TV series.
- Harry Potter Studio Tour in London, England – Experiencing the behind-the-scenes of the Harry Potter movie series.
Genealogy tourism, or ancestry tourism, involves individuals traveling to explore their family roots and heritage. This journey often includes visiting ancestral hometowns, exploring archives and libraries, and connecting with distant relatives.
It’s a personal form of tourism that provides a deeper understanding of one’s family history and cultural background.
Examples of genealogy tourism :
- Visiting Ellis Island, USA – Exploring the gateway for millions of immigrants and searching historical records.
- Ancestral Villages in China – Travelers visit their ancestral villages to learn about family history and participate in traditional customs.
- Genealogy Research in Ireland – Utilizing resources like the National Library of Ireland to trace Irish ancestry and visiting ancestral homes.
Geotourism focuses on the geographical characteristics of a destination, including its culture, aesthetics, heritage, and well-being of its inhabitants. It emphasizes a deep respect and appreciation for the intrinsic natural and cultural features of a place.
Geotourism often involves exploring unique geological features, landscapes, and local traditions in a sustainable manner.
Examples of geotourism :
- Grand Canyon, USA – Marveling at one of the world’s most renowned geological wonders.
- Icelandic Geothermal Springs – Experiencing geysers, hot springs, and volcanic landscapes.
- The Great Barrier Reef, Australia – Exploring the world’s largest coral reef system, renowned for its vibrant marine life.
Halal tourism caters to Muslim travelers who wish to adhere to their Islamic beliefs while traveling. This includes access to Halal food, prayer facilities, and accommodation that aligns with Islamic practices.
Halal tourism also often involves experiences that respect Islamic culture and heritage.
Examples of halal tourism :
- Istanbul, Turkey – Offering a rich Islamic heritage, Halal-friendly hotels, and mosques.
- Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia – Known for its Halal culinary scene and Islamic art museums.
- Dubai, UAE – Providing luxury Halal travel experiences, from shopping to accommodation.
Health tourism involves traveling to improve one’s physical or mental health, often including medical treatments, wellness retreats, or fitness programs.
This type of tourism can range from spa and wellness retreats to undergoing medical procedures or therapies in specialized facilities abroad.
Examples of health tourism :
- Spa Retreats in Bali, Indonesia – Offering holistic wellness experiences, including traditional Balinese treatments.
- Yoga Retreats in Rishikesh, India – Known as the ‘Yoga Capital of the World’, offering a range of yoga and meditation retreats.
- Thermal Baths in Budapest, Hungary – Famous for its thermal springs and spa culture.
Heritage tourism involves visiting sites of historical or cultural significance to understand and appreciate the past. It includes exploring ancient ruins, historical landmarks, museums, and culturally rich neighborhoods.
This type of tourism is about connecting with the history, traditions, and heritage of a place.
Examples of heritage tourism :
- The Pyramids of Giza, Egypt – Exploring one of the most significant archaeological sites in the world.
- The Historic Center of Rome, Italy – Immersing in the rich history of the Roman Empire.
- The Great Wall of China – Visiting the iconic symbol of China’s historical defense architecture.
Honeymoon tourism caters to newlyweds seeking a romantic and memorable experience post-wedding. It often involves luxury accommodations, picturesque settings, and romantic activities.
Destinations range from tropical beaches to cozy mountain retreats, tailored to provide an intimate and special experience for couples.
Examples of honeymoon tourism :
- Maldives – Known for its overwater bungalows and idyllic island settings.
- Paris, France – Often dubbed the ‘City of Love’, popular for its romantic ambiance.
- Santorini, Greece – Famous for its stunning sunsets, white-washed buildings, and beautiful beaches.
Industrial tourism involves visiting industrial sites, factories, or other facilities to learn about their history, operations, and contributions to society. This type of tourism offers insight into various industries, from traditional manufacturing to high-tech sectors.
Visitors get a chance to see how products are made and understand the industrial heritage of a region.
Examples of industrial tourism :
- Boeing Factory Tour, Seattle, USA – Observing the assembly of airplanes in the world’s largest building by volume.
- Guinness Storehouse, Dublin, Ireland – Exploring the history and production of the famous beer.
- BMW Welt, Munich, Germany – Showcasing the brand’s history and offering insights into modern car manufacturing.
Jungle tourism focuses on exploring dense rainforests or jungles, offering an immersive experience in rich, biodiverse environments. This type of tourism often includes guided treks, wildlife watching, and learning about the ecosystem and indigenous cultures.
It’s popular among nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers.
Examples of jungle tourism :
- Amazon Rainforest, Brazil – Experiencing the world’s largest tropical rainforest and its diverse wildlife.
- Taman Negara, Malaysia – Exploring one of the world’s oldest rainforests with guided jungle treks.
- Madagascar – Visiting unique ecosystems with a vast array of endemic species, from lemurs to exotic plants.
Justice tourism is a form of travel concerned with social justice and human rights. It involves visiting places significant to historical or contemporary struggles for justice and equality.
This type of tourism aims to educate travelers about issues like poverty, oppression, and civil rights, often involving interactions with local communities.
Examples of justice tourism :
- Robben Island, South Africa – The prison where Nelson Mandela was held, now a symbol of the struggle against apartheid.
- Civil Rights Trail, USA – Visiting key sites of the American Civil Rights Movement.
- Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe, Berlin, Germany – Reflecting on the history and impact of the Holocaust.
LGBT tourism caters to members of the LGBT community and is focused on destinations, accommodations, and events that are welcoming and inclusive. This type of tourism includes pride festivals, cruises, and destinations known for their supportive and vibrant LGBT scenes.
It promotes a safe and open environment for LGBT travelers.
Examples of LGBT tourism :
- San Francisco, USA – Known for its inclusive and vibrant LGBT community and history.
- Amsterdam, Netherlands – Hosting one of the world’s most famous pride parades and offering a welcoming atmosphere.
- Mykonos, Greece – A popular LGBT-friendly island with a lively nightlife and beautiful beaches.
Literary tourism involves visiting locations associated with famous authors, literary works, or literary history. This can include authors’ homes, settings of famous novels, or literary festivals.
It appeals to book lovers and those interested in the world of literature and storytelling.
Examples of literary tourism :
- Stratford-upon-Avon, England – The birthplace of William Shakespeare, with various related sites and theaters.
- Brontë Parsonage Museum, England – The former home of the Brontë sisters, set in the landscape that inspired their novels.
- Joyce’s Dublin, Ireland – Exploring the city through the lens of James Joyce’s works, particularly “Ulysses.”
Medical tourism involves traveling to another country for medical care, often driven by lower costs, higher quality services, or access to specific treatments not available in one’s home country.
This can include a wide range of medical services, from elective procedures like cosmetic surgery to complex treatments such as organ transplants or fertility therapy.
Examples of medical tourism :
- Bangkok, Thailand – Renowned for high-quality medical care at affordable prices, especially in cosmetic and reconstructive surgery.
- India – Offers advanced medical treatments like cardiac surgery and orthopedics at competitive prices.
- South Korea – Known for its advanced medical technology, particularly in areas like dermatology and plastic surgery.
Militarism heritage tourism involves visiting sites significant to military history, such as battlefields, war memorials, and military museums.
This type of tourism is aimed at understanding the historical context of wars and conflicts and honoring the memory of those who served.
Examples of militarism heritage tourism :
- Normandy, France – Visiting the D-Day landing beaches and war cemeteries from World War II.
- Gettysburg, USA – Exploring the site of the pivotal battle in the American Civil War.
- Hiroshima Peace Memorial, Japan – Reflecting on the impact of the atomic bomb and promoting peace.
Music tourism is travel motivated by the love of music, whether it’s visiting famous music destinations, attending concerts and festivals, or exploring the history of certain music genres.
This type of tourism can include a variety of musical experiences, from classical music concerts to rock festivals.
Examples of music tourism :
- Nashville, USA – Known as the “Music City” and famous for its country music scene and attractions like the Grand Ole Opry.
- Vienna, Austria – Celebrated for its classical music heritage and venues like the Vienna State Opera.
- New Orleans, USA – Renowned for its jazz music, lively music festivals, and vibrant street performances.
Nautical tourism encompasses activities and experiences related to sailing and boating. This can include yacht chartering, sailing regattas, and visiting maritime museums.
Nautical tourism is popular among those who enjoy the sea and water-based activities.
Examples of nautical tourism :
- Greek Islands Yacht Tour – Exploring the Aegean Sea and visiting various Greek islands by boat.
- Croatian Coastline – Offering sailing experiences along its scenic Adriatic coast.
- Monaco Yacht Show – One of the most prestigious nautical events showcasing luxury yachting.
Ocean tourism focuses on activities and experiences in and around the ocean. This includes a wide range of water-based activities such as scuba diving, snorkeling, ocean kayaking, and whale watching.
It’s ideal for those who wish to explore marine life and oceanic environments.
Examples of ocean tourism :
- Great Barrier Reef, Australia – World-famous for scuba diving and snorkeling, showcasing an array of marine life.
- Whale Watching in Maui, Hawaii – Offering opportunities to see humpback whales in their natural habitat.
- Surfing in Bali, Indonesia – Known for its excellent surfing spots and vibrant marine life.
Photography tourism caters to those who travel specifically to capture photographs of scenic, cultural, or unique subjects. This can include wildlife photography safaris, visits to picturesque landscapes, or urban photography tours.
It’s ideal for both amateur and professional photographers looking to expand their portfolios with diverse and compelling images.
Examples of photography tourism :
- Iceland – Popular for capturing natural phenomena like the Northern Lights and dramatic landscapes.
- Masai Mara, Kenya – A prime destination for wildlife photography, especially during the Great Migration.
- Paris, France – Offering classic urban photography opportunities with iconic landmarks like the Eiffel Tower.
Political tourism involves traveling to sites of significant political interest, including historical landmarks, political institutions, or locations known for political events.
This type of tourism is aimed at those interested in political history, activism, or contemporary political scenes.
Examples of political tourism :
- Washington D.C., USA – Visiting the U.S. Capitol, White House, and various political memorials.
- Berlin, Germany – Exploring sites like the Berlin Wall and Reichstag building, rich in political history.
- Beijing, China – Home to the Forbidden City and Tiananmen Square, significant in Chinese political history.
Rail tourism is centered around journeys on trains, offering a unique way to view landscapes and explore regions. This can range from luxury train experiences to scenic rail routes that traverse through picturesque countryside, mountains, or coastal areas.
It appeals to those who enjoy the romance and nostalgia of train travel.
Examples of rail tourism :
- Trans-Siberian Railway, Russia – One of the world’s longest train journeys, crossing diverse landscapes from Moscow to Vladivostok.
- The Ghan, Australia – A coast-to-coast rail journey across the Australian continent, from Darwin to Adelaide.
- Glacier Express, Switzerland – Renowned for its panoramic views of the Swiss Alps.
Regenerative tourism goes beyond sustainability, aiming to leave a place better than it was found. This approach involves engaging in travel practices that restore and enhance the environment, local culture, and community well-being.
It’s about creating a positive impact and contributing to the regeneration of the ecosystems and communities visited.
Examples of regenerative tourism :
- Reforestation Projects in the Amazon Rainforest, Brazil – Participating in efforts to replant and restore parts of the rainforest.
- Cultural Preservation Programs in Bali, Indonesia – Supporting initiatives that maintain and rejuvenate traditional Balinese arts and crafts.
- Ecosystem Restoration Camps, Various Locations – Joining camps that focus on restoring degraded landscapes and promoting ecological health.
Religious tourism, or pilgrimage, involves traveling to religious sites, temples, churches, or regions significant to specific faiths.
This type of tourism can be a spiritual journey or a way to explore the historical and cultural aspects of different religions.
Examples of religious tourism :
- Mecca, Saudi Arabia – The holiest city in Islam, visited by millions of Muslims for the Hajj pilgrimage.
- Vatican City – Attracting millions of Christian pilgrims and tourists to St. Peter’s Basilica and the Sistine Chapel.
- Varanasi, India – One of the oldest and most sacred cities in Hinduism, famous for its ghats and temples.
Rural tourism focuses on visiting rural areas to experience and understand the rural lifestyle, culture, and traditions. It often involves staying in villages, farmhouses, or homestays, and participating in activities like hiking, local crafts, and agriculture.
This type of tourism is popular among those seeking a tranquil and authentic experience away from urban centers.
Examples of rural tourism :
- Tuscany, Italy – Known for its picturesque countryside, vineyards, and traditional farm stays.
- Shirakawa-go, Japan – Offers a unique experience in traditional thatched-roof villages.
- Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, USA – Provides insight into the Amish lifestyle and culture.
Science tourism is centered around visiting sites of scientific interest, such as observatories, science museums, and research facilities. It appeals to those interested in learning about various scientific fields, from astronomy to geology.
This type of tourism often includes educational tours and interactive experiences designed to enhance understanding of scientific principles and discoveries.
Examples of science tourism :
- CERN, Switzerland – Touring the world’s largest particle physics laboratory.
- Kennedy Space Center, Florida, USA – Exploring NASA’s launch complex and space exploration exhibits.
- Galapagos Islands, Ecuador – Known for their unique biodiversity, offering insights into evolutionary biology.
Senior tourism caters to older travelers, often offering tailored travel experiences that are accessible and comfortable for them. This can include cultural tours, cruise trips, and leisure destinations with a focus on health, relaxation, and low-impact activities.
Senior tourism prioritizes ease of access, quality of services, and opportunities for social interaction.
Examples of senior tourism :
- Cruise trips in the Mediterranean – Providing accessible and leisurely travel experiences with stops at historical cities.
- Health resorts in Baden-Baden, Germany – Offering therapeutic spa treatments in a serene environment.
- Cultural tours in Japan – Guided tours with a focus on comfort and accessibility, exploring traditional Japanese culture.
Sex tourism involves traveling to engage in sexual activities, often with commercial sex workers. This controversial and often illegal form of tourism raises significant ethical and legal concerns.
It’s important to approach this topic with an understanding of the legal, social, and human rights implications involved.
Examples of sex tourism :
- Bangkok, Thailand – Known for its red-light districts, though this aspect is controversial and subject to legal and ethical scrutiny.
- Amsterdam, Netherlands – Notable for its legalized and regulated Red Light District, though the city has been taking measures to address issues related to sex tourism.
- Nevada, USA – Certain areas in Nevada have legal brothels, though this is a highly regulated industry.
Slow tourism emphasizes taking time to enjoy and experience the destination deeply rather than trying to see everything in a rush. It’s about immersing oneself in the local culture, environment, and way of life, often involving longer stays, and sustainable and mindful travel practices.
Examples of slow tourism :
- Canal Boating in France – Exploring the countryside at a leisurely pace through its network of canals.
- Walking tours in Tuscany, Italy – Enjoying the landscape, cuisine, and culture at a relaxed pace.
- Stay in a Ryokan, Japan – Experiencing traditional Japanese hospitality and culture in a serene setting.
Slum tourism involves visiting impoverished urban areas to see firsthand the life of residents in these communities. While it can raise awareness about poverty and social issues, it also raises ethical concerns about exploitation and voyeurism.
Responsible slum tourism should focus on respectful engagement and supporting local communities.
Examples of slum tourism :
- Dharavi, Mumbai, India – Guided tours that aim to break stereotypes and highlight the industriousness of the community.
- Township tours in South Africa – Visits to townships with a focus on cultural exchange and understanding the local history and social challenges.
- Favela tours in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil – Offering insights into the vibrant culture and community resilience in favelas.
Snow and ice tourism is all about travel experiences in cold and snowy environments. This type of tourism is popular for winter sports enthusiasts and those who enjoy the beauty of snowy landscapes.
Activities include skiing, snowboarding, ice skating, and visiting ice hotels or festivals.
Examples of snow and ice tourism :
- Skiing in Aspen, Colorado, USA – Offering world-class ski resorts and winter sports facilities.
- Ice Hotel Stay in Jukkasjärvi, Sweden – Experiencing unique accommodation entirely made of ice and snow.
- Harbin Ice Festival, China – Visiting one of the world’s largest ice and snow sculpture festivals.
Space tourism represents the cutting-edge of travel, offering civilians the opportunity to experience space. This emerging type of tourism includes suborbital flights that provide a few minutes of weightlessness and an incredible view of Earth from space.
It’s a frontier for wealthy adventurers and science enthusiasts.
Examples of space tourism :
- Virgin Galactic – Offering suborbital spaceflights for tourists.
- SpaceX – Developing orbital space tourism missions.
- International Space Station – Proposed private visits facilitated by companies like Axiom Space.
Sports tourism involves traveling to participate in or observe sporting events. This includes international competitions like the Olympics, marathons, football matches, or golf tournaments.
Sports tourism appeals to fans and athletes alike, offering them a chance to experience the excitement and camaraderie of sports in different locales.
Examples of sports tourism :
- FIFA World Cup, Various Locations – Attending one of the most prestigious and widely-viewed sports events in the world.
- Boston Marathon, USA – Participating or spectating in one of the oldest annual marathons.
- The Masters Golf Tournament, Augusta, USA – Observing one of the four major championships in professional golf.
Sustainable tourism focuses on traveling in a way that minimizes environmental impact and promotes conservation while benefiting local communities.
It involves responsible travel practices, supporting eco-friendly accommodations, and participating in activities that respect local culture and the environment.
Examples of sustainable tourism :
- Eco-lodges in Costa Rica – Staying in accommodations dedicated to conservation and sustainability.
- Community-based Eco Tours in Kenya – Participating in wildlife safaris that support conservation efforts and community development.
- Responsible Trekking in Nepal – Following eco-friendly practices and supporting local Sherpa communities.
Virtual tourism offers the experience of visiting a place through digital means, such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), or online tours. It’s a way to explore destinations from home, making travel accessible to those unable to travel physically.
Virtual tours can cover historic sites, museums, natural wonders, and more.
- Virtual Reality Tours of the Louvre, France – Exploring the world-famous museum from the comfort of home.
- Online Guided Tours of the Great Wall of China – Experiencing one of the world’s most iconic landmarks digitally.
- Augmented Reality Experiences of Rome’s Ancient Sites – Using AR technology to see historical ruins in their original glory.
Voluntourism combines travel with volunteering for a cause, typically involving work towards environmental conservation, education, or community development.
While it allows travelers to contribute to positive change, it’s important to choose programs that genuinely benefit the local community and environment.
Examples of voluntourism :
- Teaching English in Rural Schools, Nepal – Assisting in educational institutions in underprivileged areas.
- Marine Conservation in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia – Participating in coral reef restoration and research projects.
- Community Building Projects – Helping construct basic infrastructure like schools and healthcare facilities.
War tourism involves visiting sites significant to wartime history, such as battlefields, war memorials, and museums.
It’s a form of tourism that seeks to understand the history of conflicts and honor the memories of those who fought in them.
Examples of war tourism :
- Vietnam War Sites, Vietnam – Exploring locations like the Cu Chi Tunnels and War Remnants Museum.
- Normandy Beaches, France – Visiting WWII D-Day landing sites and memorials.
- Somme Battlefields, France – Touring sites and cemeteries from one of the largest battles of the First World War.
Wellness tourism is centered around health and well-being, offering activities and experiences that promote physical, mental, and spiritual health. This type of tourism often includes spa retreats, yoga and meditation workshops, fitness programs, and holistic wellness therapies.
Examples of wellness tourism :
- Yoga Retreats in Rishikesh, India – Engaging in yoga and meditation in the birthplace of yoga.
- Thermal Spas in Iceland – Relaxing in natural hot springs surrounded by unique landscapes.
- Wellness Resorts in Bali, Indonesia – Participating in holistic wellness programs in a serene, tropical setting.
Wildlife tourism involves traveling to observe and interact with animals in their natural habitats. It’s a way for tourists to experience wildlife up close while promoting conservation and awareness of biodiversity.
Activities can include safaris, wildlife sanctuaries, and bird watching.
Examples of wildlife tourism :
- African Safaris, Kenya or Tanzania – Experiencing the diverse wildlife of the African savannah, including the “Big Five.”
- Gorilla Trekking in Rwanda and Uganda – Encountering mountain gorillas in their natural rainforest habitat.
- Penguin Colonies in Antarctica – Observing penguins and other Antarctic wildlife in one of the most remote areas of the world.
Zoological tourism focuses on visiting zoos, aquariums, and wildlife parks where visitors can see and learn about various animal species.
This form of tourism is educational, often highlighting conservation efforts and providing insights into animal behavior and habitats.
Examples of zoological tourism :
- San Diego Zoo, USA – Known for its vast variety of species and conservation efforts.
- Singapore Zoo, Singapore – Offering an immersive experience with its open-concept enclosures and diverse wildlife.
- Monterey Bay Aquarium, USA – Renowned for its marine life exhibits and ocean conservation education.
Have we missed any types of tourism that you think should be included on this list? Are there other examples you’d like to share? Send us a message and let us know what else should be included on this list.
6 Steps To Create an Ideal Customer Profile for Travel and Tourism

The Ultimate Guide to Brand Archetypes in Travel & Tourism
Travel Tips and Trivia
Last Updated: January 23, 2024
40 Different Types of Tourists [2021 Tourism Types Guide]
Want to learn all about the different types of tourists? Check out this post to read all about 40 unique tourism types and their individual characteristics!
Danny Newman

Trying to find out about the different types of tourists? I hope this post helps!
News just in:
Not all tourists are made equal!
Sure, we’re all going from place to place to enjoy the various attractions on offer in our chosen destinations.
But everything from our reasons for travelling to our style of travel can vary, right?
So it turns out tourism’s actually this big umbrella term, under which sit all sorts of different types of tourists .
In fact, it can actually get a bit confusing…
From what I can tell, there’s no actual consensus on how many tourism types exist!
Some articles list 3 main types of tourism, others 10, a few make up their own ones for a bit of fun, and I’ve even seen some that detail 60+ !
To satisfy my own curiosity and help anyone else who might be looking into this topic, I thought I’d do some digging and put together a post about the main categories of tourism that seem to crop up again and again.
Sound good? Keep reading for a detailed look at 40 different types of tourist and tourism!
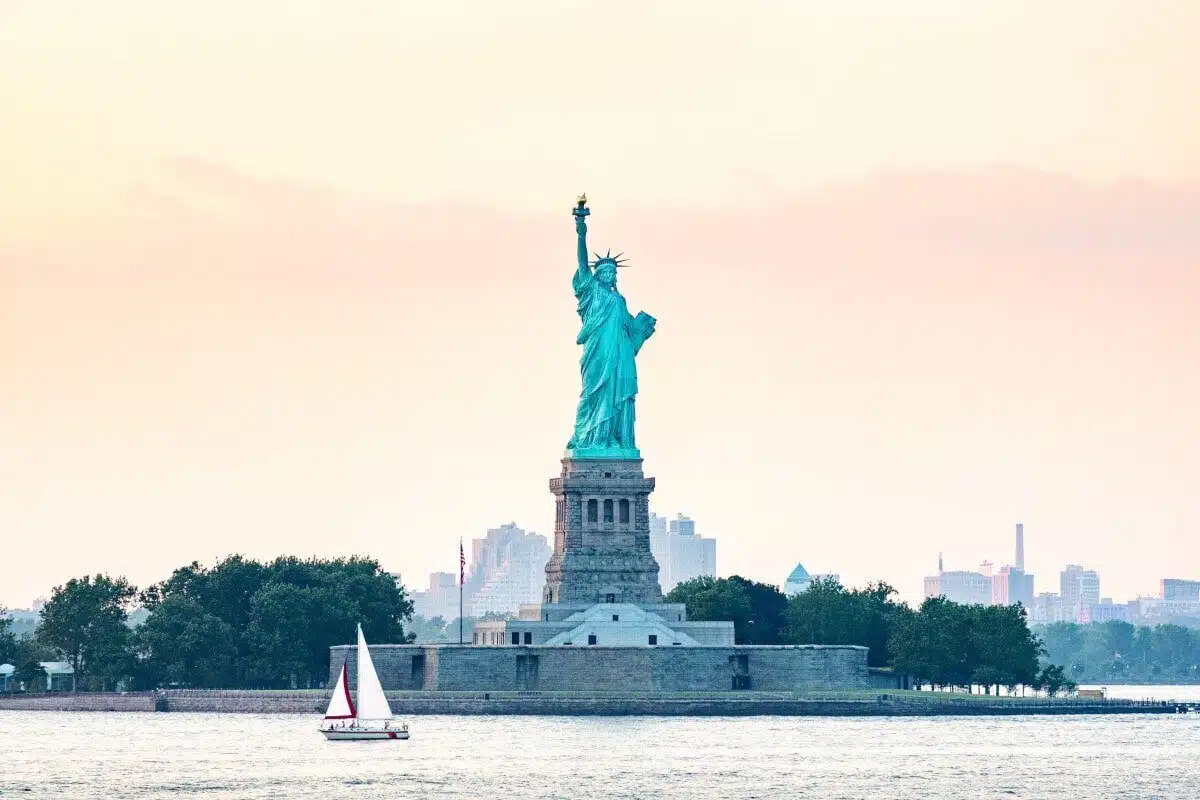

Here we go then: 40 different tourism types worth knowing about!
You might like these posts too!
- 10 Primary Disadvantages of Tourism
- A Complete Guide to Eco Travelling
- 10 Best Types of Vacations
- How to Say Thank You Around the World
- 30 Different Types of Travelling
- Comprehensive Guide to Responsible Tourism
- 20 Benefits of Solo Travel
- The Best Jobs for Adventurers
3 Main Types of Tourism
Some sources, like this one , divide the overarching category of “tourism” into three primary forms: domestic, inbound, and outbound tourism.
Let’s go through each one in turn!
First, though, here’s a fun fact: to be classed as any type of tourist, it’s generally accepted that you’re not leaving home to stay in a chosen country for more than a year . Extend your stay beyond 12 months and I’m not exactly sure what you become (a resident, maybe?). Yet, by all accounts, you’re no longer a tourist !
1. Domestic
Domestic tourism’s basically when you visit somewhere within your own country but outside the specific place you live.
Imagine a Brit who lives in London. They’d be classed as a domestic tourist if they left London to explore another part of the UK.
Inbound tourism’s the opposite.
This, according to the source above, is “the activities of a visitor from outside [their] country of residence”.
So, if that same Brit left the UK to travel around France, or Spain, or anywhere that isn’t England, Wales, Scotland, or Northern Ireland, they’d be classed by their chosen destination as an inbound tourist.
3. Outbound
And, finally, outbound tourism is when you leave your home country to explore somewhere else.
So, technically, you can be an inbound and outbound tourist at the same time!
For instance, the Brit who leaves the UK to go on holiday in France is an outbound tourist from the UK’s perspective and an inbound tourist from France’s.

Which type of tourism most appeals to you? And what type of tourist do you think you are?! Find out in the next section…
4 Types of Tourist?
In some pieces of tourist-related literature ( like this one ), those 3 official tourism types give way to 4 different types of tourists .
I find these ones far more interesting to think about!
They’re essentially different types of travellers . Learn the definitions and you can start working out which category you (and the people you meet on the road) fit into.
FYI, I’ve taken the following definitions from the source I’ve linked to above.
4. The Drifter
Drifters are tourists who pick novelty over familiarity every single time.
They revel in adventure, immerse themselves in the local community, and, whether they’re alone or in a group, tend to move without a plan or set itinerary.
5. The Explorer
Explorers favour novelty over familiarity too, just not to the same extent as drifters!
Preferring to travel solo , they also enjoy a semblance of comfort, structure, and certainty on the road. If they can see fascinating places with a reliable form of transport, then they’re happy bunnies.
6. The Individual Mass Tourist
The tables turn with individual mass tourists, who prefer familiarity over novelty.
However, they do choose to go it alone, opting for solo travel over group exploration whenever possible. They’ll follow a relatively structured itinerary and stick to certain times in particular parts of town.
7. The Organized Mass Tourist
Finally, there’s the organized mass tourist.
These guys are on the other end of the spectrum to drifters, picking familiarity over novelty every time. They’re the tourists who follow a tour guide whenever possible, try to create and stick to an itinerary, and leave nothing up to chance.

According to the literature, different types of travellers seem to fit into two distinct categories. More on these next…
2 Personality Tourist Types
To confuse things further, you see some sources (like this one ) discuss just two main tourist types!
This time, though, the definitions revolve around tourist personalities .
8. Allocentric (AKA “Venturers”)
Allocentric tourists are, according to the above source, “outgoing, self-confident, and adventurous”.
They tend to fly to their country of choice and will pick off-the-beaten-path destinations over more crowded/touristic ones.
From that description, allocentric travellers seem to resemble the drifters and explorers in the previous section. However, that’s very much my own interpretation! Experts in the field of tourism may disagree entirely.
9. Psychocentric (AKA “Dependables”)
As “self-inhibiting, nervous, and non-adventurous”, psychocentric tourists are basically the polar opposite of allocentric ones.
They “often refuse to travel by air for psychological reasons rather than financial of other practical concerns”, preferring familiar destinations to which they can travel by car and that have a solid tourist infrastructure.
Enjoying tour packages and well-organized itineraries, the psychocentric tourist sounds very much like the organized mass and individual mass tourists above.
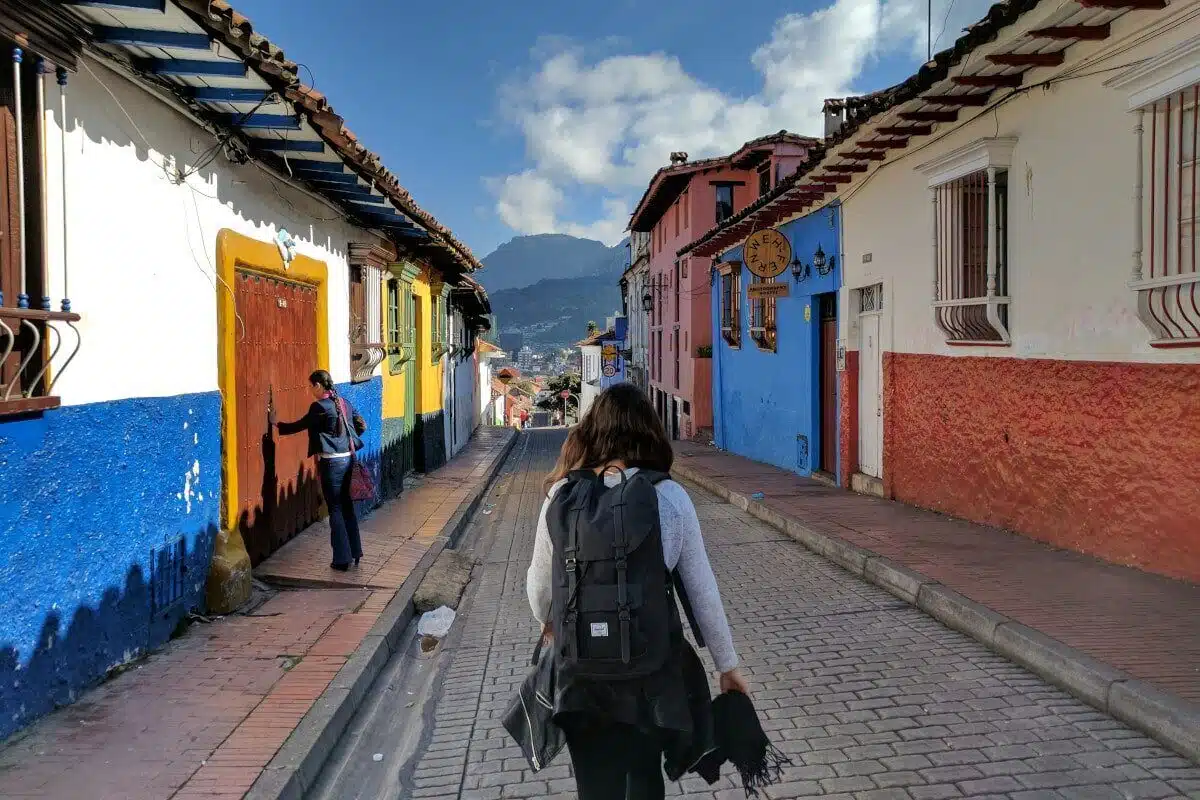

Time to move onto a long list of the main categories of tourism talked about in tourist circles!
General Subcategories of Tourism
With the technical and official forms of tourism down, let’s move onto the many different categories that tourism boards talk about online!
In alphabetical order, these ones usually revolve around peoples’ reasons for travelling versus their specific personality or style of exploration.
10. Art Tourism
Love going to new places to get involved in the art scene? Maybe you go to art festivals, explore art galleries, or attend specific artistic events.
Whatever the case, you’re officially an “art tourist”.
Even things like going to famous museums and wine tasting events supposedly fall under the bracket of art tourism.
11. Backpacking/Youth Tourism
Sometimes referred to as “youth tourism” because of its typical demographic, backpacking (or backpacker) tourism is basically when you slap your stuff into a backpack and hit the road!
From what I can tell, it’s usually associated with a younger generation and often associated with gap year travel.
12. Budget Tourism
Quick heads up: I’m not sure this is an official type of tourism or one that’s been invented by the international travelling community!
Nevertheless, as someone who travels on a budget all the time, I can vouch for its legitimacy! Budget travel/tourism is the act of exploring on a shoestring. With close ties to backpacking tourism, you try to see and do what you can without having access to huge sums of cash.

Business tourism may be one of the better-known forms of tourism on this list.
13. Business Tourism
Business tourism seems to be one of the largest, most accepted, and most talked about tourism types out there.
It’s essentially when you have to travel for work!
A business traveller might attend meetings, go to trade shows, pitch ideas to international companies, and so on.
14. Cultural Tourism
In contrast to business tourism, the definition of cultural tourism seems to be far more slippery and less agreed upon in the literature.
I guess that makes sense though. After all, defining “culture” itself isn’t easy.
Regardless, the basic principle behind cultural tourism is that you travel somewhere to experience its cultural traditions/activities (whether you’re just watching or actively partaking in them). This might involve going to a religious festival in India or Carnival in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, for example.
15. Dark Tourism
Anyone who’s watched the “Dark Tourist” TV show will have a solid grasp of dark tourism already!
For anyone who’s new to the whole shebang, though, this is the slightly shady act of exploring places associated with death and/or tragedy.
Two examples would be:
- Going to Cambodia to see the Killing Fields, or to
- Mexico for El Dia de los Muertos (the Day of the Dead).
…As an aside, attending Mexico’s Day of the Dead celebrations would probably constitute cultural tourism as well.

Dental tourism is one type of tourism that fewer people know about, but that’s becoming increasingly popular.
16. Dental Tourism
Dental tourists are people who travel to a foreign country to receive dental treatment.
Sounds crazy, right?
However, it starts making far more sense when you realize you can get really high-quality dental care at a fraction of the cost overseas!
17. Disaster Tourism
Disaster tourism reminds me a bit of dark tourism. This time, though, it involves visiting places that have suffered some sort of environmental disaster.
Whether the disaster’s man-made or natural, people decide to take a look at the aftermath and it isn’t long before businesses start cropping up to cater to them.
18. Ecotourism
Ecotourism’s talked about a lot these days- especially among avid travellers who can’t imagine life without adventure, yet wish to preserve and protect the incredible places they’re lucky enough to visit.
Alas, with jet fuel often required to get efficiently from one place to another, living by these ideals is easier said than done!
Ethical dilemmas aside, ecotourism’s when you visit natural areas responsibly.
In other words, you travel in a way that both conserves the environment and benefits (instead of hinders) the local population.

Want to teach overseas? You’ll be partaking in educational tourism!
19. Educational Tourism
Often shortened to “edu-tourism”, this type of tourism involves travelling to a foreign country for educational purposes .
The education itself may involve learning a language or learning information on the country’s history, culture, or social practices. Specific examples include going on a school trip or going to study abroad.
20. Ethnic Tourism
An ethnic tourist is someone who chooses to experience with their own two eyes the lifestyle, customs, and practices of another culture.
Sounds similar to cultural tourism, right?
However, according to this source , ethnic tourism involves a closer, more direct, and “intimate” glimpse into another culture, whereas cultural tourism involves a more indirect manner.
21. Event Tourism
As far as I can tell, event tourism involves hosting and marketing events of one form or another that function as specific tourist attractions.
In other words, you hold an event to:
- Encourage people to visit your country and
- Shed your country in a positive light.
An event tourist is someone who’s left their country of origin to visit that destination for that event (be it for business or pleasure) and stayed overnight . If they don’t stay, then they’re deemed an “event visitor”.
You can find more information here .

Family tourism’s another commonplace type of tourism worth knowing about.
Enjoying this post about the different types of tourism? You might also like these…
- 50 Fascinating Facts About Travel
- 85+ Road Trip Trivia Questions & Games
- 75 Essential Things to Pack for Travel
- Key Features of the Experience of Travel
- 100 Reasons I love to Travel (& You Will Too)
22. Family Tourism
Family tourism seems like a fairly vague and overarching term that involves all forms of tourist activity done as a family unit .
For example, you might travel somewhere with your family and go to a theme park, or try any other kid-friendly attractions in the area.
Family tourism would also include paying a visit to your friends and relatives overseas.
23. Festival Tourism
This type of tourist is nice and simple:
A festival tourist’s someone who travels somewhere specifically to attend a festival!
Whether it’s Glastonbury, Burning Man, Tomorrowland, or any of the other countless festivals happening around the world, attending them all constitutes festival tourism.
24. Food/Gastronomy Tourism
Travelling somewhere to sample its gastronomical delights and learning a thing or two about the culture as a result?
Well, you’re officially a food tourist!
Food tourism is the arena in which you’ll operate. You could be taking a cooking class, visiting local producers, sampling the street food, or taking a local wine tour.

Of all the tourism types on this list, heritage/historical tourism is one of my personal favourites.
25. Health/Medical Tourism
Medical tourism’s similar to dental tourism. This time, though, you’re travelling abroad to get treatment of the medical instead of the dental variety!
It can work in two ways.
- First, someone from a less-developed country may travel to a more developed one in order to access treatment that’s unavailable at home.
- Second, someone from a more developed country may travel to a less developed one to benefit from cheaper treatment.
26. Historical/Heritage Tourism
In a nutshell, historical tourism (otherwise known as heritage tourism) involves going overseas to enjoy its historical sites, sights, and attractions!
It’s the person who visits Rome to explore the Colosseum, Egypt to see the Sphinx, or Peru to visit Machu Picchu. Sure, you enjoy the other tourism attractions in these places as well, but your primary focus is on the history.
Read more about historical tourism here .
27. Hobby Tourism
As you’d expect, hobby tourism is when you travel alone or in a group to watch or partake in your particular hobby of choice.
Things like “football tourism” (e.g. going somewhere to watch your favourite football team play) and “music tourism” (e.g. going somewhere to see your favourite artist perform live) are two popular examples that fit within this overarching category.

International tourism is one of the main types that crop up again and again.
28. International Tourism
Another wide, general, and overarching category of travel, international tourism is the opposite of domestic tourism (discussed above):
You cross national borders to visit and explore your given destination.
29. Leisure Tourism
To borrow a definition from USA Today , leisure travel involves:
“Travel in which the primary motivation is to take a vacation from everyday life.”
So, the leisure tourist might be staying in resorts, dining out, lazing on beaches, going on guided tours, and doing whatever they can to take a much-needed break from the norm.
30. Local Tourism
Local tourism basically involves spending your time and money in foreign destinations as one of the locals would!
You’re shopping in local markets, paying a local taxi driver for a ride instead of a big international company like Uber, dining in local establishments and partying where the locals go.
The goal? To:
- Experience what life in this destination’s really like, and
- Spend your cash in a way that supports the local population.
Want to learn more about a similar topic? Here’s my guide to local travel .

Leisure tourists look for an escape from everyday life and see travel as the perfect solution.
31. National Tourism
Remember the definitions of domestic and outbound tourism I talked about before?
Well, according to the World Tourism Organization , national tourism is a category of tourism that encapsulates them both.
In their words:
“That is to say, the activities of resident visitors within and outside the country of reference, either as part of domestic or outbound tourism trips”.
32. Nature Tourism
Nature tourism’s another straight-forward form of tourism to wrap your head around:
You simply travel somewhere to revel in its natural, undeveloped areas and/or to enjoy the native wildlife on offer there!
33. Recreational Tourism
I’ve seen recreational (or recreation) tourism defined in two different ways.
The first (and most common) is that it involves travelling in order to participate in recreational activities- usually in nature- or to be a participant. Golf, fishing, hiking, and kayaking are a few examples.
The second, less common description (that nonetheless ranks at the top of Google results) is that it’s “the movement of people in their free time in the aims of rest required to restore the physical and mental strength of a person”.

Love nature and want to spend more time outdoors? Nature and recreational tourism are two different types of tourism worth looking into!
34. Religious Tourism
Are you a person of faith? Are you travelling alone or in a group to do something related to your religion?
Well, technically speaking, whether you’re going on pilgrimage, travelling as a missionary, or simply having fun, you’d be considered a religious tourist .
Heads up, you’ll also see religious tourism referred to as faith tourism .
35. Shopping Tourism
A relative newbie as far as the different types of tourists go, shopping tourism is exactly what you’d expect it to be:
Where the purpose of travelling to new places revolves largely around the desire to buy stuff . So, whether you’re going to London, Paris, or New York, your primary focus is on the goods you can acquire there.
36. Social Tourism
A more complicated and nuanced category of tourism, examples of social tourism include helping a charity build schools somewhere overseas, or teaching English to students there, and so on.
Simply put, the central focus of travel here isn’t just on personal pleasure. You’re trying to do something good for local communities in which you’re exploring.

Third-age tourism is another key tourism category in the travel industry! First, though, let’s talk about sports tourism…
37. Sport Tourism
Going somewhere new to participate in or watch a sporting event?
Well, you’re a sport tourist!
Imagine going overseas to see the next football/soccer world cup or to be in the stands at the next Olympics. This is sports tourism in its purest form. However, it could also involve going somewhere to train as a yoga instructor, or to learn martial arts.
38. Third-Age Tourism
Third-age tourism is also known as senior tourism or “silver tourism”.
This is the section of the tourist industry aimed at people who are going somewhat “grey around the edges”; who may have retired and now have expendable income and lots of free time on their hands.
So, if you love to travel and are getting a little longer in the tooth, then you’re probably classed as a senior tourist.
39. Urban Tourism
Another type of tourism for which you can probably guess the definition, urban tourism involves travelling to and around non-rural destinations.
This is the weekend trip to London, or the short break in Berlin.
You’re exploring the cities or towns, immersing yourself in the myriad metropolitan attractions on offer there.
40. Winter/Ski Tourism
Love cutting lines down powdered peaks? Well, you’re already familiar with winter/ski tourism!
From getting involved in winter sports (like skiing, snowboarding, or ice-skating) to watching them from the side-lines, a winter tourist travels to enjoy all-things cold and snow/ice-covered.
Remember (and try!) These Tourism Types
There you have it then: 40 different types of tourists.
As you can tell, although most of us have a basic definition of “tourism” in our head, the industry itself breaks down into dozens of individual tourism types !
If you’ve been trying to gain a greater understanding of these different categories of tourism, then I hope this post has helped!
Know of any other types of tourist for me to add to the list? Drop a comment below!
1 thought on “40 Different Types of Tourists [2021 Tourism Types Guide]”
Wonderful explanation. Would like to add another one that is combination of above mentioned types.
Comments are closed.

The 17 different types of travel
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Travel and tourism is a diverse industry and there are many different types of travel. The type of travel will determine the methods of business, the types of customer that it attracts and the the destination type that is facilitating tourism. In this article I will tell you all about the main types of travel and give you some examples of each.
The different types of travel
Short breaks, city breaks, countryside breaks, stag and hen parties, special events, mice tourism, short-term work contracts, types of specialist travel, vfr: migrants and expats, types of day trips, to conclude: types of travel, further reading.
Separating the different types of travel into clear segments or categories isn’t always an easy task.
Some types of travel may span more than one category- for example a person can go on a short break that is also corporate travel.
And others may be somewhat subjective- what is a short break? Is it two days? Is it four days? This is not clear-cut.
However, whilst accurately segregating types of travel into distinct categories may not be an easy task, it can be useful to have general classifications.
Categorising holidays into different types of travel helps us to better understand and assess the market segment in question. It also enables better tourism management and planning .
So what are the different types of travel? If video is your thing, watch the short video below, which covers all of the different types of travel, if not, read on…
Leisure travel
Leisure travel generally refers to travel that is undertaken for the purpose of pleasure, enjoyment, relaxation or special interests.
Leisure travel is an important component of tourism , and makes up a significant part of the tourism industry .
There are different ways that someone can undertake leisure travel. I have outlined these below.
Short breaks have become increasingly popular since the advent of the low cost airline .
Cheaper fares and regular flights have meant that people have been able to jet off for a weekend break that may not have previously been possible. In fact, [pre COVID] trends have shown that many people are now choosing to take 2-3 short breaks each year rather than a singular, more traditional summer holiday.
Short breaks are especially popular in areas that are well-connected. In Europe, for instance, it is easy to go on a short break from London to Paris. However, if you lived in Australia , the vast distances between destinations may mean that short breaks are less feasible.
City breaks are a popular type of travel.
Cities have lots to offer such as entertainment options (eating out, shows, events etc), as well as a range of tourist attractions and business tourism opportunities.
Cities are usually well connected by transport, making them easily reachable for tourists.
Rural tourism is very popular since the COVID pandemic. Countryside breaks enable people to enjoy the fresh air and to be socially distant from others.
There are many things to do on a countryside break, from hiking the Mendips , to adventure sports such as rock climbing in places like Cheddar Gorge .
It is a tradition for brides and grroms-to-be to celebrate their forthcoming marriage with a stag party or hen party. Whilst this might last for just a few hours, many people are now choosing to travel to a place outside of their home for a short break.
There are many destinations that are popular for stag or hen parties. These are usually destinations which have a substantial nightlife scene.
In Europe, many people go on a stag or hen party to Riga , Barcelona, Manchester, London, Lisbon, Benidorm, Krakow, Liverpool, Amsterdam… to name but a few.
There are different types of holidays that constitute leisure tourism.
Throughout the history of tourism , package holidays have been a popular type of travel. Packages are put together by tour operators and are then sold by different types of travel agent . This makes travel easier for the consumer.
Many people also choose to undertake independent travel. Whether tourists choose to create a dynamic package or travel on the fly, this is a popular method of leisure travel.
Cruise tourism has also grown considerably in recent years. Cruise ships come in all shapes and sizes and are popular with a wide variety of tourist types. Cruising is a form of enclave tourism .
Many people who travel for leisure are doing so to spectate or be involved in a major sporting event .
There are a large number of events that make up an important part of the sports tourism industry. Some examples include the annual Wimbledon Tennis tournament, the Formula 1 Grand Prix and the Football World Cup.
There are also other major events that people may choose to travel for. This could be, for example, the Chelsea Flower Show in London, the Day of the Dead festival in Mexico , Songkran in Thailand or the Glastonbury music festival.

Corporate travel
One of the most important (but often forgotten about!) types of travel is corporate travel.
Corporate travel, also referred to as business tourism , is any travel that is associated with or related to a person’s job or work.
Corporate travel may or may not involve staying away from home overnight.
Some types of corporate travel that you may encounter include:
MICE stands for- meetings, incentives, conferences, exhibitions. These are four important areas of the corporate travel market.
Many people will travel to attend meetings. Although, with the growth of the shut-in economy and software programmes such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams, travel for meetings has decreased significantly.
Incentive travel is travel which is given as a reward for good performance at work. It is designed to act as a motivator for staff; encouraging them to worker harder, ac hive better results and ultimately make more money for the business.
Conferences and exhibitions are an important tool for sharing ideas and networking. Similarly to meetings, many of these have now been moved online. However, it is unlikely that the conference market will disappear completely, as networking via a computer screen will never yield the same benefits as having a face-to-face conversation.
Training courses are, and will continue to be, essential to successful tourism operations management. Staff need to be trained for the position that they will/are working in and will need to be regularly unskilled.
Staff may also wish to undertake extra training for promotions or to keep up to date with industry developments.
Training courses can be in your place of work, but they can take place in alternative destinations; meaning that they facilitate a form of corporate travel.
Corporate travel can also consist of temporary work contracts. This is when a person is required to work in a location outside of their home environment for a specified period of time.
Whilst the time-frame is not clearly defined, if somebody relocates for work, they are then classified as an expatriate rather than a business tourist.
Work contracts such as these can be based within the employee’s home country or they can be based overseas.
Specialist travel
Specialist travel, often referred to as special interest tourism, is a form of niche tourism. It groups together an indefinite number of types of tourism that are specialist in nature.
Specialist tourism is often linked to a personal hobby, sport or interest. It may also be a type of travel that meets a specific need of a particular tourist or group of tourists.
I have outlined over 150 different types of specialist tourism in my types of tourism glossary – I told you, there are A LOT of different tourism types!
Some of the most common types of tourism include adventure tourism, health tourism, educational tourism, heritage and cultural tourism , gap year travel, conservation, sustainable tourism , responsible tourism and honeymoon tourism.
Visiting Friends and Relatives (VFR)
Visiting friends and relatives (VFR) is one of the biggest market segments in travel and tourism and is one of the most important types of travel.
People travel all around the world to visit their friends and relatives. This is an important form of domestic tourism as well as inbound tourism and outbound tourism .
Sometimes VFR will involve an overnight stay, and other times it will not. Travellers may choose to stay with their friends or relatives in their home or they may book accommodation of their own.
VFR is an especially prominent type of travel in areas with high migration or expatriation. For example, there are thousands of tourists who travel from the UK to India and Poland each year to visit family and friends, This is because there are a high number of Indian and Polish migrants in the UK.
Another important type of travel is day trips. Whilst according to some definitions of tourism, one may not technically be classified as a tourist unless they stay away from home overnight, they are nonetheless a valuable contribution to the tourism economy.
Most people who undertake a day trip will be visiting friends and relatives or in search of leisure or business.
Many people will choose to take a day trip to visit a tourist attraction, to go shopping, to attend an event, to visit the countryside or to take part in various activities.
A day trip can take part close to your home or it can form part of a holiday, i.e. you take a tour from your hotel whilst on holiday.
As you can see, there are many different types of travel, which can broadly be categorised as: leisure travel, corporate travel, specialist travel, visiting friends and relatives and day trips. All of these types of travel provide important contributions to the wider tourism industry and segmentation in this way allows us to assess and organise the industry according to the types of travel that are under scrutiny.
- The 3 Major Types Of Airlines + How They Work
- 50 types of transport from around the world
- 21 Types of Tourists Around The World
- 20 Popular Types of Hotels Around The World
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
Liked this article? Click to share!
Tourism – Definition, Types & Forms, History & Importance of Tourism
Tourism is one of the world’s fastest-growing industries and a major foreign exchange and employment generation for many countries. It is one of the most remarkable economic and social phenomena.
The word ‘tour’ is derived from the Latin word tornus, meaning ‘a tool for making a circle.’ Tourism may be defined as the movement of people from their usual place of residence to another place ( with the intention to return) for a minimum period of twenty-four hours to a maximum of six months for the sole purpose of leisure and pleasure.
According to WTO (1993), ” Tourism encompasses the activities of persons traveling and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business, and other purposes.”
The Rome conference on tourism in 1963 defined tourism as ‘ a visit to a country other than one’s own or where one usually resides and works. This definition, however, did not take into account domestic tourism, which has become a vital money-spinner and job generator for the hospitality industry.
The UNWTO defines tourists as ‘ people who travel to and stay in place outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes not related to the exercise of an activity remunerated from within the place visited.
According to the Tourism Society of Britain ,” tourism is the temporary short-period movement of people to destination outside the places where they usually live, work; and activities during their stay at these destinations.” This definition includes the movement of people for all purposes.
The development of technology and transportation infrastructure, such as jumbos jets, low-cost airlines, and more accessible airports, have made tourism affordable and convenient. There have been changes in lifestyle – for example, now retiree-age people sustain tourism around the year. The sale of tourism products on the internet, besides the aggressive marketing of the tour operators and travel agencies , has also contributed to the growth of tourism.
27 September is celebrated as world tourism every year. This date was chosen as on that day in 1970, the Statutes of UNWTO were adopted. The purpose of this day is to raise awareness of the role of tourism within the international community.
History of Travel and Tourism
Inbound tourism, outbound tourism, domestic tourism, forms of tourism, classification of tourism, nature of tourism, importance of tourism, economic impacts, social impacts, cultural impacts, environmental impact, industries related to tourism, tourism products.
Travel is as old as mankind on earth. At the beginning of his existence, man roamed about the planet’s surface in search of food, shelter, security, and better habitat. However, with time, such movements were transformed into wanderlust.
About five thousand years ago, climate changes, dwindling food and shelter conditions hostile invaders made the people leave their homes to seek refuge elsewhere like the Aryans left their homes in Central Asia due to climate changes. Perhaps, this leads to the development of commerce, trade, and industry.
Religion, education, and cultural movement began during the Hindu and Chinese civilizations. Christian missionaries, Buddhist monks, and others traveled far and wide carrying religious messages and returned with fantastic images and opinions about alien people.
For centuries movement of people continued to grow due to the efficiency of transport and the assistance and safety with which the people could travel. By the end of the 15th century, Italy had become Europe’s intellectual and cultural center. It represented the classical heritage both for the intelligentsia and the aristocracy.
During the 16th century, travel came to be considered an essential part of the education of every young Englishman. Travel thus became a means of self-development and education in its broadest sense. The educational travel was known as the ‘ Grand Tour .’
The industrial revolution brought about significant changes in the pattern and structure of British society. Thus, the economy of Britain was greatly responsible for the beginning of modern tourism. It also created a large and prosperous middle class. Because of remarkable improvement in transportation systems in the latter half of the 18th century and the first quarter of the 19th century, an increasing number of people began to travel for pleasure.
Travel was inspired initially by the need for survival (food, shelter, and security), the desire to expand trade, and the quest to conquer. As the transportation system improved, the curiosity for transforming the vast and virgin world into a close neighborhood created a new industry, i.e., Travel and Tourism .
However, the developments of rails, roads, steamships, automobiles, and airplanes helped to spread technology across the globe. Earlier travel was a privilege only for wealthy people, but with the industrial revolution, the scenario altogether changed. Transportation, as well as accommodation, became affordable to middle and working-class citizens.
Essentially, with the development of jet travel, communication, new technology, tourism, and travel became the world’s largest and fastest-growing industry.
Travel and tourism have recently emerged as a dominant economic force on the global scene, accounting for more than 12% of total world trade and growing at 8 percent annually.
Types of Tourism
Tourism has two types and many forms based on the purpose of visit and alternative forms of tourism. Tourism can be categorized as international and domestic tourism .
Tourism has two types and various forms. Based on the movement of people, tourism is categorized into two kinds. These are the following:
International Tourism
When people visit a foreign country, it is referred to as International Tourism . To travel to a foreign country, one needs a valid passport, visa, health documents, foreign exchange, etc.
International tourism is divided into two types; Inbound Tourism & Outbound Tourism.
This refers to tourists of outside origin entering a particular country. Traveling outside their host/native country to another country is called inbound tourism for the country where they are traveling. For example, when a tourist of Indian origin travels to Japan, it is Inbound tourism for Japan because foreign tourists come to Japan.
This refers to tourists traveling from the country of their origin to another country. When tourists travel to a foreign region, it is outbound tourism for their own country because they are going outside their country. For example, when a tourist from India travels to Japan, it is outbound tourism for India and Inbound tourism for Japan.
The tourism activity of the people within their own country is known as domestic tourism . Traveling within the same country is easier because it does not require formal travel documents and tedious formalities like compulsory health checks and foreign exchange. A traveler generally does not face many language problems or currency exchange issues in domestic tourism.
Tourism has various forms based on the purpose of the visit and alternative forms. These are further divided into many types according to their nature. Forms of tourism are the following:
Some most basic forms of tourism are the following:
- Adventure Tourism
- Atomic Tourism
- Bicycle Tours
- Beach Tourism
- Cultural Tourism
- Industrial Tourism
- Medical Tourism
- Religious Tourism
- Rural Tourism
- Sex Tourism
- Space Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Sustainable Tourism
- Virtual Tourism
- War Tourism
- Wildlife Tourism
Tourism can be classified into six distinct categories according to the purpose of travel. These are the following:
1) Recreational : Recreational or leisure tourism takes a person away from the humdrum of everyday life. In this case, people spend their leisure time in the hills, sea beaches, etc.
2) Cultural tourism satisfies cultural and intellectual curiosity and involves visits to ancient monuments, places of historical or religious importance, etc.
3) Sports/Adventure : Trips taken by people with a view to playing golf, skiing and hiking, fall within this category.
4) Health : Under this category, people travel for medical, treatment or visit places where there are curative possibilities, for example, hot springs, spa yoga, etc.
5) Convention Tourism : It is becoming an increasingly important component of travel. People travel within a country or overseas to attend conventions relating to their business, profession, or interest.
6) Incentive Tourism : Holiday trips are offered as incentives by major companies to dealers and salesmen who achieve high targets in sales. This is a new and expanding phenomenon in tourism, These are in lieu of cash incentives or gifts, Today incentive tourism is a 3 billion dollar business in the USA alone.
Tourism as a socio-economic phenomenon comprises the activities and experiences of tourists and visitors away from their home environment and are serviced by the travel and tourism industry and host destination. The sum total of this activity experience and services can be seen as a tourism product.
The tourism system can be described in terms of supply and demand. Tourism planning should strive for a balance between demands and supply. This requires an understanding not only of market characteristics and trends but also of the planning process to meet the market needs.
Often tourists from core generating markets are identified as the demand side; the supply side includes all facilities, programs, attractions, and land uses designed and managed for the visitors. These supply-side factors may be under the control of private enterprises, non-profit organizations, and the government. New and innovative forms of partnerships are also evolving to ensure the sustainable development and management of tourism-related resources.
The supply and demand side can be seen to be linked by flows of resources such as capital, labor, goods, and tourist expenditures into the destination, and flows of marketing, promotion, tourist artifacts, and experiences from the destination back into the tourist generating region.
In addition, some tourist expenditures may leak back into the visitors generating areas through repatriation of profits of foreign tourism investors and payment for improved goods and services provided to tourists at the destination. Transportation provides an important linkage both to and from the destination.
For planning purposes, the major components that comprise the supply side are:
- Various modes of transportation and other tourism-related infrastructure.
- Tourist information.
- Marketing and promotion.
- The community of communities within the visitor’s destination area.
- The political and institutional frameworks for enabling tourism.
The tourism system is both dynamic and complex due to many factors linked to it and because of the existence of many sectors contributing to its success. These factors and sectors are linked to the provision of the tourist experience and the generation of tourism revenue and markets .
The dynamic nature of the tourism system makes it imperative to scan the external and internal environment of the destinations on a regular basis so as to make changes when necessary to ensure a healthy and viable tourism industry.
Thus, it is now an accepted fact that tourism development can no longer work in isolation of the environment and the local communities, nor can it ignore the social and cultural consequences of tourism.
Tourism and hospitality , which are inextricably linked to each other, are among the major revenue-earning enterprises in the world. They happen to be among the top employers too. There has been an upmarket trend in tourism over the last few decades as travel has become quite common. People travel for business, vacation, pleasure, adventure, or even medical treatments.
Tourism constitutes an important industry today. It has opened up new vistas for the play of economic emancipation. It provides a very potent contribution by strengthening and developing the financial resources of a country. Moreover, it is a process in which mutual material and mental benefits occur. Furthermore,
- Tourism fetches foreign exchange in the form of invisible exports, which results in the manifold progress of the nation.
- Tourism generates jobs. These employments are the main contribution of tourism to generating national income. But one should remember that employment in the tourism industry is often seasonal.
- Tourism often leads to the commercialization of art forms and especially handicrafts. Art items with cultural or religious meaning are sought by tourists as souvenirs. As more and more tourists visit a destination, souvenir production has increased, often leading to mass production. This production also generates income.
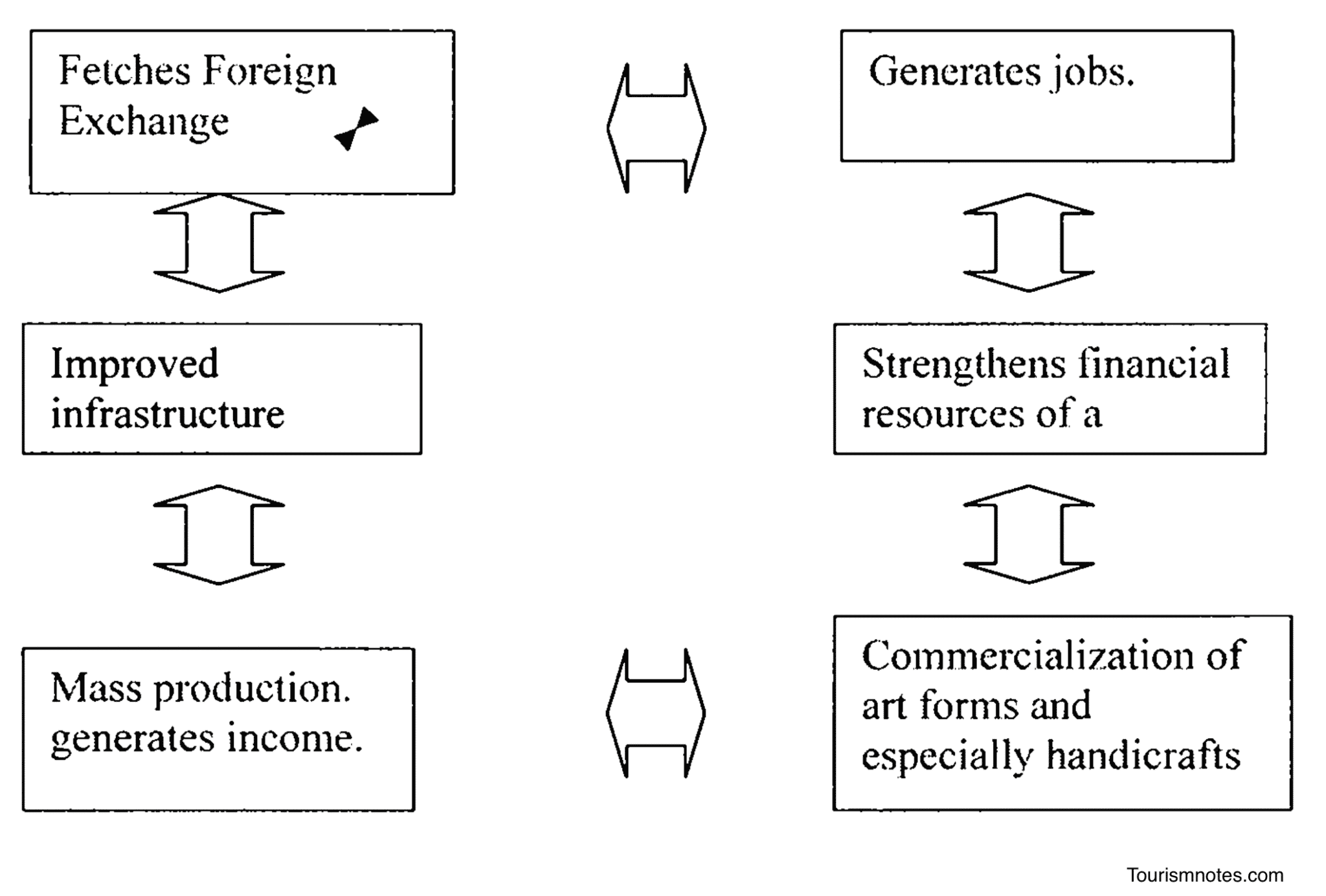
With several business-related activities associated with tourism, the industry has a tremendous potential to generate employment as well as earn foreign exchange. Many countries, such as Mauritius, Malaysia, Singapore, Fiji, and the Caribbean, whose economies are primarily driven by tourism. Tourism can contribute to the economic growth of a country in the followings ways:
Employment Generation
It creates a large number of jobs among direct services providers (such as hotels , restaurants, travel agencies , tour operators , guide and tour escorts, etc.) and among indirect services providers (such as suppliers to the hotels and restaurants, supplementary accommodation, etc.)
Infrastructure Development
Tourism spurs infrastructure development. In order to become an important commercial or pleasure destination, any location would require all the necessary infrastructure, like good connectivity via rail, road, and air transport , adequate accommodation, restaurants, a well-developed telecommunication network, and, medical facilities, among others.
Foreign Exchange
The people who travel to other countries spend a large amount of money on accommodation, transportation, sightseeing, shopping, etc. Thus, an inbound tourist is an important source of foreign exchange for any country.
The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) predict in 1997 that the twenty-first-century economy would be dominated by three industries: telecommunications, information technology, and tourism. The travel and tourism industry has grown by 500 percent in the last 25 years.
Now withstanding this bright outlook and prospects, the tourism and hospitality industries are very vulnerable to the fluctuations of national economies and happenings in the world, especially terrorist attacks that have at times dealt severe blows to business.
In recent years, there have been a few setbacks in tourism, such as the terrorist siege of the Taj and Oberoi in Mumbai, India (26 November 2008); the attack on the World Trade Centre in the United States of America (11 September 2001); bombing in a hotel on the Indonesian island of Bali (12 October 2002); tsunami in Southeast Asia and South Asia on 26 December 2004, in which thousands of the lives where lost and consequently tourism was hit. Nonetheless, the sector is now getting back to business.
Impacts of Tourism
Tourism is a multi-dimensional activity. The scope of tourism activities is so wide and varied that it cannot be restricted to any particular field of activity. Tourism has ramifications in almost all sectors and is influenced by the performance of each of these sectors directly or indirectly. Tourism in any country can be an apt reflection of the nation’s economic and social endowment apart from its natural wealth.
Tourism has vast potential to bring about changes in the country’s economic, environmental, societal, and cultural edifice. Tourism has two basics: the supply of facilities and the demand for participation. The twin market forces of supply and demand interact to produce tourism patterns. These patterns are associated with economic, social, cultural, environmental, and ecological impacts.
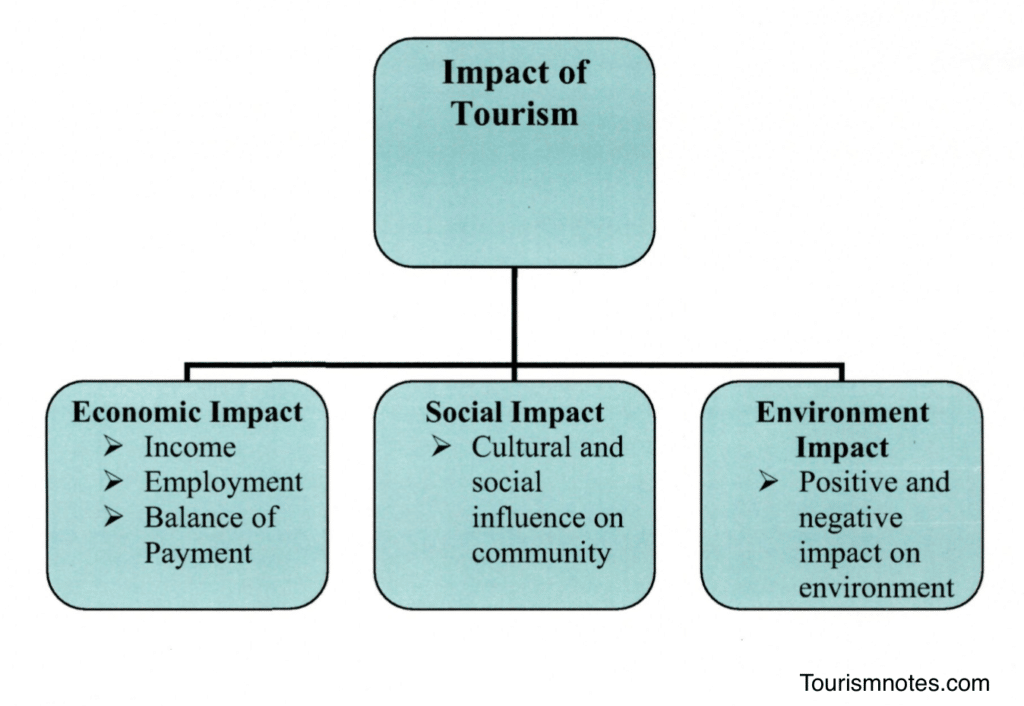
Establishing or developing a tourism industry involves expenditure, gains, costs, and benefits. If these impacts are considered from the outset of planning, strengths and opportunities can be maximized while weaknesses and threats can be minimized.
Each destination will be different in terms of tourism characteristics . The cost and benefits of tourism will vary in each destination and can change over time, depending on tourism and other activities in a destination’s local and regional context.
Tourism activities impact the economy of the country as well as the local economy of the destination.
Economics Benefits
- Tourism generates local employment, directly in the tourism sector and in the support and resource management sectors.
- Tourism stimulates profitable domestic industries, hotels and other lodging facilities, restaurants and food services, transportation systems, handicrafts, and guide services.
- Tourism generates foreign exchange for the country and injects capital and new money into the local economy.
- Tourism helps to diversify the local economy.
- Improved tourism infrastructure.
- Increase tax revenues from tourism.
Economic Costs
- Higher demand created by tourism activity may increase the price of land, housing, and a range of commodities necessary for daily life.
- Demands for health services provision and police service increase during the tourist seasons at the expense of the local tax base.
Tourism also affects the society of the destination in good as well as bad ways. It benefits and costs the local communities.
Social Benefits
- The quality of a community can be enhanced by economic diversification through tourism.
- Recreational and cultural facilities created for tourism can be used by local communities as well as domestic/international visitors.
- Public space may be developed and enhanced through tourism activity.
- Tourism Enhances the local community’s esteem and provides an opportunity for greater understanding and communication among people of diverse backgrounds.
Social Costs
- Rapid tourism growth can result in the inability of local amenities and institutions to meet service demands.
- Without proper planning and management, litter, vandalism, and crime often accompany tourism development.
- Tourism can bring overcrowding and traffic congestion.
- Visitors bring with them material wealth and apparent freedom. The youths of the host community are particularly susceptible to the economic expectations these tourists bring which can result in complete disruption of traditional community ways of life.
- The community structure may change, e.g. community bonds, demographics, and institutions.
- The authenticity of the social and cultural environment can be changed to meet tourism demands.
Tourism activities also affect the culture of the host country. There are many positive and negative cultural impacts of tourism.
Cultural Benefits
- Tourism can enhance local cultural awareness.
- Tourism can generate revenue to help pay for the preservation of archaeological sites, historic buildings, and districts.
- Despite criticism about the alteration of cultures to unacceptable levels, the sharing of cultural knowledge and experience can be beneficial for hosts and guests of tourism destinations and can result in the revival of local traditions and crafts.
Cultural Costs
- Youth in the community begin to emulate the speech and attire of tourists.
- Historic sites can be damaged through tourism development and pressures.
- There can be long-term damage to cultural traditions and the erosion of cultural values, resulting in cultural change beyond a level acceptable to the host destination.
Tourism impacts the environment in positive as well as negative ways. These impacts are following below.
Environmental Benefits
- Parks and nature preserves may be created and ecological preservation supported as a necessity for nature-based tourism.
- Improved waste management can be achieved.
- Increased awareness and concern for the environment can result from nature-based tourism activities and development.
Environmental Costs
- A negative change in the physical integrity of the area.
- Rapid development, over-development, and overcrowding can forever change the physical environment and ecosystems of an area.
- Degradation of parks and preserves.
Over the years, tourism has become a popular global activity. Depending upon the nature and purpose of their travel, tourists, need and demand certain facilities and services. This has given rise to a wide range of commercial activities that have acquired industry proportions. Thus travel and tourism nowadays represent a broad range of related industries.
Hotels are a commercial establishment that provides accommodation, meals, and other guest services. In the travel and tourism industry, the hotel industry plays a very significant role, as all tourists need a place to stay at their destinations, and require many more services and facilities to suit their specific needs and tastes.
Restaurants
Restaurants are retail establishments that serve prepared food and beverages to customers. In the travel and tourism industry, restaurants and other food and beverage outlets are very important as tourists like to experiment with the local cuisines of the places they are visiting.
Retail and Shopping
The retail industry is very important as tourists shop for their day-to-day necessities as well as look for mementos and souvenirs. In recent years, some cities in the world have been promoted as shopping destinations to attract people with a penchant for shopping by offering various products, such as garments, electronic goods, jewelry, and antiques. New York, Paris, London, and Milan in Italy are famous as fashion havens of the world.
Transportation
It is the movement of people and goods from one place to another. A well-developed transport industry, as well as infrastructure, is integral to the success of any travel and tourism enterprise.
Travel Agencies
A travel agency is a retailing business that sells travel-related products and services, particularly package tours, to customers on the behalf of suppliers such as airlines, car rentals, cruise liners, hotels, railways, and sightseeing.
Travel agencies play a very important role as they plan out the itinerary of their clients and make the necessary arrangements for their travel, stay, and sightseeing, besides facilitating their passport, visa, etc.
Tour Operators
A tour operator assembles the various elements of a tour. It typically combines tour and travel components to create a holiday. Tour operators play an important role in the travel and tourism industry.
Tourist Destinations
A tourist attraction is a place of interest for tourists, typically for its inherent or exhibited cultural value, historical significance, nature or building beauty or amusement opportunities. These are the basic fundamentals of the tourism industry.
Cultural Industries
Cultural or creative industries are responsible for the creation, production, and distribution of goods and services that are cultural in nature and usually protected by intellectual property rights. As tourists like to visit places of cultural significance and soak in the culture of the area, the cultural industry is very important to travel and tourism.
Leisure, Recreation, and Sport
Leisure or free time is a period of time spent out of work and essential domestic activity. Recreation or fun is spending time in a manner designed for therapeutic refreshment of the body or mind. While leisure is more like a form of entertainment or rest, recreation requires active participation in a refreshing and diverting manner.
As people in the world’s wealthier regions lead an increasingly sedentary lifestyle, the need for recreation has increased. These play a significant role in the travel and tourism sector.
A tourism/tourist product can be defined as the sum of the physical and psychological satisfaction it provides to tourists, during their ‘traveling and sojourn’ en route at the destinations.
Since the travel and tourism industry is an agglomeration of too many sectors that promote travel-related services. These sectors are referred to as travel vendors and their services and goods are called ‘travel products’. A tourism product includes five main components such as physical plant, services, hospitality, freedom of choice, and a sense of involvement.
Thus, whatever the natural and man-made resources and services brought about the consumption of tourists are called tourism products .
Charecterstatics Of Tourism Products
By now, you must have understood what a tourism product is. Now let us look at some of its characteristics:-
1) Intangible : Tourism is an intangible product means tourism is such a kind of product that can not be touched or seen and there is no transfer of ownership, But the facilities are available for a specified time and for a specified use. For e.g. a room in the hotel is available for a specified time.
2) Psychological : The main motive to purchase a tourism products is to satisfy the psychological need after using the product, by getting an experience while interacting with a new environment. And experiences also motivate others to purchase that product.
3) Highly Perishable : Tourism product is highly perishable in nature means one can not store the product for a long time. Production and consumption take place while a tourist is available. If the product remains unused, the chances are lost i.e. if tourists do not purchase it.
A travel agent or tour operator who sells a tourism product cannot store it. Production can only take place if the customer is actually present. And once consumption begins, it cannot be stopped, interrupted, or modified. If the product remains unused, the chances are lost i.e. if tourists do not visit a particular place, the opportunity at that time is lost. It is due to tourism reason that heavy discount is offered by hotels and transport-generating organizations during the offseason.
4) Composite Product : Tourist product is a combination of different products. It has not a single entity in itself. In the experience of a visit to a particular place, various service providers contribute like transportation The tourist product cannot be provided by a single enterprise, unlike a manufactured product.
The tourist product covers the complete experience of a visit to a particular place. And many providers contribute to the tourism experience. For instance, the airline supplies seats, a hotel provides rooms and restaurants, travel agents make bookings for stay and sightseeing, etc.
5) Unstable Demand : Tourism demand is influenced by seasonal, economic political, and other factors. There are certain times of the year that see greater demand than others. At these times there is a greater strain on services like hotel bookings, employment, the transport system, etc.
Guide To Different Types Of Tourism And Their Features
Home » Corporate Travel » Guide To Different Types Of Tourism And Their Features
Since the beginning of time, travel has been an indispensable part of human life. In the modern world, the various aspects of travel have been accommodated into an organized word ‘Tourism’. With the ease of booking travel, the industry has grown rapidly over the past few decades. Therefore, it becomes important to segregate the industry into various types for convenience of defining the purpose of each kind of travel. Let us explore some of the main types of tourism and how they differ from each other.
Different types of tourism
1. leisure tourism.
Evident from the names, leisure tourism entails the activities and locations that will help one unwind, relax and enjoy the various aspects of their trip. Typically, leisure tourism includes an escape into the natural landscape, exploring manmade architectures while staying at a comfortable and hospitable accommodation. The tourists on leisure travel will book a stay in the luxury resort or can take shelter in offbeat homestays. It is generally an amalgamation of numerous things to do such as trying local cuisine, going shopping in the regional market, and participating in recreational activities.
- Focuses on relaxation and enjoyment
- Involves sightseeing, shopping, and cultural experiences
- Often centered around beach vacations, city breaks, and entertainment
- Offers a break from routine and an opportunity to recharge
2. Business Tourism (MICE)

Business tourism or MICE tourism (Meetings, incentives, conferences and exhibitions) explores the realm of trips taken by the employees of various organizations. As working professionals, individuals are expected to attend meetings, conferences, seminars, exhibitions and other events to expand the reach of the business. Business tourism requires meticulous planning, budget forecasting, and comprehensive reporting by the admins and employees both.
- Serves professionals attending meetings, conferences, and exhibitions
- Provides networking opportunities and knowledge sharing
- Contributes to economic development and industry growth
- Requires specialized facilities and services to cater to business needs
3. Adventure Tourism
Among the most exciting types of tourism, adventure tourism brings in the opportunity to indulge in thrilling activities revolving around natural settings. The exhilaration and physical challenges involved in this kind of tourism makes it rank among the top tourism types. The activities include skydiving, paragliding, base jumping, rafting, dune bashing, and whatnot. The excitement only gets elevated when friends and family are involved during the activities.
- Emphasizes exciting and challenging experiences
- Includes activities like trekking, rock climbing, and bungee jumping
- Appeals to thrill-seekers and those seeking adrenaline rushes
- Provides opportunities for personal growth and pushing boundaries
4. Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism allows travelers to immerse themselves in the traditions, history, and lifestyle of a destination. The engagement required in cultural tourism is of the highest level. Tourists can visit various museums, historical sites, art galleries, traditional markets and much more. Additionally, the opportunity to meet the local community and participate in various events increases the fun all the more.
- Centers around exploration of a region’s history, traditions, and arts
- Involves visiting museums, historic sites, and attending cultural events
- Encourages interactions with locals to learn about their way of life
- Enhances cross-cultural understanding and appreciation
Suggested Read: Top 10 Business Travel Management Companies In India
5. Ecotourism

It is the type of tourism that deals with responsible travel to natural areas. Ecotourism promotes conservation of natural resources for the utilization of the future generations and consolidates sustainability. Travelers experience nature firsthand through activities like bird watching, nature walks, and wildlife safaris. The goal is to appreciate and protect the environment while supporting local authorities and communities.
- Focuses on responsible travel to natural areas
- Aims to support conservation efforts and sustainable practices
- Includes wildlife observation, nature walks, and eco-friendly accommodations
- Offers opportunities to connect with nature and learn about ecosystems
6. Culinary Tourism
Culinary tourism is a delightful and immersive way to experience the heart of any destination – its food. It focuses on inviting travelers to try top authentic food of any specific country or region. Travelers savor the flavors, aroma, and traditional cooking techniques of local cuisines. The journey involves visiting numerous restaurants, participating in food events, going to offbeat destinations for original tastes, meeting worldwide chefs and much more. Travelers may also be enticed to cook alongside a teacher and learn new ways of cooking.
- Revolves around exploring local cuisine and food culture
- Includes food tasting, cooking classes, and market visits
- Provides insights into regional flavors, ingredients, and cooking techniques
- Celebrates the role of food in cultural identity
7. Pilgrimage
Religious tourism or pilgrimage is a type of tourism involving spiritual upliftment of the travelers by visiting sacred sites, places of worship, and participating in religious events. It offers travelers a chance to know more about various religions while learning about the different practices of diverse cultures. Many travelers and worshippers believe it to be an opportunity to unite with God and find peace in their lives.
- Focuses on visiting sacred sites, pilgrimage destinations, and religious events
- Provides spiritual experiences and connections to faith traditions
- Involves participating in rituals, ceremonies, and cultural practices
- Encourages reflection and personal growth
8. Wellness Tourism
To calibrate well-being, individuals can head to wellness tourism. Rooting from the seeds of self-care, well tourism provides the various leaves and branches for a holistic development and rejuvenation. Common activities may include spa escapes, yoga practices, sampling nourishing and healthy food, massages, etc. Hiking and trekking can also be part of the wellness plan. Tourists can visit various wellness centers for the betterment of body and mind.
- Centers on promoting physical and mental well-being
- Involves spa treatments, yoga retreats, and meditation practices
- Offers relaxation, stress relief, and rejuvenation
- Emphasizes self-care and a healthy lifestyle
9. Rural Tourism
Rural tourism presents a serene escape to the idyllic countryside. It’s a journey that invites individuals to step away from the bustling urban landscape and embrace the simplicity and authenticity of rural living. Encompassing an array of enriching experiences, rural tourism offers the chance to participate in hands-on activities such as farming, tending to animals, and partaking in time-honored rural traditions.
- Offers a retreat to rural areas and countryside
- Involves farm stays, agricultural activities, and rural experiences
- Provides a chance to reconnect with nature and experience traditional lifestyles
- Supports local communities and sustainable agriculture
Tourism is a vast industry expanding with every day of the year. Though there are numerous types of tourism, embarking on the journey with a purpose remains constant. Hope the blog was able to provide you with the basics of various types of tourism and how the industry spreads out in several other branches.
Suggested Read: 7 First Time Business Travel Tips For A Flawless Trip
Types Of Tourism FAQs
What are the key features of leisure tourism.
Leisure tourism emphasizes relaxation and enjoyment, involves sightseeing, cultural experiences, and is often centered around beach vacations, city breaks, and entertainment. It offers a break from daily routines and a chance to recharge.
What are the distinctive features of business tourism (MICE)?
Business tourism provides networking opportunities, contributes to economic development, and requires meticulous planning, budgeting, and reporting.
What is ecotourism, and what is its primary focus?
Ecotourism is a type of tourism that promotes responsible travel to natural areas. Its primary focus is on conservation of natural resources, sustainability, and experiencing nature firsthand through activities like wildlife observation, nature walks, and eco-friendly accommodations.
Pratyush is a traveling enthusiast who always looks for innovations in business travel management. He has 5 years of experience writing content on corporate travel management and working closely with expert business travel facilitators.
Related Posts

Top Tips On Corporate Hotel Booking In Dubai
Dubai is a city of wonders and one of the biggest business centers in the Gulf. It has numerous corporate offices, tourist destinations, and shopping complexes. The continuous influx of professionals and tourists have offered Read more…

Corporate Travel
4 grand business hotels in pune, maharashtra.
Pune, a city renowned for its thriving business environment, is home to a selection of top-tier hotels that cater to the discerning needs of business travelers. These establishments seamlessly blend modern amenities, strategic locations, and Read more…

Top Car Rental Apps With Pros And Cons
Availing car rentals sounds like a task that involves long queues and tons of paperwork. However, the ground reality has changed drastically over the years. Modern day car rental services use intuitive applications for conducting Read more…
Let's get started!
Thanks for submitting your details.
We'll get back to you shortly.
Beyond Domestic & International: Guide To Every Tourism Type
There are more than 20 different types of tourism, each of which serves a unique purpose for the journey of each traveler.
There's a revival of traveling happening and with it, different types of tourism that go beyond the traditional 'domestic' and 'international.' Going into 2022, there will likely be even more travel trends that go beyond the nearly 20 types of tourism that exist today. From dark tourism to nature tourism, there's something for everyone with a trip tailored to each traveler's needs.
So, how can one be sure of which type of tourism is best-suited for them? By knowing the difference between the tourism types, of course! While some are branches of main tourism types, it's good to know which types of major tourism exist so that a traveler's next trip can be as rewarding and memorable as possible.
Going Beyond Domestic And International Borders
Gone are the days when tourism came down to two main types: domestic and international. At one point, a traveler was either remaining within their country and engaging in domestic tourism to learn more about their own backyard. If a traveler was visiting another country, the trip automatically fell into the category of international tourism, requiring a passport and, occasionally, a visa.
However, there are many breakdowns that fall within the two, as well. To clarify, a tourism type is different from a vacation type. For example, a type of vacation can include any of the following:
- A backpacking trip
- A resort vacation
- An all-inclusive vacation
- A pilgrimage
- A multi-day hike or trek
- A road trip
When it comes to the types of tourism that exist , these refer more to the theme of the trip. The type of tourism one partakes in is indicative of their interests or the goals they wish to achieve while traveling or once they arrive at their destination. Thus, it's entirely separate from the means by which (i.e. a cruise or road trip) or type of trip (i.e. backpacking or all-inclusive).
The types of tourism that exist to date are:
- Wildlife tourism
- Wellness Tourism
- Pilgrimage and spiritual tourism
- Cultural tourism
- Dark tourism
Culinary Tourism
- Celebrity tourism or Film Tourism
- Educational tourism
- Cruise tourism
- Rural tourism
- Space Tourism
- Outbound Tourism
- Business tourism
- Adventure tourism
- Medical tourism
- Atomic Tourism
- Beach Tourism
- Bicycle Tours
- Eco-Tourism
- Geo-Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Industrial Tourism
- Sustainable Tourism
The two additional types of tourism are international and domestic, as mentioned before.
Related: The Best Tips For Using Credit Cards, Withdrawing Cash, and Money Exchanges While Traveling
What Do These Tourism Types Mean?
Those interested in discovering different types of tourism should first know what each type is. For example, 'medical' tourism sounds a bit strange, and might not be what many think it is. Just like 'rural' tourism doesn't necessarily mean that a traveler will be destined to temporarily live in the woods with minimal amenities. While it would be easy enough to dive into every single type of tourism, one should at least know about the most popular options.
Eco-, Sustainable-, or Wildlife-Tourism
As the names imply, this type of tourism relates to nature and wildlife. Eco-tourism often relates to the exploration of ecosystems or natural landscapes, whether it be via a guided tour or self-exploratory hike, or trek. Wildlife tourism is very similar but maintains a focus on the animal species in the area. Sustainable tourism involves nature in a different way and maintains an emphasis on sustainable travel by the least disruptive means possible. This also means giving back to local communities and ensuring that travel to that destination is sustained for years to come, usually be partaking in activities that help the local economy.
Dark Tourism & Atomic Tourism
These two, while similar, are quite different. Dark tourism includes a broad spectrum of destinations that could be considered somewhat unsafe, untraveled, or generally off the beaten path due to its dark or tragic history. Atomic tourism is technically a subset of dark tourism and includes any site that relates to nuclear or atomic activity, including museums on the subject.
Wellness, Medical, Spiritual, And Pilgrimage Tourism
Those who travel to expand the mind or for mental health will likely be drawn to these trips. Whether it's a spiritual yoga retreat or a pilgrimage hike in a sacred place, there are plenty of tourism options that take one away from the hustle and bustle of a city. Medical tourism is somewhat of a subset of wellness tourism, which involves the traveler going to a new destination for some kind of treatment.
Rural And Cultural Tourism
Rural tourism may include traveling to remote places but that's not always the case. Sometimes, it could include something such as a farm stay or even a hostel in the countryside. Cultural tourism has an emphasis on the culture of a place, such as an interest in the local people or their way of life - this can also include historical tourism vacations.
One type of tourism that's getting plenty of attention is culinary tourism. This type of tourism, as is obviously implied by its name, relates to travel for the sake of flavor. This can include any type of food tour trip or simply a vacation planned around the culinary cuisine and history of a place.
Next: Paris Won't Break The Bank: These Sights Are Completely Free

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 7. Travel Services
7.1 Components of Travel Services
The travel services sector helps travellers arrange and reserve their vacation or business trips (StatsCan, 2018). This sector is made up of businesses and organizations that work in a coordinated effort to provide travellers with seamless arrangements to maximize their travel experience. Go2HR describes travel services experiences and employment opportunities as follows:
Within this sector, you have the flexibility of working in various capacities with event and conference planning organizations, travel companies and organizations, as well as associations, government agencies and companies that specialize in serving the needs of the tourism sector as a whole. (go2HR, Essential Tips – Travel Services, 2020)
Before we move on, let’s explore the term travel services a little more. As detailed in Chapter 1 , Canada, the United States, and Mexico have used the NAICS guidelines, which define the tourism industry as consisting of transportation, accommodation, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and travel services (Tourism HR Canada, 2020). These five sectors are defined and further detailed in B.C. by the B.C. government (BC Government, 2014) and go2HR on their website (go2HR, Career Explorer, 2020).
For many years, however, the tourism industry was classified into eight sectors: accommodations, adventure and recreation, attractions, events and conferences, food and beverage, tourism services, transportation, and travel trade (Yukon Department of Tourism and Culture, 2020; go2HR, 2020, What is Tourism? – Travel Services).
Tourism services support industry development and the delivery of guest experiences, and some of these are missing from the NAICS classification. To ensure you have a complete picture of the tourism industry in BC, this chapter will cover both the NAICS travel services activities and some additional tourism services.
First, we’ll review the components of travel services as identified under NAICS, as well as exploring popular careers within:
- Travel agencies (brick and mortar)
- Online Travel Agencies/OTA
- Tour operators
- Destination marketing organizations (DMOs)
Other Organizations
Following these definitions and descriptions, we’ll take a look at some other support functions that fall under tourism services. These include sector organizations, tourism and hospitality human resources organizations, training providers, educational institutions, government branches and ministries, economic development and city planning offices, and consultants.
Finally, we’ll look at issues and trends in travel services, both at home, and abroad.
While the application of travel services functions are structured somewhat differently around the world, there are a few core types of travel services in every destination. Essentially, travel services are those processes used by guests to book components of their trip. Let’s explore these services in more detail.
Travel Agencies

A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveller (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travellers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveller and hotels, car rentals, and tour companies (Goeldner & Ritchie, 2003). Travel agencies can be small and privately owned or part of a larger entity.
A travel agent is the direct point of contact for a traveller who is researching and intending to purchase packages and experiences through an agency. Travel agents can specialize in certain types of travel including specific destinations; outdoor adventures; and backpacking, rail, cruise, cycling, or culinary tours, to name a few. These specializations can help travellers when they require advice about their trips. Some travel agents operate at a fixed address and others offer services both online and at a bricks-and-mortar location. Travellers are then able to have face-to-face conversations with their agents and also reach them by phone or by email. To promote professionalism within the travel industry, travel counsellors can apply for a specialized diploma or certificate in travel from ACTA (ACTA, 2020a; go2HR, 2020a).
Today, travellers have the option of researching and booking everything they need online without the help of a travel agent. As technology and the internet are increasingly being used to market destinations, people can now choose to book tours with a particular agency or agent, or they can be identified as seeking Domestic Independent Travel (DIT) or Foreign Independent Travel (FIT) , by creating their own itineraries from a number of suppliers.
Online Travel Agents (OTAs)
Increasing numbers of travellers are turning to online travel agents (OTAs), companies that aggregate accommodations and transportation options and allow users to choose one or many components of their trip based on price or other incentives. Examples of OTAs include iTravel2000, Booking.com, Expedia.ca, Hotwire.com, and Kayak.com. OTAs continue to gain popularity with the travelers; in 2012, they reported online sales of almost $100 billion (Carey, Kang, & Zea, 2012) and almost triple that figure, upward of $278 billion, in 2013 ( The Economist , 2014).
In early 2015 Expedia purchased Travelocity for $280 million, merging two of the world’s largest travel websites. Expedia became the owner of Hotels.com, Hotwire, Egencia, and Travelocity brands, facing its major competition from Priceline (Alba, 2015).
Although OTAs can provide lower-cost travel options to travellers and the freedom to plan and reserve when they choose, they have posed challenges for the tourism industry and travel services infrastructure. As evidenced by the merger of Expedia and Travelocity, the majority of popular OTA sites are owned by just a few companies, causing some concern over lack of competition between brands. Additionally, many OTAs charge accommodation providers and operators a commission to be listed in their inventory system. Commission-based services, as applied by Kayak, Expedia, Hotwire, Hotels.com, and others, can have an impact on smaller operators who cannot afford to pay commissions for multiple online inventories (Carey, Kang & Zea, 2012). Being excluded from listings can decrease the marketing reach of the product to potential travellers, which is a challenge when many service providers in the tourism industry are small or medium-sized businesses with budgets to match.
While the industry and communities struggle to keep up with the changing dynamics of travel sales, travellers are adapting to this new world order. One of these adaptations is the ever-increasing use of mobile devices for travel booking. The Expedia Future of Travel Report found that 49% of travellers from the millennial generation (which includes those born between 1980 and 1999) use mobile devices to book travel (Expedia Inc., 2014), and these numbers are expected to continue to increase. Travel agencies are reacting by developing personalized features for digital travellers and mobile user platforms (ETC Digital, 2014). With the number of smartphone users expected to reach 1.75 billion in 2014 (CWT Travel Management Institute, 2014) these agencies must adapt as demand dictates.

A key feature of travel agencies’ (and to a growing extent transportation carriers) mobile services includes the ability to have up-to-date itinerary changes and information sent directly to consumers’ phones (Amadeus, 2014). By using mobile platforms that can develop customized, up-to-date travel itineraries for clients, agencies and operators are able to provide a personal touch, ideally increasing customer satisfaction rates.
Take a Closer Look: PATA — The Future of Travel is Personalisation at Scale
“The industry has changed monumentally over the past decade. The rise of meta-search websites and sharing economy services like Airbnb is giving travellers more control and choice than ever before. However, this is nothing compared to the changes that are on the horizon as technologies like mobile, AR, AI, and VR become mainstream.
One thing is certain; the pace of change is accelerating. Against this backdrop, the travel industry as a whole will need to fundamentally shift its focus to continuous innovation.” (PATA, 2019)
Despite the growth and demand for OTAs, brick and mortar travel agencies are still in demand by travellers (IBISWorld, 2019) as they have both an online presence and physical locations. The COVID-19 pandemic may see an increase in travellers relying on personal contact with brick and mortar travel agencies but at a distance through mail and phone.
Tour Operators

A tour operator packages all or most of the components of an offered trip and then sells them to the traveller. These packages can also be sold through retail outlets or travel agencies (CATO, 2020; Goeldner & Ritchie, 2003). Tour operators work closely with hotels, transportation providers, and attractions in order to purchase large volumes of each component and package these at a better rate than the traveller could if purchasing individually. Tour operators generally sell to the leisure market.
Inbound, Outbound, and Receptive Tour Operators
Tour operators may be inbound, outbound, or receptive:
- Inbound tour operators bring travellers into a country as a group or through individual tour packages (e.g., a package from China to visit Canada).
- Outbound tour operators work within a country to take travellers to other countries (e.g., a package from Canada to the United Kingdom).
- Receptive tour operators (RTOs) are not travel agents, and they do not operate the tours. They represent the various products of tourism suppliers to tour operators in other markets in a business-to-business (B2B) relationship. Receptive tour operators are key to selling packages to overseas markets (Destination BC, 2020) and creating awareness around possible product.
Destination Marketing Organizations
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs) include national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus around the world. DMOs promote “the long-term development and marketing of a destination, focusing on convention sales, tourism marketing and service” (Destinations BC, 2020).
Spotlight On: Destinations International
Destinations International is the global trade association for official DMOs. It is made up of over 600 official DMOs in 15 countries around the world. DMAI provides its members with information, resources, research, networking opportunities, professional development, and certification programs. For more information, visit the Destinations International website.
With the proliferation of other planning and booking channels, including OTA s, today’s DMOs are shifting away from travel services functions and placing a higher priority on destination management components.
Working Together
One way tour operators, DMOs, and travel agents work together is by participating in familiarization tours (FAMs for short). These are usually hosted by the local DMO and include visits to different tour operators within a region. FAM attendees can be media, travel agents, RTO representatives, and tour operator representatives. FAMs are frequently low to no cost for the guests as the purpose is to orient them to the tour product or experience so they can promote or sell it to potential guests.
The majority of examples in this chapter so far have pertained to leisure travellers. There are, however, specialty organizations that deal specifically with business trips.
Spotlight On: Global Business Travel Association (GBTA) Canada
“GBTA Canada is the voice of the Canadian business travel industry. We believe in providing the business travel and meetings community with a global platform to serve as a resource library for their peers, to implement world-class Conferences, workshops and virtual meetings, and to foster an interactive network of innovation and support.” The GBTA state that their economic impact contributes $23.5 billion CAD in Canadian business travel (Economic Impact Study) and “$435+ billion CAD of business travel and meetings expenditures represented globally.” Visit the GBTA website .
Business Travel Planning and Reservations
Unlike leisure trips, which are generally planned and booked by end consumers using their choice of tools, business travel often involves a travel management company, or its online tools. Travel managers negotiate with suppliers and ensure that all the trip components are cost effective and comply with the policies of the organization.
Many business travel planners rely on global distribution systems (GDS) to price and plan components. GDS combine information from a group of suppliers, such as airlines. In the past, this has created a chain of information from the supplier to GDS to the travel management company. Today, however, there is a push from airlines (through the International Air Transport Association’s Resolution 787) to dissolve the GDS model and forge direct relationships with buyers (BTN Group, 2014).
Destination Management Companies
According to the Association of Destination Management Executives International (ADMEI), a destination management company (DMC) specializes in designing and implementing corporate programs, and “is a strategic partner to provide creative local experiences in event management, tours/activities, transportation, entertainment, and program logistics” (ADMEI, 2020). The packages produced by DMCs are extraordinary experiences rather than general business trips. These are typically used as employee incentives, corporate retreats, product launches, and loyalty programs. DMCs are the one point of contact for the client corporation, arranging for airfare, airport transfers, ground transportation, meals, special activities, and special touches such as branded signage, gifts, and decor (ADMEI, 2020). The end user is simply given (or awarded) the package and then liaises with the DMC to ensure particular arrangements meet his or her needs and schedule.
As you can see, travel services range from online to personal, and from leisure to business applications. Now that you have a general sense of the components of travel services, let’s look at some examples in Canada and BC.
Under NAICS, businesses and functions that assist with planning and reserving components of the visitor experience.
Other services that work to support the development of tourism and the delivery of guest experiences.
A business that provides a physical location for travel planning requirements.
An individual who helps the potential traveller with trip planning and booking services, often specializing in specific types of travel.
A trade organization established in 1977 to ensure high standards of customer service, engage in advocacy for the trade, conduct research, and facilitate travel agent training.
A service that allows the traveller to research, plan, and purchase travel without the assistance of a person, using the internet on sites such as Expedia.ca or Hotels.com.
An operator who packages suppliers together (hotel + activity) or specializes in one type of activity or product.
An operator who packages products together to bring visitors from external markets to a destination.
An operator who packages and sells travel products to people within a destination who want to travel abroad.
Someone who represents the products of tourism suppliers to tour operators in other markets in a business-to-business (B2B) relationship.
Also known as a destination management organization; includes national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus.
Tours provided to overseas travel agents, travel agencies, RTOs, and others to provide information about a certain product at no or minimal cost to participants. The short form is pronounced like the start of the word "family" (not as each individual letter).
A company that creates and executes corporate travel and event packages designed for employee rewards or special retreats.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION
Home | About WTO | News & events | Trade topics | WTO membership | Documents & resources | External relations
Contact us | Site map | A-Z | Search
español français
- trade topics
- sector-by-sector
- tourism and travel-related services
SERVICES: SECTOR BY SECTOR
Tourism and travel-related services
Tourism plays an important role for nearly all WTO members, especially in terms of its contribution to employment, GDP, and the generation of foreign exchange. Tourism-related services are typically labour-intensive, with numerous links to other major segments of the economy, such as transport, cultural and creative services, or financial and insurance services.
Tourism and travel-related services include services provided by hotels and restaurants (including catering), travel agencies and tour operator services, tourist guide services and other related services.
A crucial aspect of trade in tourism services is the cross-border movement of consumers (mode 2). This permits a variety of workers, including those in remote areas, to become services exporters — for instance, by guiding tourists, performing in local events, or working in tourist accommodation. While digitalisation offers great potential for many aspects of tourism services, the sector continues to depend highly on the cross-border movement of both customers and employees, and remains strongly linked to transport services.

Current commitments and exemptions
Tourism commitments have been undertaken by over 133 WTO members, more than in any other service sector. This indicates the desire of most members to expand their tourism sectors and to increase inward foreign direct investment (FDI) as part of their efforts to promote economic growth.
The level of commitments by sub-sector varies widely for tourism and travel-related services. Commitments on services provided by hotels and restaurants are the most frequent, with a significantly smaller number of WTO members making commitments on travel agencies and tour operator services. Only about half of members with commitments on tourism have included tourist guide services, and only a few members have made commitments for the “other” tourism services category.
- Schedules of WTO Members with Specific Commitments on Tourism Services
Treatment of the sector in negotiations
Tourism services, like other services covered by the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS), were included in the services negotiations that began in 2000.
One of the earliest documents was a proposal for a GATS Annex on Tourism, originally sponsored by the Dominican Republic, El Salvador and Honduras ( S/C/W/127 and S/C/W/127/Corr.1 ). The proposal had two main aspects: more comprehensive treatment of the tourism sector (with respect to classification issues), and the prevention of anti-competitive practices. As part of the plurilateral process, a joint request was made by a group of developing countries, asking for improved tourism commitments for all modes of supply.
- Proposals and related negotiating documents on tourism services
Additional information
Search Documents Online These links open a new window: allow a moment for the results to appear.
- Secretariat background notes on tourism services (Document code S/C/W/* and keyword “tourism and Background Note”) > search > help
- Tourism services (Document code S/CSS/W/* or TN/S/W/* and Title Tourism) > search
You can perform more sophisticated searches from the Documents Online search facility by defining multiple search criteria such as document symbol (i.e. code number), full text search or document date.
Some useful links
- World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
- World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC)
- OECD Tourism Unit (Centre for Entrepreneurship, SMEs, Regions and Cities)
Problems viewing this page? If so, please contact [email protected] giving details of the operating system and web browser you are using.
See how Cvent can solve your biggest event challenges. Watch a 30-minute demo.

The Complete Guide to Virtual Tourism
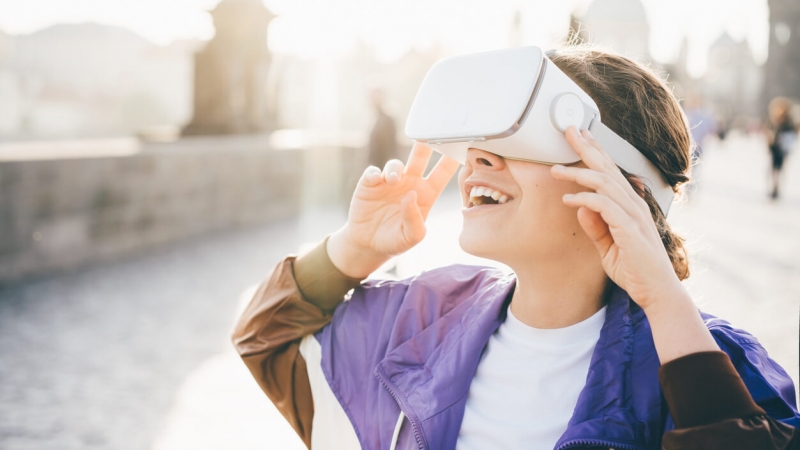

With the COVID-19 pandemic limiting where people have been able to go over the past couple of years, hotels, destinations, and travelers alike have felt the effects.
However, creative marketing and new virtual offerings can make a big difference in the years to come. Virtual tourism and travel are taking off, and hotels and destinations that know how to capitalize on the trend will set themselves up for success as the world returns to normal and more and more travelers once again pack their bags.
Take a look at our expert advice below to learn all about virtual tourism and the benefits it can offer. Plus, explore examples from some of the top virtual tourism campaigns across the world.
What is virtual tourism?
Virtual tourism presents viewers with an immersive experience of an activity, location, or destination through the use of technology. There are tons of different types of virtual tourism offerings, but there's usually a combination of virtual reality, still images, video, audio, narration, interactivity, and other multimedia formats to provide an experience of a destination that a user cannot get through images or websites alone.
Viewers can access virtual tourism content using a virtual reality headset for the most immersive experience, but they can also usually view the content on a normal computer or even a mobile device.

What are the benefits of virtual tourism?
Because viewers can experience activities, locations, and destinations from the comfort of their own homes, there are many clear benefits to virtual tourism. The most obvious of these benefits is that viewers can see and experience a destination without traveling to it, which means they aren’t limited by available flights, travel logistics, safety concerns, and whether destinations are open. They don’t even have to think about time zones or weather conditions.
The other huge benefit for viewers is cost. Virtual tourism makes destinations accessible to millions of people who may otherwise not be able to afford to travel to them. Viewers are embracing the rise in virtual tourism destinations and the increasing quality and availability of virtual reality technology to see and experience things they never thought possible.
For hotels and destinations, the clear benefit is the ability to stay top-of-mind with potential customers and to highlight a location, amenities , and offerings. Viewers who have experienced a hotel or location through virtual tourism are more likely to book a future stay, and will eagerly anticipate experiencing the activity in the “real world.”
There are also great marketing opportunities offered by virtual tourism technology. Potential guests can see a 360-degree view of a property and its amenities, rather than the flat images on a brochure or website. Experiencing a property this way increases the chances that viewers will want to visit in the future, and means that they can easily share the virtual offerings with their friends and family.
And that’s not all. Virtual tourism has a handful of other benefits:
- The immersive experience allows the viewer to imagine themselves at a travel destination.
- The viewer can control what they see of a destination, experiencing 360 degrees of a location.
- All aspects of a destination can be showcased in high resolution.
- Hotels, Convention and Visitors Bureaus (CVBs) , and travel agencies can stand out from the crowd.
- The impact of tourism on vulnerable destinations is reduced.
How is virtual tourism used?
There are lots of great ways for hotels and destinations to take advantage of this technology and the demand for virtual tourism, and it goes well beyond COVID-19.
CVBs have been using virtual tourism for years to highlight the unique aspects of a location, including everything from history and culture to exciting activities, local attractions, and fun trivia.
Hotels, CVBs, and local governments use 360-degree VR video to capture everything about a destination in an immersive way. This lets viewers experience a remote mountaintop, an idyllic beach, a network of hiking trails, or a buzzing city with the press of a button.
VR photography, on the other hand, captures still images and pieces them together using specialized software, creating an immersive image where a user can look in any direction. This technology is great for showing hotel interiors, artwork, museum exhibits, and anything that can be fully experienced without motion or sound.
Finally, fully immersive VR experiences let users get in on the action, interacting with the environment and discovering more through their actions. This is often a curated experience focusing on one aspect of the location, like the food scene, music, history, or art. Virtual reality yoga classes, nature walks, stargazing, and bird watching have all become popular ways for a location to show off everything it has to offer.

What are some examples of virtual tourism?
Below are a handful of our favorite virtual tourism campaigns from across the world. While each campaign offers something different, the common theme is that each one was created to give users easy, safe, and interactive access to a location.
The Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands created a virtual tourism campaign once COVID-19 began to give people an alternative option to traveling to the location.
"Early on in this global crisis, we sat and wondered how we could recreate a Faroe Islands’ experience for those who had to cancel or postpone their trip to the Faroe Islands – and for everyone else stuck in insolation around the world," reads the virtual tourism segment on Faroe Islands' website . "We had an idea. What if we could allow people anywhere in the world to explore the islands as virtual tourists through the eyes of a local? Or even better; what if the virtual tourists could control the movements of the local in real time?"
Bristol From Home
Similar to the Faroe Islands, Visit Bristol (England) created an immersive experience due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Bristol From Home features a collection of travelers' favorite ideas, inspirations, and resources "so that you can continue to enjoy Bristol, during social distancing measures, from the comfort of your own home."
The website features a myriad of virtual options, including tours of a luxury Victorian ship, hot-air balloon rides, gin tastings, and much more, all in one place.
Tour the awe-inspiring architecture of Dubai with Dubai 360 — an immersive virtual tourism experience that allows users to travel the city through a bird's-eye view and learn all about the locations scattered throughout.
"Our services help increase online presence, which is crucial to marketing anything in the present," reads Dubai360's website. "We aim to raise you above your competition by presenting a professional and high quality look, and improving your customers' first impressions. This service is equally useful for Hotels, Restaurants, Malls, Real Estate, or anything that can be presented visually."
Great Barrier Reef
Yes, even the Great Barrier Reef has virtual tourism offerings. The interactive journey is headlined by legendary broadcaster and historian, David Attenborough, who takes viewers throughout the world's largest coral reef system. This is much more than simply a replacement for Great Barrier Reef tours — it's an experience in and of itself, and it showcases just how versatile virtual tourism can be.
What does virtual tourism mean for the hospitality industry?
Virtual tourism is one of the many keys to the travel industry’s resilience and ability to bounce back from an unprecedented time. Showcasing everything that a property or destination has to offer is a great way to build excitement for “normal” travel and keep the destination top of mind once travelers are able to vacation again.
Virtual tourism has been lauded as a way for hotels and destinations to highlight the intangibles of their location, capturing the special feel of the place and drawing interest from travelers who might not otherwise consider it.
"A true gift of virtual travel is that we can safely and efficiently access experiences we've always wanted to access," Dennis Watkins, owner of The Magic Parlour in Chicago, said in an article for marthastewart.com. "People separated by oceans can look each other in the eyes and share stories, cultures, and ideas. When I do a show for a single family who logs in from London, Leeds, Norway, or Chicago, I start to see the power of the virtual space ... and I think we're just now starting to understand and leverage that power."
How can hotels capitalize on the virtual tourism trend?
To strategize how best to use virtual tourism, hotels should go back to the basics of their hotel marketing plan . What audience are you trying to reach? What amenities, offerings, or features make your hotel and its location unique and interesting? What aspects of your property or destination do you want to highlight? The answers to these questions will form the foundation of your virtual tourism offerings.
If you have a few experiences that guests return for time and time again, these are a great place to start with your virtual tourism experience. Give viewers a tour of your on-site vineyard, sandy beach, art deco decor, or spectacular views.
Because you can create many different virtual reality experiences, you can craft custom offerings for all of the different types of guests who stay at your property. A street art tour may be a perfect fit for young adult travelers, while an immersive symphony orchestra performance may be perfect for older guests. Try creating three or four experiences targeting guests who you would like to see at your hotel in the future, and follow through on the virtual experiences with custom packages, content marketing , and targeted informational emails.
As you craft your unique virtual tourism offerings, keep in mind that this medium isn’t limited to the traditional perspective with which your guests normally see your destination. With virtual tourism, guests could fly over your property in a hot air balloon, swim in your lake without getting wet, ski down to sit by a roaring fire in your lobby, or zip-line through the trees. By adding experiences that guests may not be able to get in person, you’ll move beyond the idea of replacing "real" travel.
Additionally, hotels can use the virtual tourism boom to appeal to planners and their event attendees as well. Not all offerings have to be limited to guests. Do you have a breathtaking ballroom with a state-of-the-art A/V system? What about extensive meeting space in your beachside bungalows? Utilize innovative 3D technology to create a virtual experience highlighting what sets you apart and creating demand.
In other words, the sky really is the limit when it comes to virtual tourism offerings. If you can think of an experience in the real world, you can likely recreate it in some fashion through virtual reality.
Now you know all about virtual tourism!
Bookmark our blog to stay up to date on all the trends and happenings from throughout the hospitality industry, as well as high-level overviews, industry-leading tips and advice, and much more.
Learn more about virtual tourism, travel, and events

Laura Fredericks
Laura brings a decade of insight to improving marketing, as she has worked in technology since 2010. She has experience starting and scaling a business, driving customer marketing, and speaking at live events, including WeDC Fest 2018. She founded Describli and Paradigm Labs, and currently works with companies to improve their customer relationship management and content strategy.
LinkedIn | Website
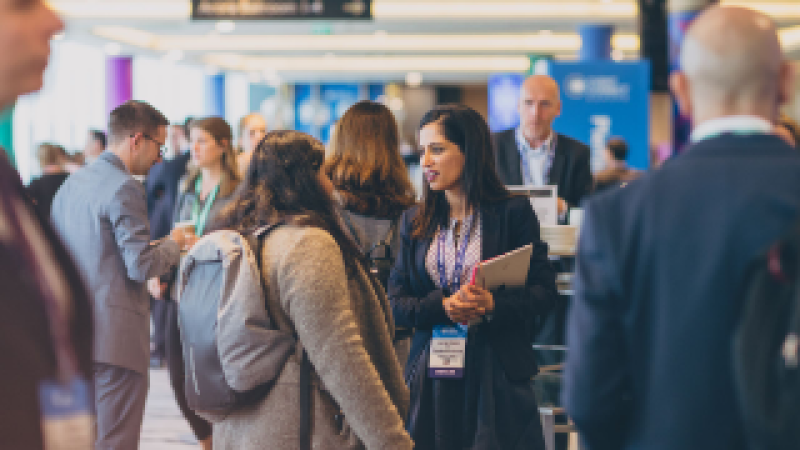

More Reading
The discovery of a lifetime – atlantis bahamas, kempinski hotel cancun: the premier fusion of business innovation and leisure, how to market to corporate event planners.
Subscribe to our newsletter
- Business Travel
- Home Inspiration
- Sustainable Living
- Wellbeing & Wellness
- Area Guides
- Whitepapers

Business Travel Guide
12 different types of tourism you need to know.

Tourism is a vast and diverse industry that has been growing steadily over the years. It is a significant contributor to the global economy, and its impact is felt across various sectors. Tourism can be defined as the act of travelling for pleasure or business purposes. It involves visiting places of interest, exploring new cultures, and experiencing different types of tourism, and each has its unique characteristics and attractions.
Cultural tourism is one of the most common types of tourism, and it involves visiting places of historical and cultural significance. Eco-tourism is a type of tourism that focuses on the conservation of natural resources and the promotion of sustainable tourism. Health tourism is another type of tourism that involves travelling to destinations for medical treatment or wellness purposes.
Key Takeaways
- Tourism is a diverse industry that involves travelling for pleasure or business purposes.
- There are various types of tourism, including cultural tourism, adventure tourism, eco-tourism, and health tourism.
- Each type of tourism has its unique characteristics and attractions, and they contribute to the growth of the global tourism industry.
1. Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism is one of different types of tourism that involves travelling to experience the culture and heritage of a destination. It is a way to explore the customs, traditions, history, and art of a place. Cultural tourism is a popular form of tourism that attracts millions of visitors each year.
- Historical visits
Historical visits are a popular form of cultural tourism. Many people travel to historical sites to learn about the past and experience the culture of a destination. Historical sites can include ancient ruins, castles, and museums. These sites offer a glimpse into the history and culture of a place and can be a great way to learn about the past.
- Culinary exploration
Culinary exploration is another popular form of cultural tourism. Many people travel to experience the food and drink of a destination. This can include trying local cuisine, visiting food markets, and taking cooking classes. Culinary tourism is a great way to experience the culture of a place through its food and drink.
- Art and literature tours
Art and literature tours are a great way to experience the culture of a destination. Many people travel to explore the art and literature of a place. This can include visiting museums, galleries, and historic sites related to art and literature. Art and literature tours can provide a deeper understanding of the culture and heritage of a place.
Business Tourism
Business tourism, also known as corporate travel , refers to travel that is done for work-related purposes. It is a subset of regular tourism and involves individuals who are still working and being paid while away from both their workplace and home. Business tourism can take many forms, including attending conferences, meetings, trade shows, and exhibitions.
According to Yahoo , corporate travel is expected to reach a global market value of $1.5 trillion by 2028, which is nearly three times itis 2020 levels. This is not surprising, given the extraordinary ROI of business travel. For every $1 a company spends on travel arrangements, they get back $12.5 in revenue.
Business tourism can be divided into four main categories, which are:
- Meetings: A meeting is an event where people come together to discuss a specific topic or issue. Meetings can be held for various purposes, such as to share information, make decisions, or solve problems. They can be held in a variety of venues, such as hotels, conference centres, or offices.
- Incentives: An incentive in corporate travel is a reward given to employees or customers for achieving a specific goal or target. Incentive travel is a form of business tourism that involves rewarding employees or customers with a trip or holiday.
- Conventions: A convention is a large meeting or conference that is usually held over several days. Conventions are often held by professional associations or trade organisations and can attract thousands of attendees.
- Exhibitions: An exhibition is an event where companies or organisations showcase their products or services. Exhibitions can be industry-specific or open to the general public.
Business tourism is an important part of international tourism, and it is expected to continue to grow in the future. It provides opportunities for individuals and companies to network, learn, and do business with others from around the world.
Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism is a type of tourism that involves travelling to remote and exotic locations outside of one’s comfort zone. It is characterised by activities that are physically and mentally challenging, and often involve an element of risk. There are many different types of adventure tourism, each with its own unique experiences and challenges.
- Mountain climbing
Mountain climbing is a popular form of adventure tourism that involves climbing to the summit of a mountain. This activity requires a high level of fitness, as well as technical skills and equipment. Some of the most popular mountain climbing destinations include Mount Everest in Nepal, Kilimanjaro in Tanzania, and the Matterhorn in Switzerland.
- Scuba diving
Scuba diving is another popular form of adventure tourism that involves exploring the underwater world. This activity requires specialised equipment and training and can be done in a variety of locations, including coral reefs, shipwrecks, and underwater caves. Some of the most popular scuba diving destinations include the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, the Red Sea in Egypt, and the Galapagos Islands in Ecuador.
- Safari expeditions
Safari expeditions are a type of adventure tourism that involves exploring wildlife reserves and national parks in search of exotic animals. This activity can be done on foot, by vehicle, or even by hot air balloon. Some of the most popular safari destinations include the Serengeti in Tanzania, Kruger National Park in South Africa, and the Masai Mara in Kenya.
Adventure tourism is a great way to explore the world and push oneself to new limits. However, it is important to remember that these activities can be dangerous and should only be undertaken with proper training and equipment.
Eco-Tourism
Eco-tourism is a type of tourism that focuses on responsible travel to natural areas while conserving the environment and improving the well-being of local people. It involves activities that are designed to minimize the negative impact on the environment and promote conservation efforts.
- Wildlife sanctuaries
Wildlife sanctuaries are an important part of eco-tourism. They provide a safe haven for endangered species and help to preserve their natural habitat. Visitors can observe wildlife in their natural environment while learning about conservation efforts. Wildlife sanctuaries also offer opportunities for research and education.
- Conservation projects
Conservation projects are another important aspect of eco-tourism. These projects are designed to protect the environment and promote sustainable development. Visitors can participate in activities such as tree planting, beach clean-ups, and wildlife monitoring. These projects not only help to protect the environment but also provide economic benefits to local communities.
- Eco villages
Eco-villages are communities that are designed to be environmentally sustainable. They use renewable energy sources, organic farming, and other eco-friendly practices. Visitors can learn about these practices while experiencing the local culture and way of life. Eco-villages also provide opportunities for visitors to participate in community projects and learn about sustainable living.
Overall, eco-tourism is a great way to promote conservation efforts while providing economic benefits to local communities. By choosing eco-tourism, visitors can have a positive impact on the environment and support sustainable development.
Health Tourism
Health tourism is a growing industry that involves travelling to another country to receive medical treatment or improve one’s health and well-being. This type of tourism is divided into two main categories: spa and wellness retreats and medical treatments abroad.
- Spa and wellness retreats
Spa and wellness retreats are a popular form of health tourism that involves staying at a resort or hotel that offers a range of wellness services, such as massages, yoga classes, and healthy meals. These retreats are designed to help individuals relax, rejuvenate, and improve their overall health and well-being.
Some of the most popular spa and wellness retreat destinations include Bali, Thailand, and India. These countries offer a range of wellness services at affordable prices, making them attractive destinations for those looking to improve their health and well-being.
- Medical treatments abroad
Medical treatments abroad are another form of health tourism that involves travelling to another country to receive medical treatment. This type of tourism is particularly popular among those who live in countries with limited medical resources or high healthcare costs.
Some of the most common medical treatments received abroad include dental work, cosmetic surgery, and fertility treatments. Countries such as Thailand, India, and Mexico are popular destinations for medical tourism due to their lower medical costs and high-quality medical facilities.
It is important to note that medical treatments abroad carry certain risks, such as language barriers, differences in medical practices, and lack of follow-up care. Therefore, it is important to thoroughly research the medical facility and treatment before making any travel arrangements.
Sports Tourism
Sports tourism is a type of tourism that involves travel to participate in or observe sporting events. It is a fast-growing sector of the global travel industry, with a wide range of activities and events available to tourists.
- international sporting events
One of the most popular forms of sports tourism is attending international sporting events. These events can include the Olympics, the World Cup, and other major tournaments. Tourists can travel to different countries to watch their favourite teams and athletes compete against each other. These events can also be a great way to experience the local culture and cuisine of the host country.
- Golf vacations
Golf vacations are another popular form of sports tourism. Golfers can travel to different destinations around the world to play on some of the best golf courses. These vacations can include all-inclusive packages that provide accommodation, meals, and access to the golf course. Some of the most popular golf destinations include Scotland, Ireland, and the United States.
- Skiing holidays
Skiing holidays are a popular winter sports tourism activity. Tourists can travel to different ski resorts around the world to ski or snowboard on the slopes. These resorts offer a range of activities, including skiing, snowboarding, and other winter sports. They also provide accommodation, meals, and other amenities to make the holiday more enjoyable.
Religious Tourism
Religious tourism is a type of tourism that involves travelling for religious purposes or to see things of religious importance. It is also known as faith tourism and incorporates a wide range of activities, including pilgrimages and spiritual retreats.
- Pilgrimages
Pilgrimages are a type of religious tourism that involves travelling to a holy site or shrine. They are often undertaken for spiritual or religious reasons and can be a powerful way for individuals to connect with their faith. Pilgrimages can be short or long and may involve walking, cycling, or travelling by other means of transportation. They can also be group or solo experiences.
- Spiritual retreats
Spiritual retreats are another type of religious tourism that involves spending time in a quiet, peaceful environment to reflect on one’s spiritual beliefs. These retreats can be led by a spiritual leader or taken individually. They can be a way for individuals to deepen their connection with their faith and find inner peace.
Religious tourism is a significant aspect of the tourism industry in many countries around the world. It can have a positive impact on local economies, providing jobs and income for local businesses. It can also have a positive impact on individuals, providing them with a way to connect with their faith and find inner peace.
Educational Tourism
Educational tourism is a type of tourism that involves travelling to a destination with the primary purpose of learning something new. It is an excellent way for individuals to gain knowledge and skills while experiencing new cultures and environments.
- Student exchange programs
Student exchange programs are a popular form of educational tourism. These programs allow students to study abroad for a semester or a year while attending a foreign university. Students can learn a new language, experience a new culture, and gain valuable academic experience. Some universities offer exchange programs with partner institutions, while others offer independent study options.
- Research trips
Research trips are another form of educational tourism. These trips are designed for individuals who want to conduct research in a particular field or area. They can be organised by academic institutions, research organisations, or individuals. Research trips can be a great way to gain first-hand experience, collect data, and develop new skills.
Overall, educational tourism is an excellent way for individuals to gain knowledge and skills while experiencing new cultures and environments. Whether it’s through student exchange programs or research trips, educational tourism can provide a valuable learning experience for individuals of all ages.
Cruise Tourism
Cruise tourism is a type of tourism that involves travelling on a cruise ship for leisure purposes. It is a luxurious form of travelling that offers an all-inclusive holiday on a cruise ship for at least 24 hours. Passengers on a cruise ship have access to a wide range of amenities and recreational facilities on board, such as swimming pools, casinos, and theatres.
The Caribbean, Mediterranean, and Arctic regions of the world are among those where cruise travel is most popular. Cruise ship passengers can take advantage of a set and detailed itinerary that includes many ports and city visits. This allows them to travel to several locations and take in various cultures all in one vacation.
There are different types of cruise ships available for passengers to choose from, depending on their preferences and budget. Some of the major types of cruise ships include:
- Luxury cruise: These are high-end cruise ships that offer luxurious amenities and services to passengers.
- Expedition cruise: These are small ships that are designed for adventure and exploration. They are ideal for passengers who want to explore remote and exotic destinations.
- Mega cruise: These are large cruise ships that can accommodate thousands of passengers. They offer a wide range of amenities and services, including multiple restaurants, bars, and entertainment options.
- Themed cruise: These are cruise ships that are designed for specific interests, such as music, food, or sports.
- Adventure cruise: These are cruise ships that are designed for adventure activities, such as hiking, kayaking, and snorkelling.
- Single cruise: These are cruise ships that are designed for solo travellers. They offer a range of activities and social events to help solo travellers meet other passengers.
Dark Tourism
Dark tourism is a type of tourism that involves visiting places associated with death, tragedy, and suffering. It is also known as grief tourism, black tourism, or thanatourism. The term “ dark tourism ” was first coined by two researchers, John Lennon and Malcolm Foley, in 1996.
According to Tourism Teacher , there are seven main types of dark tourism sites. These include:
- Death and tragedy sites: These are places where death or tragedy has occurred, such as battlefields, disaster sites, and places of execution.
- Genocide and atrocities sites: This is any place where large-scale violence, such as genocide, has occurred, such as concentration camps, killing fields, and memorials.
- Cemeteries and mausoleums: This is where the dead are buried or interred, such as graveyards, tombs, and catacombs.
- Museums and exhibitions: These are places that exhibit objects or information related to death and tragedy, such as holocaust museums, crime museums, and medical museums.
- Dark fun factories: These are places that offer entertainment related to death and tragedy, such as escape rooms, zombie chases, and theatrical activities.
- Literary and film locations: These are places associated with famous works of literature or film that deal with death and tragedy, such as the locations used in the Harry Potter series or the film Schindler’s List.
- Dark natural sites: These are natural sites associated with death and tragedy, such as volcanoes, caves, and mountains where people have died.
Space Tourism
Space tourism is a relatively new type of tourism that involves commercial space travel for recreational purposes. It has become increasingly popular in recent years, with several companies offering different types of space tourism experiences.
Types of Space Tourism
There are three main types of space tourism: suborbital, orbital, and lunar.
Suborbital space tourism
Suborbital space tourism involves taking passengers to the edge of space, providing them with a view of Earth from above and a taste of weightlessness. In these missions, spacecraft reach altitudes between 80 to 100 kilometres before returning to Earth. Suborbital flights last a few minutes and are designed to give passengers a brief experience of space travel. Companies such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin are currently working on suborbital space tourism programs.
Orbital space tourism
Orbital space tourism involves taking passengers into Earth’s orbit, allowing them to experience several days or weeks in space. This type of space tourism is more expensive and requires more training than suborbital space tourism. In 2001, American businessman Dennis Tito became the first space tourist to visit the International Space Station (ISS). Since then, several other space tourists have visited the ISS, including Guy Laliberté, the founder of Cirque du Soleil.
Lunar space tourism
Lunar space tourism involves taking passengers to the Moon, allowing them to explore its surface and experience the Moon’s low-gravity environment. This type of space tourism is still in development, with only a few companies, such as SpaceX and Blue Origin, currently working on lunar space tourism programs.
Space tourism is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to become a significant industry in the future. As technology advances and becomes more affordable, more people may have the opportunity to experience space travel. However, safety concerns and high costs are still major obstacles that need to be addressed before space tourism can become a mainstream industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main categories of tourism?
The main categories of tourism are leisure tourism, business tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, educational tourism, medical tourism, religious tourism, and eco-tourism. Each category is defined by the primary motivation of the traveller and the activities they undertake during their trip.
How do different types of tourism impact the economy?
Tourism has a significant impact on the economy of many countries. The tourism industry creates jobs, generates revenue, and contributes to the development of infrastructure. The economic impact of different types of tourism can vary depending on the destination and the activities undertaken by travellers.
What are the characteristics that define each tourism type?
Each type of tourism has unique characteristics that define it. For example, leisure tourism is characterised by relaxation and enjoyment, while adventure tourism is characterised by risk-taking and physical activity. Cultural tourism focuses on experiencing local traditions and customs, while eco-tourism emphasises sustainability and environmental conservation.
In what ways do tourism types vary internationally?
Tourism types can vary significantly between countries and regions. For example, religious tourism may be more prevalent in countries with a strong religious heritage, while eco-tourism may be more popular in countries with unique natural environments. The popularity of different types of tourism can also be influenced by factors such as climate, geography, and cultural traditions.
Can you list the primary sectors within the tourism industry?
The primary sectors within the tourism industry include accommodation, food and beverage, transportation, attractions and activities, and travel services. Each sector plays a vital role in supporting the tourism industry and contributing to the overall tourism experience.
How is tourism classified according to traveller motivation?
Tourism can be classified according to traveller motivation into three categories: domestic tourism, inbound tourism, and outbound tourism. Domestic tourism refers to travel within the traveller’s own country, while inbound tourism refers to travel by foreign visitors to the country. Outbound tourism refers to travel by residents of a country to other countries. Each category is characterised by different motivations and travel patterns.
Read more Business Travel Guide articles

Understanding Flight ID Requirements for Business Travel in 2024

9 Corporate Credit Card Policy Best Practices

What is MICE Travel? Everything You Need to Know in 2024

A Complete Guide to Corporate Travel Allowance

13 Types of Tourism That You Need to Know
- August 7, 2023
Table of Contents
Welcome, wanderlust seekers and adventure enthusiasts, to a thrilling exploration of the world’s diverse tapestry of tourism! Embark on a captivating journey as we unveil the tantalising realm of travel, introducing you to the mesmerising array of types of tourism that will ignite your wanderlust. From the adrenaline-pumping escapades of adventure tourism to the enriching experiences of cultural and heritage tourism, we delve deep into each captivating category, revealing the hidden gems, unique opportunities, and travel solutions that await you.
Whether you’re a passionate foodie yearning for culinary delights or an eco-conscious traveller seeking sustainable adventures, our comprehensive guide will unlock the secrets to immersing yourself in the rich tapestry of travel. So pack your bags, unleash your curiosity, and join Qoni Travel as we unravel the thrilling world of 13 different types of tourism you need to know about!
13 Types of Tourism
Adventure tourism.
Embarking on an awe-inspiring escapade filled with adrenaline-fueled thrills is the ultimate recipe for infusing your travel adventures with excitement. Adventure tourism, the realm where extraordinary tales are born, encompasses an array of heart-pounding activities. From the intrepid pursuit of conquering majestic peaks through hiking and mountaineering to the audacious ascent of vertical cliffs during rock climbing expeditions, the possibilities for daring exploits are boundless.
For those who possess an insatiable appetite for exhilaration, the heart-stopping leap of faith in bungee jumping or the wild ride down untamed rapids in white-water rafting are exhilarating options that promise to set pulses racing. Adventure tourism, a siren call to intrepid souls, offers the chance to revel in unforgettable experiences amidst breathtaking natural landscapes, satisfying the yearning for extraordinary encounters and leaving an indelible imprint on the adventurous spirit within.
Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism emerges as an irresistible allure for wanderers seeking to unravel the rich heritage that unfurls before them. This enchanting form of exploration beckons travellers to step into a realm of boundless wonders, where they traverse the hallowed halls of museums, trace the footprints of history at ancient sites, marvel at the brushstrokes of artistic genius within vibrant galleries, and partake in the rhythmic dance of time-honoured festivals that awaken the senses.
Eco-Tourism
In the past few years, a remarkable surge in consciousness about the significance of sustainable travel practices has emerged. Embracing this movement, eco-tourism has emerged as a captivating way to immerse oneself in the wonders of the natural world while meticulously safeguarding its delicate balance.
Drawing adventurers to breathtaking national parks, serene nature reserves, and hallowed protected areas, eco-tourism enthusiasts enthusiastically partake in eco-friendly activities, such as observing magnificent wildlife, marvelling at feathered wonders, and embarking on enlightening nature walks. With each step, these mindful explorers tread lightly, ensuring that their footprints leave no lasting scars while simultaneously nurturing their connection to the awe-inspiring tapestry of life.
Through this immersive odyssey, cultural tourism serves as a gateway to enlightenment, allowing intrepid souls to embrace the intricacies of local customs, traditions, and the very essence of existence while nurturing a profound cross-cultural empathy and an unwavering appreciation for the beauty that lies within the tapestry of humanity.
Sustainable Tourism
Sustainable tourism goes hand in hand with eco-tourism, significantly emphasising conscientious and mindful travel practices that prioritise environmental preservation, uphold local communities and foster socio-economic growth. By opting for eco-friendly accommodations, supporting locally owned enterprises, and actively participating in community-based tourism projects, sustainable tourism catalyses preserving our invaluable natural wonders and cultural legacies, ensuring their unspoiled existence for generations to come.
Wellness Tourism
Amid our modern, high-speed existence, wellness tourism emerges as a blissful sanctuary, beckoning individuals to rediscover harmony within their minds, bodies, and spirits. Embracing an ethos of tranquillity and self-nurturing, this captivating form of travel encompasses an array of activities designed to alleviate stress, restore vitality, and enhance personal growth.
Encountering a world of possibilities, wellness tourists embark on transformative journeys, seeking solace in serene spa retreats, immersing themselves in the serene embrace of yoga and meditation centres, indulging in the lavish comforts of wellness resorts, and embracing the transformative power of healing retreats. With wellness tourism, holistic well-being becomes a destination and a transformative expedition that transcends the boundaries of time and space.
Culinary Tourism
Indulge your taste buds and embark on a tantalising journey with culinary tourism, an adventure tailored for avid food lovers seeking to immerse themselves in the rich tapestry of flavours and culinary customs across the globe. Prepare for a mouthwatering experience as you partake in captivating food tours, where every bite unlocks the secrets of local cuisines and cooking classes that reveal the artistry behind cherished recipes.
Let your senses dance as you savour regional delicacies, uncover the historical and cultural significance woven into each dish, and witness the transformative power of food as it bridges the gap between diverse communities. With culinary tourism, every destination becomes a delectable playground waiting to be explored, ensuring a truly unforgettable and palate-pleasing voyage.
Historical Tourism
Step back in time and embark on a captivating journey through the annals of the past with historical tourism. This enticing adventure beckons history enthusiasts and inquisitive globetrotters alike. Immerse yourself in the tapestry of bygone eras as you traverse ancient ruins, wander through majestic castles, explore awe-inspiring archaeological sites, and meander through heritage cities that whisper tales of yore.
Unravel the secrets and significance of monumental events and iconic landmarks as every step unveils the captivating stories and the vibrant heritage that have shaped the world we know today. Historical tourism is your gateway to a remarkable fusion of discovery and reverence, offering a chance to unlock the mysteries of history and forge an unbreakable bond with the past.
Wildlife Tourism
Enthrals the hearts of passionate nature lovers and devoted animal enthusiasts, captivating them with the extraordinary allure of the natural realm. Embracing many exhilarating activities, from riveting safaris to stunning whale watching, this immersive experience transports individuals to ethereal bird sanctuaries and enlightening animal conservation centres. Amidst these ventures, one is blessed with the extraordinary privilege of beholding an exquisite tapestry of diverse wildlife species in their untamed habitats, fostering a deep connection and igniting a genuine commitment to the noble cause of conservation.
Religious Tourism
Is a captivating journey that immerses travellers in destinations with spiritual significance. It encompasses diverse experiences, from embarking on pilgrimages to revered holy sites to partaking in profound religious ceremonies. By venturing into these sacred realms, pilgrims and seekers of faith embark on a soul-stirring quest to strengthen their connection to their beliefs. As they traverse the enchanting landscapes, they marvel at awe-inspiring sacred architecture that is a testament to human devotion.
From the majestic Vatican City, home to the spiritual heart of the Catholic world, to the sacred and revered Mecca, drawing millions of devout Muslims every year, or the ancient and captivating Angkor Wat temple complex, religious tourism serves as a gateway to profound encounters with divine history, offering an unforgettable odyssey of faith and spirituality.
Educational Tourism
Embark on an extraordinary journey where the pursuit of knowledge intertwines with the allure of travel. Step beyond the walls of conventional classrooms and delve into the captivating realm of educational tourism. Immerse yourself in a tapestry of enlightening encounters as you traverse the halls of renowned educational institutions, wander amidst the whispers of history at awe-inspiring sites, and unveil the treasures within the hallowed halls of museums. Engage in immersive workshops and cultural exchange programs, fostering a vibrant tapestry of understanding and appreciation. Through educational tourism, watch as your horizons expand, your perspectives deepen, and the fire of lifelong learning is kindled within your soul.
Sports Tourism
This extraordinary form of travel allows passionate sports enthusiasts to fuse their love for athletics with unforgettable journeys. Whether you’re a spectator at thrilling sporting events, a contender in heart-pounding competitions, or an adventurer seeking sports-themed vacations, sports tourism offers an unparalleled opportunity to ignite your passion. Picture yourself bellowing cheers for your beloved team at the grandeur of the World Cup or gracefully gliding down awe-inspiring slopes as you ski through breathtaking landscapes. Get ready for a rollercoaster of exhilaration and exploration as sports tourism unlocks a world of electrifying experiences you won’t miss.
Volunteer Tourism
Discover the remarkable realm of volunteer tourism, a captivating adventure where intrepid explorers can leave a lasting mark while embarking on thrilling journeys to uncharted destinations. This extraordinary endeavour entails actively engaging in awe-inspiring community service projects, conservation endeavours, and humanitarian initiatives. As you immerse yourself in this transformative experience, an enchanting tapestry of cultural exchange unfolds, igniting profound empathy and fostering personal growth. Embark on this global quest to revolutionise lives and empower communities, embracing the boundless possibilities of volunteer tourism to create a brighter future for all.
Medical Tourism
Is an exhilarating blend of healthcare and adventure that entices individuals to embark on an international voyage in pursuit of top-notch medical care and exclusive procedures. It encompasses the exciting concept of jetting off to foreign lands, where one can embrace high-quality medical services without breaking the bank or discovering cutting-edge treatments that remain elusive within their homelands. With medical tourism , the boundaries of healing are surpassed as patients traverse borders, unlocking a world of possibilities for their well-being.
In a world bursting with wanderlust seekers and adventure enthusiasts, our thrilling exploration of the diverse tapestry of tourism has come to an exhilarating conclusion. Throughout this captivating journey, we have unveiled the tantalising realm of travel, introducing you to the mesmerising array of 13 types of tourism that ignite the flames of wanderlust within. From heart-pounding escapades in adventure tourism to the profound immersion in cultural and heritage tourism, each category has taken us deep into a world of hidden gems and unique opportunities.
Whether you’re a passionate foodie yearning for culinary delights or an eco-conscious traveller seeking sustainable adventures, our comprehensive guide has unlocked the secrets to immersing yourself in the rich tapestry of travel. As you pack your bags and unleash your curiosity, remember that the world awaits, ready to unravel the thrilling world of these 13 types of tourism you need to know about. So, embark on this transformative journey, and let the wanderlust within guide you to the extraordinary experiences that await, leaving an indelible imprint on your adventurous spirit. Stay tuned with Qoni Travel for more information.
Get in touch with our sales

As an employee, business travel and trips are often fun and productive. Booking travel can be a hectic task. With numerous routes and fares, it

The hospitality industry is one of the most dynamic and diverse fields that play a significant role in the world economy. This industry is evolving

Travelling is essential to business, and small businesses often require personalised support and cost-effective solutions. Choosing the right corporate travel agency can help small businesses

Traveling is among the biggest industries in the world that contributes a significant portion of the entire e-commerce business. It makes a high contribution to

Connect with us
Travel services managed by.
Hype DMC Travel Sdn Bhd Co. Reg: 258404-A | KPL: 6430 No.167A, 1st Floor, Jalan Maharajalela 50150 Kuala Lumpur
S AMASTA TOUR & TRAVEL Jl. Tampak Siring Raya, Daan Mogot Baru, Blok KJ-F/3A, RT.8/RW.12, Kalideres, Kec. Kalideres, Kota Jakarta Barat, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta 11840, Indonesia
Operated by Travel Ideas Online Sdn Bhd Empowering journeys through innovative technology

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.1: Components of Travel Services
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 9340

- Morgan Westcott & Wendy Anderson et al.
The travel services sector helps travellers arrange and reserve their vacation or business trips (StatsCan, 2018). This sector is made up of businesses and organizations that work in a coordinated effort to provide travellers with seamless arrangements to maximize their travel experience. Go2HR describes travel services experiences and employment opportunities as follows:
Within this sector, you have the flexibility of working in various capacities with event and conference planning organizations, travel companies and organizations, as well as associations, government agencies and companies that specialize in serving the needs of the tourism sector as a whole. (go2HR, Essential Tips – Travel Services, 2020)
Before we move on, let’s explore the term travel services a little more. As detailed in Chapter 1, Canada, the United States, and Mexico have used the NAICS guidelines, which define the tourism industry as consisting of transportation, accommodation, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and travel services (Tourism HR Canada, 2020). These five sectors are defined and further detailed in B.C. by the B.C. government (BC Government, 2014) and go2HR on their website (go2HR, Career Explorer, 2020).
For many years, however, the tourism industry was classified into eight sectors: accommodations, adventure and recreation, attractions, events and conferences, food and beverage, tourism services, transportation, and travel trade (Yukon Department of Tourism and Culture, 2020; go2HR, 2020, What is Tourism? – Travel Services).
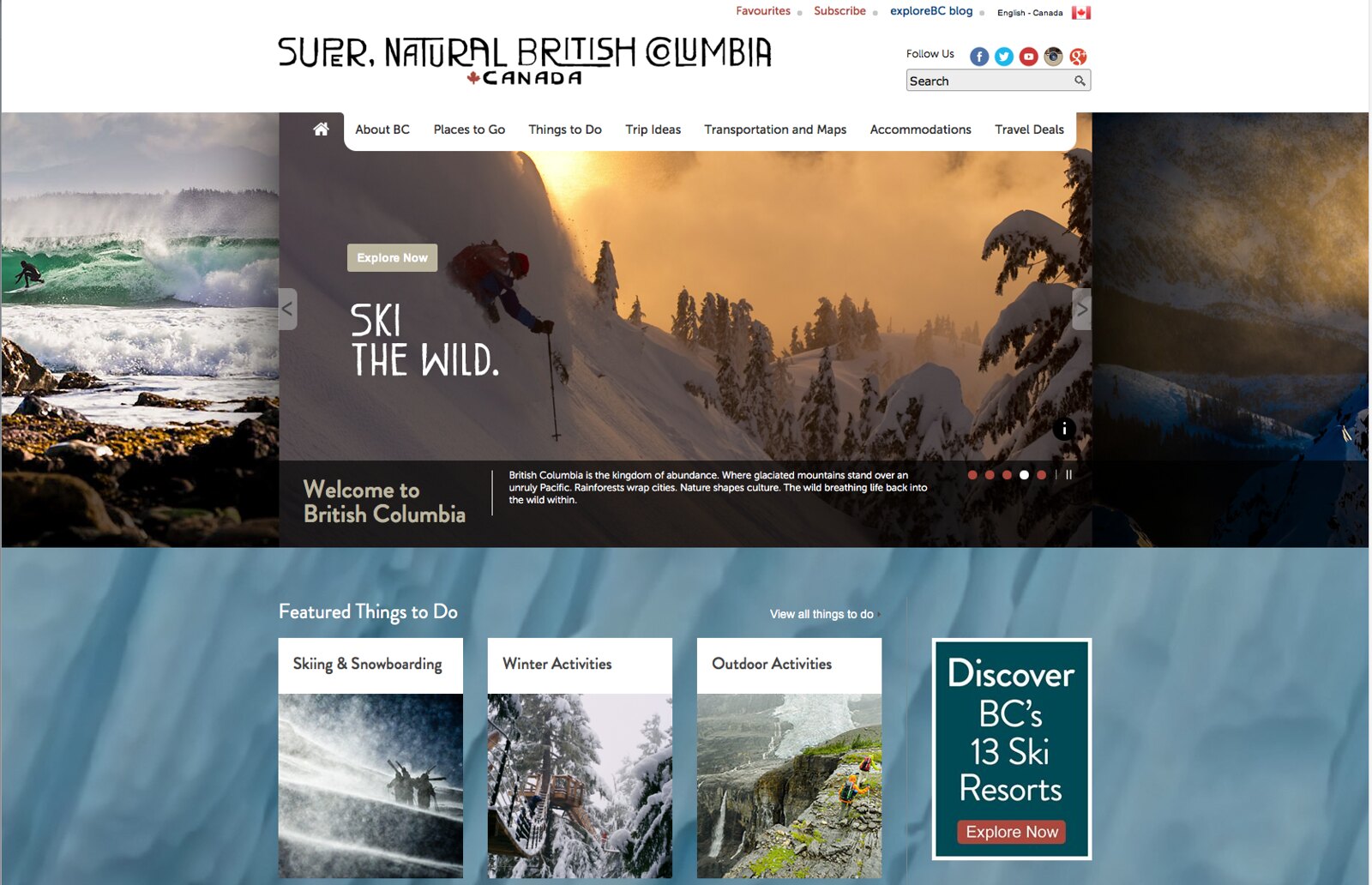
Tourism services support industry development and the delivery of guest experiences, and some of these are missing from the NAICS classification. To ensure you have a complete picture of the tourism industry in BC, this chapter will cover both the NAICS travel services activities and some additional tourism services.
First, we’ll review the components of travel services as identified under NAICS, as well as exploring popular careers within:
- Travel agencies (brick and mortar)
- Online Travel Agencies/OTA
- Tour operators
- Destination marketing organizations (DMOs)
Other Organizations
Following these definitions and descriptions, we’ll take a look at some other support functions that fall under tourism services. These include sector organizations, tourism and hospitality human resources organizations, training providers, educational institutions, government branches and ministries, economic development and city planning offices, and consultants.
Finally, we’ll look at issues and trends in travel services, both at home, and abroad.
While the application of travel services functions are structured somewhat differently around the world, there are a few core types of travel services in every destination. Essentially, travel services are those processes used by guests to book components of their trip. Let’s explore these services in more detail.
Travel Agencies

A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveller (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travellers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveller and hotels, car rentals, and tour companies (Goeldner & Ritchie, 2003). Travel agencies can be small and privately owned or part of a larger entity.
A travel agent is the direct point of contact for a traveller who is researching and intending to purchase packages and experiences through an agency. Travel agents can specialize in certain types of travel including specific destinations; outdoor adventures; and backpacking, rail, cruise, cycling, or culinary tours, to name a few. These specializations can help travellers when they require advice about their trips. Some travel agents operate at a fixed address and others offer services both online and at a bricks-and-mortar location. Travellers are then able to have face-to-face conversations with their agents and also reach them by phone or by email. To promote professionalism within the travel industry, travel counsellors can apply for a specialized diploma or certificate in travel from ACTA (ACTA, 2020a; go2HR, 2020a).
Today, travellers have the option of researching and booking everything they need online without the help of a travel agent. As technology and the internet are increasingly being used to market destinations, people can now choose to book tours with a particular agency or agent, or they can be identified as seeking Domestic Independent Travel (DIT) or Foreign Independent Travel (FIT) , by creating their own itineraries from a number of suppliers.
Online Travel Agents (OTAs)
Increasing numbers of travellers are turning to online travel agents (OTAs), companies that aggregate accommodations and transportation options and allow users to choose one or many components of their trip based on price or other incentives. Examples of OTAs include iTravel2000, Booking.com, Expedia.ca, Hotwire.com, and Kayak.com. OTAs continue to gain popularity with the travelers; in 2012, they reported online sales of almost $100 billion (Carey, Kang, & Zea, 2012) and almost triple that figure, upward of $278 billion, in 2013 ( The Economist , 2014).
In early 2015 Expedia purchased Travelocity for $280 million, merging two of the world’s largest travel websites. Expedia became the owner of Hotels.com, Hotwire, Egencia, and Travelocity brands, facing its major competition from Priceline (Alba, 2015).
Although OTAs can provide lower-cost travel options to travellers and the freedom to plan and reserve when they choose, they have posed challenges for the tourism industry and travel services infrastructure. As evidenced by the merger of Expedia and Travelocity, the majority of popular OTA sites are owned by just a few companies, causing some concern over lack of competition between brands. Additionally, many OTAs charge accommodation providers and operators a commission to be listed in their inventory system. Commission-based services, as applied by Kayak, Expedia, Hotwire, Hotels.com, and others, can have an impact on smaller operators who cannot afford to pay commissions for multiple online inventories (Carey, Kang & Zea, 2012). Being excluded from listings can decrease the marketing reach of the product to potential travellers, which is a challenge when many service providers in the tourism industry are small or medium-sized businesses with budgets to match.
While the industry and communities struggle to keep up with the changing dynamics of travel sales, travellers are adapting to this new world order. One of these adaptations is the ever-increasing use of mobile devices for travel booking. The Expedia Future of Travel Report found that 49% of travellers from the millennial generation (which includes those born between 1980 and 1999) use mobile devices to book travel (Expedia Inc., 2014), and these numbers are expected to continue to increase. Travel agencies are reacting by developing personalized features for digital travellers and mobile user platforms (ETC Digital, 2014). With the number of smartphone users expected to reach 1.75 billion in 2014 (CWT Travel Management Institute, 2014) these agencies must adapt as demand dictates.

A key feature of travel agencies’ (and to a growing extent transportation carriers) mobile services includes the ability to have up-to-date itinerary changes and information sent directly to consumers’ phones (Amadeus, 2014). By using mobile platforms that can develop customized, up-to-date travel itineraries for clients, agencies and operators are able to provide a personal touch, ideally increasing customer satisfaction rates.
Take a Closer Look: PATA — The Future of Travel is Personalisation at Scale
“The industry has changed monumentally over the past decade. The rise of meta-search websites and sharing economy services like Airbnb is giving travellers more control and choice than ever before. However, this is nothing compared to the changes that are on the horizon as technologies like mobile, AR, AI, and VR become mainstream.
One thing is certain; the pace of change is accelerating. Against this backdrop, the travel industry as a whole will need to fundamentally shift its focus to continuous innovation.” (PATA, 2019)
Despite the growth and demand for OTAs, brick and mortar travel agencies are still in demand by travellers (IBISWorld, 2019) as they have both an online presence and physical locations. The COVID-19 pandemic may see an increase in travellers relying on personal contact with brick and mortar travel agencies but at a distance through mail and phone.
Tour Operators

A tour operator packages all or most of the components of an offered trip and then sells them to the traveller. These packages can also be sold through retail outlets or travel agencies (CATO, 2020; Goeldner & Ritchie, 2003). Tour operators work closely with hotels, transportation providers, and attractions in order to purchase large volumes of each component and package these at a better rate than the traveller could if purchasing individually. Tour operators generally sell to the leisure market.
Inbound, Outbound, and Receptive Tour Operators
Tour operators may be inbound, outbound, or receptive:
- Inbound tour operators bring travellers into a country as a group or through individual tour packages (e.g., a package from China to visit Canada).
- Outbound tour operators work within a country to take travellers to other countries (e.g., a package from Canada to the United Kingdom).
- Receptive tour operators (RTOs) are not travel agents, and they do not operate the tours. They represent the various products of tourism suppliers to tour operators in other markets in a business-to-business (B2B) relationship. Receptive tour operators are key to selling packages to overseas markets (Destination BC, 2020) and creating awareness around possible product.
Destination Marketing Organizations
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs) include national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus around the world. DMOs promote “the long-term development and marketing of a destination, focusing on convention sales, tourism marketing and service” (Destinations BC, 2020).
Spotlight On: Destinations International
Destinations International is the global trade association for official DMOs. It is made up of over 600 official DMOs in 15 countries around the world. DMAI provides its members with information, resources, research, networking opportunities, professional development, and certification programs. For more information, visit the Destinations International website.
With the proliferation of other planning and booking channels, including OTAs, today’s DMOs are shifting away from travel services functions and placing a higher priority on destination management components.
Working Together
One way tour operators, DMOs, and travel agents work together is by participating in familiarization tours (FAMs for short). These are usually hosted by the local DMO and include visits to different tour operators within a region. FAM attendees can be media, travel agents, RTO representatives, and tour operator representatives. FAMs are frequently low to no cost for the guests as the purpose is to orient them to the tour product or experience so they can promote or sell it to potential guests.
The majority of examples in this chapter so far have pertained to leisure travellers. There are, however, specialty organizations that deal specifically with business trips.
Spotlight On: Global Business Travel Association (GBTA) Canada
“GBTA Canada is the voice of the Canadian business travel industry. We believe in providing the business travel and meetings community with a global platform to serve as a resource library for their peers, to implement world-class Conferences, workshops and virtual meetings, and to foster an interactive network of innovation and support.” The GBTA state that their economic impact contributes $23.5 billion CAD in Canadian business travel (Economic Impact Study) and “$435+ billion CAD of business travel and meetings expenditures represented globally.” Visit the GBTA website .
Business Travel Planning and Reservations
Unlike leisure trips, which are generally planned and booked by end consumers using their choice of tools, business travel often involves a travel management company, or its online tools. Travel managers negotiate with suppliers and ensure that all the trip components are cost effective and comply with the policies of the organization.
Many business travel planners rely on global distribution systems (GDS) to price and plan components. GDS combine information from a group of suppliers, such as airlines. In the past, this has created a chain of information from the supplier to GDS to the travel management company. Today, however, there is a push from airlines (through the International Air Transport Association’s Resolution 787) to dissolve the GDS model and forge direct relationships with buyers (BTN Group, 2014).
Destination Management Companies
According to the Association of Destination Management Executives International (ADMEI), a destination management company (DMC) specializes in designing and implementing corporate programs, and “is a strategic partner to provide creative local experiences in event management, tours/activities, transportation, entertainment, and program logistics” (ADMEI, 2020). The packages produced by DMCs are extraordinary experiences rather than general business trips. These are typically used as employee incentives, corporate retreats, product launches, and loyalty programs. DMCs are the one point of contact for the client corporation, arranging for airfare, airport transfers, ground transportation, meals, special activities, and special touches such as branded signage, gifts, and decor (ADMEI, 2020). The end user is simply given (or awarded) the package and then liaises with the DMC to ensure particular arrangements meet his or her needs and schedule.
As you can see, travel services range from online to personal, and from leisure to business applications. Now that you have a general sense of the components of travel services, let’s look at some examples in Canada and BC.
Travel With - The Holiday Story
18 Different Types of Tourism | Globally Accepted
Last few years, tourists and their demands have frequently been changing. Also, the tourism industry is changing based on needs. This article elaborates on different types of tourism, tourists, planning, activities, products, travel , etc. It helps your travel planning as well.
Along with recreation, tourism has become one of the growing industries, and it’s the source of income for many people.
“Life is all about adventure, so pack your bags and start the tour.”

Different Types of Tourism
What is tourism.

Tourism is a process of spending time away from daily routine or home to pursue recreation, relaxation, and pleasure while using the commercial provision of services.
Tourism in a country has many benefits: it creates employment, boosts revenue, develops infrastructure, helps in cultural exchange, etc. Travel duration under tourism must be less than 12 months (a consecutive year).
So, What comes first to mind when we hear the word Tourism?
The most common thought is to pack the rucksack and travel away from day-to-day life. That means the movement of people from their usual residence to another place.
Suppose your friend’s aim for the tour might differ from yours. For example, you may travel for recreation, but he may go for business.
Classification of Tourism
According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism involves the movement of people in the country’s natural environment or outside the country for personal or other purposes. These different purposes classified the tourism industry in many ways.
This article lists the main tourism classifications: Domestic tourism, International tourism, Business tourism, Adventure tourism, Medical tourism, Educational tourism, etc.
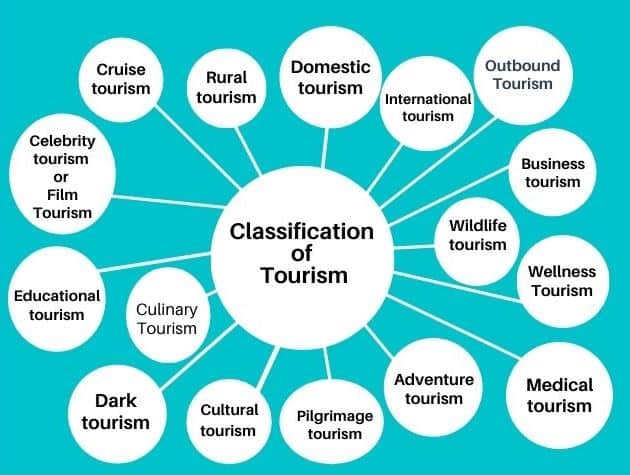

Importance of Tourism – Why is tourism important?
Tourism has a direct impact on any country’s economy. The role of tourism in economic development is important. A vast amount of job possibilities can develop through public relations in tourism. Knowing another state/country’s taste culture is a great filling from a traveler’s perspective.
Mainly how many types of tourism are there
Mainly three types of tourism are found in any country. The classes are domestic tourism, International tourism, and outbound tourism. But nowadays, many types of tourism newly evolved.
18 Different Types of Tourism
The various types of tourism are developed nowadays and become popular; they are:-
- Domestic tourism
- International tourism
- Outbound tourism
- Business tourism
- Adventure tourism
- Wildlife tourism
- Medical tourism
- Wellness tourism
- Pilgrimage and spiritual tourism
- Cultural tourism
- Dark tourism
- Culinary tourism
- Celebrity tourism or Film tourism
- Educational tourism
- Cruise tourism
- Rural tourism
- Beach tourism
- Space tourism
Let’s discuss how many flavors and categories of tourism can be found in any country and accepted globally.
1. Domestic Tourism
Domestic tourism involves traveling in one’s own country, and tourists don’t cross international borders or entry points. Domestic tourism is used to minimize poverty, enhance infrastructure, and boost the economy’s growth and generation of employment.
2. International Tourism
Travel outside your country needs a visa and passport; called International tourism. For example, if you want to explore The UK from Sri Lanka, you need documents to enter another country.
Read How to Listen to Music on a Plane
3. Outbound Tourism
This tourism defines a tourist traveling for a holiday to a different country, like your residents in Bali and traveling to Barcelona . It is an example of outbound Tourism.
4. Business Tourism
This tourist travels to meetings, officially gets together for conferences, etc.
Business tourism plays a vital role in the tourism sector. Sometimes, people stay out of their typical environment for more than a year for business purposes and spend their vacations there.
General activities related to business tourism include attending meetings, officially getting together, conferences, seminars, visiting exhibitions and trade fairs, etc. This tourism levels up the purchasing power.

5. Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism is a person’s travel from one place to another to seek fresh adventures and activities. This form of tourism is most famous among young tourists and people who like to explore remote areas. It encourages us to leave our comfort zone by undertaking activities like hiking , rafting, climbing, diving, etc.
Adventure tourism is increasing day by day. You could also try whitewater rafting, the Ladakh tour, the Kedarnath tour, Port Blair, and Andaman and Nicobar tour for the adventure.

6. Wildlife Tourism
Wildlife tourism is people’s travel to different places to observe and interact with wildlife, flora, and fauna in their natural habitat. Safaris, visiting the animal rescue center, swimming with dolphins, etc., are examples of wildlife tourism.
Because of exotic species of wildlife, this tourism became recognized. The Sariska Wildlife or Hyde Park Sanctuary , Keoladeo Gana National Park, and Corbett National Park are renowned for wildlife tourism. The Great Barrier Reef is also famous in Australia.

7. Medical Tourism
Many people travel for treatment, and several medical institutes cure foreign patients. Thailand has recorded 6000,000 new patients every year. Malaysia also treated over 100,00 tourists in 2005. 45% of foreign tourists come to Chennai for medical treatment.

8. Wellness Tourism
Wellness tourism has been a significant part of tourism since ancient times. This tourism mainly attracts those tourists who want to regain their health. Wellness tourism will help you to get rid of mental and health stress.
Tourists recover their health issues through physical, spiritual, or psychological activities. All around the world, plenty of destinations are popular for improving health.
Examples include Mexico Temazcal Beach Resort Spa, Caribbean wellness cruise, California weight loss and detox retreats, Colorado Hiking and Mountain Yoga retreat, and China Hot Spring Resorts TCM.
Ayurveda, Yoga , Meditation, Panchakarma, and Rejuvenation Therapy are the oldest Therapy of treatments to improve health and the best way to develop wellness tourism.

9. Pilgrimage and Spiritual Tourism
Pilgrimage or spiritual tourism is when a person journeys to other places for spiritual or religious reasons.
Spiritual tourism helps support local cultural activities and handicrafts, generating employment and revenue. Trips to Jerusalem, Bodh Gaya , Hajj, etc., are pilgrimage or spiritual tourism.
This tour has been famous for ages, but It’s popular among older people mainly. Vaishno Devi, Golden Temple, Char Dham, and Mathura Vrindavan are some places famous for Pilgrimage tours.
10. Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism is a person’s journey to learn and participate in local festivals, rituals, and cultural activities of other places. It’s more than a commercial activity.
This form of tourism helps spread aboriginal communities’ culture, traditions, diversity, and richness to the rest of the world.
Visit the historical sites and the artistic features of that country too. Famous cultural tourism places are:-
- India – Durga puja in Kolkata , Temples at Banaras, Jaipur, known as the pink city Palace in Rajasthan. Forts and monuments in Delhi, Agra, UP.
- UK – Tower of London, The British Museum, Big Ben, London Durga puja , etc.
- Kenya – The main attraction is the dance of the Maasai tribe.
- Morocco – The main attractions are the Olive Festival and Honey Festival.
- Jordan – The main attraction- is Jerash, famous for Roman architecture Petra, the red-rose curved rock city and one of the seven world wonders, and Shoubak with its Montreal Crusader Castle.
- Greece – The main attraction- is the Lion Gate of Mycenae.
- Turkey – the main attraction- Sultan Ahmed. Mosque, House of the Virgin Mary.
- Vietnam – The main attraction- is Sapa Market.
- Ireland tour – Cliffs of Moher, Dublin, Killarney National Park, etc.

11. Dark Tourism
Dark tourism, Black tourism, or grief tourism are related to people’s travel to historical places involved with tragedy and death. Since 2016, dark tourism has significantly increased (over 1200%). Chornobyl, cemeteries, Ground Zero, historical museums, and Auschwitz are popular dark tourism destinations.
It is referred to as mourning tourism. Dark tourism involves visiting those places and sites that have witnessed the greatest tragedies in history. Besides this history of human suffering and bloodshed, these locations are famous for their historical value.
So, those sites that carry potent pesticides have become popular tourist destinations and attract many tourists yearly.
Like Famous sites In Japan, Hiroshima & Nagasaki bombing locations, Ground Zero, New York, USA . The War Remnants Museum, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; Auschwitz concentration camp, Auschwitz, Germany; Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, etc.

12. Culinary Tourism
Culinary or food tourism involves tasting and experiencing local and traditional food in a specific country, region, city/town/village.
It is significant that besides accommodation and infrastructure. Here, food is one of the prime components. Therefore, lots of tours are organized here to experience the culinary culture.
Today, with the overall growth of this sector, tourism has expanded and developed to the next level.
Every year, Different states of India organize food festivals at different times in different states. Thousands of people from abroad join this festival to enjoy traditional food.
Everyone knows India is called “The land of spices.” And every state has unique kinds of food culture. Today, it is a significant part of tourism.
Culinary Tourism includes where people visit certain regions like California, Napa Valley, Catalonia, USA, and Spain) to enjoy foreign wines.
Famous Destinations : London, France, Beijing, Mexico, Italy, etc.

13. Celebrity Tourism or Film Tourism
Celebrities are the primary source of attraction for celebrity or film tourism. In this form of tourism, tourists visit places where a celebrity currently lives or has lived. Management organizations use celebrity tourism to promote a place or attraction.
Although no celebrities are present, only you can see the entire studio. Many Destination Management organizations (DMOs) use celebrity tourism to promote destinations as an attraction.
Popular celebrity tourism destinations are – Hollywood, Harry Potter Studios, Ramoji Film City India, Cannes Film Festival, Hong Kong, and Madame Tussauds.

14. Educational Tourism
Educational tourism is a new pattern of tourism that comprises learning new things. It’s the journey a person takes to leave his hometown or country for educational or learning purposes. Educational tourism is famous in Japan, Australia, the UK, etc.
An educational tourist can be away from his hometown for many days. Education and learning are the key reasons for their travels, and it is learning knowledge from historical places, cultural and social events, and understanding a language.
It’s used as a tool to complement education by gathering travel experience. Many educational institutes combine these trends in primary schools and are compulsory in higher education.
15. Cruise Tourism
Holidays based partially or wholly on a cruise ship are considered cruise tourism. It provides tourists with a multi-centered holiday experience. Cruise ships (like small yachts, big ships, etc.) take people on a tour of oceans, fjords, or rivers.
Throughout their trip, tourists can enjoy time at various destinations. The Mediterranean, Caribbean, Arctic, Antarctica, etc., are famous destinations. It’s the newest and fastest-growing part of the world’s tourism industry.
The world’s famous coastline and inland waterways have the potential to develop cruise and houseboat tourism like Quark Expeditions, OZ Cruising, and A-ROSA River Cruises.
India has many types of tourist cruises. Soon, India will be including Ocean Cruise, River Cruises, and Lake Cruises.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by ⚓️ Iglu Cruise (@iglucruise)
16. Rural Tourism
There are many forms of tourism, and It’s divided into many parts. In this category, a tourist spends leisure time in rural areas or villages. Visitors can make a plan to visit the rural area for some days or a couple of months.
Especially Solo travelers can visit those places to enjoy their lonely time. They join all the local activities that happen in this village.
Rural tourism is included in a ‘country holiday’ where tourists spend much of their leisure time. Thus, they taste the recreational activities in the rural environment.
Like Farming in Rural Punjab, The Spiti Valley Rural Tourism, Sundarban and Jodhpur Village Life, Bhubandanga West Bengal, and Community Tourism in Kutch.

17. Beach Tourism
Beach tourism is how a beach plays a major element in the holiday, and it’s the most modern form and the staple of tourism.
In beach tourism, tourists travel to a beach for leisure, recreation, or business purposes. People who like the clear blue sight of a beach undertake this journey.
Popular Beach Destinations: The Maldives, Seychelles, Turks And Caicos, French Polynesia, Africa , Queensland, Australia, Philippines, Thailand, Bali In Indonesia, Lakshadweep, Goa, Puri, etc.
Why is Beach Tourism important?
- Beach tourism has brought about many economic benefits.
- It has led to the building of many attractions, resorts, etc.
- Beach resorts help in meeting the increase in intra-regional demand and domestic demand.
- This type of tourism creates numerous employment opportunities.

Negative Impacts of Beach Tourism
- It leads to the wastage of a lot of resources and space.
- Beach tourism pollutes water and environmental resources.
- Building new berths, marinas, etc., hurts coastal and marine life.
18. Space Tourism
We have seen significant changes in the aviation industry in the last 100 years. What was once used for warfare and cargo transport is now used for traveling.
Human development has now broken all bounds to take this journey to the vast emptiness of space.
Russia has been the pioneer in this field. Soyuz spacecraft conducted its first space trip with American businessman Dennis Tito in April 2001.
It was a government spacecraft that conducted seven space expeditions within the next six years. This surge in public interest led other organizations worldwide to dive into this area.

There are different types of space tourism
Orbital Space Tourism: These flights remain within an orbit around the Earth at a speed higher than suborbital space flights. These flights orbit the world constantly for their entire stay in outer space.
Sub-orbital Space Tourism : This was the beginning of space tourism. The spacecraft launches with a substantial initial velocity that pushes it out of the Earth’s atmosphere. But this doesn’t throw it entirely out of the gravitational sphere. The power is insufficient for orbiting, so it freezes once the engines are shut off.
SpaceX C.E.O. Elon Musk proposed the prospect of lunar tourism. In 2018, he announced the ‘Dear Moon Project,’ the highly anticipated first lunar space tourism mission. They will carry out this project in 2022 with Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa.
Space Tourism cost
The cost of each sub-orbital trip on the Soyuz spacecraft is reported to be 200,000-250,000 million U.S. dollars. Other trips carried out by different organizations were priced around the same margin.
Virgin Galactic recently announced that each ticket would cost 450,000 USD for the upcoming missions.
Space Tourism companies
Even though the industry is still up and coming, massive companies dominate the market. Space Adventures of Virginia, U.S.A, was the first successful space tourism company.
Elon Musk’s SpaceX, Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic, and Amazon C.E.O. Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origin are all set to launch their space tourism business by 2022. Blue Origin recently conducted its debut flight with Jeff Bezos.
Oliver Daemen and Wally Funk were the world’s youngest and oldest men in space, respectively.
Space Tourism advantages
The universe and outer space have always been intriguing subjects for people on Earth. Yet, there were limited resources to satisfy their curiosity. The option of space tourism thus connects people with space in a unique way and solves its mystery. A more ecological advantage is the waste policy.
There is minimum pollution associated with these travels. Also, this allows a whole new sector of job opportunities for highly educated professionals and ambitious youth.
Top 13 list of space tourists
- Dennis Tito (American): April 28 – May 6, 2001
- Richard Branson
- Gennady Padalka
- Guy Laliberté
- Eytan Stibbe
- Sian Proctor
- Mark Shuttleworth (South African / British): April 25 – May 5, 2002
- Gregory Olsen (American): October 1 – October 11, 2005
- Anousheh Ansari (Iranian / American): September 18 – September 29, 2006
- Charles Simonyi (Hungarian): April 7 – April 21, 2007[8]
- Richard Garriott (American): October 12 – October 23, 2008[9]
- Sheikh Muszaphar Shukor (Malaysian): October 10 – October 23, 2007
Space Tourism in India
Space activities, in general, have been quite a staggering section in India. Last year, the government announced a policy that opens space exploration to private sectors, but hardly any company has taken action on it.
Entrepreneur Santhosh George Kulangara will be the first Indian space tourist as he booked his spot on a Virgin Galactic space flight in 2007. Hopefully, he will join Dennis Tito, Mark Shuttleworth, Gregory Olsen, and many more this year.
Forms of Tourism
- Atomic Tourism
- Beach Tourism
- Bicycle Tours
- Eco-Tourism
- Geo-Tourism
- Industrial Tourism
- Rural Tourism
- Space Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Sustainable Tourism
- Virtual Tourism
- War Tourism
What is the main purpose of tourism?
- Economic Sustainability: It ensures the effectiveness and competitiveness of tourism destinations and enterprises. It helps continue improvement, which is beneficial in the long run.
- Local enrichment: Tourist destination prosperity is an enormous part of tourism. The tourism business continuously maximizes the economic growth of the host destination.
- Employment Standards: Tourism supported the level of wages, terms of service, and availability for all. It creates local jobs without discrimination based on gender, race, disability, or other means.
- Local management: Involve local communities and empower local people for planning and decision-making. The community and tourism management team helped to develop this.
- Community Welfare: Maintain and boost the local community’s lifestyle. They are part of social structures. But surely, this process should take place with no social humiliation or exploitation.
- Natural Integration : Maintain and improve the quality of both urban and rural landscapes. It avoids natural and visual degradation of the environment.
- Natural Integration: Maintain and improve the quality of both urban and rural landscapes. It avoids natural and visual degradation of the environment.
- Biodiversity: Another purpose of tourism is to assist in conserving wildlife and natural wildlife areas and reducing losses.
- Environmental cleanness: Besides the purpose of tourism, all tourists must reduce air, water, and land pollution and waste generation.
- Tourism is a significant part of national integration .
- Tourism always motivates tourists to understand their traditions, heritage, culture, and religion.
- Tourism’s most significant part is economic growth or the business part of the destination. It encourages local people to create handicraft items and prepares local food items, souvenirs, dresses, etc., for sale.
- Tourism is one such thing that constantly boosts the country economically.
Niche Tourism
This tourism focuses on a specific aspect of traveling. It also focuses on the consumer market segment’s interest. It makes the destination more exciting and marketable. Niche Tourism is one of the fastest-growing sectors. Niche tourism indicates a specific feature of travel.
For example, some tourists want a museum, some wish to visit old architectural monuments, buildings, palaces, etc., and some want to eat in a famous restaurant. Thus, niche Tourism shows a particular activity that is not the only focus of travel.

Types of Niche Tourism
- Macro-Niche
- Micro-Niche
What is Macro-Niche?
Macro-niche tourism can be explained as a niche with broad customer interest categories such as rural tourism, Business tourism, sports tourism, medical tourism, environmental travel, etc.
What is Micro-Niche?
It is a small group trip, such as gastronomy tourism, cycling tourism, and geo-tourism.
Niche tourism in South Africa
South Africa is an attractive destination because of the wide diversity of animal and bird species. As a result, tourism professionals found this country has considerable potential.
Advantages of Niche Tourism
- Even if niche tourism is smaller than mainstream markets, it spreads more.
- It has more potential to grow.
- It creates quality jobs that require specialized skills.
What are the different types of tourists?
When we visit a place, we find different kinds of travelers. The aim of each traveler is different. Let us discuss the types of visitors. Five types of tourists are found mostly :-
- Incentive tourists – These tourists did not plan for the tour earlier. Suppose you have been rewarded with two tickets from the office because of your performance. You and your colleagues came for the trip.
- Business tourist – This type of tourist travels for business. They will always prefer a hotel with a conference room. They don’t come to enjoy luxury, but they want the hotel to serve everything on time.
- Leisure tourist – This type of tourist comes to enjoy the vacation. They love those hotels that serve them something extra, like drinks. They choose hotels that give them comfort and luxury at their best.
- Special interest tourists – They often plan their tours very well. This tourist doesn’t need comfort but loves to do adventure.
- The Foodie tourist – This type is quite common. They wish to taste various foods in various places. The signature dishes of those areas and various kinds of foods.
Types of a Tourist Attraction
We have to keep in mind that attraction varies from person to person. For example, suppose Rahul and Sheela are traveling to Kashmir. Rahul is interested in climbing the mountains to see snowfall, whereas Sheela is excited to visit the temples in Kashmir.
Tourist attractions could be classified into the following two categories:-
- Natural attraction – If you are a nature lover, don’t miss The Valley of Flowers in Uttarakhand, Coorg, known as the ‘Scotland of India.’
- Events and heritage attractions – Goa is a place for heritage lovers. So pack your bag, take the camera, and start your journey towards Goa. I am sure you will have an unforgettable lesson in Goa’s history. Fort Aguada, Chandor, and some famous museums are places to visit.
What is Tourism Planning?
Perfect planning is always a matter of the success of any activity. Whenever we plan something and implement it, we get a better result. It’s the same with tourism. But it is neither guaranteed nor forever. It’s a process where the people’s needs are determined using the best resources, programs, and activities.
How do these tourism plans help us?
A tourism plan makes guidelines for the areas. Then, it helps the government and private sectors to develop those areas. Most importantly, we must remember a few steps involved in tourism planning.
Main types of tourism planning
- Financial planning
- To establish the objective
- Human resource planning
- Monitoring progress
- Human resource planning.
Types of Tourism Activities
There are various kinds of tourism activities. Like-
- Heritage trails
- Swimming with dolphins

Name of some international tourist organization-
- American Society of Travel Agents : Founded 1931, Headquarter- New York
- International Academy of Tourism : Founded-1951, Headquarter- Monge Carlo
- International Bureau of Social Tourism : Founded 1963, Headquarters- Brussels
- International Touring Alliance: Founded-1919, Headquarters- Europe
- World Tourism Organization : Founded 1975, Headquarter- Madrid.
Types of Tourism packages
For different categories of tourists, everybody needs a separate package. Let’s discuss the various types of Packages that are available.
1. Adventure Tourism Package
This tourism encourages people to come out of their comfort zone to feel the thrill of nature closely in life. It is found that people are taking adventure more often. It shows potential growth in recent years.
The most exotic and adventurous destinations are Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Jammu, and Kashmir.
2. Wildlife Tourism Package
In every country, wildlife tourism is famous. But, if you love wildlife, you must choose the right package. This package is exclusively for wildlife lovers who love taking their snaps.
3. Medical tourism package
It has been observed that medical tourism has grown rapidly in Asia-specific countries.
4. Pilgrimage tourism package
Many foreigners visit various temples in India, Sri Lanka, and Singapur. However, the major attraction is the traditional architecture, art forms, and rituals performed.
Famous pilgrimage areas are the Meenakshi Temple, Golden Temple, Jagannath Temple, Santa Cruz Cathedral Basilica, Atala Mosque, etc. Therefore, this type of package is chosen based on your religious beliefs.
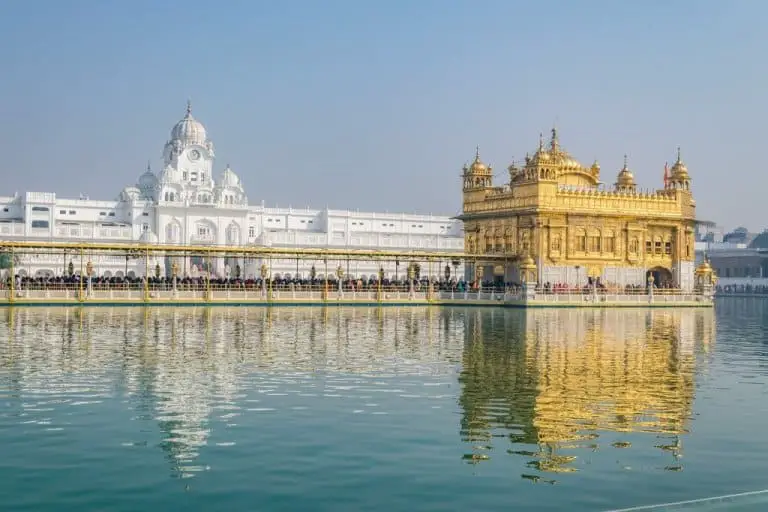

5. Eco-tourism Package
This type of tourism has become one of the fascinating travel forms. Although eco-tourism is more of a travel philosophy, it attracts many tourists. Some eco-tourism destination areas are Kerala, Galgibaga Beach, Goa, and Coorg.
6. Cultural Tourism Package
The social richness of any country draws visitors from every corner of the world to witness sheer celebrations. The cultural tour package offers you a comprehensive exploration of the different shades. Moreover, this package will bring a tourist a closer view of traditions and architecture.
Along with these, we found tourism packages like-
7. Family Tourism Package
A family tour package is designed keeping in mind the family’s needs. It gives assurance of total relaxation and fun pastimes.
The package includes adults, kids, and the elderly. This package includes sightseeing trips, tours of historical places, and adventure trips.
8. Honeymoon Tourism Package
Couples, after their marriages, take a honeymoon tour package, and it provides newlyweds with all the perquisites to make their trip memorable.
The honeymoon tourism package includes lodgings, dining, food & drinks, etc. Famous destinations for a honeymoon tour package are Maldives, Bali, Mauritius, etc.
9. Wellness Tourism Package
Traveling to other places for health and well-being takes a wellness tourism package. Tourists take this package to visit sites that provide recuperation facilities. Wellness tourism has seen a significant boost in the modern years.
Popular destinations for a wellness tourism package are Ayurveda centers, Iceland (for its spas), Bali (for yoga), etc.
10. Cruise Tourism Package
A cruise tourism package provides tourists with a journey filled with fun and recreational activities onboard and excursions onshore.
Tourists get an all-planned ship or boat trip for a specific date to a particular location at a specific price. These packages are curated as per the needs of the tourists.
What are Tourism Products?
According to the market’s needs, the customer supplies anything in the market for use/consumption, called a product.
A product can be offered in the market observation, purchase, use, or any need or demand.
A tourism product is provided to the tourist during their traveling. It mainly focuses on facilities and services designed to meet the needs.
It includes physical objects, services, personalities, places, and ideas. The above components are provided by one company or any group of companies. Tourism products can be given to tourists in a tourist destination.
Products are needed for leisure, pleasure, religious, or business purposes. These products are provided in the market at a cost.
The main reason for choosing a tourist destination is a tourism product. It gives an economic boost to the destination. So it needs to be marketed and stored in a hassle manner.
Services are designed for the visitor to fulfill their needs. Therefore, it is a combination of products. Thus, the country’s total tourism and tourist satisfaction depend on the sum of its attractions, transportation, accommodation, entertainment, etc.
Individual service providers, such as hotels, airlines, travel agencies, etc, provide every element of a tourism product. Therefore, you can analyze these products’ attractiveness, accommodation, and accessibility.
Types of Tourism Products
Attractions: It is one of the main elements. Tourists will not be encouraged to visit certain places without attractions. Attractions are the ingredients. The product determines the choice of a particular tourist to visit a specific destination.
Attractions include archaeological, cultural, and historical buildings, monuments, beach resorts, mountains, flora and fauna, national parks, trade fairs, arts and music festivals, exhibitions, games, etc. Nowadays, tourists are susceptible to changes in fashion.
Accessibility: That means by which a visitor can reach the attraction place. Tourists visit the attraction destination by different transport modes. Visitors visit his predetermined location by car, motorcycle, train , ship or boat, airplane, or cycle.
The place becomes very cheap if any destinations do not have good transport systems. Tourist centers should be located near tourist-producing markets. It is connected to a network of efficient transportation to receive the largest number of tourists.
Accommodation: Another tourism product is accommodation. It is an essential part of tourism—the tourist destination location must-have hotels, guest houses, camping, and homestay. An alternate arrangement should exist if accommodation is not possible at the central location. At least some distance away.
Hospitality: It is a major factor for a tourist destination that will develop in the future. The location’s restaurants, pubs, cafes, foods, and beverage serving style increase location attractiveness.
Natural tourism products: Our nature is beautiful and precious to us. Nature has arranged amazing things in different parts of the world, such as – hills, mountains, caves, glaciers, sea, islands, beaches, waterfalls, rivers, lakes, wildlife, deserts, etc.
The tourism product utilizes those natural gifts as a Natural tourism product, such as snow-capped mountains in Kashmir, Dudhsagar Falls in Goa, palm-fringed beaches of Goa, the wildlife of Kaziranga National Park in Assam, the Thar Desert in Jaisalmer, etc.
Read Things to do in Bainbridge Island, Seattle Washington
Human-created tourism products
Artificial tourism products are those that humans create. Human-made tourism products’ primary purpose is to attract tourists, such as Temples, Forts, palaces, museums, theme parks, etc.
The destination’s tradition and culture play a vital role in tourism. Humans maintain it to attract tourists through- classical dance – music, folk dance, paintings, handicrafts, festivals, fairs, etc.

Examples: Machu Picchu World Heritage Site, Egyptian pyramids , Taj Mahal, Red Fort in Agra, Lothal in Gujarat, Mexican pyramids, or Mesoamerican pyramids are important archaeological sites.
The Bhangra dance form of Punjab, the Kolkata Book Fair, the Durga puja in Kolkata, the Brass work of Muradabad, etc., are also included in human-made tourism products.
Tour guides are another main aspect of traveling. It is also a parameter for tourism. National and international travelers need a travel guide to discover a new place. Sometimes, national travelers may visit any tourist destination on their own.
But an international traveler always wants a good tourist guide. How do you present the location, and how much information do you provide to understand the place? It depends on a guided tour and a travel guide. This parameter upgrades the tourist destination’s level.
What are the different types of tourist destinations?
Types of tourism and types of tourist destinations may sound synonymous. However, the two have slight conceptual differences. Tourism is a broader concept, including the aspects of tourism and hospitality.
At the same time, a tourist destination is a narrower concept applying to places of tourist attraction. Based on the type of place and the causes of interest, the tourist’s destinations are:
- Coastal Destinations – Preferred mostly for the ample sunshine and salty waters lining lands adjoining the sea. Be it domestic or international coastal locations, they are great for fun and relaxation. They are favored mostly by people living in inland areas away from the sea.
- Beaches – The meeting point of land with the ocean offers a great tourist attraction. Waves hitting the shores of sandy beaches are great for tourists. In addition, new beach activities like parasailing, beach biking, etc., also attract tourists immensely.
- Island – A land in the middle of the sea or ocean on all sides is an island. Tourists are taken mainly by boat from the mainland to explore these islands. Islands standing in between a river are called riverine islands.
- Mangroves – It offers a panoramic view amidst the confluence of a river with the sea/ocean. Example: Sundarbans of India.
- Inland Destinations – Travel away from the coast is an inland destination. A variety of sub-classifications can come in under like:
Based on the type of region:
- Hill stations – Offering a surreal view from an altitude, all mountains and hills are great tourist destinations.
- Jungles – Trekking/hiking/driving through the wild greenery are great tourist attractions. Protected areas like Reserve Forests and National Park serve the twin purpose of tourism and conservation.
Based on the population structure
- Rural – For a change, get away from the fast-paced urban life to taste village life. Touring rural locations is gaining popularity because of lower population density, greener areas, and a serene environment.
- Urban – Posh urban destinations offer a pull factor for tourists to experience ultra-modern and urban life. Examples: New York, Shanghai, etc.
- Offbeat – Previously undiscovered newer locations around famous tourist spots are offbeat destinations. With lower tourist popularity, the exclusiveness of these places is retained.
Based on the type of activity
- Hiking and Camping – Places, where tourists come mostly for hiking or camping (day/night), are fast gaining popularity. These places are primarily amidst nature and come under adventure tourism.
- Preserved sites – Sites like UNESCO World Heritage sites have become popular tourist destinations. The rich natural/cultural value owes them their status.
Based on historical/religious importance
- Historical Places & Monuments – Tourists flock to places holding remnants of the past. Areas having historic architecture and events give an insight into the past culture. Examples: Taj Mahal and Jalianwallah Bagh, etc.
- Pilgrimages & Holy Shrines: Religious tourism has flourished here, making it a spiritual destination. Example: Hajj of Mecca, Bethlehem for Christians.
- Museums and buildings: Places where artifacts and remnants of historical culture are well preserved. Famous among tourists of all ages.
Based on entertainment
- Luxury destinations: Locations that only promote high-end tourism are luxury destinations. Example: Bali.
- Carnival: Annually, countries host cultural events to celebrate any occasion for a short period. When tourists travel here to enjoy themselves, it becomes a popular destination. Example: Christmas Carnival in Toronto.
- Amusement Park and Zoo: Famous for the lot is Disney Land, a great tourist destination for children. Singapore Zoo, which ushers in global tourists.

Tourism Destinations
According to UNWTO in the “World’s Top Tourism Destination,” the first four places for International tourism are France, Spain, the USA, and China.
A tourism destination is the endpoint of the journey. But, of course, we all have some goals in every field, so it’s the same with tourism.
There are various types of tourist destinations. They are as follows:-
- Centered Destination
- Based Destination
- Multi-centre Destination
- Touring Destination
- Transit Destination
Types of Tourist Attractions
- Historial attractions
- Cultural attractions
- Political significance
- The natural or scenic beauty
- Leisure travel
- Fun and Amusement
How many Types of Tourism are there in India?
There are 16 Different kinds of tourism in India , but the list may increase.
Is there anything about tourism that I’ve missed?
Over the past 75 years, the travel industry has made great strides in harmoniously uniting strangers, travelers, and locals. As a result, visits and travel are more than adventure, learning new skills, rejuvenating, and achieving perfection.
Tourism has changed from providing services like rooms, flights, and meals that people were satisfied with ten years ago. Now, people want to experience whale watching or mountain biking.
In the luxury sector, wealthy people spend more money on an experience than objects. It is called experience economics, and there is an idea that the memories of tourist values are compared to some physical resources. The rate of global tourists is increasing daily, and every country is trying to make its tourism more developed and successful.
As you can see, the tourism industry is vast and diverse. There are different kinds of tourism here; some have been around for decades, and others are just emerging.
A tour to the Grand Canyon would fall under which type of tourism?
Grand Canyon tour would fall into natural adventure tourism. Here, you can enjoy – The floor Landing Helicopter Tour, ATV, Gold Mine Tour, White Water Adventure Tour, and Rim Airplane Tour.
Kindly Stay 5 Seconds More and Share this Article.
HI TRAVELLER …Myself Ruma Dey Baidya. I’ve been backpacking for the last 20+ years. Photography and travelling have been my passion since my childhood. Whenever I got an opportunity, I never missed it. I am not a solo backpacker, so I always try group travel. I prefer budget travel, and it also helps me to save expenses. We know that memories are not constant, so I decided to document them and created this travel diary. This website [ TheHolidayStory ] is dedicated to those who passionate about travel like me. Please feel free for any information related to my blog. I am always happy to reply. Mail id – ruma[@]theholidaystory.com
How do travel and tourism distribution channels work?

By Kevin Tjoe — 29 Nov 2021
tourism distribution channels
Updated January 2023 – A tourism distribution channel refers to the stakeholders and methods involved in taking a tourism product from the supplier to the consumer. Typically, the chain of distribution in tourism refers to the businesses and platforms involved in selling, distributing, and bundling tourism products. However, more components are involved across the entire distribution chain, including suppliers, wholesalers, resellers, and consumers.
By aligning your business with existing distribution channels, you connect with important stakeholders in the industry. This creates more efficiency in your marketing efforts and ultimately grows your tourism and activity business.
What is a distribution channel?

Tourism distribution channels are the avenues tourism products and services are made accessible to consumers. Typically, tourism products are sold directly by the primary provider or through a series of intermediaries. If brokers or travel wholesalers are involved, this is called indirect distribution. Consumers can access these products via various mediums, including traditional channels such as travel agents, government bodies such as information centers, and even other tour and activity operators .
How it works
While direct bookings may still account for a large part of business, branching out through additional distribution channels can help you to maximize your brand exposure, reduce risk and ultimately boost your bookings. Many distribution channels will have access to much larger marketing spend or broader customer bases. This can provide you with access to more exposure and quality bookings.
Typically speaking you’ll provide your availabilities to them, and they’ll, in turn, bring in bookings at a pre-agreed commission rate.
The chain of distribution
The chain of distribution in tourism refers to the businesses and platforms involved in selling, distributing, and bundling tourism products. This process begins with the primary tour and activity provider all the way to the end consumers experiencing it.
Generally, there are four steps to the distribution chain:
1. Suppliers/principals
2. Wholesales
3. Resellers
4. End consumers
The distribution chain for a particular product can go through all of the steps depending on its distribution channel. For example, direct distribution won’t require wholesalers or resellers, as suppliers sell their products directly to consumers, whereas indirect distribution requires intermediaries.
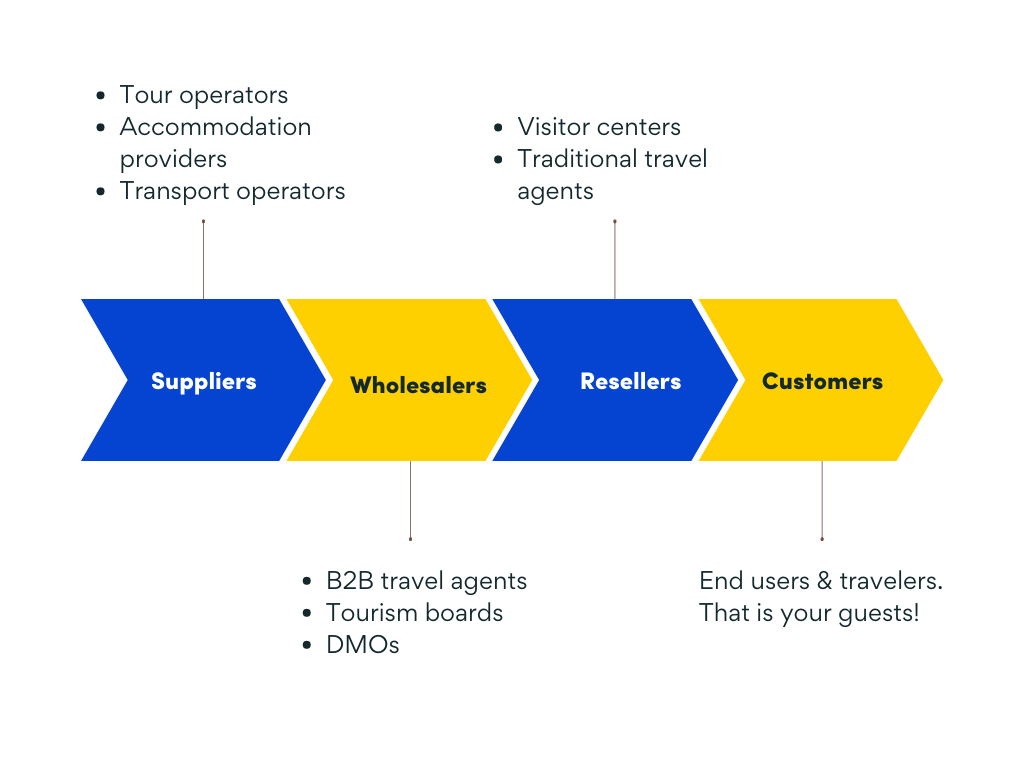
Suppliers or principals include the primary providers across accommodation, transportation and car hire companies, attractions, and experiences. Examples include hotels, Airbnb hosts, airlines, and the attractions such as the Empire State Building.
Wholesalers
Wholesalers develop packages of travel products for retailers to sell on, though in some cases they may actually sell directly to the consumer. These packages or itineraries might include tours, activities, accommodation, transport, and/or travel insurance.
Wholesalers can include:
- Destination Management Organisations (DMOs) or inbound tour operators, such as government tourism boards or tourism authorities
- Global Distribution Systems (GDSs), are used by retailers such as OTAs to easily see an inventory of availability from tourism operators.
Resellers purchase and bundle experiences to be sold directly to the consumer. A common example includes traditional travel agents, which create personalized travel packages. However, online travel agents (OTAs) such as Expedia and Tripadvisor are more commonly used these days. They provide accessibility to a range of tourism products such as airline tickets, hotel bookings, tours and activities, and more.
Consumers are the most critical component of the distribution chain. That is because they are the end user of the product. The choices and decisions consumers make have a huge impact on the rest of the distribution chain. Trends in consumer behavior, or individual decisions all influence how tourism products are marketed and sold.
Advantages of tourism distribution channels

Broadening your distribution channels involve heaps of advantages. Here are the top five:
Connectivity
By aligning your tour and activity business with the broader industry, you can connect with important stakeholders across every step of the tourism distribution chain. Forming strategic partnerships with resellers and tourism platforms enables you to access a broader customer base. This provides you with a greater opportunity to increase your sales.
Generating 100% of your revenue via direct marketing requires a great deal of investment in time and money. Existing distribution channels generally have larger marketing budgets that they can spend to attract more customers.
Typically, as the supplier, you’d only pay a fee when a booking has been made via their channel – making your marketing and sales costs predictable. This means you gain additional resources to expend on other areas of your business, such as improving your customer experience.
Flexibility
Given the wide array of potential partners, you have the freedom and flexibility to test and experiment with different methods of promoting your business. Plus, it’s more convenient for your customers to book your services through an array of trusted partners. This helps to increase customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Transparency
Utilizing existing distribution channels can make the entire booking process more transparent for both you and the end consumer. On the tour operator side, it provides you with a clearer understanding of your customer behavior and adjusts your marketing strategies for better outcomes. And on the customer side, information such as reviews displayed on your profile allows them to create informed decisions before choosing to book your services.
Accessibility
Promoting your tourism products via numerous distribution channels means that your customers can book your services where they like; when they like. Furthermore, your products and services will be found across multiple avenues – enabling a wider array of customers to book with you. In fact, operators are using an average of 14 distribution channels according to Arival’s Operator Insights 2021-2022 report.
What are the main types of tourism distribution channels?

There are many ways to get in front of customers, even more so since the rise of digital channels. From travel agents to mobile apps, tourism suppliers have never had more choices regarding promoting their products and services. There are four main distribution channel types. These include:
Traditional channels
Traditional distribution channels often refer to real-world marketing channels separate from online and mobile experiences. Indirect traditional distribution channels can include travel distribution services such as travel agents, tourism information centers, flyers and print/ digital brochures , promotional marketing services, and tour operators . Depending on your products and services, wholesalers can also make up part of your business’ traditional distribution channel.
Online channels
In recent years, online travel agencies (OTAs) have dominated the tourism industry. These online experiences allow users to plan, book, and pay for personalized travel plans through an easy-to-use centralized platform. Often flights, hotel bookings, car hire , and local experiences can be bundled and purchased through a single site, making the process convenient and intuitive. These platforms can also be cheaper due to the relatively low cost of maintaining a website over a brick-and-mortar travel agency.
Mobile channels
Like online channels, mobile distribution channels rely on digital platforms, such as apps, to promote and sell tourism products. Many popular mobile apps which centralize the tourism buying experience have cropped up in recent years. In addition, airlines, hotels, and other major suppliers have begun developing apps to improve customer loyalty and engagement. Other forms of mobile marketing can include SMS marketing, mobile advertising, and cold calling.
Direct channels
Direct marketing and sales channels include anything your business has direct control over and does not involve an intermediary. This type of marketing can occur through traditional, online, and mobile mediums. For example, direct online channels can include your website, direct bookings via a booking system, online chat assistance, and your social media accounts.
While direct marketing efforts via mobile can consist of sending promotional text messages to previous customers, cold calling potential customers, and sending personalized email marketing messages . More traditional measures may include brochures and flyers, a storefront, and salespeople.
Choosing the right tourism distribution channels
As a tour company, it’s essential to understand which distribution channels will achieve the most significant results for your business. While trial and error can bring results over the long run, understanding what makes a channel right for your business can accelerate your path to success.

Identify target market
To understand whether online or offline marketing, direct or indirect distribution, or mobile versus online platforms are best for your business, you need to understand your customers.
Demographics such as age, country of origin, the number of travelers in a party, and the number of children arriving can greatly impact how you communicate and effectively sell your services. For example, an older demographic may be more likely to use traditional channels such as a travel agent, while a young family might be found via online and social media . First, check over your previous customers and try to pull out any obvious trends amongst your clientele, then research which channels best suit your audience.
Research channels
It’s important to research which channels are available to promote your services. But also, it’s essential to understand the reputation of your potential strategic partners. When engaging in indirect marketing, you are aligning your brand with your distributors, so choosing platforms and businesses which align with your values is important. It’s also essential to understand the costs and benefits of each channel and make informed decisions based on what will work for your business.
Evaluate costs and benefits
Each platform and distribution channel will have different pricing models. Some may charge a flat fee for promotional services, others may purchase and resell your services, while others may charge a fee when you receive a booking. It’s essential to understand what level of return you can expect. If you are starting out, finding performance-based pricing options will allow you to pay as you go. Alternatively, flat fee services can sometimes provide a higher return as your budget can go directly to marketing spend.
Track performance
Once you choose one or more channels to distribute your services, ensure you track the performance versus how much it costs to attain them. By understanding the performance of your partnership, it enables you to eliminate ineffective channels and double down on your marketing efforts, thus, cutting you costs.
How can you manage all distribution channels easily?
It can take a lot of time to form and manage strategic partnerships with multiple resellers. Luckily, technology is here to help. A channel manager such as Rezdy Channel Manager can be accessed regardless of your booking system or size of business, and makes it simple to negotiate agreements, manage inventory, rates and manage commissions with a vast range of resellers, from local visitor centers to the big-name OTAs. Live availability of your tours, activities or attractions are visible from one dashboard, dropping the risk of pesky double bookings as well.
You can access the broadest reach of resellers in the industry, connect with desired resellers and easily distribute rates and availability in real-time. Rezdy is integrated with a number of alternative reservation systems and is continuously adding more, providing suppliers access to channel management tools, directly from their existing system. Suppliers with a custom built booking system can connect with Rezdy Channel Manager as well. For Rezdy booking software customers, channel management is included.
Find out more about how Rezdy’s channel management platform can support your business .
Ready to join the thousands of Rezdy customers that managed to grow their bookings by over 25% in 2022? Book a free channel manager demo with a product specialist to see how our products can fit the needs of your tour business. If you are interested in Rezdy’s booking software that includes channel management, you can start a free 21-day trail trial.
If you enjoyed this article, be sure to sign up to receive the Rezdy newsletter , a valuable resource for those who want to stay up-to-date on the latest industry happenings.
Want to know more about reseller commission rates? Read our guide to industry standard commission rates
Broaden your distribution channels with Rezdy
Enjoy 21 days to take a look around and see if we are a good fit for your business.
No obligations, no catches, no limits, nada
Distribution

eBook: Guide to growing your tourism business through distribution & channel management tools

How to navigate API connections with resellers

Case Study: Wendella Tours & Cruises

What Are Tourism Services Examples?
By Michael Ferguson
Tourism services refer to the various products or facilities that cater to the needs and preferences of tourists. These services can be anything from accommodation, transportation, food, and activities. In this article, we’ll explore some examples of tourism services.
Accommodation Services
One of the most basic and essential tourism services is accommodation. Tourists need a place to stay while they explore a new destination.
Accommodation services range from budget-friendly hostels to luxury hotels. Some popular types of accommodation include:
- Hotels: These are establishments that offer paid lodging typically with amenities like a restaurant, swimming pool, and gym.
- Hostels: These are budget-friendly accommodations that offer communal living spaces such as shared kitchens and dormitory-style bedrooms.
- Vacation Rentals: These are private homes or apartments that can be rented out for short-term stays through websites like Airbnb or VRBO.
Transportation Services
Another crucial component of tourism services is transportation. Tourists need a way to get around a new destination efficiently and safely. Transportation services include:
- Taxis: Taxis are an easy and convenient mode of transportation for tourists who don’t want to rent a car.
- Buses and Trains: Public transportation options like buses and trains are often affordable options for tourists who want to explore a city or region on their own.
- Rental Cars: Rental cars provide tourists with the flexibility to travel at their own pace without relying on public transportation schedules.
Food Services
Food is an essential aspect of any travel experience! Tourists love to try new dishes and explore local cuisine. Some examples of food services include:
- Restaurants: Restaurants offer a wide range of dining experiences from casual to fine dining.
- Street Food: Local street food vendors offer tourists the opportunity to try authentic local dishes and flavors.
- Cafes and Bakeries: Cafes and bakeries are popular spots for tourists to grab a quick coffee or pastry while exploring a new destination.
Activity Services
Tourists often want to engage in activities that allow them to experience the local culture and landscape. Activity services include:
- Tours: Tours can be anything from walking tours of a city to guided hikes through a national park.
- Museums and Attractions: Museums and attractions offer tourists the opportunity to learn about the history, culture, and art of a destination.
- Adventure Activities: Adventure activities like zip-lining, bungee jumping, or white-water rafting provide tourists with an adrenaline rush while experiencing the natural beauty of a destination.
In Conclusion
6 related question answers found, what is tourism industry example, what are the types of tourism services, what is tourism example, what are ancillary services in tourism examples, what is tourism service and who are its user, what is tourism give an example, backpacking - budget travel - business travel - cruise ship - vacation - tourism - resort - cruise - road trip - destination wedding - tourist destination - best places, london - madrid - paris - prague - dubai - barcelona - rome.
© 2024 LuxuryTraveldiva
Typology of senior travellers as users of tourism information technology
- Original Research
- Published: 27 August 2015
- Volume 15 , pages 233–252, ( 2015 )
Cite this article

- Juho Pesonen 1 ,
- Raija Komppula 2 &
- Annina Riihinen 3
1701 Accesses
30 Citations
55 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The importance of senior travellers as a travel segment for the tourism industry is continuously increasing as the number of pensioners increases in the Western world. These new senior travellers differ from earlier generations in many ways, one of which has to do with the increasing use of information and communication technologies as part of their information search process. This study examines senior travellers as users of tourism information technology. A qualitative approach was adopted to provide insights into the topic, and nine Finnish seniors were interviewed. The results were analysed using content analysis. The results show that senior travellers comprise a quite heterogeneous market with respect to the use of tourism information technology. However, there is no special marketing or website design that senior travellers really need: a good website will cater to both the needs of younger as well as older consumers. The study also presents a tentative typology of three different types of senior travellers based on their use of online travel services: Adventurous Experimenters, Meticulous Researchers and Fumbling Observers. This typology contributes to our understanding of the heterogeneous use of tourism information technology by senior travellers.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Senior Travellers as Users of Online Travel Services: A Qualitative Enquiry

Tourism’s Use of Web-Based Information Systems and the Influence of Tourism Trends

The Impact of Ageing on the Tourism Industry: An Approach to the Senior Tourist Profile
Alen E, Losada N, de Carlos P (2015) Profiling the segments of senior tourists throughout motivation and travel characteristics. Current Issues Tour. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2015.1007927
Google Scholar
Amadeus (2007) Future Traveller Tribes 2020. Report for the Air Travel Industry. Developed by Henley Centre Headlight Vision in partnership with Amadeus. http://www.amadeus.com/amadeus/documents/corporate/TravellerTribes.pdf
Backman K, Backman S, Silverberg K (1999) An investigation into the psychographics of senior nature-based travellers. Tour Recreat Res 24(1):13–22
Article Google Scholar
Benckenforff P, Sheldon P, Fesenmaier D (2014) Tourism information technology, 2nd edn
Buhalis D, Law R (2008) Progress in information technology and tourism management: 20 years on and 10 years after the Internet—the state of eTourism research. Tour Manag 29(4):609–623
Czaja S, Sharit J, Ownby R, Roth D, Nair S (2001) Examining age differences in performance of a complex information search and retrieval task. Psychol Aging 16(4):564–579
Daintith J (2012) A dictionary of physics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Dinet J, Brangier E, Michel G, Vivian R, Battisti S, Doller R (2007) Older people as information seekers: exploratory studies about their needs and strategies. Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction. Coping with Diversity. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4554. Springer, Berlin, pp 877–886
Eriksson P, Kovalainen A (2008) Qualitative methods in business research. SAGE Publications, London
Book Google Scholar
Eskola J, Suoranta J (1998) Johdatus laadulliseen tutkimukseen. Vastapaino, Tampere
Eurostat (2015) Internet use and activities. http://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/submitViewTableAction.do
Faranda W, Schmidt S (2000) Segmentation and the senior traveler: implications for today’s and tomorrow’s aging consume. J Travel Tour Mark 8(1):3–27
Finnish Ministry of Employment and the Economy (2006) Suomen matkailustrategia vuoteen 2020 and Toimenpideohjelma vuosille 2007–2013. Elinkeino-osasto. KTM Julkaisuja 21/2006. http://julkaisurekisteri.ktm.fi/ktm_jur/ktmjur.nsf/All/3D61DB118241A034C22571800022FEC4/$file/jul21elo_2006_netti.pdf
Fodness D, Murray B (1997) Tourist information search. Ann Tour Res 24(3):503–523
Gitelson RJ, Crompton JL (1983) The planning horizons and sources of information used by pleasure vacationers. J Travel Res 21(3):2–7
Gummesson E (2000) qualitative method in management research, 2nd edn. Sage Publications, New York
Hartman J, Qu H (2007) The senior travel market. J Qual Assur Hosp Tour 8(2):67–81
Horneman L, Carter RW, Wei S, Ruy H (2002) Profiling the senior traveler: an Australian perspective. J Travel Res 41(1):23–37
Javalgi R, Edward T, Rao SR (1992) Consumer behavior in the U.S. pleasure travel marketplace: an analysis of senior and non-senior travelers. J Travel Res 31(2):14–20
Johnson M (1990) Age difference in decision making: a process methodology for examining strategic information processing. J Gerontol 45(2):75–78
Kamakura W, Kim B-D, Lee J (1996) Modeling preference and structural heterogeneity in consumer choice. Mark Sci 15(2):152–172
Kau AK, Tang YE, Ghose S (2003) Typology of online shoppers. J Consum Mark 20(2):139–156
Kim J, Wei S, Ruys H (2003) Segmenting the market of West Australian senior tourists using an artificial neural network. Tour Manag 24(1):25–34
Klein L, Ford G (2003) Consumer search for information in the digital age: an empirical study of prepurchase search for automobiles. J Interact Mark 17(3):29–49
Kohijoki A-M, Marjanen H (2012) Choice orientation segments of ageing grocery shoppers—an age-related comparison. In: 19th Recent Advances in Retailing & Services Science Conference (EIRASS), July 9–12, 2012. Vienna, Austria
Kotler P, Keller K (2006) Marketing management, 12th edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Kurniawan S, King A, Evans D, Blenkhorn P (2006) Personalising web page presentation for older people. Interact Comput 18(3):457–477
Lambert-Pandraud R, Laurent G (2010) Why do older consumers buy older brands? The role of attachment and declining innovativeness. J Mark 74(5):104–121
Laslett P (1987) The Emergence of the Third Age. Ageing Soc 7(2):133–160
Lohmann M, Danielsson J (2001) Predicting travel patterns of senior citizens: how the past may provide a key to the future. J Vacation Mark 7(4):357–366
Luo M, Feng R, Cai L (2004) Information search behaviour and tourist characteristics. The Internet vis-à-vis other information sources. J Travel Tour Mark 17(2–3):15–25
Manafy M, Gautschi H (2011) Dancing with digital natives: staying in step with the generation that’s transforming the way business is done. CyberAge Books, Medford
Morris M, Venkatesh V (2000) Age differences in technology adoption decisions: implications for a changing work force. Pers Psychol 53(2):375–403
Moschis GP (1994) Marketing strategies for the mature market. Quorum books, Westport
Moschis GP (2003) Marketing to older adults: an updated view of present knowledge and practice. J Consum Mark 20(6):516–525
Newbold KB, Scott DM, Spinney JEL, Kanaroglou P, Paez A (2005) Travel behaviour within Canada’s older population: a cohort analysis. J Transp Geogr 13(4):340–351
Nielsen K (2014) Approaches to seniors’ tourist behaviour. Tour Rev 69(2):111–121
Niemelä-Nyrhinen J (2007) Baby boom consumers and technology: shooting down stereotypes. J Consum Mark 24(5):305–312
Norman W, Daniels M, McGuire F, Norman C (2001) Whither the mature market: an empirical examination of the travel motivations of neo-mature and veteran-mature markets. J Hosp Leisure Mark 8(3/4):113–130
Peacock SE, Künemund H (2007) Senior citizens and Internet technology. Eur J Ageing 4(4):191–200
Pesonen J (2013) Developing market segmentation in tourism: insights from a Finnish Rural Tourism Study. Publications of the University of Eastern Finland. Dissertations in Social Sciences and Business Studies, No 69, Savonlinna
Porter C, Donthu N (2006) Using the technology acceptance model to explain how attitudes determine Internet usage: the role of perceived access barriers and demographics. J Bus Res 59(9):999–1007
Reece W (2004) Are senior leisure travellers different? J Travel Res 43(1):11–18
Reisenwitz T, Iyer R (2007) A comparison of younger and older baby boomers: investigating the viability of cohort segmentation. J Consum Mark 24(4):202–213
Rohm AJ, Swaminathan V (2004) A typology of online shoppers based on shopping motivations. J Bus Res 57(7):748–757
Segdley D, Pritchard A, Morgan N (2011) Tourism and ageing. A transformative research agenda. Ann Tour Res 38(2):422–436
Statistics Finland (2012a) Internetin käytön muutokset. Tieto- ja viestintätekniikan käyttö -tutkimus 2012. Tilastokeskus, Helsinki. http://www.stat.fi/til/sutivi/2012/sutivi_2012_2012-11-07_kat_001_fi.html
Statistics Finland (2012b) Verkkokauppa. Tieto- ja viestintätekniikan käyttö -tutkimus 2012. Tilastokeskus, Helsinki. http://www.stat.fi/til/sutivi/2012/sutivi_2012_2012-11-07_kat_002_fi.html
Statistics Finland (2012c) Internetin käyttö muualla kuin kotona tai työpaikalla 2012. Tieto- ja viestintätekniikan käyttö -tutkimus 2012. Tilastokeskus, Helsinki. http://www.stat.fi/til/sutivi/2012/sutivi_2012_2012-11-07_kat_003_fi.html
Statistics Finland (2012d) Yhteisöpalvelujen käyttö. Tieto- ja viestintätekniikan käyttö -tutkimus 2012. Tilastokeskus, Helsinki. http://www.stat.fi/til/sutivi/2012/sutivi_2012_2012-11-07_kat_004_fi.html
Sudbury L, Simcock P (2009a) A multivariate segmentation model of senior consumers. J Consum Mark 26(4):251–262
Sudbury L, Simcock P (2009b) Understanding older consumers through cognitive age and the list of values: a UK perspective. Psychol Mark 26(1):22–38
Thébault M, Picard P, Ouedraogo A (2013) Seniors and tourism: an international exploratory study on the use of the internet for researching recreational information. Int Bus Res 6(3):22–28
Topo P (2008) Ikääntyminen ja teknologia [Ageing and technology]. In: Heikkinen E, Rantanen T (eds) Gerontologia [Gerontology]. Duodecim, Helsinki, pp 515–522
Vigolo V, Confente I (2014) Older tourists: an exploratory study on online behaviour. In: Xiang Z, Tussydiah I (eds) Information and communication technologies in tourism. ENTER 2014 proceedings. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 439–452
You X, O’Leary J (1999) Destination behaviour of older UK travellers. Tour Recreat Res 24(1):23–34
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Tourism Studies, University of Eastern Finland, Kuninkaankartanonkatu 7, P.O. Box 86, 57101, Savonlinna, Finland
Juho Pesonen
Business School, University of Eastern Finland, Yliopistonkatu 2, P.O. Box 111, 80101, Joensuu, Finland
Raija Komppula
JAMK University of Applied Sciences, Rajakatu 35, P.O. Box 207, 40101, Jyväskylä, Finland
Annina Riihinen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Juho Pesonen .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Pesonen, J., Komppula, R. & Riihinen, A. Typology of senior travellers as users of tourism information technology. Inf Technol Tourism 15 , 233–252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40558-015-0032-1
Download citation
Received : 25 March 2015
Revised : 13 August 2015
Accepted : 13 August 2015
Published : 27 August 2015
Issue Date : October 2015
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40558-015-0032-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Senior travellers
- Information search
- Website design
- Information technology
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

4 Digital Marketing Strategies for B2B Companies
How to write a marketing plan in 9 steps, 5 marketing strategies for events, 4 keys to using instagram for businesses , 5 keys to master sms marketing.

- Acquisition
Tourism Marketing: 4 Strategies to Attract More Tourists
[covid-19] to help mitigate covid’s impact on tourism businesses , kolau is waiving the cost of creating a forbes award-winning website with e-commerce enabled., create your website quickly and easily clicking here – offer available for a limited time only..
?blog_origin=blog-
If you are in the tourism and hospitality industry and are looking to boost your business and increase your bottom line, a better marketing strategy can help. Whether you own a hotel, restaurant, travel agency, or a transport company there are things you can do to help gain visibility, attract customers, and build a loyal following. These four tourism marketing strategies can help you figure out the best way to enhance your business and stay present in the industry.
The travel and tourism industry is one of the largest in the world and has experienced stable growth over the last five years. It’s also a very fragmented industry. According to a report by IBISWorld , it’s estimated that the four main companies in this industry represent less than 10 percent of the total market share.
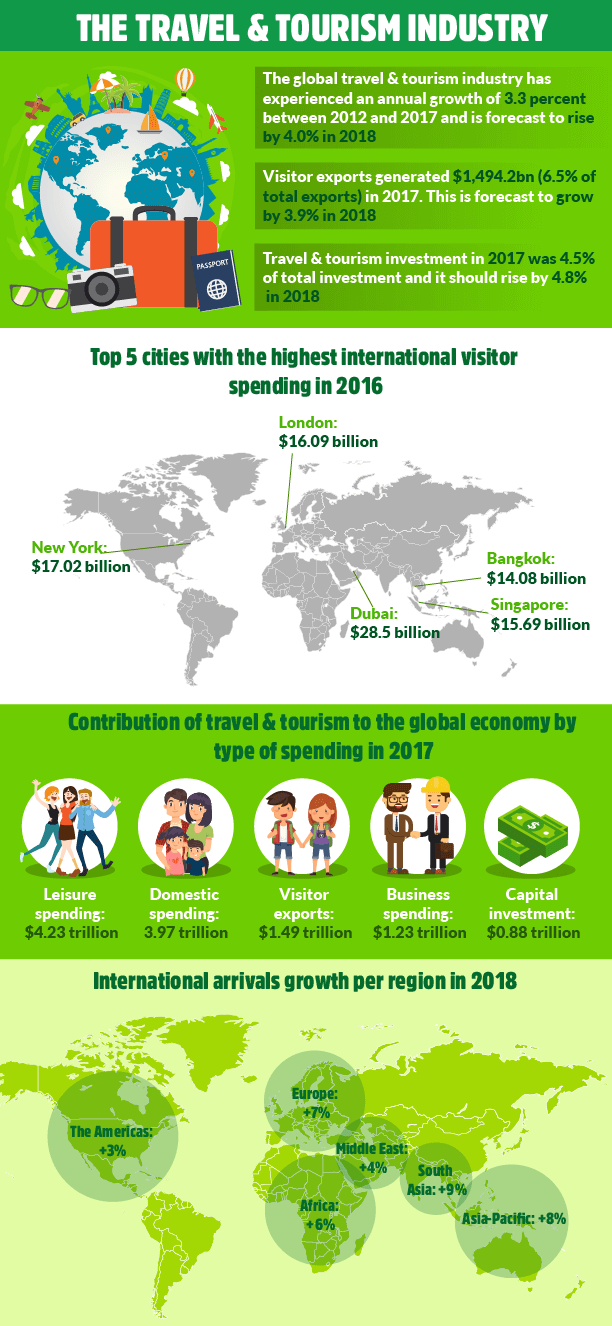
Many segments of the industry are dominated by small businesses and this facilitates access to all those who wish to build their own business. Given this opportunity, implementing the right tourism marketing strategies is crucial to stand out from the competition and to establish yourself as an authority in the industry.
With all the available opportunities for growth and development, creating a solid marketing plan with the four following strategies can be your key to success and the difference between breaking even and making a profit.
#1 Apply storytelling on your social media posts
According to HubSpot , consumers today (among them, tourists) process more than 100,500 digital words a day. Every time they want to know something they ask Google and they can compare prices instantly in three clicks. It’s not that everyone wants to ignore your marketing messages, but given a large amount of information they are exposed to, it’s inevitable that your efforts can get lost in the shuffle. Therefore, it’s necessary to find new ways to communicate to get their attention and get them to interact with your brand .
In a TED Talk , Simon Sinek, founder of Start With Why, said:
People don’t buy what you sell, they buy why you sell it.
When designing your marketing messages on social media it’s not effective to only describe the characteristics of the products or services you offer.
To effectively capture the attention of your target audience and generate more engagement, tell them why your service is made for them while also explaining what they will experience if they decide to buy your product or use your service.
In this sense, stories have enormous power. They generate empathy, transmit confidence, are easy to remember and, most importantly, are easy to share. Storytelling is a technique that allows you to link your product or service with a concrete, symbolic and emotional experience through a story and take advantage of its full potential.
When coming up with stories about your business, try to link them to your product or to the daily activities of your business in subtle ways and put them in your company’s social media posts.
Here are some examples of tourist establishments that use this technique in their Instagram, Facebook and Twitter posts:
If your content on social media doesn’t get “likes” or isn’t shared on Facebook or similar platforms, another proven resource that can help you is creating a mascot or character associated with your brand that acts as the protagonist of your stories.
For example, the travel company Travelocity has associated a traveling gnome with their brand. He appears as the protagonist in several of their publications. In addition, this travel company has created additional social profiles for the character including a fan page on Facebook, a Twitter account and an Instagram account through which they offer exclusive discounts to their followers.
In this way, they manage to promote their trips in an entertaining way that captures the attention of the users, generates engagement and manages to create a community of fans around their character and, therefore, around their brand. On Twitter alone, they’ve got more than 210,000 followers.
#2 Use augmented reality to offer memorable experiences
Within the tourism sector, offering an incredible experience is essential to get customers to remember you, recommend your brand or use your service again. Using new technologies such as augmented reality in your marketing strategy can help you create innovative and memorable experiences for your visitors and, at the same time, differentiate yourself from your competitors.
If you’re not familiar with the term augmented reality, TechTerms provides a very simple definition:
Augmented reality, commonly abbreviated as “AR,” is computer-generated content overlaid on a real-world environment.
Surely you’ve heard of Pokémon Go , a mobile augmented reality game whose launch in 2016 was a massive success. This game uses the GPS of your mobile to locate, capture and engage in battles with virtual creatures (Pokémon). By activating the camera, players can see these creatures through the screen as if they were in a real location. This is augmented reality.
The potential of this technology in the tourism industry is enormous and many tourist establishments are already using it to offer different experiences to tourists. According to a Zenith analysis , in 2018 the pervasiveness of smartphones will reach 66 percent, which means that more than half of the world uses a smartphone.
Hotels were one of the first industries to apply this technology to their marketing actions. For example, the Casa Madrona Hotel in New York used this technology to show tourists walking the street the impressive balcony views of one of its 360-degree suites, as you can see in the following video:
Augmented reality also offers great possibilities for the transportation industry . With a travel app with augmented reality, you could point the camera to a transport vehicle and discover your route, the next stop and places of interest you pass through, something very useful if you are a foreigner.
For example, the transport company, Tunnel Vision , created an app that transforms the New York subway map into an interactive guide in different languages, as you can see in the following video:
According to an analysis of augmented reality published in Harvard Business Review , the three elements that allow the massive adoption of augmented reality apps are:
- Relevant content
- A realistic and compelling interaction of the virtual with the physical environment
- A unique value that goes beyond what other technologies offer
To design a successful augmented reality app that offers a memorable experience, you must make sure it has these three elements.
#3 Create valuable content and optimize your website for SEO
According to a study by Aberdeen , conversion rates are six times higher for those who adopt content marketing than for those who don’t.
Since content marketing is incredibly important, to ensure you get the best results, consider hiring an SEO specialist to help you design a tailored strategy for your business is recommended. That being said, there are things you can do on your own. Here are a few basic tips to help you create a content and SEO strategy for your tourism marketing plan.
- Include a blog on your website and publish content that provides valuable information for your target audience: According to Ascend2, 72 percent of marketers say that creating relevant content was the most effective SEO tactic . Constructing high-quality content that provides valuable information about topics related to your tourism business (such as travel tips or interesting places to visit) can help you increase the authority of your website and, therefore, improve your positioning on Google.
If you manage to publish really interesting posts, they’re more likely to be shared or linked by other sites. This way you will get high-quality inbound links that Google will look at when positioning your website. For example, Jerry’s Motel in Los Angeles incorporates a blog in its website that publishes posts with useful and practical tips for traveling to the city.
- Choose long keywords (more than three terms) that have a high search volume and a low level of competition: According to WordStream, 50 percent of Internet searches have four or more words. You must make sure that the keywords you insert in your content are long and describe your business, products, services or—if it’s a blog post—the subject you are dealing with. Look at the number of times users search for them. This should be a significant figure relative to your pages’ click rates.
Similarly, there will be more chances of getting a good position on Google if the level of competition for your keywords is low. You have tools at your fingertips that help you discover this type of data such as the Keyword planner through Google AdWords, SEMrush or Moz .
- Take care of SEO on your website: There are several factors that influence to a greater or lesser extent the positioning of a website on search engines like Google. SEO experts agree that for Google to position your page or your post for the keyword you have chosen, you must add it in the beginning of the title of the page, in the subtitles , in the first paragraph of the content, repeat it several times throughout the content, in the URL , in the “Alt” tags of the images and in the meta tags (the summaries that appear in the Google’s results pages).
On the other hand, you must also create internal links that allow users to navigate between the different pages of your website. You should also aim to get external links (those that appear on third-party websites and direct visitors to your website). Make sure that your website has a fast loading speed and that it adapts to mobile device screens (responsive design) as Google started penalizing non-responsive websites in 2015.
- Create long and interesting content: Content marketing has changed a lot since Google no longer recognizes short articles with superfluous content. Instead, it gives the first positions to websites that publish pages with long and substantiated content that provides interesting information about a topic. Several studies agree that longer pages or posts tend to get a better position on Google which translates into more traffic. For example, HubSpot discovered that the posts that got more organic visits were those that contained between 2,250 and 2,500 words.
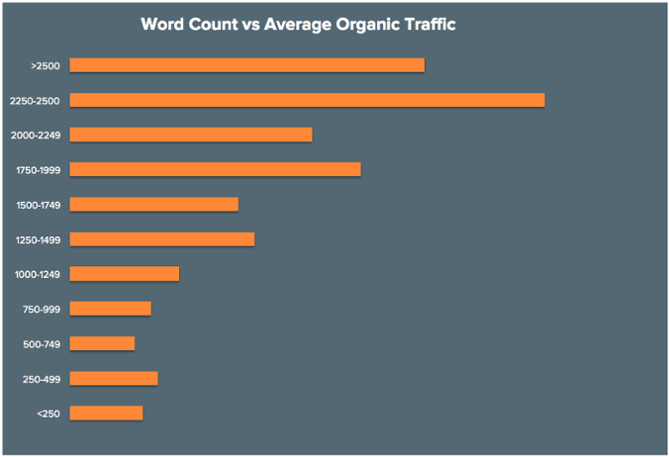
Source: HubSpot
- Create localized content: The tourism sector is a local industry so you can take advantage of this feature to create localized content which will allow you to reduce competition and attract only your potential customers. If your tourism business is located in London, try to create content that deals with topics related to travel and tourism applied to London making sure to include the term “London” in your keywords. For example, a tourist guide agency in London can create a post about “hidden places in London that you have never visited.”
#4 Manage your reviews on TripAdvisor
TripAdvisor is the largest travel review platform in the world and has more than 450 million users and more than 570 million reviews. If you are the owner of a hotel, a restaurant, a theme park or a provider of tourist activities you should know that reviews play an important role in the tourist’s decision. A survey carried out by PhoCusWright reported that 70 percent of travelers read TripAdvisor reviews before choosing a hotel and that 53 percent do not decide to make any reservations before having read reviews .
While it’s true that reviews can be as beneficial as they are harmful to your business, if you manage them well you can avoid having your image seriously affected by a bad review. Responding to negative comments in an assertive and polite manner is the best way to do this. The PhoCusWright survey also revealed that 87 percent of users believe that an appropriate response to a negative review improves their impression of the establishment .
However, you have to be very careful not to create the opposite effect. In order to respond successfully to a negative review you should :
- Respond as quickly as possible
- Do it politely
- Thank the user for sharing his opinion
- Apologize, if necessary
- Demonstrate that your company takes user comments seriously
- Demonstrate that your team will be fully involved to improve the service
- Try to offer a solution whenever possible
Here’s how the Gray Line San Francisco tour company responded cautiously to a negative review on TripAdvisor, following these recommendations:
Even so, you shouldn’t see criticism as a threat since the opinions of your customers can provide you with valuable information to implement improvements in your business and thus offer a better experience to future visitors. You should also know that, according to the PhoCusWright survey, 66 percent of users tend to ignore extreme comments when they read reviews, so while positive reviews predominate, you shouldn’t worry too much about the destructive ones.
Taking into account that the reviews are, many times, a key factor in a tourist’s decision when booking a table in a restaurant, a room in a hotel, a tour or when buying tickets for a theme park, not having a full profile on TripAdvisor means closing doors to a community of more than 450 million users willing to discover new sites and miss a great opportunity to promote your company and generate more sales.
There are also other review platforms that are gaining popularity, such as Yelp , which currently receives about 130 million unique visits and has more than 70 million reviews.
Unlike TripAdvisor, Yelp is not intended exclusively for the tourism and travel industry (there are reviews on all types of businesses), but it has an important base of reviews on restaurants, hotels and other companies operating within the tourism sector. If you want to discover how to incorporate this platform into your marketing plan, read How to increase reviews on Yelp .
The implementation of these four tourism marketing strategies will help you increase the visibility of your business, attract your target audience and get a better return on your marketing investment. Although these techniques can be applied in most cases within the tourism scope, take into account the needs of your business and choose those that best suit it.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Interview with nuh gluten – msme digitalization plan in jamaica, how to increase visibility on google, what is google adsense and how to monetize your hobbies , guide to youtube ads for ecommerce, 4 best practices for local magazine advertising, marketing automation for beginners, marketing para peluquerías: 5 ideas, marketing for clothing store: 5 strategies to better “dress” your business, 3 jewelry marketing ideas to attract more customers, marketing para clínicas veterinarias: 5 estrategias, editor picks, interview with develop digitally limited – msme digitalization plan in jamaica, interview with camaria school – msme digitalization plan in jamaica, interview with health and wellness consultant to travelers – msme digitalization..., popular posts, popular category.
- Strategy 14
- Acquisition 10
- Food Services 5
- Real Estate 4
- Minority-Owned Business 2
- Massage Therapy 2
- Email Marketing 2
- GK for competitive exams
- General Awareness for Bank Exams
- Current Affairs
- Govt Schemes
- Financial Awareness
- Computer GK
- Social Issues
- General Knowledge for Kids
Types of Tourism
- Types Of Resources
- Types Of Sensors
- Types of Surveys
- Types of Transistors
- Types of GST Returns
- Types of Pollution
- Types of Quadrilaterals
- Types of Polygons
- Types of Reflexes
- Types of Seller
- Types of Crops
- Types of Fractions
- Types of Personal Loan
- Types of Business Services
- Types of Chemical Reactions
- Types of Ads Formats
- Types of Tides
- Types of Transmission Technology
- Types of URL
- List of States & Territories in USA - Check the 50 States of the USA
- States and Capitals in India - List of 28 States & 8 UT 2024
- 10 Most Beautiful Women in the World 2024
- Top 10 Most Powerful Country in the World by Military Strength [2023]
- Valentine Week List 2024 : All Day Name from 7 Feb to 14 Feb
- Top 10 IT Companies in the World [2023]
- 7 Colours of the Rainbow - VIBGYOR
- List of Countries by Inflation Rate 2023
- 12 Months Name in English and Hindi
- 7 Continents Name List in Order with Countries, Oceans, & Size
Types of Tourism: The travel and tourism industry plays a big role in many countries’ local economies. Before the pandemic, it made up 10.3% of the world’s total economic output (GDP), and it’s expected to bounce back.
Now, let’s explore the various types of tourism. The UNWTO (UN’s World Tourism Organization) categorizes tourism into three main types: domestic, inbound, and outbound tourism. In this article, we’ll look into the different types of tourism, examining how each is defined.
Let’s get started!
Three Tourism Categories
Domestic tourism.
Domestic tourism means traveling within your own country for business or fun. It’s usually easier to plan than going abroad because you don’t need extra paperwork or health checks. You can just take a domestic flight, bus, or train to your destination. For example, if you live in London and spend the weekend in Manchester, that’s domestic tourism.
Unlike international trips, you won’t face language barriers or culture shock in domestic tourism, which makes it less stressful, at least in most cases.
Inbound Tourism
When you go to a different country, it’s called inbound tourism for that place. For example, if you go from the USA to Spain, it’s inbound tourism for Spain. Inbound tourism is part of international travel. It’s important to get all the needed paperwork ready beforehand. Also, you may have to do extra things like vaccinations and health checks.
Outbound Tourism
Outbound tourism is when you leave your own country to visit another. Using the previous example, if you travel from the USA to Spain, it’s outbound tourism for the USA because you’re leaving the country.
This type of travel involves certain formal requirements, but travel agents know about them and can help make the journey smoother. However, if you prefer going solo, you can handle the paperwork on your own. Numerous online travel agencies specialize in outbound tourism.
Also Read: Significance of Tourism as a Trade
Different Types of Tourism
Here’s a list of different types of tourism:
Also Read: Rural Tourism
Industries Related to Travel and Tourism
When people travel, they require specific facilities and services, leading to a variety of related industries in travel and tourism. These include:
- Hotel and Lodging Services : Accommodations for travelers, such as hotels and lodges.
- Food and Beverage Industry : Restaurants, cafes, and catering services for tourists.
- Transportation : Services that help people move around, like airlines, buses, and rental cars.
- Cultural Industries : Attractions like museums, historical sites, and entertainment venues.
- Tour Operators : Companies that organize and manage guided tours and activities.
- Travel Agencies : Businesses that assist with travel planning, bookings, and related services.
- Industry dealing with Real Estate, Finance, Leasing, and Insurance : Services related to property, finances, rental agreements, and insurance for travelers.
People Also View:
- Tourism Marketing: Meaning, Importance, Types and Strategies
- Road Transport – Definition, Types, Examples
- History of Transportation
FAQs on Types of Tourism
What are the 4 types of tourism planning.
1) Socio-economic development of areas. 2) Increasing employment opportunities. 3) Developing domestic tourism especially for the budget category. 4) Preservation of National heritage and environment.
What is the 5 A’s of tourism?
The five vital components of tourism system are Attraction, Accessibility, Accommodation, Amenities and Activities .
What are the 5 C’s of tourism?
The 5 C’s of Luxury Travel are: Culture, Cuisine, Community, Content and Customization.
What is the difference between travel and tourism?
In simple terms, travel means moving from one place to another, while tourism is organized travel with a specific purpose. Travelers are individuals who prefer spontaneous journeys, avoiding organized tours. They might choose to book accommodation wherever they feel like staying at the moment. On the flip side, tourism comes in various forms, but the relevant ones usually include overnight stays. So, when we talk about tourism, we’re often focusing on the types of travel experiences that involve spending the night somewhere.
What is the most popular type of tourism?
Determining the most popular type of tourism is tricky because it depends on factors like where you are, the time of year, and personal interests. Yet, some widely enjoyed types of tourism include beach vacations, city breaks, cultural and historical tourism, as well as nature and wildlife tourism.
What is sustainable tourism?
Sustainable tourism is a kind of tourism that aims to reduce its harm to the environment and local communities. At the same time, it strives to aid in the preservation of natural and cultural heritage. This type of tourism means traveling in a manner that values and respects the local environment and culture while also promoting the well-being of the local people.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Geography-MAQ
- General Knowledge
- SSC/Banking

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Beyond the ones we listed, there are plenty of other types of tourism, such as medical tourism, religious tourism, wellness tourism, dark tourism, and more. Broadly speaking, however, we could consider leisure and business tourism to be among the two main categories based on travelers' motivation. Categories.
The tourism sector is constantly evolving, expanding beyond the basics of domestic, inbound, and outbound tourism. As travel agencies, it is crucial to stay informed about the diverse range of tourism types to develop effective strategies and fuel the growth of your business. This comprehensive guide presents 62 types of tourism, offering ...
Contents hide 1 Introduction 2 Types of Tourism 2.1 Adventure Tourism 2.2 Cultural Tourism 2.3 Eco-Tourism 2.4 Medical Tourism 2.5 Beach Tourism 2.6 Religious Tourism 2.7 Business Tourism 2.8 Sports Tourism 2.9 Educational Tourism 2.10 Heritage Tourism 2.11 Culinary Tourism 3 Other Types of Tourism 3.1 Annual Holiday Tourism 3.2 Pleasure Tourism 3.3 Relaxation; Rest […]
Travel Marketing School January 8, 2024. Welcome to our ultimate guide to types of tourism! This collection is a comprehensive exploration of the diverse world of travel. In this guide, we delve into an extensive array of tourism types, each offering unique experiences and perspectives on the world. From thrill-seekers to animal enthusiasts and ...
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
You could be taking a cooking class, visiting local producers, sampling the street food, or taking a local wine tour. Of all the tourism types on this list, heritage/historical tourism is one of my personal favourites. 25. Health/Medical Tourism. Medical tourism's similar to dental tourism.
In this article I will tell you all about the main types of travel and give you some examples of each. Contents. The different types of travel. Leisure travel. Short breaks. City breaks. Countryside breaks. Stag and hen parties. Holidays.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest-growing industries and a major foreign exchange and employment generation for many countries. It is one of the most remarkable economic and social phenomena. The word 'tour' is derived from the Latin word tornus, meaning 'a tool for making a circle.'. Tourism may be defined as the movement of ...
6. Culinary Tourism. Culinary tourism is a delightful and immersive way to experience the heart of any destination - its food. It focuses on inviting travelers to try top authentic food of any specific country or region. Travelers savor the flavors, aroma, and traditional cooking techniques of local cuisines.
Bicycle Tours. Eco-Tourism. Geo-Tourism. Sports Tourism. Industrial Tourism. Sustainable Tourism. The two additional types of tourism are international and domestic, as mentioned before. The Best Tips For Using Credit Cards, Withdrawing Cash, and Money Exchanges While Traveling.
A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveller (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travellers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveller and hotels, car rentals, and ...
Tourism and travel-related services include services provided by hotels and restaurants (including catering), travel agencies and tour operator services, tourist guide services and other related services. A crucial aspect of trade in tourism services is the cross-border movement of consumers (mode 2). This permits a variety of workers ...
The Complete Guide to Virtual Tourism. With the COVID-19 pandemic limiting where people have been able to go over the past couple of years, hotels, destinations, and travelers alike have felt the effects. However, creative marketing and new virtual offerings can make a big difference in the years to come. Virtual tourism and travel are taking ...
There are various types of tourism, including cultural tourism, adventure tourism, eco-tourism, and health tourism. Each type of tourism has its unique characteristics and attractions, and they contribute to the growth of the global tourism industry. 1. Cultural Tourism.
So pack your bags, unleash your curiosity, and join Qoni Travel as we unravel the thrilling world of 13 different types of tourism you need to know about! 13 Types of Tourism Adventure Tourism. Embarking on an awe-inspiring escapade filled with adrenaline-fueled thrills is the ultimate recipe for infusing your travel adventures with excitement.
A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveller (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travellers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveller and hotels, car rentals, and ...
Famous cultural tourism places are:-. India - Durga puja in Kolkata, Temples at Banaras, Jaipur, known as the pink city Palace in Rajasthan. Forts and monuments in Delhi, Agra, UP. UK - Tower of London, The British Museum, Big Ben, London Durga puja, etc. Kenya - The main attraction is the dance of the Maasai tribe.
The concept of Tourism as a Service (TaaS) takes inspiration from Mobility as a Service (MaaS), that is, the integration of various transport services into a standalone service the users can plan, book and pay for. MaaS provides a convenient way for more sustainable travel, helping to battle the congestion of road networks (Giesecke et al. 2016).
The chain of distribution in tourism refers to the businesses and platforms involved in selling, distributing, and bundling tourism products. This process begins with the primary tour and activity provider all the way to the end consumers experiencing it. Generally, there are four steps to the distribution chain: 1. Suppliers/principals.
Tourism is the act of traveling to a different location for leisure or business purposes. It can include activities such as sightseeing, visiting historical landmarks, attending cultural events, and enjoying natural attractions. ... Types of Tourism Service: There are various types of tourism services that cater to the diverse needs and ...
The study also presents a tentative typology of three different types of senior travellers based on their use of online travel services: Adventurous Experimenters, Meticulous Researchers and Fumbling Observers. This typology contributes to our understanding of the heterogeneous use of tourism information technology by senior travellers.
The potential of this technology in the tourism industry is enormous and many tourist establishments are already using it to offer different experiences to tourists. According to a Zenith analysis, in 2018 the pervasiveness of smartphones will reach 66 percent, which means that more than half of the world uses a smartphone.
3D virtual tourism allows travelers to explore a place without physically traveling, using smartphones or computers. 59. Dark Tourism. Dark tourism or tombstone tourism involves individuals interested in the history of famous deaths, cemeteries, epitaphs, and gravestone rubbing. 60.