Travel and Expense
What is a travel allowance definitions and insights.
A travel allowance can be an effective way to manage employee travel expenses and manage costs for the employee.
When employees travel for business, there are myriad expenses, from hotels to taxis or ride-sharing services. Using a travel allowance can help give travelers flexibility and control while increasing compliance with tax regulations.

What Is a Travel Allowance?
A travel allowance is compensation paid by an employer to employees to cover expenses incurred when traveling for business. In addition to lodging and transportation, travel allowances are typically used for airfare, meals, and other expenses related to business travel. It is business travel compensation, provided either before or after travel is completed.
Managing business travel compensation can be complex and hard to manage. The way businesses handle travel compensation is changing, as leaders look to implement tools that aid travelers and companies alike.
Technology is transforming how companies manage all aspects of employee travel , including the creation and coordination of travel allowances.
Types of Travel Allowance
There are many types of travel allowances, which can be given upfront or based on a reimbursement schedule. Here is a look at some of the most common.
Fixed Travel Allowance
A fixed travel allowance is a flat rate that is offered to an employee, irrespective of the level of expenses incurred. Employees are responsible for managing their travel expenses and determining how to use the money best to accommodate their needs. It is commonly used with employees for short trips or who travel infrequently.
Typically, with a fixed allowance, if the employee spends less than the allocated amount, the employee can keep the difference. If the employee spends more, they are responsible for making up the difference. Businesses using fixed travel allowance should work with their tax professional to understand the implications of this practice.
Daily Travel Allowance
Also called a per diem, a daily travel allowance is an amount used for each day of travel and can be used for lodging, transportation, meals, and other travel expenses. Typically, a traveler will reconcile the per diem by submitting an expense report and receipts. The traveler will be reimbursed for any expenses they spent in excess and will return money that was unspent.
Travel Reimbursement
This travel allowance requires the traveler to submit receipts for actual expenses incurred, which are then reimbursed. This process can be cumbersome and time-consuming for the traveler. If reimbursement is not done in a timely manner, it can be burdensome for the employee, who is essentially lending money to the company. Fortunately, there are technologies available today to simplify this work.
Mileage Allowance
This type of allowance pays the employee for miles traveled on business. It is typically used when employees use their own car for business-related travel. Technologies can tracking and reimbursing for mileage simpler and more accurate.
Methods for Calculating Travel Allowances
When using travel allowances as part of a corporate travel program, one key consideration is how the travel allowances are calculated.
The process often has to consider the distance traveled and the time spent traveling. Here is one way to calculate a travel allowance.
Location and Days of Travel
Start by determining the location of the traveler at midnight on each day of travel. A day of travel is defined as a 24-hour period an employee is conducting business while traveling.
The day of travel ends when the next day starts or they return home from a business trip to their home or office. For example, if an employee leaves for a trip at 4 p.m., the first day of travel is from 4 p.m. that day until 4 p.m. the next.
Lodging allowances are provided based on whether an employee spends the night in accommodations other than their own home. Typically, lodging allowances are based on the location and the current price rates for various hotel categories, based on company preferences for the level of hotels allowed.
Unlike with other categories, usually lodging is an either/or determination. Employees are either allowed the lodging allowance or not based on the circumstances of the trip.
Like with lodging, meal allowances are usually based on the prevailing costs of meals in each location. It assumes that a traveler will have three meals a day.
Typically, a meal allowance covers both meals and incidentals, such as snacks. Often it is prorated based on the time in any given day a traveler is on the road.
The meal allowance may also be reduced if there are meals provided as part of the work travel, such as part of a conference registration fee or transportation ticket.
Managing Travel Allowances
Managing travel allowances is a complex task. Here are some tips on how to effectively implement and manage a program:
- Develop a Clear Policy. Travelers need to understand the specifics in your travel program and how allowances are used. The policy needs to spell out, for example, what expenses are allowed and not allowed and the ways in which allowances are calculated. Transparency is essential to ensure all employees understand how travel expenses are covered
- Consider Incidentals. Business travelers face many complexities and challenges. You want a policy that makes it easy for travelers to navigate while on the road. Be sure your policy covers costs that may arise, including parking, fuel, tips, laundry services, printing, internet fees, and luggage check fees
- Analyze Data. You need a system in place that collects and reports on travel data to allow you to better understand trends, shifts and challenges. With visibility into your travel program, you can make timely, well-informed decisions
Developing Travel Allowance Policies and Guidelines
If your company wants to develop a travel allowance policy, where should you begin?
The policy should be rooted in a broader travel policy which should consider the following:
- Scope. What aspects of business travel will your policy cover?
- Coverage. Determine which elements of travel the policy will cover, such as air travel, lodging, meals, incidentals, and ground transportation
- Reimbursement Types. Will your company use travel allowances and, if so, which types?
- Participation. How will policies be determined? Be sure to include staff from human resources, finance, and departments that frequently travel, in determining the policy
- Safety. Be sure your policy provides protection for employees while they are traveling
- Expense Reporting. Develop tools or adopt that will be used for the reporting of travel expenses, with an emphasis on scalability, technology integration, and ease of use
Technological Advancements in Travel Allowance Management
Technology is changing the way companies manage business travel . There are powerful platforms available today that integrate travel policies, allow for the booking of travel and itinerary management and provide robust data collection and travel.
Employees need access to easy-to-use tools that allow for the recording of receipts and other transactions, let them reconcile expenses and generate expense reports, and simplify approvals and routing.
SAP Concur solutions can provide companies with integrated business travel, expense, and invoice solutions. With SAP Concur solutions, companies can book travel, manage expenses, integrate with business systems, manage invoices, and more.
Learn more about how SAP Concur solutions can simplify your travel management .
- Accounts Payable Software
- Accounts Receivable Software
- Travel & Expense Management
- Payment Automation
- Cash Flow Management
- Account Payable
- Account Receivable
- Travel & Expense
- Press Release
- Get Started
Travel Allowance: A Guide to Enhance Employee Experience
Managing employee travel expenses efficiently is crucial for both employees and employers. From understanding the types of travel allowance to the reimbursement process , we’ll explore key strategies and roadblocks encountered along the way. In the blog, we will discuss best practices for optimizing employee travel allowance to empower your workforce.
What is Travel Allowance?
Travel allowance is a crucial component of employee compensation, particularly for those who frequently embark on business-related journeys. Essentially, it serves as a reimbursement or coverage for expenses incurred during such trips, encompassing various aspects like transportation, accommodation, meals, and incidental costs.
In other words, travel allowance is a financial aid mechanism that ensures employees aren’t burdened financially when carrying out their professional duties away from the office.
Types of Travel Allowance
- Per Diem Allowance: This is a fixed daily allowance provided to cover meals, lodging, transportation, and other miscellaneous expenses. It offers simplicity and flexibility, as employees receive a predetermined amount for each day of travel, regardless of actual expenditure.
- Reimbursed Expenses: Some companies opt for a reimbursement model, wherein employees pay for their travel allowance upfront and then submit expense receipts for reimbursement. This approach requires thorough documentation but ensures that employees are reimbursed for their actual expenses.
- Flat Travel Allowance: In this scenario, employees receive a fixed amount of money upfront to cover their travel costs. They’re then responsible for managing these funds efficiently throughout their trip.
What is Covered as a Business Travel Allowance?
Business travel allowance typically extends to various aspects of travel, including:
- Airfare: Covering the cost of flights or other modes of transportation required for business travel.
- Lodging: Reimbursing expenses related to hotel accommodations or other lodging arrangements necessary during the trip.
- Meals: Providing funds or reimbursement for meals consumed during the business trip.
- Incidentals: This may include expenses like ground transportation, parking fees, Wi-Fi charges, and other miscellaneous costs incurred while traveling for work.
How Does the Travel Allowance Process Work?
Employees can request travel allowance by following a structured process set by their employer. Here’s a typical step-by-step guide for requesting a travel allowance:
1. Review Travel Allowance Policy
Before requesting travel allowance, employees should review their company’s travel allowance policy to understand the eligibility criteria, covered expenses, and the reimbursement process.
2. Submit a Travel Request
If the travel is planned, employees may need to submit a travel request or travel authorization form. This form typically includes details such as the purpose of travel, dates, destination, estimated expenses, and any pre-approved budget or allowance.
3. Expense Estimates
Based on the travel request, employees should estimate their expenses for transportation, accommodation, meals, and other incidentals. This helps in planning and budgeting for the trip.
4. Travel Approval
Once the travel request is submitted, it goes through an approval process . Managers or the finance team may review and approve the request based on the company’s policies and budget constraints.
5. Travel Booking
After approval, employees can proceed with booking their travel arrangements, such as flights, hotels, and rental cars. It’s essential to keep all booking receipts and confirmations for reimbursement.
6. Submit Expense Report
Upon completion of the trip, employees are required to submit an expense report . This report details all expenses incurred during the trip, along with receipts and any other required documentation.
7. Reimbursement Request
Along with the expense report, employees can request reimbursement for the total amount of expenses incurred or up to the approved travel allowance limit. The reimbursement request should be submitted according to the company’s reimbursement process, which may involve submitting the report through an online portal or directly to the finance department.
8. Approval and Payment
The submitted expense report and reimbursement request are reviewed and approved by the appropriate department. Once approved, the employee will receive payment for the approved amount, either through direct deposit or a check.
Roadblocks Encountered During Travel Allowance Process
Processing travel allowances can pose several challenges for employees. One of the main issues is the complexity of the reimbursement process, which often involves submitting detailed expense reports, collecting and organizing receipts, and adhering to strict company policies. This can be time-consuming and cumbersome, especially for employees who are not familiar with the process or have limited administrative support.
Another challenge is the potential for delays in reimbursement. Due to the manual nature of processing travel allowance, there may be delays in reviewing and approving expense reports, which can result in employees having to wait longer to receive their reimbursement. This can be frustrating for employees, especially if they have incurred significant expenses during their trip.
Additionally, there may be discrepancies in how travel allowance is interpreted and reimbursed. Employees may find it challenging to understand what expenses are eligible for reimbursement and what documentation is required, leading to confusion and potential disputes with the finance department.
Travel allowance processing can result in a frustrating and time-consuming experience for employees, highlighting the need for companies to streamline and simplify the reimbursement process to ensure a smoother experience for all parties involved.
How can Companies Improve Travel Allowance Processing for Employees?
To make the travel allowance processing more efficient and employee-friendly, companies can implement several strategies:
1. Clear Policies
Establishing transparent and easily accessible travel allowance policies is crucial. Clearly outline who is eligible for travel allowance, what expenses are covered, and the reimbursement process. Ensure that employees understand the policies and know where to find relevant information.
2. Utilize Technology
Implementing travel management software can streamline the reimbursement process. This software can automate expense tracking, submission, and approval, reducing manual errors and processing time. It can also provide real-time visibility into travel expenses, helping employees and managers make informed decisions.
3. Monitor and Adjust Per Diem Rates
Regularly review and update per diem rates to ensure they are in line with current travel costs. Consider factors such as inflation, seasonal variations, and changes in travel patterns. Providing competitive per diem rates can help attract and retain talent.
4. Data Analysis
Use data analytics to identify trends and patterns in travel expenses . This can help identify areas where costs can be reduced or processes can be improved. For example, analyzing data may reveal that certain travel routes are more cost-effective, allowing companies to optimize travel plans.
5. Consider Employee Needs
Recognize that business travelers have unique needs. Consider offering additional allowances or support for employees traveling with families or for extended periods. Providing flexibility in travel allowances can improve employee satisfaction and productivity.
Closing Thoughts
Travel allowance plays a pivotal role in facilitating business travel and ensuring that employees are adequately compensated for their expenses. By implementing transparent policies, leveraging technology, and monitoring expenses diligently, companies can optimize their travel allowance programs to benefit both employees and the organization as a whole.
Peakflo’s Travel and Expense Management solution plays a crucial role in simplifying and enhancing the employee travel allowance process. By leveraging Peakflo’s advanced features, such as automated expense tracking, real-time visibility into travel expenses, and seamless reimbursement workflows, companies can streamline their travel allowance processing. This not only reduces the administrative burden on employees but also ensures compliance with travel policies and timely reimbursement.
Peakflo empowers companies to provide a more efficient and employee-friendly travel allowance experience, ultimately enhancing employee satisfaction and productivity.

- travel and expense
Mastering Corporate Travel Policy: Best Practices for Creation and Implementation
The ultimate guide to travel requests: streamlining your business travel process, a comprehensive guide to reimbursable expenses: definition & examples, latest post, ditching legacy systems: the key to a sustainable finance landscape, split payment: streamlining transactions for marketplaces, future-proofing b2b payments: the payment automation handbook, what is the accounting cycle 8 steps explained, uplevelling finance operations with rpa adoption.
- Accounts Payable
- Accounts Receivable
- Travel and Expense Management
- B2B Payment Software
- Invoice Management
- Procurement Software
- Product Tour
- Saving Calculator
© 2023 by Peakflo. All rights reserved.
- English (CA)
- Deutsch (DE)
- Deutsch (CH)
What is a business travel allowance?
Are business travel allowances a legal requirement, what does a business travel allowance usually cover.
- Transportation expenses for additional travel outside employees' regular commute. This can encompass airfares, taxi or local transportation costs, car hire, motorway tolls, parking fees, and standard mileage rates when staff use their personal vehicles.
- A meal allowance for food and drink consumed on the business trip. Usually, this will cover breakfast and dinner only when there has been an overnight travel.
- Accommodation provisions.
- Cover for incidental expenses such as tips and gratuities.
- Entertainment expenses for cases where travelers need to step outside their food and beverage stipend for business meals or drinks with clients.
- Travel insurance policies purchased for the business trip.
- Costs for medical considerations such as vaccinations for international travel.
- Provisions for dry cleaning or other laundry services when employees are required to stay away from their usual work location for extended periods.
What is a per diem allowance?
How can companies standardize their procedures for business travel allowances, how to improve travel policy compliance with travelperk, where can you define your business travel expense policy, what is a realistic business travel allowance.
?)
Make business travel simpler. Forever.
- See our platform in action . Trusted by thousands of companies worldwide, TravelPerk makes business travel simpler to manage with more flexibility, full control of spending with easy reporting, and options to offset your carbon footprint.
- Find hundreds of resources on all things business travel, from tips on traveling more sustainably, to advice on setting up a business travel policy, and managing your expenses. Our latest e-books and blog posts have you covered.
- Never miss another update. Stay in touch with us on social for the latest product releases, upcoming events, and articles fresh off the press.
?)
Everything you need to know about civil service rates for mileage allowance in Ireland
?)
ATO Cents Per KM: 2024 Car allowance guide
?)
Measure these 9 top KPIs for travel management success
- Business Travel Management
- Offset Carbon Footprint
- Flexible travel
- Travelperk Sustainability Policy
- Corporate Travel Resources
- Corporate Travel Glossary
- For Travel Managers
- For Finance Teams
- For Travelers
- Thoughts from TravelPerk
- Careers Hiring
- User Reviews
- Integrations
- Privacy Center
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Modern Slavery Act | Statement
- Supplier Code of Conduct

Travel Allowance: Meaning, Rules & More
What is travel allowance.
An employee may receive a travel allowance from their employer to help cover the costs associated with work travel. This kind of allowance is usually given on top of an employee's base pay or salary and is intended to cover the costs of business travel. The amount of travel reimbursement may differ based on the employer's policies, the nature and length of the journey, and the destination.
What are the Types of Travel Allowances?
Depending on the nature of the job, travel frequency, budget constraints of the company, and more such factors, different types of travel allowances can be offered to an employee.
1. Fixed Travel Allowance
A fixed travel allowance in salary implies that this is a fixed amount offered to the employee irrespective of the actual expenses incurred.
2. Daily Travel Allowance
As the name suggests, a daily travel allowance is offered to employees on a per-day basis, which covers their travel, meals, accommodation, and other such expenses.
3. Mileage Allowance
Employers can also provide a miles-based travel allowance to their employees, which depends on the number of miles they travel for business.
4. Travel Reimbursement
A travel reimbursement depends on the actual expense proofs submitted by an employee, which can include travel by air, rail or road.
The type of travel allowance offered by an employer may depend on various factors such as the nature of the job, frequency of travel, and budget constraints.
What are the Rules Applicable for Travel Allowance?
In India, there are specific tax rules governing travel allowances. Some of the basic travel allowance rules applicable to employees are as follows:
Exemption Limit
The exemption limit for travel allowances is determined by the Indian government and is subject to change. The exemption limit for travel allowance in India is ₹1,600 per month or ₹19,200 per year, as per FY 2022-2023. Read about taxation related to business travel in this blog .
Proof of Travel
The employer needs to provide proof of travel to claim the travel allowance, such as travel tickets, boarding passes, etc.
Actual Expenses
According to the travel allowance rules, if the amount of travel allowance exceeds the actual expenses incurred by the employee during travel, the excess amount is liable for a tax deduction.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
If the amount of travel allowance in salary exceeds the exemption limit, the excess amount is subject to TDS, at a rate of 5%.
Clubbing with Salary
The travel allowance is considered a part of the employee's salary and is subject to taxation accordingly.
Both employers and employees need to understand tax-related travel allowance rules. Employees must keep proper records of travel expenses and provide valid proof to claim the exemption. Employers should also ensure that they deduct TDS at the correct rate and report the travel allowance as a part of the employee's salary in their tax returns.
In conclusion
In conclusion, travel allowances are provided by employers to cover the expenses associated with work travel. Different types of travel allowances, such as fixed allowances, daily allowances, mileage allowances, and travel reimbursements, may be offered based on various factors. It is important for both employers and employees to understand the tax rules and regulations governing travel allowances, including exemption limits, proof of travel, taxation on excess amounts, TDS deductions, and the inclusion of travel allowances in the employee's salary. Compliance with these rules ensures proper documentation and accurate reporting of travel allowances for taxation purposes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. is travel allowance fully exempted.
If the tax allowance amount in an employee’s CTC structure is less than ₹1,600, then the entire allowance would be tax-free. Anything above that is applicable for a standard tax deduction.
2. How do you use travel allowance?
Employees can use travel allowance by opting for road, rail, or air travel within the country.
3. Is travel allowance part of the salary?
Yes, an employer pays a travel allowance in salary to cover the employee's travel expenses. Travel allowance is part of an employee’s cost-to-company and can be claimed annually.
4. Who can claim a travel allowance?
According to the travel allowance rules, employees can claim the allowance to meet travel-related expenses. The eligibility for claiming travel allowance depends on the company's policies, the nature of the employer’s job, and more such factors.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
What Can I Bring?
Planning ahead and packing properly can facilitate the screening process and ease your travel experience at the airport. Know what you can pack in your carry-on and checked baggage before arriving at the airport by reviewing the lists below. Even if an item is generally permitted, it may be subject to additional screening or not allowed through the checkpoint if it triggers an alarm during the screening process, appears to have been tampered with, or poses other security concerns. Read about civil penalties for prohibited items .
- Twitter: @AskTSA
- Facebook Messenger: www.fb.com/AskTSA
- Apple Business Chat: AskTSA
- Text Message: Text "Travel" to AskTSA (275-872)
The final decision rests with the TSA officer on whether an item is allowed through the checkpoint.
Officers may ask you to power up your electronic device, including cell phones. Powerless devices will not be permitted onboard the aircraft. TSA does not read or copy information from your device.

Search by A-Z
Aerosol Insecticide
- Carry On Bags: No
- Checked Bags: Yes (Special Instructions)
Aerosol insecticides are not allowed in carry-on; however they are allowed in checked bags as long as they are not labeled as hazardous material (HAZMAT).
Air Mattress with Built-in Pump
- Carry On Bags: Yes (Special Instructions)
- Checked Bags: Yes
Air mattresses with built-in pump are allowed in carry-on bags. Please check with your airline for any size or weight restrictions.
Airbrush Make-up Machine
Devices containing lithium metal or lithium ion batteries should be carried in carry-on baggage. Most other consumer devices containing batteries are allowed in carry-on and checked baggage.
For more information to portable electronic devices, see the FAA regulations.
Alcoholic beverages
- Carry On Bags: Yes (Less than or equal to 3.4oz/100 ml allowed)
Check with your airline before bringing any alcohol beverages on board. FAA regulations prohibit travelers from consuming alcohol on board an aircraft unless served by a flight attendant. Additionally, Flight Attendants are not permitted to serve a passenger who is intoxicated.
Alcoholic beverages with more than 24% but not more than 70% alcohol are limited in checked bags to 5 liters (1.3 gallons) per passenger and must be in unopened retail packaging. Alcoholic beverages with 24% alcohol or less are not subject to limitations in checked bags.
Mini bottles of alcohol in carry-on must be able to comfortably fit into a single quart-sized bag.
For more information, see FAA regulation: 49 CFR 175.10(a)(4).
Alcoholic beverages over 140 proof
- Checked Bags: No
Alcoholic beverages with more than 70% alcohol (over 140 proof), including grain alcohol and 151 proof rum. For more information, see FAA regulation: 49 CFR 175.10(a)(4).
Check with your airline if ammunition is allowed in checked bags. Small arms ammunitions must be securely packed in fiber, wood or metal boxes or other packaging specifically designed to carry small amounts of ammunition. Ask the airline about limitations or fees. Read the guidelines for traveling with firearms.
When traveling, be sure to comply with the laws concerning possession of firearms as they vary by local, state and international government.
- Carry On Bags: Yes
You may transport this item in carry-on or checked bags. For items you wish to carry on, you should check with the airline to ensure that the item will fit in the overhead bin or underneath the seat of the airplane.
Arc Lighters, Plasma Lighters, Electronic Lighters, E-Lighters
Measures must be taken to prevent unintentional activation of the heating element while on board the aircraft. Examples of effective measures to prevent unintentional activation include, but are not limited to: removing the battery from the lighter; placing the lighter into a protective case; and/or using a protective cover, safety latch, or locking device on the lighter's activation button.
Each lithium ion battery must not exceed a Watt-hour (Wh) rating of 100 Wh; or for lithium metal batteries, a lithium content of 2 grams.
Recharging of the devices and/or the batteries on board the aircraft is not permitted.
See FAA regulations for more information.
Artificial Skeleton Bones
Axes and hatchets, sharp objects, household & tools, sporting & camping, miscellaneous.
Would you like to view this website in another language?
How Leave Travel Allowance Works: A Complete Guide
- Written by: Rinaily Bonifacio
- Last updated: 25 April 2024

This guide will walk you through what Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) is, why it’s beneficial to offer it, and who qualifies for it under U.S. labor laws.
Table of contents
What is leave travel allowance?
Who is eligible to receive lta, leave travel allowance rules for different modes of transport, components of leave travel allowance, how to claim leave travel allowance, frequently asked questions.
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) is a type of benefit employers can offer to their employees to cover travel costs for vacations. Essentially, it's a way to encourage employees to take time off and travel, helping them refresh and return to work re-energized.
This allowance typically covers travel expenses incurred by the employee during their leave. Importantly, under the Income Tax Act, certain conditions allow this allowance to be tax-free, which means employees can claim LTA tax exemption on travel expenses without increasing their net taxable income.
Should you provide leave travel allowance to your employees?
Offering leave travel allowance can be a smart move for your business. Here’s why:
Boosts employee morale : Providing LTA shows that you care about your employees' well-being outside of work. This can boost job satisfaction and improve company loyalty.
Tax benefits : Both you and your employees can enjoy tax exemptions on travel costs. This means while your employees save on taxes, your company can also benefit from reduced payroll taxes.
Attracts talent : In competitive job markets, offering LTA can make your company stand out. Potential hires often look for benefits that enhance work-life balance , and LTA does exactly that.
Eligibility for leave travel allowance is generally outlined by an employer’s policies. Typically, full-time employees are eligible for LTA, but there are nuances depending on the company's specific regulations and the agreements in place. Here are some common criteria used to determine eligibility:
Employment status : Full-time employees are usually eligible, whereas part-time or temporary employees may not be.
Length of service : Some companies require employees to have been with the company for a certain period, e.g., at least one year.
Performance metrics : In some cases, eligibility might be tied to meeting certain performance goals or criteria.
Conditions under which LTA is granted
LTA is not automatically given for any travel. Here are the conditions typically required for an employee to claim leave travel allowance:
Travel with dependents : Often, LTA can be claimed when traveling with family members such as spouses, children, or dependent parents.
Approved leave duration : The travel must occur during a period of approved leave from the company. The duration of this leave might also be specified in the LTA policy.
Domestic travel : Typically, LTA covers domestic travel expenses. International travel may not qualify unless specified by the employer.
LTA offers tax benefits on travel expenses under certain conditions as per the Income Tax Act. These benefits, however, can vary based on the mode of transport used during travel. Here's an overview of how LTA rules apply to different modes of transport:
1. Air travel
Eligibility : LTA covers economy class airfare for domestic flights.
Coverage : Only the airfare for the shortest route to the destination is eligible.
Documentation : Airline tickets and boarding passes must be preserved and submitted to claim LTA.
2. Rail travel
Eligibility : All classes of train travel within the country are covered by LTA.
Coverage : Like air travel, only the fare for the shortest route is considered.
Documentation : Train tickets or e-tickets, along with proof of journey such as reservation slips, are required for LTA claims.
3. Road travel
Eligibility : If the destination is connected by rail but the journey is performed by other modes of road transport, LTA covers first-class or deluxe class fare of such transport, typically up to the amount that would have been incurred if the journey had been undertaken using the highest class of train available to the destination.
Coverage : For places not connected by rail, LTA is allowed as per the first-class or deluxe rate of fare by the shortest route to that place.
Documentation : Bus tickets, taxi receipts, or fare details are necessary when claiming LTA.
4. Waterways
Eligibility : Travel by cruise or ship within the country can also be claimed, but it’s less common.
Coverage : As with other forms, only the fare for the shortest route is eligible.
Documentation : Tickets or proof of travel expenses incurred are needed.
Special considerations:
Combination of modes : In cases where multiple modes of transport are used to reach the destination, each segment of the trip needs to be documented separately, and each needs to adhere to the LTA rules applicable to that mode of transport.
Non-covered expenses : Expenses related to accommodation, meals, and personal entertainment are not covered under LTA, regardless of the transport mode.
International travel : Typically, LTA only covers domestic travel expenses. International travel is generally not eligible for LTA unless specified by the employer.
These rules aim to provide a framework for employees and employers to understand what expenses can be claimed and the necessary documentation needed to support such claims.
Leave travel allowance is a beneficial component in an employee's salary package that helps cover costs associated with travel during leave periods. This section will delve into what types of expenses LTA can cover, what it typically does not include, and the limits and caps that apply to these allowances.
What expenses are covered under LTA?
LTA mainly aims to cover the actual travel costs incurred by an employee during official holidays or leave periods. The primary expenses that can be claimed under LTA include:
Airfare : LTA covers economy class airfare for domestic travel as per the conditions outlined by the Income Tax Act 1961.
Rail and bus fares : Tickets for trains and state-operated buses are eligible for LTA claims, providing they are the shortest routes to the destination.
Taxi fares : In cases where public transportation is not available, taxi fares between the nearest transport hub and the destination can be covered.
It’s important for employers and employees to keep receipts, boarding passes, and other proof of travel, as these are required by tax authorities to claim LTA exemption on these travel expenses.
What is not included in LTA?
While LTA covers a range of travel-related expenses, there are specific costs that are generally excluded:
Accommodation : Hotel stays and other types of lodging are not covered under LTA.
Meals and personal expenses : Food, shopping, and other personal expenditures incurred during travel are not eligible for LTA.
International travel : Only domestic travel within the country is eligible for LTA claims. Expenses for international trips are not included under standard LTA policies.
Housing loan interest : Any interest paid on housing loans during the travel period cannot be claimed as part of LTA.
Understanding these exclusions is crucial for effectively managing and claiming LTA.
Limits and caps on LTA amounts
The limits on LTA are typically defined by the employer's policy and the guidelines set forth by the Income Tax Department. Some common stipulations include:
Frequency of claims : LTA can generally be claimed twice in a block of four calendar years. Unclaimed LTA can sometimes be carried forward, but specific rules apply.
Cap on amounts : There might be a cap on the amount that can be claimed, which usually depends on the actual travel costs incurred. Employers often set these caps based on the level of the employee within the organization.
Financial year consideration : Claims must align with the financial year in which the travel occurred, influencing when and how LTA can be utilized.
Employers need to clearly communicate these limits and caps to ensure that both they and their employees can maximize the benefits of LTA while complying with all regulatory requirements.

Claiming leave travel allowance can significantly reduce employee taxable income by covering some of the travel expenses incurred during your leave. Here's a simple, step-by-step process to help you successfully claim LTA, ensuring you meet all necessary requirements and maximize your benefits.
Step 1. Check eligibility and plan your travel:
Begin by confirming eligibility for LTA with the HR department . Understand the specific terms, such as the allowed frequency of claims and permissible travel periods.
Employees should plan their travel within the scope of these terms, focusing on only domestic travel if international trips are not covered.
Step 2. Undertake the travel:
Once the leave is approved, undertake the travel. Remember, to claim LTA, employee must travel within the country and follow the shortest possible route to your destination.
Keep it in mind that LTA covers only the actual travel costs such as air, rail, or bus fares.
Step 3. Gather required documentation:
During and after the travel, collect all necessary documents that verify travel expenses. These include tickets, boarding passes, and receipts.
Ensure these documents clearly show the dates of travel, the amount paid, and the mode of transportation, as these details are crucial for LTA claims.
Step 4. Submit your LTA claim:
Fill out the LTA claim form provided by the employer. Attach all collected documents as proof of travel.
Submit this form to your HR or accounts department, depending on your company’s policy, within the specified deadline.
Step 5. Verification and approval:
The employer will verify the details of the LTA claim, ensuring all provided documents match the LTA policy’s criteria.
Once verified and approved, the claimed amount will be processed and reimbursed, or adjusted against the taxable income, as per the Income Tax Act 1961 provisions.
By following these steps and ensuring the correct documentation, employees can smoothly claim leave travel allowance and enjoy the tax benefits it offers.
.png?width=323&height=124&name=img-16%20(1).png)
Employee scheduling and Time-tracking software!
- Easy Employee scheduling
- Clear time-tracking
- Simple absence management
Understanding and implementing LTA in the company's benefits package can significantly enhance employee satisfaction and retention , offering both financial and morale-boosting advantages.
By familiarizing yourself with the rules, eligibility criteria, and claiming process outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your organization and its employees make the most out of this valuable benefit. Whether it's improving work-life balance or providing tax-efficient travel opportunities, LTA can be a cornerstone of a more motivated and committed workforce.
Is it possible to carry over unclaimed LTA from one block year to the next?
Yes, unclaimed LTA can be carried forward to the first year of the next block period only. However, it must be claimed in the first year of the new block; otherwise, it will be forfeited.

Can employees Claim LTA in case of a job change?
Yes, employees can claim LTA even if they change jobs, as long as they fulfill the other conditions related to the allowance, such as undertaking the travel and providing necessary documentation within the stipulated time frames of their employment period in each job.
Can LTA be claimed for family members' travel expenses alone if the employee does not travel?
No, the employee must be part of the travel. LTA cannot be claimed for the travel expenses of family members if the employee themselves does not travel. The allowance is intended to cover the travel costs incurred by the employee along with their family.
Written by:
Rinaily Bonifacio
Rinaily is a renowned expert in the field of human resources with years of industry experience. With a passion for writing high-quality HR content, Rinaily brings a unique perspective to the challenges and opportunities of the modern workplace. As an experienced HR professional and content writer, She has contributed to leading publications in the field of HR.
Please note that the information on our website is intended for general informational purposes and not as binding advice. The information on our website cannot be considered a substitute for legal and binding advice for any specific situation. While we strive to provide up-to-date and accurate information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information on our website for any purpose. We are not liable for any damage or loss arising from the use of the information on our website.
Ready to try Shiftbase for free?
- Leave Travel Allowance
- Employee Absence Management
- Emergency Leave
- Leave Management
- Grievance Leave

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Are Travel Expenses?
Understanding travel expenses, the bottom line.
- Deductions & Credits
- Tax Deductions
Travel Expenses Definition and Tax Deductible Categories
Michelle P. Scott is a New York attorney with extensive experience in tax, corporate, financial, and nonprofit law, and public policy. As General Counsel, private practitioner, and Congressional counsel, she has advised financial institutions, businesses, charities, individuals, and public officials, and written and lectured extensively.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/MichellePScott-9-30-2020.resized-ef960b87116444b7b3cdf25267a4b230.jpg)
For tax purposes, travel expenses are costs associated with traveling to conduct business-related activities. Reasonable travel expenses can generally be deducted from taxable income by a company when its employees incur costs while traveling away from home specifically for business. That business can include conferences or meetings.
Key Takeaways
- Travel expenses are tax-deductible only if they were incurred to conduct business-related activities.
- Only ordinary and necessary travel expenses are deductible; expenses that are deemed unreasonable, lavish, or extravagant are not deductible.
- The IRS considers employees to be traveling if their business obligations require them to be away from their "tax home” substantially longer than an ordinary day's work.
- Examples of deductible travel expenses include airfare, lodging, transportation services, meals and tips, and the use of communications devices.
Travel expenses incurred while on an indefinite work assignment that lasts more than one year are not deductible for tax purposes.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers employees to be traveling if their business obligations require them to be away from their "tax home" (the area where their main place of business is located) for substantially longer than an ordinary workday, and they need to get sleep or rest to meet the demands of their work while away.
Well-organized records—such as receipts, canceled checks, and other documents that support a deduction—can help you get reimbursed by your employer and can help your employer prepare tax returns. Examples of travel expenses can include:
- Airfare and lodging for the express purpose of conducting business away from home
- Transportation services such as taxis, buses, or trains to the airport or to and around the travel destination
- The cost of meals and tips, dry cleaning service for clothes, and the cost of business calls during business travel
- The cost of computer rental and other communications devices while on the business trip
Travel expenses do not include regular commuting costs.
Individual wage earners can no longer deduct unreimbursed business expenses. That deduction was one of many eliminated by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017.
While many travel expenses can be deducted by businesses, those that are deemed unreasonable, lavish, or extravagant, or expenditures for personal purposes, may be excluded.
Types of Travel Expenses
Types of travel expenses can include:
- Personal vehicle expenses
- Taxi or rideshare expenses
- Airfare, train fare, or ferry fees
- Laundry and dry cleaning
- Business meals
- Business calls
- Shipment costs for work-related materials
- Some equipment rentals, such as computers or trailers
The use of a personal vehicle in conjunction with a business trip, including actual mileage, tolls, and parking fees, can be included as a travel expense. The cost of using rental vehicles can also be counted as a travel expense, though only for the business-use portion of the trip. For instance, if in the course of a business trip, you visited a family member or acquaintance, the cost of driving from the hotel to visit them would not qualify for travel expense deductions .
The IRS allows other types of ordinary and necessary expenses to be treated as related to business travel for deduction purposes. Such expenses can include transport to and from a business meal, the hiring of a public stenographer, payment for computer rental fees related to the trip, and the shipment of luggage and display materials used for business presentations.
Travel expenses can also include operating and maintaining a house trailer as part of the business trip.
Can I Deduct My Business Travel Expenses?
Business travel expenses can no longer be deducted by individuals.
If you are self-employed or operate your own business, you can deduct those "ordinary and necessary" business expenses from your return.
If you work for a company and are reimbursed for the costs of your business travel , your employer will deduct those costs at tax time.
Do I Need Receipts for Travel Expenses?
Yes. Whether you're an employee claiming reimbursement from an employer or a business owner claiming a tax deduction, you need to prepare to prove your expenditures. Keep a running log of your expenses and file away the receipts as backup.
What Are Reasonable Travel Expenses?
Reasonable travel expenses, from the viewpoint of an employer or the IRS, would include transportation to and from the business destination, accommodation costs, and meal costs. Certainly, business supplies and equipment necessary to do the job away from home are reasonable. Taxis or Ubers taken during the business trip are reasonable.
Unreasonable is a judgment call. The boss or the IRS might well frown upon a bill for a hotel suite instead of a room, or a sports car rental instead of a sedan.
Individual taxpayers need no longer fret over recordkeeping for unreimbursed travel expenses. They're no longer tax deductible by individuals, at least until 2025 when the provisions in the latest tax reform package are due to expire or be extended.
If you are self-employed or own your own business, you should keep records of your business travel expenses so that you can deduct them properly.
Internal Revenue Service. " Topic No. 511, Business Travel Expenses ."
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 463, Travel, Gift, and Car Expenses ," Page 13.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 5307, Tax Reform Basics for Individuals and Families ," Page 7.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 463, Travel, Gift, and Car Expenses ," Pages 6-7, 13-14.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 463, Travel, Gift, and Car Expenses ," Page 4.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 5307, Tax Reform Basics for Individuals and Families ," Pages 5, 7.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TaxHome-3b9f1ac36f6c4e28889c34943d991fc9.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Explore sell to government
- Ways you can sell to government
- How to access contract opportunities
- Conduct market research
- Register your business
- Certify as a small business
- Become a schedule holder
- Market your business
- Research active solicitations
- Respond to a solicitation
- What to expect during the award process
- Comply with contractual requirements
- Handle contract modifications
- Monitor past performance evaluations
- Explore real estate
- 3D-4D building information modeling
- Art in architecture | Fine arts
- Computer-aided design standards
- Commissioning
- Design excellence
- Engineering
- Project management information system
- Spatial data management
- Facilities operations
- Smart buildings
- Tenant services
- Utility services
- Water quality management
- Explore historic buildings
- Heritage tourism
- Historic preservation policy, tools and resources
- Historic building stewardship
- Videos, pictures, posters and more
- NEPA implementation
- Courthouse program
- Land ports of entry
- Prospectus library
- Regional buildings
- Renting property
- Visiting public buildings
- Real property disposal
- Reimbursable services (RWA)
- Rental policy and procedures
- Site selection and relocation
- For businesses seeking opportunities
- For federal customers
- For workers in federal buildings
- Explore policy and regulations
- Acquisition management policy
- Aviation management policy
- Information technology policy
- Real property management policy
- Relocation management policy
- Travel management policy
- Vehicle management policy
- Federal acquisition regulations
- Federal management regulations
- Federal travel regulations
- GSA acquisition manual
- Managing the federal rulemaking process
- Explore small business
- Explore business models
- Research the federal market
- Forecast of contracting opportunities
- Events and contacts
- Explore travel
- Per diem rates
- Transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.)
- State tax exemption
- Travel charge card
- Conferences and meetings
- E-gov travel service (ETS)
- Travel category schedule
- Federal travel regulation
Travel policy
- Explore technology
- Cloud computing services
- Cybersecurity products and services
- Data center services
- Hardware products and services
- Professional IT services
- Software products and services
- Telecommunications and network services
- Work with small businesses
- Governmentwide acquisition contracts
- MAS information technology
- Software purchase agreements
- Cybersecurity
- Digital strategy
- Emerging citizen technology
- Federal identity, credentials, and access management
- Mobile government
- Technology modernization fund
- Explore about us
- Annual reports
- Mission and strategic goals
- Role in presidential transitions
- Get an internship
- Launch your career
- Elevate your professional career
- Discover special hiring paths
- Events and training
- Agency blog
- Congressional testimony
- GSA does that podcast
- News releases
- Leadership directory
- Staff directory
- Office of the administrator
- Federal Acquisition Service
- Public Buildings Service
- Staff offices
- Board of Contract Appeals
- Office of Inspector General
- Region 1 | New England
- Region 2 | Northeast and Caribbean
- Region 3 | Mid-Atlantic
- Region 4 | Southeast Sunbelt
- Region 5 | Great Lakes
- Region 6 | Heartland
- Region 7 | Greater Southwest
- Region 8 | Rocky Mountain
- Region 9 | Pacific Rim
- Region 10 | Northwest/Arctic
- Region 11 | National Capital Region
- Per Diem Lookup
Travel resources
Per diem look-up, 1 choose a location.
Error, The Per Diem API is not responding. Please try again later.
No results could be found for the location you've entered.
Rates for Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. Territories and Possessions are set by the Department of Defense .
Rates for foreign countries are set by the State Department .
2 Choose a date
Rates are available between 10/1/2021 and 09/30/2024.
The End Date of your trip can not occur before the Start Date.
Traveler reimbursement is based on the location of the work activities and not the accommodations, unless lodging is not available at the work activity, then the agency may authorize the rate where lodging is obtained.
Unless otherwise specified, the per diem locality is defined as "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city, including independent entities located within those boundaries."
Per diem localities with county definitions shall include "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city as well as the boundaries of the listed counties, including independent entities located within the boundaries of the key city and the listed counties (unless otherwise listed separately)."
When a military installation or Government - related facility(whether or not specifically named) is located partially within more than one city or county boundary, the applicable per diem rate for the entire installation or facility is the higher of the rates which apply to the cities and / or counties, even though part(s) of such activities may be located outside the defined per diem locality.
City Pair airfares
Visit City Pair Program to learn about its competitive, federally-negotiated airline rates for 7,500+ domestic and international cities, equating to over 13,000 city pairs.
- Search for contract fares
Note: All fares are listed one-way and are valid in either direction. Disclaimer - taxes and fees may apply to the final price
Taxes and fees may apply to the final price
Your agency’s authorized travel management system will show the final price, excluding baggage fees. Commercial baggage fees can be found on the Airline information page.
Domestic fares include all existing Federal, State, and local taxes, as well as airport maintenance fees and other administrative fees. Domestic fares do not include fees such as passenger facility charges, segment fees, and passenger security service fees.
International
International fares do not include taxes and fees, but include fuel surcharge fees.
Note for international fares: City codes, such as Washington (WAS), are used for international routes.
Federal travelers should use their authorized travel management system when booking airfare.
- E-Gov Travel Service for civilian agencies.
- Defense Travel System for the Department of Defense.
If these services are not fully implemented, travelers should use these links:
- Travel Management Center for civilian agencies.
- Defense Travel Management Office for the Department of Defense.
GSA lodging programs
Shop for lodging at competitive, often below-market hotel rates negotiated by the federal government.
FedRooms provides federal travelers on official business with FTR compliant hotel rooms for transient and extended stays (up to 29 days). The program uses FEMA and ADA-compliant rooms with flexible booking terms at or below per diem rates. Federal employees should make reservations, including FedRooms reservations, via their travel management service.
Visit GSALodging for more details on FedRooms and for additional programs offering meeting space, long term lodging, and emergency lodging.
Privately owned vehicle (POV) mileage reimbursement rates
GSA has adjusted all POV mileage reimbursement rates effective January 1, 2024.
* Airplane nautical miles (NMs) should be converted into statute miles (SMs) or regular miles when submitting a voucher using the formula (1 NM equals 1.15077945 SMs).
For calculating the mileage difference between airports, please visit the U.S. Department of Transportation's Inter-Airport Distance website.

Plan a trip
Research and prepare for government travel.
Per diem, meals & incidental expenses (M&IE) Passenger transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.) Lodging Conferences/meetings Travel charge card State tax exemption

Services for government agencies
Programs providing commercial travel services.
Travel Category Schedule (Schedule L) E-Gov Travel Service (ETS) Emergency Lodging Services (ELS) Employee relocation

Travel reporting
Federal Travel Regulation Table of contents Chapter 300—General Chapter 301—Temporary Duty (TDY) Travel allowances Chapter 302 - Relocation allowances
Track mileage automatically
Travel allowance, in this article, what is a travel allowance, how travel allowances work, providing travel allowances in the usa.
A travel allowance is provided to individuals embarking on business trips, work-related travel, or programs across the United States. In this article, learn all about:
- what a travel allowance is
- how it works, and
- how to make sure you follow the regulations around receiving it.
A travel allowance is an amount of money provided to individuals to cover the costs associated with traveling for business, work-related purposes, or as part of a government program. It is designed to reimburse travelers for their expenses while away from home, including meals, lodging, transportation, and incidentals.
Using your personal vehicle to travel for work? Automate business mileage logging with the Driversnote mileage tracker app .
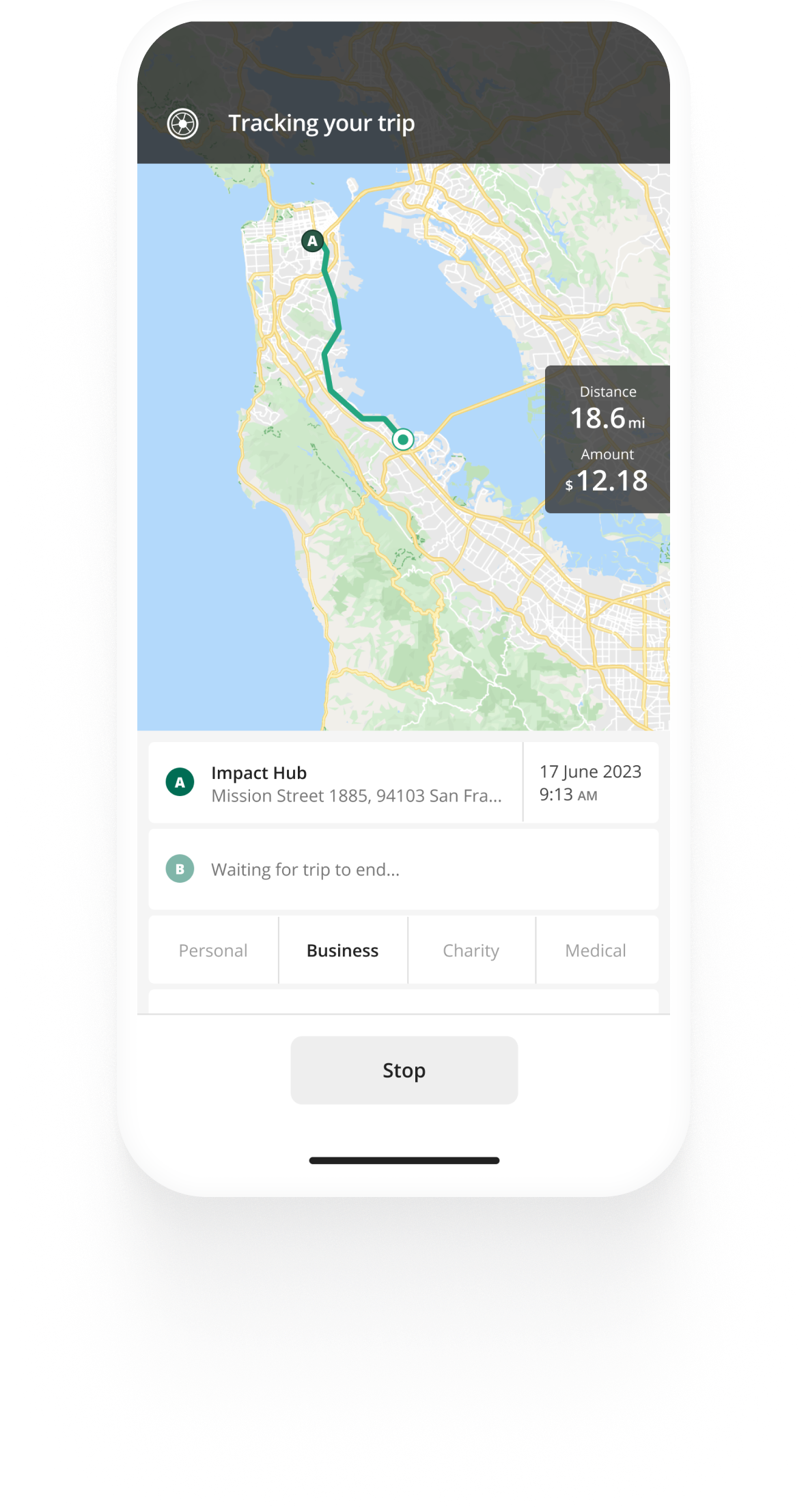
Mileage tracking made easy
Trusted by millions of drivers
When you receive a travel allowance, it is typically provided as a daily or weekly amount, depending on the duration of your trip. The specific allowance may vary depending on factors such as the purpose of travel, destination, and the organization or company you are affiliated with. Travel allowances are governed by specific guidelines and regulations set by the IRS to ensure fairness and transparency.
Travel allowances cover transportation costs, including flights, train tickets, rental cars, taxi fares, or public transportation expenses. Some companies may have their own specific policies regarding the mode of transportation or reimbursement limits.
Besides transportation, travel allowances also include meals, lodging, business calls, dry cleaning and other relevant incidental expenses.
Find out more about receiving employee reimbursement for your meal and lodging expenses and travel-related expenses .
Travel allowances are commonly provided by employers, government agencies, educational institutions, and other organizations. The specific rules and regulations around the allowance can vary depending on your organization and the purpose of travel, but the IRS sets the base for travel allowance payouts and deductions.
Firstly, business travel allowances are available when employees travel away from their tax home or main place of work for business reasons. Travel expenses must be ordinary and necessary. They can't be lavish, extravagant or for personal purposes.
To receive a travel allowance, you will typically need to submit an expense report or a detailed record of your expenses, supported by receipts or other relevant documentation. Adhering to the guidelines and providing accurate information is crucial to ensure a smooth reimbursement process.
How to automate your mileage logbook
Automate your logbook
Related posts, per diem allowance.
Wondering what a per diem allowance is? Learn everything there is to know about these allowances, how they work and if you could receive one.
IRS Mileage Guide
Mileage reimbursement in the US — rates and rules for employees, self-employed and employers in the US.
IRS Mileage Rates 2024
The standard mileage rate for business will be 67 cents per mile, effective Jan. 1st, 2024 - up 1.5 cents from the 2023 rate of 65.5 cents.
Choose your Country or region
UNCLASSIFIED (U)
allowable travel and miscellaneous expenses
(CT:LOG-392; 03-20-2024) (Office of Origin: A/LM)
14 FAM 561 POLICY AND AUTHORITIES
14 FAM 561.1 Policy
(CT:LOG-381; 09-26-2023)
It is the general policy of the U.S. Government that less-than-premium-class accommodations must be used for all modes of passenger transportation. The policies in 14 FAM 567 govern the use of common carrier accommodations and apply to travel while on official U.S. Government business.
14 FAM 561.2 Exercising Care in Incurring Expenses
An employee traveling on official business is expected to exercise the same care in incurring expenses that a prudent person would exercise if traveling on personal business and expending personal funds. Excess costs, circuitous routes, delays, or luxury accommodations and services unnecessary or unjustified in the performance of official business are not acceptable under this standard. Employees will be responsible for excess costs and any additional expenses incurred for personal preference or convenience.
14 FAM 561.3 Authorities
In addition to the authorities listed in 14 FAM 511.4 , the following authorities apply:
(1) State Department Delegation of Authority No. 462, dated January 9, 2019, delegates the Secretary of State's travel authority to the Under Secretary and Deputy Under Secretary of State for Management;
(2) 22 U.S.C. 4081 is the travel payment authorization provision of the Foreign Service Act that provides for a domestic relocation allowance;
(3) The Federal Travel Regulation (FTR) 41 CFR 301.10-124 addresses coach-class seating upgrade programs;
(4) FTR 41 CFR Part 301-13 addresses travel of employees with special needs, and
(5) The General Services Agency's (GSA) FTR Bulletin FTR 09-02, dated 31 Dec. 2008, clarifies the seat choice options and other miscellaneous fees Federal agencies may reimburse their employees while on official travel.
14 FAM 562 EXPENSES ALLOWABLE
14 FAM 562.1 Miscellaneous Expenses not Covered by Per Diem
(CT:LOG-392; 03-20-2024)
a. The following travel expenses, when actually incurred and necessary, can be itemized and reimbursed over and above the per diem allowance for lodging and meals and incidental expenses (M&IE):
(1) Official telephone calls and faxes in connection with official business; internet access fees while performing official business. Reimbursement for expenses must be authorized in advance of travel on the travel authorization;
(2) Commissions for conversion of currency; fees to obtain travelers checks, money orders and certified checks; transaction fees for use of ATMs and other vendors such as hotels when using a U.S. Government contractor-issued charge card. For locally employed (LE) staff who use their personal charge cards and for other travelers who the Department has determined may not be issued a U.S. Government charge card or who have been authorized to use their personal charge cards for official travel, transaction fees for the use of ATMs and other vendors such as hotels may be allowed, if stated on the travel authorization in advance of travel;
(3) Lodging taxes in domestic and nonforeign areas (see FTR, 41 CFR 301-11.27); energy surcharge and lodging resort fees when such fees are not optional;
NOTE : Lodging taxes and mandatory fees in foreign areas are incorporated into the per diem rate for lodging for those areas. In order to be fully reimbursed, the sum total cost of lodging plus mandatory taxes and fees in foreign areas must be within the prescribed lodging component of per diem for that area;
(4) Fees in connection with the issuance of passports and visas and other legally required costs; photographs for passports and visas; certificates of birth, health and identity, and affidavits attesting thereto; foreign country entrance and exit fees;
(5) Inoculations that cannot be obtained for free through a Federal dispensary (reimbursement must be authorized on the travel authorization before travel begins). For yellow fever inoculations, there is no requirement for prior authorization for reimbursement; and
(6) Expenses associated with the transport of human milk expressed by an employee or Eligible Family Member (EFM) while on TDY, approved medical travel, or on PCS travel (including for the authorized PCS travel to post for new infants following a parent's authorized obstetrical medevac) in accordance with the FTR, 41 CFR 301-13.2, up to a maximum of $1000. Reimbursement for expenses must be authorized in advance on the travel authorization and the traveler must submit all receipts, regardless of amount, with the travel voucher. Expenses may include commercial shipping fees, excess baggage, disposable storage bags, cold shipping packages, refrigeration, transport, and non-durable containers. Durable containers that are not reimbursable include canvas, polypropylene, and soft- or hard-sided containers . For special cases of TDY travel where expenses exceed $1000, the traveler may receive reimbursement above $1000 only when authorized in writing by the EX Director (or agency equivalent) of the funding bureau in advance of travel. Such authorization must also accompany the travel authorization and the travel voucher. Travelers are ultimately responsible for arranging all transport of human milk and for handling all related logistics. See 3 FAM 3860 for more information on the Department’s lactation policy.
b. For Agriculture only : Foreign Agricultural Service allows for reimbursement of authorized telephone calls of a personal nature during official travel. For foreign travel, the maximum reimbursement is $15.00 per day. For domestic travel, the maximum reimbursement is $5.00 per day. The maximum aggregate amount that may be approved for each travel period (i.e., consecutive days of official travel) cannot exceed the amount equal to the daily reimbursement rate multiplied by the number of lodging nights. This reimbursement is not an automatic claim and should only be reflected on a voucher if actual expenses were incurred while in a TDY travel status.
c. For USAID only : ADS 633.3.6.1 Financial Management Aspects of TDY, and ADS 549, Telecommunications Management, defines some telephone calls to family as “Official” and allows for reimbursement of those telephone calls when an employee is traveling on government business. See those ADS chapters for further details.
14 FAM 562.2 Transportation Expenses
a. The following transportation expenses, when actually incurred and necessary, can be itemized and reimbursed if not paid directly by the U.S. Government:
(1) Travel on railroads, aircraft, sailing vessels, buses, streetcars, and other usual means of common carrier conveyance;
(2) Transfer, storage, and checking of baggage necessary for the purpose of the official travel;
(3) Charges for transfer, storage, checking, and porters' fees and tips for handling U.S. Government property carried by the traveler;
(4) Transportation charges for authorized excess official baggage;
(5) Shipments by express or freight of U.S. Government property not classed as baggage and not admissible to the mail (normally made on U.S. Government bills-of-lading (GBLs) where feasible);
(6) Packing and necessary preparation for shipment, cost of unboxing at destination, and necessary cartage of unaccompanied baggage or personal effects, or baggage accompanying traveler;
(7) Hire of a boat, automobile, taxicab, aircraft, or other conveyance when authorized or approved as advantageous to the U.S. Government and when employee is engaged in official business within or outside employee's post of duty;
(8) Daily travel to procure meals or lodging at the nearest available place when such cannot be procured at a temporary duty station; and
(9) Transportation by bus, subway, streetcar, taxicab, transportation network company (TNC), or innovative mobility technology company (IMTC) (see 14 FAM 511.3 for definitions):
(a) Between places of business;
(b) Between place of lodging and place of business at a temporary duty station;
(c) Between place of lodging or employee’s home and common carrier transportation terminal in connection with official travel;
(d) From employee's office to a common carrier transportation terminal on the day of departure from the office on an official trip requiring at least one night's lodging.
b. Use of taxicabs, TNCs, or IMTCs (see 14 FAM 511.3 for definitions):
(1) When suitable common carrier transportation is available for travel between points other than those listed above, but the traveler elects to use a taxicab or TNC, or IMTC, detailed remarks noting the circumstances must be furnished on the travel voucher;
(2) Taxicab, TNC, or IMTC reimbursement in excess of $75.00 plus tip must be supported by a receipt along with a statement justifying the use of such conveyance;
(3) The maximum tip allowable under this section is 20 percent of the reimbursable fare;
(4) In lieu of the use of a taxicab, TNC, or IMTC as provided in this section, payment on a mileage basis at the approved rate, as described in 14 FAM 566.2-2 , is allowed for the mileage of a privately owned automobile used for a purpose detailed above, provided that the amount of reimbursement for mileage does not exceed the estimated taxicab, TNC, or IMTC cost, including allowable tip, for transportation between the applicable points;
(5) Membership or application fees, tickets, fines, cancellation fees or fees charged for waiting for the traveler, or other such expenses associated with TNCs or IMTCs are not reimbursable. Only actual usage charges, booking charges, and reservation charges made directly with the TNC or ITMC (not a third-party company) are eligible for reimbursement; and
(6) Travelers may not know prior to beginning a trip what ground transportation options will be available at a particular location. Thus, travel authorizations that contain advance authorization for a taxi, a TNC, or an IMTC are considered to confer authority to use any or all of those ground transportation options. When completing a travel voucher, however, it is necessary to specify whether a taxi, TNC, or IMTC was actually utilized for each instance of ground transportation in order to facilitate preparation of certain congressionally mandated reports.
14 FAM 562.3 Unaccompanied Minor Charges
Most airlines provide a service for children traveling unaccompanied on their airline without the presence of a legal guardian, but fees for this service differ by airplane. This charge is reimbursable when:
(1) The EFM child (16 years of age or younger) is the only individual entitled to travel at U.S. Government expense for the type of official travel authorized (e.g., travel of children of separated families, educational travel, educational allowance, or on authorized or ordered departure); and
(2) The child is engaged in direct travel with no deviation from the authorized itinerary; and
(3) The fee is authorized on the travel authorization in advance of travel.
14 FAM 563 EXPENSES NOT ALLOWABLE
14 FAM 563.1 Items Included in Per Diem
The following items are included within the lodging and/or meals and incidentals (M&IE) portions of the per diem allowance (see definition in 14 FAM 511.3 ) and may not be paid, itemized, or reimbursed separately:
(1) Charges for lodging, including:
(a) Overnight sleeping facilities;
(b) Personal use of room and bath during daytime;
(c) Telephone access fee; and
(d) Service charges for fans, televisions, air conditioning, heaters, microwaves, and refrigerators in rooms;
(2) Charges for meals, including:
(a) Expenses for breakfast, lunch, and dinner; and
(b) Related tips and taxes;
(3) Incidental expenses, including:
(a) Fees and tips given to waiters, porters, baggage handlers, bellhops, hotel personnel, restaurant staff, and similar employees;
(b) Transportation between place of lodging or business and places where meals are taken, except as specified in 14 FAM 562.2 , subparagraph a(8); and
(c) Bottled water;
(4) Complimentary meals provided by common carriers or hotels (e.g., complimentary breakfast meals on airplanes, etc.) have no impact on per diem rates paid per FTR, 41 CFR 301-11.17.
14 FAM 563.2 Personal and Other Expenses
Costs of a personal nature are not reimbursable, such as:
(1) Personal telephone calls or faxes, including messages, requesting leave, inquiring as to status of salary, expense vouchers, advance of funds, and reply thereto, or any other matter of personal nature. This section does not apply to Agriculture or USAID employees (see exceptions for Agriculture employees in 14 FAM 562.1 , paragraph b, and for USAID employees in 14 FAM 562.1 , paragraph c);
(2) Internet access fees for conducting personal business; internet service provider (ISP) fees (e.g., monthly charges for satellite, fiber, cable, or DSL internet access);
(3) Transaction fees for use of ATMs and other vendors, such as hotels, with a personal charge card except when authorized in accordance with 14 FAM 562.1 , subparagraph a(2);
(4) Laundry, dry cleaning, and pressing when traveling OCONUS or when traveling in CONUS for less than four consecutive nights;
(5) Alcoholic beverages;
(6) Entertainment expenses;
(7) Any expenses incurred for other persons; and
(8) Miscellaneous service fees (i.e., administrative, booking, and third-party fees) resulting from booking transportation or lodging outside a government-contracted travel management center or government lodging program (e.g., FedRooms).
14 FAM 564 Fare types
14 FAM 564.1 Unrestricted Fare Policy
(CT:LOG-381; 09-26-2023) (State and USAID)
a. In general and when possible, the Department utilizes the lowest-cost unrestricted fares available for travel between authorized origin and destination, respecting the terms of the General Services Administration (GSA) city-pair program, for all official travel.
b. An individual may request the purchase of a restricted or penalty fare for official travel based on personal convenience (e.g., taking an indirect route for personal reasons or wishing to travel in a class of service other than the one authorized), but the individual is responsible for any and all additional costs and/or penalties incurred in connection with such fares regardless of whether those costs are due to official or personal reasons. See 14 FAM 561 for an employee's responsibility to exercise due care.
c. When an individual is authorized an unrestricted fare but engages in indirect (cost-constructed) travel and elects to use a restricted fare, the cost of that restricted fare, in the class of service and the route used by the traveler, must be compared to the cost of an unrestricted fare along the authorized route in the authorized class of service in order to determine whether the individual’s deviation results in an additional cost to the U.S. Government:
(1) If an additional cost would be incurred because of the individual’s decision to engage in indirect travel and/or travel in a class of service other than the one authorized, the individual must pay, to the TMC or air carrier issuing the ticket, the difference in fare between the restricted fare elected by the traveler and the unrestricted fare that would have been purchased by the U.S. Government; and
(2) If no additional cost would be incurred, the U.S. Government may purchase the restricted fare along the indirect route and/or in the class of service other than the one authorized. Any cost saving associated with the purchase of a restricted fare in this case is not transferrable to the traveler, and a fare saving may not be used to offset change or cancellation fees incurred as a result of the individual’s decision to use a restricted fare.
d. Whenever a cost comparison is made, documentation of the specific flight itineraries and their respective costs must be retained and included in the travel authorization for future reference and to meet auditing requirements.
14 FAM 564.2 Restricted Fare Policy
a. Restricted penalty fares should be authorized for official travel only when their use is practical and economical to the U.S. Government. Round-trip tickets with such fares should be authorized only when, based on the journey as planned, the traveler knows or reasonably anticipates that such tickets will be utilized in accordance with their restrictions (see 14 FAM 542 for details of contract city-pair fares). The use of prohibited ticketing practices, such as “throw-away,” “hidden city,” or “back-to-back” ticketing, is not permitted for any part of either authorized or cost constructed travel itineraries because those tactics violate air carrier contracts of carriage.
b. A mission or bureau has the option of developing a policy requiring the use of restricted, penalty fares subject to the conditions set out in paragraph a of this section. The authorizing mission or bureau will assume financial responsibility for any penalties associated with these fares, should changes or cancellations be required by the U.S. Government. The employee will be responsible for any penalties incurred for personal convenience.
c. If a mission or bureau chooses to use restricted, penalty fares, the mission or bureau must provide the travel management center with a written policy for the use of these fares and the appropriate fare type (restricted or unrestricted) must be indicated in the remarks of each travel authorization. At posts where a travel management center does not exist, the written policy must be provided to the travel section in the general services office.
d. When an employee is authorized a restricted fare under 14 FAM 564.2 , paragraph b, and engages in indirect (cost-constructed) travel also using a restricted fare, penalties incurred due to changes or cancellations required by the U.S. Government are reimbursable up to the cost that would have been incurred for similar modifications to the authorized routing. The employee will be responsible for any penalties incurred for personal reasons.
14 FAM 564.3 Disposition of Airline Promotional Items
a. All Department employees, their dependents, and others whose travel is funded by the Department may retain for personal use promotional items (i.e., frequent flyer miles, upgrades, access to carrier lounges) earned from official travel under terms available to the general public and at no extra cost to the U.S. Government.
b. Travelers may accept free upgrades of services to business-class or first-class accommodations if they are obtained under terms available to the general public and at no extra cost to the U.S. Government.
c. Travelers may redeem frequent flier miles (or use personal funds) to upgrade to business or first-class accommodations when performing official travel.
d. It is the responsibility of each traveler to communicate directly with a service provider to establish his or her frequent travel promotional benefits account. Costs associated with establishing this account are to be paid by the traveler and are not a reimbursable expense.
e. Travelers need not report as taxable income promotional items obtained from official travel.
14 FAM 564.4 Compensation Received from Airlines for Denied Boarding
a. Voluntary : A traveler may keep payments from a carrier for voluntarily vacating a transportation seat. However, no additional expenses (per diem or miscellaneous reimbursable) may be paid because of the traveler’s delay. Additional travel expenses incurred because of voluntarily giving up a seat are the traveler’s financial responsibility.
b. Involuntary : If a traveler is involuntarily denied a transportation seat, the traveler enters an onward travel status for per diem and miscellaneous travel expense reimbursement. Any monetary compensation (including meal and/or lodging vouchers) for the denied seat belongs to the U.S. Government.
14 FAM 565 CANCELED RESERVATIONS
14 FAM 565.1 Service/Cancellation Expenses
When a train, sailing vessel, or hotel reservation is canceled because of unavoidable, nonpersonal delay or because of official necessity, the cost of a service fee or cancellation expense charged by the service provider is allowed. Fees paid for cancellations of reservations for personal reasons or avoidable delays in notifying the service provider are not reimbursable.
14 FAM 565.2 Liquidated Damage Payments to Traveler
a. When carrier tariffs require liquidated damage payments to travelers for the carrier's failure to provide confirmed reserved space, such payments by the liable carrier are to be by check, made payable to the "Treasurer of the United States." In no case is the traveler permitted to accept from the carrier a check showing the traveler as payee.
b. The traveler is to acknowledge receipt of the check and submit a copy of the acknowledgment and the check with travel voucher. Payment of denied boarding compensation to the Treasurer of the United States is a U.S. Government requirement and is no reflection on the carrier (see 4 FAM 470 ).
14 FAM 566 TRAVEL BY PRIVATELY OWNED VEHICLE OR PRIVATELY OWNED CONVEYANCE
14 FAM 566.1 Policy
a. Travel by common carrier is generally considered the most advantageous method to perform official travel. Other methods of transportation may be authorized if they are determined to be more advantageous to the U.S. Government. A determination that another method of transportation is more advantageous to the U.S. Government than common carrier transportation will not be made based on personal preference or inconvenience to the traveler.
b. In determining whether the use of a privately owned vehicle is advantageous to the U.S. Government, consider:
(1) The feasibility of using common carrier transportation or U.S. Government-owned conveyances based on availability, suitability of schedules, and other applicable requirements;
(2) The total cost to the government, including per diem, overtime, lost work time, actual transportation costs, total distance of travel, number of points visited on official travel, the number of travelers, and energy conservation;
(3) The advantages resulting from the more expeditious transactions of the public business, economy, and employee performance effectiveness; and
(4) Any other advantages and/or disadvantages to the U.S. Government in the particular case.
c. The authority to travel by privately owned vehicle (POV) contained in this section is applicable to the employee and/or other family member(s) authorized to travel. The vehicle to be used must be the property of the employee or family member prior to the initiation of travel and must be driven or shipped to the ultimate destination stipulated in the travel orders. Only such vehicles as are eligible for shipment at U.S. Government expense are authorized to be driven on a mileage per diem basis under this provision.
d. Any reimbursement for travel by POV, under the mileage (see 14 FAM 566.2-1 ) per diem basis authorized by this section is limited to the actual mileage between authorized points on a direct route plus related per diem, not to exceed 10 days to each authorized destination.
14 FAM 566.2 Use Advantageous to the U.S. Government
14 FAM 566.2-1 General
(CT:LOG-388; 01-19-2024)
a. When the authorized travel from origin to destination (combined with TDY, consultation and/or home leave, as applicable) can be performed entirely using a privately owned vehicle (POV), such use may be authorized.
b. Travel by POV to separation address in the United States, when not otherwise covered under 14 FAM 566.1 , is hereby authorized from the port of discharge of the vehicle to the separation address via consultation point (as applicable). In accordance with 14 FAM 618.4 , however, this authorization does not apply to vehicles acquired en route to a separation point.
c. When an employee's vehicle is authorized emergency storage in accordance with 14 FAM 626 , an authorizing officer may determine that it is advantageous for the vehicle to be driven all or part of the distance to the designated storage point.
d. An employee who acquires a vehicle at a point on a direct route to the post of assignment abroad, and who has not previously shipped a vehicle under the provisions of the authorizing travel orders, may drive the POV to the destination. The point of acquisition is considered the point of origin. In no case may the cost of driving the vehicle from where it is acquired exceed the cost to the U.S. Government had the vehicle been shipped from the point of origin specified in the travel authorization to the authorized destination.
e. Travel by a POV is considered advantageous to the U.S. Government when the authorized or actual point of origin and the final destination are:
(1) Connected by a hard-surface, all-weather highway or by vehicular ferry, or both (see 14 FAM 615.1 ); and
(2) Within the continental United States or Canada or one of the following Mexican border posts:
(a) Ciudad Juárez;
(b) Matamoros;
(c) Nuevo Laredo;
(d) Tijuana; or
(e) Nogales.
f. When use of a rental vehicle in the United States is authorized, reimbursement for rental fees and actual expenses for fuel (gas, diesel, electricity, etc.) and tolls is authorized. U.S. Government-contracted rental vehicle services should be used whenever possible. Collision damage waiver (CDW) is included in the contract amount and should not be accepted at extra cost. When renting from companies not on the U.S. Government contracting list, travelers will not be reimbursed for CDW. However, payments for damages to a rental car company or reimbursement to the employee, up to the deductible amount contained in the rental contract, are authorized, providing the employee was acting within the scope of his or her employment at the time of the incident.
g. When use of a rental vehicle abroad is authorized, reimbursement may include rental fees, including value added tax (VAT), and actual expenses for fuel and tolls. U.S. Government-contracted rental vehicle services should be used whenever possible. The contract rate includes CDW, VAT, and unlimited mileage. When renting from companies not on the U.S. Government contracting list, CDW, VAT, and unlimited mileage will not usually be included. CDW is a reimbursable expense abroad. In addition, payments for damages to a rental car company or reimbursement to the employee are authorized up to the deductible amount contained in the rental contract, providing the employee was acting within the scope of his or her employment at the time of the incident.
h. When use of a rental vehicle is authorized for official travel, the least expensive “compact” car available must be used unless one of the following exceptions for another class of vehicle applies and is indicated on the travel authorization:
(1) When use of other than a compact car is necessary to accommodate a medical disability or other special need, and all applicable requirements set forth in 41 CFR 301-10.450(c)(1) have been met;
(2) When additional room is required to accommodate multiple employees authorized to travel together in the same rental vehicle;
(3) When security circumstances (as defined in writing by DS or the RSO) require a larger vehicle;
(4) When necessary for other safety reasons, such as during severe weather or having to travel on rough or difficult terrain;
(5) When travelers must carry a large amount of U.S. Government material incident to their official business, and a compact rental vehicle does not contain sufficient space; or
(6) When the cost of other than a compact car is less than or equal to the cost of the least expensive compact car.
i. For non-electric rental vehicles, t ravelers may not be reimbursed for purchasing prepaid refueling options. Therefore, travelers must refuel prior to returning the rental vehicle to the drop-off location. NOTE : If it is not possible to refuel completely prior to returning the vehicle because of safety issues or due to the location of closest fueling station, travelers will be reimbursed for vendor refueling charges. For electric rental vehicles, travelers may be reimbursed for pre-paid charging costs and/or necessary costs paid via credit card or billed back to the rental vehicle company to recharge the vehicle before return.
j. Travelers will not be reimbursed for fees associated with rental car loyalty points or the transfer of points charged by car companies.
14 FAM 566.2-2 Mileage Reimbursement
Mileage reimbursement rates for automobiles (including trucks, vans, etc.), airplanes, motorcycles, and motor scooters are set by GSA. The current rates may be found on the GSA website.
14 FAM 566.3 Privately Owned Vehicle (POV) Use for Personal Convenience
14 FAM 566.3-1 General
When no determination of advantage to the U.S. Government is made (see 14 FAM 566.2 ), the employee may elect to use a privately owned vehicle for personal convenience. Any reimbursement for expenses for travel will be the lesser of:
(1) Mileage for the authorized mode of travel at the rates provided in 14 FAM 566.2-2 , plus related per diem; or
(2) For the portion of the route connected by air service, reimbursement may not exceed the constructive cost of the authorized U.S. Government fare for the authorized mode of travel on a direct route, plus related per diem and other expenses. For any portion of the route not connected by air service, reimbursement may not exceed the constructive cost of commercial fares on a surface common carrier.
14 FAM 566.3-2 Use of Rental Vehicle
When the employee elects to use a rented vehicle for personal convenience, and use of the rental vehicle has not been specifically authorized, per 14 FAM 566.2-1 , paragraphs f and g, reimbursement for travel expenses will be the lesser of:
(1) Mileage, plus per diem and other expenses allowable on the authorized mode of transportation stated in the travel authorization; or
(2) The constructive cost of the U.S. Government airfare on a direct route, plus per diem and other expenses. For any portion of the journey not connected by air service, reimbursement may not exceed the constructive cost of less than premium-class accommodations on a surface common carrier.
14 FAM 566.4 Computing Expenses
14 FAM 566.4-1 Distances
When travel is performed by a privately owned motor vehicle, distances are to be determined by use of standard highway mileage guides. Travelers must explain any substantial deviation from distances shown in the standard highway mileage. When travel is performed by privately owned airplanes, distances are to be determined from airways charts issued by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce. If a detour is necessary on account of adverse weather, mechanical difficulty, or other unusual conditions, the additional highway or charted air mileage may be included but must be explained.
14 FAM 566.4-2 Allowable Travel Time
Allowable time for travel by privately owned conveyance is limited to that which is reasonably required. Variations in driving conditions do not permit the establishment of daily mileage requirements. In the United States, however, 360 miles per day is considered the average normal driving distance. Where road, climate, and other factors beyond the control of the traveler cause interruptions and deviations resulting in longer than normal travel time, the traveler will include a full explanation on the travel voucher. The traveler must also explain any unusual circumstances that influence the elapsed time for travel by privately owned aircraft.
14 FAM 566.4-3 Shared Expenses
When two or more authorized travelers share the same privately owned conveyance, payment of mileage expenses is made to only one of them.
14 FAM 567 ACCOMMODATIONS
14 FAM 567.1 Accommodations on Trains and Vessels
a. U.S. Government employees who travel by train or sailing vessel (ship/ferry) are authorized the lowest class of accommodation on the train or sailing vessel. For overnight train travel, employees must use slumber coach sleeping accommodations or the lowest level of economy sleeping accommodations available. For overnight travel on a sailing vessel, employees must use the lowest-cost stateroom. First-class train or steamer accommodations may be used only as permitted in 14 FAM 567.1-2 .
b. In some countries, the lowest class of train or sailing vessel service available locally may be considered by posts to be unacceptable by U.S. standards and not comparable to what would be considered as a reasonable basic class of accommodation as defined in 14 FAM 511.3 . For example, train service described as first class at some posts may only equate to the coach-class definition in the United States. Accordingly, posts may establish a policy re-defining the acceptable level of local train accommodations that would meet each definition and document this in a written policy for travelers, inspectors, and U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) auditors.
c. If a train has only two classes of accommodation available (i.e., first and business), then the business class accommodation is deemed to be classified as coach class for the purposes of official travel since it is the lowest class offered. In such cases, the travel authorization should reflect that use of the lowest class of service available is authorized. While such travel may take place in the train’s business class compartment, is not reportable to GSA as premium class travel and no Form DS-4087 is required.
14 FAM 567.1-1 Authorization and Approval for the Use of Business- or First-Class Train or Sailing Vessel Accommodations
a. First class : Heads of agencies, or their designees as listed in 14 FAM 567.2-3 , may authorize or approve the use of first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations under criteria specified in 14 FAM 567.1-2 .
b. Business class : Officials listed in 14 FAM 567.2-4 may authorize or approve the use of business-class train or sailing vessel accommodations under criteria specified in 14 FAM 567.1-2 .
14 FAM 567.1-2 Use of Business- or First-Class Train or Sailing Vessel Accommodations
The use of business- or first-class accommodation may not be authorized strictly based on position or rank. When business- or first-class accommodations are authorized under the following circumstances, only the next higher available accommodations satisfying the needs may be used; for example, business-class accommodations should be utilized before going to first-class accommodations. Circumstances justifying the use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations are limited to those listed below ( NOTE : 14 FAM 567.1-2 , subparagraph (4), applies only to trains):
(1) No reasonably available coach-class train accommodations or lowest class sailing vessel accommodations :
(a) Trains : The use of business-class train accommodations may be authorized when no coach-class train accommodations are reasonably available. For this paragraph, "reasonably available" means coach-class train accommodations that are scheduled to leave within 24 hours of the employee's proposed departure time or scheduled to arrive within 24 hours of the employee's proposed arrival time. In the case of a direct route that requires overnight travel, "reasonably available” must be based on the availability of slumber coach, or lowest economy, sleeping accommodations. "Reasonably available" does not include any accommodation with a scheduled arrival time that is later than the employee's required reporting time at the duty site, or with a scheduled departure time that is earlier than the time the employee is scheduled to complete duty;
(b) When the traveler determines that coach seats are unavailable for reservation for the day he or she must travel to arrive at a destination in time to conduct official business, the traveler may proceed to obtain a reserved seat in the next higher class where a reserved seat is available. This is only permissible when the traveler has made a good-faith effort to obtain a reservation in coach class at the earliest practicable time, i.e., the employee cannot unreasonably delay or postpone making reservations and travel plans to justify premium class travel; and
(c) Sailing vessels : The use of the next higher-class accommodations may be authorized or approved only when lowest-class accommodations are not available on the vessel;
(2) Travel on trains or sailing vessels by an employee with a disability : The use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations may be authorized or approved when necessary to accommodate an employee's disability or other physical impairment, and the employee's condition and need for business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations are substantiated in writing by MED or the regional medical officer or other competent medical authority. The use of business- or first-class accommodations may also be authorized for an attendant, when the employee is authorized use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations and MED, or the regional medical officer or other competent medical authority certifies that the employee's disability or other physical impairment requires the services of an attendant en route;
(3) Security reasons aboard trains or sailing vessels : The use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations may be authorized or approved when exceptional security circumstances require such travel. Exceptional security circumstances include but are not limited to:
(a) Travel by an employee whose use of coach train or lowest-class sailing vessel accommodations would endanger the employee's life or U.S. Government property;
(b) Travel by agents in charge of protective details and accompanying individuals authorized business- or first-class accommodations; or
(c) Travel by couriers or control officers accompanying controlled pouches or packages and the lowest-class accommodations cannot fulfill the mission; and
(4) Inadequate foreign coach-class train accommodations (foreign trains only) : The use of business- or first-class train accommodations may be authorized or approved when coach-class accommodations on a foreign rail carrier lack adequate sanitation or health standards.
14 FAM 567.1-3 Reporting Requirements for Business- or First-Class Travel on a Train or Sailing Vessel
a. Refer to 14 FAM 567.2-5 for instructions on reporting the use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel travel to GSA.
b. Extra-fare train service does not need to be reported to GSA if the traveler was ticketed in the lowest class of service offered, even if that class of service was business class.
c. Travel that has been authorized under 14 FAM 567.1-2 , subparagraph (4) for inadequate sanitation or health standards does not need to be reported to GSA.
14 FAM 567.1-4 Extra-Fare Train Service (Express Trains)
a. Extra-fare train service is enhanced performance (i.e., faster speed or fewer stops) relative to other trains available between the same origin and destination.
b. Use of extra-fare trains is not authorized unless determined more advantageous to the U.S. Government or required for security reasons.
c. To justify time savings as an advantage to the U.S. Government, the extra-fare train must reduce overall journey time by one hour or more. Authorizing officials are reminded that air travel may be less expensive than extra-fare trains and, if so, should be the authorized mode of transportation.
d. To justify cost savings as an advantage to the U.S. Government, a ticket for the lowest class of service available on an extra-fare train must, relative to a ticket for the lowest class of service available on a standard train:
(1) Have the same restrictions;
(2) Be less expensive; and/or
(3) Depart within 3 hours of the standard train that would otherwise be booked.
e. Authorizing officials listed in 14 FAM 567.1-1 must approve this and the requirements of 14 FAM 567.1-2 must be met to authorize business class (when it is other than the lowest class of service offered on the train) or first class on an extra-fare train.
14 FAM 567.2 Airplanes
a. See 14 FAM 583 .
b. U.S. Government employees who use commercial air carriers for domestic and international travel on official business must be authorized coach-class airline accommodations. When available, the use of contract-air carriers offering discount (city-pair) fare is mandatory (see 14 FAM 542 , paragraph b). First-class air accommodations may be authorized only as permitted in 14 FAM 567.2-3 . Business-class air accommodations may be authorized only as permitted in 14 FAM 567.2-4 .
14 FAM 567.2-1 Seat Selection and Assignment
a. Each traveler, regardless of age, is entitled to occupy a seat on an airplane.
b. The policies and business practices of the airline(s) operating and/or marketing a particular flight determine whether a seat selection is available and, if they are available, whether a fee must be paid to obtain a seat.
c. Inability to obtain a seat selection or assignment, either for "free" or upon payment of a fee, does not confer an exception to the mandatory use of contract carriers ( 14 FAM 543 ), the provisions of the Fly America Act ( 14 FAM 583 ), or the requirement to authorize travel on the carrier offering the lowest fare that is consistent with all travel regulations.
d. Except as specified in subparagraphs d(1) through d(3) of this section, travelers are eligible for reimbursement of charges to obtain an economy class seat selection in an amount not to exceed $300 (each way) between any two authorized duty locations (i.e., origin and destination pairs), as indicated on a travel authorization. When a traveler qualifies for and is authorized a rest stop, the rest stop location is not considered a separate duty location for the purposes of this provision:
(1) If a bureau/post has a written policy stating that it wishes to limit this benefit, a traveler’s authorizing official may cap reimbursement at a lower amount for a particular instance of travel. In such cases, the authorizing official must specify, in advance of travel, the amount authorized for reimbursement between each duty location and should offer the traveler an explanation for the reduction;
(2) Seat selection fees are not reimbursable for any segment(s) of travel:
(a) Conducted in an indirect manner; or
(b) For which a traveler has cost-constructed to use accommodation in business or first class; or
(c) For which a traveler has been authorized business class or first-class accommodations; and
(3) The "value" of a seat selection fee cannot be applied towards the cost of obtaining a ticket in an other-than-coach class of service or be considered as part of any cost-construct calculation.
e. Payment of a seat selection fee must be made directly to the airline by the traveler. TMCs are not authorized to pay for seat selection fees, either by charging them directly to the U.S. Government or by facilitating payment on behalf of the traveler.
f. Reimbursement for a seat selection fee must be approved on the travel authorization prior to commencing travel and can only be approved for authorized direct travel (see 14 FAM 511.3 ).
g. Receipts are required for reimbursement of seat selection fees, regardless of amount.
h. For the purposes of determining eligibility for reimbursement, a seat selection in any cabin except business class or first class will be considered an economy class seat selection. Travelers may purchase any seating product, including those that offer increased seat width, additional legroom (formerly referred to as “extended economy seating”), or which are bundled/packaged with enhanced onboard or on-ground service, if the seating product is not business class or first class. For example, whether an airline calls a seating product Economy Plus, Premium Economy, or Preferred Seats has no bearing on eligibility for reimbursement as long as the seats are not business or first-class seats.
i. Travelers, not the TMC or airline, are responsible for making accurate determinations regarding whether a particular airline product is eligible for reimbursement as an economy-class seat assignment. Because some airlines have developed branded names that do not give direct indication of their product’s status as business or first class (e.g., United Polaris, Delta One, Copa Dreams Class), travelers who are uncertain whether a product qualifies for reimbursement as an economy class seat selection fee may request a determination of eligibility, before travel commences, by contacting [email protected].
14 FAM 567.2-2 Requirements
14 FAM 567.2-2(A) Authorization
a. Authorization for first-class or business-class air accommodations must be made in advance of the actual travel and must be documented in accordance with 14 FAM 567.2-2(B) . The designated approving official must not be subordinate to the traveler except that the Executive Secretary may approve first-class or business-class air accommodations for the Secretary and the Deputy Secretaries.
b. If the documents required under 14 FAM 567.2-2(B) cannot be completed in advance of travel due to an emergency, the employee must obtain advance approval from an agency official not subordinate to the traveler or from the chief of the agency’s transportation and travel management division or other designated office and must submit the required documents with the appropriate signatures at the earliest possible time.
c. If the employee does not obtain written authorization in accordance with this section, the employee is responsible for the difference between the first-class or business-class air accommodations used and the authorized coach-class or equivalent accommodations.
14 FAM 567.2-2(B) Documentation
a. Authorization : All requests for authorization must contain the name, grade, and position of the travelers; points between which first-class or business-class air accommodations are authorized; additional cost to the U.S. Government resulting from the difference between first-class or business-class and coach-class air accommodations; beginning date of travel; and an explanation of circumstances justifying the use of first-class or business-class air accommodations:
(1) Authorization for first-class air accommodations must be reflected in the travel authorization and accompanied by a memo from the appropriate agency head or designee (see 14 FAM 567.2-3 );
(2) Authorization for business-class air accommodations must be reflected in the travel authorization and accompanied by the appropriate form signed by the designated approving official (see 14 FAM 567.2-4 ):
(a) State : Form DS-4087, Authorization Request for Business-Class Air Travel; or Form DS-4086, Special Seating Request Form for Air Travel, if the justification for use of premium-class accommodations is authorized for disability or special need under 14 FAM 567.2-4 , subparagraph (b)(3);
(b) USAID : Form AID-522-2, Business Class Memorandum to M/MS/TTD;
(c) Commerce : Form CD-334, Request for Approval of Other Than Coach-Class Accommodations;
(d) USDA/FAS : Memo requesting premium-class travel;
(e) APHIS : Memo to approving official; and
(f) USAGM : Memo to approving official.
b. Ticketing : The travel management center (where applicable) will not ticket first-class or business-class accommodations without the appropriate documentation. Posts that do not have a travel management center must retain the required documentation for the record.
c. Blanket orders : The use of blanket travel authorizations for first-class or business-class accommodations is prohibited (State Department personnel). Each trip involving first- or business-class travel accommodations must be separately authorized.
d. Couriers : A courier who flies first class when business-class air accommodations are not available, must complete and sign Form DS-3031, Certification for Use of First-Class Air Accommodations. A copy of the certification must be retained by the courier and the original is to be maintained in the courier's regional office.
14 FAM 567.2-3 First-Class Travel
a. Authorization or approval : Authority to approve the use of first-class air accommodations is limited to the respective agency heads (the Secretary of State, the Administrator of USAID, the Secretary of Commerce, the Director of the U.S. International Broadcasting Bureau of the Broadcasting Board of Governors (USAGM/IBB), and the Secretary of Agriculture) or their designees. Designees are as follows:
(1) State : The Under Secretary for Management (M) per State Department Delegation of Authority No. 198, dated September 16, 1992, except that the Executive Secretary may approve the use of first-class air accommodations for the Secretary and the Deputy Secretary;
(2) USAID : The Deputy Administrator;
(3) Commerce : The Chief Financial Officer and the Assistant Secretary for Administration except in cases of medical necessity or emergency evacuation when the Deputy Assistant Secretary for International Operations is delegated authority to approve. First-class travel will only be authorized if no other commercial service is reasonably available or such travel is necessary for reasons of disability or medical condition (for details on Commerce’s policy on use of business-class accommodations, contact the Office of Foreign Service Human Capital);
(4) USDA/FAS : The Administrator, Foreign Agricultural Service;
(5) APHIS : The Under Secretary for Marketing and Regulatory Programs; and
(6) USAGM : The Director of the International Broadcasting Bureau or as specified in the Manual of Administration.
b. Use of first-class accommodations : Circumstances justifying the use of first-class air accommodations are limited to those listed below:
(1) No other reasonably available accommodations : The use of first-class air accommodations may be authorized or approved when coach-class air accommodations or business-class air accommodations are not reasonably available. "Not reasonably available" means no other class of accommodations other than first-class accommodations is available on any scheduled flight in time to accomplish the purpose of the official travel;
(2) Travel by an employee with a disability : The use of first-class air accommodations may be authorized or approved when necessary to accommodate an employee's disability or other physical impairment, and the employee's condition and need for first-class air accommodations are substantiated in writing by MED or the regional medical officer or other competent medical authority. The use of first-class air accommodations also may be authorized for an attendant(s) who is authorized to accompany the employee, when the employee is authorized first-class air accommodations and MED or the regional medical officer or other competent medical authority or the Disability/Reasonable Accommodation Division (GTM/ER/DRAD) certifies in writing that the employee's disability or other physical impairment requires the services of the attendant(s) en route;
(3) Security reasons : The use of first-class air accommodations may be authorized or approved when exceptional security circumstances require such travel. Exceptional security circumstances include but are not limited to:
(a) Travel by couriers or control officers accompanying controlled pouches or packages when business-class air accommodations are not available (see 14 FAM 567.1-2 , subparagraph (3)(c)); or
(b) Travel by agents in charge of protective details accompanying first-class travelers; and
(c) When required because of agency mission.
14 FAM 567.2-4 Business-Class Travel
a. Authorization or approval :
(1) State : For PCS travel, the designated approving official is the Executive Director, Bureau of Global Talent Management (GTM/EX). Except where otherwise indicated, business-class air accommodations may be authorized only with approval from the officials below (or their designated representative(s)) as provided to TMP. For travelers not mentioned below, the designated approving official must not be subordinate to the traveler:
(2) USAID : The Chief of the Travel and Transportation Division (M/MS/TTD), the director of the funding bureau, office, or mission or designee;
(3) Commerce : The Chief Financial Officer and the Assistant Secretary for Administration except in cases of medical necessity or emergency evacuation when the Deputy Assistant Secretary for International Operations is delegated authority to approve. Business-class travel will only be authorized if no other commercial service is reasonably available or such travel is necessary for reasons of disability or medical condition (for details on Commerce's policy on the use of business-class accommodations, contact the Office of Foreign Service Human Capital);
(4) USDA/FAS : The Under Secretary for Farm and Foreign Agricultural Services and the USDA Chief Financial Officer;
(5) APHIS : The Under Secretary for Marketing and Regulatory Programs and the USDA Chief Financial Officer; and
b. Justification : Travelers may use business-class air accommodations when an approving/authorizing official specifically approves or authorizes the travel in accordance with one or more of the following reasons:
(1) Coach-class air accommodations not available : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when regularly scheduled flights between the authorized origin and destination points (including connection points) provide only business-class air accommodations;
(2) No space available in coach-class air accommodations : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when space is not available in coach-class accommodations on any scheduled flight in time to accomplish the purpose of the official travel;
(3) Travel by an individual with a disability or special need : Upon the recommendation of the Bureau of Medical Services (MED), other competent medical authority in exigent circumstances, or the Disability/Reasonable Accommodation Division (GTM/ER/DRAD), business-class air accommodations may be authorized when necessary to accommodate an employee's disability or special need. Other competent medical authority must certify in writing (to include the supporting clinical findings) the traveler’s condition and need for business-class air accommodations. Upon the recommendation of MED or, in exigent circumstances, other competent medical authority, business-class air accommodations may also be authorized for an attendant authorized to accompany the traveler when the traveler is authorized use of business-class air accommodations. Authorization for an attendant to accompany the traveler, by other competent medical authority, must include written certification that the traveler’s disability or other special need requires the services of the attendant en route;
(4) Security or exceptional circumstances : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when such accommodations are required for security purposes or because exceptional circumstances, as determined by the agency head, or his or her designee, make their use essential to the successful performance of the agency's mission. NOTE : Exceptional circumstances may include, but are not limited to, a chief of mission (COM) and their eligible family member spouse (whether traveling together or at different times) going to post for the first time or leaving post the last time, in accordance with protocol and diplomatic practice for a COM. The tandem spouse of a COM assigned to the same post may also be authorized business class on this basis. Other eligible family members who accompany either the COM or spouse may be authorized business class. If consultations are authorized en route to and from post, business-class accommodations may be authorized to and from the consultation location(s);
(5) Overall cost savings : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when such accommodations would result in an overall savings to the U.S. Government, including by avoiding additional subsistence costs, overtime, or lost productive time while awaiting coach class accommodations. Whenever a cost comparison is made, documentation of the specific flight itineraries and their respective costs must be retained and included in the travel authorization for future reference and to meet auditing requirements:
(a) If a traveler is otherwise authorized an unrestricted economy fare and seeks to be authorized a business-class fare under this provision, the unrestricted economy fare must be compared to the cost of an unrestricted business-class fare;
(b) If a traveler is otherwise authorized a restricted economy fare and seeks to be authorized a business-class fare under this provision, the restricted economy fare must be compared to the cost of a restricted business-class fare;
(6) Agency mission : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when required due to agency mission. State only : Business-class travel of 14 hours or less based on this criteria must be approved by the traveler's under secretary or equivalent in their supervisory chain. Deputy secretary and under secretary business-class travel is approved by the Executive Secretary;
(7) Acceptance of payment from non-Federal source : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when the employee's transportation is paid in full through agency acceptance of payment from a non-Federal source in accordance with 2 FAM 962.12 (g) and 41 CFR 304-5.5; and
(8) Travel in excess of 14 hours for temporary duty (TDY) travel, or medical evacuation travel (exception : USAGM; for further USAGM guidance on when business-class accommodations can be authorized, refer to USAGM’s Manual of Operations and Administration (MOA) directive PART IV Section 636.3, Business-Class Travel Exceptions):
(a) TDY travel to receive training: Business-class air accommodations are not authorized for TDY travel over 14 hours where the primary purpose of the travel, as determined by the funding bureau or post approving/authorizing officer, is for the traveler to receive training or instruction;
(b) TDY travel not related to training: For TDY travel over 14 hours, travelers are authorized economy-class accommodations with a rest stop or a paid day pass to a business-class lounge at an intermediate point on the traveler’s authorized itinerary. However, the funding bureau's executive director or authorizing official at post may determine that circumstances warrant issuance of a business-class ticket provided the following criteria are met:
(i) The origin and/or destination is outside the continental United States;
(ii) The scheduled flight time (including stopovers, but not including rest stops) on the usually traveled route is in excess of 14 hours;
(iii) The purpose of the trip is urgent and cannot be postponed. The traveler must physically report to the duty location immediately upon arrival or the following day, and work until the urgent requirements are fulfilled; and
(iv) Travelers taking leave during or near the dates of their travel indicate that there are no urgent duties requiring the traveler’s immediate departure or return. Travelers who do not report for duty immediately upon arrival or no later than the next day, or take leave within days of their TDY travel should not be authorized business class travel. The traveler may be held liable for excess business class accommodations;
(c) Travelers in U.S. Government-funded business class are not entitled to a U.S. Government-funded rest stop en route to or upon arrival at the duty site. They are not eligible for a U.S. Government-funded business-class lounge day pass, (see 14 FAM 584 ). For definition of travel in excess of 14 hours and rest stop en route, see 14 FAM 567.2-4 , subparagraph b(10)(d);
(d) Medical evacuation travel: Premium-class travel is not authorized for medical evacuation unless MED, in consultation with the Foreign Service medical provider, or in an exigent situation, authorizes business-class accommodations for medical reasons. Travelers authorized by MED to use premium accommodations may not be authorized a rest stop en route or a rest period upon arrival at destination, unless specifically authorized by MED. Travel over 14 hours in duration that is not deemed medically necessary for premium class by MED, will be authorized economy class with a rest stop or a U.S. Government-funded day pass to a business-class lounge at the intermediate point;
(e) Other official travel: Business-class air accommodations may not be authorized or approved for other types of official travel more than 14 hours (such as R&R, PCS, home leave/return to post, educational travel, EVT, etc.) unless justified under one of the other provisions (see 14 FAM 567.2-4 ); and
(f) Calculation of 14-hour travel period:
(i) The “14-hour travel time" is defined as the scheduled flight time on the most expeditious available routing from your point of origin to scheduled arrival at point of destination (wheels up at origin to wheels down at destination). It does not include rest stops or travel from residence/hotel to the airport. Travel in excess of 14 hours includes a leg of travel (a travel segment) in excess of 14 hour or continuous legs of travel (continuous travel segments) without a U.S. Government-funded rest stop in excess of 14 hours on the most direct route;
(ii) The time zone dislocation provision for a rest period upon arrival ( 14 FAM 584.5 ) does not apply to business-class travel. However, business-class travelers may arrive the night before a meeting and be provided per diem for the night if such arrival is necessary to ensure attendance at the meeting. This is not considered a rest period upon arrival; and
(iii) The traveler will not be penalized and deprived of business-class accommodations if travel is delayed or accelerated due to airline schedules rather than to accommodate a traveler’s personal convenience. This is not a rest period or rest stop.
c. Use of the lowest upgradeable fare : In cases where business-class travel is authorized in accordance with the justifications above, but not funded by the bureau or post, the bureau or post may approve the lowest-cost upgradable fare if the traveler commits to upgrading to a business-class fare at their own expense:
(1) Travelers are responsible for obtaining approval for the lowest-cost upgradable fare from the authorizing official by completing a Form DS-4087 prior to travel;
(2) The cost of the upgradable fare may not exceed the cost of the business-class fare for which the traveler is eligible;
(3) When available and approved by the authorizing official, the discounted GSA city-pair YCA fare may qualify as the lowest upgradable fare in lieu of the CA fare;
(4) When a GSA city-pair fare is not available, the authorizing official may approve a fare up to and including the full "Y" fare as the lowest upgradable fare;
(5) A traveler may be authorized the upgradable fare only when the cost of the upgrade is borne by the traveler; and
(6) Rest stops or day passes to a business-class lounge are not authorized when a traveler elects this option.
d. Business-class travel within the United States : U.S. domestic flights do not usually offer separate and distinct business-class seats. The U.S. Government, however, cannot directly book employees eligible for business-class into first-class accommodations. When business-class accommodations are authorized and the airline places the individual in first-class seating at no additional cost for the part of the routing within the United States via a connection, such seating would be considered business-class accommodations for the purpose of this rule.
e. Traveler-paid or airline-provided business class : When a traveler is authorized economy class but actually travels in business class, such as by redeeming airline miles or points, completion of a Form DS-4087 is not necessary. Such instances are also not included in the annual premium-class travel report since they do not change the authorized class of accommodation or expend more U.S. Government funds than would have been spent on the authorized class of service.
f. Exceptions : The Under Secretary for Management or designee may make exceptions to this section to the extent consistent with the law.
14 FAM 567.3 Premium-Class Travel Reporting
a. Each post and domestic office that issues travel tickets must submit a premium-class (first-class and business-class) travel report identifying all premium-class commercial travel (i.e., airplanes, trains, vessels) ticketed and utilized during the fiscal year. The only exception for reporting premium-class travel is outlined in 14 FAM 567.1-3 . A negative report is required if no premium-class travel was utilized. The Department is required to report to the General Services Administration (GSA) no later than October 31 each year. Travel on U.S. Government aircraft is reported separately and is covered in 14 FAM 558 .
b. When the traveler was ticketed in the lowest class of service offered, or use is authorized under 14 FAM 567.1-2 , subparagraph (4), travel on an extra-fare train does not need to be reported to GSA.
c. State only : The Department ‘s Travel Management and Policy Division (A/LM/OPS/TMP) will compile the premium-class travel report from each post with a report from the domestic TMC including domestically issued tickets and submit a consolidated report to GSA in accordance with the guidelines in 41 CFR 300-70.100-103 of the Federal Travel Regulations.
14 FAM 568 AIRLINE LUGGAGE ALLOWANCE
14 FAM 568.1 Authorized Luggage
a. Each traveler is authorized to check, at U.S. Government expense, two pieces of luggage which do not exceed the airline's size limitations or are not considered "oversized" by the operating air carrier, and which weigh up to 50 pounds (23 kilograms) per piece. This allowance constitutes "authorized luggage." It applies to all types of travel and to/from all locations.
b. If a traveler checks items that exceed this authorized weight, size, and/or quantity limitation, reimbursement from the U.S. Government is limited to the cost that would have been incurred to transport “authorized luggage.”
c. Up to two additional pieces of luggage (a maximum of four), which do not exceed the airline's size limitations and which weigh up to 50 pounds per piece, per authorized traveler, may be approved in lieu of an allowable unaccompanied baggage (UAB) entitlement for direct travel if approved in the travel authorization prior to commencing travel.
d. If, for a particular segment of a journey, an air carrier makes a more generous (weight, quantity, or size) checked luggage allowance available to a traveler at no, or no additional, cost to the U.S. Government, the traveler is welcome to utilize the more generous allowance for that segment. This privilege does not , however, increase the “authorized luggage” allowance for subsequent segments.
e. Authorized luggage for indirect (cost-constructed) travel : When a traveler elects to engage in indirect (cost-constructed) travel, the total amount that may be reimbursed by the U.S. Government for checked luggage fees is limited to the sum of expenses that would have been incurred to transport authorized luggage along all segments of the direct route.
14 FAM 568.2 Excess Luggage
a. Luggage exceeding the weight, size, or quantity limit for “authorized luggage” is considered “excess luggage.” To be transported at U.S. Government expense, excess luggage must be required for an official purpose and be specifically authorized in advance of travel. Travel orders that include authorization for the transport of excess luggage must include a justification detailing the specific official purpose necessitating the transport and an estimated cost of such transport.
b. Travel orders for an individual required to transport a checked luggage piece or pieces entirely comprised of U.S. Government materials should include authorization for the transport of those pieces as excess luggage to ensure that the traveler’s personal authorized luggage allowance is not diminished.
c. Excess luggage is not authorized at U.S. Government expense for permanent change-of-station, rest-and-recuperation, family-visitation, and/or emergency-visitation travel. For medical travel, please refer to 16 FAM 310 .
14 FAM 568.3 Receipts
Receipts are required for reimbursement of checked luggage fees in any amount, including fees assessed by an air carrier to transport “authorized luggage.”
14 FAM 569 UNASSIGNED
- ATO Community
- Legal Database
- What's New
Log in to ATO online services
Access secure services, view your details and lodge online.
Declaring your travel allowance and claiming expenses
What to do if you receive a travel allowance to cover your travel expenses when travelling for work.
Last updated 25 April 2023
Deductible travel allowance expenses
Receiving a travel allowance from your employer does not automatically entitle you to claim a deduction for travel expenses.
A travel allowance expense is a deductible travel expense :
- you incur when you're travelling away from your home overnight to perform your employment duties
- that you receive an allowance to cover
- for accommodation, meals (food or drink), or incidentals.
You incur a travel allowance expense when you either:
- actually pay an amount for an expense
- have an obligation to pay an amount for the expense.
You can't claim a deduction if your employer either pays for or reimburses you for the expense.
If you don't incur any deducible travel allowance expenses, there is no need to consider if a travel allowance record keeping exception applies .
Example: no deductible travel allowance expenses incurred
Ainsley lives in Melbourne and is the regional manager of a clothing store chain. She must travel to Sydney for 3 days to attend the annual conference of managers.
Ainsley’s employer pays for her accommodation in Sydney, but she buys her own meals. When she returns to the office, Ainsley puts in a reimbursement claim for her meals, and her employer reimburses her for these expenses.
As Ainsley doesn't incur accommodation expenses and receives a reimbursement for the meal expenses, she can't claim a deduction for these expenses.
Since Ainsley hasn't received an allowance and she can't claim a deduction for her accommodation and meals, she doesn't need to consider whether she can rely on the travel allowance record keeping exception.
What to do if you receive a travel allowance
If your travel allowance is shown as an allowance on your annual income statement or payment summary, you:
- must include the allowance as income in your tax return
- can claim a deduction for the amount you spent on deductible travel allowance expenses
- you don't need to keep detailed records if your deduction for travel allowance expenses is within the reasonable amounts we specify.
If your travel allowance isn't shown on your annual income statement or payment summary and you spent the whole amount on deductible expenses, you:
- don't include the allowance as income in your tax return
- can't claim any deduction for your travel allowance expenses
- don't need to keep written evidence or travel records.
If you do this, you will not pay any income tax on your travel allowance.
However, if you spent more than your travel allowance on deductible travel allowance expenses, you:
- include the allowance as income in your tax return
- can claim a deduction for your travel allowance expenses
- you don't need to keep detailed records if your deduction for travel expenses is within the reasonable amounts we specify.
Example: travel allowance on income statement
William works for a company in Sydney. William’s employer requires him to visit clients in country New South Wales once a month. This involves William sleeping away from his home for 3–4 nights.
William’s employer pays him an allowance of $150 per night to cover accommodation, meal and incidental expenses, and includes the allowance on his income statement.
As William’s employer reports the travel allowance on his income statement, William must include the allowance as income in his tax return. He can claim a deduction for the amount he spends on accommodation, meals and incidental expenses while he is travelling away from his home overnight for work.
Unless he can rely on the travel allowance record keeping exception, William will have to keep receipts or other written evidence for all his accommodation, meals and incidental expenses.
Example: travel allowance not reported on income statement
George's employment duties require him to occasionally travel away from his home overnight. When he travels overnight for work, his employer pays him an allowance of $80 to cover accommodation expenses and reimburses him for the cost of his meals. George's employer doesn't show the allowance on his income statement.
When George travels overnight for work he stays in the same place, which costs him $100 per night.
As the travel allowance isn't on George's income statement and he has spent the entire allowance on deductible travel allowance expenses, he doesn't need to:
- declare the travel allowance as income in his tax return
- keep written evidence of his accommodation expenses.
George also can't claim a deduction for the expenses.
However, as George has spent more than the amount of the allowance on deductible travel allowance expenses, he can include the amount as income in his tax return. He can then claim a deduction for the amount he spent on accommodation. Unless George can rely on the travel allowance record keeping exception, he will have to keep written evidence.
Language selection
- Français fr
Travel allowance
Part-time employee.
You may give a part-time employee a reasonable allowance or reimbursement for travelling expenses incurred by the employee going to and from a part-time job. If so, and you and the part-time employee are dealing at arm's length, you do not have to include that amount in the employee's income. This applies to:
- teachers and professors who work part-time in a designated educational institution in Canada, providing service to you as a professor or teacher, and the location is not less than 80 kilometres from the employee's home
- part-time employees who had other employment or carried on a business, and they did the duties at a location no less than 80 kilometres from both the place of the employee's home and the place of the other employment or business
Salesperson and clergy
You may pay a reasonable travel allowance for expenses other than for the use of an automobile (such as meals, lodging, per diem allowance) to a salesperson or member of the clergy. You do not have to include the allowance in the employee's income if it was for expenses related to the performance of duties of the office or employment and the employee is either of the following:
- an agent selling property or negotiating contracts for the employer
- a member of the clergy
Other employees
You have to include reasonable travel allowances in the income of employees, other than a salesperson or member of the clergy, who travel to perform the duties of the office or employment, unless the allowances are received by the employee for travelling away from the municipality and the metropolitan area where the employer's establishment is located and where the employee ordinarily works or reports.
In some situations, you may provide an allowance to your employee for travel (other than an allowance for the use of a motor vehicle) within a municipality or metropolitan area so your employee can perform their duties in a more efficient way during a work shift.
This allowance is not a taxable benefit and can be excluded from the employee's income if all of the following conditions are met:
- The employee travels away from the office
- The allowance is reasonable. The CRA generally considers a value of up to $23 for the meal portion of the travel allowance to be reasonable
- You are the primary beneficiary of the allowance
- The allowance is not an additional form of remuneration
This means that you do not have to include this type of travel allowance if its main reason is so that your employee's duties are performed in a more efficient way during a work shift.
For examples of situations where a travel allowance is considered a taxable benefit, go to Examples – Travel allowance .
Reasonable travel allowances
Whether an allowance for travel expenses is reasonable is a question of fact. You should compare the reasonable costs for travel expenses that you would expect your employee to incur against the allowance you pay to the employee for the trip.
If the travel allowance is reasonable, you do not have to include it in your employee's income. If it is not reasonable, the allowance has to be included in your employee's income.
For more information, see paragraph 48 in Interpretation Bulletin IT-522R Archived, Vehicle, Travel and Sales Expenses of Employees .
Your employee may be able to claim certain employment expenses on their income tax and benefit return. For more information, see Employee's allowable employment expenses .
Payroll deductions
If the allowance is taxable , it is also pensionable and insurable. Deduct income tax, CPP contributions, and EI premiums.
Reporting the benefit on the T4 slip
Report the taxable allowance in box 14 "Employment income" and in the "Other information" area under code 40 at the bottom of the T4 slip . For more information, see T4 – Information for employers .
Forms and publications
- Income Tax Folio S2-F3-C2, Benefits and Allowances Received from Employment
- Interpretation Bulletin IT522R Archived, Vehicle, Travel and Sales Expenses of Employees
Page details
Thank you for signing up!
AI Summary to Minimize your effort
Transport Allowance for Salaried Employees - Meaning, Exemption, Calculation, Rules
Updated on : Mar 19th, 2024
11 min read
Transport Allowance is an allowance a company or employer provides to employees to compensate for their travel from their residence to the workplace. It is a type of special allowance. Like other allowances, transport allowance is a part of CTC and has fixed pay.
As the employee’s income tax computation is done by their employers for tax deduction purposes, salaried taxpayers may or may not be very concerned about their salary structuring and details of various kinds of allowances and exemptions available to them even before arriving at gross total income. However, understanding allowances and exemptions provided on such allowances is also significant for tax planning. This helps them choose the right CTC structure and lawfully claim the tax benefit to which they are entitled. Additionally the availability of the exemption depends on the tax regime chosen by the taxpayer.
This article will discuss one such allowance, i.e., transport allowance and its tax provisions.
What is Transport Allowance?
Transport allowance could mean allowance provided for the purpose of transport from residence to the place of work . However, transport allowance under Section 10(14) of Income-tax Act,1961 read with rule 2BB of Income-tax rules can be either of the following:
- Allowance granted to an employee to meet his expenditure for the purpose of commuting between his place of residence and office/place of duty
- Allowance granted to an employee working in the transport business to meet his personal expenditure during his duty performed in the course of running such transport from one place to another place provided the employee is not in receipt of daily allowance
Transport allowance is taxable in the hands of the employee since it is added to their gross salaries. However, employees can claim tax exemption for transport allowance as per the exemption limit.
Quantum of Exemption
Section 10(14) read with Rule 2BB provides for transport allowance exemption. The amount of exemption is as follows:
Changes by Finance Act, 2018
From the financial year 2018-2019, the tax exemption for medical and transport allowances has been merged. The Income Tax Department introduced a standard deduction in place of transport and medical allowance. From the financial year 2019-2020, the standard deduction is Rs 50,000, which covers the transport and medical allowance.
Thus, employees can claim the deduction of Rs 50,000 while filing their ITR without producing any bills or documents. Employers will consider the standard deduction to compute the net taxable salary while calculating the TDS. This change shall take effect from the financial year 2018-19. Accordingly, no separate transport allowance of Rs 1,600 per month is available to employees other than physically challenged employees and employees of a transport business. The limit of Rs 40,000 has been increased to Rs 50,000 in the Interim Budget 2019. Know the highlights of the Interim Budget 2019 here.
Difference Between Transport Allowance and Conveyance Allowance
A transport allowance is an allowance given to meet commuting expenses between the place of residence and office or to meet the personal expenditure of an employee of a transport business.
A conveyance allowance is an allowance granted to meet the expenditure on conveyance in the performance of office duty.
Transport allowance is fully taxable for all employees in both regimes. However it is exempt under both tax regimes to the extent of 3,200 per month for the employees who are physically challenged such as blind/deaf/dumb or orthopedically handicapped with disability of lower extremities. C onveyance allowance is exempt from tax only to the extent of actual expenditure incurred.
Illustration
Let us derive the taxable income of an employee for the FY 2017-18, FY 2018-19, FY 2019-20 and onwards.
Let us look the same illustration for an employee who is specially abled.
Transport Allowance Under the New Tax Regime
From the FY 2020-21, the government introduced the new tax regime for individual and HUF taxpayers under section 115BAC. In the new tax regime, there are flat tax rates and no deductions or exemptions. For example, an individual opting for the new tax regime cannot claim exemptions for HRA and others. Also, the individual cannot claim deductions for any tax-saving investments. However, the new tax regime allows an individual to claim the following tax-exempt allowances:
- Allowance by the employer to meet the cost of travel on tour or transfer. It includes an allowance towards the cost of travel, such as airfare, rail fare and other transportation costs.
- Any allowance by the employer to meet the ordinary daily charges incurred by an employee on account of absence from the usual place of duty. The allowance should be in respect of the tour or for the period of the journey in connection with a transfer. The allowance includes expenses an employee incurs for food and other daily costs while travelling.
- Allowance to meet conveyance expense incurred while performing duties of an office or employment of profit. However, in this case, the employer should not provide a free conveyance to the employee. The allowance includes travelling expenses an employee incurs while performing official duties.
In the case of an employee who is blind, deaf and dumb, or orthopedically handicapped, with a disability of lower extremities can claim transport allowance to meet expenditure on commuting between residence and the place of duty. The benefit is up to Rs 3,200 per month. The same would be fully taxable in the case of an employee with no disabilities.
How to Claim Transport Allowance While Filing Income Tax Return for an employee who is specially abled ?
Usually, employers take care of the tax exemption on transport allowance while deducting TDS from the paycheck. In such cases, employees have to enter the amount mentioned in Form 16 part B in the ‘Income from Salary’ column of their ITR Form .
But when an employer has given a tax benefit on transport allowance or forgotten to give the tax benefit in Form 16 , you can claim tax exemption by following the below process:
- Check the CTC structure from the salary slip.
- Check whether the amount of transport allowance is part of the CTC.
- If the amount in the CTC structure is less than Rs 3,200 per month, the entire travel allowance would be tax-free.
- If the amount in the CTC structure is more than Rs 3,200 per month, the tax-free amount would only be Rs 3,200 per month.
Related Articles
Income tax allowances and deductions Special allowance taxation Allowances and deductions available to a salaried
Frequently Asked Questions
A normal employee (other than a handicapped employee) cannot claim transport allowance for commuting between residence and place of work or employment.
The standard deduction is a flat deduction available from the taxable salary or pension income. The deduction amount is Rs. 40,000 for FY 2018-19, whereas it is increased to Rs.50,000 from FY 2019-20 and onwards.
You can furnish the proof or invoices of relocation expenses to your employer and claim tax-free reimbursement.
The tax exemption for medical reimbursement is no longer applicable. From the FY 2018-19, the fixed medical reimbursement and transport allowance stand replaced by a standard deduction.
No, if there is a company-run transportation service facility, they will not pay you a conveyance allowance whether you use the service or not.
No, your employer can pay whatever amount they find appropriate. However, only specially abled employees can avail the exemption against such allowances.
An employee who is handicapped can get the exemption of transport allowance up to Rs. 3,200 per month.
Yes, a handicapped employee can get an exemption of up to 3,200 per month if he pays taxes in any of the regime.
No, transport allowance is fully taxable in the case of a normal employee if he pays taxes in any regime.
70% of such allowance up to a maximum of Rs.10,000 per month will be exempted if he has not received daily allowance. Suppose If he receives a daily allowance, then he would not be eligible for this exemption.
Quick Summary
Was this summary helpful.
Clear offers taxation & financial solutions to individuals, businesses, organizations & chartered accountants in India. Clear serves 1.5+ Million happy customers, 20000+ CAs & tax experts & 10000+ businesses across India.
Efiling Income Tax Returns(ITR) is made easy with Clear platform. Just upload your form 16, claim your deductions and get your acknowledgment number online. You can efile income tax return on your income from salary, house property, capital gains, business & profession and income from other sources. Further you can also file TDS returns, generate Form-16, use our Tax Calculator software, claim HRA, check refund status and generate rent receipts for Income Tax Filing.
CAs, experts and businesses can get GST ready with Clear GST software & certification course. Our GST Software helps CAs, tax experts & business to manage returns & invoices in an easy manner. Our Goods & Services Tax course includes tutorial videos, guides and expert assistance to help you in mastering Goods and Services Tax. Clear can also help you in getting your business registered for Goods & Services Tax Law.
Save taxes with Clear by investing in tax saving mutual funds (ELSS) online. Our experts suggest the best funds and you can get high returns by investing directly or through SIP. Download Black by ClearTax App to file returns from your mobile phone.
Cleartax is a product by Defmacro Software Pvt. Ltd.
Company Policy Terms of use
Data Center
SSL Certified Site
128-bit encryption

How Many Bags Are Allowed on International Flights?
E mbarking on your first international journey can be an exciting yet daunting experience, especially when it comes to understanding the nuances of baggage requirements. While there are similarities between domestic and international flights, the rules for luggage can differ significantly.
- International Flight Baggage Allowance: Discover the standard luggage limits for international travel.
- Luggage Size and Weight Guidelines for International Flights: Keep carry-ons within 22x14x9 inches and checked luggage under 70 pounds to sail smoothly through check-in.
- Managing Excess Baggage on International Trips: Over your limit? Expect to pay about $100 or more for extra or overweight bags. Pro tip: Shipping luggage can be a budget-friendly alternative to airline fees.
International Flight Baggage Requirements: A Closer Look
For those accustomed to the more relaxed baggage policies of domestic flights, navigating international flight luggage allowances can be a bit of a challenge.
Typically, international airlines permit passengers to carry one piece of hand luggage and one or two pieces of checked baggage without extra charges. However, additional bags or overweight luggage will incur fees.
Carry-On and Checked Baggage Allowances on International Flights
On most international flights, passengers are allowed to bring along a personal item (like a small bag, backpack, or laptop case) and a carry-on bag free of charge.
The allowance for checked luggage usually includes one or two pieces per passenger. These allowances can vary based on the airline, the destination, and the origin of the flight. Some airlines might allow two checked bags for specific destinations while limiting it to one for others.
It's essential to verify the specific baggage policies with your airline, as what is included in your ticket can vary. Sometimes, the cost of checked luggage might already be factored into your ticket price.
Additionally, budget airlines may impose higher baggage fees to offset operational costs like fuel prices.
Advice for Managing Overweight or Excess Luggage
If your luggage exceeds the allowed limits or weight, purchasing extra space or paying overweight charges is always an option. Generally, airlines start charging from around $100 for additional or overweight bags.
To save costs, consider pre-purchasing extra luggage space or weight, as fees tend to be higher at the airport.
Understanding Luggage Size and Weight Restrictions
For carry-on bags, a typical size limit is 22 x 14 x 9 inches , with a weight restriction of around 40-45 liters .
Checked luggage should ideally weigh between 50-70 pounds and measure under 62 linear inches (height + width + depth). Exceeding these limits might lead to extra charges.
Insider Tip: For checked luggage, it's usually smarter to go with fabric luggage, unless it's extremely durable, such as the [amazon link="B003BFFRQ8" title="Pelican cases"]. That's because less durable hardside suitcases will crack more often when they're thrown around in the airplane's cargo hold. A good fabric checked suitcase would be something from Samsonite or Travelpro, such as the [amazon link="B07QWF3FDZ" title="Travelpro Crew Versapack"] (full review over here .)
Restrictions and Guidelines for Checked Luggage Contents
Most airlines have standard policies regarding items permitted in checked luggage.
Items like lighters without fuel, gels, electronic devices, and certain other items are generally not allowed in checked baggage but can be carried in hand luggage.
Handling Special Luggage Situations
When traveling with items like musical instruments or sports equipment on international flights, it's important to be aware that these items are often treated differently than regular luggage. Each airline has its own set of rules and guidelines for handling such specialized equipment, and it's crucial to be informed about them before you travel.
Musical instruments, due to their value and fragility, might require special handling or even additional fees. Some airlines allow small instruments as carry-ons, while larger ones may need to be checked in with special arrangements or protective casing. In some cases, you might even have to purchase an extra seat to accommodate a large instrument.
Similarly, sports equipment like skis, golf clubs, or surfboards typically falls under a different category in baggage rules. These items are usually larger and have specific shape requirements, and airlines might charge extra fees for transporting them. They might also have weight and size restrictions separate from standard baggage.
It's always a good idea to contact your airline well in advance to inquire about their policies regarding musical instruments and sports equipment. This way, you can make the necessary preparations, whether it's packing your items in a certain way or budgeting for additional fees. Checking these details ahead of time will help ensure a smooth and hassle-free travel experience with your special items.
What Can I Do Instead of Checking In Extra Luggage?
If you know your bags are going to go overweight or you have a lot more bags than allowed and you don’t want to check them in the airport, there’s always the option of shipping them straight to your final destination instead.
Several companies offer you the option of shipping your luggage from your house to your next destination in almost any corner of the world. When you’re on the way back home, you can also opt to ship your bags straight home instead. This is especially helpful if you don’t want to have to wait long lines while checking in your luggage or if you want to avoid excess baggage fees.
Here are some of the companies that can ship your luggage worldwide:
- Luggage Concierge
- Luggage Forward
- Luggage Free
Additional Considerations for International Flights
Remember, international flights require earlier arrival at the airport compared to domestic flights, often around three hours before departure, to allow time for baggage check-in and immigration procedures. Utilizing online check-in services can save time and hassle at the airport.
Final Thoughts on International Travel and Baggage
Embarking on international travel, particularly for the first time, can feel like navigating uncharted waters, with luggage considerations being a significant part of the voyage. The key to a stress-free journey lies in understanding and preparing for the differences in baggage rules and regulations.
The nuances of international flight luggage policies, from carry-on allowances to checked baggage fees , can vary widely across airlines and destinations. Being informed about these differences is crucial. Checking your airline's specific baggage policies beforehand can prevent unexpected surprises and additional costs at the airport. Remember, what might be a standard practice for one airline could be an extra charge on another.
When it comes to managing your luggage, think strategically. Packing efficiently can not only save space but also potentially reduce costs. Investing in luggage that meets standard international size and weight limits can be a wise decision in the long run. Moreover, consider the nature of your travel: business, leisure, adventure, or a mix, and pack accordingly.
In cases where you have extra or overweight luggage, explore alternatives like shipping your bags or pre-purchasing additional luggage allowance online, as these options might be more economical than paying at the airport. Remember, airlines often offer discounts for managing your luggage online before the flight.
Lastly, embrace the learning experience that comes with international travel. Each journey will teach you something new about navigating different airline policies, packing efficiently, and managing travel logistics. With each trip, you'll become more adept at handling the complexities of international travel, transforming from a novice explorer into a seasoned globetrotter. So pack your bags, check your documents, and embark on your adventure with confidence and a sense of preparedness. Remember, every journey is an opportunity to learn, grow, and experience the wonders of our world.
What are the typical size and weight limits for carry-on luggage on international flights?
Generally, carry-on bags should not exceed 22 x 14 x 9 inches and weigh around 40-45 liters.
Can I bring additional bags on international flights, and what are the fees?
Yes, you can usually bring additional bags, but fees start around $100 and vary by airline.
Are there items I can't pack in my checked luggage on international flights?
Yes, items like lighters without fuel, certain gels, and electronics are typically not allowed in checked luggage but can be in a carry-on.
What's the best way to handle special items like musical instruments or sports equipment?
Check with the airline for specific guidelines, as these items may have unique handling requirements.
Is it cheaper to ship my luggage than check it on an international flight?
It can be, especially if you're facing overweight or excess baggage fees. Shipping services offer an alternative that can sometimes be more cost-effective.
- American Airlines
- Delta Airlines
- A Guide to carry-on luggage from Skyscanner

How our family sticks to a budget with 2 teenagers while also teaching them about finance
- Inflation is prompting families to rethink their household budgets.
- We developed an allowance plan that teaches our two teenagers about budgeting and family finances.
- For instance, allowance is given weekly but not tied to chores.
Inflation over the last couple of years has a lot of people rethinking how they manage their household budgets . This is no different in our family of four, which includes two teenagers.
As our daughters, aged 13 and 14, grew older and neared high school, my spouse and I knew that their financial demands would grow as well. For instance, we could see their fashion needs were getting more expensive, and their entertainment requirements had outgrown Chuck E. Cheese. This presents a particular challenge when we are also trying to tighten the budget to deal with rising prices .
To fit the needs and wants of two teenagers into our family budget, we first came up with a new plan for their allowance in 2022 that encouraged good habits. The next step was to get them involved in the family finances to teach them about budgeting and the importance of being smart about money.
Since we adjusted the family finances, we have seen patience grow in terms of saving money and waiting to see if a purchase is truly necessary. We have also seen them become more interested in budgeting and smarter with money.
Here are several ways that we budget around two teenagers and teach them about money at the same time.
Allowance is given weekly and not tied to chores
When my spouse and I came up with a financial plan for our daughters as they got older and a bit more independent, we first understood that they would need regular spending money. However, we did not want the allowance to be performance-based . That is, we decided not to require the completion of chores or other tasks, like homework, for them to receive their allowance.
Every week, they each receive $25, which we think of as a guaranteed basic income program . It also creates a fixed monthly expense in our family budget.
The allowance is a guaranteed amount they can count on each month, and the money does not come with any strings attached.
There is an old saying that once you pay somebody to do something, they will never do it for free again. Our goal is to have our daughters be responsible, not paid workers. We also try our best to reward good behavior and effort instead of punishing them for not helping around the house.
We also budget monthly bonuses for our daughters
Instead of giving the girls $35 every week and taking some away when they don't meet a list of demands, we started at a minimum of $25 each week and give them occasional bonuses.
Bonuses are tied to good patterns of completing chores, being kind, being helpful, trying hard in school, and getting exercise. For example, we might give one daughter a $5 or $10 bonus one week for helping their grandmother without being asked and something similar to the other for working hard on a school assignment.
We then tell them why they received the bonus to reinforce the positive behavior.
There is no set pattern of how often or how much the bonuses are because we don't want them to become an expectation. These are a little more challenging to budget for, but after a while, we settled into a pattern where the bonuses are fairly consistent each month.
We profit-share with our daughters to discourage excessive spending
We have another bonus system for the girls based on how well the family sticks to the monthly budget.
In our family, the budget is not a secret. We encourage our children to be involved in the family finances to expose them to budgeting early on.
At the end of each month, we all review how the month went, where we did well, and what we could have done better. And if we came in under our budget, we give the girls a profit-sharing bonus.
There is no set amount or rate for the budget bonus. We discuss it as a family and assign the bonuses to each daughter. We will also designate a third "bonus" to our vacation fund, which might ultimately mean an extra day at Disney or a little extra spending cash for the girls in New York City.
We use an allowance app to encourage good money habits
There are many ways to budget with teenagers in mind, including good, old-fashioned pen and paper. However, we prefer apps that speed up and automate many steps.
The first is YNAB , which stands for "you need a budget," where the entire family's budget is kept. We also use Greenlight , which is specifically designed for children.
In addition to giving the girls debit cards, Greenlight automates allowance payments and even has games to teach them about money.
The other key feature is that the girls cannot see each other's finances. In a previous app, everything was out in the open for the entire family, often leading to conflicts when one daughter wanted to know why the other had more money or got a little extra one week.
Our girls are very different, and they have different needs. So the money they earn is just between them and us. We don't tell one sister what the other gets, but we try to be balanced and fair.
We distinguish between needs and wants
The girls have a basic monthly income, but we don't want them spending that on basic needs. Therefore, every potential purchase in our budget is defined as "household needs" or "household wants."
In general, if something is a "need," such as hair conditioner or clothes for school, the money comes from the family budget. If it is just something they "want," like tickets to see Olivia Rodrigo in concert, they have to use their own money.
Of course, everything can feel like a need to a teenager, and distinguishing between needs and wants can be tricky.
One daughter might need new shoes, but she doesn't "need" a new pair of Nike Dunk Low Pandas for $115. In these cases, we might give an amount that we think fits the budget, and if they still want that specific item, they can pay the difference.
Of course, we don't always win those battles. Teenagers can be quite convincing and relentless at times. Besides, it is nice to give them a few "wins" occasionally if they put in the effort, and it seems that important.
We also encourage delayed gratification
If you have ever known a teenager, one of the toughest things to instill in them is a sense that some things can wait.
Amazon is a great convenience, but delaying gratification can be a challenge when it is so easy to place an order and have it delivered as early as that day.
We deal with this by having an Amazon list called "do we really want this?" If something is not an immediate need, such as a new Lego set, it goes on this list. Every Saturday, we meet as a family, review the list, and see what we still want.
We often find that the desire for the item has waned, or we have thought of something we would rather have instead. It also can be quite jarring to see all the items simultaneously, and everybody realizes how much it would cost to order everything. The wait encourages everybody to be selective about what is most important.
When we started doing this, our "household wants" line in the budget was almost instantly slashed in half by several hundred dollars. Even for teens, when they sleep on something for a few days, a potential purchase can stop feeling like life or death.
The lessons our daughters have learned about money are worth the extra effort
We have used this plan with our family for about 18 months, and both daughters have become excellent savers.
When they want something special like a limited edition signed vinyl from Conan Gray or a new hoodie from Lululemon, instead of asking us and then my wife and I going through the push and pull of "can we" or "should we," they save up their money.
The excitement on their faces when they reach the magic numbers is priceless.
The next step is to find out how to encourage long-term savings. We are working on that. They are still teenagers, after all.
Have you adjusted your family finances or come up with any tips or tricks for budgeting with children? Reach out to this reporter at [email protected] .
- Main content
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Airlines are ordered to give full refunds instead of vouchers and to stop hiding fees

Travelers and their luggage in a terminal at Los Angeles International Airport in August 2023. Mario Tama/Getty Images hide caption
Travelers and their luggage in a terminal at Los Angeles International Airport in August 2023.
WASHINGTON — In an effort to crack down on airlines that charge passengers steep fees to check bags and change flights, the U.S. Department of Transportation has announced new regulations aimed at expanding consumer protections .
One of the final rules announced Wednesday requires airlines to show the full price of travel before passengers pay for their tickets. The other will force airlines to provide prompt cash refunds when flights are canceled or significantly changed.
"Passengers deserve to know upfront what costs they are facing and should get their money back when an airline owes them - without having to ask," said Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg in a statement announcing the new rules.

Taking on junk fees is popular. But can it win Biden more voters?
Surprise junk fees have become a large and growing source of revenue for airlines in recent years, according to the DOT.
"Today's announcements will require airlines to both provide passengers better information about costs before ticket purchase, and promptly provide cash refunds to passengers when they are owed — not only saving passengers time and money, but also preventing headaches," Buttigieg said.
The airline industry is unlikely to welcome the new rules. At a hearing on the proposed fee rule in March 2023, an industry lobbying group representing American, Delta and United said it would be too difficult for airlines to disclose their charges more clearly.
"The amount of unwanted and unneeded information forced upon passengers" by the new policy would only cause "confusion and frustration," warned Doug Mullen, the deputy general counsel at Airlines for America . "Very few, if any, need or want this information, and especially when they are initially trying to understand schedule and fare options."
But the DOT insists its new rule will give consumers the information they need to better understand the true costs of air travel.
Transportation Department cracks down on airline 'junk fees'
"I believe this is to the benefit of the sector as a whole," Buttigieg said in an interview with NPR's Morning Edition , because passengers will have "more confidence in the aviation sector."
The new rules require airlines to disclose all baggage, change, and cancellation fees, and to share that information with third-party booking sites and travel agents.
The regulation also prohibits bait-and-switch tactics, the DOT says, that disguise the true cost of flights by advertising a low base fare that does not include all mandatory fees.
"This is really about making sure that we create a better experience for passengers, and a stronger aviation sector in the United States," Buttigieg said in the NPR interview.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Travel allowance is a type of compensation employers provide to cover employee travel expenses incurred when traveling for business purposes. It helps with employee travel costs, such as transportation, lodging, meals, and other incidentals while on the job. Depending on the company policy, travel allowance may be given in cash or as reimbursed ...
Regularly requires you to travel away from home and, during any single trip, usually involves travel to areas eligible for different standard meal allowance rates. If this applies, you can claim a standard meal allowance of $69 a day ($74 for travel outside the continental United States) for travel in 2023.
Business travel deductions are available when employees must travel away from their tax home or main place of work for business reasons. A taxpayer is traveling away from home if they are away for longer than an ordinary day's work and they need to sleep to meet the demands of their work while away. Travel expenses must be ordinary and ...
A travel allowance is compensation paid by an employer to employees to cover expenses incurred when traveling for business. In addition to lodging and transportation, travel allowances are typically used for airfare, meals, and other expenses related to business travel. It is business travel compensation, provided either before or after travel ...
Liquids Rule. You are allowed to bring a quart-sized bag of liquids, aerosols, gels, creams and pastes in your carry-on bag and through the checkpoint. These are limited to travel-sized containers that are 3.4 ounces (100 milliliters) or less per item. Placing these items in the small bag and separating from your carry-on baggage facilitates ...
Travel allowance plays a pivotal role in facilitating business travel and ensuring that employees are adequately compensated for their expenses. By implementing transparent policies, leveraging technology, and monitoring expenses diligently, companies can optimize their travel allowance programs to benefit both employees and the organization as ...
What is a business travel allowance? Organizations establish business travel allowances to cover expenses incurred by staff during their corporate trips. Typically these reimbursements are made to cover the cost of hotel rooms, meals, and transportation. However, policies should extend to include anything required for the employee to conduct ...
Per diem rates. Rates are set by fiscal year, effective Oct. 1 each year. Find current rates in the continental United States, or CONUS rates, by searching below with city and state or ZIP code, or by clicking on the map, or use the new per diem tool to calculate trip allowances.
Topic no. 511, Business travel expenses. Travel expenses are the ordinary and necessary expenses of traveling away from home for your business, profession, or job. You can't deduct expenses that are lavish or extravagant, or that are for personal purposes. You're traveling away from home if your duties require you to be away from the general ...
1. Fixed Travel Allowance. A fixed travel allowance in salary implies that this is a fixed amount offered to the employee irrespective of the actual expenses incurred. 2. Daily Travel Allowance. As the name suggests, a daily travel allowance is offered to employees on a per-day basis, which covers their travel, meals, accommodation, and other ...
Each year the government determines an amount for travel day per diem in two categories: lodging and meals. These amounts vary by geographical location and take the local cost of living into account.
Alcoholic beverages with more than 24% but not more than 70% alcohol are limited in checked bags to 5 liters (1.3 gallons) per passenger and must be in unopened retail packaging. Alcoholic beverages with 24% alcohol or less are not subject to limitations in checked bags. Mini bottles of alcohol in carry-on must be able to comfortably fit into a ...
Components of leave travel allowance. Leave travel allowance is a beneficial component in an employee's salary package that helps cover costs associated with travel during leave periods. This section will delve into what types of expenses LTA can cover, what it typically does not include, and the limits and caps that apply to these allowances.
Travel expenses are costs associated with traveling for the purpose of conducting business-related activities. Travel expenses can generally be deducted by employees as non-reimbursed travel ...
The Federal Travel Regulation Chapter 300, Part 300-3, under Per Diem Allowance, describes incidental expenses as: Fees and tips given to porters, baggage carriers, hotel staff, and staff on ships. How often is a study conducted on the M&IE expense rates?
Per diem rates look-up Allowances for lodging, meal and incidental costs while on official government travel. Mileage reimbursement rates Reimbursement rates for the use of your own vehicle while on official government travel.
Providing travel allowances in the USA. Travel allowances are commonly provided by employers, government agencies, educational institutions, and other organizations. The specific rules and regulations around the allowance can vary depending on your organization and the purpose of travel, but the IRS sets the base for travel allowance payouts ...
The Per Diem Travel and Transportation Allowance Committee (PDTATAC), or Per Diem Committee, has oversight of the JTR, per DoD Instruction 5154.31, Volume 5 [PDF, 8 pages]. Two working level advisory panels support the subcommittee - the Military Advisory Panel (MAP) and the Civilian Advisory Panel (CAP). The Defense Travel Management Office ...
14 FAM 562 EXPENSES ALLOWABLE. 14 FAM 562.1 Miscellaneous Expenses not Covered by Per Diem. (CT:LOG-392; 03-20-2024) a. The following travel expenses, when actually incurred and necessary, can be itemized and reimbursed over and above the per diem allowance for lodging and meals and incidental expenses (M&IE):
Per diem is an allowance paid to your employees for lodging, meals, and incidental expenses incurred when travelling. This allowance is in lieu of paying their actual travel expenses. Return to top 2. What is the federal per diem rate for my area? Publication 1542, Per Diem Rates provides the rates for all continental U.S. areas. Return to top 3.
Leave Travel Allowance/Leave Travel Concession is a type of allowance given by an employer to their employee for travelling to any place in India: either on leave, after retirement or after the termination of his service. Though it sounds simple, many factors need to be kept in mind before you plan to claim an LTA exemption.
Travel allowance is a payment made to an employee to cover accommodation, food, drink or incidental expenses they incur when they travel away from their home overnight in the course of their duties. Allowances folded into your employee's salary or wages are taxed as salary and wages and tax has to be withheld, unless an exception applies. You ...
A travel allowance expense is a deductible travel expense: for accommodation, meals (food or drink), or incidentals. You incur a travel allowance expense when you either: have an obligation to pay an amount for the expense. You can't claim a deduction if your employer either pays for or reimburses you for the expense.
Reasonable travel allowances. Whether an allowance for travel expenses is reasonable is a question of fact. You should compare the reasonable costs for travel expenses that you would expect your employee to incur against the allowance you pay to the employee for the trip. If the travel allowance is reasonable, you do not have to include it in ...
Allowance by the employer to meet the cost of travel on tour or transfer. It includes an allowance towards the cost of travel, such as airfare, rail fare and other transportation costs. Any allowance by the employer to meet the ordinary daily charges incurred by an employee on account of absence from the usual place of duty.
International Flight Baggage Allowance: Discover the standard luggage limits for international travel. Luggage Size and Weight Guidelines for International Flights: Keep carry-ons within 22x14x9 ...
The allowance is a guaranteed amount they can count on each month, and the money does not come with any strings attached. There is an old saying that once you pay somebody to do something, they ...
The employer may elect to add taxable fringe benefits to employee regular wages and withhold on the total or may withhold on the benefit at the supplemental wage flat rate of 22% (for tax years beginning after 2017 and before 2026). Treas. Regs. 31.3402(g)-1 and 31.3501(a)-1T.
The new rules require airlines to disclose all baggage, change, and cancellation fees, and to share that information with third-party booking sites and travel agents.
PER DIEM, TRAVEL, AND TRANSPORTATION ALLOWANCE COMMITTEE 4800 MARK CENTER DRIVE, SUITE 05E22 ALEXANDRIA, VA 22350-9000 April 25, 2024 MEMORANDUM FOR: MILITARY ADVISORY PANEL SUBJECT: UTD for MAP 26-24(R) "Temporary Lodging Expense (TLE) Extension Recertification - Portsmouth, NH/Kittery, ME (NH194)" 1.