Brazilian wandering spiders: Bites & other facts
The spider's name means "murderess" in Greek, which is appropriate for the deadly arachnid.


Classification/taxonomy
Size & characteristics, bites and venom, additional resources.
The Brazilian wandering spider, also called armed spiders or banana spiders, belongs to the genus Phoneutria , which means "murderess" in Greek. And it's no wonder why — it's one of the most venomous spiders on Earth . Its bite, which delivers neurotoxic venom, can be deadly to humans, especially children, although antivenom makes death unlikely.
Guinness World Records has previously named the Brazilian wandering spider the world's most venomous spider multiple times (though the current record-holder is the Sydney funnel-web spider, Atrax robustus , according to Guinness ). But, as the late Jo-Anne Sewlal, who was an arachnologist at the University of the West Indies in Trinidad and Tobago, told Live Science, "classifying an animal as deadly is controversial," as the amount of damage depends on the amount of venom injected.
Jo-Anne Sewlal was a noted arachnologist from Trinidad and Tobago. While completing her PhD, she received the National Institute of Higher Education, Research, Science and Technology (NIHERST) 2012 Award for Excellence in Science and Technology for Junior Scientist. In 2013, She received a doctorate in zoology from the University of the West Indies. She discovered several species of spiders in her home country, surveyed the arachnids across several countries the Caribbean and appeared as an expert on the topic on The Science Channel. She died of an allergic reaction in January 2020.
There are nine species of Brazilian wandering spider, all of which are nocturnal and can be found in Brazil. Some species also can be found throughout Central and South America, from Costa Rica to Argentina, according to a 2008 article in the journal American Entomologist . Study author Richard S. Vetter, a research associate in the department of entomology at the University of California, Agriculture and Natural Resources, wrote that specimens of these powerful arachnids have been mistakenly exported to North America and Europe in banana shipments. However, Vetter noted, in many cases of cargo infestation, the spider in question is a harmless banana spider (genus Cupiennius ) that is misidentified as a Phoneutria . The two types of spiders look similar.
The taxonomy of Brazilian wandering spiders, according to the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS) , is:
Kingdom : Animalia Subkingdom : Bilateria Infrakingdom : Protostomia Superphylum : Ecdysozoa Phylum : Arthropoda Subphylum : Chelicerata Class : Arachnida Order : Araneae Family : Ctenidae Genus : Phoneutria
- Phoneutria bahiensis
- Phoneutria boliviensis
- Phoneutria eickstedtae
- Phoneutria fera
- Phoneutria keyserlingi
- Phoneutria nigriventer
- Phoneutria pertyi
- Phoneutria reidyi
- Phoneutria depilata , according to a 2021 study published in the journal ZooKeys , which found that Phoneutria boliviensis actually included two separate species from different habitats.
Brazilian wandering spiders are large, with bodies reaching up to 2 inches (5 centimeters) and a leg span of up to 7 inches (18 cm), according to the Natural History Museum in Karlsruhe, Germany. The species vary in color, though all are hairy and mostly brown and gray, although some species have lightly colored spots on their abdomen. Many species have bands of black and yellow or white on the underside of the two front legs, according to the University of Florida .

These arachnids "are called wandering spiders because they do not build webs but wander on the forest floor at night, actively hunting prey," Sewlal told Live Science in an interview conducted in 2014, before her death. They kill by both ambush and direct attack.
They spend most of their day hiding under logs or in crevices, and come out to hunt at night. They eat insects, other spiders and sometimes, small amphibians, reptiles and mice.
Research into one species of Brazilian wandering spider, Phoneutria boliviensis , revealed that these spiders eat a mix of arthropods and reptiles. DNA metabarcoding, a technique that examines the DNA and RNA in a sample, of the guts of 57 spiders identified 96 prey species, including flies, beetles, butterflies, moths, grasshoppers, locusts and crickets, according to research from the University of Tolima and the University of Ibagué in Colombia . Some of the female spiders also ate lizards and snakes.
While their bites are powerful and painful, "their bites are a means of self-defense and only done if they are provoked intentionally or by accident," Sewlal said.

In the Brazilian wandering spider, just as in most spider species, the female is larger than the male. Males approach females cautiously when attempting to mate, according to the biology department at the University of Wisconsin-La Crosse . Males perform a dance to get females' attention, and males often fight each other over the female. The female can be picky, and she often turns down many males before choosing a mating partner. Once she does pick one, the male needs to watch out; females often attack the males once copulation is finished.
The female then can store the sperm in a separate chamber from the eggs until she is ready to fertilize them. She will lay up to 1,000 eggs at a time, which are kept safe in a spun-silk egg sac.
Brazilian wandering spiders typically live for one or two years.
Brazilian wandering spiders' venom is a complex cocktail of toxins, proteins and peptides, according to the Natural History Museum in Karlsruhe, Germany. The venom affects ion channels and chemical receptors in victims' neuromuscular systems.
After a human is bitten by one of these spiders, he or she may experience initial symptoms such as severe burning pain at the site of the bite, sweating and goosebumps, Sewlal said. Within 30 minutes, symptoms become systemic and include high or low blood pressure , fast or a slow heart rate , nausea, abdominal cramping, hypothermia, vertigo, blurred vision, convulsions and excessive sweating associated with shock. People who are bitten by a Brazilian wandering spider should seek medical attention immediately.
Their venom is perhaps most famous for triggering painful and long-lasting erections . For that reason, in a 2023 study, scientists reported that they were testing the venom in humans as a potential treatment for erectile dysfunction in those for whom Viagra didn't work.
However, these bites are rare, and envenomations, or exposure to these toxins from a spider bite, are usually mild, Vetter said. For instance, a 2000 study in the journal Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo found that only 2.3% of people with bites who came to a Brazilian hospital over a 13-year period were treated with antivenom. (The other bites did not contain enough venom to require it.) Most of the bites were from the species P. nigriventer and P. keyserlingi in eastern coastal Brazil. About 4,000 bites reportedly happen each year in Brazil, but only 0.5% of those cases are severe, according to a 2018 study in the journal Clinical Toxinology in Australia, Europe, and Americas . Meanwhile, 15 deaths have been attributed to Phoneutria in Brazil since 1903, the 2018 study reported.
"It is unlikely that the spider would inject all of its venom into you, as this venom is not only needed as a means of defense but to immobilize prey," Sewlal said. "So if it did inject all of its venom, it [would] have to wait until its body manufactured more before it could hunt." That would also leave the spider vulnerable to being attacked by predators.
Furthermore, Sewlal pointed out that venom production requires a lot of a spider's resources and time. "So if the spider were to attack frequently and use up all of its venom, it [would] be safe to assume that it has a ready food supply to replace the energy and resources used. This situation does not exist in the wild."
- Learn more about Brazilian wandering spiders from the University of Wisconsin-La Crosse .
- Read about several species of Brazilian wandering spiders, including several images of the arachnids at the University of Florida .
- Find a spider in your bananas? It may or may not be a deadly species, according to the University of California, Riverside .
This article was originally published on Nov. 20, 2014.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Jessie Szalay is a contributing writer to FSR Magazine. Prior to writing for Live Science, she was an editor at Living Social. She holds an MFA in nonfiction writing from George Mason University and a bachelor's degree in sociology from Kenyon College.
- Laura Geggel Editor
Giant, invasive Joro spiders with 6-foot webs could be poised to take over US cities, scientists warn
Diving bell spider: The only aquatic arachnid that creates a web underwater to live in
'Hostilities began in an extremely violent way': How chimp wars taught us murder and cruelty aren't just human traits
Most Popular
- 2 2,500-year-old Illyrian helmet found in burial mound likely caused 'awe in the enemy'
- 3 Cave of Crystals: The deadly cavern in Mexico dubbed 'the Sistine Chapel of crystals'
- 4 Why do dogs sniff each other's butts?
- 5 'Lost' satellite finally found after orbiting undetected for 25 years
- 2 Japan captures 1st image of space debris from orbit, and it's spookily stunning
- 3 1,900-year-old Roman legionary fortress unearthed next to UK cathedral
- 4 2,500-year-old Illyrian helmet found in burial mound likely caused 'awe in the enemy'

Understanding the Wandering Spider: Quick Essential Facts
Wandering spiders are a group of venomous arachnids found primarily in South America.
Among these, the Brazilian wandering spider is particularly known for its potent venom and unique behavior. They are often referred to as “banana spiders” due to their frequent encounters with humans in banana plantations.
As a reader, you might be interested in learning more about these fascinating creatures, including their habitat, hunting techniques, and the effects of their venom.
In this article, we will delve into the world of wandering spiders and provide you with all the essential information to satisfy your curiosity.

Scientific Classification and Naming
The wandering spider belongs to the genus Phoneutria , which is a part of the Ctenidae family.
These spiders are known for their potent venom and aggressive behavior. Here is the scientific classification of the wandering spider:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Chelicerata
- Class: Arachnida
- Order: Araneae
- Family: Ctenidae
- Genus: Phoneutria
Within the genus Phoneutria, two species are particularly noteworthy: Phoneutria fera and Phoneutria nigriventer, also known as P. nigriventer . These spiders are primarily found in South America and other tropical regions.
Phoneutria fera and P. nigriventer differ in some aspects. Let’s compare their features using a table:
Some key characteristics of the wandering spiders in the genus Phoneutria include:
- Potent venom that can be dangerous to humans
- Nocturnal hunters and are active at night
- Equipped with long, spiny legs for capturing prey
- Aggressive defenders of their territory
By understanding the scientific classification and differences between Phoneutria species, you can better appreciate the diversity and fascinating biology of these wandering spiders.
Identification and Appearance
Color and size.
The wandering spider, also known as the banana spider, has a distinctive appearance that can help you easily identify it in the wild.
They usually have a combination of hairy brown and black colors on their body. Their size can vary, but they are generally considered large spiders. Their size can range from 1 to 2 inches in body length.

When it comes to wandering spider’s leg span, these creatures can have an impressive reach. Their leg span can extend up to 5-6 inches.
Some key characteristics of a wandering spider’s legs include:
Habitat and Distribution
Wandering Spiders are known to inhabit various environments, including rainforests and tropical forests.
These spiders can adapt to different habitats based on their needs and availability of food sources. They prefer warm and humid places, as these conditions suit their growth and reproduction.
Geographical Coverage
Wandering spiders are found in Central and South America .
They live in forests from Costa Rica to Argentina, including Colombia, Venezuela, The Guianas, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, and Northern Argentina.
They may also be present in some parts of the United States, particularly in the northern part of southern America.
However, they don’t inhabit countries like Australia. In summary, the Wandering Spider is mostly prevalent in the following areas:
- South America
- Central America
- Southern parts of the United States
Types of Wandering Spiders
Here’s a brief description of the major types of wandering spiders.
Brazilian wandering spiders
Also known as armed or banana spiders, these spiders are nocturnal and don’t make webs.
They are known to have been transported outside of South America in banana shipments.
Phoneutria nigriventer
These spiders contain neurotoxins that can cause cerebral changes and breakdown of the blood-brain barrier .
Their venom is medically significant and has been used in manufacturing drugs. Their bites may be fatal to children.
Ctenus captiosus
Also known as the Florida false wolf spider or tropical wolf spider, this species is found in the United States.
Some species of these spiders are large and scary-looking, but they’re only mildly venomous. Their venom is comparable to a bee sting.
Other types of wandering spiders include: Acantheis, Acanthoctenus, Africactenus, and Afroneutria.

Behavior and Diet
Aggression level.
Wandering spiders, as their name suggests, are known for their aggressive behavior .
While they won’t attack without provocation, if they feel threatened, they will not hesitate to defend themselves.
This is especially true during mating season.
Prey and Predators
In their natural habitat, wandering spiders primarily feed on insects and small vertebrates, such as:
- Insects like ants and moths
- Small amphibians
This diverse diet allows them to thrive in various ecosystems.
However, they are not top predators, as their natural predators include larger birds, mammals, and other spiders.
Nocturnal Activities
Wandering spiders are nocturnal creatures , which means they are active during the night.
During the day, they remain hidden in their retreats, often made from rolled-up leaves or small crevices.
At night, they leave their hiding spots to search for prey using their strong hunting skills.

Venom and Its Effects
Composition of venom.
The venom of the wandering spider is a complex mixture containing several toxic components.
Its main component is a potent neurotoxin, which can have severe effects on your nervous system 1 . Here’s a brief overview of its composition:
- Neurotoxins
Symptoms and Severity
A wandering spider’s venomous bite can cause a wide range of symptoms, depending on the severity of envenomation. These symptoms may include 2 :
- Mild to moderate pain
- Redness and swelling at the bite site
- Irregular heartbeat
- Difficulty breathing
- Blurred vision
- High blood pressure
Some severe cases may result in life-threatening complications, such as respiratory failure or even death 2 .
Medical Treatment and Antivenom
If bitten by a wandering spider, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Treatment often involves the following steps:
- Cleaning and immobilizing the affected area
- Monitoring and managing the symptoms
- Administering antivenom if it’s available and appropriate, depending on the severity of envenomation 3
Antivenom is specific to the venom of the wandering spider and can help neutralize its effects.
However, the availability of antivenom may be limited in some regions 3 .
Always remember that prevention is better than cure: learning how to identify and avoid wandering spiders is the best way to stay safe.

Reproduction and Mating
Mating ritual.
When it’s time for reproduction, the wandering spider undergoes an intriguing mating ritual.
The male spider performs a dance to attract the female by displaying his brightly colored legs and vibrating his body.
During the process, the male also produces a sperm web and transfers his sperm to the female’s reproductive organs using his pedipalps.
Egg Sacs and Offspring
After the mating process, the female wandering spider will create an egg sac to protect her eggs.
The sac consists of silk and can hold hundreds of eggs. She then attaches it to a safe hiding place, usually against a protective surface or within a secure web.
The female often guards the egg sac to ensure the protection of her offspring until they hatch.
Once the spiderlings hatch, they are known to be highly independent.
They disperse quickly and start their own journey, fending for themselves soon after emerging from the egg sac.
As they grow, they’ll go through a series of molts before reaching adulthood and beginning their own reproductive cycle.
Danger and Defense Mechanisms
The Wandering Spider is known to be one of the most dangerous spiders in the world.
Although they can potentially kill humans, fatalities are rare due to their reluctance to bite.
Oddly enough, their venom can cause an involuntary erection in men, alongside other painful symptoms.
Here are some ways the Wandering Spider protects itself and displays its dangerous nature:
- Fangs : These spiders are equipped with strong, sharp fangs that can easily pierce human skin, allowing them to inject their venom with ease.
- Venom : Their venom is potent and can cause severe pain, inflammation, and other adverse effects. In rare cases, it can even lead to death.
While interacting with Wandering Spiders, be cautious and observe them from a safe distance.
Knowing their defense mechanisms will help you respect their space and avoid any unpleasant encounters.
Remember, it’s essential to be informed and aware when dealing with these fascinating, yet dangerous creatures.

Comparison with Other Dangerous Spiders
Comparison to black widow.
The black widow spider is notorious for its potent venom, but the wandering spider has a stronger venom overall.
Both spiders are capable of causing severe symptoms, but the black widow’s venom is primarily neurotoxic, affecting your nervous system.
In contrast, the wandering spider’s venom can cause both neurotoxic and cytotoxic effects, potentially damaging your nerves and cells.
- Potent neurotoxic venom
- Red hourglass marking
- Stronger venom (neurotoxic and cytotoxic)
- No distinct marking
Comparison to Brown Recluse
The brown recluse spider is known for its necrotic venom that can lead to tissue damage and sometimes requires medical intervention.
While both the brown recluse and wandering spider can produce venomous bites, wandering spiders are considered more dangerous due to the potency of their venom and the severity of their bite symptoms.
- Necrotic venom
- Dark violin-shaped marking
Comparison to Wolf Spider
Wolf spiders are frequently mistaken for more dangerous spiders due to their size and appearance.
Although they can bite, their venom is not particularly potent and generally only causes mild itching, redness, and swelling.
In comparison, the wandering spider’s venom is far more dangerous, and its bite can result in serious symptoms, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Large and hairy
- Smoother appearance
Comparison to Sydney Funnel-Web Spider
The Sydney funnel-web spider is another highly venomous spider known for its potentially lethal bites.
While both spiders possess powerful venom, the wandering spider has a broader range of symptoms due to the combination of neurotoxic and cytotoxic effects.
In conclusion, wandering spiders are more dangerous than wolf spiders but their venom’s effects are more varied compared to black widows, brown recluses, and Sydney funnel-web spiders.
Be cautious around these spiders and seek medical help if bitten.
Interesting Facts and Guinness World Records
The Wandering Spider, also known as the Brazilian Wandering Spider, is a fascinating creature that has caught the attention of many.
They belong to the genus Phoneutria , which means “murderess” in Greek, giving you an idea of their potency. Let’s explore some interesting facts about this spider and its place in the Guinness World Records.

First, you might be curious about their venom. The Wandering Spider is known for having one of the most potent venoms among spiders.
In fact, it holds the Guinness World Record for the most venomous spider. Their venom contains a potent neurotoxin that can cause severe symptoms, including difficulty breathing, high blood pressure, and intense pain.
Apart from their venom, their behavior is also quite intriguing. These spiders are called “wandering” because they are known for actively hunting their prey rather than spinning webs to catch them.
They are mostly nocturnal creatures and, during the day, can be found hiding in logs or dark crevices.
Here are a few more notable characteristics of the Wandering Spider:
- Females are larger than males, with a body length of up to 1.6 inches (4 cm).
- They have eight eyes, arranged in two rows, which help them in hunting.
- The Wandering Spider is primarily found in Central and South America, particularly in Brazil.
- They are known to show aggression when threatened.
While the Wandering Spider is a marvel of the arachnid world, it’s essential to keep a safe distance from them due to their venomous nature.
However, their unique characteristics and record-breaking venom potency make them a fascinating subject for those interested in the natural world.
Prevention and Safety Measures
To protect yourself from wandering spiders, there are some simple safety measures you can take.
Firstly, be cautious in areas where these spiders may live, such as dark and warm spaces. For example, avoid reaching into crevices or lifting piles of wood without inspecting them first.
Always wear appropriate shoes when outdoors, particularly in wooded or grassy areas. This can help prevent bites on your feet or ankles.
Reduce the risk of wandering spiders entering your home by sealing gaps and cracks. This minimizes the chance of the spiders finding a way inside.
Regularly clean your living spaces, paying special attention to dark and hidden areas. By maintaining a clean environment, you’ll discourage wandering spiders from making themselves at home.
When out in nature, avoid disturbing spider habitats like webs or egg sacs. This can prevent agitating wandering spiders, reducing your chance of accidental encounters.
Remember, wandering spiders can be dangerous, but by taking these precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of encountering them or being bitten. Stay safe and always be aware of your surroundings.
In summary, wandering spiders, particularly those in the genus Phoneutria, are a group of venomous arachnids predominantly found in Central, South America and parts of Southern United States.
These spiders, including the Brazilian wandering spider, are known for their potent venom, nocturnal hunting habits, and aggressive defense mechanisms.
Their venom, containing neurotoxins and other components, can cause severe symptoms in humans, making them one of the most dangerous spider species.
Despite their fearsome reputation, fatalities are rare, and they play a vital role in their ecosystems.
It’s important to respect their space and take preventive measures to avoid encounters. Understanding these spiders’ behavior, habitat, and characteristics can help in appreciating their role in nature while ensuring safety.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2857337/ ↩
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3851068/ ↩ ↩ 2
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6560916/ ↩ ↩ 2
Reader Emails
Over the years, our website, whatsthatbug.com has received hundreds of letters and some interesting images asking us about wandering spiders. Scroll down to have a look at some of them.
Letter 1 – Wandering Spider from Ecuador

Hi Michele, There is a resemblance to the Dolomedes Fishing Spiders, and finding it near a river lends credence to that possibility. Eric Eaton noticed this posting and has this to say: ” Ok, the spiders from Ecuador and Costa Rica: They are most likely NOT wolf spiders, but wandering spiders, either in the family Ctenidae or Sparassidae. They tend to be more common, and even larger than, wolf spiders in the tropics. At least one species, Phoneutria fera, is extremely aggressive, with potentially deadly venom. Do not mess with large spiders in Central and South America! The venomous types are very difficult to distinguish from harmless species, and in any event, a bite is going to be really painful. These spiders sometimes stow away in bananas, houseplants, and other exported goods, so they can show up in odd places. Be careful where you put your hands.”
Update: May 14, 2013 We now have a confirmation that this is a Wandering Spider, Phoneutria fera , and it is a dangerous species. See Encyclopedia Britannica and Animal Corner .
Letter 2 – Brazilian Wandering Spider: Most Venomous Animal

Hi Martin, We are happy you were able to write to us after your encounter with this Brazilian Wandering Spider and are thrilled to be able to post your story and photos to our site. We started to research, and our first hit has a different species name. Phoneutria fera is described as: “The Brazilian Wandering Spider is not for the ‘pet keeper’. Brazilian Wandering Spiders are extremely fast, extremely venomous, and extremely aggressive. These large and dangerous true spiders are ranked among the most venomous spiders known to man. In fact, the Brazilian Wandering Spider is the most venomous spider in the New World! In South America, these true spiders are commonly encountered in peoples’ homes, supposedly hiding in peoples’ shoes, hats, and other clothes. The Brazilian Wandering Spider does not remain on a web, rather, it wanders the forest floor, hence the name.” Our favorite information on Wikipedia is that Phoneutria is Greek for “murderess”. Here is one final tidbit about the effect of the bite of the Brazilian Wandering Spider on the human male .
Letter 3 – Possibly Wandering Spider from Ecuador

Dear Mike, This is really an interesting Spider, but other than to say it appears to be a hunting spider that does not build a web to entrap prey, we aren’t sure about its identity. Many hunting spiders can jump quite well. It looks very much like the spider in a posting in our archives, also from Ecuador, that we identified as possibly a Wandering Spider in the genus Phoneutria, a venomous and potentially dangerous genus . The spotted legs on your individual look like the spotted legs on an individual in an image on Wikipedia of a Wandering Spider in the genus Phoneutria . There are many images of Brazilian Wandering Spiders on Primal Shutter and we believe that might be a correct identification for your individual.
Thank you for the information. After reading more about the spider, I’m glad it didn’t jump! Mike
Letter 4 – Possibly Wandering Spider from Ecuador

Dear Carl, We believe, though we are not certain, that this might be a Wandering Spider in the genus Phoneutria, and you may read more about Wandering Spiders on the Museum für Naturkunde Karlsruhe website where it states: “There is no doubt that the venom of some of the species is quite potent for mammals, including humans.” We eagerly welcome additional opinions on this identification. Perhaps Cesar Crash of Insetologia can provide something. In the future, please submit a single species per submission form as it makes it extremely difficult for us to categorize postings with multiple species.
Letter 5 – Wandering Spider from Belize

Hi Karl, Thanks for allowing us to post your excellent image of a Wandering Spider, Cupiennius salei . The species is pictured on iNaturalist .
Bugman aka Daniel Marlos has been identifying bugs since 1999. whatsthatbug.com is his passion project and it has helped millions of readers identify the bug that has been bugging them for over two decades. You can reach out to him through our Contact Page .
View all posts

Piyushi is a nature lover, blogger and traveler at heart. She lives in beautiful Canada with her family. Piyushi is an animal lover and loves to write about all creatures.
8 thoughts on “Understanding the Wandering Spider: Quick Essential Facts”
Hi Michele, I am an Ecuadorian scientist and specialized on spiders, I would like to find one like yours, I can say that, almost without doubt, you found the Phoneutria itself, it is the Phoneutria fera, look at this picture: http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://4.bp.blogspot.com/-bFH9qzT0F7U/T_2sZuk6xAI/AAAAAAAAAGY/8jnMVcPOcNI/s1600/phoneutria_fera2.jpg&imgrefurl=http://rangerbaiano.blogspot.com/2012/07/animais-peconhentos-e-venenosos.html&usg=__iCWEz7S86xub6RAyvXTER6HBaco=&h=864&w=834&sz=215&hl=es-419&start=6&zoom=1&tbnid=jjOROVO9h-vKXM:&tbnh=145&tbnw=140&ei=99eRUY6xKo2K9QTLvYCoDQ&prev=/search%3Fq%3Dphoneutria%2Bfera%26sa%3DN%26hl%3Des-US%26sout%3D1%26tbm%3Disch%26prmd%3Divns&itbs=1&sa=X&ved=0CDYQrQMwBQ Can you see the similarities?, unfortunately the spider might be in a better life today 🙂 Another thing, when you want identifications you should take a picture in front, the under part, and the upper part, as well as some characteristics about behaviour like how they react when you approach. The Phoneutria is a very agressive one.. best wishes, bye.
Hi Miguel, Thanks so much for the comment. This is a seven year old posting and we did not have the ability to post comments when it was originally posted online. We have made an update on What’s That Bug? and your comment is greatly appreciated.
Ah, there is also needed the size and the picture of its face so we can see the eye arrangement, depending on that it could also be pisauridae, but I stay in Ctenidae..
This is a female Cupiennius sp. wandering spider.
Perhaps surprisingly, this ubiquitous large spider of the Mindo area appears to be undescribed to species level.
Although one is indeed best advised to exercise caution in the presence of large ctenids, members of the genus Cupiennius are not known to be dangerously venomous (Barth, 2002). By way of confirmation, my girlfriend, Shannon Bowley, managed to be bitten by a mature female of this Mindo species in 2013 – she felt only mild effects, equivalent to a bee sting.
Thanks for this valuable information.
I’m planning a trip to Ecuador and I’m fearing these spiders. Do they get in houses? Any tips to keep them out, so I can sleep at night?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail. You can also subscribe without commenting.
Medical Information

First Aid for Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite
What is a brazilian wandering spider bite.
Brazilian wandering spiders, also known as banana spiders, are one of the most venomous spiders in the world. They are found primarily in South and Central America and are known for their aggressive behavior and wandering tendencies.
Identification:
- Brazilian wandering spiders have a brown body with distinctive yellow markings on their legs
- They have long and slender legs that are covered in spines
- They have a small body, but their legs can span up to 6 inches (15 centimeters)
- They have two large fangs that are often visible when they open their mouth
What are the Causes of Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite?
Brazilian wandering spiders are venomous and are capable of causing serious envenomation when they bite.
- The venom of the spider contains a neurotoxin that attacks the nervous system, causing muscle spasms, breathing difficulties, and other severe symptoms
- The venom can also cause an excessive release of serotonin, leading to increased heart rate, sweating, and elevated blood pressure
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite?
The following signs and symptoms of Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite may be noted:
- Severe pain at the site of the bite that may radiate to other parts of the body
- Sweating and tingling sensations in the mouth and tongue
- Muscular twitching, spasms, and cramps
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain
- Increased heart rate and high blood pressure
- Unconsciousness and convulsions
How is First Aid administered for Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite ?
Immediate actions:
- Clean the bite site with soap and water
- Put a wet, cold cloth, or an ice pack on the bite site
- Seek urgent medical attention, and bring the spider with you to help with identification, when possible
First aid administration:
- The First Aid for Brazilian Wandering Spider Bites includes cleaning the bite area and seeking medical attention
Who Should Administer First Aid for Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite?
- First aid for Brazilian Wandering Spider Bites should be administered by someone who is trained in providing first aid, such as a medical professional, a paramedic, or a trained first-aider
- If there is no one available with appropriate training, attempt to apply the pressure immobilization bandage and seek urgent medical attention
What is the Prognosis of Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite?
The prognosis for Brazilian Wandering Spider Bites depends on the severity of the symptoms and the timing of the treatment.
- If prompt medical attention is given, most patients can recover fully without any long-term effects
- However, delayed or inadequate treatment can lead to serious complications and even death
Long-term effects:
- There are generally no long-term effects of Brazilian Wandering Spider Bites if prompt medical attention is given
- However, in rare cases, patients may develop allergic reactions or experience chronic pain, muscle weakness, or other symptoms that persist long after the bite
How can Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite be Prevented?
A few helpful tips to prevent Brazilian Wandering Spider Bites include:
- Wear shoes and gloves when working in the garden or bush
- Check bedding and clothing before use, especially when stored in dark and cool areas
- Keep the house and garden free from clutter, including piles of rocks, leaves, and wood
- Install screens on doors and windows to prevent spiders from entering the house
- Use insecticides and spider repellents
What are certain Crucial Steps to be followed?
- If you live in areas where Brazilian wandering spiders are prevalent, it is essential to take necessary precautions to prevent being bitten.
- Learn how to identify Brazilian wandering spiders and their habitats to avoid them.
- If you suspect that you have been bitten by a Brazilian wandering spider, follow the immediate actions and first aid administration guidelines outlined above.
- Seek urgent medical attention, and bring the spider with you to help with identification.
- Do not attempt to catch or handle the spider, as this can increase the risk of being bitten.
In conclusion, Brazilian wandering spiders are a potentially deadly species of spider found in South and Central America. If you suspect that you have been bitten by a Brazilian wandering spider, it is crucial to seek urgent medical attention as soon as possible. Prevention is key to avoid being bitten, so take necessary precautions to keep yourself and your family safe from these dangerous spiders.
Hashtags: #BananaSpider #FirstAid #SouthAmericanWildlife #SpiderBites #SafetyTips
On the Article

Krish Tangella MD, MBA

Robert Ben Johnston, MD
Please log in to post a comment.
Related Articles
Test your knowledge, asked by users, related centers, related specialties, related physicians, related procedures, related resources, join dovehubs.
and connect with fellow professionals
Related Directories
At DoveMed, our utmost priority is your well-being. We are an online medical resource dedicated to providing you with accurate and up-to-date information on a wide range of medical topics. But we're more than just an information hub - we genuinely care about your health journey. That's why we offer a variety of products tailored for both healthcare consumers and professionals, because we believe in empowering everyone involved in the care process. Our mission is to create a user-friendly healthcare technology portal that helps you make better decisions about your overall health and well-being. We understand that navigating the complexities of healthcare can be overwhelming, so we strive to be a reliable and compassionate companion on your path to wellness. As an impartial and trusted online resource, we connect healthcare seekers, physicians, and hospitals in a marketplace that promotes a higher quality, easy-to-use healthcare experience. You can trust that our content is unbiased and impartial, as it is trusted by physicians, researchers, and university professors around the globe. Importantly, we are not influenced or owned by any pharmaceutical, medical, or media companies. At DoveMed, we are a group of passionate individuals who deeply care about improving health and wellness for people everywhere. Your well-being is at the heart of everything we do.
For Patients
For professionals, for partners.
Animal Corner
Discover the many amazing animals that live on our planet.
Brazilian Wandering Spider
The Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria fera) is an aggressive and highly venomous spider . It was first discovered in Brazil hence its name. However, this genus is known to exist elsewhere in South and Central America .
The Brazilian Wandering spider is a member of the Ctenidae family of wandering spiders.
The Brazilian Wandering spider appeared in the Guinness Book of World Records 2007 for being the most venomous animal .
In this particular genus, there are five known similar species whose members are also highly venomous. They include some of the relatively few species of spiders that present a threat to human beings.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Characteristics
The Brazilian wandering spider can grow to have a leg span of up to 4 – 5 inches. They are large hairy spindly-looking spiders who have eight eyes, two of which are large. Brazilian wandering spiders are fast-moving spiders, their legs are strong and spiny and they have distinctive red jaws which they display when angered.
The Brazilian wandering spider is not a Tarantula . Brazilian wandering spiders are not even in the same family group. Tarantulas are harmless to humans and are mostly ambush killers who wait for prey to come to them. Brazilian wandering spiders are active hunters. Brazilian wandering spiders and Tarantulas do have one thing in common, however, they do not eat bananas.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Habitat and Spider Webs
The Brazilian Wandering spider is so-called because it wanders the jungle floor, rather than residing in a lair or maintaining a web. This is another reason it is considered so dangerous. In densely populated areas, the Brazilian Wandering spider will usually search for cover and dark places to hide during daytime, leading it to hide within houses, clothes, cars, boots, boxes and log piles. This usually causes accidents when people disturb them.
The Brazilian Wandering spider is also called the ‘banana spider’ as it is occasionally found within shipments of bananas. As a result, any large spider appearing in a bunch of bananas should be treated with due care.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Diet
Adult Brazilian Wandering spiders eat crickets, other large insects, small lizards and mice. Spiderlings of this species eat flightless fruit flies and pinhead crickets.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Reproduction
All spiders produce silk, a thin, strong protein strand extruded by the spider from spinnerets most commonly found on the end of the abdomen. Many species use it to trap insects in webs, although there are many species that hunt freely such as the Brazilian Wandering spider. Silk can be used to aid in climbing, form smooth walls for burrows, build egg sacs, wrap prey and temporarily hold sperm, among other applications.
Brazilian Wandering spiders reproduce by means of eggs, which are packed into silk bundles called egg sacs. The male spider must (in most cases) make a timely departure after mating to escape before the females normal predatory instincts return.
Mature male spiders have swollen bulbs on the end of their palps for this purpose and this is a useful way to identify whether the spider is male or female. Once the sperm is inside the female spider, she stores it in a chamber and only uses it during the egg-laying process, when the eggs come into contact with the male sperm for the first time and are fertilized. The Brazilian Wandering spiders life cycle is 1 – 2 years.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Venom
Bites from the Brazilian Wandering spider may result in only a couple of painful pinpricks to full-blown envenomed. In either case, people bitten by this spider or any Ctenid should seek immediate emergency treatment as the venom is possibly life threatening.
The Phoneutria fera and Phoneutria nigriventer (two species of wandering spider) are the two most commonly implicated as the most vicious and deadly of the Phoneutria spiders.
The Phoneutria not only has a potent neurotoxin, but is reported to have one of the most excruciatingly painful envenoms of all spiders due to its high concentration of serotonin. They have the most active venom of any living spiders.
One of their members, the Brazilian Huntsman, is thought to be the most venomous spider in the world. Brazilian wandering spiders are certainly dangerous and bite more people than any other spiders.
Check out more animals that begin with the letter B
More Fascinating Animals to Learn About
About joanne spencer.
I've always been passionate about animals which led me to a career in training and behaviour. As an animal professional I'm committed to improving relationships between people and animals to bring them more happiness.
UK Edition Change
- UK Politics
- News Videos
- Paris 2024 Olympics
- Rugby Union
- Sport Videos
- John Rentoul
- Mary Dejevsky
- Andrew Grice
- Sean O’Grady
- Photography
- Theatre & Dance
- Culture Videos
- Fitness & Wellbeing
- Food & Drink
- Health & Families
- Royal Family
- Electric Vehicles
- Car Insurance Deals
- Lifestyle Videos
- UK Hotel Reviews
- News & Advice
- Simon Calder
- Australia & New Zealand
- South America
- C. America & Caribbean
- Middle East
- Politics Explained
- News Analysis
- Today’s Edition
- Home & Garden
- Broadband deals
- Fashion & Beauty
- Travel & Outdoors
- Sports & Fitness
- Sustainable Living
- Climate Videos
- Solar Panels
- Behind The Headlines
- On The Ground
- Decomplicated
- You Ask The Questions
- Binge Watch
- Travel Smart
- Watch on your TV
- Crosswords & Puzzles
- Most Commented
- Newsletters
- Ask Me Anything
- Virtual Events
- Betting Sites
- Online Casinos
- Wine Offers
Thank you for registering
Please refresh the page or navigate to another page on the site to be automatically logged in Please refresh your browser to be logged in
Brazilian wandering spider: Where are they from and how deadly are they?
One was found in a bunch of supermarket bananas in london, article bookmarked.
Find your bookmarks in your Independent Premium section, under my profile

Sign up to the Independent Climate email for the latest advice on saving the planet
Get our free climate email, thanks for signing up to the independent climate email.
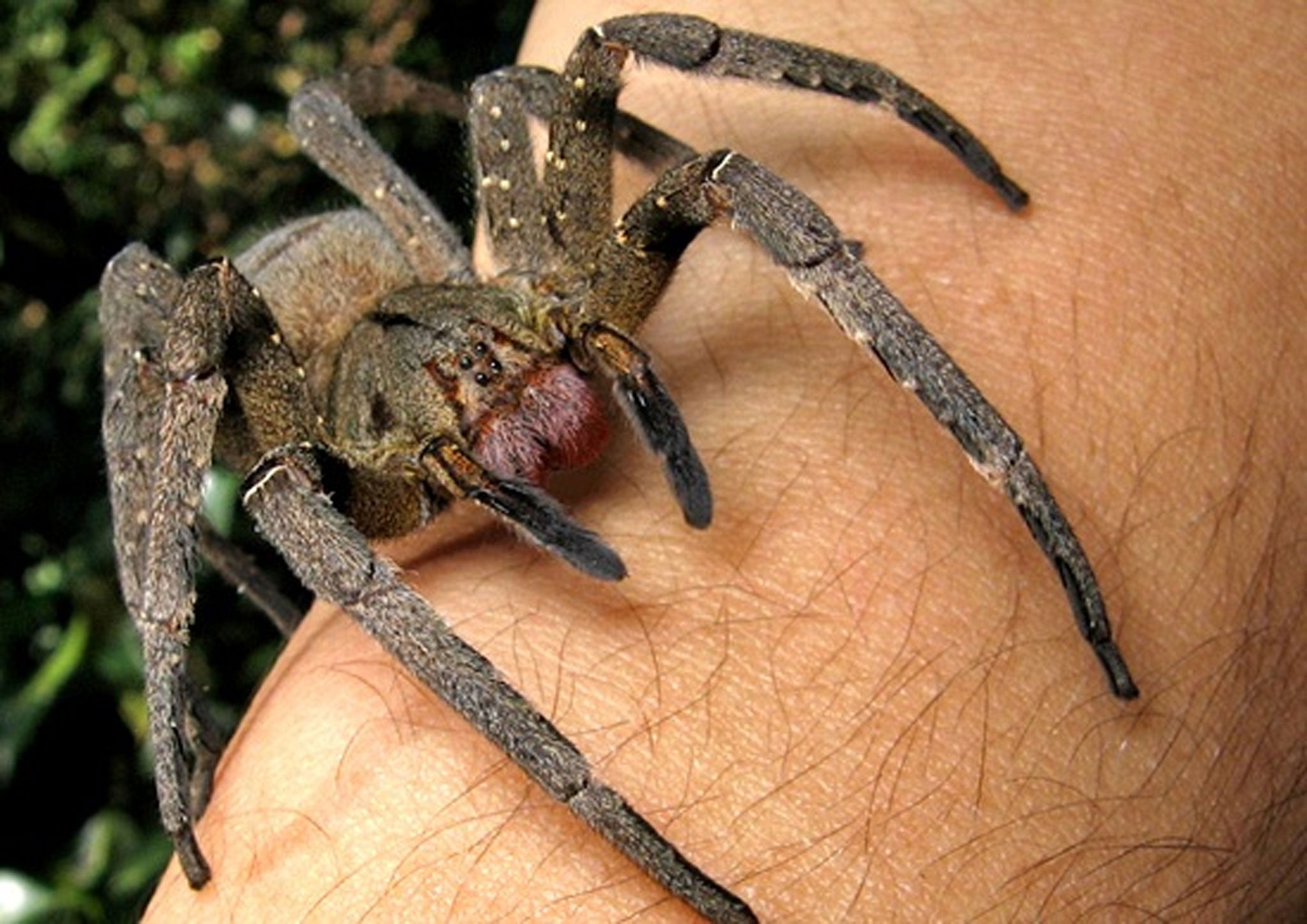
The world’s most venomous spider has been delivered to a south London home in a bunch of bananas.
Specialists were called in to trap the Brazilian wandering spider, which ripped its leg off in a bid to escape and left an egg sac full of thousands of baby spiders behind.
The family who received the deadly arachnid in their Waitrose online shop told the Mail on Sunday they were “too traumatised to remain in the house”, while the supermarket apologised for the “distressing” incident.
It was not the first time a Brazilian wandering spider made the long journey to the UK.
In 2005, a chef in Somerset was bitten by a stowaway that had been hiding in bananas delivered to his pub.
He was saved by anti-venom administered after a nearby zoo identified the arachnid from a picture he took on his phone before passing out.
The spiders and their eggs have also been found in bananas from a Tesco in Essex and One Stop in Staffordshire.
Where are they from?
Fortunately, it is very rare to find Brazilian wandering spiders in the UK or anywhere outside their natural habitat in South America.
They live in the forests of Costa Rica, Columbia, Peru, Brazil, and Paraguay and gain their name from the habit of moving across jungle floors at night in search of food.
In the day, they like hiding in places that are dark and moist and are known to favour piles of wood, garages, cupboards, shoes and even heaps of clothes.
The apparent tendency to hide in banana bunches – like in the latest incident – has given them the nickname “banana spider”.
Their scientific name translates as “murderess” in Greek and they are also known as the “armed spider”, because of their unusual attacking stance, and “horse stinger”.
How deadly is it?
The Guinness Book of World Records has named it the most venomous spider in the world for possessing the most active neurotoxic venom of any living spider.
The toxin PhTx3 causes extreme pain, swelling, paralysis, skin cell destruction, fatal breathing complications, heart attacks and painful erections (priapism) in men lasting up to four-hours.
Victims of a Brazilian wandering spider bite can reportedly be killed in an hour.
But few deaths occur because an effective anti-venom is available in Brazil and Guinness claims that people are killed, it is usually in children under the age of seven.
Scientists have reportedly considered investigating the use of the deadly venom as a possible ingredient for drugs treating erectile dysfunction.
What do Brazilian wandering spiders look like?
There are eight known species, with the most dangerous being the Phoneutria fera and the Phoneutria nigriventer.
All vary slightly in appearance but are known for their size, with a leg span of up to 15 cm (6 ins) and body length of up to 5 cm (2 ins).
They are covered with hair and usually dark brown in colour, with some displaying bright red hairs on their venom glands.
When Brazilian wandering spiders feel threatened, they adopt a distinctive “attacking” stance with their front legs in the air, swaying from side to side.
How do they attack?
The spiders use bites as their main form of attack but do not always deliver venom, using it only in an estimated third of bites.
They eat insects and small mammals, including other spiders, amphibians, reptiles and mice, hunting them on the ground and killing with an ambush or direct attack.
- Venomous spider delivered by supermarket
- Brazilian wandering spider eggs found in Essex
- Spider nest found in shop-bought bananas
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.
New to The Independent?
Or if you would prefer:
Want an ad-free experience?
Hi {{indy.fullName}}
- My Independent Premium
- Account details
- Help centre
- Share full article

Deadly Venom From Spiders and Snakes May Also Cure What Ails You
Efforts to tease apart the vast swarm of proteins in venom — a field called venomics — have burgeoned in recent years, leading to important drug discoveries.
A rattlesnake at the Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum, which keeps snakes and scorpions for their venom. Credit... Ash Ponders for The New York Times
Supported by
By Jim Robbins
- Published May 3, 2022 Updated May 6, 2022
TUCSON, Ariz. — In a small room in a building at the Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum, the invertebrate keeper, Emma Califf, lifts up a rock in a plastic box. “This is one of our desert hairies,” she said, exposing a three-inch-long scorpion, its tail arced over its back. “The largest scorpion in North America.”
This captive hairy, along with a swarm of inch-long bark scorpions in another box, and two dozen rattlesnakes of varying species and sub- species across the hall, are kept here for the coin of the realm: their venom.
Efforts to tease apart the vast swarm of proteins in venom — a field called venomics — have burgeoned in recent years, and the growing catalog of compounds has led to a number of drug discoveries. As the components of these natural toxins continue to be assayed by evolving technologies, the number of promising molecules is also growing.
“A century ago we thought venom had three or four components, and now we know just one type of venom can have thousands,” said Leslie V. Boyer, a professor emeritus of pathology at the University of Arizona. “Things are accelerating because a small number of very good laboratories have been pumping out information that everyone else can now use to make discoveries.”
She added, “There’s a pharmacopoeia out there waiting to be explored.”
It is a striking case of modern-day scientific alchemy: The most highly evolved of natural poisons on the planet are creating a number of effective medicines with the potential for many more.

One of the most promising venom-derived drugs to date comes from the deadly Fraser Island funnel web spider of Australia, which halts cell death after a heart attack .
Blood flow to the heart is reduced after a heart attack, which makes the cell environment more acidic and leads to cell death. The drug, a protein called Hi1A, is scheduled for clinical trials next year. In the lab, it was tested on the cells of beating human hearts. It was found to block their ability to sense acid, “so the death message is blocked, cell death is reduced, and we see improved heart cell survival,” said Nathan Palpant, a researcher at the University of Queensland in Australia who helped make the discovery.
If proven in trials, it could be administered by emergency medical workers, and might prevent the damage that occurs after heart attacks and possibly improve outcomes in heart transplants by keeping the donor heart healthier longer.
“It looks like it’s going to be a heart attack wonder drug,” said Bryan Fry, an associate professor of toxicology at the University of Queensland, who is familiar with the research but was not involved in it. “And it’s from one of the most vilified creatures” in Australia.
The techniques used to process venom compounds have become so powerful that they are creating new opportunities. “We can do assays nowadays using only a couple of micrograms of venom that 10 or 15 years ago would have required hundreds of micrograms,” or more, Dr. Fry said. “What this has done is open up all the other venomous lineages out there that produce tiny amounts of material.”
There is an enormous natural library to sort through. Hundreds of thousands of species of reptile, insect, spider, snail and jellyfish, among other creatures, have mastered the art of chemical warfare with venom. Moreover, the makeup of venom varies from animal to animal. There is a kind of toxic terroir: Venom differs in quantity, potency and proportion and types of toxin, according to habitat and diet, and even by changing temperatures due to climate change.
Venom is made of a complex mix of toxins, which are composed of proteins with unique characteristics. They are so deadly because evolution has honed their effectiveness for so long — some 54 million years for snakes and 600 million for jellyfish.
Venom is the product of a biological arms race over that time; as venom becomes more deadly, victims evolve more resistance, which in turn makes venom even deadlier. Humans are included in that dynamic. “We are made of protein and our protein has little complex configurations on it that make us human,” said Dr. Boyer, who founded the Venom Immunochemistry, Pharmacology, and Emergency Response Institute, or VIPER. “And those little configurations are targets of the venom.”
The specific cellular proteins that the venom molecules have evolved to target with pinpoint accuracy are what make the drugs derived from them — which use the same pathways — so effective. Some proteins, however, have inherent problems that can make new drugs from them unworkable.
There is usually no need to gather venom to make these drugs. Once they are identified, they can be synthesized.
There are three main effects from venom. Neurotoxins attack the nervous system, paralyzing the victim. Hemotoxins target the blood and local tissue toxins attack the area around the site of poison exposure.
Numerous venom-derived drugs are on the market. Captopril, the first, was created in the 1970s from the venom of a Brazilian jararaca pit viper to treat high blood pressure. It has been successful commercially. Another drug, exenatide, is derived from Gila monster venom and is prescribed for Type 2 diabetes. Draculin is an anticoagulant from vampire bat venom and is used to treat stroke and heart attack.
The venom of the Israeli deathstalker scorpion is the source of a compound in clinical trials that finds and illuminates breast and colon tumors.
Some proteins have been flagged as potential candidates for new drugs, but they have to journey through the long process of manufacture and clinical trials, which can take many years and cost millions of dollars. In March, researchers at the University of Utah announced that they had discovered a fast-acting molecule in cone snails . Cone snails fire their venom into fish, which causes the victims’ glucose levels to drop so rapidly it kills them. It holds promise as a drug for diabetes. Bee venom appears to work with a wide range of pathologies and has recently been found to kill aggressive breast cancer cells .
In Brazil researchers have been looking at the venom of the Brazilian wandering spider as a possible source of a new drug for erectile dysfunction — because of what happens to human victims when they are bit. “A characteristic of their envenomation is that males get extraordinary painful, incredibly long-lasting erections,” Dr. Fry said. “They have to separate it from its lethal factor, of course, and find a way to dial it back.”
Some scientists have long suspected that important secrets are locked up in venom. Scientific interest first surfaced in the 17th century. In the mid-18th century the Italian physician and polymath Felice Fontana added to the body of knowledge with his treatise, and in 1860 the first research to look at venom components was conducted by S. Weir Mitchell in Philadelphia.
The medicinal use of venom has a long history, often without scientific support. Venom-dipped needles are a traditional form of acupuncture. Bee sting therapy, in which a swarm of bees is placed on the skin, is used by some natural healers. The rock musician Steve Ludwin claims to have routinely injected himself with diluted venom, believing it to be a tonic that builds his immune system and boosts his energy.
The demand for venom is increasing. Ms. Califf of the Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum said she had to travel to the desert to find more bark scorpions, which she hunts at night with a black light because they glow in the dark. Arizona, Dr. Boyer said, is “venom central,” with more venomous creatures than in any other U.S. state, making it well suited for this kind of production.
Scorpion venom is harvested by applying a tiny electrical current to the arachnid, which causes it to excrete a small drop of the amber liquid at the tip of its tail. With snakes, venom glands are gently massaged as they bare their fangs over a martini glass. After they surrender their venom, the substance is sent to researchers around the globe.
Pit vipers, including rattlesnakes, have other unusual adaptations. The “pit” is the site of the biological equipment that allows snakes to sense the heat of their prey. “You can blindfold a snake and it will still strike the target,” Dr. Boyer said.
But it’s not just venom that’s far better understood these days. In the last few years, there has been a well-heeled and concerted search for antivenom.
In 2019 the Wellcome Trust created a $100 million fund toward the pursuit. Since then there have been numerous research efforts around the world looking for a single universal treatment — one that can be carried into remote areas to immediately help someone bitten by any type of venomous snake. Currently, different types of snakebites have different antivenom.
It has been difficult. The wide array of ingredients in venom that benefit new drug research has also made it difficult to find a drug that can neutralize them. One promising universal antivenom, varespladib, is in clinical trials.
Experts hope the role of venom will lead to more respect for the fear-inducing creatures who create them. Dr. Fry, for his work on anticoagulants, is studying the venom of Komodo dragons, which, at 10 feet long and more than 300 pounds, is the largest lizard in the world. It is also highly endangered.
Work on the Komodo, “allows us to talk about the broader conservation message,” he said.
“You want nature around because it’s a biobank,” he added. “We can only find these interesting compounds from these magnificent creatures if they are not extinct.”
Advertisement
Press ESC to close
The brazilian wandering spider: threats and treatments.
Imagine being bitten by a spider that not only causes excruciating pain, but also induces a painful and prolonged erection. This peculiar arachnid is no other than the Brazilian Wandering Spider, a creature that strikes fear into the hearts of many. This article explores the threats posed by this venomous spider and examines the treatments available for its bite. Prepare to discover the terrifying world of the Brazilian Wandering Spider and the measures taken to combat its deadly effects.
Table of Contents
Overview of the Brazilian Wandering Spider
Introduction to the Brazilian Wandering Spider
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, scientifically known as Phoneutria, is a species of venomous spider found primarily in South and Central America, with Brazil being its native habitat. These spiders are known for their distinct hunting techniques, potent venom, and the ability to wander, hence their name. With its aggressive nature and potentially lethal bite, the Brazilian Wandering Spider poses a significant threat to humans and animals alike.

Preferred Habitat and Distribution
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are adaptable creatures that can thrive in various habitats, ranging from tropical rainforests to urban areas. They prefer dark and secluded areas like tree stumps, piles of leaves, and crevices, typically found in the wilderness. However, due to deforestation and human encroachment, these spiders have also adapted to urban environments, often found hiding in woodpiles, sheds, and even inside homes.
Physical Characteristics
The Brazilian Wandering Spider is a large arachnid, with a leg span that can reach up to 6 inches. They have a brownish appearance with darker markings, aiding in their camouflage amidst bark and leaves. These spiders possess strong legs, enabling them to move quickly and gracefully. The most distinguishing feature of the Brazilian Wandering Spider is their characteristic defensive posture, where they raise their front legs to display their fangs.
Behavior and Hunting Techniques
Unlike most spiders that build webs for hunting, Brazilian Wandering Spiders are active hunters. They spend their nights on the move, searching for prey and avoiding potential predators. These spiders have excellent eyesight and rely on their acute senses to detect movements and vibrations. When hunting, they employ a unique technique known as “lurking,” where they stay hidden, waiting for their prey to approach before quickly pouncing on it.
Diet of Brazilian Wandering Spiders
Brazilian Wandering Spiders have a varied diet, which includes insects, small rodents, and even lizards. Their venomous bite immobilizes their prey, making it easier for the spider to handle and consume. While they primarily feed on live prey, these versatile spiders can also scavenge for food when necessary, increasing their chances of survival in harsh environments.
Venomous Threats Posed by Brazilian Wandering Spiders
Potency of brazilian wandering spider venom.
The venom of the Brazilian Wandering Spider is considered one of the most potent among spider species. It contains a neurotoxin called PhTx3, which affects the nervous system, causing severe pain, muscle spasms, and potentially life-threatening reactions. Due to its toxicity, the venom of this spider is not only harmful to humans but can also be lethal to animals, including pets.
Signs and Symptoms of Spider Bites
When bitten by a Brazilian Wandering Spider, the symptoms can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the amount of venom injected. Common signs of spider bites include intense pain, redness, swelling, and local tissue damage. In severe cases, individuals may experience systemic effects like muscle cramps, increased heart rate, sweating, and even difficulty breathing. It is crucial to seek medical attention immediately if bitten by this spider.

Health Risks and Potential Complications
Being bitten by a Brazilian Wandering Spider can lead to various health risks and potential complications. The neurotoxic effects of the venom can cause paralysis, respiratory failure, and in extreme cases, death. Additionally, some individuals may develop allergic reactions to the venom, further exacerbating the severity of the bite. Prompt medical treatment is essential to minimize the risks and complications associated with these spider bites.
Comparison to other Venomous Spiders
Compared to other venomous spiders, such as the Black Widow or Brown Recluse, the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s bite is known to be more lethal due to its potent venom. While the Black Widow and Brown Recluse spiders are found in different regions, their venom can cause severe local tissue damage and systemic symptoms as well. Each spider species presents unique risks, and understanding their differences is crucial in providing appropriate medical treatment.
Fatalities and Incidents Reported
Fatalities related to Brazilian Wandering Spider bites are rare, thanks to the availability of antivenom and timely medical interventions. However, incidents of spider bites resulting in immediate hospitalization and severe complications have been documented. Particularly vulnerable to these bites are children, the elderly, and those with underlying health conditions. Prompt reporting and proper management of spider bites are crucial to prevent tragic outcomes.
Medical Treatments for Brazilian Wandering Spider Bites
Emergency response and first aid measures.
In the event of a Brazilian Wandering Spider bite, immediate action is necessary. First and foremost, it is essential to stay calm and seek medical help without delay. While waiting for medical professionals to arrive, follow basic first aid measures, including cleaning the wound with mild soap and water, applying a cold compress to reduce swelling, and keeping the affected limb immobilized to minimize venom spread.
Antivenom Administration for Spider Bites
Antivenom is the primary treatment for Brazilian Wandering Spider bites. It contains antibodies that neutralize the venom’s effects, reducing pain and preventing further complications. Medical professionals will carefully administer the antivenom, closely monitoring the patient’s vital signs and ensuring appropriate dosage. Antivenom therapy is vital in counteracting the potent neurotoxin and providing the best chance for a successful recovery.
Management of Pain and Swelling
To alleviate pain and reduce swelling associated with spider bites, various medications can be prescribed. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to decrease inflammation and relieve discomfort. In some cases, opioids may be necessary to manage severe pain. Applying ice packs to the bite site and elevating the affected limb can also help reduce swelling.
Treatment Approaches for Systemic Effects
When systemic effects occur due to a Brazilian Wandering Spider bite, additional treatment approaches are required. Muscle relaxants and anticonvulsant medications may be administered to control muscle spasms and reduce the risk of convulsions. Supportive care, such as intravenous fluids and oxygen therapy, may also be provided to maintain hydration and ensure respiratory stability.

Long-Term Effects and Follow-Up Care
Even after the initial treatment of a Brazilian Wandering Spider bite, long-term effects may persist. Some individuals may experience residual pain, muscle weakness, or psychological trauma. Follow-up care is vital to monitor and manage any lingering symptoms. Physical therapy and counseling may be recommended to aid in rehabilitation and promote psychological well-being.
Prevention and Control Measures
Understanding spider behavior and habitats.
Understanding the behavior and habitats of Brazilian Wandering Spiders is crucial for effective prevention and control. Being aware of their preference for dark, secluded areas allows individuals to take proactive measures to minimize encounters. Regularly inspecting and cleaning potential hiding spots and sealing any gaps or cracks in homes and buildings can significantly reduce the chances of a spider infestation.
Spider Bite Prevention Tips
To prevent spider bites, adopting certain preventive measures is advisable. Avoid reaching into dark spaces without proper visibility, especially when gardening or working with woodpiles. Shake out clothing and shoes before wearing them, as spiders may seek refuge in these items. Using gloves when handling items in potential spider habitats can also provide a line of defense against accidental bites.
Safety Measures for Homes and Buildings
Creating a spider-free environment within homes and buildings can be achieved through implementing safety measures. Regularly clean and declutter living spaces, as spiders are attracted to dark and undisturbed areas. Installing screens on windows and doorways can prevent spiders from entering, and using weatherstripping to seal gaps will minimize entry points. Additionally, keeping outdoor lights off or changing the color to be less attractive to insects can also deter spiders.
Protective Clothing and Gear
When venturing into areas known for spider activity, wearing protective clothing and gear is essential to minimize the risk of bites. Long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and closed-toe shoes can provide a physical barrier between the spider and the skin. Additionally, using gloves, hats, and face shields can further protect vulnerable areas, reducing the chances of accidental bites.
Insecticides and Pest Control Methods
In cases where spider infestations become significant and pose a threat, the use of insecticides and professional pest control methods may be necessary. It is important to follow local regulations and recommendations when applying insecticides, as some may be harmful to humans and pets. Seeking the assistance of licensed pest control experts ensures effective treatment while prioritizing safety.
Research and Studies on Brazilian Wandering Spiders
Scientific studies and species classification.
Scientific studies play a crucial role in expanding our knowledge of Brazilian Wandering Spiders. Researchers conduct studies to better understand their taxonomy, behavior, and venom composition. Species classification helps identify specific variations within the Phoneutria genus, allowing for more targeted research and providing a foundation for conservation efforts.

Venom Extraction and Composition
Extracting and analyzing the venom of Brazilian Wandering Spiders is essential for developing effective antivenom and understanding the biochemical properties of the venom. Researchers aim to identify the specific toxins present, their mechanisms of action, and potential therapeutic applications. Studying venom composition can uncover valuable insights into the spider’s hunting strategies and aid in the development of novel pharmaceuticals.
Antivenom Development and Efficacy
Research on antivenom development focuses on improving the efficacy and safety of existing treatments. Scientists work to refine antivenom formulations, ensuring they neutralize the spider’s venom effectively. Testing the antivenom’s efficacy against various species of Brazilian Wandering Spiders is crucial to provide broad coverage and maximize the chances of successful treatment.
Environmental Impact and Conservation
Understanding the environmental impact of Brazilian Wandering Spiders is essential for effective conservation strategies. Research delves into the spider’s role in the ecosystem, its interactions with other species, and the potential consequences of population decline. By assessing their conservation status and identifying threats, scientists and policymakers can develop measures to protect this species and preserve its natural habitats.
Future Research Directions
As scientific advancements continue, future research on Brazilian Wandering Spiders will focus on areas such as genetic studies, venom evolution, and behavior analysis. Deepening our understanding of their genetics can provide insights into their adaptability and evolutionary history, aiding in conservation efforts. Additionally, studying behavioral patterns can enhance our ability to predict their movements and prevent human encounters.
Emerging Concerns and Cases of Brazilian Wandering Spider
Global spread and entry into new regions.
The global spread of the Brazilian Wandering Spider is a growing concern. Due to international trade and transportation, these spiders have been inadvertently introduced to regions outside their native habitat. Their ability to adapt to new environments increases the risk of establishing invasive populations, impacting local ecosystems and potentially posing a threat to human health.
Importance of Surveillance and Reporting
Surveillance and reporting systems are vital in monitoring and preventing the spread of Brazilian Wandering Spiders. Prompt and accurate reporting of potential sightings ensures swift action can be taken to mitigate the risks associated with these spiders. Encouraging public involvement and providing education on spider identification can help improve surveillance efforts and enable effective measures to be implemented.
Documented Cases Outside Brazil
While the Brazilian Wandering Spider is primarily found in Brazil, documented cases of encounters and bites have been reported in other countries. This highlights the potential for these spiders to establish populations beyond their native range and emphasizes the need for international cooperation in addressing this emerging concern. Sharing knowledge and experiences across borders is crucial in managing and preventing spider-related incidents.

Impact on Tourism and International Trade
The presence of Brazilian Wandering Spiders in areas heavily reliant on tourism and international trade can have significant economic implications. Fear of spider encounters and bites may deter tourists and affect the tourism industry. Moreover, the risk of transporting spiders through international trade, particularly in goods such as fruits or plants, poses a biosecurity concern that requires strict monitoring and prevention measures.
Legal and Regulatory Measures
To address the emerging concerns associated with the Brazilian Wandering Spider, legal and regulatory measures are necessary. Countries need to establish and enforce regulations on the import and export of potentially infested goods, ensuring adequate inspection protocols are in place. Collaboration between governments, organizations, and industries is crucial in establishing effective policies to minimize the risks posed by these spiders.
Interactions and Reactions from Local Communities
Fear and anxiety-related reactions.
The presence of Brazilian Wandering Spiders often elicits fear and anxiety among local communities. The aggressive behavior and potential dangers associated with these spiders contribute to a negative perception. Understanding the psychological impact of these fears is essential to develop educational programs and support services that address community concerns and promote emotional well-being.
Education and Awareness Programs
Educational initiatives and awareness programs play a vital role in mitigating the fears surrounding Brazilian Wandering Spiders. Providing accurate information about the spiders, their behavior, and the appropriate actions to take in case of encounters or bites can help alleviate anxiety and empower individuals to respond effectively. School programs, community workshops, and online resources are valuable tools to disseminate information and promote awareness.
Myths, Folklore, and Cultural Beliefs
Brazilian Wandering Spiders often find themselves entwined in myths, folklore, and cultural beliefs. Some local communities associate these spiders with superstitions and consider them to be omens or symbols of danger. Understanding these cultural beliefs and engaging in respectful dialogue is crucial to dispel myths, foster a better understanding of the spiders, and promote a harmonious coexistence.
Spider as a Symbol in Art and Media
The intriguing nature of the Brazilian Wandering Spider makes it a subject of fascination in art, literature, and media. Artists incorporate the spider’s image into various forms of expression, creating artwork that captures its mystique and intricate details. It serves as a reminder of the spider’s significance in both natural and cultural contexts, sparking conversations and encouraging further exploration.
Local Efforts for Spider Conservation
Communities residing in areas populated by Brazilian Wandering Spiders often play a crucial role in their conservation. Local conservation efforts may involve initiatives such as promoting sustainable land use, raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity, and establishing protected areas or nature reserves. Engaging local communities in spider conservation fosters a sense of ownership and shared responsibility for safeguarding these fascinating creatures.
Comparison with Other Dangerous Spider Species

Brown Recluse Spider
The Brazilian Wandering Spider and the Brown Recluse Spider both pose threats to humans, but they have distinct characteristics. While the Brazilian Wandering Spider is known for its wandering nature and highly potent neurotoxic venom, the Brown Recluse Spider is recognized for its reclusive behavior and venom that can cause necrotic skin lesions. Understanding the differences between these species is crucial in providing appropriate medical treatment for bites.
Black Widow Spider
Both the Brazilian Wandering Spider and the Black Widow Spider are venomous, but their venom composition and effects differ. While the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s venom primarily affects the nervous system, the Black Widow Spider’s venom contains neurotoxins that target the neuromuscular junctions. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate medical treatment are essential in managing bites from these spiders.
Sydney Funnel-Web Spider
The Brazilian Wandering Spider and the Sydney Funnel-Web Spider are both known for their potent venom and aggressive behavior. However, the Sydney Funnel-Web Spider is native to Australia, while the Brazilian Wandering Spider is found in South and Central America. Despite their geographical differences, both spiders require urgent medical attention in the case of bites due to the potential severity of their venom.
Redback Spider
The Redback Spider, native to Australia, is similar to the Brazilian Wandering Spider in terms of venom potency and potentially lethal bites. They both belong to the family of spiders known for their neurotoxic venom. While the Brazilian Wandering Spider is more active and known for its wandering behavior, the Redback Spider tends to build webs and wait for their prey. Understanding their distinct characteristics is essential in providing targeted medical treatment.
Taipan Spider
The Taipan Spider, also known as the Coastal Taipan or Australian Tarantula, is another venomous spider species found in Australia. Its unique venom composition makes it distinct from the Brazilian Wandering Spider. The Taipan Spider is known for its highly potent neurotoxic venom, but its behavior and physical characteristics differ significantly from those of the Brazilian Wandering Spider. Recognizing the differences helps in accurately identifying and managing spider encounters.
Misidentification and Popular Misconceptions
Confusion with harmless spider species.
Spider misidentification is a common occurrence, leading to unnecessary panic and fear. The Brazilian Wandering Spider may be mistaken for non-venomous species, such as harmless Huntsman or Wolf spiders, due to a superficial resemblance. Educating the public about distinguishing features and encouraging accurate identification can prevent unnecessary concern and promote a better understanding of these spiders.
Spider Hoax and Urban Legends
Urban legends and hoaxes involving spiders, including the Brazilian Wandering Spider, have contributed to public misconceptions. Sensationalized stories on social media or unreliable sources often exaggerate the dangers associated with these spiders, perpetuating unnecessary fears. Encouraging critical thinking and relying on reputable sources for information can help dispel myths and prevent the spread of false information.
Exaggerated Claims and Sensationalism
Exaggerated claims and sensationalism in media portrayals of the Brazilian Wandering Spider can contribute to public hysteria. Highlighting the spiders’ aggressive behavior and potential lethality without providing accurate context can create unnecessary panic. Promoting responsible journalism that presents factual information and provides balanced perspectives is essential to ensure accurate public understanding of these spiders.
Social Media Impact on Public Perception
Social media platforms have a significant influence on public perception and understanding of the Brazilian Wandering Spider. Misinformation can spread rapidly, contributing to fear and misunderstanding. It is crucial to encourage responsible sharing of information, verify facts before sharing, and promote scientific literacy to combat the spread of inaccuracies and ensure accurate portrayals of these spiders.
Expert Clarifications and Reliable Sources
Experts and reliable sources play a vital role in clarifying misconceptions surrounding the Brazilian Wandering Spider. Educating the public about the spiders’ behavior, venom potency, and risks through reputable sources is crucial. Scientists, researchers, and medical professionals can provide accurate and evidence-based information, addressing concerns and dispelling myths surrounding these spiders.
Conservation Efforts and Habitat Protection
Need for conservation initiatives.
Conservation initiatives are crucial to protect the Brazilian Wandering Spider and its natural habitats. The preservation of biodiversity, including these unique arachnids, is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems. By recognizing the ecological importance of spiders and their role in pest control, conservation efforts can be integrated into broader strategies aimed at preserving the planet’s biodiversity.
Preserving Natural Habitats
Preserving the natural habitats of Brazilian Wandering Spiders is paramount to their long-term survival. Protecting forests, wetlands, and other ecosystems ensures the spiders have suitable areas to thrive. Implementing sustainable land use practices and conservation policies that consider the needs of these spiders and their habitats can help safeguard their populations for future generations.
Captivity Breeding Programs
In certain cases, captivity breeding programs may be established to support the conservation of Brazilian Wandering Spiders. These programs provide controlled environments for breeding and rearing these spiders, ensuring genetic diversity and maintaining healthy populations. Collaboration between reputable institutions and regulatory bodies is crucial in developing and implementing successful breeding programs.
Community Involvement in Spider Protection
Engaging local communities in spider protection efforts fosters a sense of responsibility and promotes the overarching goal of conservation. Encouraging the participation of local residents in monitoring spider populations, reporting sightings, and supporting sustainable land use practices can enhance the effectiveness of conservation initiatives. Community involvement ensures that the conservation efforts reflect the needs and values of the people living in close proximity to these spiders.
Role of Zoos, Sanctuaries, and Research Institutions
Zoos, sanctuaries, and research institutions play a vital role in the conservation of Brazilian Wandering Spiders. These establishments provide controlled environments for the spiders, conduct research, and educate the public. By supporting scientific studies, raising awareness, and participating in breeding programs, these institutions contribute to the long-term conservation of these fascinating arachnids.
In conclusion, the Brazilian Wandering Spider, with its potent venom and unique hunting techniques, poses both a venomous threat and an ecological fascination. Understanding its behavior, venom, and appropriate medical treatments is crucial in mitigating risks associated with potential encounters. Conservation efforts, public education, and responsible reporting play essential roles in preserving the natural habitats of these spiders and dispelling myths surrounding them. By promoting a better understanding of the Brazilian Wandering Spider, we can foster a sense of coexistence and ensure the well-being of both humans and these remarkable arachnids.
Share this:
Mike Benkert
I'm a bug enthusiast and creator of BugsWorldWide, a blog sharing his 15 years of my experience caring for bugs. I've traveled the world bird watching and I'm committed to helping others with bug care. Contact me at [email protected] for assistance.
The Art of Life Organization
Understanding the behavior of juvenile silverfish, recent posts.
- Do Grasshoppers Have Backbones
- Pet Scorpion Species
- Moth Wing Patterns
- Insect Photography
- Beetle Larvae
- Grasshopper Species
- Cricket Anatomy
Discover more from BugsWorldWide
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Venomous spider found in Waitrose shopping 'beautiful but aggressive'
While most spiders scurry away when confronted, the Brazilian wandering spider stands its ground, says David Clarke of London Zoo
Killer spider found in family’s supermarket shopping
- How dangerous are Britain’s household spiders
The Brazilian wandering spider – which according to reports over the weekend emerged from a South London family’s Waitrose delivery – is one of the most infamous species of venomous spider.
It is actually a very beautiful spider, quite big, with about a 15-centimetre (six-inch) leg span. It is also quite aggressive, and while most spiders run away when confronted, the Brazilian wandering spider might stand its ground and has a particularly impressive stance – it rears up on its back legs and looks quite menacing. If it feels threatened it adopts an “attack first, ask questions later” sort of defence.
The species of Brazilian wandering spider that people tend to talk about are Phoneutria fera and Phoneutria nigriventer , which sometimes come into the UK – mainly because of things like fruit being imported. Accidentally imported spiders such as the one encountered by the family in South London are rare these days, however, because importers tend to clean off the fruit very well. There’s still the slight chance that one might be hidden away in a hand of bananas and get through.
Venom and bites
Although many types of spider have a venomous bite, the Brazilian wandering spider is one of the four types that have a more potent venom, and as such you would need a Dangerous Wild Animals (DWA) licence to keep it as a pet. Although spider bites do happen in South America, where this species is common, they are incredibly rare in the UK, and antivenins are available to counteract their venom.
As with most spiders, the Brazilian wandering spider will tackle things that are its own size. So in most cases that’s going to be large insects, but it will also take on small snakes, frogs and anything else it comes across that it can grab hold of. The venom is there mainly to subdue prey, but also as a warning: they have red hairs around the fangs and so a lot of animals know to leave them alone. It is a bit of an evolutionary quirk that some species have venom that has such a potent effect on big mammals such as ourselves.
Once the prey has been bitten, the venom immobilises and kills it, then the spider injects enzymes that break down the body tissues. The spider is then able to consume it.
Any time people are badly affected by a spider bite, the news tends to be plastered all over the press, blowing it out of proportion. Very few people get bitten by spiders or get a serious reaction to the bite. So it’s worth putting this in context. There are relatively few cases where the Brazilian wandering spider has actually caused any problems.
Can it survive the Great British weather?
The Brazilian wandering spider can’t survive our climate. It is a tropical species and there’s no expectation that it will be able to survive our harsh winters – that’s one thing we’re kind of lucky about if you want to look at it that way. What’s more, a centrally heated home during winter is a dry habitat that is not a good atmosphere for tropical spiders, and it probably won’t provide enough food for them.
We run the Friendly Spider Programme at ZSL London Zoo to treat people with arachnophobia because fear of spiders is very common. We teach people that houses are generally not great habitats for spiders.
But these are very valuable creatures. We’d be in serious trouble if there weren’t spiders around. In particular they act as biological controls, eating lots of other pests and creatures that might be more of a problem and pass on disease to humans. So the odd reported case of a spider bite is not that bad considering the enormously positive things they do generally.
Dave Clarke, head of invertebrates at ZSL London Zoo , was speaking to Guardian trainee journalist Aisha Gani
- Animal behaviour

Scorpion found in London home of BBC 6 Music presenter Ben Watt
Ed Balls photobombed by spider on BBC News

Spider photobombs BBC Scotland news

You call that a deadly spider? Australia's funnel web can kill in 15 minutes
Spider photobombs bbc scotland news - video.

Spider season is upon us – and so are the scare stories

Attack of the killer spiders and other stories sure to upset all arachnophobes

Spider app launched by ecologists

Essex woman finds eggs of world's most venomous spider in her shopping

Most viewed

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Brazilian wandering spider, also called the banana spider, is one of the planet's most venomous spiders. ... "So if the spider were to attack frequently and use up all of its venom, it [would ...
Phoneutria is a genus of spiders in the family Ctenidae.They are mainly found in northern South America, with one species in Central America. Members of the genus are commonly referred to as Brazilian wandering spiders. Other English names include armed spiders (armadeiras in Brazilian Portuguese) and banana spiders (a name shared with several others).
Brazilian wandering spiders are known for being aggressive, thanks to the alarming toxicity of their bite. However, interestingly, that behavior is actually a defense mechanism. When threatened or under attack, they raise their first two pairs of legs, indicating to their predators that the they are ready to attack.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider is a hunter of incredible power and once it targets its victim, the outcome is certain. Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubs...
Here are a few more notable characteristics of the Wandering Spider: Females are larger than males, with a body length of up to 1.6 inches (4 cm). They have eight eyes, arranged in two rows, which help them in hunting. The Wandering Spider is primarily found in Central and South America, particularly in Brazil.
Phoneutria nigriventer is a species of medically significant spider in the family Ctenidae, found in the Southern Cone of South America (Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay, and Argentina). Along with other members of the genus, they are often referred to as Brazilian wandering spiders.. Its bite can cause severe symptoms, including increased pulse, blood pressure, and respiratory rate; extraordinary ...
Clean the bite site with soap and water. Put a wet, cold cloth, or an ice pack on the bite site. Seek urgent medical attention, and bring the spider with you to help with identification, when possible. First aid administration: The First Aid for Brazilian Wandering Spider Bites includes cleaning the bite area and seeking medical attention.
The Brazilian wandering spider can grow to have a leg span of up to 4 - 5 inches. They are large hairy spindly-looking spiders who have eight eyes, two of which are large. Brazilian wandering spiders are fast-moving spiders, their legs are strong and spiny and they have distinctive red jaws which they display when angered.
Victims of a Brazilian wandering spider bite can reportedly be killed in an hour. But few deaths occur because an effective anti-venom is available in Brazil and Guinness claims that people are ...
Wandering spiders (Ctenidae) are a family of spiders that includes the Brazilian wandering spiders.These spiders have a distinctive longitudinal groove on the top-rear of their oval carapace similar to those of the Amaurobiidae. They are highly defensive and venomous nocturnal hunters. Wandering spiders are known to hunt large prey, for example hylid species Dendropsophus branneri.
Neurotoxins attack the nervous system, paralyzing the victim. ... In Brazil researchers have been looking at the venom of the Brazilian wandering spider as a possible source of a new drug for ...
Discover the threats of the Brazilian Wandering Spider, a venomous creature causing excruciating pain and prolonged erections. Explore its habitat, physical characteristics, hunting techniques, and diet. Learn about the potency of its venom, signs of bites, health risks, and potential complications. Find out the treatments available, including antivenom administration and management of pain ...
Please subscribe to the channelAttack/Defense of brazilian wandering spider - the world's most venomous spiderPhoneutria, commonly known as Brazilian wanderi...
The venom of the tiger wandering spider, a large and venomous arachnid, targets the muscles and the nervous system of its prey with two different strategies. It disrupts ion channels and causes paralysis, and it also disturbs the balance of the body and causes a blood sugar spike. Learn more about the venom's components, the neurotoxins, and the potential for new treatments.
wandering spider, (family Ctenidae), any member of the family Ctenidae (order Araneida), a small group of large spiders of mainly tropical and subtropical regions, commonly found on foliage and on the ground. Their first two legs are armed with strong bristles on the lower side. Cupiennius salei, found in rainforests in Central and South America, has a characteristic banding pattern on its ...
Other articles where Brazilian wandering spider is discussed: wandering spider: The Brazilian wandering spiders, Phoneutria fera and P. nigriventer, are sometimes also referred to as banana spiders because they are frequently found on banana leaves. They have an aggressive defense posture, in which they raise their front legs straight up into the air.
Brazilian wandering spiders are classified among the most venomous spiders on Earth, as their bites can be deadly to humans, especially children. - Articles from The Weather Channel | weather.com
The Brazilian wandering spider - which according to reports over the weekend emerged from a South London family's Waitrose delivery - is one of the most infamous species of venomous spider ...
SCATTERED SPIDER Exploits Windows Security Deficiencies with Bring-Your-Own-Vulnerable-Driver Tactic in Attempt to Bypass Endpoint Security. January 10, 2023. CrowdStrike Intelligence Team Counter Adversary Operations. In December 2022, CrowdStrike reported on a campaign by SCATTERED SPIDER, targeting organizations within the telecom and ...
The Brazilian wandering spider or banana spider is the most venomous spider in the world! This dangerous arachnid delivers toxic venom whose bite requires im...
Please subscribe to the channelPhoneutria - Armadeira - Brazilian Wandering Spider Atack/DefenseBites from the Brazilian Wandering spider may result in only ...
Discover the natural world like never before: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p4SjIjUJkek&list=PLFsd00e8nq8oDNoFvqxp6-loCskE6XNhG&pp=gAQBiAQBI'm always asked...
Scattered Spider, also referred to as UNC3944 among other names, is a hacking group mostly made up of individuals aged 19 to 22 as of September 2023. The group, whose name was first tagged by cybersecurity researchers, gained notoriety for hacking Caesars Entertainment and MGM Resorts International, two of the largest casino and gambling companies in the United States.
Giant, tarantula-sized spider that approached our house in the middle of the day. It attacked my shoe repeatedly, as shown in the video, and finally sunk it...