Skip navigation


World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Ux mapping methods compared: a cheat sheet.

November 5, 2017 2017-11-05
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
Designing and developing a product often involves a large team of people with different backgrounds and experiences who must be on the same page about the project goals, the user needs and behaviors, and even the component processes involved. This common understanding is often built with visualizations (commonly referred to as mappings). Mappings make sense of and describe various aspects and processes associated with a product.
In This Article:
Four types of mapping, empathy mapping, customer journey mapping, experience mapping, service blueprinting, three-step decision framework, use all four ux mapping methods.
This article gives an overview of four commonly used mappings, their defining characteristics, and when to use which:
- Empathy mapping
- Customer journey mapping
- Experience mapping
- Service blueprinting

Additionally, this article will outline the decisions that must be made before creating any of these mappings in a simple three-step approach framework.
Empathy maps help team members understand the user’s mindset.

Empathy map : A tool used to articulate what we know about a particular type of user. It externalizes user knowledge in order to 1) create a shared understanding, and 2) aid in decision making.
Characteristics:
- The map is split into 4 quadrants: Says, Thinks, Feels, Does.
- It shows user’s perspective regarding the tasks related to the product.
- It is not chronological or sequential.
- There is one empathy map for each persona or user type (1:1 mapping).
Why use it:
- To build empathy for your users
- To force alignment and understanding about a user type
When to use it:
- Beginning of any design process
- When categorizing research notes from a user interview
Customer journey maps focus on a specific customer’s interaction with a product or service.

Customer journey map : A visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal tied to a specific business or product. It’s used for understanding and addressing customer needs and pain points.
In its most basic form, journey mapping starts by compiling a series of user goals and actions into a timeline skeleton. Next, the skeleton is fleshed out with user thoughts and emotions in order to create a narrative. Finally, that narrative is condensed into a visualization used to communicate insights that will inform design processes.
- The map is tied to a specific product or service.
- It is split into 4 swim lanes: phases, actions, thoughts, mindsets/emotions.
- Including her mindset, thoughts, and emotions
- Leaving out most process details
- It is chronological.
- There is one map per persona/user type (1:1 mapping).
- To pinpoint specific customer journey touchpoints that cause pain or delight
- To break down silos to create one shared, organization-wide understanding of the customer journey
- To assign ownership of key touchpoints in the journey to internal departments
At any point in the design process, as a reference point amongst a team throughout a product design cycle
Experience maps generalize the concept of customer-journey maps across user types and products.

Experience map: A visualization of an entire end-to-end experience that a “generic” person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. This experience is agnostic of a specific business or product. It’s used for understanding a general human behavior (as opposed to a customer journey map, which is more specific and focused on related to a specific business).
- It is not tied to a specific product or service.
- It offers a general human perspective; it is not a specific to a particular user type or product/service.
- It depicts events in chronological order.
- To understand a general human behavior
- To create a baseline understanding of an experience that is product/service agnostic
- Before a customer journey map in order to gain understanding for a general human behavior
- When converging multiple experiences (tool and specific user agnostic) into one visualization
Service blueprints are counterparts to customer journey maps, focused on the employees.

Service blueprint : A visualization of the relationships between different service components — people, props (physical or digital evidence), and processes — that are directly tied to touchpoints in a specific customer journey.
Think of service blueprints as a part two to customer journey maps. Similar to customer journey maps, blueprints are instrumental in complex scenarios spanning many service-related offerings. Blueprinting is an ideal approach to experiences that are omnichannel, involve multiple touchpoints, or require a crossfunctional effort (that is, coordination of multiple departments).
- It is tied to a specific service.
- It is split into 4 swim lanes: customer actions, frontstage actions, backstage actions, and support processes.
- Focusing on the service provider and employees
- Leaving out most customer details
- It is chronological and hierarchical.
- To discover weaknesses in the organization
- To identify opportunities for optimization
- To bridge crossdepartment efforts
- To break down silos and create one shared, organization-wide understanding of how the service is provided
- After customer journey mapping
- Before making organizational or process changes
- When pinpointing a funnel or breakpoint internally
Before beginning any mapping effort (regardless of the type), 3 decisions must be made:
1. Current (as-is) vs. future (to-be)
This decision involves the actions and states depicted in the visualization: do they reflect the current state of the world or a desired state of the world?
- Current mappings are based on an actual “today” state of what you are mapping. This approach is ideal when the mapping goal is to identify and document existing problems and pain points. Use current state maps to help analyze research or align a team around a data-validated problem.
- Future mappings are based on an “ideal” state for a user type, experience, or a to-be service structure. Future state maps help reinvent and conceive how a user or experience would feel in the future. Use future state maps to set a benchmark or goal for the ideal form of your product or service.
2. Hypothesis vs. research
This decision depends on the type of input that you will use to build your mapping.
- Hypothesis mappings are based on an accumulation of existing understanding within a team or organization. This approach is a great way to merge multiple existing team views, create a research plan (based on the gaps that emerge from your hypothesis map), and make a first step towards a higher-fidelity, research-based map.
- Research mapping is based on data gathered specifically for building the map. This approach is best when there are time and resources dedicated to creating a research plan. While this method creates the best maps, it takes time and significant buy-in. Regardless of where you start, your maps should be iterative and constantly updated with new findings.
3. Low-fidelity vs. high-fidelity
This decision pertains to the quality of the final map visualization.
- Low-fidelity maps are unpolished and often created with sticky notes in a flexible, unrefined manner. These maps are best in an early part of the process. Low fidelity means little commitment or creation effort and empowers people to collaborate, revise, and update as needed. Use sticky notes (physically on the wall or digitally with tools like Mural.co) or collaborative excel sheets.
- High-fidelity maps are polished, created digitally, and look final. High fidelity maps are the best for creating an artifact that is going to be shared amongst many. High fidelity can be easier to read but less flexible because of the “finished” nature of the product. These maps are often created digitally and then dispersed.
All UX maps have two-fold benefits. First, the process of creating a map forces conversation and an aligned mental model. Second, the shared artifact resulting from the mapping can be used amongst your team, organization, or partners to communicate an understanding of your user or service. This artifact can also become the basis for decision making as the team moves forward.
Using one mapping method over another will not make or break a project. Ideally, a combination of all four will be used as needed at different points in your process to create an in-depth understanding of your users and organization.
Kyle, Beth. Pregnancy Experience Map. http://www.bethkyle.com/portfolio-item/pregnancy-experience-map/
Related Courses
Generating big ideas with design thinking.
Unearthing user pain points to drive breakthrough design concepts
Interaction
Orchestrate people, props, and processes that are core to your digital experience
Journey Mapping to Understand Customer Needs
Capture and communicate UX insights across complex interactions
Related Topics
- Customer Journeys Customer Journeys
- Design Process
Learn More:
Please accept marketing cookies to view the embedded video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2YpC3R1zNdA
UX Mapping Methods: When to Use Which

The Role of Design
Don Norman · 5 min

Design Thinking Activities
Sarah Gibbons · 5 min

Design Thinking: Top 3 Challenges and Solutions
Related Articles:
Building Interactive UX Maps
Megan Brown · 6 min
User Journeys vs. User Flows
Kate Kaplan · 4 min
The 5 Steps to Service Blueprinting
Sarah Gibbons · 4 min
Service Design 101
Design Thinking Builds Strong Teams
Design Thinking: Study Guide
Kate Moran and Megan Brown · 4 min
NN/g Journey Mapping Template

A customizable journey mapping template from Nielsen Norman Group to get you started creating interactive UX maps. Add your own interactions, branding, styles, and more to tailor it to your needs.
- Building Interactive UX Maps
- Journey Mapping 101
Enroll in Live Training: Journey Mapping to Understand Customer Needs
Subscribe to our Newsletter: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/subscribe/
Follow us and stay connected:
Linkedin: Nielsen Norman Group
Youtube: @NNgroup
Instagram: @nngux
Twitter: @NNgroup

- Tech Talks (New!)
- What is SEO
- SEO Checklist
- Search Engines
- International SEO
- Google Algorithm Updates
- Google Ranking Factors
- Content SEO
- Link Building
- Social Media SEO
- Site Architecture
- Adwords Tips
- Paid Search Marketing
- Landing Pages
- Display Advertising
- Twitter Ads
- Facebook Ads
- Adwords Features
- Paid Social Media
- Remarketing/Retargeting
- Quality Score
- PPC Strategy
- PPC Management/Software/Tools
- Competitor Analysis – PPC
- Guide to Google Analytics
- SEO Analytics
- Local SEO Tips
- Local SEO for Small Business
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
- Mobile Attribution
- Video Optimisation
Development
- search search
- News & Insights keyboard_arrow_down
Information
- Contact SEW
- Submit an article
- Advertise on SEW
- Content & Licensing
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Website Terms of Use
Guide: How to effectively incorporate customer journey mapping into your marketing strategy
A comprehensive customer journey mapping guide that helps you understand the role of digital transformation and customer experience in your company’s success.
30-second summary:
- A customer journey map is a visual representation of every interaction between you and your customers. Proper customer journey mapping can make a huge difference in conversions and help you create a more customer-centric marketing strategy.
- Customer journey mapping starts with identifying your user personas. This way, you’ll know exactly which customer segment to market.
- Next, you identify and map out every touchpoint or experience along the customer journey. This will help you learn and later predict customer behavior and buying decisions.
- Chief content writer, Connie Benton guides you through the customer journey mapping process outline with some great examples and tools to help you.
When it comes to building a robust marketing strategy, most beginner entrepreneurs have nothing to start off with except expert advice they find on digital marketing blogs, let alone the idea of customer journey mapping. While this alone will last you a long way, ultimately, you’re borrowing experiences from somebody else’s business, not building on your own. This is why large corporations spend so much on big data and analytics.
But it’s not just the corporations that do that. According to OnePath, 67% of SMEs spend over $10,000 a year on analytics . Why do they pay this huge price?
The answer is simple. You can only go this far using somebody else’s analytics. At some point, you should start gathering and interpreting data yourself. Without this, you can’t possibly expect to understand your thousands of clients.
If you’re looking for a point where you can start, you can postpone getting into behavioral segmentation and other advanced analytics, and follow a strategy that can yield great results on a shoestring budget . Create a customer journey map. Here’s all the information and tools you’ll need to create one.
How to create a customer journey map
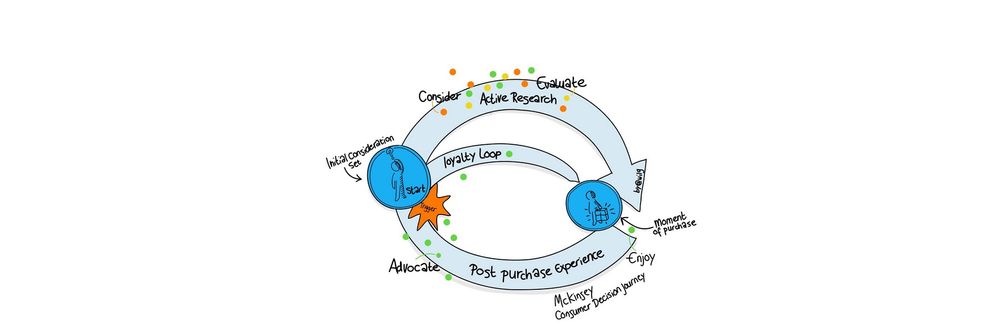
A customer journey map (CJM) is exactly what it sounds to be. A map of the path that a customer makes from their decision to make a purchase or any other action, to successfully making it. Here’s an example of what it looks like from the NNGroup.
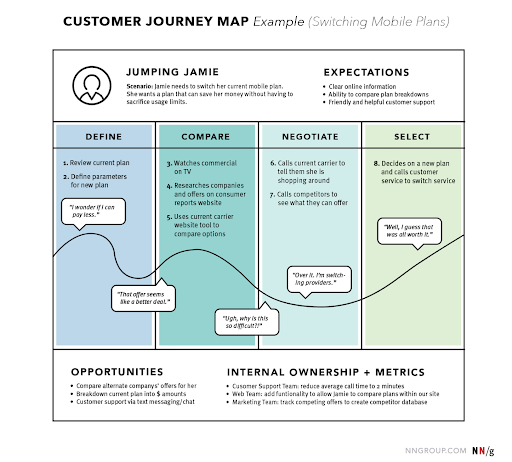
Source: NNGroup
You can create a customer journey map for most processes that involve customer decisions and use this map for different purposes. A detailed map of going from the latest stage of the sales funnel to making a purchase can be used to improve conversions. A map of making purchases after the initial conversion will help you increase customers’ lifetime value.
For now, we’ll concentrate on the basics and look at how to create a general customer journey map that covers a customer’s path from being interested in your product to making a purchase. It will help you improve your overall marketing strategy.
The first thing you’ll need to do is to set the frame of the customer map, where it should start and where it should end. Since we’re making a general map that covers the whole funnel, let’s set the start at being interested in the market, and the end at making the first purchase.
The most important thing, though, is to find the right path to trace. Most businesses have different types of clients that have different journeys. Let’s start by defining your user personas.
Analytics The 2023 B2B Superpowers Index
Analytics data analytics in marketing, digital marketing the third-party data deprecation playbook, digital marketing utilizing email to stop fraud-ecommerce client fraud case study, 1. define user personas.
Needless to say that a user looking for online shopping websites will differ from someone in search of the best online business ideas . That’s why defining user personas is so important for successful customer journey mapping.
Before you trace the customer’s journey, you need to have an idea of who’s making that journey. To do this, you need to know at least these four core data sets about your customer:
- Demographic information (for example, age, gender, country)
- What problems do they solve with your product
- What do they value from the product
- Where do they get information
With these points, you’ll be able to learn more about the customers themselves and their journey. Here’s how you can gather this information.
Tools to use
- Sign-up forms
- Google Analytics
- Facebook Analytics
- Pop-up surveys (Hotjar or similar)
- Email surveys (MailChimp or similar)
You can easily gather the most basic demographic information on your leads with the sign-up form. When they’re registering on the website or grabbing a freebie, ask them to fill a bit more than their email address, and you already have a decent database. While you’re at it, you can also gather employment information, which is extremely helpful if you run a B2B company.
If that’s not an option, gather that data with Google or Facebook analytical tools. You can also get an insight into what your users are interested in by looking up Affinity Categories in Google Analytics.
Most likely, you have not one but several main demographics. Look for the largest age and sex groups and run Affinity Category reports on them. You may find that say, men and women in their 30s that buy from you have different interests on average.
The answers to why people buy from you and what do they value the most can only be inferred from user surveys. Do it via pop-ups or send surveys to your newsletter subscribers.
That said, these are just the basic tools that will cover most needs. Feel free to use any advanced analytics tools at your disposal.
2. Identify touchpoints
Once you know who your customer is, it’s time to begin tracing their path towards the purchase. You’ll need to track the touchpoints they have with your brand as they go through every step of the sales funnel.
Asking them how they ended up on your website may not be the perfect idea as a lot of touchpoints will be forgotten before the purchase. Here’s how you can do it more efficiently.
- Lead scoring software (HubSpot or similar)
Let’s start by looking at the off-website touchpoints. These are the touchpoints that lead a customer to your website: social media, ads, blog articles in Google search, and other similar online portals. You can gauge these easily by looking at where the traffic comes from in the Google Analytics panel.
Don’t forget to add UTM markers to different links you leave around the web to make sure you’re getting the full picture.
You can also get an approximate picture by including a question like “How did you find us” in your sign-up forms. However, this only shows the bottom of the funnel, and won’t provide the full picture.
The idea behind it is to award more points to actions that lead to conversion. You can use this system to first track what actions do lead to a conversion.
This way, you’ll know what set of actions a potential buyer performs on the website. The other method to learn is to use the ‘Reverse Goal Path’ in Google Analytics.
This tab lets you take a goal from your campaign and see what actions did a person who ended up converting did on the website. This shows you the majority of the on-site customer journey.
3. Draw the map
Now you know who your customers are and what set of actions do they perform before making a purchase. All you have left to do is to actually draw the customer journey map.
You can do it whatever way you want, just make sure it will always be handy for future use.
- Drawing tool of choice: A piece of paper, an online mindmap, Photoshop, or any such platform that you’re comfortable using
Start with defining the user persona for the map you’re drawing. Since different user personas may have different journeys, you may need to draw several maps.
For now, let’s assume your customer is a 25 to 35-year-old male or female who owns an online store and is looking for SaaS software to help run it. Let’s call them Jessie since it’s a good gender-neutral name.
Start with what drives Jessie to make the purchase. Point out their motivation in this search. Then, track their behavior off-site. Maybe they search for the product reviews online or see several ads before they finally click on one of them.
Follow their path on your website based on the data you received from website analytics, and end the journey on their first purchase. Make sure to state how many users leave at a certain touchpoint and do not covert further.
In the end, you’ll have something like this.
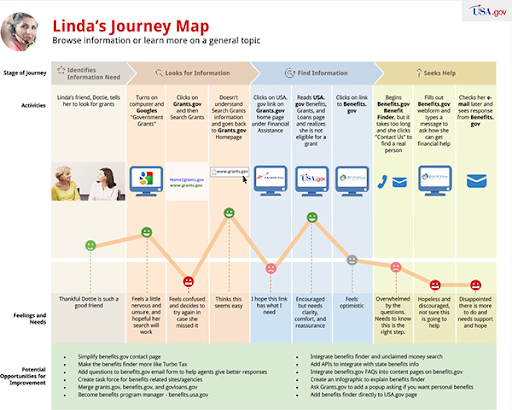
Source: Digital.gov
How to improve marketing strategy with CJM
There you have it, you’ve successfully created your first customer journey map. Now, let’s dig into how you can use it to improve your marketing efforts.
1. Search for insights
No customer journey map is complete without the insights, or potential opportunities for improvement, as noted in the map above. Gather your team if you haven’t already, and brainstorm the opportunities for improvement that you can infer from the map.
There’s no single way to go about it and it all depends on the situation you have on the map. For instance, if you see that a particular touchpoint has a conversion rate far below the rest, it’s probably something you should address.
Do more research on it, come up with a hypothesis as to why it underperforms, and try to improve it.
2. Improve messaging
Your customer’s motivation to make a purchase is a huge factor in how they decide what company to stick with. If you find that what your customers are looking for is not what you advertise, it’s a clear sign you should improve it.
3. Focus tangential interests
If you’re doing content marketing, your findings from the ‘Affinity Categories’ could be of good use. Some users can discover your product while reading articles on topics connected to it. For instance, Jessie’s journey to discovering a SaaS tool they need may have begun from reading an article on SMM.
Look up the data on affinity categories, and you can add a few more topics to your content marketing arsenal.
4. Focus on high-converting channels
While we’re on the topic of content marketing, customer journey mapping also allows for figuring out what marketing channels work best. Look at what channels are the most prevalent in the first half of the customer journey and figure out why they work best.
From then on, you have two options. You can either try to fix the channels that do not bring you enough customers or double down on the ones that already bring you the best ROI.
5. Improve on-site conversion
CJM provides some of the best analytics on the on-site actions of your customers. This gives you an opportunity to see what exactly are your customers doing on the website before they convert and improve the whole process.
This goes far beyond just improving the touchpoints you have. You can also change your on-site conversion strategy and add new touchpoints.
For instance, you may notice that people who grab freebies or attend webinars convert much more than regular visitors. You may start including these converting assets in pop-ups, or on the bottom of your blog posts.
If the issue is that your sales reps can’t keep up with the number of customers, you may need a sales funnel software to automate some of the tasks and work with bigger loads.
Improve every business aspect with customer journey mapping
A customer journey map is a tool that helps you visualize so much data about your customers and their path to conversion. Create a map that reflects how customers really do, not what you think they’re doing, and you can see all the mistakes your business does in attracting them further to conversion. Gather the data continuously and update the map to see how customer behavior changes, especially during unusual situations like a pandemic .
But it doesn’t stop there. You can improve most business processes that involve customers taking a set of actions towards a goal with a customer journey map. All you have to do is to set another frame and go through every process in this guide again.
This way, you can improve anything from increasing viewership on your blog to reducing customer churn.
Connie Benton is a chief content writer, guest contributor, and enthusiastic blogger who helps B2B companies reach their audiences more effectively. You can find her on Twitter at @ConnieB34412379 .
More about:
Get the Latest daily news and insights about search engine marketing, SEO and paid search.
The Merkle B2B 2023 Superpowers Index outlines what drives competitive advantage within the business culture and subcultures that are critical to success. It is the indispensable guide for B2B marketers to deliver world-class experiences and keep pace with the dynamic environment. Download Now
The ClicData survey found that various challenges exist that prevent organizations from achieving such gains. These challenges included inaccessible data formats and limited flexibility in displaying data in dashboards. Download Now
The need for fraud prevention in the digital world is critical now more than ever. Why? Thinking about your own behavior, consider how you complete transactions and how this has changed over the last 5 years. Download Now
The 2023 B2B Superpowers Index
Data analytics in marketing, the third-party data deprecation playbook, utilizing email to stop fraud-ecommerce client fraud case study, related articles, fospha’s insights to unlock ecommerce growth in 2024, is user data truly protected in the google analytics universe, how to use seo for a great abm strategy, using seo data analytics to identify business gaps, seven first-party data capturing opportunities your business is missing out..., four ways to use your website data to discover missed sales opportunities, cross-channel and cookieless: how measurement will evolve in 2021, what affiliate marketers have missed about google analytics, subscribe to the latest news & insights.
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Customer Journey Maps
What are customer journey maps.
Customer journey maps are visual representations of customer experiences with an organization. They provide a 360-degree view of how customers engage with a brand over time and across all channels. Product teams use these maps to uncover customer needs and their routes to reach a product or service. Using this information, you can identify pain points and opportunities to enhance customer experience and boost customer retention.
“ Data often fails to communicate the frustrations and experiences of customers. A story can do that, and one of the best storytelling tools in business is the customer journey map.” — Paul Boag, UX designer, service design consultant & digital transformation expert
In this video, Frank Spillers, CEO of Experience Dynamics, explains how you can include journey maps in your design process.
- Transcript loading…
Customer Journey Maps – Tell Customer Stories Over Time
Customer journey maps are research-based tools. They show common customer experiences over time To help brands learn more about their target audience.
Maps are incredibly effective communication tools. See how maps simplify complex spaces and create shared understanding.
Unlike navigation maps, customer journey maps have an extra dimension—time. Design teams examine tasks and questions (e.g., what-ifs) regarding how a design meets or fails to meet customers’ needs over time when encountering a product or service.
Customer journey maps should have comprehensive timelines that show the most essential sub-tasks and events. Over this timeline framework, you add insights into customers' thoughts and feelings when proceeding along the timeline. The map should include:
A timescale - A defined journey period (e.g., one week). This timeframe should include the entire journey, from awareness to conversion to retention.
Scenarios - The context and sequence of events where a user/customer must achieve a goal. An example could be a user who wants to buy a ticket on the phone. Scenarios are events from the first actions (recognizing a problem) to the last activities (e.g., subscription renewal).
Channels – Where do they perform actions (e.g., Facebook)?
Touchpoints – How does the customer interact with the product or service? What actions do they perform?
Thoughts and feelings – The customer's thoughts and feelings at each touchpoint.
A customer journey map helps you understand how customer experience evolves over time. It allows you to identify possible problems and improve the design. This enables you to design products that are more likely to exceed customers’ expectations in the future state.

How to Create a Customer Journey Map for Exceptional Experiences?
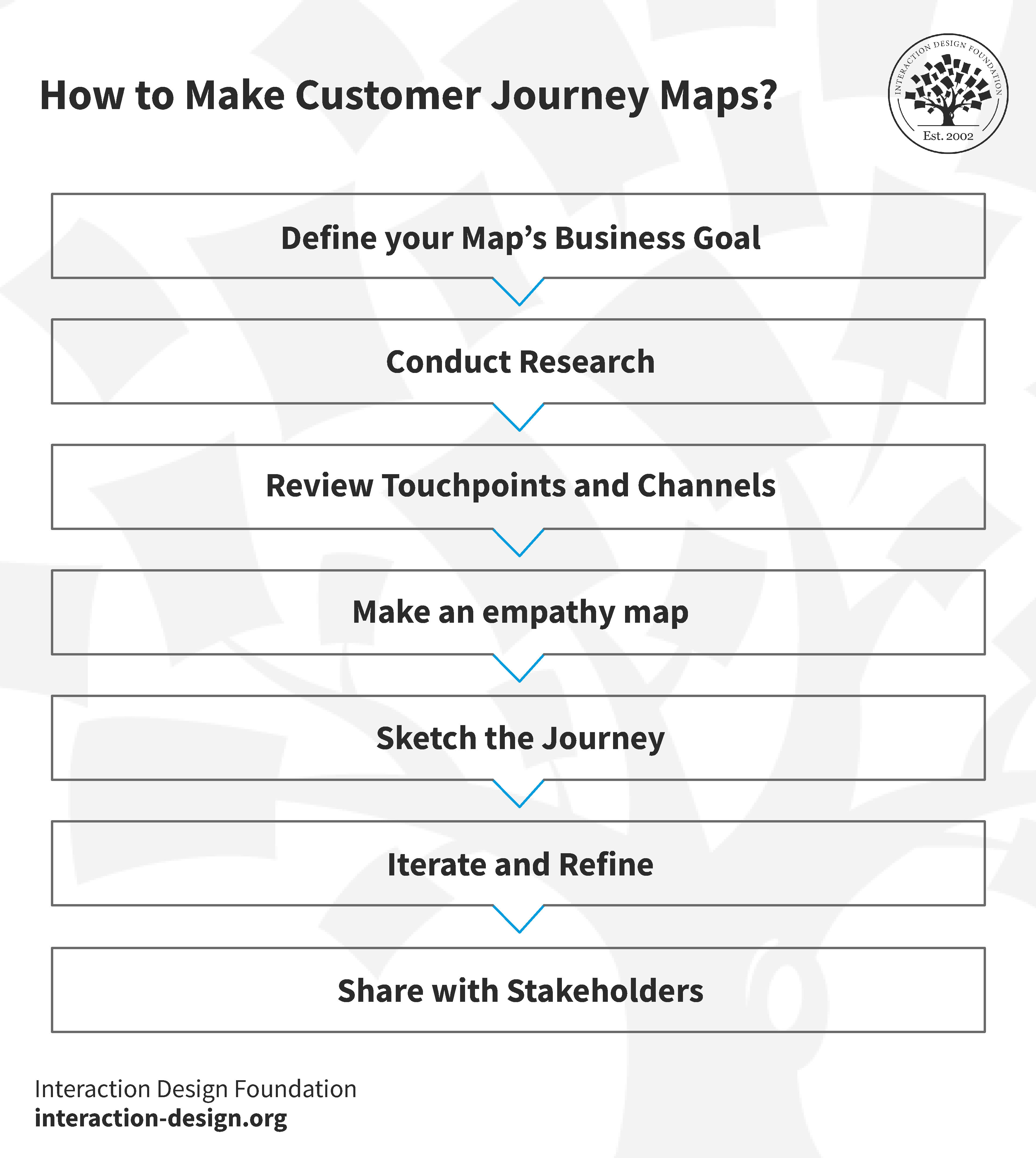
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Define Your Map’s Business Goal
Before creating a customer journey map, you must ask yourself why you're making one in the first place. Clarify who will use it and what user experience it will address.
Conduct Research
Use customer research to determine customer experiences at all touchpoints. Get analytical/statistical data and anecdotal evidence. Leverage customer interviews, surveys, social media listening, and competitive intelligence.
Watch user researcher Ditte Hvas Mortensen talk about how user research fits your design process and when you should do different studies.
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://pixabay.com/en/clay-hands-sculpting-art-69...
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-black-shirt-an...
- Copyright holder: Indecent Proposer. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/indecent_proposal/14...
- Copyright holder: Anna Langova. Copyright terms and license: CC0 1.0 Link: http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/view-image.php...
- Copyright holder: Conmongt. Copyright terms and license: CC0 Public Domain Link: https://pixabay.com/en/hourglass-time-time-lapse-clock-1623517/
Review Touchpoints and Channels
List customer touchpoints (e.g., paying a bill) and channels (e.g., online). Look for more touchpoints or channels to include.
Make an Empathy Map
Pinpoint what the customer does, thinks, feels, says, hears, etc., in a given situation. Then, determine their needs and how they feel throughout the experience. Focus on barriers and sources of annoyance.
Sketch the Journey
Piece everything—touchpoints, timescale, empathy map output, new ideas, etc.). Show a customer’s course of motion through touchpoints and channels across the timescale, including their feelings at every touchpoint.
Iterate and Refine
Revise and transform your sketch into the best-looking version of the ideal customer journey.
Share with Stakeholders
Ensure all stakeholders understand your map and appreciate how its use will benefit customers and the organization.
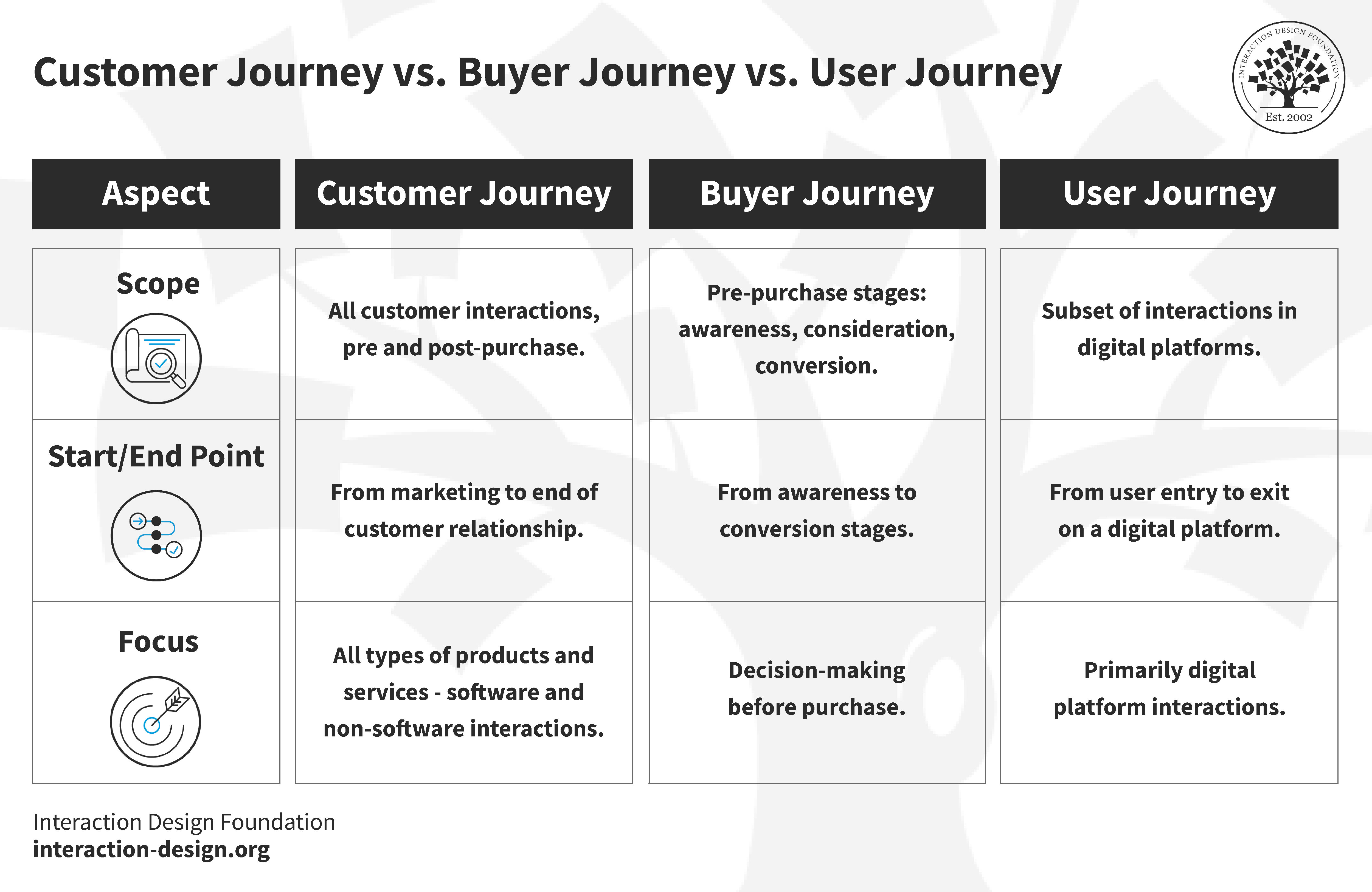
Buyer Journey vs User Journey vs Customer Journey: What's the Difference?
You must know the differences between buyer, user, and customer journeys to optimize customer experiences. A customer journey map is often synonymous with a user flow diagram or buyer journey map. However, each journey gives unique insights and needs different plans.
Customer Journey
The customer journey, or lifecycle, outlines the stages a customer goes through with a business. This journey can vary across organizations but includes five key steps:
1. Awareness : This is the first stage of the customer journey, where the customers realize they have a problem. The customer becomes aware of your brand or product at this stage, usually due to marketing efforts.
2. Consideration : Once customers know about your product or service, they start their research and compare brands.
3. Purchase : This is the stage where the customer has chosen a solution and is ready to buy your product or service.
4. Retention : After the purchase, it's about retaining that customer and nurturing a relationship. This is where good customer service comes in.
5. Advocacy : Also called the loyalty stage, this is when the customer not only continues to buy your product but also recommends it to others.
The journey doesn't end when the customer buys and recommends your solution to others. Customer journey strategies are cyclical and repetitive. After the advocacy stage, ideally, you continue to attract and retain the customers, keeping them in the cycle.
There is no standard format for a customer journey map. The key is to create one that works best for your team and product or service. Get started with customer journey mapping with our template:
This customer journey map template features three zones:
Top – persona and scenario.
Middle – thoughts, actions, and feelings.
Bottom – insights and progress barriers.
Buyer Journey
The buyer's journey involves the buyer's path towards purchasing. This includes some of the steps we saw in the customer journey but is specific to purchasing :
1. Awareness Stage : This is when a prospective buyer realizes they have a problem. However, they aren't yet fully aware of the solutions available to them.
2. Consideration Stage : After identifying their problem, the buyer researches and investigates different solutions with more intent. They compare different products, services, brands, or strategies here.
3. Decision Stage : The buyer then decides which solution will solve their problem at the right price. This is where the actual purchasing action takes place.
4. Post-Purchase Evaluation : Although not always included, this stage is critical. It's where the buyer assesses their satisfaction with the purchase. It includes customer service interactions, quality assessment, and attitudinal loyalty to the brand.
All these stages can involve many touchpoints, including online research, social media interactions, and even direct, in-person interactions. Different buyers may move through these stages at different speeds and through various channels, depending on a wide range of factors.
User Journey
The user journey focuses on people's experience with digital platforms like websites or software. Key stages include:
1. Discovery : In this stage, users become aware of your product, site, or service, often due to marketing efforts, word-of-mouth, or organic search. It also includes their initial reactions or first impressions.
2. Research/Consideration : Here, users dig deeper, exploring features, comparing with alternatives, and evaluating if your offering suits their needs and preferences.
3. Interaction/Use : Users actively engage with your product or service. They first-hand experience your solution's functionality, usability, and usefulness to achieve their goal.
4. Problem-solving : If they encounter any issues, how they seek help and resolve their issues fall into this stage. It covers user support, troubleshooting, and other assistance.
5. Retention/Loyalty : This stage involves how users stay engaged over time. Do they continue using your product, reduce usage, or stop altogether? It includes their repeated interactions, purchases, and long-term engagement over time.
6. Advocacy/Referral : This is when users are so satisfied they begin to advocate for your product, leaving positive reviews and referring others to your service.
Download this user journey map template featuring an example of a user’s routine.

Understanding these stages can help optimize the user experience, providing value at each stage and making the journey seamless and enjoyable.
Always remember the journey is as important as the destination. Customer relationships start from the first website visit or interaction with marketing materials. These initial touchpoints can influence the ongoing relationship with your customers.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0
Drawbacks of Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is valuable yet has limitations and potential drawbacks. Recognize these challenges and create more practical and realistic journey maps.
Over-simplification of Customer Experiences
Customer journey maps often risk simplifying complex customer experiences . They may depict varied and unpredictable customer behaviors as straightforward and linear. This simplification can lead to misunderstandings about your customers' needs and wants. As a result, you might overlook customers' diverse and unique paths.
Always remember that real customer experiences are more complex than any map. When you recognize this, you steer clear of decisions based on simple models.
Resource Intensity
Creating detailed customer journey maps requires a lot of resources and time. You must gather extensive data and update the maps to keep them relevant. This process can strain small businesses or those with limited resources.
You need to balance the need for comprehensive mapping with available resources. Efficient resource management and prioritization are crucial to maintaining effective journey maps.
Risk of Bias
Creating customer journey maps carries the inherent risk of biases . These biases can arise from various sources. They can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the maps.
Alan Dix, an expert in HCI, discusses bias in more detail in this video.
Common biases in customer journey mapping include:
Assumption Bias: When teams make decisions based on preconceived notions rather than customer data.
Selection Bias: When the data doesn’t represent the entire customer base..
Confirmation Bias : When you focus on information that supports existing beliefs and preferences. Simultaneously, you tend to ignore or dismiss data that contradicts those beliefs.
Anchoring Bias : Relying on the first information encountered (anchor) when making decisions.
Overconfidence Bias : Placing too much trust in the accuracy of the journey map. You may overlook its potential flaws.
These biases may misguide the team, and design decisions based on these maps might not be effective.
To address these biases, review and update journey maps with real user research data. Engage with different customer segments and gather a wide range of feedback to help create a more accurate and representative map. This approach ensures the journey map aligns with actual customer experiences and behaviors.
Evolving Customer Behaviors
Customer behaviors and preferences change with time. A journey map relevant today can become outdated. You need to update and adapt your maps to reflect these changes. This requires you to perform market research and stay updated with trends and customer feedback.
Getting fresh data ensures your journey map stays relevant and effective. You must adapt to evolving customer behaviors to maintain accurate and valuable customer journey maps.
Challenges in Capturing Emotions
Capturing emotions accurately in customer journey maps poses a significant challenge. Emotions influence customer decisions, yet you may find it difficult to quantify and represent them in maps. Most journey maps emphasize actions and touchpoints, often neglecting the emotional journey.
You must integrate emotional insights into these maps to understand customer experiences. This integration enhances the effectiveness of customer engagement strategies. You can include user quotes, symbols such as emojis, or even graphs to capture the ups and downs of the users’ emotions..
Misalignment with Customer Needs
Misalignments in customer journey maps can manifest in various ways. It can impact the effectiveness of your strategies. Common misalignments include:
Putting business aims first, not what customers need.
Not seeing or serving the varied needs of different customer types.
Not using customer feedback in the journey map.
Thinking every customer follows a simple, straight path.
Engage with your customers to understand their needs and preferences if you want to address these misalignments. Incorporate their direct feedback into the journey map. This approach leads to more effective customer engagement and satisfaction.
Over-Reliance on the Map
Relying too much on customer journey maps can lead to problems. These maps should serve as tools rather than definitive guides. Viewing them as perfect can restrict your responsiveness to customer feedback and market changes. Treat journey maps as evolving documents that complement direct customer interactions and feedback.
Make sure you get regular updates and maintain flexibility in your approach. Balance the insights from the map with ongoing customer engagement. This approach keeps your business agile and responsive to evolving customer needs.
Data Privacy Concerns
Collecting customer data for journey mapping poses significant privacy concerns. Thus, you need to create a balance. You must adhere to data protection laws and gather enough information for mapping.
You need a careful strategy to ensure customer data security. Stay vigilant to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and customer expectations. This vigilance helps maintain trust and compliance.

Learn More about Customer Journey Maps
Take our Journey Mapping course to gain insights into the how and why of journey mapping. Learn practical methods to create experience maps , customer journey maps, and service blueprints for immediate application.
Explore this eBook to discover customer journey mapping .
Find some additional insights in the Customer Journey Maps article.
Questions related to Customer Journey Maps
Creating a customer journey map requires visually representing the customer's experience with your product or company. Harness the strength of visual reasoning to understand and present this journey succinctly. Instead of detailing a lengthy narrative, like a book, a well-crafted map allows stakeholders, whether designers or not, to grasp the journey quickly. It's a democratized tool that disseminates information, unifies teams, and aids decision-making by illuminating previously unnoticed or misunderstood aspects of the customer's journey.
The customer journey encompasses five distinct stages that guide a customer's interaction with a brand or product:
Awareness: The customer becomes aware of a need or problem.
Consideration: They research potential solutions or products.
Purchase: The customer decides on a solution and makes a purchase.
Retention: Post-purchase, the customer uses the product and forms an opinion.
Advocacy: Satisfied customers become brand advocates, sharing their positive experiences.
For a comprehensive understanding of these stages and how they intertwine with customer touchpoints, refer to Interaction-Design.org's in-depth article .
A perspective grid workshop is a activity that brings together stakeholders from various departments, such as product design, marketing, growth, and customer support, to align on a shared understanding of the customer's journey. These stakeholders contribute unique insights about customer needs and how they interact with a product or service. The workshop entails:
Creating a matrix to identify customers' jobs and requirements, not initially linked to specific features.
Identifying the gaps, barriers, pains, and risks associated with unmet needs, and constructing a narrative for the journey.
Highlighting the resulting value when these needs are met.
Discuss the implied technical and non-technical capabilities required to deliver this value.
Brainstorming possible solutions and eventually narrowing down to specific features.
The ultimate aim is to foster alignment within the organization and produce a user journey map based on shared knowledge.
Learn more from this insightful video:
Customer journey mapping is vital as it harnesses our visual reasoning capabilities to articulate a customer's broad, intricate journey with a brand. Such a depiction would otherwise require extensive documentation, like a book. This tool offers a cost-effective method to convey information succinctly, ensuring understanding of whether one is a designer or lacks the time for extensive reading. It also helps the team to develop a shared vision and to encourage collaboration. Businesses can better comprehend and address interaction points by using a journey map, facilitating informed decision-making and revealing insights that might otherwise remain obscured. Learn more about the power of visualizing the customer journey in this video.
Pain points in a customer journey map represent customers' challenges or frustrations while interacting with a product or service. They can arise from unmet needs, gaps in service, or barriers faced during the user experience. Identifying these pain points is crucial as they highlight areas for improvement, allowing businesses to enhance the customer experience and meet their needs more effectively. Pain points can relate to various aspects, including product usability, communication gaps, or post-purchase concerns. Explore the detailed article on customer journey maps at Interaction Design Foundation for a deeper understanding and real-world examples.
Customer journey mapping offers several key benefits:
It provides a holistic view of the customer experience, highlighting areas for improvement. This ensures that products or services meet users' needs effectively.
The process fosters team alignment, ensuring everyone understands and prioritizes the customer's perspective.
It helps identify pain points, revealing opportunities to enhance user satisfaction and loyalty.
This visualization allows businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring resources target the most impactful areas.
To delve deeper into the advantages and insights on journey mapping, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on key takeaways from the IXDF journey mapping course .
In design thinking, a customer journey map visually represents a user's interactions with a product or service over time. It provides a detailed look at a user's experience, from initial contact to long-term engagement. Focusing on the user's perspective highlights their needs, emotions, pain points, and moments of delight. This tool aids in understanding and empathizing with users, a core principle of design thinking. When used effectively, it bridges gaps between design thinking and marketing, ensuring user-centric solutions align with business goals. For a comprehensive understanding of how it fits within design thinking and its relation to marketing, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on resolving conflicts between design thinking and marketing .
A customer journey map and a user journey map are tools to understand the experience of users or customers with a product or service.
A customer journey map is a broader view of the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It considers physical and digital channels, multiple user personas, and emotional and qualitative aspects.
A user journey map is a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service. It only considers digital channels, one user persona, and functional and quantitative aspects.
Both are useful to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. However, they have different scopes, perspectives, and purposes. A customer journey map provides a holistic view of the entire customer experience across multiple channels and stages. A user journey map provides a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service.
While user journeys might emphasize specific tasks or pain points, customer journeys encapsulate the entire experience, from research and comparison to purchasing and retention.
Customer journey maps and service blueprints are tools to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. A customer journey map shows the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It focuses on the front stage of the service, which is what the customers see and experience. It considers different user personas and emotional aspects.
A service blueprint shows how a service is delivered and operated by an organization. It focuses on the back stage of the service, which is what the customers do not see or experience. It considers one user persona and functional aspects. What are the steps that the customer takes to complete a specific task or goal within the service? What are the channels and devices that the customer interacts with at each step?
For an immersive dive into customer journey mapping, consider enrolling in the Interaction Design Foundation's specialized course . This course offers hands-on lessons, expert guidance, and actionable tools. Furthermore, to grasp the course's essence, the article “4 Takeaways from the IXDF Journey Mapping Course” sheds light on the core learnings, offering a snapshot of what to expect. These resources are tailored by industry leaders, ensuring you're equipped with the best knowledge to craft impactful customer journey maps.
Literature on Customer Journey Maps
Here’s the entire UX literature on Customer Journey Maps by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Customer Journey Maps
Take a deep dive into Customer Journey Maps with our course Journey Mapping .
This course will show you how to use journey mapping to turn your own complex design challenges into simple, delightful user experiences . If you want to design a great shopping experience, an efficient signup flow or an app that brings users delight over time, journey mapping is a critical addition to your toolbox.
We will begin with a short introduction to mapping — why it is so powerful, and why it is so useful in UX. Then we will get familiar with the three most common types of journey map — experience maps, customer journey maps and service blueprints — and how to recognize, read and use each one. Then you will learn how to collect and analyze data as a part of a journey mapping process. Next you will learn how to create each type of journey map , and in the final lesson you will learn how to run a journey mapping workshop that will help to turn your journey mapping insights into actual products and services.
This course will provide you with practical methods that you can start using immediately in your own design projects, as well as downloadable templates that can give you a head start in your own journey mapping projects.
The “Build Your Portfolio: Journey Mapping Project” includes three practical exercises where you can practice the methods you learn, solidify your knowledge and if you choose, create a journey mapping case study that you can add to your portfolio to demonstrate your journey mapping skills to future employers, freelance customers and your peers.
Throughout the course you will learn from four industry experts.
Indi Young will provide wisdom on how to gather the right data as part of your journey mapping process. She has written two books, Practical Empathy and Mental Models . Currently she conducts live online advanced courses about the importance of pushing the boundaries of your perspective. She was a founder of Adaptive Path, the pioneering UX agency that was an early innovator in journey mapping.
Kai Wang will walk us through his very practical process for creating a service blueprint, and share how he makes journey mapping a critical part of an organization’s success. Kai is a talented UX pro who has designed complex experiences for companies such as CarMax and CapitalOne.
Matt Snyder will help us think about journey mapping as a powerful and cost-effective tool for building successful products. He will also teach you how to use a tool called a perspective grid that can help a data-rich journey mapping process go more smoothly. In 2020 Matt left his role as the Sr. Director of Product Design at Lucid Software to become Head of Product & Design at Hivewire.
Christian Briggs will be your tour guide for this course. He is a Senior Product Designer and Design Educator at the Interaction Design Foundation. He has been designing digital products for many years, and has been using methods like journey mapping for most of those years.
All open-source articles on Customer Journey Maps
14 ux deliverables: what will i be making as a ux designer.

- 1.2k shares
What are Customer Touchpoints & Why Do They Matter?
- 3 years ago
How to Visualize Your Qualitative User Research Results for Maximum Impact

- 2 years ago
How to Resolve Conflicts Between Design Thinking and Marketing

How to Create a Perspective Grid
- 11 mths ago
4 Takeaways from the IxDF Journey Mapping Course
The Power of Mapping
User Story Mapping in Design
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!

11 Customer Journey Mapping
The Nielsen Norman Group has a comprehensive website that provides how-to information on the most popular types of user experience activities such as customer journey mapping ( https://www.nngroup.com/articles/journey-mapping-101/ ). In addition, they provide an overview article of when to utilize what type of methodology such as directly engaging with users vs observing, collecting self-reported data https://www.nngroup.com/articles/which-ux-research-methods/ .
One popular method is that of customer journey mapping which as we noted before is the external-facing version of the service blueprint https://blog.practicalservicedesign.com/the-difference-between-a-journey-map-and-a-service-blueprint-31a6e24c4a6c . Journey maps allow users to tell you what they are experiencing and feeling during each step of a particular service or activity. Customer journey maps are a great way to put yourself in your users’ shoes so that you are seeing their challenges and successes with fresh eyes which will help you make improvements or test out a new offering. Here too, creating a flowchart of each stop along the journey will help you analyze the action with the corresponding experience. Customer journey maps typically involve the following steps https://www.ngdata.com/how-to-create-a-customer-journey-map/ :
- Understanding your “typical” user persona so that you can extrapolate from a few to the overall population
- Timeline (is it a one-time event or does it occur across a longer time span?)
- Touchpoints are all of the things and people where the user is interacting with a particular element or in this case, their data processes
- Asking open ended questions will help users fill in their own thoughts and feedback
This is the first step in the design thinking process where you are trying to understand your stakeholder’s perspective. This is a much more direct method of collecting the actual experiences of researchers rather than hearing about them and it allows us to be able to structure future questions more meaningfully as opposed to asking something like what their challenges are. You will see that the design thinking document contains very specific questions which we were able to derive from the templates and which we might not have uncovered had we simply started with a focus-group like scenario first.
Broad questions to consider to assist with this section:
- How long does your data need to be preserved?
- What kind of descriptors are necessary for later retrieval of the data?
- How will you provide context for the stored data?
- Who will need to be able to access the data?
- How will you make the data accessible?
- Will your data be embargoed?
Tools for RDS Copyright © 2022 by Kay Bjornen is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Guides » User Journey Map » User Journey Map Examples
Register Now to Beegin Your Journey!
Register Now For Free to Beegin Your Journey!

User Journey Map Examples
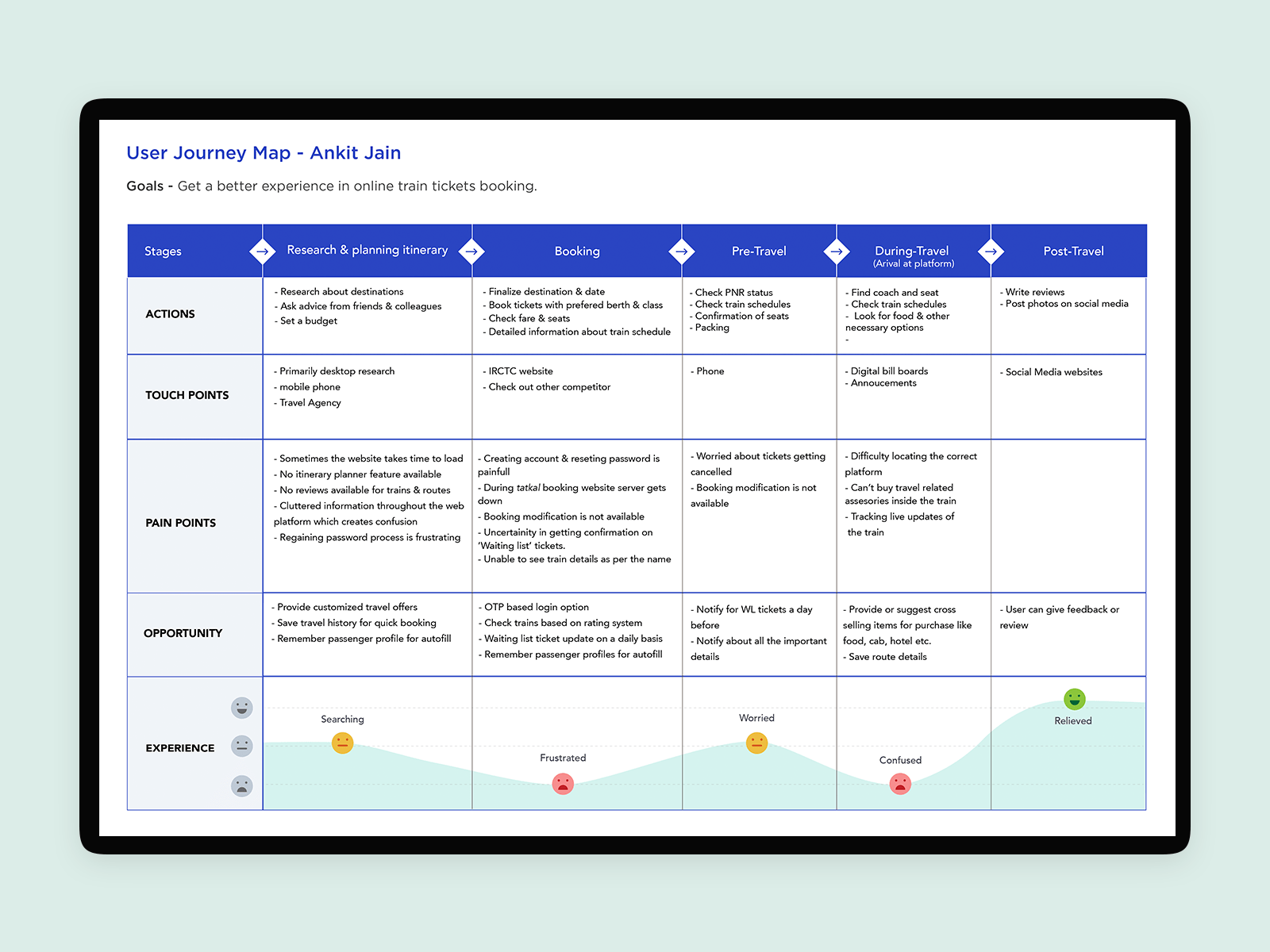
In this part of the guide we are going to present you some user journey map examples, describing their types, components and differences..

Last update 13.07.2023
User journey maps come in all shapes and sizes, depending on the type of product, persona and the goals you’ve defined for the research project. We understand it can be confusing to come up with your own structure suitable for your specific use case. That’s why we gathered 5 different user journey map examples to make sure you have something to look up to when working on your own map.
It’s always easier to create something based on the examples of professionals who’ve already done it!
In examples below we go through user journey maps of :
- Indian Railways
Improve your product’s UX with UXtweak
The only UX research tool you need to visualize your customers’ frustration and better understand their issues
Example 1: NN/group
We chose NN/group ’s user journey map as the first example for one reason. It’s very simple and easy to recreate and can serve as the most basic template with all the crucial components inside. In this particular case, we’re looking at the user journey map of the Jumping Jamie, who is looking to switch her mobile plans in order to save money.
The map perfectly outlines the 4 user stages she goes through: define, compare, negotiate, select .
We can see that at each stage Jamie completes different steps on the way to her final goal. We can also see the feelings she has along the way and the line which represents her emotions, going from the low to high points, depending on her satisfaction with the experience. The bottom of the map serves as the conclusion, defining the opportunities for improving the customer journey and internal ownership.
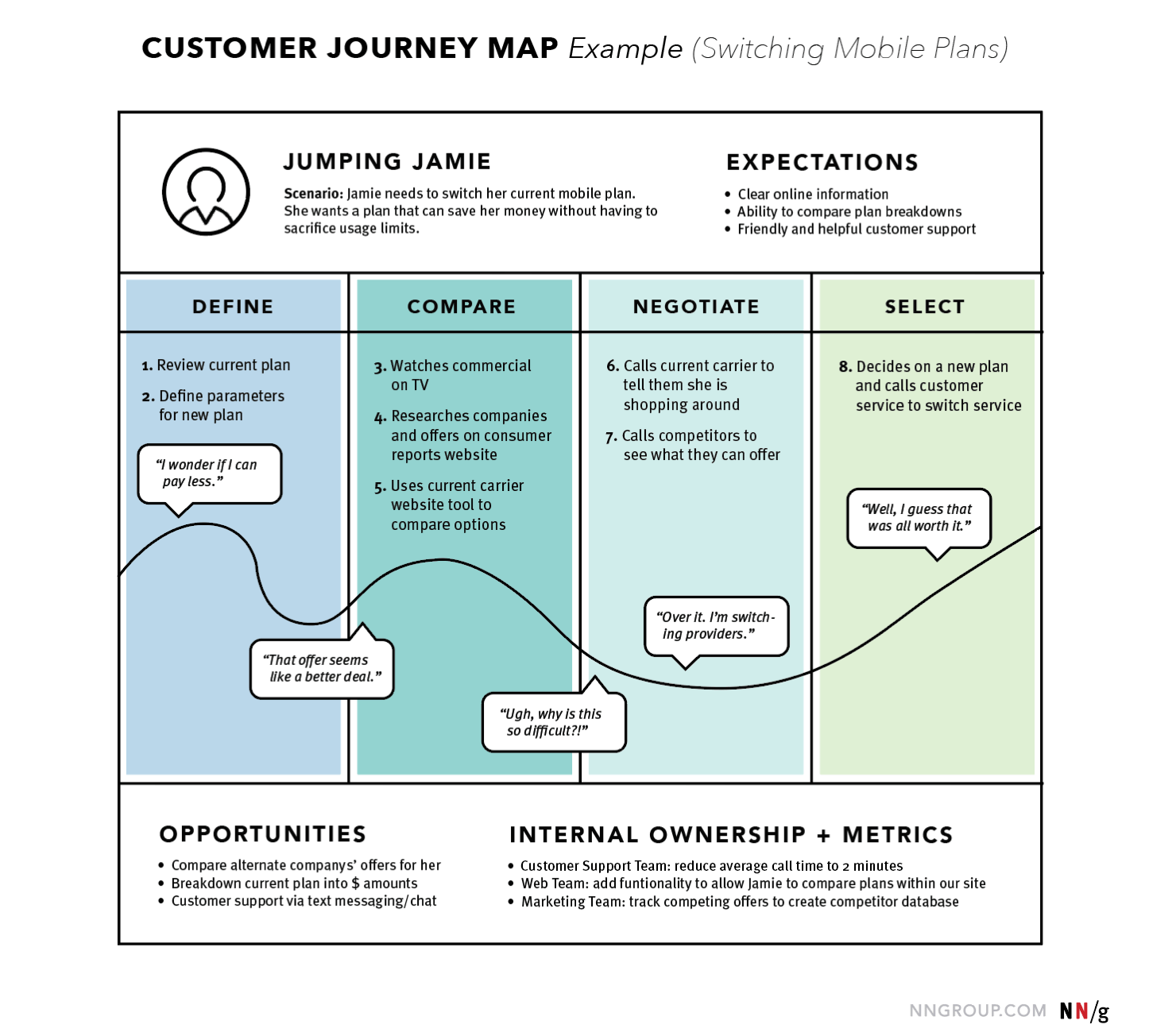
Source: NN/group
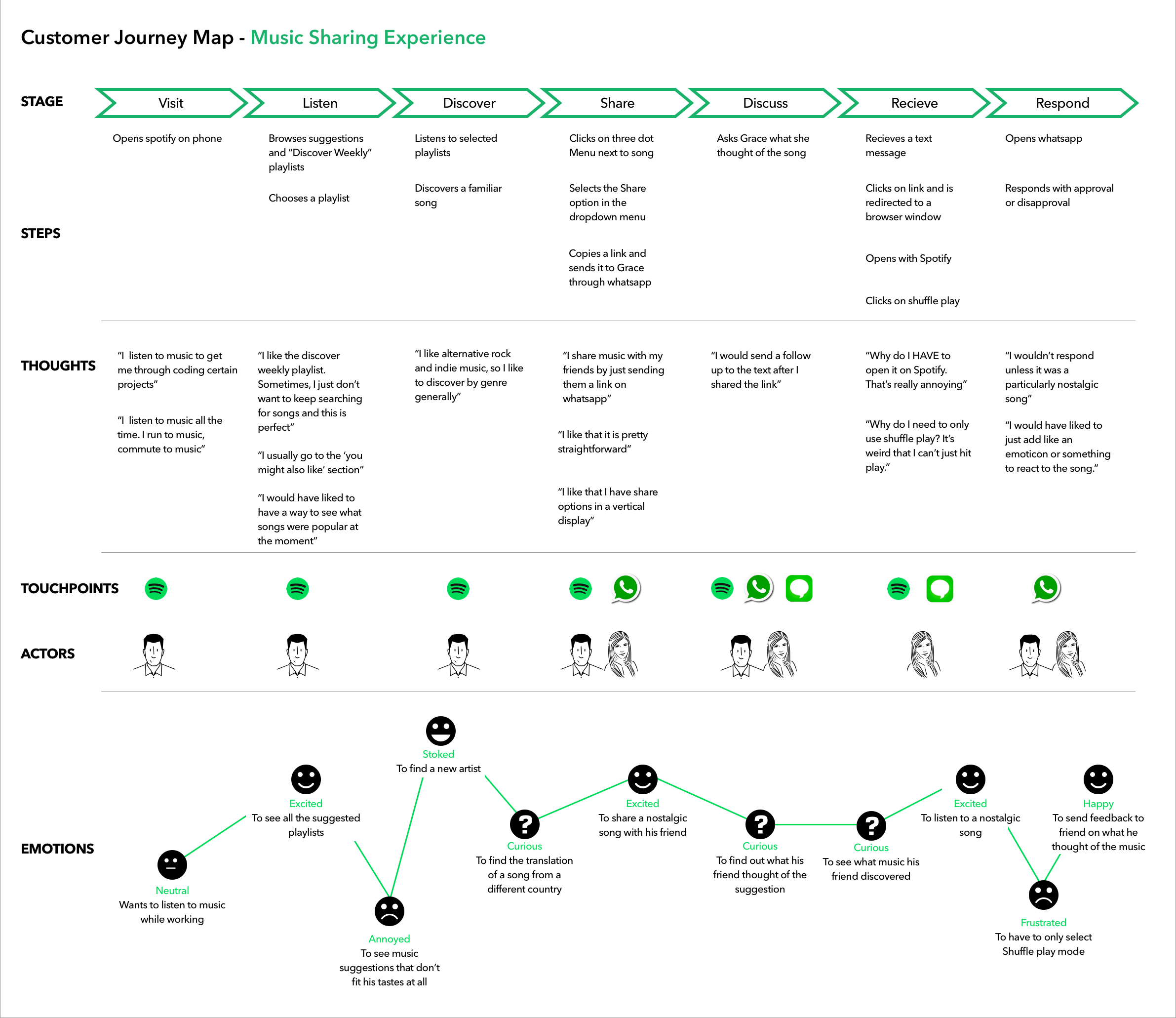
Example 2: Spotify
Spotify’s map for improving their music sharing experience is a great example of a B2C customer journey map . It was created as a part of a design project with the goal to add a music sharing feature that would allow listeners to send each other playlists and songs either within the platform or using other platforms. The project included customer journey mapping together with developing a persona as a part of the research stage. Check out the full Spotify case study to learn more.
As we can see on this map, there are a lot more stages a typical Spotify user goes through. Their thoughts and actions are described a lot more detailed and there are also additional sections such as touchpoints and actors. This map helped the design team understand at which point and why users get motivated to share music with each other. One of the key insights was that users are much more likely to share a song when the sharing feature is visible to them.
Meghana Bowen , a UX designer who worked on the project talks about pain points they uncovered: “ The biggest pain points discovered during the research stage was that the participants were worried about being judged for their music habits, as well as, most users were not aware of a share functionality existing.”
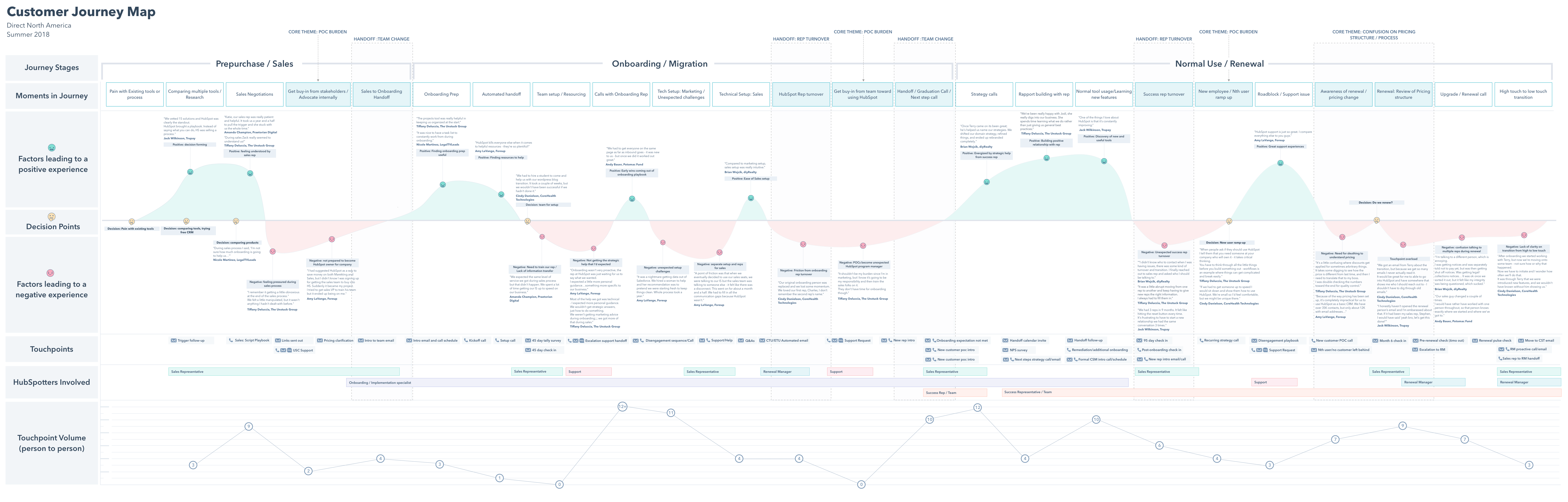
Example 3: Hubspot
In 2018 Hubspot created their own customer journey map and wrote a whole article about it providing you tips to create your own.
They chose a classical linear structure and used color-coding to make it more readable. A great idea was to add testimonials of their actual customers dealing with the product during the user research stage. This helped to empathize with them better, make existing problems feel more real and urgent and justify the data about their feelings.
It’s also a great thing to add for those who you’ll be presenting your user journey map to. These people will not be completely familiar with the research process behind it, but reading the testimonials could help them get more context on what’s going on at each stage of the journey.
Example 4: UXPressia
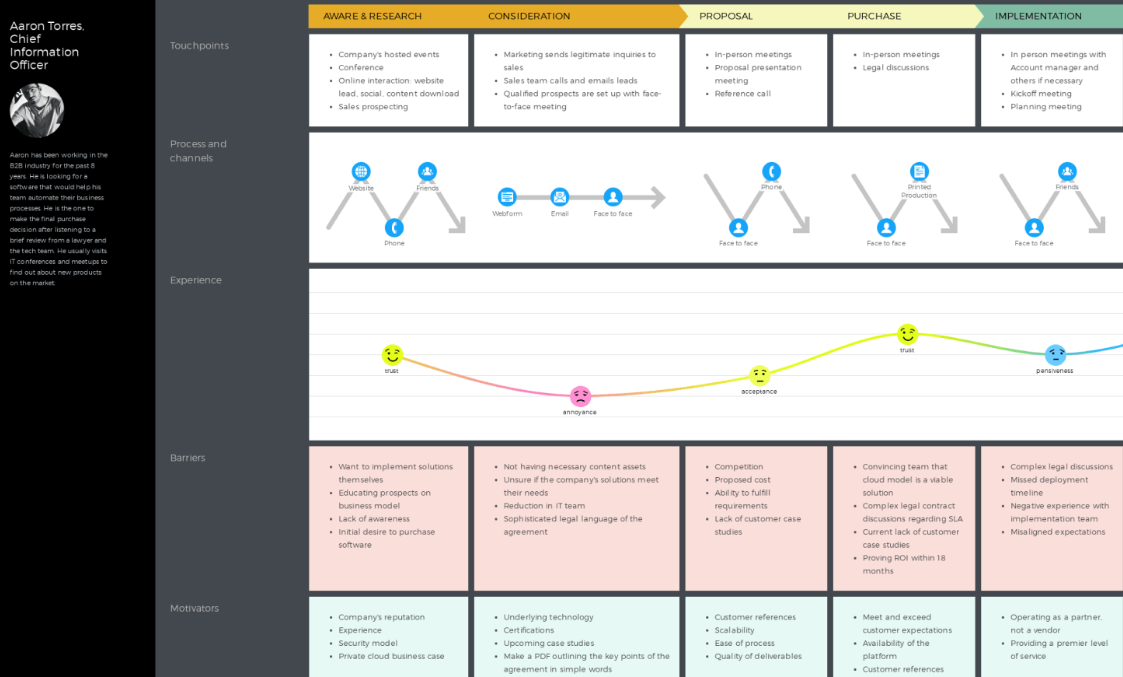
Another user journey map example, this time by UXPressia. It perfectly represents the B2B customer journey , outlining the stages a user goes through while making a purchase, from awareness to bonding or detachment.
UXPressia’s user journey map also includes 2 handy sections: barriers and motivators, that they describe under each stage. We can see that while there are no detailed emotions described at this map (as in the previous ones, for example), it’s still informative due to the motivators and barriers sections.
That again proves that user journey maps can and should look differently, as long as they are informative and clearly represent your user’s POV.
Example 5: Indian Railways
Our last example will be a user journey map created by Deepika Sinha from a research case study found on Behance. The study was conducted with a goal of improving the mobile UX of an Indian Railway app. You can check out the whole case study here .
This is a great example of how you can make an informative user journey map while still keeping it clean, visually appealing and not scary to read. The map shows the experience of booking tickets through the app, describes the pain points a user goes through and the opportunities for designers to improve the experience.
How to create a user journey map?
Creating a user journey map is an iterative process that not only includes building a map itself, but also a lot of user research and usability testing done throughout the whole process.
Creating a user journey map for your specific persona helps to look at the product from their point of view, uncover pain points and opportunities for fine-tuning the user flow in order to make it more intuitive.
To create a user journey map we recommend following these 7 steps:
- Set the objectives
- Define user personas
- Get to know your audience
- Define the journey phases
- Map out each phase
- Validate the user journey
- Identify confusions and areas of improvement
Check out our user journey map page, where we explain each of the steps in detail and walk you through the process of creating your own map.
Get access to actionable templates and examples! Learn how to create the perfect customer journey map today with our free ebook guide. ⬇️
Customer Journey Ebook
How to create a customer journey for your business
User Journey Map Tools
User journey map template, topics: user journey map.
- 01. User Journey Map
- 02. User Journey Map Tools
- 03. User Journey Map Examples
- 04. User Journey Map Template

User Journey Map
- Card Sorting
- Tree Testing
- Preference Test
- Five Second Test
- Session Recording
- Mobile Testing
- First Click Test
- Prototype Testing
- Website Testing
- Onsite Recruiting
- Own Database
- Documentation
- Product features
- UX Glossary
- Comparisons

COMMENTS
Definition of a Journey Map. Definition: A journey map is a visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. In its most basic form, journey mapping starts by compiling a series of user actions into a timeline. Next, the timeline is fleshed out with user thoughts and emotions in order to create a narrative.
See below for diagram annotations. Zone A: The lens provides constraints for the map by assigning (1) a persona ("who") and (2) the scenario to be examined ("what"). Zone B: The heart of the map is the visualized experience, usually aligned across (3) chunkable phases of the journey. The (4) actions, (5) thoughts, and (6) emotional ...
This customer journey template offers a starting point for your own customer journey map. Identify the point of view. In your own copy of the template, identify the lens (rows 2-4) of your customer-journey map. Includes the map title, persona, scenario (the specific experience being mapped), and corresponding goals and expectations of the user.
Journey maps visualize the process that a user goes through to accomplish a goal. They provide a holistic view of the customer experience, highlighting both positive and negative moments from the user's point-of-view.. Leading a journey-mapping initiative is no small challenge. It takes product knowledge and research savvy, along with project- and stakeholder-management skills.
Journey mapping reveals a holistic view of the customer experience by uncovering moments of both frustration and delight throughout a series of interactions. Find opportunities to streamline the experiences you create and differentiate your brand. "This is a great course which not only gives you a wealth of knowledge and information that you ...
In addition, most practitioners (64%) reported creating the journey maps collaboratively, with 34% collaborating over physical tools (e.g., sticky notes and paper) and 30% using digital tools (e.g., Miro, Mural, Google Sheets). In contrast, 36% reported creating the map as a solo activity using either physical tools (10%) or digital tools (26%).
UX Mapping Methods Compared: A Cheat Sheet. Sarah Gibbons. November 5, 2017. Summary: Empathy maps, customer journey maps, experience maps, and service blueprints depict different processes and have different goals, yet they all build common ground within an organization. Designing and developing a product often involves a large team of people ...
The 5 components of a journey map and the benefits of using this qualitative method as part of a UX design process to discover, document, and share the bigge...
customer journey map template phase 2 phase 3 scenario user expectations phase 4 insights internal ownership doing thinking saying. title: jmtemplate created date:
User Journey Map. A customizable journey mapping template from Nielsen Norman Group to get you started creating interactive UX maps. Add your own interactions, branding, styles, and more to tailor it to your needs. Read more: Building Interactive UX MapsJourney Mapping 101Enroll in Live Training: Journey Mapping ...
Customer journey maps come in two flavors: current-state and future-state mapping. Mapping can be based on hypotheses or on real user data.
Introduction. A journey map is a visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. (nngroup) A Customer journey map (user journey map) is a visual representation of the customer's experience when they fulfill a need/goal tied to the business/product. It represents the customer's actions, thoughts, feelings, pain points, etc.
A map of the path that a customer makes from their decision to make a purchase or any other action, to successfully making it. Here's an example of what it looks like from the NNGroup. Source: NNGroup. You can create a customer journey map for most processes that involve customer decisions and use this map for different purposes.
Customer journey maps are visual representations of customer experiences with an organization. They provide a 360-degree view of how customers engage with a brand over time and across all channels. Product teams use these maps to uncover customer needs and their routes to reach a product or service. Using this information, you can identify pain ...
3. Types of journey maps. Depending on the requirement, journey maps can be used to map the existing experiences or the desired future experience. The current-state journey maps depict the existing experiences of the users with products and services. Whereas a future-state journey map can be used to plan and envision a best case, ideal-state ...
Type #1: Hypothetical Journey Map. Project Phase: This is usually done at the start of the project when the team convenes to establish scope, timeline and define the start and end of the customer journey. Best Use for: Visualising a customer journey with a product or service that exists today. Purpose: Aggregate team's current knowledge and awareness on the customers' journey and create ...
Journey maps allow users to tell you what they are experiencing and feeling during each step of a particular service or activity. Customer journey maps are a great way to put yourself in your users' shoes so that you are seeing their challenges and successes with fresh eyes which will help you make improvements or test out a new offering.
Nielsen Norman Group offers evidence-based user experience (UX) research, training, and consulting. The company was founded by Jakob Nielsen and Don Norman. ...
Helvetica Neue,Regular" 2 000000 . Helvetica Neue,Regular" 2 000000 [Your Journey Map Title Goes Here] [Replace this icon with a visual representation of the persona the map is about]
A user journey map (also called a customer journey map) visually represents a typical user's path when using a product. It's a popular user experience research technique that reveals how users interact with and use a product over time - starting with your new user onboarding flow.. The purpose of journey mapping is to get inside the head of your users, allowing you to make meaningful ...
Another user journey map example, this time by UXPressia. It perfectly represents the B2B customer journey, outlining the stages a user goes through while making a purchase, from awareness to bonding or detachment. UXPressia's user journey map also includes 2 handy sections: barriers and motivators, that they describe under each stage.
Real-time mapping in-game or your browser as you explore. 216.8M Downloads | Mods
nngroup.com. Journey Mapping 101. A journey map is a visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. Kiele Schneckloth. 6 followers. Travel Book. Travel Journal. Drawing Books For Kids. Book Report Templates. Larry Page.