Here to help you grow
Whether you're looking to build your business, develop your career, or pick up a new digital skill, we can help you get started.

What can we help you with?
And what would you like to do?
- Show me everything
- Prepare for a new job
- Develop communication skills
- Increase my productivity
- Learn about digital marketing
- Learn coding & development skills
- Get started with artificial intelligence
- Get started with cloud computing
- Stay safe online
- Learn design skills
- Improve my digital wellbeing
- Champion diversity
- Learn about sustainability
- Understand my audience
- Start selling online
- Expand internationally
- Keep my business safe online
Grow your career
Whether you're writing your first CV or deepening your technical knowledge, our library is full of ways to sharpen your digital skillset.

Google Career Certificates
Earn a Google Career Certificate to prepare for a job in a high-growth field like Data Analytics, UX Design, and more.

Introductory digital skills courses
Get started with a range of digital skills, with entry level courses in everything from online marketing to coding.

Cloud computing fundamentals
From intro to advanced-level learning, find out more about cloud computing principles and career paths.

Google product trainings
Learn how to get the most out of the Google products you use, like Google Ads or Analytics.
Grow your business
From bringing your business online for the first time to growing its reach internationally, our library of online learning and tools can help you take your business further.

Your Digital Essentials Guide
Get an introduction to the products, tools and tips that can help you build an online presence for your small business.

Flexible online training
Learn online, at your own pace, with a library of training made to help strengthen your business with digital skills.

Resources for startups
Google for Startups connects you to the right people, products and best practices to help your business thrive.
Helpful tools for small business owners

Google Business Profile
Manage how your business shows up on Google Search and Maps to help new customers find you more easily.

Market Finder
Identify new potential markets and start selling to customers at home and around the world.
Growth stories
Meet people all over Europe who are using technology to adapt and grow their business or career.
About Grow with Google
Grow with Google is a programme that helps people to grow their careers or businesses by learning new skills and making the most of digital tools. We partner with governments and local organisations to develop digital skills and tools where they are needed most.
- Get started Get started for free
Figma design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Prototyping
- Design systems
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Product managers
Organizations
Config 2024
Register to attend in person or online — June 26–27

Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Stories about bringing new ideas to life
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center
How to create an effective user journey map
No matter what you’re working on, the key to customer satisfaction and business growth is understanding your users. A user journey map helps you uncover pain points, explore the touchpoints from their perspective, and learn how to improve your product.
Imagine you just launched a new ecommerce platform. Shoppers fill their carts with products, but they abandon their carts before checkout. With a user journey map, you can pinpoint where the customer experience is going wrong, and how to enable more successful checkouts.
Read on to find out:
- What is a user journey map, and how it captures user flows and customer touchpoints
- Benefits of user journey mapping to refine UX design and reach business goals
- How to make user journey maps in five steps, using FigJam’s user journey map template
What is a user journey map?
Think about the path a user takes to explore your product or website. How would you design the best way to get there? User journey maps (or user experience maps) help team members and stakeholders align on user needs throughout the design process, starting with user research. As you trace users' steps through your user flows, notice: Where do users get lost, backtrack, or drop off?
User journey maps help you flag pain points and churn, so your team can see where the user experience may be confusing or frustrating for your audience. Then you can use your map to identify key customer touchpoints and find opportunities for optimization.
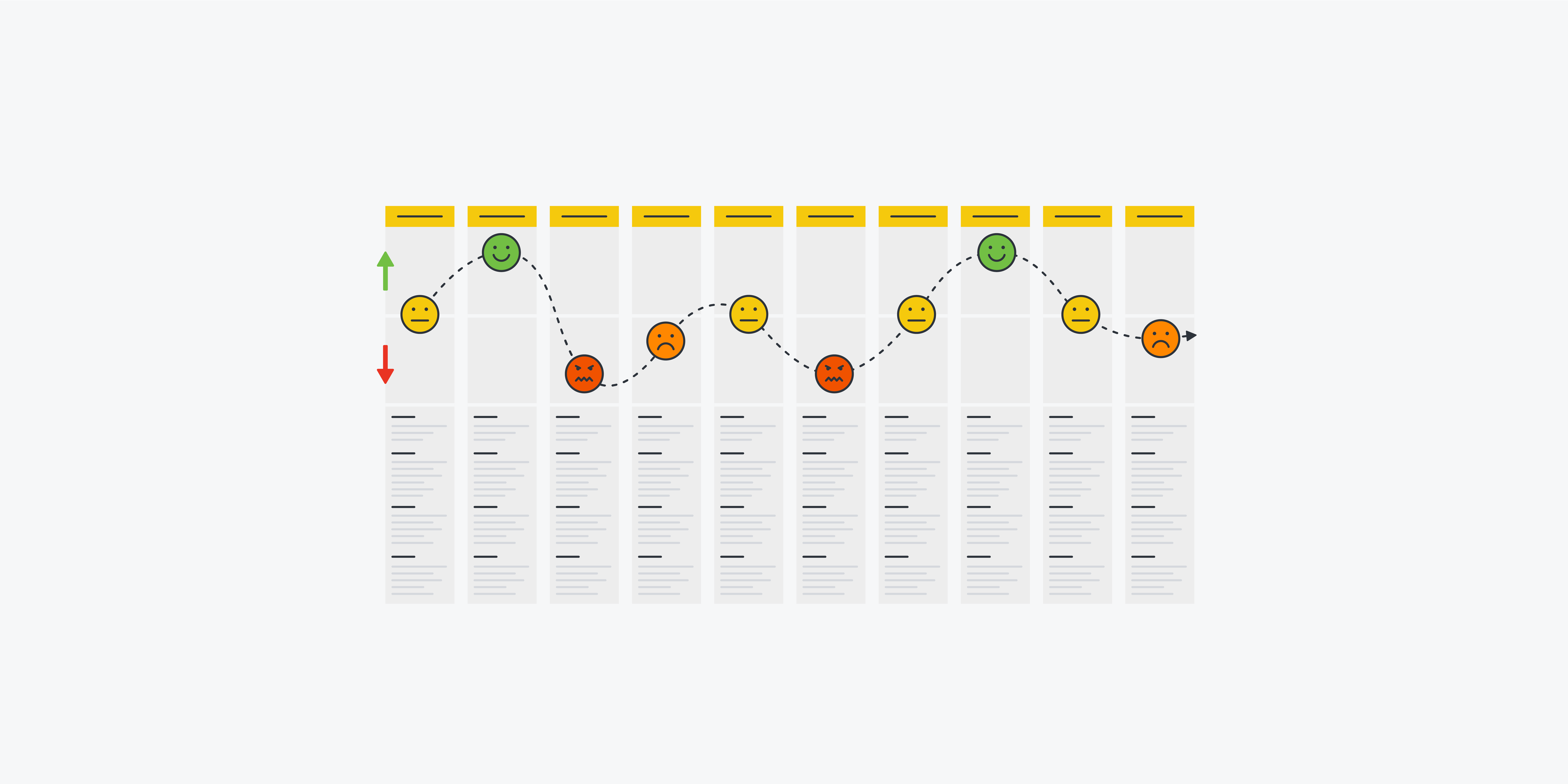
How to read a user journey map
Most user journey maps are flowcharts or grids showing the user experience from end to end. Consider this real-life journey map example of a freelancing app from Figma's design community. The journey starts with a buyer persona needing freelance services, and a freelancer looking for a gig. Ideally, the journey ends with service delivery and payment—but customer pain points could interrupt the flow.
Start your user journey map with FigJam
5 key user journey map phases.
Take a look at another Figma community user journey template , which uses a simple grid. Columns capture the five key stages of the user journey: awareness, consideration, decision, purchase, and retention (see below). Rows show customer experiences across these stages—their thoughts, feelings, and pain points. These experiences are rated as good, neutral, and bad.
To see how this works, consider a practical example. Suppose a new pet parent wants to learn how to train their puppy and discovers your dog-training app. Here's how you might map out the five key user journey stages:
- Awareness. The user sees a puppy-training video on social media with a link to your product website. They're intrigued—a positive experience.
- Consideration. The user visits your product website to preview your app. If they can't find a video preview easily, this could be a neutral or negative experience.
- Decision. The user clicks on a link to the app store and reads reviews of your app and compares it to others. They might think your app reviews are good, but your price is high—a negative or neutral experience.
- Purchase. The user buys your app and completes the onboarding process. If this process is smooth, it's a positive experience. If not, the customer experience could turn negative at this point.
- Retention. The user receives follow-up emails featuring premium puppy-training services or special offers. Depending on their perception of these emails, the experience can range from good (helpful support) to bad (too much spam).
2 types of user journey maps—and when to use them
User journey maps are helpful across the product design and development process, especially at two crucial moments: during product development and for UX troubleshooting. These scenarios call for different user journey maps: current-state and future-state.
Current-state user journey maps
A current-state user journey map shows existing customer interactions with your product. It gives you a snapshot of what's happening, and pinpoints how to enhance the user experience.
Take the puppy training app, for example. A current-state customer journey map might reveal that users are abandoning their shopping carts before making in-app purchases. Look at it from your customers' point of view: Maybe they aren't convinced their credit cards will be secure or the shipping address workflow takes too long. These pain points show where you might tweak functionality to boost user experience and build customer loyalty.
Future-state user journey maps
A future-state user journey map is like a vision board : it shows the ideal customer journey, supported by exceptional customer experiences. Sketch out your best guesses about user behavior on an ideal journey, then put them to the test with usability testing. Once you've identified your north star, you can explore new product or site features that will optimize user experience.
How to make a user journey map in 5 steps
To start user journey mapping, follow this step-by-step guide.
Step 1: Define user personas and goals.
Gather user research and data like demographics, psychographics, and shopping behavior to create detailed customer personas representing your target audience. In your dog-training app example, one key demographic may be parents. What’s their goal? It isn't necessarily "hire a puppy trainer"—it could be "teach kids how to interact with a puppy."
Step 2: Identify customer touch points.
Locate the points along the user journey where the user encounters or interacts with your product. In the dog training app example, touchpoints might include social media videos, app website, app store category search (e.g., pets), app reviews, app store checkout, in-app onboarding, and app customer support.
Step 3: Visualize journey phases.
Create a visual representation of user journey phases across key touchpoints with user flow diagrams , flowcharts , or storyboards .
Step 4: Capture user actions and responses.
For each journey stage, capture the user story: at this juncture, what are they doing, thinking, and feeling ? This could be simple, such as: "Potential customer feels frustrated when the product image takes too long to load."
Step 5: Validate and iterate.
Finally, show your map to real users. Get honest feedback about what works and what doesn’t with user testing , website metrics , or surveys . To use the dog-training app example, you might ask users: Are they interested in subscribing to premium how-to video content by a professional dog trainer? Apply user feedback to refine your map and ensure it reflects customer needs.
Jumpstart your user journey map with FigJam
Lead your team's user journey mapping effort with FigJam, the online collaborative whiteboard for brainstorming, designing, and idea-sharing. Choose a user journey map template from Figma's design community as your guide. With Figma's drag-and-drop design features, you can quickly produce your own professional, presentation-ready user journey map.
Pro tip: Use a service blueprint template to capture behind-the-scenes processes that support the user journey, bridging the gap between user experience and service delivery.
Ready to improve UX with user journey mapping?
16 MIN READ
SHARE THIS POST
Product best practices
- Product Management
- UX research
User Journey Map Guide with Examples & FREE Templates
18 April, 2024

Senior UX Researcher

Customer journey mapping is also a popular workshop task to align user understanding within teams. If backed up by user data and research, they can be a high-level inventory that helps discover strategic oversights, knowledge gaps, and future opportunities.
Yet, if you ask two different people, you will likely get at least three different opinions as to what a user journey looks like and whether it is worth the hassle. Read on if you want to understand whether a UX journey map is what you currently need and how to create one.
You can get the templates here:
Click here to download a high-resolution PDF of this template.
What is user journey mapping?
Imagine your product is a supermarket and your user is the person wanting to refill their fridge. They need to:
Decide what to buy, and in what supermarket will they be able to find and afford it
Remember to bring their coupons
Park there
Find everything
Save the new coupons for the next shopping trip
Dive Deeper: Mobile Product Management Certification
If you want to learn more about how to optimize your user journeys, we recommend enrolling in our course "Mastering Mobile App Product Management" for free.
Unlock the secrets of user-centric design with our course
Gain practical skills in identifying user needs and crafting engaging, intuitive UX designs
Get 15+ templates and frameworks
Our modules, including "How to Map Out Your Discovery" and "User Research for Mobile Apps," ensure you create visually stunning and highly functional user experiences.
Enroll for free here.
Mobile App Product Management Certification
- Upskill for free
- Career growth
- Expert Instructors
- Practical Insights

Three ways to understand customer journey maps
Now, there are at least three ways to look at the customer journey.
1. Workflow maps for usability optimization
Some imagine a user journey map as a wireframe or detailed analysis of specific flows in their app . This could be, for example, a sign-up flow or the flow for inviting others to a document. In our supermarket example, it’s a closer look at what they do inside your supermarket, maybe even only in the frozen section. Or you could define what you want them to do in the frozen aisle.
.css-61w915{margin-right:8px;margin-top:8px;max-height:30px;}@media screen and (min-width: 768px){.css-61w915{margin-right:38px;max-height:unset;}} The focus here is on getting the details of the execution right, not how it fits into the bigger picture of what the user needs.
It is more or less a wireframe from a user perspective. Such a product-focused understanding is not what we want to discuss in this article, though many examples for the best user journey maps you might come across are exactly this. There are good reasons to do such an analysis as well, since it helps you smooth out usability for the people who have already found their way into your supermarket because of your excellent ice cream selection. Workflow maps won’t help you notice that your lack of parking spots is one of the reasons why you are missing out on potential customers in the first place. By only looking at what they do inside the supermarket, you might also miss out on an opportunity for user retention: You could help them get their ice cream home before it melts.
2. Holistic user journey maps for strategic insights
With a more holistic view of what people experience when trying to achieve a goal, product makers gain strategic insights on how their product fits into the big picture and what could be in the future. Because this journey document covers so much ground, it is usually a linear simplification of what all the steps would look like if they were completed. Going back to our supermarket example, it would start from the moment the person starts planning to fill the fridge and ends when the fridge is full again — even if the supermarket building is only relevant in a few phases of this journey. Creating this version of a user journey map requires quite some time and research effort. But it can be an invaluable tool for product and business strategy. It is an inventory of user needs that can help you discover knowledge gaps and future opportunities. Service blueprints are the most comprehensive version of a user journey map since they also lay out the behind-the-scenes of a service, usually called backstage. In our supermarket example, that could be:
the advertising efforts
logistics required to keep all shelves stocked
protocols the staffers follow when communicating with customers
3. Journey mapping workshops as an alignment method
In a user journey mapping workshop, stakeholders and team members share their knowledge and assumptions about the users. Some of these assumptions might need to be challenged — which is part of the process. The goal is not the perfect output, but rather to get everyone into one room and work out a common understanding of the users they are building products for. It forces everyone to organize their thoughts, spell out what they know and assumed was common knowledge — and ideally meet real users as part of the workshop. If done right, this establishes a more comprehensive understanding of what users go through and helps overcome the very superficial ideas one might have about the lives and needs of people outside their own social bubble.
Hence, such a workshop helps create aha moments and gives the consequences of great and poor product decisions a face. So at the end of the day, it is one of many methods to evangelize user-centricity in an organization.
What are the benefits of user experience (UX) mapping?
We already discussed the benefits and shortcomings of workflow maps, but what are the reasons you should consider a UX journey map and/or a journey mapping workshop ?
1. Switching perspectives
Empathy: Like any other UX method and user research output, user journey maps are supposed to foster empathy and help product makers put themselves into the shoes of a user. Awareness: It creates awareness of why users do all the things they do. And it challenges product makers to resist the temptation of building something because it’s feasible, not because it’s needed that way.
2. Aligned understanding
Given the team is involved in creating the user experience map (either as a workshop, in expert interviews, observing the user research, or at least as a results presentation), it forces a conversation and offers a shared mental model and terminology — the foundation for a shared vision.
3. Seeing the big picture
Imagine the vastly different perceptions Sales reps, Customer Support teams, C-level, and backend engineers might have since they all meet very different segments at very different stages of their journey. Day-to-day, it makes sense to be an expert in the stages of a user journey you are responsible for. A journey map helps to step back from this and see the bigger picture, where your work fits in, and where assumptions about the majority of users were wrong. It might even help define KPIs across teams that don’t cancel each other out.
4. Uncovering blind spots and opportunities
A user journey map gives you a structured and comprehensive overview of which user needs are already tackled by your product and which ones are either underserved or solved with other tools and touchpoints. Which moments of truth do not get enough attention yet? These are the opportunities and blind spots you can work on in the future.
When is customer journey mapping just a waste of time?
In all honesty, there are also moments when creating a user journey map or running a journey mapping workshop is destined to fail and should better be put on hold. It’s a lot of work, so don’t let this energy go to waste. User journey maps only make sense when there is an intention to collaboratively work on and with them. Here are some of the scenarios and indicators that it’s the wrong moment for a journey map:
No buy-in for the workshop: The requirements of a successful journey workshop are not met, e.g., there is not enough time (60 minutes over lunch won’t do the trick), only a few team members are willing to attend, and/or key stakeholders refuse to have their assumptions challenged.
Isolated creation: The whole creation process of the user journey map happens isolated from the team, e.g., it is outsourced to an agency or an intern. Nobody from the team observes or runs the user research, or is consulted for input or feedback on the first drafts. There is no event or presentation planned that walks the team through the output. Finally, a very detailed, 10-foot-long poster appears in a hallway, and none of the team members ever find time to read, process, or discuss it with each other.
UX theater: For one reason or another, there is no time/resources allocated to user research or reviewing existing insights whilst creating the map (usability tests with non-users do not count in this case, though). Such an approach, also known as, can do more harm than good since the resulting user journey may only reinforce wrong assumptions and wishful thinking about your users.
Unclear objectives: The user journey map is only created because it is on your UX design checklist, but the purpose is unclear. If you are unsure what you or your stakeholders want to achieve with this journey map, clarify expectations and desired output before investing more energy into this. E.g., there is a chance you were only meant to do a usability review of a bumpy app workflow.
The good news is: UX maturity in an organization can change rapidly, so even if you run into one of the obstacles above, it is worth revisiting the idea in the future. Once you’re good to go, you can get started with the user journey map examples and templates below.
User journey mapping: examples, templates & tools
There is more than one way to do it right and design a great user journey map. Every organization and industry has its own templates, tools and approaches to what elements are most important to them. The following examples and template will give you an idea of what a user journey map can look like if you decide to create one yourself. Make it your own, and change up the sections and design so they make sense for your product and use cases.
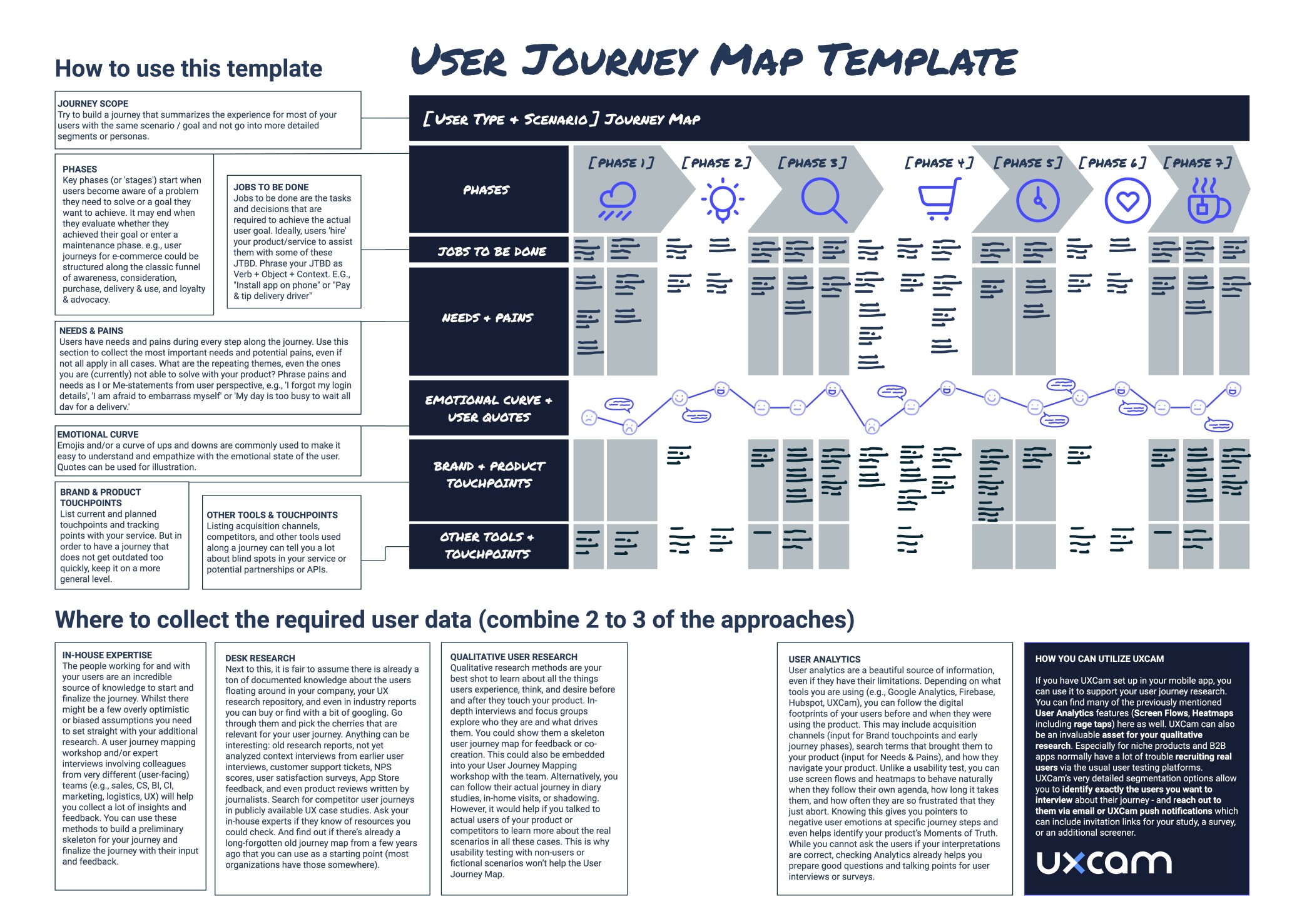
User journey map template and checklist
To give you a first orientation, you can use this user journey template and check the two fictional examples below to see how you could adapt it for two very different industries: instant meal delivery and healthcare.
Click here to download a high-resolution PDF of the user journey map template.
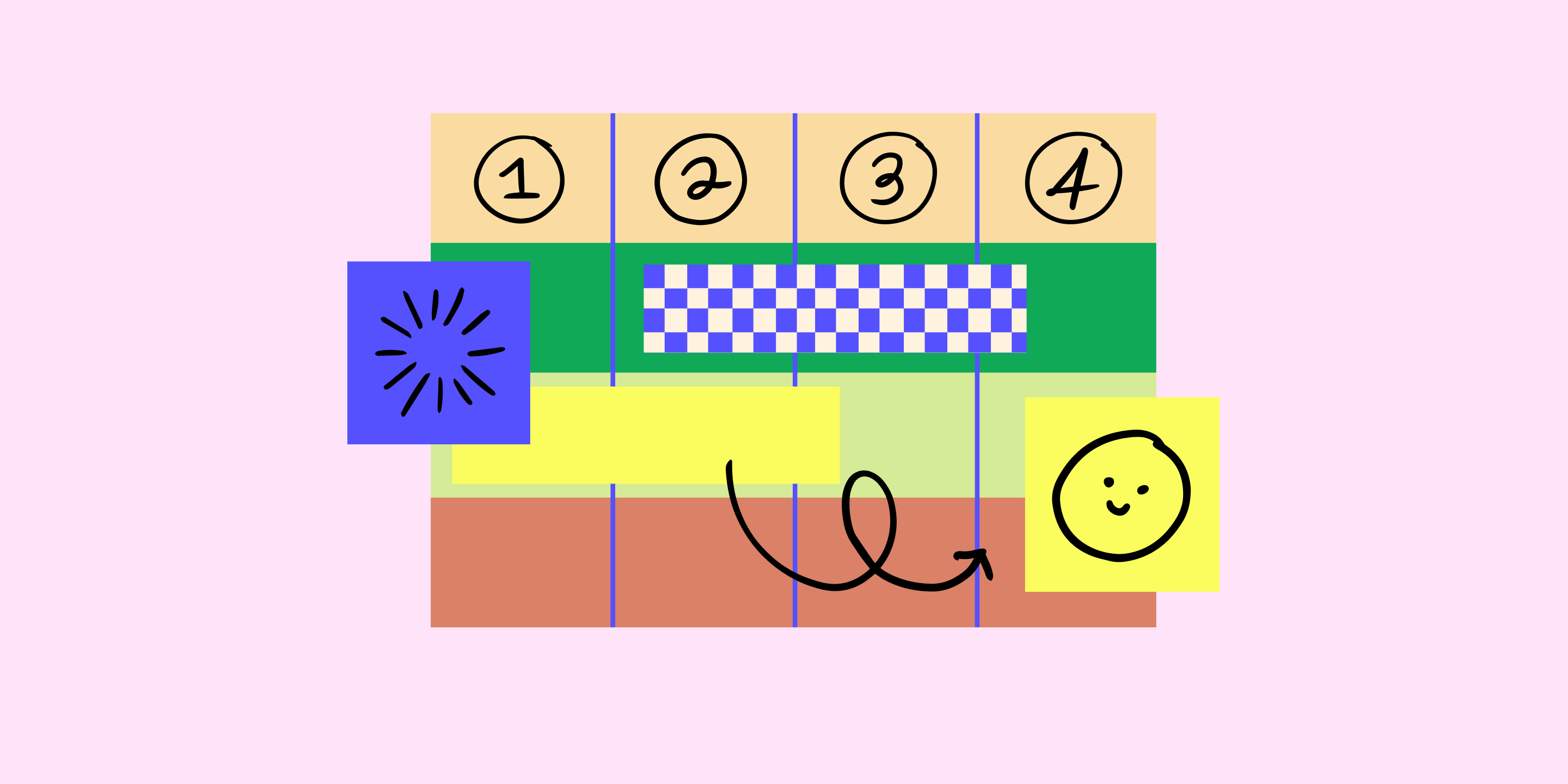
While there is no official standard, most other user journey maps contain the following elements or variations of them:
Key phases (or ‘stages’) start when users become aware of a problem they need to solve or a goal they want to achieve and may end when they evaluate whether they achieved their goal or enter a maintenance phase. E.g., user journeys for e-commerce could be structured along the classic funnel of:
Consideration
Delivery & use
Loyalty & advocacy
2. Jobs to be done
Whilst some other user journey templates might call this section ‘steps’ or ‘tasks’, it can be very beneficial to structure the stages into ‘jobs to be done’ (JTBD) instead. This framework helps you distinguish better between the actual goal of a user vs. the tasks required to get there . For example, safe online payments are never a goal of a user, this is just one of many jobs on the long way to get new sneakers on their feet. Ideally, users ‘hire’ your product/service to assist them with some of the JTBD on their journey. Phrase your JTBD as verb + object + context . Examples:
Install app on phone
Tip delivery driver
Buy new shoes
Naturally, the stages closest to your current (and future) solution require a more detailed understanding, so you might want to investigate and document deeper what JTBDs happen there.
3. Needs and pains
Users have needs and pains every step along the journey. Use this section to collect the most important needs and potential pains, even if not all apply in all cases. Ask:
What are the repeating themes, even the ones you are (currently) not able to solve with your product?
Phrase pains and needs as I- or me-statements from the user perspective, e.g., ‘I forgot my login details, ‘I am afraid to embarrass myself’ or ‘My day is too busy to wait for a delivery.’
Which are the pains and needs that are so severe that, if not solved, they can become real deal-breakers for your product or service?
On the last point, such deal-breaker and dealmaker situations, or ‘ moments of truth ’, require particular attention in your product decisions and could be visually highlighted in your journey. In a meal delivery, the taste and temperature of the food are such a moment of truth that can spoil the whole experience with your otherwise fantastic service.
4. Emotional curve
An emotional curve visualizes how happy or frustrated users are at certain stages of their journey. Emojis are commonly used to make it easy to understand and empathize with the emotional state of the user across the whole journey. It can be a surprising realization that users are not delighted with your witty microcopy, but you already did a great job by not annoying them. It is also a good reminder that what might personally excite you is perceived as stressful or overwhelming by most other users. Strong user quotes can be used for illustration.
5. Brand and product touchpoints
Here, you can list current and planned touchpoints with your brand and product, as well as. Whilst the touchpoints when using your product might be obvious, others early and late in the journey are probably less obvious to you but critical for the user experience and decision to use or return to your product. This is why it is worthwhile to include them in your map. Make sure your journey does not get outdated too soon, and don’t list one-off marketing campaigns or very detailed aspects of current workflows — just what you got in general so there is no major revision needed for a couple of years.
6. Other tools and touchpoints
This may seem the least interesting aspect of your journey or a user interview, but it can tell you a lot about blind spots in your service or potential partnerships or APIs to extend your service. E.g., Google Maps or WhatsApp are common workaround tools for missing or poor in-app solutions.
User journey map example 1: health industry
The following example is for a fictional platform listing therapists for people in need of mental health support, helping them find, contact, schedule, and pay for therapy sessions. As you can see, the very long journey with recurring steps (repeated therapy sessions) is cut short to avoid repetition.
At the same time, it generalizes very individual mental health experiences into a tangible summary. While it is fair to assume that the key phases happen in this chronological order, JTBD, timing, and the number of sessions are kept open so that it works for different types of patients.
You can also see how the journey covers several phases when the platform is not in active use. Yet, these phases are milestones in the patient’s road to recovery. Looking at a journey like this, you could, for example, realize that a ‘graduation’ feature could be beneficial for your users, even if it means they will stop using your platform because they are feeling better.
This user journey map is fictional but oriented on Johanne Miller’s UX case study Designing a mental healthcare platform .
User journey map example 2: delivery services
What the example above does not cover is the role of the therapist on the platform — most likely they are a second user type that has very different needs for the way they use the platform. This is why the second example shows the two parallel journeys of two different user roles and how they interact with each other.
Nowadays, internal staff such as delivery drivers have dedicated apps and ideally have a designated UX team looking out for their needs, too. Creating a frictionless and respectful user experience for ‘internal users’ is just as critical for the success of a business as it is to please customers.
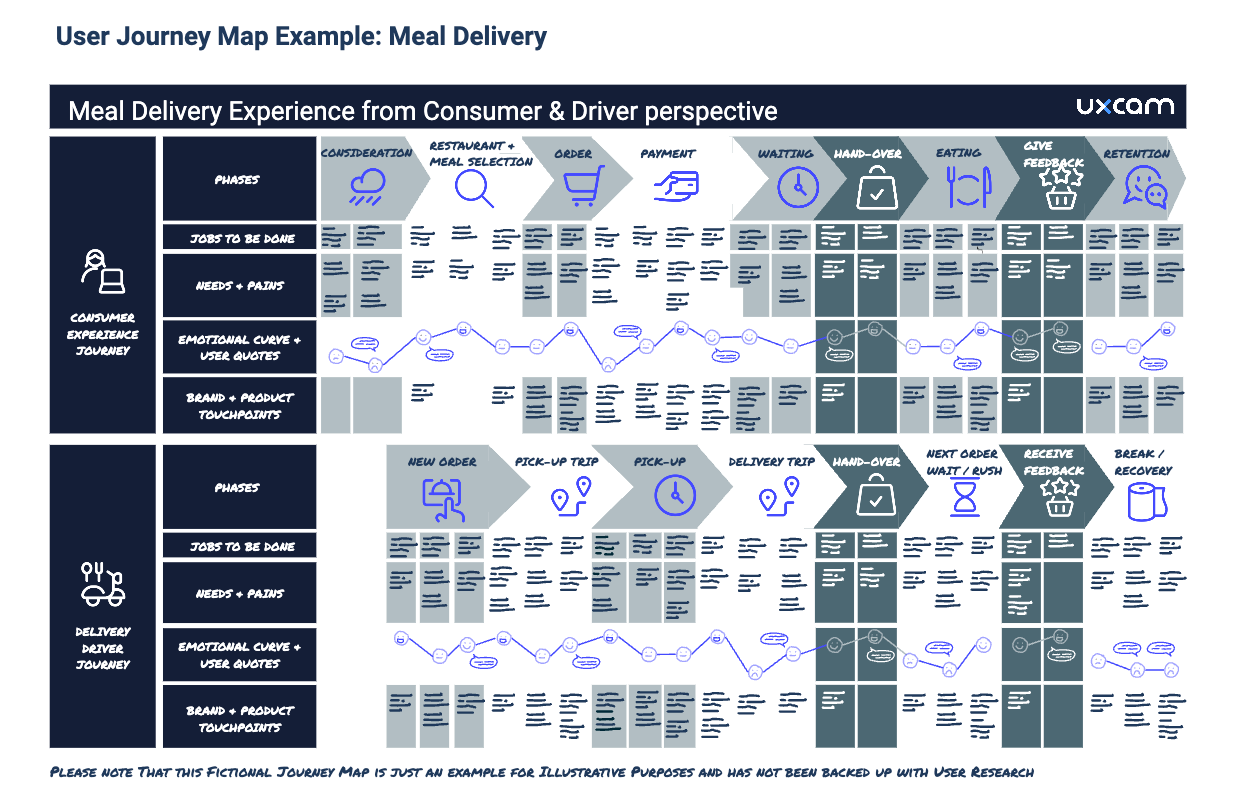
User journey map example: meal delivery. Please note that this fictional journey map is just an example for illustrative purposes and has not been backed up with user research.
For more inspiration, you can find collections with more real-life user journey examples and customer journey maps on UXeria , eleken.co & userinterviews.com , or check out free templates provided by the design tools listed below.
Free UX journey mapping tools with templates
No matter whether you’re a design buff or feel more comfortable in spreadsheets, there are many templates available for free(mium) tools you might be already using.
For example, there are good templates and tutorials available for Canva , Miro and even Google Sheets . If you are more comfortable with regular design software, you can use the templates available for Sketch or one of these two from the Figma (template 1 , template 2 ) community. There are also several dedicated journey map tools with free licenses or free trials, e.g., FlowMapp , Lucidchart and UXPressia , just to name a few.
Be aware that the first draft will require a lot of rearrangement and fiddling until you get to the final version. So it might help to pick where this feels easy for you.
How do I collect data for my app user journey?
User journey maps need to be rooted in reality and based on what users really need and do (not what we wish they did) to add value to the product and business strategy. Hence, user insights are an inevitable step in the creation process.
However, it’s a huge pile of information that needs to be puzzled together and usually, one source of information is not enough to cover the whole experience — every research method has its own blind spots. But if you combine at least two or three of the approaches below, you can create a solid app user journey .
1. In-house expertise
The people working for and with your users are an incredible source of knowledge to start and finalize the journey. Whilst there might be a few overly optimistic or biased assumptions you need to set straight with your additional research, a user journey mapping workshop and/or expert interviews involving colleagues from very different (user-facing) teams such as:
customer service
business intelligence
customer insights
will help you collect a lot of insights and feedback. You can use these methods to build a preliminary skeleton for your journey but also to finalize the journey with their input and feedback.
2. Desk research
Next to this, it is fair to assume there is already a ton of preexisting documented knowledge about the users simply floating around in your company. Your UX research repository and even industry reports you can buy or find with a bit of googling will help. Go through them and pick the cherries that are relevant for your user journey. Almost anything can be interesting:
Old research reports and not-yet-analyzed context interviews from earlier user interviews
NPS scores & user satisfaction surveys
App store feedback
Customer support tickets
Product reviews written by journalists
Competitor user journeys in publicly available UX case studies
Ask your in-house experts if they know of additional resources you could check. And find out if there’s already a long-forgotten old journey map from a few years ago that you can use as a starting point (most organizations have those somewhere).
3. Qualitative user research
Qualitative research methods are your best shot to learn about all the things users experience, think, and desire before and after they touch your product. In-depth interviews and focus groups explore who they are and what drives them. You could show them a skeleton user journey for feedback or co-creation .
This could also be embedded into your user journey mapping workshop with the team. Alternatively, you can follow their actual journey in diary studies , in-home visits or shadowing . However, in all these cases it is important that you talk to real users of your product or competitors to learn more about the real scenarios. This is why usability testing with non-users or fictional scenarios won’t help much for the user journey map.
4. Quantitative research
Once you know the rough cornerstones of your user journey map, surveys could be used to let users rate what needs and pains really matter to them. And what their mood is at certain phases of the journey. You can learn how they became aware of your product and ask them which of the motives you identified are common or exotic edge cases. Implementing micro-surveys such as NPS surveys , CES , and CSAT embedded into your product experience can give additional insights.
5. User analytics
User analytics is a beautiful source of information, even if it has its limits. Depending on what tools you are using (e.g., Google Analytics, Firebase, Hubspot, UXCam), you can follow the digital footprints of your users before and when they were using the product. This may include acquisition channels (input for brand touchpoints and early journey phases), search terms that brought them to your product (input for needs and pains), and how they navigate your product.
Unlike a usability test, you can use screen flows and heatmaps to understand how your users behave naturally when they follow their own agenda at their own pace — and how often they are so frustrated that they just quit. Knowing this gives you pointers to negative user emotions at certain journey steps and even helps identify your product’s moments of truth. Whilst you cannot ask the users if your interpretations are correct, checking analytics already helps you prepare good questions and talking points for user interviews or surveys.
Curious to know how heatmaps will look in your app? Try UXCam for free — with 100,000 monthly sessions and unlimited features.
How can I utilize UXCam to collect App User Journey data?
If you have UXCam set up in your mobile app, you can use it to support your user journey research. You can find many of the previously mentioned user analytics features ( screen flows and heatmaps , including rage taps ) here as well.
UXCam can also be an invaluable asset for your qualitative research . Especially for niche products and B2B apps that normally have a lot of trouble recruiting real users via the usual user testing platforms.
UXCam’s detailed segmentation options allow you to identify exactly the users you want to interview about their journey — and reach out to them via either email or UXCam push notifications , which can include invitation links for your study, a survey or an additional screener.
Where can I learn more?
Don’t feel ready to get started? Here are a few additional resources that can help you dive deeper into user journey mapping and create the version that is best for your project.
Creating user journey maps & service blueprints:
Mapping Experiences by Jim Kalbach
Journey Mapping 101
How to create customer journey maps
Customer Journey Stages for Product Managers
The Perfect Customer Journey Map
Planning and running user journey mapping workshops:
Journey mapping workshop
Jobs to be done:
The Theory of Jobs To Be Done
Moments of truth in customer journeys:
Journey mapping MoTs
What is a user journey map?
A user journey map is a visual representation of the process that a user goes through to accomplish a goal with your product, service, or app.
What is a user journey?
A user journey refers to the series of steps a user takes to accomplish a specific goal within a product, service, or website. It represents the user's experience from their point of view as they interact with the product or service, starting from the initial contact or discovery, moving through various touchpoints, and leading to a final outcome or goal.
How do I use a user journey map in UX?
User journey maps are an essential tool in the UX design process, used to understand and address the user's needs and pain points.
Related Articles
Best behavioral analytics tools to optimize mobile app UX
20+ powerful UX statistics to impress stakeholders
Mobile UX design: The complete expert guide
Alice Ruddigkeit
Get the latest from uxcam.
Stay up-to-date with UXCam's latest features, insights, and industry news for an exceptional user experience.
Related articles

10 Fantastic Remote Usability Testing Tools You Can Use Now
Usability testing tools that will put your mind at...

Jonas Kurzweg
Growth Lead

Curated List
7 best ab testing tools for mobile apps.
Learn with examples how qualitative tools like funnel analysis, heat maps, and session replays complement quantitative...

Content Director
User Journey Map Guide with Examples & FREE Templates
Learn experience mapping basics and benefits using templates and examples with mixed-methods UX researcher Alice...
Product Design Bundle and save
User Research New
Content Design
UX Design Fundamentals
Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
- UX training for teams
- Hire our alumni
- Student Stories
- State of UX Hiring Report 2024
- Our mission
- Advisory Council
Education for every phase of your UX career
Professional Diploma
Learn the full user experience (UX) process from research to interaction design to prototyping.
Combine the UX Diploma with the UI Certificate to pursue a career as a product designer.
Professional Certificates
Learn how to plan, execute, analyse and communicate user research effectively.
Master content design and UX writing principles, from tone and style to writing for interfaces.
Understand the fundamentals of UI elements and design systems, as well as the role of UI in UX.
Short Courses
Gain a solid foundation in the philosophy, principles and methods of user experience design.
Learn the essentials of software development so you can work more effectively with developers.
Give your team the skills, knowledge and mindset to create great digital products.
Join our hiring programme and access our list of certified professionals.
Learn about our mission to set the global standard in UX education.
Meet our leadership team with UX and education expertise.
Members of the council connect us to the wider UX industry.
Our team are available to answer any of your questions.
Fresh insights from experts, alumni and the wider design community.
Success stories from our course alumni building thriving careers.
Discover a wealth of UX expertise on our YouTube channel.
Latest industry insights. A practical guide to landing a job in UX.
How to design a customer journey map (A step-by-step guide)
A customer journey map is a visual representation of how a user interacts with your product. Learn how to create a customer journey map in this practical step-by-step guide.
The State of UX Hiring Report 2024
Learn how to start your UX career with hard facts and practical advice from those who have gone before you. In this report, we look at UX hiring trends in 2024 to help you break into the industry.
Successful UX design is rooted in empathy. The best designers are able to step into their users’ shoes and imagine what they think, feel, and experience as they interact with a product or service.
One of the most effective ways to foster user empathy and consider different perspectives is to create customer journey maps—otherwise known as customer journey maps.
If you’re new to journey mapping, look no further than this guide. We’ll explain:
- What is a customer journey map?
Why create customer journey maps?
When to create customer journey maps, what are the elements of a customer journey map, how to create a customer journey map (step-by-step).
If you want to skip straight to the how-to guide, just use the clickable menu to jump ahead. Otherwise, let’s begin with a definition.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UX]
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map (otherwise known as a user journey map) is a visual representation of how a user or customer interacts with your product. It maps out the steps they go through to complete a specific task or to achieve a particular goal—for example, purchasing a product from an e-commerce website or creating a profile on a dating app.
Where does their journey begin? What’s their first point of interaction with the product? What actions and steps do they take to reach their end goal? How do they feel at each stage?
You can answer all of those questions with a user journey map.
A user journey map template from Miro .
Creating customer journey maps helps to:
- Centre the end user and foster empathy. Creating a user/customer journey map requires you to step into the end user’s shoes and experience the product from their perspective. This reminds you to consider the user at all times and fosters empathy.
- Expose pain-points in the user experience. By viewing the product from the user’s perspective, you quickly become aware of pain-points or stumbling blocks within the user experience. Based on this insight, you can improve the product accordingly.
- Uncover design opportunities. User journey maps don’t just highlight pain-points; they can also inspire new ideas and opportunities. As you walk in your end user’s shoes, you might think “Ah! An [X] feature would be great here!”
- Get all key stakeholders aligned. User journey maps are both visual and concise, making them an effective communication tool. Anybody can look at a user journey map and instantly understand how the user interacts with the product. This helps to create a shared understanding of the user experience, building alignment among multiple stakeholders.
Ultimately, user journey maps are a great way to focus on the end user and understand how they experience your product. This helps you to create better user experiences that meet your users’ needs.
User journey maps can be useful at different stages of the product design process.
Perhaps you’ve got a fully-fledged product that you want to review and optimise, or completely redesign. You can create journey maps to visualise how your users currently interact with the product, helping you to identify pain-points and inform the next iteration of the product.
You can also create user journey maps at the ideation stage. Before developing new ideas, you might want to visualise them in action, mapping out potential user journeys to test their validity.
And, once you’ve created user journey maps, you can use them to guide you in the creation of wireframes and prototypes . Based on the steps mapped out in the user journey, you can see what touchpoints need to be included in the product and where.
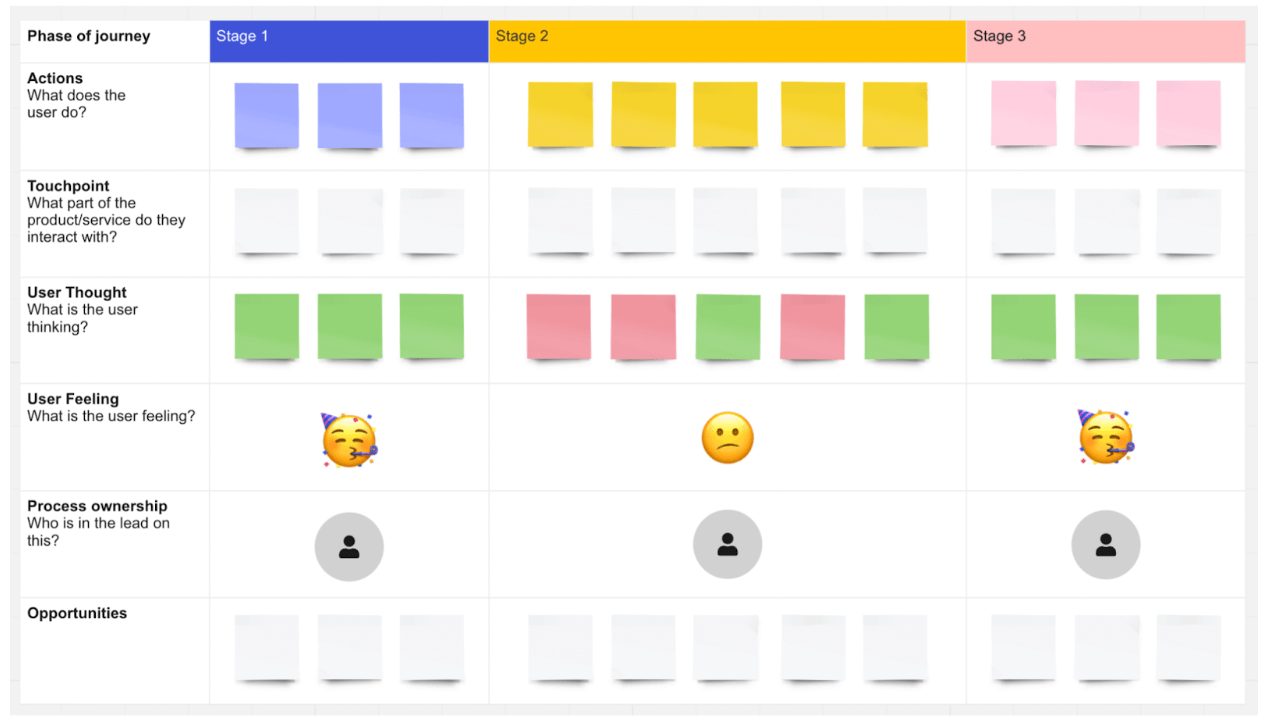
No two user journey maps are the same—you can adapt the structure and content of your maps to suit your needs. But, as a rule, user journey maps should include the following:
- A user persona. Each user journey map represents the perspective of just one user persona. Ideally, you’ll base your journey maps on UX personas that have been created using real user research data.
- A specific scenario. This describes the goal or task the journey map is conveying—in other words, the scenario in which the user finds themselves. For example, finding a language exchange partner on an app or returning a pair of shoes to an e-commerce company.
- User expectations. The goal of a user journey map is to see things from your end user’s perspective, so it’s useful to define what their expectations are as they complete the task you’re depicting.
- High-level stages or phases. You’ll divide the user journey into all the broad, high-level stages a user goes through. Imagine you’re creating a user journey map for the task of booking a hotel via your website. The stages in the user’s journey might be: Discover (the user discovers your website), Research (the user browses different hotel options), Compare (the user weighs up different options), Purchase (the user books a hotel).
- Touchpoints. Within each high-level phase, you’ll note down all the touchpoints the user comes across and interacts with. For example: the website homepage, a customer service agent, the checkout page.
- Actions. For each stage, you’ll also map out the individual actions the user takes. This includes things like applying filters, filling out user details, and submitting payment information.
- Thoughts. What is the user thinking at each stage? What questions do they have? For example: “I wonder if I can get a student discount” or “Why can’t I filter by location?”
- Emotions. How does the user feel at each stage? What emotions do they go through? This includes things like frustration, confusion, uncertainty, excitement, and joy.
- Pain-points. A brief note on any hurdles and points of friction the user encounters at each stage.
- Opportunities. Based on everything you’ve captured in your user journey map so far, what opportunities for improvement have you uncovered? How can you act upon your insights and who is responsible for leading those changes? The “opportunities” section turns your user journey map into something actionable.
Here’s how to create a user journey map in 6 steps:
- Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
- Define your persona and scenario
- Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions
- Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
- Identify opportunities
- Define action points and next steps
Let’s take a closer look.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UI DESIGN]
1. Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
The easiest way to create a user journey map is to fill in a ready-made template. Tools like Miro , Lucidchart , and Canva all offer user/customer journey map templates that you can fill in directly or customise to make your own.
Here’s an example of a user journey map template from Canva:
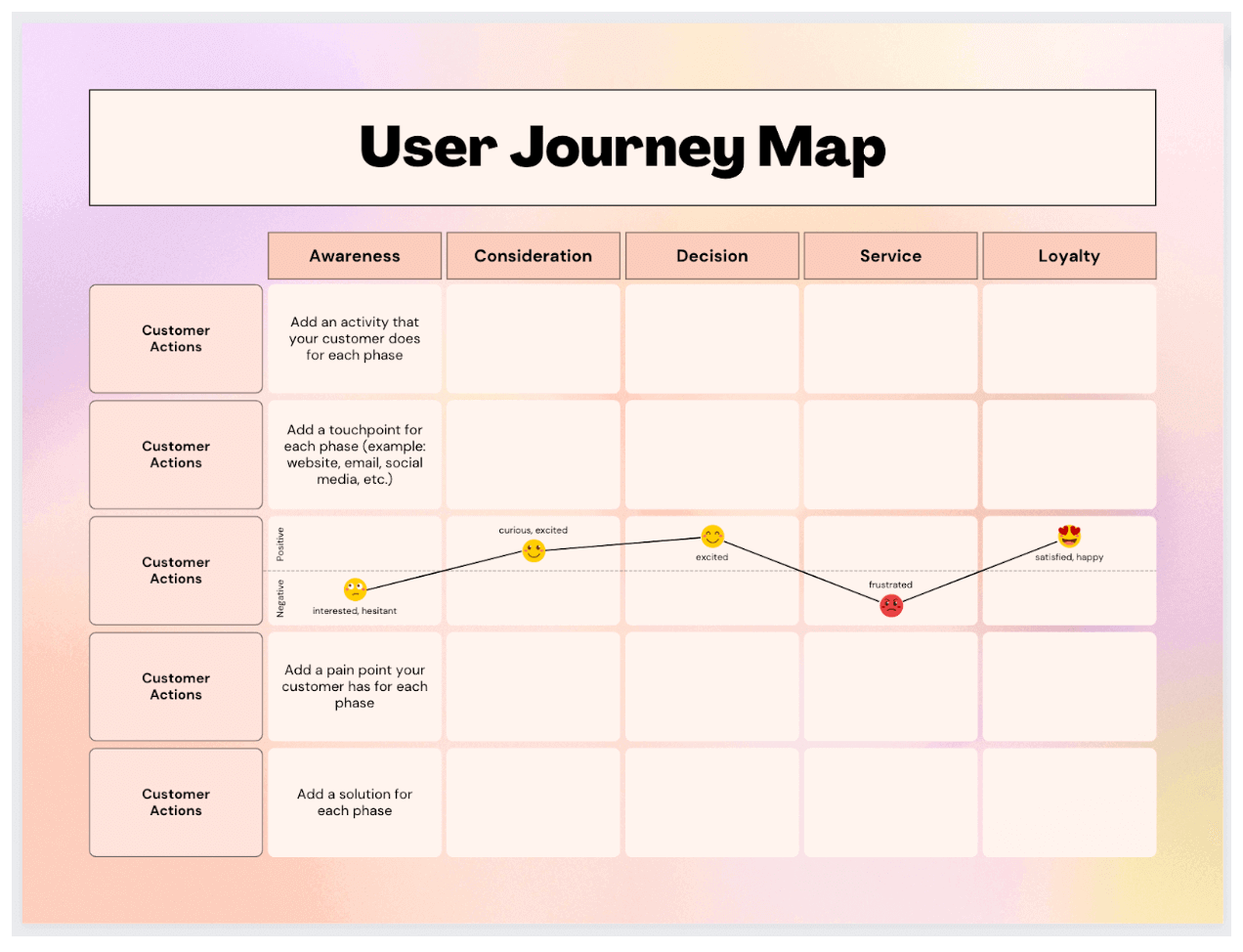
2. Define your persona and scenario
Each user journey map you create should represent a specific user journey from the perspective of a specific user persona. So: determine which UX persona will feature in your journey map, and what scenario they’re in. In other words, what goal or task are they trying to complete?
Add details of your persona and scenario at the top of your user journey map.
3. Outline key stages, actions, and touchpoints
Now it’s time to flesh out the user journey itself. First, consider the user scenario you’re conveying and think about how you can divide it into high-level phases.
Within each phase, identify the actions the user takes and the touchpoints they interact with.
Take, for example, the scenario of signing up for a dating app. You might divide the process into the following key phases: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Service, and Advocacy .
Within the Awareness phase, possible user actions might be: Hears about the dating app from friends, Sees an Instagram advert for the app, Looks for blog articles and reviews online.
4. Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
Next, step even further into your user’s shoes to imagine what they may be thinking and feeling at each stage, as well as what pain-points might get in their way.
To continue with our dating app example, the user’s thoughts during the Awareness phase might be: “ I’ve never used online dating before but maybe I should give this app a try…”
As they’re new to online dating, they may be feeling both interested and hesitant.
While looking for blog articles and reviews, the user struggles to find anything helpful or credible. This can be added to your user journey map under “pain-points”.
5. Identify opportunities
Now it’s time to turn your user pain-points into opportunities. In our dating app example, we identified that the user wanted to learn more about the app before signing up but couldn’t find any useful articles or reviews online.
How could you turn this into an opportunity? You might start to feature more dating app success stories on the company blog.
Frame your opportunities as action points and state who will be responsible for implementing them.
Here we’ve started to fill out the user journey map template for our dating app scenario:
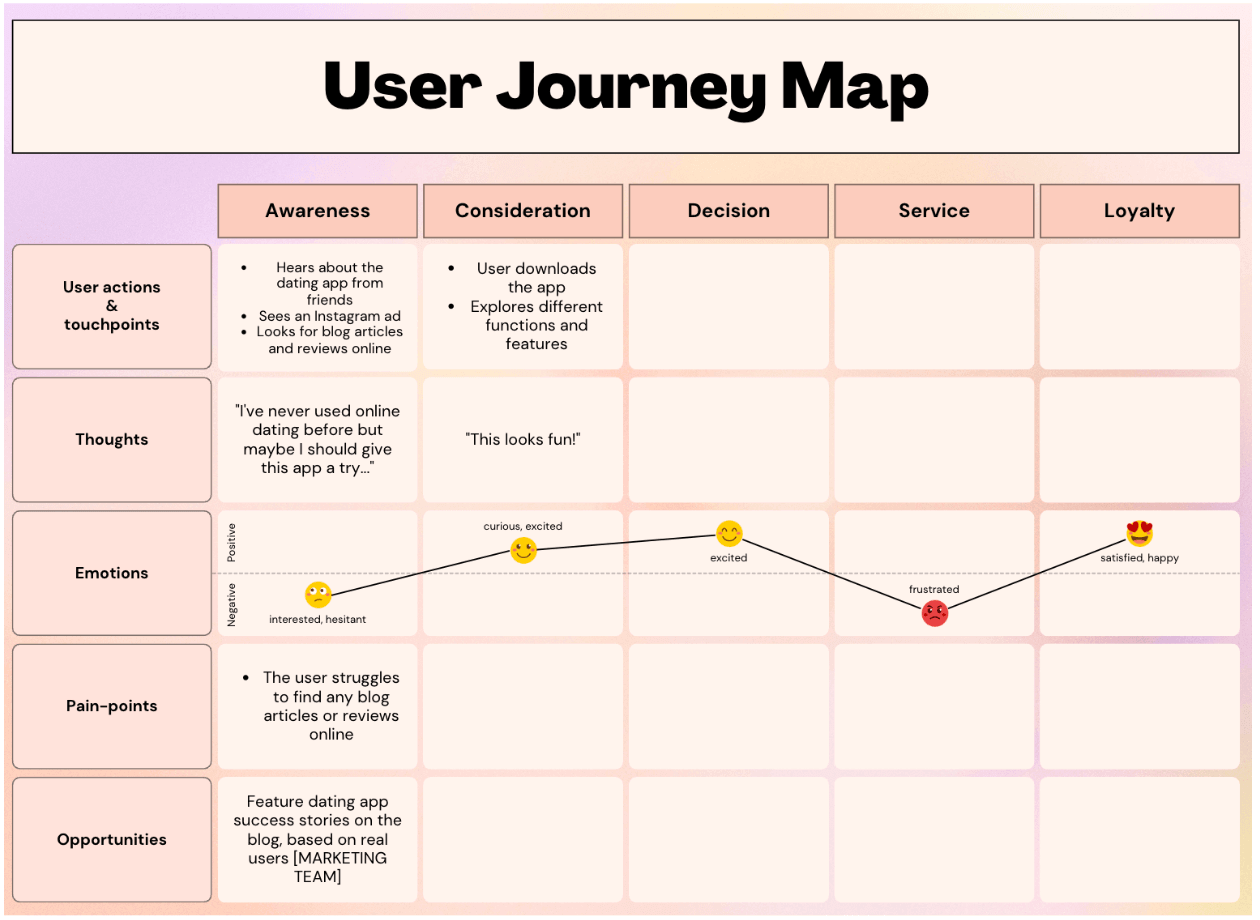
Repeat the process for each phase in the user journey until your map is complete.
6. Define action points and next steps
User journey maps are great for building empathy and getting you to see things from your user’s perspective. They’re also an excellent tool for communicating with stakeholders and creating a shared understanding around how different users experience your product.
Once your user journey map is complete, be sure to share it with all key stakeholders and talk them through the most relevant insights.
And, most importantly, turn those insights into clear action points. Which opportunities will you tap into and who will be involved? How will your user journey maps inform the evolution of your product? What are your next steps?
Customer journey maps in UX: the takeaway
That’s a wrap for user journey maps! With a user journey map template and our step-by-step guide, you can easily create your own maps and use them to inspire and inform your product design process.
For more how-to guides, check out:
- The Ultimate Guide to Storyboarding in UX
- How to Design Effective User Surveys for UX Research
- How to Conduct User Interviews
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the best UX insights and career advice direct to your inbox each month.
Thanks for subscribing to our newsletter
You'll now get the best career advice, industry insights and UX community content, direct to your inbox every month.
Upcoming courses
Professional diploma in ux design.
Learn the full UX process, from research to design to prototyping.
Professional Certificate in UI Design
Master key concepts and techniques of UI design.
Certificate in Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
Collaborate effectively with software developers.
Certificate in UX Design Fundamentals
Get a comprehensive introduction to UX design.
Professional Certificate in Content Design
Learn the skills you need to start a career in content design.
Professional Certificate in User Research
Master the research skills that make UX professionals so valuable.
Upcoming course
Build your UX career with a globally-recognised, industry-approved certification. Get the mindset, the skills and the confidence of UX designers.
You may also like

The ultimate guide to mobile app design: Follow these UI principles & best practices
The best online survey tools to use in 2024

What is colour theory? A complete introductory guide
Build your UX career with a globally recognised, industry-approved qualification. Get the mindset, the confidence and the skills that make UX designers so valuable.
A Beginner’s Guide To User Journey Mapping
To design a great product, you need to understand what the user does with it. A user journey map will help you to answer that question for the product’s entire lifecycle.
“How do people actually use this product?” is a fundamental question that every product creator must answer. In order to do so, product designers need to understand the essence of the whole product experience from the user’s perspective. Fortunately, user journey mapping is an excellent exercise that can shed light on the ways in which the users interact with the product.
What Is a User Journey Map?
More From Nick Babich What Is Microcopy?
What Design Problems Does a User Journey Map Solve?
A user journey map is an excellent tool for UX designers because i t visualizes how a user interacts with a product and allows designers to see a product from a user’s point of view. This fosters a more user-centric approach to product design, which ultimately leads to a better user experience.
User journey maps help a product team to find the answer to the “What if?” questions. Also, a user journey map can be helpful when a company tracks quantitative key performance indicators . In this case, a user journey map can become a cornerstone for strategic recommendations.
The 8-Step Process of User Journey Mapping
Before creating a user journey map, review the goals of your business or service. This knowledge will help you align the business and user goals.
- Choose a scope.
- Create a user persona.
- Define the scenario and user expectations.
- Create a list of touchpoints.
- Take user intention into account.
- Sketch the journey.
- Consider a user’s emotional state during each step of the interaction.
- Validate and refine the user journey.
1. Choose a Scope
The scope of the user journey map can vary from a high-level map that shows end-to-end experience (e.g., creating a smart home in your house) to a more detailed map that focuses on one particular interaction (for instance, adding a new device to your smart home ecosystem).
2. Create a User Persona
Who is your user?
A user journey map is always focused on the experience of one main actor — a user persona who experiences the journey.
A user persona should always be based on information that you have about your target audience. That’s why you should always start with user research . Having solid information about your users will prevent you from making false assumptions.
Gather and analyze all available information about your target audience:
- Interview your real or potential users.
- Conduct contextual inquiry. This is an ethnographic field study that involves in-depth observation of people interacting with your product.
- Conduct and analyze the results of user surveys.
3. Define the Scenario and User Expectations
The scenario describes the situation that the journey map addresses. It can be real or anticipated. It’s also important to define what expectations a user persona has about the interaction. For example, a scenario could be ordering a taxi using a mobile app with the expectation of getting the car in five minutes or less.
4. Create a List of Touchpoints
Touchpoints are user actions and interactions with the product or business. You need to identify all the main touchpoints and all channels associated with each touchpoint. For example, for the touchpoint “Buy a gift,” the associated channels could be purchasing online or buying in the store.
5. Take User Intention Into Account
What motivates your user to interact with your product? Similarly, w hat problem are users looking to solve when they decide to use your product? Different user segments will have different reasons for adopting it.
Let’s take an e-commerce website. There is a big difference between a user who is just looking around and one who wants to accomplish a specific task like purchasing a particular product.
For each user journey, you need to understand:
- Motivation. Why are the users trying to do this action?
- Channels. Where the interaction takes place.
- Actions . The actual behaviors and steps the users take.
- Pain points . What are the challenges users are facing?
Also, ensure that the user is getting a consistent experience across all channels.
6. Sketch the Journey
Put together all the information you have and sketch a journey in the format of a step-by-step interaction. Each step demonstrates an experience that the persona has with a service/product or another person.
You can use a tool called a storyboard, which is a graphic representation of how a user does something, step by step. It can help you show how users can interact with a product. Using storyboards, you can visually depict what happens during each step.
7. Consider a User’s Emotional State During Each Step of the Interaction
What does a user feel when interacting with your product?
The products we design need to mirror the states of mind of our users. When we consider a user’s emotional state, this knowledge will help us to connect with them on a human level. That’s why it’s important to add an emotional lane to the user journey map. By visualizing the emotional ups and downs of the experience, you’ll find the areas that require refinement.
You can create an empathy map to better understand how the user feels. Try to mitigate the emotional downs and reinforce emotional ups with good design.
8. Validate and Refine the User Journey
Journey maps should result in truthful narratives, not fairy tales. Even when a user journey is based on research, you must validate it. Use the information from usability testing sessions and app analytics to be sure that your journey resembles a real use case.
Gather and analyze information about your users on a regular basis. For example, user feedback can be used to improve your understanding of the user journey.
More in Design + UX Hey Designers, Stop Using Users
Map the User Journey
Remember that the goal of making a user journey map is to create a shared vision within your product team and stakeholders. That’s why, once you create a user journey map, you should share it with your peers. Make it possible for everyone in your team to look at the entire experience from the user’s standpoint and draw on this information while crafting a product.
Recent Expert Contributors Articles

Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Journey mapping 101.

December 9, 2018 2018-12-09
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
Journey maps are a common UX tool. They come in all shapes, sizes, and formats. Depending on the context, they can be used in a variety of ways. This article covers the basics: what a journey map is (and is not), related terminology, common variations, and how we can use journey maps.
In This Article:
Definition of a journey map, key components of a journey map, journey-map variations, why use journey maps.
Definition: A journey map is a visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal.
In its most basic form, journey mapping starts by compiling a series of user actions into a timeline. Next, the timeline is fleshed out with user thoughts and emotions in order to create a narrative. This narrative is condensed and polished, ultimately leading to a visualization.

The terms ‘user journey map’ and ‘customer journey map’ can be used interchangeably. Both reference a visualization of a person using your product or service.
While the argument can be made that the term ‘customer’ does a disservice to the method (because, especially for certain business-to-business products, not all of end users are technically customers, i.e., product buyers), alignment on what you call the map is far less important than alignment on the content within the map.
Journey maps come in all shapes and sizes. Regardless of how they look, journey maps have the following 5 key elements in common:
Scenario + Expectations
Journey phases, actions, mindsets, and emotions, opportunities.
The actor is the persona or user who experiences the journey. The actor is who the journey map is about — a point of view. Actors usually align with personas and their actions in the map are rooted in data.
Provide one point of view per map in order to build a strong, clear narrative. For example, a university might choose either a student or a faculty member as actor — each would result in different journeys. (To capture both viewpoints, the university will need to build two separate maps, one for each of the two user types.)
The scenario describes the situation that the journey map addresses and is associated with an actor’s goal or need and specific expectations. For example, one scenario could be switching mobile plans to save money, and expectations for it include to easily find all the information needed to make a decision.
Scenarios can be real (for existing products and services) or anticipated — for products that are yet in the design stage.
Journey maps are best for scenarios that involve a sequence of events (such as shopping or taking a trip), describe a process (thus involve a set of transitions over time), or might involve multiple channels .
Journey phases are the different high-level stages in the journey. They provide organization for the rest of the information in the journey map (actions, thoughts, and emotions). The stages will vary from scenario to scenario; each organization will usually have data to help it determine what these phases are for a given scenario.
Here are some examples:
- For an ecommerce scenario (like buying Bluetooth speakers), the stages can be discover, try, buy, use, seek support.
- For big (or luxury) purchases (like buying a car), the stages can be engagement, education, research, evaluation, justification.
- For a business-to-business scenario (like rolling out an internal tool), the stages could be purchase, adoption, retention, expansion, advocacy.
These are behaviors, thoughts, and feelings the actor has throughout the journey and that are mapped within each of the journey phases.
Actions are the actual behaviors and steps taken by users. This component is not meant to be a granular step-by-step log of every discrete interaction. Rather, it is a narrative of the steps the actor takes during that phase.
Mindsets correspond to users’ thoughts, questions, motivations, and information needs at different stages in the journey. Ideally, these are customer verbatims from research.
Emotions are plotted as single line across the journey phases, literally signaling the emotional “ups” and “downs” of the experience. Think of this line as a contextual layer of emotion that tells us where the user is delighted versus frustrated.
Opportunities (along with additional context such as ownership and metrics) are insights gained from mapping; they speak to how the user experience can be optimized. Insights and opportunities help the team draw knowledge from the map:
- What needs to be done with this knowledge?
- Who owns what change?
- Where are the biggest opportunities?
- How are we going to measure improvements we implement?

There are several concepts closely related and thus easily confused with journey maps.
It is important to note that this section is only meant to help your personal understanding and clarification of these terms. It is not advised to debate or attempt to shift a whole organization’s language to abide by the definitions stated here. Instead, use these definitions to guide you towards aspects of another method that your team has not previously considered.
Journey Map vs. Experience Map
Think of an experience map as a parent to a journey map. A journey map has a specific actor (a singular customer or user of a product) and specific scenario (of a product or service), while an experience map is broader on both accounts — a generic human undergoing a general human experience.
The experience map is agnostic of a specific business or product. It’s used for understanding a general human behavior; in contrast, a customer journey map is specific and focused on a particular business or product.
For example, imagine the world before the ridesharing market existed (Uber, Lyft, Bird, or Limebike, to name a few). If we were to create an experience map of how a person gets from one place to another, the map would likely include walking, biking, driving, riding with a friend, public transportation, or calling a taxi. Using that experience map we could then isolate pain points: unknown fares, bad weather, unpredictable timing, paying in cash, and so on. Using these pain points, we would then create a future journey map for specific product: how does a particular type of user call a car using the Lyft app?

Journey Map vs. Service Blueprint
If journey maps are the children to experience maps, then service blueprints are the grandchildren. They visualize the relationships between different service components (such as people or processes) at various touchpoints in a specific customer journey.
Think of service blueprints as a part two to customer journey maps. They are extensions of journey maps, but instead of being focused on the user (and taking the user’s viewpoint), they are focused on the business (and take its perspective).
For the Lyft scenario above, we would take the journey map and expand it with what Lyft does internally to support that customer journey. The blueprint could include matching the user to a driver, contacting the driver, calculating fares, and so on.
Journey Map vs. User Story Map
User stories are used in Agile to plan features or functionalities. Each feature is condensed down to a deliberately brief description from a user’s point of view; the description focuses on what the user wants to do, and how that feature will help. The typical format of a user story is a single sentence: “As a [type of user], I want to [goal], so that [benefit].” For example, “As a checking account holder, I want to deposit checks with my mobile device, so that I don’t have to go to the bank.”
A user story map is a visual version of a user story. For example, take the user story above (“As a checking account holder, I want to deposit checks with my mobile device, so that I don’t have to go to the bank.”) and imagine writing out the different steps that the team plans for the user to take when using that functionality. These steps could be: logging in, beginning deposit, taking picture of check, and entering transaction details. For each step, we can document required features: enabling camera access, scanning check and auto filling numbers, and authorizing signature. In a user story map, these features are written on sticky notes, then arranged based on the product release that each functionality will be added to.
While, at a glance, a user story map may look like a journey map, journey maps are meant for discovery and understanding (think big picture), while user story maps are for planning and implementation (think little picture).
Although a journey map and user story map may contain some of the same pieces, they are used at different points of the process. For example, imagine our journey map for Lyft indicated that a pain point appeared when the user was in a large group. To address it, the team may introduce a multicar-call option. We could create a user story map to break this feature (multicar call) into smaller pieces, so a product-development team could plan release cycles and corresponding tasks.
The benefits of journey maps (and most other UX mappings ) are two-fold. First, the process of creating a map forces conversation and an aligned mental model for the whole team. Fragmented understanding is a widespread problem in organizations because success metrics are siloed; it is no one’s responsibility to look at the entire experience from the user’s standpoint. This shared vision is a critical goal of journey mapping, because, without it, agreement on how to improve customer experience would never take place.
Second, the shared artifact resulting from the mapping can be used to communicate an understanding of your user or service to all involved. Journey maps are effective mechanisms for conveying information in a way that is memorable, concise, and that creates a shared vision. The maps can also become the basis for decision making as the team moves forward.
Journey mapping is a process that provides a holistic view of the customer experience by uncovering moments of both frustration and delight throughout a series of interactions. Done successfully, it reveals opportunities to address customers’ pain points, alleviate fragmentation, and, ultimately, create a better experience for your users.
Additional articles are available, discussing:
- When to create customer journey maps
- The 5-step process
- Journey mapping in real life
Free Downloads
Related courses, journey mapping to understand customer needs.
Capture and communicate UX insights across complex interactions
Omnichannel Journeys and Customer Experience
Create a usable and cohesive cross-channel experience by following guidelines to resolve common user pain points in a multi-channel landscape
Interaction
Generating Big Ideas with Design Thinking
Unearthing user pain points to drive breakthrough design concepts
Related Topics
- Customer Journeys Customer Journeys
- Design Process
Learn More:
Please accept marketing cookies to view the embedded video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2W13ext26kQ
Customer Journey Mapping 101

UX Design Critiques: 3 Tips for Effective Feedback
Megan Brown · 4 min

Journey Mapping: 2 Decisions to Make Before You Begin
Kate Kaplan · 3 min

Scenario Mapping for Design Exploration
Kim Salazar · 3 min
Related Articles:
The 5 Steps of Successful Customer Journey Mapping
Kate Kaplan · 6 min
Parking Lots in UX Meetings and Workshops
Sarah Gibbons · 5 min
When and How to Create Customer Journey Maps
User Experience vs. Customer Experience: What’s The Difference?
Kim Salazar · 5 min
Journey Mapping: 9 Frequently Asked Questions
Alita Joyce and Kate Kaplan · 7 min
Luxury Shopping User Groups and Journeys
Kate Moran · 14 min
- How to Use This Site
- Usability Testing
- Domain Modeling
Taxonomy Design
- Wireframing
- Accessibility Evaluation
- Journey Mapping
- See All Methods A-Z
- Content Strategy
- Information Architecture
- Interaction Design
- Usability Evaluation
- User Research
- Visual Design

Photo by UX Indonesia via Unsplash
Journey Mapping Method
A journey map is a holistic, visual representation of a user’s experience with a product or service over time. Journey maps combine data and insight from other research and discovery methods to provide a detailed description from the user’s point of view of steps taken, decisions made, successes, pain points, and emotions felt.
Journey maps help designers understand the user’s motivations and needs at each step of a process, from the earliest earliest phases of researching a product or service all the way through adoption, providing crucial insight for designing solutions that better meet user and business needs. The journey map’s visual and storytelling elements also help it communicate research data and findings to broader audiences within an organization.
Preparation
Journey Mapping is often more effective when it is informed by these complementary methods.

Contextual Interviewing
Observation of users performing tasks in their own environment

Task Analysis
Observe users in action to understand how they perform tasks to achieve goals

Written descriptions of how users will perform tasks with your product or on your website

A specific user's context, motivations, and goals for visiting a website or app

Stakeholder Interviewing
Understanding the perspective and influence of those invested in a project's success

User Interviewing
Understand the tasks and motivations of the user group for whom you are designing
- Define business and user goals Clearly articulate the organizational goals for the product or service, the design and business goals for the mapping exercise, and the goals of the target user the map is to represent.
- Gather research data Effective journey maps are based on qualitative and quantitative data collected across a range of activities. Review and incorporate existing research as you create your journey map, and note where gaps in understanding indicate the need for additional research.
- Identify touchpoints and channels Touchpoints describe what users do and how they do it. Channels describe where the interaction takes place (e.g. website, call center, native app, or in-store).
- Create an Empathy Map Empathy maps describe what users do, think, feel, say, and hear in a given situation. They help you understand and articulate users’ emotional state, and provide the basis for illustrating the peaks and valleys of frustration, anxiety, happiness, etc.
- Sketch the journey Visualize the order in which users exhibit behaviors, use information, make decisions, and feel emotions. Group elements into phases related to the narrative of each user. Integrate touchpoints, channels, empathy insights, and other research to show the user’s course of motion across the timescale as a whole. Include the user’s feelings at each touchpoint.
- Review, refine, and revise Review your draft journey with team members and subject matter experts to gain new insight and integrate new perspectives. Use these to identify additional opportunities to make your journey map more accurate, more expressive of the data, and more useful for the design process. From time to time, evaluate your map to make sure it remains accurate. Revise as necessary to account for evolving research, product development, and user and business needs.
Journey Mapping typically produces insight and solutions focused on these areas:
User Preference
Elements, arrangements, or qualities of experience design that user state or show are valuable to them.
User Behavior
Information about how users currently use a site, service, or resource.
Journey Mapping Resources

10 most interesting examples of Customer Journey Maps
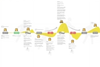
7 Interesting Real Life Customer Journey Map Examples

Customer journey maps for content: Untangle complex insights and create better experiences
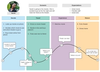
144 Best Customer Journey Map Templates and Examples

Category Design
Creating structures and schemes that make the location and use of content clear

Persona Creation
Development of research-informed representations of target user goals, behaviors, and pain points
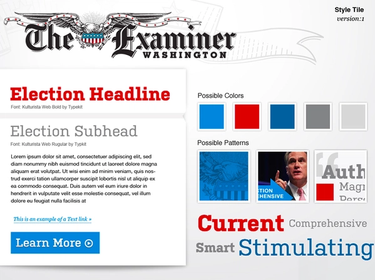
Style Tile Creation
Communicate the use of fonts, colors, and interface elements in a design system

Define a system for labeling and classifying content to make it easier to find, understand, and use
Journey Mapping Method details last edited on Sunday, February 6, 2022
- Graphic Design
- Web Development
- Web Hosting
- Online Guides
- Small Business
- Social Media
- Photography
- Graphic Designer Salaries (by State)
Enhancing User Experiences With Journey Maps
5 Best Practices for Search Results UI

Neumorphism: Is This Controversial UI Trend Making a Comeback?

What is the Customer Journey? 5 Stages Explained
Journey mapping in UX design
Last updated
21 February 2023
Reviewed by
Jean Kaluza
Customers are essential to the success of a business. Without them, the company would cease to exist. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand the stages customers go through when interacting with a brand. You can use a journey map to visualize this across all digital channels over time.
If you’re looking to create user-friendly, intuitive experiences for your customers, journey mapping is a key part of UX design . Find out everything you need to know about journey mapping in this guide.
- What are the four stages of journey mapping?
A journey map should accurately represent your user’s experience from when they first find you and start to interact with you, through to them making a purchase and becoming a loyal customer.
The stages of a journey map will therefore depend on your product. The four stages of a customer’s buying cycle are:
During this stage, customers are looking for solutions to a problem. They become aware of your brand, services, or products via advertisements or other marketing vehicles.
Social media is a powerful tool that companies use to boost awareness. During the awareness stage, the brand should share pertinent information, such as business goals, ethics, and values.
Consideration
At this stage, customers consider the brand against similar companies offering the same products and services.
You need to give potential customers a deeper understanding of what you’re offering and why your brand is a better choice. They may engage with the business by signing up for a newsletter or visiting a brick-and-mortar store.
Customers have decided what they want and make a purchase. They have gathered the information they need before committing to a purchase. They may find this information in email confirmations, FAQs on billing and shipping, and online ordering pages.
Customer loyalty
This is the last stage, after customers have made their purchase and are evaluating the overall experience. This phase is about creating loyal, returning clients by offering membership programs and future discounts.
- How to make a simple journey map
Each customer journey is unique, so journey maps vary depending on the scenarios experienced by customers. Although the maps vary widely, the same steps are involved in creating them.
Let’s look at a step-by-step approach to making a simple journey map.
Step 1: Scope definition
The first step is to clearly define your goals. What are you hoping to achieve from this journey map? Do you want to make a particular aspect of the purchasing cycle more user-friendly? Or are you trying to find out why potential customers don’t follow through with a purchase?
Setting a goal will provide guide rails around the particular customer path you’re trying to understand. This will drive UX designers throughout the journey.
Step 2: Create user personas
Next, get a grasp of who your customers are. Gather information to create different personas to improve your knowledge of the different segments of your target audience. This helps you to:
Define your target market
Create better products and services
Appeal to them through your marketing
Step 3: List channels and touchpoints
Touchpoints are points of interaction between the user and the product. The channels may be through social media platforms, the path a user would take through your product, and other supporting applications or communication necessary to complete their goal.
List all the channels and touchpoints in the journey scenarios. Identify the touchpoints with higher engagement and those that need to be optimized.
Step 4: Collect customer feedback
Gathering customer feedback helps gauge how your users feel about your product or service. Methods used to gather information include:
Questionnaires
Rating systems
Your aim is to see your product through the eyes of your customers.
Step 5: Define pain points and points of friction
Using the customer feedback you gathered in the previous stage, identify gaps in the user journey that make it difficult to move through stages. Identify when they happen and what triggers them.
This will help you to smooth out potential friction points in the customer journey.
Step 6: Improve and re-evaluate
The last step is to improve the overall experience of your customers. Once you have identified the pain points, opportunities, and goal metrics, brainstorm solutions to the identified flaws and implement necessary changes.
Regularly conduct further research and re-evaluate the customer journey.
- What are the elements of a journey map?
A journey map is made up of the following elements:
Persona (actor)
The persona is the one who experiences the journey; it may be a customer or a product user. Depending on the scenario, it could be a group or an individual.
The scenario is what the actor or persona is trying to achieve. A scenario describes the situation that the journey addresses. It primarily includes goals and expectations and can be real or imaginary.
Journey phase
Phases are the different stages of a journey, from awareness to purchasing and beyond. In each phase, try to visualize how you can meet the customer’s goals.
Thoughts and emotions
This refers to how the customer feels as they interact with your brand. Thoughts help the UX designer understand what the customer is experiencing, for example, relief, anxiousness, or frustration. Emotions allow the UX designer to focus on encouraging positive thoughts.
User actions
The action element details what the actor does in each phase to achieve their goal. It defines the actual steps taken by an actor throughout the journey.
Opportunities
This element offers the brand a chance to improve the customer's experience . They are insights gained from journey mapping and used to make informed decisions.
- Why are journey maps important?
Journey mapping brings the following benefits for a company.
Customer-centric philosophy
Using journey maps, UX designers can focus on how customers feel and think about the product being designed.
Journey maps help businesses understand their customers better, resulting in improved decision-making.
Broader business perspective
A journey map helps you to visualize situations experienced by a customer when interacting with your brand. The goal of a journey map is to remove obstacles and make the purchasing process intuitive and efficient.
Customer journey mapping helps a business owner gain an overview of their product or service from multiple viewpoints.
Improved customer experience
A journey map is the first step toward gaining a deeper understanding of customer engagement and fostering the flow of customer experience. It can help you to smooth out the customer experience and personalize it across all touchpoints.
Identification of opportunities
In complex business environments, gaps and breakdowns are common. Mapping out how a user interacts with your brand and/or product may reveal design flaws and areas that need change.
By charting the entire process, a journey map helps identify gaps and opportunities for improvement that will enhance customer experience.
Competitive advantage
Journey mapping helps a company eliminate design flaws and make its product stand out. Once a UX designer has improved customer experience, this becomes a differentiation factor among competitors in the market.
- How does a customer journey map help?
A detailed and well-researched journey map will help you to:
Build a customer-centric organization
Improve customer retention
Identify unmet opportunities that competitors may have missed
Understand the target audience
Align brand position with target market needs and expectations
Meet customer expectations
Understand different buyer personas
Optimize customer onboarding process
- How much does journey mapping cost?
The cost of journey mapping varies widely. The pricing depends on who’s doing it, how much research you want to do, and the complexity of the customer's journey.
- Designing journey maps
Journey maps are unique since they should represent whatever product or service they emulate. Variations of journey maps include:
Experience map
Empathy map
Service blueprint
You can use a third-party tool to build a well-designed journey map, such as:
Omnigraffle
However, there are no rules around what you use to build your journey map and can build it using a whiteboard, PDF format, and even Microsoft Paint. As long as it’s an accurate representation of the user’s journey, that’s what counts.
Experience maps
Experience maps are a zoom-out from journey maps. While journey maps represent a single persona’s behavior at each phase of the customer journey, experience maps can include multi-players that may interact with that user, additional products that customers typically use, or perhaps entirely different methods outside technology that users engage with to complete their goals.
Empathy maps
Empathy maps are used to understand customer personas . They do not follow a particular sequence of events along the journey. Empathy maps are divided into four parts and track what the customer does, thinks, says, and feels when using a product.
These can be helpful when defining who the persona is within your journey map.
Service blueprints
Service blueprints focus on how a brand delivers its products and services to customers rather than being customer-centric. In other words, they describe the behind-the-scenes details of the process.
They are mainly concerned with actions performed by every stakeholder in the purchase process. By focusing on service, gaps or friction points are identified and can be eliminated.
- Map your brand's path to success
Journey mapping offers many benefits to a company. Once your customer journey map is in place, you will fully understand your customers’ experience.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 January 2023
Last updated: 27 April 2023
Last updated: 26 March 2024
Last updated: 24 June 2023
Last updated: 29 May 2023
Last updated: 28 February 2023
Last updated: 14 November 2023
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Last updated: 21 June 2023
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 6 April 2023
Last updated: 31 July 2023
Last updated: 22 June 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Website Design Packages
- UX Audit (Heuristic Evaluation)
- UX Consulting
- UX Optimization
- Website Design
- UX Content Writing
- Web App Design
- Responsive Web Design
- Widespread (Electrical Supplier)
- (302) 223 4432
- Let’s Talk
What is a User Journey Map in UX?

Introduction to UX Journey Mapping
Definition and purpose.
UX journey mapping is a strategic exercise aimed at creating a holistic view of the customer experience by outlining every touchpoint and interaction a customer has with a brand. This visualization helps designers, stakeholders, and team members understand and address the needs, challenges, and opportunities within the customer experience. The purpose of UX journey mapping is not merely to document, but to foster a deep empathy towards the users, enabling teams to design more intuitive and user-centered products and services. Through this comprehensive overview, organizations gain invaluable insights into customer motivations, behaviors, and pain points, which can then be leveraged to enhance customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, business outcomes.
Journey mapping begins with the compilation of data from various sources including market research, user research, and analytics. This information forms the backbone of the journey map, detailing the user’s actions, emotions, and mindset throughout their interaction with the product or service. The exercise of mapping out these interactions encourages a shift from a business-centric to a customer-centric perspective, ensuring that user experience design decisions are grounded in real user needs and preferences rather than assumptions.
The Importance of Journey Maps in UX Design
Journey maps are vital in UX design as they provide a bird’s-eye view of the user experience, highlighting how customers interact with a product or service across multiple channels and touchpoints. This panoramic perspective is critical in identifying friction points that may hinder customer engagement and satisfaction. Moreover, journey maps serve as a shared language among cross-functional teams, facilitating better communication and alignment on the goals and vision of the user experience.
The significance of journey maps extends beyond problem identification; they are pivotal in uncovering hidden opportunities for innovation and improvement. By understanding the customer journey in its entirety, companies can anticipate user needs and craft experiences that exceed expectations, thereby fostering a strong emotional connection with the brand. This connection is the key to building a loyal customer base and achieving competitive advantage in the market.
Components of a Successful Journey Map
Identifying your user persona.
A user persona is a semi-fictional character that represents a segment of your target audience, crafted based on user research and data. Personas are crucial for journey mapping as they ensure the map reflects the experiences of real users rather than hypothetical ones. Each persona should include demographic information, goals, motivations, and pain points, providing a comprehensive profile that guides the mapping process.
Mapping Out User Scenarios and Expectations
User scenarios and expectations set the stage for the journey map, outlining the sequence of actions a user takes to achieve a goal. These scenarios are grounded in user research and feedback, ensuring they accurately represent the tasks and objectives users are trying to accomplish. By mapping these out, designers can visualize the path users take, from initial awareness to final action, and identify potential barriers to completion.
Key Elements of Journey Maps: Actions, Mindsets, and Emotions
The heart of a journey map lies in its ability to depict the user’s actions, mindsets, and emotions at each touchpoint. This triad offers a comprehensive view of the user experience, combining what users do, think, and feel. Actions refer to the steps users take, mindsets to their attitudes and expectations, and emotions to their responses to the interaction. Highlighting these elements in the journey map enables teams to empathize with users and tailor experiences to meet their needs.
Creating Your Journey Map
Steps to build an effective journey map.
The process of building a journey map starts with gathering comprehensive user data through methods like interviews, surveys, and usability testing. This data is then synthesized into a coherent narrative that represents the typical user journey. The mapping process involves several key steps:
- Define the scope and objectives of the journey map.
- Identify user personas to focus on.
- Outline key stages and touchpoints in the user journey.
- Detail actions, thoughts, and emotions for each stage.
- Visualize the journey through diagrams or software tools, making it accessible and understandable for all stakeholders.
Tools and Techniques for Journey Mapping
Several tools and techniques facilitate the journey mapping process, ranging from simple pen and paper to advanced software applications. Digital tools like UX mapping software enable dynamic visualization and easy updates, while traditional methods offer simplicity and tangibility. The choice of tool depends on the complexity of the journey and the preferences of the team. Regardless of the method, the aim is to create a clear, actionable map that guides the design and optimization of the user experience.
Analyzing and Utilizing Journey Maps
Identifying pain points and opportunities.
Analyzing a journey map involves looking for patterns and anomalies that indicate pain points or opportunities for enhancement. Pain points are moments of friction or dissatisfaction that detract from the customer experience, while opportunities are areas where improvements can significantly impact satisfaction and engagement. This analysis should be grounded in empathy, considering the emotional journey of the customer as well as the practical aspects of their experience.
Implementing Insights to Enhance User Experience
The ultimate goal of journey mapping is to apply the insights gained to improve the user experience. This may involve redesigning touchpoints, streamlining processes, or introducing new features that address users’ needs more effectively. Implementation should be strategic, prioritizing changes that will have the most significant impact on customer satisfaction and business objectives. Continuous testing and iteration are essential to ensure that modifications truly enhance the user experience.
Advanced Concepts in Journey Mapping
Journey map variations and their applications.
Journey maps can take various forms, each suited to different aspects of the user experience. For example, service blueprints provide a more detailed view of the service delivery process, including backend actions and interactions that support the customer journey. Other variations focus on specific aspects of the experience, such as emotional journey maps that highlight users’ feelings throughout their interaction with a product or service. Choosing the right type of journey map depends on the specific goals and needs of the project.
Integrating Journey Maps into Broader UX Strategy
Journey maps are most effective when integrated into a broader UX strategy. They should inform and be informed by other UX research and design activities, ensuring a cohesive understanding of the user experience. This integration enables a more strategic approach to design and development, where decisions are made with a comprehensive view of the user’s journey, rather than in isolation. The ultimate aim is to create a seamless, engaging user experience that meets users’ needs and exceeds their expectations at every touchpoint.
In conclusion, UX journey mapping is a powerful tool for understanding and improving the customer experience. By visualizing the journey from the customer’s perspective, organizations can identify pain points, uncover opportunities, and design experiences that truly resonate with their users. The journey map is not an end in itself but a means to a more empathetic, user-centered design approach that fosters loyalty, satisfaction, and business success.
Build your perfect SEO campaign with
Build your perfect SEO campaign with. Build your.
RELATED ARTICLES
Frequently asked questions.
The stages of the UX user journey typically include Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Advocacy. These stages represent the user’s journey from becoming aware of a product or service to becoming a loyal customer and advocate for the brand.
A UX experience map is a visualization that represents the overall experience a user has with a product or service, encompassing all touchpoints and channels. Unlike journey maps, which focus on specific tasks or interactions, experience maps provide a broader view of the user’s relationship with the brand, capturing emotions, motivations, and barriers across different contexts.
To conduct user journey mapping, follow these steps:
- Define the goals of the mapping exercise and the target persona.
- Gather data through user research to understand the persona’s needs, goals, and behaviors.
- Map out the key touchpoints and stages in the user’s journey with the product or service.
- Identify the user’s actions, thoughts, and emotions at each touchpoint.
- Analyze the map to identify pain points, opportunities for improvement, and moments of delight.
- Prioritize and implement changes based on insights gained from the journey map.
Creating a journey map in design thinking involves several steps:
- Empathize: Conduct research to understand the user’s needs, pain points, and the context of their interactions with the product or service.
- Define: Clearly articulate the user’s problem or need that the journey map will address.
- Ideate: Brainstorm the stages, touchpoints, and experiences that comprise the user’s journey.
- Prototype: Visualize the journey map, detailing the user’s actions, emotions, and challenges at each stage.
- Test: Share the journey map with stakeholders and users to gather feedback and refine your understanding. Design thinking emphasizes a user-centered approach, ensuring that the journey map reflects real user experiences and drives meaningful improvements.
Get more knowledagble

0 minutes read
what is usability testing
8 minutes read
How to Choose a Web Design Agency
12 minutes read
Maximizing Nonprofit Growth: Strategies for Impactful Web Design

17 minutes read
How User Experience (UX) Affects SEO

13 minutes read
What is CMS in Web Design: Answered in a Guide

9 minutes read
Unlocking UX Potential: The Importance of Interaction Design
Web design vs. web development: a comprehensive guide.

Exploring UX Design: Understanding its Connection with User Research

What are Customer Journey Maps and Why Do They Matter?

A customer journey map is an excellent way to visualize how your users navigate your user experience. But what is a customer journey map, exactly? Let’s find out.
Customer experience (CX) has become quite a hot topic in the brand and product design field. While it’s still important to turn out top-notch products for a fair price, consumers are beginning to put more value in their overall experience with a company rather than how high quality their products are. This means forming meaningful long-term relationships with customers through thoughtful and smooth customer experiences.
Recent research conducted by Forrester, a well-known consulting and analytics firm, shows that customers will spend more money for a quality lifetime relationship with an organization rather than just an impressive product. Organizations that have a solid grasp on who their customers are and what they expect to achieve when interacting with the business, are more likely to grow their bottom line and reach company goals. One of the best ways to do this is to create a customer journey map.
But what is a customer journey and why should you map it out? We’ll answer those questions and more in this informative guide. Here’s what you can expect to learn:
- What is a customer journey?
- What is a customer journey map?
How are customer journey maps used?
- Why are customer journey maps important?
- Key takeaways
Ready to learn all about customer journey maps? Let’s get started.
1. What is a customer journey?
A customer journey is the experience an established or prospective customer has with your company when trying to accomplish a certain goal. The customer journey takes into account every point of contact a customer has with a business, not just their interaction with a single product. For instance, say someone wants to find a way to learn French language quickly. Their customer journey would include their realization of the problem or goal, researching about the different solutions available to them, deciding on a product, using it, and discontinuing its use. While the product-level interaction is an important step, the customer journey takes into account how the product was marketed to the customer, customer service and support experiences, the purchasing experience, all the way to the discontinuation of use.
2. What is a customer journey map?
Customers usually have a certain goal they would like to achieve when dealing with an organization or business. A journey map gives a visual depiction of the steps it takes for them to achieve that goal and how they felt about it along the way. Using journey maps allow businesses to take a walk in their customer’s shoes and accurately experience their brand as their users would. Often this helps identify gaps or pain points in the customers experience that the organization can then address and remedy.
A customer journey map can be made with pencil and paper, sticky notes on a white board, or displayed in an Excel spreadsheet. Some businesses will even incorporate meaningful graphics into their maps to help better visualize the customer journey. These maps may focus on a certain aspect of a customer journey like service and support or they may have a broader scope and look at their customer’s daily experience.
Here are examples of some different maps and templates:
CareerFoundry: Customer journey map template

CareerFoundry’s downloadable journey map template . You can also follow this 7-step guide to build your first customer journey map .
Hubspot’s This A Day In the Life template map via HubSpot.com focuses on consumer’s needs throughout the day.
This Preact map is a good example of a more traditional map.
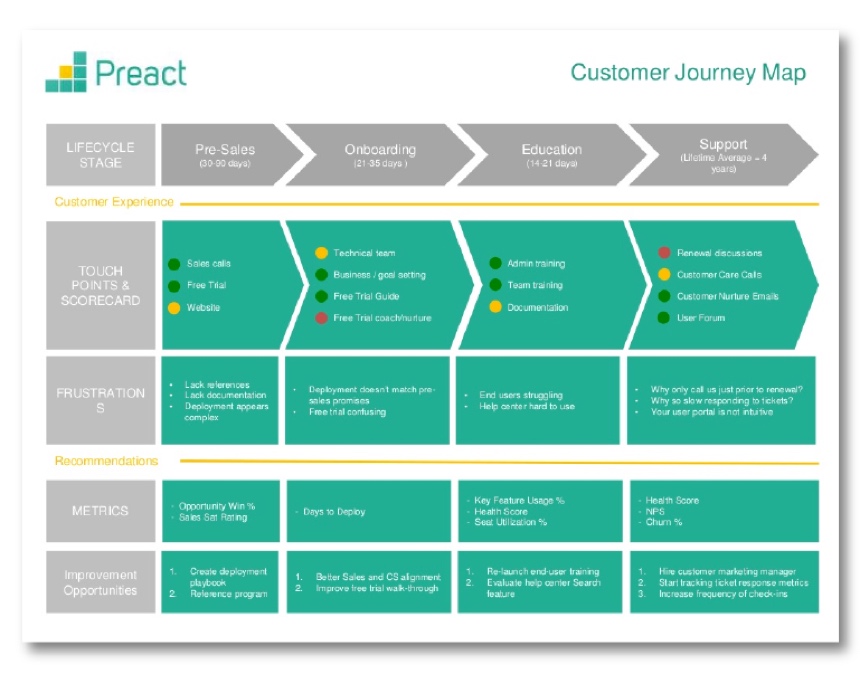
This Starbucks customer journey map is very linear and prioritizes the customer timeline.
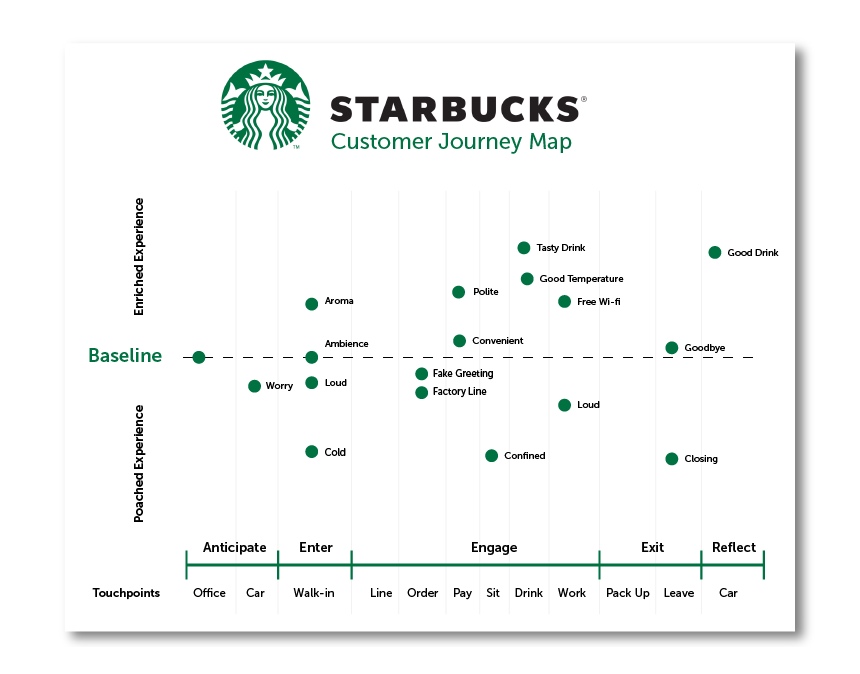
This map from UXPressia uses meaningful and memorable graphics to display the customer journey.
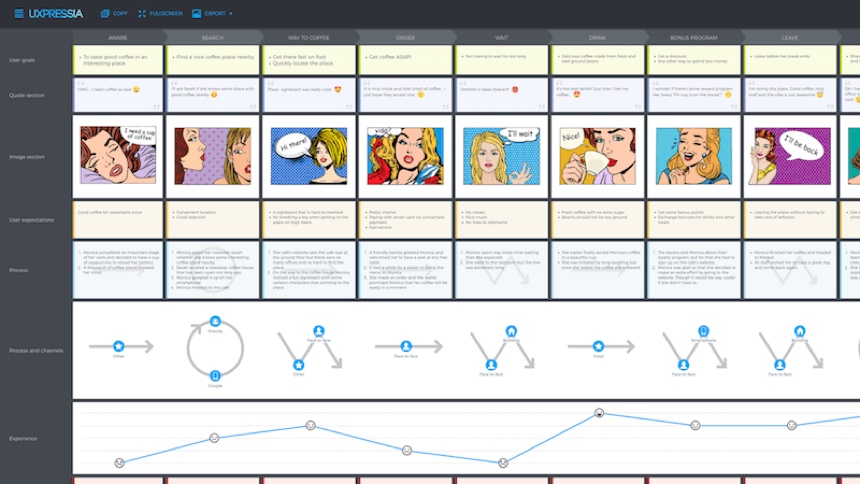
3. How are customer journey maps used?
Now that we’ve explained what a customer journey map is, let’s look a little bit further into who uses them, when, and how.
Who uses customer journey maps?
Since customer journey maps have such a large scope, their use spans a variety of professional titles. CEOs, company managers, UX/UI designers, and copywriters can all gain unique insight from customer journey maps. Designers may use them to understand where the user has come from before using the product and where they will go next while a company manager might be more interested in seeing how customer’s approach and move through the sales process.
When are customer journey maps created and used?
To make the most out of a customer journey map, they should constantly be being referenced and updated as a company and their audience evolves. However, the earliest you’ll see a customer journey map in use is usually after a business starts to have a solid grasp on who their customers are and what sort of steps they take when trying to achieve their goal. Customer journey maps are regularly revisited as a company grows.
So, once you’ve created a customer journey map, you may be wondering how best to use it. The main objective when creating a customer journey map is to keep the customer and their experience in the front of everyone’s mind. Many will choose to display customer journey maps in the workspace or ensure they are easily accessible to all employees. This way, all staff members can refer to it at any point in the design process to ensure the needs of the user are constantly being considered.
Be sure to keep your map research-based and up-to-date as well. If your map does not accurately portray the customer’s experience, it will be rendered useless. The best way to validate your results is by showing your map to customers and receiving their feedback.
4. Why are customer journey maps important?
The practice of moving through an experience as customers do helps businesses understand who their customers are and how they feel about their brand overall. These maps help create efficient work environments to create a brand that users feel happy to interact with as a whole.
Safeguards a brand’s promise
Looking through a customer’s eyes without bias can be difficult. Customer journey maps help compare what an organization may be claiming they provide to what their patrons are actually experiencing. Often, there can be stark differences between the two that, if left unaddressed, can have negative impacts on brand trust .
Narrows down the customer base
Along with understanding what it takes for a customer to achieve a certain goal, customer journey maps can also help narrow down exactly who a business’s customers are. Understanding your patrons is crucial to making sure you’re catering your services to the right people, in the right field, in the right way. Customer journey maps give a more personalized and complete picture of who businesses need to be reaching and connecting with.
Prioritizes the customer’s needs
One of the best ways to help customers succeed is to identify where their roadblocks may be and how to remove them. The visual nature of a customer journey map makes it easy to see what a customer’s pain points are and what can be done to move them along their journey with ease. Because journey maps look at the life-long relationship between customer and company, they give designers and businesses greater context when learning how to solve their customers’ needs.
Improves company communication
It can be common for consumers to express difficulty navigating between different divisions of a company. They may experience a great sales process but have trouble contacting support. Design tools that help all the different departments of an organization communicate effectively are almost invaluable. Customer journey maps help all sections of a company understand how their consumers move and what their goals are. This knowledge helps each department understand where the customer is coming from and gives them the ability to assist the customer along their journey by providing next steps.
5. Key takeaways
Understanding consumers through the creation of a customer journey map can help identify what customers need to have a positive overall experience with a brand.
While customer journey maps can provide deep insight into their customers’ experience, companies should be sure to combine this knowledge gained with other user research tools like empathy maps , user personas , and storyboarding. Used together, these design aids can help all aspects of a business create stellar experiences and products for their key audiences and consumers.
To learn more about how to craft great user/customer experiences, check out these articles:
- What exactly is CX (customer experience)?
- UX vs. CX: What’s the difference?
- What is user experience (UX) design?
- 11 Best online courses to learn UX design

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn where and how user journey mapping is used in the design process with Google's course Start the UX Design Process: Empathize, Define, and Ideate. You'll craft user stories, develop user journey maps, and more, in 21 hours or less. Build your UX design knowledge with Google's UX Design Professional Certificate. The popular series includes ...
Core Method. Collected by Google. User Journey Mapping is a common Design Sprint method that maps out a user's experience step by step as they encounter your problem space or interact with your product. This method enables the team to get into the mindset of the user and illuminates pain points, identifying opportunities to create new or ...
Create empathy maps, personas, user stories, and user journey maps to understand user needs; Develop problem statements to define user needs; Generate ideas for possible solutions to user problems; ... The Google UX Design Certificate was designed and built by subject-matter experts and senior practitioners at Google. This certificate has been ...
2 types of user journey maps—and when to use them. User journey maps are helpful across the product design and development process, especially at two crucial moments: during product development and for UX troubleshooting. These scenarios call for different user journey maps: current-state and future-state. Current-state user journey maps
Alice Ruddigkeit. Senior UX Researcher. The user journey map , also known as customer journey map or user experience journey map is a way to visually structure your knowledge of potential users and how they experience a service. Customer journey mapping is also a popular workshop task to align user understanding within teams.
Here's how to create a user journey map in 6 steps: Choose a user journey map template (or create your own) Define your persona and scenario. Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions. Fill in the user's thoughts, emotions, and pain-points. Identify opportunities.
A user journey map is an excellent tool for UX designers because i t visualizes how a user interacts with a product and allows designers to see a product from a user's point of view. This fosters a more user-centric approach to product design, which ultimately leads to a better user experience.
Because User 2 and User 4 had similar painpoints and experiences, I merged their empathy maps to create the user persona "Aryan". Due to busy florist stores, they both found it difficult to choose the perfect flowers every day and for festivals. User 4 needed flowers daily because they were used as an offering to god in daily prayers.
UX Course 2 Week 2 — User Journey Maps. This week was all about journey maps. My assignment was to take one of the user persona's I created and make a user journey map. I have actually never done one of these before and the experience was very useful. It really helps to put yourself into the user's shoes and think about what they're ...
2. Business goals. Basically, know the reason why you are creating a journey map. For example: Wanting to better understand a particular user's behavior, refocusing organizational perspective to consider real human experiences, learning where your customer's pain points are, etc.
User journey mapping is a valuable tool in UX design, helping designers understand the needs, goals, and pain points of users, identify opportunities for improvement, and align stakeholders. By following the steps outlined in this article, designers can create effective user journey maps that inform design decisions and improve the user experience.
Definition of a Journey Map. Definition: A journey map is a visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. In its most basic form, journey mapping starts by compiling a series of user actions into a timeline. Next, the timeline is fleshed out with user thoughts and emotions in order to create a narrative.
The same idea applies to the user journey map. a user journey map help UX designer create obstacles free path for users. That's the first benefit of user journey mapping. Another example is, a user journey map reduces the impact of designer bias, which I the tendency for the designer to design according to their own needs and wants instead of ...
Steps. Define business and user goals Clearly articulate the organizational goals for the product or service, the design and business goals for the mapping exercise, and the goals of the target user the map is to represent.; Gather research data Effective journey maps are based on qualitative and quantitative data collected across a range of activities. . Review and incorporate existing ...
User actions: Each stage maps out the user's steps or tasks. Emotions: Indicates how the user feels at different points.These include happiness, frustration, or confusion. Touchpoints: The places where the user interacts with the product, like a website, app, or physical store. These parts of the journey map allow design teams to assess the user's experience at every touchpoint and uncover ...
A journey map helps UX designers identify stress points and missing connections in the product to eliminate inefficiency. Journey mapping makes products functional, intuitive, and easy to use. If you're looking to create user-friendly, intuitive experiences for your customers, journey mapping is a key part of UX design.
The Importance of Journey Maps in UX Design. Journey maps are vital in UX design as they provide a bird's-eye view of the user experience, highlighting how customers interact with a product or service across multiple channels and touchpoints. This panoramic perspective is critical in identifying friction points that may hinder customer ...
A user journey map tells a story of the person trying to accomplish a specific task or goal using your product. Here are six things that you need to remember when creating a journey map: 1. Know your business goals. The business objectives are the first things you must consider when designing a user journey map.
The main job of a UX designer is to make products intuitive, functional, and enjoyable to use. By creating a user journey map, you're thinking about a product from a potential customer's point of view. This can help in several ways. User journey maps foster a user-centric mentality. You'll focus on how a user might think and feel while ...
Key elements. Journey maps come in all shapes and sizes but usually, they will contain some or all of the following: Persona — An instance of a user, real or imagined, who experiences the journey.. Scenario — Describes the situation that the journey map is trying to address. This is associated with a specific user goal, need, or expectation.
Customer journey maps help all sections of a company understand how their consumers move and what their goals are. This knowledge helps each department understand where the customer is coming from and gives them the ability to assist the customer along their journey by providing next steps. 5. Key takeaways.
A user journey map is a visual representation of the "story" from a customer's perspective. The user journey helps you visualize your product from the customer's point of view via a user journey map. It helps focus the lens on how customers experience your product or service. Creating a journey map may be more common in the marketing ...
A breakdown of a customer journey map from Nielsen Norman Group.. What is the difference between a customer journey map and a user journey map? Not a whole lot. Sometimes, user journey maps refer to specific maps UX designers make during the design process to understand potential points of friction in the customer journey. But typically, the difference is semantic: The terms "user journey ...