

June’s Journey Status
I spy a mystery! Find the hidden objects to crack every case. Love True Crime? Solve mind teasing mysteries in the glamorous 1920s! Dive into June Parker's captivating quest to unveil a scandalous, hidden family secret.
Are you having issues? Select the issue you are having below and provide feedback to June’s Journey.
problems reported in the last 24 hours
Reported issues: 81 comments.
By Margaret Galuppo 5 months ago
Purchases scenes not loading on screen. I cleared out my cache, etc. still not working
By Sharon Rizzo 6 months ago
As everyone else states, JJ keeps crashing. Sometimes it will not load. Tried ALL WOOGA suggestions and nothing works. I believe ads have created a virus. WOOGA does not care. They give out prizes and trips but won’t fix their game. I use to love playing JJ. Now it’s just a pain and not worth the effort when you cannot effectively play the game or group comps. Doesn’t give the proper credit for drinks or when hints are bought. I could go on and on.
By Susan Bales 7 months ago
Crashes during Mountain Chateau ad. Over 10 times, when ad almost finishes, game ends and back to iPad desktop. I still can’t get reward.
By JoAnne Smith 8 months ago
The last few days game is constantly crashing! Please get it fixed! I keep losing my energy for that scene when it does it! Tired of this crap!
By Sylvia Allen 9 months ago
My screen froze up yesterday 7/16. I had made a purchase and was going to make the second half of the purchase and the screen froze. Still is🙁
By Patricia Boller 9 months ago
There are offers presented, but when I click on them, I get the message "Store unavailable". How can I get these offers? When I close out the game using the X, or the Exit, does it really close out the game? Or is there something else I need to do?
By Lynn Traverso 9 months ago
Since the most recent update (two days ago) game crashes every minute and loses progress and never advances. I have to constantly restart in order to move forward. It started with the ads, but now it just crashes. Contact developer, but of course, they want me to reinstall the app and hope for the best. At this point, I am probably finished with the game, since I can't play now and will lose all my progress if I reinstall. This is the developer problem and they refuse to even try to correct it.
By Angela Przybylski 10 months ago
This used to be my favorite game. The last week or so I cannot see ads to continue the game. Black screen with a PAC MAN (seriously?) and the number 30. I'm about to give up and find another game. This is extremely annoying. FIX IT.
By Kathy 10 months ago
Used to be my favorite game, but now I can’t even play. It continually crashes. It’s so annoying!
By Marlene Whittaker 10 months ago
Every time I uninstall June's journey it reinstall suit reinstalls. I want to remove it re .I dont play games.
By Mary Jane 11 months ago
This is the second time I've started June's Journey over. This time a new level was opened and I was asked if I wanted to watch an ad. I did and during the 'ad' (or game) it froze. I have a black screen with a number 4 in the upper right hand corner. If I have to start this game over for the third time I may pass....As much as I enjoy the game this sort of thing shouldn't happen repeatedly.
By betty 11 months ago
This is ridiculous, this app crashes every 5 minutes, I think its because of the thousands of ads that you have to watch to do anything on this game. I am beginning to hate the game, not fun anymore.
'Connection Error - Try Again' is the message when I click on June's Journey but I can't click on the Try Again and get it to clear. We have wi-fi. If shows 'unable to connect with the server' but when I plug it next to the server I get the same message. I'm using an I Pad. No other windows are open.
By Joan 1 year ago
Have the flowers for 1197 but the game won’t let me pass level 1195.
By Mary 1 year ago
It shouldn’t be called June’s Journey, it should be called June’s Crashes. It use to happen once in awhile, now it happens with any adds, and now it’s even happening for no reason at all.
By Francie 1 year ago
Lost yesterday's (4/13) game play. I started playing in level 173 and ended in 175. Came in today and I am back in 173. My progress in Detectives Needed was lost; I was set back to the start.
By Dianne 1 year ago
Keep getting kicked off the game Losing points What gives
By Kim 1 year ago
Videos keep crashing
By Sharon 1 year ago
Upgrades to the main island (ie wedding scene, flipping whales, tug boat races, etc) are showing up on sunflower island as well overlapping the sunflower island area. Closing the app & restarting my android has done nothing. Happening on 4/1/23.
By Victor 1 year ago
Game will not load at all. Aside from that, when it DOES decide to load it takes 2-3 minutes. What is going on???
By Smiff 1 year ago
I am trying to remove the chewing gum from hospital room I pick up the tweezers but then I get circle with Red Cross and also can’t place snippets help please
By Delena 1 year ago
I can't play my game anymore because my phone won't let me download the new update and the game won't let me play without the new update so now I can't play my game to get my daily rewards. I'm very upset.
By Cindy Worley 1 year ago
I've been playing June's Journey for months and have completely decorated Orchid Island and am in the process of decorating Sunflower Island. For some reason I lost the whole game while playing. The game is no longer there and it wants me to start a new game. Where the heck is the game I have been working on and completing? Is this your way of dumping me?
By Bonnie Carnes 1 year ago
Game freezing up
By Diane 1 year ago
Required to do update. Update will not load
By Barbara Harris 1 year ago
Ads won't load on game #cyd2-nwew-4t9r
By Andrea Fowler 1 year ago
I’ve updated it & for close to a year it will only load to 28-34% then goes back to my home screen on my iPad! I don’t want to start over but I need sum help please! Thank u
By Bella Finder 1 year ago
JJ keeps dropping out & that means l am losing points the last lime l had just made 8 goes with the purple on & l did not get the credit for it. Also when l did my fb name for both JJ & PP Wooga put it as Bella finger l asked for it to be fixed but was not & l gave up checking, l did not friend anyone in my team because l wanted the right name.
By Sheila Hobson 1 year ago
I seem to have 2 June's Journey installed and I need to install one of them. I recently went onto Windows 11 on my laptop {notebook) and I'm still getting used to it at 71 years of age......... I play on Facebook but one says App and it doesn't come on full screen.
By Live Love Laugh (Janet) 1 year ago
Connection problem..... always get the "Reload" error message. Spent money today on diamonds that I never received. Most frustrating day today (11/07/22).
By Susan richardson 1 year ago
Junes not working four hours
By Linda Wilson 1 year ago
It always crashes after watching a video. It seems most of the complaints have the same problem. I hope you fix it soon.
By GAIL Lynch 1 year ago
Every time I have to watch an add it knocks me out of June's Journey.
By Toni Jones 1 year ago
The game keeps freezing trying to play video of birds and kicks me out there and other places
By Kelley Mountain 1 year ago
Been playing about 3 years, and just like all the other comments, the game keeps crashing. Unable to really contribute to the team, missing out on prizes, to say nothing of how incredibly annoying it is. Wooga, you have a serious issue that needs to be addressed. I doubt I will keep attempting to play the game, it’s just too frustrating.
By Linda wilson 1 year ago
I have the same problem as all the complaints above. It is frustrating! I have played this game for a long time and never had it constantly crash. I am also disappointed that you lose flamingos and whales in order to get the deck and orcas. It is so stupid!
By Jo Ann 1 year ago
Please help me. Junes Journey keeps crashing. Done everything to keep from crashing. Nothing has worked!
By Judith Hord 1 year ago
won the whales and afraid of completing the game to win the dophins; my sister won the dophins and the whales disappeared; the same happened when she won the beach wedding, her flamingos disappeared. Is there any way you can retrive the lost items.
By Eileen 1 year ago
I have had crashing problem on iPad for months. I tried all suggestions on how to clear cache and restart. I connected game to Facebook and then deleted game. I reinstalled game and have had no more problems. Perhaps you have to uninstall game to clear cache in app. I don’t know just that it worked.
By Debbie 1 year ago
I’m with everyone who has provided feedback. I’m glad to learn it’s not just me that is constantly crashing when playing on my iPad. At this point the game really is unplayable. I’m trying other games and If they don’t fix it soon, they’ll likely lose me for good.
By Bob 1 year ago
I have an iPad which works just fine except when I try to play Junes Journey. Simply stated, I get 20 to 30 seconds of play and then it crashes. Been doing this for a month. Sixty nine percent of player complaints are about crashing. Wooga you have a problem. Love the game but I quit as it seems sixty nine percent doesn’t seem to capture your attention.
By Deborah Bennett 1 year ago
Constantly crashes when trying to play on iPad. Can barely make any progress. Any word on when you will try to address this? Looks like a longstanding problem.
By Kaye Brown 1 year ago
30 second videos get stuck and when I try to fix it is disappears and I dont get my flowers or my energy. Happened 2 times this morning. this afternoon it started to happen again so I pushed go to website and it corrected itself. the 30 second videos are not working and I have lost a lot of stuff. That should not happen. It took me 10 days of playing to get to the end of Mountain Chateau and then did not get the flowers.
By Joanne Thompson 1 year ago
WHAT A SHAME!! Ive been playing JJ for about 3 yrs & never encountered the problems I have most recently. Every problem review on file at this time is what Im experiencing on my tablet. Something is real wrong when this many players are having problems. Wooga is either incapable or unwilling to correct the issue(s). Such a beautiful & well layed out game it can be when working correctly....Sorry, I give up playing or recommending this game to anyone in the future!!!
By Martin 1 year ago
I have been playing junes journey now for several years and for the last month or so after I played for a while it kicks me out of the game and I lose my points or my place in a competition. It appears this has been an ongoing problem after reading the other complaints from other players. Why can this not be rectified? It makes playing the game very frustrating and almost make someone want to stop playing all together. Please fix this problem!
By Lila 1 year ago
Very frustrated with being disconnected from the game so often and losing energy, coins and even points when playing detective tournament rounds. There have been times when playing a 110 energy round that it will disconnect 7-8 times. Hoping you will please check into this issue and get it corrected soon!!! I am connected to FB and have tried the suggestions you have listed with no change in the status of disconnecting. Thanks!!
By Douglas 1 year ago
Game keeps crashing
By cindy lou 1 year ago
.I do hope the issue gets fixed, as of 4 days back loading problems, now when I play or get to play it goes to a black screen then back to the game in like 20 sec, for those who enjoy playing the game, Hopefully the issues will be solved soon enough.
By Leanne Owen 1 year ago
Why are so many complaints has nothing been done to fix all the problems with this game. We are all having the same issues, which is nearly everything about the game. Even after many years wooga have done nothing. Obviously they couldn't give a damn and what they say to do for the problem is a load of rubbish. 🤬
By Marijana Janevska 1 year ago
JJ kicks me out constantly. While watching an ad, during playing a scene even while counting the score… I lose the reward, the energy used and the progress. I load and reload many many times just to collect club member drinks during coffee time… your help would be very much appreciated. I love Playing JJ for almost 2 years now
By Sylvain Dufour 1 year ago
I keep getting kicked out of the game. Approx every 15 min or so, mostly when I watch your Ads.
By Cindy Mullen 1 year ago
Game crashes every 30 seconds. I have trouble shooted and do everything you say to do. This is your issue not my phone or wifi connection. Why don’t you fix this!!!!!
Still crashing on iPad. When will this be fixed?
By Tina 1 year ago
I keep getting booted out. I have everything up to date and am playing on iPad app. Last night I played a competition and got kicked out and I had to restart 8 times...I was so frustrated. If this keeps happening I will have too quit playing...I love this game but not the frustration...It cannot happen when playing competition.
By Joyce Bass 1 year ago
Very frustrating!!!!!!!!!!!! Game keeps crashing and I keep losing my coins and progress. Wooga stinks as far as service and repair goes. Do something or get out of the business.
By Mary Dubay 1 year ago
The game keeps crashing resulting in me wasting energy and not getting the coins I earned playing a scene.
By Margaret Jones 1 year ago
Fed up with completing a science getting box, the JJ CRASHES so lig back in box gone along with my energy. Team also having problems. What's the point in playing. Can't finish the fortune wheel as I can't progress. Cumon wooga get your act together. You take our money quick enough. Thanks
By Tricia Edwards 1 year ago
Constantly having to restart the game, give drinks which expire before being used. My device is an iPad with all the updates in place.
By Joelle 1 year ago
I’m on an iPad Pro iOS 15.5. I’ve been playing June’s Journey since mid 2020. First week of December 2021 I updated my iOS from 14 to 15. Everything was fine until JJ did an update around December 5-7 a couple of days after updating my iOS and I have been crashing ever since. December 2021 there were hardly any updates maybe 2-3. The updates didn’t help. I play maybe 2-3 minutes sometimes less and crash. Just like everyone is saying, losing energy, getting booted off of competitions. Don’t get me started on the hat game. I always lose my tickets and and have to play to get them again and start over only to lose everything again. I also lose my Snippets packs after crashing so frustrating. I even called my internet provider who came to my house replaced my modem rewired my internet and the problem has not been resolved. My internet is 1 gig download the fastest I can have here in California for home. I’m able to upload and download terabytes of media for my job and have no issues only with June’s Journey and no I don’t play while I’m working. Wooga keeps blaming our internet but the timeline proves otherwise. I also went to my friends post production facility where there speeds are super fast to accommodate production to troubleshoot and had the same problem. Needless to say not really playing much anymore. Sorry for the long post.
The app still crashing. I keep loosing points. I have done updates and tried everything. Please help fix this problem. I am using an iPad.
By Mary Losekamp 1 year ago
Game has been crashing repeatedly while using my ipad. This has happened for the past month. I love this game but I'm getting very tired of it. Wooga FIX YOUR GAME for us ipad users!
By Linda 1 year ago
Game keeps crashing, so frustrating I keep loosing my energy. Will stop playing if this continues.
By Linda Sauls 1 year ago
Repeated problem loading june’s journey. Then, when I get on & begin playing the picture goes away & I’m back onto my homepage. It’s a constant interruption during team competitions. This has been happening for a week now. switched from google to google chrome & I’ve restarted numerous times. Still problematic. I’ve been playing for a year and this is the worst, yet. Thank you for allowing me to vent.
By JodiB 1 year ago
Game keeps crashing in IOS on iPad. Have reinstalled many times. Seems to work if I do not connect to Facebook, but that means I lose all of my past history and levels.
By margaret palmer 1 year ago
Often crashes after watching ad, making me restart and watch the ad AGAIN. Slow loading as well. I just collected coins which were not added to my total. Fun game, but getting to be too much trouble.
I have tried everything suggested and my iPad continues to crash during play? Cleared cache, restarted, updated, etc. Any suggestions?
By Christine 1 year ago
Game will not load anymore what is t he issue? Have reported this many times with no response
By Eileen aka Sweet Find Dude 1 year ago
Game keeps crashing on iPad. I have looked for updates and restarted iPad it doesn’t help. Please help us. We all love this game.
By Lisa Rene Gunnison 1 year ago
I can no longer load the game because it crashes. For the past 2 months I have been experiencing crashes in the app. 12-14 times a day. Now the team is wondering why I am not playing competitions. Throws me out before Times Up and I waste time trying to reload.
By Pierre Vermeulen 1 year ago
Scene 1293 contains ' mushrooms' to find, but they're not in the scene. The 'help' lamp leads to something outside thé screen. System blocks. The only thing you can do is stop the game. Tried to start the scene again 4 times. Nothing helps. A shame for the spilled energy and time, and leaving my team in distress.
By Margaret Knoester 1 year ago
June's journey only loads to 90% for the last week
By Dianne Armstrong 1 year ago
Game keeps crashing. Been going on for about 2 weeks
By Kat 1 year ago
Sorry..you are wrong. App keeps crashing, over and over. My whole team is very very frustrated. Does not happen anywhere else for team members. It’s the game’s problem, not all of ours. K
By Leigh 1 year ago
Game constantly crashes. Very frustrating.
By Opulent Sue Boudreau 1 year ago
Hi guys, In one of my wanted cases the object is to collect coins but the last 3 times when I have it does not get tabulated for the case. This is not the first time it has occurred. My name on there is Thomasina. Your help would be greatly appreciated. Have an awesome week🙂. Thanks.
By June H. 1 year ago
In the past couple weeks, while playing game, JJ keeps crashing and I lose ⚡️ earned. I’m using an Apple IPad 8th version. Love this game but getting tired of it constantly crashing. Looks from messages on internet I’m not alone, when can this issue be addressed?
By Kim hornsby 1 year ago
Game crashes repeatedly. So I lose progress of the task and the energy for the scene. I have cleared cash, restarted. Reinstalled the app. At a loss what to do.
By Donna DeGain 1 year ago
By Kathy 1 year ago
Can't get the game to load? It's been about 24 hours now. It continues to show the "find 5 cats" screen. Is it me or the game?
By PAMELA NELSON 2 years ago
I just purchased a new Samsung Galaxy Tablet and would like to know how I can transfer my June's Journey to my new tablet from the old one. I have been playing this game for long time and don't want to lose what I have. Please reply.
Common dislikes about June’s Journey app
- Story itself is not always a fan.
- Cost too much to open the next scene.
- Have to spend all of Gems to speed up buildings.
- Have to buy a bunch of cheaper decorations.
- Have to spend real money in the game.
- Rewards you get aren’t worth the money you have to spend.
- Developers are very stingy with many parts of this game.
Have a Problem with June’s Journey: Hidden Objects? Report Issue
Leave a comment:
Common June’s Journey Problems & Solutions. Troubleshooting Guide
Complete guide to troubleshoot June’s Journey app on iOS and Android devices. Solve all June’s Journey app problems, errors, connection issues, installation problems and crashes.
Table of Contents:
- June’s Journey iPhone Issues and Solutions
- June’s Journey iOS app crashes, not working, errors
- June’s Journey iOS app network issues
- June’s Journey on iOS has black/white screen
- June’s Journey Android App Issues and Solutions
- June’s Journey has errors/crashing/not working
- June’s Journey server network connectivity issues
- June’s Journey has black screen

Some issues cannot be easily resolved through online tutorials or self help. So we made it easy to get in contact with the support team at wooga, developers of June’s Journey.
86.67% Contact Match
Developer: Wooga
E-Mail: [email protected]
Website: Visit June’s Journey Website
Escape to an era of opulence and romance as you search for hidden clues through hundreds of stunning mind-teasing puzzles! * KEEN-EYED DETECTIVES WANTED – Engage your sense of observation to find all hidden clues and spot the differences. * YOUR 1ST CLASS TICKET TO THRILLS – Mystery! Danger! Romance! June's Journey does not require payment to download and play, but it also allows you to purchase virtual items with real money inside the game. You can also find more information about the functionality, compatibility, and interoperability of June's Journey in the above description and additional app store information. You may require an internet connection to play June's Journey and access its social features. Dive into June Parker's captivating quest to unveil a scandalous, hidden family secret. By downloading this game, you agree to future game updates as released on your app store or social network. Find the hidden objects to crack every case. Love True Crime? June's Journey is intended for those 18 and older. June's Journey may also contain advertising. Where will each new chapter take you? * A NEW EPISODE EVERY WEEK – Just like your favorite TV series, look forward to a new mystery in each new chapter, and a new chapter every week! You may choose to update this game, but if you do not update, your game experience and functionalities may be reduced. Solve mind teasing mysteries in the glamorous 1920s! You can disable in-app purchases in your device’s settings. I spy a mystery!
Solve Problems with Similar Apps:

June's Journey Server Status: Is June's Journey Down Right Now?

No problems detected at June's Journey Current June's Journey status is up, with no reported problems.
Currently, there are no surges in user-reported problems at June's Journey within the past 24 hours. Are you encountering issues with June's Journey ? Please cast a vote or leave a message in the comment section.
Please let us know the problems you are currently facing with June's Journey :
Server Connection
Online Play
June's Journey Outages and Problems
0 complaint.
Within the past 24 hours
The interactive chart above illustrates the number of problems reported by users. It is the total amount of reports that were received for June's Journey over the past 24 hours. An outage is decided when the number of user complaints is higher than average
About June's Journey
Search by Games:
June's Journey Information
- First Release Date : Oct, 04 2017
- Total Reported Problems: 1,217
Game Engines
Player perspective.

June’s Journey Guide: Tips, Tricks & Strategies to Solve All Mysteries
By: Author Rachel Robbins
Posted on Last updated: February 16, 2024
Everyone loves a good mystery. There’s undoubtedly a measure of excitement in trying to solve crimes, ghost sightings, or other events that need more than commonplace logic to be explained. Mysteries beget intrigue, and humans are inherently drawn toward strange happenings if only to satisfy our curiosity and break the monotony of the everyday.
It’s why cartoons like Scooby Doo or shows like CSI , Ghost Hunters , or even Ancient Aliens have become such hits, there’s always an element of mystery to them, a puzzle that needs to be solved, a story to be unraveled. Of course, one cannot discount the importance of the Sherlock Holmes or Nancy Drew books, which have given readers the chance to step into these mysterious stories long before they’ve become staples of the big screen.
It’s no surprise then that games like June’s Journey can deftly pull players into a world of intrigue, romance, and crime. Set in the roaring ’20s, June’s Journey is a hidden objects game wherein you’re presented with a scene and are tasked to find objects corresponding to a set of words. The mechanics of the game seem simple enough at the onset, but there’s more to it than meets the eye, just like the mystery surrounding the deaths of June’s sister Clare and Clare’s husband, Harry.

Before giving an overview of how the game is played, let’s first talk about the story in which the game revolves so we can have some context into June’s motivation, which, by extension, also serves as your motivation as the player: June’s Journey begins with June Parker receiving news that her sister Clare had been killed by her husband, Harry, just before Harry himself committed suicide.
With their teenage daughter Viriginia left in the estate, June takes it upon herself to travel to her late sister’s house, which also happens to be the scene of the crime. Here, June discovers that her hunch had been right: that there was something awfully suspicious about the circumstances surrounding her sister and brother-in-law’s deaths. Though without any experience as a detective, June has nevertheless made up her mind to find out what truly happened to Clare and Harry.

Determined to get to the bottom of things, June sets off to find more clues, and this is where you, as the player, will come in.
In following the story, you will be, as mentioned, provided with scenes containing a set of words that pertain to specific objects found in that particular scene. Some of these objects can be easily spotted while others are hidden, testing your observation skills. Your goal is to find all the objects until every word in the list has been crossed out.

In some cases, an object included in that list is a clue that drives the story forward. Every time you play a round of a specific scene, the list of words and objects you have to find will change.

For every object that you click correctly, you stand to gain multipliers that will give you bonus points. The faster you click on the right objects, the higher the multipliers and your score will be.
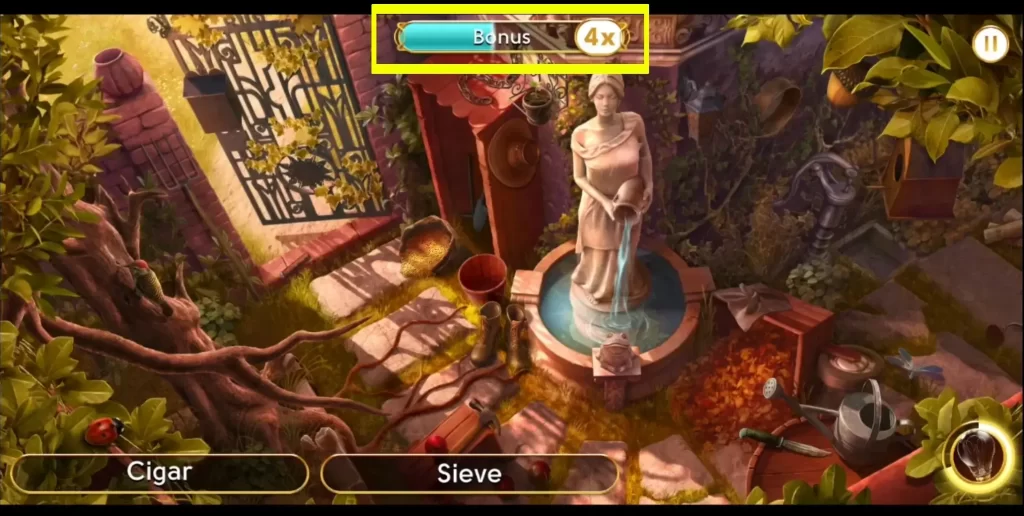
Scores are calculated based on your speed, accuracy, and whether or not you’ve availed of hints. Using hints will decrease your score.
Scenes are considered as levels and playing a single round will require you to spend energy. Completing a round will earn you points that can gain you stars. Each level has a maximum of 5 stars, which will earn you Mastery of that level. There are multiple levels in each chapter and you may only proceed to the next chapter if you’ve achieved all its requirements, which may consist of stars and flowers.
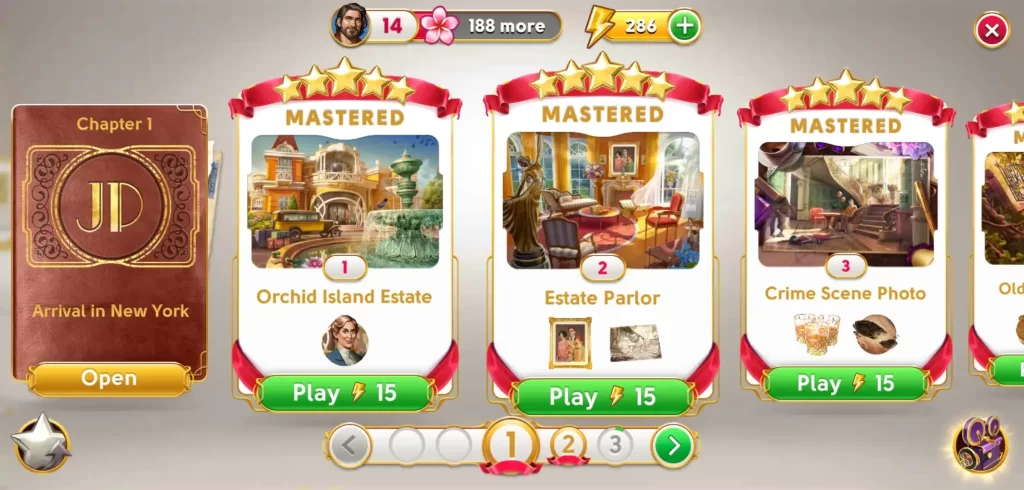
If stars can be earned by mastering a level, flowers can be earned by buying decor for Orchid Island, which is where Clare’s estate is. As June, you’ve become the unofficial caretaker of the estate. Every piece of decor costs a varying amount of coins, which can be earned by completing rounds. Placing certain types of decor will also yield a varying amount of flowers. Aside from being used to access new chapters, flowers are also needed to level up your overall account. Increasing your account level will grant you access to more decor, more levels, more chapters, and so on.
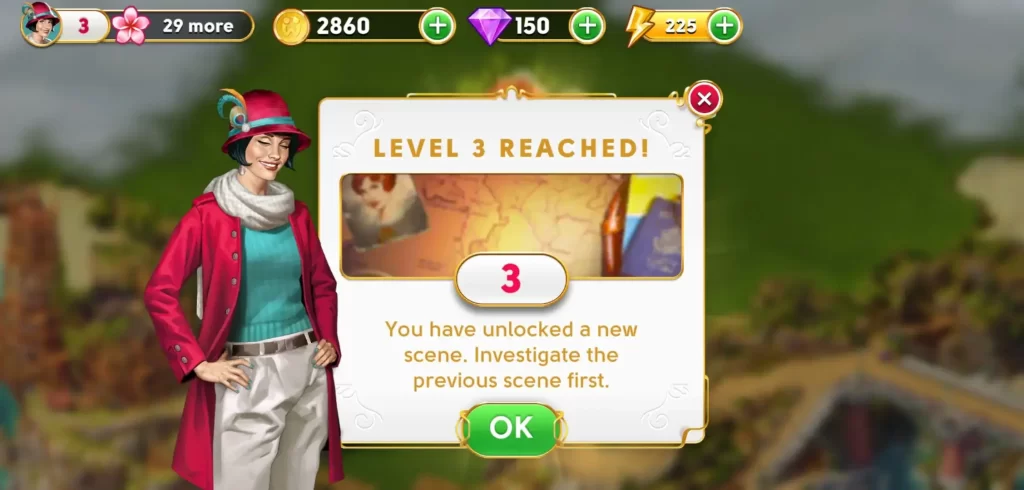
The estate itself, which is considered an individual building, can be leveled up. Completing rounds may get you construction materials, which are necessary for the upgrade. Only specific decor can be leveled up, which can yield flowers after the upgrade has been completed. Buildings also passively produce coins, which can be collected after a waiting period.
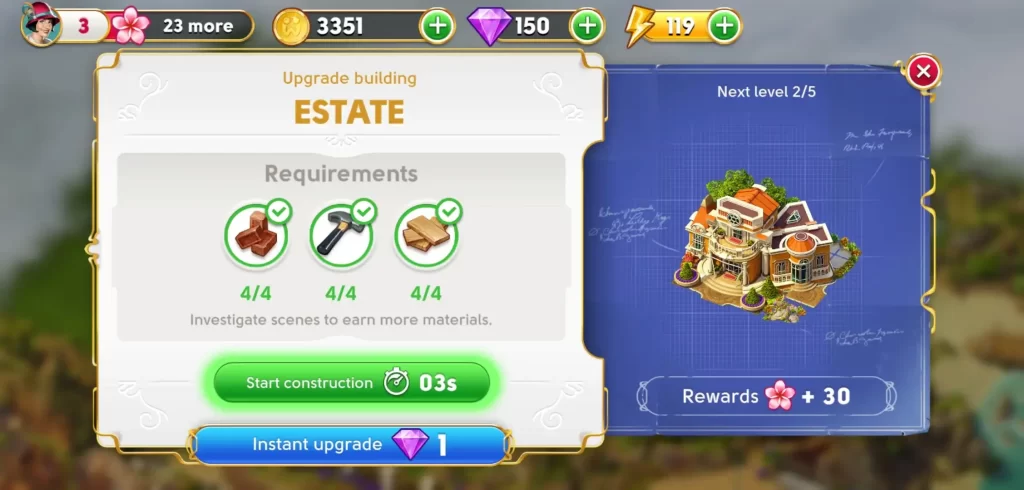
Additionally, you may eventually expand accessible spots in Orchid Island when you collect compasses, which are used in exchange for expanding your plot. Reaching certain chapters in the main story or getting enough stars will also grant you access to different places around Orchid Island, such as the lighthouse, the hangar, or the shipyard.
Of course, you can get all of these rewards and open up more locations when you play the main hidden objects game following Clare and Harry’s murder mystery. But while the mechanics of the game sound rather simple, just find an object and click on it, it’s a lot more challenging than you might think.
With our beginner’s guide for June’s Journey, we’ll teach you some tricks to find objects in the fastest way possible, as well as tips to get those high scores, not waste a drop of energy, and decorate Orchid Island into a vintage paradise that will be the envy of your neighbors, and solve the murder mystery along the way, of course.
Spend Your Energy Well
As we mentioned earlier, playing a round will always require energy. As a beginner, you have roughly a maximum of 110 energy points. Each round costs a minimum of 15 energy points. Depending on how well you do in a round, you can either gain a star or portion of a star.
This means that if a level has a maximum of 5 stars to achieve Mastery, you likely have to play it more than 5 times as completing a round does not automatically mean gaining 1 whole star. Sometimes, you might gain only 12% of a star or 30% of a star.
Again, it depends on how quickly and accurately you find all the objects included in the word set. If you do extremely well in a round, perhaps even get a “Perfect” rating, then you might be able to get, say, 50% of a star.
However, if you do poorly, you might get only 12% of a star, for example. If you consistently get low percentages, this basically means that you’re spending a lot of energy without getting much in return. Additionally, 1 energy point regenerates every 2 minutes so waiting times can feel quite lengthy.
This brings us to the two ways you may choose to approach the game so you can allocate energy points in the most productive way: you can either gain mastery of one level at a time or find all the clues first to complete a whole chapter.
What difference do these two approaches make? They both have their pros and cons and here’s what sets them apart:
Gaining Mastery of a Level First
Gaining Mastery of one level means earning all 5 stars for that level. Again, this will likely take more than 5 rounds as the game doesn’t seem to let you earn 1 whole star with every round, even if you do manage to get a “Perfect” rating.
This can seem a little tedious at first, but the advantage of gaining Mastery of a level is that you’re only focused on one scene and though there will be objects added to it every time you play a round, you’ve already become familiar with most of where the objects are hidden that you’re more likely to get Perfect ratings even if the difficulty increases. As the saying goes, practice makes perfect, so playing a level over and over to earn all 5 stars is definitely good practice.
Eventually, you would become quite familiar with the scene and the locations of objects that you’ll complete rounds faster without using hints. This then maximizes the energy you spend. Additionally, after attaining Mastery of a level, you get to open a 5-Star Box, which often contains Rare, Marvelous, and Special items.
The downside to this approach, however, is that the story won’t progress as fast and you won’t be able to unlock other areas in Orchid Island until later.
Finding Clues First
On the other hand, you may opt to complete searching for clues first then moving on to the next level instead of earning Mastery for one level. The way the game works is that in every level, you get to find 2 clues, the first of which you’ll encounter upon starting the level and the second when you’ve reached a certain number of stars for that scene.
Once you’ve found all the clues, you may unlock the next level (provided you also have enough of the flowers required) and proceed to play that scene. The advantage to this is that you’ll be able to drive the story forward and unlock more levels, chapters, and other features of the game such as unlockable locations around Orchid Island.
The downside is that most of the time, accessing the final level of a chapter requires a certain number of stars, which you’ll have to earn from previous levels. This means you may have to gain a Mastery rating of certain levels anyway.
Between these two approaches, gaining Mastery of each level may be the more productive approach when it comes to maximizing your energy points. It might seem slow in terms of story progression, but you won’t have to worry about going back to previous levels and trying to reacquaint yourself with a specific scene all over again.
You only have to focus on one scene at a time, raising your chances of getting a high score and Perfect ratings since you’re already familiar with the objects that can be found in the scene. Additionally, stars (alongside compasses) are also required to expand the plot around your estate, which is surrounded by fog. Certain decor items may also be unlocked when you earn a number of stars.
That said, you can consider gaining Mastery as the slow but steady approach that will ultimately lead to more rewards in the long run. All you need to do is be patient about your progression.
Thoroughly Study the Scene

As mentioned, high scores for each round depend on how quickly and accurately you find the right objects in a scene. During your first few tries, this can seem a little difficult and may take some time getting used to.
Many objects are cleverly hidden wherein some are shrouded in shadows, placed behind a more prominent object, or look as though they’re part of what our vision perceives as the background. Thus, you need to thoroughly study the scene to become familiar with what objects it contains from the get-go. But how exactly do you do that? Here are a few tips we’d like you to consider:
Pick the Image Apart
The first time you encounter a particular scene, you’ll be given an overall view of what it looks like. You’ll quite literally get to see the entire picture but not all the details, at least, not immediately. Upon encountering a scene, we strongly recommend zooming into it first before clicking on any object as listed in the word set.
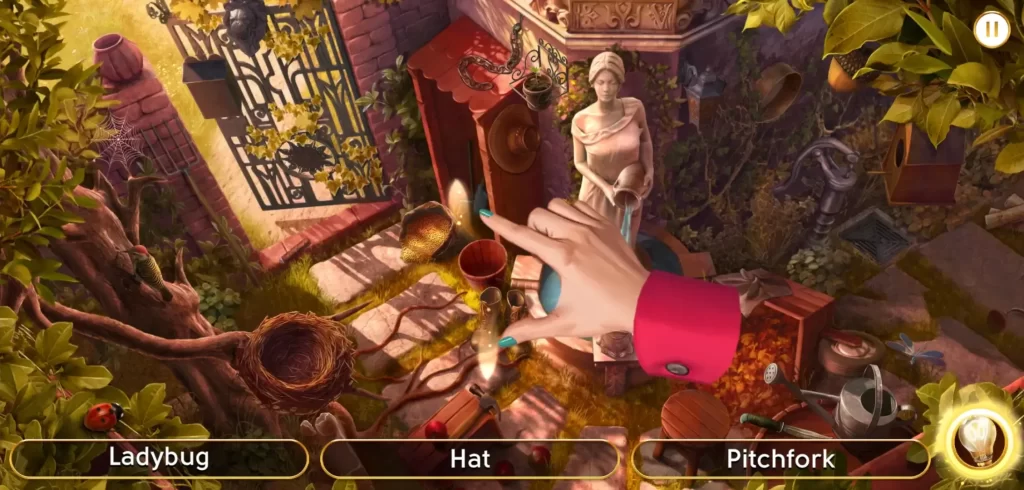
This is because clicking an object automatically begins the round, and how fast you find objects will be taken into account when tallying up your final score. Thus, it’s better to pick the image apart first before beginning the round so you don’t waste time zooming the picture in and out when the invisible timer has begun.
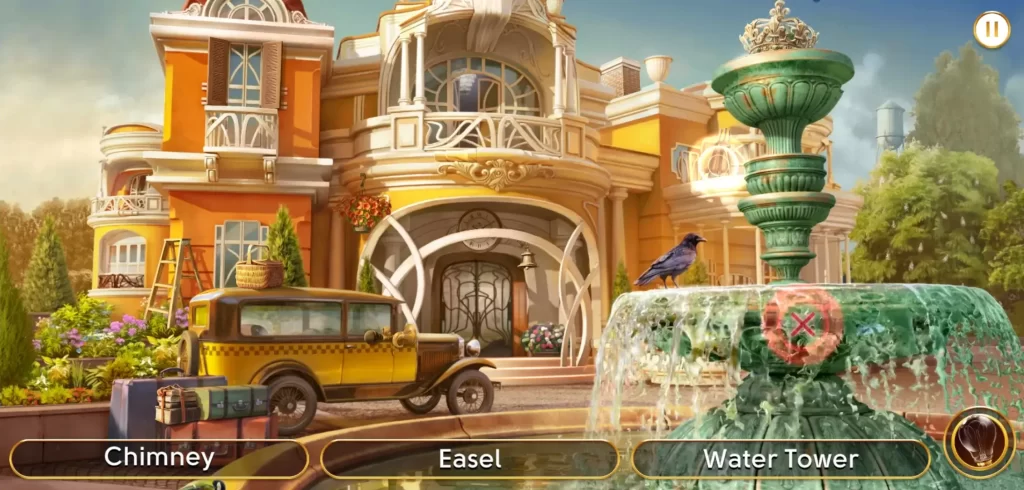
When zooming into portions of the scene, try to be methodical about it. One thing you can do is try to imagine lines dividing the picture into several parts. Let’s take this scene for example:
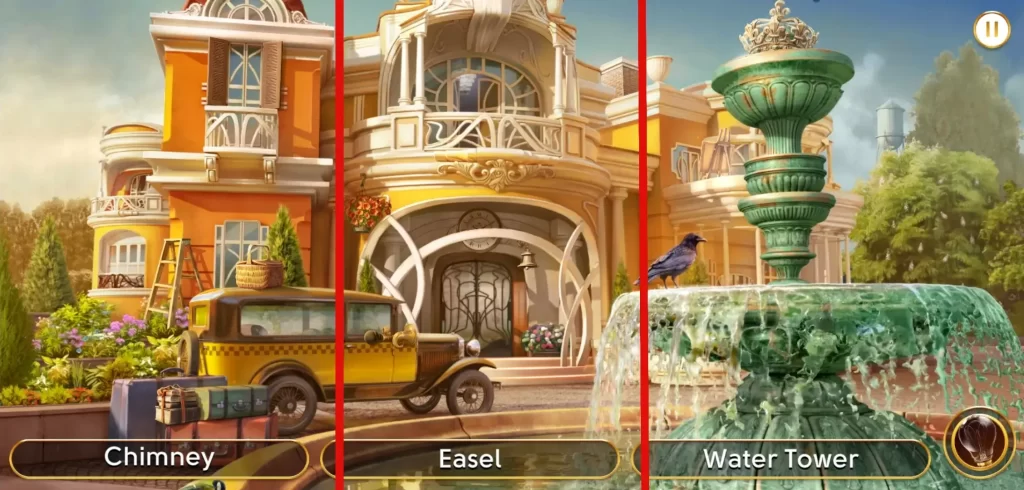

As you can see from the image above, we’ve divided the scene into three. Let’s look at the rightmost portion first. The most obvious objects are the big ones or those closest to the foreground, so take note of those first:

Smaller objects which may be mistaken as part of the background or can be easily overlooked include:

- Easel on the balcony
- Water tower beside the trees
- Crown on top of the fountain
At the center portion, the most obvious objects may include:

- Hanging flowers
- Flower bush
Further breaking the image into smaller objects, we can see the following:

- Lights on the second floor
- Clock on top of the front door
- Heart shapes on the front door
- Horn at the side of the car
- Steps to the entrance
- Golden decor on the balcony
The left side of the image also has a lot of small things that may be included in the word set:

- Basket on top of the car
- A stack of books on top of a suitcase
- Flowers of different colors
- Foggy windows from the car
- Small balcony
- Exclamation point
You might think that the last item sounds strange, but there will be times when numbers, shapes, and even Zodiac symbols will be part of the word set. This is why it’s important to take note of every small detail that you come across since they might be included as an object you have to find.
Take your time when doing this and go back and forth zooming in and out of the scene until you have a good grasp of all the objects you can possibly recognize. Don’t start until you’re confident that you’ve managed to discern most, if not all, objects in the scene.
Take Note of Additional Items
Apart from recognizing hidden objects, the other challenging aspect in this game is that every round you play may have other objects added to what you’ve already encountered. Take for example these two images below:

It can be rather subtle, but the scene on the right has more objects in it, any one of which may be included in that round’s word set. This brings us back to our first tip, wherein it’s a good idea to pick the image apart as thoroughly as you can.
Additionally, you need to treat each round as though you’re encountering a new scene since objects will occasionally be added or even removed from it. Reacquaint yourself with the scene each time you play it and take note of what’s been added or what’s been removed. This way, you don’t get caught off-guard when a new word suddenly springs up from the word set.
Remember the Words and Their Locations
Now it can be extremely difficult to memorize each and every object in every scene. Fortunately, some words get repeated, allowing you to better remember the object corresponding to this word.
Aside from just knowing what the object looks like, also take note of its general location. Keep in mind that you have about 2 to 3 seconds before bonus multipliers disappear, which may be enough time to find a specific object when you know its general location.
As for encountering new words in the set, their location might not always be where you expect as some objects are placed in spots that don’t always make sense, like a letter M on a fireplace…
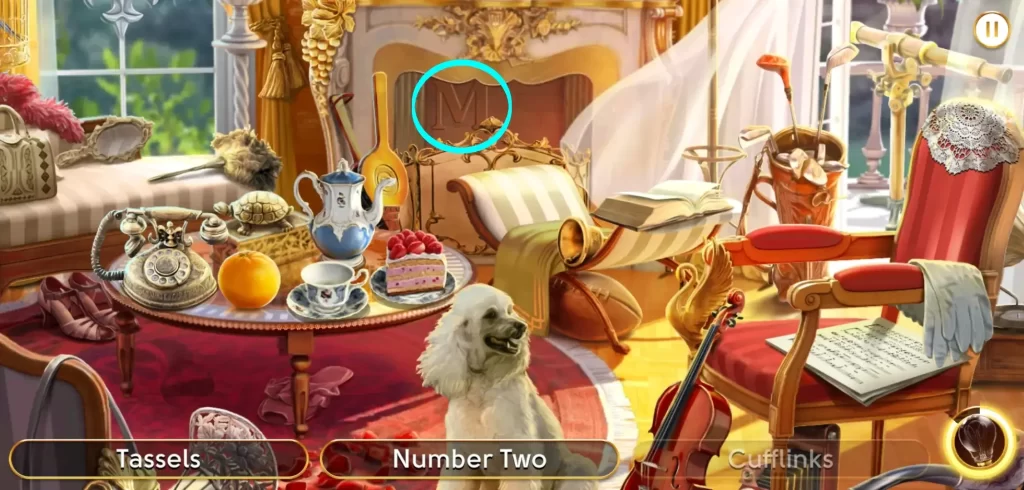

… or a figure eight on a sofa.
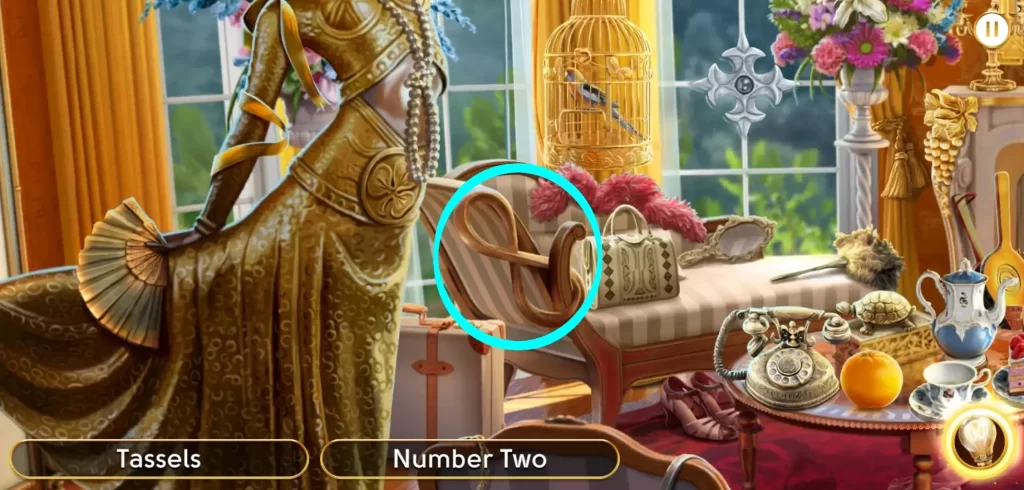

If you’ve zoomed in and out of the scene before beginning the round, these odd locations can work as markers that will help you remember an object’s general location better.
Don’t Just Click Objects at Random
You might think that it’s a clever move to just start clicking at random and hope to find the object indicated in the word set, especially if you’ve been staring at the scene for what feels like ages. Surely, you’re bound to get lucky and click on the correct object, right?
While that may be somewhat true, keep in mind that accuracy is also taken into account when tallying your overall score. This means that for every mistaken click, you lose points.
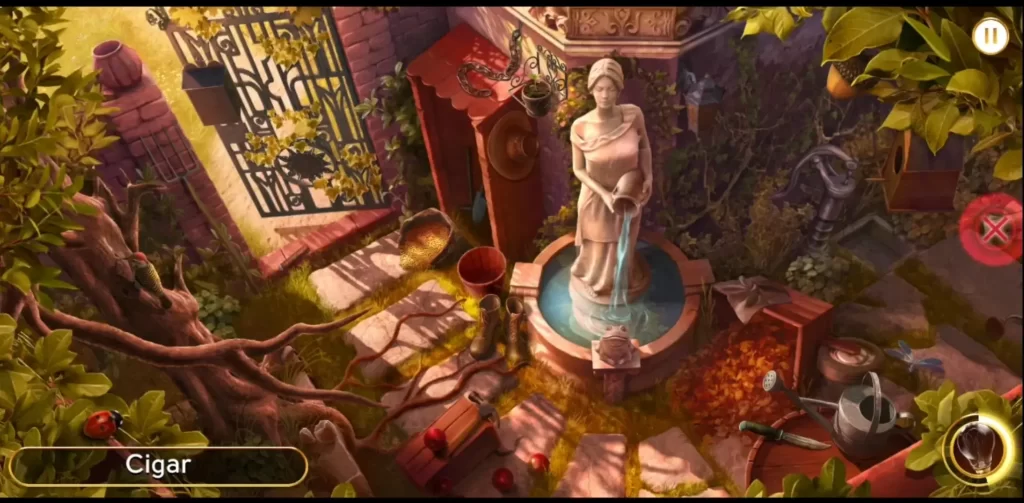

How many points are lost seem to be arbitrary, but suffice it that they do affect your final score, thus lowering your chances of getting a high percentage when it comes to earning stars. That said, it may be better to lose just speed points instead of losing both speed and accuracy points. After all, you’ve already spent some time trying to find the object that you might as well click on the right thing.
Use Hints Only When Necessary
Sometimes, there’s just that one object you can’t seem to find in the scene. You’ve zoomed in and out of the image, stared intently at the picture, but this particular object remains hidden from view. In this case, you may click the hint button, which is the light bulb on the lower right-hand corner of the screen. Upon clicking the hint button, it will illuminate the object you’re looking for, allowing you to spot it. Below is one case where we used the hint button because the chapel was extremely difficult to see and looked deceptively part of the background.

Of course, using hints will decrease your overall score. You may use hints multiple times but the button has a waiting period before it can be used again. That said, use hints only when absolutely necessary. If you really can’t find the object, then it may be time to use a hint, especially if it’s the last item on the word set.
Similarly, you may want to use the hint button if the last word on the list is one you’ve yet to encounter and you don’t want to lose the speed multiplier bonus. Click the hint button just before the multiplier bonus appears so you can still at least have a decent high score even if some points will be deducted.
Don’t Expect Items to Look the Way You Imagined
As we’ve mentioned earlier, June’s Journey is set in the 1920s, so characters, scenes, and other features of the game are all made to align with this era’s vintage aesthetic. This poses a new challenge as objects from the word list might not look like the way you imagined.
For instance, in Chapter 1, in the Old Garden Gate (Level 4), you might be asked to find a thermometer. Of course, our idea of a thermometer looks different from the way it used to in the 1920s. This is how it’s presented in the Old Garden Gate:
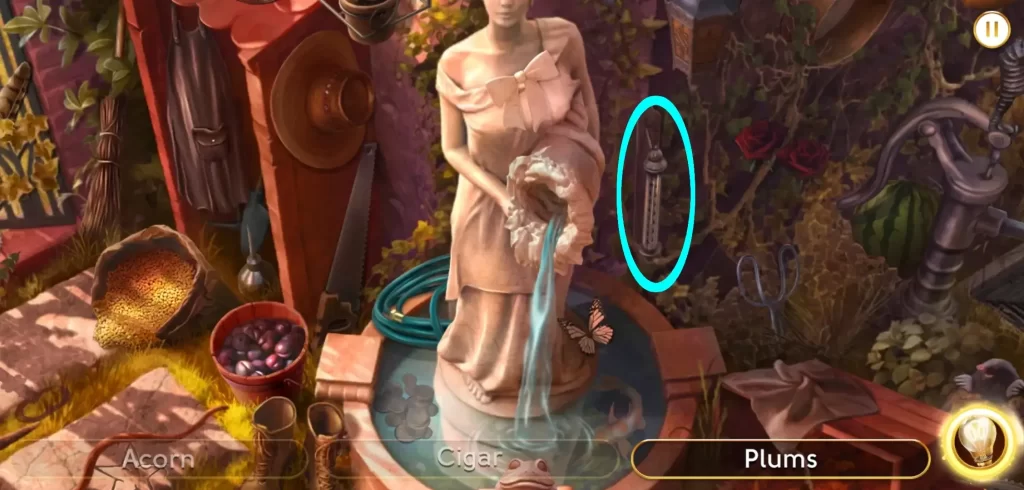

You’ll encounter a similar instance in Chapter 2, when you play the scene for Harry’s Yacht (Level 7). Here’s how the thermometer in this scene looks like:
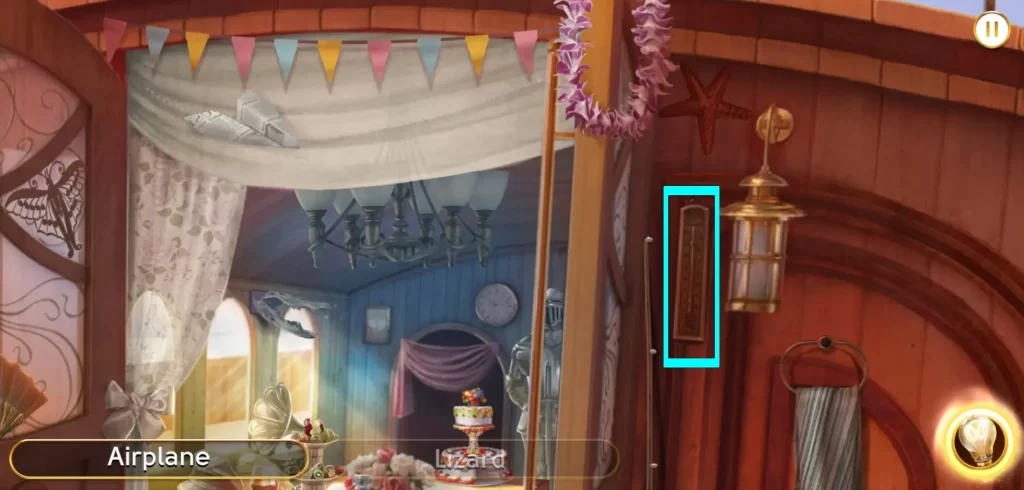

Neither of these images look the same, and neither of them are likely familiar to people today, but both of these images will be listed as “thermometer” if they pop out on the word set.
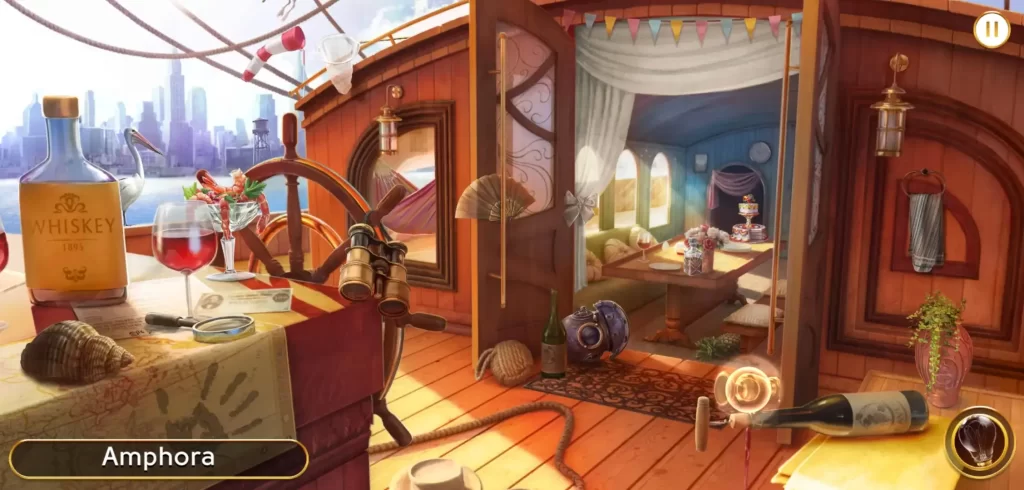
On the other hand, you might encounter a word that may be totally unfamiliar to you. One example is, again, in Harry’s Yacht (Level 7), where the word “Amphora” might spring up. Amphora isn’t an everyday word so we had to use the hint button to find out where the corresponding object is. It turns out that an amphora is an ancient Greek or Roman jar with a narrow neck and two handles.

Other times, the word included in the list can also be pretty vague or just simply isn’t what you’d expect. For instance, the word airplane or plane is something you might encounter once or twice, but it can mean either an actual plane, a paper plane, or even a poster of a plane.
The word star can mean a literal star in the sky, a carving shaped into a star, or even a starfish. Grapes can mean the literal fruit or might even pertain to stone grapes that are part of a statue or decor.
You won’t really be able to tell unless you’ve actually found the object for a particular scene so it’s best not to associate a certain word with what you might think it looks like since this can keep you from finding the right object when your eyes are looking for a specific appearance based on word-image association. As much as you can, keep both your eyes and your mind open to all sorts of possibilities so you can find the right objects even if they can be tricky.
Don’t Panic!

Last but not least, panic is definitely your worst enemy! With the way the game operates, you’ll be put under time pressure not to break your streak and the pressure to click objects correctly every single instance just to get a high score and earn bigger portions of stars. You’ll soon discover, as we did, that the game can be a little stingy when it comes to earning stars.
In this case, panicking won’t help as it can sometimes lead to paralysis and you’ll lose the chance to find an object as opposed to when you approach a scene calmly and methodically. When you don’t know which object a specific word is referring to, leave that word for now and move on to the other two words flashed on the screen.
Find the objects that are most familiar to you or those whose locations or appearances you can remember best. Upon correctly finding an object, a new word will be flashed so you can turn your attention towards that first until such time you can focus on an object or objects you’re not familiar with.
Additionally, it’s easier to be calm and find the right objects when you’re in an environment that has minimal distractions. If you’re the type to concentrate better in a quiet place, play the game at a location without too much noise. You may even choose to mute the game altogether if you find the music distracting (although this is hardly the case as the music playing for each scene is rather soft and relaxing).
Also, try not to play when you’re sleepy, if your eyes feel tired, or while you’re in a spot without ample light to avoid straining your vision. Your environment may play a significant role in keeping you calm and focused so it’s best to play in a setting that fosters these.
All in all, your performance in each round will rely on your skillfulness as an observer. It can take some time getting used to but it’ll be easier once you get the hang of things. Keep our tips in mind and don’t panic!
Claiming Rewards

Though June’s Journey can be a little bit stingy when it comes to giving rewards, there are a few avenues in which you can get some extra coins, energy, and other items just by playing the main game. Here are a few of them:
Opening Boxes

Occasionally, you’ll be able to earn both 1-star and 5-star boxes during and after playing scenes. Naturally, 1-star boxes typically give out common materials and are earned at random. On the other hand, 5-star boxes are usually earned after gaining Mastery of a level. Upon acquiring boxes, they’ll simply be kept unopened in your inventory so make sure to open them up when you’ve finished a round or have run out of energy to play.
Both 1-star and 5-star boxes have a varying chance of giving the following items:
- Coins: Used to purchase decor for Orchid Island.
- Gems: Used similarly as coins, but may also be spent for speedups and other purchases like decor.
- Compass: Used in exchange for expanding plots in Orchid Island.
- Energy: What you spend playing scenes.
- Construction materials: Used to upgrade certain buildings and fixtures in Orchid Island.
- Character cards: Can be collected so you can discover more about the characters indicated in cards. When you complete character cards, you’ll be able to play a mini game where you’ll put a fragmented picture of the character together.
Once you’ve acquired a number of these rewards, you may be able to play more scenes with additional energy, buy more decor, expand plots in Orchid Island, or get additional story-related information.
Daily Deliveries
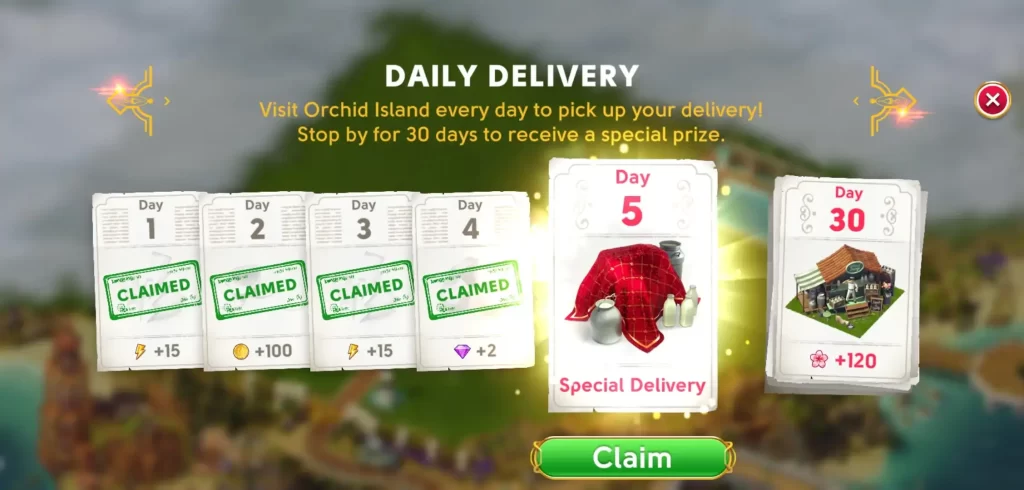
You can get random rewards from the Daily Deliveries every day you log into the game. Fortunately, the reward counter won’t reset if you forget to login and you’ll simply be able to claim the next delivery. Any of the items mentioned above can be earned through the Daily Deliveries. At the end of five days each week, you’ll be able to get a special prize and a fancy decor item by the end of 30 days.
Opening Mail
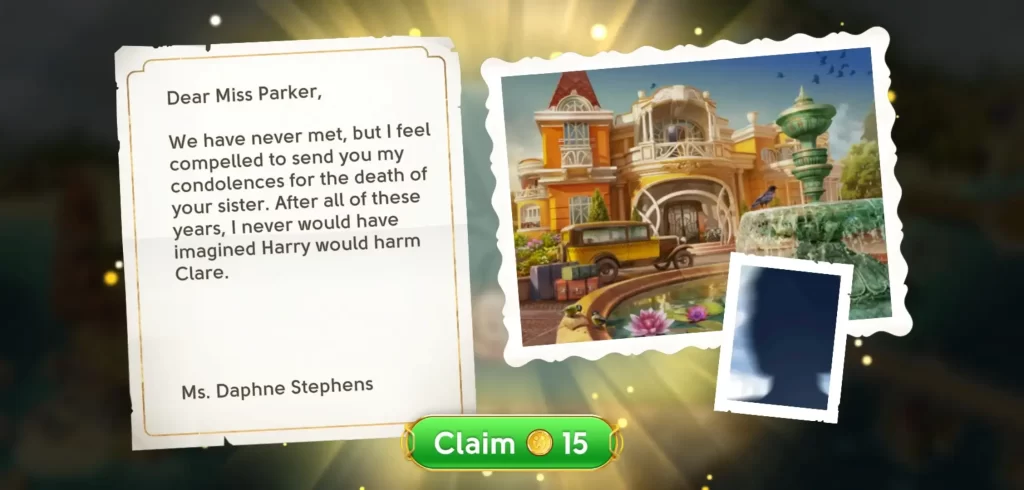
There are times when you’ll receive letters from other characters, even those you might not have met yet. Included in these letters are small rewards such as a handful of coins. That said, check your mail from time to time in case you have a letter alongside a tiny reward.
Decorate and Expand Orchid Island
Speaking of decoration and expansion, these are two important activities that you need to accomplish aside from playing scenes and finding clues. As we briefly mentioned in the beginning, decorating Orchid Island will let you earn flowers, which are needed to level up your overall account. Flowers are also required to unlock levels, particularly the last level of a chapter.
You can earn flowers by buying decor, which will often cost coins, though some can be acquired by spending gems. You will gradually unlock more decor when you keep playing scenes and earning stars.
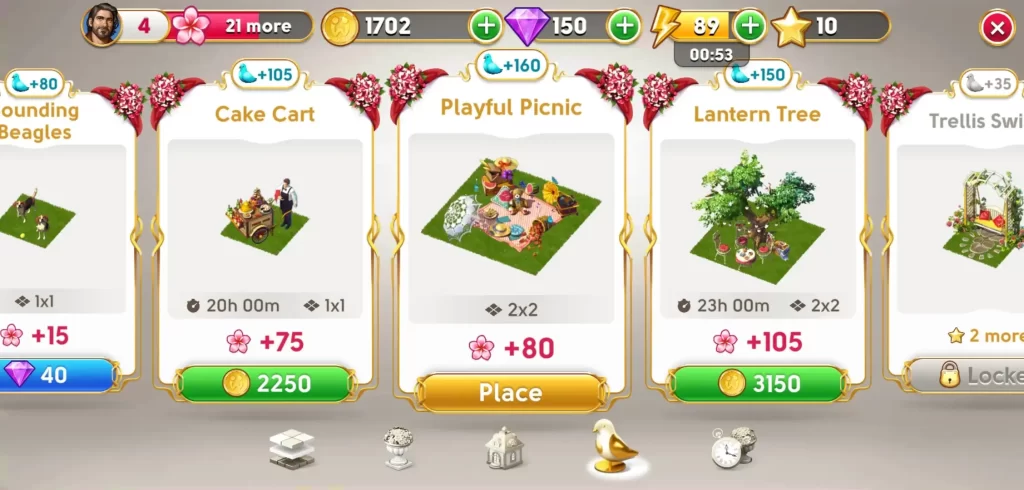
Some decor can be expensive but yield more flowers, while cheaper decor will only give you a handful of flowers. Often, decor that earns a lot of flowers will ask you to accomplish a long waiting period, which can last between 2 to 12 hours or much more.
Taking waiting times into account, it may be best to accumulate as many coins as you can so you can afford more expensive decor items instead of buying a multitude of cheaper ones. Basically, you can play the hidden objects game over and over to earn coins and open boxes, then buy the more costly decor by the end of the day so they’ll be ready the next time you log back into the game.
On the other hand, you can still buy cheaper decor if you only need a very small amount of flowers to level up your account or unlock a particular scene. This way, you don’t have to wait too long for just a handful of flowers to progress.
Upgrading your estate, too, requires a certain waiting period, but this is something you can start anytime, provided you have all the required construction materials. Upgrading your estate or other buildings like the fountain will take several hours so the earlier you can begin this, the better.
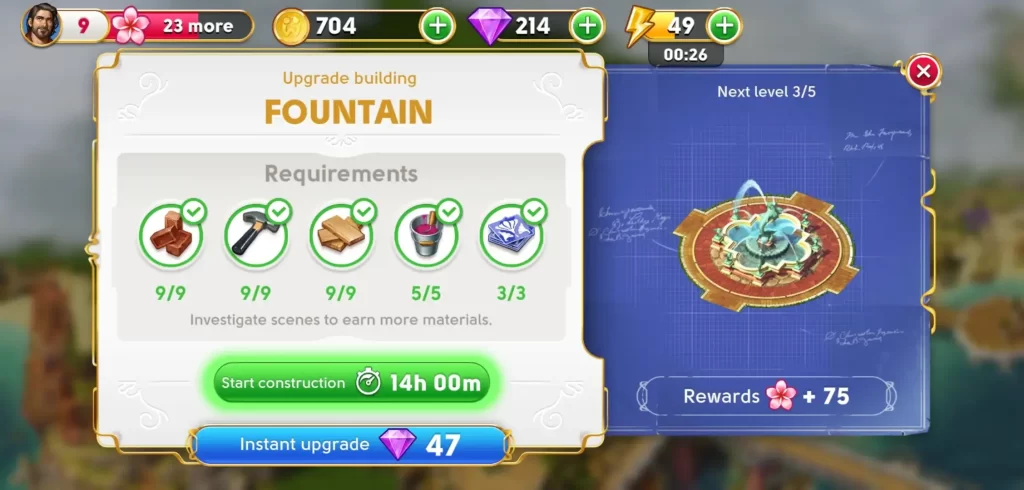
When this is done, you’ll be able to collect extra coins from these spots. The higher the level of these buildings, the more coins you can get.
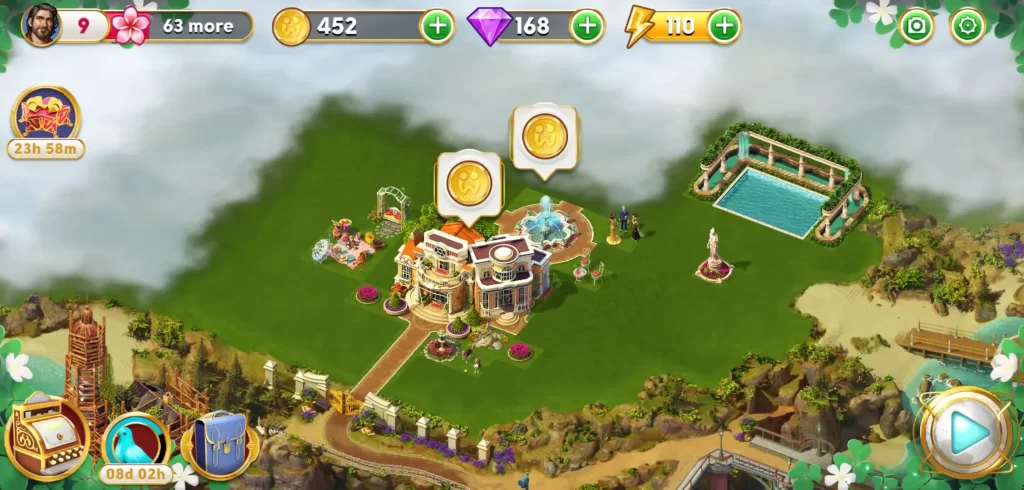
Barring aside how many flowers you can earn, you can always just have fun decorating Orchid Island and the area surrounding your estate. Of course, you will need ample space to place all the decor you’ve bought, so don’t forget to click on the foggy areas to know how many stars and compasses you need to unlock those spots.
Each expandable spot requires a different number of compasses and stars so you technically can’t choose which foggy area you want to access first because of these varying requirements, unless you skip the expansion for one spot and pick the one you desire when you’ve earned enough stars and compasses for it. Otherwise, keep playing the hidden objects game and claiming rewards so you can accumulate expansion requirements.

Similarly, progressing the main story by unlocking more chapters may also give you access to other spots in Orchid Island. For instance, you can start renovating the lighthouse when you reach Chapter 3. When you reach Chapter 7, you’ll be able to access the hangar to the west of the island.
Some other spots, on the other hand, will require the complete renovation of other areas to be accessed. For example, this cottage on the northeast side of the estate can only be accessed when the lighthouse has been completely renovated.
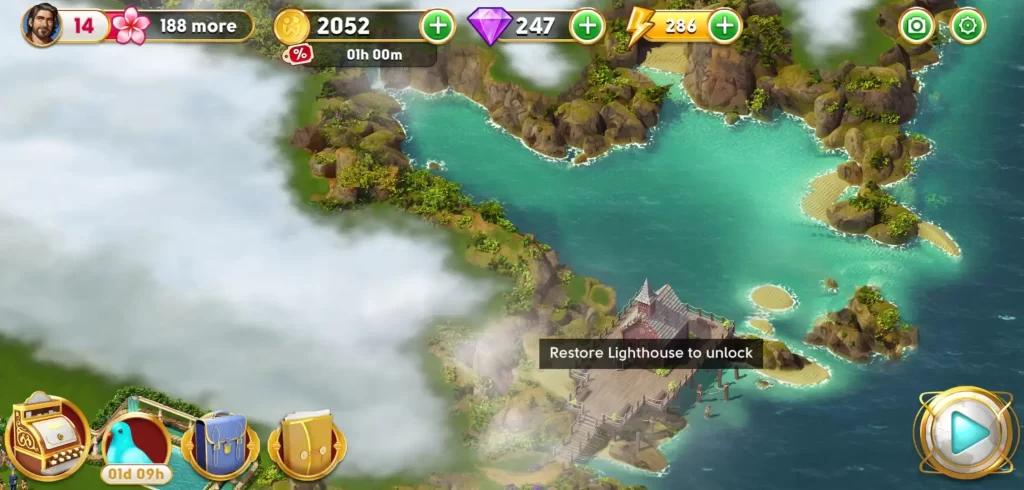
On the other hand, the airplane on the east side can only be unlocked when you’ve earned 60 stars.
Occasionally check what needs to be upgraded and renovated in Orchid Island so you can unlock more features and, consequently, more modes and rewards.
Complete Challenges and Tasks
As with any mobile game, tasks and challenges will spring up from time to time. These are avenues from which you can earn additional rewards apart from playing the main game. During our run, we were able to catch the event for the Elegant Gazebo, which is an exclusive decor piece you can gain by earning points from buying specific decor.
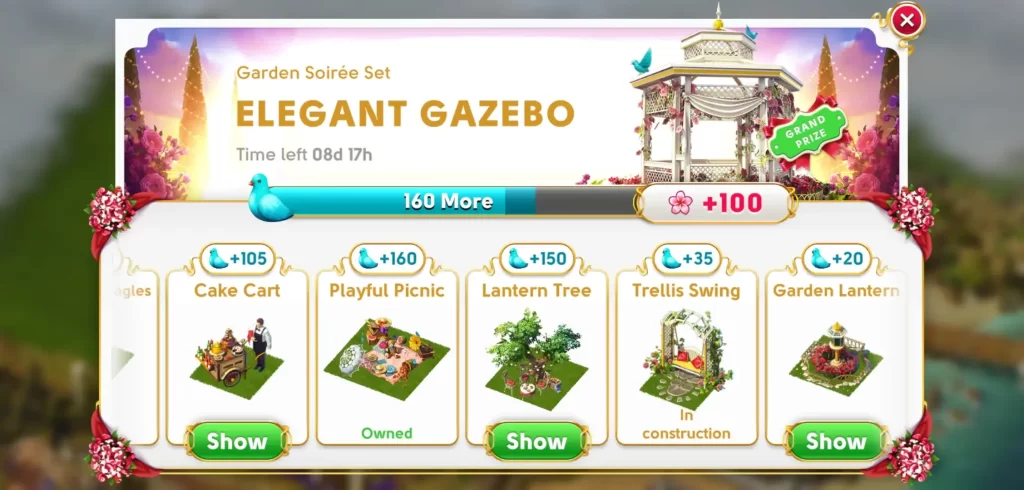
Basically, you simply need to buy the decor indicated in the list to earn the Elegant Gazebo. Each time you buy these specific decor, you gain points that will fill up a bar. Once the bar has been filled, you’ll be rewarded the Elegant Gazebo, which will give you an extra 100 flowers.
Similarly, we also caught the Help Wanted challenge, which is a set of tasks you can accomplish to earn rewards like energy or coins. Tasks can include just about anything, from finding a certain amount of hidden objects to playing a number of scenes, and so on.
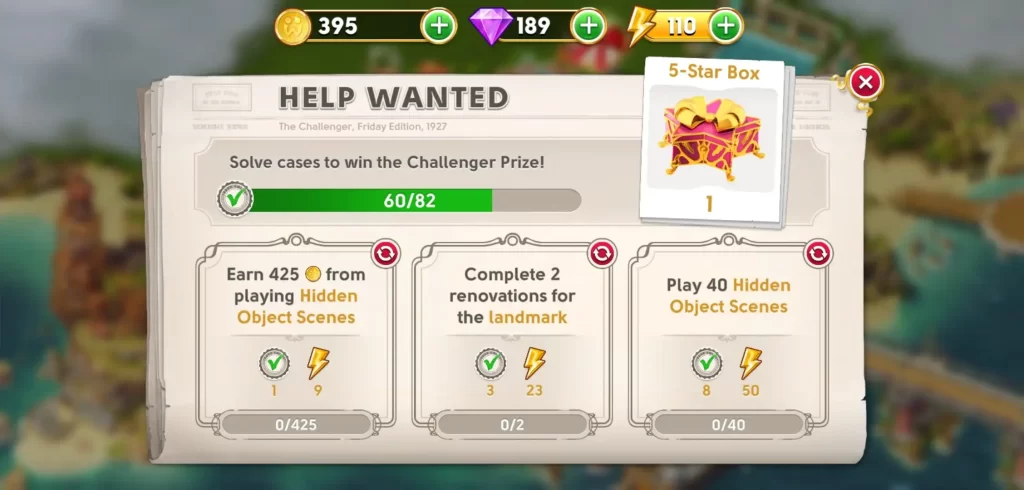
Frequently check which tasks are needed to be fulfilled so you can gain additional rewards. Don’t forget to claim these rewards as well so the task will refresh into a new one. Upon claiming rewards for a completed task, you will have to wait a few hours to view the new task, unless you watch an ad.
Watch Ads for Perks
Ah yes, ads, they’re a staple in mobile games. Though they can sometimes break your immersion from the game, ads in June’s Journey are helpful in that they offer a handful of perks in exchange for 30 to 45 seconds of watch time. Here are just some of the things that you can gain whenever you watch ads:
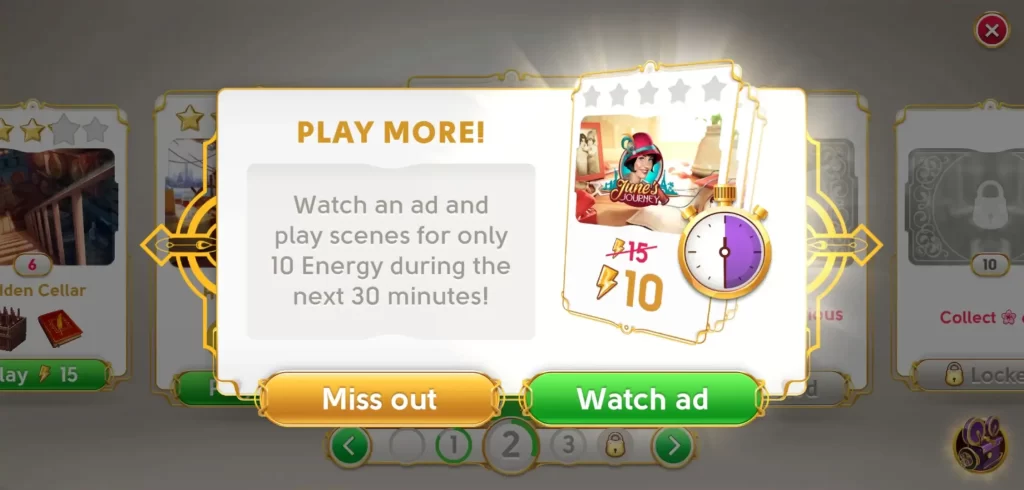
- Reduced energy expenditure: Before playing any scene, you can click on the purple button at the lower right-hand side of the screen so you can watch ads. Doing this will lessen the cost of playing scenes from 15 energy to just 10 energy for a duration of 10 minutes. Once your 10 minutes are up, you may watch another ad so you can bring the energy cost back down to 10 once more.
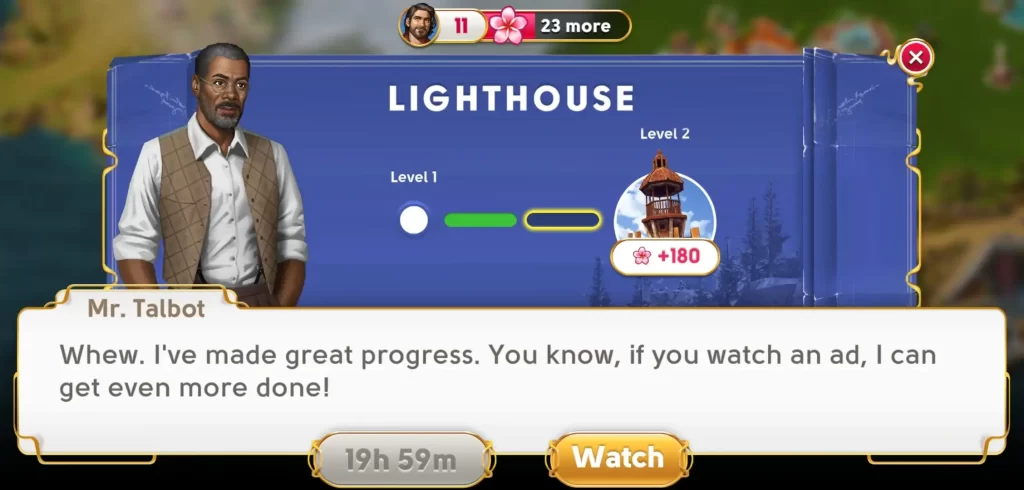
- Building renovation: Let’s say you’ve unlocked the lighthouse, which is in need of renovation. The only way you can actually renovate this spot is by watching ads. Depending on how far you’ve progressed into the renovation phase, you’ll need to watch a minimum of 1 to 2 ads. Once the renovation phase is completed, you’ll have to wait around 20 hours to be able to continue renovating the area. This way, you don’t have to watch ads continuously and the game actually gives you sort of a break from playing.
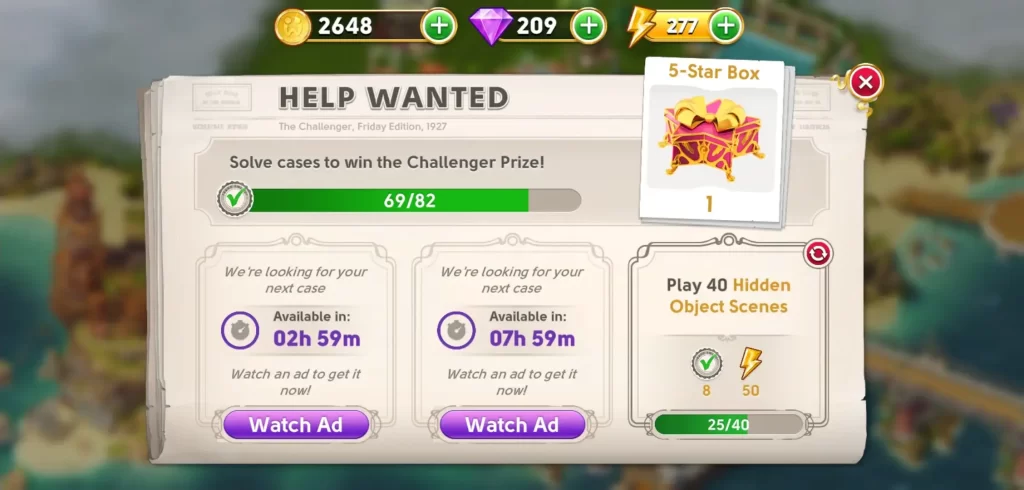
- Refresh tasks instantly: This one specifically applies to when you’ve encountered the Help Wanted challenge or other similar challenges. As we mentioned in the previous section, you’ll have to wait a couple of hours before you can view new tasks. However, you can skip this waiting time once you watch an ad for each new task you want to view instantly. Between waiting a couple of hours and watching a short ad, the latter sounds like a reasonable compromise so you can continue completing tasks and not waste energy without gaining additional rewards.
This brings us to the conclusion of our beginner’s guide for June’s Journey! Hopefully, our bag of tips and tricks are able to help you find objects faster, complete scenes with higher scores, maximize your energy points, and earn more rewards! Who do you think is the real killer? What’s the object you had the most difficult time finding? Do you have other tips for your fellow detectives? Share your thoughts in our comment section below!
Monday 22nd of April 2024
What are the golden keys and silver skips for?
Wednesday 14th of February 2024
I lost everything, I was already on the 3rd island
lucille Traylor
Monday 5th of February 2024
How to get rid of Big Box being charged to amazon
How to rid hidden box
Saturday 13th of January 2024
i like june's journey except for the snakes that are in the puzzles so much

In-game ad troubleshooting tips for mobile devices
- Please quit and reopen the app
- Restart your device - yes, we know “Have you tried turning it off and on again?”...but it does work most of the time!
- Please ensure that you are running your device on a stable connection. Anything above 5mbs down should be adequate. You can test your connection here . We recommend running our games on a wifi connection to ensure the best performance and to avoid any additional carrier charges.
- Please ensure your game is up to date by visiting the relevant App Store page. If you see an “Open” button, then you are running the latest game version available.
- Please make sure that you are also running the latest available operating system for your device. For Android: Settings > System Updates > Check for Updates For iOS: Settings > General > Software Update
- Allow your ads to be tracked - in your device settings. Enabling Limited Ad Tracking or changing your Ad ID may cause issues with in-game ads such as availability or seeing the same ads displayed repeatedly.We recommend having this option disabled for optimal performance. For Android: Settings -> Google -> Ads -> Uncheck “Opt out of Personalized Ads” For iOS: Settings > Privacy > Advertising -> Uncheck “Limit Ad Tracking”Please do not “Reset Advertising ID” on either device.
- The subject of the ad
- At what point in the game was the ad shown?
- Was there a close button?
- If available, screenshots are very helpful.
Related articles
Need more help?

Hot Five: Niantic has a new star, Epic warns of "degradation in quality", and new games hit the market
- Multi-platform
- Monster Hunter Now

Week in Views - What caught our eyes in the last seven days
- Week That Was
- Cross-platform
- Honkai: Star Rail
- Mobile Ports

PocketGamer.biz Podcast - Hot gaming trends and ad formats that are losing steam

Mobile Mavens: Can we preserve classic mobile games forever?
- Mobile Mavens
- Preservation
- mobile gaming

PocketGamer.biz podcast - Finding and growing your niche
- Sports Management

PocketGamer.biz Podcast - gaming for good

Week in Views - What caught our editorial eyes in the last seven days
- Hypercasual
- interstitial ads
- Intrinsic ads
- weekly digest

Hall of Fame: Jani Karlsson and pioneering the earliest days of the mobile games industry
- Hall of Fame

Subscription services are growing fast, but unlikely to become the dominant form of monetisation
- Monetisation
- Subscription
- Xbox Game Pass

What is driving the insatiable demand for mergers and acquisitions?
- Acquisition

Top 10 games industry jobs to apply for this week
- Jobs in Games
- Jobs Weekly
- United Kingdom

How does Hot Wheels Unlimited monetise?
- IAP Inspector

Pokemon Day: How are The Pokemon Company's recent mobile releases performing?
- Pokemon Masters
- Pokemon Home

2017 - the year not much happened in mobile games, says Verto
- Chart of the Week

The internet reacts to the Nintendo Switch reveal
- Nintendo Switch

The Promiscuous Gamer enters a Marvel Avengers Alliance (2) and meets his Dream Girlfriend
- Promiscuous Gamer

Why we need more games without Nolan North's voice in them
- Going Global

Why it's significant Kabam has gifted all The Hunger Games' players $0.14
- Reciprocity

Not immune but Finland has given GamerGate the cold shoulder

PG.biz week that was: 100m Android devices, 33.5% of Infinity Blade's revenues from IAP, GREE's Q3 sales up 77% to $198m, and ngmoco is lost in translation

PG.biz week that was: Gamevil likes Amazon Appstore, Honeycomb will be open, AGON stops, Zipline starts, HTC profits, Xoom hasn't, 4th & Battery rejected, and Apple gets game PR

Hot Five: Flying the freemium flag, Disney scores a direct hit and why CSR Racing haters are xenophobes

AI everywhere: Using neural networks for asset creation, marketing and more
- Artificial Intelligence
- neural networks

Hear MORE from the experts - eight MORE fabulous fireside chats from PGC London 2024
- pocket gamer connects london

Mobile Mavens: What's the state of play for the MENA region?

King’s Paula Ingvar: a games industry journey from "I’m not worthy!" to Candy Crush Soda’s VP of product
- Swedish Games Industry
- Candy Crush
- Careers in Games
- industry insight

Hot Five: Supercell’s Squad Busters levels up, retro Nintendo on iOS, and Genshin Impact’s worst month yet
- Soft Launch
- Squad Busters
- retro games

Week in Views - Squads busted, Apple crushed, War zoned and Snoozin' with the Snorlax…
- Augmented Reality

Speaker Spotlight: Dubai Future Foundation's Faisal Kazim on leading Dubai's gaming charge
- Speaker Spotlight

Have Supercell's changes supercharged its revenue?

48 top mobile games in soft launch: Squad Busters, CSR 3, Plants vs. Zombies 3, LEGO Hill Climb Adventures, and more

"Gaming in MENA is just starting. Investment will bring more attention to the region and create more opportunities"

King’s Trevor Burrows on the power of art: "We could see our numbers literally dropping"
- Art direction
- Player-feedback

New release roundup: The best new mobile games from cartoony cats to sports stars
- Rhythm Games

ESL FACEIT and Qiddiya Gaming discuss establishing gaming district in the KSA amidst MENA growth

Nifty Craft founder Vince Ghossoub on making a card battler MMO and growth in the MENA region

Maysalward, Tamatem and Nifty Craft CEOs on Savvy Games Group's KSA and MENA investment


Speaker Spotlight: Dubai NEXT's Aisha Alazab on transforming ideas into successful campaigns and funding

Speaker Spotlight: Applovin's Pankaj Choudhary talks 360 strategies for successful app marketing

"Squad Busters is a love letter to Supercell IPs"

Supercell’s Head of Live Games Sara Bach talks company changes, world-beating live ops, and how to get back on top
- Company Development

“We’re making it so anyone can create anything on Roblox. The only limit is their own creativity”
- User Generated Content
- Generative AI
- App Store Metrics
- Company Directory
- The Charticle
- The IAP Inspector
- Advertising
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Sign up to PGBN

Roblox launches video ads, partnering with IAS to deliver transparent metrics
- Video Advertising
- Immersive Ads

LinkedIn gets games as three puzzlers go live on the workplace social service
- Social Media
- mobile games

Brawl Stars has already earned more in 2024 than the entirety of 2023
- Brawl Stars
- Revenue Growth

Revolutionising feedback: Pocket Gamer Connects partners with AI-powered tool Voop
- user feedback

Partner events are the latest trend in Monopoly GO!, Royal Match and Project Makeover
- In-game Events
- Dubai GameExpo Summit

Belka Games lays off 20% of workforce as it becomes "more critical" of future titles
- Restructure

How user consent for personalised ads can significantly increase your Android revenue

Supercell invests in web3 startup GFAL led by King, EA and Activision Blizzard veterans

Everyone loves Nintendo… Delta emulator hits 4.4 million downloads in its first week
- Alternative App stores
- Sideloading

Supercell's Squad Busters launches globally on May 29th

Supercell’s Squad Busters soft launches today with over 100,000 Google Play downloads

Supercell’s Squad Busters ranks No. 1 for App Store game downloads in all soft launch countries

Pika fight… Pokémon Go just put prices up 1300% in Turkey

Carv raises $10M series A to simplify data monetization for gamers

Meta's VR/AR woes continue with new $3.8 billion loss
Dubai gameexpo summit 2024.
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
The MENA Games Industry Awards 2024
Gamedev atlantic 2024, mobidictum meetup berlin may 2024.
Berlin, Germany
Mobidictum Meetup Tallinn May 2024
Tallinn, Estonia
Israel Mobile Summit 2024
Tel Aviv, Israel
WN Conference Istanbul 2024
İstanbul, Turkey
DevGAMM Vilnius 2024
Vilnius, Lithuania
Pocket Gamer Connects Helsinki 2024
Helsinki, Finland
Develop: Brighton 2024
Brighton, UK
Mobidictum Meetup Barcelona September 2024
Barcelona, Spain

AppsFlyer’s Adam Smart on why cross-platform is the future

The key to successful hypercasual prototypes
- Game Development

Rusty Lake co-founder Robin Ras celebrates success and shares what's next for the studio

Sybo and Outplay on the collaboration behind Subway Surfers Blast
- Subway Surfers

Fingersoft CEO Jaakko Kylmäoja on the future of their hit Hill Climb Racing
- Hill Climb Racing

Are in-game ads the answer for developers? We asked Marc Merrill of Riot Games

A recipe for success: bringing intrinsic in-game ads to Cooking Diary
- Development

Five reasons why it’s more critical than ever to look to in-game advertising
- In-game Advertising

Phoenix Games acquires live operations studio PopReach Games India

Kwalee moves into casual games for Text Express: Word Adventure
- Partnerships

Multi-million funding to ignite growth for UK games studios

Auctus Capital Partners and Remote Control to invest in European games companies

A16Z doubles gaming investment with $600M fund as part of $7.2B fundraise

Indie gamers Avalon gear up for global launch with $10 million investment

Honkai: Star Rail zooms beyond $1 billion on its first anniversary
- Anniversary

Call of Duty Warzone: Mobile generated 'just' $6.92 million in its first month
- Global launch
- Call of Duty

Honkai: Star Rail earned more than double Genshin Impact’s revenue in March
- Revenue Gap
- Genshin Impact

Ramadan sparks rise in Middle East mobile app downloads and purchases

War Robots blasts past $900 million as shooter celebrates 10 years since launch

UK video games market hits £7.82 billion valuation with mobile up 4.5%

Hear from the experts - eight fabulous fireside chats from PGC London 2024

Microsoft and Activision Blizzard: The complete timeline
- Activision Blizzard Acquisition

From Wooga to Innplay Labs: Inside Playtika’s shopping spree

The Top 50 Mobile Game Makers of 2023
- Top 50 Mobile Game Makers 2023

Marvel Strike Force, Stumble Guys, and GSN: What has Savvy Games Group bought?
- Marvel Strike Force
- WWE: Champions

Seven more fireside chats with the mobile world's movers & shakers from PGC London 2023

Eight fireside chat interviews with the industry’s best and brightest at PGC London 2023
- Pocket Gamer Connects

Pocket Gamer Connects Advent Calendar: Days 23-24: A final thank you and happy holidays!
- Advent Calendar
- PGC London 2023
Count of active applications in the App Store
Total Active App (currently available for download): 5,605,622
Total Inactive Apps (no longer available for download): 213,606
Total Apps Seen in US App Store: 5,819,228
Number of Active Publishers in the US App Store: 1,725,655
Application Category Distribution
Most Popular Categories
- Games (1,101,794 active)
- Business (566,699 active)
- Education (487,705 active)
- Lifestyle (472,561 active)
- Utilities (389,966 active)
Making history and smashing milestones with June's Journey
Wooga’s vice president of games martin müller celebrates june's journey $1billion milestone.

A subsidiary of Playtika, Wooga, announced in November that its flagship title, June’s Journey, had achieved $1 billion in revenue . In addition, this also meant it was the first German mobile game to reach such heights in the past six years. June’s Journey stands as the highest-grossing hidden object game on both the App Store and Google Play, with a large number of female players accounting for its player base.
We spoke with Wooga ’s vice president of games, Martin Müller, who shared his insight into why June’s Journey has been able to achieve such highs and how an inclusive and diverse audience has not only played a part in that success but also how it plays a significant role in Wooga’s workplace culture.
PocketGamer.biz: June's Journey recently reached the massive milestone of the $1 billion mark. How do you feel about this accomplishment and what do you believe made it possible?
Martin Müller: I’m incredibly proud of the Wooga team for this outstanding achievement. The key factor contributing to our success lies in our continuous commitment to listening to our players. By understanding their gameplay habits and motivations, we have enhanced and expanded the game over the past six years, leading to this impressive milestone.
Since the beginning of Wooga, our goal has been to develop games that are inclusive and engaging for a diverse audience.
A huge percentage of June’s Journey players are women over 55, an audience that is overlooked in many other games but has been a critical factor for success here. How did you engage so deeply with these players and nurture a loyal fanbase?
Since the beginning of Wooga, our goal has been to develop games that are inclusive and engaging for a diverse audience. As a natural outcome, our games have garnered a large female player base. One way we’ve strengthened this relationship with our longtime players is through special annual events celebrating the anniversary of June’s Journey. These events involve inviting players to take part in contests, creating opportunities for face-to-face interactions.
This deliberate initiative has played a crucial role in fostering a community and establishing lasting connections with our players. However, engaging our community of players goes far beyond yearly anniversary celebrations. Throughout the year, the game provides many ways for our players to form tight-knit gaming communities by engaging with our club features or via in-game events.
How could other developers do more to make their games more inclusive? Any advice you could offer?
For us, embracing diversity, equity, and inclusion is of utmost importance. It goes beyond our hiring practices and workplace culture all the way to our stories and in-game characters. Creating a rich and inclusive narrative starts by forming a diverse team responsible for writing the stories and developing characters.
We also place a high priority on thorough testing with players, actively seeking their input through processes like UX testing. Embracing diversity will always remain a fundamental aspect of our approach. The key for me is to not have an agenda or try to place specific messages into the story. The world is a rich and diverse place and our stories reflect that. We neither exaggerate nor shy away.
June’s Journey is also the fastest German mobile game ever to reach these heights and is now the highest-grossing hidden object game worldwide! What do you think sets the game apart from others?
The game offers an immersive experience by captivating players with an engaging story set in the vast world of June. Over the years, we have consistently introduced new features and extensions to cater to a wide range of player interests. For example, story enthusiasts can delve into additional side stories, social players can collaborate with their club members to solve cases, and those seeking competition and challenge can participate in competitive events.
How do you reflect on the game’s journey so far and what comes next?
We face challenges in acquiring new users due to rule changes across various platforms, such as IDFA two years ago and subsequent adjustments by Google.
Looking ahead, we are dedicated to continuously serving our players and community for the long haul. We have numerous ideas to improve and broaden the June's Journey experience. With players actively involved for over five years in our in-game community, our ongoing goal is to consistently bring joy and inspiration to these dedicated participants.
What do you think are some of the biggest market challenges right now and how can we combat them?
As a market leader in our genre, it is our responsibility to generate innovative ideas that improve the experience, making sure our game remains enjoyable, engaging, and immersive in the ever-changing world of gaming. To achieve this, we prioritise a continual and thorough understanding of our user base.
In addition, we face challenges in acquiring new users due to rule changes across various platforms, such as IDFA two years ago and subsequent adjustments by Google. These changes have impacted user acquisition strategies across the gaming industry. To address this, we are placing a strong emphasis on building a robust community and encouraging word-of-mouth promotion. Our goal is to cultivate advocates within our player base, ensuring ongoing engagement and long-term gameplay.
What about the mobile market in general excites you most right now?
The most exciting aspect is the heartfelt appreciation we receive from players. The ability to hear firsthand how our work positively impacts their lives is one of the reasons why working in this industry is truly fantastic. Games are no longer played exclusively by hardcore gamers on stationary game devices. We can entertain anyone now, anywhere at any time.
Finally is there anything else you can tell us about what Wooga is working on or what we should be on the lookout for?
I assure you that our team is tirelessly working on innovative projects that we believe will bring a lot of excitement and entertainment to our players.
- Hidden object
- Demographic

Paige is the Deputy Editor on PG.biz who, in the past, has worked in games journalism covering new releases, reviews and news. Coming from a multimedia background, she has dabbled in video editing, photography, graphic and web design! If she's not writing about the games industry, she can probably be found working through her ever-growing game backlog or buried in a good book.
Related Articles
Hot five: unity 6, monopoly go’s major milestone and supercell’s creator support, june’s journey’s $1billion revenue makes german gaming history, wooga celebrates $500 million milestone, june's journey saw 178,000 try to solve its railway riddles campaign, wooga is bringing its players together to solve a new murder mystery in june's journey.
Get Pocket Gamer Biz in your inbox
- Daily Updates
- Weekly Updates
Top Stories

Games Industry Jobs

Popular Stories

GameFounders' Kadri Harma On Unlocking The MENA Game Market

Fireside Chat: How AI is Shaking up Game Development in 2024, Craig Chapple SM & Tom Pigott, Ludo.ai
Pgbiz on facebook, to get pocket gamer biz in your inbox.

- WALKTHROUGHS
- Cheats & Tips
- Redeem Codes
- Game Guides
Questions and Answers for June's Journey - Hidden Object
This is our page for asking and answering questions for June's Journey - Hidden Object. If you have a question you can ask it below and please check through the questions that have already been asked to see if you can answer any.
Ask a question for June's Journey - Hidden Object
The members with the know how for June's Journey - Hidden Object
AppGamer - Mobile Game Guides and News since 2008.
AppGamer.com is owned by Web Media Network Limited , UK company number 3783771.
© 2023 Web Media Network Limited, 86-90 Paul Street, London. EC2A 4NE. United Kingdom.
All rights reserved. No part of this website or its content may be reproduced without the copyright owner's permission.
This site is not affiliated in any way with Google, Apple or any video game publishers.
- Introduction
- Hints and Tips for June's Journey
- How to get support in June's Journey
- How to change the Text Color in Messages
- How to add icons in your club chat messages
- June's Journey - Hidden Object Redeem Codes (May 2024)
Display Name
Age -- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
The Secret Push That Could Ban TikTok
U.s. lawmakers have long worried that the chinese government could use the app to spread propaganda..
This transcript was created using speech recognition software. While it has been reviewed by human transcribers, it may contain errors. Please review the episode audio before quoting from this transcript and email [email protected] with any questions.
From “The New York Times,” I’m Sabrina Tavernise. And this is “The Daily.”
[THEME MUSIC]
American lawmakers have tried for years to ban the video app TikTok over concerns that its ties to China pose a national security risk. Last week, they passed a law that might finally do it. Today, my colleague, Sapna Maheshwari, on the secret effort behind the law and what a ban would mean for the company’s 170 million American users.
It’s Tuesday, April 30.
So Sapna, tell me about this law that just passed that potentially bans the social media app TikTok. We’ve seen efforts in the past to rein in TikTok, but this one really seems like the most substantial yet.
It’s a huge deal. What this law really does is it puts the future of this hugely popular app with 170 million American users into question. TikTok has reshaped the way many people listen to music. It’s changed the way we cook. It’s made a whole different kind of celebrity.
But it’s never been able to shake these concerns around the fact that it has really close ties to China. It’s owned by a Chinese company, ByteDance. And lawmakers, for years, have been worried that the Chinese government could somehow use ByteDance and TikTok to get information on Americans or possibly spread propaganda.
President Trump tried to ban it in 2020. The State of Montana tried to ban this app last year. TikTok has largely survived those challenges, but this time it could actually be banned in the United States.
So let’s talk about this. Why did this effort succeed where the other ones failed?
So it’s an interesting story.
Here we go.
The committee will come to order.
And it really dates back to this hearing about a year ago that Congress had with Shou Chew, the CEO of TikTok.
Mr. Chew, you are here because the American people need the truth about the threat TikTok poses to our national and personal security.
Members of the committee, thank you for your time.
— TikTok has repeatedly said that it has addressed these national security concerns and that there’s no issue here. And you can hear that when Shou Chew testified.
Let me start by addressing a few misconceptions about ByteDance of which we are a subsidiary. ByteDance is not owned or controlled by the Chinese government.
He’s saying American investors are behind ByteDance.
Now, TikTok itself is not available in mainland China. We’re headquartered in Los Angeles and in Singapore.
And I myself am Singaporean. I live in Singapore.
The bottom line is this — American data, stored on American soil, by an American company, overseen by American personnel.
And we are actually going above and beyond what American technology companies do to keep things safe.
And I look forward to your questions. Thank you very much.
And is Congress convinced by that?
Congress is not convinced by that.
ByteDance is a Chinese company?
Well, ByteDance owns many businesses that operates in China.
Is it or is it not a Chinese company?
Congressman, the way we look at it, it was founded by Chinese entrepreneurs.
No, no, no, no. I’m not asking how you look at it. Fact, is it a Chinese company or not? For example, Dell is a company —
It was this really fiery, five-hour hearing, where Republicans and Democrats asked really contentious questions.
We do not promote or remove content at the request of the Chinese government. Will you repeat —
The question is, are you percent certain that they cannot use your company to promote such messages?
It is our commitment to this committee and all our users that we will keep this free from any manipulation by any government.
OK. If you can’t say it 100 percent certain I take that as a no.
There’s this underlying sense of distrust around the company and its ties to China.
I will remind you that making false or misleading statements to Congress is a federal crime.
I understand. Again, you can go on our platform. You will find that content.
And it becomes clear through the hearing that, across the board, Republicans and Democrats largely feel the same way.
Mr. Chew, I got to hand it to you. You’ve actually done something that in the last three to four years has not happened except for the exception of maybe Vladimir Putin. You have unified Republicans and Democrats.
So within weeks of this hearing, this small group of lawmakers gets together. And they say, let’s come up with a law that works where all the other ones have failed and actually make TikTok answer to its Chinese connections once and for all.
So tell me about this small group of lawmakers. Who are they?
So it starts with Republicans. Among them is Steve Scalise, one of the most powerful Republicans in the House. And a small group sort of works together for a few months, but they realize that in order to really make this law work, they’re going to need Democrats. So they end up working through this House Committee that’s focused on China and competition. And this is where the bulk of the work on this bill takes place.
And just to note, this is a really small group. There’s less than 20 key players who are working on this. And all throughout, they are keeping this very, very secret.
And why exactly are they keeping it secret? What’s the point of that?
So this group really wanted to keep this out of the eyes of TikTok, which has a huge lobbying presence in DC, and has successfully worked to kill bills that targeted TikTok in the past. And what they’re really doing is looking at all of the past efforts to either force a sale or a ban of TikTok, and trying to work their way through why those plans didn’t succeed and what they can do differently.
But while the lawmakers are working on this bill, something big happens that kind of changes the politics around it. And that’s October 7.
Your social media feeds are unique to you, but could they be shaping how you view the Israel-Gaza War? The BBC’s —
As the war breaks out and people start getting information about it, a lot of people are getting information about the Israel-Hamas War on TikTok, especially young people.
Social media algorithms seem to be driving some users towards increasingly divisive posts —
And there’s this big messy argument spilling out into living rooms and all over the internet, and, of course on TikTok. And it’s getting very heated. For instance, there’s this moment in the fall where a bunch of TikTok users start sharing this old manifesto.
I read Osama bin Laden’s “Letter to America.”
It’s wild, and everyone should read it.
Go read “A Letter to America.” Seriously, go read it.
That was actually written by Osama bin Laden, defending the 9/11 attacks and criticizing the United States’ support of Israel. TikTok users start trying to tie it to the modern day conflict.
Reading this letter, it becomes apparent to me that the actions of 9/11 were all just the buildup of our government failing other nations.
The way this letter is going viral right now is giving me the greatest sense of relief. Now it’s all coming to light because of Palestine.
And there’s these accusations that TikTok may be promoting one side of the conflict over the other. And a couple of researchers look at hashtags around Palestine, and they say that the data they pulled shows that TikTok is showing way more pro-Palestine videos and not so much for Israel. And this sets off huge alarm bells for this small group of lawmakers.
But isn’t that just a function of the fact that TikTok, at this point, is the public square in the United States for young people? I mean, this is what young people were talking about, and this is where they’re doing the talking.
TikTok has pushed back really forcefully against these accusations. They said that Gallup polls show that young people view Israel differently than older generations. They say that they’re not the ones influencing what people post, that the hashtags and the videos are a reflection of the user base and nothing that they’re doing to influence.
But for lawmakers, this doesn’t really make their concerns go away. Instead, this conflict shows them how TikTok could be used to spread propaganda. It made lawmakers feel that TikTok could be really dangerous when it comes to shaping the views of Americans on foreign policy, on US elections. And what it also does is, it provides this driving force to this group that’s drafting this bill. And they suddenly see that this might be a way to bring more people into their effort.
And so heading into November against this backdrop, they even bring in the White House and the Justice Department to help work on this bill. And with the White House, they want to make sure that this is a bill that the president will support. And they work with the Justice Department to shore up the language in the bill to help defend against court challenges.
Because the Justice Department, of course, would be the one that would have to defend the bill, right?
That’s exactly right. And so they’re trying to make it as rock solid as possible so that they can win in court when TikTok challenges this law. And so March rolls around, and they decide that it’s time to unveil this bill that they’ve been working on for close to a year.
The battle over TikTok on Capitol Hill is intensifying.
This morning, House lawmakers have agreed unanimously to move a bill to a full floor vote.
And TikTok is caught completely flat footed. They didn’t see this coming. And this is just what the group wanted. So TikTok has this army of lobbyists that’s suddenly scrambling. And they go into damage control mode. They start reaching out to members of Congress.
This app is so much more than just an app for dumb TikTok dances.
They fly a group of TikTok stars and small businesses to come to DC —
This is a life-changing apps.
— and lobby on the steps of the Capitol and meet with lawmakers.
Standing up here with all these amazing TikTokers behind me is a complete honor, and every single one of them would voice their opinion just like this. This is how we feel. This has to stop.
They set up interviews between these TikTok creators, as they’re known, and big TV shows and news programs. And they’re doing everything they can to fight against this bill before it goes any further. And then they decide to do something unusual, which is use TikTok itself to try and derail this bill.
How exactly do they do that?
So days after this bill is announced, a ton of TikTok users get a message when they open the TikTok app that basically says, call Congress and tell them not to ban TikTok.
Hmm. OK. So like, literally this window comes up and says, call Congress. Here you go.
Exactly. You can enter your zip code, and there’s a button that appears. And you can press it, and the call goes straight to your representative.
So offices are quickly overwhelmed by calls. And TikTok sent out this message to users on the same day that a House committee is going into vote on this bill and whether to move it forward. And so the stunt happens. They go into vote, and they come out, and it’s 50 to 0 in support of the bill.
One of the representatives who worked on the bill said that this stunt by TikTok turned a lot of no’s into yeses and yeses into, quote, “hell yeses.”
[LAUGHS]: so the whole episode sounds like it actually backfired, right? Like, TikTok’s stunt essentially just confirmed what was the deepest fears of lawmakers about this company, that the app could be used to influence American politics.
That’s definitely how a lot of lawmakers viewed it. And when this bill is brought to the full House a week later, it passes by an overwhelming majority. And weeks later, it passes in the Senate as part of a broader aid package. And on Wednesday, it’s signed into law by President Biden.
But now the question is, what does it mean? Like, how will this actually work? And how will it affect the tens of millions of Americans who use TikTok every day?
[MUSIC PLAYING]
We’ll be right back.
So Sapna, now that Biden has signed this bill, what does it actually mean in practice for TikTok? What does the law do?
So the law is really trying to push ByteDance, the company that owns TikTok, to sell to a non-Chinese owner. And the company basically has nine months for this sale to happen. There’s an option for President Biden to add another three months to that clock. And if the company doesn’t find a buyer or refuses to be sold, it will be banned.
And what would a ban actually mean, Sapna? I mean, people would still have the app on their phones, right? So it wouldn’t disappear overnight.
Yeah, no one’s coming to pick up your phone and to forcibly delete this thing. What the law says is that app stores and web hosting services wouldn’t be allowed to carry TikTok anymore. So basically, it would kind of die a slow death over time, where it wouldn’t be updated and just kind of peter out.
So the bottom line here is that the clock has started on this potential sale, right? They have 12 months to find a buyer. So what are the obstacles here? I mean, it sounds pretty ferociously complicated.
There’s a ton of challenges here. And it’s a very messy choose-your-own adventure. So one of the first big questions is who could buy this?
ByteDance and TikTok are private. We don’t know their financials. But analysts estimate that it will cost tens of billions of dollars. That narrows the buying pool pretty quickly. And a lot of the companies that could afford to buy it, like Meta, the owner of Facebook, or Google, which owns YouTube, would probably be kicked out of the running because they are simply too big. Regulators would say, you already own these big apps. You can’t possibly add this to your stable.
There’d be a monopoly concern there.
Exactly. And then, there’s a lot of questions around how this would work, technically. ByteDance and TikTok are very much global organizations. You have the CEO in Singapore. They have huge operations in Ireland. They have this big workforce in the US. And of course, they do have engineers in China.
So how do you extract all those things, make it all work? It’s a very big international transaction.
And then there is the chance that the Chinese government blocks this sale and says, you cannot do this, ByteDance. We will not allow it.
So Sapna, how does that actually work, though, in terms of China? I mean, can China actually just ban the sale of this company? I mean, it is a private company after all, right?
Well, here’s one way it could work. The Chinese government could block the export of TikTok’s algorithm. And let me explain that in kind of plain English.
They could basically block the technology that fuels the TikTokiness of this app, the recommendations, the magic of it, why you see what you see when you’re looking at TikTok.
TikTokiness, is that an adjective?
That is now an adjective.
[LAUGHS]: Nice.
And there’s a chance that Beijing could say, hey, you can’t export this technology. That is proprietary. And if that happens, that suddenly makes TikTok way, way less valuable.
So the Chinese government could let the sale go through potentially, but as a kind of an empty shell, right? The thing that makes TikTok TikTok, the algorithm, wouldn’t be part of the company. So that probably isn’t very appealing for a potential buyer.
Exactly. And I mean, the role of the Chinese government here is really interesting. I’ve talked to experts who say, well, if the Chinese government interferes to try and block a sale of this app, doesn’t that underscore and prove all the concerns that have been expressed by American lawmakers?
If you’re worried about China being in control of this thing, well, that just confirmed your fears.
Exactly. And I mean, it’s an interesting thing that ByteDance and TikTok have to grapple with.
So bottom line here — selling TikTok is quite complicated, and perhaps not even possible for these reasons that you’re giving, right? I mean, not least of which because the Chinese government might not allow the algorithm to leave the country. And that’s not something that the US Congress has a lot of control over.
So is this law fundamentally just a ban, then?
That’s what TikTok is calling it. Right after this bill was signed into law on Wednesday —
Make no mistake, this is a ban, a ban on TikTok and a ban on you and your voice.
— Tiktok’s CEO made a TikTok — what else?— that explained the company’s position.
Because the freedom of expression on TikTok reflects the same American values that make the United States a beacon of freedom.
He actually argued that TikTok reflects American values.
TikTok gives everyday Americans a powerful way to be seen and heard. And that’s why so many people have made TikTok part of their daily lives.
And he said that this law infringes on the First Amendment free speech rights of Americans who love it and who use it every day.
The facts and the Constitution are on our side, and we expect to prevail again.
So it’s very clear that TikTok plans to challenge this law in court. And the court fight to follow will determine the fate of TikTok’s future in the US.
So is that First Amendment argument that the TikTok CEO is making here going to work?
Nobody wants to put money on that. I mean, the company is really approaching this with the idea that the First Amendment rights of Americans are being infringed on. But if you remember, the government has been working on this law. They’ve been anticipating those challenges. And they can justify an infringing of First Amendment rights in certain cases, including with national security concerns. And so it’ll be up to a judge on whether those concerns pass muster and justify this sale and even a potential ban of TikTok.
Got it. So TikTok will argue free speech, First Amendment. And the government will counter by saying, look, this is about China. This is about America’s national security interests.
That’s right. And the legal experts that I’ve spoken with say this is a really big and sticky area of the law, and it’s a huge case. And they really think that this will go to the Supreme Court, regardless of who wins in the first round of this.
So where does that leave the millions of Americans who use TikTok, and many of them, of course, who earn a living on the platform?
I mean, it’s really uncertain what happens now with the company, and the clock has started ticking. When I’ve looked at TikTok and looked at videos from users —
This is about the impending TikTok ban. And it just triggered me so much. It makes my blood boil, and I have to get this out there.
There’s a lot of shock —
The most success I’ve had has been here on TikTok, and now they’re trying to take it away.
This is so stupid!
— and anger.
You can’t ban apps! You can’t ban things from people!
People are confused.
Word on the street is that in the next 9 to 12 months, TikTok could be banned.
And they’re also caught a bit off guard, just because there have been these years of efforts to do something about TikTok. People on the app have been hearing about a TikTok ban, really, since 2020.
The government can take away a literal app on our phones, and we’re supposed to believe we’re free?
A few TikTokers have said, how can this be the thing that the government is pushing through so quickly?
Can we stop funding a genocide? No. Can we get free COVID tests? No. Can we stop killing the planet? No. Can we at least watch videos on an app of people doing fun things and learn about the world around us? No.
So there’s this sense of distrust and disappointment for many people who love this app.
We got rid of TikTok. You’re welcome. Protecting you from China. You know that phone was made in China. Ah!
And I think there’s also this question, too, around what about TikTok makes it so harmful? Even though it has increasingly become a place for news, there’s plenty of people who simply use this app for entertainment. And what they’re seeing out of Washington just doesn’t square with the reality they experience when they pull out their phones.
And I wonder, Sapna, I mean, just kind of stepping back for a second, let’s say this ban on TikTok succeeds. If it goes through, would Americans be better off?
It depends who you ask. For the users who love TikTok, if it actually disappeared, it would be the government taking away a place where maybe they make money, where they get their entertainment, where they figure out what to read or what to cook next. To free speech advocates, this would be dystopian, unheard of for the government to crack down on an app with such wide usage by Americans.
But for the American political class And the National security establishment, this is a necessary move, one that was years in the making, not something that was just come up with on the fly. And ultimately, it all comes down to China and this idea that you can’t have a social media app like this, a source of news like this, that is even at all at risk of being influenced by the Chinese government and our greatest adversaries.
Sapna, thank you.
Here’s what else you should know today. On Monday, in its latest high-profile showdown with pro-Palestinian protesters, Columbia University gave students until 2:00 PM to clear out from an encampment at the center of campus or face suspension. It appeared to be an effort to remove the encampment without relying on New York City Police, whose removal of a previous encampment there two weeks ago inspired similar protests on campuses across the country.
Free Palestine!
Hi, this is Sharon Otterman reporting for “The New York Times.”
00 PM deadline for protesters to clear out of the encampment at the center of Columbia University has come and gone, and there’s still quite a large contingent inside the encampment.
But Monday’s warning seemed only to galvanize the Columbia protesters and their supporters.
And hundreds of students and others from around the campus have come out to support them. They are currently walking around in a picket around the encampment.
Hundreds of students, standing for or five people deep, encircled the encampment in a show of solidarity. They were joined by members of the Columbia faculty.
There’s also dozens of faculty members, who are prepared to stand in lines in front of the main entrance to the encampment, in case Public Safety or the NYPD move in. But as of 2:00, there was no sign of that happening.
Then, on Monday evening, Columbia announced it had begun to suspend students who had failed to leave the encampment. It was unclear exactly how many students had been suspended.
[PRO-PALESTINE CHANTING]:
Today’s episode was produced by Will Reid, Rachelle Banja, and Rob Szypko. It was edited by Marc Georges and Liz O. Baylen, contains original music by Dan Powell and Marion Lozano, and was engineered by Chris Wood. Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sharon Otterman.
That’s it for “The Daily.” I’m Sabrina Tavernise. See you tomorrow.

- May 1, 2024 • 35:16 The New Abortion Fight Before the Supreme Court
- April 30, 2024 • 27:40 The Secret Push That Could Ban TikTok
- April 29, 2024 • 47:53 Trump 2.0: What a Second Trump Presidency Would Bring
- April 26, 2024 • 21:50 Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
- April 25, 2024 • 40:33 The Crackdown on Student Protesters
- April 24, 2024 • 32:18 Is $60 Billion Enough to Save Ukraine?
- April 23, 2024 • 30:30 A Salacious Conspiracy or Just 34 Pieces of Paper?
- April 22, 2024 • 24:30 The Evolving Danger of the New Bird Flu
- April 19, 2024 • 30:42 The Supreme Court Takes Up Homelessness
- April 18, 2024 • 30:07 The Opening Days of Trump’s First Criminal Trial
- April 17, 2024 • 24:52 Are ‘Forever Chemicals’ a Forever Problem?
- April 16, 2024 • 29:29 A.I.’s Original Sin
Hosted by Sabrina Tavernise
Featuring Sapna Maheshwari
Produced by Will Reid , Rachelle Bonja and Rob Szypko
Edited by Marc Georges and Liz O. Baylen
Original music by Marion Lozano and Dan Powell
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
American lawmakers have tried for years to ban TikTok, concerned that the video app’s links to China pose a national security risk.
Sapna Maheshwari, a technology reporter for The Times, explains the behind-the-scenes push to rein in TikTok and discusses what a ban could mean for the app’s 170 million users in the United States.
On today’s episode

Sapna Maheshwari , who covers TikTok, technology and emerging media companies for The New York Times.

Background reading
A tiny group of lawmakers huddled in private about a year ago, aiming to bulletproof a bill that could ban TikTok.
The TikTok law faces court challenges, a shortage of qualified buyers and Beijing’s hostility .
Love, hate or fear it, TikTok has changed America .
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
Special thanks to Sharon Otterman .
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Sapna Maheshwari reports on TikTok, technology and emerging media companies. She has been a business reporter for more than a decade. Contact her at [email protected] . More about Sapna Maheshwari
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For more tutorial videos, check out our June's Journey YouTube channel!Q: My game takes a long time to load.A: The first thing that you shou... Need Help? If you're looking at this on an Android device, tap on the Speech Bubble icon in the upper right corner of the screen.
Firstly, before playing June's Journey, close any other open tabs in your browser. Secondly, close any other non-essential programs that are running. Both of these will free up more memory for the game to load. Another thing you can do to help the game is clear your browser's cache. The game runs best on a 64-bit browser.
#June'sJourney #NotOpen #NotWorking #ProblemIn this video Tutorial, i will show you How to Fix June's Journey App Not Working Problem in Android & Ios Mobile...
Common June's Journey Problems & Solutions. Troubleshooting Guide. Complete guide to troubleshoot June's Journey app on iOS and Android devices. Solve all June's Journey app problems, errors, connection issues, installation problems and crashes. Table of Contents: June's Journey iPhone Issues and Solutions.
Discover June's Journey, the brand new hidden object game from the makers of Pearl's Peril. Find hidden clues and solve exciting puzzles across beautiful locations that draw you right into the heart of the mystery! Surprises at every turn, stunning hand drawn scenes, and a cast of glamorous characters await you in a globetrotting story game. From the heart of 1920s America to the perfect ...
To recruit for new club members, find a club, and new player information, sort your feed from NEW POSTS to HOT and COMMENT UNDER the designated sticky posts. This is a fan run subreddit for the mobile hidden objects game Junes Journey.
In this video, we will go through a few troubleshooting steps you can try if you cannot access your game and ways you can get fast, comprehensive help with any issue that may arise. Subscribe to us on YouTube for more upcoming how-to videos and extra June's Journey content! ==> https://woo.ga/JJYouTube
Rec Room is the best place to build and play games together. Party up with friends from all around the world to chat, hang out, explore MILLIONS of player-created rooms, or build something new and amazing to share with us all. Rec Room is free, and cross plays on everything from phones to VR headsets.
Click "advanced" tab. For ads: personalized. If it's already checked, then uncheck it/or vice versa. It doesn't matter what setting it is just it if not checked or uncheck if already checked. This has happened to me three times and all I have to do to get ads to play is adjust that setting. 2.
Set in the roaring '20s, June's Journey is a hidden objects game wherein you're presented with a scene and are tasked to find objects corresponding to a set of words. The mechanics of the game seem simple enough at the onset, but there's more to it than meets the eye, just like the mystery surrounding the deaths of June's sister Clare ...
June's Journey - Hey Detectives! 👋 The video ads in our... Hey Detectives! 👋 The video ads in our game help us keep it free to play, but if they do not work properly it can be frustrating. We have found that this...
Please make sure that you are also running the latest available operating system for your device. For Android: Settings > System Updates > Check for Updates. For iOS: Settings > General > Software Update. Allow your ads to be tracked - in your device settings. Enabling Limited Ad Tracking or changing your Ad ID may cause issues with in-game ads ...
The environments in June's Journey are full of weird intricacies, some of which don't even make sense. If you see something elaborate that doesn't appear in the object list in one round ...
I can play on pc, and then switch to my phone or tablet by connecting to my Fb account. 2. If the game on one device has a glitch and I have to reinstall it, the Fb connection allows me to easily restore my game progress, which I've had to do on multiple occasions. 3. If the game is disconnected from your Fb account, customer support can re ...
Tweedlepillar. • 2 yr. ago. I suggest you use Blokada (ad blocker app). It used to skip ads entirely but now counts down 35 seconds. I'd rather stare at a 35 sec countdown than "watch" any ad, especially ones that crash the game. It stops ads from playing altogether so you won't have this crashing problem. 7. Share.
sweetie4555_ Answered: I have the same problem. The game slider works but the right side of the main page doesn't. I also get a list of games on that side but only the # of people playing them. There is a " collapse " icon there, also, so you can use it to get rid of the list of games. Then you are able to play in full screen.
A subsidiary of Playtika, Wooga, announced in November that its flagship title, June's Journey, had achieved $1 billion in revenue. In addition, this also meant it was the first German mobile game to reach such heights in the past six years. June's Journey stands as the highest-grossing hidden object game on both the App Store and Google ...
Gold stars 564. It .. In order to win Sherlock level prizes in June's Journey, does your team only .. Hi. So if the change to cafe was to make things fair what was the reason to .. Hi if my account for June's journey is linked to my Facebook and I am logged .. Hi.
American lawmakers have tried for years to ban TikTok, concerned that the video app's links to China pose a national security risk. Sapna Maheshwari, a technology reporter for The Times ...