The remarkable twin Voyager spacecraft continue to explore the outer reaches of the solar system decades after they completed their surveys of the Outer Planets. Launched in 1977 (September 5 for Voyager 1 (V1) and August 20 for Voyager 2 (V2), whose trajectory took it past Jupiter after Voyager 1), the spacecraft pair made many fundamental discoveries as they flew past Jupiter (March 1979 for V1, July 1979 for V2) and Saturn (November 1980 for V1, August 1981 for V2). The path of Voyager 2 past Saturn was targeted so that it continued within the plane of the solar system, allowing it to become the first spacecraft to visit Uranus (January 1986) and Neptune (August 1989). Following the Neptune encounter, both spacecraft started a new phase of exploration under the intriguing title of the Voyager Interstellar Mission.

Five instruments continue to collect important measurements of magnetic fields, plasmas, and charged particles as both spacecraft explore different portions of the solar system beyond the orbits of the planets. Voyager 1 is now more than 118 astronomical units (one AU is equal to the average orbital distance of Earth from the Sun) distant from the sun, traveling at a speed (relative to the sun) of 17.1 kilometers per second (10.6 miles per second). Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s.

This processed color image of Jupiter was produced in 1990 by the U.S. Geological Survey from a Voyager image captured in 1979. The colors have been enhanced to bring out detail. Zones of light-colored, ascending clouds alternate with bands of dark, descending clouds. The clouds travel around the planet in alternating eastward and westward belts at speeds of up to 540 kilometers per hour. Tremendous storms as big as Earthly continents surge around the planet. The Great Red Spot (oval shape toward the lower-left) is an enormous anticyclonic storm that drifts along its belt, eventually circling the entire planet.
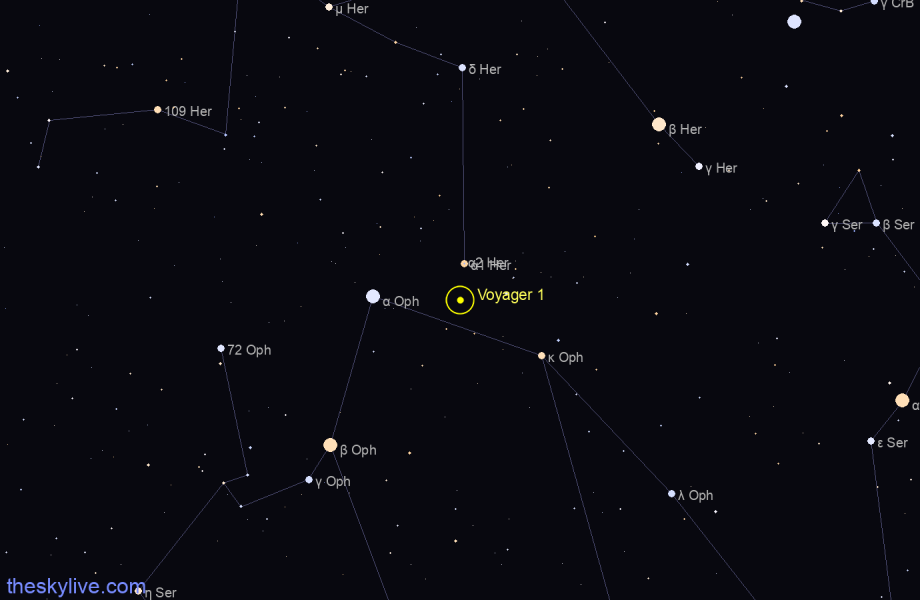
As seen in the night sky at Earth, Voyager 1 is within the confines of the constellation Ophiuchus, only slightly above the celestial equator; no telescope can see it, but radio contact is expected to be maintained for at least the next ten years. Voyager 2 is within the bounds of the constellation Telescopium (which somehow sounds quite appropriate) in the far southern night sky.

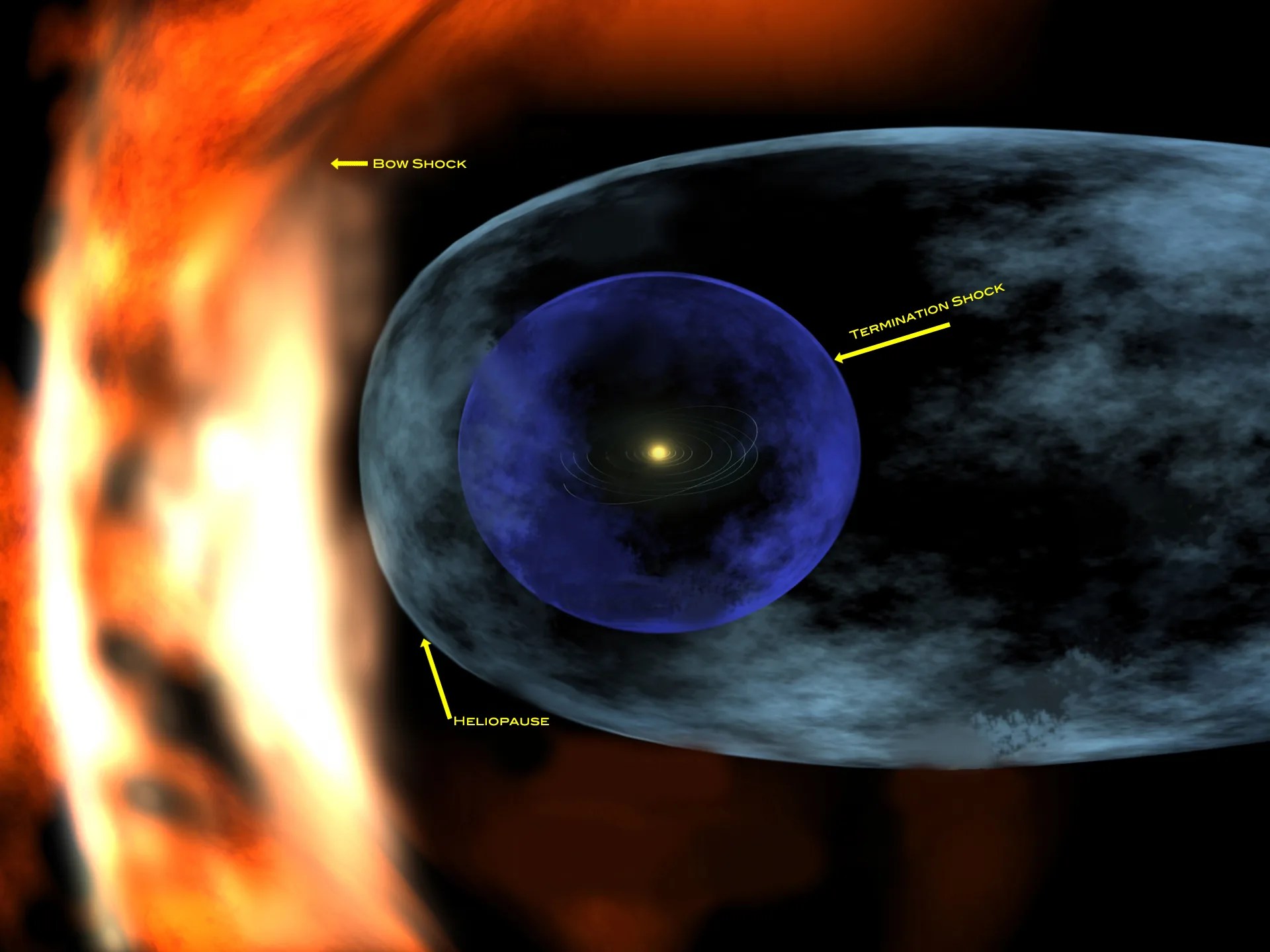
Both spacecraft have already passed something called the Termination Shock † (December 2004 for V1, August 2007 for V2), where the solar wind slows as it starts to interact with the particles and fields present between the stars. It is expected that both spacecraft will encounter the Heliopause, where the solar wind ceases as true interstellar space begins, from 10 to 20 years after crossing the Termination Shock. Theories exist for what should be present in interstellar space, but the Voyagers will become the first man-made objects to go beyond the influences of the Sun, hopefully returning the first measurements of what it is like out there. Each spacecraft is carrying a metal record with encoded sounds and sights from Earth, along with the needle needed to read the recordings, and simplified instructions for where the spacecraft came from, in case they are eventually discovered by intelligent extra-terrestrials.

Keep track of the Voyager spacecraft on the official Voyager Interstellar Mission website or follow @NASAVoyager2 on Twitter. † The sun ejects a continuous stream of charged particles (electrons, protons, etc) that is collectively termed the solar wind. The particles are traveling extremely fast and are dense enough to form a very tenuous atmosphere; the heliosphere represents the volume of space where the effects of the solar wind dominate over those of particles in interstellar space. The solar wind particles are moving very much faster than the local speed of sound represented by their low volume density. When the particles begin to interact with interstellar particles and fields (the interaction can be either physically running into other particles or experiencing an electromagnetic force resulting from a charged particle moving within a magnetic field), then they start to slow down. The point at which they become subsonic (rather than their normal hypersonic speed) is the Termination Shock.
We rely on the generous support of donors, sponsors, members, and other benefactors to share the history and impact of aviation and spaceflight, educate the public, and inspire future generations. With your help, we can continue to preserve and safeguard the world’s most comprehensive collection of artifacts representing the great achievements of flight and space exploration.
- Get Involved
- Host an Event

Thank you. You have successfully signed up for our newsletter.
Error message, sorry, there was a problem. please ensure your details are valid and try again..
- Free Timed-Entry Passes Required
- Terms of Use

Ephemeris Calculator
Compute Voyager 1 ephemerides for any date and time between 01 Jan 1970 and 01 Jan 1970 and display the predicted position in an interactive sky map.
- Where is Voyager 1?
Voyager 1 is currently in the constellation of Ophiucus . The current Right Ascension is 17h 15m 59s and the Declination is +12° 21’ 18”.
Right now, from the selected location (Greenwich, United Kingdom edit_location_alt ), Voyager 1 can be observed looking in the South-West direction at an altitude of 44° degrees above the horizon (view Voyager 1 position on a interactive sky map ).
emoji_objects If you access this data frequently and would like to have a more synthetic view, you can create a Quick Access Page for this object and bookmark it or add it to your Home Screen.
See also the following additional resources about Voyager 1
- Voyager 1 Information on TheSkyLive.com
- How far is Voyager 1 from Earth?
- When does Voyager 1 rise and set?
- Interactive sky map
- Live position tracker
Voyager 1 Trajectory through the Solar System
- Released Thursday, August 31, 2017
- Visualizations by:
- Tom Bridgman
This visualization tracks the trajectory of the Voyager 1 spacecraft through the solar system. Launched on September 5, 1977, it was one of two spacecraft sent to visit the giant planets of the outer solar system. Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter and Saturn before being directed out of the solar system. To fit the 40 year history of the mission into a short visualization, the pacing of time accelerates through most of the movie, starting at about 5 days per second at the beginning and speeding up to about 11 months per second after the planet flybys are past. The termination shock and heliopause are the 'boundaries' created when the plasma between the stars interacts with the plasma flowing outward from the Sun. They are represented with simple grid models and oriented so their 'nose' is pointed in the direction (Right Ascension = 17h 24m, declination = 17 degrees south) represented by more recent measurements from other missions.
Visualization centered on the Voyager 1 trajectory through the solar system.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.HD1080i_p30.mp4 (1920x1080) [120.3 MB]
- Voyager.ChaseV1.HD1080i_p30.webm (1920x1080) [15.4 MB]
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_2160p30.mp4 (3840x2160) [210.8 MB]
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate (1920x1080) [256.0 KB]
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate (3840x2160) [256.0 KB]
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.HD1080i.03905_print.jpg (1024x576) [96.8 KB]
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.HD1080i.03905_searchweb.png (320x180) [68.6 KB]
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.HD1080i.03905_thm.png (80x40) [4.4 KB]
Voyager 1's 'Family Portrait' On Valentine's Day 1990, Voyager 1's camera were pointed back at the solar system to image the planets. Check out Voyager at NASA/JPL for more information.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.UHD3840.00000_print.jpg (1024x576) [104.9 KB]
Opening view of Earth orbit looking outward to the rest of the solar system.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.UHD3840.00550_print.jpg (1024x576) [117.4 KB]
Voyager 1 (and 2) cross the orbit of Mars, slightly above the ecliptic plane to avoid the asteroid belt between Mars & Jupiter.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.UHD3840.01490_print.jpg (1024x576) [113.3 KB]
The camera moves out ahead of the Voyagers for a view back at the inner solar system.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.UHD3840.01990_print.jpg (1024x576) [102.3 KB]
Voyager 1 just after the Jupiter flyby on March 5, 1979.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.UHD3840.02420_print.jpg (1024x576) [101.8 KB]
Voyager 1 just before the Saturn flyby on November 12, 1980.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.UHD3840.02990_print.jpg (1024x576) [123.1 KB]
With a gravity-assist from the Saturn flyby, Voyager 1 is directed above the plane of the solar system and continues outward. This is near the time of the Voyager 1 'Family Portrait'. The orbit of Pluto is the grey orbit visible above the orbits of the other planets.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.UHD3840.03350_print.jpg (1024x576) [97.5 KB]
Voyager 1 crosses the termination shock of the solar wind. For simplified and symmetric termination shock model, the timing is not accurate. In reality, this crossing occurred around December of 2004.
- Voyager.ChaseV1.clockSlate_Track.UHD3840.03900_print.jpg (1024x576) [99.4 KB]
Voyager 1 (and 2) beyond the heliopause near the end of 2017.
A slightly sped-up version of the Voyager 1 visualization above, reducing the time for the Voyagers to cross the asteroid belt.
- Voyager1SpedUp.m4v (1920x1080) [123.0 MB]
- Voyager1SpedUp.webm (1920x1080) [12.2 MB]
- Voyager1_Sped_Up-HD1080p.mov (1920x1080) [185.8 MB]
- Voyager1_Sped_Up.mov (1920x1080) [1.7 GB]
- Voyager_1_Sped_Up_4k-H264.mov (3840x2160) [639.6 MB]
- Voyager_1_Sped_Up_4k_ProRes.mov (3840x2160) [7.2 GB]
- Voyager1SpedUp.00500_print.jpg (1024x576) [122.6 KB]
- Solar System
Please give credit for this item to: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
- Kathalina Tran (KBR Wyle Services, LLC)
- Genna Duberstein (USRA)
- Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
Project support
- Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, August 31, 2017. This page was last updated on Wednesday, November 15, 2023 at 12:05 AM EST.
- Voyager @ 40
- Voyager Retrospective
Datasets used in this visualization
Planetary ephemerides SPICE kernel
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.
Hubble’s Brand New Image of Jupiter
Where is the edge of the solar system, voyager 2 trajectory through the solar system, revisiting the pale blue dot at 30, you may also like..., no results., an error occurred. please reload this page and try again..
Subscribe or renew today
Every print subscription comes with full digital access
Science News
‘humanity’s spacecraft’ voyager 1 is back online and still exploring.
After five months of glitching, the spacecraft is talking to Earth again from interstellar space

The Voyager 1 spacecraft (illustrated) is back online after a few months of transmitting garbled data. It’s now poised to continue its exploration of interstellar space.
JPL-Caltech/NASA
Share this:
By Ramin Skibba
April 26, 2024 at 11:45 am
After months of challenging trouble-shooting and suspenseful waiting, Voyager 1 is once again talking to Earth.
The aging NASA spacecraft, about 24 billion kilometers from home, began transmitting garbled data in November. On April 20, NASA scientists got the probe back online after uploading new flight software to work around a chunk of onboard computer memory that had failed. They’re now receiving data about the spacecraft’s health and hope to hear from its science instruments again in a few weeks, says Suzanne Dodd, the mission’s project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
That means the iconic craft could be on a path to recovery — and to continue its exploration of interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 briefly visited Jupiter and Saturn before eventually departing the solar system. It and its twin, Voyager 2, are the longest-operating space probes, now tasked with studying far-flung solar particles and cosmic rays. In particular, the probes have been monitoring the changing of the sun’s magnetic field and the density of plasma beyond the solar system, yielding information about the farthest reaches of the sun’s influence .
“The spacecraft is really remarkable in its longevity. It’s incredible,” Dodd says. “We want to keep Voyager going as long as possible so we have this time record of these changes.”
Voyager 1 and 2, cruising along diverging paths, made history by crossing the heliopause in 2012 and 2018 , respectively ( SN: 9/12/13; SN: 12/10/18 ). At nearly 18 billion kilometers from the sun, that’s long been considered the outer extent of our star’s magnetic field and the solar wind, the boundary before interstellar space.
Since then, Dodd says, the science team has made some surprising findings ( SN: 11/4/19 ). For one, they’ve determined that the heliosphere, the huge bubble of space dominated by the solar wind, might not be spherical but have one or two tails, making it shaped like a comet or a croissant.
And thanks to Voyager, scientists now know that, despite expectations otherwise, the sun’s magnetic field and charged particles actually remain significant even beyond the heliopause, says David McComas, a Princeton University astrophysicist not involved in the mission.
Some theories predicted a serene environment in the distant oceans of interstellar space, but the Voyagers keep passing through waves of charged particles, indicating that the solar magnetic field still holds some sway there. What’s more, the probes’ data have shown how ripples in the field form bubbles at the edge of the solar system, which is more frothy and dynamic than expected.
Other missions have begun building on Voyager’s solar physics research. These include NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, and the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe, or IMAP, which is set to launch next year. Earth-orbiting IBEX has been measuring high-energy particles to map the heliosphere for 15 years, whereas IMAP will orbit between the sun and Earth, giving it an uninterrupted view of the sun as it monitors the galactic cosmic rays that manage to filter through the heliosphere.
“There’s a huge synergy between the Voyagers and both IBEX and IMAP,” says McComas, principal investigator of the latter two missions. “We were all really scared when Voyager 1 stopped phoning home.”
It will be decades until another mission could accomplish what the Voyagers have done. NASA’s New Horizons soared by Pluto in 2015 and kept going ( SN:8/9/18 ). It’s heading toward the edge of the solar system, but it’s cruising slowly and will run out of power before it can collect data beyond the heliopause.
The Voyagers can fly forever, but power for their instruments is waning. Over the next few years, NASA will shut some down to conserve energy for the rest.
That means Voyager 1’s days of collecting science data are numbered. “It’s a very beloved mission,” Dodd says. “It’s humanity’s spacecraft, and we need to take care of it.”
More Stories from Science News on Space

Separating science fact from fiction in Netflix’s ‘3 Body Problem’

Pluto’s heart-shaped basin might not hide an ocean after all

Our picture of habitability on Europa, a top contender for hosting life, is changing

Jupiter’s moon Io may have been volcanically active ever since it was born

50 years ago, scientists found a lunar rock nearly as old as the moon

How a sugar acid crucial for life could have formed in interstellar clouds

What Science News saw during the solar eclipse

During the awe of totality, scientists studied our planet’s reactions
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber? Become one now .
Ship Traffic .net
VOYAGER 1 Current Position and Live Map Location
Where is the current location of voyager 1 right now ship voyager 1 is a passenger ship navigating under the unspecified flag. the imo number is 8891613 and mmsi number is 1. general vessel particulars are as follows length overall (loa) of 23 m and beam (max width) of n.a. m. live maps below show the following voyage data - present position, next port of call, estimated (eta) and predicted time of arrival (pta), current speed, course, draught, photos, videos, local time, utc time..
Full Screen
Refresh Map
Open this map on your mobile by scanning a QR code
Open this map on your mobile by scanning the QR code image with your camera
20 emails/day for more ask
Send 0 emails out of 20 today

Interstellar Messengers

Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018.
Mission Type
Science Targets
Voyager 1 & 2

Mission Updates
Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth.
Latest News
NASA’s Voyager Team Focuses on Software Patch, Thrusters

NASA’s Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy

Edward Stone Retires After 50 Years as NASA Voyager’s Project Scientist

Engineers Solve Data Glitch on NASA’s Voyager 1
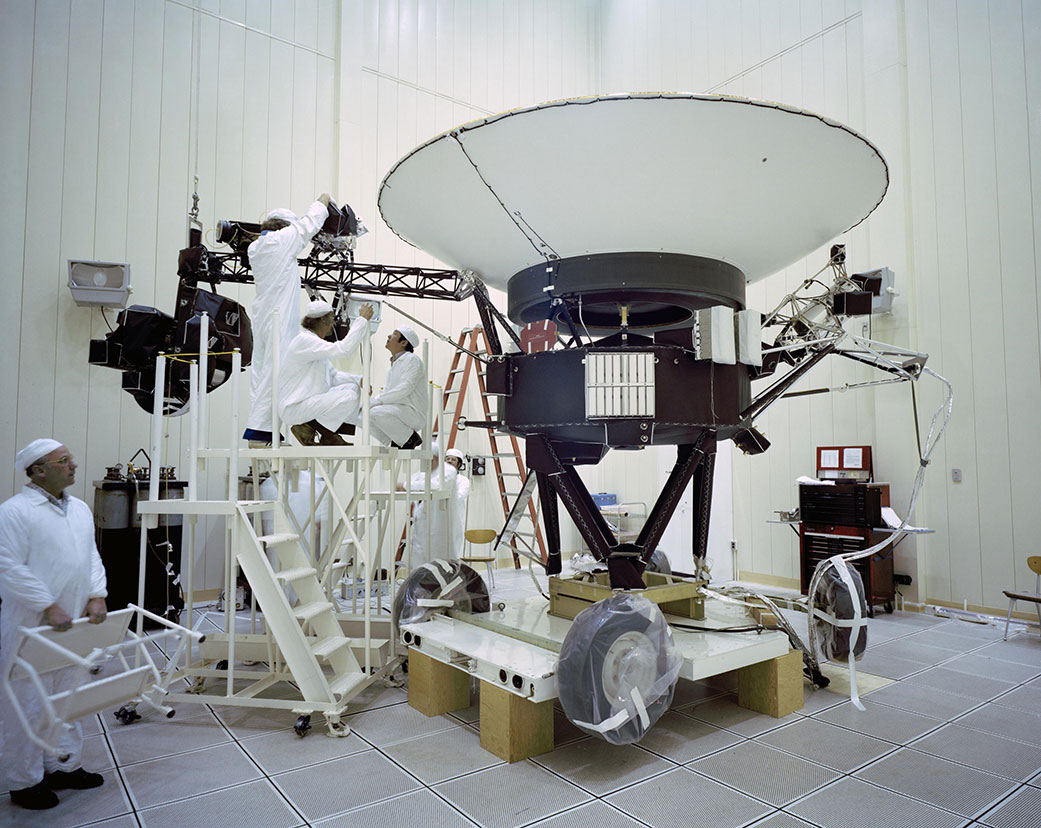

Voyager, NASA’s Longest-Lived Mission, Logs 45 Years in Space
The Interstellar Mission
After completing the first in-depth reconnaissance of the outer planets, the twin Voyagers are on a new mission to chart the edge of interstellar space.
The Golden Record
The contents of the golden record were selected for NASA by a committee led by Carl Sagan of Cornell University.
The Spacecraft
The twin Voyagers are escaping our solar system in different directions at more than 3 astronomical units (AU) a year.

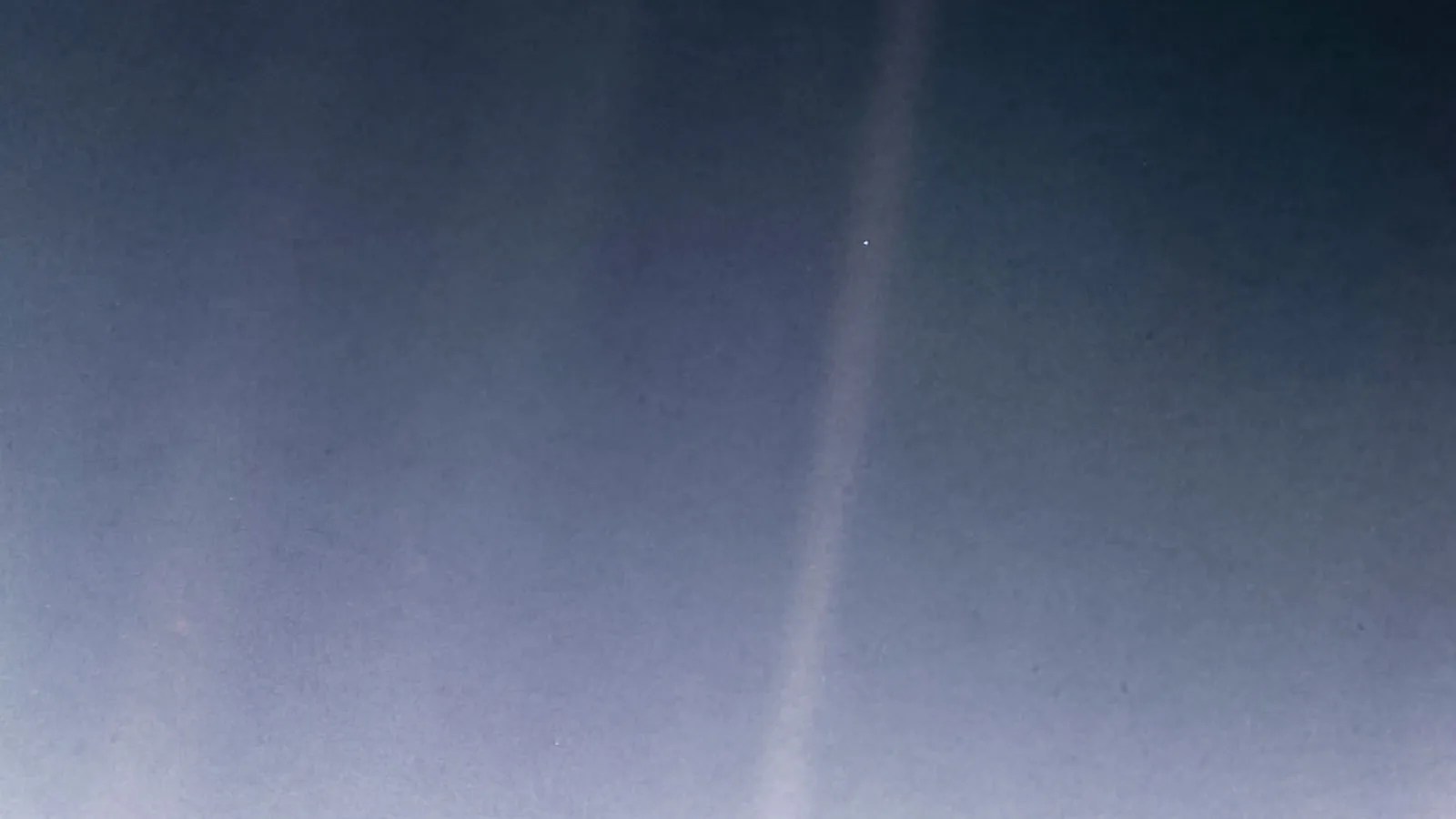
The Pale Blue Dot
The behind-the-scenes story of the making of Voyager 1's iconic image of Earth as "a mote of dust suspended in a sunbeam."

Discover More Topics From NASA

Our Solar System

Heliosphere

Voyager 1 is sending data back to Earth for the first time in 5 months
Sign up for CNN’s Wonder Theory science newsletter. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more .
For the first time in five months, NASA engineers have received decipherable data from Voyager 1 after crafting a creative solution to fix a communication problem aboard humanity’s most distant spacecraft in the cosmos.
Voyager 1 is currently about 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away, and at 46 years old, the probe has shown multiple quirks and signs of aging in recent years.
The latest issue experienced by Voyager 1 first cropped up in November 2023, when the flight data system’s telemetry modulation unit began sending an indecipherable repeating pattern of code .
Voyager 1’s flight data system collects information from the spacecraft’s science instruments and bundles it with engineering data that reflects its current health status. Mission control on Earth receives that data in binary code, or a series of ones and zeroes.
But since November, Voyager 1’s flight data system had been stuck in a loop. While the probe has continued to relay a steady radio signal to its mission control team on Earth over the past few months, the signal did not carry any usable data.
The mission team received the first coherent data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems on April 20. While the team is still reviewing the information, everything they’ve seen so far suggests Voyager 1 is healthy and operating properly.
“Today was a great day for Voyager 1,” said Linda Spilker, Voyager project scientist at JPL, in a statement Saturday. “We’re back in communication with the spacecraft. And we look forward to getting science data back.”
The breakthrough came as the result of a clever bit of trial and error and the unraveling of a mystery that led the team to a single chip.
Troubleshooting from billions of miles away
After discovering the issue, the mission team attempted sending commands to restart the spacecraft’s computer system and learn more about the underlying cause of the problem.
The team sent a command called a “poke” to Voyager 1 on March 1 to get the flight data system to run different software sequences in the hopes of finding out what was causing the glitch.
On March 3, the team noticed that activity from one part of the flight data system stood out from the rest of the garbled data. While the signal wasn’t in the format the Voyager team is used to seeing when the flight data system is functioning as expected, an engineer with NASA’s Deep Space Network was able to decode it.
The Deep Space Network is a system of radio antennae on Earth that help the agency communicate with the Voyager probes and other spacecraft exploring our solar system.
The decoded signal included a readout of the entire flight data system’s memory.
By investigating the readout, the team determined the cause of the issue: 3% of the flight data system’s memory is corrupted . A single chip responsible for storing part of the system’s memory, including some of the computer’s software code, isn’t working properly. While the cause of the chip’s failure is unknown, it could be worn out or may have been hit by an energetic particle from space, the team said.
The loss of the code on the chip caused Voyager 1’s science and engineering data to be unusable.
Since there was no way to repair the chip, the team opted to store the affected code from the chip elsewhere in the system’s memory. While they couldn’t pinpoint a location large enough to hold all of the code, they were able to divide the code into sections and store it in different spots within the flight data system.
“To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole,” according to an update from NASA . “Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the (flight data system) memory needed to be updated as well.”
After determining the code necessary for packaging Voyager 1’s engineering data, engineers sent a radio signal to the probe commanding the code to a new location in the system’s memory on April 18.
Given Voyager 1’s immense distance from Earth, it takes a radio signal about 22.5 hours to reach the probe, and another 22.5 hours for a response signal from the spacecraft to reach Earth.
On April 20, the team received Voyager 1’s response indicating that the clever code modification had worked, and they could finally receive readable engineering data from the probe once more.
Exploring interstellar space
Within the coming weeks, the team will continue to relocate other affected parts of the system’s software, including those responsible for returning the valuable science data Voyager 1 is collecting.
Initially designed to last five years, the Voyager 1 and its twin, Voyager 2, launched in 1977 and are the longest operating spacecraft in history. Their exceptionally long life spans mean that both spacecraft have provided additional insights about our solar system and beyond after achieving their preliminary goals of flying by Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune decades ago.
The probes are currently venturing through uncharted cosmic territory along the outer reaches of the solar system. Both are in interstellar space and are the only spacecraft ever to operate beyond the heliosphere, the sun’s bubble of magnetic fields and particles that extends well beyond the orbit of Pluto.
Voyager 2, which is operating normally, has traveled more than 12.6 billion miles (20.3 billion kilometers) from our planet.
Over time, both spacecraft have encountered unexpected issues and dropouts, including a seven-month period in 2020 when Voyager 2 couldn’t communicate with Earth. In August 2023, the mission team used a long-shot “shout” technique to restore communications with Voyager 2 after a command inadvertently oriented the spacecraft’s antenna in the wrong direction.
The team estimates it’s a few weeks away from receiving science data from Voyager 1 and looks forward to seeing what that data contains.
“We never know for sure what’s going to happen with the Voyagers, but it constantly amazes me when they just keep going,” said Voyager Project Manager Suzanne Dodd, in a statement. “We’ve had many anomalies, and they are getting harder. But we’ve been fortunate so far to recover from them. And the mission keeps going. And younger engineers are coming onto the Voyager team and contributing their knowledge to keep the mission going.”
For more CNN news and newsletters create an account at CNN.com


Voyager Probes Heliosphere Chart

This graphic shows the position of the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes, relative to the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun that extends well past the orbit of Pluto. Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause, or the edge of the heliosphere, in 2012. Voyager 2 is still in the heliosheath, or the outermost part of the heliosphere.
The Voyager spacecraft were built by JPL, which continues to operate both. JPL is a division of Caltech in Pasadena. California. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington. For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit https://www.nasa.gov/voyager and https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov .
share this!
April 22, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
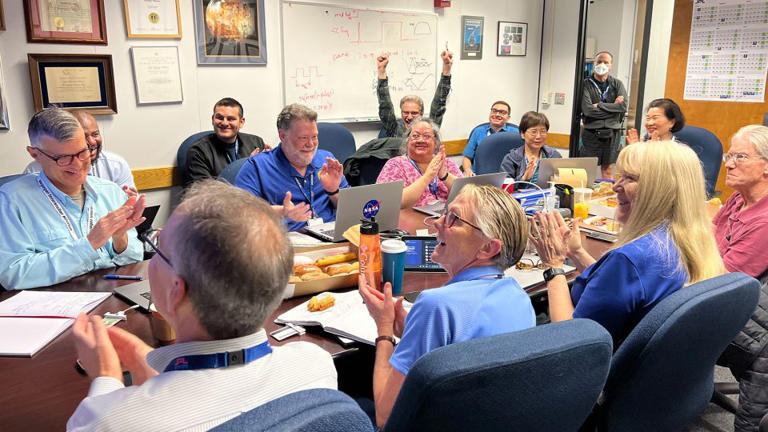
NASA's Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth

For the first time since November, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems. The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft's three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it's sent to Earth.
The team discovered that a single chip responsible for storing a portion of the FDS memory—including some of the FDS computer's software code—isn't working. The loss of that code rendered the science and engineering data unusable. Unable to repair the chip, the team decided to place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. But no single location is large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
So they devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS. To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole. Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated as well.
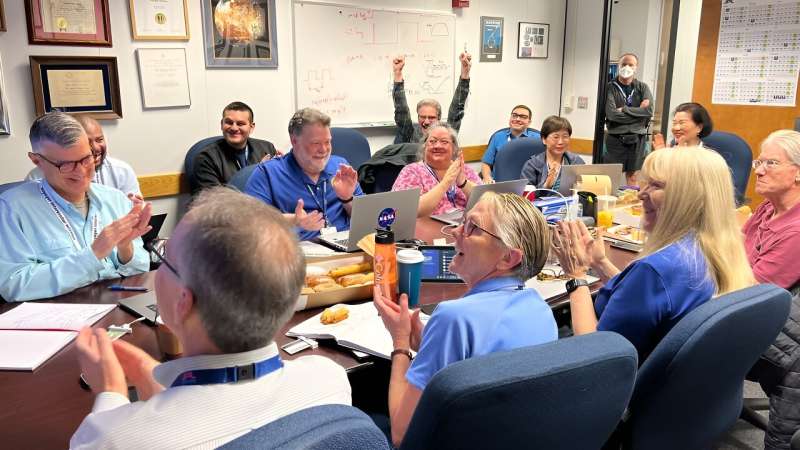

The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft's engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22.5 hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22.5 hours for a signal to come back to Earth. When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification had worked: For the first time in five months, they were able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago, the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history. Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
Provided by NASA
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Global study shows a third more insects come out after dark
13 hours ago

Cicada-palooza! Billions of bugs to blanket America
16 hours ago

Getting dynamic information from static snapshots

Ancient Maya blessed their ballcourts: Researchers find evidence of ceremonial offerings in Mexico

Optical barcodes expand range of high-resolution sensor
Apr 26, 2024

Ridesourcing platforms thrive on socio-economic inequality, say researchers

Did Vesuvius bury the home of the first Roman emperor?

Florida dolphin found with highly pathogenic avian flu: Report

A new way to study and help prevent landslides

New algorithm cuts through 'noisy' data to better predict tipping points
Relevant physicsforums posts, need help simplifying standard error formula for redshift, our beautiful universe - photos and videos.
Apr 25, 2024
Solar Activity and Space Weather Update thread
'devil' comet visible tonight 21.04.24, waves in space, documenting the setup of my new telescope.
Apr 24, 2024
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

Engineers working to resolve issue with Voyager 1 computer
Dec 13, 2023

NASA hears signal from Voyager 2 spacecraft after mistakenly cutting contact
Aug 1, 2023

NASA listens for Voyager 2 spacecraft after wrong command cuts contact
Jul 31, 2023

NASA's Voyager team focuses on software patch, thrusters
Oct 20, 2023

NASA's Voyager will do more science with new power strategy
Apr 27, 2023

Engineers investigating NASA's Voyager 1 telemetry data
May 18, 2022
Recommended for you

Japan's moon lander wasn't built to survive a weekslong lunar night. It's still going after 3

Simulated microgravity affects sleep and physiological rhythms, study finds
Apr 22, 2024

'Tube map' around planets and moons made possible by knot theory
Apr 17, 2024

NASA's Ingenuity Mars helicopter team says goodbye—for now

NASA confirms mystery object that crashed through roof of Florida home came from space station
Apr 16, 2024

NASA is seeking a faster, cheaper way to bring Mars samples to Earth
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
Interstellar Science

Science Investigations
- Magnetic field investigation (MAG)
- Low energy charged particle investigation (LECP)
- Plasma investigation (PLS)
- Cosmic ray investigation (CRS)
- Plasma wave investigation (PWS)
There are currently five science investigation teams participating in the VIM. The science teams for these investigations are currently collecting and evaluating data on the strength and orientation of the Sun's magnetic field; the composition, direction and energy spectra of the solar wind particles and interstellar cosmic rays; the strength of radio emissions that are thought to be originating at the heliopause, beyond which is interstellar space; and the distribution of hydrogen within the outer heliosphere.
There are 4 operating instruments on-board the Voyager 1 spacecraft. These instruments directly support the five science investigations teams. The Planetary Radio Astronomy Investigation (PRA) is no longer working on the Voyager 1 spacecraft and the Ultraviolet Spectrometer Subsystem (UVS) is no longer working on Voyager 1 or Voyager 2.
Science Data Acquisition Strategy
Science data are returned to earth in real time at 160 bps. Real time data capture uses 34 meter Deep Space Network (DSN) resources with the project goal to acquire at least 16 hours per day of real time data per spacecraft. This goal is not always achieved due to the competition for DSN resources with prime mission projects and other extended mission projects.
Three times per week, Voyager 1 has 48 seconds of high rate (2.8 kbps) PWS data recorded onto the Digital Tape Recorder (DTR) for later playback. Voyager 1 has six playbacks per year. The playbacks require 70 meter and 34 meter DSN support for data capture. After transmission of the data (either real time or recorded) to JPL, it is processed and made available in electronic files to the science teams located around the country for their processing and analysis.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year. Distance from Sun: This is a real-time indicator of Voyagers' straight-line distance from the sun in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi ...
Voyager 1 live position and data. This page shows Voyager 1 location and other relevant astronomical data in real time. The celestial coordinates, magnitude, distances and speed are updated in real time and are computed using high quality data sets provided by the JPL Horizons ephemeris service (see acknowledgements for details). The sky map shown in the background represents a rectangular ...
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. Missions. ... Voyager 1 Present Position. Voyager 2 Present Position. Voyager's Grand Tour Timeline. Mission Status. Voyager 1. Voyager 2. Launch Date. Monday, Sep 5, 1977 12:56:00 UTC.
Map showing Voyager 1 in Ophiucus on April, 27 2024. Field of view: 50x30 degrees View interactive star map. The current Right Ascension of Voyager 1 is 17h 16m 00s and the Declination is +12° 21' 10 " (topocentric ... The position of Voyager 1 and the planets along their orbits in this diagram accurately represents the current ...
Voyager 1 has been exploring our solar system for more than 45 years. The probe is now in interstellar space, the region outside the heliopause, or the bubble of energetic particles and magnetic fields from the Sun. Voyager 1 is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space. Voyager 1 discovered a thin ring around Jupiter and ...
Site Manager: Jon Nelson Webmasters: Anil Natha, Luis Espinoza Webmasters: Anil Natha, Luis Espinoza
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
In about 40,000 years, after the spacecraft will no longer be operational and will not be able to gather new data, it will pass within 1.6 light-years of the star Gliese 445, in the constellation Camelopardalis. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 10.5 billion miles from Earth, and will pass 1.7 light-years from the star Ross 248 in about 40,000 years.
About the mission. Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
Voyager 1 is literally venturing into the great unknown and is approaching interstellar space. Traveling at a speed of about one million miles per day, Voyager 1 could cross into interstellar space within the next 10 years. "Interstellar space is filled with material ejected by explosions of nearby stars," Stone said.
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the ...
Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s. This processed color image of Jupiter was ...
Voyager 1 is currently in the constellation of Ophiucus.The current Right Ascension is 17h 16m 02s and the Declination is +12° 20' 48".. Right now, from the selected location (Greenwich, United Kingdom edit_location_alt), Voyager 1 can be observed looking in the South-East direction at an altitude of 40° degrees above the horizon (view Voyager 1 position on a interactive sky map).
This visualization tracks the trajectory of the Voyager 1 spacecraft through the solar system. Launched on September 5, 1977, it was one of two spacecraft sent to visit the giant planets of the outer solar system. Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter and Saturn before being directed out of the solar system.To fit the 40 year history of the mission into a short visualization, the pacing of time ...
Heliocentric positions of the five interstellar probes (squares) and other bodies (circles) until 2020, with launch and flyby dates. Markers denote positions on 1 January of each year, with every fifth year labelled. Plot 1 is viewed from the north ecliptic pole, to scale. Plots 2 to 4 are third-angle projections at 20% scale. In the SVG file, hover over a trajectory or orbit to highlight it ...
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
Voyager 1 and 2, cruising along diverging paths, made history by crossing the heliopause in 2012 and 2018, respectively (SN: 9/12/13; SN: 12/10/18). At nearly 18 billion kilometers from the sun ...
VOYAGER 1 Current Position and Live Map Location Where is the current location of VOYAGER 1 right now? Ship VOYAGER 1 is a passenger ship navigating under the Unspecified flag. The IMO number is 8891613 and MMSI number is 1. General vessel particulars are as follows length overall (LOA) of 23 m and beam (max width) of n.a. m. Live maps below show the following voyage data - Present Position ...
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018. Mission Type.
In 1977, NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft embarked on an incredible journey to the outer planets and beyond. After delivering stunning images of Jupiter, Satur...
The consensus of the Voyager science team is that Voyager 1 has not yet reached interstellar space. "The Voyager team is aware of reports today that NASA's Voyager 1 has left the solar system," said Edward Stone, Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif. "It is the consensus of the Voyager ...
NASA Voyager Status Update on Voyager 1 Location. Artist concept of NASA's Voyager spacecraft. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech › larger image. "The Voyager team is aware of reports today that NASA's Voyager 1 has left the solar system," said Edward Stone, Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif.
The latest issue experienced by Voyager 1 first cropped up in November 2023, when the flight data system's telemetry modulation unit began sending an indecipherable repeating pattern of code ...
Voyager Probes Heliosphere Chart. Oct. 3, 2018. This graphic shows the position of the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes, relative to the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun that extends well past the orbit of Pluto. Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause, or the edge of the heliosphere, in 2012. Voyager 2 is still in the heliosheath, or ...
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, ... 'Tube map' around planets and moons made possible by knot theory. Apr 17, 2024.
Voyager's 30-Year Plan. The Voyager Interstellar Mission has the potential for obtaining useful interplanetary, and possibly interstellar, fields, particles, and waves science data until around the year 2020 when the spacecraft's ability to generate adequate electrical power for continued science instrument operation will come to an end ...