- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Sweepstakes
- Space Travel + Astronomy

Space Tourism Is Here: Booking a Trip to the Final Frontier
The next era of space exploration and innovation is here — and we're all invited. A billionaire space race is underway as Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, SpaceX, and others are testing the technology to take us to places previously visited only by highly trained astronauts. Space tourism is officially taking flight, and it might just save the Earth.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Jamie-Carter-618d9aa6e45f4ecf9b9dcaabbec68029.jpg)
In July 2021, we watched as Richard Branson and Jeff Bezos took to the skies in a giant leap for the space tourism industry, but their launches to the edge of space weren't timed particularly well. Against the backdrop of a global pandemic and climate emergency, two billionaires taking joy rides to space may not have been good optics, but don't underestimate what just happened — and how important it could be for the future of humanity.
With the first crewed launches of Virgin Galactic's supersonic space plane and Blue Origin's reusable rocket, a world of commercial space travel is taking its first step. Both companies plan to begin regular, scheduled trips for paying space tourists in the near future, but their visions stretch back many years to the beginning of human spaceflight.
The Space Race: Then and Now
Bezos's Blue Origin chose an auspicious day to send its first crew to space. July 20, 2021 was exactly 52 years after Apollo 11 astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the moon. But that wasn't the only major space travel anniversary celebrated in 2021.
April 12 was the 60th anniversary of Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin becoming the first human to not only reach space, but also go into orbit around Earth. Meanwhile, May 5 saw the 60th anniversary of NASA's Freedom 7 mission, which launched Alan Shepard on a suborbital flight that lasted 15 minutes. He reached an altitude of 101 miles to become the first American in space before his capsule parachuted to splashdown in the ocean.
The name of Blue Origin's New Shepard launch system is no coincidence. Its mission profile is almost identical to America's inaugural 1961 spaceflight, save for billionaire-grade comfy seats and large windows. From Launch Site One near Van Horn in the West Texas desert, that rocket fires a capsule containing up to six people (but no pilot) into space, which then parachutes down 15 minutes later.
The Virgin Galactic experience is different. Its supersonic rocket-powered spaceplane SpaceShipTwo VSS Unity seats six passengers and two highly trained pilots. It takes off on a runway from Spaceport America near Truth or Consequences, New Mexico, while strapped to a mothership. At 52,000 feet, it detaches and burns its rocket engine for one minute to reach Mach 3 speeds and touch the edge of space. After a few minutes of weightlessness (and a chance for passengers to see the curvature of Earth against the blackness of space), it glides back to land on a runway.
The Price for a Ticket to Space
These short trips are anticipated to cost between $250,000 and $500,000, but in January 2022, expect to see a truly out-of-this-world private trip to space with an even more astronomical price tag. It will come from the other, arguably much more important billionaire in the space tourism bubble: Elon Musk. Axiom Mission 1 will see his company, SpaceX, launch four private astronauts on behalf of Houston-based space tourism company Axiom Space. An American real estate investor, a Canadian investor, a former Israeli Air Force pilot, and an ex-Space Shuttle pilot will launch on an incredible orbital mission in its Crew Dragon spacecraft.
At $55 million per ticket, this is ultra-aspirational space tourism of the highest order. "The experience is drastically different because they will be launching on a SpaceX rocket and going to the International Space Station (ISS) for 10 days," says Christina Korp, cofounder of Space for a Better World . "They will be doing what real astronauts do, and I don't think it's an accident that Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin did their flights before Axiom's mission." Axiom Space intends to launch a private space station — the first "space hotel" — as early as 2024 to give space tourists somewhere to visit.
The Future of Space Tourism — and of Our Planet
Musk talks of Mars colonies and humanity spreading out into the cosmos, but since 2012, SpaceX has made a lot of money from NASA contracts to launch supplies to the ISS. In the summer of 2020, it began ferrying NASA astronauts there, too. SpaceX's Starship — currently being tested — will land two NASA astronauts, the first woman and the next man, on the moon in 2024.
You see, space tourism is just a sideshow to a bigger and more worthy goal of saving the planet. Next year, Blue Origin plans to test its reusable New Glenn rocket — named after John Glenn, the first American to orbit the Earth in 1962 — which will be able to take cargo and astronauts into orbit. Bezos has said he thinks we need to go to space to save Earth, specifically by protecting the planet from pollution by moving heavy industry into space. That can only happen when space travel is safe, scheduled, and affordable. Space tourism will help create a competitive space economy, just as mass tourism has lowered the cost of flying.
Similarly, Branson's aim is to increase access to space. "We are at the vanguard of a new space age…Our mission is to make space more accessible to all," he said after his inaugural flight. A microgravity experiment was on board that first flight on July 11, with similar plans for all subsequent trips. Meanwhile, sister company Virgin Orbit's LauncherOne sends small satellites and science payloads into orbit via a small rocket launch from underneath the wing of a Boeing 747.
The scientific spin-offs for all of us down on Earth are currently unknown, but the space community has an incredible track record when it comes to innovation. "Clean energy as solar power is from the space program," says Korp. "Solar panels were invented to power satellites and refined to power spacecraft." Cue GPS, weather forecasting, telecommunications, and even internet access. There are also fleets of satellites large and small that observe how our planet is behaving and changing. "It's the space industry that's monitoring climate change, tracking hurricanes, and learning how to survive in the extreme environment of space — including experiments to grow food with almost no water, for example," says Korp. Every single space mission, including suborbital and even zero-gravity flights, have environmental experiments on board as default.
"This is not about escaping Earth," said Bezos after the flight. "The whole point is, this is the only good planet in the solar system and we have to take care of it." Bezos wants to scale up into affordable space travel. That will enable long-term, commercial projects that ultimately may help prevent further climate change, or at least help us cope with its consequences.
However, Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, and SpaceX won't be the only way to reach space. Russian space agency Roscosmos is expected to take "citizen space explorers" to the ISS soon, but the most affordable way to get "black sky time" may be with Space Perspective , which will launch a pressurized capsule propelled by a high-performance space balloon.
The six-hour flight will cost around $125,000 per person and launch from Space Coast Spaceport in Florida in 2024. "Unlike short-lived, adrenaline-fueled moments of weightlessness, Space Perspective flights bring you space calm," says Jane Poynter, founder, co-CEO, and CXO of Space Perspective. The flights on Spaceship Neptune involve a gentle ascent at just 12 miles per hour for a six-hour tour of Earth's biosphere, culminating in a view of our beautiful planet from space.
Space tourism is here at last. Instagram had better get ready for "Earth selfies."
Program Credits
Editorial Lead: Elizabeth Rhodes Contributors: Jamie Carter and Stefanie Waldek Visuals Editor: Mariah Tyler Art Director: Jenna Brillhart Designer: Sarah Maiden
You Won’t Hear Much About the Next Chapter of Space Travel
Space tourism is getting less transparent, and more like traveling by private jet.

Listen to this article
Listen to more stories on hark
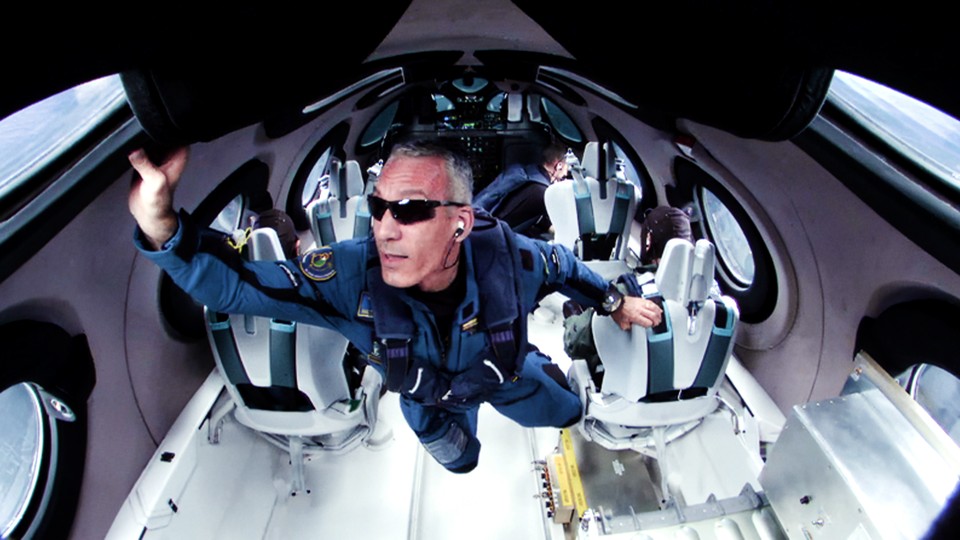
Of all the high-flying tourism ventures spawned by space-obsessed billionaires, Virgin Galactic, founded by Richard Branson, offers perhaps the most unconventional approach. It doesn’t use big rockets or gumdrop-shaped capsules. Instead, an airplane takes off with a spacecraft strapped to its wing. The spacecraft, shaped like a plane itself, holds the paying customers and more pilots. When the airplane reaches a certain altitude, it releases the spacecraft. The spacecraft’s pilots then ignite its engine, and the vehicle soars straight up, to the fuzzy boundary that separates us from the rest of the universe, before gliding back down and landing on a runway.
The spaceplane experience is a stark contrast to Blue Origin’s suborbital jaunts and SpaceX’s orbital missions, but Virgin Galactic’s passengers still have a few surreal minutes of weightlessness, and they get to see the planet gleaming against the darkness of space. Those passengers have included the first former Olympian to reach space, as well as the first mother-daughter duo and, most recently, the first Pakistani .
In the midst of all that, Virgin Galactic clocked a first that raised some eyebrows: The company withheld the passenger list from the public before a takeoff last month, divulging the travelers’ names only after they had landed. The company never publicly explained its preflight secrecy. (Virgin Galactic did not respond to a request for comment.) Yesterday, Virgin Galactic announced its next flight, scheduled for November; the company kept one of the three listed passengers anonymous, saying only that the person is “of Franco-Italian nationality.”
Virgin is of course within its rights to withhold passenger names before takeoff. After all, airlines and railroads keep private the names of their customers. But Virgin Galactic’s choice to do so marks a subtle shift—the latest in U.S. spaceflight’s arc from a publicly funded national mission to private tourism. NASA, as a taxpayer-funded organization, has always had to provide the public with launch lists and livestreams. But the age of space tourism raises a host of questions: How much openness do space-tourism companies owe the public? How much privacy do they owe their customers? Before the Virgin flight returned home last month, it operated almost like a privately chartered plane, its movements known to relevant aviation agencies but its passengers’ names undisclosed to the public. Commercial spaceflight and air travel are still far from alike, but in this particular aspect, the space-tourism industry may be drifting toward its private-jet era.
Read: The new ‘right stuff’ is money and luck
In practice, the space-tourism industry is barely more than two years old, and it’s “still finding its norms,” says Carissa Christensen, a space consultant and the CEO of BryceTech, an analytics and engineering firm. The first passenger rosters were marquee news in 2021, when Branson and Jeff Bezos were racing to be the first to ride their own spacecraft , and Elon Musk’s SpaceX was working to send a quartet of private astronauts with zero spaceflight experience into orbit.
All three of their companies publicized, and even hyped, the passenger lists, in some cases months in advance. Wally Funk, an octogenarian aviator who had outperformed male candidates in astronaut tests during the 1960s but was kept out of the astronaut corps because she was a woman, flew alongside Bezos . Jared Isaacman, a billionaire businessman, paid for three other people to fly into orbit with him on SpaceX; all of them gave countless interviews before launch. And who can forget the hype ahead of William Shatner’s flight, and the Star Trek star’s unfiltered, emotional remarks after landing?
The rosters became less noteworthy as time went on: The customers were no longer memorable guests who got free rides, but simply very wealthy people who could afford the trips on their own. Last month’s temporarily secret Virgin Galactic fliers included a real-estate investor from Las Vegas, a South African entrepreneur, and a British engineer who founded a company that builds race cars. Michelle Hanlon, a space lawyer and the executive director of the University of Mississippi’s Center for Air and Space Law, told me that she was mildly surprised by Virgin Galactic’s decision to withhold the passengers’ identities before takeoff, but that the decision did not strike her as inappropriate.
“From a paparazzi standpoint, if it’s Ashton Kutcher, the world’s gonna care a little bit more than if it’s Michelle Hanlon,” Hanlon said. (Kutcher did, in fact, purchase a Virgin Galactic ticket in 2012, but he later sold it back to the company after his wife and fellow actor, Mila Kunis, talked him out of going.) And from a legal standpoint, nothing inappropriate occurred, Hanlon said; there are no existing requirements for a private company to disclose passenger names. Space travelers must sign waivers from the Federal Aviation Administration outlining the risks associated with the activity, she said, but the companies they’re flying with are not required to provide the agency with a passenger list.
Read: Jeff Bezos knows who paid for him to go to space
Passenger names aren’t the only details of commercial spaceflight that are becoming more opaque. When SpaceX launched its first set of private astronauts, the company shared significantly less live footage of their experience in orbit than they did when NASA astronauts test-drove the capsule a year earlier. During its last two flights, Virgin Galactic decided not to provide a livestream, giving updates on social media instead.
Because there are no regulations, it’s difficult to say when the companies’ right to privacy becomes a concerning level of secrecy. NASA overshares when it comes to its astronauts and their mission, because the public—which funds the agency—expects it. Americans might also expect a good look at SpaceX customers who visit the International Space Station, which relies on billions of dollars of taxpayer money, and where private visitors share meals with government astronauts. But what about other kinds of SpaceX missions, which go into orbit without disembarking at any government-owned facility? The company developed its crewed launch services with significant investment from NASA, so virtually every SpaceX trip indirectly involves government money. That doesn’t necessarily mean SpaceX is obligated to share as the space agency does, even if people on the ground feel that it should.
Another major difference between NASA missions and private ones, of course, is that astronauts are at work, whereas many space tourists are presumably just having fun. Caryn Schenewerk, a consultant who specializes in commercial spaceflight at her firm CS Consulting, told me that she thinks commercial spaceflight will adopt the practices of other forms of adventure tourism. Take skydiving, for example: Schenewerk said that she has signed paperwork granting the skydiving company permission to use footage of her experience for its own purposes. “There’s some expectation of privacy on the individual’s behalf that then has to be actively waived for the company’s benefit,” she said.
The once-anonymous Virgin Galactic passengers on the September flight have since publicly shared their stories , basking in the awe of their experience. Christensen told me that most future tourists will likely do the same. “A big part of the fun is other people knowing that you’ve done it,” she said. Flying to space isn’t exactly something to be modest about: Fewer than 700 people have done it since human beings first achieved the feat, in the early 1960s, and we know all of their names. If Virgin’s new mystery passenger doesn’t reveal their name, they really will make history.
Read: Seeing Earth from space will change you
Many spacefarers—the Soviet cosmonauts who inhabited the first space station, the American astronauts who shuttled their way into orbit, the Chinese astronauts living in space right now, all of the people who have flown commercial—have spoken about the transformational wonder of seeing Earth from space, a phenomenon known as the overview effect . They reported that they better understood the reality of our beautiful, fragile planet, and that they felt a duty to share their impressions with people on the ground. Gene Cernan, one of the dozen men who walked on the lunar surface, once said, “If only everyone could relate to the beauty and the purposefulness of it … It wouldn’t bring a utopia to this planet for people to understand it all, but it might make a difference.” In this sense, for a space traveler to remain unknown forever would be a sort of anti–overview effect: Just as they may have the right to request some privacy, they have no obligation to bring the transcendent power of their journey back to Earth.
Three years ago, two NASA astronauts made a historic flight on a new SpaceX astronaut capsule. Ahead of the mission, I asked NASA what Doug Hurley and Bob Behnken were going to have for breakfast on the morning of the launch. It was a question with a long tradition in spacefaring history: During the Apollo days, the public was privy to the final Earth-bound meals of history-making astronauts. NASA officials balked, saying they couldn’t divulge that information for privacy reasons. But on the day of the launch, Hurley, as if to sate the space press corps, posted a picture of his steak and eggs on Twitter (as it was still known then).
Hurley and Behnken’s preflight hours seemed like fair game; after all, these men were government employees, doing their job on their assigned mission. But future passengers may decide that we have no business knowing their breakfast order—or even their name.
Space Tourism: Can A Civilian Go To Space?

2021 has been a busy year for private space tourism: overall, more than 15 civilians took a trip to space during this year. In this article, you will learn more about the space tourism industry, its history, and the companies that are most likely to make you a space tourist.
What is space tourism?
Brief history of space tourism, space tourism companies, orbital and suborbital space flights, how much does it cost for a person to go to space, is space tourism worth it, can i become a space tourist, why is space tourism bad for the environment.
Space tourism is human space travel for recreational or leisure purposes . It’s divided into different types, including orbital, suborbital, and lunar space tourism.
However, there are broader definitions for space tourism. According to the Space Tourism Guide , space tourism is a commercial activity related to space that includes going to space as a tourist, watching a rocket launch, going stargazing, or traveling to a space-focused destination.
The first space tourist was Dennis Tito, an American multimillionaire, who spent nearly eight days onboard the International Space Station in April 2001. This trip cost him $20 million and made Tito the first private citizen who purchased his space ticket. Over the next eight years, six more private citizens followed Tito to the International Space Station to become space tourists.
As space tourism became a real thing, dozens of companies entered this industry hoping to capitalize on renewed public interest in space, including Blue Origin in 2000 and Virgin Galactic in 2004. In the 2000s, space tourists were limited to launches aboard Russian Soyuz aircraft and only could go to the ISS. However, everything changed when the other players started to grow up on the market. There are now a variety of destinations and companies for travels to space.
There are now six major space companies that are arranging or planning to arrange touristic flights to space:
- Virgin Galactic;
- Blue Origin;
- Axiom Space;
- Space Perspective.
While the first two are focused on suborbital flights, Axiom and Boeing are working on orbital missions. SpaceX, in its turn, is prioritizing lunar tourism in the future. For now, Elon Musk’s company has allowed its Crew Dragon spacecraft to be chartered for orbital flights, as it happened with the Inspiration4 3-day mission . Space Perspective is developing a different balloon-based system to carry customers to the stratosphere and is planning to start its commercial flights in 2024.
Orbital and suborbital flights are very different. Taking an orbital flight means staying in orbit; in other words, going around the planet continually at a very high speed to not fall back to the Earth. Such a trip takes several days, even a week or more. A suborbital flight in its turn is more like a space hop — you blast off, make a huge arc, and eventually fall back to the Earth, never making it into orbit. A flight duration, in this case, ranges from 2 to 3 hours.
Here is an example: a spaceflight takes you to an altitude of 100 km above the Earth. To enter into orbit — make an orbital flight — you would have to gain a speed of about 28,000 km per hour (17,400 mph) or more. But to reach the given altitude and fall back to the Earth — make a suborbital flight — you would have to fly at only 6,000 km per hour (3,700 mph). This flight takes less energy, less fuel; therefore, it is less expensive.
- Virgin Galactic: $250,000 for a 2-hour suborbital flight at an altitude of 80 km;
- Blue Origin: approximately $300,000 for 12 minutes suborbital flight at an altitude of 100 km;
- Axiom Space: $55 million for a 10-day orbital flight;
- Space Perspective: $125,000 for a 6-hour flight to the edge of space (32 km above the Earth).
The price depends, but remember that suborbital space flights are always cheaper.
What exactly do you expect from a journey to space? Besides the awesome impressions, here is what you can experience during such a trip:
- Weightlessness . Keep in mind that during a suborbital flight you’ll get only a couple of minutes in weightlessness, but it will be truly fascinating .
- Space sickness . The symptoms include cold sweating, malaise, loss of appetite, nausea, fatigue, and vomiting. Even experienced astronauts are not immune from it!
- G-force . 1G is the acceleration we feel due to the force of gravity; a usual g-force astronauts experience during a rocket launch is around 3gs. To understand how a g-force influences people , watch this video.
For now, the most significant barrier for space tourism is price. But air travel was also once expensive; a one-way ticket cost more than half the price of a new car . Most likely, the price for space travel will reduce overtime as well. For now, you need to be either quite wealthy or win in a competition, as did Sian Proctor, a member of Inspiration4 mission . But before spending thousands of dollars on space travel, here is one more fact you might want to consider.
Rocket launches are harmful to the environment in general. During the burning of rocket fuels, rocket engines release harmful gases and soot particles (also known as black carbon) into the upper atmosphere, resulting in ozone depletion. Think about this: in 2018 black-carbon-producing rockets emitted about the same amount of black carbon as the global aviation industry emits annually.
However, not all space companies use black carbon for fuel. Blue Origin’s New Shepard rocket has a liquid hydrogen-fuelled engine: hydrogen doesn’t emit carbon but simply turns into water vapor when burning.
The main reason why space tourism could be harmful to the environment is its potential popularity. With the rising amount of rocket launches the carbon footprint will only increase — Virgin Galactic alone aims to launch 400 of these flights annually. Meanwhile, the soot released by 1,000 space tourism flights could warm Antarctica by nearly 1°C !
Would you want to become a space tourist? Let us know your opinion on social media and share the article with your friends, if you enjoyed it! Also, the Best Mobile App Awards 2021 is going on right now, and we would very much appreciate it if you would vote for our Sky Tonight app . Simply tap "Vote for this app" in the upper part of the screen. No registration is required!
Finding the Universe
Travel tales, photography and a dash of humor

Space Tourism: How to Visit Space as a Tourist
Last updated: August 28, 2023 . Written by Laurence Norah - 4 Comments
Despite the name of this blog, I have been distressingly earth bound for all of my years thus far. Given recent developments in space exploration technology though, hope is not yet lost for the dream of going into space as a tourist – without having to shell out the millions of dollars that past tourists have paid!
In today’s post, I’m going to talk about a few things. I’m going to cover where space travel & exploration is today.
I’m going to talk about what options we have now, and may have in the future, for getting into space as a tourist. And I’m also going to cover a few ways those of us stuck on Earth without access to a giant pile of cash can still get our space fix around the world!
The State of Space Travel as a Tourist in 2023

Huge strides are happening right now in space exploration, particularly with private companies looking at opening up space to your average person. Admittedly, right now, space tourism isn’t exactly accessible.
Up to 2009, only 7 people made it into space as tourists, all travelling with the Russian Space Agency, and all paying in excess of USD $20 million.
These weren’t exactly hop-on hop-off trips either, with the participants undergoing months of training, and many of them actively running their own experiments in space. So to call them space tourists is perhaps a bit of a misnomer.
However, things have now changed, and trips into space are becoming more affordable. Admittedly, they aren’t exactly “budget”, but they are less than $20 million a go.
So what’s changed?
Well, put simply, private investment. Whilst massive government organisations like NASA , the Russian Space Agency and the European Space Agency are always researching and expanding their space exploration efforts, their focus isn’t exactly on getting folks like you and me into space – at least not in the near term. Their focus is on long term scientifically focused exploration missions, with perhaps the most exciting being NASA’s Journey to Mars .
Other organisations though, see the potential for space based tourism as a way to generate funds and publicity for their projects. There are three main players in the space tourism business right now – Virgin Galactic , SpaceX and Blue Origin .
Let’s take a look at the main players with whom you have a real chance of getting into space within the next few years.
How to Go To Space As A Tourist
Other than flagging down a passing UFO Ford Prefect style, or signing up to be an astronaut with a government agency, getting into space is a bit tricky. But that’s all changing, and these are the companies with whom you are most likely to be able to travel into space.

1. Virgin Galactic
Part of the Virgin Group headed up by Sir Richard Branson, Virgin Galactic currently offers sub-orbital flights to paying passengers aboard their SpaceShipTwo and SpaceShipThree craft.
Sub-orbital means that you’re not high enough to actually orbit the earth, but as the goal you do pass the 100km line that marks the edge of space, you will technically be in space, and also experience weightlessness. Hurrah!
The good news is that as of June 2023, commercial space flights have actually commenced. Trips are scheduled to go monthly, and you can now buy tickets for a voyage into space with Virgin Galactic. They are currently on sale for $450,000.
Admittedly, $450,000 USD isn’t exactly small change, but it’s a lot less expensive than the $20 million that previous space travellers have paid. For your money, you get three days of training at Spaceport America in New Mexico, a flight into space, a somewhat incredible view and a period of weightlessness. Not too bad.
2. Blue Origin
Owned by Amazon billionaire Jeff Bezos, Blue Origin is a private company which initially appeared to be focusing on sub-orbital flight, much like Virgin Galactic.
Unlike Virgin Galactic though, which uses a combination of a normal plane and a rocket plane to achieve the necessary space altitude, Blue Origin are using more conventional rocket technology, with a focus on re-usable components that cut the cost of launches.
Other than the spacecraft, the experience is largely the same – a sub-orbital flight that comprises a few days of training in Texas, a journey lasting around 11 minutes to up beyond the 100km line, weightlessness and some incredible views.
The technology to do this will look familiar to any fans of existing space flight technologies, including the capsule that returns to Earth by parachute, meaning that there are fewer technical hurdles to overcome.
As of 2021, flights have commenced on the New Shepherd, with Jeff Bezos being the first into space. The ticket for the first commercially available seat in the July 2021 launch was auctioned off for a cool $28 million.
Since that launch, there have been a number of flights with paying customers.
Regular pricing isn’t set, although it’s currently rumored to be around $1 million per seat. A timeframe for general availability of commercial flights isn’t yet known. You can sign up to be kept informed and updated however.
Perhaps even more excitingly than the New Shepherd program is its successor – the New Glenn program. This should offer longer duration, possibly even orbital flights, although details are currently sparse on the ground, with operations aimed to launch in late 2024. We do know however that priority on these trips will be given to New Shepherd customers.
Last in our trio of serious contenders for firms that will take your money and send you into space in the next few years is SpaceX .
SpaceX is owned by Elon Musk, who is particularly famous for being the CEO and co-founder of Tesla Inc, the electric car and battery manufacturer, amongst other things.
SpaceX largely focuses on commercial launch capabilities, with a particular focus on reusable rocket technologies that bring down the cost of putting payloads into orbit.
They’ve been hugely successful in this field, with multiple achievements, including being the first privately funded company to successfully launch, orbit and recover a spacecraft.
They were also the first private company to send a spacecraft to the International Space Station, and have since flown many missions to the ISS.
Whilst the majority of their work is on commercial and government contracts for putting things like satellites into orbit, some recent developments have put SpaceX firmly on the space tourism map.
First, in 2017 they announced that they had been contracted by two private individuals who want to go on a trip around the moon. This was originally due to launch in 2018, but has been postponed until at least 2024. It will be by far the most ambitious space tourism endeavor to date by any company, and you can read more about the project here .
SpaceX are also starting to sell tickets on their Crew Dragon capsule, which is the launch system NASA is using to shuttle astronauts to the ISS. These are not generally available, but a 3-day mission consisting entirely of tourists took place in 2021, with further missions expected. These are still priced in the tens of millions of dollars though, so don’t bank on these becoming affordable for a while to come.
Next, SpaceX is actively working on technology to colonise Mars, with a lofty goal of setting up a permanent colony on the red planet, home to over a million people, within the next 100 years.
Whilst the current estimate of cost for such a ride is in the region of $10 billion USD per person, SpaceX is aiming to bring that down to $100,000 through the development of their Interplanetary Transport System . This won’t happen in the near-term, but by the end of the century tourism to Mars might be a real possibility, with lunar and earth-orbital flights the norm by then.
4. Other Contenders
So those are the main players who, in my opinion, have the most realistic chances of taking you to space in the coming decade. But they aren’t the only players in the space tourism arena! Here are a few others to be aware of who might give you a chance of getting off Planet Earth.
Bigelow Aerospace: Bigelow Aerospace are actually a pretty major name when it comes to space technology, and if you ever happen to find yourself in a hotel on the moon or floating around the Earth, it’s likely going to be inside one of their inflatable habitats.
This isn’t theoretical either, they’ve got an inflatable capsule attached to the International Space Station already undergoing feasibility testing. Owner Robert Bigelow made his fortune in hotels, and he sees no reason why we can’t have them in space too.
Space Perspective: Space Perspective are taking a slightly different approach to everyone else, in that their route to space is to fly passengers 100,000ft above the ground in capsule carried aloft by a gigantic hydrogen filled balloon.
Ok, so 100,000ft isn’t exactly space, but it is high enough to see the curvature of the earth. It’s likely to be a more sedate and relaxed experience as well, compared to firing yourself into space on some sort of rocket at least. And whilst experiencing zero-gee isn’t going to be on the cards, you should be able to enjoy the views from the wraparound windows whilst enjoying a tipple from the on-board bar!
Tickets for 2024 flights have already sold out, but you can book for 2025 at a cost of $125,000 per person.
Boeing: Boeing are currently under contract with NASA to build a crew transport vehicle that would be compatible with a number of rocket systems, primarily for the purpose of shuttling astronauts to the ISS. It was originally due to start those flights in late 2018. However, testing did not start until late 2019, and the current timetable for crewed flights is now 2023.
As part of their contract, this CST-100 Starliner was specified to include one seat specifically for the purposes of space tourism , allowing one passenger to just tag along for the ride as it were. For a price, naturally. That price is currently unknown, although the original goal was to have it price competitive with the Russian Space Agency, so don’t expect it to come under the tens of millions mark!
Mars One: Mars One was an organisation with a goal of establishing a permanent human colony on Mars by the year 2035. Announced in 2012, it encouraged members of the public to sign up for the one-way mission, which resulted in over 200,000 applicants. That was whittled down to 100, and then a final 24 candidates.
Unfortunately, the project was dogged by criticism, particularly around the technical and financial feasibility of the plan. Finally, Mars One entered administration in 2019.

The Best Space Sights and Activities on Earth
Ok, so based on all the above, you’re probably realising that space is still a pretty tough place to get to right now, and even over the next few years it’s still going to be pretty darn expensive for a fairly brief jaunt.
Don’t fret though. Planet Earth is a pretty cool place, and there are a lot of space-related activities you can take part in without re-mortgaging your house and strapping yourself to a rocket.
Here are a few places you can learn about space and space travel in the meantime! Let’s look at these.
1. Active Spaceports
Whilst you might not get into space right now, you can still visit a spaceport and dream of the future! I’ve picked three spaceports for you to think about visiting.
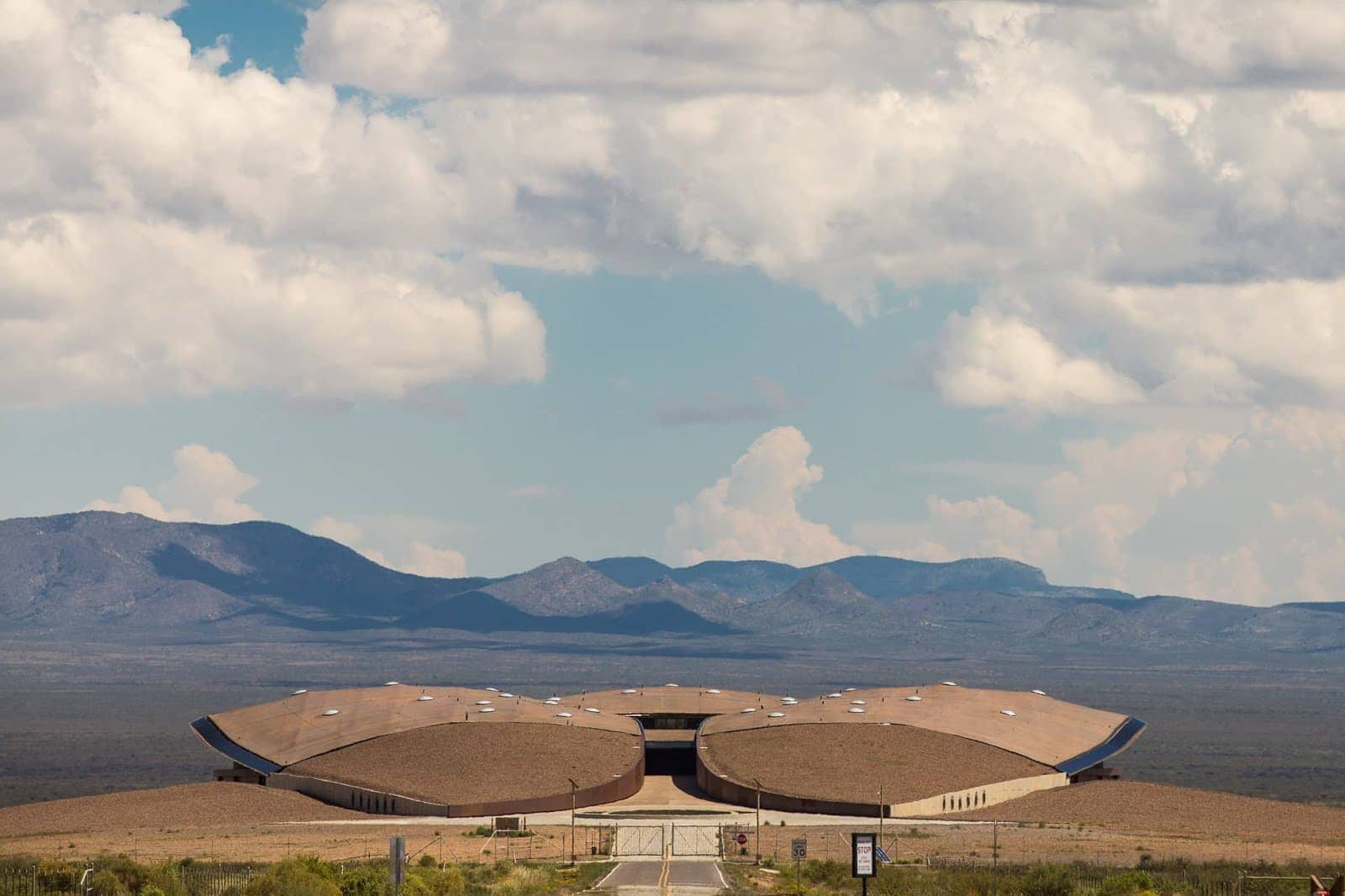

Spaceport America, USA. Set in the high New Mexican desert, Spaceport America is the world’s first purpose-built commercial spaceport, meaning it’s designed for commercial users. Yes, people like you and me. It’s the home base of Virgin Galactic, and is where that company will be operating from when they finally launch their space tourism flights. SpaceX also conduct some of their testing here. Unfortunately, you still can’t board a space trip here, but it’s a worthwhile place to visit, if only to get a tantalising glimpse of a possible future.
Kennedy Space Center, USA. Found in Florida, Kennedy Space Center is the main launch pad for NASA’s operations, and is where Apollo and Space shuttle launches took place. It’s a massive facility, spanning 144,000 acres. There’s a visitor centre on site, where you can learn all about NASA and it’s space operations, see an actual space shuttle and even experience a simulated space shuttle launch. Kennedy Space Center is still very much an active launch site, and you can also come here to watch rockets blast off into space – see their website for the launch schedule .
Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan. One of the world’s most famous spaceports, and certainly the oldest and largest, Baikonur Cosmodrome is where the majority of Russia’s space program has operated from, including the first man into space, Yuri Gagarin. It’s still very active, and you can in theory visit, however prices are steep for a one day tour ($700+), and can only be arranged via a specialist tour operator in a complex process that needs to be booked weeks in advance.
2. Space Museums
As well as active space ports, there are a lot of museums around the world dedicated to sharing man’s activities in space. Here are a few of the best.
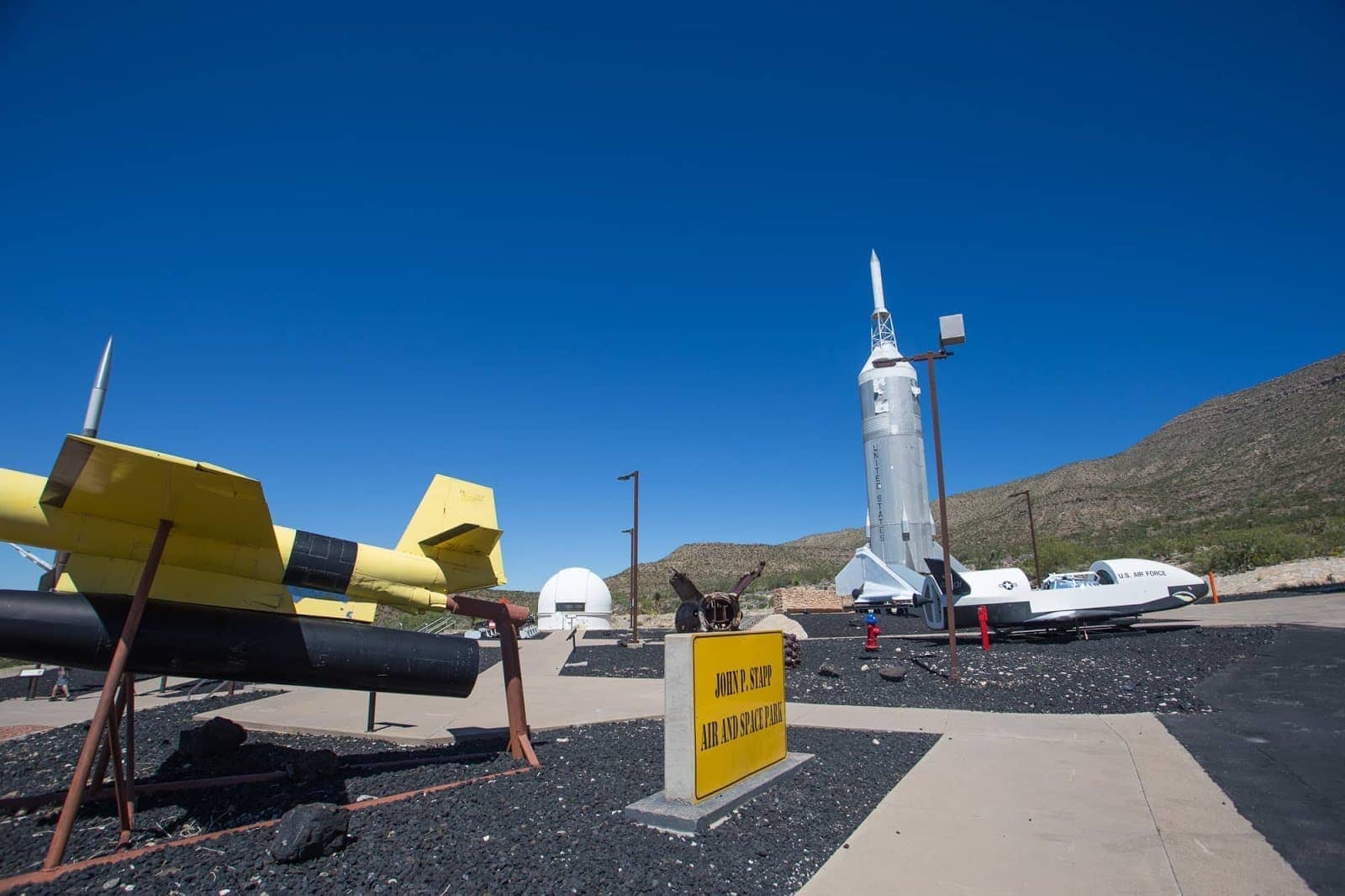

Space Center Houston, USA. The official visitor centre for NASA’s center for human spaceflight activities, Space Center Houston is an excellent place to come and learn all about NASA’s efforts around getting people into space. It has a number of artifacts from our explorations to date, including a lunar module replica and various actual capsules that have been into space. Tip – if you’re visiting a few sights in Houston, you can save money by investing in a CityPASS card which will get you into the Space Center as well as a number of other attractions in the city.
New Mexico Museum of Space History, USA. Found in Alamogordo in southern New Mexico, the five storey New Mexico Museum of Space History is full of information about man’s efforts to get into space, with everything from information on early rocket technology through to more modern day exhibits including a space shuttle landing simulator. It’s also home to the International Hall of Space Fame, a planetarium, and offers fantastic views across the White Sands National Monument.
Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum , USA . Found in Washington, D.C., this enormous museum is home to the world’s largest collection of historic aircraft and spacecraft in the world, including the Apollo 11 module and clothing worn by astronauts. With over 60,000 objects on display, you won’t run out of things to look at!
The National Space Centre, UK. Both a museum and an educational resource, the National Space Center in Leicester, UK, is home to six interactive galleries and the UK’s largest planetarium. A highlight though is the 42 metre high Rocket Tower , which houses a number of upright rockets, really giving you a feel for the enormity of these machines.
The U.S. Space and Rocket Center. Found in Huntsville, Alabama, right next door to NASA Marshall. The U.S. Space and Rocket Center has loads of information on the history of space flight, including two full size Saturn V rockets! This is also where you can attend Space Camp , a hands-on multi day training program for all ages, which will take you through a range of training similar to that which real astronauts do!
3. Space Themed Sights
We may be currently fairly stuck on the planet, but that doesn’t mean we’re not still hurtling through space, a small rock in a vast galaxy. Here are a few ways to help remind ourselves that there’s more out there than our horizon.
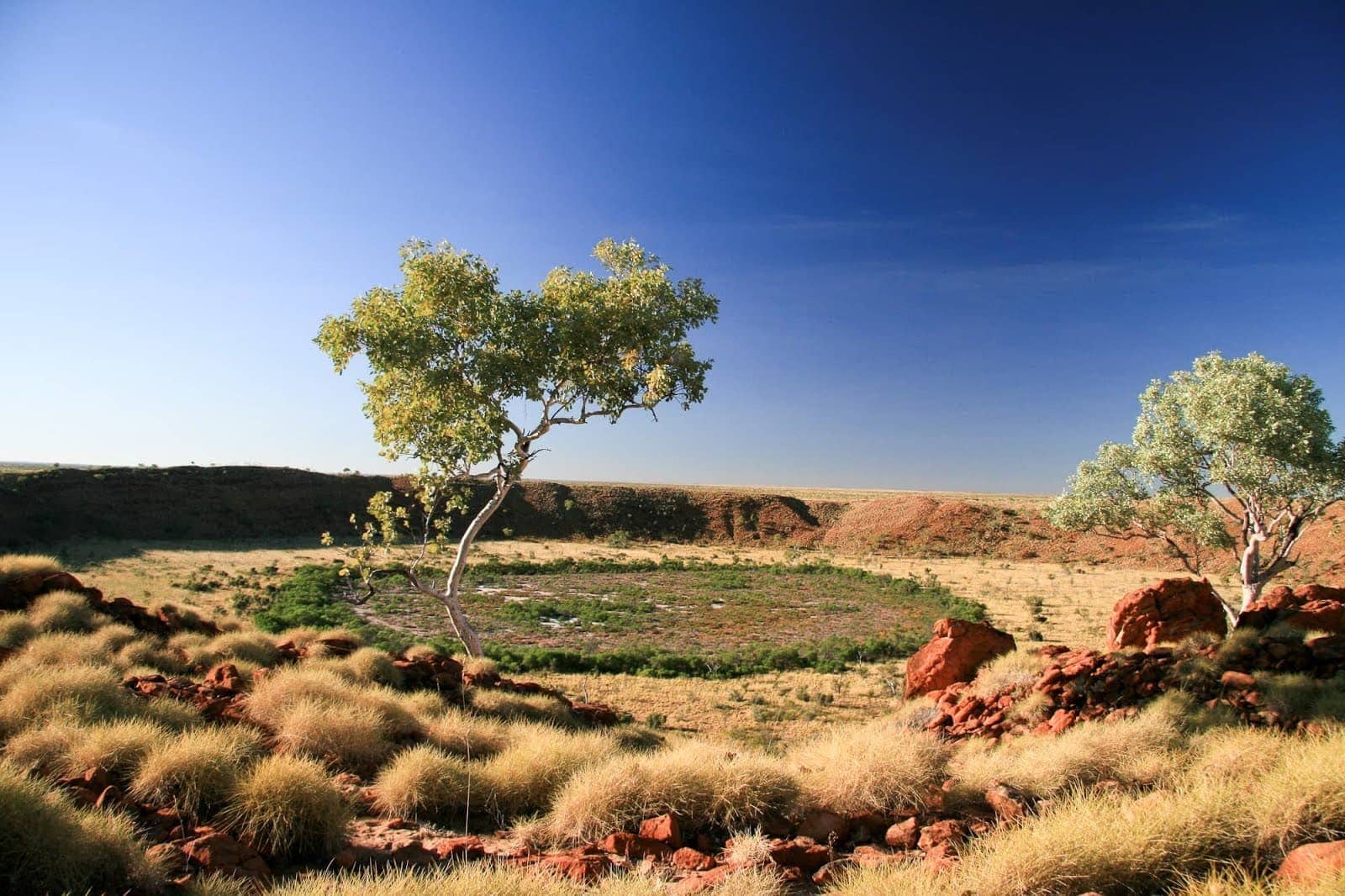

Meteor Craters. On our journey through space we regularly bump into errant lumps of space debris – around 100 tons a day in fact. Most often these lumps are so small (dust-specks really) that they just burn up in our atmosphere, creating beautiful shooting stars. However, anything larger than a marble has a chance of making to earth, although there are a lot of factors at work.
According to NASA , it’s the lumps that are around the size of a football field and up that make the most impact, and one of these hits us every couple of thousand of years. They can cause significant damage and leave a lasting impact. Two worth mentioning that you can visit are the aptly named “ Meteor Crater ” in Arizona, USA, and the Wolfe Creek Meteorite Crater in Western Australia. Both of these are around a kilometre in diameter, meaning you can see the whole structure with the naked eye and really get a feel for the force required to create such a hole. Of course you can also find smaller ones all over the world.
Star Gazing. You might not be able to get to the stars, but that doesn’t mean you can’t appreciate them. I always find that just lying back and staring into the vastness of space from a really dark location is a very powerful experience. You need to be somewhere far away from light pollution to get the best views of the night sky – there are dark sky preserves (and even festivals !) where you can get a great view, otherwise, head as far away from the lights as you can and just look up.
4. Giant Telescopes
How about if you can’t get into space, you try just looking at it through a really big magnifying glass and pretend you’re there? It might be as close as you can currently get to space for free, whilst also being wowed by humanities technological accomplishments. Below are four locations around the world where you can learn all about the art of looking into space. Of course, there are many more sites around the world and you can find a list of some of the major telescopes here although not all can be visited by the public.

The Very Large Array, USA. Far out in the New Mexico wilderness, the Very Large Array is one of the world’s largest and most impressive radio telescopes. Unlike an optical telescope, which look at visible light waves, a radio telescope looks at radio waves, and from that we can learn all sorts of things from how black holes are formed through to the creation of the universe itself. These radio waves require a very large telescope, which is why the VLA is actually made up of 27 dishes, which work together to capture radio waves. There’s a small visitor centre and self-guided walking trail, and there are guided tours on the first Saturday of the month. See the official website for more details.
Jodrell Bank, UK. If you’re in the UK , then a trip to Jodrell Bank is a good option for viewing impressively large radio telescopes. In fact, Jodrell Bank is home to the world’s third largest steerable radio telescope, as well as a number of other active telescopes. There’s a visitor centre where you can learn all about the telescopes, and all sorts of other space-related things.
The Very Large Telescope, Chile. Way up high in the mountains of Chile is the world’s most advanced visible-light astronomical observatory – the aptly named “ Very Large Telescope ”. Operated by the European Southern Observatory, this is the most impressive optical instrument in the world to date, consisting of four main mirrors that are over eight meters in diameter, as well as four 1.8m diameter mirrors. These work together to create a final image, and the telescope is powerful enough that it would be able to make out a cars headlights on the moon. It’s fairly remote, what with it being on a mountain top in Chile, but you can visit – check here for more information on tours.
Green Bank Observatory, USA – At time of writing, Green Bank Observatory is home to the worlds largest steerable radio telescope, the Green Bank Telescope. Constructed in 2001, it’s one of the newest US telescopes, and with a total collecting area of 2.3 acres, is certainly impressive to behold. You can take a tour of the observatory, and there are also weekly and monthly events at the site.
5. Extra-terrestrial spots
If you’re really desperate to get off planet, you might want to frequent a location which has a history of extra-terrestrial activity such as UFO sightings. Whilst E.T. is yet to make formal contact, who knows, you might get lucky and have the chance to hop on a passing spaceship!

Roswell, USA. If you want to learn about aliens, then the town of Roswell in New Mexico has definitely got to be on your list. It became famous as the alleged site of a huge government cover-up of a supposed alien spaceship crash at a nearby ranch property, and the town has since embraced it’s position as the world’s most famous UFO hotspot. There are a number of alien themed attractions here – we’d recommend visiting the Roswell UFO museum as a good starting point.
El Enladrillado, Chile. Central Chile is well known as a UFO spotting hotzone. So much so in fact, that the country’s national tourism board established a UFO trail, a 30km long designated trail in the Andes mountains that centres around the town of San Clemente. This is definitely a good place to come to spot UFO’s, although the national tourism authority is keen to stress that a sighting isn’t guaranteed.
Nullabor Plain, Australia. When I was travelling in Australia, I had a memorable evening out in the outback on the vast Nullabor Plain with a chap who was convinced he was regularly visited by aliens. He might have been on to something of course, with this region of Australia being particularly famous for UFO sightings. And if you don’t see a UFO, fear not, the star gazing here is pretty epic too!
HR Giger Museum, Switzerland. If you prefer your aliens of the fantastical science fiction type, then a visit to the HR Giger museum in Gruyères, Switzerland, should definitely be on your list. It’s home a large collection of works by Swiss artists HR Giger, who famously created the monsters from the sci-fi classic horror movie Alien (and its sequels). Definitely one for the sci-fi fans.
Further Reading for your Space Trip
Well, that was a lot about space. Hopefully you’ve learnt a bit about your options for getting into space as a tourist, as well as some slightly more cost-effective ways to get your space fix on! Here are a few resources that you might find useful.
- Our favourite sights along the New Mexico Space Trail , USA. Plus a guide to attending the Albuquerque International Balloon Fiesta if you’re in New Mexico.
- Our guide to visiting Jasper National Park for their annual Dark Sky Festival
- A guide to attending Space Camp USA , as well as visiting the U.S Space and Rocket Center
- Official websites for Virgin Galactic , Blue Origin and SpaceX , for when you’ve saved up enough for that ticket to space
- The NASA Instagram feed , for mind blowing space images
- John Glenn’s memoir, to give you an insight into what it was like to be the first American to orbit the earth.
- Chris Hadfield’s book “ An Astronaut’s Guide to Life on Earth ”, helping you understand how to make the impossible a reality, which seems like a good place to end this post!

Well, that was a lot to write about space travel and space tourism! We’re not quite there yet, but with the pace of developments I see no reason why, in the coming years and decades, that I won’t finally be able to realise my dream of heading up into space for real. Let me know in the comments if heading into space is a dream of yours!

Enjoyed this post? Why not share it!
There are 4 comments on this post
Please scroll to the end to leave a comment
Lynn Magnuson says
17th February 2024 at 8:16 am
Traveling into space is something I’ve wanted to do ever since I was a child. I remember sitting in class and I think it was the third grade and watching Alan Shepard blast off. I knew at that point that someday I wanted to do the same thing. It hasn’t happened yet, but as time goes by the chance to do so, becomes more and more a possibility. I hope someday I do get the chance.
I love your article. Very well written and very informative. Keep up the great writing. That’s another thing I share a passion for. Writing
Laurence Norah says
20th February 2024 at 1:45 am
I’m right there with you! I really hope you get the chance to get into space some day soon. It’s definitely getting closer as a possibility 🙂
Safe travels, be they earthbound or not!
roshmand says
2nd July 2023 at 6:57 pm
amazing poat. thanks
4th July 2023 at 9:39 am
thank you very much 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Let me know when there's a reply to my comment (just replies to your comment, no other e-mails, we promise!)
Subscribe to our monthly Newsletter where we share our latest travel news and tips. This also makes you eligible to enter our monthly giveaways!
We only ask for your e-mail so we can verify you are human and if requested notify you of a reply. To do this, we store your data as outlined in our privacy policy . Your e-mail will not be published or used for any other reason other than those outlined above.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Virgin Galactic successfully flies tourists to space for first time
Six individuals were aboard VSS Unity space plane, including first mother-daughter duo to venture to space together
Virgin Galactic’s VSS Unity, the reusable rocket-powered space plane carrying the company’s first crew of tourists to space, successfully launched and landed on Thursday.
The mission, known as Galactic 02, took off shortly after 11am ET from Spaceport America in New Mexico .
Aboard the spacecraft were six individuals total – the space plane’s commander and former Nasa astronaut CJ Sturckow, the pilot Kelly Latimer, as well as Beth Moses, Virgin Galactic’s chief astronaut instructor who trained the crew before the flight.
The spacecraft also carryied three private passengers, including the health and wellness coach Keisha Schahaff and her 18-year-old daughter, Anastasia Mayers, both of whom are Antiguan.
According to Space.com, Schahaff won her seat onboard the Galactic 02 as part of a fundraising competition by Space for Humanity, a non-profit organization seeking to democratize space travel. Mayers is studying philosophy and physics at Aberdeen University in Scotland. Together, Schahaff and Mayers are the first mother-daughter duo to venture to space together.

“When I was two years old, just looking up to the skies, I thought, ‘How can I get there?’ But, being from the Caribbean, I didn’t see how something like this would be possible. The fact that I am here, the first to travel to space from Antigua, shows that space really is becoming more accessible,” Schahaff said in a statement last month.
The mission also marks the most women flown in a single mission to space.
Onboard the flight was also the former Olympian Jon Goodwin, who participated in the 1972 Olympics in Munich as a canoeist. At 80 years old, Goodwin was the second passenger with Parkinson’s disease and the first Olympian to embark on a trip to space.
“When I was diagnosed with Parkinson’s in 2014, I was determined not to let it stand in the way of living life to the fullest. And now for me to go to space with Parkinson’s is completely magical,” he said in a news release. “I hope this inspires all others facing adversity and shows them that challenges don’t have to inhibit or stop them from pursuing their dreams,” Goodwin said .
Galactic 02 is a suborbital flight. However, despite VSS Unity not reaching orbit, the trajectory allows passengers to experience several minutes of weightlessness at an altitude high enough for them to see the Earth’s curvature, Space.com explains .
Following liftoff, Virgin Galactic’s carrier plane VMS Eve transported VSS Unity to an altitude of about 44,300ft. Eve then dropped Unity, which then fired its own rocket motor and ascended to suborbital space. Passengers onboard experienced approximately 3Gs.

Live footage inside the spacecraft showed the passengers unstrapping themselves from their seats and peering out down to Earth through the windows as they floated throughout the spacecraft.
In a press conference after the flight, Schahaff recounted her experience, saying: “Looking at Earth was the most amazing … It was so comfortable. It really was the best ride ever. I would love to do this again.
“This experience has given me this beautiful feeling that if I can do this, I can do anything,” she added.
Mayers, who is the second-youngest person to go to space, said: “I was shocked at the things that you feel. You are so much more connected to everything than you would expect to be. You felt like a part of the team, a part of the ship, a part of the universe, a part of Earth. It was incredible and I’m still starstruck.”
To Goodwin, the experience was far more dramatic than he expected.
after newsletter promotion
“The pure acceleration, Mach 3 [2,301mph, 3,378 ft per second] in eight and a half seconds was completely surreal. The re-entry was a lot more dramatic than I imagined it would be. In fact, I would have said it was out of control if I didn’t know anything different,” he said.

“It was a completely surreal experience. But the most impressive thing was looking at Earth from space. The pure clarity was very moving, quite surreal. It was without a doubt the most exciting day of my life,” he added.
In a statement released following the flight, Sturckow said: “It is a surreal and humbling experience to have flown Unity today. The wonder and excitement of spaceflight never loses its magic.”
Latimer echoed similar sentiments, saying: “In my entire career, from the Air Force Academy to being a test pilot for Nasa, nothing tops what I have just experienced at the controls of VSS Unity. Going to space today fulfilled an ambition I’ve had since I was a child.”
The Virgin Galactic founder, Sir Richard Branson, also hailed the flight, tweeting: “Today we flew three incredible private passengers to space: Keisha Schahaff, Anastatia Mayers and Jon Goodwin. Congratulations Virgin Galactic commercial astronauts 011, 012 and 013 – welcome to the club!”
Despite Galactic 02 being Virgin Galactic’s second commercial spaceflight mission, it is the first flight to carry private customers. In June, Galactic 01 carried three crew members from the Italian air force and the National Research Council of Italy.
In July 2021, Branson traveled to space and back onboard the VSS Unity, a mission that marked the billionaire’s entry into the new era of space tourism helmed by other billionaires including the SpaceX founder, Elon Musk, and Blue Origin founder, Jeff Bezos.
According to Virgin Galactic, the company has already booked a backlog of about 800 customers. Tickets have ranged from $250,000 to $450,000.
Galactic 03, the company’s third commercial spaceflight, is planned for September.
- Virgin Galactic
Most viewed

The future of space tourism: op-ed

Dylan Taylor is a global entrepreneur, investor and philanthropist who acts as the Chairman and CEO of Voyager Space Holdings and the founder of Space for Humanity , a nonprofit organization that seeks to democratize space exploration. He has also served as an active advocate and philanthropist in the space manufacturing industry and a strategic advisor for the Archmission and the Human Spaceflight Program while also acting as the co-founding patron of the Commercial Spaceflight Federation. He contributed this article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Opinions and Insights .
It's true that 2020 spawned a collective feeling of retreat coupled with a FOMO (fear of missing out) that inspires us to escape a chaotic world. For now, we have the silence of nature or an eventual trip abroad, but the future can provide a more adventurous escape: one to the stars.

The NewSpace industry has its sights set on space tourism , a growing market expected to be worth at least $3 billion by 2030 . As companies like SpaceX test reusable rocket technology to make spaceflight more affordable and accessible for humans, other private firms, including Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin, are investing in suborbital space tourism to take Earthlings into the very edge of space and back. While only uber-wealthy passengers and private researchers will have access to space tourism in the immediate future, the long term holds promises for ordinary citizens.
The evolution of technology plays a vital role in sending more tourists to space and a few influential trends will determine the future of space tourism, along with the progress we make both on and off our home planet.
Related: Space tourists will face big risks, as private companies gear up for paid suborbital flights
Commercial suborbital trips
Suborbital travel will likely be the space tourism subsector to materialize first, but it may also be the most short-lived. However, Blue Origin , backed by Jeff Bezos, is testing its New Shepard system that will launch customers to the edge of space in a capsule which separates from a small rocket and retreats back to Earth under parachutes. Richard Branson's company Virgin Galactic relies on a space plane, dropped from a carrier aircraft, with a rocket motor that speeds up and takes passengers high into the atmosphere.
Both companies' shuttle systems are designed to fly passengers over 50 miles above Earth's atmosphere, allowing customers to experience the feeling of weightlessness for a few minutes. Virgin Galactic's SpaceShipTwo will launch its next human spaceflight test on Dec. 11 as Blue Origin eyes early 2021.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
These brief spaceflights hold opportunities for tourism and scientific research and present unique experiences for space observation at varying trajectories and regulatory requirements. However, Axios reports concerns over declined public interest in suborbital tourism as a passing interest due to high costs and a short-lived ride. This may deflate the market as passengers await new developments in the field.
But there's some hope. Some experts look to commercial suborbital trips to take the place of long-distance air travel that can eventually cater to everyday citizens. SpaceX plans to use its Starship rocket to fly 100 people around the world in mere minutes. The company stated that a 15-hour flight to Shanghai from New York would be capable of flying in 39 minutes. According to UBS, if even only 5% of the average 150 million passengers that travel on 10 hour or longer flights pay $2,500 per trip, then returns could skyrocket to $20 billion per year in today's value.
A recent UBS report mentions, "Space tourism could be the stepping stone for the development of long-haul travel on earth serviced by space."
Related: Virgin Galactic wants to send people on superfast trips across Earth

Orbital vacations
Orbital tourism, which entails remaining in space for at least one full orbit, is another major focus of governmental agencies and private space companies, all of which have the long-term goal to inhabit the moon and Mars. Projects from Boeing, SpaceX and Axiom Space plan to start launching tourists to the International Space Station on commercial spacecraft beginning as early as this year. SpaceX is also partnering with Space Adventures to send four tourists to low Earth orbit for a few days in late 2021 or early 2022.
As more companies consider in-space tourism, orbital vacations are set to become a popular trend. Orbital vacationing infrastructure, including orbital and lunar-based hotels, is positioned to become lucrative as space infrastructure companies already hauled in a combined $3.6 billion so far this year .
Much of this infrastructure remains in preliminary stages, but the first approach may be to establish low-orbit hotels. One hotel design expects to send guests in a hydrogen-filled balloon with a pressurized capsule, utilizing Earth's gravity. Other options include designing or renovating an existing space station to accommodate guests. NASA, for instance, is opening up the International Space Station for commercial tourism . The Aurora Station , a planned luxury hotel that will host six guests for a $9.5 million, 12-day stay in low Earth orbit, will charge $9.5 million for the trip. It's pricey, but experts predict prices will fall like they did in the tech industry for computers and mobile phones.
A proposal for expandable space habitats may also serve as orbital hotels. Made of unique materials and easily stored at home, they are launched to space where they're inflated to true size. Bigelow Space invented the B330 , a space habitat that enlarges to form a hotel or living area for humans in space. As demand increases, they are interconnected to other inflatable habitats to increase their size. Bigelow also plans to develop an attached inflated module to the International Space Station as one of the first hotels in space. In-space vacations will eventually be the gateway for moon and Mars habitation.
Nurturing the space and world economies
Private space companies are devotedly investing across space tourism and firms like UBS consider access to space an enabler to broader opportunities for investment.
More next-generation engineers will enter the space tourism sector for the scope of opportunities and innovation, eventually decreasing the barriers to entry that will increase competition, lower costs, and ultimately democratize space travel for everyday citizens.
Of course, there are crucial safety, comfort and health factors to consider. Training, medical screenings and liability waivers will need to be examined before tourists head to space.
Space tourism will be a small subsector of the industry, but it will bolster the entire NewSpace industry. Once space tourism does become mainstream, it will also positively impact many socioeconomic factors on Earth: creating jobs, educating citizens about space and fostering a new solar-based energy infrastructure. The sweet escape to the stars can eventually awaken us to the awe-inspiring potential of space exploration while also giving us a better appreciation of home.
Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
SpaceX rocket launches 11 satellites, including one for South Korea, on Bandwagon-1 rideshare flight (photos)
SpaceX fires up huge Super Heavy booster ahead of 4th Starship test flight (photos, video)
Total solar eclipse 2024: Live updates
Most Popular
By Jeff Spry April 07, 2024
By Robert Lea April 07, 2024
By Tariq Malik April 06, 2024
By Space.com Staff April 06, 2024
By Joe Rao April 06, 2024
By Josh Dinner April 06, 2024
By Mike Wall April 06, 2024
By Monisha Ravisetti April 06, 2024
By Robert Lea April 06, 2024
By Elizabeth Howell April 06, 2024
- 2 In Indiana, the best spot to see the 2024 solar eclipse is wherever you are
- 3 Chasing the 2024 solar eclipse means dorm life for some New York spectators (including me)
- 4 The total solar eclipse 2024 is happening today! Here's what you need to know
- 5 Maya nobility performed bloodletting sacrifices to strengthen a 'dying' sun god during solar eclipses

The Past, Present, and Future of Space Tourism
It’s been more than 20 years since the first space tourist took flight, but there’s a lot more to come in the emerging industry of space tourism..
- Copy Link copied

Are space vacations in our near future?
Illustration by Delcan & Co.
When Austrian journalist Gerhard Pistor requested to book a trip to the moon in 1964, his travel agency forwarded his query to Pan American World Airways—Pan Am. The now-defunct airline accepted the reservation and noted that the first flights to the moon would take off in the year 2000. So began a years-long space-tourism marketing stunt in which some 93,000 people joined Pan Am’s First Moon Flights Club, a waiting list for the first civilian trips to the moon.
That, of course, never happened. But as the Space Age advanced, space tourism did, too. In 2001, American entrepreneur Dennis Tito became the first true space tourist, launching aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft and spending more than a week aboard the International Space Station (ISS)—reportedly spending $20 million to do so.
Today, we’re in a new era of space tourism, with growing numbers of civilians leaving Earth for brief moments through private enterprises focusing on such endeavors. And in the coming decades, we may even see the dawn of regular long-duration space vacations.
The Birth of Space Tourism
After the Apollo era, companies investigated opportunities to send civilians rather than government professionals—that is, NASA astronauts—into space. In the 1970s, manufacturing conglomerate Rockwell International, a contractor for NASA’s Space Shuttle program, researched the possibility of passenger modules that could fit into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle, with similar concepts developed by other companies over the subsequent decade. None came to fruition.
NASA did open up its spaceflights to nongovernment professionals, though, primarily as payload specialists, who were tasked to complete specific in-flight projects by companies outside of NASA. NASA also developed the Teacher in Space and Journalist in Space programs to open up spaceflight to several civilians annually. But the programs were ended after the Challenger disaster in 1986, which killed the first Teacher in Space participant, Christa McAuliffe, along with her six crew members. The program was considered for a revival, but that, too, was ended after a Space Shuttle failure—this one, the fatal Columbia disaster in 2003.
Space tourism finally became successful in 2001 with Tito’s launch to the ISS. That trip was organized by a company called Space Adventures, which ultimately saw eight other space tourists take trips to the ISS through 2009, each launched on a Russian Soyuz spacecraft. But these tourist flights ended after the retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle program in 2011. Because the only spacecraft capable of human spaceflight at that time was the Soyuz , every seat on every launch was needed for professional astronauts from around the world, and tourism was put on the back burner.
Space Tourism Today
For the past decade, private space tourism companies have been developing spacecraft to take passengers on suborbital flights, which bring them to the edge of space and back down to Earth in relatively short “hops” lasting anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours. By comparison, the first nine Space Adventure clients flew orbital missions that encircled the planet for days.
The method of flight varies by company. Blue Origin , for instance, launches vertically like most rockets, whereas Virgin Galactic flies a rocket-powered space plane that is launched from the belly of a carrier aircraft. While these two companies are the only suborbital companies cleared by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) for launches—both have already carried passengers to space—other companies are preparing for liftoff. That includes space-balloon companies Space Perspective and World View , which offer a far more leisurely journey than rocket-powered ascents, gently lifting passengers to high altitudes in a high-tech version of a hot air balloon. Across all suborbital space tourism companies, prices range from approximately $50,000 to $450,000 per seat.
Orbital tourism has also made a comeback, though at far higher prices: tens of millions of dollars per seat. SpaceX , which is contracted by NASA to launch astronauts to the ISS, is also available for private charters. In 2021, entrepreneur Jared Isaacman organized the Inspiration4 mission, the world’s first all-civilian mission, during which he and three crewmates orbited the Earth in a SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule as a fundraiser for St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. In 2022, SpaceX provided the launch vehicle for the Axiom mission 1 (Ax-1), the world’s first all-civilian mission to the ISS, during which four crew members spent eight days onboard the orbiting research facility.
Space Adventures is also back in business; it organized a flight to the ISS for Japanese entrepreneur Yusaku Maezawa, who traveled to space in December 2021. Maezawa intends to charter SpaceX’s under-development Starship spacecraft for a moon mission called the dearMoon project, taking with him eight civilians on the journey.
What’s Next for Space Tourism
Space tourism remains in its nascent phase, with plenty of work to be done. Existing suborbital companies are still tweaking launch vehicles and increasing launch cadence to approach regularity, while upcoming ones are waiting for FAA approval to begin their operations. And, hopefully, the space tourism companies will eventually be able to reduce the cost of flights, too.
But many enterprises are already eyeing the future when it comes to space tourism—a future in low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA itself is investing in that future through the Commercial LEO Development Program, through which it is funding the development of private space stations. As NASA and its international partners move toward retiring the ISS in the next decade or so, the agency hopes to rent facilities from private stations that will be able to host not only its professional astronauts but also commercial visitors.
Four projects have received funding from NASA’s Commercial LEO Development Program, including Axiom Space, the company that launched the Ax-1 mission. Axiom has partnered with avant-garde interior designer Philippe Starck to work on its Axiom Station. Another funded project, Starlab by Voyager Space and its subsidiary Nanoracks, has partnered with Hilton to develop astronaut accommodations.
Three of the four companies are expecting to launch their space stations by the end of the decade, but as space programs go, delays are highly likely. (NASA’s current Artemis program, for instance, was hoping to land humans on the moon in 2024, but that deadline has been pushed back to at least 2025.) Still, the future is bright for space tourism and certainly within the realm of reality—all we have to do is wait. And for travelers who have always wished to be among the stars, that wait will be worth it.

clock This article was published more than 1 year ago
How to travel to space, Earth’s hottest new destination
Go boldly, but pack lightly.
The space just above our planet is booming . Off-world trips are rapidly increasing: 42 of the 51 commercial astronauts recognized by the Federal Aviation Administration left Earth within the past two years.
The FAA predicts their ranks will balloon in the next decade — which may also bring new destinations, such as a rotating space hotel whose construction, planners claim, will begin in 2026 — and some experts have expressed optimism that relatively affordable space travel could be possible by the middle of this century.
For now, though, costs remain enormous. A $450,000 ticket reserves a spot on Virgin Galactic’s space plane, which flies 50 miles above Earth — six times a passenger plane’s cruising altitude. Expect to pay even more to go higher. Blue Origin’s 11-minute journey by rocket, which reportedly cost more than $1 million, shoots above the 62-miles-high Kármán line, the generally agreed-upon boundary between Earth and space. Others spend days in space. In September 2021, four civilian Americans orbited for three days aboard a SpaceX Dragon capsule. No word on how much it cost them.
For $55 million , Axiom Space will send astronauts via a SpaceX rocket to the International Space Station, a laboratory that circles Earth once every 90 minutes. For two weeks last April, the ISS’s first Axiom crew members worked in the lab while forgoing proper showers.
The New Space Age
Space “ought to be on everybody’s bucket list,” said former NASA astronaut Michael López-Alegría , the Axiom Space vice president who commanded the April mission. “We’d be the first to admit that it’s not quite democratic yet, because it’s still pretty expensive, but we’ll get there.” The Houston-based company has already begun to build a segment of what will be a private space station.
Here’s how to pack and prep for Earth’s hottest new destination.
Getting ready
Training takes days to months. Axiom Space crew members spent at least 700 hours learning new tasks: how to run experiments, dock a transport vehicle to the ISS and respond to fires.
They also practiced on a centrifuge, the rapidly spinning machine that simulates the extreme acceleration of space travel. You don’t need to be in tiptop shape — floating in microgravity is effortless, López-Alegría said — but you will have to endure intense G-force as you exit and reenter the atmosphere.
You should be mentally prepared for a unique psychological experience called the overview effect , which occurs when people witness their home planet from above. “When we came back to Earth, I could not stop crying,” said aerospace PhD student Sara Sabry, founder of the Deep Space Initiative , who traveled to space last August via Blue Origin (whose founder, Jeff Bezos, owns The Washington Post).
Aboard SpaceX, you’ll wear spacesuits: sleek, pressurized white outfits with black-visored helmets. On Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin flights, the fit is closer to a jet pilot’s, with gear that’s not designed for loss of pressure. Sabry said her suit was comfy and custom-tailored. Under Armour makes the clothes — underwear, jumpsuit and zip-up boots — for Virgin Galactic, which founder Richard Branson wore in his July 2021 journey to space’s edge.
Going boldly, packing lightly
Space may be the one place you can fly without packing an ID or passport . “When we walk onto the vehicle, we’re wearing our spacesuits and pretty much nothing else,” López-Alegría said.
Expect to leave the rest of your worldly possessions on Earth, with a few exceptions. Sabry packed three pounds of mementos in a bag, including photographs and a single dirty sock belonging to her niece. On Inspiration4, the Earth-orbiting SpaceX mission, one astronaut brought his ukulele to serenade his teammates in the capsule.
Snapping selfies
Don’t plan on filling your Instagram feed with your space travels to make your friends jealous. You won’t have your phone.
On Sabry’s Blue Origin flight, a few people had a GoPro strapped to their wrists to capture video — especially of the three minutes of weightlessness.
The ISS provides cameras to use. Astronauts can browse the internet on the space station, but posting requires help. Pictures snapped in space are beamed to Earth, López-Alegría said, where someone on the ground uploads them to social media.
Eating and drinking
There wasn’t any snacking on the Blue Origin craft, Sabry said, and the up-and-down trips don’t leave time for in-flight meals. Hot food isn’t always an option with other carriers, either. The first course served on the orbiting Dragon capsule was cold pizza, though SpaceX founder Elon Musk apologized for the unheated pie and promised future astronauts would have a food warmer.
Why NASA and other space agencies want to return to the moon
That’s how the crew heats dinner on the ISS, which boasts a varied menu: about 200 options , mostly freeze-dried or thermostabilized. Tortillas replace bread to avoid crumbs; what’s just a tabletop mess on Earth becomes a hazard when bits can float into electronics or eyeballs. There’s no soda or beer because, according to NASA, carbonation bubbles would be unpleasantly routed through the digestive system without gravity to help an astronaut burp.
Staying clean-ish
Space is like backcountry camping. Both lack laundry machines and require some hygienic compromises. When astronauts must bathe, they squeeze packets of soap and water on their skin and apply rinseless shampoo to their hair. Toilets on the ISS and Dragon Capsule collect waste via suction hoses and fans. On the space station, urine is recycled into drinkable water . Toothbrushes and paste are the same, but without sinks, there’s no spitting.
Falling asleep
You’ll roll out sleeping bags in the SpaceX spacecraft or as an Axiom crew member on the ISS. Vehicles are temperature-regulated because the outside of the ISS can swing from minus-250 in the shadows to 250 degrees in the sun. Still, some modules, or sections, of the ISS can be chillier than others: López-Alegría said he donned long underwear to be cozier when drifting off in space.
Illustrations by Elizabeth von Oehsen. Editing by Amanda Finnegan.


Everything you need to know about space tourism
Posted: October 12, 2023 | Last updated: October 12, 2023

Between floating in weightlessness, witnessing 16 sunrises a day and gazing into the infinite void, space travel sure sounds like an out-of-this-world experience. And now, it’s no longer a thing of the future.
That’s right, soon interstellar awe will be open to (almost) anyone, as billionaires Richard Branson, Jeff Bezos, and Elon Musk are pushing the space tourism industry to a higher orbit.

What is space tourism?
Well, it’s almost like regular tourism: travel for recreational and leisure purposes… but in outer space. Some organizations like the Commercial Spaceflight Federation and the Citizens in Space project prefer to use the terms “personal spaceflight” or “citizen space exploration,” though.
In a nutshell, it’s space travel for non-astronauts.

Who can travel to space?
Anyone ! Well, that is, anyone with enough money. No need to have any previous science qualifications or NASA training, especially since a trained crew will escort tourists on their galactic journey.
According to Virgin Galactic, future space tourists will be between 10 and 90 years old, and come from diverse professional and cultural backgrounds.
The only thing you need? The desire to explore the universe!

What is orbital travel?
The main difference between orbital and suborbital flights lies in the trajectory and speed of the vessels.
To go into orbit, a rocket or spaceship needs to follow a path that goes around the Earth at the very fast minimum speed of 7.7 kilometres (4.8 miles) per second, in order to keep circling and never fall back down.
It allows astronauts and travellers to stay in space for extended periods of time, hence it is for now the preferred type of flight.

What is suborbital travel?
A suborbital flight , which is what Branson and Bezos did, “just” requires enough energy to blast off to space and then naturally fall back to Earth, making a huge arc.
It requires less energy and is less costly than orbital flights, thus opening doors for relatively affordable space tourism in the future.
Passengers would experience up to six minutes of weightlessness and a grandiose view.

How do you prepare?
Although Virgin Galactic doesn’t explicitly list its physical requirements, they did say astronauts would have to pass certain medical checkups and training programs. Blue Origin, on the other hand, has said that training for suborbital trips will only take a day.
And of course, any space tourist will also have to pass a series of thorough tests to determine whether they’re fit to fly up there.
Once in space, you may have to perform small bouts of exercise to prevent muscle wasting , which takes place after just seven days.

What is lunar tourism?
As its name hints, lunar tourism is the project of sending paying travellers to the moon. The first one could happen as soon as 2023, and would consist of a loop flight.
But three types of lunar tourism could be available in the near future: circumlunar trajectory, lunar orbit, and even lunar landing.
How cool would it be to say to someone, upon returning from a lunar vacation, “I’ve literally loved you to the moon and back”?

Where does space tourism take place?
Admittedly, space is a vast place. So where exactly would tourists go ?
First, any space travel begins with the Kármán line , which lies at 100 kilometres (62 miles) above sea level and is commonly accepted as the limit between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space.
Then, there are several options: orbital, suborbital, and lunar space tourism.

Have touristic space travels already occurred?
Yes! From 2001 to 2009, the Russian space agency and the U.S.-based space tourism company Space Adventures took seven (very wealthy) members of the public for several orbital space travels to the International Space Station.
The flights took place aboard the famous spacecraft Soyuz but stopped in 2010, since the crew of actual astronauts grew bigger and left no more seats available for paying space tourists.

Who were the first space tourists?
The American businessman Dennis Tito became officially the first space tourist in April 2001, when he stayed for seven days on the International Space Station.
He was followed by six multimillionaire fellows from various countries: South African entrepreneur Mark Shuttleworth, American scientist Gregory Olsen, Iranian engineer Anousheh Ansari (the first female space tourist), Hungarian-American computer programmer Charles Simonyi, British video game mogul Richard Garriott, and Canadian businessman Guy Laliberté.
On July 11, 2021, billionaire Richard Branson, along with three Virgin Galactic employees and two pilots, reached an altitude of 85 kilometres (53 miles) above Earth aboard his Virgin Galactic rocket plane, the Unity. Less than 10 days later, on July 20, the world’s richest man, Amazon’s Jeff Bezos, briefly entered space on Blue Origin , his private space company’s reusable rocket. He was joined by his younger brother Mark, Dutch teenager Oliver Daemen, and Wally Funk, who, at 82 years old, became the oldest astronaut.
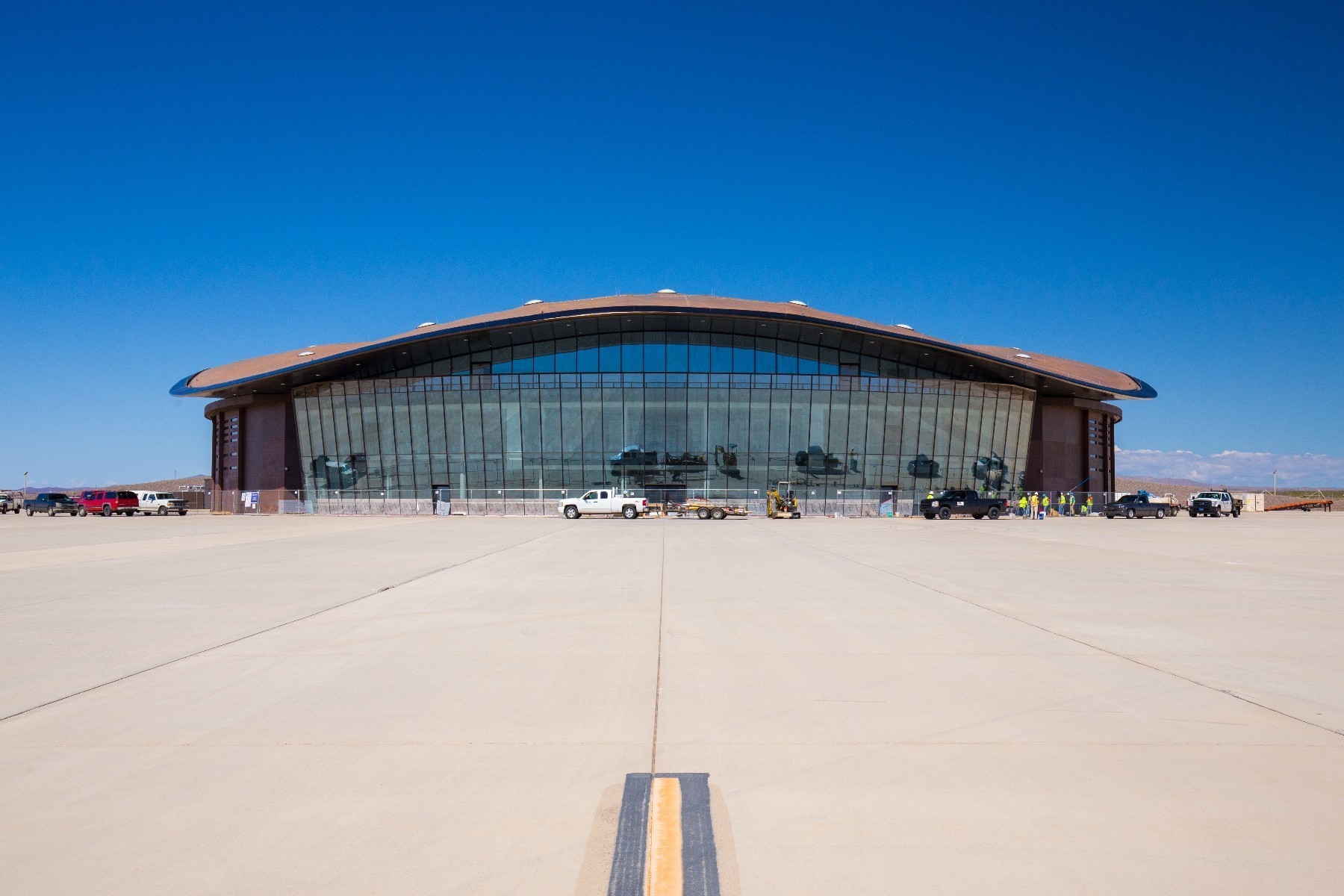

Who would be the space tourism “agencies”?
Unlike past tourism experiments, which took place aboard vessels sent off for scientific purposes, future travels will happen on private companies’ flights set up solely for space tourism.
Those pioneering aerospace companies are Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic ; SpaceX, founded by Tesla co-founder Elon Musk ; and Blue Origin , created by Amazon founder Jeff Bezos.

When will space tourism happen?
Sooner than you think. According to Forbes , Virgin Galactic’s successful trip means the company could start sending civilians up into space as soon as early 2022. Likewise, Blue Origin, which has a Federal Aviation Administration licence for human space travel through August 2021, could officially enter the space tourism game by early 2022.

How much will it cost?
It’s not exactly clear at the moment, but there have been some indications. For example, Virgin Galactic began selling ticket reservations for US$250,000 and sold roughly 600, before a test crash in 2014 brought sales to a halt. They’re expected to start selling tickets again in 2022, but at a much higher price.
It was reported in 2018 that seats on Bezos’s Blue Origin would also cost in the ballpark of US$200,000 to US$300,000, but that could change given how high demand is. At a recent auction, the winning bid for a seat aboard the company’s first spaceflight was a whopping US$28 million .
The bottom line is, those hoping to take a trip around the stars will either need to know someone or have hundreds of thousands (likely even millions) of dollars to spare.
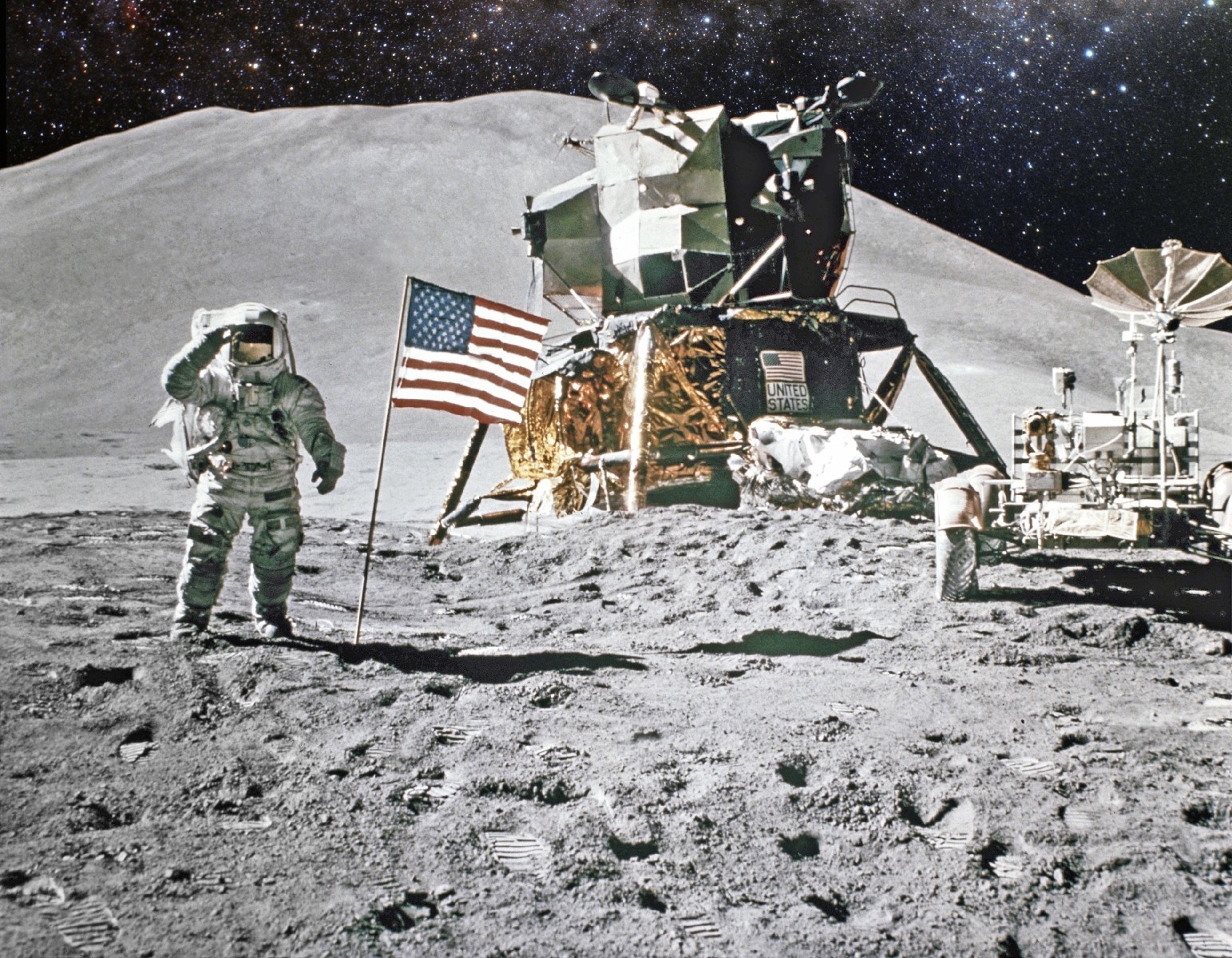

How do we get there?
The development of space tourism vehicles is still an ongoing project.
But a few options already exist, like Virgin Galactic’s spaceplanes that can carry up to eight people, or SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft , launched by the Falcon Heavy rocket.
Blue Origin’s New Shepard looks more like a regular rocket that takes off and lands vertically, but also claims to offer the biggest windows of any spacecraft—a good selling point. It comfortably sits six people and is fully autonomous, meaning no pilot onboard.
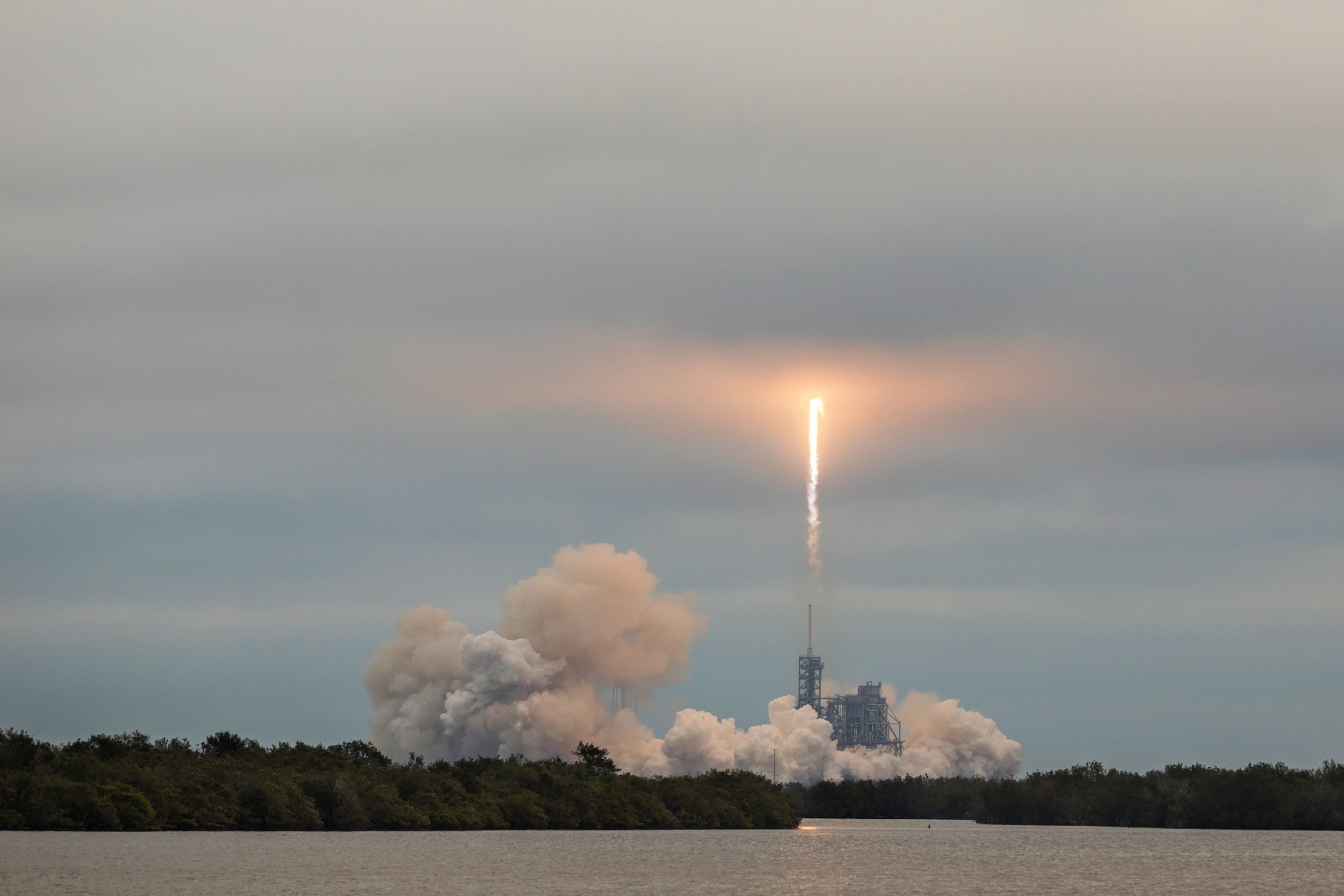


What does it feel like?
Needless to say, travelling to space is no walk in the park.
You’re eager to experience the joys of floating in microgravity? You better also get prepared to endure several physical discomforts: nausea and sea sickness, dizziness, headache, disorientation, puffy face, and bloodshot eyes.
But astronauts and previous space tourists agree that the body adjusts fairly quickly, getting used to its spatial environment in about three days.

Is it safe?
Safety is a reasonable concern , considering the many hazards involved in space travel: the probability of a crash, exposure to cosmic radiation, and even unknown dangers that could emerge with this new industry. But here is the real question for any adventurer: is the thrill worth the risk?

What is the food like?
For many tourists, food is a crucial criterion for a successful vacation. But outer space is no place for gourmets, at least not yet. Interstellar tourists can expect to enjoy mostly canned, modified, and pre-packaged meals (such as space burritos and freeze-dried ice cream). But soon, thanks to NASA’s veggie farm , space tourists might be able to savour space-grown salads.

What about the accommodations?
Orbital space travel allows you to stay up there for a few days or even weeks. At that point, you might want to stretch your legs outside of the spacecraft, right? Well, in the future, space stations could be used as hotels: the Genesis inflatable habitats by Bigelow Aerospace and the Space Island Project are existing examples. Make sure to book a room with a view of planet Earth!
How to pack a space suitcase?
Packing a suitcase for a trip through the cosmos is actually less of a headache than doing so for a weekend vacation on Earth. Just keep in mind that it’s impossible to do laundry in space, so pack clothes accordingly : stock up on underwear, light clothing (space station temperature is controlled at about 22 degrees Celsius, or 72 degrees Fahrenheit), and exercise outfits. Outerwear will be provided: an orange suit for takeoff and re-entry, and a white one for potential space strolls.
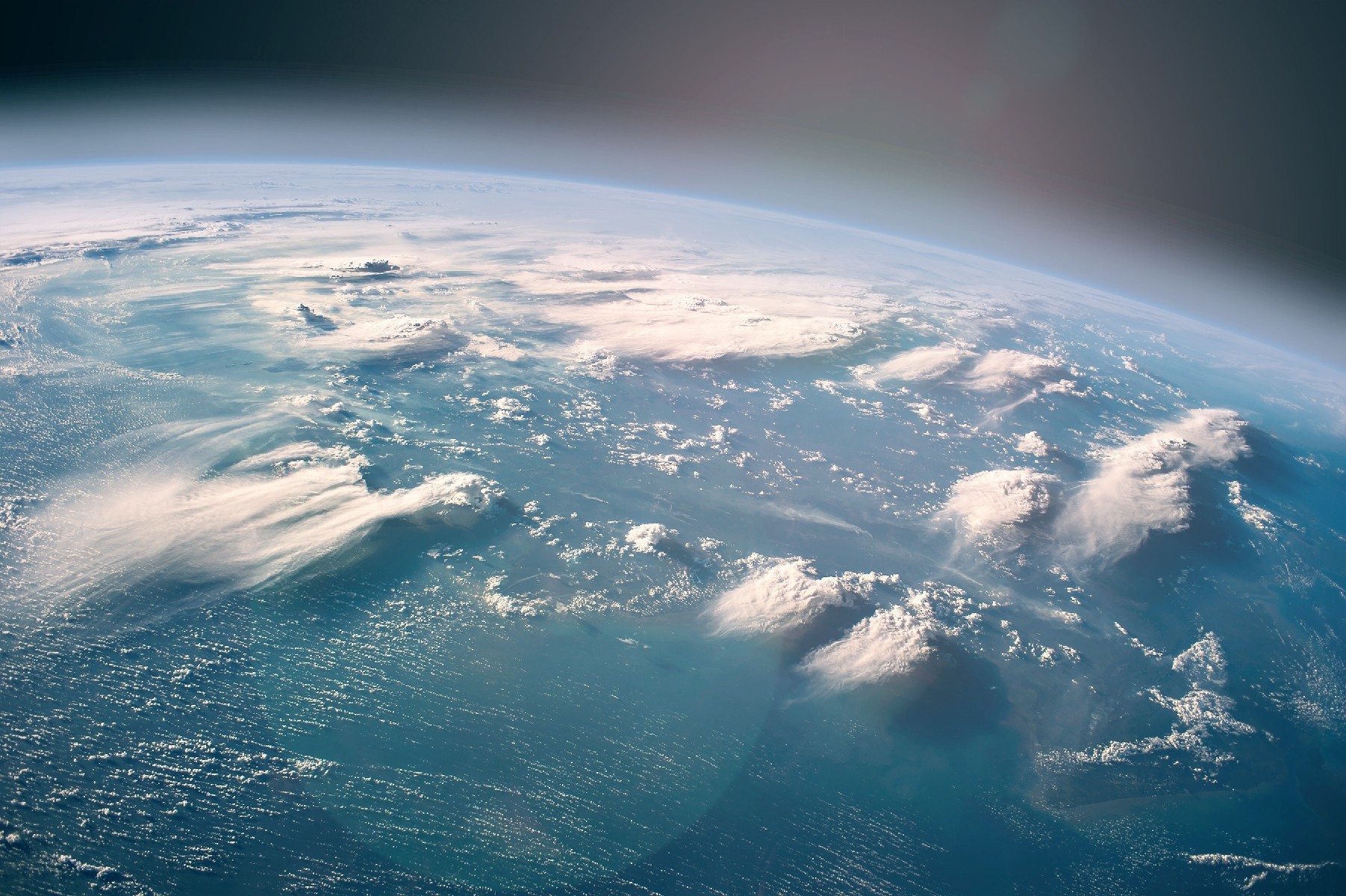

Is it eco-friendly?
With ecotourism being a growing trend and concern over the last few years, the question is legitimate. Well, bad news: space travel could have a negative impact by accelerating global warming . This would be caused by the black carbon released into the stratosphere after suborbital launches. But of course, entrepreneurs in the industry claim that the carbon footprint of space tourism would be minimal. The truth is, rockets emit 50 to 100 times more CO₂ per passenger than a regular flight. Considering that Virgin Galactic plans to do 400 trips per year, that’s a lot of CO₂ entering the atmosphere.
More for You
Russian Missile Ship on Fire in 'NATO Lake': Report
50 iconic movie lines that you have probably quoted at least once
The Best And Worst Breakfast Biscuits From 8 Fast Food Chains
One Piece: Characters With Most Victories
Chicken Cordon Bleu Casserole
Former pro basketball player Jimmer Fredette calls Caitlin Clark a 'threat'
5 Netflix movies to watch when the kids have gone to bed
30 slang words you may not realize came from TV and movies
Trump Suing N.Y. Judge Just One Week Before Hush Money Trial, Report Says
Solo Leveling Breaks One of Anime's Biggest Storytelling Tropes
The 31 Best Grammys Red Carpet Outfits Ever
25 Healthy Fast-Food Orders That You Can Grab and Go
Peanuts by Charles Schulz
What Is Red Diesel Fuel, And What Happens If You Put It In Your Truck?
Scientists discover highly toxic material in human urine: 'Raises important new questions'
‘What’s Up, Doc?’: 15 Trivia Tidbits About Bugs Bunny
20 actors who passed up iconic roles
How to Make Spaghetti Carbonara Sauce – Recipe
Luka Dončić, Kyrie Irving leave even their Mavericks teammates ‘starstruck’
The Discontinued McDonald's Sandwich That Inspired 3 Sauces
INTERSTELLAR TRIPS

Explore Beyond
Join the waiting list for our exclusive services.
Thanks for joining!
Space Tours
It’s Time to Explore More
Let Interstellar Trips help you find your perfect space vacation. We offer a wide range of luxury space tours, including private trips with our partners SpaceX and Virgin Galactic. All of our trips are designed for first-class customers, who value their privacy and want the most luxurious experience possible.

ORBIT EXPEDITION
Stratosphere trips are a type of space tourism experience that involves traveling to the stratosphere, the layer of Earth's atmosphere that lies between approximately 6 and 30 miles (10 and 50 kilometers) above the Earth's surface. Stratosphere trips offer passengers the opportunity to experience weightlessness and breathtaking views of the Earth and the stars.
Space Expeditions
Space Travel Expeditions involve traveling beyond the Earth's atmosphere into outer space. These trips can take a variety of forms, including trips to the International Space Station (ISS), lunar missions, and trips to other destinations in the solar system.

First-Class Services

Exclusive Experience

VIP Concierge

Personalised Training & Support

Why Travel With Us?
Your Personal Travel Guide

The Ultimate Space Adventure
Space travel is exciting for a number of reasons. One of the most unique and exciting aspects of space travel is the opportunity to experience weightlessness. This can be a thrilling and unforgettable experience, as it allows travellers to feel what it's like to float freely in a microgravity environment. Space travel also offers travellers the opportunity to see the Earth from a perspective that is not possible from the surface. From space, travellers can see the curvature of the Earth and the stunning beauty of our planet from a completely new angle.
Adventures In The Final Frontier
In addition to these exciting experiences, space travel also offers the opportunity to explore the unknown. Space is an enormous and largely unexplored frontier, and space travel offers the opportunity to explore this vast and mysterious realm. For many people, the idea of being able to explore new worlds and discover what lies beyond our planet is a truly exciting prospect. Furthermore, many space travel missions are designed to gather scientific data and conduct experiments that can help us understand more about the universe and our place in it. For people who are interested in science and discovery, the opportunity to participate in these types of missions can be very exciting. Finally, the thrill of adventure is also a major part of the appeal of space travel. Whether it's the excitement of launching into space or the thrill of exploring new worlds, space travel offers a unique and thrilling adventure that is unlike anything else.

Bookings have already began
123-456-7890
Thanks for submitting!
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
NASA Picks 3 Companies to Help Astronauts Drive Around the Moon
The agency’s future moon buggies will reach speeds of 9.3 miles per hour and will be capable of self-driving.

By Kenneth Chang
NASA will be renting some cool wheels to drive around the moon.
Space agency officials announced on Wednesday that they have hired three companies to come up with preliminary designs for vehicles to take NASA astronauts around the lunar south polar region in the coming years. After the astronauts return to Earth, these vehicles would be able to self-drive around as robotic explorers, similar to NASA’s rovers on Mars.
The self-driving capability would also allow the vehicle to meet the next astronaut mission at a different location.
“Where it will go, there are no roads,” Jacob Bleacher, the chief exploration scientist at NASA, said at a news conference on Wednesday. “Its mobility will fundamentally change our view of the moon.”
The companies are Intuitive Machines of Houston, which in February successfully landed a robotic spacecraft on the moon ; Lunar Outpost of Golden, Colo.; and Venturi Astrolab of Hawthorne, Calif. Only one of the three will actually build a vehicle for NASA and send it to the moon.
NASA had asked for proposals of what it called the lunar terrain vehicle, or L.T.V., that could drive at speeds up to 9.3 miles per hour, travel a dozen miles on a single charge and allow astronauts to drive around for eight hours.
The agency will work with the three companies for a year to further develop their designs. Then NASA will choose one of them for the demonstration phase.
The L.T.V. will not be ready in time for the astronauts of Artemis III, the first landing in NASA’s return-to-the-moon program , which is currently scheduled for 2026 .
The plan is for the L.T.V. to be on the lunar surface ahead of Artemis V, the third astronaut landing that is expected in 2030, said Lara Kearney, manager of the extravehicular activity and human surface mobility program at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
“If they can get there earlier, we’ll take it earlier,” Ms. Kearney said.
The L.T.V. contract will be worth up to $4.6 billion over the next 15 years — five years of development and then a decade of operations on the moon, most of it going to the winner of this competition. But Ms. Kearney said the contracts allow NASA to later finance the development of additional rovers, or allow other companies to compete in the future.
The contract follows NASA’s recent strategy of purchasing services rather than hardware.
In the past, NASA paid aerospace companies to build vehicles that it then owned and operated. That included the Saturn V rocket, the space shuttles and the lunar roving vehicles — popularly known as moon buggies — that astronauts drove on the moon during the last three Apollo missions in 1971 and 1972.
The new approach has proved successful and less expensive for the transportation of cargo and astronauts to the International Space Station. NASA now pays companies, notably Elon Musk’s SpaceX, fixed fees for those services, more akin to plane tickets or FedEx shipments.
For the company chosen to build the L.T.V., the vehicle will remain its property, and that company will be able to rent it to other customers when it is not needed by NASA.
“It’s commercially available for us as a commercial business to sell capacity on that rover,” said Steve Altemus, the chief executive of Intuitive Machines, “and do that for international partners and for other commercial companies and space agencies around the world.”
The competition created alliances between small startups and larger, more established aerospace companies, as well as car companies. The Intuitive Machines team includes Boeing, Northrop Grumman and Michelin, the tire maker. Lunar Outpost added to its team Lockheed Martin, Goodyear and General Motors, which had helped design the Apollo moon buggies.
Astrolab is working with Axiom Space of Houston, which has sent private astronauts to the space station and is building a commercial module to the International Space Station. Astrolab announced last year that it had signed an agreement to send one of its rovers to the moon on a SpaceX Starship rocket as early as 2026. That mission is independent of whether it is selected by NASA, a company spokesman said.
While Lunar Outpost is competing with Intuitive Machines on this contract, it plans to work with the company separately, sending smaller robotic rovers to the moon on the company’s lunar landers.
Kenneth Chang , a science reporter at The Times, covers NASA and the solar system, and research closer to Earth. More about Kenneth Chang
What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
Scientists may have discovered a major flaw in their understanding of dark energy, a mysterious cosmic force . That could be good news for the fate of the universe.
A new set of computer simulations, which take into account the effects of stars moving past our solar system, has effectively made it harder to predict Earth’s future and reconstruct its past.
Dante Lauretta, the planetary scientist who led the OSIRIS-REx mission to retrieve a handful of space dust , discusses his next final frontier.
A nova named T Coronae Borealis lit up the night about 80 years ago. Astronomers say it’s expected to put on another show in the coming months.
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Slovenščina
- Science & Tech
- Russian Kitchen
The best places in Moscow for space lovers

The Memorial museum of Cosmonautics, Moscow. Source: Lori/Legion-Media
In Moscow lovers of the films “Interstellar” and “Gravity” can begin their space tour as soon as they arrive by staying at the Cosmos Hotel, located in what could be called the “space” part of town. From there they can cross the street to the Cosmos Pavilion at VDNKh and the Moscow Museum of Cosmonautics.
Choose the planetarium that fits you best: a fancy one full of wild amusements or a small and cosy Soviet one hidden among the trees of Ekaterininsky Park. For a tour of Zvezdny Gorodok (Star Village) reservations often must be made two months in advance.
Cosmic canine pioneers
At the end of World War II it was still unknown if a living being could survive a space flight. In the USSR, given Professor Pavlov’s previous experience, experiments went forward with dogs, while in the U.S. and France scientists chose monkeys and cats respectively. In the USSR dogs were taken from shelters, as family dogs were considered too soft. Scientists needed dogs with a real “Soviet character,” in other words tough and full of self-denial.
In August 1960 Belka and Strelka accomplished 17 orbits around the Earth and their comeback was a triumph. They spent the rest of their lives in glory, and were often paraded around in kindergartens and schools. When they died their bodies were stuffed with straw and put on display at the Museum of Cosmonautics in Moscow.

Source: RIA Novosti/Ruslan Krivobok
Nikita Khrushchev gave Pushinka, a puppy of the heroine Strelka, as a gift to President Kennedy’s daughter. The gift was intended as a hint: the First Secretary of the Communist Party wanted to demonstrate that the USSR had beaten the U.S. in the space race. Once the CIA checked it for listening devices, Pushinka became the Kennedys’ pet, soon pairing it off with their Welsh terrier Charlie. She gave birth to four puppies.
The Museum of Cosmonautics

Source: Lori/Legion-Media
The museum has a rich collection including the first satellite, a space WC, the capsule where space dogs Kozyavka and Otvazhnaya lived, the personal belongings of the first astronaut, specimens from the moon and recreations of space flights. Authentic space food is sold in the gift shop.
Everything has been left untouched at Korolev’s Memorial House Museum located nearby. He lived there for six years during an intense period of work, fully devoting himself to projects aimed at conquering space, the most important of which was the launch of the Earth’s first artificial satellite and the first space flight of a man.
Prospekt Mira 111 Metro: VDNKh +7 (495) 683-79-68 www.kosmo-museum.ru Hours of operation: Tue, Wed, Fri-Sun 10:00-19:00, Thu 10:00-21:00; closed Mondays Entrance fee: 200 rubles (3,5$) for adults; 50 rubles (80 cents) for children; free for children under six Guided tour: 350 rubles (6$); photo or video: 230 rubles (4$) Admission to the Buran-2 interactive space flight: 200 rubles (3,5$)
Zvezdny Gorodok (Star City)

Source: Photoxpress
The Astronauts’ Training Center and the Museum of Space Exploration can be found at the closed settlement Zvezdny Gorodok. Here you can learn about the history of spacecraft, see the first Soviet rocket, spacesuits and flight simulators for the training of astronauts. If you submit to a quick medical check-up, you can try all this yourself. But strolling around the grounds through this quiet town is also worthwhile as it’s a fascinating glimpse into Soviet scientific settlements. In order to visit the museum, you need to book a tour by phone or e-mail at least 35 days in advance.
Zvezdny Gorodok, 23 kilometers from MKAD, Sholkovskoe Shosse, Moscow Region +7 (495) 526-38-74 www.zvezdniygorodok.ru (in Russian) E-mail: [email protected] Entrance fee: 500 rubles (9$) for adults, 400 rubles (7$) for children
Moscow Planetarium

Source: TASS/Vladimir Astapkovich
The Moscow Planetarium was recently reconstructed and has once again become a major destination for entertainment mixed with a scientific and educational mission. There are Large and Small Star Halls, the Lunarium interactive museum, a 4D cinema and an observatory.

Source: TASS/Anna Salynskaya
The planetarium is located in the Large Star Hall, which projects stars and planets on the ceiling and shows a documentary film on black holes and the collision of galaxies. In the Lunarium you can make the Sun explode with a virtual meteorite, take a walk on Mars, launch a hydrogen-fuelled rocket or give shape to an extra-terrestrial. This is not Moscow's only such facility, as there is also a small but pleasant planetarium in Ekaterininsky Park: www.planetarium-cc.ru (in Russian)
Sadovaya-Kudrinskaya ul. 5/1 Metro: Krasnopresnenskaya, Barrikadnaya +7 (495) 221-76-90 www.planetarium-moscow.ru/en Hours of operation: Mon, Wed-Sun 10:00–21:00; closed Tuesdays Entrance fee: 120–700 rubles (2-12,5$)
The Cosmos Pavilion at VDNKh
The Cosmos Pavilion Museum at VDNKh park features a full-size interactive model of the future Mars-Tefo space station. It is part educational project and part interactive museum dedicated to the exploration of Mars. It is also a place where you can experience the role of the astronaut and explorer of distant worlds.

Source: TASS/Milkhail Japaridze
There are three ways to experience Mars-Tefo: you can look, touch or try yourself. Visitors can get on a simulator that mimics a walk on the surface of Mars with views of its landscapes. The walk leads to the station, where you can observe sandstorms.

There are fantastic images of Mars’ surface as well as a panorama of the Gale Crater shot by the Curiosity space probe in 2012. Additionally, visitors can enter the teleport zone and go into the future to a time when humans can explore Mars and a screening room where you can see Mars and a film on the exploration and conquest of the Red Planet.
Prospekt Mira 119, VDNKh, Pavilion 34 Metro: VDNKh +7 (495) 215-13-41 or +7 (495) 215-13-48 The pavilion is open Tues-Sun, although tours must be booked in advance Entrance fee: 500–2000 rubles (9$-36$), with a five-percent discount if tickets are purchased online www.marstefo.ru (in Russian)
All rights reserved by Rossiyskaya Gazeta.
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox
This website uses cookies. Click here to find out more.

- Moscow Tours
- Customized tours
- Moscow for kids
- Evening activities
- Moscow evening activities
- St Petersburg evening activities
- Day trips out of Moscow
- Golden Ring tours
- St Petersburg tours
- Russian tour destinations
- Package tours
- Moscow highlights
- Travel Tips
- Upcoming group tours
- Moscow events
Memorial Museum of Space Exploration Tour

Request form

We use cookies to improve your experience on our website, and to facilitate providing you with services available through our website. By continuing to use our website, you accept our use of cookies, the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service . I agree
- Ethics & Leadership
- Fact-Checking
- Media Literacy
- The Craig Newmark Center
- Reporting & Editing
- Ethics & Trust
- Tech & Tools
- Business & Work
- Educators & Students
- Training Catalog
- Custom Teaching
- For ACES Members
- All Categories
- Broadcast & Visual Journalism
- Fact-Checking & Media Literacy
- In-newsroom
- Memphis, Tenn.
- Minneapolis, Minn.
- St. Petersburg, Fla.
- Washington, D.C.
- Poynter ACES Introductory Certificate in Editing
- Poynter ACES Intermediate Certificate in Editing
- Ethics & Trust Articles
- Get Ethics Advice
- Fact-Checking Articles
- International Fact-Checking Day
- Teen Fact-Checking Network
- International
- Media Literacy Training
- MediaWise Resources
- Ambassadors
- MediaWise in the News
Support responsible news and fact-based information today!
Is CERN activating the world’s most powerful particle accelerator for the April 8 eclipse? No
CERN restarted its Large Hadron Collider after a regular winter stop for maintenance. It is unrelated to the eclipse.

As people around the country await the April 8 total eclipse, conspiracy theories about a Switzerland-based nuclear research facility have some social media users on edge. In their view is CERN, also known as the European Organization for Nuclear Research.
“Why is CERN being reactivated on April 8, the same day as the infamous eclipse?” asked a March 29 Facebook post , referencing what it called the group’s plan to activate “the large hadron collider” on the day of the eclipse. “My gut instinct is that something really big is being planned for that day… perhaps a total takedown of both the grid and society in general worldwide.” In another post April 1, a man in a baseball cap speculated that CERN is deliberately starting back up April 8 to “open up a gateway, a portal.”

(Screenshot/Facebook)
These posts were flagged as part of Meta’s efforts to combat false news and misinformation on its News Feed. (Read more about our partnership with Meta , which owns Facebook and Instagram.)
It is not unusual for scientists to conduct research during an eclipse, when the sun’s corona becomes visible and areas in totality go briefly dark in the moon’s shadow. Total solar eclipses allow researchers “to study Earth’s atmosphere under uncommon conditions.” NASA, for example, is launching three sounding rockets on the day of the eclipse to study its effects on the ionosphere (a mission that also became a subject of misinformation ).
But CERN’s research is different. The primary research focus of CERN — an acronym derived from the French name “Conseil Européen pour la Recherche Nucléaire” — is particle physics , or “the study of the fundamental constituents of matter and the forces acting between them.” The organization seeks to find answers about the universe’s fundamental structure .
CERN houses the Large Hadron Collider, the most powerful particle accelerator in the world , which measures around 16.8 miles (27 kilometers) in circumference. The collider’s aim, as Britannica explains , is to “understand the fundamental structure of matter by re-creating the extreme conditions that occurred in the first few moments of the universe according to the big-bang model.”
CERN spokesperson Sophie Tesauri told PolitiFact in an email that the collider’s activities have nothing to do with the April 8 eclipse.
“What we do at CERN is doing particle physics with accelerators such as the LHC, and this has little to do with astrophysics in a direct way,” Tesauri said. “So there is no link between the solar eclipse on Monday 8th April, and what we do at CERN.”
CERN has an accelerator complex composed of machines with “increasingly higher energies.” A beam of particles is injected by one machine to the next one, bringing the beam to a higher energy — and the Large Hadron Collider is the last element in this complex.
“Hadrons” are a group of particles that include protons and ions. In the Large Hadron Collider, two beams travel in opposite directions at nearly light speed and are made to collide. In 2012, Large Hadron Collider experiments led to the discovery of the Higgs boson particle , a particle named for British physicist Peter Higgs, who in the 1960s postulated about the existence of a particle that interacted with other particles at the beginning of time to provide them with their mass.
Tesauri told PolitiFact that the accelerator complex is restarted every year after a brief winter technical stop, when beam production ceases so that the accelerators can undergo maintenance. Restarting an accelerator like the Large Hadron Collider “requires a full commissioning process in order to check that all equipment works properly.”
“Now that all the checks have been performed, the LHC is ready to provide particle collisions to the LHC experiments, and first collisions for this year should actually happen today 5th April,” Tesauri said in her email. “This will mark the beginning of the physics run for 2024.”
The beams were initially expected to enter collision April 8, according to a March 14 report . It said, “Depending on how work progresses, this milestone may shift forwards or backwards by a few days.”
On April 5, CERN announced that the Large Hadron Collider achieved its first stable beams in 2024, “marking the official start of the 2024 physics data-taking season.” The statement said that from March 8 to April 5, the Large Hadron Collider was set up to handle the beam and tested for any issues.
“Although the solar eclipse on 8 April will not affect the beams in the LHC, the gravitational pull of the moon, like the tides, changes the shape of the LHC because the machine is so big,” CERN’s announcement said. This phenomenon is not unique to an eclipse; a 2012 news release discussed distortions in the machine brought about by a full moon.
According to CERN’s frequently asked questions page, the Large Hadron Collider is expected to run over 20 years , “with several stops scheduled for upgrades and maintenance work.”
Conspiracy theories surrounding CERN’s work have been circulating for years . In a statement to Verify fact-checkers, CERN said that its research “captures the imagination of lots of people, which is why CERN has been featured in a lot of science fiction books / even movies, around the world.” CERN said works inspired by its research are fictional and “should not be confused with the actual scientific research.”
False claims about the group’s work are so common that the organization addresses some common theories on its FAQ page : No, it won’t “open a door to another dimension,” and no, it won’t “generate black holes in the cosmological sense.”
We rate the claim that CERN is activating its Large Hadron Collider in connection with the April 8 solar eclipse False.
More from Poynter:
- MAN ON MOON: Reflections on how mankind and the media came together on the surface of the moon 50 years ago
Gannett journalists in the solar eclipse’s path go on strike
- What if newsrooms treated every day like eclipse day?

Here’s your chance to train with a journalist so dedicated, he’ll walk to work in a blizzard
Kerwin Speight is leading the Poynter Producer Project, a workshop designed to enhance the skills of TV and video producers

Opinion | Women’s basketball takes the spotlight with sensational performances … on and off the court
This weekend’s games shattered ESPN’s viewership numbers for all basketball games — men and women, college and professional.

Unionized workers at the Austin American-Statesman and the Rochester Democrat and Chronicle are striking over stalled contract negotiations

Associated Press Stylebook makes Merriam-Webster its official dictionary
If a term isn’t listed in the stylebook, its entry in Merriam-Webster will be considered AP style.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Start your day informed and inspired.
Get the Poynter newsletter that's right for you.
NEWS... BUT NOT AS YOU KNOW IT
‘Tacky’ and ‘bleak’ tourist attraction named one of most popular in the UK

Share this with

From Royal palaces to theme parks, the UK has a lot to offer the almost 40 million tourists that visit each year.
But a new ranking has revealed one of the most popular tourist attractions in the UK, and it’s sure to leave people confused.
Attracting 5 million visitors each year, Blackpool Pleasure Beach is the UK’s second most popular tourist attraction outside of London – but it doesn’t exactly receive rave reviews.
In fact, TripAdvisor users have called it ‘tacky’ and ‘bleak’. Ouch.
Perhaps it’s the long history that keeps tourists flocking to the resort every single year. Found on Blackpool’s South Shore in Lancashire , Blackpool Pleasure Beach has been going since the Victorian Era, founded in 1896 as seaside visits became more accessible for all classes. Think Punch & Judy shows and donkey rides along the beach.

And today, the park is famous for holding numerous record titles, including the largest collection of wooden roller coasters of any theme park in the UK: the Big Dipper, Blue Fryer, Grand National and Nickelodeon Streak.
Likewise, when it was first unveiled in 1994, The Big One was the tallest and steepest coaster in the world, attracting adrenaline-seeking fans.
But these days, visitors argue that the ‘golden days’ of Blackpool Pleasure Beach are over.
‘Not what it once was. Despite being less than busy and small queues it still took a long time to get onto most of the rides,’ Philip S wrote in a disgruntled Tripadvisor review.

‘It has been allowed to fall into a state of neglect.’
Another review described Blackpool as ‘tired’ and ‘run-down.’
‘Blackpool is so tired and actually becoming run-down,’ Sharr1964 penned.
‘Just unpleasant to look at, it seriously needs an injection of money to bring everywhere up to date.’
The UK’s top 10 most popular attractions
- Royal Albert Dock, Liverpool: 6.3 million visitors per year
- Blackpool Pleasure Beach: 5 million
- Palace Pier, Brighton: 4.6 million
- Alton Towers, Stoke-on-Trent: 2.3 million
- National Museum of Scotland, Edinburgh: 2 million
- Chester Zoo: 1.8 million
- Windsor Castle: 1.5 million
- Edinburgh Castle: 1.4 million
- Roman Baths, Bath: 1.3 million
- Stonehenge, Wiltshire: 970,000.
The news comes after Blackpool was also dubbed the friendliest town in the UK , which is also likely to be a big plus for tourists.
Despite it’s ‘marmite’ reputation, the town scored highly for life satisfaction, hospitality, and personal life satisfaction of residents, in a ranking by LNER.
Elsewhere on the list of most popular UK tourist attractions, the Royal Albert Dock in Liverpool claimed the top spot, according to The Great British Attraction Index.

A whopping 6.3 million visitors each year, taking in the museums, including Tate Liverpool and The Beatles Story, as well as wondering around the shops and grabbing a bite to eat at the many restaurants and bars.
Your Weekly Horoscope

What does the week have in store? Your tarot horoscope reading for April 8 to April 14
Further south, another seaside town, Brighton Palace Pier was in third place with 4.6 million visitors each year, whilst Alton Towers ranked fourth with 2.3 million – one that might annoy Thorpe Park fans out there which didn’t place anywhere on the list.
Do you have a story to share?
Get in touch by emailing [email protected] .
MORE : Pilot forced to return to airport after ‘wee from broken toilet flows into cabin’
MORE : For Barcelona without the tourists, try Spain’s ‘sunshine coast’ with flights from £50
MORE : Easter travel chaos for hundreds of Brit tourists with ‘three hour’ airport queues

Get need-to-know travel news, inspiration and advice from Metro every week.
Sign up here....
Privacy Policy
Your name was Oscar, aged 27, very tall and extrovert, and wearing a boxy…
You were tall dark and handsome, wearing a purple jumper, which you took…

Enter your birthday for your free daily horoscope sent straight to your inbox!
Get us in your feed
This diagram shows what happens during a total solar eclipse
- A total solar eclipse will be visible from Texas to Maine on Monday.
- This cosmic event occurs when the Earth, sun, and moon align perfectly.
- One diagram shows how a total solar eclipse works, and why it darkens the sky in the middle of the day.
A total solar eclipse will turn afternoon skies dark from Texas to Maine on Monday.
During the eclipse, the moon will cross between the Earth and the sun, completely blocking out the sun's light. If you're in the moon's shadow, the sky will go dark for about three to four minutes, depending on your location.
It's the climax of a cosmic dance between our planet , the moon, and the sun.
What causes a total solar eclipse
During a total solar eclipse, three key conditions happen at the same time: The moon is in the "new moon" phase; the moon crosses the plane of the Earth's orbit ; and the moon is at its closest point to Earth in its orbit.
When those conditions are just right, the Earth, sun, and moon line up. This diagram shows how that looks:
Then, if you're in the path of totality — which is basically the center of the moon's shadow, called the umbra — the moon appears to obscure the sun.
If you're in the penumbra — the outer region of the moon's shadow — you'll see a partial solar eclipse , where the moon appears to partially overlap the sun.
A total solar eclipse happens somewhere on Earth about every 18 months on average. It's rare for one to occur in any single place, though, because of the complex movements of the Earth and moon.
The moon orbits Earth every 29.5 days, while Earth has its own orbit around the sun. The moon's orbit is tilted about five degrees, which is large enough to keep its shadow off the Earth and the Earth's shadow off the moon most of the time.
There are two points — called nodes — where the moon's orbit crosses the Earth's plane. In the diagram above, the moon is lined up on a node.
Related stories
The moon aligns with the nodes and the sun about twice per year, which is how we get eclipses. A solar eclipse happens when the moon is between the Earth and sun. A lunar eclipse happens when the moon is on the other side of the Earth, farthest from the sun.
What the total solar eclipse will look like
In the path of totality on Monday, where the moon's umbra falls over Earth, the total solar eclipse will have 10 distinct phases , each with different amounts of the sun visible from the ground.
The phenomenon kicks off with what's called first contact, when the moon starts to pass across the sun. After about an hour, the moon will almost completely mask the sun, and you'll start to see a bright light radiate out of the sliver of remaining sun, known as the "diamond ring."
Then the moon will fully eclipse the sun, turning the sky dark in the middle of the day.
During totality only the sun's outermost atmosphere, called the corona, will be visible glowing around the dark disc of the moon.
After that, the moon will continue to travel across the sky to form another crescent. The eclipse ends when the moon ceases to cover the sun.
Types of solar eclipses
There are three types of solar eclipses .
Total solar eclipses, like this one, occur when the moon appears to completely cover the sun. If the moon only somewhat covers the sun, that's a partial eclipse . Many people who are near the path of totality, but not in it, on Monday will see a partial eclipse.
The third type, an annular eclipse , occurs when the moon is too far from Earth to fully block out the sun from our perspective. The outer edge of the sun remains visible as a bright ring around the moon.
A total solar eclipse is considered the most spectacular. Globally, only about a third of all solar eclipses are total.
The next total solar eclipse in the contiguous US will be in 2044.
How to watch the eclipse
If you plan to watch the eclipse, make sure you are wearing ISO-certified eclipse glasses . These are 1,000 times darker than regular sunglasses. Without them, staring at the sun could damage your eyes.
The only safe time to look at the eclipse without glasses is during totality.
Leanna Garfield and Anaele Pelisson contributed to an earlier version of this post .
Watch: Why the sun has two giant holes, and what that means for Earth
- Main content
We, and third parties, use cookies for technical and analytical purposes, for marketing purposes and for integration with social media. For more information, refer to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Consent . By clicking on ‘I agree’, you consent to the use of these cookies.
We, and third parties, use cookies for technical and analytical purposes, for marketing purposes and for integration with social media. Refer to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Consent .
Sign in using your email ID
Don't Have a tourHQ Account?

Please enter your email address below
Already a TourHQ member

Explore the world with tourHQ

- I am a Traveller
- I am a Guide
- I am a Tour Company
- USD US, dollar
- GBP British Pounds
- Space travel

- write a review
Space Travel
License/ certification.

Not licensed/ License details not provided
About company.
Space Travel is DMC, based in Russia, Moscow.
We provide different type of services from booking transfers to building full itinerary for your trip.
TourHQ ID: RU15404
Private Tours Operator in: Moscow
Other Guiding City: Grozny, Urus-Marten, Lake Kezenoyam
Languages spoken by our guides: Arabic, English, German, Russian, Spanish
Review Rating
No review submitted as yet, my tour calendar.
- Subscribe Now (Opens in new window)
Your Air Force
- Pentagon & Congress
- Army Times (Opens in new window)
- Marine Corps Times (Opens in new window)
- Navy Times (Opens in new window)
- Defense News (Opens in new window)
- Flashpoints
- Benefits Guide (Opens in new window)
- Military Pay Center
- Military Retirement
- VA Loan Center (Opens in new window)
- Military Benefits
- Discount Depot
- Military Culture
- Military Fitness
- Gear Scout (Opens in new window)
- Military Movies & Video Games
- Military Sports
- Transition Guide (Opens in new window)
- Military History
- Black Military History (Opens in new window)
- Congressional Veterans Caucus (Opens in new window)
- Military Appreciation Month (Opens in new window)
- Vietnam Vets & Rolling Thunder (Opens in new window)
- Hall of Valor (Opens in new window)
- Service Members of the Year (Opens in new window)
- Create an Obituary (Opens in new window)
- Pay It Forward (Opens in new window)
- Medals & Misfires
- Installation Guide (Opens in new window)
- Battle Bracket
- Task Force Violent
- CFC Givers Guide
- Photo Galleries
- Early Bird Brief
- Long-Term Care Partners
- Navy Federal
- Newsletters (Opens in new window)
- Digital Edition (Opens in new window)
Air Force offers new bonuses to entice troops to move to cold bases
The Air Force is offering airmen and guardians a new incentive to warm them up to the idea of taking on assignments at some of the chilliest bases in the United States: more money.
Effective April 1, airmen and guardians who agree to yearlong tours at one of seven bases where temperatures often drop to -20 degrees or colder are eligible to receive a one-time, lump-sum bonus ranging from $1,000 to $4,000. The incentive pay, available to all regardless of rank or position, runs through Dec. 31, 2026, and is subject to change, according to a March 29 memo .
Air Force again dangles $600,000 in bonuses to keep pilots in uniform
Annual bonus pay programs aim to keep airmen around to blunt the effects of a pilot shortage that has lasted decades..
Eligible locations include Minot and Grand Forks Air Force Bases and Cavalier Space Force Base, North Dakota; Eielson AFB, Clear Space Force Station, and Joint Base Elmendorf-Richardson, Alaska; and Malmstrom AFB, Montana.
The payment is meant to ease the financial burden of buying cold-weather essentials, including clothing and snow tires, and help the Air Force entice personnel to serve in places that can be hard to staff because of their weather.
According to the Air Force, troops at Minot, Grand Forks, Malmstrom, Cavalier and JBER, where temperatures can drop below -29 degrees, may receive $2,000 if they have dependents or $1,000 if they do not. Those at Eielson and Clear, which can reach a teeth-rattling -49 degrees, can nab $2,000 without dependents. Those with dependents at Eielson can earn $4,000; tours at Clear are unaccompanied assignments.
“Airmen and guardians living in extremely cold conditions [face] unique out-of-pocket costs,” said Alex Wagner , assistant secretary of the Air Force for manpower and reserve affairs. “In addition to the assignment and retention benefits of the pay, it also comes down to making sure we do our best to take care of our service members and their families stationed at these critical installations.”
The first bonuses will be paid out July 1.
“We want to ensure airmen, guardians and their families have the resources needed to safely live and work in an extreme cold-weather environment,” Wagner said.
Air Force spokesperson Master Sgt. Deana Heitzman told Air Force Times that the service is also considering cold-weather incentives for foreign assignments as well. Those options are still in the works.
Courtney Mabeus-Brown is the senior reporter at Air Force Times. She is an award-winning journalist who previously covered the military for Navy Times and The Virginian-Pilot in Norfolk, Va., where she first set foot on an aircraft carrier. Her work has also appeared in The New York Times, The Washington Post, Foreign Policy and more.
In Other News
Lawmakers push for cost-of-living boost in veterans benefits next year
Legislation introduced in the senate would guarantee a cost-of-living boost in veterans benefits in 2025..
Military pharmacies resume regular operations after cyberattack
Military pharmacies no longer have to manually process prescriptions following a february cyberattack that disrupted pharmacy operations around the world..
Empty shelves at commissaries? Officials aim to beef up the supply
"what grocery store runs out of potatoes" asked one military wife in south korea..
Defense, VA budget work begins on Capitol Hill as Congress returns
Defense and veterans hearings on capitol hill for the week of april 8, 2024..
US-Chinese military talks resume on safety in the air and at sea
U.s. and chinese defense officials met to discuss unsafe and aggressive ship and aircraft incidents between the two militaries in the pacific..

IMAGES
COMMENTS
An American real estate investor, a Canadian investor, a former Israeli Air Force pilot, and an ex-Space Shuttle pilot will launch on an incredible orbital mission in its Crew Dragon spacecraft ...
Jason Lyon. By Debra Kamin. May 7, 2022. Ilida Alvarez has dreamed of traveling to space since she was a child. But Ms. Alvarez, a legal-mediation firm owner, is afraid of flying, and she isn't ...
The tickets cost $75,000 per person, and you can request info on their website. As of 2019, World View Enterprises suggested they might be focusing less on space tourism and more on research and commercial business, but they're still a contender! 9. Bigelow Aerospace.
Isaacman — who will become the third billionaire to self-fund a trip space in the past three months and the first to buy a trip to orbit on a SpaceX capsule — is billing this mission as one ...
00:00. 09:13. Listen to more stories on hark. Of all the high-flying tourism ventures spawned by space-obsessed billionaires, Virgin Galactic, founded by Richard Branson, offers perhaps the most ...
What is space tourism? Space tourism is human space travel for recreational or leisure purposes. It's divided into different types, including orbital, suborbital, and lunar space tourism. However, there are broader definitions for space tourism.
CNN —. Virgin Galactic — the space tourism company founded by British billionaire Richard Branson — finally launched its first space tourists to the edge of the cosmos, a major step toward ...
Space tourism is human space travel for recreational purposes. There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital, suborbital and lunar space tourism. During the period from 2001 to 2009, seven space tourists made eight space flights aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft to the International Space Station, brokered by Space Adventures in conjunction with Roscosmos and RSC Energia.
5) SpaceX stacks tallest booster ever with Starship. SpaceX's first orbital Starship SN20 is stacked atop its massive Super Heavy Booster 4 for the first time on Aug. 6, 2021 at the company's ...
The US space agency has changed its tune on space tourism since Tito's historical trip, announcing back in 2019 plans to open the ISS to tourists. 2020 is when private spaceflight just got ...
Up to 2009, only 7 people made it into space as tourists, all travelling with the Russian Space Agency, and all paying in excess of USD $20 million. These weren't exactly hop-on hop-off trips either, with the participants undergoing months of training, and many of them actively running their own experiments in space.
Virgin Galactic's VSS Unity, the reusable rocket-powered space plane carrying the company's first crew of tourists to space, successfully launched and landed on Thursday.. The mission, known ...
According to UBS, if even only 5% of the average 150 million passengers that travel on 10 hour or longer flights pay $2,500 per trip, then returns could skyrocket to $20 billion per year in today ...
That includes space-balloon companies Space Perspective and World View, which offer a far more leisurely journey than rocket-powered ascents, gently lifting passengers to high altitudes in a high-tech version of a hot air balloon. Across all suborbital space tourism companies, prices range from approximately $50,000 to $450,000 per seat.
Space tourism, recreational space travel, either on established government-owned vehicles such as the Russian Soyuz and the International Space Station (ISS) or on vehicles fielded by private companies. Space tourism has gained new prominence as more opportunities have become available.
No word on how much it cost them. For $55 million, Axiom Space will send astronauts via a SpaceX rocket to the International Space Station, a laboratory that circles Earth once every 90 minutes ...
1 / 20. Everything you need to know about space tourism ©Shutterstock. Between floating in weightlessness, witnessing 16 sunrises a day and gazing into the infinite void, space travel sure sounds ...
Interstellar Trips offers a unique space tourism experience, partnering with leading companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin to provide access to the final frontier. Join us for an unforgettable journey beyond our planet and discover the wonders of space through our space travel packages.
NASA had asked for proposals of what it called the lunar terrain vehicle, or L.T.V., that could drive at speeds up to 9.3 miles per hour, travel a dozen miles on a single charge and allow ...
Lopez-Alegría, 63, took of four trips to space between 1995 and 2007 during his time with NASA. He left the space agency in 2012, and he joined Axiom a few years later with the aim of going back ...
The pavilion is open Tues-Sun, although tours must be booked in advance Entrance fee: 500-2000 rubles (9$-36$), with a five-percent discount if tickets are purchased online www.marstefo.ru (in ...
The museum was opened in 1981 to celebrate the 20th anniversary of the first manned space flight, completed by Yuri Gagarin. The various displays trace the history of space exploration: the first satellite - Sputnik - launched in 1957; the first dogs in space; the first human flights; and the first spacewalk.
As people around the country await the April 8 total eclipse, conspiracy theories about a Switzerland-based nuclear research facility have some social media users on edge.
Several states are preparing for massive tourism numbers as Americans travel to witness the solar eclipse on Monday. Monday's total solar eclipse will make landfall along Mexico's Pacific coast and cross into Texas and 14 other U.S. states, before exiting over Canada.
Attracting 5 million visitors each year, Blackpool Pleasure Beach is the UK's second most popular tourist attraction outside of London - but it doesn't exactly receive rave reviews. In fact ...
During a total solar eclipse, three key conditions happen at the same time: The moon is in the "new moon" phase; the moon crosses the plane of the Earth's orbit; and the moon is at its closest ...
Space Travel is a local tour operator in Moscow, Grozny, Urus-Marten & Lake Kezenoyam with tours that focus on Eco Tourism, Adventure Sports, Airport Transfer and more! Read about the company's reviews, custom tours and more at tourHQ.com.
According to the Air Force, troops at Minot, Grand Forks, Malmstrom, Cavalier and JBER, where temperatures can drop below -29 degrees, may receive $2,000 if they have dependents or $1,000 if they ...
The 20th Ho Chi Minh City Tourism Festival from 4 to 7 April, at 23/9 Park, District 1, with the theme "20 years of Going Green of Vibrant Touch". The Festival will offer lots of promotional packages with preferential prices up to 50%, along with many attractive gifts and services. Some new tourism products will be introduced at the Festival as: Ho Chi Minh City - the emotional journeys; art ...