Aims and Objectives of Ecotourism
by Magda Healey
Published on 21 Mar 2018
Tourism is bigger now than ever before. International tourist arrivals quadrupled between 1960 and 1990 and then doubled again between 1990 and 2010. The most remote places, from the Amazon rainforest to ice-bound Antarctic, have become respectable leisure destinations. No corner of the Earth remains untouched, and many countries rely on tourism for their income. This unparalleled growth in leisure travel has prompted concerns about its impact on fragile ecosystems and traditional communities and led to the appearance of ecotourism.
As adventurous travelers strayed off the path of a standard sea-sun-and-sand vacation, they rejected mass provision of package trips, searching instead for the pristine and the authentic. Ecotourism has became one of the ways the green sensitivities of affluent westerners manifest themselves. According to the International Ecotourism Society, ecotourism combines travel to natural areas with principles of sustainability, conservation and direct benefits to local people. Martha Honey, a co-founder and co-Director of the Center on Ecotourism and Sustainable Development and the author of "Ecotourism and Sustainable Development," proposes an expanded definition, focusing on: minimizing impact, building environmental awareness, providing benefits to conservation and local people, respecting local culture and supporting human rights.

Minimizing Impact
Ecotourism aims to reduce environmental impact that comes with mass tourism and its vast, often resource-heavy, infrastructure. This impact reduction includes using locally available, often traditional and, at other times, recycled materials and supporting designs of infrastructure that are environmentally friendly and that fit within traditions and sensibilities of local culture. Minimizing impact also means controlling numbers and acceptable behaviors of tourists. These efforts can range from limiting traffic on national park trails to controlling the numbers of game shot during community-run hunting expeditions. Another way to lessen the impact of tourism is to use renewable energy and to carefully dispose of waste. Culturally, ecotourism aims to respect the local communities and traditions, to alleviate the exploitive aspects of leisure travel and to benefit, rather than damage, the communities.
Building Awareness
Ecotourism aims to teach as well as to entertain and relax. This objective applies to environmental as well as cultural matters. Visitors who participate in ecotourism projects should receive information on the ecology and conservation issues pertinent to the local area. Guides and other staff should be able to effectively communicate with the tourists, helping them to interpret the natural environment and pointing out the sensitive areas and fragile ecosystems. The cultural exchange important to ecotourism through which visitors learn about local customs and social mores should, ideally, involve sensitivity and balance. In many situations, traditions function as exotic backdrop for tourists, with locals compelled toward primitive and folksy affectation for the benefit of tourists seeking authenticity.
Financial Benefits
Ecotourism must provide direct financial benefits for conservation projects and environmental protection, either directly through charges for tours, admission fees and donations or indirectly through taxes on travel or accommodation. The financial benefits of ecotourism should extend not only to the conservation of natural heritage, but to the local population. They must benefit from tourism and travel, either by being employed in or, ideally, running the tourist infrastructure or by benefiting from local developments such as transport links, sanitation, water and health provision.
Human Rights and Democracy
According to Honey's criteria, ecotourism should also strive to support human rights, economic empowerment and democratic movements in host communities. In addition to increasing awareness about political issues of the host country, one way of empowering people is to support local, particularly small scale, businesses and providers and their struggles to achieve control of land and assets. This political aim of ecotourism is the most contentious and often the hardest to define clearly. For example, boycotting certain destinations may prove to be a double-edged sword, and it's important to ascertain whether long-term gains achieved by political pressure will be offset by short-term economic losses.
What Is Ecotourism? Definition, Examples, and Pros and Cons
- Chapman University
- Sustainable Fashion
- Art & Media
Ecotourism Definition and Principles
Pros and cons.
- Examples of Ecotourism
- Frequently Asked Questions
Ecotourism is about more than simply visiting natural attractions or natural places; it’s about doing so in a responsible and sustainable manner. The term itself refers to traveling to natural areas with a focus on environmental conservation. The goal is to educate tourists about conservation efforts while offering them the chance to explore nature.
Ecotourism has benefited destinations like Madagascar, Ecuador, Kenya, and Costa Rica, and has helped provide economic growth in some of the world’s most impoverished communities. The global ecotourism market produced $92.2 billion in 2019 and is forecasted to generate $103.8 billion by 2027.
A conservationist by the name of Hector Ceballos-Lascurain is often credited with the first definition of ecotourism in 1987, that is, “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals, as well as any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas.”
The International Ecotourism Society (TIES), a non-profit organization dedicated to the development of ecotourism since 1990, defines ecotourism as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education [both in its staff and its guests].”
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) looks at ecotourism as a significant tool for conservation, though it shouldn’t be seen as a fix-all when it comes to conservation challenges:
“There may be some areas that are just not appropriate for ecotourism development and some businesses that just won’t work in the larger tourism market. That is why it is so important to understand the basics of developing and running a successful business, to ensure that your business idea is viable and will be profitable, allowing it to most effectively benefit the surrounding environment and communities.”
Marketing an ecosystem, species, or landscape towards ecotourists helps create value, and that value can help raise funds to protect and conserve those natural resources.
Sustainable ecotourism should be guided by three core principles: conservation, communities, and education.
Conservation
Conservation is arguably the most important component of ecotourism because it should offer long-term, sustainable solutions to enhancing and protecting biodiversity and nature. This is typically achieved through economic incentives paid by tourists seeking a nature-based experience, but can also come from the tourism organizations themselves, research, or direct environmental conservation efforts.
Communities
Ecotourism should increase employment opportunities and empower local communities, helping in the fight against global social issues like poverty and achieving sustainable development.
Interpretation
One of the most overlooked aspects of ecotourism is the education component. Yes, we all want to see these beautiful, natural places, but it also pays to learn about them. Increasing awareness about environmental issues and promoting a greater understanding and appreciation for nature is arguably just as important as conservation.
As one of the fastest growing sectors of the tourism industry, there are bound to be some downsides to ecotourism. Whenever humans interact with animals or even with the environment, it risks the chance of human-wildlife conflict or other negative effects; if done so with respect and responsibility in mind, however, ecotourism can reap enormous benefits to protected areas.
As an industry that relies heavily on the presentation of eco-friendly components to attract customers, ecotourism has the inevitable potential as a vessel for greenwashing. Part of planning a trip rooted in ecotourism is doing research to ensure that an organization is truly providing substantial benefits to the environment rather than exploiting it.
Ecotourism Can Provide Sustainable Income for Local Communities
Sustainably managed ecotourism can support poverty alleviation by providing employment for local communities, which can offer them alternative means of livelihood outside of unsustainable ones (such as poaching).
Research published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that communities in regions surrounding conservation areas in Costa Rica had poverty rates that were 16% lower than in areas that weren’t near protected parks. These protected areas didn’t just benefit from conservation funds due to ecotourism, but also helped to reduce poverty as well.
It Protects Natural Ecosystems
Ecotourism offers unique travel experiences focusing on nature and education, with an emphasis on sustainability and highlighting threatened or endangered species. It combines conservation with local communities and sustainable travel , highlighting principles (and operations) that minimize negative impacts and expose visitors to unique ecosystems and natural areas. When managed correctly, ecotourism can benefit both the traveler and the environment, since the money that goes into ecotourism often goes directly towards protecting the natural areas they visit.
Each year, researchers release findings on how tourist presence affects wildlife, sometimes with varying results. A study measuring levels of the stress hormone cortisol in wild habituated Malaysian orangutans found that the animals were not chronically stressed by the presence of ecotourists. The orangutans lived in the Lower Kinabatangan Wildlife Sanctuary, where a local community-managed organization operates while maintaining strict guidelines to protect them.
Ecotourism May Also Hurt Those Same Natural Ecosystems
Somewhat ironically, sometimes ecotourism can hurt ecosystems just as much as it can help. Another study in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution found that ecotourism can alter animal behaviors in ways that put them at risk. If the presence of humans changes the way animals behave, those changes may make them more vulnerable by influencing their reaction to predators or poachers.
It's not just the animals who are at risk. As ecotourism activities become too popular, it can lead to the construction of new infrastructure to accommodate more visitors. Similarly, more crowds mean more pressure on local resources, increased pollution, and a higher chance of damaging the soil and plant quality through erosion. On the social side, these activities may displace Indigenous groups or local communities from their native lands, preventing them from benefiting from the economic opportunities of tourism.
Ecotourism Offers the Opportunity to Experience Nature
Renown conservationist Jane Goodall has a famous quote: “Only if we understand, will we care. Only if we care, will we help. Only if we help, shall all be saved.” It can be difficult to understand something that we haven’t seen with our own eyes, and ecotourism gives travelers the opportunity to gain new experiences in natural areas while learning about the issues they face.
Ecotourism also educates children about nature, potentially creating new generations of nature lovers that could someday become conservationists themselves. Even adult visitors may learn new ways to improve their ecological footprints .
EXAMPLES OF ECOTOURISM
The East African country has some competitive advantages over its neighbors thanks to its rich natural resources, paired with the fact that it has allocated over 25% of its total area to wildlife national parks and protected areas. Because of this, an estimated 90% of tourists visit to Tanzania seeking out ecotourism activities. Ecotourism, in turn, supports 400,000 jobs and accounts for 17.2% of the national GDP, earning about $1 billion each year as its leading economic sector.
Some of Tanzania’s biggest highlights include the Serengeti, Mount Kilimanjaro , and Zanzibar, though the country still often goes overlooked by American tourists. Visitors can take a walking safari tour in the famous Ngorongoro Conservation area, for example, with fees going to support the local Maasai community.
The country is also known for its chimpanzees , and there are several ecotourism opportunities in Gombe National Park that go directly towards protecting chimpanzee habitats.
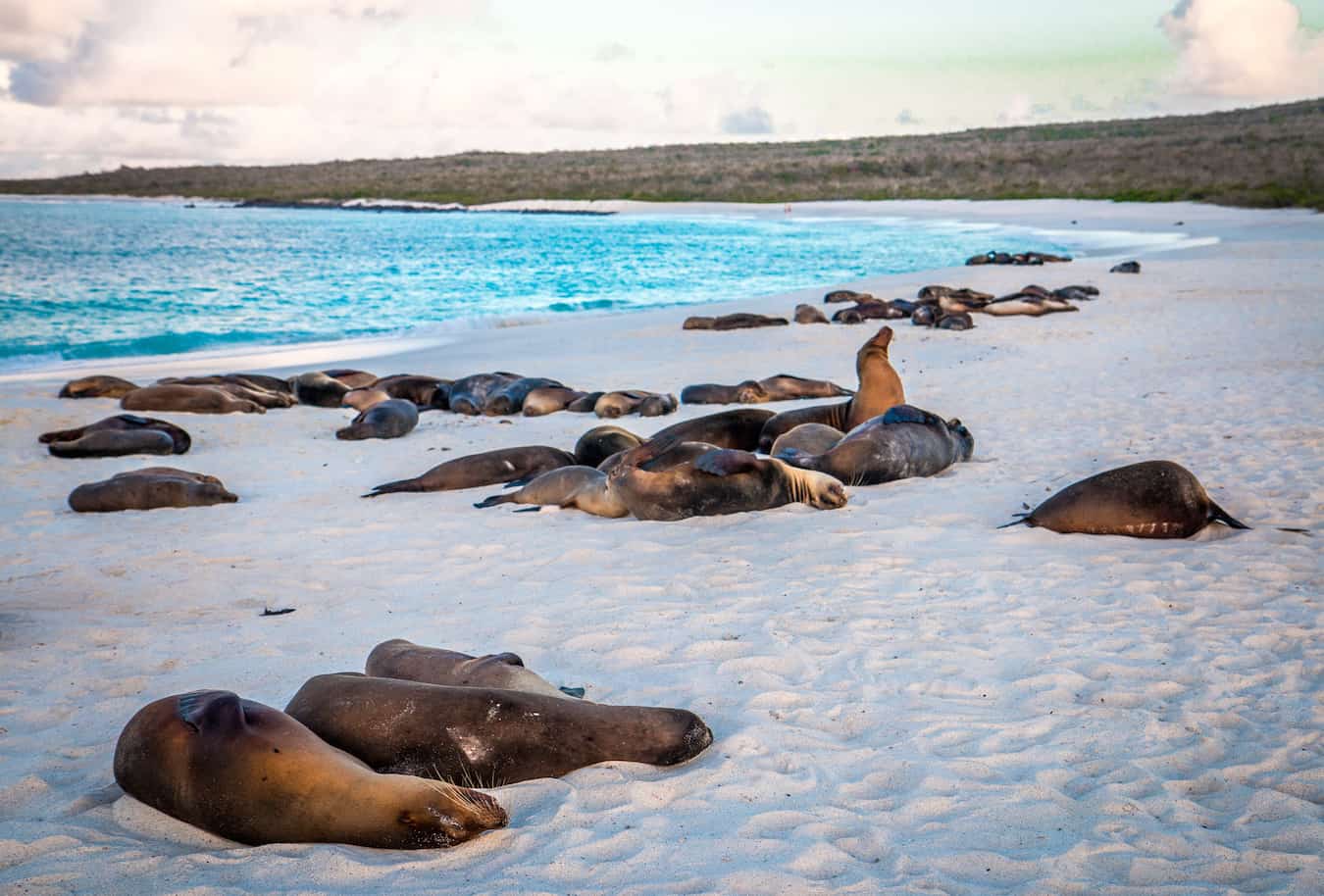
Galapagos Islands
It comes as no surprise that the place first made famous by legendary naturalist Charles Darwin would go on to become one of the most sought-after ecotourism destinations on Earth, the Galapagos Islands .
The Directorate of the Galapagos National Park and the Ecuadorian Ministry of Tourism require tour providers to conserve water and energy, recycle waste, source locally produced goods, hire local employees with a fair wage, and offer employees additional training. A total of 97% of the land area on the Galapagos is part of the official national park, and all of its 330 islands have been divided into zones that are either completely free of human impact, protected restoration areas, or reduced impact zones adjacent to tourist-friendly areas.
Local authorities still have to be on their toes, however, since UNESCO lists increased tourism as one of the main threats facing the Galapagos today. The bulk of funding for the conservation and management of the archipelago comes from a combination of governmental institutions and entry fees paid by tourists.
Costa Rica is well-known throughout the world for its emphasis on nature-based tourism, from its numerous animal sanctuaries to its plethora of national parks and reserves. Programs like its “Ecological Blue Flag” program help inform tourists of beaches that have maintained a strict set of eco-friendly criteria.
The country’s forest cover went from 26% in 1983 to over 52% in 2021 thanks to the government’s decision to create more protected areas and promote ecotourism in the country . Now, over a quarter of its total land area is zoned as protected territory.
Costa Rica welcomes 1.7 million travelers per year, and most of them come to experience the country’s vibrant wildlife and diverse ecosystems. Its numerous biological reserves and protected parks hold some of the most extraordinary biodiversity on Earth, so the country takes special care to keep environmental conservation high on its list of priorities.
New Zealand
In 2019, tourism generated $16.2 billion, or 5.8% of the GDP, in New Zealand. That same year, 8.4% of its citizens were employed in the tourism industry, and tourists generated $3.8 billion in tax revenue.
The country offers a vast number of ecotourism experiences, from animal sanctuaries to natural wildlife on land, sea, and even natural caves. New Zealand’s South Pacific environment, full of sights like glaciers and volcanic landscapes, is actually quite fragile, so the government puts a lot of effort into keeping it safe.
Tongariro National Park, for example, is the oldest national park in the country, and has been named by UNESCO as one of only 28 mixed cultural and natural World Heritage Sites. Its diverse volcanic landscapes and the cultural heritage of the indigenous Maori tribes within the create the perfect combination of community, education, and conservation.
How to Be a Responsible Ecotourist
- Ensure that the organizations you hire provide financial contributions to benefit conservation and find out where your money is going.
- Ask about specific steps the organization takes to protect the environment where they operate, such as recycling or promoting sustainable policies.
- Find out if they include the local community in their activities, such as hiring local guides, giving back, or through initiatives to empower the community.
- Make sure there are educational elements to the program. Does the organization take steps to respect the destination’s culture as well as its biodiversity?
- See if your organization is connected to a non-profit or charity like the International Ecotourism Society .
- Understand that wildlife interactions should be non-invasive and avoid negative impacts on the animals.
Ecotourism activities typically involve visiting and enjoying a natural place without disturbing the landscape or its inhabitants. This might involve going for a hike on a forest trail, mountain biking, surfing, bird watching, camping, or forest bathing .
Traveling in a way that minimizes carbon emissions, like taking a train or bike instead of flying, may also be part of an ecotourism trip. Because these modes of travel tend to be slower, they may be appreciated as enjoyable and relaxing ecotourism activities.
The Wolf Conservation Center ’s programing in New York State is an example of ecotourism. This non-profit organization is dedicated to the preservation of endangered wolf species. It hosts educational sessions that allow visitors to observe wolves from a safe distance. These programs help to fund the nonprofit organization’s conservation and wildlife rehabilitation efforts.
Stonehouse, Bernard. " Ecotourism ." Environmental Geology: Encyclopedia of Earth Science , 1999, doi:10.1007/1-4020-4494-1_101
" What is Ecotourism? " The International Ecotourism Society .
" Tourism ." International Union for Conservation of Nature .
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1307712111
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033357
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.09.010
https://doi.org/10.5897/JHMT2016.0207
" Galapagos Islands ." UNESCO .
" About Costa Rica ." Embassy of Costa Rica in Washington DC .
https://www.stats.govt.nz/information-releases/tourism-satellite-account-2019
- Costa Rica’s Keys to Success as a Sustainable Tourism Pioneer
- What Is Sustainable Tourism and Why Is It Important?
- What Is Community-Based Tourism? Definition and Popular Destinations
- How to Be a Sustainable Traveler: 18 Tips
- What Is Overtourism and Why Is It Such a Big Problem?
- Defeating Deforestation Through Rum, Chocolate, and Ecotourism
- Empowering Communities to Protect Their Ecosystems
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Sustainable Travel
- Why Bonobos Are Endangered and What We Can Do
- Why Are National Parks Important? Environmental, Social, and Economic Benefits
- IUCN President Tackles Biodiversity, Climate Change
- The World’s Smallest Tiger Is Inching Towards Extinction
- Ecuador Expands Protected Galapagos Marine Reserve by More Than 23,000 Square Miles
- What Is Voluntourism? Does It Help or Harm Communities?
- Regenerative Travel: What It Is and How It's Outperforming Sustainable Tourism
- New Zealand Aims to Become World's Largest 'Dark Sky Nation'

What Is Ecotourism?
Conservation, offering market-linked long-term solutions, ecotourism provides effective economic incentives for conserving and enhancing bio-cultural diversity and helps protect the natural and cultural heritage of our beautiful planet., communities, by increasing local capacity building and employment opportunities, ecotourism is an effective vehicle for empowering local communities around the world to fight against poverty and to achieve sustainable development., interpretation, with an emphasis on enriching personal experiences and environmental awareness through interpretation, ecotourism promotes greater understanding and appreciation for nature, local society, and culture., the definition., ecotourism is now defined as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education” (ties, 2015). education is meant to be inclusive of both staff and guests., principles of ecotourism, ecotourism is about uniting conservation, communities, and sustainable travel. this means that those who implement, participate in and market ecotourism activities should adopt the following ecotourism principles:.
- Minimize physical, social, behavioral, and psychological impacts.
- Build environmental and cultural awareness and respect.
- Provide positive experiences for both visitors and hosts.
- Provide direct financial benefits for conservation.
- Generate financial benefits for both local people and private industry.
- Deliver memorable interpretative experiences to visitors that help raise sensitivity to host countries’ political, environmental, and social climates.
- Design, construct and operate low-impact facilities.
- Recognize the rights and spiritual beliefs of the Indigenous People in your community and work in partnership with them to create empowerment.
Privacy Overview
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Climate Change
- Policy & Economics
- Biodiversity
- Conservation
Get focused newsletters especially designed to be concise and easy to digest
- ESSENTIAL BRIEFING 3 times weekly
- TOP STORY ROUNDUP Once a week
- MONTHLY OVERVIEW Once a month
- Enter your email *
Explainer: What Is Ecotourism?

The world has slowly become more connected over time. People take an interest in other cultures and want to experience them themselves. Traveling is an exciting part of life because it broadens your horizons and provides excellent educational opportunities, but how can you do so sustainably? To celebrate World Tourism Day 2023 under the theme “Tourism and green investment”, we dive deep into the world of ecotourism and explore new and innovative solutions to promote the movement of people around the world.
What Is Ecotourism?
Ecotourism involves traveling sustainably. When you vacation, domestically or abroad, you stay conscious of the environment as much as possible. Ecotourists try to limit their carbon footprint and support local ecosystems by contributing positively. For example, they could eat at a local restaurant or refrain from using plastic on their trip. Ecotourism has become critical as people try to expand their worldview while staying environmentally conscious.
Why Should You Practice Ecotourism?
Tourism is vital for many communities worldwide. Vacationers spend their money to help small businesses thrive and to stimulate local economies. However, tourism can negatively impact the environment. A 2022 study found that tourism is responsible for nearly 8% of the world’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, most of which came from food and waste management.
The pandemic hit the tourism industry with a steep 74% decline in international travel. Many countries had lockdowns in place to prevent COVID-19 transmission from foreign places. While this contributed to a significant drop in carbon emissions in 2020, tourist-dependent nations suffered huge economic losses.
Three years after the first case was detected in Wuhan, China, the pandemic is finally winding down and international travel is resuming, with air traffic set to reach 2019 levels soon. Last year saw a 153% increase in air travel compared to 2021 and about 62% pre-pandemic levels. In 2023, air traffic is expected to continue rising as most countries lift restrictions.
The bounce-back of tourism means the same will happen in terms of emissions. In 2022, GHG emissions increased by 7% in the first quarter compared to 2020.
It is critical to practice ecotourism as global warming becomes more apparent. You’ll benefit from learning and becoming a better friend to the environment. Implementing ecotourism comes with many benefits:
- Educate yourself: The most significant benefit of ecotourism is educating yourself on environmental issues. If you find ways to be environmentally conscious on your trip, you are more likely to repeat those behaviors at home. Reading literature and research from scientists puts into perspective how the planet needs your help to survive.
- Protect resources: Sustainable travel means using natural and renewable resources to improve the planet’s health. You’re protecting the environment around you from the negative impacts of travel. If you believe in leaving something better than when you found it, ecotourism is the way to go.
- Help economies: Practicing ecotourism means other vacationers behind you also get to enjoy a clean environment . One way is by spending your money at local businesses. These shops are the heart of communities and give the location its remarkable personality. Patronising these companies helps them grow and continue their services for future visitors.
How Can You Be Mindful on Vacation?
It’s challenging to be perfect regarding your carbon footprint when traveling, but there are ways to limit your environmental impact abroad and contribute positively to the area. These five ways show how you can be a mindful ecotourist on your next trip.
1. Research Ecotourism Locations
Ecotourism starts before you travel. Research as thoroughly as possible to see what destinations are the most conducive to ecotourism and find ways to be an ecotourist at the location. For example, you could look for hotels with biophilic designs. These spaces combine buildings with nature to maintain a connection with the environment. You may see natural materials like hardwood , stones, and trees inside the facility.
Ecotourism means accounting for your environmental impact, but you should also examine how the area cares about green practices. When planning a trip, search for cities that implement eco-friendly policies to promote ecotourism. For example, Seattle, Washington, uses hydroelectric power for nearly 100% of its energy consumption.
2. Beware of Greenwashing
Talking about environmentally friendly practices is one thing, but implementing them and supporting the planet are the next steps that some businesses do not take. You may know this strategy as greenwashing . Due diligence can tell you which organisations stay true to their word and which only use eco-friendliness as a marketing term.
It is essential to be able to spot greenwashing when you travel. Research hotels and businesses in the area and review their practices. How do they align with environmentally positive initiatives that they claim? For example, in 2018, Hilton said it would reduce CO2 emissions. However, critics accused the company of greenwashing because it cut down palm and mangrove trees to build its resort in the Maldives. Tearing down palm trees significantly affects carbon levels in the atmosphere.
One way to research a company like Hilton for greenwashing is to examine its environmental, social and governance (ESG) scores. These metrics track companies’ operations and give an objective measurement to gauge practices. Organisations like Bloomberg developed databases that show exhaustive lists of ESG scores. They monitor thousands of businesses worldwide, so it is easier to see which are telling the truth beyond their ‘green’ campaigns.
3. Visit a Wildlife Refuge
Part of ecotourism is finding ways to limit your environmental impact, but you can make positive contributions while still having fun. Visit a wildlife refuge when on vacation. These sanctuaries are some of the best places to support wildlife conservation and educate yourself.

Photo by Joshua J. Cotten on Unsplash
Wildlife refuges provide large, safe, and green spaces for animals to thrive. Many of them risk extinction and can thrive in a sanctuary. The money you spend at the refuges goes toward keeping the facilities standing and funding research to examine these animals. There are wildlife sanctuaries in all 50 states and five territories in the U.S. Internationally, there are numerous opportunities on every continent to support conservation.
Seeing wildlife is a terrific experience, but remember to be mindful when visiting. For example, do not disturb animals by calling or touching them, and refrain from feeding them, even if they approach you. These creatures have special diets and oftentimes, human food is not suitable for them. If you bring food, clean up your waste afterward. Curious wildlife may get their heads stuck in plastic containers or eat things they are not supposed to.
4. Use Green Transportation Methods
Another way to practice ecotourism is to use green transportation methods. This strategy is something you can do abroad and practice at home. Eco-friendly transit reduces your carbon footprint significantly because it reduces greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and negative environmental impacts.

Photo by freestocks on Unsplash
Depending on your destination, you should search for ways to take public transportation. These options may include buses, trains and metro lines. Public transit is more efficient than passenger vehicles because it emits 45% fewer CO2 emissions than cars on the road. Use bicycles and other low-emissions options if it’s not available.
5. Learn Local Customs
Ecotourism goes hand-in-hand with mindful traveling. When you vacation, try to be one with the culture and immerse yourself. That’s how you get the most out of your travels. Learn local customs and find out what the residents do. They say when in Rome, do as the Romans do — and that’s a solid start for being an ecotourist.
Eating local food is an excellent way to immerse yourself and be an ecotourist. Ask a guide or resident where the best places to eat are. Small businesses and restaurants are likelier to have a lower carbon footprint than tourist traps. Find establishments that source their food locally. The shortened supply chain delivers delicious items at a lower price than you may see in chains.
Being an Ecotourist Worldwide
Calls for sustainability are growing as humans begin recognising their negative environmental impact. You can find ways to lower your carbon footprint at home, and you should keep the same mindful attitude when traveling abroad. Focus on being an ecotourist and helping the environment wherever you go.
You might also like: Can EcoTourism Save Coral Reefs?

15 Biggest Environmental Problems of 2024

International Day of Forests: 10 Deforestation Facts You Should Know About

13 Major Companies Responsible for Deforestation
Hand-picked stories weekly or monthly. We promise, no spam!
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Boost this article By donating us $100, $50 or subscribe to Boosting $10/month – we can get this article and others in front of tens of thousands of specially targeted readers. This targeted Boosting – helps us to reach wider audiences – aiming to convince the unconvinced, to inform the uninformed, to enlighten the dogmatic.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Green Global Travel
World's largest independently owned Ecotourism / Green Travel / Sustainable Travel / Animal & Wildlife Conservation site. We share transformative Responsible Travel, Sustainable Living & Going Green Tips that make a positive impact.
What Is Ecotourism? (The History & Principles of Responsible Travel)

Disclaimer: This post may contain affiliate links. All hosted affiliate links follow our editorial policies .
What is ecotourism? How does it work? Why does it matter? And how can we, as travelers, put the core principles of ecotourism into practice?
In recent years, the growth of interest in responsible travel has outpaced that of traditional sun/sand tourism by an increasingly wide margin.
With some experts estimating that ecotourism now represents 11.4% of all consumer spending, these sorts of questions have become more and more common.
And, as we continue to see more negative impacts of mass tourism on beloved destinations around the world, the answers to these questions will become increasingly vital.
Part of the confusion surrounding sustainable travel is the plethora of names being used for it within the industry.
E cotourism, a movement that began to take shape back in the 1980s, is the oldest and most commonly used word for it.
More recent industry buzzwords include sustainable tourism, green tourism, nature tourism, responsible tourism, ethical tourism, mindful travel, conscious travel, pro-poor tourism, and many others.
Regardless of what you call it, the central concepts that these philosophies share in common are that the travel industry as a whole should adopt more environmentally friendly practices, protect the natural and cultural heritage of a destination, and support local communities.
With the United Nations designating 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development , this seems like a great time to deepen the conversation about what ecotourism is and why it’s important for the future of travel.
Here we’ll explain the definition of ecotourism, examine its history and evolution, explore its core principles and benefits, and look at 10 ways that each of us as responsible travelers can ensure our adventures ultimately make a positive impact.
READ MORE: How Mass Tourism is Destroying Destinations

- The Definition of Ecotourism
- A Brief History of Ecotourism
- Ecotourism in the ’90s & Beyond
- The Principles of Ecotourism
- Ecotourism Principles in Action
The Benefits of Ecotourism
- Other Articles on Ecotourism

THE DEFINITION OF ECOTOURISM
According to The Oxford English Dictionary , the word “ecotour” was first recorded in 1973, followed by “ecotourism” in 1982.
There, the word is defined as, “Tourism to areas of ecological interest (typically exotic and often threatened natural environments), especially to support conservation efforts and observe wildlife; spec. access to an endangered environment controlled so as to have the least possible adverse effect.”
Ecotourism was perhaps best defined in 1990 by Megan Epler Wood, the co-founder of The International Ecotourism Society (TIES) and author of six influential books on the subject.
Her latest, Sustainable Tourism on a Finite Planet: Environmental, Business and Policy Solutions , was released in 2017.
Now the director of the International Sustainable Tourism Initiative at Harvard, Epler Wood’s original definition was more simple and to the point. She described ecotourism as, “Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and improves the well-being of local people.”
In simple words, the meaning of ecotourism is travel that makes a positive impact on both the ECO logy and ECO nomy of a given destination.
One mistake many people make is assuming that ecotourism is all about conserving nature and wildlife by any means necessary. But if a destination or business’ tourism development strategy does not actively provide concrete financial benefits for the indigenous people, it’s not truly ecotourism.
Other NGOs, such as The Center for Responsible Travel (CREST, whose co-founder Dr. Martha Honey also served as the Executive Director of TIES for four years), have since expanded on Epler Wood’s concept to provide more in-depth definitions of ecotourism.
CREST currently defines ecotourism as, “Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, socially and economically sustains the well-being of local people, and creates knowledge and understanding through interpretation and education of all involved (including staff, travelers, and community residents).”
Other responsible travel organizations may have their own take on what ecotourism is, but these three are the most significant definitions.
READ MORE: Megan Epler Wood on the Evolution of Ecotourism

A BRIEF HISTORY OF ECOTOURISM
Ecotourism’s earliest origins arguably began with the Sierra Club’s Outing program. Launched in 1901, these annual expeditions took hikers into the Sierra Nevada’s backcountry in order to show members natural wonders, “so that those persons could become active workers for the preservation of the forests.”
The modern movement began to take root in the environmental activism of the 1970s. Some sources suggest that the term ecotourism was originally coined by Mexican architect-turned-environmentalist Héctor Ceballos-Lascuráin . He used the word to describe traveling to undisturbed areas in order to enjoy their natural beauty and culture.
In 1981 Ceballos-Lascuráin became the founding president of the Mexican Association for the Conservation of Nature, the most influential Mexican NGO in the conservation arena. In 1984 he founded the first Mexican ecotourism agency, ECOTOURS.
His 315-page book on Tourism, Ecotourism, and Protected Areas was published in 1996 by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN). He served for many years as an Ecotourism Advisor to both the IUCN and United Nations World Tourism Organization.
Megan Epler Wood was another one of the ecotourism movement’s earliest adopters. She was a young wildlife biologist hired by World Wildlife Fund founder (and former EPA director) Russell Train right out of grad school in the early ’80s.
Their all-star team at the time also included Russell Mittermeier (now President of Conservation International) and Thomas Lovejoy , who’s known as the “godfather of biodiversity.”
“In the 1980s the idea of sustainable development was new,” Epler Wood recalls. “There was a big conversation about finding ways to benefit local people who wanted to conserve natural areas. A few years later my husband and I lived in Colombia on a joint Fulbright scholarship. [We realized that] people visiting the rainforest were bringing a majority of the benefits those locals were seeing.
READ MORE: Top Ecotourism Destinations According to Experts

ECOTOURISM IN THE ’90s & BEYOND
After she returned home in 1988, Epler Wood went on to produce The Environmental Tourist for PBS. She started pitching conservation NGOs a documentary on ecotourism that would be “the very first global investigation of how tourism could contribute to conservation of natural resources and local well-being.”
When that project lost its funding, she tapped into her contacts and started The International Ecotourism Society. The organization’s goal was to contribute to the development of ecotourism as a viable tool for conservation, protection of bio-cultural diversity, and sustainable community development.
Epler Wood left TIES in 2002 to start her own consulting firm. She was replaced by Dr. Martha Honey, the veteran journalist/historian who wrote the seminal book, Ecotourism and Sustainable Development: Who Owns Paradise? in 1999. She was Executive Director of the organization from 2003 to 2006, and eventually founded the Center for Responsible Travel in Washington, DC.
I had the pleasure of interviewing Dr. Honey during a keynote presentation at the TBEX Travel Blogging Conference in Cancun, Mexico in 2014. When I asked about the changes she’s seen in the ecotourism industry over the past 20 years, Dr. Honey insisted that they were positive for the most part.
“It hasn’t lost or changed its core values, which are essentially that tourism should be done in a way that’s beneficial to environmental conservation and local communities and respectful of local cultures…The Slow Food movement, organic agriculture, travel philanthropy, concern about human trafficking and child sexual abuse, fair trade , carbon offsets, and animal welfare are all branches on the original tree.
There have been countless other ecotourism icons over the past 30 years, from Jonathan Tourtellot (NatGeo’s Destination Stewardship Center) and Jeff Greenwald (founder of Ethical Traveler) to eco-design authority Hitesh Meta.
Now ecotourism is considered one of the fastest-growing sectors in the travel industry (about 5% annually), accounting for around 6% of the world’s gross domestic product. Even as the market for traditional tourism grew stagnant, the UNWTO’s global forecast projected rapid growth in the ecotourism industry over the next decade.
READ MORE: Q&A With Dr. Martha Honey on Ecotourism

THE PRINCIPLES OF ECOTOURISM
Ecotourism is essentially all about bringing nature/wildlife conservationists, local communities, and the responsible travel industry together to ensure development focused on long-term sustainability rather than short-term profits.
The goal is to develop tourist accommodations, activities, and attractions that benefit everyone involved– the local flora/fauna, the local people, travel industry stakeholders, and travelers alike.
With this mission in mind, the ecotourism industry has collectively developed a number of core guiding principles over the past few decades. Although international regulation and accreditation have remained elusive, these guidelines provide a general blueprint for responsible tourism development.
Many of these principles align with those of the Global Sustainable Tourism Council , which developed an extensive list of criteria for sustainable destinations, hotels, and tour operators.
1. Build Environmental & Cultural Awareness
Education is a key aspect of ecotourism initiatives, for locals and visitors alike. Most of these efforts are focused on improving awareness, sensitizing people to environmental issues, and encouraging them to be conscious of their impact on the places they visit.
Some tour operators create conservation education programs for local schools. Many offer interpretative guides, naturalists, and guest lecturers to help deepen travelers’ understanding of their experiences.
Immersive interactions with local cultures are also becoming increasingly common. These experiences often emphasize interaction rather than a typical performer-audience relationship with visitors.
2. Design & Operate Low-Impact Eco Tours/Facilities
Remember the old environmental adage, “Take only pictures, leave only footprints”? Today’s ecotourism industry strives to take it one step further.
The focus is all about sustainability, minimizing the negative carbon footprint travel often leaves on the environment. But these days the big picture goal is to create positive, rather than merely neutral impact.
From using alternative energy sources and ensuring all building materials are locally sourced to limiting eco tour group sizes, conscious consideration should be made to ensure low impact at every stage, from development to implementation.
3. Provide Financial Benefits for Conservation
The idea of using the revenue generated by ecotourism to help fund the conservation of nature and wildlife is not a new idea. In fact, it dates back more than 100 years, to the creation of the US National Parks Service .
Referred to by documentarian Ken Burns as “America’s Best Idea,” this concept has since been applied to more than 6,000 national parks in nearly 100 different countries around the world.
When managed properly, ecotourism can help provide a revenue-generating alternative to urbanization, deforestation, unsustainable agriculture, and poaching. And though critics claim ecotourism often fails to deliver on its promise, recent scientific studies continue to illustrate its conservation benefits.
4. Provide Financial Benefits for Local People
Critics have similarly pointed out that some ecotourism initiatives have created more problems for local people than they solve. Poorly managed programs can lead to conflicts over land and resources, unfair profit distribution, and cultural exploitation.
This is what happens when the phenomenon known as greenwashing – the disinformation disseminated by an organization so as to present an environmentally responsible public image– rears its ugly head.
True ecotourism MUST provide financial benefits to local people, whether through direct (tours, admission fees, and donations) or indirect means (such as taxes on travel or accommodation). It generally works best when there is smaller scale, slower growth, and greater involvement by local communities in all steps of the tourism development process.
5. Support Human Rights
Ecotourism initiatives should always strive to support human rights, economic empowerment, and democratic movements in a given destination.
In addition to increasing awareness about sociopolitical and environmental issues facing a given destination, ecotourism initiatives should support local businesses and the rights of indigenous inhabitants to control their land and assets.
This principle is arguably the most problematic and contentious. Should tour companies or travelers boycott a given destination due to human rights abuses or unfair treatment of its indigenous population? In many cases, such boycotts don’t punish the powers-that-be nearly as harshly as the locals who rely heavily on tourism revenue to survive.
READ MORE: Why Responsible Travel Matters
ECOTOURISM PRINCIPLES IN ACTION
Becoming a more responsible traveler is the best way to ensure your adventures are positive for the local people and the planet.
Whe n the core principles of ecotourism are applied, it can stimulate financial growth in developing nations, strengthening the global economy.
Individually, one person taking these baby steps to going green might not seem to make much of an impact. But if we all take simple strides towards being more conscious of our choices, collectively we can m ake a world of difference. Here’s how!
Lightening up your load saves money on baggage fees and increases plane fuel-efficiency.
Pack items that can be washed in the sink and are quick drying so they can be worn multiple times during your trip.
We recommend (but do not receive compensation from) the ExOfficio brand, and wear it everywhere we travel.
Take shorter showers, turn off the faucet while shaving and brushing your teeth, and re-use towels for multiple days.
And NEVER use the hotel laundry, as they typically wash each guest’s clothes separately, even if there are only a few items.
READ MORE: The Best Travel Clothing For 7 Travel Styles (An Epic Guide)

SAVE ENERGY
When you leave your hotel room, turn off the lights, heat/AC and TV.
Consider leaving the “Do Not Disturb” sign on the door so that the housekeeping staff won’t clean your room every day.
This will save on harsh chemical cleaning supplies and the electricity of vacuuming and washing bed linens.
REDUCE/REUSE/RECYCLE
Take a BPA-free water bottle you can refill, use just one bar of soap for both sink and shower.
Return brochures and maps once you’re finished using them, and hold on to your trash until you find a place to recycle it.
Seek out indigenous artisans and learn about their craft.
When we were in the Riviera Maya near Coba, we saw tons of assembly line art.
But instead we wound up buying from a man who taught local children and tourists the ancient craft of Mayan pottery and distributed profits equally among families in his village.
READ MORE: What Is An Eco Lodge? A Guide to Eco-Friendly Accommodations

LEAVE ONLY FOOTPRINTS
Stick to marked trails to avoid harming native flora, and consider taking a bag to pick up trash along your journey.
Not only is it a great way to help keep the outdoors beautiful, but it also protects wildlife that might eat or get tangled in the garbage.
BE A TRAVELER, NOT A TOURIST
Take time to immerse yourself in the local music, art and cuisine. Embrace the cultural differences that make it unique.
Get to know the locals and how they view life. You might be surprised at the things you learn when you open your mind to new ideas!
HONOR LOCAL TRADITIONS
Some cultures have very different traditions from yours.
Women are forbidden to show skin in some Muslim countries. For some, being photographed in like having your soul stolen.
Understand and respect these traditions, or risk offending the people whose culture you’re there to experience.
READ MORE: Embracing the Culture of the Maasai People of Tanzania

Developing nations are badly in need of basic necessities most people take for granted.
Traveling gives you a unique experience that stays with you for the rest of your life.
In return, consider giving something back, such as bringing school supplies on tours in which you know you’ll interact with locals.
SHOP SMARTER
Read labels, and ask questions like “What is this item made from?”
All over the planet people sell items made from non-sustainable hardwoods, endangered species, and ancient artifacts.
It may be alright in their country to sell them, but you can still vote with your wallet by refusing to buy them.
READ MORE: The Problem with Animal Selfies

THE BENEFITS OF ECOTOURISM
To quote CREST founder Dr. Martha Honey during our Keynote session at TBEX Cancun in 2014, we earnestly believe that ecotourism is “ simply a better way to travel . ” Here’s a look at how this transformational approach to travel benefits conservation, increases cross-cultural understanding, and ultimately turns travelers into environmental advocates:
Benefits to Wildlife
To see how ecotourism benefits nature and wildlife, let’s look at endangered species such as African Elephants . Ivory from Elephant tusks is worth $1500 a pound on the black market, which has led to a dramatic increase in poaching.
But Elephants are worth 76 times more alive than dead . When you consider the revenue from wildlife photography tours , luxury safari camps, and other ecotourism offerings, a single Elephant is worth $1.3 million over the course of its lifetime!
Other heavily poached species, such as Lions and Rhinos , have shown to be similarly valuable alive. Ecotourism offers a long-term alternative to exploitation, generating sustainable revenue and ensuring better overall health of the ecosystem.
Benefits to the Environment
Nature reserves and national parks help prevent deforestation and pollution, while also protecting the habitat of endemic species.
The revenue that ecotourism provides can help replace profits from exploitative practices such as mining or slash ‘n’ burn agriculture. It can also help ensure the long-term financial viability of the area.
Naturalist guides also help travelers understand the value of a pristine ecosystem, and teach them about the importance of conservation. This ultimately help to create a more mindful and conscious legion of travelers.
Benefits to Local People
When managed properly, ecotourism can offer locals alternative revenue streams. In wildlife-rich countries such as Rwanda , former poachers are often employed as guides or trackers, capitalizing on their knowledge of the animals and their habitat.
In Costa Rica , unemployment has fallen to less than 10% since the country started building its ecotourism infrastructure in the 1970s. The country now enjoys the highest standard of living in Central America .
Involving local communities in tourism management empowers them by ensuring that more revenue is reinvested locally. Ecotourism also offers indigenous peoples an opportunity to remain on ancestral land, conserve it, and preserve traditional culture.
Benefits to Travelers
In the words of United Nations Secretary General Talib Rifai, the Year of Sustainable Tourism provided “a unique opportunity to advance the contribution of the tourism sector to the three pillars of sustainability– economic, social and environmental– while raising awareness of the true dimensions of a sector which is often undervalued.”
Sure, being a responsible traveler takes a greater level of commitment to being conscious and mindful of the impact we have on the destinations we visit. But ecotourism also offers us incredible, transformative experiences, allowing us to develop closer personal relationships to the nature, wildlife, and local people we encounter during our adventures.
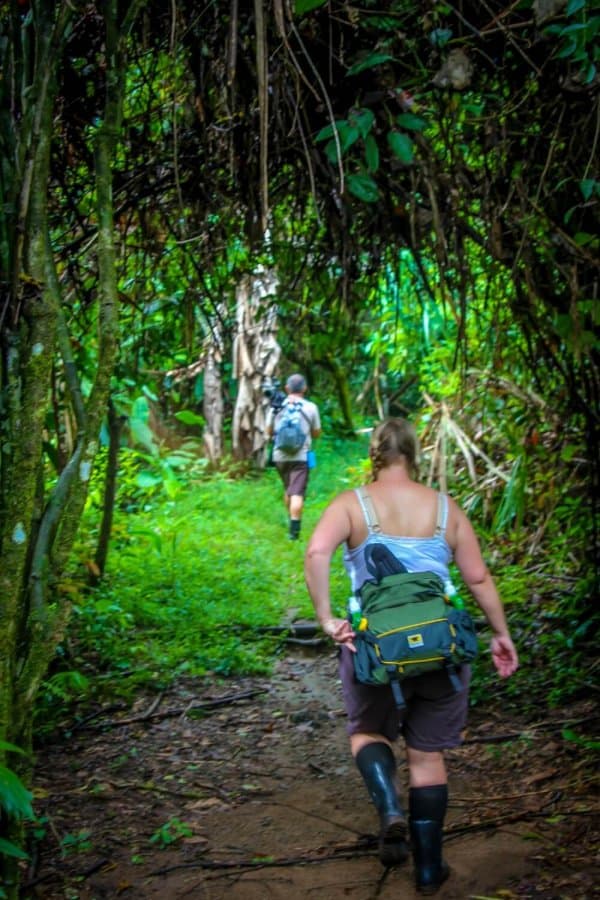
Learning about ecotourism during my life-changing experience in South Africa in 2000 permanently changed my understanding of mankind’s role in our planetary ecosystem. And I firmly believe that, once you’ve had that sort of travel experience, you’ll never want to travel the traditional way again. –Bret Love; photos by Bret Love & Mary Gabbett unless otherwise noted

OTHER ARTICLES ON ECOTOURISM
How Mass Tourism is Destroying Destinations Travelers Love
Why Responsible Tourism is Better
7 Harmful Practices Tourists Should Never Support
Why Slow Travel is Better
Why Community Based Tourism is Vital to Responsible Travel
What Is An Eco Lodge? A Guide to Eco-Friendly Accommodations
What Is Glamping? An Intro to Luxury Camping
10 Steps to Becoming a More Responsible Traveler
Green Travel Tips: The Ultimate Guide to Sustainable Travel
How to Choose a Green Hotel
How to Choose a Responsible Scuba Diving Tour Operator
How to Eat Ethically When You Travel
Top 10 Latin American Ecotourism Adventures
Top 10 Off the Beaten Path Ecotourism Destinations
Ecotourism in Costa Rica
Ecotourism in Jordan
Ecotourism in Antarctica
Ecotourism in Australia
Ecotourism in Cancun
Ecotourism in Egypt
Ecotourism in Ireland
Ecotourism in Jamaica
Ecotourism in New Zealand
Ecotourism in Northern Italy
Ecotourism in Sabah, Borneo
Ecotourism in Spain
Ecotourism in Taipei
Ecotourism in Tonga

About the Author
Green Global Travel is the world's #1 independently owned ecotourism website encouraging others to embrace sustainable travel, wildlife conservation, cultural preservation, and going green tips for more sustainable living.
We've been spotlighted in major media outlets such as the BBC, Chicago Tribune, Forbes, The Guardian, Lonely Planet, National Geographic, Travel Channel, Washington Post and others.
Owned by Bret Love (a veteran journalist/photographer) and Mary Gabbett (business manager/videographer), USA Today named us one of the world's Top 5 Travel Blogging Couples. We were also featured in the 2017 National Geographic book, Ultimate Journeys for Two, for which we contributed a chapter on our adventures in Rwanda. Other awards we've won include Best Feature from both the Caribbean Tourism Organization and the Magazine Association of the Southeast.
As Seen On…

Join the 300,000+ people who follow Green Global Travel’s Blog and Social Media

- Travel Updates
A Complete Guide To Understanding Ecotourism
Terms like ecotourism, green tourism, and sustainable tourism have been popping up in discussions easily, and unfortunately, they are being used interchangeably. Here, we will take a look at what is ecotourism and what are the principles of ecotourism.

Over the years, ecotourism has been gaining a lot of importance, especially considering that more and more travellers are looking to be more responsible and follow environment-friendly practices. However, many are still not clear about exactly what is ecotourism or the principles of ecotourism. There is a misconception that ecotourism, green tourism, and sustainable tourism are the same thing, and while they all promote responsible tourism, they all mean different things and have different scopes.
In this article, while trying to give a deeper understanding of what is ecotourism, we will give you information about ecotourism like the meaning of ecotourism, ecotourism tourism definition, and the principles of ecotourism. By the end of this article, we hope you will have a clearer understanding of the term and its evolution.
Also read: What is the difference between eco tourism, green tourism and sustainable tourism?
What Is Ecotourism?
Eco-tourism or ecological tourism has been defined as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education” by The International Ecotourism Society (TIES, 2015). To answer the question “What is ecotourism?” in a simpler way, it is a form of tourism that is about going out into the natural world and is more about what you do in a place than where you stay. It is more than just travelling around the whole world and sightseeing.
It is the kind of tourism where fragile and/or pristine natural environments are visited in a way that the impact of the visit is minimised. The environment and local communities should benefit in such a way that the latter is motivated to keep the local environment pristine.
Another way to explain what is ecotourism is to say that it involves travel to places where flora, fauna, and cultural heritage are the main attractions. It supports conservation efforts through the education of tourists, giving them an insight into the human impact on the environment, and helping them gain a better appreciation of natural habitats. It may also benefit the environment through direct investment in conservation efforts.
Also read: 10 simple ways to become a responsible traveller
History Of Ecotourism

Although the term ecotourism has been gaining popularity in recent years, it is not a new concept. However, there is no clarity as to the origins of the term as there are several different claims as to when it came into use.
Some claim that the term ecotourism was popularised by Hector Ceballos-Lascurian, who also claimed to have coined the term in the year 1983. This is when he was in the dual role of founding president of PRONATURA (an influential Mexican conservationist NGO) and Director General of Standards and Technology of SEDUE (the Mexican Ministry of Urban Development and Ecology). To him, ecotourism meant travelling to undisturbed areas to enjoy the natural beauty and culture. Later, in 1984, he founded ECOTOURS, Mexico’s first ecotourism agency. Ceballos-Lascurian even served as an Ecotourism Advisor to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature and the United Nations World Tourism Organisation for many years.
Some others claim that the term was coined in 1965 by Claus-Dieter (Nick) Hetzer, who was an academic and adventurer from the Forum International, Berkeley, USA. He is also believed to have run the first eco-tours in Yucatán in the early 1970s.
[What is an eco-tour?: Tours that involve visits to scenic or remote natural areas and are designed to minimise negative impacts on the environment and local inhabitants.]
There is another claim that eco tourism originated even earlier, in 1901 in fact, with the Sierra Club’s Outing program. These were annual expeditions that took hikers into the Sierra Nevada’s backcountry, showing them its natural wonders so that they could actively work for the preservation of the forests.
Over the past decades, there have been many icons of ecotourism and now, this form of tourism has been gaining a lot of importance. Ecotourism is considered to be one of the fastest-growing tourism sectors in the industry (about 5 percent annually) and there are no signs of it slowing down, even though more traditional forms of tourism have seen a stagnation.
Principles Of Ecotourism
Now that we have seen what is ecotourism and taken a look at its history, we will go over the principles that guide the ecotourism industry. Ecotourism is essentially about bringing together communities, conservation, and sustainable travel.
Many tour packages are being classified as “eco-tours” even though they do not emphasise conservation, education, or social and cultural participation, and low impact on the places visited. Therefore, to help you understand which tours are actually eco-tours, here are the principles of ecotourism:
1. Building Environmental And Cultural Awareness And Respect

The major focus of ecotourism is to sensitise people towards environmental issues, improve awareness, and encourage people to be conscious of the effect on the places they visit. Following this principle, a few tour operators create educational programs on conservation for local schools. Interpretive guides, naturalists, and guest lecturers are also offered by other operators to help visitors get a deeper understanding of their experiences. Some operators also offer immersive interactions with local cultures (that are becoming more common) that emphasise proper interactions instead of a usual performer-audience relationship.
2. Minimize Physical, Social, Behavioural, And Psychological Impacts By Operating Low-Impact Eco Tours

The ecotourism industry’s focus is sustainability, and minimising the negative impact that conventional tourism leaves on the environment. Over time, however, the concept has evolved to include making a positive impact, rather than merely having a neutral impact on the environment and the locals. Maintaining small groups and avoiding under-managed or over-visited destinations is a good way to minimise the impact of the group on the areas visited.
3. Provide Direct Financial Benefits For Conservation

One of the main objectives of ecotourism is to help local conservation efforts by inviting financial benefits. Visiting national parks is one way for tourists to contribute towards the conservation of nature and wildlife. When ecotourism gains more importance and practitioners, more revenue generation opportunities are created that are environmentally better alternatives to urbanisation, deforestation, unsustainable agriculture, and poaching.
Also read: How to be a more responsible wildlife tourist
4. Generate Financial Benefits For Locals And Private Industry

Another important principle of ecotourism is the generation of financial benefits for local communities. Through direct or indirect means, locals must get the financial benefits of eco-tourism. This could be through tours, admission fees, donations, and taxes on travel and accommodation. Community tours are a good way to generate financial benefits for local communities.
5. Deliver Memorable Interpretative Experiences For The Visitors

Although ecotourism is geared towards reducing a negative impact on the environment and the local communities and generating a positive impact on the same, it doesn’t mean that the tours have to be all about work. Any tour (conventional or not) should be designed in such a way that visitors should enjoy their trip. If the eco-tours are tough and/or too boring, there is a fair chance that many may start losing interest in more responsible tour packages, thereby having a negative impact on the communities that depend on these tours.
6. Recognise The Rights And Spiritual Beliefs Of The Indigenous People And Work With Them

Tourists who are part of eco-tours are encouraged to respect the rights and spiritual beliefs of the locals/indigenous population of the destinations instead of just getting in their faces and taking their photos without their permission. Like any other individual, the local communities value their privacy and it would always be better to first interact and have meaningful conversations with them and, only once permission is received, take a picture of them.
Beware Of Greenwashing!
While you are in safe waters when you practice ecotourism, sustainable tourism, or responsible (all of which are eco-friendly), you must always be careful of tour operators and tourism companies that only pretend to be eco-friendly in order to attract more business, a practice widely known as greenwashing. A good way to make sure that the company or tour operator to whom you are giving your business is legitimately eco-friendly, you will have to do a bit of digging and gathering of all the facts. Once you are convinced that the company is legitimate, go ahead and book your eco-tour and contribute to a better and happier world.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Unveiling the wonders of culture and tradition!

Are you ready to embark on a journey filled with adventure, culture, tradition, and exciting attractions? Let your explorer's spirit soar and make unforgettable memories as you explore the beauty of our diverse world.
- What is Ecotourism?

Ecotourism is a type of tourism that involves visiting pristine, fragile, and relatively uninterrupted natural areas, planned as a small scale alternative and low-impact tour as an alternative to standard commercial tourism. Ecotourism promotes conservation, and aims to have a positive socio-economic impact on the local people surrounding the attraction. The primary objective for ecotourism may be to provide finances for the conservation of ecology, to champion for the respect of different cultures, to educate the traveler or to politically empower local communities. Environmentalists have considered ecotourism as a critical endeavor since the 1980s, when the environmental "green" movement was just starting to emerge.
An Overview On Ecotourism
In general, ecotourism handles interaction with living things that shape an ecosystem of the natural environments while focusing on environmental sustainability, personal growth, and socially responsible travel. Typically, ecotourism involves going to places where cultural heritage together with flora and fauna are the main attractions. The primary intention for ecotourism was to provide tourists with insight on the effects of human beings on the environment thus encouraging the appreciation of the existing natural habitats.
The History Of Ecotourism
The term ecotourism traces its history back to the late twentieth century. It is believed that ecotourism was first recorded in 1982 after the word ecotour which was recorded in 1973. While ecotourism refers to tourism in areas that are of ecological interest for purposes of conserving the environment, ecotour refers to a visit to areas that are of ecological interest for purposes of education. However, there are some accounts that the term ecotourism had been used earlier than 1970s. Some say that Claus-Dieter Hetzer, an adventurer and academician from Berkeley, California, was the first person who supposedly came up with the word ecotourism in 1965 and conducted the first ecotours during the early 1970s in the Yucatán.
Benefits Of Ecotourism
An ecotourist is different from a regular tourist in the sense that they are more mindful of their surroundings and they help contribute to the sustainability of natural environments. Ecotourism is beneficial because it promotes water conservation, recycling, and energy efficiency together with the development of economic opportunities for the local communities living in such areas. Other benefits include the potential to spread environmental awareness to the rest of the world, respecting the cultures of different people, protecting the ecosystem and the conservation of both cultural and biological diversities which go hand in hand with supporting democratic movements and human rights.
Ecotourism And Economy
Ecotourism is not only a marginal activity used in the financing of environmental protection but also a significant industry that boosts the national economy of many countries. Ecotourism in countries like Ecuador, Madagascar, Costa Rica, Kenya, Nepal and territories such as Antarctica represent an important sector of the economic activity and gross domestic product (GDP). Due to the confusion of ecotourism and tourism, there have been moves to establish international and national programs for accrediting ecotourism. However, the process of accreditation might be controversial. There have been national ecotourism certification programs established in different countries where ecotourism is popular such as Kenya, Costa Rica, and Australia.
More in Travel

13 Most Underrated Towns In New York To Take A Trip To

Tales in Transit: The Twists & Turns of World Travel

13 Most Underrated Towns In Massachusetts To Take A Trip To

9 Most Underrated Towns In Washington To Take A Trip To

Riding The Rails Across Europe: A Haphazard Adventure
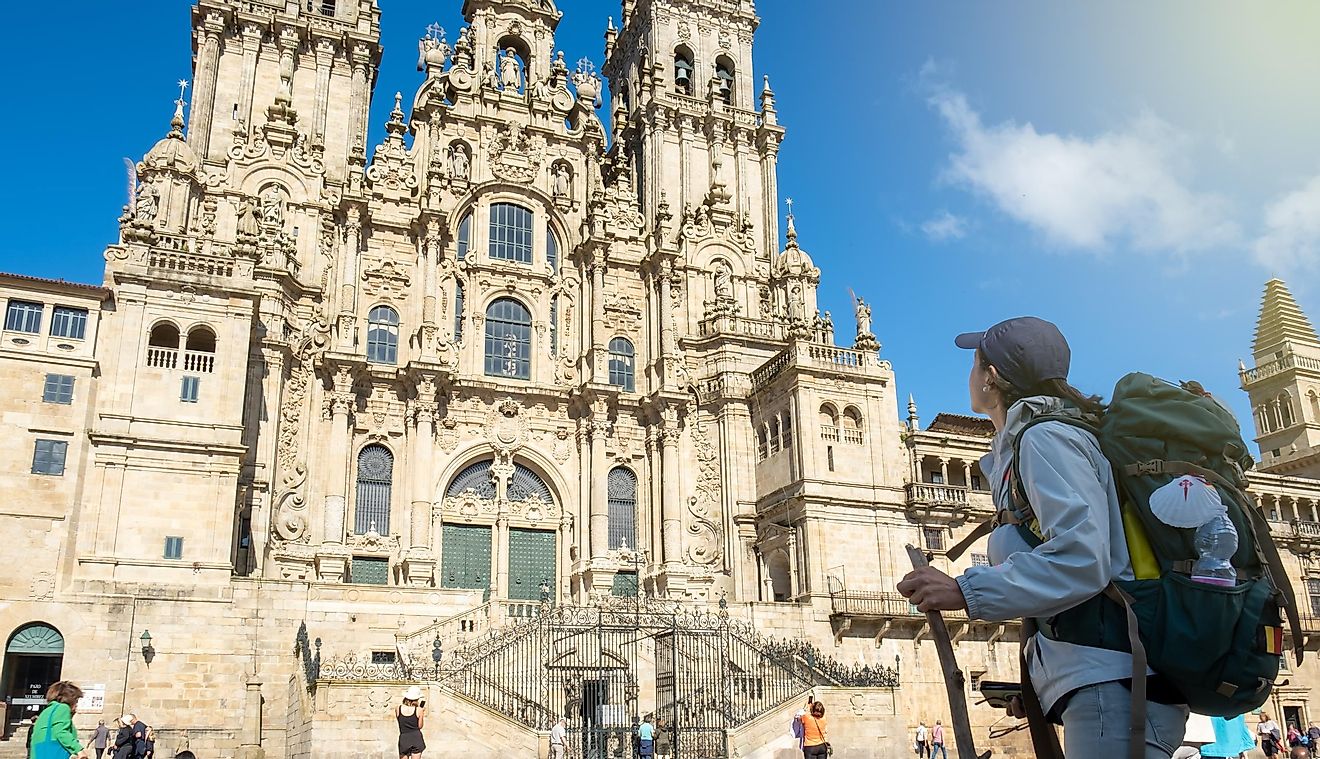

An American's Guide for the Camino de Santiago
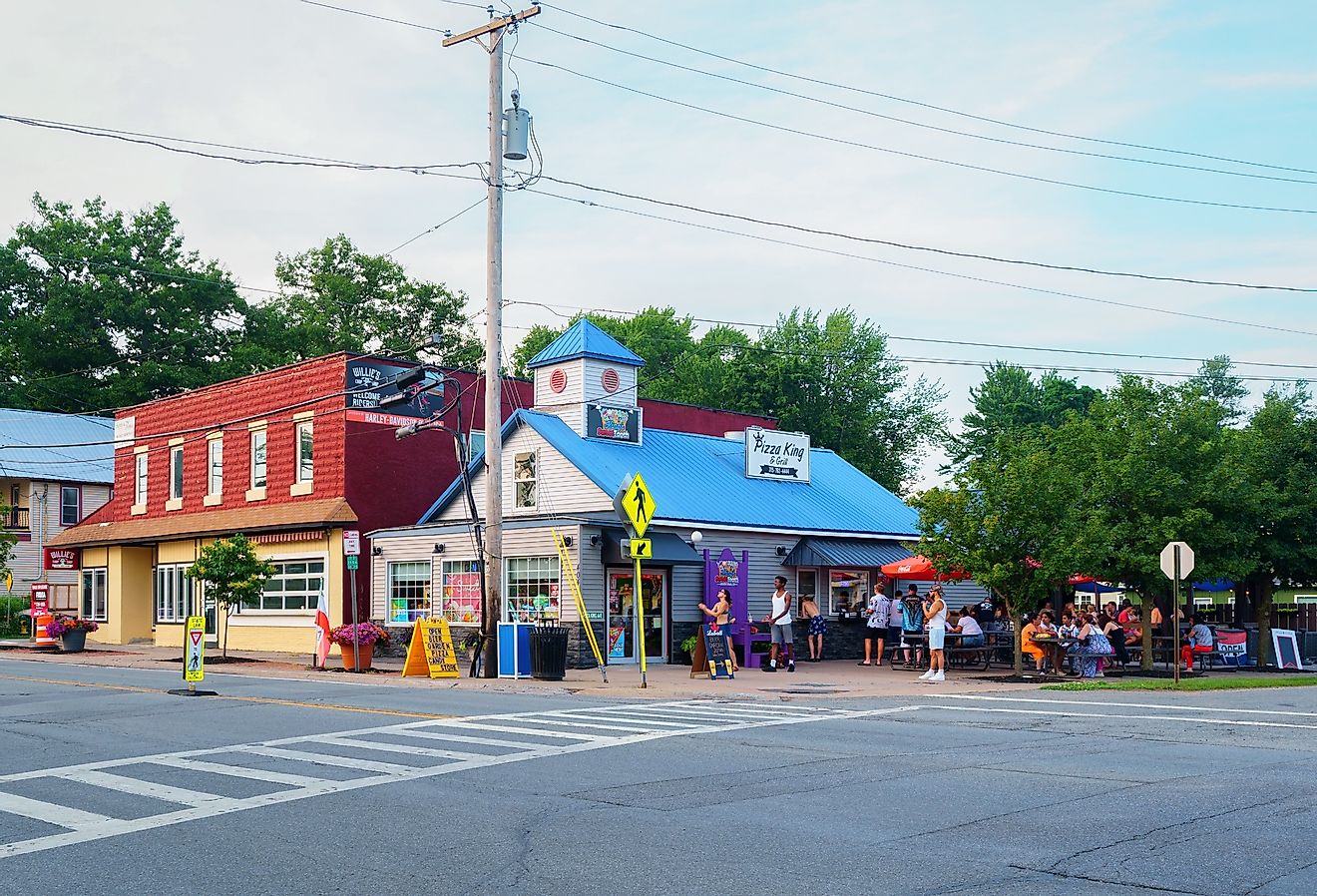

13 Most Underrated Towns In Upstate New York To Take A Trip To
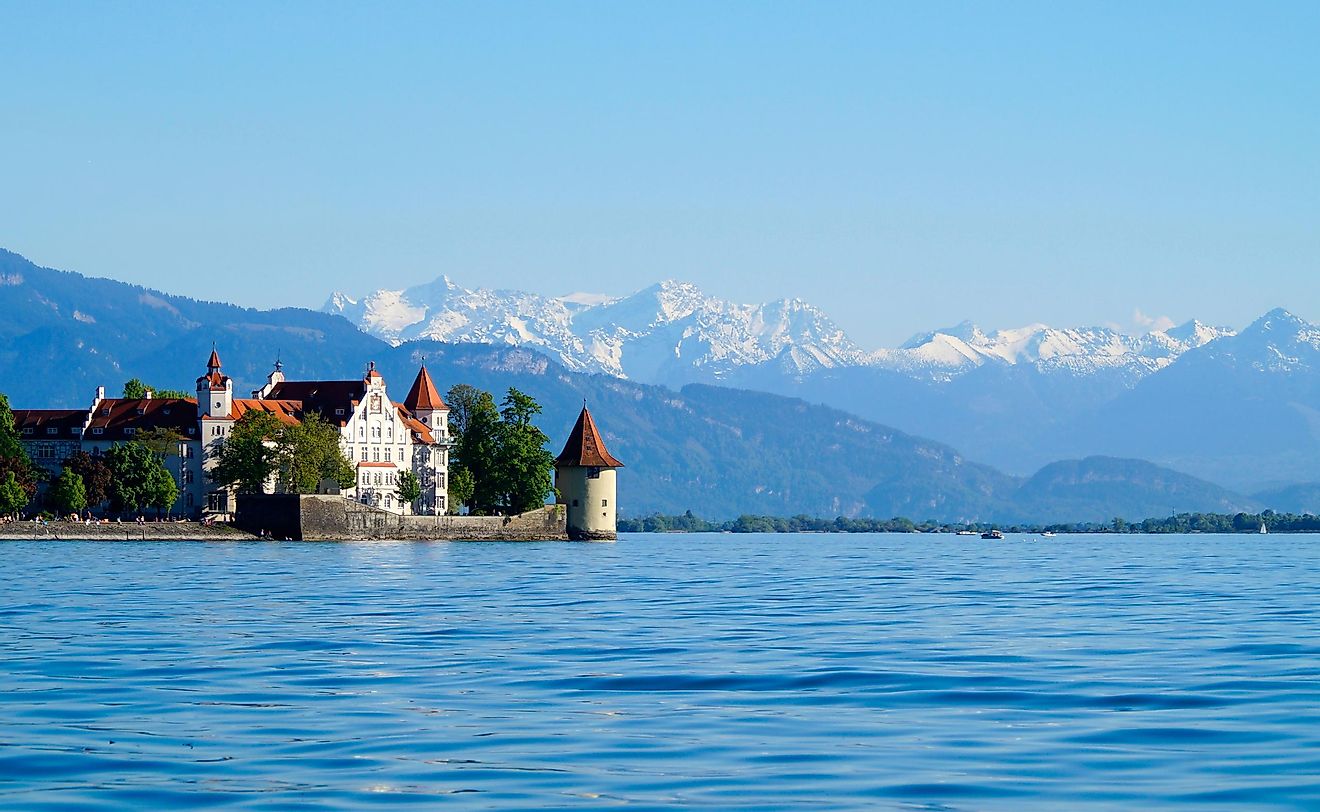

Explore The Most Charming Spots To Visit Around Lake Constance
Advertisement
Ecotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends
- Published: 21 February 2022
- Volume 25 , pages 2977–3003, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
- Lishan Xu 1 , 2 ,
- Changlin Ao ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8826-7356 1 , 3 ,
- Baoqi Liu 1 &
- Zhenyu Cai 1
19k Accesses
21 Citations
Explore all metrics
With the increasing attention and awareness of the ecological environment, ecotourism is becoming ever more popular, but it still brings problems and challenges to the sustainable development of the environment. To solve such challenges, it is necessary to review literature in the field of ecotourism and determine the key research issues and future research directions. This paper uses scientometrics implemented by CiteSpace to conduct an in-depth systematic review of research and development in the field of ecotourism. Two bibliographic datasets were obtained from the Web of Science, including a core dataset and an expanded dataset, containing articles published between 2003 and 2021. Our research shows that ecotourism has been developing rapidly in recent years. The research field of ecotourism spans many disciplines and is a comprehensive interdisciplinary subject. According to the research results, the evolution of ecotourism can be roughly divided into three phases: human disturbance, ecosystem services and sustainable development. It could be concluded that it has entered the third stage of Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline. The research not only identifies the main clusters and their advance in ecotourism research based on high impact citations and research frontier formed by citations, but also presents readers with new insights through intuitive visual images.
Similar content being viewed by others
Three pillars of sustainability: in search of conceptual origins
Ben Purvis, Yong Mao & Darren Robinson
Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism
Qadar Bakhsh Baloch, Syed Naseeb Shah, … Asia Umar Khan

Anthropocentrism: More than Just a Misunderstood Problem
Helen Kopnina, Haydn Washington, … John J Piccolo
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Ecotourism, which has appeared in academic literature since the late 1980s, is a special form of nature-based tourism that maintains the well-being of the local community while protecting the environment and provides tourists with a satisfying nature experience and enjoyment (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1996 ; Higgins, 1996 ; Orams, 1995 ). With years of research and development, ecotourism has risen to be a subject of investigation in the field of tourism research (Weaver & Lawton, 2007 ). In 2002, the United Nations declared it the International Year of Ecotourism (IYE), and the professional Journal of Ecotourism was established in the same year.
With the progress and maturity of ecotourism as an academic research field, countless scholars have put forward standards and definitions for ecotourism (Sirakaya et al., 1999 ; Wight, 1993 ). The main objectives of ecotourism emphasize long-term sustainable development (Whitelaw et al., 2014 ), including the conservation of natural resources, the generation of economic income, education, local participation and the promotion of social benefits such as local economic development and infrastructure (Ardoin et al., 2015 ; Coria & Calfucura, 2012 ; Krüger, 2005 ; Oladeji et al., 2021 ; Ross & Wall, 1999 ; Valdivieso et al., 2015 ). It can also boost rural economies and alleviate poverty in developing countries (Snyman, 2017 ; Zhong & Liu, 2017 ).
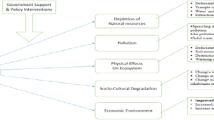
With unrestricted increasing attention to the ecological environment and the improvement of environmental awareness, ecotourism is becoming ever more prevalent, and the demand for tourism is increasing year by year (CREST, 2019 ). This increase, however, leads to a number of environmental, social and economic challenges in the development of ecotourism. For example, due to the low public awareness of ecotourism, the increase in tourists has brought a series of negative impacts on the local ecological environment, culture and economy, including disrespect for local culture and environmental protection, as well as more infrastructure construction and economic burden to meet the needs of tourists (Ahmad et al., 2018 ; Chiu et al., 2014 ; Shasha et al., 2020 ; Xu et al., 2020 ). Such challenges and contradictions are urgent problems to be tackled by the sustainable development of ecotourism. Especially against the backdrop of the current pandemic, tourism has experienced a severe blow, but climate change and other environmental issues have not been improved (CREST, 2020 ). In this context, facing these challenges and difficulties, it is essential to re-examine the future development path of ecotourism, to explore how government agencies can formulate appropriate management policies while preserving the environment and natural resources to support sustainable tourism development. Accordingly, it is necessary to consult literature in the field of ecotourism to understand the research progress and fundamental research issues, to identify challenges, suitable methods and future research direction of ecotourism.
Some previous reviews of ecotourism offer a preview of research trends in this rapidly developing area. Weaver and Lawton ( 2007 ) provide a comprehensive assessment of the current state and future progress of contemporary ecotourism research, starting with the supply and demand dichotomy of ecotourism, as well as fundamental areas such as quality control, industry, external environment and institutions. Ardoin et al. ( 2015 ) conducted a literature review, analyzing the influence of nature tourism on ecological knowledge, attitudes, behavior and potential research into the future. Niñerola et al. ( 2019 ) used the bibliometric method and VOSviewer to study the papers on sustainable development of tourism in Scopus from 1987 to 2018, including literature landscape and development trends. Shasha et al. ( 2020 ) used bibliometrics and social network analysis to review the research progress of ecotourism from 2001 to 2018 based on the Web of Science database using BibExcel and Gephi and explored the current hot spots and methods of ecotourism research. These reviews have provided useful information for ecotourism research at that time, but cannot reflect the latest research trends and emerging development of ecotourism either of timeliness, data integrity, research themes or methods.
This study aims to reveal the theme pattern, landmark articles and emerging trends in ecotourism knowledge landscape research from macro- to micro-perspectives. Unlike previous literature surveys, from timeliness, our dataset contains articles published between 2003 and 2021, and it will reveal more of the trends that have emerged over the last 3 years. Updating the rapidly developing literature is important as recent discoveries from different areas can fundamentally change collective knowledge (Chen et al., 2012 , 2014a ). To ensure data integrity, two bibliographic datasets were generated from Web of Science, including a core dataset using the topic search and an expanded dataset using the citation expansion method, which is more robust than defining rapidly growing fields using only keyword lists (Chen et al., 2014b ). And from the research theme and method, our review focuses on the area of ecotourism and is instructed by a scientometric method conducted by CiteSpace, an analysis system for visualizing newly developing trends and key changes in scientific literature (Chen et al., 2012 ). Emerging trends are detected based on metrics calculated by CiteSpace, without human intervention or working knowledge of the subject matter (Chen et al., 2012 ). Choosing this approach can cover a more extensive and diverse range of related topics and ensure repeatability of analysis with updated data (Chen et al., 2014b ).
In addition, Shneider’s four-stage theory will be used to interpret the results in this review. According to Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline (Shneider, 2009 ), the development of a scientific discipline is divided into four stages. Stage I is the conceptualization stage, in which the objects and phenomena of a new discipline or research are established. Stage II is characterized by the development of research techniques and methods that allow researchers to investigate potential phenomena. As a result of methodological advances, there is a further understanding of objects and phenomena in the field of new subjects at this stage. Once the techniques and methods for specific purposes are available, the research enters Stage III, where the investigation is based primarily on the application of the new research method. This stage is productive, in which the research results have considerably enhanced the researchers’ understanding of the research issues and disclosed some unknown phenomena, leading to interdisciplinary convergence or the emergence of new research directions or specialties. The last stage is Stage IV, whose particularity is to transform tacit knowledge into conditional knowledge and generalized knowledge, so as to maintain and transfer the scientific knowledge generated in the first three stages.
The structure of this paper is construed as follows. The second part describes the research methods employed, the scientometric approach and CiteSpace, as well as the data collection. In the third part, the bibliographic landscape of the core dataset is expounded from the macroscopic to the microscopic angle. The fourth part explores the developments and emerging trends in the field of ecotourism based on the expanded dataset and discusses the evolution phase of ecotourism. The final part is the conclusion of this study. Future research of ecotourism is prospected, and the limitations of this study are discussed.
2 Methods and data collection
2.1 scientometric analyses and citespace.
Scientometrics is a branch of informatics that involves quantitative analysis of scientific literature in order to capture emerging trends and knowledge structures in a particular area of study (Chen et al., 2012 ). Science mapping tools generate interactive visual representations of complex structures by feeding a set of scientific literature through scientometrics and visual analysis tools to highlight potentially important patterns and trends for statistical analysis and visualization exploration (Chen, 2017 ). At present, scientometrics is widely used in many fields of research, and there are also many kinds of scientific mapping software widely used by researchers and analysts, such as VosViewer, SCI2, HistCite, SciMAT, Gephi, Pajek and CiteSpace (Chen, 2011 , 2017 ; Chen et al., 2012 ).
Among these tools, CiteSpace is known for its powerful literature co-citation analysis, and its algorithms and features are constantly being refined as it continues to evolve. CiteSpace is a citation visual analysis software developed under the background of scientometrics and data visualization to analyze the basics that are included in scientific analysis (Chen, 2017 ; Chen et al., 2012 ). It is specialized designed to satisfy the need for systematic review in rapidly changing complicated areas, particularly with the ability to identify and explain emerging trends and transition patterns (Chen et al., 2014a ). It supports multiple types of bibliometric research, such as collaborative network analysis, co-word analysis, author co-citation analysis, document co-citation analysis, and temporal and spatial visualization (Chen, 2017 ). Currently, CiteSpace has been extensively used in more than 60 fields, including computer science, information science, management and medicine (Abad-Segura et al., 2019 ; Chen, 2017 ).
In this paper, we utilize CiteSpace (5.8.R1) to analyze acquired bibliographies of ecotourism to study emerging trends and developments in this field. From macro to micro, from intuitive to complex, from whole to part and from general to special, the writing ideas are adopted. Figure 1 presented the specific research framework of this study.
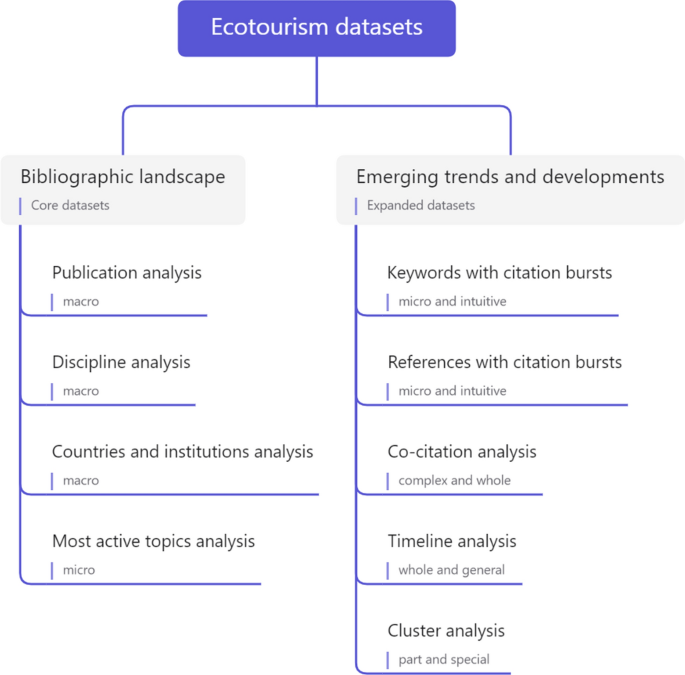
The research framework of this study
2.2 Data collection
Typical sources of scientific literature are Web of Science, Scopus and Google Scholar. Considering the quantity and quality of data, the Web of Science database was expected to provide the original data in this research. In order to comprehend the research status and development trends of ecotourism, this study systematically reviewed the ecotourism literature collected on the Web of Science Core Collection. The Web of Science Core Collection facilitates access to the world’s leading scholarly journals, books and proceedings of conferences in the sciences, social sciences, art, and humanities, as well as access to their entire citation network. It mainly includes Science Citation Index Expanded from 2003 to current and Social Sciences Citation Index from 2004 to present. Therefore, the data obtained in this study are from 2003 and were consulted on June 3, 2021.
In the process of data retrieval, it is frequently confronted with the choice between recall rate and precision rate. To address the problem of low recall rate in keyword or topic retrieval, Chen et al. ( 2014a , b ) expanded the retrieval results through ‘citation expansion’ and ‘comprehensive topic search’ strategies. However, when the recall rate is high, the accuracy rate will decrease correspondingly. In practical standpoint, instead of refining and cleaning up the original search results, a simpler and more efficient way is to cluster or skip these unrelated branches. Priority should be placed on ensuring recall rate, and data integrity is more important than data for accuracy. Therefore, two ecotourism documentation datasets, the core dataset and the expanded dataset, were obtained from the Web of Science by using comprehensive topic search and citation expansion method. The latter approach has been proved more robust than using keyword lists only to define fast-growing areas (Chen et al., 2014b ). A key bibliographic landscape is generated based on the core dataset, followed by more thorough research of the expanded dataset.
2.2.1 The core dataset
The core dataset was derived through comprehensive subject retrieval in Web of Science Core Collection. The literature type was selected as an article or review, and the language was English. The period spans 2003 to 2021. The topic search query is composed of three phrases of ecotourism: ‘ ecotour* ’ OR ‘ eco-tour* ’ OR ‘ ecological NEAR/5 tour* ’. The wildcard * is used to capture related variants of words, for example, ecotour, ecotourism, ecotourist and ecotourists. The related records that are requested include finding these terms in the title, abstract or keywords. The query yielded 2991 original unique records.

2.2.2 The expanded dataset
The expanded dataset includes the core dataset and additional records obtained by reference link association founded on the core dataset. The principle of citation expansion is that if an article cites at least one article in the core dataset, we can infer that it is related to the topic (Garfield, 1955 ). The expanded dataset is comprised of 27,172 unique records, including the core dataset and the articles that cited them. Both datasets were used for the following scientometrics analysis.
3 Bibliographic landscape based on the core dataset
The core dataset consists of a total of 2991 literature from 2003 to 2021. This study utilized the core dataset to conduct an overall understanding of the bibliographic landscape in the field of ecotourism.
3.1 Landscape views of core dataset
The distribution of the yearly publication of bibliographic records in the core and expanded datasets is presented in Fig. 2 . It can be observed that the overall number of ecotourism-related publications is on the rise, indicating that the scholarly community is increasingly interested in ecotourism. After 2018, the growth rate increased substantially. And in 2020, the number of publications in the expanded dataset is close to 5000, almost double that of 2017 and 5 times that of 2011. This displays the rapid development of research in the field of ecotourism in recent years, particularly after 2018, more and more researchers began to pay attention to this field, which also echoes the trend of global tourism development and environmental protection. With the increase in personal income, tourism has grown very rapidly, and with it, tourism revenue and tourist numbers, especially in developing states. For instance, the number of domestic tourists in China increased from 2.641 billion in 2011 to 6.06 billion in 2019, and tourism revenue increased from 1930.5 billion RMB in 2011 to 5725.1 billion RMB in 2019 (MCT, 2021 ). However, due to the lack of effective management and frequent human activities, the rapid development of tourism has led to various ecological and environmental problems, which require corresponding solutions (Shasha et al., 2020 ). This has played an active role in promoting the development of ecotourism and triggered a lot of related research. In addition, since 2005, the expanded dataset has contained numerous times as many references as the core dataset, demonstrating the importance of using citation expansion for literature retrieval in scientometric review studies.
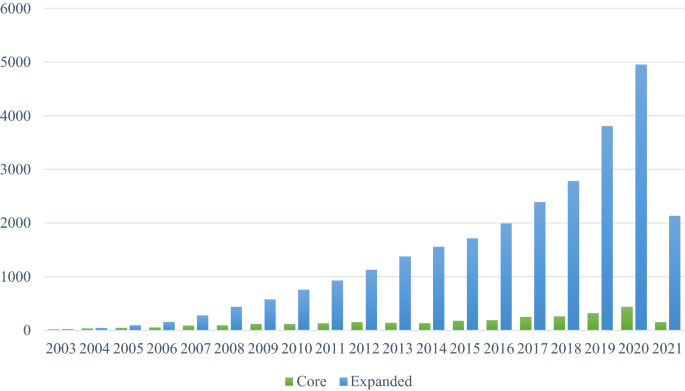
The distribution of bibliographic records in core and expanded dataset. Note The data were consulted on June 3, 2021
The data were consulted on June 3, 2021
The dual-map overlay of scientific map literature as Fig. 3 shows, against the background of global scientific map from more than 10,000 journals covered by Web of Science, represents the distribution and connections on research bases and application fields across the entire dataset of the research topics (Chen & Leydesdorff, 2014 ). Colored lines are citation links, and numbered headings are cluster labels. On the left side is the journal distribution which cites literature, regarding the field application of ecotourism, mainly covers multiple disciplines such as 3. Ecology, Earth, Marine, 6. Psychology, Education, Health, 7. Veterinary, Animal Science and 10. Economics, Economic and Political. On the right side is the distribution of journals of cited literature, representing the research basis of ecotourism. As can be observed from the figure, ecotourism research is based on at least five disciplines on the right, including 2. Environmental, Toxicology, Nutrition, 7. Psychology, Education, Social, 8. Molecular, Biology, Genetics, 10. Plant, Ecology, Zoology and 12. Economics, Economic, Political. It can be viewed that the research field of ecotourism spans multiple disciplines and is a comprehensive and complex subject. The dual-map overlay provides a global visualization of literature growth of the discipline level.
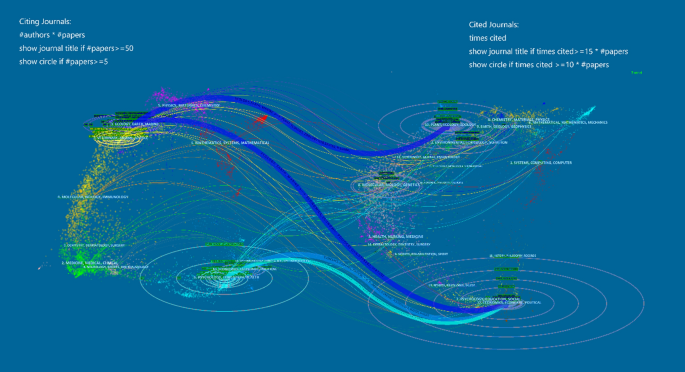
A dual-map overlay of ecotourism literature
The total number of papers issued by a country or an institution reflects its academic focus and overall strength, while centrality indicates the degree of academic cooperation with others and the influence of published papers. The top 15 countries and institutions for the number of ecotourism papers published from 2003 to 2021 are provided in Table 1 . Similar to the study of Shasha et al. ( 2020 ), the ranking of the top six countries by the number of publications remains unchanged. As can be seen from the table, the USA ranks first in the world, far ahead in both the number of publications and the centrality. China ranks second in global ecotourism publications, followed by Australia, England, South Africa and Canada. While the latest data show that Taiwan (China), Turkey and South Korea appear on the list. Overall, the top 15 countries with the most publications cover five continents, containing a number of developed and developing, which shows that ecotourism research is receiving global attention. In terms of international academic cooperation and impact of ecotourism, Australia and England share second place, Italy and France share fourth place, followed by South Africa and Spain. China’s centrality is relatively low compared to the number of publications, ranking eighth. Academic cooperation between countries is of great significance. Usually, countries with high academic publishing level cooperate closely due to similar research interests. International academic cooperation has enhanced each other’s research capacity and promoted the development of ecotourism research. Therefore, although some countries have entered this list with the publication number, they should attach importance to increase academic cooperation with other countries and improving the international influence of published papers.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences and its university are the most prolific when it draws to institutions’ performance. It is the most important and influential research institute in China, especially in the field of sustainable development science. Australia has four universities on the list, with Griffith University and James Cook University in second and third place. USA also includes four universities, with the University of Florida in fourth place. South Africa, a developing country, gets three universities, with the University of Cape Town and the University of Johannesburg fifth and sixth, respectively. In comparison with previous studies (Shasha et al., 2020 ), Iran and Mexico each have one university in the ranking, replacing two universities in Greece, which means that the importance and influence of developing countries in the field of ecotourism is gradually rising. Based on the above results, it can be summarized that the USA, China, Australia and South Africa are relatively active countries in the field of ecotourism, and their development is also in a relatively leading position.
3.2 Most active topics
The foam tree map and the pie chart of the focal topics of ecotourism based on the core dataset generated by Carrot2 through the title of each article is illustrated in Fig. 4 . Developing and developed, case study, protected areas, sustainable tourism, tourism development and developing ecotourism are leading topics in the field of ecotourism research, as well as specific articles under the main topics. The lightweight view generated by Carrot2 provides a reference for the research, and then, co-word analysis is employed to more specifically reflect the topics in the research field.
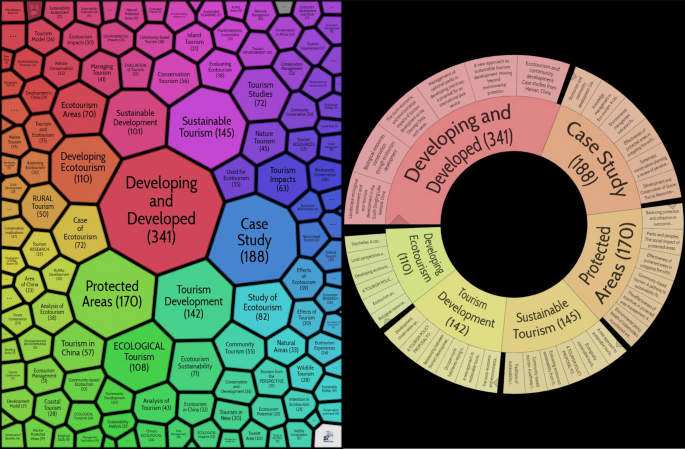
Foam tree map and pie chart of major topics on ecotourism
The topics covered by ecotourism could be exposed by the keywords of the articles in the core dataset. Figure 5 displays the keywords analysis results generated based on the core dataset. From the visualization results in the figure, it can infer that ecotourism, conservation, tourism, management, protected area, impact, biodiversity, sustainability, national park and community are the ten most concerned topics. Distinct colors set out at the time of co-citation keywords first appear, and yellow is generated earlier than red. In addition, Fig. 5 can also reflect the development and emerging topics in the research field, such as China, Mexico, South Africa and other hot countries for ecotourism research; ecosystem service, economic value, climate change, wildlife tourism, rural tourism, forest, marine protected area and other specific research directions; valuation, contingent valuation, choice experiment and other research methods; willingness to pay, preference, benefit, perception, attitude, satisfaction, experience, behavior, motivation, risk, recreation and other specific research issues.
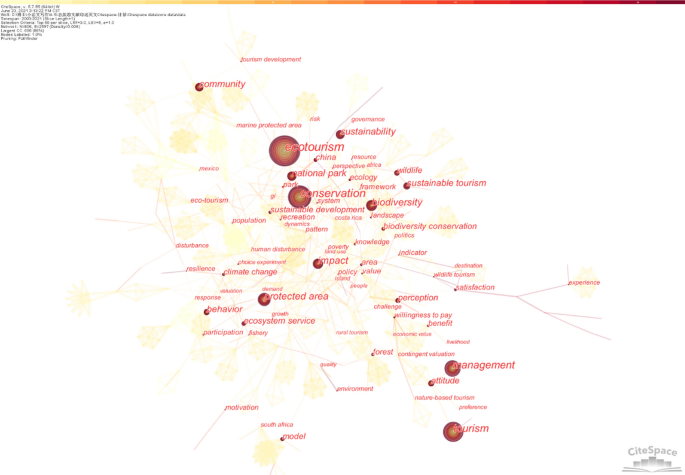
A landscape view of keywords based on the core dataset
4 Emerging trends and developments based on the expanded dataset
The expanded dataset, consisting of 27,172 records, is approximately nine times larger than the core dataset. This research applies the expanded dataset to profoundly explore the emerging trends and developments of ecotourism.
4.1 Keywords with citation bursts
Detection of citation bursts can indicate both the scientific community’s interest in published articles and burst keywords as an indicator of emerging tendencies. Figure 6 displays the top 30 keywords with the strongest citation bursts in the expanded dataset. Since 2003, a large number of keywords have exploded. Among them, the strongest bursts include ecotourism, bird, disturbance, reserve, Africa, challenge, sustainable development and strategy. Keywords with citation burst after 2017 are experience, challenge, sustainable development, willingness to pay, perspective, strategy, quality and satisfaction, which have continued to this day. The results indicate dynamic development and emerging trends in research hotspots in the field of ecotourism.
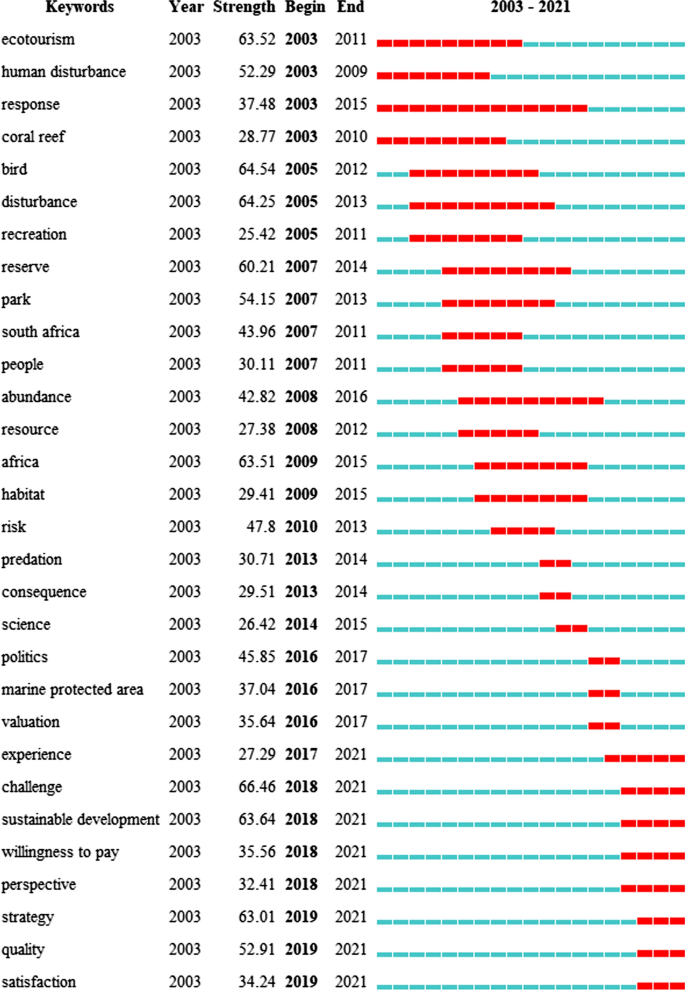
Top 30 keywords with the strongest citation bursts
4.2 References with citation bursts
Figure 7 sets out the top 30 references in the expanded dataset with citation bursts. The articles with the fastest growing citations can also contribute to describe the dynamics of a field. References with high values in strength column are important milestones of ecotourism research. The two articles with strong citation bursts prior to 2010 focused on the human impact on the environment and animals. West et al. ( 2006 ) discussed the relationship between parks and human beings and the social impact of protected areas, and Köndgen et al. ( 2008 ) studied the decline of endangered great apes caused by a human pandemic virus. The paper with the strongest citation burst in the entire expanded dataset was released by Fairhead et al. ( 2012 ), which looked at ‘green grabbing,’ the appropriation of land and resources for environmental purposes. Milcu et al. ( 2013 ) conducted a semi-quantitative review of publications dealing with cultural ecosystem services with the second strongest citation burst, which concluded that the improvement of the evaluation method of cultural ecosystem service value, the research on the value of cultural ecosystem service under the background of ecosystem service and the clarification of policy significance were the new themes of cultural ecosystem service research. In addition, many articles with citation burst discussed the evaluation method of ecosystem services value (Costanza et al., 2014 ; Groot et al., 2010 ), the evaluation of cultural ecosystem service value (Plieninger et al., 2013 ) and its role in ecosystem service evaluation (Chan et al., 2012 ; Chan, Guerry, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Daniel et al., 2012 ). The most fresh literature with strong citation burst is the article of D’Amato et al. ( 2017 ) published in the Journal of Cleaner Production, which compared and analyzed sustainable development avenues such as green, circular and bio economy. In addition, it is worthwhile noting the use of R in ecotourism, with the persuasive citation burst continuing from 2012 to the present, as indicated by the orange arrow in Fig. 7 .
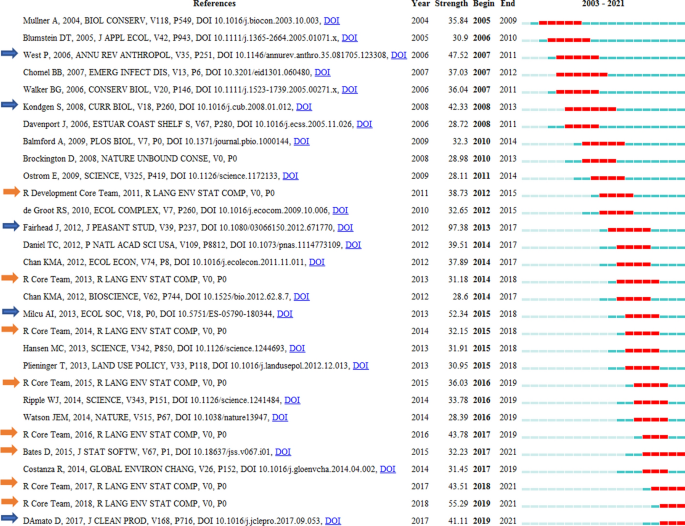
Top 30 references with the strongest citation bursts
4.3 Landscape view of co-citation analysis
The landscape view of co-citation analysis of Fig. 8 is generated based on the expanded dataset. Using g -index ( k = 25) selection criteria in the latest edition of CiteSpace, an annual citation network was constructed. The final merged network contained 3294 links, 2122 nodes and 262 co-citation clusters. The three largest linked components cover 1748 connected nodes, representing 82% of the entire network. The modularization degree of the synthetic network is 0.8485, which means that co-citation clustering can clearly define each sub-field of ecotourism. Another weighted mean silhouette value of the clustering validity evaluation is 0.9377, indicating that the clustering degree of the network is also very superior. The harmonic mean value amounts to 0.8909.
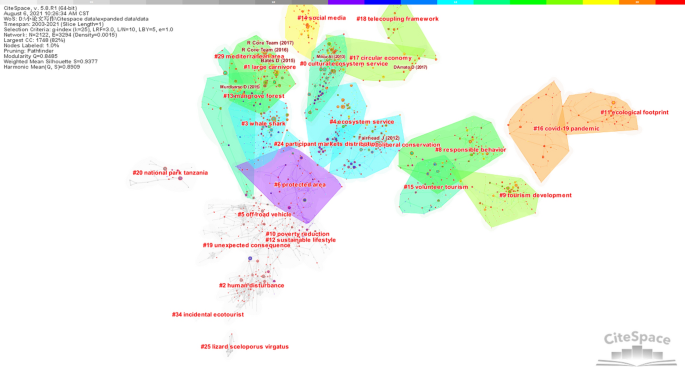
A landscape view of the co-citation network based on the expanded dataset
In the co-citation network view, the location of clusters and the correlation between clusters can show the intellectual structure in the field of ecotourism, so that readers can obtain an overall understanding of this field. The network falls into 25 co-citation clusters. The tags for each cluster are generated founded on the title, keywords and abstract of the cited article. Color-coded areas represent the time of first appeared co-citation links, with gray indicating earlier and red later. The nodes in the figure with red tree rings are references to citation bursts.
4.4 Timeline view
In order to further understand the time horizon and study process of developing evolution on clusters, after the generation of co-citation cluster map, the Y -axis is cluster number and the year of citation publication is X -axis, so as to obtain the timeline view of the co-citation network, shown as Fig. 9 . Clusters are organized vertically from largest to smallest. The color curve represents co-citation link coupled with corresponding color year, with gray representing earlier and red representing newer. Larger nodes and nodes with red tree rings indicate high citation or citation burst. The three most cited references of the year demonstrate below each node, in vertical order from least to most.
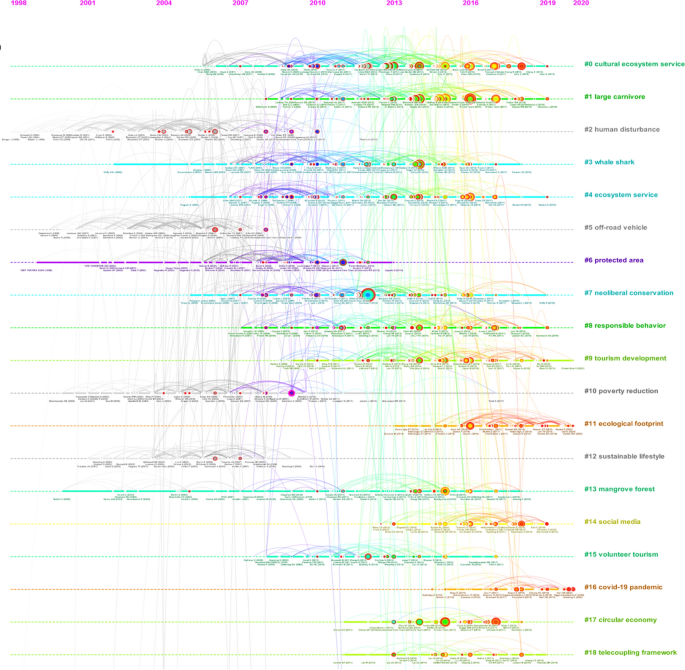
A timeline visualization of the largest clusters
The timeline view provides a reasonably instinctual and insightful reference to understand the evolutionary path of every subdomain. Figure 9 shows 19 clusters ranging from #0 to #18, with #0 being the largest cluster. As can be seen from the figure, the sustainability and activeness of each cluster are contrasting. For example, the largest cluster has been active since 2006, while the gray and purple clusters are no longer active.
4.5 Major clusters
Taking clustering as a unit and analyzing at the level of clustering, specifically selecting large or new type clustering, is the foothold of co-citation analysis, which can help to understand the principal and latest research fields related to ecotourism. Table 2 displays a summary of the foremost 19 clusters, the first nine of which are all over 100 in size. The silhouette score of all clusters is greater than 0.8, indicating that the homogeneity of each cluster is high. The mean year is the average of the publication dates of references in the cluster. By combining the results in Table 2 , Figs. 8 and 9 , it can be observed that the five largest clusters are #0 cultural ecosystem services, #1 large carnivore, #2 human disturbance, #3 whale shark and #4 ecosystem service. A recent topic is cluster #16 COVID-19 pandemic. #11 Ecological footprint and #14 social media are two relatively youthful fields.
The research status of a research field can be demonstrated by its knowledge base and research frontier. The knowledge base consists of a series of scholarly writing cited by the corresponding article, i.e., cited references, while the research frontier is the writing inspired by the knowledge base, i.e., citing articles. Distinct research frontiers may come from the same knowledge base. Consequently, each cluster is analyzed based on cited references and citing articles. The cited references and citing articles of the five largest clusters are shown in Online Appendix A. Fig a) lists the 15 top cited references with the highest Σ (sigma) value in the cluster, where Σ value indicates that the citation is optimal in terms of the comprehensive performance of structural centrality and citation bursts. Fig b) shows the major citing articles of cluster. The citation behavior of these articles determines the grouping of cited literature and thus forms the cluster. The coverage is the proportion of member citations cited by citing articles.
4.6 Phase evolution research
Through the above analysis of the core dataset and the expanded dataset of ecotourism, we can see the development and evolution of the research field of ecotourism. The research process of ecotourism has gone through several stages, and each stage has its strategic research issues. Research starts with thinking about the relationship between humans and nature, moves to study it as a whole ecosystem, and then explores sustainable development. Hence, the evolution of ecotourism can be roughly parted into three phases.
4.6.1 Phase I: Human disturbance research stage (2003–2010)
This phase of research concentrates on the influence of human activities such as ecotourism on the environment and animals. Representative keywords of this period include ecotourism, human disturbance, response, coral reef, bird, disturbance, recreation, reserve, park, South Africa and people. Representative articles are those published by West et al. ( 2006 ) and Köndgen et al. ( 2008 ) of human impact on the environment and animals. The representative clustering is #2 human disturbance, which is the third largest one, consisting of 130 cited references from 1998 to 2012 with the average year of 2004. This cluster has citation bursts between 2002 and 2010 and has been inactive since then. As showed in Fig S3 a) and b), the research base and frontier are mainly around the impact of human disturbances such as ecotourism on biology and the environment (McClung et al., 2004 ). And as showed in Fig. 8 and Fig. 9 , clusters closely related to #2 belong to this phase and are also no longer active, such as #5 off-road vehicle, #6 protected area, #10 poverty reduction and #12 sustainable lifestyle.
4.6.2 Phase II: Ecosystem services research stage (2011–2015)
In this stage, the content of ecotourism research is diversified and exploded. The research is not confined to the relationship between humans and nature, but begins to investigate it as an entire ecosystem. In addition, some specific or extended areas began to receive attention. Typical keywords are abundance, resource, Africa, risk, predation, consequence and science. The most illustrative papers in this stage are Fairhead et al. ( 2012 )’s discussion on green grabbing and Milcu et al. ( 2013 )’s review on cultural ecosystem services. Other representative papers in this period focused on the evaluation methods of ecosystem service value and the role of cultural ecosystem service in the evaluation of ecosystem service value. Most of the larger clusters in the survey erupted at this stage, including #0 cultural ecosystem services, #1 large carnivore, #3 whale shark, #4 ecosystem services. Some related clusters also belong to this stage, such as #7 neoliberal conservation, #8 responsible behavior, #9 tourism development, #13 mangrove forest, #15 volunteer tourism, #17 circular economy and #18 telecoupling framework.
Cluster #0 cultural ecosystem services are the largest cluster in ecotourism research field, containing 157 cited references from 2006 to 2019, with the mean year being 2012. It commenced to have the citation burst in 2009, with high cited continuing until 2019. Cultural ecosystem services are an essential component of ecosystem services, including spiritual, entertainment and cultural benefits. Thus, in Fig. 8 , the overlap with #4 ecosystem services can obviously be seen. In Cluster #0, many highly cited references have discussed the trade-offs between natural and cultural ecosystem services in ecosystem services (Nelson et al., 2009 ; Raudsepp-Hearne et al., 2010 ) and the important role of cultural ecosystem services in the evaluation of ecosystem services value (Burkhard et al., 2012 ; Chan, Guerry, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Fisher et al., 2009 ; Groot et al., 2010 ). As non-market value, how to evaluate and quantify cultural ecosystem services is also an important issue (Hernández-Morcillo et al., 2012 ; Milcu et al., 2013 ; Plieninger et al., 2013 ). Besides, the exploration of the relationship among biodiversity, human beings and ecosystem services is also the focus of this cluster research (Bennett et al., 2015 ; Cardinale et al., 2012 ; Díaz et al., 2015 ; Mace et al., 2012 ). The citing articles of #0 indicate the continued exploration of the connotation of cultural ecosystem services and their value evaluation methods (Dickinson & Hobbs, 2017 ). It is noteworthy that some articles have introduced spatial geographic models (Havinga et al., 2020 ; Hirons et al., 2016 ) and social media methods (Calcagni et al., 2019 ) as novel methods to examine cultural ecosystem services. In addition, the link and overlap between #0 cultural ecosystem service and #17 circular economy cannot be overlooked.
Ecosystem services relate to all the benefits that humans receive from ecosystems, including supply services, regulatory services, cultural services and support services. Research on cultural ecosystem services is based on the research of ecosystem services. It can be viewed in Fig. 9 that the research and citation burst in #4 was all slightly earlier than #0. Cluster #4 includes 118 references from 2005 to 2019, with an average year of 2011. In its research and development, how to integrate ecosystem services into the market and the payment scheme to protect the natural environment is a significant research topic (Gómez-Baggethun et al., 2010 ). In Cluster #4, the most influential literature provides an overview of the payment of ecosystem services (PES) from theory to practice by Engel et al. ( 2008 ). Many highly cited references have discussed PES (Kosoy & Corbera, 2010 ; Muradian et al., 2010 ), including the effectiveness of evaluation (Naeem et al., 2015 ), social equity matters (Pascual et al., 2014 ), the suitability and challenge (Muradian et al., 2013 ), and how to contribute to saving nature (Redford & Adams, 2009 ). The cluster also includes studies on impact assessment of protected areas (Oldekop et al., 2016 ), protected areas and poverty (Brockington & Wilkie, 2015 ; Ferraro & Hanauer, 2014 ), public perceptions (Bennett, 2016 ; Bennett & Dearden, 2014 ) and forest ecosystem services (Hansen et al., 2013 ). The foremost citing articles confirm the dominant theme of ecosystem services, especially the in-depth study and discussion of PES (Muniz & Cruz, 2015 ). In addition, #4 is highly correlated with #7 neoliberal protection, and Fairhead et al. ( 2012 ), a representative article of this stage, belongs to this cluster.
As the second largest cluster, Cluster #1 contains 131 references from 2008 to 2019, with the median year of 2014. As Fig S2 a) shows, the highly cited literature has mainly studied the status and protection of large carnivores (Mace, 2014 ; Ripple et al., 2014 ), including the situation of reduction (Craigie et al., 2010 ), downgrade (Estes et al., 2011 ) and even extinction (Dirzo et al., 2014 ; Pimm et al., 2014 ), and the reasons for such results, such as tourist visits (Balmford et al., 2015 ; Geffroy et al., 2015 ) and the increase in population at the edge of the protected areas (Wittemyer et al., 2008 ). The conservation effects of protected areas on wildlife biodiversity (Watson et al., 2014 ) and the implications of tourist preference heterogeneity for conservation and management (Minin et al., 2013 ) have also received attention. It is worth noting that the high citation rate of a paper using R to estimate the linear mixed-effects model (Bates et al., 2015 ) and the use of R in this cluster. The relationship between biodiversity and ecotourism is highlighted by the representative citing articles in research frontier of this cluster (Chung et al., 2018 ).
Cluster #3 refers to marine predator, and as shown in Fig. 8 , which has a strong correlation with #1. A total of 125 references were cited from 2002 to 2018, with an average year of 2011. References with high citation in #3 mainly studied the extinction and protection of marine life such as sharks (Dulvy et al., 2014 ), as well as the economic value and ecological impact of shark ecotourism (Clua et al., 2010 ; Gallagher & Hammerschlag, 2011 ; Gallagher et al., 2015 ). The paper published by Gallagher et al. ( 2015 ) is both the highly cited reference and main citing article, mainly focusing on the impact of shark ecotourism. It is also noteworthy that #6 protected area, #13 mangrove forest and #29 Mediterranean areas are highly correlated with these two clusters (Fig. 8 ).
Moreover, some clusters are not highly correlated with other clusters, but cannot be neglected at this stage of research. Cluster #8 responsible behavior includes 107 citations with the average year 2013, and mainly studied environmentally responsible behaviors in ecotourism (Chiu et al., 2014 ). Cluster #9 tourism development contains 97 cited references with mean year of 2015, focusing on the impact of such factors as residents’ perception on tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Cluster #15 volunteer tourism consists of 52 citations, with an average year of 2011, which mainly considers the role of volunteer tourism in tourism development and sustainable tourism (Wearing & McGehee, 2013 ). Cluster #18 telecoupling framework has 26 cited references with the mean year being 2015, and the application of the new integrated framework of telecoupling Footnote 1 in ecotourism can be seen (Liu et al., 2015 ).
At this stage, it can be seen that the research field of ecotourism begins to develop in the direction of diversification, including the value evaluation and related research of ecosystem services and cultural ecosystem services, as well as the exploration of wild animals and plants, marine animals and plants and biodiversity. Neoliberal conservation, tourists’ responsible behavior, tourism development, volunteer tourism and circular economy are all explored. Some new research methods have also brought fresh air to this field, such as the introduction of spatial geographic models and social media methods, the discussion of economic value evaluation methods, the widespread use of R and the exploration of telecoupling framework. Therefore, from this stage, research in the field of ecotourism has entered the second stage of scientific discipline development (Shneider, 2009 ), featured by the use and evolution of research tools that can be used to investigate potential phenomena.
4.6.3 Phase III: Sustainable development research stage (2016 to present)
This stage of research continues to explore a series of topics of the preceding phase and further extends the research field on this basis. The keywords at this stage are politics, marine protected area and valuation. Some other keywords are still very active today, such as experience, challenge, sustainable development, willingness to pay, perspective, strategy, quality and satisfaction. The representative article is about sustainable development published by D'Amato et al. ( 2017 ), as shown in Fig. 8 belonging to #17 circular economy. The emerging clusters in this period are #11 ecological footprint, #14 social media and #16 COVID-19 pandemic. Cluster #11 contains 70 cited references from 2013 to 2020 with the mean year 2017. This clustering study mainly used the ecological footprint as an environmental indicator and socioeconomic indicators such as tourism to investigate the hypothesis of environmental Kuznets curve (Ozturk et al., 2016 ; Ulucak & Bilgili, 2018 ). Cluster #14 includes 52 cited references, with an average year of 2016. It can be seen that the introduction of social media data has added new color to research in the field of ecotourism, such as using social media data to quantify landscape value (Zanten et al., 2016 ) and to understand tourists’ preferences for the experience of protected areas (Hausmann et al., 2018 ), as well as from a spatial perspective using social media geo-tagged photos as indicators for evaluating cultural ecosystem services (Richards & Friess, 2015 ). As the latest and most concerned topic, cluster #16 contains 48 cited references, with mean year of 2018. This cluster mainly cites research on over-tourism (Seraphin et al., 2018 ) and sustainable tourism (Higgins-Desbiolles, 2018 ) and explores the impact of pandemics such as COVID-19 on global tourism (Gössling et al., 2021 ).
These emerging clusters at this phase bring fresh thinking to the research of ecotourism. First of all, the analysis of ecological footprint provides a tool for measuring the degree of sustainability and helps to monitor the effectiveness of sustainable programs (Kharrazi et al., 2014 ). Research and exploration of ecological footprint in ecotourism expresses the idea of sustainable development and puts forward reasonable planning and suggestions by comparing the demand of ecological footprint with the carrying capacity of natural ecosystem. Secondly, the use of social media data brings a new perspective of data acquisition to ecotourism research. Such large-scale data acquisition can make up for the limitations of sample size and data sampling bias faced by survey data users and provide a new way to understand and explore tourist behavior and market (Li et al., 2018 ). Finally, the sudden impact of COVID-19 in 2020 and its long-term sustainability has dealt a huge blow to the tourism industry. COVID-19 has highlighted the great need and value of tourism, while fundamentally changing the way destinations, business and visitors plan, manage and experience tourism (CREST, 2020 ). However, the stagnation of tourism caused by the pandemic is not enough to meet the challenges posed by the environment and the climate crisis. Therefore, how to sustain the development of tourism in this context to meet the challenges of the environment and climate change remains an important issue in the coming period of time. These emerging clusters are pushing the boundaries of ecotourism research and the exploration of sustainable development in terms of research methods, data collection and emerging topics.
Despite the fact that the research topics in this stage are richer and more diversified, the core goal of research is still committed to the sustainable development of ecotourism. The introduction of new technologies and the productive results have led to a much-improved understanding of research issues. All this commemorates the entrance of research into the third stage of the development of scientific disciplines (Shneider, 2009 ). In addition to continuing the current research topics, the future development of the field of ecotourism will continue to focus on the goal of sustainable development and will be more diversified and interdisciplinary.
5 Conclusion
This paper uses scientometrics to make a comprehensive visual domain analysis of ecotourism. The aim is to take advantage of this method to conduct an in-depth systematic review of research and development in the field of ecotourism. We have enriched the process of systematic reviews of knowledge domains with features from the latest CiteSpace software. Compared with previous studies, this study not only updated the database, but also extended the dataset with citation expansion, so as to more comprehensively identify the rapidly developing research field. The research not only identifies the main clusters and their advance in ecotourism research based on high impact citations and research frontiers formed by citations, but also presents readers with new insights through intuitive visual images. Through this study, readers can swiftly understand the progress of ecotourism, and on the basis of this study, they can use this method to conduct in-depth analysis of the field they are interested in.
Our research shows that ecotourism has developed rapidly in recent years, with the number of published articles increasing year by year, and this trend has become more pronounced after 2018. The research field of ecotourism spans many disciplines and is a comprehensive interdisciplinary subject. Ecotourism also attracts the attention of numerous developed and developing countries and institutions. The USA, China, Australia and South Africa are in a relatively leading position in the research and development of ecotourism. Foam tree map and pie chart of major topics, and the landscape view of keywords provide the hotspot issues of the research field. The development trend of ecotourism is preliminarily understood by detecting the citation bursts of the keywords and published articles. Co-citation analysis generates the main clusters of ecotourism research, and the timeline visualization of these clusters provides a clearer view for understanding the development dynamics of the research field. Building on all the above results, the research and development of ecotourism can be roughly divided into three stages: human disturbance, ecosystem services and sustainable development. Through the study of keywords, representative literature and main clusters in each stage, the development characteristics and context of each stage are clarified. From the current research results, we can catch sight that the application of methods and software in ecotourism research and the development of cross-field. Supported by the Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline (Shneider, 2009 ), it can be thought that ecotourism is in the third stage. Research tools and methods have become more potent and convenient, and research perspectives have become more diverse.
Based on the overall situation, research hotspots and development tendency of ecotourism research, it can be seen that the sustainable development of ecotourism is the core issue of current ecotourism research and also an important goal for future development. In the context of the current pandemic, the tourism industry is in crisis, but crisis often breeds innovation, and we must take time to reconsider the way forward. As we look forward to the future of tourism, we must adopt the rigor and dedication required to adapt to the pandemic, adhering to the principles of sustainable development while emphasizing economic reliability, environmental suitability and cultural acceptance. Post-COVID, the competitive landscape of travel and tourism will change profoundly, with preventive and effective risk management, adaptation and resilience, and decarbonization laying the foundation for future competitiveness and relevance (CREST, 2020 ).
In addition, as can be seen from the research and development of ecotourism, the exploration of sustainable development increasingly needs to absorb research methods from diverse fields to guide the formulation of policy. First of all, how to evaluate and quantify ecotourism reasonably and scientifically is an essential problem to be solved in the development of ecotourism. Some scholars choose contingent valuation method (CVM) and choice experiment (CE) in environmental economics to evaluate the economic value of ecotourism, especially non-market value. In addition, the introduction of spatial econometrics and the use of geographic information system (GIS) provide spatial scale analysis methods and results presentation for the sustainable development of ecotourism. The use of social media data implies the application of big data technology in the field of ecotourism, where machine learning methods such as artificial neural networks (ANN) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) are increasingly being applied (Talebi et al., 2021 ). The measurement of ecological footprint and the use of telecoupling framework provide a reliable way to measure sustainable development and the interaction between multiple systems. These approaches all have expanded the methodological boundaries of ecotourism research. It is worth noting that R, as an open source and powerful software, is favored by scholars in the field of ecotourism. This programming language for statistical computation is now widely used in statistical analysis, data mining, data processing and mapping of ecotourism research.
The scientometrics method used in this study is mainly guided by the citation model in the literature retrieval dataset. The range of data retrieval exercises restraint by the source of retrieval and the query method utilized. While current methods can meet the requirements, iterative query optimization can also serve to advance in the quality of the data. To achieve higher data accuracy, the concept tree function in the new version of CiteSpace can also serve to clarify the research content of each clustering (Chen, 2017 ). In addition, the structural variation analysis in the new edition is also an interesting study, which can show the citation footprints of typical high-yielding authors and judge the influence of the author on the variability of network structure through the analysis of the citation footprints (Chen, 2017 ).
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Web of Science.
Telecoupling, an integrated concept proposed by Liu et al. ( 2013 ), encompasses both socioeconomic and environmental interactions among coupled human and natural systems over distances. Liu et al. ( 2013 ) also constructed an integrated framework for telecoupling research, which is used to comprehensively study and explain multiple human-nature coupling systems at multiple spatial–temporal scales to promote the sustainable development of global society, economy and environment, and has been applied to ecotourism, land change science, species invasion, payments for ecosystem services programs, conservation, food trade, forest products, energy and virtual water, etc. (Liu et al., 2015 ).
Liu, J., Hull, V., Batistella, M., DeFries, R., Dietz, T., Fu, F.,... Zhu, C. (2013). Framing Sustainability in a Telecoupled World. Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 26. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-05873-180226
Abad-Segura, E., Cortés-García, F. J., & Belmonte-Ureña, L. J. (2019). The sustainable approach to corporate social responsibility: A global analysis and future trends. Sustainability, 11 (19), 5382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195382
Article Google Scholar
Ahmad, F., Draz, M. U., Su, L., Ozturk, I., & Rauf, A. (2018). Tourism and environmental pollution: Evidence from the one belt one road (OBOR) provinces of Western China. Sustainability, 10 (10), 3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103520
Article CAS Google Scholar
Ardoin, N. M., Wheaton, M., Bowers, A. W., Hunt, C. A., & Durham, W. H. (2015). Nature-based tourism’s impact on environmental knowledge, attitudes, and behavior: A review and analysis of the literature and potential future research. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 23 (6), 838–858. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2015.1024258
Balmford, A., Green, J. M. H., Anderson, M., Beresford, J., Huang, C., Naidoo, R., Walpole, M., & Manica, A. (2015). Walk on the wild side: Estimating the global magnitude of visits to protected areas. PLoS Biology, 13 (2), e1002074. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002074
Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B., & Walker, S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67 (1), 132904.
Bennett, N. J. (2016). Using perceptions as evidence to improve conservation and environmental management. Conservation Biology, 30 (3), 582–592. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.12681
Bennett, E. M., Cramer, W., Begossi, A., Cundill, G., Díaz, S., Egoh, B. N., Geijzendorffer, I. R., Krug, C. B., Lavorel, S., Lazos, E., Lebel, L., Martín-López, B., Meyfroidt, P., Mooney, H. A., Nel, J. L., Pascual, U., Payet, K., Harguindeguy, N. P., Peterson, G. D., … White, G. W. (2015). Linking biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human well-being: Three challenges for designing research for sustainability. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 14 , 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2015.03.007
Bennett, N. J., & Dearden, P. (2014). Why local people do not support conservation: Community perceptions of marine protected area livelihood impacts, governance and management in Thailand. Marine Policy, 44 , 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2013.08.017
Brockington, D., & Wilkie, D. (2015). Protected areas and poverty. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 370 (1681), 20140271. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2014.0271
Burkhard, B., Kroll, F., Nedkov, S., & Müller, F. (2012). Mapping ecosystem service supply, demand and budgets. Ecological Indicators, 21 , 17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.06.019
Calcagni, F., Maia, A. T. A., Connolly, J. J. T., & Langemeyer, J. (2019). Digital co-construction of relational values: Understanding the role of social media for sustainability. Sustainability Science, 14 , 1309–1321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-019-00672-1
Cardinale, B. J., Emmett Duffy, J., Gonzalez, A., Hooper, D. U., Perrings, C., Venail, P., Narwani, A., Mace, G. M., Tilman, D., Wardle, D. A., Kinzig, A. P., Daily, G. C., Loreau, M., Grace, J. B., Larigauderie, A., Srivastava, D. S., & Naeem, S. (2012). Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature, 486 , 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11148
Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. C. (1996). Tourism, ecotourism, and protected areas: The state of nature-based tourism around the world and guidelines for its development. World Congress on National Parks and Protected Areas, 4th, Caracas.
Chan, K. M. A., Guerry, A. D., Balvanera, P., Klain, Sarah, Satterfield, T., Basurto, X., Bostrom, A., Chuenpagdee, R., Gould, R., Halpern, B. S., Hannahs, N., Levine, J., Norton, B., Ruckelshaus, M., Russell, R., Tam, J., & Woodside, U. (2012). Where are cultural and social in ecosystem services? A framework for constructive engagement. BioScience, 62 (8), 744–756.
Google Scholar
Chan, K. M. A., Satterfield, T., & Goldstein, J. (2012b). Rethinking ecosystem services to better address and navigate cultural values. Ecological Economics, 74 , 8–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.11.011
Chen, C. (2011). Predictive effects of structural variation on citation counts. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 63 (3), 431–449. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21694
Chen, C. (2017). Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Data and Information Science, 2 (2), 1–40. https://doi.org/10.1515/jdis-2017-0006
Chen, C., Dubin, R., & Kim, M. C. (2014a). Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine a scientometric update (2000–2014). Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 14 (9), 1295–1317. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2014.920813
Chen, C., Dubin, R., & Kim, M. C. (2014b). Orphan drugs and rare diseases: A scientometric review (2000–2014). Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 2 (7), 709–724. https://doi.org/10.1517/21678707.2014.920251
Chen, C., Hu, Z., Liu, S., & Tseng, H. (2012). Emerging trends in regenerative medicine a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 12 (5), 593–608. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2012.674507
Chen, C., & Leydesdorff, L. (2014). Patterns of connections and movements in dual-map overlays: A new method of publication portfolio analysis. Journal of the Association for Information Science, 65 (2), 334–351. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22968
Chiu, Y.-T.H., Lee, W.-I., & Chen, T.-H. (2014). Environmentally responsible behavior in ecotourism: Antecedents and implications. Tourism Management, 40 , 321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.06.013
Chung, M. G., Dietz, T., & Liu, J. (2018). Global relationships between biodiversity and nature-based tourism in protected areas. Ecosystem Services, 34 , 11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.09.004
Clua, E., Buray, N., Legendre, P., Mourier, J., & Planes, S. (2010). Behavioural response of sicklefin lemon sharks Negaprion acutidens to underwater feeding for ecotourism purposes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 414 , 257–266. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps08746
Coria, J., & Calfucura, E. (2012). Ecotourism and the development of indigenous communities: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Ecological Economics, 73 , 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.10.024
Costanza, R., de Groot, R., Sutton, P., van der Ploeg, S., Anderson, S. J., Kubiszewski, I., Stephen Farber, R., & Turner, K. (2014). Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Global Environmental Change, 26 , 152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.04.002
Craigie, I. D., Baillie, J. E. M., Balmford, A., Carbone, C., Collen, B., Greena, R. E., & Hutton, J. M. (2010). Large mammal population declines in Africa’s protected areas. Biological Conservation, 143 (9), 2221–2228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2010.06.007
CREST. (2019). The Case for Responsible Travel: Trends & statistics 2019 . https://www.responsibletravel.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/213/2021/03/trends-and-statistics-2019.pdf
CREST. (2020). The Case for Responsible Travel: Trends & statistics 2020 . https://www.responsibletravel.org/docs/trendsStats2020.pdf
D’Amato, D., Droste, N., Allen, B., Kettunen, M., Lähtinen, K., Korhonen, J., Leskinen, P., Matthies, B. D., & Toppinen, A. (2017). Green, circular, bio economy: A comparative analysis of sustainability avenues. Journal of Cleaner Production, 168 , 716–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.053
Daniel, T. C., Muhar, A., Arnberger, A., Aznar, O., Boyd, J. W., Chan, K. M. A., Costanza, R., Elmqvist, T., Flint, C. G., Gobster, P. H., Gret-Regamey, A., Lave, R., Muhar, S., Penker, M., Ribe, R. G., Schauppenlehner, T., Sikor, T., Soloviy, I., Spierenburg, M., … von der Dunk, A. (2012). Contributions of cultural services to the ecosystem services agenda. PNAS, 109 (23), 8812–8819. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114773109
Díaz, S., Demissew, S., Carabias, J., Joly, C., Lonsdale, Mark, Ash, N., Larigauderie, A., Adhikari, J. R., Arico, S., Báldi, A., Bartuska, A., Baste, I. A., Bilgin, A., Brondizio, E., Chan, K. M. A., Figueroa, V. E., Duraiappah, A., Fischer, M., Hill, R., … Zlatanova, D. (2015). The IPBES conceptual framework-connecting nature and people. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 14 , 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2014.11.002
Dickinson, D. C., & Hobbs, R. J. (2017). Cultural ecosystem services: Characteristics, challenges and lessons for urban green space research. Ecosystem Services, 25 , 179–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.04.014
Dirzo, R., Young, H. S., Galetti, M., Ceballos, G., Isaac, N. J. B., & Collen, B. (2014). Defaunation in the anthropocene. Science, 345 (6159), 401–406. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1251817
Dulvy, N. K., Fowler, S. L., Musick, J. A., Cavanagh, R. D., Kyne, P. M., Harrison, L. R., Carlson, J. K., Davidson, L. N., Fordham, S. V., Francis, M. P., Pollock, C. M., Simpfendorfer, C. A., Burgess, G. H., Carpenter, K. E., Compagno, L. J., Ebert, D. A., Gibson, C., Heupel, M. R., Livingstone, S. R., … White, W. T. (2014). Extinction risk and conservation of the world’s sharks and rays. Life, 3 , e00590. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00590.001
Engel, S., Pagiola, S., & Wunder, S. (2008). Designing payments for environmental services in theory and practice: An overview of the issues. Ecological Economics, 65 (4), 663–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.03.011
Estes, J. A., Terborgh, J., Brashares, J. S., Power, M. E., Berger, J., Bond, W. J., Carpenter, S. R., Essington, T. E., Holt, R. D., Jackson, J. B. C., Marquis, R. J., Oksanen, L., Oksanen, T., Paine, R. T., Pikitch, E. K., Ripple, W. J., Sandin, S. A., Scheffer, M., Schoener, T. W., … Wardle, D. A. (2011). Trophic downgrading of planet earth. Science, 333 (6064), 301–306. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1205106
Fairhead, J., Leach, M., & Scoones, I. (2012). Green Grabbing: A new appropriation of nature? The Journal of Peasant Studies, 39 (2), 237–261. https://doi.org/10.1080/03066150.2012.671770
Ferraro, P. J., & Hanauer, M. M. (2014). Quantifying causal mechanisms to determine how protected areas affect poverty through changes in ecosystem services and infrastructure. PNAS, 111 (11), 4332–4337. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1307712111
Fisher, B., Turner, R. K., & Morling, P. (2009). Defining and classifying ecosystem services for decision making. Ecological Economics, 68 (3), 643–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.09.014
Gallagher, A. J., & Hammerschlag, N. (2011). Global shark currency: The distribution, frequency, and economic value of shark ecotourism. Current Issues in Tourism, 14 (8), 797–812. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2011.585227
Gallagher, A. J., Vianna, G. M. S., Papastamatiou, Y. P., Macdonald, C., Guttridgeg, T. L., & Hammerschlag, N. (2015). Biological effects, conservation potential, and research priorities of shark diving tourism. Biological Conservation, 184 , 365–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2015.02.007
Garfield, E. (1955). Citation indexes for science: A new dimension in documentation through association of ideas. Science, 122 (3159), 108–111. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.122.3159.108
Geffroy, B., Samia, D. S. M., Bessa, E., & Blumstein, D. T. (2015). How nature-based tourism might increase prey vulnerability to predators. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 30 (12), 755–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.09.010
Gómez-Baggethun, E., de Groot, R., Lomas, P. L., & Montes, C. (2010). The history of ecosystem services in economic theory and practice: From early notions to markets and payment schemes. Ecological Economics, 69 (6), 1209–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.007
Gössling, S., Scott, D., & Hall, C. M. (2021). Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 29 (1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2020.1758708
de Groot, R. S., Alkemade, R., Braat, L., Hein, L., & Willemen, L. (2010). Challenges in integrating the concept of ecosystem services and values in landscape planning, management and decision making. Ecological Complexity, 7 (3), 260–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecocom.2009.10.006
Hansen, M. C., Potapov, P. V., Moore, R., Hancher, M., Turubanova, S. A., Tyukavina, A., Thau, D., Stehman, S. V., Goetz, S. J., Loveland, T. R., Kommareddy, A., Egorov, A., Chini, L., Justice, C. O., & Townshend, J. R. G. (2013). High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science, 342 (6160), 850–853. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1244693
Hausmann, A., Toivonen, T., Slotow, R., Tenkanen, H., Moilanen, A., Heikinheimo, V., & Minin, E. D. (2018). Social media data can be used to understand tourists’ preferences for nature-based experiences in protected areas. Conservation Letters, 11 (1), e12343. https://doi.org/10.1111/conl.12343
Havinga, I., Bogaart, P. W., Hein, L., & Tuia, D. (2020). Defining and spatially modelling cultural ecosystem services using crowdsourced data. Ecosystem Services, 43 , 101091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2020.101091
Hernández-Morcillo, M., Plieninger, T., & Bieling, C. (2012). An empirical review of cultural ecosystem service indicators. Ecological Indicators, 29 , 434–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.01.013
Higgins, B. R. (1996). The Global structure of the nature tourism industry: Ecotourists, tour operators, and local businesses. Journal of Travel Research, 35 (2), 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728759603500203
Higgins-Desbiolles, F. (2018). Sustainable tourism: Sustaining tourism or something more? Tourism Management Perspectives, 25 , 157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2017.11.017
Hirons, M., Comberti, C., & Dunford, R. (2016). Valuing cultural ecosystem services. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 41 , 545–574. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-110615-085831
Kharrazi, A., Kraines, S., Hoang, L., & Yarime, M. (2014). Advancing quantification methods of sustainability: A critical examination emergy, exergy, ecological footprint, and ecological information-based approaches [Review]. Ecological Indicators, 37 , 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.10.003
Köndgen, S., Kühl, H., N’Goran, P. K., Walsh, P. D., Schenk, S., Ernst, N., Biek, R., Formenty, P., Mätz-Rensing, K., Schweiger, B., Junglen, S., Ellerbrok, H., Nitsche, A., Thomas Briese, W., Lipkin, I., Pauli, G., Boesch, C., & Leendertz, F. H. (2008). Pandemic human viruses cause decline of endangered great apes. Current Biology, 18 (4), 260–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2008.01.012
Kosoy, N., & Corbera, E. (2010). Payments for ecosystem services as commodity fetishism. Ecological Economics, 69 (6), 1228–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.002
Krüger, O. (2005). The role of ecotourism in conservation: Panacea or Pandora’s box? Biodiversity & Conservation, 14 , 579–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-004-3917-4
Li, J., Xu, L., Tang, L., Wang, S., & Li, L. (2018). Big data in tourism research: A literature review. Tourism Management, 68 , 301–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.03.009
Liu, J., Hull, V., Batistella, M., DeFries, R., Dietz, T., Fu, F., & Zhu, C. (2013). Framing sustainability in a telecoupled world. Ecology and Society, 18 (2), 26. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-05873-180226
Liu, J., Hull, V., Junyan Luo, W., Yang, W. L., Viña, A., Vogt, C., Zhenci, Xu., Yang, H., Zhang, J., An, Li., Chen, X., Li, S., Ouyang, Z., Weihua, X., & Zhang, H. (2015). Multiple telecouplings and their complex interrelationships. Ecology and Society, 20 (3), 44. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-07868-200344
Mace, G. M. (2014). Whose conservation? Science, 345 (6204), 1558–1560. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254704
Mace, G. M., Norris, K., & Fitter, A. H. (2012). Biodiversity and ecosystem services: A multilayered relationship. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 27 (1), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2011.08.006
McClung, M. R., Seddon, P. J., Massaro, M., & Setiawan, A. N. (2004). Nature-based tourism impacts on yellow-eyed penguins Megadyptes antipodes: Does unregulated visitor access affect fledging weight and juvenile survival? Biological Conservation, 119 (2), 279–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2003.11.012
MCT. (2021). Statistical Bulletin on Culture and Tourism Development 2020 . Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China. Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-07/05/content_5622568.htm
Milcu, A. I., Hanspach, J., Abson, D., & Fischer, J. (2013). Cultural ecosystem services: A literature review and prospects for future research. Ecology and Society, 18 (3), 44. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-05790-180344
Minin, E. D., Fraser, I., Slotow, R., & MacMillan, D. C. (2013). Understanding heterogeneous preference of tourists for big game species: Implications for conservation and management. Animal Conservation, 16 (3), 249–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1795.2012.00595.x
Muniz, R., & Cruz, M. J. (2015). Making nature valuable, not profitable: Are payments for ecosystem services suitable for degrowth? Sustainability, 7 (8), 10895–10921. https://doi.org/10.3390/su70810895
Muradian, R., Arsel, M., Pellegrini, L., Adaman, F., Aguilar, B., Agarwal, B., Corbera, E., Ezzine de Blas, D., Farley, J., Froger, G., Garcia-Frapolli, E., Gómez-Baggethun, E., Gowdy, J., Kosoy, N., Le Coq, J. F., Leroy, P., May, P., Méral, P., Mibielli, P., … Urama, K. (2013). Payments for ecosystem services and the fatal attraction of win-win solutions. Conservation Letters, 6 (4), 274–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-263X.2012.00309.x
Muradian, R., Corbera, E., Pascual, U., Kosoy, N., & May, P. H. (2010). Reconciling theory and practice: An alternative conceptual framework for understanding payments for environmental services. Ecological Economics, 69 (6), 1202–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.006
Naeem, S., Ingram, J. C., Varga, A., Agardy, T., Barten, P., Bennett, G., Bloomgarden, E., Bremer, L. L., Burkill, P., Cattau, M., Ching, C., Colby, M., Cook, D. C., Costanza, R., DeClerck, F., Freund, C., Gartner, T., Goldman-Benner, R., Gunderson, J., … Wunder, S. (2015). Get the science right when paying for nature’s services. Science, 347 (6227), 1206–1207. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa1403
Nelson, E., Mendoza, G., Regetz, J., Polasky, S., Tallis, H., Cameron, D., Chan, K. M. A., Daily, G. C., Goldstein, J., Kareiva, P. M., Lonsdorf, E., Naidoo, R., Ricketts, T. H., & Shaw, M. (2009). Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 7 (1), 4–11. https://doi.org/10.1890/080023
Niñerola, A., Sánchez-Rebull, M.-V., & Hernández-Lara, A.-B. (2019). Tourism research on sustainability: A bibliometric analysis. Sustainability, 11 (5), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051377
Oladeji, S. O., Awolala, D. O., & Alabi, O. I. (2021). Evaluation of sustainable ecotourism practices in Oke-Idanre Hills, Ondo-State, Nigeria [Article; Early Access]. Environment Development and Sustainability . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01550-6
Oldekop, J. A., Holmes, G., Harris, W. E., & Evans, K. L. (2016). A global assessment of the social and conservation outcomes of protected areas. Conservation Biology, 30 (1), 133–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.12568
Orams, M. B. (1995). Towards a more desirable form of ecotourism. Tourism Management, 16 (1), 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0261-5177(94)00001-Q
Ozturk, I., Al-Mulali, U., & Saboori, B. (2016). Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23 , 1916–1928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5447-x
Pascual, U., Phelps, J., Garmendia, E., Brown, K., Corbera, E., Martin, A., Gomez-Baggethun, E., & Muradian, R. (2014). Social equity matters in payments for ecosystem services. BioScience, 64 (11), 1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biu146
Pimm, S. L., Jenkins, C. N., Abell, R., Brooks, T. M., Gittleman, J. L., Joppa, L. N., Raven, P. H., Roberts, C. M., & Sexton, J. O. (2014). The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science, 344 (6187), 1246752. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1246752
Plieninger, T., Dijks, S., Oteros-Rozas, E., & Bieling, C. (2013). Assessing, mapping, and quantifying cultural ecosystem services at community level. Land Use Policy, 33 , 118–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.12.013
Raudsepp-Hearne, C., Peterson, G. D., & Bennett, E. M. (2010). Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. PNAS, 107 (11), 5242–5247. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907284107
Redford, K. H., & Adams, W. M. (2009). Payment for ecosystem services and the challenge of saving nature. Conservation Biology, 23 (4), 785–787. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2009.01271.x
Richards, D. R., & Friess, D. A. (2015). A rapid indicator of cultural ecosystem service usage at a fine spatial scale: Content analysis of social media photographs. Ecological Indicators, 53 , 187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.01.034
Ripple, W. J., Estes, J. A., Beschta, R. L., Wilmers, C. C., Ritchie, E. G., Hebblewhite, M., Berger, J., Elmhagen, B., Letnic, M., Nelson, M. P., Schmitz, O. J., Smith, D. W., Wallach, A. D., & Wirsing, A. J. (2014). Status and ecological effects of the world’s largest carnivores. Science, 343 (6167), 1241484. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241484
Ross, S., & Wall, G. (1999). Ecotourism: Towards congruence between theory and practice. Tourism Management, 20 (1), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5177(98)00098-3
Seraphin, H., Sheeran, P., & Pilato, M. (2018). Over-tourism and the fall of Venice as a destination. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 9 , 374–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2018.01.011
Sharpley, R. (2014). Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management, 42 , 37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.10.007
Shasha, Z. T., Geng, Y., Sun, H.-P., Musakwa, W., & Sun, L. (2020). Past, current, and future perspectives on eco-tourism: A bibliometric review between 2001 and 2018. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27 , 23514–23528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08584-9
Shneider, A. M. (2009). Four stages of a scientific discipline; four types of scientist. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 34 (5), 217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2009.02.002
Sirakaya, E., Sasidharan, V., & Sönmez, S. (1999). Redefining ecotourism: The need for a supply-side view. Journal of Travel Research, 38 (2), 168–172. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728759903800210
Snyman, S. (2017). The role of private sector ecotourism in local socio-economic development in southern Africa. Journal of Ecotourism, 16 (3), 247–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/14724049.2016.1226318
Talebi, M., Majnounian, B., Makhdoum, M., Abdi, E., & Omid, M. (2021). Predicting areas with ecotourism capability using artificial neural networks and linear discriminant analysis (case study: Arasbaran Protected Area, Iran). Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23 , 8272–8287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00964-y
Ulucak, R., & Bilgili, F. (2018). A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 188 , 144–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.191
Valdivieso, J. C., Eagles, P. F. J., & Gil, J. C. (2015). Efficient management capacity evaluation of tourism in protected areas. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 58 (9), 1544–1561. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2014.937479
Watson, J. E. M., Dudley, N., Segan, D. B., & Hockings, M. (2014). The performance and potential of protected areas. Nature, 515 , 67–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13947
Wearing, S., & McGehee, N. G. (2013). Volunteer tourism: A review. Tourism Management, 38 , 120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.03.002
Weaver, D. B., & Lawton, L. J. (2007). Twenty years on: The state of contemporary ecotourism research. Tourism Management, 28 (5), 1168–1179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2007.03.004
West, P., Igoe, J., & Brockington, D. (2006). Parks and peoples: The social impact of protected areas. Annual Review of Anthropology, 35 , 251–277.
Whitelaw, P. A., King, B. E. M., & Tolkach, D. (2014). Protected areas, conservation and tourism-financing the sustainable dream. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 22 (4), 584–603. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2013.873445
Wight, P. (1993). Ecotourism: Ethics or eco-sell. Journal of Travel Research, 31 (3), 3–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728759303100301
Wittemyer, G., Elsen, P., Bean, W. T., Burton, A. C. O., & Brashares, J. S. (2008). Accelerated human population growth at protected area edges. Science, 321 (5885), 123–126. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1158900
Xu, L., Ao, C., Mao, B., Cheng, Y., Sun, B., Wang, J., Liu, B., & Ma, J. (2020). Which is more important, ecological conservation or recreational service? Evidence from a choice experiment in wetland nature reserve management. Wetlands, 40 , 2381–2396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-020-01348-8
Zanten, B. T. V., Berkel, D. B. V., Meentemeyer, R. K., Smith, J. W., Tieskens, K. F., & Verburg, P. H. (2016). Continental-scale quantification of landscape values using social media data. PNAS, 113 (46), 12974–12979. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1614158113
Zhong, L., & Liu, L. (2017). Ecotourism development in China: Achievements, problems and strategies. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 8 (5), 441–448. https://doi.org/10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.05.001
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study is funded by Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (1451MSYYB013) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.71874026 and No.71171044).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Management Science and Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, 150030, China
Lishan Xu, Changlin Ao, Baoqi Liu & Zhenyu Cai
Faculty of Economic and Management, Mudanjiang Normal University, Mudanjiang, 157011, China
College of Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, 150030, China
Changlin Ao
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
In this study, LX proposed the research topic, designed the research methodology and framework, and made the data analysis. She was the major contributor in writing the manuscript. CA contributed to the design of the whole paper, including the research topic and methodology, and also participated in the writing and revision of the manuscript. BL and ZC were involved in data collection and analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Changlin Ao .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval and Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Additional information, publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 1035 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Xu, L., Ao, C., Liu, B. et al. Ecotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends. Environ Dev Sustain 25 , 2977–3003 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02190-0
Download citation
Received : 29 October 2021
Accepted : 03 February 2022
Published : 21 February 2022
Issue Date : April 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02190-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Sustainable development
- Research trends
- Scientometrics
- Web of Science
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 May 2023
Eco-tourism, climate change, and environmental policies: empirical evidence from developing economies
- Yunfeng Shang 1 ,
- Chunyu Bi 2 ,
- Xinyu Wei 2 ,
- Dayang Jiang 2 ,
- Farhad Taghizadeh-Hesary ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5446-7093 3 , 4 &
- Ehsan Rasoulinezhad ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7726-1757 5
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 275 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
7132 Accesses
7 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental studies
Developing ecotourism services is a suitable solution to help developing countries improve the status of sustainable development indicators and protect their environment. The primary purpose of this paper is to find out the effects of green governance variables and carbon dioxide emissions on ecotourism for 40 developing economies from 2010 to 2021. The results confirmed a uni-directional causal relationship between the green governance indicator and the inflation rate of the ecotourism indicator. In addition, with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. In comparison, with a 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries, ecotourism will increase by 0.32%. Moreover, ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to macroeconomic variables changes than in developed economies. Geopolitical risk is an influential factor in the developing process of ecotourism. The practical policies recommended by this research are developing the green financing market, establishing virtual tourism, granting green loans to small and medium enterprises, and government incentives to motivate active businesses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Comprehensive green growth indicators across countries and territories
Samuel Asumadu Sarkodie, Phebe Asantewaa Owusu & John Taden

Role of foreign direct Investment and political openness in boosting the eco-tourism sector for achieving sustainability
Yunfeng Shang, Qin Yang & Yuanjie Pu
Ways to bring private investment to the tourism industry for green growth
Fengxiao Gong & Hui Chen
Introduction
The challenge of climate change has become a primary threat to living on the Earth in the last centuries (Rasoulinzhad and Taghizadeh-Hesary, 2022 ). Many meetings of the countries at the regional and international level are held on the topics of environment and climate change. Regardless of environmental issues, population growth, and the lack of control of greenhouse gas emissions, industrialization has been the most crucial cause of the climate change crisis. Chao and Feng ( 2018 ) address human activity as the leading cause of climate change and express that this challenge is a potential threat to living on Earth. Woodward ( 2019 ) argued that climate change threats include the rise in global temperature, the melting of polar ice caps, and unprecedented disease outbreaks. Therefore, urgent policies and solutions are essential to control and lower the risk of global change. One of the signs of climate change is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s surface. Figure 1 shows the temperature data from 1910 to 2021 for the four continents of Asia, Europe, Africa, and North America.
Source: Authors from NOAA ( https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/climate-at-a-glance/global/time-series ).
The data in Fig. 1 shows that the air temperature has increased significantly over the past century, which has been more prominent in Asia and Europe. In 2021, we saw a decrease in temperature changes due to the spread of the Corona disease and a decrease in the rate of greenhouse gas emissions. However, the role of the Asian continent in increasing the global temperature has been more than other continents due to its large population and excessive consumption of fossil fuels.
During the past decades, the world’s countries have tried to formulate and implement various environmental policies collectively in the form of agreements or separately to fight environmental threats. Regarding international agreements, such things as the Paris Agreement of 2015, the Kyoto Protocol of 1997, the Montreal Protocol of 1987, and the Vienna Convention on the Protection of the Ozone Layer in 1985 can be addressed whose primary purpose is to integrate the goals and motivation of the international community to the world’s environmental threats. However, a group of earlier studies, such as Zheng et al. ( 2017 ), Takashima ( 2018 ), and Roelfsema et al. ( 2022 ), emphasized the inefficiency of these global agreements, especially after the left the USA from the Paris Agreement on 1 June 2017. The most important cause of this inefficiency has been the need for more motivation of countries to fulfill their international obligations towards environmental issues. However, many governments consider the threat of climate change only within their geographical boundaries and have tried to formulate and implement green policies to advance their environmental protection goals. These policies include green financial policies (green taxes, green subsidies), monetary policies (such as green loans and green financing), and cultural and social policies in line with sustainable development. The ultimate goal of these green policies is a green economy, an environmentally friendly economy, a zero carbon economy, or a sustainable economy. Lee et al. ( 2022 ) define the green economy as a broad concept comprising green industry, agriculture, and services. Centobelli et al. ( 2022 ) express that environmental sustainability should be more attention in the service sector owing to its penetration into social life and interactions.
Tourism and travel-related services are among countries’ main parts of the service sector. By creating the flow of tourists, tourism services can lead to capital transfer, job creation, cultural exchange (globalization), and increasing welfare in the country hosting the tours. According to the Yearbook of Tourism Statistics published by the World Tourism Organization, international tourism has increased from 522.2 billion US dollars in 1995 to nearly 1.86 trillion US dollars in 2019. This increase shows the importance of tourism services in generating income for countries, especially in the era of Corona and post-corona. Casado-Aranda et al. ( 2021 ) express that tourism services can be a central driver of economic growth recovery in post COVID era. Jeyacheya and Hampton ( 2022 ) argue that tourism can make high incomes for host countries leading to job creation and economic flourishing in destination cities for tourists.
An important issue mentioned in the corona era and relies on the post-corona era is the revitalizing of green economic growth. An important issue mentioned in the corona era and relying on the post-corona era is the revitalizing green economic growth (Bai et al., 2022 ; Werikhe, 2022 ), an opportunity that countries should pay more attention to in order to rebuild their economic activities. In other words, countries should plan their return to economic prosperity with environmental issues in mind. To this end, the issue of tourism finds a branch called Ecotourism or sustainable tourism which has environmental concerns and tries to help countries to improve environmental protection policies. Ecotourism is an approach based on environmental criteria, which is opposed to over-tourism (a type of tourism that disrupts the protection of the environment and destroys natural resources). The International Ecotourism Society defines Ecotourism as an efficient way to conserve the environment and improve local people’s well-being. It can be said that Ecotourism, along with various economic advantages (income generation, job creation, globalization, poverty alleviation), will bring environmental protection to the world’s countries, achieving the goals of green economic growth recovery and sustainable development. Xu et al. ( 2022 ) consider Ecotourism as one of the essential components of achieving sustainable development in the post-corona era.
Ecotourism in developing countries has more priorities compared to developed economies. Firstly, developing countries are often countries with financial problems of the government, and the governments in these countries need more capital to advance sustainable development goals. Therefore, developing ecotourism services can be a suitable solution to help these countries improve the status of sustainable development indicators and protect their environment. Second, due to the spread of the Corona disease, developing countries have experienced numerous bankruptcy in the tourism services sector. Therefore, promoting ecotourism in these countries is of great importance in the post-corona era. Third, developing countries have a high share in the emission of greenhouse gases in the world due to their high dependence on fossil fuels and the lack of advanced green technologies. Fourth, due to bureaucratic processes, high cost, and lack of market transparency, greenwashing may happen in developing economies’ ecotourism industry, meaning that a company serving ecotourism services makes its activities seem more sustainable and ethical than they are. The term “greenwashing” can harshly impact the future development path of the ecotourism industry in developing economies. According to the reasons mentioned above, developing ecotourism in developing countries can be an essential factor in controlling and reducing greenhouse gas emissions in these countries.
This paper tries to contribute to the existing literature from the following aspects:
Calculating the ecotourism index for selected countries based on the criteria for measuring sustainable tourism stated by the World Tourism Organization in the United Nations. Considering that there is no specific index for ecotourism, the calculation of ecotourism in this article will be innovative.
Measuring the green governance index as a proxy for environmental policies for selected countries based on the Environment Social and Governance (ESG) data.
Selecting a sample of 40 developing countries from different geographical regions to calculate the interconnections between ecotourism, green governance, and climate change
Making a further discussion to address the role of uncertainty and the developing level of countries in the relationship between ecotourism and explanatory variables.
The main results confirm the existence of a uni-directional causal relationship running from the green governance indicator and inflation rate to the ecotourism indicator. In addition, with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. A 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries accelerates ecotourism by 0.32%.
Moreover, ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to macroeconomic variables changes than in developed economies. Geopolitical risk is an influential factor in the developing process of ecotourism. The practical policies recommended by this research are developing the green financing market, establishing virtual tourism, granting green loans to small and medium enterprises, and government incentives to motivate active businesses.
The paper in continue is organized as follows: section “Literature review” provides a short literature review to determine the gaps this research seeks to fill. Section “Data and model specification” argues data and model specification. The following section represents empirical results. Section “Discussion” expresses discussion, whereas the last section provides conclusions, policy implications, research limitations, and recommendations to research further.
Literature review
This part of the article analyzes and classifies the previous literature on ecotourism and sustainable development in a rational and structured way. The importance of tourism in economic growth and development has been discussed in previous studies. However, the study of the effect of tourism on climate change has received little attention. Especially the relationship between sustainable tourism, climate change, and environmental policies is a problem that has yet to receive the attention of academic experts.
A group of previous studies has focused on the place of tourism in economic development and growth. Holzner ( 2011 ) focused on the consequences of tourism development on the economic performance of 134 countries from 1970 to 2007. They found out that excessive dependence on tourism income leads to Dutch disease in the economy, and other economic sectors need to develop to the extent of the tourism sector. In another study, Sokhanvar et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the causal link between tourism and economic growth in emerging economies from 1995 to 2014. The main results confirmed that the linkage is country-dependent. Brida et al. ( 2020 ) studied 80 economies from 1995 to 2016 to determine how tourism and economic development are related. The paper’s conclusions highlighted tourism’s-positive role in economic activities.
Another group of previous studies has linked tourism to sustainability targets. Sorensen and Grindsted ( 2021 ) expressed that nature tourism development has a positive and direct impact on achieving sustainable development goals of countries. In a new study, Li et al. ( 2022 ) studied the impacts of tourism development on life quality (as one of the sustainable development goals defined by the UN in 2015) in the case of Japan. They found that tourism development positively impacts the quality of life of age groups in the country. Ahmad et al. ( 2022 ) explored the role of tourism in the sustainability of G7 economies from 2000–2019. The primary findings revealed the positive impact of tourism arrivals on sustainable economic development. Zekan et al. ( 2022 ) investigated the impact of tourism on regional sustainability in Europe. They concluded that tourism development increases transport, leading to increased carbon dioxide emissions. Therefore, tourism development causes environmental pollution.
Tourism that can pay attention to environmental issues is called “ecotourism.” Many new studies have studied different dimensions of ecotourism. Lu et al. ( 2021 ) expanded the concept of the ecotourism industry. The significant results expressed that smart tourist cities are essential for efficient ecotourism in countries. Thompson ( 2022 ) expressed the characteristics of ecotourism development through survey methodology. The results confirmed the importance of transparent regulations, government support, and social intention to promote ecotourism. In another study, Heshmati et al. ( 2022 ) employed the SWOT analysis method to explore the critical success factors of ecotourism development in Iran. They found that legal documentation and private participation are major influential factors in promoting ecotourism in Iran. In line with the previous research, Hosseini et al. ( 2021 ) tried to explore the influential factors in promoting ecotourism in Iran by employing a SWOT analysis. They depicted that attracting investors is essential to enhance ecotourism projects in Iran. Hasana et al. ( 2022 ) reviewed research to analyze the earlier studies about ecotourism. The conclusions expressed that ecotourism is necessary for environmental protection. However, it is a challenging plan for the government, and they should carry out various policies toward ecotourism development. Kunjuraman et al. ( 2022 ) studied the role of ecotourism on rural community development in Malaysia. The significant results confirmed that ecotourism could transfer-positive impacts.
Several earlier studies have concentrated on the characteristics of ecotourism in different developed and developing economies. For example, Ruhanen ( 2019 ) investigated the ecotourism status in Australia. The paper concluded that the country could potentially make a larger share of ecotourism to the entire local tourism industry. Jin et al. ( 2022 ) studied the role of local community power on green tourism in Japan. They concluded that the concept of agricultural village activity and regional support positively influences the development of green tourism in Japan as a developed economy. Choi et al. ( 2022 ) sought to find aspects of ecotourism development in South Korea. The preliminary results confirmed the importance of green governance and efficient regulation to promote a sustainable tourism industry. Baloch et al. ( 2022 ) explored the ecotourism specifications in the developing economy of Pakistan. They found that Pakistan’s ecotourism needs government support and the social well-being of the visited cities. Sun et al. ( 2022 ) studied ecotourism in China. They concluded that there is imbalanced development of ecotourism among Chinese provinces due to the need for more capital to invest in all ecotourism projects throughout the Chinese cities. Tajer and Demir ( 2022 ) analyzed the ecotourism strategy in Iran. They concluded that despite various potentials in the country, insufficient capital, lack of social awareness, and political tension are the major obstacles to promoting a sustainable tourism industry in Iran.
Another group of earlier studies has drawn attention to promoting eco-tourism in the post COVID era. They believe that the corona disease has created an excellent opportunity to pay more attention to environmental issues and that countries should move towards sustainable development concepts such as sustainable (eco) tourism in the post-corona era. Soliku et al. ( 2021 ) studied eco-tourism in Ghana during the pandemic. The findings depicted the vague impacts of a pandemic on eco-tourism. Despite the short-term negative consequence of the pandemic on eco-tourism, it provides various opportunities for developing this sector in Ghana. Hosseini et al. ( 2021 ) employed the Fuzzy Dematel technique to find solutions for promoting eco-tourism during COVID-19. They found out that planning to increase the capacity of eco-tourism and incentive policies by governments can help promote the eco-tourism aspect under the pandemic’s consequences. Abedin et al. ( 2022 ) studied the consequence of COVID-19 on coastal eco-tourism development. The primary findings confirmed the negative impacts of a pandemic on the development of eco-tourism.
A review of previous studies shows that tourism can positively impact green growth and sustainable development. Sustainable tourism can be used as a policy to deal with the threat of climate change. This issue needs more attention in the corona and post-corona eras. Because in the post-corona era, many countries have sought to revive green economic growth, and ecotourism can be one of the tools to achieve it. As observed, a detailed study of the relationship between climate change, ecotourism, and environmental policies has yet to be done. Therefore, this research will address and fill this literature gap.
Data and model specification
Data description.
The paper seeks to find the relationship between climate change, ecotourism, and environmental policy for the panel of 40 developing economies from different regions from 2010 to 2021 (480 observations). The sample size could have been more extensive due to the lack of information on some variables. However, there are 480 observations in the data analysis of the data panel; therefore, the number of samples selected is acceptable.
To determine the proxies for main variables, CO2 emissions per capita are selected as the proxy for climate change. Many earlier studies (e.g., Espoir et al., 2022 ) have employed this variable as an appropriate variable representing the status of climate change. Regarding ecotourism, the World Tourism Organization proposed some measurements of sustainable tourism, and also following Yusef et al. ( 2014 ), the entropy weight method is employed to calculate a multi-dimensional ecotourism indicator comprising per capita green park area (square meters), gross domestic tourism revenue (US dollars), the ratio of good air quality (%), green transport, renewable water resources (km3) and deforestation rate (%). It is a novel ecotourism indicator that can show the ecotourism status in countries.
In addition, the green governance index is calculated as a proxy for environmental policy. Principally, the Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) data from World Bank are gathered to calculate this variable. With the improvement of the Green Governance Index, the quality of environmental policies will also increase, and vice versa. With the adverseness of the Green Governance Index, the efficiency of environmental policies will decrease.
Regarding control variables, the inflation rate as an influential factor in tourism flows is selected. The importance of this variable to promoting/declining tourism flows has been drawn to attention by some earlier studies, such as Liu et al. ( 2022 ). The inflation rate can raise the total cost of travel, causing a reduction in tourism flows, while any reduction in the inflation rate can increase the intention of tourists to travel. In addition, the KOF globalization index provided by the KOF Swiss Economic Institute is another control variable. A country with a higher degree of globalization means more readiness to accept tourists from countries with different cultures and religions.
Model specification
According to the variables mentioned above, 40 examined developing countries from 2010 to 2021, the panel co-integration model can be written as Eq. 1 :
ETOR indicates the ecotourism index, while CO2, GGI, INF, and GLOB denote Carbon dioxide emissions per capita, green governance index, inflation rate, and globalization index, respectively. i is 1,2,…,40 and shows examined developing economies, while t is time and contains 2010, 2011,..,2021.
Prior to the estimation of coefficients of Eq. 1 , the panel unit root tests are employed to find out whether the series is stationary. To this end, three tests of LLC (Levin et al., 2002 ), Breitung’s test ( 2000 ), and the PP-Fisher test (Philips and Perron, 1988 ). If all the variables are stationary at the first level of difference (I(1)), a panel co-integration test can be conducted to explore whether the model is spurious. To this end, Kao’s co-integration test ( 1999 ) and Pedroni’s residual co-integration test ( 2004 ) are conducted. If the co-integration relationship exists among variables, the panel causality test can be run to determine the causal linkages among variables. In this paper, the two steps of Engle and Granger (1987)‘s test, which is based on the error correction model (ECM) is used as Eqs. 2 – 6 :
In the above Equations, Δ is the first differences of variables, while θ and ECT represent the fixed country effect and error correction term.
The next step is the long-run panel co-integration estimations. To this end, Fully Modified OLS (FMOLS) and Dynamic OLS (DOLS) as robustness checks are conducted, which are two famous panel co-integration estimators (Rasoulinezhad, 2018 ). The FMOLS estimator has various advantages. It allows serial correlation, endogeneity, and cross-sectional heterogeneity (Erdal and Erdal, 2020 ).
Empirical results
In this section, we will implement the experimental research model. The purpose of implementing an econometric model based on panel data is to find the effects of green governance variables and carbon dioxide emissions on ecotourism. As the first step, the panel unit root tests are conducted. The results are reported in Table 1 as follows:
According to Table 1 , all three-panel unit root tests depict that all series are non-stationary at the level and become stationary after a first difference. Next, the panel co-integration tests are conducted, and their results are represented in Tables 2 and 3 :
The two-panel co-integration tests’ findings confirm the presence of co-integration linkages among variables.
The panel causality test studies the short-term and long-term causal relationship among variables. Table 4 reports the results of the panel causality check as follows:
According to Table 4 , there is a uni-directional causal relationship between the green governance indicator and the inflation rate of the ecotourism indicator. At the same time, there is a bi-directional causal relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and ecotourism indicators, confirming the existence of the feedback effect. In addition, there is only short-term causality from the green governance indicator to carbon dioxide emissions. In contrast, ecotourism and the globalization index have a uni-directional causal linkage. In the short term, improving ecotourism can cause globalization and reduce carbon emissions in developing economies. Regarding the long-term causality, it can be concluded that the ECT of ecotourism, green governance index, and globalization index are statistically significant. These three variables are major adjustment variables when the system departs from equilibrium.
In the last stage, the long-run estimations are done through FMOLS and DOLS estimators. Table 5 lists the results of the estimations by these two-panel co-integration estimators:
Based on FMOLS estimation, it can be concluded that the Green Governance index has a positive and significant coefficient in such a way that with a 1% improvement in the green governance index of developing countries, the ecotourism of these countries will increase by 0.43%. By improving the state of green governance, the quality of formulated and implemented green policies in these countries will increase, improving the conditions of ecotourism development. This finding aligns with Agrawal et al. ( 2022 ) and Debbarma and Choi ( 2022 ), who believe that green governance is essential to sustainable development. In the case of carbon dioxide emissions, the coefficient of this variable is not statistically significant. In other words, the variable of carbon dioxide emissions per capita has no significant effect on ecotourism in developing countries. The inflation rate has a significant negative effect on ecotourism. With a 1% increase in the general prices of goods and services in developing countries, ecotourism will decrease by 0.34%. This finding aligns with Rahman ( 2022 ), who showed a negative relationship between inflation and sustainable development in their research. An increase in inflation means an increase in the total cost of a tourist’s trip to the destination country, inhibiting the growth of tourist services.
Regarding the globalization variable, this variable has a significant positive effect on the ecotourism of developing countries. With a 1% increase in the globalization index of these countries, ecotourism will increase by 0.32%. Globalization means more interaction with the world’s countries, acceptance of different cultures and customs, more language learning in society, more acceptance of tourism, and development of tourist services in the country. This finding is consistent with the results of Akadiri et al. ( 2019 ), who confirmed that globalization is one of the crucial components in tourism development.
The DOLS estimator was also used to ensure the obtained findings’ validity. The results of this method are shown in Table 5 . The signs of the coefficients are consistent with the results obtained by the FMOLS method. Therefore, the validity and reliability of the obtained coefficients are confirmed.
In this section, we will briefly discuss the relationship between ecotourism and climate change and the environmental policy considering the uncertainty and the relationship between variables in developed and developing countries.
Consideration of uncertainty
Uncertainty as a primary reason for risk has become a research issue in recent decades. Uncertainty can make the future unpredictable and uncontrollable, affecting economic decision-making. Regarding tourism, the impacts of uncertainty have been drawn to attention by several earlier studies (e.g., Dutta et al., 2020 ; Das et al., 2020 ; and Balli et al., 2019 ; Balli et al., 2018 ). In general, uncertainty in the tourism industry reflects tourists’ concerns and consumption habits in the way that by increasing uncertainty, it is expected that tourists make sense of risks and postpone their tourism activities, and vice versa; in the sphere of certainties, the various risks are clear, and tourists can make rational decisions for their tourism plans and activities. In order to explore the impacts of uncertainties on eco-tourism of the examined developing economies, the geopolitical risk index (GPR) as a proxy for economic policy uncertainty index is gathered and added as a control variable to Eq. 1 . The estimations results by FMOLS are reported in Table 6 as follows.
According to Table 6 , the uncertainty (geopolitical risk) has a negative coefficient meaning that with a 1% increase in geopolitical risk, the eco-tourism industry in the examined developing countries decreases by approximately 0.69%. The signs of coefficients of other variables align with the earlier findings, represented in Table 5 . In addition, the magnitude of the impact of geopolitical risk is larger than the impacts of other variables highlighting the importance of lower geopolitical risk in these economies to reach sustainable tourism targets.
Difference in developed and developing economies
Considering the different structures and financial power of these two groups of countries, the relationship between the variables mentioned in these two groups is expected to be different. In the previous section, the results for the group of developing countries showed that the Green Governance index has a positive and significant coefficient. In the case of carbon dioxide emissions, the coefficient of this variable is not statistically significant. The inflation rate has a significant negative effect on ecotourism. Regarding the globalization variable, it can be mentioned that this variable has a significant positive effect on the ecotourism of developing countries. In order to analyze the relationship between variables in the developed countries, the top 10 countries with the highest HDI in 2021 are selected (Switzerland (0.962), Norway (0.961), Iceland (0.959), Hong Kong (0.952), Australia (0.951), Denmark (0.948), Sweden (0.947) and Ireland (0.945)). The selected variables, explained in section “Data and model specification”, are collected from 2010 to 2021. The panel unit root tests confirmed that all series are non-stationary at the level and become stationary after a first difference. In addition, the presence of co-integration linkages among variables is revealed by the panel co-integration test. The panel co-integration estimator of FMOLS is employed to study the long-term relationship among variables. The findings are reported in Table 7 as follows:
According to the estimated coefficients, the green governance indicator positively and statistically significantly impacts ecotourism in the examined developed economies. However, the magnitude of the impact of this variable is more considerable for developing countries because these countries have more imbalances in markets and regulations. Therefore, the presence of good green tourism can have a more positive effect on advancing the goal of ecotourism. Contrary to the findings of developing countries, carbon dioxide emission in developed countries has a negative and significant effect, meaning that with an increase of 1% in carbon dioxide in developed countries, the level of ecotourism becomes more unfavorable by 0.034%. Moreover, inflation and globalization variables have significant negative and positive coefficients, respectively. However, the magnitudes of these two variables’ coefficients are also higher in developing countries. Ecotourism in developing countries is more sensitive to changes in macroeconomic variables such as green governance, globalization, and inflation.
Another difference between eco-tourism in developed and developing economies may be interpreted through the term “greenwashing,” introduced by Westerveld in 1986 (Maichum et al., 2016 ). In developing countries, due to the economic structure, limited knowledge, bureaucratic process, lack of legal eco-certification, and imperfect competition, a company involved in the eco-tourism industry makes an unsubstantiated claim to deceive consumers into accepting the company’s services are in line with environmental protection policies. Hence, green governance in developing countries should have another role in regulating the eco-tourism market to lower the threat of greenwashing in eco-tourism services.
Conclusions and policy recommendations
Concluding remarks.
The findings of econometric modeling revealed the relationship between environmental policies, climate change, and ecotourism. Based on the findings of the econometric model, the following conclusions can be presented:
A uni-directional causal relationship runs from the green governance indicator and inflation rate to the ecotourism indicator, which means that any changes in green governance and inflation rate cause changes in ecotourism, which is vital for developing economies where governance and inflation rate are two crucial issues.
There is a bi-directional causal relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and ecotourism indicators, confirming the existence of the feedback hypothesis, expressing that in developing economies, any policies related to ecotourism cause changes in CO2 emissions and vice versa.
There is only short-term causality from the green governance indicator to carbon dioxide emissions, whereas there is a uni-directional causal linkage from ecotourism to the globalization index. In other words, in the short term, improving ecotourism can cause globalization and reduce carbon emissions in developing economies.
By improving green governance in developing economies, the quality of formulated and implemented green policies in these countries will increase, improving the conditions of ecotourism development.
An increase in the inflation rate raises the total cost of a tourist’s trip to developing economies, inhibiting the growth of eco-tourist services.
Globalization means more interaction with the world’s countries, acceptance of different cultures and customs, more language learning in society, more acceptance of tourism, and development of tourist services in developing countries.
Policy implications
In order to achieve the promotion of ecotourism in developing countries, the implementation of integrated and effective strategic and practical policies is of great importance. According to the concluding remarks mentioned, practical policies are presented as follows for enhancing ecotourism in developed countries. The development of ecotourism requires the improvement of various infrastructures and mechanisms, which depends on the implementation of projects related to ecotourism in developing countries. Because most countries do not have enough financial power to invest in such projects, developing the green financing market can be one of the critical practical solutions. The green financing tool can increase the investment risk and return on investment in such projects, and as a result, the participation of the private sector in these projects will increase. With information and communication technology development, virtual tourism can solve many environmental issues related to human physical presence. Virtual tourism is one of the branches of tourism services that provide people with destinations, places of interest, and tourist attractions with full quality but in virtual form. Another practical policy is granting green loans to small and medium enterprises active in ecotourism. Despite the organizational agility, these companies do not have the significant financial power to develop different sectors of ecotourism; therefore, the cooperation of the banking industry of developing countries by providing green loans (with low-interest rates) can motivate small and medium-sized companies in the field of activities related to ecotourism. Government incentives to motivate businesses active in ecotourism and government deterrent policies (green tax) from businesses active in the field of tourism to lead them to increase the share of ecotourism in their activities can be a proper operational strategy. In developing countries, the role of government and green governance is vital in advancing the goals of ecotourism. By improving the level of its green governance, the government can create efficient policies, regulations, and social tools to create motivation and desire to accept ecotourism, an essential and undeniable issue in developing societies. Creating a guarantee fund for ecotourism companies in developing countries is another practical policy to support these companies financially. Guarantee funds can be established with the participation of the people of ecotourism destinations in order to strengthen the financial strength of ecotourism companies in these destinations.
Limitations and recommendations to further research
This research had a practical and innovative contribution to the literature on ecotourism in developing countries. The findings obtained from the econometric model analysis provided appropriate practical and strategic policies to the policymakers of countries interested in the development of ecotourism. However, access to data related to the ecotourism index and sustainable development of developing countries due to the lack of community in a specific database is considered one of the critical limitations of this research. This limitation caused many developing countries to be excluded from the research sample, which may have created a deviation in the research. Adding more countries to the test sample in future research is suggested to obtain complete and accurate results. Also, due to the outbreak of the Corona pandemic at the end of 2019 and the Russia-Ukraine war since the beginning of 2022, it is suggested that these two variables be included in the econometric model as an illusion in order to analyze their effects on the ecotourism of the countries of the world. Using other econometric methods, such as artificial neural networks, is suggested to model ecotourism in different countries. Complex modeling by taking into account trends and trends to predict the relationship between variables in the future will be an essential step in formulating effective programs in ecotourism.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abedin Z, Handayani W, Zaky E, Faturrahman A (2022) Perceived risk and attitude’s mediating role between tourism knowledge and visit intention during the COVID-19 pandemic: implementation for coastal-ecotourism management. Heliyon 8(10):e10724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10724
Article Google Scholar
Agrawal A, Brandhorst S, Jain M, Liao C, Pradhan N, Solomon D (2022) From environmental governance to governance for sustainability. One Earth 5(6):615–621
Article ADS Google Scholar
Ahmad N, Youjin L, Hdia M (2022) The role of innovation and tourism in sustainability: why is environment-friendly tourism necessary for entrepreneurship? J Clean Prod 379(Part 2):134799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134799
Akadiri S, Alola A, Akadiri A (2019) The role of globalization, real income, tourism in environmental sustainability target. Evidence from Turkey. Sci Total Environ 687:423–432
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bai X, Wang K, Tran T, Sadiq M, Trung L, Khudoykulov K (2022) Measuring China’s green economic recovery and energy environment sustainability: econometric analysis of sustainable development goals. Econ Anal Policy 75:768–779
Balli F, Shahzad SJH, Uddin GS (2018) A tale of two shocks: what do we learn from the impacts of economic policy uncertainties on tourism? Tour Manag68:470–475
Balli F, Uddin GS, Shahzad SJH (2019) Geopolitical risk and tourism demand in emerging economies. Tour Econ 25(6):997–1005
Baloch Q, Shah S, Iqbal N, Sheeraz M, Asadullah M, Mahar S, Khan A (2022) Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism. Environ Sci Pollut Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22496-w
Breitung J (2000) The local power of some unit root tests for panel data. In: Baltagi B (ed.). Nonstationary panels, panel cointegration, and dynamic panels, advances in econometrics. vol. 15. JAI Press, Amsterdam. pp. 161–178
Brida J, Gomez D, Segarra V (2020) On the empirical relationship between tourism and economic growth. Tour Manag 81:104131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104131
Casado-Aranda L, Fernandez J, Bastidas-Manzano A (2021) Tourism research after the COVID-19 outbreak: insights for more sustainable, local and smart cities. Sustain Cities Soc 73:103126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103126
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Centobelli P, Cerchione R, Esposito E (2022) Environmental sustainability in the service industry of transportation and logistics service providers: systematic literature review and research directions. Transp Res Part D Trans Environ 53:454–470
Chao Q, Feng A (2018) Scientific basis of climate change and its response. Glob Energy Interconnect 1(4):420–427
Google Scholar
Choi Y, Oh C, Chon J (2022) Applying the resilience principles for sustainable ecotourism development: a case study of the Nakdong Estuary, South Korea. Tour Manag 83:104237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104237
Das D, Dutta A, Bhadra A, Uddin GS (2020) Role of presidential uncertainties on the hotel industry. Ann Tour Res 81:102762
Debbarma J, Choi Y (2022) A taxonomy of green governance: a qualitative and quantitative analysis towards sustainable development. Sustain Cities Soc 79:103693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103693
Dutta A, Mishra T, Uddin GS, Yang Y (2020) Brexit uncertainty and volatility persistence in tourism demand. Curr Issue Tour 24(16):2225–2232
Erdal H, Erdal G (2020) Panel FMOLS model analysis of the effects of livestock support policies on sustainable animal presence in Turkey. Sustainability 12:3444. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083444
Espoir D, Mudiangombe B, Bannor F, Sunge R, Tshitaka J (2022) CO2 emissions and economic growth: Assessing the heterogeneous effects across climate regimes in Africa. Sci Total Environ 804:150089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150089
Hasana U, Swain S, George B (2022) A bibliometric analysis of ecotourism: a safeguard strategy in protected areas. Region Sustain 3(1):27–40
Heshmati M, Gheitury M, Shadfar S (2022) Factors affecting possibility of ecotourism development and sustaining natural resources using SWOT approach in west Iran. Int J Geoheritage Parks 10(2):173–183
Holzner M (2011) Tourism and economic development: the beach disease. Tour Manag32(4):922–933
Hosseini S, Paydar M, Keshteli M (2021) Recovery solutions for ecotourism centers during the Covid-19 pandemic: utilizing Fuzzy DEMATEL and Fuzzy VIKOR methods. Exp Syst Appl 185:115594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115594
Hosseini S, Paydar M, Triki C (2021) Implementing sustainable ecotourism in Lafour region, Iran: applying a clustering method based on SWOT analysis. J Clean Prod 329:129716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129716
Jeyacheya J, Hampton M (2022) Pathway choice and post-Covid tourism: Inclusive growth or business as usual? World Dev Sustain 1:100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wds.2022.100024
Jin C, Takao M, Yobuta M(2022) Impact of Japan’s local community power on green tourism. Asia Pacific J Region Sci 6:571–591
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Economet 90(1):1–44
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Kunjuraman V, Hussin R, Aziz R (2022) Community-based ecotourism as a social transformation tool for rural community: a victory or a quagmire. J Outdoor Recreat Tour 39:100524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jort.2022.100524
Lee C, Wang C, Ho S (2022) The dimension of green economy: Culture viewpoint. Econ Anal Policy 74:122–138
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CS (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Economet 108(1):1–24
Li J, Ridderstaat J, Yost E (2022) Tourism development and quality of life interdependence with evolving age-cohort-based population. Tour Manag 93:104621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2022.104621
Liu A, Kim Y, Song H (2022) Toward an accurate assessment of tourism economic impact: a systematic literature review. Ann Tour Res Empirical Insight 3(2):100054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annale.2022.100054
Lu C, Huang J, Chen C, Shu M, Hsu C, Bapu T (2021) An energy-efficient smart city for sustainable green tourism industry. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 47:101494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101494
Maichum K, Parichatnon S, Peng KC (2016) Application of the extended theory of planned behavior model to investigate purchase intention of green products among Thai consumers. Sustainability 8:1077
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economet Theory 20(3):597–625
Phillips PCB, Perron P (1988) Testing for a unit root in time series regressions. Biometrika. 75(2):335–346
Rahman M (2022) The effect of taxation on sustainable development goals: evidence from emerging countries. Heliyon 8(9):e10512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10512
Rasoulinezhad E (2018) A new evidence from the effects of Russia’s WTO accession on its foreign trade. Eur Econ Rev 8(1):73–92
Rasoulinezhad E, Taghizadeh-Hesary F (2022) Role of green finance in improving energy efficiency and renewable energy development. Energy Efficiency 15(2):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-022-10021-4
Roelfsema M, Soest H, Elzen M, Coninck HH, Kuramochi T, Harmsen M, Dagnomilis I, Hohne N, Vuuren D (2022) Developing scenarios in the context of the Paris Agreement and application in the integrated assessment model IMAGE: a framework for bridging the policy-modelling divide. Environ Sci Policy 135:104–116
Article CAS Google Scholar
Ruhanan L (2019) The prominence of eco in ecotourism experiences: an analysis of post-purchase online reviews. J Hosp Tour Manag 39:110–116
Sokhanvar A, Ciftcioglu S, Javid E (2018) Another look at tourism-economic development nexus. Tour Manag Perspect 26:97–106
Soliku O, Kyiire B, Mahama A, Kubio C (2021) Tourism amid COVID-19 pandemic: impacts and implications for building resilience in the eco-tourism sector in Ghana’s Savannah region. Heliyon 7(9):e07892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07892
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sorensen F, Grindsted T (2021) Sustainability approaches and nature tourism development. Ann Tour Res 91:103307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2021.103307
Sun Y, Ding W, Yang G (2022) Green innovation efficiency of China’s tourism industry from the perspective of shared inputs: Dynamic evolution and combination improvement paths. Ecol Indica 138:108824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108824
Tajer E, Demir S (2022) Ecotourism strategy of UNESCO city in Iran: applying a new quantitative method integrated with BWM. J Clean Prod 376:134284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134284
Takashima N (2018) International environmental agreements between asymmetric countries: a repeated game analysis. Jpn World Econ 48:38–44
Thompson B (2022) Ecotourism anywhere? The lure of ecotourism and the need to scrutinize the potential competitiveness of ecotourism developments. Tour Manag 92:104568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2022.104568
Werikhe A (2022) Towards a green and sustainable recovery from COVID-19. Curr Res Environ Sustain 4:100124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crsust.2022.100124
Woodward A (2019) Climate change: disruption, risk and opportunity. Glob Trans 1:44–49
Xu L, Ao C, Liu B, Cai Z (2022) Cotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends. Environ Dev Sustain https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02190-0
Yusef N, Rahman F, Jamil M, Iranmanesh M (2014) Measuring the quality of ecotourism services: case study–based model validation. Sage Open, https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244014538270
Zekan B, Weismayer C, Gunter U, Schuh B, Sedlacek S (2022) Regional sustainability and tourism carrying capacities. J Clean Prod 339:130624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130624
Zheng H, Dai H, Lai H, Wang W (2017) U.S. withdrawal from the Paris agreement: reasons, impacts, and China’s response. Adv Clim Change Rese 8(4):220–225
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Hospitality Administration, Zhejiang Yuexiu University, Zhejiang, China
- Yunfeng Shang
School of Economics, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin, China
Chunyu Bi, Xinyu Wei & Dayang Jiang
School of Global Studies, Tokai University, Tokyo, Japan
Farhad Taghizadeh-Hesary
TOKAI Research Institute for Environment and Sustainability (TRIES), Tokai University, Tokyo, Japan
Faculty of World Studies, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
Ehsan Rasoulinezhad
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Yunfeng Shang , Dayang Jiang or Ehsan Rasoulinezhad .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shang, Y., Bi, C., Wei, X. et al. Eco-tourism, climate change, and environmental policies: empirical evidence from developing economies. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 275 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01777-w
Download citation
Received : 11 November 2022
Accepted : 18 May 2023
Published : 31 May 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01777-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Spatial effects of green finance development in chinese provinces under the context of high-quality energy development.
- Fangbin Qian
Economic Change and Restructuring (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Moscow City Walks and Areas
The best way to explore Moscow is to go for a walk in one of the central neighborhoods or parks.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Ecotourism and sustainable development: a scientometric review of global research trends
1 Department of Management Science and Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, 150030 China
2 Faculty of Economic and Management, Mudanjiang Normal University, Mudanjiang, 157011 China
Changlin Ao
3 College of Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, 150030 China
Associated Data
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Web of Science.
With the increasing attention and awareness of the ecological environment, ecotourism is becoming ever more popular, but it still brings problems and challenges to the sustainable development of the environment. To solve such challenges, it is necessary to review literature in the field of ecotourism and determine the key research issues and future research directions. This paper uses scientometrics implemented by CiteSpace to conduct an in-depth systematic review of research and development in the field of ecotourism. Two bibliographic datasets were obtained from the Web of Science, including a core dataset and an expanded dataset, containing articles published between 2003 and 2021. Our research shows that ecotourism has been developing rapidly in recent years. The research field of ecotourism spans many disciplines and is a comprehensive interdisciplinary subject. According to the research results, the evolution of ecotourism can be roughly divided into three phases: human disturbance, ecosystem services and sustainable development. It could be concluded that it has entered the third stage of Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline. The research not only identifies the main clusters and their advance in ecotourism research based on high impact citations and research frontier formed by citations, but also presents readers with new insights through intuitive visual images.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10668-022-02190-0.
Introduction
Ecotourism, which has appeared in academic literature since the late 1980s, is a special form of nature-based tourism that maintains the well-being of the local community while protecting the environment and provides tourists with a satisfying nature experience and enjoyment (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1996 ; Higgins, 1996 ; Orams, 1995 ). With years of research and development, ecotourism has risen to be a subject of investigation in the field of tourism research (Weaver & Lawton, 2007 ). In 2002, the United Nations declared it the International Year of Ecotourism (IYE), and the professional Journal of Ecotourism was established in the same year.
With the progress and maturity of ecotourism as an academic research field, countless scholars have put forward standards and definitions for ecotourism (Sirakaya et al., 1999 ; Wight, 1993 ). The main objectives of ecotourism emphasize long-term sustainable development (Whitelaw et al., 2014 ), including the conservation of natural resources, the generation of economic income, education, local participation and the promotion of social benefits such as local economic development and infrastructure (Ardoin et al., 2015 ; Coria & Calfucura, 2012 ; Krüger, 2005 ; Oladeji et al., 2021 ; Ross & Wall, 1999 ; Valdivieso et al., 2015 ). It can also boost rural economies and alleviate poverty in developing countries (Snyman, 2017 ; Zhong & Liu, 2017 ).
With unrestricted increasing attention to the ecological environment and the improvement of environmental awareness, ecotourism is becoming ever more prevalent, and the demand for tourism is increasing year by year (CREST, 2019 ). This increase, however, leads to a number of environmental, social and economic challenges in the development of ecotourism. For example, due to the low public awareness of ecotourism, the increase in tourists has brought a series of negative impacts on the local ecological environment, culture and economy, including disrespect for local culture and environmental protection, as well as more infrastructure construction and economic burden to meet the needs of tourists (Ahmad et al., 2018 ; Chiu et al., 2014 ; Shasha et al., 2020 ; Xu et al., 2020 ). Such challenges and contradictions are urgent problems to be tackled by the sustainable development of ecotourism. Especially against the backdrop of the current pandemic, tourism has experienced a severe blow, but climate change and other environmental issues have not been improved (CREST, 2020 ). In this context, facing these challenges and difficulties, it is essential to re-examine the future development path of ecotourism, to explore how government agencies can formulate appropriate management policies while preserving the environment and natural resources to support sustainable tourism development. Accordingly, it is necessary to consult literature in the field of ecotourism to understand the research progress and fundamental research issues, to identify challenges, suitable methods and future research direction of ecotourism.
Some previous reviews of ecotourism offer a preview of research trends in this rapidly developing area. Weaver and Lawton ( 2007 ) provide a comprehensive assessment of the current state and future progress of contemporary ecotourism research, starting with the supply and demand dichotomy of ecotourism, as well as fundamental areas such as quality control, industry, external environment and institutions. Ardoin et al. ( 2015 ) conducted a literature review, analyzing the influence of nature tourism on ecological knowledge, attitudes, behavior and potential research into the future. Niñerola et al. ( 2019 ) used the bibliometric method and VOSviewer to study the papers on sustainable development of tourism in Scopus from 1987 to 2018, including literature landscape and development trends. Shasha et al. ( 2020 ) used bibliometrics and social network analysis to review the research progress of ecotourism from 2001 to 2018 based on the Web of Science database using BibExcel and Gephi and explored the current hot spots and methods of ecotourism research. These reviews have provided useful information for ecotourism research at that time, but cannot reflect the latest research trends and emerging development of ecotourism either of timeliness, data integrity, research themes or methods.
This study aims to reveal the theme pattern, landmark articles and emerging trends in ecotourism knowledge landscape research from macro- to micro-perspectives. Unlike previous literature surveys, from timeliness, our dataset contains articles published between 2003 and 2021, and it will reveal more of the trends that have emerged over the last 3 years. Updating the rapidly developing literature is important as recent discoveries from different areas can fundamentally change collective knowledge (Chen et al., 2012 , 2014a ). To ensure data integrity, two bibliographic datasets were generated from Web of Science, including a core dataset using the topic search and an expanded dataset using the citation expansion method, which is more robust than defining rapidly growing fields using only keyword lists (Chen et al., 2014b ). And from the research theme and method, our review focuses on the area of ecotourism and is instructed by a scientometric method conducted by CiteSpace, an analysis system for visualizing newly developing trends and key changes in scientific literature (Chen et al., 2012 ). Emerging trends are detected based on metrics calculated by CiteSpace, without human intervention or working knowledge of the subject matter (Chen et al., 2012 ). Choosing this approach can cover a more extensive and diverse range of related topics and ensure repeatability of analysis with updated data (Chen et al., 2014b ).
In addition, Shneider’s four-stage theory will be used to interpret the results in this review. According to Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline (Shneider, 2009 ), the development of a scientific discipline is divided into four stages. Stage I is the conceptualization stage, in which the objects and phenomena of a new discipline or research are established. Stage II is characterized by the development of research techniques and methods that allow researchers to investigate potential phenomena. As a result of methodological advances, there is a further understanding of objects and phenomena in the field of new subjects at this stage. Once the techniques and methods for specific purposes are available, the research enters Stage III, where the investigation is based primarily on the application of the new research method. This stage is productive, in which the research results have considerably enhanced the researchers’ understanding of the research issues and disclosed some unknown phenomena, leading to interdisciplinary convergence or the emergence of new research directions or specialties. The last stage is Stage IV, whose particularity is to transform tacit knowledge into conditional knowledge and generalized knowledge, so as to maintain and transfer the scientific knowledge generated in the first three stages.
The structure of this paper is construed as follows. The second part describes the research methods employed, the scientometric approach and CiteSpace, as well as the data collection. In the third part, the bibliographic landscape of the core dataset is expounded from the macroscopic to the microscopic angle. The fourth part explores the developments and emerging trends in the field of ecotourism based on the expanded dataset and discusses the evolution phase of ecotourism. The final part is the conclusion of this study. Future research of ecotourism is prospected, and the limitations of this study are discussed.
Methods and data collection
Scientometric analyses and citespace.
Scientometrics is a branch of informatics that involves quantitative analysis of scientific literature in order to capture emerging trends and knowledge structures in a particular area of study (Chen et al., 2012 ). Science mapping tools generate interactive visual representations of complex structures by feeding a set of scientific literature through scientometrics and visual analysis tools to highlight potentially important patterns and trends for statistical analysis and visualization exploration (Chen, 2017 ). At present, scientometrics is widely used in many fields of research, and there are also many kinds of scientific mapping software widely used by researchers and analysts, such as VosViewer, SCI2, HistCite, SciMAT, Gephi, Pajek and CiteSpace (Chen, 2011 , 2017 ; Chen et al., 2012 ).
Among these tools, CiteSpace is known for its powerful literature co-citation analysis, and its algorithms and features are constantly being refined as it continues to evolve. CiteSpace is a citation visual analysis software developed under the background of scientometrics and data visualization to analyze the basics that are included in scientific analysis (Chen, 2017 ; Chen et al., 2012 ). It is specialized designed to satisfy the need for systematic review in rapidly changing complicated areas, particularly with the ability to identify and explain emerging trends and transition patterns (Chen et al., 2014a ). It supports multiple types of bibliometric research, such as collaborative network analysis, co-word analysis, author co-citation analysis, document co-citation analysis, and temporal and spatial visualization (Chen, 2017 ). Currently, CiteSpace has been extensively used in more than 60 fields, including computer science, information science, management and medicine (Abad-Segura et al., 2019 ; Chen, 2017 ).
In this paper, we utilize CiteSpace (5.8.R1) to analyze acquired bibliographies of ecotourism to study emerging trends and developments in this field. From macro to micro, from intuitive to complex, from whole to part and from general to special, the writing ideas are adopted. Figure 1 presented the specific research framework of this study.

The research framework of this study
Data collection
Typical sources of scientific literature are Web of Science, Scopus and Google Scholar. Considering the quantity and quality of data, the Web of Science database was expected to provide the original data in this research. In order to comprehend the research status and development trends of ecotourism, this study systematically reviewed the ecotourism literature collected on the Web of Science Core Collection. The Web of Science Core Collection facilitates access to the world’s leading scholarly journals, books and proceedings of conferences in the sciences, social sciences, art, and humanities, as well as access to their entire citation network. It mainly includes Science Citation Index Expanded from 2003 to current and Social Sciences Citation Index from 2004 to present. Therefore, the data obtained in this study are from 2003 and were consulted on June 3, 2021.
In the process of data retrieval, it is frequently confronted with the choice between recall rate and precision rate. To address the problem of low recall rate in keyword or topic retrieval, Chen et al. ( 2014a , b ) expanded the retrieval results through ‘citation expansion’ and ‘comprehensive topic search’ strategies. However, when the recall rate is high, the accuracy rate will decrease correspondingly. In practical standpoint, instead of refining and cleaning up the original search results, a simpler and more efficient way is to cluster or skip these unrelated branches. Priority should be placed on ensuring recall rate, and data integrity is more important than data for accuracy. Therefore, two ecotourism documentation datasets, the core dataset and the expanded dataset, were obtained from the Web of Science by using comprehensive topic search and citation expansion method. The latter approach has been proved more robust than using keyword lists only to define fast-growing areas (Chen et al., 2014b ). A key bibliographic landscape is generated based on the core dataset, followed by more thorough research of the expanded dataset.
The core dataset
The core dataset was derived through comprehensive subject retrieval in Web of Science Core Collection. The literature type was selected as an article or review, and the language was English. The period spans 2003 to 2021. The topic search query is composed of three phrases of ecotourism: ‘ ecotour* ’ OR ‘ eco-tour* ’ OR ‘ ecological NEAR/5 tour* ’. The wildcard * is used to capture related variants of words, for example, ecotour, ecotourism, ecotourist and ecotourists. The related records that are requested include finding these terms in the title, abstract or keywords. The query yielded 2991 original unique records.
The expanded dataset
The expanded dataset includes the core dataset and additional records obtained by reference link association founded on the core dataset. The principle of citation expansion is that if an article cites at least one article in the core dataset, we can infer that it is related to the topic (Garfield, 1955 ). The expanded dataset is comprised of 27,172 unique records, including the core dataset and the articles that cited them. Both datasets were used for the following scientometrics analysis.
Bibliographic landscape based on the core dataset
The core dataset consists of a total of 2991 literature from 2003 to 2021. This study utilized the core dataset to conduct an overall understanding of the bibliographic landscape in the field of ecotourism.
Landscape views of core dataset
The distribution of the yearly publication of bibliographic records in the core and expanded datasets is presented in Fig. 2 . It can be observed that the overall number of ecotourism-related publications is on the rise, indicating that the scholarly community is increasingly interested in ecotourism. After 2018, the growth rate increased substantially. And in 2020, the number of publications in the expanded dataset is close to 5000, almost double that of 2017 and 5 times that of 2011. This displays the rapid development of research in the field of ecotourism in recent years, particularly after 2018, more and more researchers began to pay attention to this field, which also echoes the trend of global tourism development and environmental protection. With the increase in personal income, tourism has grown very rapidly, and with it, tourism revenue and tourist numbers, especially in developing states. For instance, the number of domestic tourists in China increased from 2.641 billion in 2011 to 6.06 billion in 2019, and tourism revenue increased from 1930.5 billion RMB in 2011 to 5725.1 billion RMB in 2019 (MCT, 2021 ). However, due to the lack of effective management and frequent human activities, the rapid development of tourism has led to various ecological and environmental problems, which require corresponding solutions (Shasha et al., 2020 ). This has played an active role in promoting the development of ecotourism and triggered a lot of related research. In addition, since 2005, the expanded dataset has contained numerous times as many references as the core dataset, demonstrating the importance of using citation expansion for literature retrieval in scientometric review studies.The data were consulted on June 3, 2021

The distribution of bibliographic records in core and expanded dataset. Note The data were consulted on June 3, 2021
The dual-map overlay of scientific map literature as Fig. 3 shows, against the background of global scientific map from more than 10,000 journals covered by Web of Science, represents the distribution and connections on research bases and application fields across the entire dataset of the research topics (Chen & Leydesdorff, 2014 ). Colored lines are citation links, and numbered headings are cluster labels. On the left side is the journal distribution which cites literature, regarding the field application of ecotourism, mainly covers multiple disciplines such as 3. Ecology, Earth, Marine, 6. Psychology, Education, Health, 7. Veterinary, Animal Science and 10. Economics, Economic and Political. On the right side is the distribution of journals of cited literature, representing the research basis of ecotourism. As can be observed from the figure, ecotourism research is based on at least five disciplines on the right, including 2. Environmental, Toxicology, Nutrition, 7. Psychology, Education, Social, 8. Molecular, Biology, Genetics, 10. Plant, Ecology, Zoology and 12. Economics, Economic, Political. It can be viewed that the research field of ecotourism spans multiple disciplines and is a comprehensive and complex subject. The dual-map overlay provides a global visualization of literature growth of the discipline level.

A dual-map overlay of ecotourism literature
The total number of papers issued by a country or an institution reflects its academic focus and overall strength, while centrality indicates the degree of academic cooperation with others and the influence of published papers. The top 15 countries and institutions for the number of ecotourism papers published from 2003 to 2021 are provided in Table Table1. 1 . Similar to the study of Shasha et al. ( 2020 ), the ranking of the top six countries by the number of publications remains unchanged. As can be seen from the table, the USA ranks first in the world, far ahead in both the number of publications and the centrality. China ranks second in global ecotourism publications, followed by Australia, England, South Africa and Canada. While the latest data show that Taiwan (China), Turkey and South Korea appear on the list. Overall, the top 15 countries with the most publications cover five continents, containing a number of developed and developing, which shows that ecotourism research is receiving global attention. In terms of international academic cooperation and impact of ecotourism, Australia and England share second place, Italy and France share fourth place, followed by South Africa and Spain. China’s centrality is relatively low compared to the number of publications, ranking eighth. Academic cooperation between countries is of great significance. Usually, countries with high academic publishing level cooperate closely due to similar research interests. International academic cooperation has enhanced each other’s research capacity and promoted the development of ecotourism research. Therefore, although some countries have entered this list with the publication number, they should attach importance to increase academic cooperation with other countries and improving the international influence of published papers.
The top 15 most productive countries and institutions on ecotourism
The Chinese Academy of Sciences and its university are the most prolific when it draws to institutions’ performance. It is the most important and influential research institute in China, especially in the field of sustainable development science. Australia has four universities on the list, with Griffith University and James Cook University in second and third place. USA also includes four universities, with the University of Florida in fourth place. South Africa, a developing country, gets three universities, with the University of Cape Town and the University of Johannesburg fifth and sixth, respectively. In comparison with previous studies (Shasha et al., 2020 ), Iran and Mexico each have one university in the ranking, replacing two universities in Greece, which means that the importance and influence of developing countries in the field of ecotourism is gradually rising. Based on the above results, it can be summarized that the USA, China, Australia and South Africa are relatively active countries in the field of ecotourism, and their development is also in a relatively leading position.
Most active topics
The foam tree map and the pie chart of the focal topics of ecotourism based on the core dataset generated by Carrot2 through the title of each article is illustrated in Fig. 4 . Developing and developed, case study, protected areas, sustainable tourism, tourism development and developing ecotourism are leading topics in the field of ecotourism research, as well as specific articles under the main topics. The lightweight view generated by Carrot2 provides a reference for the research, and then, co-word analysis is employed to more specifically reflect the topics in the research field.

Foam tree map and pie chart of major topics on ecotourism
The topics covered by ecotourism could be exposed by the keywords of the articles in the core dataset. Figure 5 displays the keywords analysis results generated based on the core dataset. From the visualization results in the figure, it can infer that ecotourism, conservation, tourism, management, protected area, impact, biodiversity, sustainability, national park and community are the ten most concerned topics. Distinct colors set out at the time of co-citation keywords first appear, and yellow is generated earlier than red. In addition, Fig. 5 can also reflect the development and emerging topics in the research field, such as China, Mexico, South Africa and other hot countries for ecotourism research; ecosystem service, economic value, climate change, wildlife tourism, rural tourism, forest, marine protected area and other specific research directions; valuation, contingent valuation, choice experiment and other research methods; willingness to pay, preference, benefit, perception, attitude, satisfaction, experience, behavior, motivation, risk, recreation and other specific research issues.

A landscape view of keywords based on the core dataset
Emerging trends and developments based on the expanded dataset
The expanded dataset, consisting of 27,172 records, is approximately nine times larger than the core dataset. This research applies the expanded dataset to profoundly explore the emerging trends and developments of ecotourism.
Keywords with citation bursts
Detection of citation bursts can indicate both the scientific community’s interest in published articles and burst keywords as an indicator of emerging tendencies. Figure 6 displays the top 30 keywords with the strongest citation bursts in the expanded dataset. Since 2003, a large number of keywords have exploded. Among them, the strongest bursts include ecotourism, bird, disturbance, reserve, Africa, challenge, sustainable development and strategy. Keywords with citation burst after 2017 are experience, challenge, sustainable development, willingness to pay, perspective, strategy, quality and satisfaction, which have continued to this day. The results indicate dynamic development and emerging trends in research hotspots in the field of ecotourism.

Top 30 keywords with the strongest citation bursts
References with citation bursts
Figure 7 sets out the top 30 references in the expanded dataset with citation bursts. The articles with the fastest growing citations can also contribute to describe the dynamics of a field. References with high values in strength column are important milestones of ecotourism research. The two articles with strong citation bursts prior to 2010 focused on the human impact on the environment and animals. West et al. ( 2006 ) discussed the relationship between parks and human beings and the social impact of protected areas, and Köndgen et al. ( 2008 ) studied the decline of endangered great apes caused by a human pandemic virus. The paper with the strongest citation burst in the entire expanded dataset was released by Fairhead et al. ( 2012 ), which looked at ‘green grabbing,’ the appropriation of land and resources for environmental purposes. Milcu et al. ( 2013 ) conducted a semi-quantitative review of publications dealing with cultural ecosystem services with the second strongest citation burst, which concluded that the improvement of the evaluation method of cultural ecosystem service value, the research on the value of cultural ecosystem service under the background of ecosystem service and the clarification of policy significance were the new themes of cultural ecosystem service research. In addition, many articles with citation burst discussed the evaluation method of ecosystem services value (Costanza et al., 2014 ; Groot et al., 2010 ), the evaluation of cultural ecosystem service value (Plieninger et al., 2013 ) and its role in ecosystem service evaluation (Chan et al., 2012 ; Chan, Guerry, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Daniel et al., 2012 ). The most fresh literature with strong citation burst is the article of D’Amato et al. ( 2017 ) published in the Journal of Cleaner Production, which compared and analyzed sustainable development avenues such as green, circular and bio economy. In addition, it is worthwhile noting the use of R in ecotourism, with the persuasive citation burst continuing from 2012 to the present, as indicated by the orange arrow in Fig. 7 .

Top 30 references with the strongest citation bursts
Landscape view of co-citation analysis
The landscape view of co-citation analysis of Fig. 8 is generated based on the expanded dataset. Using g -index ( k = 25) selection criteria in the latest edition of CiteSpace, an annual citation network was constructed. The final merged network contained 3294 links, 2122 nodes and 262 co-citation clusters. The three largest linked components cover 1748 connected nodes, representing 82% of the entire network. The modularization degree of the synthetic network is 0.8485, which means that co-citation clustering can clearly define each sub-field of ecotourism. Another weighted mean silhouette value of the clustering validity evaluation is 0.9377, indicating that the clustering degree of the network is also very superior. The harmonic mean value amounts to 0.8909.

A landscape view of the co-citation network based on the expanded dataset
In the co-citation network view, the location of clusters and the correlation between clusters can show the intellectual structure in the field of ecotourism, so that readers can obtain an overall understanding of this field. The network falls into 25 co-citation clusters. The tags for each cluster are generated founded on the title, keywords and abstract of the cited article. Color-coded areas represent the time of first appeared co-citation links, with gray indicating earlier and red later. The nodes in the figure with red tree rings are references to citation bursts.
Timeline view
In order to further understand the time horizon and study process of developing evolution on clusters, after the generation of co-citation cluster map, the Y -axis is cluster number and the year of citation publication is X -axis, so as to obtain the timeline view of the co-citation network, shown as Fig. 9 . Clusters are organized vertically from largest to smallest. The color curve represents co-citation link coupled with corresponding color year, with gray representing earlier and red representing newer. Larger nodes and nodes with red tree rings indicate high citation or citation burst. The three most cited references of the year demonstrate below each node, in vertical order from least to most.

A timeline visualization of the largest clusters
The timeline view provides a reasonably instinctual and insightful reference to understand the evolutionary path of every subdomain. Figure 9 shows 19 clusters ranging from #0 to #18, with #0 being the largest cluster. As can be seen from the figure, the sustainability and activeness of each cluster are contrasting. For example, the largest cluster has been active since 2006, while the gray and purple clusters are no longer active.
Major clusters
Taking clustering as a unit and analyzing at the level of clustering, specifically selecting large or new type clustering, is the foothold of co-citation analysis, which can help to understand the principal and latest research fields related to ecotourism. Table Table2 2 displays a summary of the foremost 19 clusters, the first nine of which are all over 100 in size. The silhouette score of all clusters is greater than 0.8, indicating that the homogeneity of each cluster is high. The mean year is the average of the publication dates of references in the cluster. By combining the results in Table Table2, 2 , Figs. 8 and and9, 9 , it can be observed that the five largest clusters are #0 cultural ecosystem services, #1 large carnivore, #2 human disturbance, #3 whale shark and #4 ecosystem service. A recent topic is cluster #16 COVID-19 pandemic. #11 Ecological footprint and #14 social media are two relatively youthful fields.
Summary of major clusters
* LLR refers to Log-Likelihood Ratio
The research status of a research field can be demonstrated by its knowledge base and research frontier. The knowledge base consists of a series of scholarly writing cited by the corresponding article, i.e., cited references, while the research frontier is the writing inspired by the knowledge base, i.e., citing articles. Distinct research frontiers may come from the same knowledge base. Consequently, each cluster is analyzed based on cited references and citing articles. The cited references and citing articles of the five largest clusters are shown in Online Appendix A. Fig a) lists the 15 top cited references with the highest Σ (sigma) value in the cluster, where Σ value indicates that the citation is optimal in terms of the comprehensive performance of structural centrality and citation bursts. Fig b) shows the major citing articles of cluster. The citation behavior of these articles determines the grouping of cited literature and thus forms the cluster. The coverage is the proportion of member citations cited by citing articles.
Phase evolution research
Through the above analysis of the core dataset and the expanded dataset of ecotourism, we can see the development and evolution of the research field of ecotourism. The research process of ecotourism has gone through several stages, and each stage has its strategic research issues. Research starts with thinking about the relationship between humans and nature, moves to study it as a whole ecosystem, and then explores sustainable development. Hence, the evolution of ecotourism can be roughly parted into three phases.
Phase I: Human disturbance research stage (2003–2010)
This phase of research concentrates on the influence of human activities such as ecotourism on the environment and animals. Representative keywords of this period include ecotourism, human disturbance, response, coral reef, bird, disturbance, recreation, reserve, park, South Africa and people. Representative articles are those published by West et al. ( 2006 ) and Köndgen et al. ( 2008 ) of human impact on the environment and animals. The representative clustering is #2 human disturbance, which is the third largest one, consisting of 130 cited references from 1998 to 2012 with the average year of 2004. This cluster has citation bursts between 2002 and 2010 and has been inactive since then. As showed in Fig S3 a) and b), the research base and frontier are mainly around the impact of human disturbances such as ecotourism on biology and the environment (McClung et al., 2004 ). And as showed in Fig. 8 and Fig. 9 , clusters closely related to #2 belong to this phase and are also no longer active, such as #5 off-road vehicle, #6 protected area, #10 poverty reduction and #12 sustainable lifestyle.
Phase II: Ecosystem services research stage (2011–2015)
In this stage, the content of ecotourism research is diversified and exploded. The research is not confined to the relationship between humans and nature, but begins to investigate it as an entire ecosystem. In addition, some specific or extended areas began to receive attention. Typical keywords are abundance, resource, Africa, risk, predation, consequence and science. The most illustrative papers in this stage are Fairhead et al. ( 2012 )’s discussion on green grabbing and Milcu et al. ( 2013 )’s review on cultural ecosystem services. Other representative papers in this period focused on the evaluation methods of ecosystem service value and the role of cultural ecosystem service in the evaluation of ecosystem service value. Most of the larger clusters in the survey erupted at this stage, including #0 cultural ecosystem services, #1 large carnivore, #3 whale shark, #4 ecosystem services. Some related clusters also belong to this stage, such as #7 neoliberal conservation, #8 responsible behavior, #9 tourism development, #13 mangrove forest, #15 volunteer tourism, #17 circular economy and #18 telecoupling framework.
Cluster #0 cultural ecosystem services are the largest cluster in ecotourism research field, containing 157 cited references from 2006 to 2019, with the mean year being 2012. It commenced to have the citation burst in 2009, with high cited continuing until 2019. Cultural ecosystem services are an essential component of ecosystem services, including spiritual, entertainment and cultural benefits. Thus, in Fig. 8 , the overlap with #4 ecosystem services can obviously be seen. In Cluster #0, many highly cited references have discussed the trade-offs between natural and cultural ecosystem services in ecosystem services (Nelson et al., 2009 ; Raudsepp-Hearne et al., 2010 ) and the important role of cultural ecosystem services in the evaluation of ecosystem services value (Burkhard et al., 2012 ; Chan, Guerry, et al., 2012 ; Chan, Satterfield, et al., 2012 ; Fisher et al., 2009 ; Groot et al., 2010 ). As non-market value, how to evaluate and quantify cultural ecosystem services is also an important issue (Hernández-Morcillo et al., 2012 ; Milcu et al., 2013 ; Plieninger et al., 2013 ). Besides, the exploration of the relationship among biodiversity, human beings and ecosystem services is also the focus of this cluster research (Bennett et al., 2015 ; Cardinale et al., 2012 ; Díaz et al., 2015 ; Mace et al., 2012 ). The citing articles of #0 indicate the continued exploration of the connotation of cultural ecosystem services and their value evaluation methods (Dickinson & Hobbs, 2017 ). It is noteworthy that some articles have introduced spatial geographic models (Havinga et al., 2020 ; Hirons et al., 2016 ) and social media methods (Calcagni et al., 2019 ) as novel methods to examine cultural ecosystem services. In addition, the link and overlap between #0 cultural ecosystem service and #17 circular economy cannot be overlooked.
Ecosystem services relate to all the benefits that humans receive from ecosystems, including supply services, regulatory services, cultural services and support services. Research on cultural ecosystem services is based on the research of ecosystem services. It can be viewed in Fig. 9 that the research and citation burst in #4 was all slightly earlier than #0. Cluster #4 includes 118 references from 2005 to 2019, with an average year of 2011. In its research and development, how to integrate ecosystem services into the market and the payment scheme to protect the natural environment is a significant research topic (Gómez-Baggethun et al., 2010 ). In Cluster #4, the most influential literature provides an overview of the payment of ecosystem services (PES) from theory to practice by Engel et al. ( 2008 ). Many highly cited references have discussed PES (Kosoy & Corbera, 2010 ; Muradian et al., 2010 ), including the effectiveness of evaluation (Naeem et al., 2015 ), social equity matters (Pascual et al., 2014 ), the suitability and challenge (Muradian et al., 2013 ), and how to contribute to saving nature (Redford & Adams, 2009 ). The cluster also includes studies on impact assessment of protected areas (Oldekop et al., 2016 ), protected areas and poverty (Brockington & Wilkie, 2015 ; Ferraro & Hanauer, 2014 ), public perceptions (Bennett, 2016 ; Bennett & Dearden, 2014 ) and forest ecosystem services (Hansen et al., 2013 ). The foremost citing articles confirm the dominant theme of ecosystem services, especially the in-depth study and discussion of PES (Muniz & Cruz, 2015 ). In addition, #4 is highly correlated with #7 neoliberal protection, and Fairhead et al. ( 2012 ), a representative article of this stage, belongs to this cluster.
As the second largest cluster, Cluster #1 contains 131 references from 2008 to 2019, with the median year of 2014. As Fig S2 a) shows, the highly cited literature has mainly studied the status and protection of large carnivores (Mace, 2014 ; Ripple et al., 2014 ), including the situation of reduction (Craigie et al., 2010 ), downgrade (Estes et al., 2011 ) and even extinction (Dirzo et al., 2014 ; Pimm et al., 2014 ), and the reasons for such results, such as tourist visits (Balmford et al., 2015 ; Geffroy et al., 2015 ) and the increase in population at the edge of the protected areas (Wittemyer et al., 2008 ). The conservation effects of protected areas on wildlife biodiversity (Watson et al., 2014 ) and the implications of tourist preference heterogeneity for conservation and management (Minin et al., 2013 ) have also received attention. It is worth noting that the high citation rate of a paper using R to estimate the linear mixed-effects model (Bates et al., 2015 ) and the use of R in this cluster. The relationship between biodiversity and ecotourism is highlighted by the representative citing articles in research frontier of this cluster (Chung et al., 2018 ).
Cluster #3 refers to marine predator, and as shown in Fig. 8 , which has a strong correlation with #1. A total of 125 references were cited from 2002 to 2018, with an average year of 2011. References with high citation in #3 mainly studied the extinction and protection of marine life such as sharks (Dulvy et al., 2014 ), as well as the economic value and ecological impact of shark ecotourism (Clua et al., 2010 ; Gallagher & Hammerschlag, 2011 ; Gallagher et al., 2015 ). The paper published by Gallagher et al. ( 2015 ) is both the highly cited reference and main citing article, mainly focusing on the impact of shark ecotourism. It is also noteworthy that #6 protected area, #13 mangrove forest and #29 Mediterranean areas are highly correlated with these two clusters (Fig. 8 ).
Moreover, some clusters are not highly correlated with other clusters, but cannot be neglected at this stage of research. Cluster #8 responsible behavior includes 107 citations with the average year 2013, and mainly studied environmentally responsible behaviors in ecotourism (Chiu et al., 2014 ). Cluster #9 tourism development contains 97 cited references with mean year of 2015, focusing on the impact of such factors as residents’ perception on tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Cluster #15 volunteer tourism consists of 52 citations, with an average year of 2011, which mainly considers the role of volunteer tourism in tourism development and sustainable tourism (Wearing & McGehee, 2013 ). Cluster #18 telecoupling framework has 26 cited references with the mean year being 2015, and the application of the new integrated framework of telecoupling 1 in ecotourism can be seen (Liu et al., 2015 ).
At this stage, it can be seen that the research field of ecotourism begins to develop in the direction of diversification, including the value evaluation and related research of ecosystem services and cultural ecosystem services, as well as the exploration of wild animals and plants, marine animals and plants and biodiversity. Neoliberal conservation, tourists’ responsible behavior, tourism development, volunteer tourism and circular economy are all explored. Some new research methods have also brought fresh air to this field, such as the introduction of spatial geographic models and social media methods, the discussion of economic value evaluation methods, the widespread use of R and the exploration of telecoupling framework. Therefore, from this stage, research in the field of ecotourism has entered the second stage of scientific discipline development (Shneider, 2009 ), featured by the use and evolution of research tools that can be used to investigate potential phenomena.
Phase III: Sustainable development research stage (2016 to present)
This stage of research continues to explore a series of topics of the preceding phase and further extends the research field on this basis. The keywords at this stage are politics, marine protected area and valuation. Some other keywords are still very active today, such as experience, challenge, sustainable development, willingness to pay, perspective, strategy, quality and satisfaction. The representative article is about sustainable development published by D'Amato et al. ( 2017 ), as shown in Fig. 8 belonging to #17 circular economy. The emerging clusters in this period are #11 ecological footprint, #14 social media and #16 COVID-19 pandemic. Cluster #11 contains 70 cited references from 2013 to 2020 with the mean year 2017. This clustering study mainly used the ecological footprint as an environmental indicator and socioeconomic indicators such as tourism to investigate the hypothesis of environmental Kuznets curve (Ozturk et al., 2016 ; Ulucak & Bilgili, 2018 ). Cluster #14 includes 52 cited references, with an average year of 2016. It can be seen that the introduction of social media data has added new color to research in the field of ecotourism, such as using social media data to quantify landscape value (Zanten et al., 2016 ) and to understand tourists’ preferences for the experience of protected areas (Hausmann et al., 2018 ), as well as from a spatial perspective using social media geo-tagged photos as indicators for evaluating cultural ecosystem services (Richards & Friess, 2015 ). As the latest and most concerned topic, cluster #16 contains 48 cited references, with mean year of 2018. This cluster mainly cites research on over-tourism (Seraphin et al., 2018 ) and sustainable tourism (Higgins-Desbiolles, 2018 ) and explores the impact of pandemics such as COVID-19 on global tourism (Gössling et al., 2021 ).
These emerging clusters at this phase bring fresh thinking to the research of ecotourism. First of all, the analysis of ecological footprint provides a tool for measuring the degree of sustainability and helps to monitor the effectiveness of sustainable programs (Kharrazi et al., 2014 ). Research and exploration of ecological footprint in ecotourism expresses the idea of sustainable development and puts forward reasonable planning and suggestions by comparing the demand of ecological footprint with the carrying capacity of natural ecosystem. Secondly, the use of social media data brings a new perspective of data acquisition to ecotourism research. Such large-scale data acquisition can make up for the limitations of sample size and data sampling bias faced by survey data users and provide a new way to understand and explore tourist behavior and market (Li et al., 2018 ). Finally, the sudden impact of COVID-19 in 2020 and its long-term sustainability has dealt a huge blow to the tourism industry. COVID-19 has highlighted the great need and value of tourism, while fundamentally changing the way destinations, business and visitors plan, manage and experience tourism (CREST, 2020 ). However, the stagnation of tourism caused by the pandemic is not enough to meet the challenges posed by the environment and the climate crisis. Therefore, how to sustain the development of tourism in this context to meet the challenges of the environment and climate change remains an important issue in the coming period of time. These emerging clusters are pushing the boundaries of ecotourism research and the exploration of sustainable development in terms of research methods, data collection and emerging topics.
Despite the fact that the research topics in this stage are richer and more diversified, the core goal of research is still committed to the sustainable development of ecotourism. The introduction of new technologies and the productive results have led to a much-improved understanding of research issues. All this commemorates the entrance of research into the third stage of the development of scientific disciplines (Shneider, 2009 ). In addition to continuing the current research topics, the future development of the field of ecotourism will continue to focus on the goal of sustainable development and will be more diversified and interdisciplinary.
This paper uses scientometrics to make a comprehensive visual domain analysis of ecotourism. The aim is to take advantage of this method to conduct an in-depth systematic review of research and development in the field of ecotourism. We have enriched the process of systematic reviews of knowledge domains with features from the latest CiteSpace software. Compared with previous studies, this study not only updated the database, but also extended the dataset with citation expansion, so as to more comprehensively identify the rapidly developing research field. The research not only identifies the main clusters and their advance in ecotourism research based on high impact citations and research frontiers formed by citations, but also presents readers with new insights through intuitive visual images. Through this study, readers can swiftly understand the progress of ecotourism, and on the basis of this study, they can use this method to conduct in-depth analysis of the field they are interested in.
Our research shows that ecotourism has developed rapidly in recent years, with the number of published articles increasing year by year, and this trend has become more pronounced after 2018. The research field of ecotourism spans many disciplines and is a comprehensive interdisciplinary subject. Ecotourism also attracts the attention of numerous developed and developing countries and institutions. The USA, China, Australia and South Africa are in a relatively leading position in the research and development of ecotourism. Foam tree map and pie chart of major topics, and the landscape view of keywords provide the hotspot issues of the research field. The development trend of ecotourism is preliminarily understood by detecting the citation bursts of the keywords and published articles. Co-citation analysis generates the main clusters of ecotourism research, and the timeline visualization of these clusters provides a clearer view for understanding the development dynamics of the research field. Building on all the above results, the research and development of ecotourism can be roughly divided into three stages: human disturbance, ecosystem services and sustainable development. Through the study of keywords, representative literature and main clusters in each stage, the development characteristics and context of each stage are clarified. From the current research results, we can catch sight that the application of methods and software in ecotourism research and the development of cross-field. Supported by the Shneider’s four-stage theory of scientific discipline (Shneider, 2009 ), it can be thought that ecotourism is in the third stage. Research tools and methods have become more potent and convenient, and research perspectives have become more diverse.
Based on the overall situation, research hotspots and development tendency of ecotourism research, it can be seen that the sustainable development of ecotourism is the core issue of current ecotourism research and also an important goal for future development. In the context of the current pandemic, the tourism industry is in crisis, but crisis often breeds innovation, and we must take time to reconsider the way forward. As we look forward to the future of tourism, we must adopt the rigor and dedication required to adapt to the pandemic, adhering to the principles of sustainable development while emphasizing economic reliability, environmental suitability and cultural acceptance. Post-COVID, the competitive landscape of travel and tourism will change profoundly, with preventive and effective risk management, adaptation and resilience, and decarbonization laying the foundation for future competitiveness and relevance (CREST, 2020 ).
In addition, as can be seen from the research and development of ecotourism, the exploration of sustainable development increasingly needs to absorb research methods from diverse fields to guide the formulation of policy. First of all, how to evaluate and quantify ecotourism reasonably and scientifically is an essential problem to be solved in the development of ecotourism. Some scholars choose contingent valuation method (CVM) and choice experiment (CE) in environmental economics to evaluate the economic value of ecotourism, especially non-market value. In addition, the introduction of spatial econometrics and the use of geographic information system (GIS) provide spatial scale analysis methods and results presentation for the sustainable development of ecotourism. The use of social media data implies the application of big data technology in the field of ecotourism, where machine learning methods such as artificial neural networks (ANN) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) are increasingly being applied (Talebi et al., 2021 ). The measurement of ecological footprint and the use of telecoupling framework provide a reliable way to measure sustainable development and the interaction between multiple systems. These approaches all have expanded the methodological boundaries of ecotourism research. It is worth noting that R, as an open source and powerful software, is favored by scholars in the field of ecotourism. This programming language for statistical computation is now widely used in statistical analysis, data mining, data processing and mapping of ecotourism research.
The scientometrics method used in this study is mainly guided by the citation model in the literature retrieval dataset. The range of data retrieval exercises restraint by the source of retrieval and the query method utilized. While current methods can meet the requirements, iterative query optimization can also serve to advance in the quality of the data. To achieve higher data accuracy, the concept tree function in the new version of CiteSpace can also serve to clarify the research content of each clustering (Chen, 2017 ). In addition, the structural variation analysis in the new edition is also an interesting study, which can show the citation footprints of typical high-yielding authors and judge the influence of the author on the variability of network structure through the analysis of the citation footprints (Chen, 2017 ).
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
This study is funded by Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (1451MSYYB013) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.71874026 and No.71171044).
Authors’ contributions
In this study, LX proposed the research topic, designed the research methodology and framework, and made the data analysis. She was the major contributor in writing the manuscript. CA contributed to the design of the whole paper, including the research topic and methodology, and also participated in the writing and revision of the manuscript. BL and ZC were involved in data collection and analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Availability of data and material
Declarations.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Not applicable.
Liu, J., Hull, V., Batistella, M., DeFries, R., Dietz, T., Fu, F.,... Zhu, C. (2013). Framing Sustainability in a Telecoupled World. Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 26. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-05873-180226
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Lishan Xu, Email: nc.ude.unjdm@0104102 .
Changlin Ao, Email: nc.ude.uaen@nilgnahcoa .
Baoqi Liu, Email: moc.qq@457115825 .
Zhenyu Cai, Email: moc.qq@697833194 .
- Abad-Segura E, Cortés-García FJ, Belmonte-Ureña LJ. The sustainable approach to corporate social responsibility: A global analysis and future trends. Sustainability. 2019; 11 (19):5382. doi: 10.3390/su11195382. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahmad F, Draz MU, Su L, Ozturk I, Rauf A. Tourism and environmental pollution: Evidence from the one belt one road (OBOR) provinces of Western China. Sustainability. 2018; 10 (10):3520. doi: 10.3390/su10103520. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ardoin NM, Wheaton M, Bowers AW, Hunt CA, Durham WH. Nature-based tourism's impact on environmental knowledge, attitudes, and behavior: A review and analysis of the literature and potential future research. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2015; 23 (6):838–858. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2015.1024258. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balmford A, Green JMH, Anderson M, Beresford J, Huang C, Naidoo R, Walpole M, Manica A. Walk on the wild side: Estimating the global magnitude of visits to protected areas. PLoS Biology. 2015; 13 (2):e1002074. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002074. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software. 2015; 67 (1):132904. doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bennett NJ. Using perceptions as evidence to improve conservation and environmental management. Conservation Biology. 2016; 30 (3):582–592. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12681. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bennett EM, Cramer W, Begossi A, Cundill G, Díaz S, Egoh BN, Geijzendorffer IR, Krug CB, Lavorel S, Lazos E, Lebel L, Martín-López B, Meyfroidt P, Mooney HA, Nel JL, Pascual U, Payet K, Harguindeguy NP, Peterson GD, Prieur-Richard A-H, Reyers B, Roebeling P, Seppelt R, Solan M, Tschakert P, Teja Tscharntke BL, Turner PH, Verburg EF, Viglizzo PCL, White GW. Linking biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human well-being: Three challenges for designing research for sustainability. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability. 2015; 14 :76–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2015.03.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bennett NJ, Dearden P. Why local people do not support conservation: Community perceptions of marine protected area livelihood impacts, governance and management in Thailand. Marine Policy. 2014; 44 :107–116. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2013.08.017. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brockington D, Wilkie D. Protected areas and poverty. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 2015; 370 (1681):20140271. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0271. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burkhard B, Kroll F, Nedkov S, Müller F. Mapping ecosystem service supply, demand and budgets. Ecological Indicators. 2012; 21 :17–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.06.019. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Calcagni F, Maia ATA, Connolly JJT, Langemeyer J. Digital co-construction of relational values: Understanding the role of social media for sustainability. Sustainability Science. 2019; 14 :1309–1321. doi: 10.1007/s11625-019-00672-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cardinale BJ, Emmett Duffy J, Gonzalez A, Hooper DU, Perrings C, Venail P, Narwani A, Mace GM, Tilman D, Wardle DA, Kinzig AP, Daily GC, Loreau M, Grace JB, Larigauderie A, Srivastava DS, Naeem S. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature. 2012; 486 :59–67. doi: 10.1038/nature11148. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. C. (1996). Tourism, ecotourism, and protected areas: The state of nature-based tourism around the world and guidelines for its development. World Congress on National Parks and Protected Areas, 4th, Caracas.
- Chan KMA, Guerry AD, Balvanera P, Klain Sarah, Satterfield T, Basurto X, Bostrom A, Chuenpagdee R, Gould R, Halpern BS, Hannahs N, Levine J, Norton B, Ruckelshaus M, Russell R, Tam J, Woodside U. Where are cultural and social in ecosystem services? A framework for constructive engagement. BioScience. 2012; 62 (8):744–756. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chan KMA, Satterfield T, Goldstein J. Rethinking ecosystem services to better address and navigate cultural values. Ecological Economics. 2012; 74 :8–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.11.011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C. Predictive effects of structural variation on citation counts. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology. 2011; 63 (3):431–449. doi: 10.1002/asi.21694. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C. Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Data and Information Science. 2017; 2 (2):1–40. doi: 10.1515/jdis-2017-0006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C, Dubin R, Kim MC. Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine a scientometric update (2000–2014) Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2014; 14 (9):1295–1317. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2014.920813. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C, Dubin R, Kim MC. Orphan drugs and rare diseases: A scientometric review (2000–2014) Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2014; 2 (7):709–724. doi: 10.1517/21678707.2014.920251. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C, Hu Z, Liu S, Tseng H. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2012; 12 (5):593–608. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C, Leydesdorff L. Patterns of connections and movements in dual-map overlays: A new method of publication portfolio analysis. Journal of the Association for Information Science. 2014; 65 (2):334–351. doi: 10.1002/asi.22968. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chiu Y-TH, Lee W-I, Chen T-H. Environmentally responsible behavior in ecotourism: Antecedents and implications. Tourism Management. 2014; 40 :321–329. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.06.013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chung MG, Dietz T, Liu J. Global relationships between biodiversity and nature-based tourism in protected areas. Ecosystem Services. 2018; 34 :11–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.09.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clua E, Buray N, Legendre P, Mourier J, Planes S. Behavioural response of sicklefin lemon sharks Negaprion acutidens to underwater feeding for ecotourism purposes. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 2010; 414 :257–266. doi: 10.3354/meps08746. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Coria J, Calfucura E. Ecotourism and the development of indigenous communities: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Ecological Economics. 2012; 73 :47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.10.024. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Costanza R, de Groot R, Sutton P, van der Ploeg S, Anderson SJ, Kubiszewski I, Stephen Farber R, Turner K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Global Environmental Change. 2014; 26 :152–158. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.04.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Craigie ID, Baillie JEM, Balmford A, Carbone C, Collen B, Greena RE, Hutton JM. Large mammal population declines in Africa’s protected areas. Biological Conservation. 2010; 143 (9):2221–2228. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2010.06.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- CREST. (2019). The Case for Responsible Travel: Trends & statistics 2019 . https://www.responsibletravel.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/213/2021/03/trends-and-statistics-2019.pdf
- CREST. (2020). The Case for Responsible Travel: Trends & statistics 2020 . https://www.responsibletravel.org/docs/trendsStats2020.pdf
- D’Amato D, Droste N, Allen B, Kettunen M, Lähtinen K, Korhonen J, Leskinen P, Matthies BD, Toppinen A. Green, circular, bio economy: A comparative analysis of sustainability avenues. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2017; 168 :716–734. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.053. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Daniel TC, Muhar A, Arnberger A, Aznar O, Boyd JW, Chan KMA, Costanza R, Elmqvist T, Flint CG, Gobster PH, Gret-Regamey A, Lave R, Muhar S, Penker M, Ribe RG, Schauppenlehner T, Sikor T, Soloviy I, Spierenburg M, Taczanowska K, Tam J, von der Dunk A. Contributions of cultural services to the ecosystem services agenda. PNAS. 2012; 109 (23):8812–8819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114773109. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Díaz S, Demissew S, Carabias J, Joly C, Lonsdale Mark, Ash N, Larigauderie A, Adhikari JR, Arico S, Báldi A, Bartuska A, Baste IA, Bilgin A, Brondizio E, Chan KMA, Figueroa VE, Duraiappah A, Fischer M, Hill R, Koetz T, Leadley P, Lyver P, Mace GM, Martin-Lopez B, Okumura M, Pacheco D, Pascual U, Pérez ES, Reyers B, Roth E, Saito O, Scholes RJ, Sharma N, Tallis H, Thaman R, Watson R, Yahara T, Hamid ZA, Akosim C, Al-Hafedh Y, Allahverdiyev R, Amankwah E, Asah ST, Asfaw Z, Gabor Bartus L, Brooks A, Caillaux J, Dalle G, Darnaedi D, Driver A, Erpul G, Escobar-Eyzaguirre P, Failler P, Fouda AMM, Bojie Fu, Gundimeda H, Hashimoto S, Homer F, Lavorel S, Lichtenstein G, Mala WA, Mandivenyi W, Matczak P, Mbizvo C, Mehrdadi M, Metzger JP, Mikissa JB, Moller H, Mooney HA, Mumby P, Nagendra H, Nesshover C, Oteng-Yeboah AA, Pataki G, Roué M, Rubis J, Schultz M, Smith P, Sumaila R, Takeuchi K, Thomas S, Verma M, Yeo-Chang Y, Zlatanova D. The IPBES conceptual framework-connecting nature and people. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability. 2015; 14 :1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2014.11.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dickinson DC, Hobbs RJ. Cultural ecosystem services: Characteristics, challenges and lessons for urban green space research. Ecosystem Services. 2017; 25 :179–194. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.04.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dirzo R, Young HS, Galetti M, Ceballos G, Isaac NJB, Collen B. Defaunation in the anthropocene. Science. 2014; 345 (6159):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1251817. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dulvy NK, Fowler SL, Musick JA, Cavanagh RD, Kyne PM, Harrison LR, Carlson JK, Davidson LN, Fordham SV, Francis MP, Pollock CM, Simpfendorfer CA, Burgess GH, Carpenter KE, Compagno LJ, Ebert DA, Gibson C, Heupel MR, Livingstone SR, Sanciangco JC, Stevens JD, Valenti S, White WT. Extinction risk and conservation of the world’s sharks and rays. Life. 2014; 3 :e00590. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00590.001. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Engel S, Pagiola S, Wunder S. Designing payments for environmental services in theory and practice: An overview of the issues. Ecological Economics. 2008; 65 (4):663–674. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.03.011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Estes JA, Terborgh J, Brashares JS, Power ME, Berger J, Bond WJ, Carpenter SR, Essington TE, Holt RD, Jackson JBC, Marquis RJ, Oksanen L, Oksanen T, Paine RT, Pikitch EK, Ripple WJ, Sandin SA, Scheffer M, Schoener TW, Shurin JB, Sinclair ARE, Soulé ME, Virtanen R, Wardle DA. Trophic downgrading of planet earth. Science. 2011; 333 (6064):301–306. doi: 10.1126/science.1205106. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fairhead J, Leach M, Scoones I. Green Grabbing: A new appropriation of nature? The Journal of Peasant Studies. 2012; 39 (2):237–261. doi: 10.1080/03066150.2012.671770. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferraro PJ, Hanauer MM. Quantifying causal mechanisms to determine how protected areas affect poverty through changes in ecosystem services and infrastructure. PNAS. 2014; 111 (11):4332–4337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307712111. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fisher B, Turner RK, Morling P. Defining and classifying ecosystem services for decision making. Ecological Economics. 2009; 68 (3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.09.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gallagher AJ, Hammerschlag N. Global shark currency: The distribution, frequency, and economic value of shark ecotourism. Current Issues in Tourism. 2011; 14 (8):797–812. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2011.585227. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gallagher AJ, Vianna GMS, Papastamatiou YP, Macdonald C, Guttridgeg TL, Hammerschlag N. Biological effects, conservation potential, and research priorities of shark diving tourism. Biological Conservation. 2015; 184 :365–379. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2015.02.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garfield E. Citation indexes for science: A new dimension in documentation through association of ideas. Science. 1955; 122 (3159):108–111. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3159.108. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Geffroy B, Samia DSM, Bessa E, Blumstein DT. How nature-based tourism might increase prey vulnerability to predators. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 2015; 30 (12):755–765. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2015.09.010. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gómez-Baggethun E, de Groot R, Lomas PL, Montes C. The history of ecosystem services in economic theory and practice: From early notions to markets and payment schemes. Ecological Economics. 2010; 69 (6):1209–1218. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gössling S, Scott D, Hall CM. Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2021; 29 (1):1–20. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1758708. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- de Groot RS, Alkemade R, Braat L, Hein L, Willemen L. Challenges in integrating the concept of ecosystem services and values in landscape planning, management and decision making. Ecological Complexity. 2010; 7 (3):260–272. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2009.10.006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hansen MC, Potapov PV, Moore R, Hancher M, Turubanova SA, Tyukavina A, Thau D, Stehman SV, Goetz SJ, Loveland TR, Kommareddy A, Egorov A, Chini L, Justice CO, Townshend JRG. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science. 2013; 342 (6160):850–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1244693. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hausmann A, Toivonen T, Slotow R, Tenkanen H, Moilanen A, Heikinheimo V, Minin ED. Social media data can be used to understand tourists’ preferences for nature-based experiences in protected areas. Conservation Letters. 2018; 11 (1):e12343. doi: 10.1111/conl.12343. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Havinga I, Bogaart PW, Hein L, Tuia D. Defining and spatially modelling cultural ecosystem services using crowdsourced data. Ecosystem Services. 2020; 43 :101091. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2020.101091. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hernández-Morcillo M, Plieninger T, Bieling C. An empirical review of cultural ecosystem service indicators. Ecological Indicators. 2012; 29 :434–444. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.01.013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins BR. The Global structure of the nature tourism industry: Ecotourists, tour operators, and local businesses. Journal of Travel Research. 1996; 35 (2):11–18. doi: 10.1177/004728759603500203. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins-Desbiolles F. Sustainable tourism: Sustaining tourism or something more? Tourism Management Perspectives. 2018; 25 :157–160. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2017.11.017. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hirons M, Comberti C, Dunford R. Valuing cultural ecosystem services. Annual Review of Environment and Resources. 2016; 41 :545–574. doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-110615-085831. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kharrazi A, Kraines S, Hoang L, Yarime M. Advancing quantification methods of sustainability: A critical examination emergy, exergy, ecological footprint, and ecological information-based approaches [Review] Ecological Indicators. 2014; 37 :81–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.10.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Köndgen S, Kühl H, N'Goran PK, Walsh PD, Schenk S, Ernst N, Biek R, Formenty P, Mätz-Rensing K, Schweiger B, Junglen S, Ellerbrok H, Nitsche A, Thomas Briese W, Lipkin I, Pauli G, Boesch C, Leendertz FH. Pandemic human viruses cause decline of endangered great apes. Current Biology. 2008; 18 (4):260–264. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.01.012. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kosoy N, Corbera E. Payments for ecosystem services as commodity fetishism. Ecological Economics. 2010; 69 (6):1228–1236. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krüger O. The role of ecotourism in conservation: Panacea or Pandora’s box? Biodiversity & Conservation. 2005; 14 :579–600. doi: 10.1007/s10531-004-3917-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li J, Xu L, Tang L, Wang S, Li L. Big data in tourism research: A literature review. Tourism Management. 2018; 68 :301–323. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2018.03.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu J, Hull V, Batistella M, DeFries R, Dietz T, Fu F, Zhu C. Framing sustainability in a telecoupled world. Ecology and Society. 2013; 18 (2):26. doi: 10.5751/ES-05873-180226. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu J, Hull V, Junyan Luo W, Yang WL, Viña A, Vogt C, Zhenci Xu, Yang H, Zhang J, An Li, Chen X, Li S, Ouyang Z, Weihua X, Zhang H. Multiple telecouplings and their complex interrelationships. Ecology and Society. 2015; 20 (3):44. doi: 10.5751/ES-07868-200344. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mace GM. Whose conservation? Science. 2014; 345 (6204):1558–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.1254704. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mace GM, Norris K, Fitter AH. Biodiversity and ecosystem services: A multilayered relationship. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 2012; 27 (1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2011.08.006. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McClung MR, Seddon PJ, Massaro M, Setiawan AN. Nature-based tourism impacts on yellow-eyed penguins Megadyptes antipodes: Does unregulated visitor access affect fledging weight and juvenile survival? Biological Conservation. 2004; 119 (2):279–285. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2003.11.012. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- MCT. (2021). Statistical Bulletin on Culture and Tourism Development 2020 . Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China. Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-07/05/content_5622568.htm
- Milcu AI, Hanspach J, Abson D, Fischer J. Cultural ecosystem services: A literature review and prospects for future research. Ecology and Society. 2013; 18 (3):44. doi: 10.5751/ES-05790-180344. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Minin ED, Fraser I, Slotow R, MacMillan DC. Understanding heterogeneous preference of tourists for big game species: Implications for conservation and management. Animal Conservation. 2013; 16 (3):249–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1795.2012.00595.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muniz R, Cruz MJ. Making nature valuable, not profitable: Are payments for ecosystem services suitable for degrowth? Sustainability. 2015; 7 (8):10895–10921. doi: 10.3390/su70810895. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muradian R, Arsel M, Pellegrini L, Adaman F, Aguilar B, Agarwal B, Corbera E, Ezzine de Blas D, Farley J, Froger G, Garcia-Frapolli E, Gómez-Baggethun E, Gowdy J, Kosoy N, Le Coq JF, Leroy P, May P, Méral P, Mibielli P, Norgaard R, Ozkaynak B, Pascual U, Pengue W, Perez M, Pesche D, Pirard R, Ramos-Martin J, Rival L, Saenz F, Van Hecken G, Vatn A, Vira B, Urama K. Payments for ecosystem services and the fatal attraction of win-win solutions. Conservation Letters. 2013; 6 (4):274–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-263X.2012.00309.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muradian R, Corbera E, Pascual U, Kosoy N, May PH. Reconciling theory and practice: An alternative conceptual framework for understanding payments for environmental services. Ecological Economics. 2010; 69 (6):1202–1208. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naeem S, Ingram JC, Varga A, Agardy T, Barten P, Bennett G, Bloomgarden E, Bremer LL, Burkill P, Cattau M, Ching C, Colby M, Cook DC, Costanza R, DeClerck F, Freund C, Gartner T, Goldman-Benner R, Gunderson J, Jarrett D, Kinzig AP, Kiss A, Koontz A, Kumar P, Lasky JR, Masozera M, Meyers D, Milano F, Naughton-Treves L, Nichols E, Olander L, Olmsted P, Perge E, Perrings C, Polasky S, Potent J, Prager C, Quétier F, Redford K, Saterson K, Thoumi G, Vargas MT, Vickerman S, Weisser W, Wilkie D, Wunder S. Get the science right when paying for nature's services. Science. 2015; 347 (6227):1206–1207. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa1403. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nelson E, Mendoza G, Regetz J, Polasky S, Tallis H, Cameron D, Chan KMA, Daily GC, Goldstein J, Kareiva PM, Lonsdorf E, Naidoo R, Ricketts TH, Shaw M. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. 2009; 7 (1):4–11. doi: 10.1890/080023. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Niñerola A, Sánchez-Rebull M-V, Hernández-Lara A-B. Tourism research on sustainability: A bibliometric analysis. Sustainability. 2019; 11 (5):1377. doi: 10.3390/su11051377. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oladeji SO, Awolala DO, Alabi OI. Evaluation of sustainable ecotourism practices in Oke-Idanre Hills, Ondo-State, Nigeria [Article; Early Access] Environment Development and Sustainability. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01550-6. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oldekop JA, Holmes G, Harris WE, Evans KL. A global assessment of the social and conservation outcomes of protected areas. Conservation Biology. 2016; 30 (1):133–141. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12568. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Orams MB. Towards a more desirable form of ecotourism. Tourism Management. 1995; 16 (1):3–8. doi: 10.1016/0261-5177(94)00001-Q. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U, Saboori B. Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2016; 23 :1916–1928. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5447-x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pascual U, Phelps J, Garmendia E, Brown K, Corbera E, Martin A, Gomez-Baggethun E, Muradian R. Social equity matters in payments for ecosystem services. BioScience. 2014; 64 (11):1027–1036. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biu146. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pimm SL, Jenkins CN, Abell R, Brooks TM, Gittleman JL, Joppa LN, Raven PH, Roberts CM, Sexton JO. The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science. 2014; 344 (6187):1246752. doi: 10.1126/science.1246752. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Plieninger T, Dijks S, Oteros-Rozas E, Bieling C. Assessing, mapping, and quantifying cultural ecosystem services at community level. Land Use Policy. 2013; 33 :118–129. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.12.013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Raudsepp-Hearne C, Peterson GD, Bennett EM. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. PNAS. 2010; 107 (11):5242–5247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907284107. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Redford KH, Adams WM. Payment for ecosystem services and the challenge of saving nature. Conservation Biology. 2009; 23 (4):785–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2009.01271.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Richards DR, Friess DA. A rapid indicator of cultural ecosystem service usage at a fine spatial scale: Content analysis of social media photographs. Ecological Indicators. 2015; 53 :187–195. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.01.034. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ripple WJ, Estes JA, Beschta RL, Wilmers CC, Ritchie EG, Hebblewhite M, Berger J, Elmhagen B, Letnic M, Nelson MP, Schmitz OJ, Smith DW, Wallach AD, Wirsing AJ. Status and ecological effects of the world’s largest carnivores. Science. 2014; 343 (6167):1241484. doi: 10.1126/science.1241484. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ross S, Wall G. Ecotourism: Towards congruence between theory and practice. Tourism Management. 1999; 20 (1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/S0261-5177(98)00098-3. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seraphin H, Sheeran P, Pilato M. Over-tourism and the fall of Venice as a destination. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management. 2018; 9 :374–376. doi: 10.1016/j.jdmm.2018.01.011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharpley R. Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management. 2014; 42 :37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.10.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shasha ZT, Geng Y, Sun H-P, Musakwa W, Sun L. Past, current, and future perspectives on eco-tourism: A bibliometric review between 2001 and 2018. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2020; 27 :23514–23528. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08584-9. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shneider AM. Four stages of a scientific discipline; four types of scientist. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2009; 34 (5):217–223. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.02.002. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sirakaya E, Sasidharan V, Sönmez S. Redefining ecotourism: The need for a supply-side view. Journal of Travel Research. 1999; 38 (2):168–172. doi: 10.1177/004728759903800210. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Snyman S. The role of private sector ecotourism in local socio-economic development in southern Africa. Journal of Ecotourism. 2017; 16 (3):247–268. doi: 10.1080/14724049.2016.1226318. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Talebi M, Majnounian B, Makhdoum M, Abdi E, Omid M. Predicting areas with ecotourism capability using artificial neural networks and linear discriminant analysis (case study: Arasbaran Protected Area, Iran) Environment, Development and Sustainability. 2021; 23 :8272–8287. doi: 10.1007/s10668-020-00964-y. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ulucak R, Bilgili F. A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2018; 188 :144–157. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.191. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valdivieso JC, Eagles PFJ, Gil JC. Efficient management capacity evaluation of tourism in protected areas. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management. 2015; 58 (9):1544–1561. doi: 10.1080/09640568.2014.937479. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watson JEM, Dudley N, Segan DB, Hockings M. The performance and potential of protected areas. Nature. 2014; 515 :67–73. doi: 10.1038/nature13947. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wearing S, McGehee NG. Volunteer tourism: A review. Tourism Management. 2013; 38 :120–130. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.03.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weaver DB, Lawton LJ. Twenty years on: The state of contemporary ecotourism research. Tourism Management. 2007; 28 (5):1168–1179. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2007.03.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- West P, Igoe J, Brockington D. Parks and peoples: The social impact of protected areas. Annual Review of Anthropology. 2006; 35 :251–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.anthro.35.081705.123308. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whitelaw PA, King BEM, Tolkach D. Protected areas, conservation and tourism-financing the sustainable dream. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2014; 22 (4):584–603. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2013.873445. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wight P. Ecotourism: Ethics or eco-sell. Journal of Travel Research. 1993; 31 (3):3–9. doi: 10.1177/004728759303100301. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wittemyer G, Elsen P, Bean WT, Burton ACO, Brashares JS. Accelerated human population growth at protected area edges. Science. 2008; 321 (5885):123–126. doi: 10.1126/science.1158900. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu L, Ao C, Mao B, Cheng Y, Sun B, Wang J, Liu B, Ma J. Which is more important, ecological conservation or recreational service? Evidence from a choice experiment in wetland nature reserve management. Wetlands. 2020; 40 :2381–2396. doi: 10.1007/s13157-020-01348-8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zanten BTV, Berkel DBV, Meentemeyer RK, Smith JW, Tieskens KF, Verburg PH. Continental-scale quantification of landscape values using social media data. PNAS. 2016; 113 (46):12974–12979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1614158113. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhong L, Liu L. Ecotourism development in China: Achievements, problems and strategies. Journal of Resources and Ecology. 2017; 8 (5):441–448. doi: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.05.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Tourism Web Portal
About the portal.
A technological tool for effective communication between the leading players in the Moscow tourism market and representatives of the foreign/regional tourism industry through online events. OBJECTIVES: • Building long-term cooperation with foreign/regional representatives • Raising awareness among foreign/regional representatives of the tourism industry of the tourism opportunities, measures and attractiveness of the city of Moscow in the field of tourist infrastructure development
Moscow City Tourism Committee
The Tourism Committee, or Mostourism, is the executive body of the Moscow City Government that oversees tourist activities in the capital. The Committee is responsible for legislative initiatives, congress and exhibition activities, and event and image projects. As the brand manager for an attractive tourism image for Moscow, Mostourism constantly analyses global trends, offers Russian and foreign tourists what they want, and also uncovers new opportunities for the capital in terms of interesting and rewarding leisure activities.
ANO «Project Office for the Development of Tourism and Hospitality of Moscow»
Syundyukova Yulia [email protected] Mezhiev Magomed [email protected]
Video materials about Moscow
- Hispanoamérica
- Work at ArchDaily
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
Moscow's Urban Movement: Is There Hope for a Better Future?

- Written by Mari Chichagova
- Published on December 09, 2015
In 2010, following the election of a new mayor, the Moscow city government began to work towards a comfortable urban environment in which citizens would feel like residents rather than mere users of the city. The emphasis was on creating public spaces in which Muscovites could fulfill their potential and feel that the city was their home.
Gorky Park was at the forefront of the changes. During the 1990s, the "Central Park of Culture and Leisure" accumulated a collection of fairground rides and became a sort of amusement park popular principally among visitors from other cities; Muscovites hardly went there. Three years ago, the city government made it their mission to overturn the park's image and bring Moscow's residents back. A full-scale reconstruction and restoration began in spring 2011.
Today, Gorky Park is a new level of urban space – one centered around people and boasting a scrupulously conceived infrastructure. All of the changes were aimed at creating a comfortable environment for life - for strolling and sport, work and study, culture and leisure. Moreover, in a short time the park has developed an effective economic model whereby it receives one half of its budget from the city and generates the other half itself.

The regeneration of Gorky Park was followed by a flurry of changes. The city began to invest intensively in the development of other Moscow parks (by 2015, 240 new parks had been opened, 160 of which were in residential areas), in cycling mobility and infrastructure (by 2015, 241.7 kilometers of cycle track and around 10,000 bike parking spaces had been installed), and in street design and refurbishment (to date, 50 streets and squares have been repaired and 72 pedestrian zones created). Pedestrians are now the priority user group in the urban environment.
The work undertaken in 2015 has been more than impressive in its scale: sidewalks have been widened; 30,000 trees have been planted; 10,000 unauthorized advertising structures have been demolished; the facades of 943 buildings have been repaired, 178 hectares of lawn have been replanted, and 1.1 million square meters of flowerbed have been arranged and planted.

The redevelopment of Krymskaya embankment , completed in 2013, is one of the most successful projects to be implemented in recent years. In accordance with the design by Wowhaus Architecture Bureau , the embankment was completely pedestrianized. Cycle paths were demarcated and later became part of a single 8 kilometer cycle track along the Moskva River linking the Pushkinskaya, Andreevskaya, and Vorobyovskaya embankments. The historical identity of the area was also taken into account: artists have sold their work on the Krymskaya embankment since Soviet times; in light of the tradition, a covered wooden arcade was built to accommodate them. Nearby, a summer cinema and a lecture theater have sprung up. Meanwhile, plentiful benches were installed, along with an open fountain which has become a favorite spot for both locals and tourists.
Triumfalnaya square, which opened in its new guise in September 2015, is another successful urban project. As part of the reconstruction, vehicular access to the square was blocked, the street-level parking was removed, and the section of road from the Garden ring onto Tverskaya Street was closed off. The concept, by the architecture studio Buromoscow , was selected as part of a competition which attracted over forty entries. The design also included new trees, swings, and benches, as well as pavilions where residents and tourists might buy tea, coffee and a newspaper, or find out information about the city.

Despite the obvious positive dynamic - Moscow's gradual transition from a city of disconnected “islands” with a closed, unfriendly urban environment to a European style city where pedestrians are the priority user group - there remain a plethora of issues.
Yes, Moscow is continually holding round tables, forums, and discussions of its future urban development. Yes, it can now be said that the government has long-term planning objectives and a concept for how the city ought to look in three, five or ten years’ time.

And yet - despite the involvement of world class experts such as Jan Gehl , Renzo Piano , and Diller Sconfidio + Renfro , despite the numerous architectural competitions involving a jury, the expert community, and the citizens themselves - the quality and implementation of this city-scale project leaves much to be desired.
A good illustration of this is the Moscow government's ongoing program "My Street," which is intended to improve Moscow's public spaces. The project sets aside 100 billion roubles for the redevelopment of 4,000 streets by 2018. Nevertheless, the quality of the work carried out over the summer of 2015 (scheduled for completion in time for the Moscow City Day celebrations in early September) was far from ideal. After the hurried redevelopment works, it was hard not to notice the high, unwieldy curbs, the drains appearing unexpectedly in the middle of cycle-tracks, the tarmac laid on top of paving slabs, or the paving slabs laid on top of tarmac.

Often, an important date (such as the 2018 FIFA World Cup or City Day) is the best motivation for civil servants to get things done. But should it be that way?
There is a flip-side to chasing after statistics. Firstly, quality of execution suffers. Secondly, the choice of contractor and the professionalism of the people hired to supervise and implement the work leaves much to be desired.
The absence of professionals with the skills, experience and enthusiasm to finish a project to a high standard is becoming increasingly apparent. The contractors' main concern is currently to finish the work as fast as possible (usually to a low standard) and pick up their pay check. Companies rarely invest in skilled personnel, preferring to hire cheap labor.

The winners of architectural contests should be permitted, at a legislative level, to supervise the realization of their spatial development concepts. If this is not done, then contracting organizations will continue to profiteer and to alter concepts at the master-planning stage, condemning the original designs to remain mere ideas, a collection of pretty architectural renders in the official documentation. If third parties continue to oversee work, as opposed to the authors of the concepts, then the question must be answered: how will the quality of future projects be guaranteed?
There is no doubt about the mayor's desire to invest in the visual face of Moscow and to improve the city's quality of life. Yet the need remains for a more careful approach to project implementation and to hiring and contracting decisions. There also needs to be more active work with citizens - they are the main users of urban space, and they, ultimately, are the clients.

Mari Chichagova graduated with honours degree from the Faculty of Philology of Lomonosov Moscow State University in 2009. In 2010 she started working at "Interior + Design," a magazine dedicated to architecture, design, culture and about people who were defining and driving those processes, from Norman Foster to Le Corbusier and Zaha Hadid. Afterwards she worked as a PR specialist at the Strelka Institute of Media, Architecture and Design , a Russian institution that is working in the field of urban studies, using a multi-disciplinary approach.
Since 2013 she has worked as a Deputy PR Director and then as an Acting PR Director at Gorky Park , Moscow ’s Central park. In addition to PR duties, she initiated contacts with other significant parks and organizations around the globe such as International Federation of Parks and Recreation Administration, the San Francisco Golden Gate Park, San Francisco Recreation and Park Department, Central Park of New York among others.
All images of Gorky Park (excluding image of Garage Museum) via Shutterstock.com
- Sustainability
世界上最受欢迎的建筑网站现已推出你的母语版本!
想浏览archdaily中国吗, you've started following your first account, did you know.
You'll now receive updates based on what you follow! Personalize your stream and start following your favorite authors, offices and users.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Building Awareness. Ecotourism aims to teach as well as to entertain and relax. This objective applies to environmental as well as cultural matters. Visitors who participate in ecotourism projects should receive information on the ecology and conservation issues pertinent to the local area. Guides and other staff should be able to effectively ...
Ecotourism, in turn, supports 400,000 jobs and accounts for 17.2% of the national GDP, earning about $1 billion each year as its leading economic sector.
Ecotourism is about uniting conservation, communities, and sustainable travel. This means that those who implement, participate in and market ecotourism activities should adopt the following ecotourism principles: Minimize physical, social, behavioral, and psychological impacts. Build environmental and cultural awareness and respect.
The bounce-back of tourism means the same will happen in terms of emissions. In 2022, GHG emissions increased by 7% in the first quarter compared to 2020. It is critical to practice ecotourism as global warming becomes more apparent. You'll benefit from learning and becoming a better friend to the environment.
She described ecotourism as, "Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and improves the well-being of local people.". In simple words, the meaning of ecotourism is travel that makes a positive impact on both the ECO logy and ECO nomy of a given destination. One mistake many people make is assuming that ecotourism ...
He defined ecotourism as; 'travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific objective of studying, admiring, and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals, ... (aka eco) tourism. The chronological development of the concept of sustainable tourism and ecotourism. Adapted from Swarbrooke (1999)
Eco-tourism or ecological tourism has been defined as "responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education" by The International Ecotourism Society (TIES, 2015). ... One of the main objectives of ecotourism is to help local conservation ...
The key objectives of eco-tourism include the protection of natural areas, production of revenue, education and local involvement, and capacity building (Coria and Calfucura 2012; Chandel and Mishra 2016; Drumm et al. 2004; Pedersen 1991; Ross and Wall 1999). It is based on the notion that ecosystem constitutes a unique local resource which ...
Ceballos Lascurain (1987) (Joshi, 2011) Ecotourism is defined as travelling to relatively undisturbed natural areas with specific objective of studying, admiring and enjoying scenery and its wild animals and plants as well as existing.
The first official definition of ecotourism from 1987 is commonly accredited to Ceballos-Lascuráin (Fennel 2003), who defined it as: 'travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific objective of studying, admiring, and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals, as well as any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in ...
Ecotourism is a form of tourism marketed as "responsible" travel (using what proponents say is sustainable transport) to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. The stated purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide funds for ecological conservation, to directly benefit the economic development and political empowerment of local ...
Sustainable Development: One of the main objectives of ecotourism is to promote sustainable development. It encourages the use of resources from local natural areas in an environmentally responsible and sustainable manner and, ensures that they remain available to support the needs of the local population and visitors alike.
The Ecotourism Definition. The simplest way to explain the concept of ecotourism is with two words: traveling responsibly. Simply put, ecotourism is tourism that centers around awareness of the environment and the local community. As eco-tourists, the goal is to visit an area with the well-being of the local people and nature in mind.
Ecotourism promotes conservation, and aims to have a positive socio-economic impact on the local people surrounding the attraction. The primary objective for ecotourism may be to provide finances for the conservation of ecology, to champion for the respect of different cultures, to educate the traveler or to politically empower local communities.
Ecotourism as a learning tool generated positive remarks as well as uncertainties. I2 believes that ecotourism can help shift the balance by focusing on the [land] treasures, and he agrees with I1 when stating that it can 'absolutely' help reaching the MaB and the ECST objectives.
Ecotourism, which has appeared in academic literature since the late 1980s, is a special form of nature-based tourism that maintains the well-being of the local community while protecting the environment and provides tourists with a satisfying nature experience and enjoyment (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1996; Higgins, 1996; Orams, 1995).With years of research and development, ecotourism has risen to ...
Developing ecotourism services is a suitable solution to help developing countries improve the status of sustainable development indicators and protect their environment. The primary purpose of ...
Ecotourism is a nature-based, sustainable, learning- and management-demanding form of tourism that encourages conservation, educates visitors and residents, and provides economic benefits to local communities [1,2,3,4,5,6].Ecotourism opportunities combine natural, environmentally aware, culturally educative, and sustainably managed conditions that give value to a place [7,8,9].
Tverskaya Area in Moscow. Tverskaya is the main street of Moscow, it starts from the Kremlin and goes north through all Moscow to change into Leningradskoe shosse, which leads to Tver and after 700 km to St. The best way to explore Moscow is to go for a walk in one of the central neighborhoods or parks.
Introduction. Ecotourism, which has appeared in academic literature since the late 1980s, is a special form of nature-based tourism that maintains the well-being of the local community while protecting the environment and provides tourists with a satisfying nature experience and enjoyment (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1996; Higgins, 1996; Orams, 1995).With years of research and development, ecotourism ...
About the portal. A technological tool for effective communication between the leading players in the Moscow tourism market and representatives of the foreign/regional tourism industry through online events. OBJECTIVES: • Building long-term cooperation with foreign/regional representatives • Raising awareness among foreign/regional ...
Yes, Moscow is continually holding round tables, forums, and discussions of its future urban development. Yes, it can now be said that the government has long-term planning objectives and a ...
The 'Moscow 2030' is a high-level strategic document that sets objectives, goals, and areas of development of Moscow as an innovative city of the future. Moscow 2030 - comfortable, educating, culturally rich and safe urban environment for everyone 'Smart City 2030' sets priorities, goals and objectives for city governance and digital ...