

International tourism, expenditures (current US$) - Cambodia

Selected Countries and Economies
All countries and economies.
- Privacy Notice
- Access to Information
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here.
Effects of Tourism Expenditure on Cambodia’ Economy: A Computable General Equilibrium Model for Cambodia
- Conference paper
- First Online: 30 July 2022
- Cite this conference paper

- Chantha Hor 5
Part of the book series: Studies in Systems, Decision and Control ((SSDC,volume 429))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference of the Thailand Econometrics Society
365 Accesses
The ten-year (2011–2020) tourism strategic development plan in Cambodia has diversified destinations into four strategic tourism destinations: Central (business tourism), Northwest (cultural tourism), Southwest (coastal tourism), and Northeast (eco-tourism). This paper analyzes the impact of a 10% increase in tourism expenditure for the tourism sector by employing a computable general equilibrium (CGE) model based on Macro-and Micro social accounting matrix year 2015. I find that 10% increased tourism expenditure stimulates the real GDP, private consumption, exports, and imports in the short run; it reduces real GDP in the long run. The estimation result suggests that a shock in tourism expenditure increases household income and improves household welfare at Cambodia’s four strategic tourism destinations.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Becken, S., & Lennox, J. (2012). Implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism. Tourism Management, 33 (1), 133–142.
Article Google Scholar
Blake, A. (2000). The economic effects of tourism in Spain. Christel DeHaan Tourism and Travel Research Institute.
Google Scholar
Blake, A., Arbache, J. S., Sinclair, M. T., & Teles, V. (2008). Tourism and poverty relief. Annals of Tourism Research, 35 (1), 107–126.
Blake, A., & Sinclair, M. T. (2003). Tourism crisis management US response to September 11. Annals of Tourism Research, 30 (4), 813–832.
Blake, A., Sinclair, M. T., & Soria, J. A. C. (2006). Tourism productivity: Evidence from the United Kingdom. Annals of Tourism Research, 33 (4), 1099–1120.
Chhuor, S. (2017). Potential roles of the export orientation of Cambodia’s agriculture and agro-industry: An application of CGE analysis. Journal of Economic Structures , 6 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40008-017-0087-6
Dwyer, L., Forsyth, P., Madden, J., & Spurr, R. (2000). Economic impacts of inbound tourism under different assumptions regarding the macroeconomy. Current Issues in Tourism, 3 (4), 325–363.
Dwyer, L., Forsyth, P., & Spurr, R. (2004). Evaluating tourism’s economic effects: New and old approaches. Tourism Management, 25 (3), 307–317.
Dyna, H., & Em, K. (2015). Impacts of Cambodia’s tariff elimination on household welfare and labor market: a CGE approach. Partnership for Economic Policy-PEP .
Ear, S., Sim, S., & Khiev, P. (2016). Macroeconomic impacts of public consumption on education—A computable general equilibrium approach. Partnership for Economic Policy-PEP .
Forsyth, P., Dwyer, L., Spurr, R., & Pham, T. (2014). The impacts of Australia’s departure tax: Tourism versus the economy? Tourism Management, 40 , 126–136.
Gül, H. (2013). Economic impacts of an increase in the foreign tourism receipts: A SAM-based income multiplier analysis. Advances in Hospitality and Tourism Research, 1 (1), 17–36.
Gül, H. (2016). Effects of foreign demand increase in the tourism industry: A CGE approach to Turkey. An International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Research, 26 (4), 598–611.
Henry, E. W., & Deane, B. (1997). The contribution of tourism to the economy of Ireland in 1990 and 1995. Tourism Management, 18 (8), 535–553.
Ihalanayake, R. (2012). Economic effects of tourism tax changes in Australia: Empirical evidence from a computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Economics, 18 (1), 181–202.
Kobayashi, S., Tanji, H., Saito, K., Huang, W., & Tada, M. (2009). The industrial structure of Cambodia and the role of agriculture and fishery in its development. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly, 43 (4), 309–316.
Narayan, P. K. (2004). The economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: Empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Economics, 10 (4), 419–433.
Njoya, E. T., & Nikitas, A. (2020). The role of air transport in employment creation and inclusive growth in the Global South: The case of South Africa. Journal of Transport Geography, 85 , 102738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2020.102738
Levy, S. (2017). Graduation-based social protection for Cambodia’s extreme poor: a general equilibrium analysis of economic and poverty impacts .
Li, S., Blake, A., & Cooper, C. (2011). Modeling the economic impact of international tourism on the Chinese economy: A CGE analysis of the Beijing 2008 Olympics. Tourism Economics, 17 (2), 279–303.
Li, S., & Song, H. (2013). Economic impacts of visa restrictions on tourism: A case of two events in China. Annals of Tourism Research, 43 , 251–271.
Lofgren, H., Harris, R. L., & Robinson, S. (2002). A standard computable general equilibrium (CGE) model in GAMs . Micro Computers in Policy Research No. 5. International Food Policy Research Institution, Washington, DC.
Mahadevan, R., Amir, H., & Nugroho, A. (2017). Regional impacts of tourism-led growth on poverty and income inequality. Tourism Economics, 23 (3), 614–631.
Meng, S. (2014). The role of inbound tourism in the Singaporean economy: A computable general equilibrium (CGE) assessment. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 31 (8), 1071–1089.
MOT. (2019). Tourism annual statistics report . Ministry of Tourism, Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
Pambudi, D., McCaughey, N., & Smyth, R. (2009). Computable general equilibrium estimates of the impact of the Bali bombing on the Indonesian economy. Tourism Management, 30 (2), 232–239.
Soubert, S., & Lay, S. (1995). Case study on the effects of tourism on culture and the environment . UNESCO.
Sugiya, G., Blake, A., & Sinclair, M. T. (2003). Tourism and globalization: Economic impact in Indonesia. Annals of Tourism Research, 30 (3), 683–701.
United Nation World Tourism Organization. (2020). International tourism highlights . https://doi.org/10.18111/9789284422456 . Accessed July 25, 2021.
World Bank. (2020). Enabling eco-tourism development in Cambodia . Washington, DC.
Yang, H. Y., & Chen, K. H. (2009). A general equilibrium analysis of the economic impact of a tourism crisis: A case study of the SARS epidemic in Taiwan. Journal of Policy Research in Tourism, Leisure and Events, 1 (1), 37–60.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
ACLEDA Institute of Business, #1397, Phnom Penh-Hanoi Friendship Blvd, Phum Anlong Kngan, Sangkat Khmuonh, Khan Saensokh, Phnom Penh, 1149, Kingdom of Cambodia
Chantha Hor
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chantha Hor .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Economics, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
Songsak Sriboonchitta
Department of Computer Science, University of Texas, El Paso, TX, USA
Vladik Kreinovich
Faculty of Economics, Center of Excellence in Econometrics, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
Woraphon Yamaka
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Hor, C. (2022). Effects of Tourism Expenditure on Cambodia’ Economy: A Computable General Equilibrium Model for Cambodia. In: Sriboonchitta, S., Kreinovich, V., Yamaka, W. (eds) Credible Asset Allocation, Optimal Transport Methods, and Related Topics. TES 2022. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, vol 429. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97273-8_32
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97273-8_32
Published : 30 July 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-97272-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-97273-8
eBook Packages : Intelligent Technologies and Robotics Intelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Cambodia - International Tourism, Expenditures 2024 Data 2025 Forecast 1995-2020 Historical
International tourism, expenditures (current us$) in cambodia was reported at 213000000 usd in 2020, according to the world bank collection of development indicators, compiled from officially recognized sources. cambodia - international tourism, expenditures - actual values, historical data, forecasts and projections were sourced from the world bank on april of 2024..

Tourism in Cambodia
Development of the tourism sector in cambodia from 1995 to 2021.
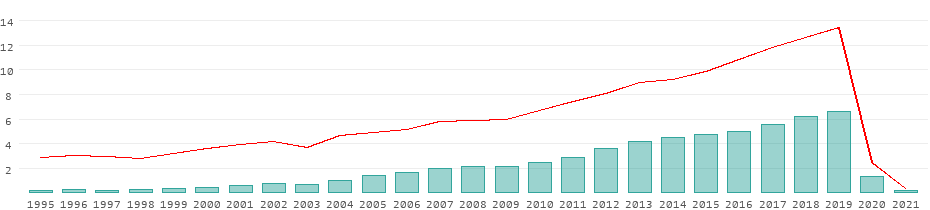
Revenues from tourism
All data for Cambodia in detail

Travel & Tourism in Cambodia (2022)
Unlock hidden opportunities in the Travel and Tourism industry

Published: July 31, 2022 Report Code: GDTTCS-22-69-MP-L5
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Threads
- Share via Email
- Report Overview
Table of Contents
Methodology.
Discover untapped potential in the Travel & Tourism industry with our Travel & Tourism in Cambodia (2022) report and make more profitable business decisions.
GlobalData’s country series report titled ‘Travel & Tourism in Cambodia (2022)’ provides a wealth of key data for the travel & tourism sector in Cambodia. The data in this report includes demands & flows data on domestic travel, international arrivals and departures. Additionally, data is provided on traveler spending patterns, the airlines, and hotel sectors. The report also identifies the key themes impacting the tourism industry.
In 2022, Cambodia welcomed 2.29 million international arrivals. The country also saw 0.5 million international departures over the same period. This report is based on data from databases compiled by GlobalData’s team of industry experts.
- Assess and seize new business opportunities in the current landscape of Cambodia’s travel and tourism sector.
- Future-proof your strategies by utilising historical and projected performance data from specific market segments that shape the industry.
- Effectively plan and allocate resources in response to evolving tourism behaviours, fostering sustainable growth.

Reasons to Buy
Uncover comprehensive data on the patterns and trends of travel within Cambodia. Dive into information related to travel destinations, purposes, and preferences of domestic tourists.
Capitalise on business opportunities by understanding how travellers allocate their expenditures based on their spending habits on accommodation, transportation, food, and other expenses.
Access data on inbound tourists arriving in Cambodia and outbound trips made by residents. This section includes popular destinations, factors driving these travel trends, and visitor demographics.
Understand occupancy rates for hotels, load factors for airlines, car rental trends, and the role of travel intermediaries in facilitating bookings and reservations.
Identify opportunities within the market and tailor your strategies to target specific customer groups in the travel and tourism industry of Cambodia.
Leverage historical and projected performance data to gauge the trajectory of the industry. Study how it has evolved over time and determine what can be expected in the future to enhance your strategies.
Key Players
Definitions & Research Methodology
Frequently asked questions
All the above details are then collated to build the end deliverable in an easy to consume format.
- Currency Conversion is for Indicative purpose only. All orders are processed in US Dollars only.
- USD - US Dollar
- AUD — Australian Dollar
- BRL — Brazilian Real
- CNY — Yuan Renminbi
- GBP — Pound Sterling
- INR — Indian Rupee
- JPY — Japanese Yen
- ZAR — South African Rand
- USD — US Dollar
- RUB — Russian Ruble
Can be used by individual purchaser only
Can be shared by unlimited users within one corporate location e.g. a regional office
Can be shared globally by unlimited users within the purchasing corporation e.g. all employees of a single company
Undecided about purchasing this report?
Get in touch to find out about multi-purchase discounts.
[email protected] Tel +44 20 7947 2745
Every customer’s requirement is unique. With over 220,000 construction projects tracked, we can create a tailored dataset for you based on the types of projects you are looking for. Please get in touch with your specific requirements and we can send you a quote.
Sample Report
Travel & Tourism in Cambodia (2022) was curated by the best experts in the industry and we are confident about its unique quality. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer free sample report to help you:
- Assess the relevance of the report
- Evaluate the quality of the report
- Justify the cost
Download your copy of the sample report and make an informed decision about whether the full report will provide you with the insights and information you need.
Below is a sample report to help you understand the structure of the report you are buying

“The GlobalData platform is our go-to tool for intelligence services. GlobalData provides an easy way to access comprehensive intelligence data around multiple sectors, which essentially makes it a one-for-all intelligence platform, for tendering and approaching customers.
GlobalData is very customer orientated, with a high degree of personalised services, which benefits everyday use. The highly detailed project intelligence and forecast reports can be utilised across multiple departments and workflow scopes, from operational to strategic level, and often support strategic decisions. GlobalData Analytics and visualisation solutions has contributed positively when preparing management presentations and strategic papers.”
“COVID-19 has caused significant interference to our business and the COVID-19 intelligence from GlobalData has helped us reach better decisions around strategy. These two highlights have helped enormously to understand the projections into the future concerning our business units, we also utilise the project database to source new projects for Liebherr-Werk to use as an additional source to pitch for new business.”
Your daily news has saved me a lot of time and keeps me up-to-date with what is happening in the market, I like that you almost always have a link to the source origin. We also use your market data in our Strategic Business Process to support our business decisions. By having everything in one place on the Intelligence Center it has saved me a lot of time versus looking on different sources, the alert function also helps with this.
Having used several other market research companies, I find that GlobalData manages to provide that ‘difficult-to-get’ market data that others can’t, as well as very diverse and complete consumer surveys.
Our experience with GlobalData has been very good, from the platform itself to the people. I find that the analysts and the account team have a high level of customer focus and responsiveness and therefore I can always rely on. The platform is more holistic than other providers. It is convenient and almost like a one stop shop. The pricing suite is highly competitive and value for our organisation.
I like reports that inform new segments such as the analysis on generation Z, millennials, the impact of COVID 19 to our banking customers and their new channel habits. Secondly the specialist insight on affluent sector significantly increases our understanding about this group of customers. The combination of those give us depth and breadth of the evolving market.
I’m in the business of answering and helping people make decisions so with the intelligence center I can do that, effectively and efficiently. I can share quickly key insights that answer and satisfy our country stakeholders by giving them many quality studies and primary research about competitive landscape beyond the outlook of our bank. It helps me be seen as an advisory partner and that makes a big difference. A big benefit of our subscription is that no one holds the whole data and because it allows so many people, so many different parts of our organisation have access, it enables all teams to have the same level of knowledge and decision support.
“I know that I can always rely on Globaldata’s work when I’m searching for the right consumer and market insights. I use Globaldata insights to understand the changing market & consumer landscape and help create better taste & wellbeing solutions for our customers in food, beverage and healthcare industries.
Globaldata has the right data and the reports are of very high quality compared to your competitors. Globaldata not only has overall market sizes & consumer insights on food & beverages but also provides insights at the ingredient & flavour level. That is key for B2B companies like Givaudan. This way we understand our customers’ business and also gain insight to our unique industry”
GlobalData provides a great range of information and reports on various sectors that is highly relevant, timely, easy to access and utilise. The reports and data dashboards help engagement with clients; they provide valuable industry and market insights that can enrich client conversations and can help in the shaping of value propositions. Moreover, using GlobalData products has helped increase my knowledge of the finance sector, the players within it, and the general threats and opportunities.
I find the consumer surveys that are carried out to be extremely beneficial and not something I have seen anywhere else. They provided an insightful view of why and which consumers take (or don’t) particular financial products. This can help shape conversations with clients to ensure they make the right strategic decisions for their business.
One of the challenges I have found is that data in the payments space is often piecemeal. With GD all of the data I need is in one place, but it also comes with additional market reports that provide useful extra context and information. Having the ability to set-up alerts on relevant movements in the industry, be it competitors or customers, and have them emailed directly to me, ensures I get early sight of industry activity and don’t have to search for news.
Related reports

Every Company Report we produce is powered by the GlobalData Intelligence Center.
Subscribing to our intelligence platform means you can monitor developments at Travel & Tourism in Cambodia (2022) in real time.
- Access a live Travel & Tourism in Cambodia (2022) dashboard for 12 months, with up-to-the-minute insights.
- Fuel your decision making with real-time deal coverage and media activity.
- Turn insights on financials, deals, products and pipelines into powerful agents of commercial advantage.
- 2 February 2023
The Royal Government of Cambodia has acknowledged the potential of the tourism industry as a source of Cambodia’s socio-economy growth, including job creation and poverty reduction. Tourism has been considered one of Cambodia’s key economic pillars, both international and domestic. In the early 2000s , the top foreign tourists to Cambodia were westerners from the United States, United Kingdom, and France. 1 Chinese tourists have topped the 2019 Cambodia arrival list accounting for 2.36 million visitors. 2 It shows an 18 percent increase from 2018. Chinese tourists remain at the top for 2020, followed by Thailand and Vietnam . 3 Other tourist arrivals are from the United States, the Republic of Korea, Japan, France, and Chinese Taipei. 4 For outbound departure, Cambodia has traveled the most to Thailand (42 percent), Vietnam (30 percent), Taiwan (12 percent), China (5 percent), Malaysia (4 percent), and the rest of the world (7 percent) in 2019. 5
In 20 19, there were approximately 11.3 million domestic and 6.61 million international tourists. 6 In 2022, Cambodia recorded 2.2 million international visitors, an 11 percent increase from the previous year. 7 International tourist revenue shared of Cambodia’s GDP was 9.44 percent in 2000 . 8 The number increased to 19.61 percent in 2019. 9 International tourist receipts are equivalent to 228 million USD in 2000 and 4,919 million USD in 2019. 10 However, the number dropped significantly in 2020 as the world was hit with COVID-19’s quarantine and travel restrictions. In 2020, international tourist receipts dropped threefold from the previous year to around 1,023 million USD. 11
Tourism directly employed 630,000 workers , of which 60 percent were women in 2019. 12 The sector is only second to the garment sector with the largest number of women employed. In terms of hotels and accommodation, a s of 2020 , a total of 1,028 hotels provide 44,428 rooms residing in 25 provinces across Cambodia. 13 Another accommodation type is the guesthouse, in which 2,755 units are divided into 35,791 rooms are available for tourists. 14 As the tourism industry grows and demand for accommodation spike over the year, the number of hotels and guesthouses also increase. In 1998, there were only 216 hotels and 147 guesthouses. It shows a growth rate of 386 percent and 1.740 percent for hotels and guesthouses, respectively. 15
Cambodia’s top tourist destination is the Angkor Archaeological Park in Siem Reap. The park covers 400 square kilometers and consists of forest areas and many ancient temples. It is home to Angkor Wat temple, the largest religious temple in the world. The temple was listed as UNESCO World Heritage in 1992. 16 Angkor Wat and other temples in the Angkor Archaeological Park have generated millions of dollars and attracted millions of local and international travelers each year. In 2019 , Angkor Wat attracted approximately 2.2 million international tourists generating 99 million USD in revenue through ticket sales. 17 Other tourist's popular destinations are coastal areas (Preah Sihanouk, Koh Rong, Kep, Koh Kong, and Kampot), mountain areas (Battambang, Rattanakiri, Mondulkiri, Pursat), and ecotourism that spread out across the countries .
Ecotourism and Communities-Based Ecotourism (CBET) in Cambodia
The United Nations World Tourism Organization defines ecotourism as “all nature-based forms of tourism in which the main motivation of visitors is the observation and appreciation of nature as well as the traditional cultures prevailing in natural areas.” 18 While communities based ecotourism involves the local communities' participation and natural resource management, who will gain direct benefits through ecotourism activities in their areas. 19 As communities-based ecotourism generate profit for the local, it also preserves the natural resources and environments. For a country with rich natural landscapes and attractions, Cambodia has the potential for ecotourism development. 20
In the last decades, ecotourism has experienced rapid growth. The main reason for the change is the government's prioritization of diversifying the sector and the need for sustainable tourism. I n 2017 , the interministerial ecotourism task force was formed to manage and develop potential communities based tourism in Cambodia. 21 In addition, i n 2021 , based on the success of the interministerial task force, the National Committee for Management and Development of Community-Based Tourism and Ecotourism (NCDCBE) was established. 22

Virachey National Park, Ratanakiri, Cambodia. Photo taken from Ministry of Tourism's Facebook page on 05 October 2017.
As of 2019, the Ministry of Tourism stated that there are around 266 ecotourism sites, 13 of which are community base ecotourism operating across Cambodia. 23 In 2019 , ecotourism shared 16 percent of the total tourist visit in Cambodia. 24 The number has accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic as the demand for domestic tourism increased due to international travel restrictions. In 2022, The Ministry of Environment approved 307 small-scale ecotourism projects, which shows a hike in ecotourism demand in the past few years. 25 Also, the Ministry of Agriculture has identified 131 agricultural communitie s that have the potential to convert into communities-based ecotourism that can improve the local’s living standard. 26
In collaborating with the World Bank, the Ministry of Environment implemented the Sustainable Landscape and Ecotourism Project (CSLEP) in 2019. The 50.66 million USD project aims to promote ecotourism and non-timber forest products in the Cardonmon mountain and Tonel Sap landscape, which they identified as potential areas for communities-based ecotourism development; namely, the Koh Kong province, Siem Reap province, and Phnom Aural protected area. 27 Under the CLSEP project, various frameworks are published including the Process Framework of the Cambodia Sustainable Landscape and Ecotourism , Indigenous People Planning Framework of the Cambodia Sustainable Landscape and Ecotourism and Resettlement Policy Framework of the Cambodia Sustainable Landscape and Ecotourism.
Tourism in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic
Having tourism as one of their main source of revenue, Cambodia felt the impact of COVID-19 . At the beginning of the pandemic, the tourism sector was drastically affected. The reason is mainly due to the travel restriction that prevents foreign tourists from traveling. 28 Foreigners visiting Cambodia dropped significantly from 6.61 million in 2019 to 1.3 million visitors in 2020. 29 It is estimated that Cambodia has lost 3 billion USD of tourism revenue to the COVID-19 pandemic. 30
I n 2020 , Tourism-related employment decreased by 21.7 percent from the previous year. 31 It was equivalent to 2.33 million in employment in 2019 to 1.82 million in 2020. 32 As of September 2020 , the Ministry of Tourism reported that about 3000 tourism-related businesses were closed or suspended. 33 About 62 percent o f the affected business were based in Siem reap, forcing nearly 15,000 workers out of jobs. 34 Most suspended or laid-off workers turn to the agricultural sector to support their daily incomes.
The government has initiated various long and short-term recovery responses to retrieve the tourism industry. Those measures include tax/fee exemptions and cash support/loans for tourism-related businesses and enterprises, vaccination campaigns and capacity development for employees in the tourism sector, and infrastructure development. For instance, on February 2020 , a policy on monthly tax exemption for all hotels and guesthouses in Siem Reap was issued. This tax exemption policy for tourism-related accommodation has been extended until March 2023 . In addition, on May 2022, the government launched 150 million USD of the Tourism Recovery Co-financing Scheme (TRCS), which comes from the RGC’s contribution of 75 million USD through the Small and Medium Enterprise Bank of Cambodia (SME Bank) and Participating Financial Institutions (PFIs) contribution of 75 million USD. The enterprises in the tourism sector affected by the COVID-19 crisis can apply for loans from participating financial institutions that are partners of SME Bank at a concessional interest rate.
The government has implemented the Roadmap for Recovery of Cambodia tourism during and post COVID-19 . The roadmap is a comprehensive guideline that aims to strengthen the tourism sector during the post-COVID-19, mitigate the negative impact of the pandemic, and promote Cambodia's prestige and tourism as a safe destination for post-pandemic. The roadmap consists of three phases of recovery such as:
- Phase 1: Crisis management in the new normal phase and planning for recovery (2020-2021)
- Phase 2: Recovery of the tourism sector in Cambodia in the post-COVID (2022-2023)
- Phase 3: Preparation for the new future of the tourism sector in Cambodia (2024-2025).
Challenge and way forward
Despite gaining a large number of international tourists each year, Cambodia’s tourism sector still has room for improvement and to capitalize on the potential. The kingdom heavily depends on Angkor Wat as the main tourist attraction has made the country’s tourism sector vulnerable to external shock. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic has presented a reality test for Cambodia’s tourism sector. The travel restrictions and border closure negatively affect all tourism-related businesses, especially in tourism-driven provinces such as Siem Reap and Preah Sihanouk.
A limited selection of destinations is also a problem. Cambodia needs to diversify the tourism sector in order to keep the average length of tourists’ stay high. In 2018, the average length of stay of international tourists was seven days, one day shorter than in 1995. 35 The longer stay usually means more spending, thus generating more revenue for the sector. Diversifying the tourism sector to more than just temple tours will attract tourists to stay longer as it offers more options for tourists to explore. The government has recognized ecotourism as a solution to diversify the tourism industry. In addition, the Strategic framework and programs for economic recovery and to promote Cambodia's economic growth in living with COVID-19 in the new normal for 2021-2023 has identify areas for tourism diversification such as the coastal areas, northeastern regions, and natural landscapes such as Tonle sap, Mekong, and Bassac river.
Another issue associated with Cambodia’s tourism is poor infrastructure and limited transportation . 36 Infrastructure and transportation in other areas besides popular international destinations are often poor quality and underdeveloped. Roads, network connectivity, electricity, clean water, and sanitation in remote tourist sites can be unsatisfactory. 37 The establishment of the Master Plan for Siem Reap Tourism Development 2021-2035 , Master Plan for Mondulkiri Tourism Development 2021-2035 , the Phnom Penh-Sihanouk expressway, the new Siem Reap international airport are the government’s attempts to enhance and diversify the sector through infrastructure and connectivity development.
For 2023, Cambodia’s government has projected to receive four million international tourists, providing a positive aspect for a post-COVID-19 recovery in the tourism sector. 38 This could generate 4 billion USD in revenue for the country. 39
Related to Tourism
- Economy and commerce
- 1 . Peter Varga, " Angkor Wat: The Impact of Mass Tourism, " EHL insight, accessed January 2023.
- 2 . Khmer Times Staff, " Chinese top tourist arrivals in 2019, " Khmer Times, February 2020, accessed January 2023.
- 3 . Ministry of Tourism, " Tourism Statistic Report December 2020 ," December 2020, accessed January 2023.
- 5 . World Travel Tourism Council, " 2022 Annual Research: key highlights, " 2022, accessed January 2023.
- 6 . Economic Diplomacy Coordinating Group, " Dashboard series about Cambodia ," Ministry of Foreign Affair and International Cooperation, November 2021, accessed January 2023.
- 7 . Hin Pisei, " International visitors top 2.2M in 2022, lifting 2023 hopes, " The Phnom Penh Post, January 2023, accessed January 2023.
- 8 . Global Economy, " Compare countries with annual data from official sources ," accessed January 2023.
- 10 . Ministry of Tourism, " Tourism Statistic Report February 2022 ," February 2022, accessed January 2023.
- 12 . Asian Development Bank, " Sector Assessment Summary: Tourism in Cambodia ," Community-Based Tourism COVID-19 Recovery Project, January 2022, accessed January 2023.
- 13 . Economic Diplomacy Coordinating Group, " Dashboard series about Cambodia ," Ministry of Foreign Affair and International Cooperation, November 2021, accessed January 2023.
- 16 . UNESCO, " UNESCO statement on a reported construction project near the World Heritage site of Angkor in Cambodia ," February 2021, accessed January 2023.
- 17 . Khmer Times Staff, " Cambodia’s famed Angkor sees more than 45,000 international tourists in first 5 months ," Khmer Times, June 2022, accessed January 2023.
- 18 . United Nations World Tourism Organization, " Ecotourism and protect areas, " accessed January 2023.
- 19 . Phe Siphannara, " Overview of community-based ecotourism for sustainable development in Cambodia ," September 2019, accessed January 2023.
- 20 . OECD, " Structural policy country note: Cambodia ," Economic outlook for Southeast Asia, China India 2019: Towards smart urban transportation, December 2019, accessed January 2023.
- 21 . Post Staff, " Hun Sen gives nod to creation of ecotourism task force ," November 2017, accessed January 2023.
- 22 . Tin Sokhavuth, " Gov’t orders formation of NCDCBE to boost tourism sector ," October 2021, accessed January 2023.
- 23 . Phe Siphannara, " Overview of community-based ecotourism for sustainable development in Cambodia ," September 2019, accessed January 2023.
- 24 . Rawlins, et al, " Enabling ecotourism development in Cambodia, " World Bank, 2020, accessed January 2023.
- 25 . Sok Sithika, " 307 small nature tourism projects approved in September, " Khmer Times, October 2022, accessed January 2023.
- 26 . Khmer Times Staff, "Ministry identifies 131 potential ecotourism communities, " Khmer Times, July 2022, accessed January 2023.
- 27 . Ministry of Environment, " Cambodia Sustainable Landscape and Ecotourism Project, " February 2020, accessed January 2023.
- 28 . Ngin Chanrith, " COVID-19 and the Tourism sector in Cambodia: impact, response and the road to recovery, " 2022, accessed January 2023.
- 30 . Ministry of Tourism, " Roadmap for Recovery of Cambodia tourism during and post COVID-19," 2021, accessed January 2023.
- 31 . World Travel Tourism Council, " 2022 Annual Research: key highlights, " 2022, accessed January 2023.
- 33 . Khmer Times Staff, " 51,000 tourism-based jobs in Cambodia vapourised because of COVID-19 pandemic ," Khmer Times, November 2020, accessed January 2023.
- 35 . Perter Varga, " Angkor Wat: The Impact of Mass Tourism, " EHL insight, accessed January 2023.
- 36 . George Styllis, " Tourism slowdown threatens Cambodian model ," July 2016, accessed January 2023.
- 38 . Khmer Times Staff, " Four million international tourists expected by Cambodia this year after China’s pandemic strategy optimization ," Khmer Times, January 2023, accessed January 2023.
- 39 . Chea Vanyuth, " Cambodia expects tourism generating $4B in 2023 ," Khmer Times, January 2023, accessed January 2023.

- Ask Question
- Report Problem
- Send Feedback
- Submit Resources
Do you have questions on the content published by Open Development Cambodia (ODC)? We will gladly help you.
Have you found a technical problem or issue on the Open Development Cambodia (ODC) website?
Do you have a new idea that could help transform the Open Development Cambodia (ODC) website? We will be glad to hear it.
Tell us how we're doing.
Do you have resources that could help expand the Open Development Cambodia (ODC) website? We will review any map data, laws, articles, and documents that we do not yet have and see if we can implement them into our site. Please make sure the resources are in the public domain or fall under a Creative Commons license.
Disclaimer: Open Development Cambodia (ODC) will thoroughly review all submitted resources for integrity and relevancy before the resources are hosted. All hosted resources will be in the public domain, or licensed under Creative Commons. We thank you for your support.
Thank you for taking the time to get in contact!

Open Development Cambodia (ODC) in collaboration with the School of International and Public Affairs at Columbia University is conducting a survey to gather feedback that helps us make our open data platform even relevant and valuable for users.
- Your feedbacks are anonymous and confidential
- This short google form survey takes about 5 minutes .
This website stores cookies on your computer. These cookies are used to collect information about how you interact with our website and allow us to remember you. We use this information in order to improve and customize your browsing experience and for analytics and metrics about our visitors both on this website and other media. To find out more about the cookies we use, see our Cookies Policy .
If you decline, your information won’t be tracked when you visit this website. A single cookie will be used in your browser to remember your preference not to be tracked.
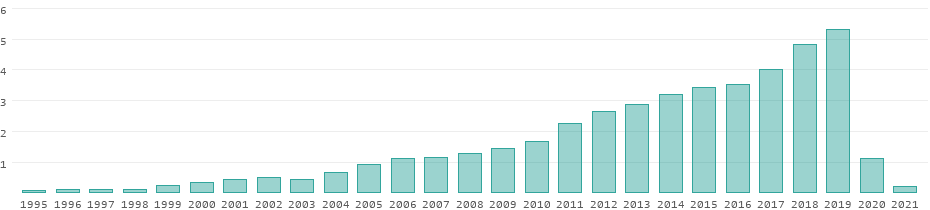
Cambodia Avg Expenditure: Per Capita
View cambodia's cambodia avg expenditure: per capita from 2004 to 2019 in the chart:.
What was Cambodia's Cambodia Avg Expenditure: Per Capita in 2019?
Related indicators for cambodia avg expenditure: per capita, accurate macro & micro economic data you can trust.
Explore the most complete set of 6.6 million time series covering more than 200 economies, 20 industries and 18 macroeconomic sectors.
Cambodia Key Series
Buy selected data, more indicators for cambodia, request a demo of ceic.
CEIC’s economic databases cover over 200 global markets. Our Platform offers the most reliable macroeconomic data and advanced analytical tools.
Explore our Data
Cambodia Can Go from Spending More to Spending Better, Public Expenditure Review Finds
PHNOM PENH, February 15, 2024 — Cambodia can do more to translate increased public spending on social services sectors into stronger health and education outcomes, a World Bank review of public expenditure released today says.
As a result of improved revenue collection and prudent management of public finances, facilitated by Cambodia’s consistent economic growth between 1995 and 2019, Cambodia has been able to mitigate the negative impacts of COVID-19 and spend more in social sectors, according to the World Bank’s Public Financial Review, Cambodia: From Spending More to Spending Better . However, this upsurge in spending was driven partly by across-the-board salary increases. The average public sector wage now surpasses that of the private sector for similar jobs.
Pay rises have yet to translate into better outcomes, particularly in social sectors, the review finds. Education outcomes have improved only slightly and remain low compared to those across the region. Use of public health facilities is low, and Cambodians spend more on medical treatment than the regional average, while public service infrastructure would benefit from improvement.
“Cambodia needs to get better value from its expenditure on public services to achieve sustainable and inclusive growth in the long term,” said Maryam Salim, World Bank Country Manager for Cambodia. “This means making spending more efficient through more strategic budget management, linking salary increases to performance, and better balancing resource allocation across levels of government.”
Cambodia can structure the next phase of its public financial management reform to build the fiscal resilience needed to meet long-term spending needs and respond to climate challenges, according to the review, which the World Bank produces at the request of the Ministry of Economy and Finance. This could be achieved by strengthening the links between planning and budgeting, and between spending and performance outcomes. Improving accountability and performance assessment in the public sector and strengthening capital budget management will also contribute to greater spending efficiency.
Authorities can improve public health delivery by addressing basic quality issues in public health services, promoting the use of health facilities, and ensuring equitable access for the poor. To ensure spending on education is more efficient, authorities can strengthen processes for recruitment, deployment, and training of teachers, and by making school operating funds more responsive to the needs of each school. Improving operational efficiency, human resource management, and staff capacity across sub-national administrations will also improve the impact of public spending, the review says.
Full Report
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
FACT SHEET: Japan Official Visit with State Dinner to the United States
Today, President Biden welcomed Prime Minister Kishida of Japan for an Official Visit with State Dinner to celebrate the deep and historic ties between our two countries. This visit also reflects the upward trajectory of the U.S.-Japan Alliance as it evolves into a global partnership that promotes a shared vision of progress and prosperity for the future. The two leaders’ ambitious efforts span the depth and breadth of the Alliance to include cooperation on defense and security; space; advanced technology and economic cooperation; diplomacy and development; and people-to-people ties.
This bilaterally coordinated fact sheet provides an overview of political understandings that were affirmed or reaffirmed during the Official Visit with State Dinner, as well as plans for further cooperative activities between the United States and Japan.
DEFENSE AND SECURITY COOPERATION
Our defense and security ties form the core of our Alliance and are the cornerstone of regional peace and security. Recognizing that the Alliance has reached new heights, we plan to further bolster our defense and security cooperation to allow for greater coordination and integration.
Upgrading Alliance Command and Control: The United States and Japan intend to bilaterally upgrade our respective command and control frameworks to enable seamless integration of operations and capabilities and allow for greater interoperability and planning between U.S. and Japanese forces in peacetime and during contingencies. More effective U.S.-Japan Alliance command and control provides strengthened deterrence and promotes a free and open Indo-Pacific in the face of pressing regional security challenges. In order to support this initiative, they reaffirm to deepen Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) cooperation and Alliance information sharing capabilities, including through the Bilateral Information Analysis Cell.
Exploring Advanced Capabilities Cooperation under AUKUS Pillar II: Recognizing Japan’s strengths and the close bilateral defense partnerships with the AUKUS countries, AUKUS partners – Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States – are considering cooperation with Japan on AUKUS Pillar II advanced capability projects.
Bolstering Regional Networked Security: As our two countries deepen cooperation and coordination within the Alliance, we also look to expand our efforts to enhance regional security. The United States and Japan intend to work together toward our vision to cooperate on a networked air defense architecture, incorporating future capabilities with Australia. We will explore enhanced cooperation, including missile defense information sharing to counter growing air and missile threats. As our two countries look to ensure a secure and peaceful region, the United States and Japan plan to conduct deterrence operations to address escalatory or provocative activities around Japan.
Deepening U.S.-Japan Defense Industry Cooperation : The United States and Japan plan to leverage our respective industrial bases to establish an Alliance defense production capacity to meet the demand for critical capabilities over the long term. We will convene a Forum on Defense Industrial Cooperation, Acquisition and Sustainment (DICAS) co-led by the U.S. Department of Defense and Japan Ministry of Defense to identify priority areas for partnering U.S. and Japanese industry, including on co-development, co-production and co-sustainment. As a part of this mutually beneficial effort, we announce our intention to explore co-production of advanced and interoperable missiles for air defense and other purposes to further bolster the Alliance deterrence posture. Our two countries also commit to establishing a working group to explore opportunities for future fighter pilot training and readiness, including AI and advanced simulators, and co-development and co-production of cutting-edge technologies such as common jet trainers to maintain combat-ready next-generation fighter airpower.
Leveraging Regional Maintenance and Repair Capabilities: The U.S. Department of Defense plans to work with U.S. Congress to authorize the U.S. Navy to use private shipyards to conduct maintenance and repairs of 90 days or less on U.S. Navy ships deployed to the Indo-Pacific from homeports in the United States, including Guam. Additionally, the U.S. Navy continues to review opportunities to conduct maintenance and repair of forward-deployed U.S. Navy ships at Japanese commercial shipyards. The United States and Japan plan to explore the possibility of conducting maintenance and repair on engines of Japan-based U.S. Air Force aircrafts including fourth generation fighters. Supporting the new DICAS’s oversight of co-sustainment, the two countries will convene the first Working Group for Ship Repair in Japan by June 2024 to coordinate future maintenance and repair opportunities
Enabling Japan’s Stand-off Defense and Counter-hypersonic Capabilities: The United States continues to support Japan’s capability development, highlighting the signing of the Letter of Offer and Acceptance for Japan to acquire U.S. Tomahawk Land Attack Missiles and the start of a training pipeline and ship modifications for Japan to acquire operational capability. The United States and Japan plan to also continue to pursue cooperative development of a Glide Phase Interceptor program to counter hypersonic threats, which aims to strengthen regional deterrence and build on long-standing missile defense cooperation between the two countries.
Advancing Trilateral Cooperation : The United States and Japan with Australia intend to seek to advance trilateral intelligence reconnaissance, and surveillance (ISR) operational coordination, including by identifying key capabilities to integrate into exercises and training. Building on the announcement at the Australia Official Visit in October 2023 to pursue trilateral cooperation with Japan on unmanned aerial systems (UAS), our three countries are pursuing cooperative opportunities in the rapidly emerging field of collaborative combat aircraft and autonomy. Continuing the momentum from the Camp David trilateral summit, we welcome progress on establishing an annual multidomain exercise between the United States, Japan, and the Republic of Korea (ROK). Recognizing the commitments made in the Atlantic Declaration and the Hiroshima Accord, and as the Indo-Pacific and Euro-Atlantic regions become ever more interlinked, both countries welcome the announcement of regular U.S.-Japan-UK trilateral exercises, beginning in 2025, as they enhance their shared and enduring security.
Deepening Cooperation on Information and Cyber Security: The two countries pledge to continue to deepen their cooperation on information and cyber security to ensure the Alliance stays ahead of growing threats and builds resilience in the information and communication technology (ICT) domain. They plan to also enhance their cooperation on the protection of critical infrastructure. The United States and Japan plan to establish a working group of relevant experts to develop an action plan on achieving mutual recognition on cybersecurity labelling schemes for Internet of Things.
Boosting our Humanitarian Response Capacity : Recognizing the importance of rapidly responding to frequent and severe climate change-related and other natural disasters, we plan to explore cooperation on the establishment of a humanitarian assistance and disaster relief hub in Japan.
Deepening U.S.-Japan Defense Science and Technology Cooperation: The United States and Japan continue to evolve bilateral science and technology cooperation through the Defense Science and Technology (S&T) Cooperation Group (DSTCG). Co-chaired by the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering (USD(R&E)) and the Commissioner for the Acquisition, Technology and Logistics Agency (ATLA), the DSTCG aims to better integrate and align U.S. and Japan defense S&T ecosystems.
Mitigating Impacts on Local Communities: In order to maintain deterrence and mitigate impact on local communities, we are firmly committed to the steady implementation of the realignment of U.S. forces in Japan in accordance with Okinawa Consolidation Plan, including the construction of the Futenma Replacement Facility at Henoko as the only solution that avoids the continued use of Marine Corps Air Station Futenma.
Cooperation on Environmental Issues: The United States and Japan affirm the importance of continued bilateral coordination on stable stationing of USFJ, including on environmental cooperation.
SPACE COOPERATION
As we further strengthen the foundation of our alliance, we also are looking to the future. Our two countries will continue to pioneer and lead on space exploration to include on the Moon.
Signing of Historic Lunar Surface Exploration Implementing Arrangement: The United States and Japan signed a historic implementing arrangement for human spaceflight cooperation on the Moon. Japan will provide and maintain a pressurized rover to support astronauts living and working on the Moon, while the United States will allocate two astronaut flight opportunities to the lunar surface for Japan on future Artemis missions . The shared goal is fora Japanese national to be the first non-American astronaut to land on the Moon on a future Artemis mission. This pressurized rover is intended to enable astronauts to travel farther and work for longer periods on the lunar surface.
Negotiating a Space Technology Safeguards Agreement: The United States and Japan commenced negotiations on a space technology safeguards agreement which is designed to provide the legal and technical framework for U.S. commercial space launch from Japan. The space technology safeguards agreement has the potential to open new commercial opportunities in a range of advanced technologies related to space.
Expanding Space Science Cooperation : Building on the 2023 U.S.-Japan Framework Agreement, Japan will participate in NASA missions, including Dragonfly and the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope. Dragonfly is NASA’s robotic mission to Saturn’s moon Titan to investigate its habitability and prebiotic chemistry wherein Japan will provide a seismometer to Dragonfly’s suite of scientific instruments. The Roman Space Telescope is NASA’s flagship next generation observatory; Japan will contribute hardware to support the Coronagraph instrument as well as ground station support. The United States and Japan plan to also collaborate on JAXA’s Next-generation Solar-observing Satellite, SOLAR-C, which is intended to investigate the mysteries of solar atmospheres by conducting spectroscopic observations of UV radiations from the Sun.
Deepening Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) Constellation Cooperation: The United States and Japan announced their intention to collaborate on a future Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV) detection and tracking constellation. This includes cooperation on demonstration, bilateral analysis, information sharing, and potential collaboration with the U.S. industrial base. The integration between U.S. and Japanese constellations of LEO satellites provides an opportunity to improve communications and increase the resilience of both nations’ space capabilities.
Enhancing Satellite Cooperation : The United States and Japan announced the completion of three new operational ground stations for Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) in Alaska, California, and Guam. The new ground stations will enhance Japan’s ability to monitor and maintain the accuracy of QZSS. Furthermore, Japan will launch two QZSS satellites hosting payloads from the Department of Defense by March 2026.
ECONOMIC, TECHNOLOGY, AND CLIMATE COOPERATION
Technology innovation will drive the alliance in the 21 st century. Our two countries pledge to continue to work closely together on critical and emerging technologies such as AI, quantum, semiconductors, and clean energy. Our enhanced collaboration and investment in these technologies provide opportunities for greater ties and prosperity for both of our countries as we seek to secure our economic and technological futures.
Economic Cooperation
Major Commercial Deals: The private sector in both of our countries recognize the incredible opportunities and promise of growing our commercial ties, especially in areas such as critical and emerging technologies. We welcome the establishment of a Japan Innovation Campus supporting Japanese startups in Silicon Valley and the “Global Startup Campus” in Tokyo, and support accelerating investment in our two countries to foster innovation. We also welcome the following major new and recent commercial deals, among the many, that demonstrate our strong and vibrant economic ties:
Private Sector Investment
- Microsoft has announced it will invest $2.9 billion over the next two years in Japan in artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing and data centers, an expanded digital skilling program to train more than three million people, the founding of a Microsoft Research lab in Japan, and cybersecurity cooperation with the Government of Japan to enhance Japan’s cybersecurity resilience.
- Google plans to invest $1 billion in digital connectivity for North Pacific Connect, which expands the Pacific Connect Initiative, with NEC, to improve digital communications infrastructure between the United States, Japan, and Pacific Island Nations.
- Daiichi Sankyo intends to invest $350 million in constructing a new manufacturing building, laboratory and warehouse at its facility in New Albany, Ohio. Daiichi Sankyo estimates the creation of 900 jobs across the United States over three years.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) has announced it will invest approximately $15 billion in Japan by 2027 to expand existing cloud infrastructure to serve as the backbone for AI and other digital services in the country. AWS estimates this planned investment could contribute up to $37 billion to Japan’s GDP and support an estimated average of more than 30,500 full-time equivalent jobs in local Japanese businesses each year.
- Toyota has announced an additional investment of nearly $8 billion that it expects will add an estimated 3,000 more jobs to increase capacity to support battery electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid vehicles battery production in Greensboro, North Carolina. This is Toyota’s first automotive battery plant in North America, and the plant’s total investment is now nearly $13.9 billion; Toyota expects it will create an estimated 5,100 jobs.
- Honda Aircraft Company has announced an additional investment of $55.7 million for production of its new HondaJet 2600 model in North Carolina. It brings the total investment in the HondaJet business in North Carolina to $573.4 million.
- UBE Corporation has invested $500 million in its Waggaman, Louisiana, a Justice40 community, electrolyte solvent facility project for batteries which it expects to create 60 new jobs.
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation is investing approximately $200 million in new manufacturing facilities for robotics and semiconductor motion solutions in the states of Wisconsin and Ohio which is expected to employ about 1,750 workers and increase the Yaskawa footprint in the United States by about 25 percent.
- MITSUI E&S, its U.S.-based subsidiary PACECO, and Brookfield are working together to reestablish final assembly of port cranes in California. This is the first time since 1989 that the United States has had this capacity, and it is expected to contribute to securing the safety of U.S. port infrastructure.
- FUJIFILM Corporation announced an investment of $200 million in two U.S. subsidiaries to expand its global cell therapy contract development and manufacturing (CDMO) capabilities. The investments are earmarked for Madison, Wisconsin and Thousand Oaks, California, and FUJIFILM estimates the investment could create up to 160 new jobs.
Collaborative Government-Private Sector Engagement:
- General Atomics Aeronautical Systems plans to provide two MQ-9B SeaGuardian unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) which will add high performance and surveillance ability to the Japan Coast Guard (JCG). This project will provide $152 million in U.S. exports and is expected to support 700 U.S. jobs.
- As the first foreign company named as a trusted partner in Japan’s Moonshot program of Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) on quantum computers, Infleqtion will collaborate with the Japanese Institute of Molecular Science (IMS) on developing a powerful quantum computer using Infleqtion’s quantum technology.
- Quantinuum, a U.S. quantum computer manufacturer, plans to provide RIKEN, a Government of Japan National Research and Development Agency, exclusive access to and use of a quantum computer for a period of five years – representing $50 million in quantum service exports.
Enhancing Financial Sector Cooperation : The United States and Japan are committed to strengthening our partnership to bolster cross-border investment and support financial stability. To this end, we intend to organize a roundtable this year, convening public and private sector stakeholders to discuss capital markets integration, identify potential key reforms, and bring to bear expertise from our respective financial sectors and regulatory authorities.
Engaging on Sustainable Investment: The United States and Japan pledge to continue to collaborate and build upon their foundation of successful public-private sector engagement. This initiative enables dialogues and forums through which to share best practices and promote mutually beneficial opportunities for U.S. and Japanese businesses in the areas of sustainable investment, risk management, and corporate value creation. By the end of next year, we intend to jointly host one or more roundtables to connect U.S. and Japanese private sector companies with investment opportunities while promoting sustainable value creation (SX).
Building Transparent, Resilient, and Sustainable Supply Chains : The United States and Japan welcome the initiation of discussions between the U.S. Department of Commerce and Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) under the framework of the U.S.-Japan Economic Policy Consultative Committee (our economic “2+2”) to accelerate joint efforts to address supply chain challenges and opportunities in mutually determined strategic sectors, such as current-generation and mature-node (“legacy”) semiconductors, along with like-minded countries, as appropriate. Both sides seek to cooperate to address supply chain vulnerabilities, such as those posed by non-market policies and practices, including by gaining a better comprehension of such vulnerabilities in strategic sectors.
Critical and Emerging Technology and Innovation
Strengthening Artificial Intelligence Research Collaboration: Building on the landmark university-corporate strategic partnerships in quantum computing and semiconductor engineering launched on the sidelines of the G7 Leaders’ Summit in Hiroshima, the United States and Japan welcome a new $110 million joint Artificial Intelligence partnership with the University of Washington and University of Tsukuba as well as Carnegie Mellon University and Keio University through funding from NVIDIA, Arm, and Amazon, Microsoft, and a consortium of Japanese companies. This innovative partnership is expected to advance AI research and development and enhance U.S.-Japan global leadership in cutting-edge technology. We welcome the initiation of AI and quantum technology cooperation between Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) and NVIDIA, exploring the potential cooperation in the field of computing and development. We welcome the new Project Arrangement on high-performance computing and AI between the U.S. Department of Energy and the Japan’s Ministry of Education Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the new Memorandum of Understanding on AI for Science between Argonne National Laboratory and RIKEN to foster collaboration. We welcome cooperation between U.S. and Japanese companies toward the development of foundation models for generative AI, including contribution of NVIDIA’s GPUs to Japanese computational resources companies such as Sakura Internet and Softbank and other computational resources from Google and Microsoft to Japanese AI foundation models development companies.
Launching Quantum Technology Partnerships: To promote our bilateral industrial cooperation on quantum computing, the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) intends to partner with Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) to build robust supply chains for quantum technology and related standardization. The University of Chicago, the University of Tokyo, and Seoul National University established a partnership to train a quantum workforce and strengthen their collective competitiveness in the global economy.
Enhancing Cooperation on Semiconductors: Building on our long history of cooperation on semiconductor technology, we welcome the initiation of discussions among Japan’s Leading-Edge Semiconductor Technology Center (LSTC) and U.S. research initiatives, such as the U.S. National Semiconductor Technology Center (NSTC) and the U.S. National Advanced Packaging Manufacturing Program (NAPMP), toward the creation of an agenda for U.S.- Japan cooperation, including an R&D roadmap and workforce development. We welcome robust U.S.-Japan private sector cooperation, especially in next-generation semiconductors and advanced packaging. U.S. and Japanese companies are exploring the wide range of possibilities available through optical semiconductors through partnerships like the Global Innovative Optical and Wireless Networks (IOWN) Forum.
The U.S. Department of Labor plans to invite Japanese counterparts in the semiconductor sector to participate in technical workshops with the U.S. private sector and educational institutions to discuss optimal ways to train the next generation of designers, builders, and professionals in advanced semiconductor research and manufacturing.
Strengthening Cooperation for Safe, Secure and Trustworthy AI: The United States and Japan are committed to further advancing the Hiroshima AI Process by expanding support from partner governments and AI actors. The United States and Japan acknowledged and plan to support each other in establishing national AI Safety Institutes and committed to future collaboration, including on interoperable standards, methods, and evaluations for AI safety. A crosswalk of Japan’s AI Guidelines for Business with the NIST AI Risk Management Framework is currently underway and is designed to promote interoperability in our policy frameworks for AI.
Reducing AI Risks and Harms from Synthetic Content: The United States and Japan pledge to cooperate on reducing risks and harms of AI-generated content. The countries commit to provide transparency to the public, to the extent possible and appropriate, by authenticating and labeling official government produced content as well as detecting and identifying AI-generated content and content altered or manipulated by AI. Both governments plan to take steps independently and cooperatively on technical research and standards development.
Establishing a New Science and Technology Partnership: The United States and Japan announce a partnership to catalyze innovation, facilitate knowledge exchange, and promote entrepreneurial endeavors that contribute to the advancement of science and technology, and through the State Department’s Global Innovation through Science and Technology (GIST) program. The United States and Japan also endorse joint efforts among their universities and companies to foster human capital for the purpose of increasing governability on digital and emerging technologies under the initiative of U.S.-Japan Digital Innovation Hub and Advanced Technology Workshop
Expanding National Science Foundation Collaboration: The United States and Japan welcome the signing of the Memorandum of Cooperation between the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) to partner on NSF’s Innovation Corps (I-Corps) program. This entrepreneurship training program aims to strengthen lab to market transition by helping researchers more effectively target their discoveries to customer needs. Through the Global Centers program, NSF has committed $25 million in awards for bioeconomy research and JST will support at least three awards. The two agencies also plan to collaborate on research on the designing materials which will revolutionize our engineering future.
Strengthening International Joint Research in Scientific and Technological Fields: The United States and Japan welcomed strengthening collaboration between the national research institutes and universities in science, technology, and innovation as well as the exchange of researchers through joint research to promote U.S.-Japan talent mobility and circulation, such as the Adopting Sustainable Partnerships for Innovative Research Ecosystem (ASPIRE) in eight areas: AI and information, biotechnology, energy, materials, quantum, semiconductors, telecommunications, and healthcare. We welcome further bilateral collaboration on global ocean observation and Arctic research. The Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) and Fukushima Institute for Research, Education and Innovation (F-REI) are pursuing a Memorandum of Cooperation to establish a collaborative relationship to increase opportunities for joint research in select topics including energy, robotics, radiation science, nuclear disaster response, and agriculture.
Promoting Open and Interoperable Approaches to Telecommunications Networks: As the world becomes more interconnected, the United States and Japan pledge to continue to promote open, standards-based approaches to telecommunications networks that are interoperable, secure, and multi-vendor in nature. The United States and Japan intend to explore opportunities to promote Open RAN commercialization in third countries, including Indo-Pacific countries. The United States and Japan commit to continuing to engage both bilaterally and with like-minded partner countries through fora such as the Quad.
Climate and Clean Energy
Expanding U.S.-Japan Clean Energy and Climate Cooperation: The United States and Japan are launching a new high-level dialogue on our two countries’ implementation of respective domestic measures and maximize respective synergies and impacts, including the Inflation Reduction Act and Green Transformation (GX) Promotion Strategy, aimed at accelerating energy transition progress this decade, promoting complementary and innovative clean energy supply chains, and improving industrial competitiveness. For the advancement of the U.S.-Japan Climate Partnership, recalling relevant CMA decisions, we further plan to aggressively implement our 2030 nationally determined contributions (NDCs) and develop ambitious 2035 NDCs in line with a 1.5C warming limit. We encourage all major economies to submit bold, 1.5C-aligned 2035 NDCs that reflect economy-wide absolute reduction targets including all greenhouse gases, sectors, and categories, and commit to prioritizing concrete and timely steps towards the goal of accelerating the phase-out of domestic unabated coal power. The United States and Japan intend to also work together to secure a successful outcome at the 29 th UN Climate Change Conference on a new collective quantified goal that reflects a realistic increment and broadened contributor base.
Expanding Quality Infrastructure Investment: The United States and Japan plan to work together and with partner countries in strategic economic corridors on fostering investment under the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGI), including cooperation in the Indo-Pacific through the PGI-IPEF InvestmentAccelerator. Our two countrieswill continue to seek cooperation on critical minerals and other projects, including those along the PGI Lobito Corridor. The United States and Japan have worked to establish a Blue Dot Network Secretariat at the OECD to certify quality infrastructure projects.
Building Resilient Critical Mineral Supply Chains: The United States and Japan resolve to explore joint projects, including through the Minerals Security Partnership and the Partnership for Resilient and Inclusive Supply-chain Enhancement (RISE), including ones that diversify key supply chains of critical minerals, and support recycling efforts for electrical and electronic scrap in the United States, Japan, and other Indo-Pacific likeminded partners. To that end, the United States welcomes the MOU between the Japan Organization for Metals and Energy Security (JOGMEC) and La Générale des Carrières et des Mines (GECAMINES) in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in alignment with our shared commitment with PGI’s development of the Lobito Corridor.
The United States and Japan intend to continue facilitating $170 million in annual U.S. e-scrap exports to Japan for environmentally sound recycling under the OECD Council Decision on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Wastes Destined for Recovery Operations and strengthen cooperation through facilitating a policy dialogue on increasing circularity of critical minerals and raw materials, which are indispensable for decarbonization and reducing negative environmental impacts.
Deepening Energy Cooperation : Both of our countries recognize the importance of clean energy as we look to combat the effects of climate change and lay the groundwork for clean and resilient economic growth this century. The United States and Japan announced the U.S.-Japan Strategic Partnership to Accelerate Fusion Energy Demonstration and Commercialization . The United States and Japan reaffirmed their commitment to accelerating the global transition to zero-emissions energy and working with other fossil energy importers and producers to minimize methane emissions across the fossil energy value chain to the fullest extent practicable. Both countries also intend to support the establishment of green shipping corridors including a new grain corridor to support global efforts to decarbonize the international shipping sector.
Today we announce Japan joins as the first international collaborator of the U.S. Floating Offshore Wind Shot. Japan recognizes the ambition of the U.S. Floating Offshore Wind Shot, which aims to reduce the cost of floating offshore wind in deep waters by more than 70 percent and reach 15GW of U.S. domestic deployment by 2035. Through the partnership, the United States and Japan will collaborate to make progress towards global ambition in line with the U.S. Floating Offshore Wind Shot, taking into consideration national circumstances, to accelerate breakthroughs across engineering, manufacturing, and other innovation areas that dramatically reduce the cost of floating offshore wind in deep waters by 2035. The United States and Japan announced they would report publicly on progress each year through CEESI. To work towards global ambition, Japan will contribute with its efforts of “the Vision for Offshore Wind Industry” and approximately 120 billion yen through the Green Innovation Fund. The United States also welcomes Japan’s newly-launched industry platform, the Floating Offshore Wind Technology Research Association (FLOWRA), aiming to reduce costs and achieve mass production of floating offshore wind through collaboration with academia. The United States will continue its efforts under the Department of Energy’s Strategy to Advance Offshore Wind Energy to leverage more than $5.8 billion in cumulative public and private sector supply chain investments under the Biden-Harris Administration. We also intend to advance research and development for perovskite solar cell technology through the Green Innovation Fund and the Perovskite PV Accelerator for Commercializing Technologies (PACT) Center, led by Sandia National Laboratory.
Expanding Infrastructure to Support Clean Energy: Our two nations acknowledge the need to expand and modernize power grids and energy infrastructure to keep pace with our ambitious goals for renewable energy deployment. We plan to explore means to boost investment in our power grids and share best practices for grid modernization. We also look to expand the use of market-based power purchase agreements by companies and industries to assist access to clean energy, including from both large nuclear reactors and advanced and small modular reactors (A/SMRs), as they attempt to meet their own decarbonization goals and drive innovation in power intensive industries such as Artificial Intelligence, quantum computing, and data centers.
Partnering to Deploy Safe and Secure Nuclear Energy: The United States and Japan recognize the crucial role of civil nuclear power to meet our overarching climate goals, as affirmed in our participation in the COP28 pledge to triple globally installed nuclear energy by 2050. In pursuit of this vision, the United States applauds the Prime Minister’s plan to restart nuclear reactors to meet its 2030 decarbonization goals. Our two countries acknowledge the transformational opportunities presented through our continued cooperation on A/SMRs, and affirm our continued partnership on joint efforts both bilaterally and multilaterally to deploy A/SMRs this decade.
Our two countries plan to launch the Fukushima Daiichi Decommissioning partnership with Tokyo Electric Power Company and U.S. national laboratories to deepen research cooperation for the steady implementation of decommissioning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, especially for fuel debris retrieval. Recognizing the important role of nuclear energy to both accelerate the energy transition and enhance energy security, the United States and Japan also resolve to promote public-private investment in enriched uranium production capacity free from Russian material.
Improving Methane Emissions Data: The United States and Japan are collaborating, including with other international partners, to share greenhouse gas emissions satellite observations data and make it freely available to the public, including providing greenhouse gas information to governments in low- and middle-income countries to support the development of climate mitigation policies. The United States and Japan intend to also leverage existing efforts, such as the International Methane Emissions Observatory, to develop and disseminate accurate, transparent methane emissions data to support methane reduction interventions globally.
Carbon Management: The United States and Japan reaffirm our commitment to the Carbon Management Challenge, Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Initiative, and to the Mission Innovation CDR Launchpad in the pursuit of developing carbon management technologies to support achieving the Paris Agreement goals. Additionally, the United States commits to supporting collaboration with Japanese counterparts to evaluate the potential for cross-border carbon dioxide transport and storage hubs between Alaska and Japan. For example, the United States is pursuing carbon dioxide shipping feasibility studies and tools such as life cycle assessment and technoeconomic analysis that can aid in this goal. We welcome the progress of ongoing projects in carbon capture, utilization, and storage, as well as carbon recycling, between U.S. and Japanese companies. On e-methane, Japanese companies have signed Letters of Intent (LOIs) with U.S. companies to avoid CO 2 double counting.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel: The United States and Japan reaffirm our joint aim of decarbonizing the aviation industry, including the goal of net-zero emissions by 2050. We recognize the importance of realizing the U.S. Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) Grand Challenge 2030 goal of three billion gallons of SAF that, compared to a petroleum-based jet fuel baseline, will provide a significant reduction in lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions, as well as Japan’s 2030 target of replacing 10% of the fuel consumed by Japanese airlines with SAF. To support achieving these goals, the United States pledges to seek to support the increase of globally available supplies of SAFs or feedstocks, including those that are ethanol-based, and commit to working in ICAO to identify solutions that accurately measure and actively reduce the carbon intensity of global SAF feedstocks and products. Simultaneously, Japan commits to advancing R&D efforts to develop and commercialize SAF technologies, including Alcohol-to-Jet (ATJ), through support measures by Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.
Collaborating on Hydrogen and its Derivatives, and Geothermal: We welcome the progress of collaboration between U.S. and Japanese companies on building hydrogen hubs, and shared expectations for further cooperation to build a large-scale and resilient global supply chains based on carbon intensity and to expand utilization of hydrogen. A Memorandum of Cooperation (MOC) on Geothermal Energy was signed between DOE-METI at the G7 Ministers’ Meeting on Climate, Energy and Environment in Sapporo in April 2023. Through this MOC, the United States and Japan have been exploring next steps for collaboration.
Investing in U.S. Infrastructure : The U.S. Department of Transportation and Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism welcomed Amtrak’s leadership of the Texas Central High Speed Rail Project, utilizing Shinkansen technologies, which was recently selected for the Federal Railroad Administration’s (FRA) Corridor Identification and Development grant program. The successful completion of development efforts and other requirements would position the project for potential future funding and financing opportunities.
Biotechnology, Biopharmaceutical, and Health-Related Cooperation
Tackling Cancer Together: In alignment with the Biden Cancer Moonshot to end cancer as we know it, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Japan’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) intend to collaborate and exchange information on oncology drug products. Specifically, under initiatives Project Nozomi and Project Orbis, FDA and PMDA intend to work to enable earlier access to cancer medication for patients and hold discussions on future drug development, including multiregional clinical trials and ways to prevent drug shortages.
Advancing Pharmaceutical Innovation: The United States and Japan welcome the Japan’s Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA)’s intent to establish an office in the Washington, D.C. metro area. This office provides opportunities to enhance PMDA’s cooperation with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and facilitate information sharing with private industry.
Opening of CDC Regional Office: The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) opened a Regional Office for East Asia and the Pacific in Tokyo in February. This new regional office provides support to 26 countries and territories in the region to strengthen core global health security capacities and collaboration to improve detection, rapid response to disease threats, and knowledge and information exchange.
Global Health Collaboration: The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) and Japan’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs will continue to discuss ways to advance shared global health priorities.
Expanding Biotechnology and Healthcare Cooperation : The United States and Japan welcome the launch of a new U.S.-Japan biotechnology and healthcare discussion, focused on promoting responsible development, protecting key technologies, and establishing reliable and secure supply chains. The exchange prioritizes efforts to advance industrial competitiveness, including joint events in close partnership with relevant U.S. and Japanese ministries and agencies, as well as academic and private sector partners. It also bolsters work to prioritize the safe, secure, and responsible development and use of emerging biotechnology through close policy coordination.
DIPLOMACY, DEVELOPMENT, AND HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE
As global leaders, the United States and Japan remain committed to ensuring a peaceful and stable Indo-Pacific region with a conviction that the security in Euro-Atlantic and Indo-Pacific regions are interlinked. Beyond these regions, our two countries recognize the global challenges we jointly face and reaffirm commitments made at the G7 Hiroshima Summit in upholding the rule of law, which protects all nations, especially the vulnerable, and continued cooperation with partners beyond the G7. To that end, we intend to launch a new strategic dialogue to coordinate global diplomacy and development efforts and to be held at the Deputy Secretary of State/Vice Minister for Foreign Affairs level. Our two countries remain committed to supporting Ukraine’s right to self-defense and its long-term security and economic recovery. The United States has contributed $74.6 billion in humanitarian, development, military, and economic assistance to Ukraine, and Japan has been providing continuous support to Ukraine, a commitment of which adds up to $12.1 billion in total. We are also committed to addressing the humanitarian crisis in Gaza. Japan has provided approximately $107 million in support of the Palestinian people and the United States has contributed $180 million in humanitarian assistance for civilians in Gaza since October 7, 2023. Moreover, the United States and Japan underscore the importance and urgency of the situation in Haiti and reiterate our support to the mandate of the UN-authorized Multinational Security Support (MSS) Mission to Haiti.
Investing in the Indo-Pacific : The U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) and the Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) have renewed an MOU that enables greater collaboration in financing projects in the Indo-Pacific and beyond.
The United States and Japan acknowledge the importance of improving the Amata Kabua International Airport in the Republic of Marshall Island (RMI) in support of sustaining RMI’s economy.
Building on the U.S.-Australia joint funding commitment for subsea cables last October, the United States and Japan will collaborate with like-minded partners to build trusted and more resilient networks and intend to contribute funds to provide subsea cables in the Pacific region, including $16 million towards subsea cable systems for Tuvalu, which will connect it for the first time in history, as well as the Federated States of Micronesia. In addition, Taiwan also plans to provide funding to deliver connectivity to Tuvalu.
In southeast Asia, the United States has announced $5 million in new funding to the Japan-U.S.-Mekong Power Partnership (JUMPP), which puts the U.S. commitment to $35 million since JUMPP’s launch in 2019. The $5 million helps fulfill Vice President Harris’ announcement that she plans to work with U.S. Congress to harness up to $20 million in new JUMPP funding. The U.S. and Japan’s work in the Mekong region has supported over 100 technical cooperation projects to expand cross-border power trade and clean energy integration in Cambodia, Lao PDR, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Strengthening the International Financial Architecture : The United States and Japan intend to continue our collaboration to strengthen the international financial architecture and support developing countries to promote our shared values. This includes advancing the MDB Evolution agenda, planned contributions that would enable more than $30 billion in new lending headroom at the World Bank to support low- and middle-income countries in addressing global challenges, securing ambitious International Development Association and Asian Development Fund replenishments, addressing debt vulnerabilities that are holding back low- and middle-income countries’ growth potential and ability to invest in critical areas like climate and development including through advancing debt treatment through the G20 Common Framework and enhancing debt transparency, and solidifying the International Monetary Fund (IMF) as a quota-based institution at the center of the global financial safety net.
Deepening our Commitment to Nuclear Disarmament and Non-proliferation and Peaceful Uses of Nuclear Energy: President Biden commended Japan’s safe, responsible, and science-based discharge of Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS) treated water into the sea. The two leaders welcomed that the U.S. Department of Energy and Japan’s MEXT have removed all excess highly enriched uranium (HEU) from the Kyoto University Critical Assembly and Japan Atomic Energy Agency’s Japan Materials Testing Reactor Critical Assembly to the United States and a new joint commitment to convert the Kindai University Teaching and Research Reactor from HEU to low-enriched uranium fuel and to return its HEU to the United States. The United States also joined the Japan-led “Fissile Material Cut-Off Treaty (FMCT) Friends” effort to demonstrate our shared commitment toward disarmament.
Combatting Gender-Based Online Harassment and Abuse : Recognizing the importance of partnerships to combat technology-facilitated gender-based violence, including the Global Partnership for Action on Gender-Based Online Harassment and Abuse, the United States and Japan concur to strengthen our work at the nexus of gender equality and digital technology. These efforts underscore our commitments to advance our shared values, including human rights and gender equality, and further Women, Peace, and Security goals in an increasingly technology-dependent world.
Countering Foreign Information Manipulation: The United States and Japan are committed to working together and last year committed to the joint U.S.-Japan Memorandum of Cooperation on Countering Foreign Information Manipulation. The United States and Japan recognize that foreign information manipulation poses a challenge to the Indo-Pacific region and beyond and warrants enhanced bilateral and multilateral cooperation.
Partnership to Combat Commercial Spyware: Japan has joined the Joint Statement on Efforts to Counter the Proliferation and Misuse of Commercial Spyware. The United States and Japan are committed to implementing domestic controls and building the international coalition to combat the misuse of such surveillance tools that pose a threat to our mutual national security interests and that enable human rights abuses.
Countering the Growing Threat of Transnational Repression: The United States and Japan are committed to reinforcing our partnership on countering transnational repression. To effectively address the rising concern of transnational repression globally it will take a coordinated multilateral response.
Bolstering Whole-of-Society Resilience : The United States and Japan welcome the National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Resilience, Japan’s MEXT, and NVIDIA’s efforts on joint research and development on nation-scale resilience.
Building Resilient and Responsible Seafood Supply Chains: Our two countries pledge to work together, as part of the efforts under the Task Force on the Promotion of Human Rights and International Labor Standards in Supply Chains, led by the U.S. Trade Representative and METI, to explore ways to combat forced labor and advance responsible labor practices in seafood supply chains. We also intend to build resilient seafood supply chains through strengthened trade channels and increased business opportunities.
Strengthening Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture : To enhance existing food security efforts, the United States and Japan recently launched the U.S.-Japan Dialogue on Sustainable Agriculture, and we plan to continue joint research on reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural production. Together, we intend to promote new technologies and climate-smart production practices to build sustainable and resilient agriculture and food systems able to feed a growing global population while conserving natural resources and mitigating climate change. As an example, the United States and Japan intend to be founding contributors to the Vision for Adapted Crops and Soils seed and soil health research This research helps bolster diverse food production in developing partner countries.
PEOPLE-TO-PEOPLE TIES
Our people-to-people ties serve as the bedrock of our Alliance. Civil society has been one of the driving factors of our close relationship over the past 170 years. Our two countries recognize the legacy of Ambassador Mansfield, the longest-serving U.S. Ambassador to Japan and his incredible contributions to the relationship through the Mansfield Center and Mansfield Foundation.
The success of the Alliance is due to the bonds between our peoples, and our two governments recognize the achievements of organizations and programs, such as Fulbright Japan, the JET Programme, the Japan Foundation, the KAKEHASHI Project, and the U.S.-Japan Council’s TOMODACHI Initiative, Asia Kakehashi Project +(Plus), and their contributions to the alliance. Our two countries celebrate the unique and historic role of the 38 Japan-America Societies located throughout the United States and 29 America-Japan Societies across Japan.
This year is the U.S.-Japan Tourism Year 2024, ahead of Japan hosting the 2025 World Expo in Osaka. For the first time since 1988, the United States approved federal funding to support the design, build, and operation of the U.S. Pavilion at the World Expo.
Our two countries remain steadfast in our commitment to foster close connections, and to promote close ties between current changemakers and future generations of leaders.
Boosting Educational Exchanges : The United States and Japan announce a new $12 million “Mineta Ambassadors Program (MAP)” education exchange endowment administered by the U.S.-Japan Council for U.S. and Japanese high school and university students who will “map” the future of the relationship, with support from Apple, the BlackRock Foundation, Toshizo Watanabe Foundation, and other founding donors. As a long-term investment in U.S.-Japan relations, the endowment plans to increase exchange opportunities in both directions. In this regard, we also welcome Japan’s new initiative to expand scholarship for Japanese students through the Japan Student Servicers Organization. We also recognize the importance of educational cooperation among high schools and universities between the two countries and enhance mid-to-long term educational exchange, including those seeking degree certificates or professional training and internship opportunities. The two governments also announce the restart of STEM scholarships in Japan via the Fulbright Program for the first time in 50 years, ensuring our flagship education exchange program supports our most important economic security priorities, and removal of the tuition cap for Japanese Fulbright participants.
Engaging the Next Generation of Leaders: President Biden and Prime Minister Kishida applaud the Japanese American National Museum’s new Toshizo Watanabe Democracy Fellowship to promote global democracy and strengthen U.S.-Japan ties. Beginning with an eight-person pilot program this summer, this new Fellowship is designed to provide opportunities for Japan’s future leaders to experience the United States, network with Japanese leaders and others who seek to strengthen democracy and the bilateral relationship and develop a cohort of up-and-coming professionals who have to promise to become advocates for stable and secure democracies in the years ahead.
We applaud the efforts of the U.S.-Japan Council’s exchange program of local high school students and leadership/professionals for Maui reconstruction. We also welcome Japan’s intention to broaden the scope of the invitation program for Japanese American leaders to raise their next generation.
Promoting Exchanges among Professionals: We welcomed the initiative of the Japan Foundation that is promoting exchanges among professionals and practitioners addressing common issues facing the Indo-Pacific region, such as climate change and disaster management, and we look forward to further development in the future. The two leaders also welcomed the establishment of the Mansfield Professor of Japanese and Indo-Pacific affairs.
Women, Peace and Security (WPS): The Women, Peace and Security (WPS) Parliamentarians’ Network Japan hosted U.S. WPS Caucus Member Rep. Sydney Kamlager-Dove and Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues Geeta Rao Gupta on April 3-4 for a legislative exchange to reaffirm our shared commitment to promote WPS globally.
Increasing Exchange Opportunities for Japanese Language Specialists in the United States: The United States and Japan signed a memorandum of cooperation to expand exchange opportunities for Japanese language specialists to observe U.S. institutions and methods in the United States and share their specialized knowledge of Japanese language education with U.S. colleagues. We also emphasize the value of in-person learning for Japanese language in the U.S. and welcome efforts to expand the Japanese Language Education Assistant Program (J-LEAP).
Enhancing Cultural and Educational Interchange: The United States and Japan reaffirmed their confidence in the role of the U.S.-Japan Conference on Cultural and Educational Interchange (CULCON) in further enhancing people-to-people ties. The United States and Japan also welcomed the inaugural U.S.-Japan High Level Policy Dialogue on Education and instruct the respective departments and ministries to accelerate the preparation of the second dialogue to examine and follow up on the issues raised above. We also acknowledge the importance of cultural exchanges including through promoting creative and cultural content industries such as in music, movies, animation and manga.
Strengthening Tourism Ties: To coincide with the U.S.-Japan Tourism Year, Airbnb has announced it will commit $1 million to an International Visitors Leadership Program to bring Japanese tourism professionals to the United States to study best practices on rural tourism and support local economies in each nation.
The United States also welcomes Japan’s intention to support the National Park Service as it begins a multi-year rehabilitation project around the Tidal Basin and West Potomac Park. Each year, millions of visitors from around the United States and indeed the world visit the National Mall for the Cherry Blossom Festival. These cherry trees, first gifted by the people of Japan to the United States in 1912, are an enduring reminder of the close bonds of friendship between Americans and Japanese.
Expanding Global Entry Program : The United States welcomes Japan’s expected full membership this year in Customs and Border Protection’s Global Entry program, a Trusted Traveler Program that allows expedited clearance for pre-approved, low-risk travelers upon arrival at U.S. airports. Japan’s full inclusion in Global Entry provides opportunity to bolster our countries’ security while facilitating travel and commerce between our nations.
Strengthening the Resilience of Democracy : President Biden and Prime Minister Kishida welcomed the launch of the U.S.-Japan Strategic Dialogue of Democratic Resilience and reaffirmed their commitment through the second round of the Strategic Dialogue on March 8, 2024.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
II.OUTBOUND TOURISM Outbound tourism in January - December 2022 Outbound tourism Change (%) 2020 2021 2022 21/20 2022*/21 Cambodia Outbound Tourists 326,199 30,517 970,292 -90.6 3079.5 International Tourists Departure 1,367,253 183,608 2,082,792 -86.6 1034.4 Thailand Vietnam China (RPC) U.S.A Lao PDR Indonesia Korea (ROK) FranceMalaysia U.K
In many countries, especially developing countries, tourism has emerged as an important engine for economic growth. Cambodia's tourism sector has been re-emerging into the Cambodian economy since 1992 after nearly two decades of suffering from civil war and political turmoil (1975-1991) [].The government of Cambodia recognized its importance for economic growth and poverty reduction in 1995.
The total number of inbound tourists to these GMS countries was 73.6 million in 2019 with the total shared between Thailand 39.8 million, Viet Nam 18.0 million, Cambodia 6.6 million, Lao PDR 4.8 million and Myanmar 4.36 million. 4. Cambodia's Tourism Profile Pre COVID-19. Tourism is a priority sector in the Cambodian government's ...
International tourism, expenditures (current US$) - Cambodia World Tourism Organization, Yearbook of Tourism Statistics, Compendium of Tourism Statistics and data files. License : CC BY-4.0
PHNOM PENH, CAMBODIA (4 April 2023) — Cambodia's economy is forecast to grow at 5.5% in 2023 and 6.0% in 2024 on a more robust tourism recovery and higher growth in the services sector, according to a report released today by the Asian Development Bank (ADB). "Despite weaker global demand, Cambodia's economy continued to perform well in ...
Cambodia has diversified destinations into four strategic tourism destinations: Central (business tourism), Northwest (cultural tourism), Southwest (coastal tourism), and Northeast (eco-tourism). This paper analyzes the impact of a 10% increase in tourism expenditure for the tourism sector by employing a computable
II.OUTBOUND TOURISM Outbound tourism in January - March 2023 Outbound tourism Change (%) 2021 2022 2023 22/21 2023*/22 Cambodia Outbound Tourists 5,509 30,410 408,978 452.0 1244.9 International Tourists Departure 63,666 119,715 1,193,596 88.0 897.0 Thailand Vietnam China (RPC) Lao PDR U.S.A Korea (ROK) France Russia U.K Indonesia
Avg Expenditure: Group Tour data is updated yearly, averaging 1,130.055 USD from Dec 2004 to 2019, with 16 observations. The data reached an all-time high of 1,329.760 USD in 2008 and a record low of 553.400 USD in 2016. Avg Expenditure: Group Tour data remains active status in CEIC and is reported by Ministry of Tourism.
II.OUTBOUND TOURISM Outbound tourism in January - April 2023 Outbound tourism Change (%) 2021 2022 2023 22/21 2023*/22 Cambodia Outbound Tourists 6,969 54,933 570,301 688.2 938.2 International Tourists Departure 80,748 189,628 1,607,887 134.8 747.9 Thailand Vietnam China (RPC) Lao PDR U.S.A Korea (ROK) France IndonesiaU.K Russia
International tourism, expenditures (current US$) in Cambodia was reported at 213000000 USD in 2020, according to the World Bank collection of development indicators, compiled from officially recognized sources.
This paper analyzes the impact of a 10% increase in tourism expenditure for the tourism sector by employing a computable general equilibrium (CGE) model based on Macro-and Micro social accounting ...
Cambodia Current Expenditures: EA: Tourism data was reported at 6,413.000 KHR mn in Dec 2023. This records an increase from the previous number of 5,872.000 KHR mn for Nov 2023. Cambodia Current Expenditures: EA: Tourism data is updated monthly, averaging 5,727.000 KHR mn from Jul 2014 to Dec 2023, with 114 observations. The data reached an all-time high of 21,886.000 KHR mn in Dec 2016 and a ...
Cambodia - Tourism expenditure in the country. 1,119,000,000 (current US dollars) in 2020. Cambodia tourism expenditure in the country was at level of 1,119 million current US dollars in 2020, down from 5,312 million current US dollars previous year, this is a change of 78.93%. The description is composed by our digital data assistant.
The latest report cited internal tourism expenditures made by Cambodians at about $650 million - or a ballpark mean of $50 per person - and noted that an average domestic trip lasts three days and two nights. ... "In 2023, Cambodia's tourism sector will see improvements compared to 2022, especially in the number of regional tourists ...
5.0 (%) in 2017. International tourism expenditures are expenditures of international outbound visitors in other countries, including payments to foreign carriers for international transport. These expenditures may include those by residents traveling abroad as same-day visitors, except in cases where these are important enough to justify separate classification. For some countries they do not ...
Tourism in Cambodia Cambodia recorded a total of 196,400.00 tourists in 2021, ranking 96th in the world in absolute terms. ... Our data on tourist numbers, revenues and expenditures are based on information from the World Tourism Organization. However, to ensure international comparability, the data for some years or countries were manually ...
The data in this report includes demands & flows data on domestic travel, international arrivals and departures. Additionally, data is provided on traveler spending patterns, the airlines, and hotel sectors. The report also identifies the key themes impacting the tourism industry. In 2022, Cambodia welcomed 2.29 million international arrivals.
919,000,000 (US dollars) in 2017. International tourism expenditures are expenditures of international outbound visitors in other countries, including payments to foreign carriers for international transport. These expenditures may include those by residents traveling abroad as same-day visitors, except in cases where these are important enough to justify separate classification. For some ...
Tourism directly employed 630,000 workers, of which 60 percent were women in 2019. 12 The sector is only second to the garment sector with the largest number of women employed. In terms of hotels and accommodation, a s of 2020, a total of 1,028 hotels provide 44,428 rooms residing in 25 provinces across Cambodia. 13 Another accommodation type is the guesthouse, in which 2,755 units are divided ...
Cambodia tourism expenditures was at level of 213 million US dollars in 2020, down from 1,162 million US dollars previous year, this is a change of 81.67%. International tourism expenditures are expenditures of international outbound visitors in other countries, including payments to foreign carriers for international transport. These expenditures may include those by residents traveling ...
Cambodia Avg Expenditure: Per Capita data was reported at 497.690 USD in Dec 2019. This records an increase from the previous number of 486.500 USD for Dec 2018. Cambodia Avg Expenditure: Per Capita data is updated yearly, averaging 479.250 USD from Dec 2004 to 2019, with 16 observations. The data reached an all-time high of 513.430 USD in 2008 and a record low of 409.400 USD in 2004.
PHNOM PENH, February 15, 2024 — Cambodia can do more to translate increased public spending on social services sectors into stronger health and education outcomes, a World Bank review of public expenditure released today says. As a result of improved revenue collection and prudent management of public finances, facilitated by Cambodia's ...
Strengthening Tourism Ties: To coincide with the U.S.-Japan Tourism Year, Airbnb has announced it will commit $1 million to an International Visitors Leadership Program to bring Japanese tourism ...
Cambodia tourism expenditures as a share of total imports was at level of 0.9 % in 2020, down from 4.6 % previous year. International tourism expenditures are expenditures of international outbound visitors in other countries, including payments to foreign carriers for international transport. These expenditures may include those by residents traveling abroad as same-day visitors, except in ...