Management of Tourism
- Living reference work entry
- Latest version View entry history
- First Online: 10 March 2024
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Abraham Pizam 3 &
- Valeriya Shapoval 3
Tourism management can be analyzed at four levels: scope, ownership, industry sector, and function. At the first level, those who are concerned with the macro-effects of the tourism industry have analyzed its consequences on the economy, the ecology, and sociocultural milieu of the host community. Economists have developed mathematical models to estimate the direct, indirect, and induced impacts of income injected by tourists into the national, regional, or local economies (Dwyer et al. 2020 ). Ecologists, geographers, and regional planners have mostly studied the negative effects of tourism on the physical environment. Tourism can have negative impacts on the destination by overusing and depleting natural resources. Therefore, environmental quality is increasingly important to ensure the future existence of destinations (Archer et al. 2005 ).
Maintaining environmental quality is essential for saving resources and maintaining the quality and competitiveness of the environment and...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.

Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Archer, B., C. Cooper, and L. Ruhanen. 2005. The positive and negative impacts of tourism. Global Tourism 3: 79–102.
Article Google Scholar
Barrows, C., T. Powers, and D. Reynolds. 2009. Introduction to Management in the Hospitality Industry . New York: Wiley.
Google Scholar
Barrows, C. W., and T. Powers. 2009. Introduction to the Hospitality Industry . Wiley: Study Guide.
Dwyer, L., P. Forsyth, and W. Dwyer. 2020. Tourism economics and policy . Bristol: Channel View.
Fenich, G. 2019. Meetings, expositions, events and conventions: An introduction to the industry . New York: Pearson.
Goeldner, C., and J.R.B. Ritchie. 2012. Tourism: Principles, practices, philosophies . New York: Wiley.
Morrison, A. 2018. Marketing and managing tourism destinations . New York: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Rizou, M., I. Galanakis, T. Aldawoud, and C. Galanakis. 2020. Safety of foods, food supply chain and environment within the COVID-19 pandemic. Trends in Food Science & Technology 102: 293–299.
Sebastia, L., I. Garcia, E. Onaindia, and C. Guzman. 2009. E-tourism: A tourist recommendation and planning application. International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools 18 (05): 717–738.
Tarlow, P. 2005. The appealing ‘dark’ side of tourism and more. In Niche tourism: Contemporary issues, trends and cases , ed. Marina Novelli, 47–57. London: Routledge.
Chapter Google Scholar
Walker, J. 2016. Introduction to hospitality management . Upper Saddle River: Pearson.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Central Florida, Orlando, USA
Abraham Pizam & Valeriya Shapoval
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Valeriya Shapoval .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Hospitality Leadership, University of Wisconsin-Stout, Menomonie, WI, USA
Jafar Jafari
School of Hotel and Tourism Management, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
Honggen Xiao
Section Editor information
Department of Tourism, Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia
Nevenka Cavlek
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Pizam, A., Shapoval, V. (2023). Management of Tourism. In: Jafari, J., Xiao, H. (eds) Encyclopedia of Tourism. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_125-2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_125-2
Received : 20 September 2021
Accepted : 29 March 2023
Published : 10 March 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-01669-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-01669-6
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Business and Management Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
Chapter history
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_125-2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_125-1
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Winter is here! Check out the winter wonderlands at these 5 amazing winter destinations in Montana
- Travel Tips
What Is Tourism Managment
Published: December 12, 2023
Modified: December 28, 2023
by Ashil Brookshire
- Plan Your Trip
- Sustainability
Introduction
Tourism is a flourishing industry that encompasses travel, accommodations, attractions, and activities for leisure, business, or educational purposes. As travel becomes more accessible and people’s desire to explore new places increases, the importance of effective tourism management becomes paramount. Tourism management plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation, sustainability, and profitability of tourism destinations and businesses.
Tourism management involves overseeing and coordinating various aspects of the tourism industry, including marketing, planning, development, operations, and customer service. It aims to provide a positive and enriching experience for tourists, while also benefiting the local communities and preserving the environment.
In this article, we will delve into the definition of tourism management, discuss its importance, explore the key elements and functions within tourism management, and highlight the challenges and emerging trends in the field.
By understanding the intricacies of tourism management, professionals in the industry can develop effective strategies to attract tourists, optimize the visitor experience, and contribute to the overall growth and sustainability of the tourism sector.
Definition of Tourism Management
Tourism management refers to the practice of planning, organizing, and coordinating all the activities and resources involved in the operation of tourism destinations, businesses, and services. It encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, including marketing, budgeting, development, operations, and customer service, with the ultimate goal of ensuring a positive and fulfilling experience for tourists.
Effective tourism management involves a comprehensive understanding of customer preferences, market trends, and destination dynamics. It requires a strategic approach to attract tourists, create memorable experiences, and maximize the economic and social benefits for the local communities. A successful tourism management plan takes into account factors such as infrastructure, transportation, accommodation, attractions, and local resources.
Tourism managers play a crucial role in coordinating the various stakeholders involved in the tourism industry, including government agencies, tourism boards, hospitality establishments, transportation companies, tour operators, and local communities. They work towards developing and implementing strategies that align with the objectives of all parties and ensure the sustainability of tourism destinations.
Furthermore, tourism management involves maintaining a delicate balance between preserving the natural and cultural heritage of a destination and providing quality experiences for tourists. It encompasses initiatives for environmental conservation, responsible tourism practices, and community engagement. By implementing sustainable measures, tourism managers can create long-term benefits and mitigate any negative impacts of tourism on the environment and local communities.
Ultimately, the goal of tourism management is to create a harmonious relationship between tourists, the destination, and the local community. By carefully examining and managing all aspects of the tourism experience, tourism managers strive to meet the demands of the modern traveler, while simultaneously promoting the social, economic, and environmental sustainability of the destination.
Importance of Tourism Management
The importance of effective tourism management cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in the sustainable development and success of tourism destinations and businesses. Here are several key reasons why tourism management is essential:
- Economic Impact: Tourism is a significant source of revenue and job creation worldwide. Tourism management helps maximize the economic benefits by attracting tourists, promoting local businesses, and ensuring the efficient utilization of resources. It stimulates economic growth, enhances employment opportunities, and generates income for the local community.
- Sustainable Development: By implementing sustainable tourism practices, tourism management aims to minimize negative impacts on the environment and culture of the destination. It fosters responsible tourism, encourages conservation efforts, and promotes the well-being of local communities. This ensures the long-term viability and preservation of the destination for future generations.
- Enhanced Visitor Experience: Tourism management focuses on providing exceptional experiences for tourists. It involves careful planning and coordination of attractions, accommodations, transportation, and activities to meet the needs and preferences of different types of travelers. By creating memorable and enjoyable experiences, tourism management fosters positive word-of-mouth recommendations and repeat visits.
- Destination Promotion: Effective tourism management plays a crucial role in destination promotion. It involves strategic marketing initiatives, digital campaigns, and partnerships to attract tourists from different regions. By showcasing the unique offerings of a destination, tourism management helps create a positive image and differentiate it from competitors in the global tourism market.
- Community Engagement: Tourism management actively engages with local communities to ensure their involvement and support in tourism activities. By promoting community participation, respect for local customs and traditions, and equitable distribution of benefits, tourism management fosters a positive relationship between tourists and the local community.
In summary, tourism management is vital for driving economic growth, environmental sustainability, and cultural preservation. It strives to enhance the visitor experience, promote responsible tourism practices, and foster positive relationships between tourists, the destination, and local communities. By prioritizing effective tourism management, destinations can thrive and maximize the benefits of tourism while mitigating potential negative impacts.
Elements of Tourism Management
Tourism management involves various elements that are essential for the successful operation and development of tourism destinations and businesses. These elements encompass the key components that contribute to the overall tourism experience. Here are the main elements of tourism management:
- Marketing and Promotion: This element focuses on creating awareness and attracting tourists to a destination or business. It involves market research, branding, advertising, digital marketing, public relations, and partnerships to effectively communicate the unique selling points of the destination or business.
- Planning and Development: This element involves strategic planning for the sustainable development of tourism destinations. It includes market analysis, infrastructure development, zoning regulations, carrying capacity assessment, and collaboration with stakeholders to ensure the optimal use of resources and development of tourism facilities.
- Operations and Logistics: This element deals with the day-to-day operations and logistical aspects of tourism businesses and destinations. It includes managing accommodations, transportation, attractions, tour operations, customer service, and ensuring smooth operations and seamless experiences for tourists.
- Customer Service and Experience: This element focuses on providing excellent customer service and creating memorable experiences for tourists. It includes training staff, implementing quality assurance measures, addressing customer feedback, and continuously improving the visitor experience to exceed customer expectations.
- Sustainability and Responsible Tourism: This element emphasizes the importance of preserving the natural and cultural heritage of a destination and promoting responsible tourism practices. It involves implementing sustainable measures, minimizing negative impacts of tourism, supporting local communities, and engaging in environmental conservation efforts.
- Economic Management: This element focuses on the financial aspect of tourism management. It involves budgeting, revenue management, pricing strategies, cost control, and financial analysis to ensure profitability and economic sustainability for tourism businesses and destinations.
- Partnerships and Collaboration: This element highlights the significance of collaboration with various stakeholders in the tourism industry. It includes establishing partnerships with government entities, tourism boards, local communities, businesses, and industry associations to foster cooperation, share resources, and work towards common goals.
By addressing and integrating these elements effectively, tourism management can create a well-rounded and holistic approach to the overall management and success of tourism destinations and businesses. It ensures a memorable and sustainable tourism experience for both tourists and the local community.
Functions of Tourism Management
Tourism management involves a range of functions that are essential for the efficient and effective operation of tourism destinations and businesses. These functions contribute to the overall success of the tourism industry and play a vital role in providing a positive experience for tourists. Here are the main functions of tourism management:
- Strategic Planning: This function involves setting goals, formulating strategies, and developing plans to achieve the desired outcomes. It includes analyzing market trends, identifying target markets, and determining the positioning and competitive advantage of the destination or business.
- Market Research: Market research is crucial for understanding customer preferences, market trends, and demand patterns. This function involves conducting surveys, collecting data, and analyzing market insights to develop marketing strategies, identify target audiences, and tailor tourism offerings accordingly.
- Product Development: This function focuses on creating tourism products and experiences that meet the needs and expectations of tourists. It involves identifying unique selling points, designing packages and itineraries, collaborating with local attractions and service providers, and ensuring product innovation to enhance the tourism experience.
- Marketing and Promotion: This function entails creating awareness, attracting tourists, and promoting tourism offerings. It includes advertising, digital marketing, public relations, social media management, content creation, and developing partnerships to effectively reach and engage with target audiences.
- Operations Management: This function deals with the day-to-day operations of tourism businesses and destinations. It includes managing accommodations, transportation, attractions, and activities, as well as ensuring efficient logistics and providing quality customer service to enhance the overall visitor experience.
- Financial Management: Financial management is crucial for the economic sustainability of tourism businesses and destinations. This function involves budgeting, revenue management, pricing strategies, cost control, and financial analysis to ensure profitability and optimize resource allocation.
- Sustainability and Responsible Tourism: This function focuses on environmental conservation, community engagement, and responsible tourism practices. It involves implementing sustainable measures, promoting cultural preservation, supporting local communities, and ensuring the long-term viability of tourism destinations.
- Customer Relationship Management: This function emphasizes building and maintaining strong relationships with customers. It includes managing customer inquiries, addressing feedback and complaints, providing personalized experiences, and fostering customer loyalty through effective communication and relationship building initiatives.
- Partnerships and Collaboration: Collaboration is crucial for the success of tourism management. This function involves establishing partnerships with government entities, tourism boards, local communities, businesses, and industry associations to collaborate, share resources, and work towards common goals for the development and growth of the tourism industry.
By fulfilling these functions, tourism management ensures the seamless operation, sustainable development, and memorable experiences for both tourists and the local community. It is a multifaceted discipline that requires a comprehensive approach to meet the ever-evolving demands of the tourism industry.
Challenges in Tourism Management
Tourism management faces various challenges that can impact the sustainability and success of tourism destinations and businesses. These challenges arise from both internal and external factors and require proactive strategies to overcome. Here are some common challenges in tourism management:
- Seasonality: Seasonality refers to the fluctuation in tourism demand based on the time of year. Many destinations experience peak tourist seasons followed by periods of low or off-peak seasons. Managing seasonality can be a challenge, as it requires finding ways to attract tourists during off-peak times and optimizing resources to accommodate peak season demands.
- Overtourism: Overtourism occurs when the number of tourists exceeds the carrying capacity of a destination, resulting in overcrowding, infrastructure strain, and negative environmental and sociocultural impacts. Managing overtourism involves implementing measures to distribute tourism flows, regulate visitor numbers, and promote sustainable tourism practices.
- Sustainability: Ensuring sustainable tourism is a challenge faced by tourism management. This involves balancing the economic, social, and environmental aspects of tourism to minimize negative impacts and maximize long-term benefits. It requires implementing sustainable practices, promoting responsible tourism, and engaging local communities in decision-making processes.
- Competition: The tourism industry is highly competitive, with destinations and businesses vying for the attention of tourists. Managing competition requires differentiating the destination or business through unique offerings, effective marketing strategies, and continuous innovation to attract and retain visitors.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Consumer behavior and travel preferences are constantly evolving. Tourism management needs to adapt to these changes by understanding emerging trends, catering to different market segments, and providing personalized experiences. This requires staying updated with technology advancements, digital marketing strategies, and consumer insights.
- Economic Volatility: Tourism can be impacted by economic factors such as recessions, exchange rate fluctuations, and political instability. These factors can influence travel decisions, tourist spending, and business operations. Tourism management needs to develop strategies to mitigate the effects of economic volatility and attract tourists during challenging times.
- Infrastructure and Resource Management: Adequate and well-maintained infrastructure is crucial for the smooth operation of tourism. However, managing limited resources, ensuring sustainability, and maintaining infrastructure can be challenging. Tourism management needs to prioritize infrastructure development, enhance resource management, and strike a balance between tourist needs and environmental conservation.
- Technology Disruptions: Rapid advancements in technology impact the tourism industry. Online platforms, social media, and mobile applications have changed the way tourists research, book, and experience travel. Tourism management needs to leverage technology to enhance marketing, distribution channels, customer service, and overall tourism experiences.
- Crisis Management: Tourism destinations are susceptible to natural disasters, political unrest, health crises, and other unforeseen events. Crisis management is crucial in ensuring safety, communication, and recovery. Tourism management should have contingency plans, crisis communication strategies, and cooperation with authorities to effectively manage crises.
Overcoming these challenges requires proactive and strategic approaches in tourism management. By addressing these issues, tourism destinations and businesses can thrive, deliver exceptional visitor experiences, and contribute to the sustainable development of the tourism industry.
Emerging Trends in Tourism Management
Tourism management is constantly evolving to adapt to changing market dynamics, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. Here are some emerging trends in tourism management that are shaping the future of the industry:
- Sustainable Tourism: The increasing emphasis on sustainability has led to a rise in sustainable tourism practices. Travelers are seeking eco-friendly and socially responsible experiences. Tourism management is embracing sustainable initiatives such as reducing carbon emissions, promoting local sourcing, and supporting community development.
- Authentic Experiences: Tourists are increasingly looking for unique and authentic experiences that provide a deeper connection with the destination and its culture. Tourism management is focusing on curating immersive activities, cultural interactions, and off-the-beaten-path experiences to meet these demands.
- Technology Integration: Technology continues to revolutionize the tourism industry. Tourism management is leveraging technologies like virtual reality, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence to enhance the booking process, improve customer service, and create engaging marketing campaigns.
- Personalization: Personalization is gaining prominence as tourists seek customized experiences tailored to their preferences. Tourism management is utilizing data analytics and customer relationship management tools to segment markets, target specific demographics, and deliver personalized recommendations and offers to travelers.
- Wellness and Health Tourism: Wellness and health tourism have witnessed significant growth. As people prioritize their well-being, tourism management is incorporating wellness activities, spa treatments, yoga retreats, and healthy dining options into destination offerings.
- Community Engagement: Tourism management is recognizing the importance of involving local communities in tourism development. Engaging with local residents, empowering them economically, and showcasing their culture and traditions contribute to sustainable destination management.
- Multi-Generational Travel: With families traveling together, tourism management is focusing on catering to the diverse needs of multi-generational travelers. Destinations are offering a variety of activities and accommodations suitable for different age groups and interests.
- Sharing Economy: The sharing economy has disrupted the traditional tourism industry. Tourism management is adapting by collaborating with sharing economy platforms, integrating home-sharing options, and exploring new business models to meet the evolving demands of travelers.
- Destination Marketing through Influencers: Influencer marketing has become a powerful tool in tourism management. Collaborating with social media influencers to create authentic content and promote destinations has become an effective way to reach and engage with target audiences.
- Accessible Tourism: The focus on inclusivity and accessibility has led to the growth of accessible tourism. Tourism management is ensuring that destinations, accommodations, and attractions are accessible to people with disabilities, providing equal opportunities for all travelers.
These emerging trends are reshaping the tourism industry and presenting new opportunities and challenges for tourism management. By embracing these trends, tourism destinations and businesses can stay competitive, attract a wider range of visitors, and deliver exceptional experiences in the ever-changing landscape of travel and tourism.
Tourism management plays a crucial role in the successful operation, development, and sustainability of tourism destinations and businesses. It encompasses various elements and functions that aim to create exceptional experiences for tourists while considering the economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of tourism management, its importance, key elements, functions, challenges, and emerging trends. It is evident that effective tourism management is essential for driving economic growth, preserving natural and cultural heritage, promoting responsible tourism practices, and enhancing the overall visitor experience.
However, tourism management also faces challenges such as seasonality, overtourism, sustainability, competition, and changing consumer behavior. These challenges require proactive strategies and innovative approaches to ensure the long-term success and development of tourism destinations.
At the same time, emerging trends in tourism management, including sustainable tourism, personalization, technology integration, and wellness tourism, present new opportunities for growth and innovation within the industry.
In conclusion, tourism management is a dynamic and evolving field that plays a vital role in shaping the tourism industry. By effectively managing tourism destinations and businesses, tourism managers can create positive synergies between tourists, the destination, and local communities, fostering economic growth, environmental preservation, and cultural enrichment.
With the constantly evolving landscape of travel, it is imperative for tourism managers to stay updated with the latest trends, embrace sustainable practices, leverage technology, and engage with diverse stakeholders. By doing so, tourism management can contribute to the growth and sustainability of the tourism industry, creating unforgettable experiences for travelers while fostering a positive and responsible approach towards tourism.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
- Welcome Message
- Mission, Vision and Values
- Meet Our Team
- Why Study With Us
- Accreditations, Memberships & Affiliations
- Industry Partnerships
- Awards and Recognition
- Facts and Figures 2021
- Diploma in Business Administration Co-op
- Diploma in Business Management Co-op
- Diploma in Business Management
- Diploma in Digital Business Management Co-op
- Diploma in Digital Marketing Specialist Co-op
- Certificate in Business Essentials Co-op
- Certificate in General Business Management
- Diploma in Hospitality and Tourism Management Co-op
- Diploma in Fundamentals of Hospitality and Tourism Co-op
- Diploma in International Hospitality Operations Management Co-op
- Advanced Diploma in Hospitality and Tourism Management Co-op
- Advanced Diploma in Hospitality and Tourism Management
- Certificate in Customer Service Excellence Co-op
- Diploma in Data Analytics Co-op
- Preparatory Course for ACCA Examination
- ACCA Part-Time Courses
- Diploma in Cybersecurity Specialist Co-op
- English for Academic Purposes
- Our Study Guides
- Our Courses
- Individual Applications
- Partner Referred Applications
- Admission Requirements
- Better Jobs Ontario Program
- English Proficiency
- Start Dates
- International Students Fees
- Domestic Students Fees
- Scholarships
- Payment options
- Get ready for TSoM
- Convocation
- Internship and Job Fairs
- TSoM Calendar
- Special Events
- Toronto School of Management Reviews & Testimonials
- International Student Advisory (ISA)
- Graduation Requirements
- Chat with our Students and Staff
- Medical Insurance
- Alumni Community
- Career Services
- Our Hiring Process
- Our Co-op Partners
- Hire TSoM Co-Op Students
- Hire TSoM Graduates
- Meet our Students and Graduates
- FAQs for Students
- FAQs for Employers
- University Canada West
- Niagara College – Toronto
- Trebas Institute
- Arden University
- Yorkville University
Scope and future of tourism management

Tourism is considered to be an important aspect of economic growth and the development of a nation. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) , global tourism is expected to reach 1.6 billion (in terms of international arrivals) by the year 2020. Tourism management is generally considered a bright and potential employment sector as it offers a wide variety of career opportunities in both the private and public sector. This article covers the details of tourism management courses and the prospective job opportunities that it can offer you.
What are the different types of tourism?
Tourism is an evolving industry that provides tourists with various experiences that help promote the country, region, or whatever type of destination they are travelling to. There are many different kinds of tourism, and each one caters to a different set of interests. Here are the three main types of tourism:
Domestic Tourism: Domestic tourism refers to travel within your own country. It entails traveling to various regions, cities, or towns within the same country for business, pleasure, or other purposes. Domestic tourism is important for the growth of the tourism business in a country because it helps the economy and encourages other people enthusiastic about promoting local tourism.
Inbound Tourism: Inbound tourism refers to tourism by foreign visitors to a destination country. It involves international travel for pleasure, commerce, or other reasons. People who want to explore new cultures, experience various lifestyles, and visit historical and natural landmarks frequently engage in inbound tourism. Inbound tourism is essential to the growth of a country’s tourism industry because it contributes to the economy and helps promote the country as a travel destination.
Outbound Tourism: Outbound tourism refers to the practice of individuals traveling outside of their country of residence for tourism, business, or other purposes. Outbound tourism plays an essential role to the development of a country’s tourism industry because it adds significantly to the economy and promotes international travel.
What is tourism management?
Tourism management is a multidisciplinary field that includes all activities related to the tourism and hospitality industries. It prepares candidates with the experience and training required to hold managerial positions in food, accommodation and tourism industry. The three major areas of tourism management are:
- Business administration (finance, human resources and marketing activities);
- Management theories and principles;
- Tourism industry (travel accommodation, environmental factors and tourism organizations)
Tourism management implements marketing efforts in attracting tourists to travel to particular destinations. This involves the management of a variety of activities such as:
- Studying tour destination;
- Planning the tour;
- Making travel arrangements;
- Providing accommodation.
Who is eligible for a tourism management course?
- You should obtain an Ontario Secondary School Diploma certificate or equivalent;
- Your age should be 18 years or older;
- You should gain a minimum IELTS score of 5.5 (or its equivalent for non-native English speakers).
What is the course structure of tourism management?
- Front Office Operations – this includes an introduction about the systems and procedures required for Front Desk Office Operations. It helps students develop skills related to reception procedures.
- Customer Service – this module elaborates on the importance of effective communication skills while dealing with customers. It provides students with a better understanding of customer relations and services.
- Food and Beverage Management – focuses on the operations related to food and beverage management. It includes the following topics:
- Food and beverage operations;
- Standard product costs and pricing strategies;
- Productions;
- Controlling;
- Facility design, layout and equipment.
- Hospitality Accounting – this module can help a student enhance their decision making process in the field of management. It provides an in-depth knowledge about the processes and practices of hotel business.
- Human Resource Management – this module is structured to train students to build a strategic and coherent approach to their organizations assets. Students get an opportunity to learn about effective business practices of the hospitality industry.
Other modules covered by a tourism management course are as follows:
- Introduction to Hospitality and Tourism;
- Housekeeping;
- Food and Beverage Operations;
- Food Sanitation, Safety and Health;
- Organizational Behavior in the Hospitality Industry;
- Facilities and Maintenance Management;
- Marketing in Hospitality and Tourism;
- Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Events;
- Issues in the Hospitality and Tourism Industry;
- Resort Management;
- Niche and Specialty Management.
How long is a tourism management course and how much does it cost?
The tourism management course is a full-time program lasting two years. It consists of 48 weeks of in-class academic sessions. The total length of the course exceeds up to 78 weeks, including scheduled breaks. The total course fee of the tourism management program is CAD 19,000.
What is the career scope of the tourism Industry?
Tour Manager (Average annual salary: $49,150 ) – they must possess language skills and knowledge about weather, customs and tourist attractions. Their main role is to ensure that the tour goes smoothly and tourists get to enjoy themselves during their holiday. Tour managers should have networking and customer service skills as well as a good grasp of the following subjects:
- Archaeology;
- Modern languages;
- Travel, tourism and leisure studies.
Let’s look at some of the responsibilities of a tour manager:
- Accompanying native and foreign groups travelling by bus, planes, boats and trains;
- Welcoming holidaymakers at the starting point and explaining travel arrangements (food, culture, itineraries and destinations) and stop-over points in detail;
- Resolving logistic issues and coordinating travel arrangements;
- Checking tickets or other relevant documents, as well as attending to special requirements such as seat allocations, passport or immigration issues;
- Making accommodation bookings on proposed dates and ensuring that the accommodation is satisfactory;
- Dealing with emergencies and responding to questions from tourists.
The career scope of the tourism industry does not only cover tours and other forms of travel; it also expands to the hospitality sector. Here’s an example of what a career as a Hotel Manager in Canada would look like:
Hotel Manager (Average annual salary: $42,967 ) – their function is to manage hotel employees and day-to-day operations of a hotel. This may include front-of-house reception, food and beverage operations, budgeting and financial management. They are expected to have an understanding of hotel management practices and relevant laws and guidelines. They execute the following tasks:
- Analysing and interpreting financial information;
- Implementing effective marketing strategies to promote the hotel’s services;
- Monitoring sales and profits;
- Supervising maintenance, supplies, renovations and furnishings;
- Dealing with suppliers, travel agencies and event planners;
- Inspecting services and property regularly by enforcing strict compliance with health and safety standards.
The scope of tourism is so diverse that you can also explore opportunities in properties and real estate! A career as a Property Manager would look like the following:
Property Manager (Average annual salary: $56,702 ) – property managers are assigned to work at a resort location to oversee the operations of a facility or assets. They are generally hired by property owners and real estate investors who are unable to manage their properties themselves. Commercial properties run by property managers include apartment complexes, retail malls and business offices. The basic responsibilities of a property manager are:
- Building an effective rental program;
- Providing customer services;
- Establishing positive relationships with long-term clients;
- Dealing with renovations;
- Coordinating group visits;
- Managing association-related business;
- Supervising and coordinating building maintenance;
- Resolving tenant concerns and complaints;
- Advertising, demonstrating and leasing vacant units;
- Collecting and depositing rent;
- Communicating with and sending updates to the property owner on the status of the property.
If you enjoy experiencing cultural exchanges, then you should opt for a tourism management career. Toronto School of Management (TSoM) offers an Advanced Diploma in Hospitality and Tourism Management course to help students enter the hospitality and tourism sector. This course can help you learn how to develop strategic plans for tourism and understand the needs of the target customers.
- What are some of the challenges facing the tourism industry? The tourism sector encounters various obstacles, including the effects of climate change, over-tourism in specific locations, geopolitical instability, evolving travel behaviours, and the emergence of accommodation alternatives.
- What are some of the opportunities for growth in the tourism industry? Despite the obstacles confronting the tourism industry, there are also numerous growth opportunities in this sector. These include the rise of responsible and sustainable tourism, the expansion of the digital economy, and potential for growth in niche markets such as adventure tourism, health and wellness tourism, and cultural tourism.
- How can individuals interested in pursuing a career in tourism management prepare for the future of the industry? Individuals pursuing a career in tourism management can prepare for a stable career by getting quality education in business management, marketing, and finance. It would also help you to have a solid grasp of the tourism industry, including its trends, challenges, and opportunities.

One Reply to “Scope and future of tourism management”
[…] is an important task of destination marketers and researchers in the field of tourism marketing as tourist experiences in destinations can correct and shape the preliminary destination image in their […]
Comments are closed.
Contact Us Today

What is tourism? A definition of tourism
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Whilst most of us have been tourists at some point during our lives, you might find yourself asking ‘what is tourism?’ or ‘what is the definition of tourism’?

Having studied, worked in and taught tourism management for many years, I can tell you that there is no straight-cut answer to this question! In fact, I do tell you- in this YouTube video below!
The tourism industry is argued to be the largest industry in the world, providing more employment than any other industry. Note, however, the use of the word ‘argued’. You see, the tourism industry is somewhat grey in nature. Elements that some may consider ‘tourism’, others may not. Some people believe they are ‘ tourists ‘, when others do not. Some things are black and white, and others are not.
In this post I will explain why there is no simple explanation in answer to the question ‘what is tourism?’. I will explain the diversity of the tourism industry and provide a range of definitions of tourism that have been developed by academics and practitioners.
What is tourism?
Tourism is the generic term used to cover both demand and supply that has been adopted in a variety of forms and used throughout the world.
Tourism essentially refers to the activities undertaken by visitors, also known as the visitor economy. The tourism industry encompasses all activity that takes place within the visitor economy.
This includes activities that are directly related to the tourist, such as staying in a hotel, ordering a meal or visiting a tourist attraction. It also includes indirect activities, such as the transport company which delivers the food to the restaurant in which the tourist eats or the laundry company that has a contract with the hotel for cleaning bed sheets.
It is largely due to the indirect contributions to tourism, that defining and measuring the tourism industry is so difficult!
Tourism comes in many different shapes and sizes and there are many different types of tourism . There is mass tourism , niche tourism and special interest tourism. There is domestic tourism and international tourism . There is inbound tourism and outbound tourism .
Whilst there is a range of different forms of tourism, they all come under the broad tourism umbrella, nonetheless. This is because they all revolve around visitors and they all feed the visitor economy in one way or another.

A definition of tourism
Tourism is a phenomenon with no universally accepted definition, owing to the complexity and individualism of the travellers themselves and the activities that they choose to undertake.
The most widely utilised definition of tourism, proposed by the World Trade Organisation (WTO) and United States (UN) Nations Statistics Division (1994), prescribes that in order to qualify as a tourist one must travel and remain in a place outside of their usual residential environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business or other purposes.
Matheison and Wall (1982) on the other hand, do not impose a timeframe, simply stating that one must travel to a destination temporarily.
Leiper (1979) believed that defining tourism is more complex than this, proposing that there are three approaches that can be taken. The economic stance focuses on tourism as a business, the technical stance focusses on the tourist in order to provide a common basis by which to collect data and the holistic stance attempts to include the entire essence of the subject.
The Cambridge Dictionary define tourism quite simply as; ‘the business of providing services such as transport, places to stay or entertainment for people who are on holiday’.
Read also: – The importance of tourism – Types of tourism: A glossary – Outbound tourism | Understanding the basics – The structure of the tourism industry – Domestic tourism tourism explained – The history of tourism
Whilst such attempts to define the concept of tourism may be useful from a generic perspective, the practical application of such definitions is difficult when applied to specific tourism types, such as those outlined in this post outlining the different types of tourism.
In fact, Robinson and Novelli (2007), in their introduction to the niche tourism phenomena, postulate that tourists have developed as consumers, becoming increasingly sophisticated in their needs and preferences as a result of an emergent culture of tourism.
Despite such acknowledgements of the progressive and adaptive nature of tourism, particularly evident through the limitless introduction of new and niche tourism forms, there appear to have been no attempts to develop the commonly accepted definitions of tourism in parallel.
As such, I would argue that there is a need the definition of tourism to be revisited by academics and industry practitioner, to ensure that it is representative of the tourism industry that operates today.
How would you define the term tourism?
For more information on what makes up the tourism industry, I recommend the key text Tourism: Principles and Practice by John Fletcher, available from Amazon here .
Liked this article? Click to share!

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
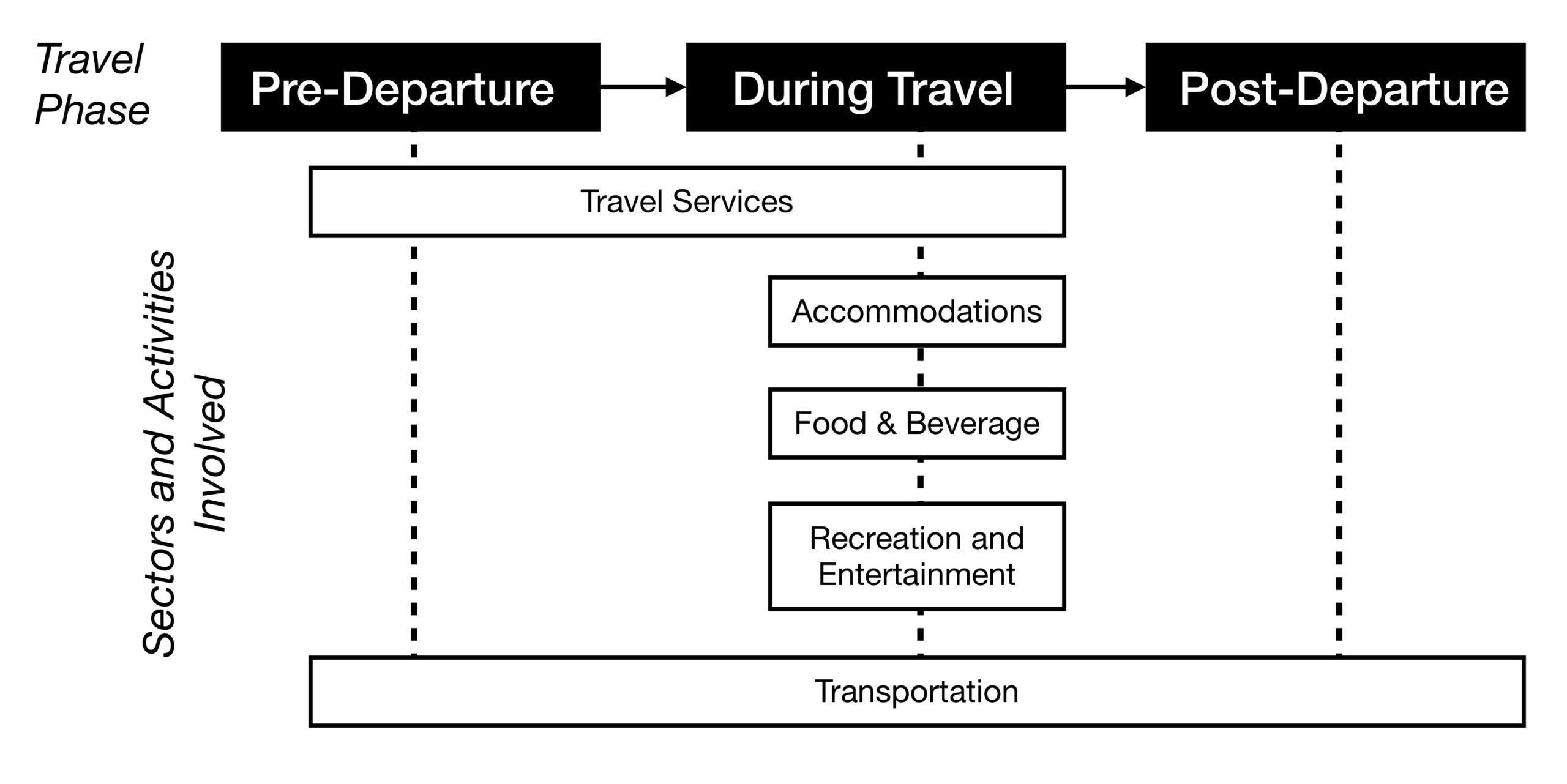
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Long Descriptions
Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the sectors and activities involved during each phase.
There are three travel phases: pre-departure, during travel, and post-departure.
Pre-departure, tourists use the travel services and transportation sectors.
During travel, tourists use the travel services, accommodations, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and transportation sectors.
Post-departure, tourists use the transportation sector.
[Return to Figure 1.2]
Media Attributions
- Front Desk by Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence .
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Tourism Management Tutorial
- Tourism Management - Home
- Tourism Basics
Tourism Management - Introduction
- Tourism Management - Types
- Tourism Management - Terminology
- Tourism Management - Factors
- Tourism Management - Demand
- Tourism Mngmt - Motivation Factors
- Maslow's Pyramid of Motivation
- Consumer Behavior in Tourism
- Tourism Management - Plog's Model
- About Tourism Destinations
- Destination Awareness
- Tourism Management - Milieus
- Tourism Management Destination
- Tools for Destination Management
- Managing Tourism
- Tourism Management - Supply
- Tourism Functional Management
- Business Departments
- Market Segmentation
- Tourism Mngmt - Marketing Mix
- Tourism Mngmt - Products & Services
- Developing Product
- Product Development Phases
- Tourism Impacts, Trends, & Future
- Tourism Management - Impacts
- Tourism Mngmt - Trends & Future
- Tourism Management Resources
- Tourism Management - Quick Guide
- Tourism Management - Resources
- Tourism Management - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Tourism has turned out to be an economic booster contributing to the economic development of many countries over the last few decades. People see holidays as a necessity, and not as luxury in the present scenario. Tourism calls for coordination and cooperation between travel agents, tour operators, and tourists. Tourism has a few major elements − destinations, attractions, sites, accommodation, and all ancillary services.
What is Tourism?
Tourism involves the activities of people travelling and staying in a place away from their home environment for leisure, business or other purposes.
Mathieson and Wall (1982) define tourism as follows −
"The temporary movement of people to destinations outside their usual places of work and residence, the activities undertaken during their stay in those destinations, and the facilities created to cater to their needs."
Tourism was mainly been traditional in its early form. With the evolution of cultures, economies, and knowledge, tourism took a different form called sustainable tourism with the aspect of well-planned tour, well-studied destination, and conservation of destination.
Factors that Motivate People to Travel
The most common reasons for the people to travel away from home are −
- To spend holidays leisurely
- To visit friends and relatives
- To attend business and professional engagements
- To get health treatment
- To undertake religious pilgrimages
- Any other personal motives
Traditional and Niche Tourism
The following table lists down a few points that differentiate traditional tourism from niche tourism −
What is Tourism Management?
It involves the management of multitude of activities such as studying tour destination, planning the tour, making travel arrangements and providing accommodation. It also involves marketing efforts to attract tourists to travel to particular destinations.
There is a subtle difference between just travelling and tourism.
Travelling is going from the place of residence or work to another distant or a neighboring place by any means of transport. Routine commutation can be termed as travelling.
Tourism is travelling with an objective. All tourism necessarily include travel but all travel does not necessarily include tourism. We can say, travelling is a subset of tourism.
One similarity between travel and tourism is, they both are temporary movements.
Tourism Web Portal
About the portal.
A technological tool for effective communication between the leading players in the Moscow tourism market and representatives of the foreign/regional tourism industry through online events. OBJECTIVES: • Building long-term cooperation with foreign/regional representatives • Raising awareness among foreign/regional representatives of the tourism industry of the tourism opportunities, measures and attractiveness of the city of Moscow in the field of tourist infrastructure development
Moscow City Tourism Committee
The Tourism Committee, or Mostourism, is the executive body of the Moscow City Government that oversees tourist activities in the capital. The Committee is responsible for legislative initiatives, congress and exhibition activities, and event and image projects. As the brand manager for an attractive tourism image for Moscow, Mostourism constantly analyses global trends, offers Russian and foreign tourists what they want, and also uncovers new opportunities for the capital in terms of interesting and rewarding leisure activities.
ANO «Project Office for the Development of Tourism and Hospitality of Moscow»
Syundyukova Yulia [email protected] Mezhiev Magomed [email protected]
Video materials about Moscow

Planning a trip to Moscow? Our travel guide contains up-to-date, personal information on everything from what to see , to when to visit , where to stay , and what to eat !
- General Information
- What to see
- How to get to Moscow
- Where to stay
- Where to eat
Why visit Moscow?
Majestic churches, impressive historic fortresses, and palatial buildings: Moscow is a fascinating city whose emblematic architecture reflects the turbulent history that has defined Russia throughout the centuries.
The traces of the USSR can be found around every corner of the city , side by side with the iconic relics of Imperial Russia , like the mythical Red Square , the imposing Kremlin , and the beautiful St Basil's Cathedral .
Discover a fascinating world of Cold War bunkers, golden-domed basilicas, world-class art museums, and the legendary "palace of the people," as the Moscow Metro has been nicknamed. Whether you fancy watching a classical Russian ballet at the Bolshoi Theatre , perusing the fine arts at the Pushkin Museum , or marveling at the sheer size of the monuments to the Soviet state's achievements at the All-Russia Exhibition Centre , this travel guide will help you on your way!
Where to start?
If you're going to travel to Moscow and you don't know much about the city yet, the first thing to do is to dive into its legendary history - understanding the past will help you understand the present. Next, check out our practical hints and tips on traveling to the city before discovering which of its most important museums , monuments , and attractions pique your interest.
Looking for a place to stay?
Booking your accommodation in advance is the best way to get great discounts. Our detailed guide on where to stay in Moscow will help you decide which neighborhood you'd like to look for hotels or apartments in, and our hotel search engine will find you the best deals!
Why is our Moscow travel guide the best?
Introducing Moscow is a city guide written by travelers for travelers and contains personalized advice to help you make the most of your trip to the city.
All the information in this guide is valid as of December 2022. If you find any errors or have any comments, please feel free to contact us .

Our travel guides
- top attractions
- where to stay
- and much more
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
COMMITTEE FOR TOURISM - MOSCOW CITY GOVERNMENT
Country: Russian Federation
Website: https://www.mos.ru/tourism/

3 Germans arrested for spying for China

King Harald of Norway is back at work after pacemaker surgeries

Will Gaza be able to rise from the ashes, once more?

Voters choose mayors in hundreds of Polish cities
Moscow city tourism committee organizes conference for indian mice market stakeholders.

New Delhi [India], April 24 (ANI): Recognising market demand, the Moscow City Tourism Committee organized a conference for representatives of the Indian MICE industry, to introduce them to the tourism strengths of the Russian capital.
MICE stands for Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Exhibitions, and is a type of tourism in which large groups, usually plan things well in advance.
The event took place on April 19 in Delhi and brought together over 100 participants from MICE agencies of both countries, corporate customers, representatives of the travel industry in Moscow, Aeroflot and the Indian branches of Sberbank.
Business tourism is one of the most promising directions for Moscow.
In 2023, the capital was visited by 3.7 million business tourists - 7 per cent more than in 2022. And India remains one of the leaders among visitors from non-CIS countries in terms of the number of business travellers.
"The Russian capital as a centre of business tourism and corporate events is already an established and a strong brand in the international arena," commented Anastasia Popova, Deputy General Director for International and Industry Cooperation of Project Office for the Development of Tourism and Hospitality in Moscow.
"Now our task is to demonstrate to our Indian partners all the possibilities of organizing high-value MICE events in Moscow in combination with already proven tourist programs," said Popova.
At the Shaping MICE Future Conference, industry experts from Russia and India pronounced statements and speeches on the future of MICE events in these two countries, a presentation of the MICE potential of Moscow was showcased, and an analytical report on the state of the outbound MICE market in India was presented to the visitors.
During the panel discussion, participants assessed the current status and interaction peculiarities with the MICE market in India and developed recommendations for the MICE industry in Moscow during the general brainstorming session.
Representatives of the Indian MICE industry participated in B2B negotiations to find new cross-partners in the Moscow business environment and among representatives of the hospitality industry.
Representatives of the MICE industry took part in the event from Moscow.
Among them were DMC (Grand Rus, Academservice, Headed Goose, Satguru Travel, Isba Rus, Hug the Bear, Mellenium Group) as well as representatives of other partners interested in the development of MICE cooperation between Russia and India: Global transfers provider i'way and hotels Edge Seligerskaya and Edge Vinogradovo Moscow by Rotana.
"In 2024, we have witnessed a significant surge (more than quadruple) in the demand for transfers by Russians visiting India, both for business and leisure purposes. Muscovites are leading the trend, with 80 per cent of transfer bookings originating from the capital since the beginning of the year. Additionally, we observe a growing interest from Indian tourism agencies in exploring Russia, resulting in a substantial increase in our collaboration," commented Dmitriy Saraykin, co-founder of Global Transfer Provider i'way.
The Shaping MICE Future conference allowed the Moscow City Tourism Committee to form a pool of MICE industry representatives in Moscow to prioritize incoming requests for events and clarify India's requirements for business and corporate events to build mutually effective work. Indian colleagues received up-to-date information about Moscow as a safe and attractive MICE destination and were able to find potential partners among representatives of the MICE industry of the Russian capital and were able to present the MICE market in India.
"The event served as a remarkable platform for fostering meaningful dialogue and collaboration within the tourism industry. The event provided us with invaluable opportunities to engage with key stakeholders from the tourism department, as well as tour operators and service providers. The insights gained during the event underscored the Moscow City Tourism Committee's keen interest in the Indian outbound market, and we are optimistic about the promising prospects for Moscow as a destination, particularly in the post-pandemic landscape. We firmly believe that with concerted efforts and strategic initiatives, Moscow has the potential to emerge as a top-choice destination for Indian tourists," said Mudit Mathur, director of Tours Delite India, representing Academ Service - Russia in India.
The conference also assessed the solutions to foreign demand for non-standard venues and elements in MICE programs, such as museums, parks, theaters and others. Holding MICE events at offbeat locations, such as the State Historical Museum, the Moscow Planetarium and Khudozhestvenny Cinema, is becoming popular.
ANI 25th April 2024, 03:27 GMT+10
Read This Next
Big News Network
- Big News Network News Agency
- Midwest Radio Network
- Mainstream Media
BIG NEWS NETWORK.COM
- Contact & Support
- Terms & Conditions
PRODUCTS & SERVICES
- News Releases
Copyright © 1998-2024 Big News Network All rights reserved. ISSN : 2616-6917

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tourism management is the oversight of all activities related to the tourism and hospitality industries. It's a multidisciplinary field that prepares people with the interest, experience, and ...
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
UNWTO Tourism Definitions is a comprehensive and authoritative source of tourism-related terms and concepts, covering different aspects of the tourism sector and its impacts. The publication provides definitions of tourism, tourist, visitor, excursionist, domestic tourism, inbound tourism, outbound tourism, and many more, in English, French and Spanish. It also includes a glossary of acronyms ...
Tourism management can be analyzed at four levels: scope, ownership, industry sector, and function. At the first level, those who are concerned with the macro-effects of the tourism industry have analyzed its consequences on the economy, the ecology, and sociocultural milieu of the host community. Economists have developed mathematical models ...
Definition of Tourism Management. Tourism management refers to the practice of planning, organizing, and coordinating all the activities and resources involved in the operation of tourism destinations, businesses, and services. It encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, including marketing, budgeting, development, operations, and customer ...
Tourism Management is the leading scholarly journal focuses on the management, including planning and policy, of travel and tourism. The journal takes an interdisciplinary approach in examining international, national and regional tourism as well as specific management …. View full aims & scope. $4550. Article publishing charge.
Tourism management refers to everything that is related to the hospitality and travel industries. Here you find extensive information about tourism.
UN Tourism works to provide guidance and share good practices on policies and governance models aimed to effectively support the tourism sector at the different levels: national, regional and local. The development and management of tourism destinations requires a holistic approach to policy and governance. Governance has two specific dimensions:
A Practical Guide to Tourism Destination Management. This publication represents a major contribution to developing professionalism in the field of destination management. It is intended as a practical guide, showing how concepts of destination management may be translated into practice. Besides it will be of considerable interest to academics ...
A Practical Guide to Tourism Destination Management. This publication represents a major contribution to developing professionalism in the field of destination management. It is intended as a practical guide, showing how concepts of destination management may be translated into practice. Besides it will be of considerable interest to academics ...
Tourism is considered to be an important aspect of economic growth and the development of a nation. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), global tourism is expected to reach 1.6 billion (in terms of international arrivals) by the year 2020.Tourism management is generally considered a bright and potential employment sector as it offers a wide variety of career ...
A Practical Guide to Tourism Destination Management. Published: 2007 Pages: 163. eISBN: 978-92-844-1243-3. Abstract: This publication represents a major contribution to developing professionalism in the field of destination management. It is intended as a practical guide, showing how concepts of destination management may be translated into ...
International Tourism Management. International Tourism Management is a degree course, whose main focuses with regard to contents consist of business basics with a tourism covering, cross cultural and social competence as well as leadership- and professional competence.
One of the leading texts in the field, Tourism Management is the ideal introduction to the fundamentals of tourism as you study for a degree, diploma or single module in the subject with a global focus. This 6 th edition has been revised and updated to include:. new content on: sports, festivals and event tourism including the impact of the Olympic Games, social media impacts on tourism and ...
Tourism is the generic term used to cover both demand and supply that has been adopted in a variety of forms and used throughout the world. Tourism essentially refers to the activities undertaken by visitors, also known as the visitor economy. The tourism industry encompasses all activity that takes place within the visitor economy.
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities ...
It involves the management of multitude of activities such as studying tour destination, planning the tour, making travel arrangements and providing accommodation. It also involves marketing efforts to attract tourists to travel to particular destinations. There is a subtle difference between just travelling and tourism.
Destination management / marketing organization (DMO): A destination management/marketing organization (DMO) is the leading organizational entity which may encompass the various authorities, stakeholders and professionals and facilitates tourism sector partnerships towards a collective destination vision. The governance structures of DMOs vary ...
It comprises four stages: (i) development of a management plan, (ii) its consequent implementation, (iii) performance evaluation and impact assessment, and (iv) feedback and response. Sign in to download hi-res image. Fig. 4. Integrated management framework for tourism industry in accordance with PDCA principle.
The Tourism Committee, or Mostourism, is the executive body of the Moscow City Government that oversees tourist activities in the capital. The Committee is responsible for legislative initiatives, congress and exhibition activities, and event and image projects. As the brand manager for an attractive tourism image for Moscow, Mostourism ...
Here you'll find everything you need to plan a trip to Russia's fascinating capital, from help booking hotels and airport transfers to detailed descriptions of the city's sights and cultural attractions. Whether you're coming to Moscow as a tourist or on business, we're confident you'll find our range of services indispensable.
Why visit Moscow? Majestic churches, impressive historic fortresses, and palatial buildings: Moscow is a fascinating city whose emblematic architecture reflects the turbulent history that has defined Russia throughout the centuries. The traces of the USSR can be found around every corner of the city, side by side with the iconic relics of Imperial Russia, like the mythical Red Square, the ...
Urban Tourism; Destination Management; Innovation, Education & Investments. Innovation Projects; Investments Strategy; Tourism Startup Competitions; UN Tourism Challenges; Ethics, Culture & Social Responsibility. ... UN Tourism is a specialized agency of the United Nations ...
"The Russian capital as a centre of business tourism and corporate events is already an established and a strong brand in the international arena," commented Anastasia Popova, Deputy General Director for International and Industry Cooperation of Project Office for the Development of Tourism and Hospitality in Moscow.
262K Followers, 61 Following, 2,890 Posts - Louvre Abu Dhabi (@louvreabudhabi) on Instagram: "A universal museum #LouvreAbuDhabi Open Tuesday - Sunday: 10.00 - Midnight Galleries & exhibitions close at 18.30(20.30 on Fri - Sun) Closed on Monday"