

Gartner Identifies Three Steps to Effectively Execute a Customer Journey Map
Next-Generation Strategies for B2B Sales and Marketing Leaders to Be Discussed at the Gartner Sales and Marketing Conference, October 9-11 in Las Vegas
STAMFORD, Conn.--( BUSINESS WIRE )--Customer journey maps are a critical component of many organizations' customer experience (CX) framework, however, almost one-third of organizations still face difficulty incorporating journey maps into their CX efforts, according to Gartner, Inc. That's because many lack governance and oversight, and that ultimately undermines even the best maps' ability to drive action.
Gartner defines customer journey mapping as a collaborative process of gathering qualitative and quantitative data to understand customers' desired journeys and identify gaps between their expectations and their perceptions of the experience delivered by a brand at steps along the journey. The main goal of journey mapping is to determine the challenges and opportunities a brand faces in improving its CX and improve satisfaction, loyalty and advocacy.
"While CX leaders have long understood the value of customer journey maps and the impact they have on an organization's ability to exceed or meet customer expectations, many still struggle to utilize them effectively in their CX initiatives," said Jane-Anne Mennella , senior research director at Gartner.
"There are a number of reasons why this happens, from stakeholders who don't understand their role, to using incomplete or incorrect data sources," added Ms. Mennella. "Essentially, many fail because they don't incorporate the governance and oversight needed to realize the journey map's true ROI."
According to Gartner, the main objectives of a customer journey map should be to (a) identify specific CX problems and opportunities, and (b) gain alignment and consensus on how to address those problems and opportunities. To execute on this effectively, and establish the appropriate governance and oversight, CX teams should follow three key steps:
- Master the Foundational Elements First: The same attention paid to laying the groundwork for journey mapping initiatives should be given to the actual creation of the journey map itself. Before building a journey map, CX leaders should consider the following: affirm leadership and key stakeholder support, build a cross-functional team composed of representatives from all departments who support the CX, assess data sources and needs, and know the audience for whom you are mapping the journey.
- Focus on the Actionable and Accurate: Determining and building successful customer journeys requires clear communication among the team and a strong understanding of the entire journey the customers take. CX leaders should start with aligning team goals and expectations. Next, the customer journey map should include the following criteria: it should be created from the customer's perspective and reflect the customer's entire journey — from evaluation, purchase, use through to loyalty, satisfaction and/or advocacy. Lastly, CX teams should consider validating the data included in the journey to ensure it accurately reflects the experience, feelings, thoughts and actions of the customers.
- Cultivate Value from Journey Maps: When journey maps fail, research shows it typically happens following the design phase. To get maximum value from customer journey maps, CX leaders must turn the insight derived from journey maps into action and experiences, ensure those journey maps are current, and develop a communications plan to reinforce progress toward realizing the customer's desired journey.
Additional details on how CX leaders can find true ROI from their customer journey maps is available to Gartner for Marketers clients in the report "Create Actionable, Insight-Driven Journey Maps." More topics like this will be discussed at Gartner's Sales & Marketing Conference in Las Vegas, NV, October 9-11, 2018.
About the Gartner Sales & Marketing Conference
Sales and marketing leaders face unprecedented changes in customer expectations, technology and the talent needed to drive results. At the Gartner Sales & Marketing Conference 2018 , taking place October 9-11 in Las Vegas, sales and marketing leaders will learn from the latest research, Gartner experts, and esteemed peers, to guide them through this time of change. Follow news and updates from the event on Twitter at #GartnerSMC .
About Gartner
Gartner, Inc. (NYSE:IT), is the world's leading research and advisory company and a member of the S&P 500. We equip business leaders with indispensable insights, advice and tools to achieve their mission-critical priorities and build the successful organizations of tomorrow.
Our unmatched combination of expert-led, practitioner-sourced and data-driven research steers clients toward the right decisions on the issues that matter most. We're trusted as an objective resource and critical partner by more than 15,000 organizations in more than 100 countries — across all major functions, in every industry and enterprise size.
To learn more about how we help decision makers fuel the future of business, visit www.gartner.com .
Gartner, Inc. Kelly Blum, 571-303-5745 [email protected]
- #digitalmarketing
- #customerexperience

Gartner Identifies Three Steps to Effectively Execute a Customer Journey Map
Next-Generation Strategies for B2B Sales and Marketing Leaders to Be Discussed at the Gartner Sales and Marketing Conference, October 9-11 in Las Vegas
Customer journey maps are a critical component of many organizations’ customer experience (CX) framework, however, almost one-third of organizations still face difficulty incorporating journey maps into their CX efforts, according to Gartner, Inc. That’s because many lack governance and oversight, and that ultimately undermines even the best maps’ ability to drive action.
Gartner Says Strong Governance and Oversight are Key to Successful Customer Journey Maps
Gartner defines customer journey mapping as a collaborative process of gathering qualitative and quantitative data to understand customers’ desired journeys and identify gaps between their expectations and their perceptions of the experience delivered by a brand at steps along the journey. The main goal of journey mapping is to determine the challenges and opportunities a brand faces in improving its CX and improve satisfaction, loyalty and advocacy.
“While CX leaders have long understood the value of customer journey maps and the impact they have on an organization’s ability to exceed or meet customer expectations, many still struggle to utilize them effectively in their CX initiatives,” said Jane-Anne Mennella , senior research director at Gartner.
Read More: Fake Artificial Intelligence (AI) Vs. Real AI: How To Tell The Difference Between The Scammers & The Real Deal
“There are a number of reasons why this happens, from stakeholders who don’t understand their role, to using incomplete or incorrect data sources,” added Ms. Mennella. “Essentially, many fail because they don’t incorporate the governance and oversight needed to realize the journey map’s true ROI.”
Read More: Cyara Empowers Contact Centers to Deliver Personalized Customer Journeys
According to Gartner, the main objectives of a customer journey map should be to (a) identify specific CX problems and opportunities, and (b) gain alignment and consensus on how to address those problems and opportunities. To execute on this effectively, and establish the appropriate governance and oversight, CX teams should follow three key steps:
- Master the Foundational Elements First: The same attention paid to laying the groundwork for journey mapping initiatives should be given to the actual creation of the journey map itself. Before building a journey map, CX leaders should consider the following: affirm leadership and key stakeholder support, build a cross-functional team composed of representatives from all departments who support the CX, assess data sources and needs, and know the audience for whom you are mapping the journey.
- Focus on the Actionable and Accurate: Determining and building successful customer journeys requires clear communication among the team and a strong understanding of the entire journey the customers take. CX leaders should start with aligning team goals and expectations. Next, the customer journey map should include the following criteria: it should be created from the customer’s perspective and reflect the customer’s entire journey — from evaluation, purchase, use through to loyalty, satisfaction and/or advocacy. Lastly, CX teams should consider validating the data included in the journey to ensure it accurately reflects the experience, feelings, thoughts and actions of the customers.
- Cultivate Value from Journey Maps: When journey maps fail, research shows it typically happens following the design phase. To get maximum value from customer journey maps, CX leaders must turn the insight derived from journey maps into action and experiences, ensure those journey maps are current, and develop a communications plan to reinforce progress toward realizing the customer’s desired journey.
Additional details on how CX leaders can find true ROI from their customer journey maps is available to Gartner for Marketers clients in the report “Create Actionable, Insight-Driven Journey Maps.” More topics like this will be discussed at Gartner’s Sales & Marketing Conference in Las Vegas, NV, October 9-11, 2018.
Read More: With Automation and AI, the Human Side of Selling Is Fast Becoming a Unique Skill Set

The STS news desk represents a team of tech journalists who coordinate trending stories and breaking news on behalf of the SalesTechStar newsroom.
Ansira Receives Industry Accolades Ahead of 100-Year Anniversary
Miller Heiman Group Launches Sales Analytics Platform Linked to Major Methodology Update
Episode 199: Top Trends in Modern B2B Marketing with Emily Singer, Head of Marketing…
Episode 198: MarTech and AI with Jeff Samuels, COO of Iterable
SalesTechStar Interview with Kevin Meeks, Chief Customer Officer at LivePerson
SalesTechStar Interview with Alon Partuk, CEO and Co-founder at Octup

- WEEKLY HIGHLIGHTS
- GUEST AUTHORS
- STAFF WRITERS
- The SalesStar Podcast – Episodes 101 to 200
- The SalesStar Podcast – Episodes 001 to 100
- The SalesStar Podcast – RSS Feed
- DemandGen Radio
- B2B Database & List Services
- Buyer Insights
- Account-Based Planning
- Content Sharing
- In App Marketing
- Incentives & Commissions
- Influencer Marketing
- Intelligent Assistants
- Privacy and Regulations
- Quote & Proposal
- Gamification
- Territory & Quota Management
- Multichannel Orchestration
- Native & Programmatic Advertising
- Online Meeting & Sharing
- Forecasting & Performance Management
- Predictive Marketing
- Pipeline & Analytics
- Pipeline Management
- Predictive & AI
- Productivity & Enablement
- Programmatic Email
- Data Visualization
- Sales Engagement
- Nimble Sales Intelligence
- Sales Activity Logging
- Sales Appraisal
- Sales Coaching
- Sales Dialer
- Sales Intelligence
- Web & Social Prospecting Tools
- Signals & Social Engagement
- Speech & Conversation Analytics
- Lead Distribution & Call Management
- People Management
- Salestechstar Podcast 2023
- Salestechstar Podcast 2024
- SalesTechStar Interviews
- The SalesStar Podcast: Episodes 192 onwards (Year: 2024)
- The SalesStar Podcast: Episodes 148 to 191 (Year: 2023)
- The SalesStar Podcast: Episodes 109 to 147 (Year: 2022)
- The SalesStar Podcast: Episodes 56 to 108 (Year: 2021)
- The SalesStar Podcast: Episodes 01 to 55 (Year: 2020)
- Lead Generation
Welcome, Login to your account.
Recover your password.
A password will be e-mailed to you.

How to create a customer journey map
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 8 min
How to Make a Customer Journey Map
- Conduct persona research
- Define customer touchpoints
- Map current states
- Map future states
Steve Jobs, the genius behind Apple’s one-of-a-kind customer experience, said, “You’ve got to start with the customer experience and work back toward the technology, not the other way around.”
Nowadays, a clear vision and strategy for customer interactions is no longer an optional “nice-to-have”—it’s essential. As you refine your customer experience, a customer journey map is one of the most powerful ways to understand your current state and future state.

A customer journey map is a diagram that shows the process your customers go through in interacting with your business, such as an experience on the website, a brick and mortar experience, a service, a product, or a mix of those things.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of a customer’s experience with your brand. These visuals tell a story about how a customer moves through each phase of interaction and experiences each phase. Your customer journey map should include touchpoints and moments of truth, but also potential customer feelings, such as frustration or confusion, and any actions you want the customer to take.
Customer journey maps are often based on a timeline of events, such as a customer’s first visit on your website and the way they progress towards their first in-product experience, then purchase, onboarding emails, cancellation, etc.
Your customer journey maps may need to be tailored to your business or product, but the best way to identify and refine these phases is to actually talk to your customers. Research your target audiences to understand how they make decisions, decide to purchase, etc. Without an essential understanding of your customers and their needs, a customer map will not lead you to success. But, a well-constructed and researched customer journey map can give you the insights to drastically improve your business’s customer experience.
The benefits of customer journey mapping
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool for uncovering insights into your customer experience, driving business goals, and building resilience in a changing market. In a 2022 report, Hanover Research found that 94% of businesses said their customer journey maps help them develop new products and services to match customer needs. Another 91% said their maps drove sales.
But understanding a customer’s journey across your entire organization does so much more than increase your revenue. It enables you to discover how to be consistent when it comes to providing a positive customer experience and retaining customer loyalty.
This was especially evident in recent years as top of improving marketing, customer journey maps emerged as a valuable way to understand evolving buyer behavior. In fact, 1 in 3 businesses used customer journey maps to help them navigate the changing landscape during the pandemic.
When done correctly, customer journey mapping helps to:
- Increase customer engagement through channel optimization.
- Identify and optimize moments of truth in the CX.
- Eliminate ineffective touchpoints.
- Shift from a company to a customer-focused perspective.
- Break down silos between departments and close interdepartmental gaps.
- Target specific customer personas with marketing campaigns relevant to their identity.
- Understand the circumstances that may have produced irregularities in existing quantitative data.
- Assign ownership of various customer touchpoints to increase employee accountability.
- Make it possible to assess the ROI of future UX/CX investments.
Following the process outlined above, customer mapping can put your organization on a new trajectory of success. Yet, according to Hanover Research, only 47% of companies currently have a process in place for mapping customer journeys. Making the investment to map your customer journey and solidify that process as part of your company’s DNA can result in significant advantages in your competitive landscape, making your solution the go-to option that customers love.
Customer journey maps can become complicated unless you keep them focused. Although you may target multiple personas, choose just one persona and one customer scenario to research and visualize at a time. If you aren’t sure what your personas or scenarios might be, gather some colleagues and try an affinity diagram in Lucidchart to generate ideas.
1. Set goals
Without a goal, it will be difficult to determine whether your customer journey map will translate to a tangible impact on your customers and your business. You will likely need to identify existing—and future—buyers so you can set goals specifically for those audiences at each stage of their experience.
Consider gathering the key stakeholders within your company—many of whom likely touch different points of the customer experience. To set a logical and attainable goal, cross-functional teamwork is essential. Gather unique perspectives and insights about each part of the existing customer journey and where improvements are needed, and how those improvements will be measured.
Pro Tip : If you don’t already have them in place, create buyer personas to help you focus your customer journey map on the specific types of buyers you’re optimizing for.
2. Conduct persona research
Flesh out as much information as possible about the persona your customer journey map is based on. Depending on the maturity of your business, you may only have a handful of records, reports, or other pre-existing data about the target persona. You can compile your preliminary findings to draft what you think the customer journey may look like. However, the most insightful data you can collect is from real customers or prospective customers—those who have actually interacted with your brand. Gather meaningful customer data in any of the following ways:
- Conduct interviews.
- Talk to employees who regularly interact with customers.
- Email a survey to existing users.
- Scour customer support and complaint logs.
- Pull clips from recorded call center conversations.
- Monitor discussions about your company that occur on social media.
- Leverage web analytics.
- Gather Net Promoter Score (NPS) data.
Look for information that references:
- How customers initially found your brand
- When/if customers purchase or cancel
- How easy or difficult they found your website to use
- What problems your brand did or didn’t solve
Collecting both qualitative and quantitative information throughout your research process ensures your business makes data-driven decisions based on the voice of real customers. To assist when conducting persona research, use one of our user persona templates .

Discover more ways to understand the Voice of the Customer
3. Define customer touchpoints
Customer touchpoints make up the majority of your customer journey map. They are how and where customers interact with and experience your brand. As you research and plot your touchpoints, be sure to include information addressing elements of action, emotion, and potential challenges.
The number and type of touchpoints on your customer journey map will depend on the type of business. For example, a customer’s journey with a SaaS company will be inherently different than that of a coffee shop experience. Simply choose the touchpoints which accurately reflect a customer’s journey with your brand.
After you define your touchpoints, you can then start arranging them on your customer journey map.
4. Map the current state
Create what you believe is your as-is state of the customer journey, the current customer experience. Use a visual workspace like Lucidchart, and start organizing your data and touchpoints. Prioritize the right content over aesthetics. Invite input from the stakeholders and build your customer journey map collaboratively to ensure accuracy.
Again, there is no “correct” way to format your customer journey map, but for each phase along the journey timeline, include the touchpoints, actions, channels, and assigned ownership of a touchpoint (sales, customer service, marketing, etc.). Then, customize your diagram design with images, color, and shape variation to better visualize the different actions, emotions, transitions, etc. at a glance.
Mapping your current state will also help you start to identify gaps or red flags in the experience. Collaborators can comment directly on different parts of your diagram in Lucidchart, so it’s clear exactly where there’s room for improvement.
5. Map future states
Now that you’ve visualized the current state of the customer journey, your map will probably show some gaps in your CX, information overlap, poor transitions between stages, and significant pain points or obstacles for customers.
Use hotspots and layers in Lucidchart to easily map out potential solutions and quickly compare the current state of the customer journey with the ideal future state. Present your findings company-wide to bring everyone up to speed on the areas that need to be improved, with a clear roadmap for expected change and how their roles will play a part in improving the customer journey.
Customer journey map templates
You have all the right information for a customer journey map, but it can be difficult to know exactly how to start arranging the information in a digestible, visually appealing way. These customer journey mapping examples can help you get started and gain some inspiration about what—and how much—to include and where.

Don’t let the possibility of a bad customer journey keep you up at night. Know the current state of the customer journey with you business, and make the changes you need to attract and keep customers happy.

Customer journey mapping is easy with Lucidchart.
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Business Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Data Center
- Data Management
- Emerging Technology
- Enterprise Applications
- IT Leadership
- Digital Transformation
- IT Strategy
- IT Management
- Diversity and Inclusion
- IT Operations
- Project Management
- Software Development
- Vendors and Providers
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- Middle East
- Italia (Italy)
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Data Analytics & AI
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Computerworld
- Network World
The customer journey map: A new playbook CIOs must master
CIOs driving digital business strategy must master customer experience. That means working with marketing on a critical initiative: the customer journey map.

The digital era has altered C-suite dynamics. Once unlikely collaborators, IT and marketing are partnering closely on new customer-facing technologies, an acknowledgment that both parties must work together to help their companies — and careers — thrive.
CIOs are also huddling with CMOs and other business line leaders on “customer journey maps,” critical documents that outline key customer touchpoints. Here’s what CIOs should know about customer journey maps and how to ensure you’re making effective use of them.
What is a customer journey map?
The customer journey map includes a chart that helps employees visualize the process by which companies attract customers and inspire loyalty. Journey mapping enables companies to identify touchpoints, find previously unknown problems and their root causes, quantify the value of improving customer experience (CX) through KPIs or other metrics, and measure improvements.
“Journey maps can also help organizations build empathy for customers by walking participants through how touchpoints influence customers’ attitudes and actions,” according to a guide to journey mapping Forrester Research published in August. This enforces customer-centric thinking and encourages good CX behaviors.
10 steps for crafting an effective journey map
The map is created in a collaborative process that relies on qualitative and quantitative data to determine and understand customer journeys, including customers’ goals, needs and expectations, Gartner analyst Jane-Anne Mennella tells CIO.com. The map also helps executives identify gaps between customers’ expectations and their experience during their journey.
Form a cross-functional team. Assemble key stakeholders from business lines, including sales, marketing, IT, operations and human resources. This team will inform and shape the map to ensure it provides a 360-degree view of customers’ desires, Mennella says. “Customer experience is a cross-functional mandate” requiring stakeholders from every business line, but especially the CIO, she says. Ideally, the CEO will govern this group, but Mennella says the CMO or CIO could lead it as well. Regardless, the leader must be “empowered to break any ties,” Mennella says.
Build personas. Craft a “persona,” or an image of the ideal customer, Mennella says. Using this outside-in view of molding digital experiences around the customer, the team should be able to build maps that detail touchpoints, interests and feelings for each persona. Different customer demographics may require different personas.
Pick your methodology. Familiarize yourself with the framing of a journey map and choose a methodology that matches project objectives, says Forrester.
Conduct research. “Listen” to social media to see what people are saying about your brand and tailor services accordingly, Mennella says. Peruse your company’s digital channels, as well as forums and online communities. Operational and transactional data are also key. “We’re seeing this increased focus on customer insights and user research,” Mennella says. The CIO is crucial here, providing customer analytics to help keep the business on a straight path to the customer. Conducting customer research helps identify and eliminate gaps in customer misunderstandings, Forrester says.
Tool up. Use a journey atlas to help visualize and organize the map. Prioritize based on customer and business value. The atlas can show how journeys interrelate, overlap and influence each other, Forrester says.
Workshop for empathy. Co-creation with stakeholders and customers ensures buy-in and validation, Forrester says. Engage in storytelling activities to get to the root of customer behavior and identify moments of truth and areas of improvement.
Correct errors. Journey mapping efforts often fail due to lack of executive buy-in or even mapping the wrong things, Forrester observes. Avoid these pitfalls by including customers as well as the right stakeholders needed to ensure the journey maps are valid.
Select KPIs. Pick metrics that matter most for customer obsession. Start by inventorying existing metrics, having your cross-functional team agree on metrics to eliminate, gaps to fill, and a data collection strategy to implement, Forrester says.
Mine data for richer insights. Journey analytics mines quantitative and qualitative data, such as customer feedback surveys, marketing data and language patterns, Forrester says. This data, ideally collected at every step of the journey, can be combined with web analytics and call center data to hypothesize how changes will improve experiences overall, thereby predicting and optimizing next best actions.
In the absence of such data, Mennella says that hypothetical journey maps are acceptable. Here, an organization outlines the steps, thoughts, feelings and actions they think their customers would take, for example, with a new mobile ordering app.
CIOs shared their customer journey map successes with CIO.com.
Customer journey map examples: Suez North America
Homeowners expect water to simply flow when they turn on a faucet. But in an era defined by Amazon.com’s frictionless and often white-glove service, utility companies realize that many consumers expect more compelling services — even from a utility.
Suez North America’s customer journey maps notes the channels, including smart and analog meters, phone, social media, Web and mobile device channels, that connect the company to consumers, says Michael Salas, CIO and CDO for the water utility, which services 7.2 million residents in New York, New Jersey, Delaware and Rhode Island.
Suez took customer “pulse” surveys, conducted on-site observations and convened workshops in which business and IT conceptualized an ideal utility experience complete with gap analysis, personas and considerations for emerging technologies such as IoT and ML.
Salas says Suez built a customer experience portal for which thousands of customers signed up to make direct debit subscriptions online, automating bill payments and reducing employee hours by the thousands. It also augmented its contact center solution with natural language processing speech recognition, resulting in a self-service rate of 40 percent.
Suez also crafted an Amazon.com Alexa skill to enable consumers to “ask” questions about bill payment and other services without waiting to speak to a human representative. “A voice assistant is a natural interface for our services,” Salas says.
Feedback mechanisms built into this journey map helped Suez further improve service, says Salas, who leveraged agile development with daily standup meetings and Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) , complete with a comprehensive change management program. “We try to put ourselves in the shoes of the customer,” says Salas, who appointed a dedicated director of customer experience, Douwe Busschops, to lead these efforts.
One of the hallmarks of the improved service is pairing better customer services and empathy. For example, smart meters, acoustic sensors and machine learning software generate actionable alerts about water waste, such as water leaks in residents’ homes. These efforts are critical for providing “cradle to grave” service to customers, Salas says.
Customer journey map examples: Adobe
Charting the customer journey proved pivotal for Adobe, which has spent the past several years pivoting from licensed software to SaaS (software-as-a-service) sales models.
To better understand customer behavior, Adobe tracks product downloads, display ad impressions, click-through rates for Adobe.com and various other signals consumers initiate online as they try, buy, use and renew software, says Mark Picone, vice president of information and data services. Tracking revenue and product consumption, including cancellations, by geography is also a key task for Adobe, which uses the information to determine whether to increase promotions and perks in certain regions, he adds.
This approach to examining customer behavior makes it easier to personalize email campaigns for consumers, a key marketing practice for Adobe. “We look at all of those events and petabytes of click-level instrumentation of how consumers are using products,” Picone tells CIO.com, adding that Adobe also created key performance indicators to monitor progress.
Information about how people consume Adobe software is also critical, Picone says, because it informs product teams how to refine software for customers.
To build a unified data architecture that enables these capabilities Adobe “normalized,” or consistently defined, and labeled each data type. The challenge? The same data types are often called different things by finance, sales, marketing and other business lines — a common challenge most enterprise face as they seek to streamline data governance.
Customer journey map mistakes to avoid
Building a customer journey map is one thing; leveraging it to bolster the customer experience is another. While 77 percent of 244 marketing leaders Gartner surveyed said they have a journey map, 30 percent struggle to use them effectively in support of their customer experience efforts, Mennella says. Here are some common pitfalls CIOs and their colleagues should avoid:
You have to start somewhere. Journey maps often fall down because organizations don’t know where to start, typically because they don’t know the customers they are targeting. Mennella says enterprises sometimes rely too much on third-party data, which puts distance between them and their customers. Here, Mennella says analytics and usage metrics can help hone your personas and goals.
Beware the product management pitfall. Sometimes enterprises are too focused on their own goals rather than what their customers need, Mennella says. Start with the outside-in approach, rather than simply building a product you think people want and trying to sell it to them.
Some customers are more valuable than others. Sometimes organizations focus on the easy, low-hanging fruit personas. Go for the big whales that are going to be loyal advocates who bring fellow customers on board to keep the flywheel spinning.
Related content
A new era for vmware cloud service provider partners begins, us proposes draft data privacy legislation, the c-suite is expanding — and it leaders are stepping up, sport analytics leverage ai and ml to improve the game, from our editors straight to your inbox, show me more, eu and us agree to chart common course on ai regulation.

The complex patchwork of US AI regulation has already arrived

CBAP certification: A high-profile credential for business analysts

Eaton CIO Katrina Redmond on optimizing AI and digital services

Tech layoffs continue, while AI prevents them from getting new jobs quickly

CIO Leadership Live Middle East with Bruno Ascencio, Head of Data Transformation at First Abu Dhabi Bank

3 Leadership Tips: John Pinard, Vice President, IT Operations, Infrastructure & Cybersecurity, DUCA Financial Services Credit Union Ltd.

3 Leadership Tips: Tina Mathas, CTO, General Bank of Canada

Sponsored Links
- IDC report: Life-cycle services can help align technology, operational, and business outcomes.
- Digital infrastructure plays a big role in business outcomes. Read this IDC report to learn more.
Moving up Gartner’s CX Pyramid with Journey Mapping

Last week I wrote about the Gartner CX Pyramid , an interesting maturity model. This week I’ll go into how to use journey mapping best practices to move up the model based on Gartner’s description of the model on their public website.
Selecting the right journey mapping approach requires you to understand where you are on the model and where you aspire to be. An inaccurate assessment will create waste; attempting to create a Proactive-level approach with only a Communication-level infrastructure will be expensive and ultimately frustrate customers instead of creating loyalty. Similarly, using a lower-level approach won’t have sufficient impact with higher-level design capabilities. Journey mapping doesn’t exist in a vacuum – it requires enough staffing and leadership to implement the changes that come out of it.
Moving from Communication to Responsive
Moving from the first to the second stage involves helping customers solve their problems from your perspective. Make it easier for customers to solve their problems with less-expensive self-service tools. While it does help your customer be more efficient, the primary focus is to save on expensive call center or sales resources. While this approach does create customer value, since it’s more efficient for them, that’s incidental. The primary goal is to save on costs.
The Customer Effort Score is an effective measurement tool here. You’re not creating delight, but you are removing friction . Said differently, you’re not building emotional loyalty, but you are removing causes of dis loyalty. There’s value to this, especially for companies who are earlier in their CX maturity.
A warning to regular readers: You may be surprised by this paragraph. This is the one situation where I will ever endorse using employee workshops as a journey mapping methodology. If your only goal is to identify ways to decrease costs in existing journeys, you can probably accomplish this by putting a bunch of employees in a room and giving them Post-It Notes. But you won’t solve customer problems, and you’ll never realize the promised benefits of journey mapping. Having employees guess what customers do isn’t a customer-centric approach.
Moving from Responsive to Commitment
This is where you start seeing the benefits of a strong CX program; this move is aspirational for most companies. Making this step requires you to listen to customers and resolve their problems in the way they want them resolved. This requires talking with customers to understand their most important needs, and then involving the team to look for solutions. Solving these problems can consistently create an emotional connection that leads customers to stay even if they could save money with competitors.
But, involving customers in journey mapping isn’t enough – moving to Commitment means solving customer needs at specific points in the journey. To do this, map a specific sub-journey and get targeted information needed to solve customer problems. Our survey on CX leaders’ experience with journey mapping showed that 60% mapped the end-to-end journey. For most companies, this will be too general to solve specific problems. To fix these issues, a team needs to go deeper and understand specific customer needs at precise points along the journey, whether that’s first-time usage, asking for help, or mastering usage of the product or service. Trying to cover all three stages in one effort will return diluted findings – a customer who is trying to master your product can’t effectively remember what it was like the first time she used it.
Moving from Responsive to Commitment requires involving customers in journey mapping and having a narrow focus to ensure you fully solve your customers’ problems. It’s probably possible to skip Responsive and move from Communication to Commitment, but it will take a huge effort. Skipping any more steps is impossible; you need to build the infrastructure to solve customer needs before attempting to become consistently Proactive. Establishing your company at the Commitment Level requires consistently doing an excellent job solving customer needs. Trying to go to Proactive without this consistency will result in overpromising customer benefit while serving an inconsistent experience that varies in delivered value.
Tomorrow we’ll move onto using journey mapping to reach the top to two levels of the Gartner CX Pyramid: Proactive and Evolution.
Keep reading .

Navigating Customer Experience Maturity: The Road to Success
By Jim Tincher

To be a change maker in CX, focus on business outcomes

Books About Customer Experience: 9 Best Reads for CX Professionals
By Shawn Phillips

Journey Mapping to Hypothesis Mapping: Creating Better CX
Stay updated with our insights ..

Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2021? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map right at the last second?

The thing is -- understanding your customer base can be extremely challenging. And even when you think you've got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

Download Now
While it isn't possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a very handy tool for keeping track of important milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I'll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents
What is the customer journey?
Customer journey stages.
- What is a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
What's included in a customer journey map, steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
- Customer Journey Map Best Practices
Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer's journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I've worked with were confused about the differences between the customer's journey and the buyer's journey. The buyer's journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don't wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process to consider, evaluate, and decide to purchase a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand's place within the buyer's journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer's journey. When you create a customer journey map, you're taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey, instead of leaving it up to chance.
Free Customer Journey Map Template
Fill out this form to access the free templates..
For example, at HubSpot, our customer's journey is divided into 3 stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
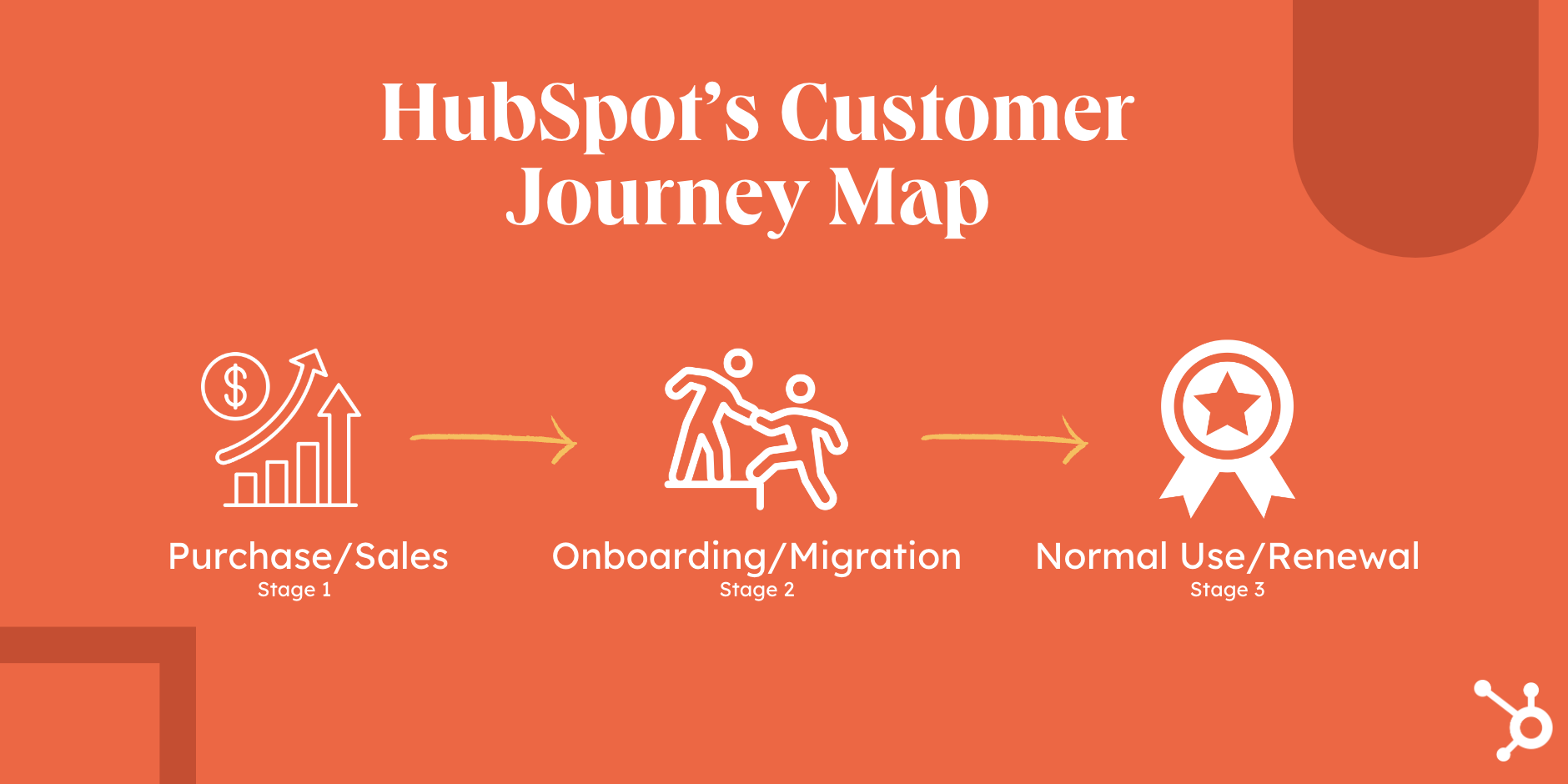
The stages may not be the same for you — in fact, your brand will likely come up with a set of unique stages of the customer journey. But where do you start? Let's take a look.
Generally, there are 5 phases that customers go through when interacting with a brand or a product: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Loyalty.
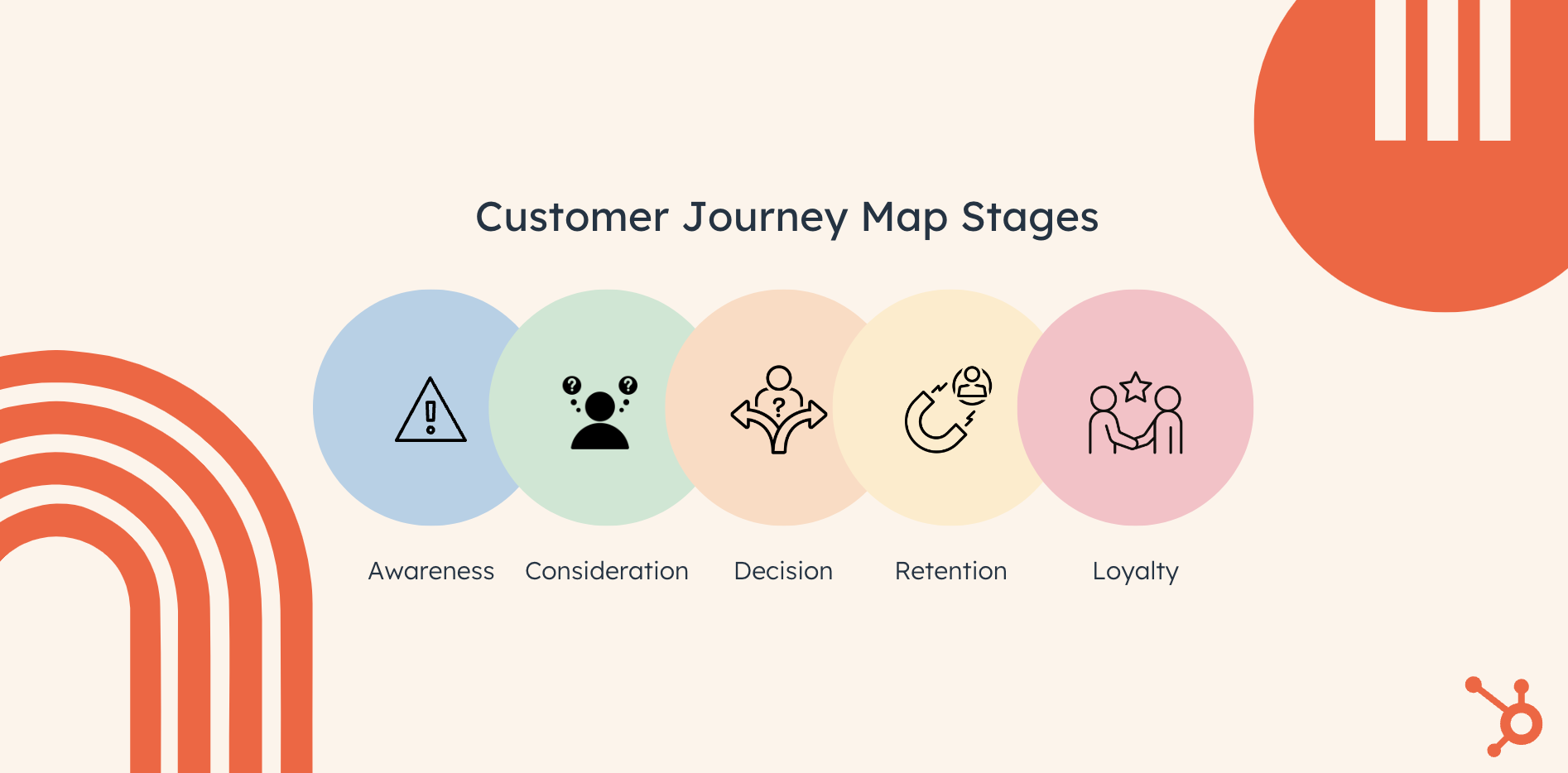
1. Awareness Stage
In the awareness stage, customers realize they have a problem. At this point, they may not know that they need a product or service, but they will begin doing research either way.
During this stage of the customer journey, brands should deliver educational content to help customers diagnose a problem and offer potential solutions. Your aim should be to help customers alleviate their pain point, not encourage a purchase.
Some educational content that I've created in the past are:
- How-to articles and guides
- General whitepapers
- General ebooks
- Free courses
Educational content may also be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Social media
- Search engines
2. Consideration
In the consideration stage, customers have done enough research to realize that they need a product or service. At this point, they begin to compare brands and offerings.
During this stage, brands should deliver product marketing content to help customers compare different offerings and, eventually, choose their product or service. The aim is to help customers navigate a crowded marketplace and move them toward a purchase decision.
Product marketing content may include:
- Product listicles
- Product comparison guides and charts
- Product-focused white papers
- Customer success stories or case studies
Product marketing content may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Your website
- Conferences
3. Decision Stage
In the decision stage, customers have chosen a solution and are ready to buy.
During this stage, your brand should deliver a seamless purchase process to make buying products as easy as possible. I wouldn't recommend any more educational or product content at this stage — it's all about getting customers to make a purchase. That means you can be more direct about wanting customers to buy from you.
Decision-stage content may include:
- Free consultations
- Product sign-up pages
- Pricing pages
- Product promotions (i.e "Sign up now and save 30%")
Decision-stage content may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
4. Retention Stage
In the retention stage, customers have now purchased a solution and stay with the company they purchased from, as opposed to leaving for another provider.
During this stage, brands provide an excellent onboarding experience and ongoing customer service to ensure that customers don't churn.
Retention-stage strategies may include:
- Providing a dedicated customer success manager
- Making your customer service team easily accessible
- Creating a knowledge base in case customers ever run into a roadblock
Retention-stage strategies may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
5. Loyalty Stage
In the loyalty stage, customers not only choose to stay with a company — they actively promote it to family, friends, and colleagues. The loyalty stage can also be called the advocacy stage.
During this phase, brands should focus on providing a fantastic end-to-end customer experience. This should span from your website content to your sales reps all the way to your social media team and your product's UX.
Most importantly, customers become loyal when they've achieved success with your product — if it works, they're more likely to recommend your brand to others.
Loyalty-stage strategies may include:
- Having an easy-to-navigate website
- Investing in your product team to ensure your product exceeds customer expectations
- Making it easy to share your brand with others via a loyalty or referral program
- Providing perks to continued customers, such as discounts
Loyalty-stage strategies may be delivered via customer touchpoints such as:
- Your products
To find out whether your customers have reached the loyalty stage, try a Net Promoter Score survey , which asks one simple question: "On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend us to a friend?" To deliver this survey, you can use customer feedback software like Service Hub .
Now, let's get to the good stuff. Let's talk about creating your customer journey map.
What is the customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the customer's experience with a company. It also provides insight into the needs of potential customers at every stage of this journey and the factors that directly or indirectly motivate or inhibit their progress.
The business can then use this information to improve the customer's experience, increase conversions, and boost customer retention.
Now, the customer journey map is not to be confused with a UX journey map. But, for clarity, let's distinguish these two below.
What is UX journey mapping?
A UX journey map represents how a customer experiences their journey toward achieving a specific goal or completing a particular action.
For example, the term "UX journey mapping" can be used interchangeably with the term "customer journey mapping" if the goal being tracked is the user's journey toward purchasing a product or service.
However, UX journey mapping can also be used to map the journey (i.e., actions taken) towards other goals, such as using a specific product feature.
Why is customer journey mapping important?
While the customer journey might seem straightforward — the company offers a product or service, and customers buy it — for most businesses, it typically isn't.
In reality, it's a complex journey that begins when the customer becomes problem-aware (which might be long before they become product-aware) and then moves through an intricate process of further awareness, consideration, and decision-making.
The customer is also exposed to multiple external factors (competitor ads, reviews, etc.) and touchpoints with the company (conversations with sales reps, interacting with content, viewing product demos, etc.).
Keep in mind that 80% of customers consider their experience with a company to be as important as its products.
By mapping this journey, your marketing, sales, and service teams can understand, visualize, and gain insight into each stage of the process.
You can then decrease any friction along the way and make the journey as helpful and delightful as possible for your leads and customers.
Customer journey mapping is the process of creating a customer journey map — the visual representation of a company's customer experience. It compiles a customer's experience as they interact with a business and combines the information into a visual map.
The goal of this process is to draw insights that help you understand how your customers experience their journeys and identify the potential bottlenecks along the way.
It's also important to note that most customer journeys aren't linear. Instead, buyers often experience a back-and-forth, cyclical, multi-channel journey.
Let's look at the stages that you should include in any customer journey.
- The Buying Process
- User Actions
- User Research
1. The Buying Process
To determine your customers' buying process, you'll want to pull data from all relevant sources (prospecting tools, CMS, behavior analytics tools, etc.) to accurately chart your customer's path from first to last contact.
However, you can keep it simple by creating broad categories using the typical buying journey process stages — awareness, consideration, and decision — and mapping them horizontally.
2. Emotions
Whether the goal is big or small, remember your customers are solving a problem. That means they're probably feeling some emotion — whether that's relief, happiness, excitement, or worry.
Adding these emotions to the journey map will help you identify and mitigate negative emotions and the pain points that cause them.
On HubSpot's journey map , we use emojis to represent potential emotions at different stages of the customer journey.
3. User Actions
This element details what a customer does in each stage of the buying process. For example, during the problem-awareness stage, customers might download ebooks or join educational webinars.
Essentially, you're exploring how your customers move through and behave at each stage of their journey.
4. User Research
Similar to the last section, this element describes what or where the buyer researches when they are taking action.
More than likely, the buyer will turn to search engines, like Google, to research solutions during the awareness stage. However, it's important to pay attention to what they're researching so you can best address their pain points.
5. Solutions
1. Use customer journey map templates.
Why make a customer journey map from scratch when you can use a template? Save yourself some time by downloading HubSpot's free customer journey map templates .
This has templates that map out a buyer's journey, a day in the life of your customer, lead nurturing, and more.
These templates can help sales, marketing, and customer support teams learn more about your company's buyer persona. Not only will this lead to improvements to your product, but also a better customer experience.
2. Set clear objectives for the map.
Before you dive into your customer journey map, you need to ask yourself why you're creating one in the first place.
What goals are you directing this map towards? Who is it for? What experience is it based upon?
If you don't have one, I would recommend creating a buyer persona . This is a fictitious customer with all the demographics and psychographics representing your average customer. This persona reminds you to direct every aspect of your customer journey map toward the right audience.
3. Profile your personas and define their goals.
Next, you should conduct research. This is where it helps to have customer journey analytics at the ready.
Don't have them? No worries. You can check out HubSpot's Customer Journey Analytics tool to get started.
Some great ways to get valuable customer feedback are questionnaires and user testing. The important thing is to only reach out to actual customers or prospects.
You want feedback from people interested in purchasing your products and services and who have either interacted with your company or plan to do so.
Some examples of good questions to ask are:
- How did you hear about our company?
- What first attracted you to our website?
- What are the goals you want to achieve with our company? In other words, what problems are you trying to solve?
- How long have you/do you typically spend on our website?
- Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, what was your deciding factor?
- Have you ever interacted with our website to make a purchase but decided not to? If so, what led you to this decision?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how easily can you navigate our website?
- Did you ever require customer support? If so, how helpful was it, on a scale of 1 to 10?
- Can we further support you to make your process easier?
You can use this buyer persona tool to fill in the details you procure from customer feedback.
4. Highlight your target customer personas.
Once you've learned about the customer personas that interact with your business, I would recommend narrowing your focus to one or two.
Remember, a UX journey map tracks the experience of a customer taking a particular path with your company — so if you group too many personas into one journey, your map won't accurately reflect that experience.
When creating your first map, it's best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
You can use a marketing dashboard to compare each and determine the best fit for your journey map. Don't worry about the ones you leave out, as you can always go back and create a new map specific to those customer types.
5. List out all touchpoints.
Begin by listing the touchpoints on your website.
Based on your research, you should have a list of all the touchpoints your customers are currently using and the ones you believe they should be using if there's no overlap.
This is essential in creating a UX journey map because it provides insight into your customers' actions.
For instance, if they use fewer touchpoints than expected, does this mean they're quickly getting turned away and leaving your site early? If they are using more than expected, does this mean your website is complicated and requires several steps to reach an end goal?
Whatever the case, understanding touchpoints help you understand the ease or difficulties of the customer journey.
Aside from your website, you also need to look at how your customers might find you online. These channels might include:
- Social channels
- Email marketing
- Third-party review sites or mentions
Run a quick Google search of your brand to see all the pages that mention you. Verify these by checking your Google Analytics to see where your traffic is coming from. Whittle your list down to those touchpoints that are the most common and will be most likely to see an action associated with it.
At HubSpot, we hosted workshops where employees from all over the company highlighted instances where our product, service, or brand, impacted a customer. Those moments were recorded and logged as touchpoints. This showed us multiple areas of our customer journey where our communication was inconsistent.
The proof is in the pudding -- you can see us literally mapping these touch points out with sticky notes in the image below.

HubSpot's free customer journey map template makes it easier than ever to visualize the buyer's journey. It saved me some time organizing and outlining my customer experience and it made it clear how a website could impact my user's lives.
The customer journey map template can also help you discover areas of improvement in your product, marketing, and support processes.
Download a free, editable customer journey map template.
Types of Customer Journey Maps and Examples
There are four types of customer journey maps , each with unique benefits. Pick the one that makes the most sense for your company.
Current State
These customer journey maps are the most widely used type. They visualize the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers currently experience while interacting with your company. They're best used for continually improving the customer journey.
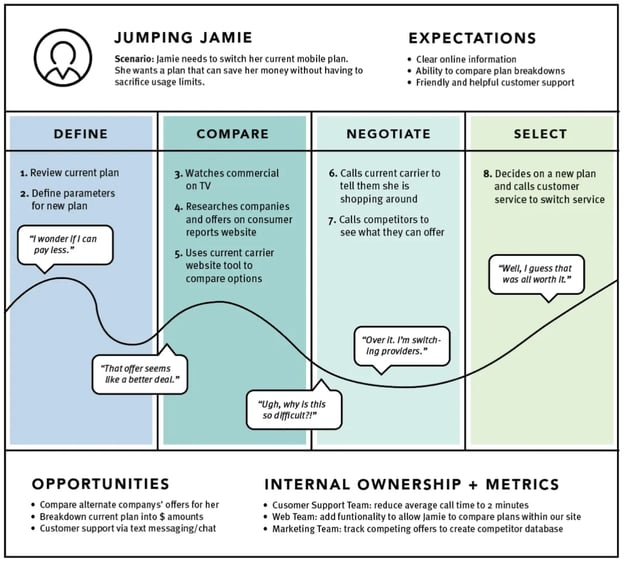
Image Source
Day in the Life
These customer journey maps visualize the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers currently experience in their daily activities, whether or not that includes your company.
This type gives a broader lens into your customers' lives and what their pain points are in real life.
Day-in-the-life maps are best used for addressing unmet customer needs before customers even know they exist. Your company may use this type of customer journey map when exploring new market development strategies .

Future State
These customer journey maps visualize what actions, thoughts, and emotions that your customers will experience in future interactions with your company. Based on their current interaction with your company, you'll have a clear picture of where your business fits in later down the road.
These maps are best for illustrating your vision and setting clear, strategic goals.
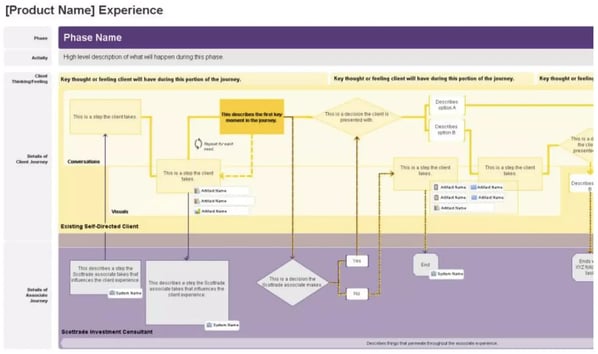
Service Blueprint
These customer journey maps begin with a simplified version of one of the above map styles. Then, they layer on the factors responsible for delivering that experience, including people, policies, technologies, and processes.
Service blueprints are best used to identify the root causes of current customer journeys or the steps needed to attain desired future customer journeys.
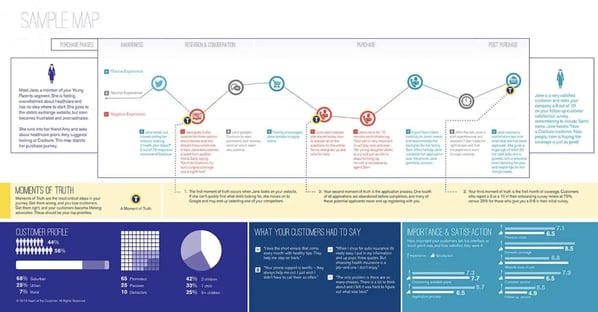
If you want a look at a real customer journey map that HubSpot has used recently, check out this interview we conducted with Sarah Flint, Director of System Operations at HubSpot. We asked her how her team put together their map (below) as well as what advice she would give to businesses starting from scratch.

Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Set a goal for the journey map.
- Survey customers to understand their buying journey.
- Ask customer service reps about the questions they receive most frequently.
- Consider UX journey mapping for each buyer persona.
- Review and update each journey map after every major product release.
- Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams.
1. Set a goal for the journey map.
Determine whether you aim to improve the buying experience or launch a new product. Knowing what the journey map needs to tell you can prevent scope creep on a large project like this.
2. Survey customers to understand their buying journey.
What you think you know about the customer experience and what they actually experience can be very different. Speak to your customers directly, so you have an accurate snapshot of the customer's journey.

3. Ask customer service reps about the questions they receive most frequently.
Sometimes, customers aren't aware of their specific pain points, and that's where your customer service reps come in.
They can help fill in the gaps and translate customer pain points into business terms you and your team can understand and act on.
4. Consider UX journey mapping for each buyer persona.
It's easy to assume each customer operates the same way, but that couldn't be further from the truth.
Demographics, psychographics, and even how long someone has been a customer can determine how a person interacts with your business and makes purchasing decisions.
Group overarching themes into buyer personas and create a UX journey map for each.
5. Review and update each journey map after every major product release.
Every time your product or service changes, the customer's buying process changes. Even slight tweaks, like adding an extra field to a form, can become a significant roadblock.
So, reviewing the customer journey map before and after implementing changes is essential.
6. Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams.
Customer journey maps aren't very valuable in a silo. However, creating a journey map is a convenient way for cross-functional teams to provide feedback.
Afterward, make a copy of the map accessible to each team, so they always keep the customer top of mind.
Breaking down the customer journey, phase by phase, aligning each step with a goal, and restructuring your touchpoints accordingly are essential steps for maximizing customer success .
Here are a few more benefits to gain from customer journey mapping.
1. You can refocus your company with an inbound perspective.
Rather than discovering customers through outbound marketing, you can have your customers find you with the help of inbound marketing.
Outbound marketing involves tactics targeted at generalized or uninterested audiences and seeks to interrupt the customers' daily lives. Outbound marketing is costly and inefficient. It annoys and deters customers and prospects.
Inbound marketing involves creating helpful content that customers are already looking for. You grab their attention first and focus on the sales later.
By mapping out the customer journey, you can understand what's interesting and helpful to your customers and what's turning them away.
2. You can create a new target customer base.
You need to understand the customer journey properly to understand your customers' demographics and psychographics.
It's a waste of time and money to repeatedly target too broad of an audience rather than people who are actually interested in your offering.
Researching the needs and pain points of your typical customers will give you a good picture of the kinds of people who are trying to achieve a goal with your company. Thus, you can hone your marketing to that specific audience.
3. You can implement proactive customer service.
A customer journey map is like a roadmap to the customer's experience.
It highlights moments where people experience delight and situations where they might face friction. Knowing this ahead of time allows you to plan your customer service strategy and intervene at ideal times.
Proactive customer service also makes your brand appear more reliable. For example, when I worked in customer support, we would anticipate a surge in tickets around the holidays. To be proactive, we'd send out a message to customers letting them know about our team's adjusted holiday hours. We would aalso tell them about additional support options if we were unavailable and what to do if an urgent problem needed immediate attention.
With expectations set, customers won't feel surprised if they're waiting on hold a little longer than usual. They'll even have alternative options to choose from — like a chatbot or knowledge base — if they need to find a faster solution.
4. You can improve your customer retention rate.
When you have a complete view of the customer journey, it's easier to pick out areas where you can improve it. When you do, customers experience fewer pain points, leading to fewer people leaving your brand for competitors.
After all, 33% of customers will consider switching brands after just one poor experience.
UX journey mapping can point out individuals on the path to churn. If you log the common behaviors of these customers, you can start to spot them before they leave your business.
While you might not save them all, it's worth the try. Increasing customer retention rates by just 5% can increase profits by 25%-95%.
5. You can create a customer-focused mentality throughout the company.
As your company grows, it can be tricky to coordinate all your departments to be as customer-focused as your customer service, support, and success teams are. That's because each department has varying goals, meaning they might not be prioritizing customer needs -- they might focusing on website traffic, leads, product signups, etc.
One way to overcome this data silo is to share a clear customer journey map with your entire organization. The great thing about these maps is that they map out every single step of the customer journey, from initial attraction to post-purchase support. And, yes, this concerns marketing, sales, and service.
For more examples of customer journey maps, read on to the next section for a few templates you can use as a baseline for your company's map.
Customer Journey Mapping Examples
To help guide your business in its direction, here are examples to draw inspiration from for building out your customer journey map.
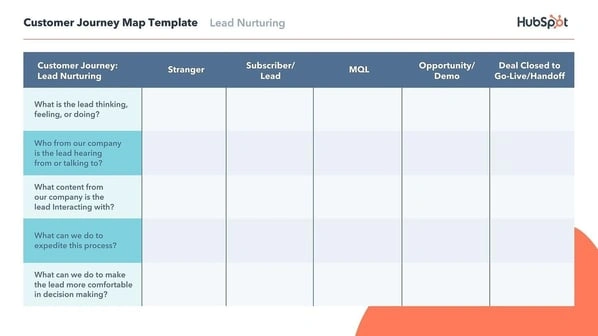
1. HubSpot's Customer Journey Map Templates
HubSpot's free Customer Journey Map Templates provide an outline for companies to understand their customers' experiences.
The offer includes the following:
- Current State Template
- Lead Nurturing Mapping Template
- A Day in the Customer's Life Template
- Customer Churn Mapping Template
- Customer Support Blueprint Template
Each of these templates helps organizations gain new insights into their customer base and help make improvements to product, marketing, and customer support processes.
Download them today to start working on your customer journey map.
2. B2B Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map clearly outlines the five steps Dapper Apps believes customers go through when interacting with them.
As you can see, it goes beyond the actual purchasing phase by incorporating initial research and post-purchase needs.
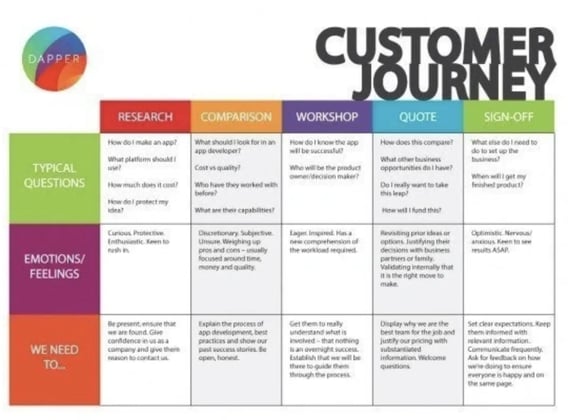
This map is effective because it helps employees get into the customers' minds by understanding the typical questions they have and the emotions they're feeling.
There are incremental action steps that Dapper Apps can take in response to these questions and feelings that will help it solve all the current problems customers are having.
3. Ecommerce Customer Journey Map Example
This fictitious customer journey map is a clear example of a day-in-the-life map.
Rather than just focusing on the actions and emotions involved in the customer's interaction with the company, this map outlines all the actions and emotions the customer experiences on a typical day.
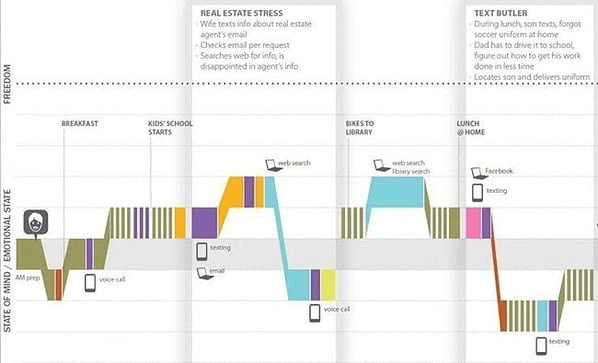
This map is helpful because it measures a customer's state of mind based on the level of freedom they get from certain stimuli.
This is helpful for a company that wants to understand what its target customers are stressed about and what problems may need solving.
4. Future B2C Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map, designed for Carnegie Mellon University, exemplifies the usefulness of a future state customer journey map. It outlines the thoughts, feelings, and actions the university wants its students to have.
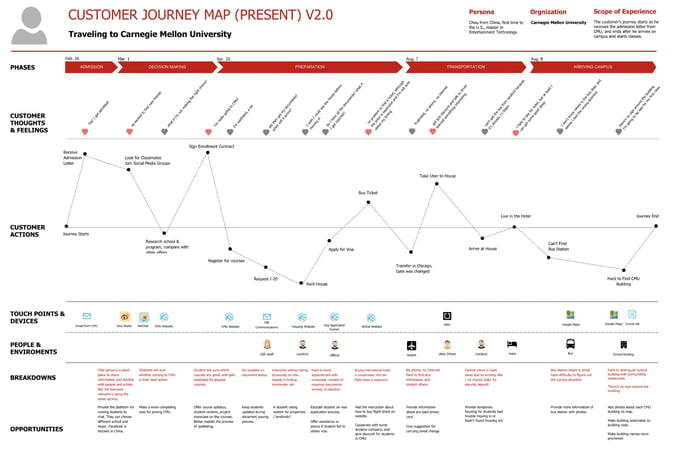
Based on these goals, CMU chose specific proposed changes for each phase and even wrote out example scenarios for each phase.
This clear diagram can visualize the company vision and help any department understand where they will fit into building a better user experience.
5. Retail Customer Journey Map Example
This customer journey map shows an in-depth customer journey map of a customer interacting with a fictitious restaurant.
It's clear that this style of map is more comprehensive than the others. It includes the front-of-stage (direct) and back-of-stage (non-direct or invisible) interactions a customer has with the company, as well as the support processes.
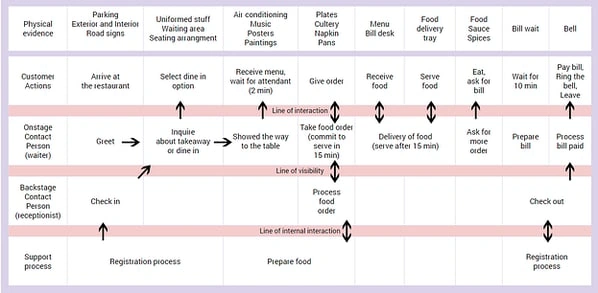
This map lays out every action involved in the customer experience, including those of the customer, employees directly serving diners, and employees working behind the scenes.
By analyzing how each of these factors influences the customer journey, a company can find the root cause of mishaps and problem-solve this for the future.
To get your business from point A — deciding to focus on customer journeys — to point B — having a journey map — a critical step to the process is selecting which customer mindset your business will focus on.
This mindset will determine which of the following templates you'll use.
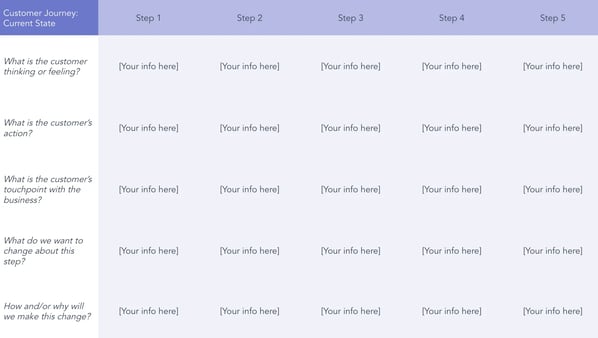
1. Current State Template
If you're using this template for a B2B product, the phases may reflect the search, awareness, consideration of options, purchasing decision, and post-purchase support processes.
For instance, in our Dapper Apps example, its phases were research, comparison, workshop, quote, and sign-off.
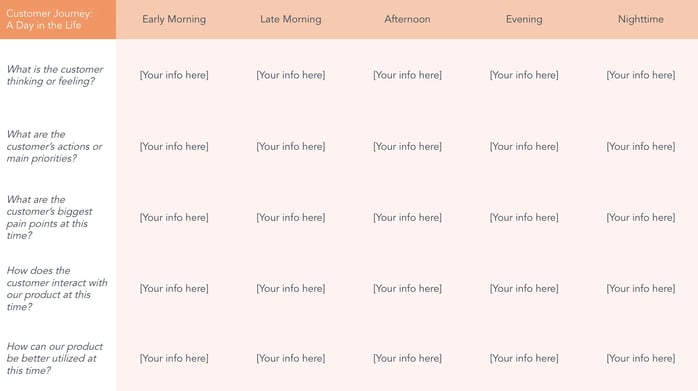
2. Day in the Life Template
Since this template reflects all the thoughts, feelings, actions, needs, and pain points a customer has in their entire daily routine — whether or not that includes your company — you'll want to map out this template in a chronological structure.
This way, you can highlight the times of day at which you can offer the best support.
Get an interactive day in the life template.
3. Future State Template
Similar to the current state template, these phases may also reflect the predicted or desired search, awareness, consideration of options, purchasing decision, and post-purchase support processes.
Since this takes place in the future, you can tailor these phases based on what you'd like the customer journey to look like rather than what it currently looks like.
Get an interactive future state template.

4. Service Blueprint Template
Since this template is more in-depth, it doesn't follow certain phases in the customer journey.
Instead, it's based on physical evidence — the tangible factors that can create impressions about the quality and prices of the service — that often come in sets of multiple people, places, or objects at a time.
For instance, with our fictitious restaurant example above, the physical evidence includes all the staff, tables, decorations, cutlery, menus, food, and anything else a customer comes into contact with.
You would then list the appropriate customer actions and employee interactions to correspond with each physical evidence.
For example, when the physical evidence is plates, cutlery, napkins, and pans, the customer gives their order, the front-of-stage employee (waiter) takes the order, the back-of-stage employee (receptionist) processes the order, and the support processes (chefs) prepare the food.
Get an interactive service blueprint template.

5. Buyer's Journey Template
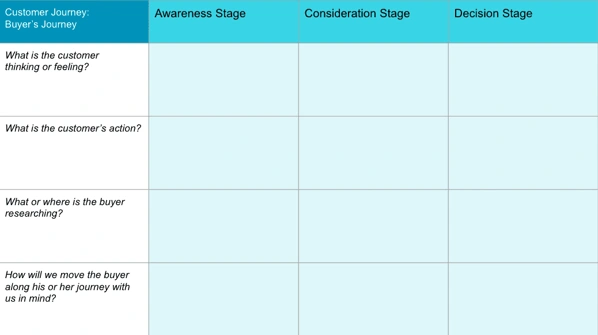
You can also use the classic buyer's journey — awareness, consideration, and decision — to design your customer journey map.
Get an interactive buyer's journey template.
Charter the Path to Customer Success
Once you fully understand your customer's experience with your business, you can delight them at every stage of their buying journey. Remember, many factors can affect this journey, including customer pain points, emotions, and your company's touchpoints and processes.
A customer journey map is the most effective way to visualize this information, whether you're optimizing the customer experience or exploring a new business opportunity to serve a customer's unrecognized needs.
Use the free templates in this article to start mapping the future of customer success at your business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August, 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![customer journey mapping gartner How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![customer journey mapping gartner How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![customer journey mapping gartner Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]
![customer journey mapping gartner How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-journey-map_13.webp)
How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2023
![customer journey mapping gartner How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
So You've Made a Customer Journey Map. Now What?
Kristen Bialik
6 steps to effectively use your customer journey map, consider using customer journey software, creating a customer journey map isn't the final destination; it's the beginning of your customer experience improvement journey..

Greetings, cartographers. You've put yourself in your customers' shoes and mapped their journey . You've added topographical nuance. Now what?
Your customer journey map isn't meant to be wall art or a fixed route that never changes. And businesses of all kinds can struggle with how to effectively leverage a journey map once it exists.
According to Gartner, 30% of marketing leaders in charge of or supporting customer journey mapping have established maps but struggle to use them effectively in identifying and prioritizing customer experience (CX) efforts (full article available to Gartner clients).
You don't have to be among that number. Your journey map is meant to be used and used effectively, not just looked at.
Let's look at how to use your map to identify pain points, connect those customer pain points to internal processes, and work toward a better customer experience.
If you've been looking at your journey map wondering what to do next, take a look at these steps to start putting your map to use.
Along the way, we'll distinguish between a customer journey map (what you've already created) and your company journey map (connecting that map to your own internal processes).
To do so, we'll look at a fictional customer-business scenario between Trey Veller—a customer interested in buying a cross-country bus tour package–and Tour De Farce—a bus company hoping to win his business.
1. Validate your map
Begin by validating your customer journey map. In other words: Make sure it's an accurate reflection of your customer experience. This validation process should confirm that the real customer journey you're interested in is accurately portrayed by your map.
Hopefully, you were able to combine quantitative and qualitative information when drafting your map. But if not, bring in whatever data you didn't focus on initially to get the full lay of the land.
Surveys, interviews, and focus groups all offer valuable contextual information to make sure you didn't miss or mischaracterize any steps in your map. Just be sure to use participants who are representative of your existing or target customers.
Whichever methodology you use, the validation process should help identify or verify:
Any touch points that are missing from your map
What customers want to achieve and/or feel at each stage of their journey
How successful customers are at achieving their goal at each stage
What customers feel are the most important moments in their journey
Once you've confirmed that your customer journey map is accurate and/or incorporated any necessary information from the validation process, you're ready for the next step.
2. Identify pain points within the customer journey
The most insightful journey mapping process doesn't only detail the specific points customers take from start to finish; it illuminates customers' feelings and actions throughout their journey.
Note and celebrate current successes, areas where the customer is happy and satisfied in their journey. But you'll get the most out of your customer map by identifying and solving moments where your customers are feeling dissatisfied or frustrated.
Are your customers calling customer service with the same set of problems? Is there a feature on your website or product that isn't functioning optimally? Are wait times for a particular service resulting in customer frustration and departures? Is there a disconnect when customers move from one channel to another?
Let's take a look at Trey Veller and his customer journey through buying and taking a bus tour with Tour De Farce. He's experienced a couple of the pain points the company is aware of from their customer journey mapping exercise:
Veller had a hard time finding the specific tour package he was interested in on the company website, since there was no good filtering mechanism to limit results by country, cost, or number of days.
After he found and booked the trip, he expected an itinerary to be emailed to him with key information about the trip. No such email arrived; he had to log in to his account on the website to get the information he needed.
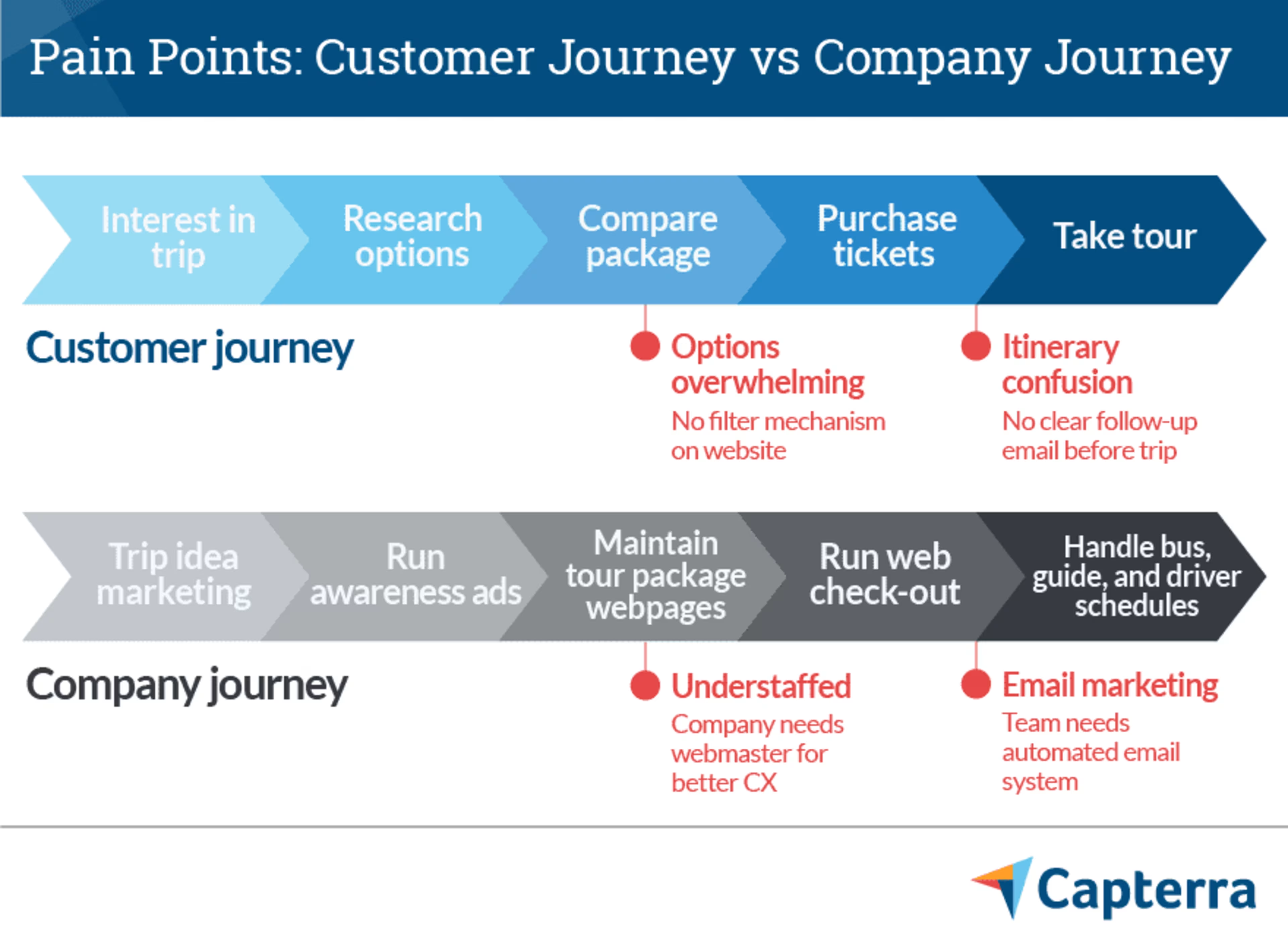
Leverage your qualitative data to really listen to your customers and understand when they're unable to meet their goals at a given stage or when the emotional experience of a touch point could be improved.
Once you've identified and prioritized the pain points you want to address, you're ready to connect them to your company journey (internal processes) and begin solving these problems.
3. Connect the outside journey to internal processes
Remember, your customer journey map is all about your customer's experience, not your company's. It's an outside-in look at your product or service.
But to improve your customer journey, you need to flip the script and look inside-out by adding an additional layer that connects external-facing touch points to internal systems, teams, and processes.
Let's say your company sends out a weekly promotional email newsletter. Opening the email, reading it, and clicking on a link that redirects to your website are all touch points on your customer journey map. Ideally, your customers see a seamless connection between the email and the webpage.
Internally, those touch points involve the newsletter marketing platform and server, your newsletter marketing team, sales department, webmasters, and possibly others.
Why does this matter? Connecting the customer journey to your company journey allows you to see all relevant stakeholders and channels you need to include when addressing a problem.
Let's go back to Tour De Farce. It knows the tour package page is a source of frustration. Customers want to filter options instead of wading through a long list. The problem? Tour De Farce doesn't have a dedicated webmaster who can implement a filter mechanism to the webpage.
The company's not sure if its current website server and platform can do what's needed. A webmaster could evaluate the website and implement a filtering mechanism but would need help from other teams on how to tag each tour. To solve this problem, multiple stakeholders need to be involved.
4. Refine your goals and troubleshoot solutions with relevant stakeholders
Often, the customer journey-mapping process reveals multiple pain points. Ideally, once you know what customers are frustrated by on the outside, you can identify who can help you fix it on the inside.
To do so, step back and prioritize what solutions should come first, then work with relevant teams to find solutions. Delivering the customer's desired experience may require cross-functional collaboration and may include overlapping systems, channels, or processes.
Tour De Farce's number one pain point priority is addressing the webpage filtering complaint. For the filter mechanism, involved stakeholders include HR (hiring a webmaster), the team currently managing the website (interviewing and onboarding the webmaster), and the team who plans the tours (providing key tagging information the webmaster will need to create the filters).
Once Tour De Farce has a dedicated website expert, the webmaster will need to work with the digital team, tour planning team, and marketing and design to determine the best way to set up the new page for customers to find their ideal tour.
5. Track key performance indicators
Once you've brainstormed solutions to your first-priority CX issues, determine what key performance indicators (KPIs) will best help you measure improvements.
Define what success looks like for each touch point, as well as how you can measure and optimize your customer experience over time. This may require continued cross-functional collaboration, as other teams may have the data you need to track performance.
How often you should track your KPIs will vary depending on the project, but schedule a recurring check to track performance at regular intervals.
In our last Tour De Farce example, let's imagine the company decided to implement an email automation program so customers would get key information by email leading up to their trip. The stakeholders involved have determined that email open and click rates are their most important metrics for success. The marketing team handling the emails looks at the open and click rates each week.
6. Update your maps
Your customer journey will change over time, especially as new channels (e.g., emerging social media platforms) alter the digital landscape, affecting how your customers find and interact with your business.
Static and outdated maps can't serve your business. As you solve problems discovered in your initial map, update the map so it reflects your progress and allows your business to shift focus to other customer experience priorities.
Knowing when or how often to update, however, can be tricky. One option is establishing a specific time frame for regular customer journey map refreshes. Another option? Leveraging customer journey mapping software.
If you're no Mercator , consider using customer journey mapping software for better visualization and collaboration capabilities.
Some software programs allow users to drill down and conduct exploratory analysis on frequent pathway variations or customer pain points, helping illuminate what CX issues leaders should prioritize. Some solutions can also track improvements and signal when to update your map.
Whatever your journey mapping priorities are, following the steps above will help you chart out a path to success.
Check out Capterra's directory of customer journey mapping tools
Was this article helpful, about the author.
Kristen Bialik is a senior specialist analyst covering customer experience for Capterra. She holds B.A.'s in English and Communications from the University of Michigan and an M.A. in Journalism Research from the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Follow her at @kebialik for insight on CX for small and midsize businesses.
Related Reading
6 top-rated ai-enabled tools for customer service, retail strategist reveals how technology can deliver personalized and frictionless experiences, capterra value report: a price comparison guide for call center software, 6 top-rated free survey tools, global thought leader on customer loyalty explores the ‘science of effort’ in ex and cx, sales researcher says ai-enabled tech is the key to uncovering b2b sales insights, 74% of companies have expanded their cx spend—here's where you should invest, according to a cx veteran, 7 top-rated free help desk software, 7 customer service mobile apps users love.
B2B Customer Journey Mapping Guide For SaaS
10 min read
Interested in building a B2B customer journey map?
It’s a challenging process, but the benefits are well worth it. At the very least, a journey map will help you easily analyze and make data-driven decisions to improve the user experience. It also helps align your teams by ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding customer interactions.
In this article, we’ll cover B2B customer journey stages, how to build a B2B customer journey map, and the right tools to use.
- A journey map is a visual representation outlining the entire customer experience from discovery to conversion and beyond.
- Customer journey mapping informs customer experience management and helps you predict and meet user expectations, driving customer success and growth for your business.
B2B customer journeys are usually not a linear process, but here’s a list of the stages involved:
- Consideration
How to build a B2B customer journey map:
1. Understand your buyer personas and user personas:
- Collect feedback from existing customers
- Use signup surveys to get new customer information
Look at user behavior in-app to spot trends
2. Define important customer touchpoints for each user persona:
Look at acquisition metrics to understand important channels
Use heatmaps and website session recordings to understand the buying process, map your sales process touchpoints, define the activation point for different personas, understand the happy paths for different personas.
3. Measure and analyze how users progress through the customer journey
- Use funnel analysis to understand friction and drop-offs in the customer’s journey
- Collect customer experience feedback to know where you need to help users progress through the journey
- Iterate on your customer experience management strategy based on the information gathered
Best customer journey mapping and analysis tools to increase customer retention: Userpilot and Miro.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation outlining the entire experience a customer goes through when interacting with your product, from discovery to conversion and beyond.
A detailed journey map will help you understand customer needs and pain points at every stage of their journey, equipping you to deliver positive experiences.
Why do you need a B2B customer journey map?
Journey maps inform customer experience management . By knowing the steps customers are expected to take at each key milestone, you can easily detect when they’re stuck and deploy means to remove friction . This will help you create a positive customer experience and boost customer retention.
Additionally, journey maps help you deliver more value by prompting account upgrades at the right stages. You’ll meet customer expectations and boost revenue.
B2B customer journey stages
The B2B customer journey is usually not linear but a complex and dynamic process influenced by various factors and multiple decision-makers.
After some research, Gartner found that B2B buyers move back and forth between key buying actions. Here’s what it looks like:

To illustrate, imagine a company identifies a need to improve its customer support process.
While exploring solutions, they realize upgrading their CRM software could help. So, they begin considering two options: get a higher tier from their current provider or find alternative software. While evaluating their choices, someone suggests implementing a chatbot solution might be a better fit.
This prompts them to revisit the problem and re-evaluate the solutions, factoring in budget and other considerations.
The above is just an example, but different shades of it happen in B2B companies all the time.
If the process is this complex, how do you win?
Your best bet is to provide decision-makers with information designed to help them move smoothly between buying stages.
To do that properly, you need to identify the key stages involved. We’ve outlined them below (still bear in mind it’s not a linear process):
- Awareness: Here, the customer understands their need and is searching for solutions. They conduct online research, ask peers, etc.
- Consideration: Customers in the consideration stage have identified potential tools or solutions that could solve their problem. They’re in the process of researching and evaluating different options.
- Evaluation: This stage involves the customer taking a concrete step to sign up for a free trial or create a free account. Customer activation happens here.
- Decision: The customer makes a buying decision, either opting for a paid subscription or becoming an active user of the freemium version.
- Adoption: After users have decided to use your tool, it’s time you make them see they made the right choice. Focus on helping this user group experience repeated value quickly, making them want to continue using your platform. Data-driven in-app onboarding is critical here. Collect customer data, tailor the onboarding to their needs, and keep analyzing to spot drop-offs.
- Expansion: This stage is where users upgrade to do more with your tool. It can happen multiple times in the user journey.
- Loyalty: At this stage, the customer is a happy and satisfied user. They continue to renew their subscription, are actively engaged with the product, and may even become brand advocates .
How to build a B2B customer journey map
So, how do you build a journey map that helps you convert customers, find user experience improvement areas, and boost customer retention?
Here are practical steps:
Understand your buyer personas and user personas
The buyer isn’t always the end user, especially in large enterprises. Buyers simply purchase the product and hand it over to end users.
For example, sales management might select SaaS tools for sales forecasting, CRM, or lead management. Their main objective when buying is to assess the tool’s impact on the sales team’s productivity and revenue generation.
On the other hand, the users will be sales reps, and their primary concern is usability and how the tool helps them meet sales goals.
Similarly, in large marketing teams, the head of marketing is responsible for buying marketing tools , but the people who actually use them are content creators, designers, social media managers, etc.
So, don’t confuse buyers for users when creating your personas . Unless you’re selling to startups, focus on developing two different personas for buyers and users.
Your personas should include multiple data points covering demographic information, behavioral data, pain points, goals, and preferences.
Wondering how to get this data? These three steps will help:
Collect customer feedback data to shape personas
Use customer satisfaction surveys to learn what brings positive customer experiences and what problems your product helps users solve.
This will enable you to understand who your best-fit users are. Once you have the survey responses, identify recurring feedback and use that to build your user persona.
Use your signup flow for data collection and define customer segments
Your signup flow is a good opportunity to learn about users from the horse’s mouth.
Keep it short, but ask questions that let you understand the main JTBD or pain points of users. You also want to ask questions that let you know how big the user is.
Here’s an example from Notion:

Dig into your analytics to understand the features your active users engage with the most.
This enables you to determine what’s valuable to different user segments.

Also, it aims to understand trends that lead to high customer lifetime value and use all the information gathered to create user personas that are not solely based on hypothetical characteristics but rooted in real user actions and preferences.

Define important customer touchpoints for each user persona
After following the steps above, you’ll have different user personas. Your next step is to define the critical touchpoints for these user groups based on their pain points.
Consider two factors: the number of traffic a channel generates and the quality of leads (in terms of ROI).
By identifying your top-performing channels, you can know where your ideal customers come from and incorporate those channels into your customer journey map.
You know the channels that bring in visitors, but how do these people behave when they land on your website and landing pages?
Use heatmaps and session recordings to find out.
Heatmaps offer a visual representation of where users click, move their cursors, or spend the most time on your web pages.
Session recordings, on the other hand, capture individual user sessions, allowing you to replay and analyze exactly how users navigate your site. You can see their cursor movements, clicks, scrolls, and interactions in real time.
Combining these two will give you an overview of the purchase process.
The touchpoints here will differ depending on whether you’re a sales-led or product-led company.
Touchpoints in a sales-led approach
- Initial outbound contact from sales reps
- Discovery calls
- Product demos
- Customized proposals
- Contract signing
For product-led companies, the touchpoints start with the product, and users progress independently with little to zero contact with a human agent. The typical touchpoints:
- Self-signup
- Account upgrades (trial to premium )
- Upsell /cross-sells
Activation is the point in the customer journey where the user experiences value. This varies for each product and can also be different for each user persona.
For example, imagine an email marketing tool used by a SaaS company and an e-commerce shop.
Ecom operators are mostly interested in recovering potential sales through abandoned cart emails. So activation for the e-commerce shop happens when they’re able to successfully trigger such emails.
For the SaaS company, they may be more interested in segmentation based on user behavior. For example, sending an email when a user completes a specific task.

The happy path refers to the ideal sequence of actions a user takes to achieve their goals with your product.
Map the ideal customer journey map for each step users need to take after activation. Highlight the features they need to discover and how often they should use them to adopt and become active users.

Measure and analyze how users progress through the customer journey
Collecting and analyzing user data helps you understand what’s happening at each stage. With the insights gathered, you’ll refine your B2B customer journey map and improve the user experience.
Here’s how:
Use funnel customer journey analysis
Use a tool like Userpilot to conduct funnel analysis and identify friction points and drop-offs in the user journey.
To gain deeper insights, pair this analysis with session recordings.
The combination will help you better understand user behavior and make informed improvements.

Collect customer experience feedback
Trigger CES surveys to gauge how easy or challenging users find specific aspects of their journey.
This feedback can uncover pain points or areas where users struggle. For example, you’ll know when they’re finding it hard to adopt a new feature, upgrade their account, comprehend your pricing structure, etc.
By pinpointing these specific issues, you’ll have a clearer roadmap for helping users progress smoothly through their journey.

Iterate on your customer experience management strategy
It’s not enough to collect qualitative and quantitative data; implement the insights to improve the customer experience.
- Trigger in-app flows to guide users across the journey where they need help.
- Adjust the customer journey map based on how your product evolves or the user needs change.
- Use in-app messaging to guide users to discover and adopt important features that will bring value to them.
For example, Rocketbots uses interactive walkthroughs to guide users through using and adopting key features :

Best customer journey mapping and analysis tools to increase customer retention
The right tool makes it easy to create a detailed B2B customer journey. While there are several products on the market, it can be hard to pick the one with the functionalities you need.
You can’t go wrong with Userpilot and/or Miro (depending on your needs).
Userpilot – for data collection
Userpilot is a product growth tool that bundles analytics , feedback , and engagement .
You can use it to collect data through in-app usage analytics and customer feedback surveys. Our platform also lets you analyze this data to spot trends and friction in the user journey.
Userpilot has features to let you trigger contextual in-app experiences to smoothen the customer journey.
For example, you could trigger an interactive walkthrough to guide users through using a feature they’re struggling with.

Miro – for visualizing the customer journey map
Miro is a collaborative online whiteboarding platform that greatly facilitates the visualization of B2B customer journey maps.
With its intuitive interface and extensive toolkit, Miro can enable your team to create, share, and collaborate on journey maps in a dynamic and visual manner.
You can easily map out each stage of the customer journey, incorporating elements like personas, touchpoints, pain points, and key interactions. Its real-time collaboration features allow you to work together seamlessly, whether you’re in the same room or distributed across the globe.
Is having a B2B customer journey map an absolute requirement for success?
Definitely not. You can thrive without one. However, journey maps help you become more customer-centric and deliver better user experiences. That’s what savvy SaaS customers want, and it will unlock growth opportunities and boost your customer retention rate, loyalty, and revenue.
To get started, book a demo call with our team and see how Userpilot helps SaaS companies create detailed B2B customer journey maps.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...

Customer Journey Map
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map (CJM) is a visual representation of the different stages and touchpoints a customer goes through while interacting with a business or brand . It provides a comprehensive understanding of the customer’s experience, highlighting their needs, motivations, pain points, and overall satisfaction with the brand . CJMs are essential tools for businesses looking to improve customer experience (CX) by identifying areas for improvement and optimizing their interactions with customers.
The concept of customer journey mapping has gained popularity in recent years, as businesses have shifted their focus from product-centric approaches to customer-centric strategies. According to a survey by Gartner, 89% of companies now expect to compete primarily on the basis of customer experience (CX) by 2022. As a result, businesses are investing more in understanding their customers’ needs and preferences and using that information to create more personalized and engaging experiences.
Creating a customer journey map involves several steps, including identifying the customer personas, mapping out the different stages of the customer journey, defining the touchpoints and interactions, and gathering feedback from customers to validate the map. A typical CJM includes four key elements: the customer persona , the journey stages, the touchpoints, and the emotional states.
Customer Persona
A customer persona is a fictional representation of the ideal customer for a business. It includes demographic information, such as age, gender, income, and education, as well as psychographic information, such as values, attitudes, and behaviors. Creating customer personas helps businesses understand their customers’ needs and preferences and design products and services that meet those needs.
Journey Stages
The customer journey is divided into several stages, typically including awareness, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase. The stages may vary depending on the nature of the business and the customer journey, but they generally represent the different phases of the customer’s interaction with the brand .
Touchpoints
A touchpoint is any interaction between the customer and the brand , whether it is through a website , a social media channel, a physical store, or a customer service call. Each touchpoint represents an opportunity for the business to create a positive experience for the customer or risk alienating them.
Emotional States
The emotional states represent the customer’s feelings and perceptions at each stage of the journey. It includes positive emotions, such as joy and excitement, as well as negative emotions, such as frustration and disappointment. Understanding the emotional states helps businesses identify pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping offers several benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved Customer Experience: CJMs provide a comprehensive understanding of the customer’s needs, preferences, and pain points, allowing businesses to create more personalized and engaging experiences that meet their customers’ expectations.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: By providing a positive and seamless customer experience, businesses can increase customer loyalty, leading to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
- Enhanced Brand Perception: A positive customer experience can enhance the brand’s perception and reputation, leading to increased brand loyalty and customer advocacy.
- Optimized Processes: CJMs help businesses identify areas for improvement in their processes and operations, allowing them to optimize their resources and improve efficiency.
- Better Communication and Collaboration: CJMs provide a shared understanding of the customer journey, facilitating communication and collaboration among different departments and stakeholders in the organization.
Examples of Customer Journey Mapping
There are numerous examples of businesses using customer journey mapping to improve their CX. One such example is Starbucks, which created a CJM to understand its customers’ needs and preferences and improve its mobile ordering experience. By mapping out the customer journey and identifying pain points, such as long wait times and confusing menus, Starbucks was able to streamline the ordering process and improve the overall customer experience.
- Lalu, N. (2021). Customer Journey Mapping: What It Is and How to Create One. Hubspot. Retrieved from https://blog.hubspot.com/service/customer-journey-mapping.
- Marr, B. (2019). What is a Customer Journey Map and Why Do You Need One? Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2019/02/13/what-is-a-customer-journey-map-and-why-do-you-need-one/?sh=4f4d45f3b4ef .
- Rosenbaum, M. (2019). How to Create a Customer Journey Map. Smartsheet. Retrieved from https://www.smartsheet.com/customer-journey-map.
- Gartner (2019). Customer Journey Mapping: A Tool to Enhance Customer Experience. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/marketing/insights/articles/customer-journey-mapping-a-tool-to-enhance-customer-experience.
- White, R. (2020). Customer Journey Mapping: The Complete Guide. Qualtrics. Retrieved from https://www.qualtrics.com/experience-management/customer/customer-journey-mapping/ .
- Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2016). Marketing Management (15th ed.). Pearson.
- Bitner, M. J. (1992). Servicescapes: The Impact of Physical Surroundings on Customers and Employees. Journal of Marketing , 56(2), 57-71.
- Meyer, C., & Schwager, A. (2007). Understanding Customer Experience. Harvard Business Review, 85(2), 116-126.
- Verhoef, P. C., Lemon, K. N., Parasuraman, A., Roggeveen, A., Tsiros, M., & Schlesinger, L. A. (2009). Customer Experience Creation: Determinants, Dynamics, and Management Strategies. Journal of Retailing, 85(1), 31-41.

Process Manager Login
Process Governance Login
Process Manager (US) Login
Process Governance (US) Login
Process Manager (APAC) Login
Process Governance (APAC) Login
Process Manager (EMEA) Login
Process Governance (EMEA) Login
Process Manager (Canada) Login
Process Governance (Canada) Login
Process Manager (Japan) Login
Process Governance (Japan) Login
The Fundamentals of Customer Journey Mapping, and Why Businesses Need It Now
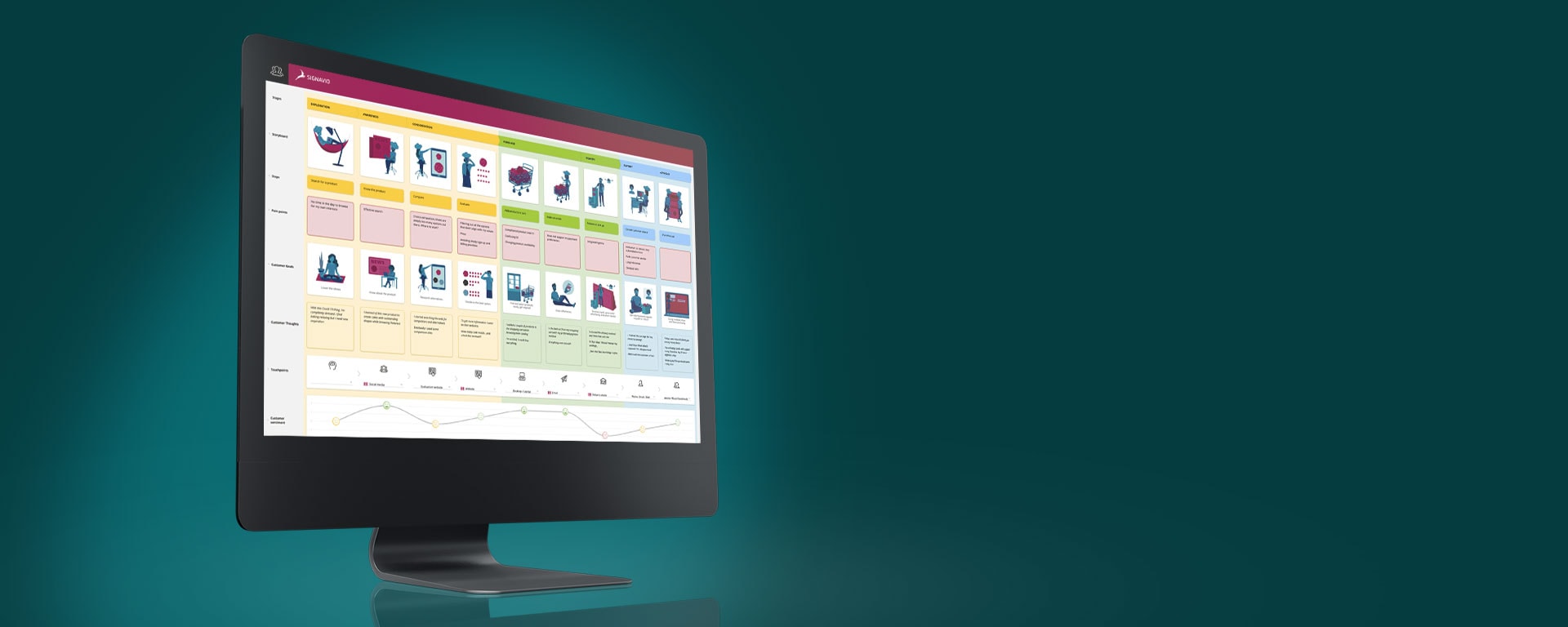
Journey mapping, in particular customer journey mapping, is a vital tool to building a customer-centric business. Read on for a comprehensive summary of customer journey mapping essentials, and how Signavio can help operationalize customer excellence in.
- Creating "frictionless" experiences
For years, we’ve been hearing about changing customer expectations, and the importance of the customer experience. The customer journey across digital and offline channels is getting more complex, meaning omnichannel customer service is the norm, and the pressure is on to provide “frictionless” experiences.
Harvard Business Review reports that “a good customer experience makes a person five times more likely to recommend a company and more likely to purchase in the future.” PwC found that “73% of all people point to customer experience as an important factor in their purchasing decisions. Yet only 49% of US consumers say companies provide a good customer experience today.” Why is creating a good — not even stellar — customer experience so difficult?
Companies are making a deliberate shift to react to the connection between customer satisfaction and business outcomes. But delivering new services into the market, or improving existing ones, often means fundamental changes within an organization. Visual tools can help cut through complexity by making the processes that impact customer experience tangible and actionable. That’s where journey mapping comes in.
Companies won’t be able to solve their customer experience problems with technology alone — it’s just the enabler. Focus on experience to realign priorities. PwC
This article introduces journey mapping as an organization-wide tool to align around the customer, also known as a customer-centric approach. We’ll explain what journey mapping is (and isn’t), how it can be used and measured, and share best practices and resources to get you started.
Table of contents
What is customer journey mapping (cjm), what exactly is a journey map, what about muce and rox, the history of journey mapping, why businesses need journey mapping now, revenue benefits, reduced costs, increased sales, greater customer and employee satisfaction, operational and organizational benefits, who leads and participates in journey mapping efforts, transformation initiatives, operational excellence, risk & compliance, journey mapping use cases, employee journey mapping, 1) have a clearly established scope for the project., 2) conduct internal research., 3) map the ‘current state’ customer journey., 4) develop and document your hypothesis about the journey., 5) conduct customer research., 6) review the journey., 7) improve the journey., why journey maps fail…and what to do about it, connect customer needs back to business results., adjust your journey map to optimize customer experience., determine future state processes., the customer journey as a whole, phases of the customer journey, journey touchpoints, examples of customer journey maps, blog posts, whitepapers and guides, on-demand webcasts, ux, cx and ex thought leadership, certification, next steps for your journey.
A customer journey informs customer journey mapping which produces a customer journey map.
In its most basic form, a journey map is a visualization of the steps that a person goes through in order to reach a goal. Customer (or buyer or user) journey mapping is the process of creating a visual map of all the touchpoints throughout a customer’s journey with your company, from discovery, to purchase, to post-purchase and retention.
Journey mapping is qualitative research that helps companies understand the experiences, challenges, and frustrations of their customers. It helps customer facing teams identify and understand customers’ needs, reactions and emotions to experiences delivered to them by the organization, and is used to influence and drive customer behavior by providing experiences that directly address the customer’s needs.
There is no one format or style for developing journey maps, however most journey maps include these elements:
- Persona (or actor): the typical customer or user the map is about.
- Scenario: the desired action or goal the persona is trying to accomplish.
- Actions: steps completed by the persona and by others during the journey.
- Motivations: user thoughts, emotions, why the persona did something.
- Moments of truth: points of pain or delight that make or break the journey for the persona.
- Opportunities: where the journey can be improved. Opportunities make the map actionable.
Two elements that show up less frequently are:
- Handoff points and ownership: where interactions transition from one team or person to another. This highlights accountability.
- Metrics: how success is judged, allowing teams to assess whether changes have actually improved the experience.
Can you have too much of a good thing? Watch out for common traps with our list of 5 Signs Your Processes May Damage Customer Satisfaction
There are many ways to show how to get from Point A to Point B. Approaches to process improvement have evolved over the last thirty years, and especially rapidly over the last decade. This means the roles which contribute to the process management profession and the terminology used to describe it have been fluid.
Each of the terms below describe something that is a visual representation, with steps or stages. The areas of difference between the terms relates to who is creating the map, who the map is about, how complex the experience represented is, and what it is trying to explain or impact.
'Mapping' vs. 'Modeling'
You'll see the terms customer journey 'mapping' and 'map' used throughout this post, in order to ensure consistency. In fact, the terms customer journey 'map' and 'model' are often used interchangeably. However, there is a difference!
The difference between an isometric customer journey map and a tabular customer journey model is like the difference between a hand-drawn map and a modern GPS app: they both get you to where you’re going but one offers better functionality, including giving the user much more information. A tabular customer journey model offers a richer picture of where customers are along their journey, in particular by connecting customer experience data with process mining analysis.
If you are just beginning your work on investigating how customers interact with your organization's internal processes, this distinction will be largely academic. As you progress along the road to building exceptional customer experiences, however, the more sophisticated and data-rich customer journey models will become increasingly important.
Important Customer Journey Mapping Terms
Here are top terms to know as you navigate the world of user and customer experience.
- Customer experience (CX): the interactions and perceptions a customer has related to a company. Customer experience is how a customer feels through the entire customer lifecycle, whereas a customer journey captures what the customer does in a stage of the lifecycle.
- User experience (UX): what a user experiences when interacting with a user interface. UXMatters offers this broader definition; “all aspects of digital products and services that users experience directly — and perceive, learn, and use — including products’ form, behavior, and content, but also encompassing users’ broader brand experience and the response that experience evokes in them.”
- Customer experience management (CEM): the process of executing, managing, and optimizing how a customer’s experience aligns with business performance.
- Design thinking : a human-centric, iterative problem-solving process focused on five phases — Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test. It is most useful to tackle problems that are ill-defined or unknown.
- Service design: Service design improves the experiences of both the user and employee or service provider by designing, aligning, and optimizing an organization’s operations to better support customer journeys. It includes customer journey mapping.
Consultancies like Gartner and PwC have introduced some new acronyms and models around the value of mapping experiences.
Multi Experience (MX) is an approach that integrates the Employee Experience (EX) with the Customer Experience (CX). The idea behind MX is that by making it easier for employees across departments to serve customers there is bi-directional benefit in removing friction from the customer experience. MUCE is MX + UX + CE+ EX and reflects the full digital experience. Gartner also calls this “total experience,” i.e. the combination of, as well as interplay between, customer experience, user experience and employee experience to impact and transform business outcomes. It is one of their top 10 tech trends for 2021 .
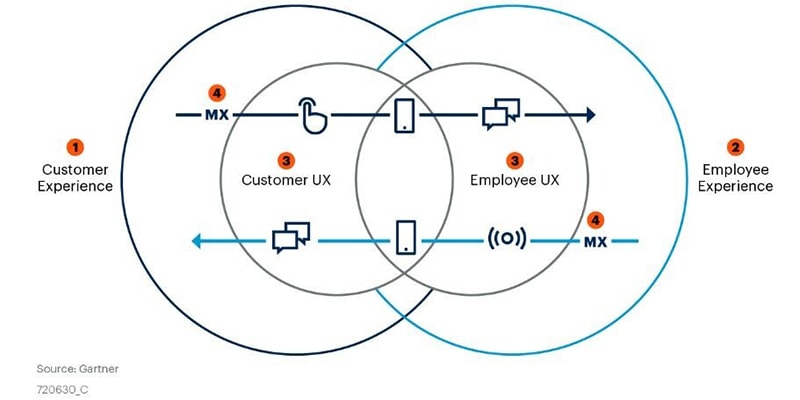
PwC adds in LX, or Leadership Experience, to how they assess a holistic approach to “outside-in” change. ROX, or Return on Experience, is what they call a “holistic approach to understanding and increasing the value of your investments across customer experience (CX), employee experience (EX) and leadership experience (LX).”
ROX requires the collaboration of the roles of the chief marketing officer (CMO), chief information officer (CIO), chief human resources officer (CHRO), and chief digital officer (CDO) for transformative change.
These models emphasize frequent communication, assessing and improving experiences by looking at where different groups intersect, and driving improvement by prioritizing customer needs vs. only bottom line or return on investment metrics.
Journey mapping has roots in product design, user experience, design thinking, and service design. ServiceDesignTools provides an illustration to show how the practices of social science, business, technology and design have developed tools that help organizations understand the people they are designing for and serving.
ServiceDesignTools also lists a number of important dates in the evolution of journey mapping, including:
- 1950s: Process improvement established as a methodology through Total Quality Management (TQM) and Quality Circles.
- 1982: “Service design” coined by G.Lynn Shostack in Harvard Business Review
- 1989: Service mapping is mentioned in the book, “Service Wisdom” by Chip Bell and Ron Zemke
- 1998: OxfordSM first uses customer journey mapping for Eurostar.
Building on this long history, a wealth of research from the last couple of years reinforces the importance of customer experience for retaining customers:
- Organizations that have and use customer journey maps are twice as likely to outperform competitors. [ Gartner ]
- CX drives over two-thirds of customer loyalty, outperforming brand and price combined. [ Gartner ]
- When Futurum Research surveyed 330 companies in North America and Europe in June 2020, 57% said their entire business model needed to be reconsidered in the wake of COVID-19. [ Forbes ]
- 81% of marketers say their companies will compete on the basis of CX in two years. Most are destined to underdeliver. [ Gartner ]
- One in three consumers (32%) say they will walk away from a brand they love after just one bad experience. [ PwC ]
- 54% of U.S. consumers say customer experience at most companies needs improvement. [ PwC ]
- 82% of the top-performing companies report paying close attention to the human experience around digital and tech. [ PwC Digital IQ ]
The Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
Great customer experience leaves consumers feeling seen, heard and valued. Mapping your customer journey means you can provide these great experiences more easily, creating a lasting positive impact on a company's bottom line, from revenue benefits to operational agility and departmental efficiency. In other words, a great customer journey map builds organizational alignment around the customer experience.
According to year-on-year growth research on customer journey mapping conducted by The Aberdeen Group, effective CJM will deliver:
Brands see almost 10x (1000%) improvement in the total cost of customer service.
CJM is essential for optimizing both sales and marketing practices. Brands that use CJM enjoy an average sales cycle that is 18 times faster, with 56% more revenue from up-selling and cross-selling efforts. Marketing practices experience a 54% greater return on marketing investment.
As customers are given the experiences they expect, satisfaction naturally increases, leading to a 24% increase in positive social media comments.
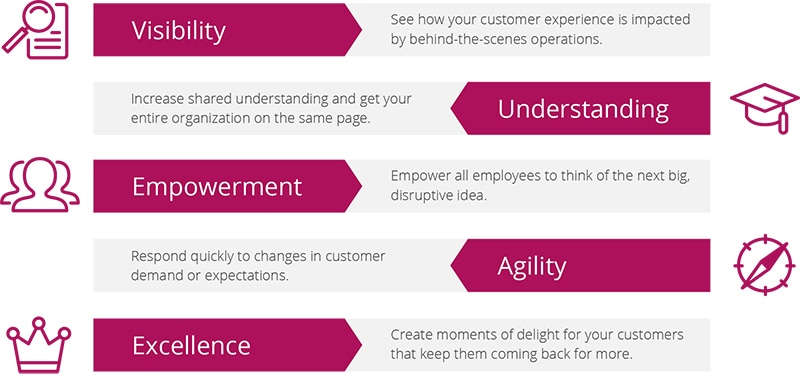
Many enterprises now have a chief customer officer (CCO) or chief experience officer (CXO) who is responsible for customer experience efforts. This is a significant change from just a few years ago, with Gartner reporting that “only around 10% of organizations have no CXO or CCO (or equivalent) today, compared to 39% two years ago. More than 70% of these leaders report directly to the CEO or COO while 18% report to the CMO.”
To discover more about the strategic role of the Chief Customer Officer, listen to our interview with Yamani Rangan, CCO at HubSpot, on Signavio's very own podcast: Art of the Pivot.
Regardless of reporting structure, the most successful process improvement efforts have a sponsor, a project leader, and a collaborative, cross-functional team contributing to the effort. The benefit of dedicated CX leadership is accountability; for measurement, governance and leadership to ensure consistency and reduce conflict between different activities aiming to enhance customer experience for an organization.
What Does Customer Journey Mapping Mean for BPM Leaders?
Customer journey mapping is a visual tool to facilitate collaboration in change management initiatives by creating a shared vision around a goal. Maps can increase customer empathy and understanding around the points of interaction businesses have with their customers.
Transformation initiatives can only succeed when companies overcome the bias towards “the way things have always been done.” Customer journey mapping gives you a fresh perspective to imagine innovative business models. It also creates excitement for change by providing employees the context and purpose of their work.
Even the most efficient process can be a waste if it isn’t contributing to the overall customer journey. Before embarking on a major operational excellence project, you first need to understand where the customer journey should be improved. Those processes should then become a priority.
Every interaction with a potential customer involves risk. Not only the risk of losing a customer, but also the risk that a non-compliant action is being taken. Customer journey mapping creates transparency around these interactions and provides visibility into underlying decisions.
With Signavio, all these initiatives can easily be communicated throughout the enterprise by creating a shared vision and single source of truth for the processes that fuel your business.
The same customer journey map may benefit different departments in different ways. For instance:
- Product: Find points of friction in task completion that can be improved
- Support: Route issues to the right teams.
- Customer Success: Improve onboarding. Reduce obstacles throughout the customer lifecycle. Benchmark your desired customer experience for customers against what they actually receive.
- Sales: Understand how different buyer personas progress through your sales funnel. Discover new opportunities to connect and engage with prospects. Assess if the transitions from marketing to sales to customer success are effective.
- Marketers: Identify gaps in content, understand where decisions are being made.
- Analytics: Generate hypotheses about what data is reflecting.
- Finance: Determine the “cost to serve” at key touchpoints to identify possible cost reductions.
The challenges of acquisition, engagement and retention don’t just apply to customers. Organizations face similar challenges with employees company-wide, as the way we work changes. The pandemic added a new perspective on remote work, collaboration, organizational culture and work-life balance.
An increasing number of organizations are taking a cue from CX by using journey mapping to improve the employee experience. Those that do invest in employee experience are more productive, valuable, attractive, innovative, and profitable. Research by Jacob Morgan, author of The Employee Experience Advantage , found that “organizations that invested most heavily in employee experience were included 11.5 times as often in Glassdoor’s Best Places to Work, listed 4.4 times as often in LinkedIn’s list of North America’s Most In-Demand Employers, 28 times more often listed among Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, and made it 2.1 times as often on the Forbes list of the World’s Most Innovative Companies.”
The approach to mapping remains the same; start with the problem you’re trying to solve. For many organizations, the problems to tackle with journey mapping could include how to:
- Ensure new hires are successful in their first 30 days;
- Attract a larger number of qualified candidates for Engineering roles;
- Provide more consistent and frequent performance feedback;
- Assess the process for internal communications; or
- Identify when and where learning and development opportunities should be introduced.
Once you identify the problem, the steps to mapping the journey remain the same, but with the added benefit of co-creating solutions with employees. This not only helps model the employee experience more accurately, but ensures employees feel a sense of ownership and investment in the way their individual jobs function, and how they fit into the larger goals of the organization.
Making sure employees feel heard will lead to a more engaged workforce, and since it's interactions with employees that can often drive customers' buying decisions, this is a triple win, offering benefits for employees, customers, and a company’s bottom line.
How To Get Started With Customer Journey Mapping
Our Ultimate Guide to Customer Journey Mapping illustrates each step of mapping customer journeys, and includes key questions to answer along the way. You can also download our handy visual guide to the 7 steps to start customer journey mapping , which covers the steps below.
The most vital thing is to define "who, what, where, and when." The map will help you show "how and why."
- Who — The persona or customer. Create one journey map per persona / point of view.
- What — The goal, action, or task you want to improve. You may wish to prioritize journeys that happen most often or have the most known issues.
- Where — The channel(s) the journey happens in.
- When — The time period in the customer journey when the customer will achieve the outcome. What is the before, during and after of the journey you are assessing?
Gather existing data around the journey. This could include website data, call center logs, social media posts, or operational data.
Identify the teams that interact with the customer persona and experience you are mapping.
What’s working well? Where do things break down? Identifying “moments of truth” — the make-or-break touchpoints in a customer’s journey — is a key component of journey mapping. It takes “twelve positive moments of truth to counter one failed moment,” according to service management researcher Richard Normann in his book Moments of Truth.
Ask research participants to detail the steps they take to complete the task you’ve decided to map in their own words. Keep questions open ended. Listen for “doing, feeling, thinking” verbs as the participant explains the steps. The language customers use matters, and may offer a clue into how they feel about a part of the journey.
Analyze the gaps between the current strategy and expectations. Use the participant’s responses to validate or disprove your team’s observations.
Put change into action by fixing what you’ve identified as a problem. Communicate the change to the teams that are involved in the journey and measure the behaviors that result from the change.
Now you know the right steps, check out how you can put them into action with our video demonstration of SAP Signavio Journey Modeler .
User experience consultancy Nielsen Norman Group surveyed user experience professionals on when journey maps fail. The top points of failure include:
- When there is no focus (36%)
- When the map is not based in reality (25%)
- When the map is not shared or used (21%)
- When there is no trust or buy-in (11%)
Each of these points of failure is avoidable. Here’s some tips on combating the top 4 reasons journey maps fail.
- When journey maps lack focus, go back to the best practice of limiting the scope of your journey to one persona, one goal, one channel.
- When journey maps are criticized because they are “not based in reality,” it is often because they draw from assumptions vs. customer research. Customer interviews and validation are a key part of the process.
- Is it because teams don’t know about your project? Engage with teams that touch your project early and often. Present your work in a company all hands so the broader organization can visualize and understand the customer experience.
- Is it because it is hard to find the file or the information is out of date? Make your map accessible to all in your organization. Integrate the customer journey into your process landscape documentation.
- Is it because teams haven’t been included throughout the process? Pain points aren't just experienced by customers. Casting a wide net for internal feedback can help improve the detail and effectiveness of a journey map.
- When there’s no trust or buy-in, it could be because journey mapping was conducted by one team to surface weaknesses in a process. By having top-down support for your program, and including the teams that intersect with the journey you are mapping, you are more likely to gain trust and buy-in for the process.
How To Successfully Put Journey Maps Into Action
Eight years into the age of the customer, just 15% of enterprises are customer-obsessed. Our research finds that executives agree with the idea…they just struggle to put it into practice. Forrester analyst Shar VanBoskirk
To deliver the competitive advantage that executive teams seek, CX teams need to reiterate “why” the customer is critical to the organization’s success — often over and over again. Here are some ways to get started.
- Add goals and metrics to your journey map to show how CX initiatives result in concrete outcomes.
- Identify and engage teams that touch the journey you are mapping, and make sure to include customer interviews and data in your analysis.
- Partner with Finance teams who may use process mapping to identify inefficiencies to add a customer lens to improvements.
- Frequently share insights and results outside of your team to help employees identify with the customer and have a voice in the customer experience.
Discuss perception gaps. Train customer facing teams on the moments of truth and pain points that you’ve discovered. Make sure that your map includes accountability and metrics so that you can show results, both as part of your stakeholder management and to drive further improvements.
Think of journey mapping as an ongoing improvement program vs. a one-off project. It helps to have a high-level executive sponsor and an ongoing program owner accountable for change. Plan improvements, and use customer insights from your interviews to drive strategy. As your business changes and new products are introduced, re-test hypotheses and review processes.
Fixing the underlying operations that deliver the experience is where most customer experience efforts fail. The value journey mapping brings is helping organizations change by thinking and acting in a more customer-focused way.
Sometimes just doing it is the best way to learn. Check out our hands-on tutorial on how to create customer journey maps.
How to Measure Customer Journey Mapping Efforts
Maps are a means to an end in getting to where you want to be. No map is 100% accurate, but it can help teams make more informed and data-driven decisions about where experiences can be improved. The value of journey mapping is in the actions teams take once the map has been created.
A Nielsen Norman Group study found that more than 80% of user experience designers don’t use metrics in their journey maps, making it difficult to then prove the value of UX improvements via data analytics.
Jennifer Clinehens of UXMagazine suggests breaking down measurement into three parts: the customer journey as a whole, the phases of the customer journey, and an individual touchpoint within the journey. Each element can then be measured with context appropriate metrics.
Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Customer Effort Score (CES) are three metrics to look at how effective the entire customer journey is. Clinehens assesses the pros and cons of each. Many teams and touchpoints impact NPS or CSAT, so consider more than just this metric to measure your efforts.
The phases of Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, Retention, and Advocacy each have business metrics associated with them. Are more customers that started the purchase process completing a purchase after journey map improvements? Are web or mobile stats reflecting behavioral change on the areas of the journey the team has optimized?
Does each touchpoint reduce friction or make the specific action more positive for the customer? Measurement may include decreasing wait or task time and generating positive feedback from surveys or stakeholder interviews.
In short, customer experience metrics are just one part of a broader system of action, pointing the way towards the steps you’ll take to improve the way customers interact with your business.
Customer journey maps can be elaborate or simple, as long as they help visualize the customer experience. Each customer journey map example below shows a different layout and approach.
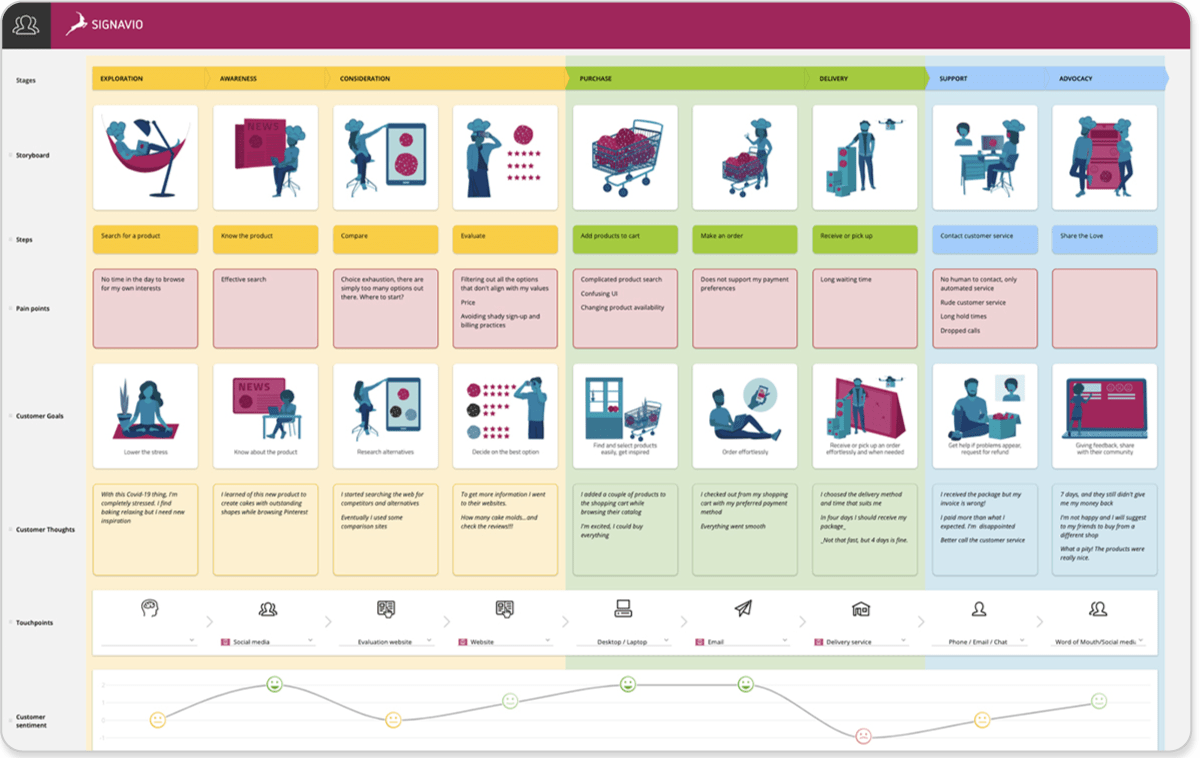
The image above shows a sample product search journey using Signavio Customer Journey Modeler . The example incorporates stages (representing customer stages or stages for other journey types), a storyboard, pain point, goals, customer verbatims, sentiment and touch points.
- The Smithsonian Institute
The Smithsonian has some of the most-visited museums in the world, and has mapped out its visitors’ journey across multiple channels and touch points of engagement.
The image below shows a healthcare insurance purchase journey map from, which incorporates a persona, phases, goals and touch points.
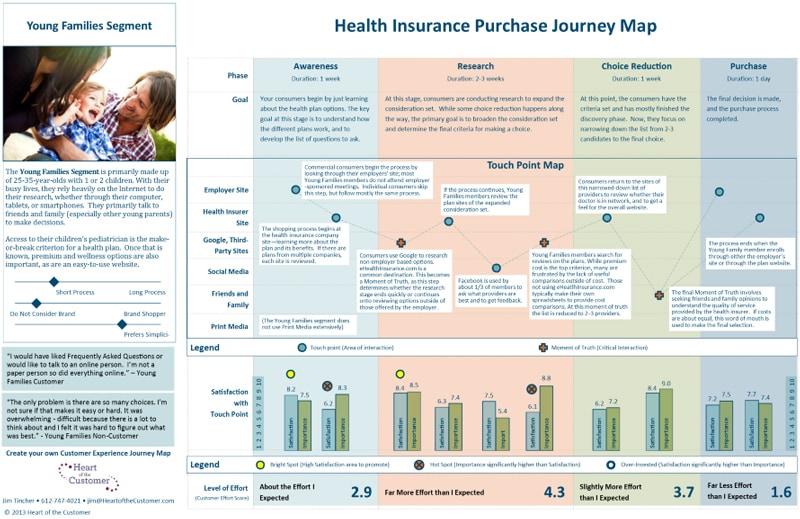
Resources for Customer Journey Mapping
Signavio has a number of blog posts and webcasts that offer a deeper dive into journey mapping.
- For a comprehensive overview of everything you need to know about customer journey mapping in 2021, we've prepared Your Ultimate Guide to Customer Journey Mapping .
- Designing Customer Journey Maps offers three tips to keep you on track with mapping efforts.
- The 7 Steps to Start Customer Journey Mapping is a handy visual guide to beginning to think about CJM in your business.
- Customer Journey Maps as a Strategic Imperative considers the broader competitive advantages of embracing journey mapping.
- An overview of all the customer journey map elements available in SAP Signavio Process Manager can be found in our customer journey maps user guide .
- “Get a Better View of Your Customer’s Journey”
- “How Telstra’s Transformation Journey Enhances its Customer Experience Offering (APAC)”
- “Introducing Next Generation CJM by Signavio (EMEA)”
Still want more customer journey mapping resources?
Here are some additional resources related to journey mapping and customer experience.
- CustomerThink: online community for customer-centered business management practices.
- Jakob Nielsen and Don Norman : pioneers of UX and founders of the Nielsen Norman Group.
- UX Magazine : online news magazine focused on experience design.
- Service Design Network : non-profit institution dedicated to expertise in service design.
- The Customer Experience Professionals Association (CXPA) offers Customer Experience Professional (CCXP) certification.
- Global user experience research and consulting firm, Nielsen Norman Group , offer UX certification, seminars and events.
First, make sure you check out our Ultimate Guide to Customer Journey Mapping .
Then, request a demo of how customer journey mapping can support your business’s operational excellence or business transformation initiative.
Or, if you're ready to get started with customer journey modeling today, register for a free 30-day trial of SAP Signavio Process Manager.
Related Articles
April 24th 2020
How to Adapt Critical Business Functions in a Crisis
January 15th 2020
Why Positive Customer Experience is Vital to Business Success
June 20th 2019
Natural balance: How sustainable process management can support a strong corporate culture
June 12th 2019
5 Signs Your Processes May Damage Customer Satisfaction
May 3rd 2019
Excellence Equals Everyone Engaged!
March 22nd 2019
Bringing customer excellence to life at #BTOES19
March 19th 2019
Customer Excellence set to become the new business imperative
February 26th 2019
Journey Modeling
February 12th 2019
It’s Not Over: The Disconnect Between OpEx and CX
November 27th 2018
3 Easy Mistakes to Avoid When Designing Customer Journey Maps
November 6th 2018
Top 5 Challenges for Telco Companies: How BPM Can Help
October 25th 2018
En Route to Success: Customer Journeys as a Strategic Imperative
October 15th 2018
Record-Breaking Signavio Wins Another "Aragon Research Hot Vendor™" Award in Customer Journey Mapping!
October 10th 2018
BPM Solutions: The Evolution of Business Process Management
September 6th 2018
The Wild Card: How Companies Punish Consumer Loyalty
September 4th 2018
Brand Awareness and (In)Fidelity: The Battle for Consumer Loyalty
July 24th 2018
Moments of Magic: Upgrade Customer Experience with CJM
May 31st 2018
Digital Transformation | What’s happening in the traditional retail sector today?
April 26th 2018
Video: 2018 is the year of BPM facts and feelings
February 26th 2018
Tomorrow’s World: Revamp the Status Quo
February 23rd 2018
Customer Centric: Revolution not Evolution
February 12th 2018
Design Thinking: Unleash Your Innovation
February 8th 2018
Hands on customer journey maps modeling
February 5th 2018
From Best Practice to Next Practice
October 17th 2017
What is a Customer Journey Map and Why Do You Need One?
November 11th 2016
Realizing Great CX: Design Thinking and BPM
- Get A Shortlist
- Industry solutions
The rise of the customer journey map
Home → Articles → The rise of the customer journey map
Gartner analyst Olive Huang explores how businesses can use customer journey mapping to better understand the customer and enrich their experience…
By understanding the behaviours, preferences, media consumption habits, technology adoption patterns and detailed day-in-the-life routines of customers, organisations can design a journey map that becomes the backbone of their customer experience strategy. A wide range of styles and tools are used in building journey maps.
In the past, organisations used customer journey maps to describe how they wanted the ideal customer journey to be and the emotions they wanted customers to feel on that journey. But they made limited use of data from sources like customer surveys, focus groups and user groups to understand the journeys that customers actually took. The customer journey maps were often created in workshops and roundtable sessions with flip charts, whiteboards and post-it notes – a very manual approach.
Tools that can help In the last few years, customer journey modelling and visualisation tools have started to become popular, often used as part of a consulting service from boutique digital agencies.
Only recently have a number of technology vendors started to invest in this space and release software with data gathering, connecting, visualising and acting capabilities to operationalise the customer journey, covering multiple channels and touchpoints.
Today, all three approaches – manual customer journey mapping, customer journey modelling and visualisation tools, and customer journey operationalisation – co-exist in the market. Some large organisations are using all three of them in combination.
Large organisations often begin their first foray into customer journey mapping by engaging digital agencies in a customer experience discovery and design exercise. At this stage, digital agencies are delivering customer journey mapping using a pencil-and-post-it manual approach, but also sometimes via customer journey modelling and visualisation tools.
After the first project, many organisations will start building these journey mapping skills and toolsets in-house using their own resources so that they can be reused on other customer experience projects.
A critical skill that needs to be developed is building customer personas to better understand the variety of experiences that different customers might encounter. It is an outside-in design approach that requires putting yourself in the shoes of a potential customer to understand what his or her experience is when engaging, or not engaging, with organisations.
Only a small number of organisations get to the third step of using technology to automate – and map, track and influence via real-time data – the customer journey.
Technology adoption will increase Gartner foresees that the maturity level of organisations’ use of customer journey mapping technologies will increase over time. Once they have gone through the initial modelling and design process manually or by using a visualisation tool, the next natural step is to operationalise customer journeys.
In these organisations, customer journey mapping will no longer be limited to a design and discovery exercise, followed by a reporting exercise. It will result in the implementation of an operational technology that delivers a customer experience that is planned and designed, then monitors and triggers responses by the organisation.
Organisations that build customer journey analytics and journey mapping capabilities in-house require a combination of data analytics skills and user experience design skills. These skills exist today in many organisations but in different departments – it’s just a matter of getting them to work together. These resources may be in a central customer experience management team, or in marketing, customer service, operations, sales or the business process competency centre.
The challenge Gartner sees is not obtaining these skills, but the lack of an intuitive and discovery-thinking culture that will make use of the skills.
How to get started To help an organisation build these capabilities, IT leaders should:
- Seek out anyone in the organisation who has internal customer journey mapping skills, then investigate which third parties are doing customer journey mapping on behalf of the organisation.
- Discuss with heads of marketing, customer service, operations, sales and business process management to decide which department(s) these resources should belong to.
- Start building expertise in customer journey mapping in the IT organisation to match the skills in the enterprise as a whole. Be aware that you may not be able to train these resources from within; instead, you will need to hire at least some from external markets.
- Research the appropriate technologies that can be used to operationalise customer journeys and encourage the use of these technologies by those doing customer journey mapping.
ABOUT OLIVE HUANG//
Olive Huang is a research director at Gartner. She is part of the CRM software research team and focuses on customer service and support, contact centres, CRM vendors and service providers, as well as CRM strategy and best practices in Asia Pacific. Olive will be presenting at the Gartner Business Transformation and Process Management Summit in Sydney, 21-22 June 2016.
About Software Shortlist
Software Shortlist is a trusted third party that provides free information and services to software buyers to help them find relevant vendors.
- Get A Shortlist : software matching service designed to connect you with the best vendors positioned to deliver your requirements
- ERP Shortlist : find an integrated system to manage your entire business. See case studies, whitepapers, articles & buyers guide.
- CRM Shortlist : improve customer and supplier engagement with the right CRM system. Free case studies, whitepapers, and articles.
- Email Newsletter : subscribe to our free e-newsletter for useful case studies, whitepapers and articles
Software Shortlist Pty Ltd (ACN: 129 547 888) is a division of iStart Limited .
Subscribe to our free e-newsletter
About istart.
iStart is Australia & New Zealand’s ICT Research Hub informing and educating business and IT decision makers on technology investment. Browse the latest research, thought leadership and tech success stories online , and subscribe to the weekly e-newsletter . If you are considering a technology investment, then iStart is where to begin.
ERP articles
- How to conduct a cost-benefit analysis for an ERP system
- Make-to-order vs make-to-stock: implications for your ERP system
- Revenue-generation now key CIO skill
- Composing a modern ERP strategy
- Entrepreneur – and Netsuite – confidence high
CRM articles
- Digitising your comms
- Is CRM the largest software market in the world?
- New CRM fresh on global market
- Dynamics takes to the field
- Equip your salespeople for on-the-road success

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Focus On The Right Solutions - Improve Your Customer Experience - Grow Your Business. TheyDo is Your All-in-One Platform for Customer-Centric Collaboration. Get Started.
Compare Top Sales Mapping App Software by Rating, Features and Cost Side-by-Side. See Why Decision Makers Love This Free Sales Mapping App Report
A customer journey map is a tool that helps marketers understand the series of connected customer experiences that customers desire and need — whether that be completing a desired task or traversing the end-to-end journey from prospect to customer to loyal advocate. It helps boost customer understanding and improve customer-facing decisions ...
Discovery: Learn new things about the customer based on data and customer research. Ideation: Identify customer pain points and generate solutions. Activation: Include stakeholders in the project prioritization and selection. "Making an impact will require more than just a map," says Nordlund. "It's going to require a plan and it's ...
Prepare for customer journey mapping. CX leaders lay the groundwork to create useful customer journey maps with these actions: Get senior support. Customer journeys touch many functions in the organization. A vocal senior leader can help generate support from other functions and motivate them to participate, which eases access to people and data.
Customer journey mapping requires data and support from others in your organization who are not necessarily within your sphere of influence or control. It will make it easier for you to get access to data, resources and other assistance you need from peers not directly accountable for the Source: Gartner journey map project. Figure 2.
Customer journey mapping has become a critical way to understand customers from their perspective, but many firms struggle with how best to start. Financial services leaders can use this research to understand the critical preceding steps in the journey mapping process. Included in Full Research
Gartner defines customer journey mapping as a collaborative process of gathering qualitative and quantitative data to understand customers' desired journeys and identify gaps between their ...
Gartner defines customer journey mapping as a collaborative process of gathering qualitative and quantitative data to understand customers' desired journeys and identify gaps between their expectations and their perceptions of the experience delivered by a brand at steps along the journey. The main goal of journey mapping is to determine the ...
Simply choose the touchpoints which accurately reflect a customer's journey with your brand. After you define your touchpoints, you can then start arranging them on your customer journey map. 4. Map the current state. Create what you believe is your as-is state of the customer journey, the current customer experience.
Move to the Top Levels of the Gartner CX Pyramid Using a Customer Journey Map. I think it's important to talk about the use of journey mapping to move to the top of the pyramid - the Proactive and Evolution levels. Getting to these levels requires significantly more investment in both customer insights and design.
A customer journey map can help businesses get this kind of information and provide guidance for future consumer interactions. ... B2B customer journey map example. Gartner's business-to-business (B2B) customer journey map highlights how not all maps need to follow the same format. The flowchart-like design emphasizes the natural thought and ...
While 77 percent of 244 marketing leaders Gartner surveyed said they have a journey map, 30 percent struggle to use them effectively in support of their customer experience efforts, Mennella says.
A customer journey map helps you gain a better understanding of your customers so you can spot and avoid potential concerns, make better business decisions and improve customer retention. The map ...
But, involving customers in journey mapping isn't enough - moving to Commitment means solving customer needs at specific points in the journey. To do this, map a specific sub-journey and get targeted information needed to solve customer problems. Our survey on CX leaders' experience with journey mapping showed that 60% mapped the end-to ...
Our survey on CX leaders' experience with journey mapping showed that 60% mapped the end-to-end journey. For most companies, this will be too general to solve specific problems. To fix these issues, a team needs to go deeper and understand specific customer needs at precise points along the journey, whether that's first-time usage, asking ...
Summary. Deploying dynamic customer engagement is a multistep journey that involves investment in people, process and technology to deliver personalized, proactive experiences at scale. Customer service and support leaders can use this strategic roadmap to effectively implement DCE.
Breaking down the customer journey, phase by phase, aligning each step with a goal, and restructuring your touchpoints accordingly are essential steps for maximizing customer success. Here are a few more benefits to gain from customer journey mapping. 1. You can refocus your company with an inbound perspective.
What customers feel are the most important moments in their journey. Once you've confirmed that your customer journey map is accurate and/or incorporated any necessary information from the validation process, you're ready for the next step. 2. Identify pain points within the customer journey. The most insightful journey mapping process doesn't ...
Mapping and connecting siloed data across the customer journey; List of Representative Vendors including Genesys; Understanding the market direction and key advancements . Gartner, Market Guide for Customer Journey Analytics & Orchestration, Christopher Sladdin, Daniel O'Sullivan, 27 February 2024.
After some research, Gartner found that B2B buyers move back and forth between key buying actions. Here's what it looks like: Map of the B2B buying journey. To illustrate, imagine a company identifies a need to improve its customer support process. ... Best customer journey mapping and analysis tools to increase customer retention.
The concept of customer journey mapping has gained popularity in recent years, as businesses have shifted their focus from product-centric approaches to customer-centric strategies. According to a survey by Gartner, 89% of companies now expect to compete primarily on the basis of customer experience (CX) by 2022. As a result, businesses are investing more in understanding their customers ...
Gartner also calls this "total experience," i.e. the combination of, as well as interplay between, customer experience, user experience and employee experience to impact and transform business outcomes. ... Customer journey mapping is a visual tool to facilitate collaboration in change management initiatives by creating a shared vision ...
Customer journey mapping is a common approach used today to discover the gaps between customers' expectations and their perceptions of the actual experience. Gartner believes that 60 percent of large organisations will develop in-house customer journey mapping capabilities by 2018.