
Written by Vasilena Markova • September 27, 2023 • 12:58 pm • Internet

Round-Trip Time (RTT): What It Is and Why It Matters
Round-Trip Time (RTT) is a fundamental metric in the context of network performance, measuring the time it takes for data packets to complete a round trip from source to destination and back. Often expressed in milliseconds (ms), RTT serves as a critical indicator for evaluating the efficiency and reliability of network connections. In today’s article, we dive into the concept of RTT, exploring how it works, why it matters in our digital lives, the factors that influence it, and strategies to enhance it. Whether you’re a casual internet user seeking a smoother online experience or a network administrator aiming to optimize your digital infrastructure, understanding this metric is critical in today’s interconnected world.
Table of Contents
What is Round-Trip Time (RTT)?
Round-Trip Time is a network performance metric representing the time it takes for a data packet to travel from the source to the destination and back to the source. It is often measured in milliseconds (ms) and is a crucial parameter for determining the quality and efficiency of network connections.
To understand the concept of RTT, imagine sending a letter to a friend through the postal service. The time it takes for the letter to reach your friend and for your friend to send a reply back to you forms the Round-Trip Time for your communication. Similarly, in computer networks, data packets are like those letters, and RTT represents the time it takes for them to complete a round trip.
How Does it Work?
The concept of RTT can be best understood by considering the journey of data packets across a network. When you request information from a web server, for example, your device sends out a data packet holding your request. This packet travels through various network devices in between, such as routers and switches, before reaching the destination server. Once the server processes your request and prepares a response, it sends a data packet back to your device.
Round-Trip Time is determined by the time it takes for this data packet to travel from your device to the server (the outbound trip) and then back from the server to your device (the inbound trip). The total RTT is the sum of these two one-way trips.
Let’s break down the journey of a data packet into several steps so you can better understand the RTT:
- Sending the Packet: You initiate an action on your device that requires data transmission. For example, this could be sending an email, loading a webpage, or making a video call.
- Packet Travel: The data packet travels from your device to a server, typically passing through multiple network nodes and routers along the way. These middle points play a significant role in determining the RTT.
- Processing Time: The server receives the packet, processes the request, and sends a response back to your device. This processing time at both ends also contributes to the Round-Trip Time.
- Return Journey: The response packet makes its way back to your device through the same network infrastructure, facing potential delays on the route.
- Calculation: It is calculated by adding up the time taken for the packet to travel from your device to the server (the outbound trip) and the time it takes for the response to return (the inbound trip).
Why does it matter?
At first look, Round-Trip Time (RTT) might seem like technical terminology, but its importance extends to various aspects of our digital lives. It matters for many reasons, which include the following:
- User Experience
For everyday internet users, RTT influences the sensed speed and responsiveness of online activities. Low Round-Trip Time values lead to a seamless experience, while high RTT can result in frustrating delays and lag during tasks like video streaming, online gaming, or live chats.
- Network Efficiency
Network administrators and service providers closely monitor RTT to assess network performance and troubleshoot issues. By identifying bottlenecks and areas with high RTT, they can optimize their infrastructure for better efficiency.
- Real-Time Applications
Applications that rely on real-time data transmission, such as VoIP calls, video conferencing, and online gaming, are highly sensitive to RTT. Low RTT is crucial for smooth, interruption-free interactions.
In cybersecurity, Round-Trip Time plays a role in detecting network anomalies and potential threats. Unusually high RTT values can be a sign of malicious activity or network congestion.
Factors Affecting Round-Trip Time (RTT)
Several factors can influence the metric, both positively and negatively. Therefore, understanding these factors is crucial, and it could be very beneficial for optimizing network performance:
- Distance: The physical distance between the source and destination plays a significant role. Longer distances result in higher RTT due to the time it takes for data to travel the network.
- Network Congestion: When a network experiences high volumes of traffic or congestion, data packets may be delayed as they wait for their turn to be processed. As a result, it can lead to packet delays and increased RTT.
- Routing: The path a packet takes through the network can significantly affect RTT. Efficient routing algorithms can reduce the time, while not-so-optimal routing choices can increase it.
- Packet Loss: Packet loss during transmission can occur due to various reasons, such as network errors or congestion. When lost, packets need to be retransmitted, which can seriously affect the Round-Trip Time.
- Transmission Medium: It is a critical factor influencing RTT, and its characteristics can vary widely based on the specific medium being used. Fiber optic cables generally offer low RTT due to the speed of light in the medium and low signal loss. In contrast, wireless mediums can introduce variable delays depending on environmental factors and network conditions.
How to improve it?
Improving Round-Trip Time (RTT) is a critical goal for network administrators and service providers looking to enhance user experiences and optimize their digital operations. While some factors affecting it are beyond our control, there are strategies and practices to optimize Round-Trip Time for a smoother online experience:
- Optimize Routing: Network administrators can optimize routing to reduce the number of hops data packets take to reach their destination. This can be achieved through efficient routing protocols and load balancing .
- Optimize Network Infrastructure: For businesses, investing in efficient network infrastructure, including high-performance routers and switches, can reduce internal network delays and improve RTT.
- Upgrade Hardware and Software: Keeping networking equipment and software up-to-date ensures that you benefit from the latest technologies and optimizations that can decrease RTT.
- Implement Caching: Caching frequently requested data closer to end-users can dramatically reduce the need for data to travel long distances. The result really helps with lowering RTT.
- Monitor and Troubleshoot: Regularly monitor your network for signs of congestion or packet loss. If issues arise, take steps to troubleshoot and resolve them promptly.
Discover ClouDNS Monitoring service!
Round-Trip Time (RTT) is the silent force that shapes our online experiences. From the seamless loading of web pages to the quality of our video calls, RTT plays a pivotal role in ensuring that digital interactions happen at the speed of thought. As we continue to rely on the Internet for work, entertainment, and communication, understanding and optimizing this metric will be crucial for both end-users and network administrators. By reducing it through strategies, we can have a faster, more responsive digital world where our online activities are limited only by our imagination, not by lag.
Hello! My name is Vasilena Markova. I am a Marketing Specialist at ClouDNS. I have a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Economics and am studying for my Master’s Degree in Cybersecurity Management. As a digital marketing enthusiast, I enjoy writing and expressing my interests. I am passionate about sharing knowledge, tips, and tricks to help others build a secure online presence. My absolute favorite thing to do is to travel and explore different cultures!

Related Posts

Ping Traffic Monitoring: Ensuring Network Health and Efficiency
March 28, 2024 • Monitoring
In an era where digital connectivity is the lifeline of businesses and individuals alike, maintaining optimal network performance is more ...
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Recent Posts
- DNS vs DHCP. Are they connected?
- What is Traffic Director?
- Telnet Explained: What Is It and How It Works?
- Decoding Error 500: Understanding, Preventing, and Resolving the Internal Server Error
- What is a Smurf DDoS attack?
- Cloud Computing
- DNS Records
- Domain names
- Load balancing
- SSL Certificates
- Web forwarding
- DNS Services
- Managed DNS
- Dynamic DNS
- Secondary DNS
- Reverse DNS
- DNS Failover
- Anycast DNS
- Email Forwarding
- Enterprise DNS
- Domain Names
- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
What is RTT(Round Trip Time)?
- What is Real-Time Linux?
- What is RTS(Real Time Streaming)?
- What is Time-To-Live (TTL)?
- Program to calculate the Round Trip Time (RTT)
- What is TCP Fast Open?
- Difference between Round trip time (RTT) and Time to live (TTL)
- Real Time Transport Protocol (RTP)
- How to subtract time in R ?
- Python time.tzset() Function
- TCP Tahoe and TCP Reno
- Ruby | Time to_time function
- Ruby | Time round function
- What is 15:00 Military Time?
- Time tuple in Python
- What Time will it be in 24 Hours From Now?
- Dart - Date and Time
- Ruby | Time utc function
- time.Time.Round() Function in Golang with Examples
- Ruby | Time to_r function
- What is OSI Model? - Layers of OSI Model
- TCP/IP Model
- Basics of Computer Networking
- Types of Network Topology
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)
- RSA Algorithm in Cryptography
- Caesar Cipher in Cryptography
- Differences between TCP and UDP
- TCP Server-Client implementation in C
- Types of Transmission Media
RTT (Round Trip Time) also called round-trip delay is a crucial tool in determining the health of a network. It is the time between a request for data and the display of that data. It is the duration measured in milliseconds.
RTT can be analyzed and determined by pinging a certain address. It refers to the time taken by a network request to reach a destination and to revert back to the original source. In this scenario, the source is the computer and the destination is a system that captures the arriving signal and reverts it back.

RTT(Round Trip Time) Measurement
What Are Common Factors that Affect RTT?
There are certain factors that can bring huge changes in the value of RTT. These are enlisted below:
- Distance: It is the length in which a signal travels for a request to reach the server and for a response to reach the browser,
- Transmission medium: The medium which is used to route a signal, which helps in faster transfer of request is transmitted.
- Network hops: It is the time that servers take to process a signal, on increasing the number of hops, RTT will also increase.
- Traffic levels: Round Trip Time generally increases when a network is having huge traffic which results in that, for low traffic RTT will also be less.
- Server response time: It is the time taken by a server to respond to a request which basically depends on the capacity of handling requests and also sometimes on the nature of the request.
Applications of RTT
Round Trip Time refers to a wide variety of transmissions such as wireless Internet transmissions and satellite transmissions. In Internet transmissions, RTT may be identified by using the ping command. In satellite transmissions, RTT can be calculated by making use of the Jacobson/Karels algorithm.
Advantages of RTT
Calculation of RTT is advantageous because:
- It allows users and operators to identify how long a signal will take to complete the transmission.
- It also determines how fast a network can work and the reliability of the network.
Example: Let us assume there are two users, one of which wants to contact the other one. One of them is located in California while the other one is situated in Germany. When the one in California makes the request, the network traffic is transferred across many routers before reaching the server located in Germany. Once the request reverts back to California, a rough estimation of the time taken for this transmission could be made. This time taken by the transmitted request is referred to as RTT. The Round Trip Time is a mere estimate. The path between the two locations can change as the passage and network congestion can come into play, affecting the total period of transmission.
How Does Round-Trip Time Work?
Consider a topology where an appliance named “Exinda” is located between the client and the server. The diagram shown below depicts how the concept of RTT works:

RTT Calculation
For the calculation of Average RTT, RTTS for server and client needs to be calculated separately. The performed calculations are shown below:
Server RTT: RTT1 = T2 – T1 RTT2 = T5 – T4
Client RTT: RTT3 = T3 – T2 RTT4 = T7 – T6
Average RTT: Avg Server RTT = (RTTs1 + RTTs2) / 2 Avg Client RTT = (RTTc1 + RTTc2) / 2 Avg Total RTT = Avg Server RTT + Avg Client RTT
You can refer to the Program to calculate RTT for more details.
Measures To Reduce RTT
A significant reduction in RTT can be made using Content Delivery Network (CDN) . A CDN refers to a network of various servers, each acquiring a copy of the content on a particular website. It addresses the factors affecting RTT in the enlisted ways:
- Points of Presence (PoP)
- Web caching
- Load distribution
- Scalability
- Tier 1 access
CDN has been largely successful in reducing the value of RTT and due to this, a decrease in RTT by 50% is achievable.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of round trip noun from the Oxford Advanced American Dictionary
Questions about grammar and vocabulary?
Find the answers with Practical English Usage online, your indispensable guide to problems in English.
Nearby words
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
Round Trip Time (RTT)
Round Trip Time (RTT) is the length time it takes for a data packet to be sent to a destination plus the time it takes for an acknowledgment of that packet to be received back at the origin. The RTT between a network and server can be determined by using the ping command.
This will output something like:
In the above example, the average round trip time is shown on the final line as 26.8ms.
- Time to First Byte (TTFB)
Home > Learning Center > Round Trip Time (RTT)
Article's content
Round trip time (rtt), what is round trip time.
Round-trip time (RTT) is the duration, measured in milliseconds, from when a browser sends a request to when it receives a response from a server. It’s a key performance metric for web applications and one of the main factors, along with Time to First Byte (TTFB), when measuring page load time and network latency .
Using a Ping to Measure Round Trip Time
RTT is typically measured using a ping — a command-line tool that bounces a request off a server and calculates the time taken to reach a user device. Actual RTT may be higher than that measured by the ping due to server throttling and network congestion.
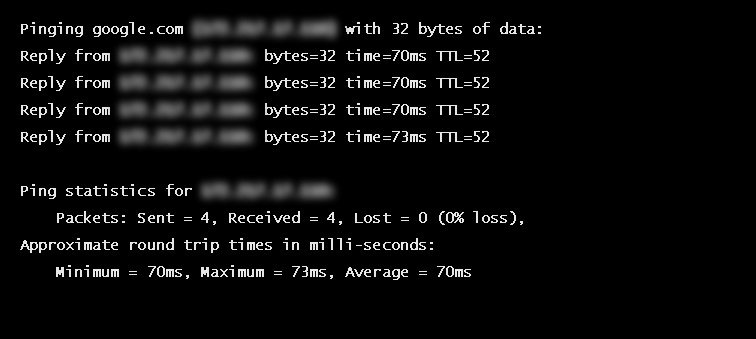
Example of a ping to google.com
Factors Influencing RTT
Actual round trip time can be influenced by:
- Distance – The length a signal has to travel correlates with the time taken for a request to reach a server and a response to reach a browser.
- Transmission medium – The medium used to route a signal (e.g., copper wire, fiber optic cables) can impact how quickly a request is received by a server and routed back to a user.
- Number of network hops – Intermediate routers or servers take time to process a signal, increasing RTT. The more hops a signal has to travel through, the higher the RTT.
- Traffic levels – RTT typically increases when a network is congested with high levels of traffic. Conversely, low traffic times can result in decreased RTT.
- Server response time – The time taken for a target server to respond to a request depends on its processing capacity, the number of requests being handled and the nature of the request (i.e., how much server-side work is required). A longer server response time increases RTT.
See how Imperva CDN can help you with website performance.
Reducing RTT Using a CDN
A CDN is a network of strategically placed servers, each holding a copy of a website’s content. It’s able to address the factors influencing RTT in the following ways:
- Points of Presence (PoPs) – A CDN maintains a network of geographically dispersed PoPs—data centers, each containing cached copies of site content, which are responsible for communicating with site visitors in their vicinity. They reduce the distance a signal has to travel and the number of network hops needed to reach a server.
- Web caching – A CDN caches HTML, media, and even dynamically generated content on a PoP in a user’s geographical vicinity. In many cases, a user’s request can be addressed by a local PoP and does not need to travel to an origin server, thereby reducing RTT.
- Load distribution – During high traffic times, CDNs route requests through backup servers with lower network congestion, speeding up server response time and reducing RTT.
- Scalability – A CDN service operates in the cloud, enabling high scalability and the ability to process a near limitless number of user requests. This eliminates the possibility of server side bottlenecks.
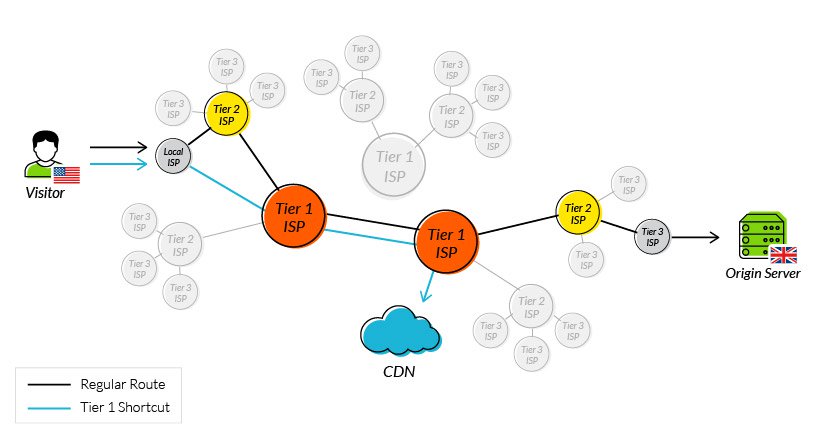
Using tier 1 access to reduce network hops
One of the original issues CDNs were designed to solve was how to reduce round trip time. By addressing the points outlined above, they have been largely successful, and it’s now reasonable to expect a decrease in your RTT of 50% or more after onboarding a CDN service.
Latest Blogs

Grainne McKeever
Feb 26, 2024 3 min read

Erez Hasson
Jan 18, 2024 3 min read

Luke Richardson
Dec 27, 2023 6 min read

Dec 21, 2023 2 min read

Dec 13, 2023 5 min read

Dec 7, 2023 6 min read

- Imperva Threat Research

, Gabi Stapel
Nov 8, 2023 13 min read

Nov 7, 2023 1 min read
Latest Articles
- Network Management
169.8k Views
103.1k Views
100.4k Views
98.4k Views
58.7k Views
54.6k Views
2024 Bad Bot Report
Bad bots now represent almost one-third of all internet traffic

The State of API Security in 2024
Learn about the current API threat landscape and the key security insights for 2024
Protect Against Business Logic Abuse
Identify key capabilities to prevent attacks targeting your business logic
The State of Security Within eCommerce in 2022
Learn how automated threats and API attacks on retailers are increasing
Prevoty is now part of the Imperva Runtime Protection
Protection against zero-day attacks
No tuning, highly-accurate out-of-the-box
Effective against OWASP top 10 vulnerabilities
An Imperva security specialist will contact you shortly.
Top 3 US Retailer
- Ponuka slovníkov
- Prihlásenie
Frázové slovesá
Slovné spojenia.
Ďalšie užitočné portály
- www.dict.com - najväčší slovníkový portál pre 34 jazykov vo všetkých kombináciách
- www.preklady-korektury.sk - kalkulátor na preklady a lokalizácie
- www.lingea.sk - predaj elektronickej a knižnej jazykovej produkcie
Rozšírené vyhľadávanie

Latency vs Round Trip Time: Understanding the Differences

As someone who works in the technology industry, I often come across the terms “latency” and “round trip time” (RTT). While both terms are related to network performance, they are not interchangeable.
Understanding latency and RTT is crucial for troubleshooting network issues and improving network performance. In this article, I will explain latency and RTT and how they differ.
Table of Contents
What is Latency?
Latency refers to the time it takes for a packet of data to travel from its source to its destination . It’s the measure of how long it takes for a packet to travel from one point to another. Latency is often measured in milliseconds (ms), and the lower the latency, the better the network performance.
Many factors can affect latency, including the distance between the source and destination, the number of hops the packet must take, and the network’s speed. For example, if you’re sending a packet from New York to Los Angeles, it will take longer for the packet to travel that distance than if you’re sending it from New York to Boston.
Similarly, if the packet must pass through multiple routers or switches, it will take longer to reach its destination than if it only had to pass through one.
What is Round Trip Time?
Round trip time, or RTT, measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from its source to its destination and then back again . It’s time it takes for a packet to make a round trip. RTT is also measured in milliseconds (ms), and like latency, the lower the RTT, the better the network performance.
RTT is affected by the same factors that affect latency, including distance, number of hops, and network speed. However, RTT also considers the time it takes for the destination to process the packet and send a response.
For example, if you’re sending a packet to a server that’s busy processing other requests, it will take longer for the server to respond, and thus, the RTT will be higher.
Differences between Latency and RTT
The main difference between latency and RTT is that latency only measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from its source to its destination, while RTT measures the time it takes for a packet to make a round trip.
Latency measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from one point to another. It’s the measure of one-way delay. RTT measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from its source to its destination and back again. It’s the measure of two-way delay.
Another important difference is that while latency only measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from one point to another, RTT considers the time it takes for the destination to process the packet and send a response.
For example, if you’re trying to access a website, the latency will measure the time it takes for the packet to travel from your computer to the server hosting it. The RTT will measure the time it takes for the packet to travel from your computer to the server hosting the website and back to the webpage.
Latency and RTT are network performance measures, but they measure differently. Latency measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from one point to another, while RTT measures the time it takes for a packet to make a round trip.
Understanding the difference between these two terms is crucial for troubleshooting network issues and improving network performance.
How to Measure Latency and RTT?
Several tools and methods can be used to measure latency and RTT. One of the most common tools is the ping command. The ping command sends a packet to a specified destination and measures the time it takes for the packet to return. The ping command can be used to measure both latency and RTT.
Another tool that can be used to measure latency and RTT is traceroute. Traceroute works by sending packets to a specified destination and measuring the time it takes for each packet to reach each hop along the way.
It also provides information about each hop, such as IP address and hostname. This tool is useful for identifying the source of network issues, as it can show where packets are getting delayed.
There are also specialized tools and services, such as Speedtest and Cloudping, that can be used to measure network performance. These tools typically provide more detailed information about network performance, such as upload and download speeds, and can be used to compare network performance between different locations and providers.
What are Some Ways to Improve Latency and RTT?
There are several ways to improve latency and RTT, but it’s important to understand that not all solutions will work in all situations. The most effective solutions will depend on the specific network and the root cause of the latency or RTT issues.
One common solution is to upgrade network hardware, such as routers and switches . This can improve network speed and reduce the number of hops packets must take, thereby reducing latency and RTT.
Another solution is to optimize network configurations. This can include optimizing routing protocols and adjusting packet size. This can help to improve network efficiency and reduce the number of hops packets must take, thereby reducing latency and RTT.
Optimizing network software and applications can also help to improve network performance. This can include optimizing web servers, databases, and other applications to reduce the time it takes for the destination to process packets and send a response.
Finally, it’s also essential to consider the physical location of network devices. For example, if devices are located in a poorly ventilated area, they may overheat and become less efficient, resulting in increased latency and RTT.
By moving the devices to a cooler location or adding additional cooling, the devices will be able to run more efficiently, which can help to improve network performance.
Latency and RTT are both important network performance measures, but they measure different things. Latency measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from one point to another, while RTT measures the time it takes for a packet to make a round trip.
Understanding these two terms’ differences is crucial for troubleshooting network issues and improving network performance. Several tools and methods can be used to measure latency and RTT.
There are several ways to improve network performance, such as upgrading network hardware, optimizing network configurations, optimizing network software and applications, and considering the physical location of network devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to understand the difference between latency and rtt.
Understanding latency and RTT is crucial for troubleshooting network issues and improving network performance. Latency and RTT are network performance measures, but they measure differently.
By understanding the difference between these two terms, you can better understand where network issues are occurring and implement solutions to improve performance.
Can latency and RTT be reduced to zero?
It’s impossible to reduce latency and RTT to zero, as there will always be some delay due to the physical distance between the source and destination.
However, latency and RTT can be minimized through various methods such as upgrading network hardware, optimizing network configurations, and reducing the number of hops packets must take.
Can you give an example of a situation where latency is more important than RTT?
One example of a situation where latency is more critical than RTT is in online gaming . When playing a game online, players expect a low latency to ensure that their actions are responsive and they have the best gaming experience.
In this case, it’s more important to minimize the time it takes for a packet to travel from the player’s computer to the game server than to measure the time it takes for a packet to make a round trip.
Related Posts

Spectrum Modem Blinking Blue And White: How to Fix
Gpu artifacts: causes, solutions, and prevention.
How Is A Microprocessor Different From An Integrated Circuit

MSI vs Lenovo: A Comprehensive Comparison for Tech Enthusiasts

How Much Do Laptops Weigh? A Comprehensive Guide

Is It Bad To Sleep With AirPods In?
Tim has always been obsessed with computers his whole life. After working for 25 years in the computer and electronics field, he now enjoys writing about computers to help others. Most of his time is spent in front of his computer or other technology to continue to learn more. He likes to try new things and keep up with the latest industry trends so he can share them with others.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Subscriber Services
- For Authors
- Publications
- Archaeology
- Art & Architecture
- Bilingual dictionaries
- Classical studies
- Encyclopedias
- English Dictionaries and Thesauri
- Language reference
- Linguistics
- Media studies
- Medicine and health
- Names studies
- Performing arts
- Science and technology
- Social sciences
- Society and culture
- Overview Pages
- Subject Reference
- English Dictionaries
- Bilingual Dictionaries
Recently viewed (0)
- Save Search
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Related Content
More like this.
Show all results sharing these subjects:
- Astronomy and Cosmology
round-trip light time
Quick reference.
The elapsed time taken by a signal travelling from the Earth to a spacecraft or other celestial body, then immediately transmitted or reflected back to the original transmission point. This is about equal to twice the one-way light time, but it varies because the motions of the Earth and space objects create different travelling times each way. RTLT to the Sun is about 17 minutes, and it was about 23 hours to the Voyager 1 probe in October 2001.
From: round-trip light time in A Dictionary of Space Exploration »
Subjects: Science and technology — Astronomy and Cosmology
Related content in Oxford Reference
Reference entries.
View all related items in Oxford Reference »
Search for: 'round-trip light time' in Oxford Reference »
- Oxford University Press
PRINTED FROM OXFORD REFERENCE (www.oxfordreference.com). (c) Copyright Oxford University Press, 2023. All Rights Reserved. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a PDF of a single entry from a reference work in OR for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice ).
date: 29 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.194.105.172]
- 185.194.105.172
Character limit 500 /500

Driving Distance Calculator
Driving distances between two cities.
Travelmath helps you find driving distances based on actual directions for your road trip. You can get the distance between cities, airports, states, countries, or zip codes to figure out the best route to travel to your destination. Combine this information with the fuel cost tool to find out how much it will cost you to drive the distance, or compare the results to the straight line distance to determine whether it's better to drive or fly. You can print out pages with a travel map.
Maybe you want to see the driving time instead? Or if you're driving a long distance, you might want to check the midpoint of your trip to find a hotel.
Home · About · Terms · Privacy


Timberwolves fans deserve to celebrate a rare trip to Round 2: ‘This is one step’
Maybe you sat in front of a projector screen in your home theater, marveling at Anthony Edwards’ fourth-quarter dunk so much that you had to freeze it on the screen and gather with your buddies to take a photo to commemorate the event.
Maybe you were watching Karl-Anthony Towns deliver one of the best performances of his life to help your Minnesota Timberwolves — yes, they are YOUR Timberwolves — sweep the Phoenix Suns with a 122-116 Game 4 victory on Sunday night and had to wonder if this was all a dream because you were so used to Wolves seasons ending in April.
Advertisement
Maybe you were lucky enough to be in the Footprint Center in Phoenix, wearing a wolf on your head while you cheered for the road team or swiping away the offer of a Suns T-shirt while supporting your brother-in-law , Jordan McLaughlin .
Maybe you had to set your alarm to get up for a 3:30 a.m. tipoff in France because there was no way you were going to miss seeing your favorite team win its first playoff series in 20 years.
Maybe you cradled your newborn in your arms in Northeast Minneapolis or r eminisced at your crib in Los Angeles about how far you have come since the last time the Timberwolves have come this far.
Wherever you were, whatever you were wearing, whoever you were with, I hope you took a moment on Sunday night to soak it all in.
For 20 years, the Timberwolves have been the butt of jokes across the league, and deservedly so. Michael Beasley once showed up to a game with scratches on his face and later said that they came from a Tasmanian Devil that had gotten out of its cage at his home. Kevin Love once said he broke his hand while doing knuckle push-ups. David Kahn passed on Steph Curry … twice, Jimmy Butler detonated the organization from the inside and Gersson Rosas was fired days before training camp opened.
That is just a sliver of the dysfunction and embarrassment that Timberwolves fans have had to endure over the years. You have watched your team change general managers more often than Mario Andretti changed tires at the Indy 500. You have seen players come and go with the frequency of cast reboots on “The Real Housewives” franchise. To be honest, you’re not even sure who owns your team .
None of that mattered on Sunday night. It did not matter that Kevin Durant and Devin Booker , for the first time this series, showed some real determination to not lose a game. It did not matter that the Wolves could not hit a shot to save their lives in the first half of the game. It did not matter that Scott Foster was the crew chief.
The only thing that mattered was that this Timberwolves team is different than any that has come before it over the last 20 years. This team has a superstar exploding onto the NBA landscape , a supporting cast as tight-knit and talented as any in the 35-year history of the franchise and a coaching staff that is capable of building a game plan to turn a team that dominated the Wolves in the regular season into a frustrated, flopping mess of a group that never stood a chance.
A series that opened with the belief that the Suns would exploit Minnesota’s size ended with a quickness so overwhelming that it led to the conclusion that it wasn’t even all that impressive for the Wolves because they were the ones who had the mismatch so heavily in their favor. A team with Durant, Booker and Bradley Beal would presumably be the kind of shooting-rich, small-ball roster that could run circles around Rudy Gobert , Towns and the bigger, slower Wolves. Instead, the Suns were suffocated by them.
The Suns have flaws, no doubt. But they won 49 games during the regular season, including 10 of their last 14 to avoid the Play-In Tournament. Two of those were decisive victories over the Wolves. But the script flipped in the postseason with Minnesota exposing Phoenix as a glass-jawed opponent, one that couldn’t withstand the pressure of Edwards on the perimeter and Towns and Gobert at the rim.
You heard the questions about Edwards’ love of the game before he was drafted and then you watched him deliver his latest jaw-dropper in Game 4, putting up 40 points, nine rebounds, six assists and two blocks in 41 minutes.
MUST. SEE. TV. 🔥🔥🔥 pic.twitter.com/RfyEyTIZO5 — Minnesota Timberwolves (@Timberwolves) April 29, 2024
You have seen Towns take all manner of criticism and derision for his lack of success on the court, his battle with Butler, even for the tone of his voice in interviews. Then you watched him deliver one of the very best games of his career, hitting shots early when no one else could to keep the team afloat and finishing with 28 points, 10 rebounds and three assists to close out the Suns.
T O U G H 😤 pic.twitter.com/FN2M1oikqL — Minnesota Timberwolves (@Timberwolves) April 29, 2024
You endured last season, the rough entry of Gobert and the ridiculing from national media about what was surely a foolish decision by president of basketball operations Tim Connelly to pair Gobert and Towns in the frontcourt. When they re-signed Naz Reid , another center?!?, last summer, the jokes kept flying. Typical Timberwolves, always a step behind the rest. Now here they are, advancing to the second round to face the winner of the Denver Nuggets – Los Angeles Lakers series.
With the way the Wolves played in this Suns series, with how connected they were on defense and how versatile they were on offense, the possibilities are endless. They have an alpha wolf in Edwards who breathes life and confidence into his teammates daily. They have a generational defense anchored by Gobert, Jaden McDaniels and Nickeil Alexander-Walker that can tear a team apart. They have a true point guard in Mike Conley to smooth things out when the going gets tough.
The way this team is playing right now, and the way the rest of the Western Conference looks, this could be just the beginning for these Wolves, your Wolves.
“ It’s great, but at the same time, we’re trying to get that championship,” Gobert told reporters in Phoenix. “And this is one step of the way. It’s not gonna get easier. So we just gotta stay focused, keep putting in the work every day and keep taking care of ourselves and we’ll be alright.”
The biggest concern at this point may be the health of coach Chris Finch, who ruptured the patellar tendon in his right knee late in the fourth quarter. But the sweep gives the Wolves some time to come up with a plan. The earliest the next round would begin is on Saturday if the Nuggets defeat the Lakers in Game 5 on Monday night. If the Lakers win Game 5, Game 1 of the next series will begin on Monday.
There will be people who snicker at your elation, who look down their noses and point at the folks celebrating a trip to the second round of the playoffs. Pay no attention to the Lakers fans and Boston Celtics fans who haven’t walked through the same fire you have for the last 20 years. They are the same holier-than-thou wet blankets who laughed when Patrick Beverley jumped onto the scorer’s table after the Play-In win over the LA Clippers two years ago. Basketball is supposed to be fun, and you have had precious few moments in which to revel over the last two decades.
You don’t want to hang a banner for this one. That would be silly. But you should enjoy this. It has been a long road to get here. The last time was in 2004, Kevin Garnett’s MVP season. This team is better than that one, deeper, more talented and just as capable of coming out of the West.
Maybe you allowed yourself to think about that while wearing a Stephon Marbury jersey in Phoenix, watching nervously until the last second ticked off the clock to make sure this was happening. Maybe you played some Prince at your home in San Diego while Ian Eagle narrated the closing seconds on TNT.
Or maybe you don’t have any rooting interest in this team at all. But maybe you’ve spent the bulk of your career chronicling the stories of the people in the jerseys , the coaches leading them and so many of the the anonymous folks behind the scenes . Maybe you would bristle when you would tell people that you cover the Minnesota Timberwolves and they would furrow their brows and ask, “Why would you waste your time with them? ” Maybe you always knew this was a basketball state, and that all the people here needed was a reason to watch.
Maybe you didn’t make the trip to Phoenix for Games 3 and 4. Maybe you watched the Wolves complete the first best-of-seven sweep in Minnesota pro sports history in the quiet of your basement with the flat screen on mute (sorry Grady and Jim Pete), while your boy, who has had to deal with health issues that no one his age should have to face, sleeps soundly on the couch next to you. Maybe you understood that as fun as it would have been to be there for a historic moment, it felt even better to be right where you needed to be.
And maybe you smiled and started to think about all the stories that this team has left to tell.
(Photo of Karl-Anthony Towns: Christian Petersen / Getty Images)
Get all-access to exclusive stories.
Subscribe to The Athletic for in-depth coverage of your favorite players, teams, leagues and clubs. Try a week on us.

Jon Krawczynski is a senior writer for The Athletic covering the Minnesota Timberwolves, the NBA and the Minnesota Vikings. Jon joined The Athletic after 16 years at The Associated Press, where he covered three Olympics, three NBA Finals, two Ryder Cups and the 2009 NFC Championship Game. Follow Jon on Twitter @ JonKrawczynski

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Obousměrné zpoždění (anglicky round-trip delay time, RTD nebo round-trip time, RTT) v telekomunikacích je doba, která uplyne od vyslání signálu z jedné komunikující stanice na druhou po návrat potvrzení zpátky na první stanici.. V případě počítačových sítí je signálem obvykle paket a obousměrné zpoždění se také označuje jako doba odezvy na ping.
The round-trip time (RTT) from the client's network to the AWS Region that the WorkSpaces are in should be less than 100ms. If the RTT is between 100ms and 200ms, the user can access the WorkSpace, but performance is affected. If the RTT is between 200ms and 375ms, the performance is degraded. If the RTT exceeds 375ms, the WorkSpaces client ...
3. Round Trip Time. The RTT is the time between sending a message from a source to a destination (start) and receiving the acknowledgment from the destination at the source point (end). We can also see RTT referred to as Round Trip Delay (RTD). Sometimes, the acknowledgment is sent from the destination to the source almost immediately after the ...
Round-Trip Time is a network performance metric representing the time it takes for a data packet to travel from the source to the destination and back to the source. It is often measured in milliseconds (ms) and is a crucial parameter for determining the quality and efficiency of network connections. To understand the concept of RTT, imagine ...
Last Updated : 13 Apr, 2023. RTT (Round Trip Time) also called round-trip delay is a crucial tool in determining the health of a network. It is the time between a request for data and the display of that data. It is the duration measured in milliseconds. RTT can be analyzed and determined by pinging a certain address.
What is round-trip time? Round-trip time (RTT) is the duration in milliseconds (ms) it takes for a network request to go from a starting point to a destination and back again to the starting point. RTT is an important metric in determining the health of a connection on a local network or the larger Internet, and is commonly utilized by network ...
In telecommunications, round-trip delay (RTD) or round-trip time (RTT) is the amount of time it takes for a signal to be sent plus the amount of time it takes for acknowledgement of that signal having been received. This time delay includes propagation times for the paths between the two communication endpoints. In the context of computer networks, the signal is typically a data packet.
Flying time between cities. Travelmath provides an online flight time calculator for all types of travel routes. You can enter airports, cities, states, countries, or zip codes to find the flying time between any two points. The database uses the great circle distance and the average airspeed of a commercial airliner to figure out how long a ...
Overview, Formula & Usage. Okta. Updated: 02/14/2023 - 11:30. Time to read: 3 minutes. Round trip time, or RTT, is a measurement of the milliseconds required for a data packet to head to a destination and for that destination server to send back an acknowledgment of the packet.
Round-trip time (RTT) in networking is the interval it takes a network request to go from a source to a destination and back. It is expressed in milliseconds (ms). RTT is influenced by propagation, transmission, processing, and queueing delays. Low RTT is preferred for responsive network applications, while high RTT can cause sluggishness. RTT ...
Definition of round trip noun in Oxford Advanced American Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.
Round Trip Time (RTT) is the length time it takes for a data packet to be sent to a destination plus the time it takes for an acknowledgment of that packet to be received back at the origin. The RTT between a network and server can be determined by using the ping command. This will output something like: In the above example, the average round ...
Travelmath provides an online travel time calculator to help you figure out flight and driving times. You can compare the results to see the effect on the total duration of your trip. Usually, the flight time will be shorter, but if the destination is close, the driving time can still be reasonable. Another popular tool is the time difference ...
Round-trip time (RTT) in networking is the time it takes to get a response after you initiate a network request. When you interact with an application, like when you click a button, the application sends a request to a remote data server. Then it receives a data response and displays the information to you. RTT is the total time it takes for ...
Factors Influencing RTT. Actual round trip time can be influenced by: Distance - The length a signal has to travel correlates with the time taken for a request to reach a server and a response to reach a browser.; Transmission medium - The medium used to route a signal (e.g., copper wire, fiber optic cables) can impact how quickly a request is received by a server and routed back to a user.
trip sb ( up) podraziť komu nohu, nastaviť komu nohu ( spôsobiť, že sa niekto potkne) 3. be tripping on sth ( hovor .) mať halucinácie / haluze po čom, byť natripovaný ( po požití drogy) 4. (kniž.) cupotať. 5. ísť na výlet. ego trip. be on an ego trip zvyšovať si sebavedomie, cítiť sa stredbodom sveta.
The main difference between latency and RTT is that latency only measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from its source to its destination, while RTT measures the time it takes for a packet to make a round trip. Latency measures the time it takes for a packet to travel from one point to another. It's the measure of one-way delay.
Travelmath helps you find the driving time based on actual directions for your road trip. You can find out how long it will take to drive between any two cities, airports, states, countries, or zip codes. This can also help you plan the best route to travel to your destination. Compare the results with the flight time calculator to see how much ...
Provide up to 26 locations and Route Planner will optimize, based on your preferences, to save you time and gas money. Find the shortest routes between multiple stops and get times and distances for your work or a road trip. Easily enter stops on a map or by uploading a file. Save gas and time on your next trip.
Round trip time, or RTT, is a measurement of the milliseconds required for a data packet to head to a destination and for that destination server to send back an acknowledgement of the packet. What is RTT in networking? Think of RTT as a type of timed confirmation receipt. As soon as you send something, the timer starts.
trip up: trip sb up i přen. podrazit komu nohy. be: It was to be his first trip. Měl to být jeho první výlet. cesta: služební cesta business trip. jet: jet na výlet go on a trip. jízdenka: zpáteční jízdenka return ticket, AmE round (-trip) ticket. lístek: zpáteční lístek BrE return ticket, AmE round-trip ticket.
Search for: 'round-trip light time' in Oxford Reference ». (RTLT)The elapsed time taken by a signal travelling from the Earth to a spacecraft or other celestial body, then immediately transmitted or reflected back to the original transmission point. This is about equal to twice the one-way light time, but it varies because the motions of the ...
Driving distances between two cities. Travelmath helps you find driving distances based on actual directions for your road trip. You can get the distance between cities, airports, states, countries, or zip codes to figure out the best route to travel to your destination. Combine this information with the fuel cost tool to find out how much it ...
But winning a playoff series for the first time since 2004 is a big deal. NBA. Teams. Playoff Bracket ... who look down their noses and point at the folks celebrating a trip to the second round of ...