What Counts as Work Time on a Business Trip?
What is counted as working time?
Does a business trip equal work time?
Business trips during and outside of work time
Is travel time work time?
While on the business trip: work time or free time?

This may also interest you.
From the heir of the Concorde to biometric boarding: new flying experiences are coming
Compensation and Refunds
Got an unexpected meeting? Need to focus? Looking for some downtime? The number of day-use hotel amenities available is on the rise.
Bleisure: connecting “business” and “leisure”
Check out our business travel offers
- ACCOR BUSINESS OFFER Receive your negotiated rates by booking in your preferred hotels from our network of over 3,500 worldwide!
- BUSINESS PLUS MULTI-BRAND CARD This flexible offer is tailored to individual travellers as well as companies and offers up to 20% discount on hotel nights worldwide.
- CORPORATE CONTRACTS Customised contracts! Select your preferred destinations and hotels and we will offer you an annual contract with specially negotiated terms and rates.
Sign up for our newsletter to keep up to date with our special offers, new destinations and information about ACCOR.

Everything You Need to Know About the Business Travel Tax Deduction
.jpeg)
Justin is an IRS Enrolled Agent, allowing him to represent taxpayers before the IRS. He loves helping freelancers and small business owners save on taxes. He is also an attorney and works part-time with the Keeper Tax team.
You don’t have to fly first class and stay at a fancy hotel to claim travel expense tax deductions. Conferences, worksite visits, and even a change of scenery can (sometimes) qualify as business travel.
What counts as business travel?
The IRS does have a few simple guidelines for determining what counts as business travel. Your trip has to be:
- Mostly business
- An “ordinary and necessary” expense
- Someplace far away from your “tax home”
What counts as "mostly business"?
The IRS will measure your time away in days. If you spend more days doing business activities than not, your trip is considered "mostly business". Your travel days are counted as work days.
Special rules for traveling abroad
If you are traveling abroad for business purposes, you trip counts as " entirely for business " as long as you spend less than 25% of your time on personal activities (like vacationing). Your travel days count as work days.
So say you you head off to Zurich for nine days. You've got a seven-day run of conference talks, client meetings, and the travel it takes to get you there. You then tack on two days skiing on the nearby slopes.
Good news: Your trip still counts as "entirely for business." That's because two out of nine days is less than 25%.
What is an “ordinary and necessary” expense?
“Ordinary and necessary” means that the trip:
- Makes sense given your industry, and
- Was taken for the purpose of carrying out business activities
If you have a choice between two conferences — one in your hometown, and one in London — the British one wouldn’t be an ordinary and necessary expense.
What is your tax home?
A taxpayer can deduct travel expenses anytime you are traveling away from home but depending on where you work the IRS definition of “home” can get complicated.
Your tax home is often — but not always — where you live with your family (what the IRS calls your "family home"). When it comes to defining it, there are two factors to consider:
- What's your main place of business, and
- How large is your tax home
What's your main place of business?
If your main place of business is somewhere other than your family home, your tax home will be the former — where you work, not where your family lives.
For example, say you:
- Live with your family in Chicago, but
- Work in Milwaukee during the week (where you stay in hotels and eat in restaurants)
Then your tax home is Milwaukee. That's your main place of business, even if you travel back to your family home every weekend.
How large is your tax home?
In most cases, your tax home is the entire city or general area where your main place of business is located.
The “entire city” is easy to define but “general area” gets a bit tricker. For example, if you live in a rural area, then your general area may span several counties during a regular work week.
Rules for business travel
Want to check if your trip is tax-deductible? Make sure it follows these rules set by the IRS.
1. Your trip should take you away from your home base
A good rule of thumb is 100 miles. That’s about a two hour drive, or any kind of plane ride. To be able to claim all the possible travel deductions, your trip should require you to sleep somewhere that isn’t your home.
2. You should be working regular hours
In general, that means eight hours a day of work-related activity.
It’s fine to take personal time in the evenings, and you can still take weekends off. But you can’t take a half-hour call from Disneyland and call it a business trip.
Here's an example. Let’s say you’re a real estate agent living in Chicago. You travel to an industry conference in Las Vegas. You go to the conference during the day, go out in the evenings, and then stay the weekend. That’s a business trip!
3. The trip should last less than a year
Once you’ve been somewhere for over a year, you’re essentially living there. However, traveling for six months at a time is fine!
For example, say you’re a freelancer on Upwork, living in Seattle. You go down to stay with your sister in San Diego for the winter to expand your client network, and you work regular hours while you’re there. That counts as business travel.
What about digital nomads?
With the rise of remote-first workplaces, many freelancers choose to take their work with them as they travel the globe. There are a couple of requirements these expats have to meet if they want to write off travel costs.
Requirement #1: A tax home
Digital nomads have to be able to claim a particular foreign city as a tax home if they want to write off any travel expenses. You don't have to be there all the time — but it should be your professional home base when you're abroad.
For example, say you've rent a room or a studio apartment in Prague for the year. You regularly call clients and finish projects from there. You still travel a lot, for both work and play. But Prague is your tax home, so you can write off travel expenses.
Requirement #2: Some work-related reason for traveling
As long as you've got a tax home and some work-related reason for traveling, these excursion count as business trips. Plausible reasons include meeting with local clients, or attending a local conference and then extending your stay.
However, if you’re a freelance software developer working from Thailand because you like the weather, that unfortunately doesn't count as business travel.
The travel expenses you can write off
As a rule of thumb, all travel-related expenses on a business trip are tax-deductible. You can also claim meals while traveling, but be careful with entertainment expenses (like going out for drinks!).
Here are some common travel-related write-offs you can take.
🛫 All transportation
Any transportation costs are a travel tax deduction. This includes traveling by airplane, train, bus, or car. Baggage fees are deductible, and so are Uber rides to and from the airport.
Just remember: if a client is comping your airfare, or if you booked your ticket with frequent flier miles, then it isn't deductible since your cost was $0.
If you rent a car to go on a business trip, that rental is tax-deductible. If you drive your own vehicle, you can either take actual costs or use the standard mileage deduction. There's more info on that in our guide to deducting car expenses .
Hotels, motels, Airbnb stays, sublets on Craigslist, even reimbursing a friend for crashing on their couch: all of these are tax-deductible lodging expenses.
🥡 Meals while traveling
If your trip has you staying overnight — or even crashing somewhere for a few hours before you can head back — you can write off food expenses. Grabbing a burger alone or a coffee at your airport terminal counts! Even groceries and takeout are tax-deductible.
One important thing to keep in mind: You can usually deduct 50% of your meal costs. For 2021 and 2022, meals you get at restaurants are 100% tax-deductible. Go to the grocery store, though, and you’re limited to the usual 50%.
{upsell_block}
🌐 Wi-Fi and communications
Wi-Fi — on a plane or at your hotel — is completely deductible when you’re traveling for work. This also goes for other communication expenses, like hotspots and international calls.
If you need to ship things as part of your trip — think conference booth materials or extra clothes — those expenses are also tax-deductible.
👔 Dry cleaning
Need to look your best on the trip? You can write off related expenses, like laundry charges.
{write_off_block}
Travel expenses you can't deduct
Some travel costs may seem like no-brainers, but they're not actually tax-deductible. Here are a couple of common ones to watch our for.
The cost of bringing your child or spouse
If you bring your child or spouse on a business trip, your travel expense deductions get a little trickier. In general, the cost of bring other people on a business trip is considered personal expense — which means it's not deductible.
You can only deduct travel expenses if your child or spouse:
- Is an employee,
- Has a bona fide business purpose for traveling with you, and
- Would otherwise be allowed to deduct the travel expense on their own
Some hotel bill charges
Staying in a hotel may be required for travel purposes. That's why the room charge and taxes are deductible.
Some additional charges, though, won't qualify. Here are some examples of fees that aren't tax-deductible:
- Gym or fitness center fees
- Movie rental fees
- Game rental fees
{email_capture}
Where to claim travel expenses when filing your taxes
If you are self-employed, you will claim all your income tax deduction on the Schedule C. This is part of the Form 1040 that self-employed people complete ever year.
What happens if your business deductions are disallowed?
If the IRS challenges your business deduction and they are disallowed, there are potential penalties. This can happen if:
- The deduction was not legitimate and shouldn't have been claimed in the first place, or
- The deduction was legitimate, but you don't have the documentation to support it
When does the penalty come into play?
The 20% penalty is not automatic. It only applies if it allowed you to pay substantially less taxes than you normally would. In most cases, the IRS considers “substantially less” to mean you paid at least 10% less.
In practice, you would only reach this 10% threshold if the IRS disqualified a significant number of your travel deductions.
How much is the penalty?
The penalty is normally 20% of the difference between what you should have paid and what you actually paid. You also have to make up the original difference.
In total, this means you will be paying 120% of your original tax obligation: your original obligation, plus 20% penalty.
.jpeg)
Justin W. Jones, EA, JD

Over 1M freelancers trust Keeper with their taxes
Keeper is the top-rated all-in-one business expense tracker, tax filing service, and personal accountant.

Sign up for Tax University
Get the tax info they should have taught us in school
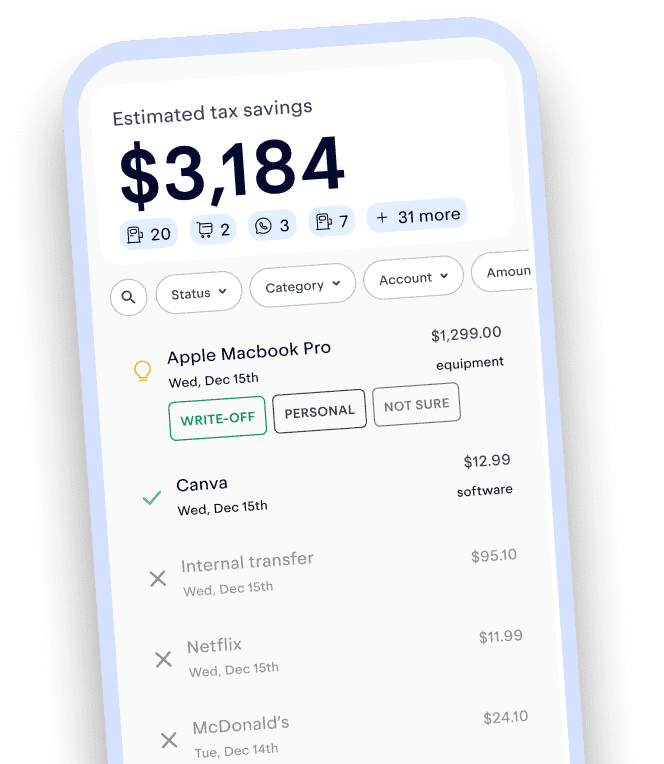
Expense tracking has never been easier
What tax write-offs can I claim?
At Keeper, we’re on a mission to help people overcome the complexity of taxes. We’ve provided this information for educational purposes, and it does not constitute tax, legal, or accounting advice. If you would like a tax expert to clarify it for you, feel free to sign up for Keeper. You may also email [email protected] with your questions.
Voted best tax app for freelancers
More Articles to Read
Free Tax Tools
1099 Tax Calculator
- Quarterly Tax Calculator
How Much Should I Set Aside for 1099 Taxes?
Keeper users have found write-offs worth
- Affiliate program
- Partnership program
- Tax bill calculator
- Tax rate calculator
- Tax deduction finder
- Quarterly tax calculator
- Ask an accountant
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Affiliate Program
- Partnership Program
- Tax Bill Calculator
- Tax Rate Calculator
- Tax Deduction Finder
- Ask an Accountant
When does work time begin and end when traveling, excluding travel time to and from local office?

TriNet Team
While your specific state may have its own regulations, the Department of Labor (DOL) has guidelines for determining which parts of time spent traveling are considered working hours. Here are a number of the key issues:
According to the DOL, for one-day business trips, the employee is compensated for all of their time spent traveling between work sites, but you may subtract time they spend commuting to the airport, bus stand, or train station they're departing from.
Overnight Trips
For multiple day business trips, the same rules apply with one exception. While all time spent working must be paid, compensable transit time may be limited to hours that fall within an employee's normal working hours. Please note that state laws vary significantly from this standard.
For example, if an employee who generally works from 9AM to 5PM were to catch a 3PM flight to Europe, 2 of those hours (from 3-5) are compensable. Working hours apply to all daysincluding weekendseven if the employee doesn't normally work on weekends.
Regarding Time Zones
If an employee's travel will take them through 2 or more time zones, the time from the starting point of their trip should be used to determine their compensable hours.
Be sure to check your state's laws regarding additional stipulations for employee travel time.
For instance, in California employees traveling for business reasons need to be compensated for a larger amount of time, including their commute to the airport, or bus station, as well as their time spent waiting to purchase tickets, check baggage, or boarding.
Another great resource is the federal mileage reimbursement standard , which summarizes optional reimbursement rates for travel by car.
Helpful Links:
Paying Employees Business Travel - nolo.com - An easily understood guide to calculating compensable travel hours
Creditable Travel Time - law.Cornell.edu - List of laws defining creditable travel time

Need a hand with payroll?
Ready to use and expert designed, our Payroll Report Templates keep you accurate and organized.
This communication is for informational purposes only; it is not legal, tax or accounting advice; and is not an offer to sell, buy or procure insurance.
This post may contain hyperlinks to websites operated by parties other than TriNet. Such hyperlinks are provided for reference only. TriNet does not control such web sites and is not responsible for their content. Inclusion of such hyperlinks on TriNet.com does not necessarily imply any endorsement of the material on such websites or association with their operators.

Inspirational stories and on-the-ground perspectives shaping the future of work.

On-demand sessions

Is a PEO right for you? Take our assessment.
Get the latest hr trends, insights, advice and more sent straight to your inbox..
- Client Portal
- Employee Login
.png)
- Community Involvement
- Meet the Team
- What We Stand For
- Why Choose Axcet?
- Certified PEO
- HR Outsource Options
- Client Reviews
- Human Resources
- Employee Benefits
- Payroll Services
- Workerss Comp. and Employee Safety Risk Management
- PEO Expertise You Can Trust
- Resource Library
- Subscribe to the Blog
- What is a PEO?
- Certified PEO FAQ
- Employee Benefits FAQs
- HR Outsourcing FAQs
- Payroll Administration FAQs
- Risk Management FAQs
- Schedule a Consultation
- PEO Frequently Asked Questions
- Options to Outsource Human Resources
- HR Outsourcing Frequently Asked Questions
- Complete List of Services
- Risk Management
- Payroll Administration
- Expertise You Can Trust
- Employee Safety & Risk Management
- All about COVID-19 in the Workplace
- Kansas & Missouri HR News
- Kansas City Interest News
- Choose Topic:
- Payroll Administrations
Understanding Business Travel Time Pay for Nonexempt Employees
By Jeanette Coleman, SPHR & SHRM-SCP on Dec 01 , 2020 2 min read 0 comment(s)
Share this:

Business travel statistics show U.S. travelers took more than 450 million domestic business trips in 2018, and more than a million business trips are taken daily. Even though the worldwide pandemic has hit the travel and hospitality industries hard, the Global Business Travel Association reports that business travel costs are expected to run over $1 trillion by 2022.
Employers have obligations under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) regarding pay for work travel. According to the Department of Labor (DOL), work travel time for nonexempt employees must be compensated, although home-to-work travel, or normal commuting, does not fall into this category. Exempt employees are paid their normal salary when traveling for work.

Business Travel Compensation Q & A
Question: Do we have to pay nonexempt employees for travel time?
Answer: Yes, the FLSA requires paying for travel time in most situations other than regular commute to work, as it’s considered hours worked.
Question: Our construction supervisor drives to various worksites during his workday to talk to clients, direct the work of crews, and inspect equipment and projects. Do we have to pay him for his driving time?
Answer: Yes, that is described as “travel that is all in a day’s work” by the DOL, and is counted as hours worked. Similarly, if an employee must travel for a special one-day assignment and returns the same day, that travel time is counted as hours worked and must be paid.
Question: We have employees who travel for their jobs and are away from home for days or weeks. Do we have to pay for their travel time?
Answer: Yes, travel for work involving overnight stay away from home is compensable when travel time falls outside of normal work hours.
Question: Do we have to pay our non-exempt employees for work performed during travel outside of normal work schedule ?
Answer: Yes, employers must pay for any time employees perform work, including time spent working during travel outside of the normal work schedule.
For example, an employee with a normal work schedule of 8 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. Monday through Friday who works on employer-directed tasks after 4:30 p.m. during weekend travel for work must receive employee travel overtime pay for all time worked after 4:30 p.m.

Considerations for Business Travel Time Compensation
Business travel policy.
It’s important to have properly recorded time records when non-exempt employees are traveling for work, recorded in the workweek in which it occurred. A detailed, but user-friendly, business travel policy is important for full compliance with FLSA and local regulations and includes definitions of types of travel time along with an outline of employees' responsibility for tracking travel time accurately.
As always, be sure to check with your state’s travel time laws, as some state laws differ from the FLSA.
Ensure Compliance and Fair Compensation: Partner with Axcet HR Solutions
At Axcet HR Solutions , we understand the complexities of business travel time pay for non-exempt employees. Don't risk non-compliance or confusion surrounding travel compensation. Partner with us, a professional employer organization (PEO) and HR company to navigate these challenges effectively.
Contact us today to ensure your employees are compensated fairly and your business stays compliant with the latest regulations. With Axcet HR Solutions by your side, you can streamline your HR processes and focus on what truly matters – growing your business.

Written by Jeanette Coleman, SPHR & SHRM-SCP
Get hr updates, table of contents, zoom shirt with sweatpants: has the pandemic forever changed employee dress codes.

It’s Christmas in Kansas City: 12 Must-See Holiday Lights Displays
Let us know what you think....
.png)
- Subscribe to Latest Resources
- [ Client Portal ]
Remove cookies
An official website of the United States government.
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Misclassification
- Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
- Pump at Work
- Maternal Health
- Retaliation
- Government Contracts
- Immigration
- Child Labor
- Agricultural Employment
- Subminimum Wage
- Employment of Workers With Disabilities
- Lie Detector Tests
- Davis Bacon Prevailing Wage Survey
- WORKER RIGHTS
- Resources For Employers
- Regulatory Library
- Interpretive Guidance
- Industry-Specific Resources
- Compliance Assistance
- elaws Advisors
- Fact Sheets
- New and Small Businesses Resources
- Presentations
- External User Portal (EUP)
- Compliance Assistance Toolkits
- New and Small Business Resources
- Publications By Language
- FLSA Compliance Videos
- Know Your Rights Video Series
- Employer.gov
- DOL Enforcement Database
- Workers Owed Wages
- Order Publications
- Laws and Regulations
- Field Handbook
- Administrator Interpretations, Opinion and Ruling Letters
- Field Bulletins
- State Minimum Wage Laws
- State Labor Law Topics
- State Labor Offices
- Resources for State and Local Governments
- NEWS RELEASES
WAGE AND HOUR DIVISION
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF LABOR
Fact Sheet #22: Hours Worked Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)
Revised July 2008
This fact sheet provides general information concerning what constitutes compensable time under the FLSA . The Act requires that employees must receive at least the minimum wage and may not be employed for more than 40 hours in a week without receiving at least one and one-half times their regular rates of pay for the overtime hours. The amount employees should receive cannot be determined without knowing the number of hours worked.
Definition of "Employ"
By statutory definition the term "employ" includes "to suffer or permit to work." The workweek ordinarily includes all time during which an employee is necessarily required to be on the employer's premises, on duty or at a prescribed work place. "Workday", in general, means the period between the time on any particular day when such employee commences his/her "principal activity" and the time on that day at which he/she ceases such principal activity or activities. The workday may therefore be longer than the employee's scheduled shift, hours, tour of duty, or production line time.
Application of Principles
Employees "Suffered or Permitted" to work: Work not requested but suffered or permitted to be performed is work time that must be paid for by the employer. For example, an employee may voluntarily continue to work at the end of the shift to finish an assigned task or to correct errors. The reason is immaterial. The hours are work time and are compensable.
Waiting Time:
Whether waiting time is hours worked under the Act depends upon the particular circumstances. Generally, the facts may show that the employee was engaged to wait (which is work time) or the facts may show that the employee was waiting to be engaged (which is not work time). For example, a secretary who reads a book while waiting for dictation or a fireman who plays checkers while waiting for an alarm is working during such periods of inactivity. These employees have been "engaged to wait."
On-Call Time:
An employee who is required to remain on call on the employer's premises is working while "on call." An employee who is required to remain on call at home, or who is allowed to leave a message where he/she can be reached, is not working (in most cases) while on call. Additional constraints on the employee's freedom could require this time to be compensated.
Rest and Meal Periods:
Rest periods of short duration, usually 20 minutes or less, are common in industry (and promote the efficiency of the employee) and are customarily paid for as working time. These short periods must be counted as hours worked. Unauthorized extensions of authorized work breaks need not be counted as hours worked when the employer has expressly and unambiguously communicated to the employee that the authorized break may only last for a specific length of time, that any extension of the break is contrary to the employer's rules, and any extension of the break will be punished. Bona fide meal periods (typically 30 minutes or more) generally need not be compensated as work time. The employee must be completely relieved from duty for the purpose of eating regular meals. The employee is not relieved if he/she is required to perform any duties, whether active or inactive, while eating.
Sleeping Time and Certain Other Activities:
An employee who is required to be on duty for less than 24 hours is working even though he/she is permitted to sleep or engage in other personal activities when not busy. An employee required to be on duty for 24 hours or more may agree with the employer to exclude from hours worked bona fide regularly scheduled sleeping periods of not more than 8 hours, provided adequate sleeping facilities are furnished by the employer and the employee can usually enjoy an uninterrupted night's sleep. No reduction is permitted unless at least 5 hours of sleep is taken.
Lectures, Meetings and Training Programs:
Attendance at lectures, meetings, training programs and similar activities need not be counted as working time only if four criteria are met, namely: it is outside normal hours, it is voluntary, not job related, and no other work is concurrently performed.
Travel Time:
The principles which apply in determining whether time spent in travel is compensable time depends upon the kind of travel involved.
Home to Work Travel:
An employee who travels from home before the regular workday and returns to his/her home at the end of the workday is engaged in ordinary home to work travel, which is not work time.
Home to Work on a Special One Day Assignment in Another City:
An employee who regularly works at a fixed location in one city is given a special one day assignment in another city and returns home the same day. The time spent in traveling to and returning from the other city is work time, except that the employer may deduct/not count that time the employee would normally spend commuting to the regular work site.
Travel That is All in a Day's Work:
Time spent by an employee in travel as part of their principal activity, such as travel from job site to job site during the workday, is work time and must be counted as hours worked.
Travel Away from Home Community:
Travel that keeps an employee away from home overnight is travel away from home. Travel away from home is clearly work time when it cuts across the employee's workday. The time is not only hours worked on regular working days during normal working hours but also during corresponding hours on nonworking days. As an enforcement policy the Division will not consider as work time that time spent in travel away from home outside of regular working hours as a passenger on an airplane, train, boat, bus, or automobile.
Typical Problems
Problems arise when employers fail to recognize and count certain hours worked as compensable hours. For example, an employee who remains at his/her desk while eating lunch and regularly answers the telephone and refers callers is working. This time must be counted and paid as compensable hours worked because the employee has not been completely relieved from duty.

Where to Obtain Additional Information
For additional information, visit our Wage and Hour Division Website: http://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd and/or call our toll-free information and helpline, available 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. in your time zone, 1-866-4USWAGE (1-866-487-9243).
This publication is for general information and is not to be considered in the same light as official statements of position contained in the regulations.
The contents of this document do not have the force and effect of law and are not meant to bind the public in any way. This document is intended only to provide clarity to the public regarding existing requirements under the law or agency policies.
- Work With Us
Perfecting the One-day Business Trip: Tips and What to Pack
Written by Becca
Updated on February 23rd, 2024

I took a very short one-day business trip, flying back the same day! Here are my best tips for how to survive and what to pack, to make this work travel worth it and easy.
This article may contain affiliate links. We earn a small commissions when you purchase via those links — and it's free for you. It's only us (Becca & Dan) working on this website, so we value your support! Read our privacy policy and learn more about us .
Table of contents
- What to pack for a same-day work trip
- Tips for taking a one-day work trip
- Final thoughts on a one-day business trip
I was recently presented with the opportunity to take a one-day business trip, departing in the morning and returning home the same night. It was mildly thrilling as I first considered it.
As a woman in her mid-thirties, I am glad to travel halfway across the US for a single in-person meeting, and go home to sleep in my own bed the same night.
How do you take a same-day business trip, though? Is there any secret hack or tip I needed to uncover? How do you survive the early morning flight, the late night return and looking fresh and put-together in between?
Take it from me: I first researched the other tips out there from business travelers who nailed the one-day business trip, and these are my best suggestions of how to do it and what to pack.

What to pack for a same-day work trip
Packing for a same-day work trip isn’t hard, but I thought through it a few times. Here’s what I went with, from the bag I strategically chose to the back-up smart items I packed in there.
Your business travel bag or luggage
While business travel websites and pro business travelers out there recommend a short carry-on suitcase like the Daily Carry-On from Away , I found it perfectly appropriate to take a professional laptop travel backpack.
I swear by the Bivy Tote Backpack from Troubadour , which is my dedicated work backpack for when I head into the my Manhattan office.
Get free shipping on orders $100+, Troubadour's 5-year guarantee and 100-day returns now!
Shop the deal

With room for a laptop and a central cavity that fits a slim packing cube , accessories and chargers, it was a no-brainer to take this awesome travel backpack on my business trip.
I was considering taking the Troubadour Adventure Carrier tote , which I also have in my closet, but decided that I didn’t want to be stressing either one of my shoulders during all that walking through airports. I’ll use this lovely and spacious tote for another occasion.
I chose the Bivy backpack for my one-day trip in order to manage weight on my shoulders effectively while walking through airports twice in one day. Here’s what it looks like.
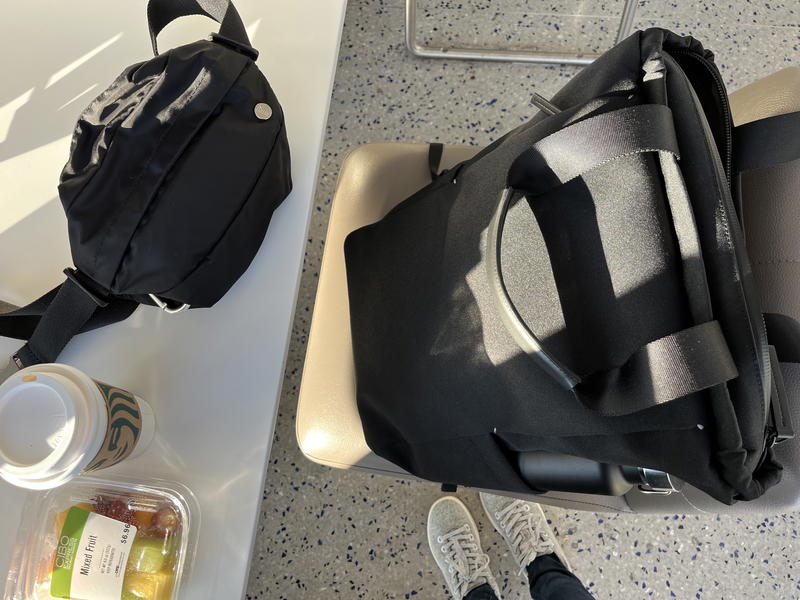

Travel (waist pack) accessory bag
I’ve mentioned in other gear articles of ours that I really like having a waist pack during travel days. During a same-day business trip, you do quite a bit of travel in just a few hours!
Shop my picks

Great for stylish women travelers (or men travelers!), it can be worn in a cute “waist” location rather than at your hip.

It fits all my daily “stuff” from hand cream, hand sanitizer, keys, cards, wallet and phone, to more random items like even an entire water bottle.

I appreciate its sleek, expandable design and multiple pockets, ideal for daily essentials and travel, with a stylish silver buckle adding a touch of elegance.
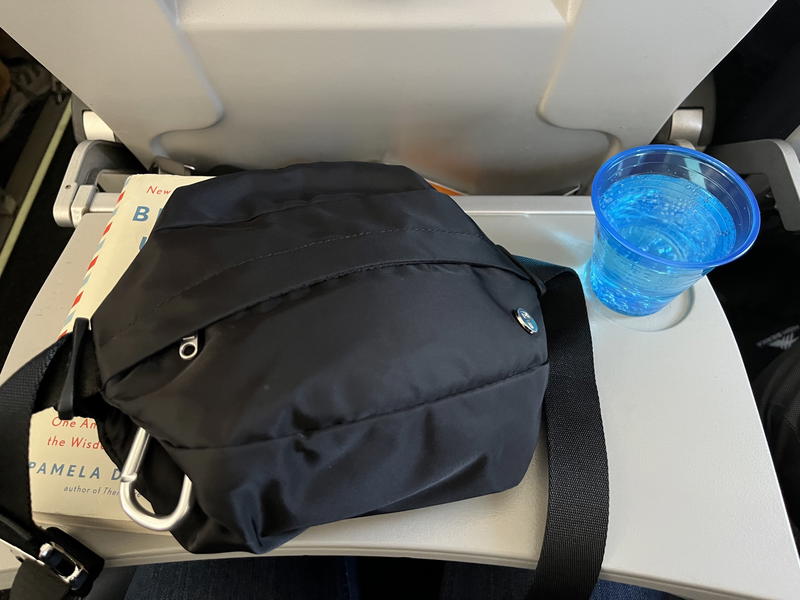
On this trip, I took the Public Rec Belt Bag , which I used both in its fanny pack method and its sling bag setup. I find this bag is to be so convenient for keeping my passport, wallet, phone and AirPods handy and close to my body. I keep it in my lap during the flight as well.
Not interested in the look of this convertible fanny pack? Check out the list of my best fanny packs for travel to see more options.

Work items to pack
Make sure to take your work laptop, laptop case (I use a simple neoprene one I bought on my own) and your laptop cable or charger. I usually pack these the night before.
One tip is to make sure you don’t take your personal laptop instead of your work computer, as that would be an unfortunate mistake. Pack these while you’re not in a rush, ideally not in the minutes before you’re running out the door.
Other travel accessories
In addition to the standard “travel things” like a phone cable and an external battery pack or power bank (great for when you have an old plane with no outlets!), you could consider bringing compression socks for the flight and a neck pillow (I recommend this easy one from BCozzy ).
You’ll also want a reusable travel water bottle! Pack the one you’d take on any trip. I recommend the YETI or the S’well bottles . Fill up your bottle at a water fountain before you board your inbound flight, so that you’re not parched and tired upon arrival.

Toiletries to bring
When leaving home for just a day, you might think, do I need toiletries?
I opted for “yes” on this question, after reading some recommendations of bringing a toothbrush and travel-sized toothpaste for these reasons:
- So that you can freshen up by brushing, after a flight, if you fall asleep and feel groggy
- In the rare case that your return flight is cancelled, you’ll be glad to had a spare toothbrush and toothpaste
I also brought aromatherapy scented travel-sized hand cream for battling the dryness of the plane, plus having an attempt at smelling nice before my meeting. I packed one tube of mascara as a quick makeup fix, one lip balm and one mini Vaseline , also to combat airplane dryness.
One more thing: a last-minute item I threw in my backpack was a travel-sized hairbrush to use post-flight in case I looked messy.
For men, you could consider bringing a beard comb or small set of travel-sized grooming items .
If you often perspire during flights, or just tend to feel smelly, opt to bring along deodorant and apply it either in the airplane bathroom before the descent, or in an airport bathroom right when you arrive.

Clothing, accessories and shoes
As my trip was during the fall, I was lucky to be able to wear a sweater as my casual top that doubled as a layer on the flight and a base that I could “dress up” before landing.
How did I do my “dressing up before landing?”
I packed a set of a matching necklace and bracelet that I could put on, along with a solid-colored pashmina that could add a pop of color to what I was wearing (which was dark jeans and gray Allbirds Pipers ).
I also expertly applied mascara as the plane was landing, by using my phone as a mirror. Luckily, I did fine.
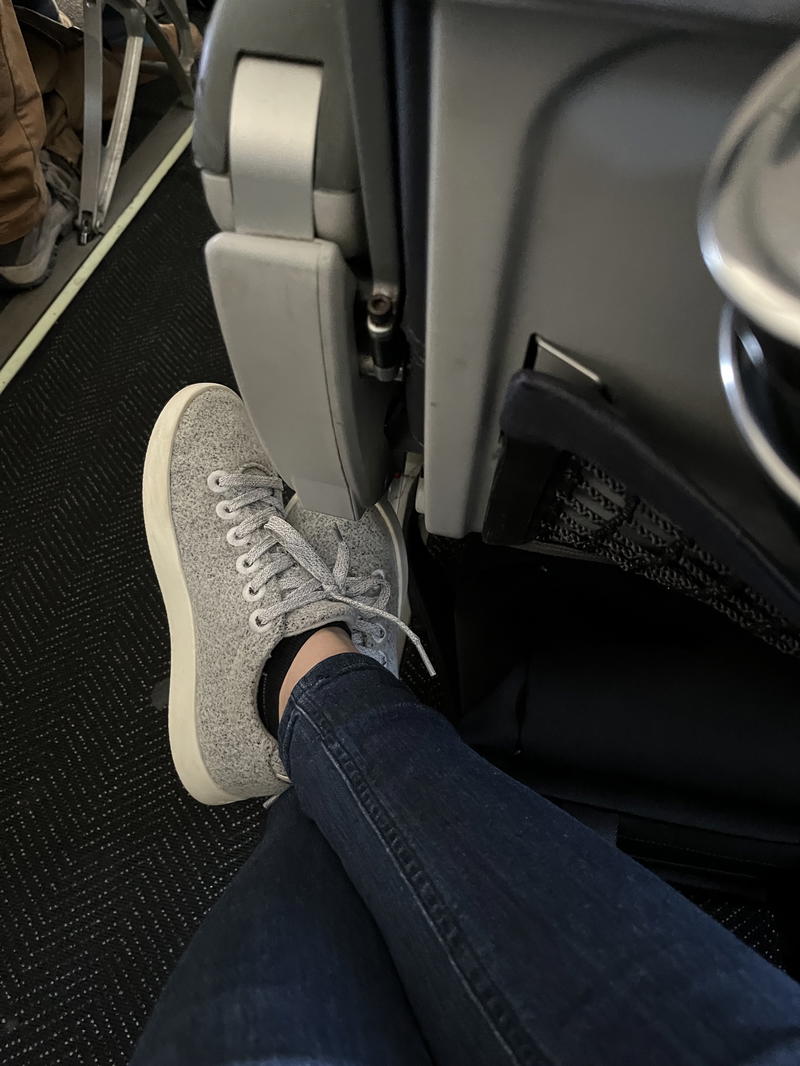

I should mention I also wore my black leather band travel watch by Victorinox , which is always a classy item to have on my wrist in professional environments.
In a small packing cube , I packed one extra pair of underwear and one extra top, along with a pair of leggings, for two possible reasons:
- In case I wanted a change of clothes for the flight home the same night
- For the same reason of (in a rare case) my return flight getting cancelled and my needing to spend a night in my destination
Tips for taking a one-day work trip
Remember: this business travel guide is for anyone taking a work trip that lasts only one calendar day, not a 24-hour trip that involves one night in a hotel. I’ve recently done one of those as well, and the difference is that you really do require a whole night’s worth of things.
For anything I mention here, it’s in regard to leaving in the morning, going to a meeting or event out of town, and coming back the same night. I’m not really speaking to red-eye flights , which would start the night before and get you into your destination in the morning, essentially. The tips here speak to waking up at a “more or less” normal morning time and getting home before midnight the same day.
Here are my best tips for making your trip successful and not getting too tired!

Get a good night of rest the night before
I really recommend trying to go to bed at 9, 10 or 11 pm the night before your same-day work trip, depending on if you have a 6, 7 or 8 am flight.
I had a 9:30 am flight out of an airport not too far from where I live, so I lucked out. I went to bed around 11 pm the night before (and of course didn’t sleep very well because I always fear I’ll miss my early morning alarm!). I left home a little after 7, and was already through security and grabbing a latte 45 minutes later.
Check into both your flights the day before
Because your flights are both on the same calendar day, you can check in online the day before you leave and save a lot of time at the airport.

Perfect that one-day work trip packing list
Despite being such a brief trip, as you can see from the packing I did above, you may be challenged by fitting all these “what-if” items into only a backpack or mini carry-on.
Pack your trip bag beforehand
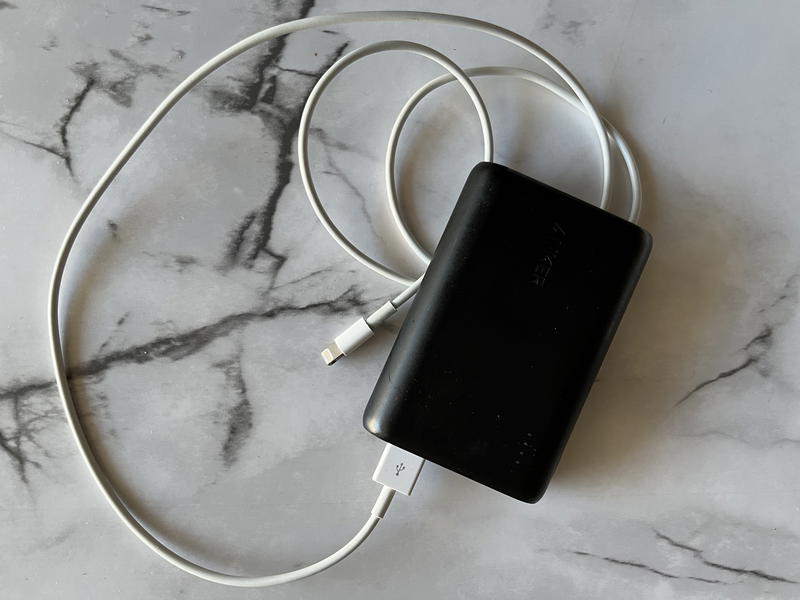
Pack your entire carry-on or backpack the night before your trip and make a short list of the finishing touches for the morning. For me, this list tends to be my phone charger, phone, battery backup power bank and a few other things.

Keep in touch with colleagues or clients
If your flight is delayed, or even if it takes off early, ping your coworkers also traveling or your client/partner on the ground at your destination to let them know your status.
I texted my coworkers as soon as I landed, and we texted the business partners with whom we’d be meeting, nearly immediately, to tell them our ETA at the office campus.

Have a freshen-up plan
For me, my plan was to put on my jewelry, fix my hair and have my makeup done before landing, as I was meeting colleagues immediately in the airport and heading right to the meeting with another company!
Your plan could look different. Think about if your tight schedule allows time to change clothes in an airport bathroom, have a meal before picking up your rental car, etc., so that you can have a game plan.
Regarding meals, we’re talking about that in just a second!

Make sure to eat on the way in
Luckily, I picked up both breakfast and snacks at airport shops in the morning and ate enough to hold myself over for a while, as well as have snacks for the afternoon if food wasn’t available or being planned. Truth is, you never know if others came from having lunch and assume everyone has eaten.
It was fortunate that I prepped in this way because I headed with colleagues to our meeting, forty minutes outside the city we landed in, and we wound up not going out to lunch for another two and a half hours. If I hadn’t been able to sneak a snack, I would’ve been starving!
(As you can see here, I’m a bit of a health nut, and I focus on nutrient-rich foods full of protein and fiber on travel days. I try to avoid chips and pure sugar junk as long as possible.)

Be communicative about your time frame
What with departing the same night back home, keep your coworkers and business partners at the meeting or event informed of your departure timeline so that no one encounters any stress.
We were in luck that we went out to a business lunch after meetings were done, and our timeline for getting in an Uber and being en route to the local airport for the flight home was absolutely perfect.
Plan around that flight back home
Sleeping in your own bed tonight is surely the end goal, so make it a priority to not miss that flight back to your origin airport!
Calculate the distance between where you’ll be spending the day, to the airport, so that you can get through security and to your gate on time. Hopefully you’ve had a chance by then to have a successful business meeting or event, and even sample some local cuisine!
For me, I went right from the airport to a meeting at an office campus in a suburb, and then went right back to the airport with coworkers to make our return flight to NYC .
Prepare for delays
This is standard travel advice and also standard business travel advice, of course. Would you ever know it? While I was with colleagues waiting for our flight home to board, we got a notification from the airline app that our flight was delayed more than 90 minutes.
I had a moment of agony and then was thankful I wasn’t alone, but surely could’ve been if I had been heading to a different home airport than the others.
Fortunately, there were food options nearby, as well as WiFi. Eventually, our delayed flight wound up being able to board earlier than expected and we made a mad dash for that!

Final thoughts on a one-day business trip
I think my same-day work trip went fairly well, considering that I did travel halfway across the US and return home in the same period of less than 16 hours. Air travel really never ceases to amaze me for how it gets you from Point A to Point B, so fast .
A few things that brought me success were staying relaxed, keeping an eye on the time and knowing that I had everything with me that I needed in case of an unexpected scenario.
I hope your same-day trip for business goes swimmingly and that these recommendations were good reminders of what you can do!
You may also like

How to Plan a Trip to NYC with a Baby (What to Know)
Going to NYC with a baby for the first time doesn’t have to be hard! In our list of local tips, find out what to do and see with your baby in New York City to make the visit easy.

Road Trip with Baby: Essential Travel Packing List & Tips
How do you take a road trip with a baby for the first time? Check out my essential travel packing list for everything your infant needs during a trip.

How to Avoid Pickpockets When Traveling (22 Tips)
Avoid pickpockets on your next trip with my best tips for keeping valuables safe. Use these tricks and hacks to ward off thieves while traveling!

36 Real Ways to Save Money While Traveling (Actionable Tips)
Here are our proven best ways to save money while traveling. When traveling on a budget, there are lots of ways to make your money last longer, even during inflation.

15 Best Ways to Eat Healthy during Travel (my Favorite Tricks)
What are some ideas for how to eat healthy during your trip? Check out our best practices and my personal tricks, for healthy eating that you can try during travel.

21 Tips for Staying in a Hotel with a Baby (Experienced Parents)
How do you survive staying in a hotel room with a baby? From my experience, I list the top tips and tricks for sharing a hotel room with an infant on a vacation.

What's up ! We’re Becca & Dan.
We created this blog to share some of the knowledge and experience that we have around travel , remote work , photography and beyond!
We're currently sitting on the couch writing travel guides.
Join the club
You’ll get emails with our latest articles, tips, advice and so much more! You won't find this content anywhere else!
This website may contain affiliate links. We earn a small commissions when you purchase via those links — and it's free for you. It's only us (Becca & Dan) working on this website, so we value your support! Read our privacy policy and learn more about us .
Among other programs, Half Half Travel is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Business Taxes
When Must I Pay Employees for Travel Time?
Travel Time vs. Commuting Time
Image by Jo Zixuan Zhou © The Balance 2020
In general, your business should pay employees for the time they spend traveling for work-related activities. You don't have to pay employees for travel that is incidental to the employee's duties and time spent commuting (traveling between home and work). Travel time can include both local trips and travel away from home.
Travel vs. Commuting Time
Commuting is going back and forth to work. Everyone (at least everyone who doesn't work at home) commutes to a job. Commuting time is personal time, not business time. The IRS does not allow businesses to deduct commuting time as a business expense, and employees should not be paid for the commuting time.
The Department of Labor (DOL) discusses employees who drive employer-provided vehicles. The DOL considers the time spent in home-to-work travel by an employee in an employer-provided vehicle, or in activities performed by an employee that are incidental to the use of the vehicle for commuting, generally is not "hours worked" and, therefore, does not have to be paid.
Here's a possible rule of thumb: If your business authorizes a trip by an employee, no matter how the employee travels (car, train, bus, etc.) you should pay for the employee's travel time.
Travel time for hourly and salaried employees may be counted differently. Pay to employees for local travel time is only applicable to non-exempt (hourly) employees, not to exempt (professional or managerial) employees. Exempt employees are paid for their expertise by the job, not by the hour.
Different Types of Travel Time:
Home to Work Travel , as explained above, is commuting time, not work time, and it's not paid.
Travel on Special One Day Assignment in Another City. The DOL says "the time spent in traveling to and return from the other city is work time," but they note that you may deduct the time the employee would spend commuting.
Sara works in an office in your company, but you send her to another city on a special assignment. She leaves from her home, goes to the city, and comes back home the same day. She spends 3 hours traveling (1 1/2 hours each way) from home to the other city. She would normally spend 30 minutes total driving from her home to work and back, so you could deduct the 30 minutes and pay her for 2 1/2 hours of travel time.
Travel That's Part of the Employee's Normal Work. Time an employee spends traveling is part of the job. You must count this time as work time. The time the employee spends going to the first job site, and home from the last job site, is commuting time and isn't paid.
An LPN (licensed professional nurse) works for a nursing facility and travels between the two locations of this facility, providing care for patients at both locations. Her daily travel time between these locations must be included in her pay because she is not commuting. But she can't count the time driving from home to the first location or the time back home from the last location.
Travel Away from Home. If travel includes an overnight stay it is travel time. The DOL doesn't include travel away from home outside regular hours as a passenger on an airplane, train, boat, bus, or car as work time. But you must count hours worked on regular working days and work hours on nonworking days (weekends and holidays).
If an employee travels from Cleveland to Pittsburgh for a two-day seminar at the direction of your company, you must pay for the hours the employee would have worked in a normal workday for each of those days, even if they were on Saturday or Sunday.
Incidental vs. Work Travel: Paid or Not Paid?
- An employee drives to work from his home every day. You ask him to stop on his way and pick up bagels for the staff meeting. This driving time is not paid. Time commuting to work is never paid time; the time to stop for the bagels is "incidental" to the commuting and is not part of the employee's job.
- You ask an employee to drive to a store on work time to get bagels for the office meeting. If the employee makes this trip during normal work hours, he or she should be paid.
Also, you might want to contact an employment attorney to discuss these issues.
Paying for Travel Expenses
In addition to paying employees for travel time, you should pay their expenses for travel. The Department of Labor doesn't require reimbursement for travel expenses, but it makes sense to pay employees if you require them to travel. Your business can deduct employee travel expenses as a business expense. If employees mix business and personal travel, you need to sort out the part that is business-related and pay only these expenses.
State Regulations on Paying for Employee Travel
Check with your state labor department to see if there are any rules which might override the federal rules. Contact the nearest local office of the U.S. Department of Labor for information on specific instances of travel time that affect your business.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 535 (2019): Business Expenses ," Page 5. Accessed May 26, 2020.
Internal Revenue Service. " Travel & Entertainment Expenses ," Page 3. Accessed May 26, 2020.
U.S. Department of Labor. " Travel Time ." Accessed May 26, 2020.
Electronic Code of Federal Regulations. " Travel Time ." Accessed May 26, 2020.
U.S. Office of Personnel Management. " Fact Sheet: Hours of Work for Travel ." Accessed May 26, 2020.
U.S. Department of Labor. " Fact Sheet #17D: Exemption for Professional Employees Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) ," Pages 1-3. Accessed May 26, 2020.
U.S. Department of Labor. " Fact Sheet #22: Hours Worked Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) ." Accessed May 26, 2020.
U.S. Department of Labor. " Opinion Letter FLSA 2018 ," Page 2. Accessed May 26, 2020.
U.S. Department of Labor. " Reimbursed Travel Expense Payments ," Page 1. Accessed May 26, 2020.
Internal Revenue Service. " Topic No. 511 Business Travel Expenses ." Accessed May 26, 2020.
For Agencies
Let's Talk: (844) 800 - 2211
Remembering Shay Litvak Our Co-Founder and CTO
November 1979 - September 2023
When Do Employers Have to Pay Employees for Travel Time?

Deanna deBara
For some small businesses, traveling to meet clients, make sales, and manage day-to-day activities is a must. For others, traveling is valuable for attending conferences, participating in networking events, or undergoing specialized training.
But if it's your employees doing the traveling, do you need to pay them for that time? Whatever your preferences are as a small business owner, the legal answer is: that depends.
Let's explore when you need to provide travel time pay for hourly employees, which employees are entitled to that pay, and, if they are entitled, how much you'll need to pay them.
Who Is Entitled to Travel Pay?
All non-exempt employees are entitled to travel pay during normal work hours and when they are actively working outside of those hours. They aren't entitled to travel pay for doing their typical commute, according to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA).
Non-exempt employees are typically paid an hourly wage and are paid less than $684 per week or $35,568 per year.
These rules don't apply to exempt employees, and therefore it's up to you whether you want to pay them to travel.
What's more—your state may have some extra rules, so make sure to check your state's Department of Labor or Wage and Hour Division website.
When Do You Have to Provide Travel Time Pay for Hourly Employees?
But when, exactly, are these employees paid to travel? Compensable work time needs to be paid when employees travel:
- Locally: You need to pay employees when they travel locally as part of their regular duties (for example, from your office to a supply store). And if that travel happens outside of the employee's regular workday hours (even if they're only waiting to travel, like sitting at a bus stop or train station)? You still need to pay.
- Between worksites: Employees get travel pay when traveling between worksites. For example, a courier who transports materials between different job sites must be paid for the time spent traveling. Similarly, plumbers who travel between customers' homes are eligible for travel pay.
- For special one-day assignments: You must provide travel pay for hourly employees who travel out of town, even if they return home at the end of the workday—though you can deduct the employee's normal commute time from the total payment. For example, let's say an employee spends a total of two hours traveling to and from a work conference (which takes place during normal working hours). Because her typical daily commute takes 30 minutes, you would only need to pay for 1.5 hours of traveling (in addition to regular hourly wages).
- Overnight: Employees traveling overnight are due travel pay during their regular working hours and any time they spend working outside of those regular hours (for example, participating in late-night conference calls while on a train). You also need to pay employees for traveling during their regular working hours, even on non-working days, like weekends, holidays, or their normal days off.
Bonus tip : The best way to track travel time for your employees? Time tracking software like Hourly . Workers clock in right from their phones, and the platform automatically tracks their location, hours and what project they're working on—which you can see in real-time. Another perk? You can run payroll with the click of a button.
How Much Do You Have to Pay Employees for Travel Time?
Employees traveling for work need to be paid at least the minimum wage, but they can be paid more or less than their normal pay rate.
If you want to pay a different rate than an employee's hourly wage, you'll need to:
- Tell the employee they will be paid a different rate before they begin their trip.
- Make sure the hourly rate for travel pay doesn't cause the employee's total pay for all workable hours to fall below minimum wage (state, local or federal—whichever is highest) or result in incorrect overtime pay.
- Ensure that you're not violating their employment contract.
This gives you the flexibility to offer a higher rate of pay as an incentive for traveling outside of regular business hours—or, if you decide to pay less than their typical rate (but still minimum wage or above!), it can help make sure that paying for travel won't interrupt your cash flow or cause other financial concerns for your company.
Ready to transform your business into a profit-pumping machine? Learn how with our monthly newsletter.
Subscription implies consent to our privacy policy.
When Do You NOT Have to Provide Travel Time Pay for Hourly Employees?
Exempt employees—like outside salespeople, executives, managers, administrators, and even IT personnel—aren't entitled to travel pay. And non-exempt workers? They're not eligible for travel pay when they are:
- Commuting: An employee's commute—the time spent driving from their home to work (and from work to home)—doesn't qualify as travel time. This also includes the time spent driving from accommodations/lodging (like a hotel) to a work location, like a client's office or conference center.
- On break or during personal time : Non-exempt employees aren't entitled to travel pay during breaks (including meal periods and time spent sleeping) or when they can spend their time how they see fit. In other words, you don't need to pay for traveling during the time an employee can go shopping, sightseeing, or out to eat.
- Away from work and not working : Employees on overnight travel or business trips don't need to be paid outside of regular working hours unless they're working during that time period. For example, an employee who regularly works 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. Monday through Friday only needs to be paid for traveling on a Saturday if they travel during their normal working hours (i.e., 9 a.m. to 5 p.m.)—unless they're working outside of those hours too (like answering customer support emails or counting inventory).
- A passenger: You don't need to pay for travel when an employee is a passenger (in any sort of vehicle) and isn't doing work outside of regular work hours. The only exceptions occur when you require an employee to drive the vehicle or be actively engaged in working (like riding to a job site while handling customer calls or riding as a passenger in a client's vehicle).
- Choosing to drive themselves : If you offer to pay for an employee's travel method (like airfare, a bus ticket, or a train ticket) and the employee requests to drive instead, the employee is only entitled to travel pay while driving during their regular work hours. In other words, if an employee requests to drive themselves vs. taking public transit, you don't need to pay for travel outside of the employee's regular shift.
In other words, a non-exempt employee isn't entitled to travel pay unless they are driving, traveling during their normal working hours, or actively working while traveling.
Does Travel Time Count Towards Overtime?
Yes, travel time counts toward overtime, and you'd owe them 1.5 times their regular rate for any hours worked over 40 while they're traveling.
What if your pay rate for traveling is different from an employee's regular wages? Then it gets a little more complicated.
In that case, you need to use the weighted average of the two overtime rates to get their final pay. Here's an example:
Let's imagine one of your employees is pulling a 40-hour week at the office. Their rate? $15 per hour. So that gives them $600 for their regular workweek (that's 40 hours multiplied by $15 per hour). Now, during that same week, they also spent 8 hours traveling as overtime, for which you're paying them $11.25 per hour. This gives them an extra $90 (which is 8 hours multiplied by $11.25 per hour).
Add these together, and their total straight-time pay for the week is $690.
Now, to figure out their average rate for the week (including travel time and regular office time), you need to divide this total pay by their total hours worked. In this case, it's 48 hours in total (40 regular hours plus 8 overtime hours). So, $690 divided by 48 hours gives you a weighted average rate of $14.375 per hour.
But they've already been paid for all 48 hours at their respective rates, right? For the 8 hours of overtime, what you owe them is an extra half of that weighted average rate. That's what we call the "overtime premium." Half of $14.375 is about $7.19. So, the overtime pay would be 8 hours (overtime) times $7.19, which comes out to $57.52.
To get their final paycheck, you add this overtime pay to their straight-time pay. So, $690 (straight-time pay) plus $57.52 (overtime pay) equals $747.52. As a business owner, using the weighted average method to calculate the overtime rate, you'd be paying out $747.52 for this employee's week of work, including their overtime.
Additionally, if you pay for travel time that isn't required to be paid (like commuting), you can't count them as hours worked for overtime purposes.
Travel Time Pay Best Practices
Handling travel pay can be complex and difficult at first. But it doesn't have to be! Use these best practices to simplify paying your employees for working on the go.
Create a Travel Policy
If your small business sends employees to different locations, you need to establish a written travel policy—and include it in your employee handbook.
Your travel policy should outline which situations result in compensable travel time (like attending conferences or visiting different job sites), as well as any exclusions where employees won't be compensated (like an employee's regular commute or traveling as a passenger on non-working days).
If you pay a different hourly rate for time spent traveling, make sure to include it in your policy. Then, have employees sign the policy to acknowledge they understand it and agree to its terms—and then add the signed document to their employee file.
Track Hours Traveled
As a small business owner, you need to track employee travel time to follow labor laws and make sure their paychecks are accurate.
Though you can ask employees to record and document the time they spend traveling—which can help you make sure your records are accurate—the responsibility for doing so is ultimately on you.
Pay for or Reimburse Travel Expenses
The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) doesn't require you to pay for your employee's travel expenses.
Still, if you're sending your employees out of town, you should pay for the cost of travel—like tickets and lodging.
If you don't, your employees are almost guaranteed to get frustrated that they have to pay for expenses out of pocket—and that frustration could lead to issues with employee engagement and retention.
When writing your travel policy, outline which travel expenses your company covers. If you expect employees to front some or all of the travel expenses, detail your procedure for requesting reimbursement and how to track expenses (like mileage or airfare).
You might also want to provide some form of per diem or stipend that helps employees pay for small travel expenses, like food.
This can either be an allowance per meal period (like $15 for breakfast, $20 for lunch, and $40 for dinner) or a specific amount that the employee can use throughout the trip (like $50 per day or $150 for the weekend). Have your employees save and submit their receipts to avoid taxation. You can also consider a company card to lessen the burden on your team's bank account.
Check With Your State's Laws
In addition to federal law, some state laws apply additional regulations to travel time. This means rules can vary based on the state you operate in. For example, compensable work time in California includes riding as a passenger in a vehicle when traveling for work.
But which set of employment laws should you follow? You should apply the set of rules that provide the highest payment to your employees. So, if your state regulations specify that certain activities qualify as compensable—even if the FLSA does not—you need to pay for time spent traveling.
(For guidance about your state's specific laws and guidelines, contact your state's Department of Labor and local Wage and Hour Division .)
FAQs About Travel Time Pay for Hourly Employees
Do remote/hybrid workers qualify for travel pay.
A remote or hybrid worker qualifies for travel pay when you require them to travel to your place of business or another venue (like a conference hall, training facility, or client location) and they:
- Live far away from the regular worksite (requiring an overnight stay or significant travel time)
- Are only expected to work on-site by request or on a day they're not normally required to be on-site
However, remote/hybrid workers aren't entitled to travel pay when:
- Your policy specifies that both an employee's home/remote office and your office are considered primary work locations
- They are expected to work on-location on certain days
- The time spent traveling to the office is considered an employee's commute (even if they are a remote or hybrid worker)
Do employees who drive/travel as part of their job qualify for travel pay?
The FLSA requires you to pay employees their regular hourly wages when they are driving or traveling as part of their job responsibilities. For example, bus or delivery drivers should be paid their regular wages while on the job.
Compensating Your Employees for Traveling Doesn't Need to Be Difficult
Traveling for business can take a toll—both on the road and off. Paying travel time for hourly employees can incentivize them to hit the road when necessary and make up for the time they spend away from their families and lives.
Once you've determined which employees qualify for travel time pay, implement a clear travel policy (that adheres to state and federal law) and use management tools (like Hourly !) to maintain accurate records and compensate your employees for time spent traveling.

What are Pre-Tax and Post-Tax Payroll Deductions?

Payroll Mistake? Send This Payroll Error Letter to Employees

The Business Owner’s Guide To Biweekly And Semi-Monthly Payroll
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

Office of Human Resources Management
- Practitioners
- Compensation Policies
- Premium Pay
Was this page helpful?
Travel time as hours of work, applicability.
This information applies to GS, FP, and FWS EXEMPT and NONEXEMPT employees.
When is Travel Compensable
Time in a travel status away from the official duty station is compensable for EXEMPT and NONEXEMPT employees when the travel is performed within the regularly scheduled administrative workweek, including regularly scheduled overtime. In addition, travel is compensable for both categories of employees for purposes of meeting the daily and weekly overtime standards when it:
- Involves the performance of work while traveling, (e.g., as a chauffeur or courier);
- Is incident to work performed while traveling (e.g., a courier's travel relative to the spot where further travel to deliver a diplomatic pouch would begin);
- Is carried out under such arduous and unusual conditions that the travel is inseparable from work; or
- Results from an event which could not be scheduled or controlled administratively, including travel by an employee to such an event and the employee's return from such an event to his or her official duty station.
For a NONEXEMPT employee, travel meeting the weekly overtime standard (but not the daily overtime standard) also includes:
- Travel as a passenger on an overnight assignment during hours on nonworkdays which correspond to regular working hours; and
- One-day travel as a passenger to and from a temporary duty station (not including travel between home and the employee's normal duty station).
Who Makes the Determination
Officials to whom authority has been delegated to authorize or approve travel on official business are responsible for determining whether travel outside the regularly scheduled workweek meets any of the conditions for hours of work.
How Much Travel Time is Creditable For Pay
When travel outside the normal workweek constitutes hours of work, the following rules will apply in determining the amount of time in a travel status that is deemed hours of work for premium pay:
When is an employee in travel status . An employee is in a travel status only for those hours actually traveling between the official duty station and the point of destination, or between two temporary duty points, and the usual waiting time which interrupts travel.
When traveling by common carrier . Time in a travel status begins with the scheduled time of departure from the common carrier terminal, and ends upon arrival at the common carrier terminal located at the destination. However, when the employee spends 1 hour or more in travel between the common carrier terminal and place of business or residence, then the entire time traveling between the carrier terminal and place of business or residence (that is actual time traveling, exclusive of waiting time at the terminal prior to the scheduled departure time) counts as hours of work.
Waiting time . Usual waiting time between segments of a trip or at common carrier terminals counts as worktime for premium pay (up to 3 hours in unusually adverse circumstances, e.g., holiday air traffic, severe weather) provided travel away from the duty station is compensable because it meets any of the conditions of this Section.
Authority to Order Noncompensable Travel
Congress has not provided a remedy whereby an EXEMPT employee who performs official but noncompensable hours of travel may be compensated (57 Comp. Gen. 43, 50, 1977). A manager does, however, have the authority to schedule official travel that is noncompensable. As a requirement of 5 CFR 610.123, the manager must record the reasons for ordering such travel in a memo to be filed with the employee's Time and Attendance Report (T&A). A copy of the memo must be given the employee if the employee requests it.
Work performed while traveling . In order to meet the intent of the law as defined in the majority of Comptroller General decisions, work performed while traveling must be work which is inherent in the employee's job and which can only be performed while traveling, e.g., chauffeuring, hurricane reconnaissance performed aboard a plane flying into the eye of the hurricane, etc. Discretionary work such as review of a scientific presentation by a scientist or treaty papers by a foreign service officer enroute to a meeting is work which could be performed in an office independently of travel and does not satisfy the definition of work while traveling and is, therefore, not compensable for purposes of overtime. (B-146288, January 3, 1975)
Work incident to work performed while traveling . Travel which is incident to work performed while traveling must also meet the definition of "work performed while traveling" above. Travel which is necessary to meet another mode of travel is compensable for overtime purposes if the traveler performs work while traveling which is an inherent part of the job and which could only be performed while traveling, for example, a motor vehicle operator who is ordered to travel by plane in order to take responsibility for a truck which he or she is then to deliver to its permanent location (57 Comp. Gen. 43 (1977), or a courier who travels to pick up and deliver a pouch (B-178458, dated June 22, 1973). Travel and incidental transport of files is not within the definition since the transportation of files is work not inherent in the job (B-181632, dated April 1, 1975).
Travel under arduous conditions . Arduous means more than the inconvenience associated with long travel delays, unbroken travel, unpleasant weather, or bad roads. Prolonged travel in heavy blowing snow which makes driving difficult but stops short of endangering the employee might be considered arduous. A distinction must be made between travel which is arduous and travel which is hazardous duty. Each case must be judged on its own merits (B-193623,
July 23, 1979).
Travel resulting from an event which could not be administratively scheduled or controlled . An event that cannot be administratively scheduled or controlled implies immediate official necessity for travel. If it is discretionary when the employee begins travel, not including the minimum necessary time to make travel arrangements, the notion of immediate necessity which is implied by an event that could not be scheduled or controlled is lacking and the intent of the law as defined by the General Accounting Office is not satisfied. Therefore, time spent in such travel would not be compensable for overtime purposes
(B-186005, August 31, 1976).
Within the agency's administrative control . Whether the scheduling or timing of the event that precipitates an employee's travel was within the administrative control of the agency is strictly interpreted in decisions of the Comptroller General (CG). Travel on overtime to and from a meeting arranged at the discretion of two Federal agencies is not compensable since agencies have it within their power to ensure that the employee travels during work time (B-146288, January 3, 1975 et alia).
For the same reason, travel to and from training which is conducted by the government, under government contract or by a private institution solely for the benefit* of the government is not compensable since the government has it within its power to ensure that the start and end times of such training allow the employee to travel on work time (B-190494, May 8, 1978; also, 66 CG 620, 1987).
*In William A. Lewis et al, 69 CG 545 (1990). The CG ruled travel on overtime to and from training that is given by a private institution is compensable because government cannot control the private institution or its scheduling of the course. The Lewis opinion further held that the notion of "immediate official necessity for travel" which prior CG decisions have held must be present in travel which responds to an event that is not schedulable or controllable was established by the start time of the class. To be present when the class began, the employees had to travel on Sunday.
NOTE : The regulations which govern training time which is compensable as overtime and travel to and from training are separate and distinct. The circumstances under which premium pay may be paid while an individual is in training are covered in the section titled Premium Pay and Training.
Meeting abroad - a matter of accommodation . An employee's claim for overtime compensation for travel overseas to be present at the opening of a conference with representatives of a foreign government was disallowed. Although the employee's agency indirectly scheduled the meeting through the USAID Mission, the Comptroller General ruled the lack of governmental control envisioned by law and regulation for travel on overtime to be deemed compensable was not present. (Gerald C. Holst, B-202694, January 4, 1982; and B-222700, dated October 17, 1986).
NOTE : The Lewis decision (see discussion above) precipitated a review of CG decisions with the result that government control of events was sufficient to validate all previous decisions except one: Gerald C. Holst, was overruled. In overruling the 1986 decision, the Comptroller General found the agency to lack control of the scheduling of the meeting to an appreciable degree. Further, the start time of the opening conference established the immediate official necessity for travel. Travel, was, therefore, compensable.
Failure to plan . An employee who travels outside his or her normal tour of duty to perform maintenance on equipment so that the equipment can perform necessary functions in accordance with operational deadlines is not performing compensable travel if the maintenance responds to gradual deterioration which could have been prevented if maintenance was scheduled on a timely basis (49 Comp. Gen. 209, 1969).
Two-day per diem rule . An employee may be required to travel on his or her own time if in order to allow the employee to travel during working hours, the agency would be required to pay two days or more per diem. However, the two-day per diem rule does not of itself support an entitlement to overtime compensation for the employee. To be compensable at the overtime rate, travel must respond to an event that could not be scheduled or controlled administratively and there must be an immediate official necessity for the travel to be performed outside the employee's regular duty hours (60 Comp. Gen. 681, 1981).
Return travel . When an employee performs compensable overtime by traveling to an event which could not be controlled or scheduled, he or she is automatically eligible for compensation for return travel to his or her duty station.
Disparity in hours of work means disparate overtime entitlement . Because FLSA provides two situations in which a NONEXEMPT employee, but not an EXEMPT employee, can be paid for travel on overtime hours, (specifically, during hours on nonworkdays which correspond to regular working hours and for one-day travel as a passenger to and from a temporary duty station), it is possible for a NONEXEMPT employee to be paid for travel when an EXEMPT employee in the same situation is ineligible for overtime pay.
Share this page
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- A–Z Index
- Operating Status

Resources For
- New / Prospective Employees
- Federal Employees
- HR Professionals
Hours of Work for Travel
Fact sheet: hours of work for travel, description.
In limited circumstances, travel time may be considered hours of work. The rules on travel hours of work depend on whether an employee is covered by or exempt from the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). For FLSA-exempt employees, the crediting of travel time as hours of work is governed under title 5 rules-in particular, 5 U.S.C. 5542(b)(2) and 5544(a)(3) and 5 CFR 550.112(g) and (j). For FLSA-covered employees, travel time is credited if it is qualifying hours of work under either the title 5 rules or under OPM's FLSA regulations-in particular, 5 CFR 551.401(h) and 551.422.
Employee Coverage
Title 5 overtime laws and regulations apply to most FLSA-exempt Federal employees, including General Schedule and prevailing rate employees. Certain employees, such as members of the Senior Executive Service, are not eligible for overtime pay or other premium pay under title 5. (See 5 U.S.C. 5541(2) and 5 CFR 550.101 for coverage rules.)
OPM's FLSA regulations apply to most FLSA-covered Federal employees. (See 5 U.S.C. 5542(b)(2) and 5544(a)(3) and 5 CFR 551.102.) An employee may determine his or her FLSA status by checking block 35 of the most recent Notification of Personnel Action (SF-50) to find out whether his or her position is nonexempt (N) or exempt (E) from the overtime pay provisions of the FLSA. Alternatively, an employee may obtain a determination from his or her servicing personnel office.
Overtime Work
In general, overtime hours are hours of work that are ordered or approved (or are "suffered or permitted" for FLSA-covered employees) and are performed by an employee in excess of 8 hours in a day or 40 hours in a workweek. (See 5 U.S.C. 5542(a), 5544(a), and 6121(6) and (7), and 5 CFR 550.111 and 551.501. Note exceptions.)
Travel That is Hours of Work Under Title 5
Under 5 U.S.C. 5542(b)(2) and 5 CFR 550.112(g), official travel away from an employee's official duty station is hours of work if the travel is-
- within the days and hours of the employee's regularly scheduled administrative workweek, including regularly scheduled overtime hours, or
- involves the performance of work while traveling (such as driving a loaded truck);
- is incident to travel that involves the performance of work while traveling (such as driving an empty truck back to the point of origin);
- is carried out under arduous and unusual conditions (e.g., travel on rough terrain or under extremely severe weather conditions); or
- results from an event that could not be scheduled or controlled administratively by any individual or agency in the executive branch of Government (such as training scheduled solely by a private firm or a job-related court appearance required by a court subpoena).
An agency may not adjust an employee's normal regularly scheduled administrative workweek solely to include travel hours that would not otherwise be considered hours of work.
Travel That is Hours of Work Under the FLSA
For FLSA-covered employees, time spent traveling is hours of work if-
- an employee is required to travel during regular working hours (i.e., during the regularly scheduled administrative workweek);
- an employee is required to work during travel (e.g., by being required to drive a Government vehicle as part of a work assignment);
- an employee is required to travel as a passenger on a 1-day assignment away from the official duty station; or
- an employee is required to travel as a passenger on an overnight assignment away from the official duty station during hours on nonworkdays that correspond to the employee's regular working hours. (See 5 CFR 551.422(a).)
Official Duty Station
"Official duty station" is defined in 5 CFR 550.112(j) and 551.422(d). An agency may prescribe a mileage radius of not greater than 50 miles to determine whether an employee's travel is within or outside the limits of the employee's official duty station for determining entitlement to overtime pay for travel.
Administrative Workweek
An administrative workweek is a period of 7 consecutive calendar days designated in advance by the head of an agency under 5 U.S.C. 6101. The regularly scheduled administrative workweek is the period within the administrative workweek during which the employee is scheduled to work in advance of the administrative workweek. (See definitions in 5 CFR 610.102. See also 5 CFR 550.103 and 551.421.)
Commuting Time
For FLSA-covered employees, normal commuting time from home to work and from work to home is not hours of work. (See 5 CFR 551.422(b).) However, commuting time may be hours of work to the extent that the employee is required to perform substantial work under the control and direction of the employing agency-i.e., productive work of a significant nature that is an integral and indispensable part of the employee's principal activities. The fact that an employee is driving a Government vehicle in commuting to and from work is not a basis for determining that commuting time is hours of work. (See Bobo decision cited in the References section.)
Similarly, for FLSA-exempt employees, normal commuting time from home to work and from work to home is not hours of work. (See 5 CFR 550.112(j)(2).) However, commuting time may be hours of work to the extent that the employee is officially ordered or approved to perform substantial work while commuting.
Normal "home-to-work/work-to-home" commuting includes travel between an employee's home and a temporary duty location within the limits of the employee's official duty station. For an employee assigned to a temporary duty station overnight, normal "home-to-work/work-to-home" commuting also includes travel between the employee's temporary place of lodging and a work site within the limits of the temporary duty station.
If an employee (whether FLSA-covered or exempt) is required to travel directly between home and a temporary duty location outside the limits of the employee's official duty station, the time the employee would have spent in normal commuting must be deducted from any hours of work outside the regularly scheduled administrative workweek (or, for FLSA covered employees, outside corresponding hours on a nonwork day) that may be credited for the travel time. (The travel time is credited as hours of work only as allowed under the applicable rules-e.g., for an FLSA-covered employee, if the travel is part of a 1-day assignment away from the official duty station.)
- 5 U.S.C. 5542(b)(2) (General Schedule employees)
- 5 U.S.C. 5544(a)(3) (Prevailing rate employees)
- 5 CFR 550.112(g) and (j), 610.102, and 610.123
- 5 CFR 551.401(h) and 551.422 (OPM's FLSA regulations)
- Decision by United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit, Jerry Bobo v. United States , 136 F.3rd 1465 (Fed. Cir. 1998) affirming Court of Federal Claims decision of same name, 37 Fed. Cl. 690 (Fed. Cl. 1997).
- Section 4 of the Portal-to-Portal Act of 1947 (61 Stat. 84) as amended in 1996 by section 2102 of Public Law 104-188. (See 29 U.S.C. 254.)
Back to Top
A self-service hub for your administrative needs
Sign up for classes, review your benefits, check your paystubs, and more.
Hourly Employees: Compensation During Business Travel
While a non-exempt, hourly employee is generally not entitled to additional compensation for commuting to and from MIT or a related local work site, if the employee is traveling for business, they must be compensated in accordance with the guidelines on this page.
A non-exempt, hourly employee is generally not entitled to additional compensation for commuting to and from MIT or a related local work site.
- Example : A non-exempt employee who normally works on campus is assigned to work at Lincoln Laboratory for the day. They are not entitled to compensation for time spent commuting between home and Lincoln Laboratory.
However, if the employee is traveling for business, as opposed to commuting, they must be compensated in accordance with the guidelines on this page.
- Example : A non-exempt employee who normally works on campus attends a mid-day meeting at Lincoln Laboratory. Time spent travelling to and from Lincoln can be compensated.
- Example : A non-exempt employee who normally works on campus is asked to attend a conference in Chicago. They are entitled to compensation under the "Hourly Travel" guidelines.
- In general, an employee should not lose or gain regular (base) earnings as a result of travel.
- "Travel status," as used in these guidelines, refers to the time between leaving home or the regular workplace to begin business travel and returning home or to the regular workplace. It includes all time an employee is working and not working, including sleeping and socializing with colleagues.
- "In transit" refers to traveling from the point of departure to the destination and returning, or traveling between points on an itinerary. It does not include travel to and from a Boston-area airport, railroad, or bus station.
- Applying these guidelines in specific situations can be difficult. Managers and administrators are encouraged to consult their Human Resources Officer for guidance before travel occurs.
Travel not involving an overnight stay
- With certain exceptions, hours spent in authorized travel on official business, when an overnight stay is not required, is considered time worked for pay purposes.
- Exceptions : No compensation is needed for meal times and commuting time between an employee's home and the airport, railroad, or bus station.
- Example : A non-exempt employee flies to New York to attend a meeting and returns home the same day. They should be compensated for travel time to and from the meeting (e.g., flight time and cab rides), but not for commuting time between home and the airport.
Travel involving an overnight stay
- All time spent in "travel status," including time spent "in transit," during the employee's regular working hours and in the regular workweek, is considered hours worked for pay purposes.
Day One: They are entitled to compensation for time spent traveling to the conference after 9 a.m. and all time at the conference or elsewhere until 5 p.m. Meal times at the conference need not be counted as hours worked unless the employee is required to attend the meal, in which case that time is counted as hours worked.
Day Two: They should be compensated for all conference-related activities between 9 a.m. and 5 p.m., but not for the time spent flying home after 5 p.m. If the conference does not end until 6 p.m., they should be paid until 6 p.m. but not for the time flying home in the evening.
Travel involving weekends and holidays
- Time spent "in transit" on Saturdays, Sundays, and holidays during hours that correspond to the employee's regular working hours should be counted as time worked for pay purposes.
- Example : An employee who regularly works Monday through Friday, 7 a.m. to 3 p.m., takes the train home on Saturday from a three-day business trip to New York. They should be paid for hours on the train between 7 a.m. and 3 p.m. If the employee took the train home on Saturday after 3 p.m., they would not be paid for hours on the train. However, if the employee drove to New York and drove home on Saturday after 3 p.m., they would need to be paid for hours spent driving home.
- However, time spent on personal activities (e.g., eating or sleeping) on Saturdays, Sundays, and holidays, but not while "in transit," is not counted as time worked for pay purposes, provided the employee has no work duties or responsibilities.
Sleeping periods while "in transit"
- Time required to be "in transit" during the customary sleeping period (typically 11 p.m. to 7 a.m.) is counted as time worked, unless the employee has adequate sleeping accommodations and can occupy the accommodations for an uninterrupted period of no less than 6 hours.
- Example: An employee should be compensated for time spent taking the "red-eye" from Los Angeles to Boston.
Travel time compensation and overtime
- A non-exempt, hourly employee who is compensated for travel time in connection with any of the scenarios noted on this "Hourly Travel" page will be paid at his/her normal wage rate.
- If this travel time causes the employee to work more than 40 hours in a work week (or over 8 hours in a day, if required by an applicable collective bargaining agreement), the employee is entitled to overtime.
Create your address on the web.
- Domain Check
- Free Domain
Move your domain name to IONOS.
Secure site traffic and build trust.
Protect your domain from threats.
Create your own website easily.
Our experts build your website.
Create your own online store.
Fast, scalable hosting for any website.
Optimized for speed, reliablity and control.
Deploy your site, app, or PHP project from GitHub.
Reach out with your own email address.
Safeguard your emails against loss.
Secure and share your data on the go.
Powerful Exchange email and Microsoft's trusted productivity suite.
Collaborate smarter with Google's cloud-powered tools.
Protect your data from viruses, ransomware, and loss.
Pay as you go with your own scalable private server.
Your fully virtualized private server.
Get enterprise hardware with unlimited traffic
Individually configurable, highly scalable IaaS cloud
- Business Name Generator
- Logo Creator
- Favicon Generator
- Whois Lookup
- Website Checker
- SSL Checker
- IP Address Check
- Validation service
- Grow Your Business

Is business travel time working time?
There are many factors dictating whether or not an employee must be compensated for travel hours during a business trip in the UK. These factors include legislation, terms of contract and labour agreements . While it may seem unfair that workers are not routinely compensated for traveling time on business trips they are undertaking at the behest of the company, it is often the norm. This can have a tough impact on the payslips of employees who are required to travel for work frequently, especially abroad since travel times can last many hours. It also disproportionately affects higher earners, since those in more senior positions are often the ones required to attend conferences and meetings with clients to represent their company.
In recent years, several other countries have experienced court rulings deeming business travel time to count as working time. While the UK has much more relaxed labour laws than some other countries, it is important to be aware of the differences in working time regulations if you are running a company that operates in multiple countries.
Regulating work time on business trips
Two case studies.
In the UK, the remuneration of travel times for business trips is regulated individually . If you have a generous employer, they are likely to consider travel time on business trips to be working time and compensate you as such: i.e. the entire business trip is considered to be working time. However, these agreements usually have to be negotiated separately. If one is applying for a job that is known to have high levels of work travel time, it is recommended to negotiate the terms of business trips and legally enshrine them in the individuals‘ working contract from the very beginning to avoid any confusion. In some companies, working time during business trips is already outlined in labour agreements and collective agreements and may apply accordingly to all or only certain employees. In the UK, travel to and from clients is generally considered to be working time.
However, there are many instances when no legal rules apply to whether or not travel times are considered working time and whether these periods should be compensated, and by how much. In practice, the case is usually that the only hours which count as working time are the same hours the employee would normally work, e.g. 9 am to 5 pm. This means that if a business trip flight lasts three hours and begins at 7 am, the employee would be compensated for the final hour of 9-10 am since this falls within their normal working hours, but the first two hours are unpaid. However, if your work superiors request that you spend the flight doing work (e.g. preparing presentation slides or corresponding via e-mail), then those hours can be considered overtime.
There are certain exceptions to these rules if a worker’s activity consists of a significant amount travel time (i.e. a primary obligation), such as truck drivers or traveling salespeople. Companies may also have differing policies for domestic and foreign travel.
Working Time Regulations 1998
Another factor which may impact remuneration for an employee during business travel time is whether or not they are covered by the Working Time Regulations . The regulations stipulate that time spent commuting to and from work is generally not considered
to be working time. Although the regulations are unclear on time spent travelling abroad, a ruling by the European Court of Justice in 2015 stipulated that mobile workers – those without a fixed place of work – must be considered to be working when travelling to and from clients or sites. In other words, employees travelling between appointments must be compensated for the time spent travelling.
Employers should also take account of how travel affects the total working time of an individual. Unless an employee has signed an opt-out agreement, they should not work more than 48 hours per week without receiving compensation.
Case study 1:
A delivery service driver has a contractually stipulated working time of 6 am to 2:30 pm daily. At 6 am, they pick up their service vehicle from the company garage and drive to the central warehouse, where the vehicle is loaded with goods from 6:30 am. After the final delivery at 2:30 pm, the driver drives back to the company premises, where they cannot park their vehicle until 4 pm due to heavy traffic at the parking lot. In this case, the total working time from 6 am to 4 pm could be considered working time, since the employee would not be able to carry out their work duties without the travel time. It can, therefore, be considered the main obligation.
Case study 2:
An insurance company employee is sent out to meet with a client who, due to unforeseen circumstances, is unable to come to the insurance company office. Meeting clients outside the office is generally outside of the employee’s remit. The employee’s usual work hours are between 8 am and 5 pm. The client meeting lasts from 4 pm to 5:30 pm, and then the employee drives straight home without first returning to work.
In this instance, only the 30 minutes spent meeting the customer count as work overtime. The return journey is not considered working time since the employee is returning home instead of back to work. If the employee’s manager had contacted them and requested that they return to the office to work late and write an additional report about the meeting, then the drive back to the office would have been considered working time, and been compensated accordingly.
Please note the legal disclaimer relating to this article.
Related articles

Maximum working hours for employees
In the UK, employees shouldn’t work more than 48 hours a week, but you can voluntarily decide to opt out of this and work extra hours. But what exactly counts as working hours? This article explains all about the maximum working hours so make sure you’re not unknowingly doing too many hours.

Time tracking – what should you know?
The laws governing employee time tracking are set out under the UK Working Time Regulations. But things like overtime and meal breaks are managed differently from company to company. However, every employer in the UK is obliged to keep records for their employees, including the hours worked each day and the total hours worked per week. What kind of data must be collected and what role does data…

Travel expense accounting: how to correctly reimburse travel expenses
Costs incurred during a business trip can be claimed back from the employer or in your own tax return. In order to do this, you need a detailed list of the individual costs in the travel expense report. But which costs can be claimed for tax purposes and to what extent? And what are the differences between business trips at home and abroad?
An official website of the United States Government
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Search Toggle search Search Include Historical Content - Any - No Include Historical Content - Any - No Search
- Menu Toggle menu
- INFORMATION FOR…
- Individuals
- Business & Self Employed
- Charities and Nonprofits
- International Taxpayers
- Federal State and Local Governments
- Indian Tribal Governments
- Tax Exempt Bonds
- FILING FOR INDIVIDUALS
- How to File
- When to File
- Where to File
- Update Your Information
- Get Your Tax Record
- Apply for an Employer ID Number (EIN)
- Check Your Amended Return Status
- Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN)
- File Your Taxes for Free
- Bank Account (Direct Pay)
- Payment Plan (Installment Agreement)
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Your Online Account
- Tax Withholding Estimator
- Estimated Taxes
- Where's My Refund
- What to Expect
- Direct Deposit
- Reduced Refunds
- Amend Return
Credits & Deductions
- INFORMATION FOR...
- Businesses & Self-Employed
- Earned Income Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Clean Energy and Vehicle Credits
- Standard Deduction
- Retirement Plans
Forms & Instructions
- POPULAR FORMS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Form 1040 Instructions
- Form 4506-T
- POPULAR FOR TAX PROS
- Form 1040-X
- Circular 230
Understanding business travel deductions
More in news.
- Topics in the News
- News Releases
- Multimedia Center
- Tax Relief in Disaster Situations
- Inflation Reduction Act
- Taxpayer First Act
- Tax Scams/Consumer Alerts
- The Tax Gap
- Fact Sheets
- IRS Tax Tips
- e-News Subscriptions
- IRS Guidance
- Media Contacts
- IRS Statements and Announcements
IRS Tax Tip 2023-15, February 7, 2023
Whether someone travels for work once a year or once a month, figuring out travel expense tax write-offs might seem confusing. The IRS has information to help all business travelers properly claim these valuable deductions.
Here are some tax details all business travelers should know
Business travel deductions are available when employees must travel away from their tax home or main place of work for business reasons. A taxpayer is traveling away from home if they are away for longer than an ordinary day's work and they need to sleep to meet the demands of their work while away.
Travel expenses must be ordinary and necessary. They can't be lavish, extravagant or for personal purposes.
Employers can deduct travel expenses paid or incurred during a temporary work assignment if the assignment length does not exceed one year.
Travel expenses for conventions are deductible if attendance benefits the business. There are special rules for conventions held outside North America .
Deductible travel expenses include:
- Travel by airplane, train, bus or car between your home and your business destination.
- Fares for taxis or other types of transportation between an airport or train station and a hotel, or from a hotel to a work location.
- Shipping of baggage and sample or display material between regular and temporary work locations.
- Using a personally owned car for business.
- Lodging and meals .
- Dry cleaning and laundry.
- Business calls and communication.
- Tips paid for services related to any of these expenses.
- Other similar ordinary and necessary expenses related to the business travel.
Self-employed individuals or farmers with travel deductions
- Those who are self-employed can deduct travel expenses on Schedule C (Form 1040), Profit or Loss From Business (Sole Proprietorship) .
- Farmers can use Schedule F (Form 1040), Profit or Loss From Farming .
Travel deductions for the National Guard or military reserves
National Guard or military reserve servicemembers can claim a deduction for unreimbursed travel expenses paid during the performance of their duty .
Recordkeeping
Well-organized records make it easier to prepare a tax return. Keep records such as receipts, canceled checks and other documents that support a deduction.
Subscribe to IRS Tax Tips
- Share full article

Planning to Combine Business and Leisure Travel? You’re Not Alone.
As employees increasingly add leisure time to their business trips, companies are trying to figure out where their duty of care obligations begin and end.
Credit... Aart-Jan Venema
Supported by
By Amy Zipkin
- April 7, 2024
On a Sunday in late January, Melinda Buchmann, who lives in Florida and supervises client relations for RevShoppe, a 30-person remote company advising organizations on sales techniques and strategies, arrived in Banff, Alberta, to help set up a four-day company meeting.
The last day of the event, her husband, Josh, a director of strategic partnerships for the delivery company DoorDash , who also works remotely, joined her. They spent two leisurely days hiking in Banff National Park and visiting Lake Louise.
“I take advantage, because I don’t know when I’m going to return,” Ms. Buchmann said of the decision to combine downtime with a business trip.
As postpandemic work life has changed, and arrangements now include full-time office attendance as well as hybrid and remote work, so, too, has business travel. The phenomenon known as bleisure, or blended business and leisure travel, was initially embraced largely by digital nomads . But such combined travel is now also popular with people outside that group . Allied Market Research, a subsidiary of Allied Analytics, based in Portland, Ore., estimated that the bleisure travel market was $315.3 billion in 2022 and would reach $731.4 billion by 2032.
As employees increasingly add leisure time to their business trips, companies are struggling to determine where their legal obligation to protect employees from harm — their so-called duty of care — begins and ends. And workers may think that because their trip started with business, they will get all the help they need if something goes wrong on the leisure end. Instead, they should generally consider the leisure part of a trip as a regular vacation where they cover all expenses and contingencies.
Companies are responsible for knowing where their employees are during a business trip, covering expenses if an accident or emergency occurs, securing new lodging if a hotel is damaged, even swapping out a broken down rental car. Still, it’s not entirely clear if that coverage ends completely after the conference or the last client meeting.
Companies recognize that threats are increasing, said Robert Cole, senior research analyst focusing on lodging and leisure travel at Phocuswright, a market research company. They are trying to figure out how to take care of a valuable company resource, the employee, without leaving themselves open to financial risk or potential litigation.
“Crafting a comprehensive policy that balances business objectives, employee well-being and legal considerations can be challenging,” Nikolaos Gkolfinopoulos, head of tourism at ICF, a consulting and technology services company in Reston, Va., wrote in an email.
Employees may be on their own without realizing it and may be surprised by out-of-pocket expenses if they require hospital care abroad or evacuation, said Suzanne Morrow, chief executive of InsureMyTrip , an online insurance travel comparison site in Warwick, R.I.
Ms. Morrow said medical coverage provided by a company “is generally only for the dates of the actual business trip abroad.” If travelers are extending the trip for personal travel, she added, “they would want to secure emergency medical coverage for that additional time abroad.”
Employers and employees are left to figure out when the business portion of the trip ends and the leisure segment begins, a significant detail if an employee has a medical emergency. “Where does the corporation liability end?” said Kathy Bedell, senior vice president at BCD Travel, a travel management company.
Companies have varying policies to deal with the new travel amalgam. The chief executive of RevShoppe, Patricia McLaren, based in Austin, Texas, said the company provided flexible travel options and allowed employees to work anywhere they choose.
Even so, there are constraints. The company requires all employees, including executives, to sign liability and insurance waivers when they are on a voluntary company-sponsored trip, such as an off-site meeting. Such waivers typically place responsibility on employees for their own well-being. And if they bring someone, they are responsible for that person’s expenses.
Employees are responsible for requesting the paid time off and notifying their managers of their whereabouts, although that part is not a requirement. Managers have to ensure adequate staffing, Ms. McLaren said.
Elsewhere, employees may not bother to mention the leisure portion of their trip. Eliot Lees, a vice president and managing director at ICF, said he had been on trips as a child with his parents when they combined business and leisure. His parents were academics, who would piggyback vacations onto conferences.
Now he does the same. “I don’t think I ever asked for approval,” he said. (ICF has no formal business-leisure travel policy. It’s allowed as part of personal time off.) After a conference in the Netherlands last year, he spent four days hiking in the northern part of the country.
“I go anywhere, and take more risks than I should,” he said. He said he didn’t carry personal travel or accident insurance.
Any nonchalance may quickly evaporate if a threat emerges. Security experts say even low-risk locations can become high-risk for a few days or weeks of the year.
“Companies are concerned about losing visibility into a traveler’s whereabouts if they booked flights and hotels outside their corporate travel management company,” Benjamin Thorne, senior intelligence manager in London for Crisis24, a subsidiary of GardaWorld, wrote in an email. “The company may think the traveler is in one city when, in reality, they could have booked a holiday package to another nearby city. This lack of visibility by the company makes it difficult to support travelers when a disaster occurs.”
He also raised the possibility that “a traveler with bleisure travel reservations and expectations may find their work trip canceled due to changes in the risk environment or company policy, disrupting their leisure plans.”
Will a company step in off hours if there’s a problem? “That depends on how you are booked,” Mr. Cole, the senior research analyst at Phocuswright, said. A rule of thumb is the further you get from corporate control, the greater the gray area gets.
Half of GoldSpring Consulting’s clients take the responsibility for the entire trip, said Will Tate, a partner at the consultancy based in Cross Roads, Texas, and a certified public accountant. They don’t want the reputational risk. The other half say: “The business trip ended Friday. That’s when we end our duty of care.”
Some companies are trying to define and narrow the gray area. “If you are clearly on personal time, there is no legal requirement for your employer to provide for you,” said Nicole Page, a lawyer whose practice includes employment law at Reavis Page Jump in New York.
Uber provides employees with advisories before a trip, travel assessments, safety tips while traveling and emergency travel assistance, including medical aid, airport travel support, urgent and emergency assistance, and lost or stolen personal property insurance whether they are on business or pleasure travel or a combination.
And at DoorDash, Chris Cherry, head of global safety and security, wrote in an email that “while personal travel is not something we track, we have received requests to extend our travel support capabilities to personal travel.” Mr. Cherry said in those cases, the company has manually added employee leisure itineraries to its travel risk management system and “provided the same level of overwatch that we do for regular business travel.”
The Buchmanns plan to travel this month to Barcelona, Spain, for the McDonald’s Worldwide Convention. DoorDash will have a booth, and Mr. Buchmann will work on the exhibit floor and also entertain clients.
Ms. Buchmann will accompany him. She plans to go sightseeing in the morning, and work in the afternoons and evenings Barcelona time. She will also take three days of paid time off and has shared her plans with Ms. McLaren, the RevShoppe chief executive.
They will stay a day after the conference and plan to visit the Dalí Theater and Museum in Figueres. “I’m sure there will be no shortage of tapas and window shopping along way,” Mr. Buchmann said. He expects to be back at work the next Monday.
Explore Our Business Coverage
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping the world of business..
Stopping a Huge Cyberattack: A Microsoft engineer noticed something was off on a piece of software he worked on. He soon discovered someone was probably trying to gain access to computers all over the world .
Hoping for an A.I. Productivity Boost: Economists doubt that A.I. is already visible in productivity data . Big companies, however, talk often about adopting it to improve efficiency.
Cashing In on Graffiti: Brands, developers and even officials are embracing the global appeal of street art , but the boom comes with questions about preserving a neighborhood’s cultural cachet.
‘Twitter Menace’ or True Believer?: The deep-pocketed tech investor Garry Tan says he wants to save San Francisco. But his pugnacious online habits are making him enemies .
A C.E.O.’s Bold Claims: Amira Yahyaoui, a human rights activist, promoted the success of her student aid start-up, Mos. Some of her statements do not add up .
Advertisement
More From Forbes
Business travel is back—jump in with these travel essentials.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
It’s time to leave your work-from-home set up and not just for a stint into the office. Business travel is once again trending and many of us have not restocked our travel bags in years. Now is the perfect time for a travel closet refresh and these items will help you look your best and be better prepared for that next official meeting.
Arrive in style with this suit
A terrific wrinkle-free suit from Bonobos
Bonobos is well known for offering key wardrobe pieces that can be easily styled and customized. An excellent choice for business travel is the Jetsetter stretch wool suit. The tailoring looks great and the material—97% wool, 3% stretch—prioritizes comfort. This all-season suit features modern notch lapels, double-button placket, double vent, non-functioning button cuffs, Bemberg lining and an interior passport pocket. You can choose between slim, regular and athletic fit and a host of colors. The wrinkle-resistant fabric guarantees you will look terrific upon arrival.
A stylish choice from Veilance
A multi functional work friendly dress from Arc’teryx
While you may shop Arc’teryx for its outstanding outdor gear, its Veilance line is geared towards fashionable urban dwellers. A perfect piece that can transition from day to night is the Icosta dress. This new wardrobe favorite offers comfort, performance and lots of extra style. The stretch polyester weave makes it easy to move around in and its moisture wicking quality will help you stay cool in stuffy meeting rooms. Small pockets are a nice, welcome touch and ultrasonic finishing throughout provides clean lines and seamless luxury.
The Surface Pro 9
Why You Should Stop Sending Texts From Your iMessage App
Apple ipad pro 2024 release date latest news on when it will launch, paris 2024 olympics morocco miss out on historic qualification zambia qualifies.
An ideal laptop from Microsoft
If it’s time to upgrade your laptop, Microsoft’s Surface Pro 9 is a great choice. The Surface Pro 9 provides terrific laptop performance and up to 19 hours of battery life for long workdays. It can also be used as a tablet and provides an ideal screen for a late-night movie in your hotel room. Another plus—it weighs less than two pounds. You can customize the device and keyboard with multiple colors and materials. And if AI is on your wish list, Microsoft’s Copilot is easily integrated into this newest Surface device.
A fashionable backpack
A sleek backpack from Thule
It is definitely time to update your backpack. The Thule Subterra 2 21L backpack is perfect for the modern traveler; it combines a streamlined look, numerous features and storage compartments for all your needs. Inside, you will find padded laptop and tablet sleeves to ensure that your tech stays safe. And an interior organization section keeps pens, chargers, keys and other essentials in place. A back “security” pocket allows you to keep your passport and wallet hidden, but easy to access. As an added bonus, the bag is bluesign® certified, meaning it is manufactured with the environment in mind.
Durable and stylish travel jewelry
Designer travel jewelry from D. Louise
If you want to look stylish, but don’t want to tote your authentic gold and diamond pieces with you when you travel, then consider a purchase form D. Louise. This British company makes incredibly fashionable pieces that are appropriate for business meetings and adventure treks. The pieces are gold-plated stainless steel and use a coating process that is 10 times stronger than standard gold plating and is environmentally friendly. This is jewelry that you can confidently swim and work out in. All pieces are guaranteed not to fade or tarnish. In addition, the packaging is sustainable and the company plants a tree for every order placed.
Cozy wool slippers
Get cozy with these wool slippers from Glerups
This Danish company has been making environmentally friendly wool footwear for decades. Wool is naturally temperature regulating, odor-resistant and breathable and these Glerups come in multiple styles and colors. Stay comfortable during long flights or in your hotel room with these extremely lightweight wool slippers. They can be ordered with leather or rubber soles and are also ideal for a quick trip to breakfast buffet. The company uses wool that is carefully sourced from Danish Gotland sheep and sheep from New Zealand on farms committed to regenerative agriculture.
Multi-purpose sunglasses
Versatile sunglasses from ROKA
You can look terrific and obtain outstanding features with the newest sunglasses from Roka. The Oslo 2.0 includes upgraded hinges, temples, and GEKO™ grip placement. These features help to create a better fit during all activities. You can gain sun protection while navigating any city and also use these during an outdoor run or a trip to the beach, so there is no need to pack multiple pairs of sunglasses. ROKA glasses come in multiple colors and lens options and are customizable. Try them on virtually to see which you prefer.
A favorite travel pillow
A favorite neck pillow from Turtl
If you struggle to get comfortable on those longer flights, consider the Turtl. This innovative neck pillow might just allow you to get a bit of a rest before your arrival. The Turtl comes in four colors and offer multiple benefits. There is complete support for your head, so you won’t bump into your seatmate and it has been demonstrated to relieve stress on your spine and muscles. The soft fleece fabric will help you feel comfy as you nod off.
Protect your phone in style
Magsafe phone case from Otterbox
The Symmetry Series soft-touch phone case is an ideal travel companion. It provides durable protection so you don’t need to worry if you accidentally drop your phone (3 times as many drops as the military standard.) The ultra slim design means it is easy to slip in and out of pockets and the soft touch material makes it easy to grip. The case comes equipped with built in magnets that lets you charge your phone from any MagSafe charging device.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Money latest: US burger chain expanding in UK; Spotify hiking prices again
American burger chain Wendy's will be recruiting for over 400 job roles as part of its expansion across the UK. Meanwhile, Spotify is raising prices again. Read about this and the rest of today's consumer and personal finance news in the Money blog, and leave a comment in the form below.
Thursday 11 April 2024 13:38, UK
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
- Spotify to hike subscription price by up to £24 a year
- Minimum income for family visa rises by £10,000
- Britons can now 'work from home' in Italy for a year
- Wendy's creating 400 jobs as part of UK expansion
- Britons buying homes, having babies, getting married and retiring later - but one key life event is happening earlier
- 'WTF is going on with the price of olive oil?'
- Could I build a home gym for less than my gym membership?
- Basically... Tax codes
- Cheap Eats : Great British Menu legend shares ultimate toastie recipe
Ask a question or make a comment
Rishi Sunak's post-Brexit rules for foreign workers are getting tough press in Italy this week - with claims they could mark the end of Italian waiters in London.
April saw the minimum salary requirement for a skilled worker visa increase from £26,200 to £38,700 - a near 50% rise as the government tries to reduce immigration.
Italian daily newspaper La Repubblica published an article on its site headlined "Italians in London, the long goodbye" after the new rule was brought in this month.
There were an estimated 342,000 Italians living in the UK in 2021, according to the latest Office for National Statistics census data.
La Repubblica said the new rule change would lead to the "end of the story" of Italy's "ancient roots" in the capital, which was founded by the Romans in 43 AD.
Separately, Italian journalist Antonio Polito wrote in the Corriere della Sera newspaper that the new salary for skilled workers was "an amount that no young novice can realistically earn".
"Thus London gives up one of its great assets, the fact of being an offshore and cosmopolitan city," he said.
Mr Sunak's post-Brexit rule change has worried hospitality bosses who are still struggling to get to grips with a post-COVID reality and rising costs.
Conor Sheridan, founder of Nory and Mad Egg restaurant chain, previously told the Money blog that roughly 14% of his 15,000 UK employee base were on working visas that could be affected.
Trade body UKHospitality also said the changes would "further shrink the talent pool that the entire economy will be recruiting from".
As the migration law came in, Home Secretary James Cleverly said it was "time to turn off the taps and end the flow of cheap workers from abroad".
"We are refocusing our immigration system to prioritise the brightest and best who have the skills our economy needs, while reducing overall numbers," he said.
Several of the UK's biggest supermarkets closed their gender pay gap in the last year - while Morrisons saw the biggest rise, figures show.
Ocado and Lidl reduced their gap by the largest amounts in 2023-24 compared to the previous year, while Tesco, Asda, Aldi, Co-op, Iceland and Waitrose owner John Lewis also saw a reduction.
The data comes from the government's gender pay gap service and states the difference in hourly rates of pay.
In contrast to other big-name brands, Morrisons saw its mean pay gap widen to 12.5% from 7.6%. M&S also saw a slight increase from 12.5% to 12.6%.
The mean figure gives the best overall view of the gender pay gap but includes extreme values which could skew the average.
Of the 11 biggest UK supermarkets, Co-op has the largest pay gap with 13.2%, followed by M&S and Morrisons.
An M&S spokesperson said: "We're committed to driving equal opportunities and making M&S a great place to work for women. Encouragingly our median pay gap has decreased, and women now make up more than 50% of our UK store management population, but we know there is more to do.
"We're making progress with the launch of new initiatives, talent programmes, and policies, including our flexible working offer – Worklife, a Job Share Finder, and our industry-leading family leave offer."
A spokesperson for Co-op said: "We are committed to treating our colleague member owners fairly, and this includes driving equitable outcomes for female colleagues. We've seen a significant reduction in our gender pay gap since we started to report data in 2017, and this year's data shows further progress towards closing it.
"It's important to reiterate that we don't pay people differently based on their gender at Co-op. The gender pay gap is caused by us having fewer females in leadership role, where salaries are higher.
"Our focus on improving representation remains, as we know this is one of the key drivers causing the gender pay gap. Today, 40% of our leadership population are female - this is not enough, which is why we’ve launched a series of development programmes and have a coaching and mentoring offer to support women with career progression.
"We know there’s still much to do in this space and will hold ourselves to account and continue to strive for gender equality."
Morrisons has also been contacted for comment.
Every Thursday we look at a different savings option, explain the pros and cons, and reveal the best deals on the market (see table below for that). This week we're talking about the best notice accounts. Savings Champion founder Anna Bowes says this...
As with the rest of the savings market, the top notice account rates have started to fall. However, there are stalwarts like the Investec 90-day notice account that are holding steady and as a result offering savers an opportunity to earn a little more, while not having to tie up their cash for too long.
A relatively unused aspect of the savings market, notice accounts offer a bit of a halfway house, with the best rates available generally paying more than the top easy access rates, but will more flexibility of access than a fixed term bond.
Just as it sounds, these savings accounts require you to give notice in order to access your money without a penalty. The usual notice period ranges from 30 to 120 days, although there are some accounts on the market that require six months or even a year's notice.
By Sarah Taaffe-Maguire , business reporter
Another record month for Heathrow. Last month was the busiest ever March for the UK's biggest airport, the second record-breaking month in a row.
It was also the busiest Easter weekend as Good Friday became the busiest ever direct departure day, when 118,000 people began their journey at the airport.
It shows, despite cost of living pressures, lots of Britons were going on holiday.
More good news for Heathrow came earlier this week as planned strike action by 600 border force officers was called off to allow for negotiations in its dispute over working patterns.
Oil prices are still high, hanging around $90. A barrel of Brent crude oil, the benchmark for oil prices, costs $90.66. The last time prices were this high was in the wake of the 7 October attacks and fears of conflict spreading throughout the Middle East.
On the currency front, £1 buys $1.2538 and €1.1678.
How old is the average Briton when they buy their first home, or finish paying their mortgage, or retire?
These are some of the questions answered in a "Journeying Through Life" data dump from the Office for National Statistics.
Here are some of the key takeaways...
Home ownership - including the one life event that's happening earlier
People are buying homes later in life, perhaps unsurprisingly given how house prices have risen in the last decade or so.
In 2022, more than half of people owned their own home (either with a mortgage or outright) by the age of 36.
That's a significant increase on 2004's figures - which showed the average age for home ownership was 32.
This graph shows what proportion of people own homes at what age.
It isn't all doom and gloom on the homes front, however, with the age at which people own their home outright (ie mortgage paid off) dropping from 63 (in 2004) to 61 in 2020.
This is pretty much the only life event happening earlier, however.
Retiring later
Again, this probably won't come as a huge surprise, but people are retiring later.
The age where more than half of people were retired increased from 64 in 2011 to 66 in 2021.
There has been a bigger increase in average retirement age for women (from 61 years in 2011, to 66 years in 2021) than for men (from 65 in 2011 to 66 in 2021).
The ONS says this is because the state pension age for women was increased from 60 to 66 during this time to match men.
Gender pay gap shrinking but still present
The latest data shows that men are still, on the whole, being paid more than women - although the gender pay gap is shown to be shrinking.
For all employees, the gender pay gap was 14% in 2023 - compared with 20% in 2013.
Despite the gap shrinking, this graph shows that men's hourly wages are higher than women's at nearly all ages.
The grey shaded area represents the pay gap.
Another part of the data shows that males start work a touch earlier than women - with half of males in full-time employment by the age of 23 (compared with females at 24) in 2021.
That data could be explained by the fact that more women attend university - some 319,000 females compared with 285,000 males in 2022.
Moving out, marrying and having children
The age at which young people move out of their family homes is increasing, too.
In 2011, half of people were not living with their parents at the age of 21 - compared with 24 in 2022.
More men live with their parents than women, with 61% of adults living at home in 2021 were male.
When it comes to having children, the average age at which women have their first baby has risen to 29.
That's up from an average of just 23 in 1970.
And finally, marriage.
The median age at first marriage has been steadily increasing since the 1960s.
For opposite sex couples married in 2020, the median age was 32 years for men and 30 years for women. For those entering into same-sex marriage, the median age was older, at 36 years for men and 32 years for women.
As well as getting married older, fewer people are getting married. In 2019, marriage rates had fallen to their lowest on record. For men, there were 18.6 marriages per 1,000 never-married men; for women, there were 17.2 marriages per 1,000 never-married women.
Spotify has announced it is hiking its subscription prices by up to £24 a year.
It is the second time in less than a year that the music streaming giant has increased its prices.
Here's how the prices will change...
Individual: £11.99 a month (up from £10.99 a month)
Duo: £16.99 a month (up from £14.99 a month)
Family: £19.99 a month (up from £17.99 a month)
When will the change kick in?
The subscription price will change from May and if you are an existing customer Spotify will email you and give you one-month's notice of the change.
If you are on a free trial you will pay the old price for one month once your trial ends.
A Spotify spokesperson told Sky News: "So that we can keep innovating and delivering value to fans, the music industry, and creators on our platform, we occasionally update our prices.
"We've begun communicating with existing subscribers in the UK to explain what this means for their account."
American burger chain Wendy's will be recruiting for over 400 job roles as part of its expansion across the UK.
The chain returned to the UK in 2021 after a 20-year break and has since opened just over 30 sites, including drive-throughs in Colchester, Peterborough, Derby and Brampton Hut.
But the chain, which was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1969, plans to open a further nine sites this year in Liverpool, Middlesbrough, and a second location in Sheffield.
New locations will include Liverpool, Middlesbrough and a second site in Sheffield.
Wendy's franchisee GH Burgers will open a first restaurant in Wood Green, London, this year.
There will also be restaurants in Southend-on-Sea, Colchester, Cambridge and Newcastle.
Michael Clarke, UK managing director for the Wendy's Company, told The Caterer : "We've seen great momentum in building Wendy's fandom in the UK, and the love and excitement for this iconic brand grows stronger with each new restaurant opening."
Changes to visa rules costing people thousands of pounds extra "destroy the notion of the UK as a place where families can thrive", campaigners have said.
The minimum income for family visas rises by more than £10,000 to £29,000 today.
It will rise further to £38,700 early next year.
Reunite Families UK claimed the values of family and love are being treated as "as yet another political football to be sacrificed in order to receive better poll or electoral results".
The government says the plans offer "an accelerated and comprehensive programme of reforms" to address "unsustainable" levels of legal migration to the UK.
Justifying its plans, the Home Office said the minimum amount had remained unchanged for more than a decade, and the new measures will help ensure families are self-sufficient and not relying on public funds.
'We just want to be with our families'
Argentinian Eugenia Morales said the uncertainty around her and her baby daughter being able to reunite with her husband in the UK had taken a toll.
The 30-year-old has been with her partner Connor White for three years but is unsure whether - after having their daughter in Argentina - she will be able to join him in England.
She said Mr White, who is based in West Sussex, cannot leave his eldest child from a previous relationship and has been working weekends in his construction job to try to boost his income to the required amount to sponsor his wife.
Ms Morales said she would be looking for a job in the UK and would not have access to benefits while applying on the family visa route anyway.
She told the PA news agency: "We don't want to be a burden to the [welfare] system, we just want to be with our families.
"It's an awful situation. We want to be together, we want the girls to grow up together but this is making it totally impossible."
Caroline Coombs, co-founder of Reunite Families UK, said people are feeling "punished" and "excluded" by the new rules.
Ms Coombs said: "This increase, together with the ones which will come into force in the next 12 months, destroy the notion of the UK as a place where families can thrive."
Athletics will become the first sport to introduce prize money at the Olympics this summer.
World Athletics, the international athletics federation, says it will pay Olympic gold medal winners $50,000 at the Paris games.
The athletics governing body said it is setting aside $2.4m (£1.89m) to pay the gold medallists across 48 events at Paris' track and field programme.
Read the full story here ...
The tweet below on the price of olive oil has gone viral - so we thought it was a good opportunity to resurface our feature from March that explains what's going on.
At the time, our spending calculator revealed the average price of a 500ml bottle of olive oil had risen from £3.54 in January 2021 to £7.45 now - an eyebrow-raising jump of 110.5%.
We spoke to experts about why - and here's what we learned...
Groves becomes graveyards
We start in Italy, where, according to a survey by the polling firm Istituto Piepoli , 45% of consumers have rediscovered seed oil in the kitchen, and the industry is facing an existential crisis.
Mike Carlucci, managing director of the Italian food importer Tenuta Marmorelle , says production in parts of Italy is becoming impossible due to a natural disaster that has nothing to do with the climate.
"The events of the past 10 years have made olive oil production in Puglia [which produces 40% of Italy's olive oil] almost impossible," he said. "This is due to the rising bacteria disease Xylella Fastidiosa."
The disease attacks and kills century-old olive trees, severely diminishing yields.
It spreads about 20km to 25km a year, Mike says, leaving a "graveyard of withered and barren trees which were once stunning beautiful olive groves".
Many producers have been forced to replace their trees with more resilient varieties but...
"Even if the new trees manage not to succumb to Xylella, it will be at least nine to 12 years before they produce a notable amount of oil," says Mike.
While prices are up across the continent, in the UK another factor is in play: Brexit.
"The cost of customs documentation leaving Europe and entering the UK is approximately £95 per shipment," says Mike.
"Transporters have all imposed a Brexit surcharge for extra admin duties performed by them in the importation of goods from Europe."
Pallets coming into the UK from the continent are now subject to more stringent fire resistance rules - meaning the cost of pallets has "tripled, even in some cases quadrupled".
'Never had a shortage like it'
Another issue, as has been widely reported, are the wildfires and droughts in southern Europe last year.
These weather events have lead people to extreme measures, according to Sarah Vachon, olive oil sommelier and founder of citizensofsoil.com .
"You can ask the elders in the villages in Greece and they've never had a shortage like this," she says.
"I see lots of producers selling their previous harvest's oils, since they're able to get a high price for it and might have held on to it over the year.
"This means the consumer is not getting fresh EVOO. And when it's not fresh, it not only loses its flavour, but it also loses a lot of the health benefits (namely antioxidants like polyphenols) which drop significantly over time."
On top of climate change, there's a flood of cheap sunflower oil coming from Ukraine - so while the price of olive oil is going up, the cost of alternatives are going down.
200 trees stolen overnight
The result is an industry in crisis - and organised criminals are taking advantage.
"Around half of the farmers I work with have a story to tell about thieves stealing their liquid gold," says Sarah.
"Sometimes it's the oil itself, or the olive fruit at the groves, or even an insane story from one of our producers about thieves coming in the night and uprooting 200 freshly planted trees."
Maria Dawson, managing director of the organic food seller Clearspring, says the industry is seeing "some of the lowest levels of olive oil production for five decades and unfortunately a shortage of supply".
The company has managed to secure a stable supply for the coming year, but Maria expects the market to remain uncertain - with no price reductions in the near future, even if 2025 brings better harvests.
Olive oil sommelier Sarah isn't hopeful, either.
"Olive oil is already facing record prices, and the way the climate is changing across the Mediterranean basin (which is warming 20% faster than the rest of the world), the shortages we've seen will likely continue."
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
COMMENTS
There is no standard regulation for business trips that take place outside of work hours. Whether the business trip can be counted as work time depends on the situation. Regulations concerning this matter can usually be found in your contract of employment or labour agreement. By the way, employees in high positions and corresponding abundant ...
The reason for a trip, your typical work hours, and the nature of the trip — overnight vs. day trip, for example — impact eligibility for travel pay. Below are a few types of work-related travel time: ... Time spent traveling on a business trip within the hours they regularly work (9 a.m. to 5 p.m., for example) is eligible for travel pay. ...
To be able to claim all the possible travel deductions, your trip should require you to sleep somewhere that isn't your home. 2. You should be working regular hours. In general, that means eight hours a day of work-related activity. It's fine to take personal time in the evenings, and you can still take weekends off.
While your specific state may have its own regulations, the Department of Labor (DOL) has guidelines for determining which parts of time spent traveling are considered working hours. Here are a number of the key issues: Day Trips. According to the DOL, for one-day business trips, the employee is compensated for all of their time spent traveling between work sites, but you may subtract time ...
Time spent traveling during normal work hours is considered compensable work time. Time spent in home-to-work travel by an employee in an employer-provided vehicle, or in activities performed by an employee that are incidental to the use of the vehicle for commuting, generally is not "hours worked" and, therefore, does not have to be paid. This provision applies only if the travel is within ...
Which Hours Must Employers Count as Work Time? By Jean Murray. Updated on September 19, 2022. Fact checked by Mrinalini Krishna. In This Article. Photo: David Burton / Getty Images. A look at what is considered work time for overtime purposes, including on-call time, travel time, attendance at events, and other time.
FLSA dictates that the legal working week consists of 40 hours over seven days. Anything over this is considered overtime and must be compensated at a payment rate of time-and-a-half. Trips made for business often result in overtime being incurred, and employees must be compensated for this. This rule does not apply to those not covered by FLSA ...
For example, an employee with a normal work schedule of 8 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. Monday through Friday who works on employer-directed tasks after 4:30 p.m. during weekend travel for work must receive employee travel overtime pay for all time worked after 4:30 p.m. Considerations for Business Travel Time Compensation. Business travel policy
A tool to track work hours during business trips. In any situation, the best thing to do to keep a record of the working day for workers who are not always in the office is to have a time tracking software with geolocation that complies with the law and is adapted to the needs of jobs that require traveling. It is all about choosing the right ...
Generally, employees should be compensated for all time spent traveling during regular business hours. This is also true for non-working days, as long as they are still on the business trip. However, if an employee is a passenger on a plane, train, or automobile, and the travel is during non-work hours, and the employee is not required to and ...
Travel That is All in a Day's Work: Time spent by an employee in travel as part of their principal activity, such as travel from job site to job site during the workday, is work time and must be counted as hours worked. Travel Away from Home Community: Travel that keeps an employee away from home overnight is travel away from home.
1. You could count business hours at the expo in one total and then keep a separate total count for business meetings (including eating out). If it isn't a business meeting, don't count it (if you're in the hotel chatting and you aren't obligated to be there, it isn't a business meeting) - Brandin. Apr 27, 2015 at 9:48.
Tips for taking a one-day work trip. Remember: this business travel guide is for anyone taking a work trip that lasts only one calendar day, not a 24-hour trip that involves one night in a hotel. I've recently done one of those as well, and the difference is that you really do require a whole night's worth of things.
15. Workout gear. Even on a business trip, it's important to focus on your well-being. Pack some workout clothes and shoes so you can continue your exercise routine in a hotel gym or by going for a run close by where you are staying during your business trip. 16. Pajamas.
Here's a possible rule of thumb: If your business authorizes a trip by an employee, no matter how the employee travels (car, train, bus, etc.) you should pay for the employee's travel time. ... "Fact Sheet: Hours of Work for Travel." Accessed May 26, 2020. U.S. Department of Labor. "Fact Sheet #17D: Exemption for Professional Employees Under ...
One-day trips. If the business sends you on a one-day business trip, the company typically pays for the time it takes you to travel to and from the destination. Depending on the company, they may pay you a portion of these travel fees only. You can calculate this by subtracting your daily commute time from time travelled on your business trip.
All non-exempt employees are entitled to travel pay during normal work hours and when they are actively working outside of those hours. They aren't entitled to travel pay for doing their typical commute, according to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Non-exempt employees are typically paid an hourly wage and are paid less than $684 per week ...
Two-day per diem rule. An employee may be required to travel on his or her own time if in order to allow the employee to travel during working hours, the agency would be required to pay two days or more per diem. However, the two-day per diem rule does not of itself support an entitlement to overtime compensation for the employee.
While working in other countries, employees can rightly expect to work the same hours and receive the same pay as specified in their employment contract. Overtime and time in lieu of business travel If it is usual practice for your business to pay overtime, employees can claim for overtime where applicable.
The rules on travel hours of work depend on whether an employee is covered by or exempt from the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). For FLSA-exempt employees, the crediting of travel time as hours of work is governed under title 5 rules-in particular, 5 U.S.C. 5542(b)(2) and 5544(a)(3) and 5 CFR 550.112(g) and (j).
Time spent "in transit" on Saturdays, Sundays, and holidays during hours that correspond to the employee's regular working hours should be counted as time worked for pay purposes. Example: An employee who regularly works Monday through Friday, 7 a.m. to 3 p.m., takes the train home on Saturday from a three-day business trip to New York. They ...
If you have a generous employer, they are likely to consider travel time on business trips to be working time and compensate you as such: i.e. the entire business trip is considered to be working time. However, these agreements usually have to be negotiated separately. If one is applying for a job that is known to have high levels of work ...
Business travel deductions are available when employees must travel away from their tax home or main place of work for business reasons. A taxpayer is traveling away from home if they are away for longer than an ordinary day's work and they need to sleep to meet the demands of their work while away. Travel expenses must be ordinary and ...
Allied Market Research, a subsidiary of Allied Analytics, based in Portland, Ore., estimated that the bleisure travel market was $315.3 billion in 2022 and would reach $731.4 billion by 2032. As ...
The Virginia Department of Transportation is committed to maintaining the safest possible work zones. We do this by: Developing highway safety policies, standards and guidelines related to work zone safety. Providing technical guidance, best practices and advice to work zone inquiries from internal and external customers.
An excellent choice for business travel is the Jetsetter stretch wool suit. The tailoring looks great and the material—97% wool, 3% stretch—prioritizes comfort. This all-season suit features ...
Italy is allowing Britons who can work remotely to apply for a year-long "digital nomad" visa. The scheme opened for applications for non-EU citizens at the end of last week - having been talked ...