- Human rights
- International
Ex. Saúde, Presidente, Governo
- TVBrasilPlay
- Carta de Serviços


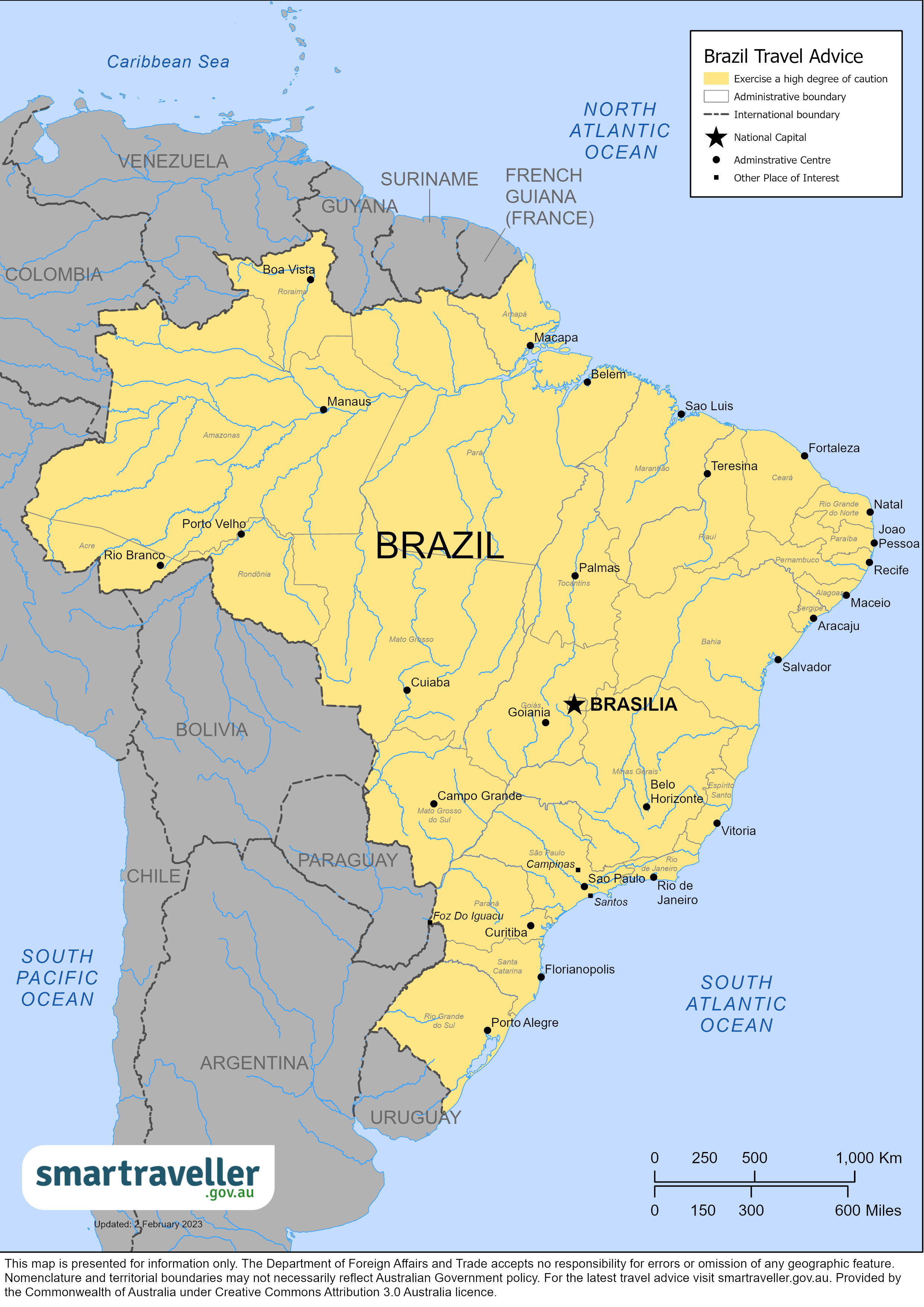
Know the rules for the entry of travelers into Brazil
Document was published in the official gazette on saturday.
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Linkedin
Published on 29/11/2021 - 15:34 By Agência Brasil - Brasília
Click to listen:.

Restrictions
Temporary flights to Brazil that originate in or pass through the following countries are prohibited: Republic of South Africa; Republic of Botswana; Kingdom of Essuatini; Kingdom of Lesotho; Republic of Namibia and Republic of Zimbabwe.
It is also temporarily suspended the authorization for foreign travelers to travel to Brazil, traveling or traveling in these countries in the last 14 days before embarking.
Entrance of Brazilians
The rules, according to Anvisa, do not restrict the entry of Brazilians, of any nature or origin. "Brazilians are not restricted from accessing the country", reinforced the agency, in a statement.
At the moment, Brazilians who have been to one of the six countries listed must complete a 14-day quarantine in their final destination city in Brazil.
It is also necessary to complete the Traveler's Health Declaration within 24 hours prior to departure to Brazil.
Travelers must also present a non-detectable (negative) RT-PCR test, performed within the last 72 hours before boarding, or a negative antigen-type test, performed within 24 hours before boarding.
Children under 12 years of age traveling with an escort do not need to present the exam, as long as all accompanying persons present documents with a negative or non-detectable result.
According to Anvisa, foreigners who have not passed through the six countries on the restriction list can enter Brazil as long as they meet the same determinations valid for Brazilian travelers.
The entry of foreign nationals traveling or with a ticket is suspended, in the last 14 days before boarding, in any of the six countries listed, with the exception of foreigners who meet one of the following criteria: foreigners with permanent residence, for a fixed or indefinite period, in Brazilian territory; foreign professional on a mission at the service of an international organization, as long as identified; foreign official accredited to the Brazilian government; foreigner who is a spouse, partner, child, parent or guardian of a Brazilian; whose entry is specifically authorized by the Brazilian government in view of the public interest or for humanitarian reasons; and holder of the National Migration Registry.
flight arrivals
Flights to Brazil that originate or pass through the Republic of South Africa, Republic of Botswana, Kingdom of Essuatini, Kingdom of Lesotho, Republic of Namibia and Republic of Zimbabwe are prohibited.
The restriction does not apply to the operation of cargo flights, handled by workers dressed in personal protective equipment (PPE), whose crew must observe the sanitary protocols specified in the Civil House ordinance.
Cruise ship travel, according to Anvisa, remains authorized, and compliance with the protocol established by Anvisa is mandatory.
Only ships that sail exclusively in Brazilian waters during the cruise season are authorized.
cargo ships
The operation of cargo ships is also authorized. Vessels, according to the agency, must follow strict protocols, which provide for examinations for the embarkation and disembarkation of crew members and quarantine in the event of a suspected or confirmed case on board.
land access
Anvisa highlights that the entry into the country of foreigners of any nationality by highways or any other land means remains prohibited.
Exceptions provided for in the ordinance include, for example, freight transport and transit between twin cities (municipalities that are crossed by the border, drought or river).
Text translated using artificial intelligence.
Relacionadas
Pandemia: cuidados devem ser mantidos com variante ômicron, covid-19: o que se sabe até agora da variante ômicron, destaques ebc.
Conteúdos extras dos outros veículos de comunicação da EBC para lhe informar mais
Comuns nos centros urbanos, pombos são vetores de doenças graves
Ouça ao vivo: flamengo e nova iguaçu duelam pelo título do campeonato carioca, todos comemoram a volta de ali para a cirurgia.

Nine out of ten Brazilians admit to having believed fake news
A quarter of the people say they have been accused of spreading falsehoods by those with a different worldview. The survey was carried out by the Locomotiva Institute and was obtained exclusively by Agência Brasil.

São Paulo inaugurates shelter for migrants
According to Nascimento, the state secretary for Social Development, most Afghans do not stay in Brazil; they are headed for Europe and the United States.

Brazil's trade balance registers $7.482 bi surplus in March
On the export front, the fall in international prices of soybeans, oil, and meat was the primary factor contributing to the decrease in Brazilian exports.

Brazil surpasses 1,000 dengue fatalities this year
There is a downward trend in the number of dengue cases in the states of Acre, Amazonas, Espírito Santo, Goiás, Minas Gerais, Piauí, Roraima, and the Federal District.

Tests detect mercury in Yanomami indigenous hair samples
A total of 287 hair samples from individuals of various age groups, including children and the elderly, were examined. 84% of them showed levels exceeding 2.0 µg/g.
Brazil now requires visas for tourists from Australia, Canada, USA
Starting April 10, tourists from these three countries must apply for an electronic visa, known as an e-Visa, through the platform: https://brazil.vfsevisa.com .

Pardon request for indigenous people victims of dictatorship approved
In its report, the National Truth Commission highlighted that at least 8,350 indigenous people were murdered, and many others endured various forms of violence and abuse.

Brazil records increase in proven oil reserves in 2023
Geologist Jorge Figueiredo notes that Brazil produces 3.5 mi barrels of oil per day, significantly exceeding its domestic consumption of around 2.5 mi barrels a day.

Rio releases new mosquitoes used to fight dengue fever
The municipality started a new release of wolbitos—mosquitoes infected with the Wolbachia bacteria. The microorganisms are used to combat arboviruses such as dengue, Zika, and chikungunya, as they prevent the viruses that cause these diseases from developing inside their main carrier.

Brazil adopts single dose of HPV vaccine
"A single vaccine will provide lifelong protection against various types of diseases and cancers caused by HPV," stated Health Minister Nísia Trindade.
- Quick access
- Government Agencies
- Access to Information
- Legislation
- Accessibility
- Reset Cookies
- Switch to high contrast mode
Ministério das Relações Exteriores

Português | Español

Consular affairs

Bilateral relations

Itamaraty Palace
Press releases, attack on humanitarian aid workers and hospital in the gaza strip, earthquake in chinese taipei, attack at iranian consulate in damascus, speeches, articles and interviews, address by minister mauro vieira at the yasser arafat foundation – ramallah, 17 march 2024, ministerial conversation on trade and sustainable development, including trade and industrial policy space for industrial development.
Address by Minister Mauro Vieira at WTO Ministerial Conference - Abu Dhabi, 26 February 2024
Address by Minister Mauro Vieira at the ministerial meeting of the Cairns Group - Abu Dhabi, February 25, 2024
- KAYAK for Business NEW
Brazil Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status
Traveling from the United States to Brazil
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces.
Ready to travel?
Find flights to brazil, find stays in brazil, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Brazil from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brazil.
Can I travel to Brazil if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Brazil without restrictions.
Can I travel to Brazil without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Brazil without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Brazil?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Brazil.
Can I travel to Brazil without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Brazil?
Mask usage in Brazil is not required in public spaces.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Brazil?
Restaurants in Brazil are open. Bars in Brazil are .
Situation in Haiti April 5, 2024
U.s. citizens in haiti, update january 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Learn about your destination
Take 90 seconds for safer travel.
Travel Advisory Levels
Enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Brazil travel advice
Latest updates: Natural disasters and climate – update of information on flooding in southeastern states
Last updated: March 26, 2024 18:16 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, brazil - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Brazil due to high crime rates and regular incidents of gang-related and other violence in urban areas.
Back to top
Crime is a serious problem throughout Brazil. Crime rates are highest in urban centres, particularly in areas adjacent to impoverished neighbourhoods of:
- Rio de Janeiro
- São Paulo
Foreign tourists are most commonly affected by theft but incidents of violent crime have also occurred, due to the high prevalence of guns coupled with the willingness of criminals and police to resort to violence. To avoid becoming a victim of crime, be aware of your surroundings at all times and follow the security directives of local authorities.
Petty crime
Street crime, including pickpocketing, purse snatching and theft from cars, is common in Brazil’s large cities. Tourists are a favourite target.
Petty theft on buses and the metro is common. It is a significant concern in Recife.
Incidents of opportunistic crime increase significantly at large-scale sporting events, international conferences and during holidays such as the Carnival and New Year’s celebrations.
Flash mob robberies ( arrastões ) have occurred sporadically on Rio’s city beaches and in other crowded tourist areas. This type of crime involves a group of thieves (often young children and youth originating from nearby favelas) that swarm an area and snatch valuable items such as cash, jewellery and cell phones.
A common ruse used by criminals is the Good Samaritan scam, where a criminal offers to help a tourist who looks lost. If you are lost, go into a nearby business or hotel to ask for help.
- Ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- Remain vigilant when visiting tourist destinations such as:
- outdoor markets
- hotel grounds
- bars and nightclubs
- airports and bus stations
- Avoid showing signs of affluence such as expensive jewellery, watches, clothing and bags
- Carry only small amounts of cash
- Keep cameras and portable electronic devices concealed
- Be aware of ploys to distract your attention
- Remain cautious with new acquaintances who ask for information or offer hospitality or assistance
- Book tours with reliable agencies
Violent crime
Armed robberies occur regularly, even during the day. They are a growing concern at restaurants, particularly in larger cities. Hold-ups can occur on Brazil’s trains. Assaults are frequently perpetrated in unofficial taxis.
Incidents of sexual assault against male and female foreigners have been reported, sometimes involving the use of sedatives.
Victims have been seriously injured or killed when resisting perpetrators, who may be armed or under the influence of drugs.
- Exercise a high degree of caution at all times
- Avoid travelling alone, especially at night
- Avoid parks or central (downtown) areas of major cities
- Avoid poorly lit and isolated streets
- Avoid walking on isolated and unsupervised beaches with poor visibility from the sidewalk
- If you are threatened by robbers, don’t resist.
Express kidnappings
The number of kidnappings in the Rio de Janeiro Metropolitan area has significantly increased since 2022.
Criminals may kidnap a victim for a few hours and force them to withdraw funds at an ATM for their release. Thieves may put drugs into food and drinks, temporarily incapacitating victims, who become quickly disoriented and are vulnerable to kidnapping.
- Use only a reputable taxi company or a trusted ride-sharing app
- Avoid showing signs of affluence, such using cell phones, headphones and wearing jewelry
- Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers
- Be wary of accepting these items from new acquaintances
Borders with Colombia and Venezuela
There is a concerning level of serious criminal activity by organized criminal groups along the border areas with countries bordering Brazil, particularly Colombia and Venezuela. Incidents of attacks on tourists and kidnapping have occurred. Be extremely cautious when crossing into bordering countries.
Vulnerable neighborhoods
Vulnerable neighborhoods (commonly referred to as “favelas”), are characterized by informal housing developments, crowded quarters, poorer conditions, and/or irregular construction.
Gang-related violence and organized crime is prevalent in these areas and police assistance is very limited.
Avoid renting accommodations in vulnerable neighborhoods, and travelling to these areas, even on a guided tour.
Police operations
Armed clashes and shootouts between police forces and alleged criminals regularly occur in vulnerable neighbourhoods. Police operations have led to retaliation by criminal gangs. Vulnerable neighbourhoods are located across major cities, as a result, there is an ongoing risk of violence spilling over to neighbouring areas, including affluent neighbourhoods and tourist destinations. There have been incidents of injuries and deaths as a result of stray bullets near, and in, vulnerable neighbourhoods.
Credit card and ATM fraud is a major problem. Be cautious when using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention when your cards are being handled by others
- use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Cybercrime is also a growing problem. Perpetrators monitor social media sites and eavesdrop on your conversations when you are in the country.
- Do not discuss travel plans or any other personal information within earshot of strangers
- Be cautious when posting information on social media
- Be particularly vigilant in internet cafes
Overseas fraud
Pirate attacks and armed robbery against ships occur in coastal waters. Mariners should take appropriate precautions.
Live piracy report - International Maritime Bureau’s Piracy Reporting Centre
Demonstrations
Demonstrations take place regularly. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
Protests can cause delays on main roads, including to airports, such as to the Guarulhos International Airport i n São Paulo . Demonstrations tend to increase in frequency and intensity during major events that attract foreign visitors.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Women’s safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse.
- Avoid travelling alone at night
- Avoid carrying purses
Advice for women travellers
Spiked food and drinks
Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
The use of sedatives to facilitate robberies of personal belongings has been reported on beaches in Rio and in crowded restaurants in São Paulo.
- Never leave your belongings unattended on city beaches
- Ask for drinks coming from sealed bottles or cans instead of in plastics glasses
- In restaurants, avoid sitting close to the entrance
Coastal waters can be dangerous.
- Swim or surf in areas where lifeguards are located
- Avoid swimming where there are strong currents
- Be wary of sharks, especially in Brazil’s north east near Recife
- Follow the instructions and warnings of local authorities.
Robberies are frequent and occur in tourist destinations, including on hiking trails. Be especially cautious on the Corcovado trail in Rio, where several robberies have happened.
If you intend on trekking:
- never do so alone
- always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you’re properly equipped and well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary, including when you expect to be back
- obtain detailed information on trekking routes before setting out
- ensure the trail doesn’t pass through a favela
- do not venture off marked trail
Adventure tourism
Amazon border regions and the Pantanal wetlands are largely uninhabited and dangerous areas.
Travel in these regions only with trained guides.
Public transportation
The subway systems in Rio and in São Paulo are generally safe during the day. Be extremely cautious using public transportation at night
There have been reports of theft and violence on city buses in Rio de Janeiro and near vulnerable neighbourhoods across the country, especially during rush hour.
Inter-city buses are generally reliable. Ensure that you use a reputable company before you book your travel.
Bus accidents occur regularly.
Major bus services charge fixed, pre-paid rates.
Do not use public vans.
Local law requires the use of the taxi meter to determine the legal fare. Adding surcharges to a fare is illegal.
Should taxi rates change and their taxi meters have not been adjusted, drivers may indicate these changes by showing an authorized paper with the new fares.
Many tourists hire “radio taxis”, also known as “commun taxis.” These taxis operate at a fixed price irrespective of the time of the day and the time it takes to arrive at your destination.
- Only use official taxis
- Upon arrival to Brazil, purchase your fare from licensed taxi offices in the airport arrival hall or near the taxi queues
- During your stay, use licensed taxis from taxi stands
Road safety
Brazil has one of the highest road accident rates in the world.
Road conditions are generally acceptable in large cities but badly maintained in the rest of the country. Poor signage and construction also pose a hazard.
Drivers do not respect traffic laws. Drivers are extremely aggressive and reckless and often drive at excessive speeds.
At night, it is common for drivers to treat red lights as stop signs to protect against hold-ups at intersections. Pedestrians and motorists proceeding through green lights during these hours should be particularly cautious.
- Be careful when stopping on the side of any highway because of traffic
- Be careful of motorbikes when changing lanes
- When driving in the city, pay particular attention to your surroundings while waiting at traffic lights
- If you feel threatened at any time, do not stop
- If you are in a traffic accident, call the police immediately
- Never confront the driver of another vehicle
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Effective April 10, 2024, Canadian passport holders will be required to obtain a visa to enter Brazil.
For more information, contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Brazil.
Useful links
- Information on visitor visas – Ministry of foreign affairs of Brazil
- Visitor visa – General consulate of Brazil
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Brazilian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Brazil.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: not required for stays of up to 90 days Business visa: not required for stays of up to 90 days without remuneration Student visa: not required for stays of up to 90 days
Length of stay
A tourist stay can be granted for up to 90 days. The permitted length of stay for tourists is determined by the immigration officer upon entry.
If you intend to stay more than 90 days, you must obtain an extension from the Federal Police for a maximum stay of 180 days per period of 12 months.
To request a visa extension, you will have to:
- request such an extension prior to the expiration of the authorized stay
- provide your detailed (long-form) birth certificate
In order for your Canadian long form birth certificate to be accepted in Brazil, it must be presented to the Brazilian Embassy or one of its consulates prior to departure from Canada. Neither the Embassy of Canada nor its consulates in Brazil can authenticate a Canadian birth certificate outside of Canada.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Dengue: Advice for travellers - 25 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is a risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is not required to enter this country.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is recommended depending on your itinerary.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites.
About Yellow Fever Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by an animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. Rabies treatment is often available in this destination.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis causes skin sores and ulcers. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
Visceral leishmaniasis (or kala azar) affects the bone marrow and internal organs. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly. It can also be transmitted by blood transfusion or sharing contaminated needles. If left untreated it can cause death. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease) is a risk in this country. It is caused by a parasite spread by infected triatomine bugs. The infection can be inactive for decades, but humans can eventually develop complications causing disability and even death.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from triatomine bugs, which are active at night, by using mosquito nets if staying in poorly-constructed housing. There is no vaccine available for Chagas disease.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Medical services and facilities
Good health care is only available in major cities. Quality of care varies greatly throughout the country.
Private hospitals and clinics located in cities are often better staffed and equipped than public or rural facilities.
Some medical facilities in the state of Rio de Janeiro have closed or are providing limited services, due to lack of funding for their operations. Private hospitals remain operational.
Certain medications may not be available.
Physicians and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment.
Medical evacuation can be very expensive and you may need it in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe.
Avoid areas of known drug trafficking. Travellers should not, under any circumstances, carry any items for strangers, especially baggage and parcels.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Child sex tourism
Brazil is actively seeking to prevent child sex tourism. A number of tourists have been convicted of offences relating to the corruption of minors.
The legal age of consent in Brazil is 18. Prison sentences are severe.
Child Sex Tourism: It’s a Crime
Identification
You must carry photo identification, such as a passport or driver’s license. Keep a photocopy of your passport in a safe place, in case it’s lost or confiscated.
Not carrying identification can lead to problems and delays if stopped by police or in case of a medical emergency.
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Brazil.
If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Brazil, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. You may also be subject to different entry/exit requirements .
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. The convention applies between Canada and Brazil.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Brazil, and if the applicable conditions are met, you may apply for the return of your child to the Brazilian court.
If you are in this situation:
- act as quickly as you can
- contact the Central Authority for your province or territory of residence for information on starting an application under The Hague Convention
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Brazil to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- List of Canadian Central Authorities for the Hague Convention
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- The Hague Convention - Hague Conference on Private International Law
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
The legal blood alcohol limit is 0.00% in Brazil. If the police suspect you of drinking and driving, they could confiscate your driver’s licence on the spot. If convicted, you can expect heavy fines and possible jail sentences.
You can drive in Brazil for up to 180 days with a valid Canadian driver’s licence. Obtain an official Portuguese translation of your Canadian driver’s licence to help when dealing with local authorities.
You should carry an international driving permit.
International Driving Permit
The currency is the real (BRL).
Canadian bank cards may not work in ATMs. They should have a pin with a maximum of 4 digits to work in Brazil.
Canadian dollars are not generally accepted, except by some exchange bureaus, most likely at airports. Do not exchange money on the street.
Carry small bills, as change is often unavailable for small transactions.
Flooding in southeastern states
On March 23, 2024, heavy rains and strong winds caused severe flooding across southeastern Brazil, resulting in several casualties. There are reports of several landslides causing significant damage to buildings and infrastructure, particularly in the states of Sao Paulo, Espirito Santo and Rio de Janeiro. Evacuation efforts are underway. More rain is expected in the hours and days to come.
The following essential services could face further disruptions :
- transportation
- power distribution
- fuel supply
- water and food supply
- telecommunications networks
- emergency services
- medical care
If you're in an affected area:
- shelter in a safe place and stay indoors
- exercise caution
- monitor local news and weather reports
- follow the instructions of local authorities, including evacuation orders
Weather alerts – National Institute of Meteorology (in Portuguese)
El Niño
The complex weather phenomenon called El Niño happens at irregular intervals of 2 to 7 years and can last 9 months to 2 years. El Niño generally generates droughts and heavy rainfalls, which could cause flooding, landslides, and mudslides, and could severely disrupt travel. Extreme droughts and heavy rains could limit access to food, drinking water, hygiene products, and medication. Severe weather could occur, such as:
- Below-average rainfall and droughts in the north and northeast
- Excessive rains in the south and southeast of the country
- Above-average temperatures in all regions
Keep informed of regional weather forecasts before and during your travels, and plan accordingly. Ensure you have adequate insurance to cover the consequences of such events, including the disruption of travel plans.
Learn about El Niño
Rainy seasons
The rainy seasons extend from:
- January to July in the north
- October to April in the south and southeast
- April to July in the northeast
Flash floods can occur outside of the rainy season.
They can hamper overland travel, especially in rural areas. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged. Travel conditions on mountain roads and on highways leading to beaches can be dangerous. Seasonal flooding can also reduce the provision of essential services. Power outages are frequent during the rainy season.
Avoid the affected areas, keep informed of regional weather forecasts and follow the instructions of local authorities.
- Weather warnings – National Institute of Meteorology (in Portuguese)
- Weather forecast – Climatempo (in Portuguese)
- More about hurricanes, typhoons, cyclones and monsoons
Landslides
Landslides are becoming more common in Brazil and are the result of heavy rainfall. During heavy rainfall, landslides are more likely to occur.
Dry season
Brasilia and the interior of the country experiences extreme dry periods between June and September. Humidity levels can drop below 10% and heat levels rise significantly.
Stay informed of regional weather forecasts and plan accordingly.
A severe drought is affecting the south east of Brazil.
The water supply in São Paulo, including to the city of São Paulo, has been significantly affected. Some areas of São Paulo are experiencing water shortages, and the water quality has diminished.
Use only bottled water for drinking and cooking.
Bush and forest fires are common between May to September, particularly in Brasilia.
The air quality in areas near active fires may deteriorate due to heavy smoke. In case of a major fire:
- stay away from the affected area, particularly if you suffer from respiratory ailments
- follow the instructions of local emergency services personnel
- monitor local media for up-to-date information on the situation
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police (military): 190
- medical assistance: 192
- firefighters: 193
Tourist police
- Rio de Janeiro: (21) 2332 2924 or 2334 6802
- São Paulo: (11) 3120 4447 or 3151 4167
- Salvador: (71) 3116-6817
- Recife: (81) 3322-4867
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Brazil, in Brasilia, or the Consulate General of Canada in São Paulo or Rio de Janeiro and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
You may call the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa toll-free at 0 800 891-6614.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Section 10 - Tanzania & Zanzibar
- Section 10 - Cusco & Machu Picchu
CDC Yellow Book 2024
Author(s): Alexandre Macedo de Oliveira
Destination Overview
Infectious disease risks, environmental hazards & risks, safety & security, availability & quality of medical care.
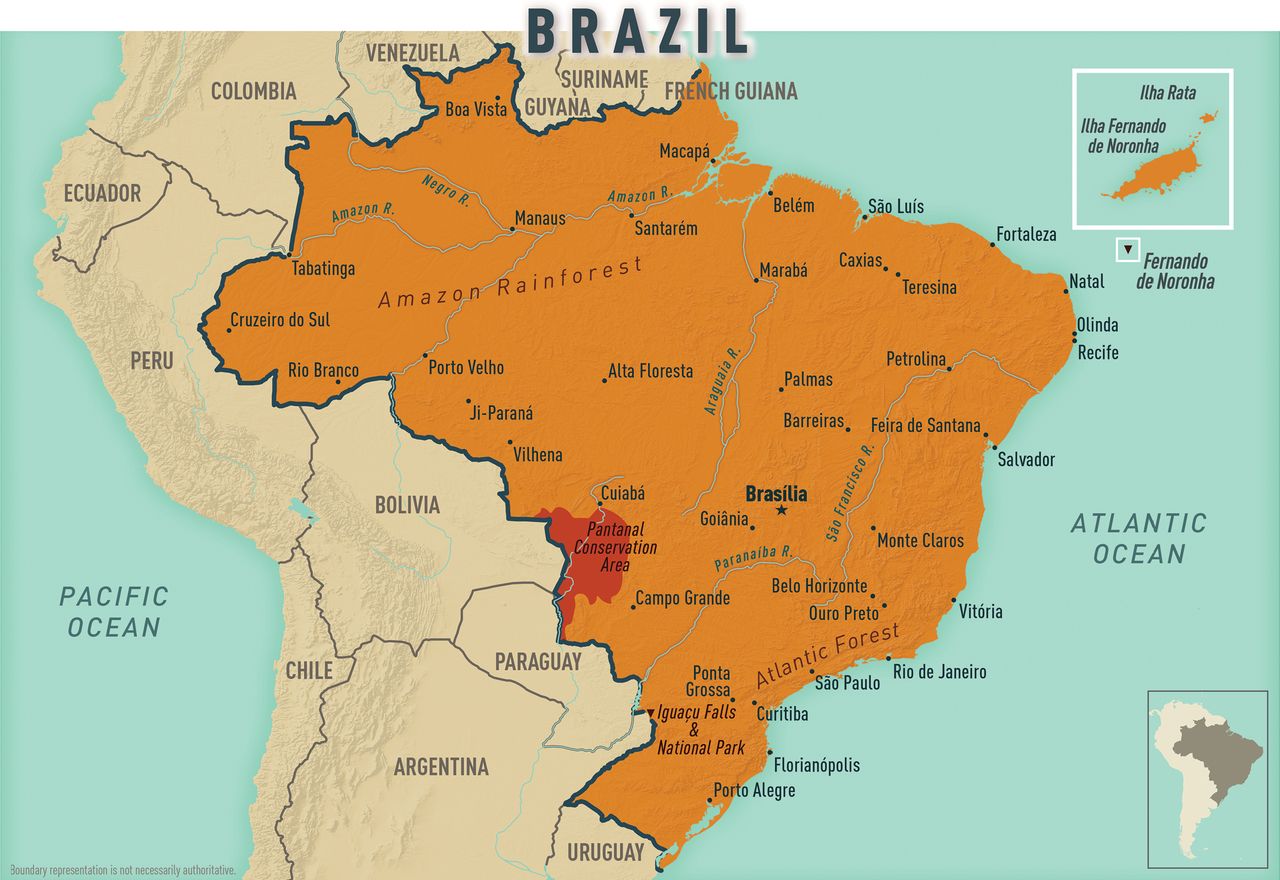
At nearly 3.3 million square miles in size, Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world and the largest country in South America, occupying nearly half the land area of the continent. With >210 million people, Brazil is home to the world’s largest Portuguese-speaking population. The world’s eighth largest economy, Brazil is classified as an upper-middle-income country. Nearly 85% of Brazilians live in urban areas.
Brazil is the most popular tourist destination in South America, and the second most popular in all Latin America. In 2018, >6 million international visitors traveled to Brazil; the country hosted the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) World Cup in 2014 and the Summer Olympic and Paralympic Games in 2016. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil’s second-largest city (population >7 million) and most frequently visited tourist destination, is famous for its beaches, landmarks, and annual Carnival festivities. São Paulo, one of the world’s largest cities with >21 million people in the greater metropolitan area, is the economic center of Brazil and the most visited destination for business travel. Brazilian people prize many of their major cities, including Florianópolis, Fortaleza, Manaus, Recife, and Salvador, for their coastlines and regional culture.
The country also boasts multiple UNESCO World Heritage sites, including Iguaçu National Park in Paraná, home to the largest waterfalls in the Americas; the historic towns of Olinda (Pernambuco), Ouro Preto (Minas Gerais), Salvador (Bahia), and São Luis (Maranhão); the modern capital of Brasília; and natural areas of the Amazon Forest and the Pantanal Conservation Area, which extends from one state (Mato Grosso do Sul) into another (Mato Grosso) and into portions of two countries (Bolivia and Paraguay). The Atlantic forests and the archipelago of Fernando de Noronha in the Atlantic Ocean are World Heritage sites (see Map 10-06 ).
The Amazon Forest, large portions of which extend into the countries that neighbor Brazil, attracts travelers in search of exotic adventures. The region presents unique risks, and careful planning and attention to travelers’ health needs before, during, and after the trip is critical. Because mosquito-borne diseases (chikungunya, dengue, malaria, yellow fever, and Zika) are endemic throughout the Amazon, advise travelers to complete all relevant vaccinations and provide them with detailed instruction on the proper use of chemoprophylaxis and mosquito avoidance. The hot and humid climate throughout the forest increases the risks for dehydration and heat stroke; travelers should practice extreme caution and, whenever possible, resist the temptation to consume potentially unsafe food and beverages.

Map 10-06 Brazil
View Larger
Travelers to Brazil should be up to date on routine vaccines, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), influenza, measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), and diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis. Hepatitis A vaccination also is recommended. Consider hepatitis B vaccination for most travelers, but especially for anyone who could be exposed to blood or other body fluids (e.g., through medical services, sexual contact, tattooing).
Enteric Infections & Diseases
Travelers’ diarrhea.
Travelers should take food and water precautions throughout Brazil, including in the big cities (see Sec. 2, Ch. 8, Food & Water Precautions ). Travelers’ diarrhea (TD) is the most common travel-related ailment, and visitors consuming raw fruits and vegetables, unpasteurized dairy products, and food from street vendors increase their risk for foodborne infections. Oral rehydration salts are available from public health clinics and in almost all pharmacies in Brazil. For further information about travelers’ diarrhea, see Sec. 2, Ch. 6, Travelers’ Diarrhea .
Typhoid Fever
Consider vaccinating “adventurous eaters” against typhoid, along with travelers who stay with friends or relatives or who visit smaller cities, villages, or rural areas (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 24, Typhoid & Paratyphoid Fever ).
Respiratory Infections & Diseases
Coronavirus disease 2019.
All travelers going to Brazil should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
Endemic Fungi
A variety of fungi (e.g., Paracoccidioides in the south and southeast) are endemic to Brazil. Inhaling the spores of fungi typically present in the soil (e.g., Coccidioides , Cryptococcus neoformans , Histoplasma , P aracoccidioides ) can cause respiratory illness and occasionally more severe disease (e.g., meningitis, bone infections). For more details, see Sec. 5, Part 4, Ch. 1, Coccidioidomycosis / Valley Fever , and Sec. 5, Part 4, Ch. 2, Histoplasmosis . Travelers should beware of bat guano in caves and use caution before disturbing soil, particularly if contaminated by bat or bird feces.
Peak influenza circulation occurs during April–September in most of Brazil but can occur throughout the year in tropical areas. The influenza vaccine recommended for use in the Northern Hemisphere each year confers protection against the virus strains circulating in the Southern Hemisphere that same year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends seasonal influenza vaccination ≥2 weeks before travel, and pneumococcal vaccination for people ≥65 years of age, and for younger adults and children with chronic medical conditions.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is prevalent in Brazil, but short-term travelers are not considered to be at high risk for infection unless visiting specific crowded environments. Before they leave the United States, consider TB testing for travelers who anticipate prolonged exposure to people known to have, or at high risk for having, TB (e.g., people in clinics, hospitals, prisons, homeless shelters). For more detailed information, see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 22, Tuberculosis , and Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 23, . . . perspectives: Testing Travelers for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection.
Sexually Transmitted Infections & HIV
The HIV infection rate in Brazil is 0.5% among adults aged 15–49 years, comparable to other countries in South America. Discuss options for preexposure prophylaxis with travelers at greater risk for acquiring HIV infection (see www.cdc.gov/hiv/prep, and Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 11, Human Immunodeficiency Virus / HIV ). In Brazil, people who use drugs, men who have sex with men, and female sex workers are more likely than the general population to be infected with HIV.
In Brazil, condoms are available free of charge in public health clinics, tourist service centers, and other distribution points in many cities. Male condoms are also available throughout Brazil in pharmacies, convenience stores, and supermarkets; female condoms are available in some locations.
Soil- & Waterborne Infections
Leptospirosis.
In urban areas of Brazil, outbreaks of leptospirosis have occurred after heavy flooding (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 10, Leptospirosis ). Travelers who have contact with standing water or mud after heavy rainfall are at increased risk. Advise travelers to avoid entering bodies of freshwater potentially contaminated with animals’ body fluids.
Schistosomiasis
Schistosoma spp. are parasites found in freshwater lakes and rivers in many states of Brazil, especially in the northeast. Advise travelers to avoid bathing, swimming, or wading in fresh, unchlorinated water, where they could contract schistosomiasis (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 20, Schistosomiasis ). Bathing or swimming in saltwater is not a source of infection.
Vectorborne Diseases
Vectorborne diseases (bacterial, viral, parasitic) are present in many areas of Brazil; these infections are among the leading causes of febrile illness in travelers returning from South America.
Chikungunya & Dengue
Risk for chikungunya and dengue infection is increased in many large Brazilian cities due to large populations of Aedes mosquitoes, which transmit these viruses (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 2, Chikungunya , and Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 4, Dengue ). During 2000–2015, cases of dengue surged throughout Brazil, with epidemics reported in large cities, including Rio de Janeiro and Salvador. Preliminary data show that in 2019, Brazil recorded ≈132,000 cases of chikungunya and ≈1.5 million probable cases of dengue. Travelers to Brazil should take measures to protect themselves from mosquito bites (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis occur in Brazil and are most common in the Amazon and northeast regions (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 14, Cutaneous Leishmaniasis , and Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 15, Visceral Leishmaniasis ). The risk for transmission is greatest from dusk to dawn because the sand fly vector typically feeds (bites) at night and during twilight hours. Ecotourists and adventure travelers might be at increased risk, but even short-term travelers in endemic areas have developed leishmaniasis. Travelers should take measures to avoid insect bites (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Lymphatic Filariasis
Brazil is actively participating in the global program to eliminate lymphatic filariasis (LF); LF is considered endemic to only 4 cities in Brazil, all located in the Recife Metropolitan Region (northeastern coast) of the country. As of 2020, all regions had achieved the targets set by the World Health Organization (WHO) to stop annual treatment, suggesting low likelihood of ongoing disease transmission and minimal risk to travelers. Brazil is still working to achieve all targets demonstrating elimination of LF as a public health problem (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 9, Lymphatic Filariasis , and the WHO website .
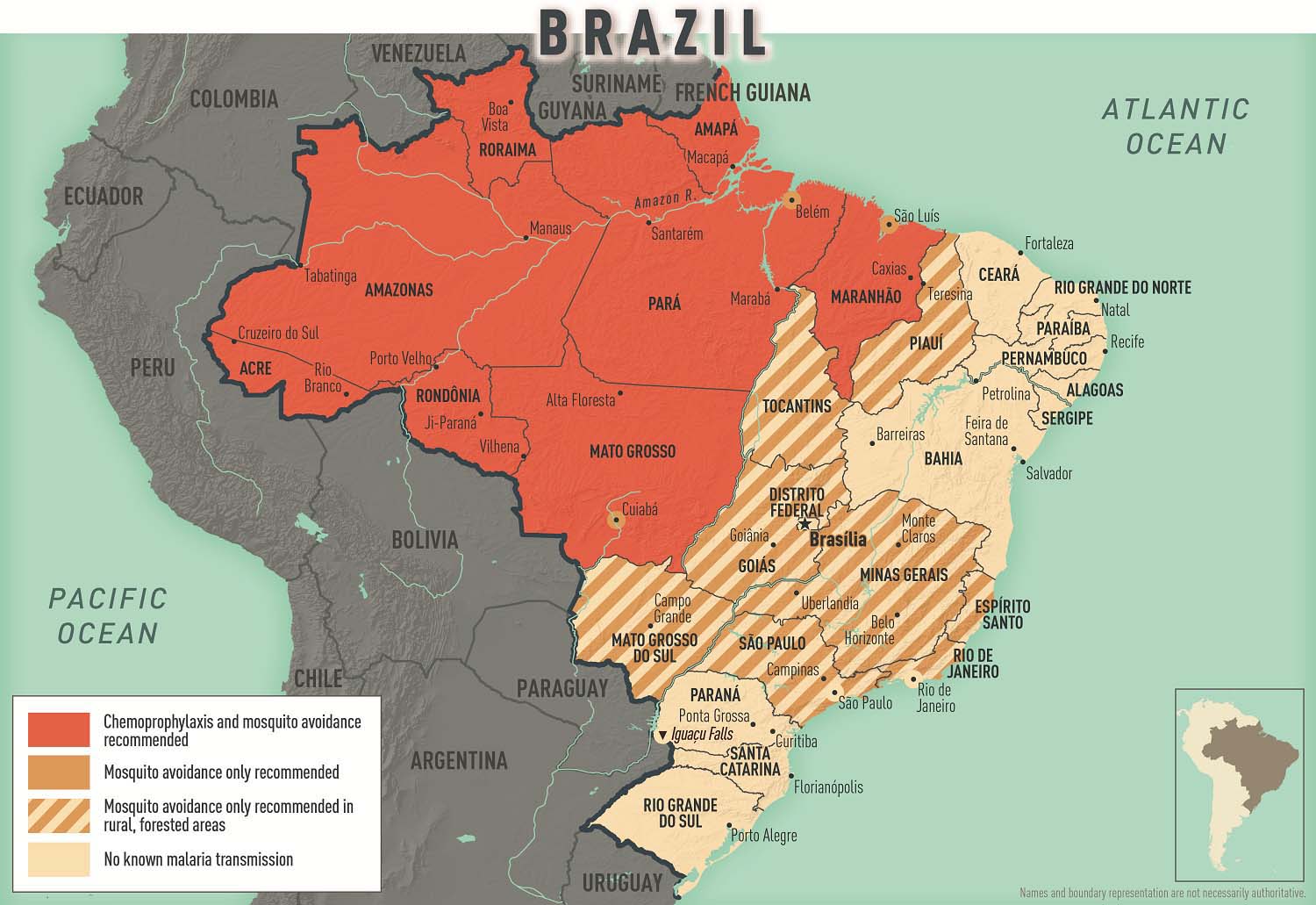
Almost all malaria in Brazil occurs in the Amazon Basin, although less competent malaria vector species are present in other parts of the country. Plasmodium vivax is the main malaria species; only ≈10%–20% of malaria cases are caused by P. falciparum . CDC recommends chemoprophylaxis for travelers going to malaria-endemic areas of Brazil (see Sec. 2, Ch. 5, Yellow Fever Vaccine & Malaria Prevention Information, by Country ; Map 2-04 ; and the CDC Malaria webpage. No malaria transmission occurs in the cities of Brasília (the capital), Rio de Janeiro, or São Paolo, or at Iguaçu Falls.
Map 2-04 Malaria prevention in Brazil
Rickettsial Diseases
Tickborne rickettsial diseases in Brazil include febre maculosa and Brazilian spotted fever, which are caused by etiologic agents from the same genus (Rickettsia) that causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever in the United States (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 18, Rickettsial Diseases ). Travelers should take precautions (e.g., wearing appropriate clothing, applying insect repellants on clothes and skin) to avoid tick bites both indoors and outdoors (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Trypanosomiasis
Except in the north of the country where cases continue to rise, most states in Brazil have eliminated Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) through improved housing conditions and insecticide spraying for the vector. Although the risk is extremely low, travelers and ecotourists staying in poor-quality housing, especially in the Amazon region, might be at greater risk for this disease.
Outbreaks have been associated with consuming food or beverages containing açaí, an Amazonian fruit eaten throughout Brazil, and sugar cane juice ( caldo de cana ). Oral transmission occurs when people consume food or beverages contaminated with triatomines—the bloodsucking insects that transmit the etiologic agent of Chagas disease ( Trypanosoma cruzi )—or their feces (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 25, American Trypanosomiasis / Chagas Disease ).
Yellow Fever
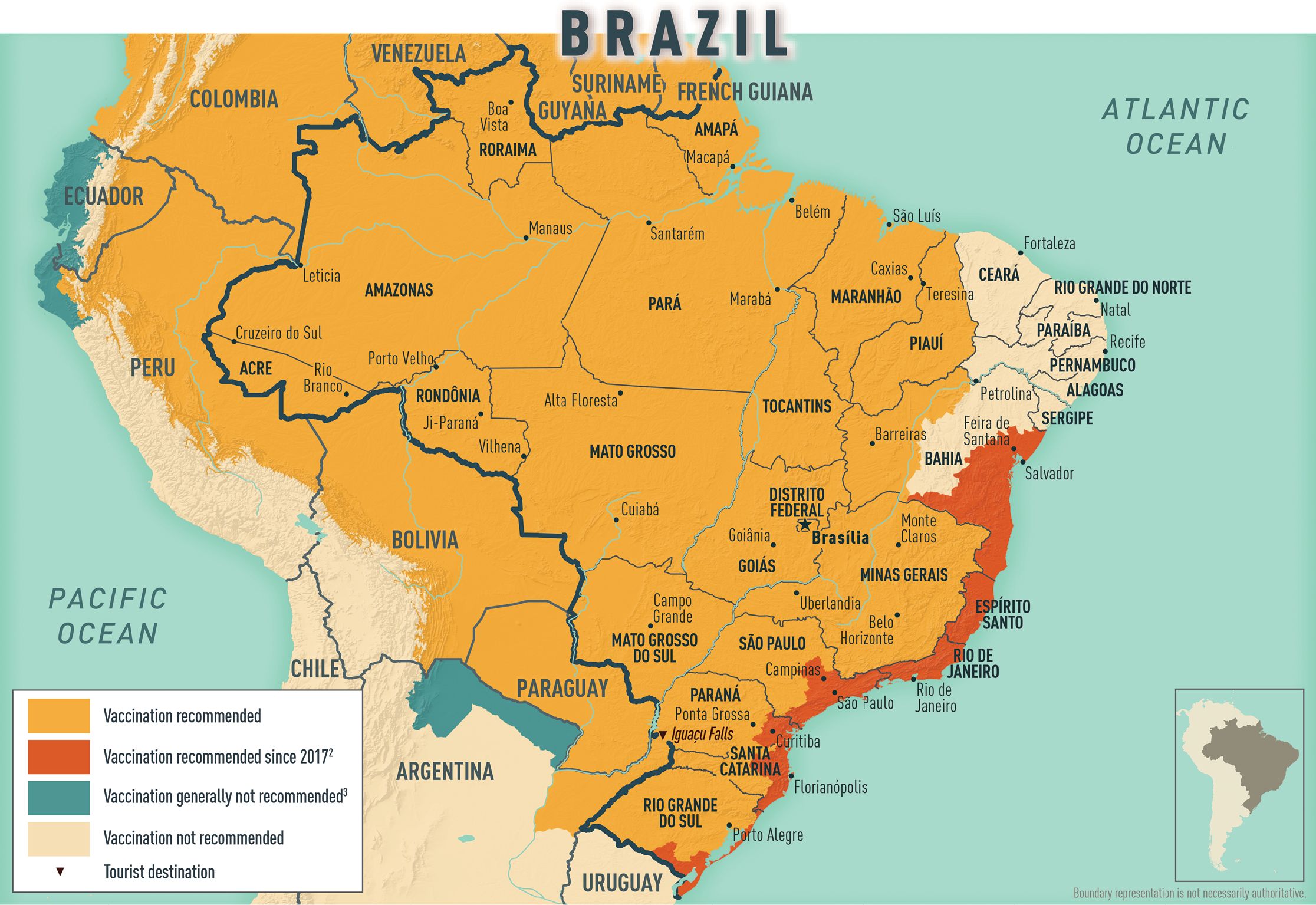
Mosquitoes that transmit yellow fever virus can be found throughout the Amazon Basin and in forested regions along all major river basins in Brazil, including Iguaçu Falls and as far south as Rio Grande do Sul. During 2016–2017, outbreaks of sylvatic yellow fever extended to the southeastern coast of Brazil, including the cities of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo, areas with historically low risk for transmission. Several unvaccinated travelers visiting these areas became ill with the disease, and some died.
Evidence of an expanded range of yellow fever transmission in Brazil led WHO and CDC to broaden their vaccination coverage recommendations for the country in 2017. Although Brazil does not require proof of vaccination against yellow fever for entry into the country, CDC recommends yellow fever vaccination for all travelers aged ≥9 months going to areas with risk for transmission. Updated information on areas of risk can be found on the CDC Travelers’ Health website; see Sec. 2, Ch. 5, Yellow Fever Vaccine & Malaria Prevention Information, by Country .
People planning travel to other countries in South America (e.g., Colombia) could be required to show proof of yellow fever vaccination at airline counters before exiting Brazil.
Map 2-03 Yellow fever vaccine recommendations for Brazil & neighboring countries
Zika virus is an arbovirus (genus Flavivirus ) transmitted mainly by mosquitoes, typically, although not exclusively, Aedes aegypti . Zika virus also can be sexually transmitted and transmitted during pregnancy to a fetus. First reported in Brazil in 2015, Zika was likely introduced to the country 2 years prior. A large Zika outbreak occurred in 2016, and >215,000 probable cases were reported. By 2019, the number of cases had dropped to 10,000.
Most Zika infections are asymptomatic and, when present, symptoms are mild. Commonly reported signs and symptoms include arthralgia, conjunctivitis, fever, and maculopapular rash; Guillain-Barré syndrome and encephalopathy have also been reported (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 27, Zika ).
Vertical transmission leads to congenital Zika virus infection; sequelae can include microcephaly with central nervous system anomalies, other serious neurologic consequences, and fetal loss. Because of the risk for birth defects in infants born to people infected with Zika during pregnancy, CDC encourages a pretravel discussion of risks with anyone who is pregnant or trying to become pregnant. Zika travel information is available at the CDC Travelers’ Health website.
Animal Bites
Overall, the risk for rabies infection in Brazil is very low. Preexposure rabies vaccination is recommended for travelers with extended itineraries, particularly children, and people planning trips to rural areas (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 18, Rabies ). For shorter stays, preexposure rabies vaccination is recommended for adventure travelers, those who might be occupationally exposed to animals, and people staying in locations >24 hours away from access to rabies immune globulin (e.g., the Amazon Forest).
Poisonous snakes are a hazard in many places in Brazil, although deaths from snake bites are rare (see Sec. 4, Ch. 7, Zoonotic Exposures: Bites, Stings, Scratches & Other Hazards ). Counsel travelers to seek immediate medical attention any time a bite wound breaks the skin, or if a snake sprays venom into their eyes. In some areas of the country, specific antivenoms are available, and being able to identify the snake species (or taking a picture) might prove critical to delivery of optimal medical care. The national toll-free number for intoxication and poisoning assistance is 0800-722-6001 (in Portuguese only).
Climate & Sun Exposure
Ensure travelers to Brazil are familiar with climatic conditions at their destinations before they go. Except in the south, where temperatures peak at 85°F (30°C), temperatures >104°F (40°C) are common in cities along the coast and in the Amazon region during October–March (see Sec. 4, Ch. 2, Extremes of Temperature ).
Travel in Brazil is generally safe, although crime remains a problem in urban areas and has spread to rural areas. The incidence of crime against tourists is greater in areas surrounding beaches, hotels, nightclubs, and other tourist destinations (see Sec. 4, Ch. 11, Safety & Security Overseas ). Drug-related violence has resulted in clashes with police in tourist areas. Several Brazilian cities have established specialized police units that patrol areas frequented by tourists and provide assistance to crime victims.
Political Unrest
Political demonstrations might disrupt public and private transportation. Encourage travelers to register with the US Department of State’s Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive advisories and alerts for areas they plan to visit.
Prostitution
Although commercial sex work is legal in Brazil, operating a brothel and financial exploitation of sex workers are both against the law.
Traffic-Related Injuries
As in many foreign countries, motor vehicle accidents in Brazil are a leading cause of injury and death among US travelers (see Sec. 8, Ch. 5, Road & Traffic Safety ). Road conditions in Brazil differ significantly from those in the United States, and driving at night can be dangerous. The national toll-free number for emergency roadside assistance (193) is in Portuguese only. Driving after drinking alcohol, even small quantities, is illegal, and travelers can expect police checkpoints during evenings and nights in many urban areas. Seatbelt use is mandatory, and motorcyclists are required by law to wear helmets.
Children aged ≤10 years must be seated in the back seat. Brazilian federal law requires infants ≤1 year of age to use rear-facing car seats, children 1–4 years of age to use forward-facing car seats, and children 4–7.5 years of age to use booster seats. Anyone traveling with small children should bring their own car or booster seats, in the event these are limited or unavailable.
Quality health care is available in most sizable Brazilian cities. Brazilian public health services are free, even for visitors. Foreign visitors can seek treatment in the emergency care network of Brazil’s public health system, known as the Unified Health System, or by its Portuguese acronym, SUS, or through private facilities. A non-comprehensive list of private medical services can be found on the US Embassy in Brazil website. The toll-free emergency number for ambulance services throughout Brazil is 192. The Brazilian Ministry of Health provides information in Portuguese for international visitors , including a list of reference hospitals for mass gathering events in Brazil.
Medical Tourism
Brazil has a growing number of private clinics that cater to international clientele and offer medical procedures using advanced technologies. Travel to Brazil for cosmetic surgery, assisted reproductive technology, or other elective medical procedures has increased in recent years, becoming a major part of the medical industry. Although the quality of care overall can vary widely, Brazil has many cosmetic surgery facilities on par with those found in the United States. Travelers seeking cosmetic surgery or other elective procedures should do their research and make sure that emergency medical services are available at their clinic of choice (see Sec. 6, Ch. 4, Medical Tourism ).
The following authors contributed to the previous version of this chapter: Joanna Gaines, Ana Carolina Faria e Silva Santelli
Bibliography
Hamer DH, Angelo K, Caumes E, van Genderen PJJ, Florescu SA, Popescu CP, et al. Fatal yellow fever in travelers to Brazil, 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(11):340–1.
Malaria Atlas Project. Country profile: Brazil. Available from: https://malariaatlas.org/trends/country/BRA .
Melo CFCAE, Vasconcelos PFDC, Alcantara LCJ, Araujo WN. The obscurance of the greatest sylvatic yellow fever epidemic and the cooperation of the Pan American Health Organization during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53:e20200787.
Ministry of Health. Epidemiological bulletin: special issue. Chagas disease World Day, 14 April; year 2 [in Portuguese]. Brasilia: The Ministry; 2021. Available from: www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/boletins-epidemiologicos/especiais/2021/boletim_especial_chagas_14abr21_b.pdf .
Ministry of Health. Ministry of Health. Epidemiological bulletin 41. Monitoring of cases of urban arboviruses transmitted by Aedes aegypti (dengue, chikungunya and Zika), epidemiological weeks 01 to 52 [in Portuguese]. Brasilia: The Ministry; 2020. Available from: www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/boletins-epidemiologicos/edicoes/2020/boletim_epidemiologico_svs_41.pdf .
Nobrega AA, Garcia MH, Tatto E, Obara MT, Costa E, Sobel J, et al. Oral transmission of Chagas disease by consumption of acai palm fruit, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15(4):653–5.
Petersen E, Wilson ME, Touch S, McCloskey B, Mwaba P, Bates M, et al. Rapid spread of Zika virus in the Americas—implications for public health preparedness for mass gatherings at the 2016 Brazil Olympic Games. Int J Infect Dis. 2016;44:11–5.
Possas C, Lourenço-de-Oliveira R, Tauil PL, Pinheiro FP, Pissinatti A, Cunha RVD, et al. Yellow fever outbreak in Brazil: the puzzle of rapid viral spread and challenges for immunisation. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2018;113(10):e180278.
Sabino EC, Buss LF, Carvalho MPS, Prete CA Jr, Crispim MAE, Fraiji NA, et al. Resurgence of COVID-19 in Manaus, Brazil, despite high seroprevalence. Lancet. 2021;397(10273):452–5.
Silva MMO, Tauro LB, Kikuti M, Anjos RO, Santos VC, Gonçalves TSF, et al. Concomitant transmission of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses in Brazil: clinical and epidemiological findings from surveillance for acute febrile illness. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(8):1353–9.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Brazil due to the threat of violent crime.
Brazil (PDF 1.24 MB)
Americas (PDF 3.25 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 192 or go to a hospital.
Call 190 or go to the local police station.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Brazil.
- Large scale protests can occur at any time in Brazil. Monitor the media. Follow the instructions of local authorities and review our guidance on staying safe when there are demonstrations .
- Violent crime, including mugging, armed robbery and carjacking is common. These occur more often in large cities and during festivals, such as Carnaval. Don't go out alone at night. Avoid isolated areas, including beaches. Crime rates are particularly high in shanty towns or 'favelas'. Don't enter favelas, even with a tour group.
- Use only prepaid or official taxis. If using rideshare apps such as Uber, ensure you enter the vehicle with the same plate number and name shown in the app. If you're driving yourself, keep doors locked and windows closed. Ensure your route avoids favelas.
- The wet season is from November to July, depending on the region. Landslides and flooding can occur, and severe storms often delay flights. Be prepared to adjust your travel plans.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Brazil experiences recurrent measles outbreaks. It is important to get vaccinated.
- Common insect-borne diseases include dengue, malaria, yellow fever, Zika virus, chikungunya, filariasis and leishmaniasis. The 2024 seasonal increase in dengue fever is much higher than usual. Protect yourself from insect bites. Get vaccinated against yellow fever where possible.
- HIV/AIDS is a serious risk. Take precautions if you're taking part in high-risk activities.
- Food-related, waterborne and other infectious diseases include cholera, typhoid and hepatitis. Drink boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
Full travel advice: Health
- Don't use or carry illegal drugs. Penalties for drug offences are severe and include long prison sentences.
- You must carry proof of identity with you. Always carry photo ID, such as a driver's licence and a photocopy of your passport.
- Dual nationals must enter Brazil on their Brazilian passport. If you're male and aged over 18, you may need to do military service. Contact a Brazilian embassy or consulate for advice.
- Same-sex relationships are legal but aren't always accepted in rural communities. Avoid public displays of affection.
- Don't drink and drive. Penalties are severe for driving with a blood-alcohol level reading over 0%.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- From 10 April, Australian passport holders will need a visa to enter Brazil. For more information, contact an embassy or consulate of Brazil .
- Entry and exit conditions may change without warning. Follow the advice of border and health authorities and comply with local regulations. Contact the nearest Brazilian embassy or consulate for the latest details.
- Brazilian children (including dual nationals) must have written consent from any non-accompanying parent to depart Brazil.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
- For full consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Brasilia or the Australian Consulate-General in São Paulo .
- The Australian Consulate in Rio de Janeiro does not provide notarial (document legalisation) services and only provides limited services, for example interviews for an Australian Passport.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Violent crime.
Violent crime, often involving weapons, is common, especially in large cities. Most crime is opportunistic. Common examples which involve tourists include the theft of valuables at the beach or from bags and valuables snatched while sightseeing. Tourists have also been robbed at knife or gunpoint. Local authorities advise against taking valuables and passports to the beach. Carry a photocopy of your passport or another form of identity.
Muggings and other violent crimes are common in and around:
- tourist spots, hotels, nightclubs and bars
- historical centres
- public transport
- public beaches
- outdoor markets
- unregistered taxis
- ATMs and currency exchange facilities
Other common crimes include:
- home invasion
- food and drink spiking
- sexual assault
- kidnapping and scams
In Rio de Janeiro, crime hotspots include:
- Copacabana Beach
- Ipanema Beach
- the Santa Teresa area
- the Lapa neighbourhood
- the Christ the Redeemer statue
- the Corcovado Trail
In São Paulo, crime hotspots are in the downtown area and around the historical centre of the city and include:
- around the São Paulo Cathedral
- Station of light (Estação da Luz)
- Princess Isabel Square
- Central market
In Brasilia, crime hotspots include the central bus station and two adjacent shopping centres.
Crime levels in shanty towns, or 'favelas', and many satellite cities are especially high.
Crimes relating to drug trafficking and illicit goods are common along Brazil's western and northern border areas. Affected areas include:
- the states of Amazonas, Acre, Rondônia, Mato Grosso, Roraima, Pará and Amapa
- the tri-border area of Argentina, Brazil (Foz do Iguaçu city) and Paraguay
Your safety is your main priority. Don't chase after a perpetrator or resist. Criminals may be armed and, if challenged, they may respond with violence. They will often have accomplices nearby. If you're robbed, report it to the local police.
To protect yourself from violent crime:
- avoid crime hotspots, especially late at night
- stay alert in public places, especially where there are lots of people, including other tourists
- leave valuables and passport in a hotel safe
- keep mobile devices and other valuables out of sight
- keep your belongings and baggage close to you when you're outside
- lock the doors and windows of your accommodation, including balcony doors
- avoid going out alone, especially at night
- avoid isolated areas on the beach
- don't leave your luggage, food or drinks unattended
- never accept drinks, food, gum or cigarettes from people you've just met
- don't enter favelas, even with a tour group
If you're a victim of violent crime, including rape, seek immediate medical help. The risk of HIV/AIDS is high.
Female survivors of domestic violence or sexual assault can access a dedicated hotline that provides access to local support services, including police, by calling 180 or via the WhatsApp phone messaging application on +55 61 99610 0180.
Partying safely
Crime levels increase before and during festivals such as Carnaval, with tourists frequently being targeted.
Make sure you follow these tips:
- watch out for drink spiking and know your alcohol limits
- don’t use drugs – penalties for drug offences in Brazil are high
- don’t drink and drive – penalties are severe for driving with a blood-alcohol reading over 0%
- keep your valuables out of sight, as petty crime, such as bag or phone snatching, is common
- be mindful of where you’re going, get recommendations from your hotel and plan your transport options in advance
More information:
Scammers take advantage of people looking for romantic partners, often via dating websites, apps or social media, by pretending to be prospective companions. Be wary of any online invitation you receive to travel to an unfamiliar location, especially if the location is changed at late notice and if someone is offering romance. The scammer may kidnap you and force you to transfer or withdraw money and then extort your loved ones for more money to secure your release.
Take caution when purchasing food and beverages from vendors, especially at the beach when paying by card. Confirm the price before and check the figure on the card machine is correct and hasn't been inflated. Don’t give your card to the vendor when making payments.
- Theft and robbery
- Scams that affect travellers
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you’re connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping occurs across the world with political, ideological and criminal motives. Foreigners, including Australians, have been kidnapped overseas while travelling. Kidnaps can happen anywhere, anytime, including in destinations that are typically at lower risk. The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
Kidnappings occur in Brazil, and in some cases, individuals of perceived wealth are targeted. There have been instances of kidnapping-for-ransom, express, tiger, and virtual kidnappings. There were more express and tiger kidnaps in Brazil than in any other country worldwide during the first half of 2023.
Civil unrest and political tension
Large-scale protests are common. Public protests and events that draw large crowds can turn violent and authorities have used tear gas and other riot-control measures.
Demonstrations and protests often interrupt traffic and public transport.
During periods of unrest:
- avoid protests and rallies
- monitor the news for possible unrest and avoid those areas
- if a protest occurs, leave if it's safe to do so
- prepare for long waits and be ready to adjust your travel plans
- follow instructions from the local authorities
You should follow the instructions of local authorities and review our guidance on staying safe when there are demonstrations .
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Major events are attractive targets for terrorists.
To protect yourself from terrorism:
- be alert to possible threats
- report suspicious activity or items to police
- monitor the news for emerging threats
- take official warnings seriously
- follow the advice from local authorities
If there's an attack, leave the affected area straight away if you can.
Avoid the affected area after an attack in case there are secondary attacks.
Swimming safety
Many beaches, including in Rio de Janeiro and Fortaleza, have strong, dangerous rips.
Shark attacks are possible, especially at many north-eastern beaches. Obey warning signs.
Climate and natural disasters
Brazil experiences severe droughts and flooding.
If there's a natural disaster :
- secure your passport in a safe, waterproof location
- keep in contact with your friends and family
- monitor the media and local sources
- follow the advice of local authorities
Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
The wet season is from January to July in the north, November to March in the south and south-east and April to July in the north-east. Landslides, flooding and flash flooding can happen, especially in poorer urban areas.
It's common for flooding and severe storms to damage transport infrastructure, including roads and bridges and can delay domestic and international flights. Monitor local media for weather advice and follow any instructions given by local authorities.
Staying safe in the heat
If you're travelling during extreme hot weather, plan your days to avoid being outside during the hottest part of the day. If you go out in the heat, rest often and stay in the shade as much as possible.
- Drink plenty of water. Even if you're not thirsty. Avoid alcohol
- Wear sunscreen, a hat and sunglasses
- Wear loose, lightweight, light-coloured clothing
Avoid strenuous outdoor activities such as hiking or biking in extreme hot weather, particularly if you're not usually active or used to high temperatures.
- Extreme hot weather
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare, or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Brazil. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a dated letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Insect-borne diseases.
Insect-borne diseases are a serious risk in Brazil. Yellow fever , dengue , malaria and the zika virus are common. Other insect-borne diseases include:
- chikungunya
- leishmaniasis
You're most at risk during the wet season, in poorer urban areas or in regional areas where there are stagnant bodies of water, including the Pantanal or Amazon.
Take the following steps to avoid insect bites:
- cover exposed skin with light-coloured long-sleeved shirts and long pants
- use insect repellents. If you use both sunscreen and insect repellent, apply the sunscreen first and then the repellent
- treat your clothing and gear with insecticides
- sleep in screened or air-conditioned rooms. Use bed nets if you can't keep mosquitoes from coming inside the room
- consider taking anti-malarial medication
- Infectious diseases
- Immunisation (Department of Health and Aged Care)
HIV/AIDS is a significant risk. Take precautions if you're taking part in activities that put you at risk of infection, such as avoiding contact with contaminated objects and sharing personal items. Practice safe sex.
Other health risks
There are recurrent measles outbreaks in Brazil. To protect yourself, stay up to date with your vaccinations, wash your hands regularly and avoid close contact with people who are sick and wild or domestic animals.
Food-related, waterborne and other infectious diseases are common, including:
- bilharzia (schistosomiasis)
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw and undercooked food, such as salads
- avoid contact with dogs and other mammals
- avoid swimming in fresh water
If you're bitten or scratched by an animal, get medical help immediately.
Make sure your vaccinations are up to date.
- Measles immunisation service
Medical care
Medical facilities.
You can access free health care at public hospitals and clinics in Brazil. The standard of emergency care is generally high but can vary, with access being more limited and of a lower standard outside of major urban areas.
When accessing public health care, you will likely experience overcrowding, longer wait times and more rudimentary facilities than you are accustomed to in Australia. It is very unlikely your treating doctor will speak English.
Private health care at hospitals and clinics in larger cities is often similar or superior to Australia. Doctors will often speak at least some English. Private medical care is very expensive, even more expensive if you need a medical evacuation. You may be charged upfront or be required to produce proof of insurance prior to receiving treatment.
Public mental health care facilities are basic and overcrowded with a focus on more severe chronic and acute care, using a pharmaceutical-based treatment approach.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Brazil has severe penalties for possession of or trafficking illegal drugs. These include long sentences in local jails.
- Carrying or using drugs
You must always carry proof of identity. Carry a photocopy of your passport with some original identification, such as your driver's licence or another government-issued identity document.
Don't drink and drive, penalties are severe for driving with a blood-alcohol level reading over 0%.
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law
Dual citizenship
Dual nationals must enter and exit Brazil using their Brazilian passport.
If you're a dual national male over 18, you'll have to do military service if you stay in Brazil for 12 months.
Contact a Brazilian embassy or consulate for advice.
- Dual nationals
Local customs
Same-sex relationships are legal but aren't always accepted. Avoid public displays of affection.
- Advice for LGBTI travellers
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
From 10 April, Australian passport holders will be required to obtain a visa to enter Brazil. For more information, contact an embassy or consulate of Brazil for details about visas, currency and customs.
Currently you don't need a visa to enter Brazil for:
- artistic or sport activities
You can stay in Brazil for 90 days over a 12-month period. This will be counted from the date of your first entry to Brazil. You can also extend your stay for another 90 days. If you require visa advice or assistance, you should contact the Brazilian Federal Police or a visa agency.
In other cases, apply for your visa through an embassy or consulate of Brazil .
If you plan to live in Brazil, you'll need to get a visa before arrival. The Brazilian Government strongly enforces immigration and entry laws.
If you need a visa and arrive without one, authorities will send you back on the next available flight.
- Brazilian Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Travel via Chile
If you’re travelling via Chile, ensure you meet all current entry or transit requirements.
- Travel advice for Chile
Other formalities
Entry and exit stamps.
When you arrive, authorities will stamp your passport. This may be inspected by immigration authorities when you leave.
If you plan to leave Brazil and return during your trip, get an exit stamp in your passport from Brazilian immigration when you leave.
Yellow fever vaccination
You may need a valid yellow fever vaccination certificate to enter Brazil. Some airlines may want to see a copy when you depart to Australia or other countries.
Find out about returning to Australia after exposure to yellow fever .
- Countries with a risk of yellow fever
Travel with children
Dual-national children must enter and exit Brazil using their Brazilian passports.
Brazilian and dual-national children travelling in the company of only one parent must provide proof of consent to travel from the non-accompanying parent. If you can't produce proof of parental consent, local authorities will stop your children from departing Brazil. Unaccompanied children, or children travelling in the company of a non-parent, will require the consent of both parents.
Parental consent will usually be in the form of an observation note inserted into the child's Brazilian passport when it is issued by the Brazilian authorities. Alternatively, a Brazilian Embassy, Consulate or Juvenile Court can witness and notarise written parental consent or proof of residence outside Brazil.
If one or both parents are deceased, you'll require a death certificate notarised by a Brazilian Embassy, Consulate or Juvenile Court.
Parents of dual-national children should contact a Brazilian embassy or consulate for advice.
- Advice for people travelling with children
Authorities won't let you enter Brazil unless your passport is valid for at least 6 months from the date of your entry. This may apply even if you're just transiting.
Some immigration authorities and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Tourists can receive conflicting advice from different sources. You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTI travellers
The local currency is the Brazilian Real (BRL).
Declare amounts over USD 10,000 (or foreign currency equivalent) when you arrive and depart. This includes all forms of currency, not just cash. US dollars are the easiest to exchange. Credit cards are widely accepted.
Ask your bank in Australia if your ATM card will work and if it has an affiliate bank in Brazil, as some local machines may be unreliable.
Credit card fraud and ATM tampering are widespread. Check your bank statements for unauthorised charges. To combat fraud and theft, many ATMs may limit the amount you can withdraw per day.
Local travel
Remote areas.
You're at risk of becoming lost or injured while trekking in remote parts of Brazil. This includes the Amazon border regions and the Pantanal wetlands.
Use an experienced guide.
Driving permit
You can drive in Brazil for up to 180 days after your arrival, as long as you carry a valid Australian driver’s licence. It is also recommended that you carry a translation of your licence. After this period, you will need to obtain a local driver’s licence.
Road travel
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in Brazil than in Australia.
Hazards on the road include:
- aggressive driving
- poorly maintained roads
- large numbers of trucks and other slow vehicles on main routes
Traffic lights are often not obeyed, especially at night in larger cities. Don't assume cars will stop.
Carjacking and other vehicle-related crimes can occur. To stay safe while driving and guard against carjacking:
- keep vehicle doors locked, windows up, and valuables out of sight, even when moving
- make sure your GPS route isn't via a favela — if in doubt, ask your hotel or tour guide
- be alert to threats, including when stopped in traffic
- when stopped in traffic, including at traffic lights, be alert to threats and maintain extra distance from other cars.
- always approach your car with the keys ready
- don't stay in a parked vehicle
If you plan to drive:
- check you have enough insurance
- learn local traffic laws and practices
- don't drink and drive – penalties are severe for driving with a blood-alcohol reading over 0%
- guard against carjacking and other vehicle-related crimes
If you're in an accident:
- call 193 for the fire department if there are injuries
- call 190 for the police if there are no injuries
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Check if your insurance policy covers you when using a motorbike, quad bike or similar vehicle.
Always wear a helmet.
Registered taxis, rideshares such as Uber and the metro are generally safe. To reduce your risk:
- only use licensed taxis or rideshare booked through apps
- find out what transport services are available at the airport before you travel; most airports have licenced taxi desks inside the baggage reclaim areas and allow payment before travel
- follow signage or advice of authorities to official taxi services only
- always ask if the driver will use the meter, or agree on the fare before you get in a taxi
- ensure you enter the vehicle with the same plate number and name as shown in the app, and don't get into a taxi or rideshare if other passengers are already inside.
- avoid using motorcycle taxis
Public transport
Brazil has a well-developed network of inter-city buses, as well as metro systems in some of the major cities such as Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo.
Travel can be risky due to poor vehicle maintenance, local driving habits and petty crime.
Be alert when using public transport, especially during busy times and at night.
Criminals often work in gangs robbing people gathered in the same place. Public transport hubs can be hotspots.
People have reported hijacking and robbery of tour buses in recent years.
- Transport and getting around safely
Boat travel
International cruise liners visit Brazil.
Commercial riverboats are common in some parts. Keep your belongings close.
Tourist operators often use basic vessels for river outings in jungle areas.
You should always wear a life jacket.
Piracy happens, particularly in the north-east. Pirates have also attacked cruise ships and lodges along the Amazon River.
The International Maritime Bureau (IMB) issues piracy reports on its website.
- Going on a cruise
- Travelling by boat
Domestic and international flight delays are common. Airport strikes also occur.
Ask your travel agent if your itinerary allows for delays.
Be prepared for the possibility of extended waits at airports.
If you need to make or change airline bookings while in Brazil, ensure your payment method will be accepted.
Most major airlines, such as LATAM, Gol and Azul, accept international credit cards, although some may only accept them on their international websites.
Travel and tour agents may also have restrictions. You may need to pay cash at the airline office or ask your Australian travel provider.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Brazil's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Operators may not speak English.
Tourist Police who speak English are available in Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and at some major airports.
Rio de Janeiro Special Police Unit for Tourism Support Av. Afrânio de Melo Franco, 159 Leblon, Rio de Janeiro – RJ Phone: +55 21 2334 6802 or +55 21 2332 2924
São Paulo Special Police Unit for Tourism Support Rua da Cantareira, 390 Centro, São Paulo - SP Phone: +55 11 3257 4475
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Brasilia , the Australian Consulate-General in São Paulo or the Consulate in Rio de Janeiro . The Consulate in Rio de Janeiro does not provide notarial (document legalisation) services and only provides limited services, for example, interviews for an Australian Passport.
Australian Embassy, Brasilia
SES QD 801, Conjunto K, Lote 07 Brasilia - DF, Brazil ZIP/CEP: 70200-010
Phone: +55 61 3226 3111 Email: [email protected] , or [email protected] Website: brazil.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Embaixada da Austrália no Brasil X: @EmbAusBrasil Instagram: australianobrasil
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
Australian Consulate-General, São Paulo
Edificio Trianon Corporate – Cerqueira Cesar Alamenda Santos 700 9th Floor, Unit 92 São Paulo - SP, Brazil ZIP/CEP: 01418-100
Phone: +55 11 2112 6200 Email: [email protected]
Australian Honorary Consulate, Rio de Janeiro
Av. Bartolomeu Mitre, 770 Leblon, Rio de Janeiro - RJ, Brazil ZIP/CEP: 22431-003
Phone: +55 21 3824 4624 Email: [email protected]
The Australian Consulate in Rio de Janeiro does not provide notarial (document legalisation) services and only provides limited services, for example interviews for an Australian Passport.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Brazil?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
Get our news on your inbox! Suscribe x
MercoPress. South Atlantic News Agency
MercoPress, en Español
Montevideo, April 7th 2024 - 01:51 UTC

Brazil: Travelers from US, Australia, and Canada will need a visa starting next week

Holders of US, Australian, and Canadian passports will be required a tourist visa to enter Brazil by air, land, or sea, effective next Wednesday (April 10), Agencia Brasil reported. Under Decree 11.875/2024, the initial Jan. 10 deadline was extended for three months to avoid the negative consequences for Brazil's tourism industry during peak season.
The visa requirement overturns a decision by former President Jair Bolsonaro, who had lifted such an imposition in March 2019 for travelers from the United States, Canada, Australia, and Japan in a unilateral decision while Brazilians continued to need a visa to travel to those countries. Hence, Itamaraty explained that the new measure stemmed from a question of reciprocity.
In May 2023, Japan was removed from this list when Brazil and the island nation signed an agreement to waive visa requirements for nationals of either country entering the other for tourism purposes for up to 90 days.
Brazil's International Tourism Promotion Agency (Embratur) has undertaken a campaign through tour operators and airlines in the three countries affected to remind their customers of the need for visas.
Travelers from those countries wishing to visit Brazil must apply for an electronic visa, the so-called e-Visa, through the platform: https://brazil.vfsevisa.com, which costs US$ 80.90, Agencia Brasil also pointed out.
The 100% electronic procedure does not require applicants to show up at a Brazilian consulate. All the necessary documentation can be uploaded digitally and the visa is also delivered via e-mail. A print-up will be needed together with a valid passport to be admitted into Brazil.
Travelers are also advised to apply for the e-visa well in advance to avoid delays or missed connections.
The e-visa will allow multiple entries and will have the same validity period as conventional visas: ten years for US nationals and five years for Canadians and Australians.
Top Comments
No comments for this story
Please log in or register (it’s free!) to comment. Login with Facebook
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
Get our news on your inbox! Suscribe

Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
beta This is a test version of the layout of this page. Take the survey to help us improve it
- Help and services around the world
- UK help and services in Brazil
Travelling to Brazil
Includes travel advice and how to get married abroad.
Subscriptions
- Get emails for this topic Travelling to Brazil
Brazil travel advice
FCDO travel advice for Brazil. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Getting married abroad
Requirements, paperwork and processes for weddings and civil partnerships overseas - registration, restrictions, fees
Reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad
How to minimise your risk, and what to do if there's a terrorist attack.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Stay up to date with notifications from The Independent
Notifications can be managed in browser preferences.
UK Edition Change
- UK Politics
- News Videos
- Paris 2024 Olympics
- Rugby Union
- Sport Videos
- John Rentoul
- Mary Dejevsky
- Andrew Grice
- Sean O’Grady
- Photography
- Theatre & Dance
- Culture Videos
- Food & Drink
- Health & Families
- Royal Family
- Electric Vehicles
- Car Insurance deals
- Lifestyle Videos
- UK Hotel Reviews
- News & Advice
- Simon Calder
- Australia & New Zealand
- South America
- C. America & Caribbean
- Middle East
- Politics Explained
- News Analysis
- Today’s Edition
- Home & Garden
- Broadband deals
- Fashion & Beauty
- Travel & Outdoors
- Sports & Fitness
- Sustainable Living
- Climate Videos
- Solar Panels
- Behind The Headlines
- On The Ground
- Decomplicated
- You Ask The Questions
- Binge Watch
- Travel Smart
- Watch on your TV
- Crosswords & Puzzles
- Most Commented
- Newsletters
- Ask Me Anything
- Virtual Events
- Betting Sites
- Online Casinos
- Wine Offers
Thank you for registering
Please refresh the page or navigate to another page on the site to be automatically logged in Please refresh your browser to be logged in
How many months do I need left on my UK passport before I travel?
Many countries across the world require you to have a few months left on your passport at the time of travel – here are the main holiday destinations to watch out for, article bookmarked.
Find your bookmarks in your Independent Premium section, under my profile

Sign up to Simon Calder’s free travel email for expert advice and money-saving discounts
Get simon calder’s travel email, thanks for signing up to the simon calder’s travel email.
You might think that you can just hop on a plane with an in-date passport and travel the world. In fact, many countries demand that visitors have months left on their passport before it expires.
Some – including Australia , Canada and the US – only require your travel document to be in date for the duration of your trip.
But others give a more restrictive time frame, with no real pattern from region to region – while most of Asia requires six months on your passport, for example, different Caribbean islands demand different time frames.
In some destinations, you can also be caught out for not having enough space left in your passport for new immigration stamps.
Here are the key passport validity rules for British passports for the world’s top holiday destinations.
- Barred from Europe: 2.4m Brits caught in post-Brexit passport chaos
- When do I need to renew my passport for travel to Europe?
- This is the best time to renew your passport to save money
Valid for the duration of your stay
These countries only ask that your passport is valid until the day you leave the country.
*While this is technically the rule for Canada, if you have six months or less on your passport, it may take longer for you to get through immigration.
Valid for one day
Costa Rica requires Britons to have one day’s validity from the day of their departure.
Valid for three months
All EU countries, plus those in the Schengen Area (excluding Ireland) require you to have three months left on your passport from the day you plan to leave. Your passport must also be less than 10 years old on the day you enter the country. This is true for the following countries:
- Republic of Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Liechtenstein
- Netherlands
- Switzerland
- Vatican City
These non-European countries also require three months’ validity on your day of departure:
- British Virgin Islands
- French Polynesia
- New Zealand
- South Korea
Valid for six months
In most cases, this means valid for six months from the date you arrive in the country, but it’s worth checking the Foreign Office’s individual entry requirements for the country you’re visiting to make sure.
- Antigua and Barbuda
- The Bahamas
- Dominican Republic
- Ecuador (& Galapagos Islands)
- Madagascar*
- Philippines
- South Africa*
- United Arab Emirates
*South Africa, Madagascar, Kenya also require you to have two blank pages left in your passport; Namibia requires one blank page.
Valid for 180 days
India requires a more specific 180 days of validity from the date you arrive. It also asks visitors to have two blank pages available for their visa.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.
New to The Independent?
Or if you would prefer:
Want an ad-free experience?
Hi {{indy.fullName}}
- My Independent Premium
- Account details
- Help centre

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
While Brazil's COVID-19 vaccination requirements may change, the CDC recommends that U.S. citizens eligible for vaccination should not travel internationally until they are fully vaccinated. T he U.S. Department of State Travel Advisory for Brazil is currently Level 4: Do Not Travel due to COVID-19. For more details on Brazil's COVID-19 ...
Still current at: 6 April 2024 Updated: 27 March 2024 Latest update: FCDO now advises against all but essential travel to parts of the Amazonas River region ('Warnings and insurance' and ...
On August 6 the Department of State updated the Travel Advisory for Brazil. Please see the Travel Advisory below: Do not travel to Brazil due to COVID-19. Exercise increased caution in Brazil due to crime. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Company, Industry and Trade; Agriculture and Livestock; Energy, Minerals and Fuels; Travel and Tourism; Justice and Security; Finance, Taxes and Public Management
The rules, according to Anvisa, do not restrict the entry of Brazilians, of any nature or origin. "Brazilians are not restricted from accessing the country", reinforced the agency, in a statement ...
Passport validity requirements. To enter Brazil, your passport must have an 'expiry date' at least 6 months after the date you arrive. Check with your travel provider that your passport and ...
Dengue in the Americas February 28, 2024 Dengue is a risk in many parts of Central and South America, Mexico, and the Caribbean. Some countries are reporting increased numbers of cases of the disease. Travelers to the Americas can protect themselves by preventing mosquito bites. Destination List: Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, French ...
Itamaraty is the Brazilian government agency responsible for issuing visas, which is done through Brazilian embassies, consulates general, consulates and vice-consulates abroad. Citizens of other countries wishing to obtain a visa to travel to Brazil should contact Brazilian consular offices abroad for more information on how to apply.
Ministerial conversation on trade and sustainable development, including trade and industrial policy space for industrial development. Address by Minister Mauro Vieira at WTO Ministerial Conference - Abu Dhabi, 26 February 2024. Feb 26, 2024 10:37 AM.
FCDO travel advice for Brazil. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
The basics. Brazil has been one of the hardest hit countries by the pandemic. The country holds the second highest Covid-19 death toll in the world, second only to the United States. At the height ...
Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Brazil such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
Brazil Travel Advisory: Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution: October 19, 2023: Cayman Islands Travel Advisory : Level 1: Exercise Normal Precautions: July 17, 2023: ... You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
The U.S. Department of State Travel Advisory for Brazil is currently Level 4: Do Not Travel due to COVID-19. Vaccines must be approved by ANVISA (Brazil's National Health Agency), the World Health Organization, the FDA, or by relevant health authorities in the country where the vaccine was administered. To be considered fully vaccinated, the ...
Check our Traveler Information Center for more information if you are a traveler with specific health needs, such as travelers who are pregnant, immune compromised, or traveling for a specific purpose like humanitarian aid work. Remember to pack extras of important health supplies in case of travel delays. Prescription medicines. Your prescriptions
Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information for Brazil. If you decide to travel to Brazil: Read the Department of State's COVID-19 page before planning any international travel, and read Embassy Brazil's COVID-19 page for detailed regulations. Be aware of your surroundings. Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country's entry rules. Regular Canadian passport. Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Brazil. Passport for official travel. Different entry rules ...
With >210 million people, Brazil is home to the world's largest Portuguese-speaking population. The world's eighth largest economy, Brazil is classified as an upper-middle-income country. Nearly 85% of Brazilians live in urban areas. Brazil is the most popular tourist destination in South America, and the second most popular in all Latin ...
Brazil has a well-developed network of inter-city buses, as well as metro systems in some of the major cities such as Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. Travel can be risky due to poor vehicle maintenance, local driving habits and petty crime. Be alert when using public transport, especially during busy times and at night.
Holders of US, Australian, and Canadian passports will be required a tourist visa to enter Brazil by air, land, or sea, effective next Wednesday (April 10), Agencia Brasil reported. Under Decree ...
Veterinary Health Certificate for Export of Dogs and Cats from the United States of America to Brazil. Certificado Zoosanitario do Brasil para Importação de Animais (Cães e Gatos) Domésticos. Veterinary Authority. UNITEDSTATESDEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE. Date Of Issue / data de emissão. Certificate Number//
Brazil travel advice. FCDO travel advice for Brazil. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Valid for three months. All EU countries, plus those in the Schengen Area (excluding Ireland) require you to have three months left on your passport from the day you plan to leave. Your passport ...
Industrial, manufacturing, financial, trading, travel, and government organizations in the U.S., Mexico, Colombia, Brazil, Argentina, Dominican Republic, Spain, and Portugal have been targeted ...