Tourism – Definition, Types & Forms, History & Importance of Tourism
Tourism is one of the world’s fastest-growing industries and a major foreign exchange and employment generation for many countries. It is one of the most remarkable economic and social phenomena.
The word ‘tour’ is derived from the Latin word tornus, meaning ‘a tool for making a circle.’ Tourism may be defined as the movement of people from their usual place of residence to another place ( with the intention to return) for a minimum period of twenty-four hours to a maximum of six months for the sole purpose of leisure and pleasure.
According to WTO (1993), ” Tourism encompasses the activities of persons traveling and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business, and other purposes.”
The Rome conference on tourism in 1963 defined tourism as ‘ a visit to a country other than one’s own or where one usually resides and works. This definition, however, did not take into account domestic tourism, which has become a vital money-spinner and job generator for the hospitality industry.
The UNWTO defines tourists as ‘ people who travel to and stay in place outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes not related to the exercise of an activity remunerated from within the place visited.
According to the Tourism Society of Britain ,” tourism is the temporary short-period movement of people to destination outside the places where they usually live, work; and activities during their stay at these destinations.” This definition includes the movement of people for all purposes.
The development of technology and transportation infrastructure, such as jumbos jets, low-cost airlines, and more accessible airports, have made tourism affordable and convenient. There have been changes in lifestyle – for example, now retiree-age people sustain tourism around the year. The sale of tourism products on the internet, besides the aggressive marketing of the tour operators and travel agencies , has also contributed to the growth of tourism.
27 September is celebrated as world tourism every year. This date was chosen as on that day in 1970, the Statutes of UNWTO were adopted. The purpose of this day is to raise awareness of the role of tourism within the international community.

History of Travel and Tourism
Inbound tourism, outbound tourism, domestic tourism, forms of tourism, classification of tourism, nature of tourism, importance of tourism, economic impacts, social impacts, cultural impacts, environmental impact, industries related to tourism, tourism products.
Travel is as old as mankind on earth. At the beginning of his existence, man roamed about the planet’s surface in search of food, shelter, security, and better habitat. However, with time, such movements were transformed into wanderlust.
About five thousand years ago, climate changes, dwindling food and shelter conditions hostile invaders made the people leave their homes to seek refuge elsewhere like the Aryans left their homes in Central Asia due to climate changes. Perhaps, this leads to the development of commerce, trade, and industry.
Religion, education, and cultural movement began during the Hindu and Chinese civilizations. Christian missionaries, Buddhist monks, and others traveled far and wide carrying religious messages and returned with fantastic images and opinions about alien people.
For centuries movement of people continued to grow due to the efficiency of transport and the assistance and safety with which the people could travel. By the end of the 15th century, Italy had become Europe’s intellectual and cultural center. It represented the classical heritage both for the intelligentsia and the aristocracy.
During the 16th century, travel came to be considered an essential part of the education of every young Englishman. Travel thus became a means of self-development and education in its broadest sense. The educational travel was known as the ‘ Grand Tour .’
The industrial revolution brought about significant changes in the pattern and structure of British society. Thus, the economy of Britain was greatly responsible for the beginning of modern tourism. It also created a large and prosperous middle class. Because of remarkable improvement in transportation systems in the latter half of the 18th century and the first quarter of the 19th century, an increasing number of people began to travel for pleasure.
Travel was inspired initially by the need for survival (food, shelter, and security), the desire to expand trade, and the quest to conquer. As the transportation system improved, the curiosity for transforming the vast and virgin world into a close neighborhood created a new industry, i.e., Travel and Tourism .
However, the developments of rails, roads, steamships, automobiles, and airplanes helped to spread technology across the globe. Earlier travel was a privilege only for wealthy people, but with the industrial revolution, the scenario altogether changed. Transportation, as well as accommodation, became affordable to middle and working-class citizens.
Essentially, with the development of jet travel, communication, new technology, tourism, and travel became the world’s largest and fastest-growing industry.
Travel and tourism have recently emerged as a dominant economic force on the global scene, accounting for more than 12% of total world trade and growing at 8 percent annually.
Types of Tourism
Tourism has two types and many forms based on the purpose of visit and alternative forms of tourism. Tourism can be categorized as international and domestic tourism .
Tourism has two types and various forms. Based on the movement of people, tourism is categorized into two kinds. These are the following:
International Tourism
When people visit a foreign country, it is referred to as International Tourism . To travel to a foreign country, one needs a valid passport, visa, health documents, foreign exchange, etc.
International tourism is divided into two types; Inbound Tourism & Outbound Tourism.
This refers to tourists of outside origin entering a particular country. Traveling outside their host/native country to another country is called inbound tourism for the country where they are traveling. For example, when a tourist of Indian origin travels to Japan, it is Inbound tourism for Japan because foreign tourists come to Japan.
This refers to tourists traveling from the country of their origin to another country. When tourists travel to a foreign region, it is outbound tourism for their own country because they are going outside their country. For example, when a tourist from India travels to Japan, it is outbound tourism for India and Inbound tourism for Japan.
The tourism activity of the people within their own country is known as domestic tourism . Traveling within the same country is easier because it does not require formal travel documents and tedious formalities like compulsory health checks and foreign exchange. A traveler generally does not face many language problems or currency exchange issues in domestic tourism.
Tourism has various forms based on the purpose of the visit and alternative forms. These are further divided into many types according to their nature. Forms of tourism are the following:
Some most basic forms of tourism are the following:
- Adventure Tourism
- Atomic Tourism
- Bicycle Tours
- Beach Tourism
- Cultural Tourism
- Industrial Tourism
- Medical Tourism
- Religious Tourism
- Rural Tourism
- Sex Tourism
- Space Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Sustainable Tourism
- Virtual Tourism
- War Tourism
- Wildlife Tourism
Tourism can be classified into six distinct categories according to the purpose of travel. These are the following:
1) Recreational : Recreational or leisure tourism takes a person away from the humdrum of everyday life. In this case, people spend their leisure time in the hills, sea beaches, etc.
2) Cultural tourism satisfies cultural and intellectual curiosity and involves visits to ancient monuments, places of historical or religious importance, etc.
3) Sports/Adventure : Trips taken by people with a view to playing golf, skiing and hiking, fall within this category.
4) Health : Under this category, people travel for medical, treatment or visit places where there are curative possibilities, for example, hot springs, spa yoga, etc.
5) Convention Tourism : It is becoming an increasingly important component of travel. People travel within a country or overseas to attend conventions relating to their business, profession, or interest.
6) Incentive Tourism : Holiday trips are offered as incentives by major companies to dealers and salesmen who achieve high targets in sales. This is a new and expanding phenomenon in tourism, These are in lieu of cash incentives or gifts, Today incentive tourism is a 3 billion dollar business in the USA alone.
Tourism as a socio-economic phenomenon comprises the activities and experiences of tourists and visitors away from their home environment and are serviced by the travel and tourism industry and host destination. The sum total of this activity experience and services can be seen as a tourism product.
The tourism system can be described in terms of supply and demand. Tourism planning should strive for a balance between demands and supply. This requires an understanding not only of market characteristics and trends but also of the planning process to meet the market needs.
Often tourists from core generating markets are identified as the demand side; the supply side includes all facilities, programs, attractions, and land uses designed and managed for the visitors. These supply-side factors may be under the control of private enterprises, non-profit organizations, and the government. New and innovative forms of partnerships are also evolving to ensure the sustainable development and management of tourism-related resources.
The supply and demand side can be seen to be linked by flows of resources such as capital, labor, goods, and tourist expenditures into the destination, and flows of marketing, promotion, tourist artifacts, and experiences from the destination back into the tourist generating region.
In addition, some tourist expenditures may leak back into the visitors generating areas through repatriation of profits of foreign tourism investors and payment for improved goods and services provided to tourists at the destination. Transportation provides an important linkage both to and from the destination.
For planning purposes, the major components that comprise the supply side are:
- Various modes of transportation and other tourism-related infrastructure.
- Tourist information.
- Marketing and promotion.
- The community of communities within the visitor’s destination area.
- The political and institutional frameworks for enabling tourism.
The tourism system is both dynamic and complex due to many factors linked to it and because of the existence of many sectors contributing to its success. These factors and sectors are linked to the provision of the tourist experience and the generation of tourism revenue and markets .
The dynamic nature of the tourism system makes it imperative to scan the external and internal environment of the destinations on a regular basis so as to make changes when necessary to ensure a healthy and viable tourism industry.
Thus, it is now an accepted fact that tourism development can no longer work in isolation of the environment and the local communities, nor can it ignore the social and cultural consequences of tourism.
Tourism and hospitality , which are inextricably linked to each other, are among the major revenue-earning enterprises in the world. They happen to be among the top employers too. There has been an upmarket trend in tourism over the last few decades as travel has become quite common. People travel for business, vacation, pleasure, adventure, or even medical treatments.
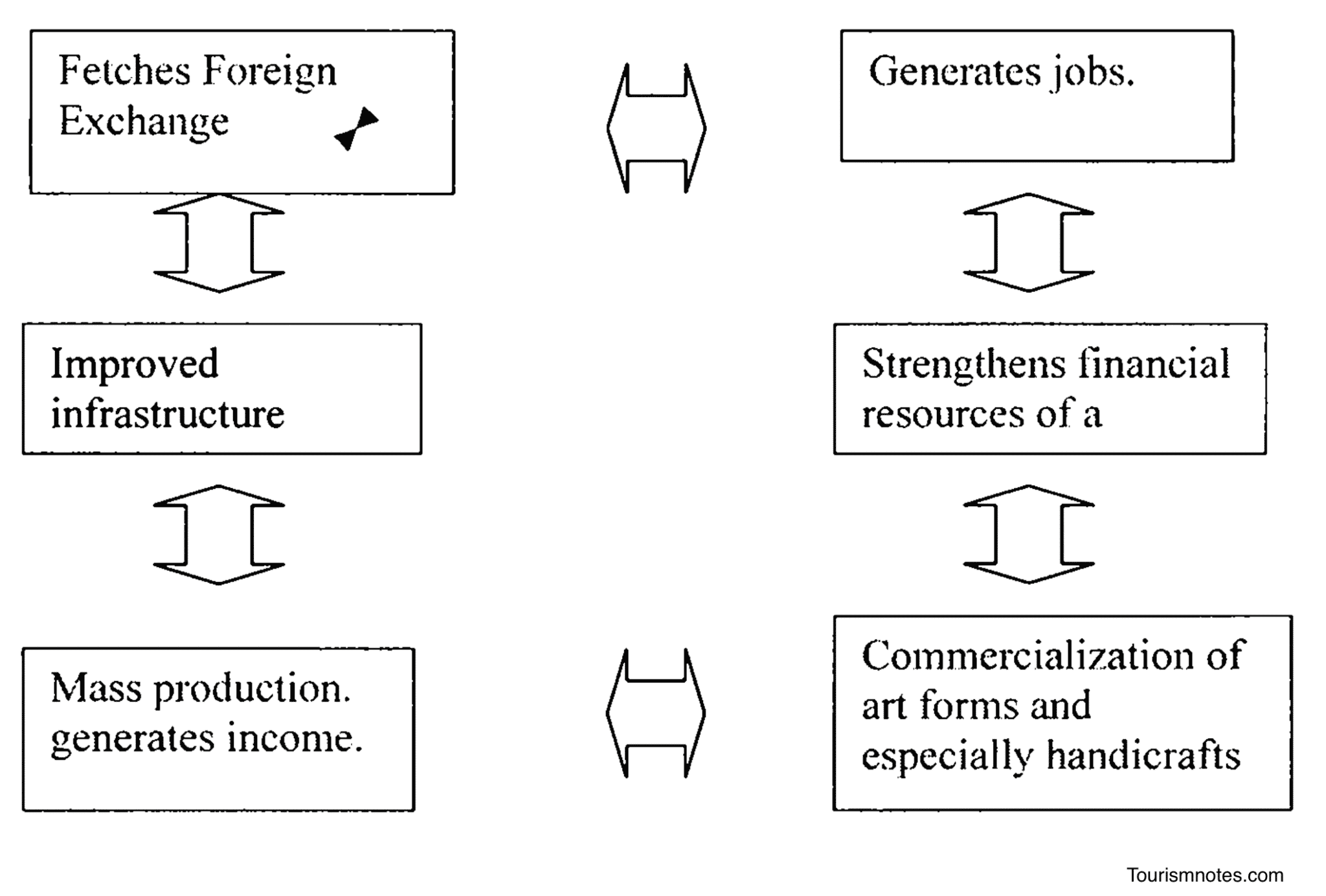
Tourism constitutes an important industry today. It has opened up new vistas for the play of economic emancipation. It provides a very potent contribution by strengthening and developing the financial resources of a country. Moreover, it is a process in which mutual material and mental benefits occur. Furthermore,
- Tourism fetches foreign exchange in the form of invisible exports, which results in the manifold progress of the nation.
- Tourism generates jobs. These employments are the main contribution of tourism to generating national income. But one should remember that employment in the tourism industry is often seasonal.
- Tourism often leads to the commercialization of art forms and especially handicrafts. Art items with cultural or religious meaning are sought by tourists as souvenirs. As more and more tourists visit a destination, souvenir production has increased, often leading to mass production. This production also generates income.
With several business-related activities associated with tourism, the industry has a tremendous potential to generate employment as well as earn foreign exchange. Many countries, such as Mauritius, Malaysia, Singapore, Fiji, and the Caribbean, whose economies are primarily driven by tourism. Tourism can contribute to the economic growth of a country in the followings ways:
Employment Generation
It creates a large number of jobs among direct services providers (such as hotels , restaurants, travel agencies , tour operators , guide and tour escorts, etc.) and among indirect services providers (such as suppliers to the hotels and restaurants, supplementary accommodation, etc.)
Infrastructure Development
Tourism spurs infrastructure development. In order to become an important commercial or pleasure destination, any location would require all the necessary infrastructure, like good connectivity via rail, road, and air transport , adequate accommodation, restaurants, a well-developed telecommunication network, and, medical facilities, among others.
Foreign Exchange
The people who travel to other countries spend a large amount of money on accommodation, transportation, sightseeing, shopping, etc. Thus, an inbound tourist is an important source of foreign exchange for any country.
The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) predict in 1997 that the twenty-first-century economy would be dominated by three industries: telecommunications, information technology, and tourism. The travel and tourism industry has grown by 500 percent in the last 25 years.
Now withstanding this bright outlook and prospects, the tourism and hospitality industries are very vulnerable to the fluctuations of national economies and happenings in the world, especially terrorist attacks that have at times dealt severe blows to business.
In recent years, there have been a few setbacks in tourism, such as the terrorist siege of the Taj and Oberoi in Mumbai, India (26 November 2008); the attack on the World Trade Centre in the United States of America (11 September 2001); bombing in a hotel on the Indonesian island of Bali (12 October 2002); tsunami in Southeast Asia and South Asia on 26 December 2004, in which thousands of the lives where lost and consequently tourism was hit. Nonetheless, the sector is now getting back to business.
Impacts of Tourism
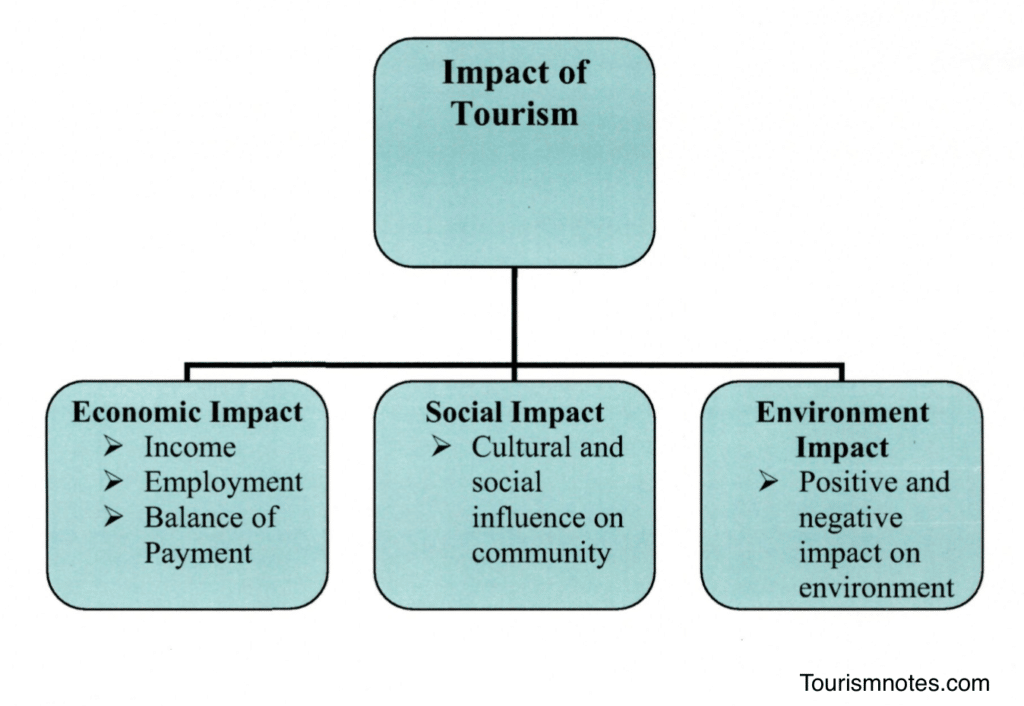
Tourism is a multi-dimensional activity. The scope of tourism activities is so wide and varied that it cannot be restricted to any particular field of activity. Tourism has ramifications in almost all sectors and is influenced by the performance of each of these sectors directly or indirectly. Tourism in any country can be an apt reflection of the nation’s economic and social endowment apart from its natural wealth.
Tourism has vast potential to bring about changes in the country’s economic, environmental, societal, and cultural edifice. Tourism has two basics: the supply of facilities and the demand for participation. The twin market forces of supply and demand interact to produce tourism patterns. These patterns are associated with economic, social, cultural, environmental, and ecological impacts.
Establishing or developing a tourism industry involves expenditure, gains, costs, and benefits. If these impacts are considered from the outset of planning, strengths and opportunities can be maximized while weaknesses and threats can be minimized.
Each destination will be different in terms of tourism characteristics . The cost and benefits of tourism will vary in each destination and can change over time, depending on tourism and other activities in a destination’s local and regional context.
Tourism activities impact the economy of the country as well as the local economy of the destination.
Economics Benefits
- Tourism generates local employment, directly in the tourism sector and in the support and resource management sectors.
- Tourism stimulates profitable domestic industries, hotels and other lodging facilities, restaurants and food services, transportation systems, handicrafts, and guide services.
- Tourism generates foreign exchange for the country and injects capital and new money into the local economy.
- Tourism helps to diversify the local economy.
- Improved tourism infrastructure.
- Increase tax revenues from tourism.
Economic Costs
- Higher demand created by tourism activity may increase the price of land, housing, and a range of commodities necessary for daily life.
- Demands for health services provision and police service increase during the tourist seasons at the expense of the local tax base.
Tourism also affects the society of the destination in good as well as bad ways. It benefits and costs the local communities.
Social Benefits
- The quality of a community can be enhanced by economic diversification through tourism.
- Recreational and cultural facilities created for tourism can be used by local communities as well as domestic/international visitors.
- Public space may be developed and enhanced through tourism activity.
- Tourism Enhances the local community’s esteem and provides an opportunity for greater understanding and communication among people of diverse backgrounds.
Social Costs
- Rapid tourism growth can result in the inability of local amenities and institutions to meet service demands.
- Without proper planning and management, litter, vandalism, and crime often accompany tourism development.
- Tourism can bring overcrowding and traffic congestion.
- Visitors bring with them material wealth and apparent freedom. The youths of the host community are particularly susceptible to the economic expectations these tourists bring which can result in complete disruption of traditional community ways of life.
- The community structure may change, e.g. community bonds, demographics, and institutions.
- The authenticity of the social and cultural environment can be changed to meet tourism demands.
Tourism activities also affect the culture of the host country. There are many positive and negative cultural impacts of tourism.
Cultural Benefits
- Tourism can enhance local cultural awareness.
- Tourism can generate revenue to help pay for the preservation of archaeological sites, historic buildings, and districts.
- Despite criticism about the alteration of cultures to unacceptable levels, the sharing of cultural knowledge and experience can be beneficial for hosts and guests of tourism destinations and can result in the revival of local traditions and crafts.
Cultural Costs
- Youth in the community begin to emulate the speech and attire of tourists.
- Historic sites can be damaged through tourism development and pressures.
- There can be long-term damage to cultural traditions and the erosion of cultural values, resulting in cultural change beyond a level acceptable to the host destination.
Tourism impacts the environment in positive as well as negative ways. These impacts are following below.
Environmental Benefits
- Parks and nature preserves may be created and ecological preservation supported as a necessity for nature-based tourism.
- Improved waste management can be achieved.
- Increased awareness and concern for the environment can result from nature-based tourism activities and development.
Environmental Costs
- A negative change in the physical integrity of the area.
- Rapid development, over-development, and overcrowding can forever change the physical environment and ecosystems of an area.
- Degradation of parks and preserves.
Over the years, tourism has become a popular global activity. Depending upon the nature and purpose of their travel, tourists, need and demand certain facilities and services. This has given rise to a wide range of commercial activities that have acquired industry proportions. Thus travel and tourism nowadays represent a broad range of related industries.
Hotels are a commercial establishment that provides accommodation, meals, and other guest services. In the travel and tourism industry, the hotel industry plays a very significant role, as all tourists need a place to stay at their destinations, and require many more services and facilities to suit their specific needs and tastes.
Restaurants
Restaurants are retail establishments that serve prepared food and beverages to customers. In the travel and tourism industry, restaurants and other food and beverage outlets are very important as tourists like to experiment with the local cuisines of the places they are visiting.
Retail and Shopping
The retail industry is very important as tourists shop for their day-to-day necessities as well as look for mementos and souvenirs. In recent years, some cities in the world have been promoted as shopping destinations to attract people with a penchant for shopping by offering various products, such as garments, electronic goods, jewelry, and antiques. New York, Paris, London, and Milan in Italy are famous as fashion havens of the world.
Transportation
It is the movement of people and goods from one place to another. A well-developed transport industry, as well as infrastructure, is integral to the success of any travel and tourism enterprise.
Travel Agencies
A travel agency is a retailing business that sells travel-related products and services, particularly package tours, to customers on the behalf of suppliers such as airlines, car rentals, cruise liners, hotels, railways, and sightseeing.
Travel agencies play a very important role as they plan out the itinerary of their clients and make the necessary arrangements for their travel, stay, and sightseeing, besides facilitating their passport, visa, etc.
Tour Operators
A tour operator assembles the various elements of a tour. It typically combines tour and travel components to create a holiday. Tour operators play an important role in the travel and tourism industry.
Tourist Destinations
A tourist attraction is a place of interest for tourists, typically for its inherent or exhibited cultural value, historical significance, nature or building beauty or amusement opportunities. These are the basic fundamentals of the tourism industry.
Cultural Industries
Cultural or creative industries are responsible for the creation, production, and distribution of goods and services that are cultural in nature and usually protected by intellectual property rights. As tourists like to visit places of cultural significance and soak in the culture of the area, the cultural industry is very important to travel and tourism.
Leisure, Recreation, and Sport
Leisure or free time is a period of time spent out of work and essential domestic activity. Recreation or fun is spending time in a manner designed for therapeutic refreshment of the body or mind. While leisure is more like a form of entertainment or rest, recreation requires active participation in a refreshing and diverting manner.
As people in the world’s wealthier regions lead an increasingly sedentary lifestyle, the need for recreation has increased. These play a significant role in the travel and tourism sector.
A tourism/tourist product can be defined as the sum of the physical and psychological satisfaction it provides to tourists, during their ‘traveling and sojourn’ en route at the destinations.
Since the travel and tourism industry is an agglomeration of too many sectors that promote travel-related services. These sectors are referred to as travel vendors and their services and goods are called ‘travel products’. A tourism product includes five main components such as physical plant, services, hospitality, freedom of choice, and a sense of involvement.
Thus, whatever the natural and man-made resources and services brought about the consumption of tourists are called tourism products .
Charecterstatics Of Tourism Products
By now, you must have understood what a tourism product is. Now let us look at some of its characteristics:-
1) Intangible : Tourism is an intangible product means tourism is such a kind of product that can not be touched or seen and there is no transfer of ownership, But the facilities are available for a specified time and for a specified use. For e.g. a room in the hotel is available for a specified time.
2) Psychological : The main motive to purchase a tourism products is to satisfy the psychological need after using the product, by getting an experience while interacting with a new environment. And experiences also motivate others to purchase that product.
3) Highly Perishable : Tourism product is highly perishable in nature means one can not store the product for a long time. Production and consumption take place while a tourist is available. If the product remains unused, the chances are lost i.e. if tourists do not purchase it.
A travel agent or tour operator who sells a tourism product cannot store it. Production can only take place if the customer is actually present. And once consumption begins, it cannot be stopped, interrupted, or modified. If the product remains unused, the chances are lost i.e. if tourists do not visit a particular place, the opportunity at that time is lost. It is due to tourism reason that heavy discount is offered by hotels and transport-generating organizations during the offseason.
4) Composite Product : Tourist product is a combination of different products. It has not a single entity in itself. In the experience of a visit to a particular place, various service providers contribute like transportation The tourist product cannot be provided by a single enterprise, unlike a manufactured product.
The tourist product covers the complete experience of a visit to a particular place. And many providers contribute to the tourism experience. For instance, the airline supplies seats, a hotel provides rooms and restaurants, travel agents make bookings for stay and sightseeing, etc.
5) Unstable Demand : Tourism demand is influenced by seasonal, economic political, and other factors. There are certain times of the year that see greater demand than others. At these times there is a greater strain on services like hotel bookings, employment, the transport system, etc.
- English (CA)
- Deutsch (DE)
- Deutsch (CH)
8 types of tourism that you need to know
The three tourism categories, domestic tourism, inbound tourism, outbound tourism, the 8 types of tourism according to motivation, business tourism.
- Meet with business partners or prospects
- Attend an event, conference, or trade show
- Visit another office location of the same company
?)
See how to save money on business travel
Leisure tourism, shopping tourism, cultural tourism, sports tourism, rural tourism, mountain tourism, urban tourism, many people travel – but for completely different reasons.
?)
Make business travel simpler. Forever.
- See our platform in action . Trusted by thousands of companies worldwide, TravelPerk makes business travel simpler to manage with more flexibility, full control of spending with easy reporting, and options to offset your carbon footprint.
- Find hundreds of resources on all things business travel, from tips on traveling more sustainably, to advice on setting up a business travel policy, and managing your expenses. Our latest e-books and blog posts have you covered.
- Never miss another update. Stay in touch with us on social for the latest product releases, upcoming events, and articles fresh off the press.
?)
5 inefficient processes affecting your business and how to fix them
?)
Duty of care in the workplace: everything you need to know
?)
CEO Roles and Responsibilities: conquer your role as CEO
- Business Travel Management
- Offset Carbon Footprint
- Flexible travel
- Travelperk Sustainability Policy
- Corporate Travel Resources
- Corporate Travel Glossary
- For Travel Managers
- For Finance Teams
- For Travelers
- Thoughts from TravelPerk
- Careers Hiring
- User Reviews
- Integrations
- Privacy Center
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Modern Slavery Act | Statement
- Supplier Code of Conduct
Travel With - The Holiday Story
18 Different Types of Tourism | Globally Accepted
Last few years, tourists and their demands have frequently been changing. Also, the tourism industry is changing based on needs. This article elaborates on different types of tourism, tourists, planning, activities, products, travel , etc. It helps your travel planning as well.
Along with recreation, tourism has become one of the growing industries, and it’s the source of income for many people.
“Life is all about adventure, so pack your bags and start the tour.”

Different Types of Tourism
What is tourism.

Tourism is a process of spending time away from daily routine or home to pursue recreation, relaxation, and pleasure while using the commercial provision of services.
Tourism in a country has many benefits: it creates employment, boosts revenue, develops infrastructure, helps in cultural exchange, etc. Travel duration under tourism must be less than 12 months (a consecutive year).
So, What comes first to mind when we hear the word Tourism?
The most common thought is to pack the rucksack and travel away from day-to-day life. That means the movement of people from their usual residence to another place.
Suppose your friend’s aim for the tour might differ from yours. For example, you may travel for recreation, but he may go for business.
Classification of Tourism
According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism involves the movement of people in the country’s natural environment or outside the country for personal or other purposes. These different purposes classified the tourism industry in many ways.
This article lists the main tourism classifications: Domestic tourism, International tourism, Business tourism, Adventure tourism, Medical tourism, Educational tourism, etc.
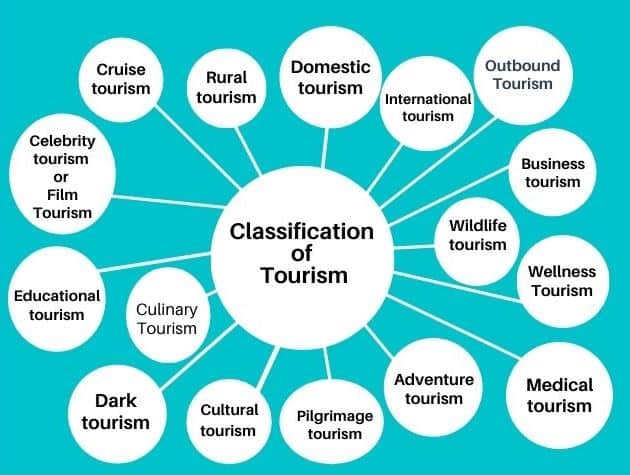

Importance of Tourism – Why is tourism important?
Tourism has a direct impact on any country’s economy. The role of tourism in economic development is important. A vast amount of job possibilities can develop through public relations in tourism. Knowing another state/country’s taste culture is a great filling from a traveler’s perspective.
Mainly how many types of tourism are there
Mainly three types of tourism are found in any country. The classes are domestic tourism, International tourism, and outbound tourism. But nowadays, many types of tourism newly evolved.
18 Different Types of Tourism
The various types of tourism are developed nowadays and become popular; they are:-
- Domestic tourism
- International tourism
- Outbound tourism
- Business tourism
- Adventure tourism
- Wildlife tourism
- Medical tourism
- Wellness tourism
- Pilgrimage and spiritual tourism
- Cultural tourism
- Dark tourism
- Culinary tourism
- Celebrity tourism or Film tourism
- Educational tourism
- Cruise tourism
- Rural tourism
- Beach tourism
- Space tourism
Let’s discuss how many flavors and categories of tourism can be found in any country and accepted globally.
1. Domestic Tourism
Domestic tourism involves traveling in one’s own country, and tourists don’t cross international borders or entry points. Domestic tourism is used to minimize poverty, enhance infrastructure, and boost the economy’s growth and generation of employment.
2. International Tourism
Travel outside your country needs a visa and passport; called International tourism. For example, if you want to explore The UK from Sri Lanka, you need documents to enter another country.
Read How to Listen to Music on a Plane
3. Outbound Tourism
This tourism defines a tourist traveling for a holiday to a different country, like your residents in Bali and traveling to Barcelona . It is an example of outbound Tourism.
4. Business Tourism
This tourist travels to meetings, officially gets together for conferences, etc.
Business tourism plays a vital role in the tourism sector. Sometimes, people stay out of their typical environment for more than a year for business purposes and spend their vacations there.
General activities related to business tourism include attending meetings, officially getting together, conferences, seminars, visiting exhibitions and trade fairs, etc. This tourism levels up the purchasing power.

5. Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism is a person’s travel from one place to another to seek fresh adventures and activities. This form of tourism is most famous among young tourists and people who like to explore remote areas. It encourages us to leave our comfort zone by undertaking activities like hiking , rafting, climbing, diving, etc.
Adventure tourism is increasing day by day. You could also try whitewater rafting, the Ladakh tour, the Kedarnath tour, Port Blair, and Andaman and Nicobar tour for the adventure.

6. Wildlife Tourism
Wildlife tourism is people’s travel to different places to observe and interact with wildlife, flora, and fauna in their natural habitat. Safaris, visiting the animal rescue center, swimming with dolphins, etc., are examples of wildlife tourism.
Because of exotic species of wildlife, this tourism became recognized. The Sariska Wildlife or Hyde Park Sanctuary , Keoladeo Gana National Park, and Corbett National Park are renowned for wildlife tourism. The Great Barrier Reef is also famous in Australia.

7. Medical Tourism
Many people travel for treatment, and several medical institutes cure foreign patients. Thailand has recorded 6000,000 new patients every year. Malaysia also treated over 100,00 tourists in 2005. 45% of foreign tourists come to Chennai for medical treatment.

8. Wellness Tourism
Wellness tourism has been a significant part of tourism since ancient times. This tourism mainly attracts those tourists who want to regain their health. Wellness tourism will help you to get rid of mental and health stress.
Tourists recover their health issues through physical, spiritual, or psychological activities. All around the world, plenty of destinations are popular for improving health.
Examples include Mexico Temazcal Beach Resort Spa, Caribbean wellness cruise, California weight loss and detox retreats, Colorado Hiking and Mountain Yoga retreat, and China Hot Spring Resorts TCM.
Ayurveda, Yoga , Meditation, Panchakarma, and Rejuvenation Therapy are the oldest Therapy of treatments to improve health and the best way to develop wellness tourism.

9. Pilgrimage and Spiritual Tourism
Pilgrimage or spiritual tourism is when a person journeys to other places for spiritual or religious reasons.
Spiritual tourism helps support local cultural activities and handicrafts, generating employment and revenue. Trips to Jerusalem, Bodh Gaya , Hajj, etc., are pilgrimage or spiritual tourism.
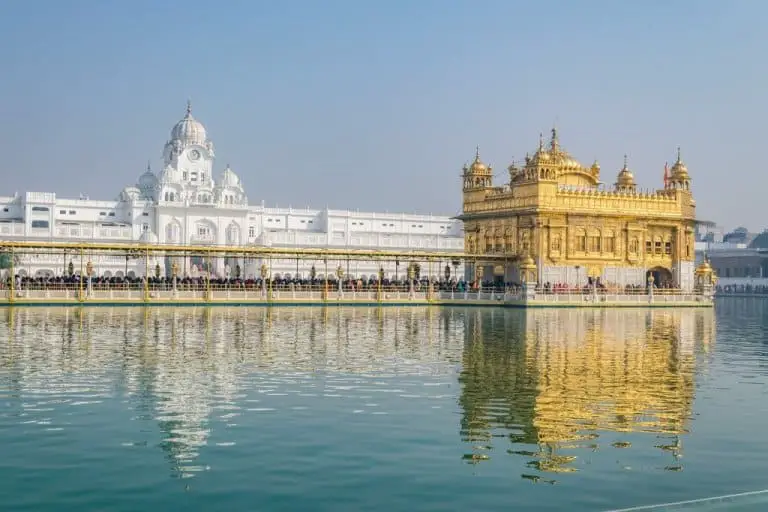
This tour has been famous for ages, but It’s popular among older people mainly. Vaishno Devi, Golden Temple, Char Dham, and Mathura Vrindavan are some places famous for Pilgrimage tours.
10. Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism is a person’s journey to learn and participate in local festivals, rituals, and cultural activities of other places. It’s more than a commercial activity.
This form of tourism helps spread aboriginal communities’ culture, traditions, diversity, and richness to the rest of the world.
Visit the historical sites and the artistic features of that country too. Famous cultural tourism places are:-
- India – Durga puja in Kolkata , Temples at Banaras, Jaipur, known as the pink city Palace in Rajasthan. Forts and monuments in Delhi, Agra, UP.
- UK – Tower of London, The British Museum, Big Ben, London Durga puja , etc.
- Kenya – The main attraction is the dance of the Maasai tribe.
- Morocco – The main attractions are the Olive Festival and Honey Festival.
- Jordan – The main attraction- is Jerash, famous for Roman architecture Petra, the red-rose curved rock city and one of the seven world wonders, and Shoubak with its Montreal Crusader Castle.
- Greece – The main attraction- is the Lion Gate of Mycenae.
- Turkey – the main attraction- Sultan Ahmed. Mosque, House of the Virgin Mary.
- Vietnam – The main attraction- is Sapa Market.
- Ireland tour – Cliffs of Moher, Dublin, Killarney National Park, etc.

11. Dark Tourism
Dark tourism, Black tourism, or grief tourism are related to people’s travel to historical places involved with tragedy and death. Since 2016, dark tourism has significantly increased (over 1200%). Chornobyl, cemeteries, Ground Zero, historical museums, and Auschwitz are popular dark tourism destinations.
It is referred to as mourning tourism. Dark tourism involves visiting those places and sites that have witnessed the greatest tragedies in history. Besides this history of human suffering and bloodshed, these locations are famous for their historical value.
So, those sites that carry potent pesticides have become popular tourist destinations and attract many tourists yearly.
Like Famous sites In Japan, Hiroshima & Nagasaki bombing locations, Ground Zero, New York, USA . The War Remnants Museum, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; Auschwitz concentration camp, Auschwitz, Germany; Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, etc.

12. Culinary Tourism
Culinary or food tourism involves tasting and experiencing local and traditional food in a specific country, region, city/town/village.
It is significant that besides accommodation and infrastructure. Here, food is one of the prime components. Therefore, lots of tours are organized here to experience the culinary culture.
Today, with the overall growth of this sector, tourism has expanded and developed to the next level.
Every year, Different states of India organize food festivals at different times in different states. Thousands of people from abroad join this festival to enjoy traditional food.
Everyone knows India is called “The land of spices.” And every state has unique kinds of food culture. Today, it is a significant part of tourism.
Culinary Tourism includes where people visit certain regions like California, Napa Valley, Catalonia, USA, and Spain) to enjoy foreign wines.
Famous Destinations : London, France, Beijing, Mexico, Italy, etc.

13. Celebrity Tourism or Film Tourism
Celebrities are the primary source of attraction for celebrity or film tourism. In this form of tourism, tourists visit places where a celebrity currently lives or has lived. Management organizations use celebrity tourism to promote a place or attraction.
Although no celebrities are present, only you can see the entire studio. Many Destination Management organizations (DMOs) use celebrity tourism to promote destinations as an attraction.
Popular celebrity tourism destinations are – Hollywood, Harry Potter Studios, Ramoji Film City India, Cannes Film Festival, Hong Kong, and Madame Tussauds.

14. Educational Tourism
Educational tourism is a new pattern of tourism that comprises learning new things. It’s the journey a person takes to leave his hometown or country for educational or learning purposes. Educational tourism is famous in Japan, Australia, the UK, etc.
An educational tourist can be away from his hometown for many days. Education and learning are the key reasons for their travels, and it is learning knowledge from historical places, cultural and social events, and understanding a language.
It’s used as a tool to complement education by gathering travel experience. Many educational institutes combine these trends in primary schools and are compulsory in higher education.
15. Cruise Tourism
Holidays based partially or wholly on a cruise ship are considered cruise tourism. It provides tourists with a multi-centered holiday experience. Cruise ships (like small yachts, big ships, etc.) take people on a tour of oceans, fjords, or rivers.
Throughout their trip, tourists can enjoy time at various destinations. The Mediterranean, Caribbean, Arctic, Antarctica, etc., are famous destinations. It’s the newest and fastest-growing part of the world’s tourism industry.
The world’s famous coastline and inland waterways have the potential to develop cruise and houseboat tourism like Quark Expeditions, OZ Cruising, and A-ROSA River Cruises.
India has many types of tourist cruises. Soon, India will be including Ocean Cruise, River Cruises, and Lake Cruises.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by ⚓️ Iglu Cruise (@iglucruise)
16. Rural Tourism
There are many forms of tourism, and It’s divided into many parts. In this category, a tourist spends leisure time in rural areas or villages. Visitors can make a plan to visit the rural area for some days or a couple of months.
Especially Solo travelers can visit those places to enjoy their lonely time. They join all the local activities that happen in this village.
Rural tourism is included in a ‘country holiday’ where tourists spend much of their leisure time. Thus, they taste the recreational activities in the rural environment.
Like Farming in Rural Punjab, The Spiti Valley Rural Tourism, Sundarban and Jodhpur Village Life, Bhubandanga West Bengal, and Community Tourism in Kutch.

17. Beach Tourism
Beach tourism is how a beach plays a major element in the holiday, and it’s the most modern form and the staple of tourism.
In beach tourism, tourists travel to a beach for leisure, recreation, or business purposes. People who like the clear blue sight of a beach undertake this journey.
Popular Beach Destinations: The Maldives, Seychelles, Turks And Caicos, French Polynesia, Africa , Queensland, Australia, Philippines, Thailand, Bali In Indonesia, Lakshadweep, Goa, Puri, etc.
Why is Beach Tourism important?
- Beach tourism has brought about many economic benefits.
- It has led to the building of many attractions, resorts, etc.
- Beach resorts help in meeting the increase in intra-regional demand and domestic demand.
- This type of tourism creates numerous employment opportunities.

Negative Impacts of Beach Tourism
- It leads to the wastage of a lot of resources and space.
- Beach tourism pollutes water and environmental resources.
- Building new berths, marinas, etc., hurts coastal and marine life.
18. Space Tourism
We have seen significant changes in the aviation industry in the last 100 years. What was once used for warfare and cargo transport is now used for traveling.
Human development has now broken all bounds to take this journey to the vast emptiness of space.
Russia has been the pioneer in this field. Soyuz spacecraft conducted its first space trip with American businessman Dennis Tito in April 2001.
It was a government spacecraft that conducted seven space expeditions within the next six years. This surge in public interest led other organizations worldwide to dive into this area.

There are different types of space tourism
Orbital Space Tourism: These flights remain within an orbit around the Earth at a speed higher than suborbital space flights. These flights orbit the world constantly for their entire stay in outer space.
Sub-orbital Space Tourism : This was the beginning of space tourism. The spacecraft launches with a substantial initial velocity that pushes it out of the Earth’s atmosphere. But this doesn’t throw it entirely out of the gravitational sphere. The power is insufficient for orbiting, so it freezes once the engines are shut off.
SpaceX C.E.O. Elon Musk proposed the prospect of lunar tourism. In 2018, he announced the ‘Dear Moon Project,’ the highly anticipated first lunar space tourism mission. They will carry out this project in 2022 with Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa.
Space Tourism cost
The cost of each sub-orbital trip on the Soyuz spacecraft is reported to be 200,000-250,000 million U.S. dollars. Other trips carried out by different organizations were priced around the same margin.
Virgin Galactic recently announced that each ticket would cost 450,000 USD for the upcoming missions.
Space Tourism companies
Even though the industry is still up and coming, massive companies dominate the market. Space Adventures of Virginia, U.S.A, was the first successful space tourism company.
Elon Musk’s SpaceX, Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic, and Amazon C.E.O. Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origin are all set to launch their space tourism business by 2022. Blue Origin recently conducted its debut flight with Jeff Bezos.
Oliver Daemen and Wally Funk were the world’s youngest and oldest men in space, respectively.
Space Tourism advantages
The universe and outer space have always been intriguing subjects for people on Earth. Yet, there were limited resources to satisfy their curiosity. The option of space tourism thus connects people with space in a unique way and solves its mystery. A more ecological advantage is the waste policy.
There is minimum pollution associated with these travels. Also, this allows a whole new sector of job opportunities for highly educated professionals and ambitious youth.
Top 13 list of space tourists
- Dennis Tito (American): April 28 – May 6, 2001
- Richard Branson
- Gennady Padalka
- Guy Laliberté
- Eytan Stibbe
- Sian Proctor
- Mark Shuttleworth (South African / British): April 25 – May 5, 2002
- Gregory Olsen (American): October 1 – October 11, 2005
- Anousheh Ansari (Iranian / American): September 18 – September 29, 2006
- Charles Simonyi (Hungarian): April 7 – April 21, 2007[8]
- Richard Garriott (American): October 12 – October 23, 2008[9]
- Sheikh Muszaphar Shukor (Malaysian): October 10 – October 23, 2007
Space Tourism in India
Space activities, in general, have been quite a staggering section in India. Last year, the government announced a policy that opens space exploration to private sectors, but hardly any company has taken action on it.
Entrepreneur Santhosh George Kulangara will be the first Indian space tourist as he booked his spot on a Virgin Galactic space flight in 2007. Hopefully, he will join Dennis Tito, Mark Shuttleworth, Gregory Olsen, and many more this year.
Forms of Tourism
- Atomic Tourism
- Beach Tourism
- Bicycle Tours
- Eco-Tourism
- Geo-Tourism
- Industrial Tourism
- Rural Tourism
- Space Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Sustainable Tourism
- Virtual Tourism
- War Tourism
What is the main purpose of tourism?
- Economic Sustainability: It ensures the effectiveness and competitiveness of tourism destinations and enterprises. It helps continue improvement, which is beneficial in the long run.
- Local enrichment: Tourist destination prosperity is an enormous part of tourism. The tourism business continuously maximizes the economic growth of the host destination.
- Employment Standards: Tourism supported the level of wages, terms of service, and availability for all. It creates local jobs without discrimination based on gender, race, disability, or other means.
- Local management: Involve local communities and empower local people for planning and decision-making. The community and tourism management team helped to develop this.
- Community Welfare: Maintain and boost the local community’s lifestyle. They are part of social structures. But surely, this process should take place with no social humiliation or exploitation.
- Natural Integration : Maintain and improve the quality of both urban and rural landscapes. It avoids natural and visual degradation of the environment.
- Natural Integration: Maintain and improve the quality of both urban and rural landscapes. It avoids natural and visual degradation of the environment.
- Biodiversity: Another purpose of tourism is to assist in conserving wildlife and natural wildlife areas and reducing losses.
- Environmental cleanness: Besides the purpose of tourism, all tourists must reduce air, water, and land pollution and waste generation.
- Tourism is a significant part of national integration .
- Tourism always motivates tourists to understand their traditions, heritage, culture, and religion.
- Tourism’s most significant part is economic growth or the business part of the destination. It encourages local people to create handicraft items and prepares local food items, souvenirs, dresses, etc., for sale.
- Tourism is one such thing that constantly boosts the country economically.
Niche Tourism
This tourism focuses on a specific aspect of traveling. It also focuses on the consumer market segment’s interest. It makes the destination more exciting and marketable. Niche Tourism is one of the fastest-growing sectors. Niche tourism indicates a specific feature of travel.
For example, some tourists want a museum, some wish to visit old architectural monuments, buildings, palaces, etc., and some want to eat in a famous restaurant. Thus, niche Tourism shows a particular activity that is not the only focus of travel.

Types of Niche Tourism
- Macro-Niche
- Micro-Niche
What is Macro-Niche?
Macro-niche tourism can be explained as a niche with broad customer interest categories such as rural tourism, Business tourism, sports tourism, medical tourism, environmental travel, etc.
What is Micro-Niche?
It is a small group trip, such as gastronomy tourism, cycling tourism, and geo-tourism.
Niche tourism in South Africa
South Africa is an attractive destination because of the wide diversity of animal and bird species. As a result, tourism professionals found this country has considerable potential.
Advantages of Niche Tourism
- Even if niche tourism is smaller than mainstream markets, it spreads more.
- It has more potential to grow.
- It creates quality jobs that require specialized skills.
What are the different types of tourists?
When we visit a place, we find different kinds of travelers. The aim of each traveler is different. Let us discuss the types of visitors. Five types of tourists are found mostly :-
- Incentive tourists – These tourists did not plan for the tour earlier. Suppose you have been rewarded with two tickets from the office because of your performance. You and your colleagues came for the trip.
- Business tourist – This type of tourist travels for business. They will always prefer a hotel with a conference room. They don’t come to enjoy luxury, but they want the hotel to serve everything on time.
- Leisure tourist – This type of tourist comes to enjoy the vacation. They love those hotels that serve them something extra, like drinks. They choose hotels that give them comfort and luxury at their best.
- Special interest tourists – They often plan their tours very well. This tourist doesn’t need comfort but loves to do adventure.
- The Foodie tourist – This type is quite common. They wish to taste various foods in various places. The signature dishes of those areas and various kinds of foods.
Types of a Tourist Attraction
We have to keep in mind that attraction varies from person to person. For example, suppose Rahul and Sheela are traveling to Kashmir. Rahul is interested in climbing the mountains to see snowfall, whereas Sheela is excited to visit the temples in Kashmir.
Tourist attractions could be classified into the following two categories:-
- Natural attraction – If you are a nature lover, don’t miss The Valley of Flowers in Uttarakhand, Coorg, known as the ‘Scotland of India.’
- Events and heritage attractions – Goa is a place for heritage lovers. So pack your bag, take the camera, and start your journey towards Goa. I am sure you will have an unforgettable lesson in Goa’s history. Fort Aguada, Chandor, and some famous museums are places to visit.
What is Tourism Planning?
Perfect planning is always a matter of the success of any activity. Whenever we plan something and implement it, we get a better result. It’s the same with tourism. But it is neither guaranteed nor forever. It’s a process where the people’s needs are determined using the best resources, programs, and activities.
How do these tourism plans help us?
A tourism plan makes guidelines for the areas. Then, it helps the government and private sectors to develop those areas. Most importantly, we must remember a few steps involved in tourism planning.
Main types of tourism planning
- Financial planning
- To establish the objective
- Human resource planning
- Monitoring progress
- Human resource planning.
Types of Tourism Activities
There are various kinds of tourism activities. Like-
- Heritage trails
- Swimming with dolphins

Name of some international tourist organization-
- American Society of Travel Agents : Founded 1931, Headquarter- New York
- International Academy of Tourism : Founded-1951, Headquarter- Monge Carlo
- International Bureau of Social Tourism : Founded 1963, Headquarters- Brussels
- International Touring Alliance: Founded-1919, Headquarters- Europe
- World Tourism Organization : Founded 1975, Headquarter- Madrid.
Types of Tourism packages
For different categories of tourists, everybody needs a separate package. Let’s discuss the various types of Packages that are available.
1. Adventure Tourism Package
This tourism encourages people to come out of their comfort zone to feel the thrill of nature closely in life. It is found that people are taking adventure more often. It shows potential growth in recent years.
The most exotic and adventurous destinations are Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Jammu, and Kashmir.
2. Wildlife Tourism Package
In every country, wildlife tourism is famous. But, if you love wildlife, you must choose the right package. This package is exclusively for wildlife lovers who love taking their snaps.
3. Medical tourism package
It has been observed that medical tourism has grown rapidly in Asia-specific countries.
4. Pilgrimage tourism package
Many foreigners visit various temples in India, Sri Lanka, and Singapur. However, the major attraction is the traditional architecture, art forms, and rituals performed.
Famous pilgrimage areas are the Meenakshi Temple, Golden Temple, Jagannath Temple, Santa Cruz Cathedral Basilica, Atala Mosque, etc. Therefore, this type of package is chosen based on your religious beliefs.

5. Eco-tourism Package
This type of tourism has become one of the fascinating travel forms. Although eco-tourism is more of a travel philosophy, it attracts many tourists. Some eco-tourism destination areas are Kerala, Galgibaga Beach, Goa, and Coorg.
6. Cultural Tourism Package
The social richness of any country draws visitors from every corner of the world to witness sheer celebrations. The cultural tour package offers you a comprehensive exploration of the different shades. Moreover, this package will bring a tourist a closer view of traditions and architecture.
Along with these, we found tourism packages like-
7. Family Tourism Package
A family tour package is designed keeping in mind the family’s needs. It gives assurance of total relaxation and fun pastimes.
The package includes adults, kids, and the elderly. This package includes sightseeing trips, tours of historical places, and adventure trips.
8. Honeymoon Tourism Package
Couples, after their marriages, take a honeymoon tour package, and it provides newlyweds with all the perquisites to make their trip memorable.
The honeymoon tourism package includes lodgings, dining, food & drinks, etc. Famous destinations for a honeymoon tour package are Maldives, Bali, Mauritius, etc.
9. Wellness Tourism Package
Traveling to other places for health and well-being takes a wellness tourism package. Tourists take this package to visit sites that provide recuperation facilities. Wellness tourism has seen a significant boost in the modern years.
Popular destinations for a wellness tourism package are Ayurveda centers, Iceland (for its spas), Bali (for yoga), etc.
10. Cruise Tourism Package
A cruise tourism package provides tourists with a journey filled with fun and recreational activities onboard and excursions onshore.
Tourists get an all-planned ship or boat trip for a specific date to a particular location at a specific price. These packages are curated as per the needs of the tourists.
What are Tourism Products?
According to the market’s needs, the customer supplies anything in the market for use/consumption, called a product.
A product can be offered in the market observation, purchase, use, or any need or demand.
A tourism product is provided to the tourist during their traveling. It mainly focuses on facilities and services designed to meet the needs.
It includes physical objects, services, personalities, places, and ideas. The above components are provided by one company or any group of companies. Tourism products can be given to tourists in a tourist destination.
Products are needed for leisure, pleasure, religious, or business purposes. These products are provided in the market at a cost.
The main reason for choosing a tourist destination is a tourism product. It gives an economic boost to the destination. So it needs to be marketed and stored in a hassle manner.
Services are designed for the visitor to fulfill their needs. Therefore, it is a combination of products. Thus, the country’s total tourism and tourist satisfaction depend on the sum of its attractions, transportation, accommodation, entertainment, etc.
Individual service providers, such as hotels, airlines, travel agencies, etc, provide every element of a tourism product. Therefore, you can analyze these products’ attractiveness, accommodation, and accessibility.
Types of Tourism Products
Attractions: It is one of the main elements. Tourists will not be encouraged to visit certain places without attractions. Attractions are the ingredients. The product determines the choice of a particular tourist to visit a specific destination.
Attractions include archaeological, cultural, and historical buildings, monuments, beach resorts, mountains, flora and fauna, national parks, trade fairs, arts and music festivals, exhibitions, games, etc. Nowadays, tourists are susceptible to changes in fashion.
Accessibility: That means by which a visitor can reach the attraction place. Tourists visit the attraction destination by different transport modes. Visitors visit his predetermined location by car, motorcycle, train , ship or boat, airplane, or cycle.
The place becomes very cheap if any destinations do not have good transport systems. Tourist centers should be located near tourist-producing markets. It is connected to a network of efficient transportation to receive the largest number of tourists.
Accommodation: Another tourism product is accommodation. It is an essential part of tourism—the tourist destination location must-have hotels, guest houses, camping, and homestay. An alternate arrangement should exist if accommodation is not possible at the central location. At least some distance away.
Hospitality: It is a major factor for a tourist destination that will develop in the future. The location’s restaurants, pubs, cafes, foods, and beverage serving style increase location attractiveness.
Natural tourism products: Our nature is beautiful and precious to us. Nature has arranged amazing things in different parts of the world, such as – hills, mountains, caves, glaciers, sea, islands, beaches, waterfalls, rivers, lakes, wildlife, deserts, etc.
The tourism product utilizes those natural gifts as a Natural tourism product, such as snow-capped mountains in Kashmir, Dudhsagar Falls in Goa, palm-fringed beaches of Goa, the wildlife of Kaziranga National Park in Assam, the Thar Desert in Jaisalmer, etc.
Read Things to do in Bainbridge Island, Seattle Washington
Human-created tourism products
Artificial tourism products are those that humans create. Human-made tourism products’ primary purpose is to attract tourists, such as Temples, Forts, palaces, museums, theme parks, etc.
The destination’s tradition and culture play a vital role in tourism. Humans maintain it to attract tourists through- classical dance – music, folk dance, paintings, handicrafts, festivals, fairs, etc.

Examples: Machu Picchu World Heritage Site, Egyptian pyramids , Taj Mahal, Red Fort in Agra, Lothal in Gujarat, Mexican pyramids, or Mesoamerican pyramids are important archaeological sites.
The Bhangra dance form of Punjab, the Kolkata Book Fair, the Durga puja in Kolkata, the Brass work of Muradabad, etc., are also included in human-made tourism products.
Tour guides are another main aspect of traveling. It is also a parameter for tourism. National and international travelers need a travel guide to discover a new place. Sometimes, national travelers may visit any tourist destination on their own.
But an international traveler always wants a good tourist guide. How do you present the location, and how much information do you provide to understand the place? It depends on a guided tour and a travel guide. This parameter upgrades the tourist destination’s level.
What are the different types of tourist destinations?
Types of tourism and types of tourist destinations may sound synonymous. However, the two have slight conceptual differences. Tourism is a broader concept, including the aspects of tourism and hospitality.
At the same time, a tourist destination is a narrower concept applying to places of tourist attraction. Based on the type of place and the causes of interest, the tourist’s destinations are:
- Coastal Destinations – Preferred mostly for the ample sunshine and salty waters lining lands adjoining the sea. Be it domestic or international coastal locations, they are great for fun and relaxation. They are favored mostly by people living in inland areas away from the sea.
- Beaches – The meeting point of land with the ocean offers a great tourist attraction. Waves hitting the shores of sandy beaches are great for tourists. In addition, new beach activities like parasailing, beach biking, etc., also attract tourists immensely.
- Island – A land in the middle of the sea or ocean on all sides is an island. Tourists are taken mainly by boat from the mainland to explore these islands. Islands standing in between a river are called riverine islands.
- Mangroves – It offers a panoramic view amidst the confluence of a river with the sea/ocean. Example: Sundarbans of India.
- Inland Destinations – Travel away from the coast is an inland destination. A variety of sub-classifications can come in under like:
Based on the type of region:
- Hill stations – Offering a surreal view from an altitude, all mountains and hills are great tourist destinations.
- Jungles – Trekking/hiking/driving through the wild greenery are great tourist attractions. Protected areas like Reserve Forests and National Park serve the twin purpose of tourism and conservation.
Based on the population structure
- Rural – For a change, get away from the fast-paced urban life to taste village life. Touring rural locations is gaining popularity because of lower population density, greener areas, and a serene environment.
- Urban – Posh urban destinations offer a pull factor for tourists to experience ultra-modern and urban life. Examples: New York, Shanghai, etc.
- Offbeat – Previously undiscovered newer locations around famous tourist spots are offbeat destinations. With lower tourist popularity, the exclusiveness of these places is retained.
Based on the type of activity
- Hiking and Camping – Places, where tourists come mostly for hiking or camping (day/night), are fast gaining popularity. These places are primarily amidst nature and come under adventure tourism.
- Preserved sites – Sites like UNESCO World Heritage sites have become popular tourist destinations. The rich natural/cultural value owes them their status.
Based on historical/religious importance
- Historical Places & Monuments – Tourists flock to places holding remnants of the past. Areas having historic architecture and events give an insight into the past culture. Examples: Taj Mahal and Jalianwallah Bagh, etc.
- Pilgrimages & Holy Shrines: Religious tourism has flourished here, making it a spiritual destination. Example: Hajj of Mecca, Bethlehem for Christians.
- Museums and buildings: Places where artifacts and remnants of historical culture are well preserved. Famous among tourists of all ages.
Based on entertainment
- Luxury destinations: Locations that only promote high-end tourism are luxury destinations. Example: Bali.
- Carnival: Annually, countries host cultural events to celebrate any occasion for a short period. When tourists travel here to enjoy themselves, it becomes a popular destination. Example: Christmas Carnival in Toronto.
- Amusement Park and Zoo: Famous for the lot is Disney Land, a great tourist destination for children. Singapore Zoo, which ushers in global tourists.

Tourism Destinations
According to UNWTO in the “World’s Top Tourism Destination,” the first four places for International tourism are France, Spain, the USA, and China.
A tourism destination is the endpoint of the journey. But, of course, we all have some goals in every field, so it’s the same with tourism.
There are various types of tourist destinations. They are as follows:-
- Centered Destination
- Based Destination
- Multi-centre Destination
- Touring Destination
- Transit Destination
Types of Tourist Attractions
- Historial attractions
- Cultural attractions
- Political significance
- The natural or scenic beauty
- Leisure travel
- Fun and Amusement

How many Types of Tourism are there in India?
There are 16 Different kinds of tourism in India , but the list may increase.
Is there anything about tourism that I’ve missed?
Over the past 75 years, the travel industry has made great strides in harmoniously uniting strangers, travelers, and locals. As a result, visits and travel are more than adventure, learning new skills, rejuvenating, and achieving perfection.
Tourism has changed from providing services like rooms, flights, and meals that people were satisfied with ten years ago. Now, people want to experience whale watching or mountain biking.
In the luxury sector, wealthy people spend more money on an experience than objects. It is called experience economics, and there is an idea that the memories of tourist values are compared to some physical resources. The rate of global tourists is increasing daily, and every country is trying to make its tourism more developed and successful.
As you can see, the tourism industry is vast and diverse. There are different kinds of tourism here; some have been around for decades, and others are just emerging.
A tour to the Grand Canyon would fall under which type of tourism?
Grand Canyon tour would fall into natural adventure tourism. Here, you can enjoy – The floor Landing Helicopter Tour, ATV, Gold Mine Tour, White Water Adventure Tour, and Rim Airplane Tour.
Kindly Stay 5 Seconds More and Share this Article.
HI TRAVELLER …Myself Ruma Dey Baidya. I’ve been backpacking for the last 20+ years. Photography and travelling have been my passion since my childhood. Whenever I got an opportunity, I never missed it. I am not a solo backpacker, so I always try group travel. I prefer budget travel, and it also helps me to save expenses. We know that memories are not constant, so I decided to document them and created this travel diary. This website [ TheHolidayStory ] is dedicated to those who passionate about travel like me. Please feel free for any information related to my blog. I am always happy to reply. Mail id – ruma[@]theholidaystory.com

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

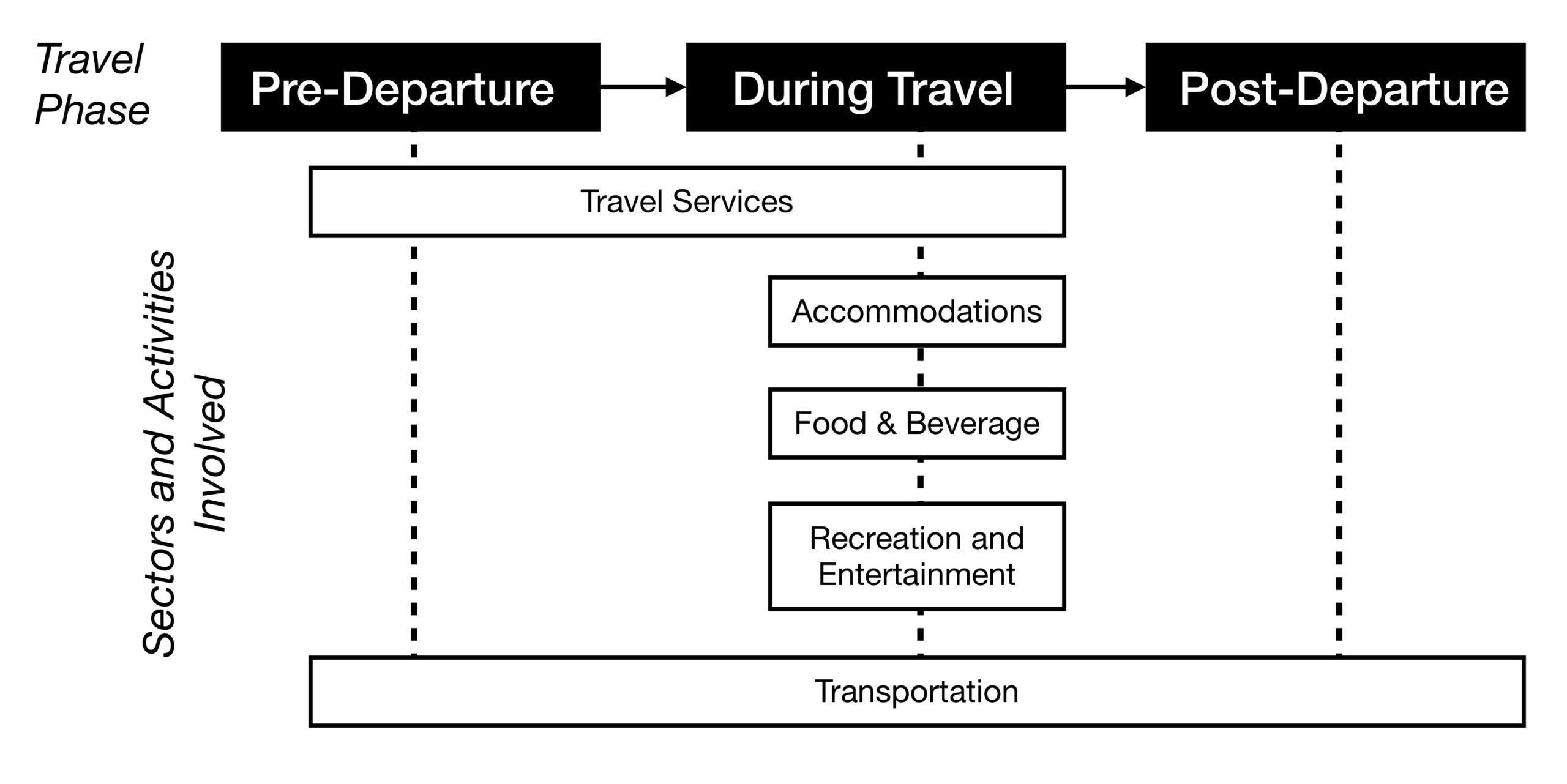
It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Long Descriptions
Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the sectors and activities involved during each phase.
There are three travel phases: pre-departure, during travel, and post-departure.
Pre-departure, tourists use the travel services and transportation sectors.
During travel, tourists use the travel services, accommodations, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and transportation sectors.
Post-departure, tourists use the transportation sector.
[Return to Figure 1.2]
Media Attributions
- Front Desk by Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence .
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Statistics of tourism

The United Nations recognizes the World Tourism Organization as the appropriate organization to collect, to analyse, to publish, to standardize and to improve the statistics of tourism, and to promote the integration of these statistics within the sphere of the United Nations system.
“Official statistics provide an indispensable element in the information system of a democratic society, serving the government, the economy and the public with data about the economic, demographic, social and environmental situation.”
Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics
The UNWTO Statistics Department is committed to developing tourism measurement for furthering knowledge of the sector, monitoring progress, evaluating impact, promoting results-focused management, and highlighting strategic issues for policy objectives.
The department works towards advancing the methodological frameworks for measuring tourism and expanding its analytical potential, designs practical guidance for their implementation in countries, supports statistical strengthening in countries through capacity building, and compiles and disseminates tourism statistics of countries all over the world.
The United Nations recognizes the World Tourism Organization as the appropriate organization to collect, to analyses, to publish, to standardize and to improve the statistics of tourism , and to promote the integration of these statistics within the sphere of the United Nations system.
Tourism Statistics Database
UNWTO systematically gathers tourism statistics from countries and territories around the world into a vast database that constitutes the most comprehensive statistical information available on the tourism sector.
COVID-19 AND TOURISM STATISTICS
With new situations emerging from the unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic, some clarifications need to be made to the UN statistical standards on tourism to maintain as far as possible data consistency and international comparability
Tourism | History, Classification, Destinations, Types And Characteristics
We explain what tourism is, how it is classified and what are the means to travel. In addition, its general characteristics and the tourist
What is tourism?
The Boy Barely Escapes A HUGE Threat
Tourism history
Touristic destinations.

Durability of tourism
Types of tourism.

- Individual tourism. It is the type of tourism that is done alone or without company. Sometimes family tourism or with a small group of friends can be considered within this category, since it is compared with mass tourism that represents the transfer of more people from one geographical point to another.
- Mass or collective tourism. It is the tourism that takes place with a group of people, whether they are known or not by the tourist.
- Adventure Turism. It is a type of tourism in which the subject climbs mountains , hills, performs sports activities such as rafting, kayaking or diving that involve a greater energy drain than other types of tourism.
- Traditional or sedentary tourism. In this tourism, high-wear actions are not designated or too many activities are scheduled. On the contrary, the activities will depend on chance and without much prior programming.
- Cultural tourism. It is a type of tourism whose destination is some event or site of generally historical cultural attraction. Archaeological tourism can be derived from this, where the purpose of the tourist visit is to observe the remains of ancient societies .
- Gastronomic tourism. It is done with the aim of tasting different dishes or typical foods of the destination that the tourist is visiting.
- Domestic tourism. It is carried out within the same national territory of residence of the tourist.
- International tourism. It exceeds the borders of the tourist's country of residence.
There are many varieties of tourism such as business tourism, sex tourism, entertainment tourism, stay tourism, community aid tourism, agrotourism or rural tourism.
Tourist displacement

In order to move to the tourist spot that the person wishes to visit, it is necessary to do so by some means such as:
- Walking. This type of tourism is better known as “backpacking”.
- By bus or car. The subject must make the purchase of a land passage or circulate in his own vehicle.
- Aerial. The most common is the plane but it can also be by helicopter.
- Maritime. This type of displacement can be by boat, cruise ship or a smaller vessel.
Tourism companies
The companies of tourism have a wide range of different destinations . From this point of view, tourism is a business or trade that provides different services to satisfy the need to travel and get to know different tourist destinations.
Tourist information

Tourism companies use brochures or films to show what the destination to which the subject wishes to visit tourist is like.
In this way, tourism companies provide useful data regarding the climate, social conditions , currency and all the information that may be useful.

A tourist is considered to be one or those people who do tourism , both individually and in a group of friends or strangers.
Economic cost for the tourist

The tourist must pay for their stay, their trips and visits to tourist spots and also, any extra expenses that may arise.
Many tourist destinations such as national parks, squares or museums do not have a monetary cost.
Tourist behavior
There are differential characteristics that mark the behavior of people who do tourism:
- Exotic thinking. In relation to the site they visit, the tourist will present a feeling of estrangement and exoticism, valuing or not what is different from their own culture .
- Ignorance of the language. If the tourist moves to a place where their language is not spoken , they will need a translator or they will communicate with signs or in a language that the inhabitants can understand.
- Clothing. Clothing is one of the most notable physical characteristics, since it varies depending on the society to which the tourist belongs. The greater the distance from the tourist's home society, the more noticeable this characteristic will be.
Kalum Talbot
MA student of the TransAtlantic Masters program at UNC-Chapel Hill. Political Science with a focus on European Studies. Expressed ideas are open to revision. He not only covers Technical articles but also has skills in the fields of SEO, graphics, web development and coding. .
Leave a reply
Social media, entertainment, recent post.

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

Essay: Definition, Structure, Features, Characteristics, How to Do It

Narrative Text: What It Is, Structure, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Cohen’s tourist typology- The 4 major types of tourists
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Cohen’s tourist typology was one of the first major typologies developed in the travel and tourism space. If you are studying travel and tourism, you will probably be introduced to Cohen’s tourist typology at some point (and that’s probably why you are here now!). If you are wondering what this tourist typology is all about and how Cohen categorised his four major types of tourists, then you have come to the right place… read on….
Who is Erik Cohen?
What is cohen’s tourist typology, cohen’s types of tourists, institutionalised tourists, noninstitutionalised tourists, cohen’s tourist typology- 4 types of tourists, the drifter, the explorer, the individual mass tourist, the organised mass tourist, why is cohen’s tourist typology beneficial, types of tourists- further reading.

Erik Cohen is an Emeritus Professor in the Department of Sociology and Anthropology, Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Erik focuses his research in Social Anthropology, Sociological Theory and Tourism Studies. Erik is most well known for his work on tourist typologies published in the 1970s.

Cohen’s tourist typology is a model that aims to categorise tourists into different types. Cohen’s theory is well known as being the first to attempt to categorise types of tourists. Cohen derived this theory on the types of tourists based on his knowledge of sociology and anthropology and applied it to the context of tourism, he is not necessary a tourism specialist. Cohen’s theory was first published in 1972 in his article entitles ‘Towards a Sociology of International Tourism .
Whilst a lot has clearly changed in the tourism industry since the 1970, Cohen’s tourist typology has continued to be used as a guide for understanding the different types of tourists throughout the years by academics and tourism industry professionals.

The types of tourists identified by Cohen in his typology are based on a continuum- a spectrum that allows tourists to be placed at some point between the familiar and the novel. Essentially, Cohen teaches us that there are many different types of tourists, some who seek familiar experiences (such as familiar food chains, branded accommodation options that they know or languages that they can speak), others who seek entirely new experiences (new cultures, new locations, new languages etc) and those who fall somewhere in between.

In Cohen’s tourist typology there are two groups of tourists- the institutionalised tourists and the noninstitutionalised tourists. Lets take a look at what these are-
Cohen describes institutionalised tourism as the organised mass tourism . This is the tourism industry that is designed to make the tourist experience as smooth and as organised as possible. There are a number of tourism agents involved with institutionalised tourism, such as travel agents , tour operators and tourism resorts. Institutionalised tourists experience novelty with the comforts of the familiar.
Cohen’s noninstitutionalised tourists are the opposite of institutionalised tourists. These types of tourists do not seek the commodified products and services that the mass tourism industry provides, instead, the institutionalised tourist seek deep immersive and experiential travel experiences that cannot be obtained through institutionalised tourism. These types of tourists travel independently and are often in search of adventure, the new and the unfamiliar and authenticity .
Cohen breaks down his tourist typology further, suggesting that there are four main types of tourists:
The first two types of tourists (the Drifter and the Explorer) are deemed noninstitutionalised tourists and the latter two (The Individual Mass Tourist and the Organised Mass Tourist) are examples of institutionalised tourists. Now, lets take a deeper a deeper look at what each of these four types of tourists are…

The Drifter is the type of tourist that is least connected with the mass tourism industry. Drifters typically have an authentic and deep immersive experience, opting for staying with members of the local community rather than in hotels and spending their time in the local community. They seek adventure and plan their own itineraries. This type of tourist always opts for novelty over familiarity- you won’t see a Drifter eating in McDonalds or shopping in Zara!

This type of tourist is similar to a Drifter in that they seek novelty over the familiar, however Explorers do often have a little more interaction with the commodities associated with the tourism industry. For example, an Explorer may travel independently and enjoy an immersive cultural experience, but they may rest their head on a hotel pillow at the end of the day. This type of tourist will generally eat and shop local, but don’t be surprised if they enjoy a Big Mac from time to time too.

In Cohen’s tourist typology the Individual Mass Tourist seeks the familiar. This type of tourist wants familiar food, they want to be able to communicate in a familiar language and they want to stay in types of accommodation that they are familiar with. However, the Individual Mass Tourist is not constrained by the likes of group tours and activities- yes, they may book their holiday through a travel or use a local tour guide, but they will typically opt for solo travel over group tours.

The last of the types of tourists outlined in Cohen’s tourist typology is the Organised Mass Tourist. The Organised Mass Tourist seeks the familiar in the same way that the The Individual Mass Tourist does, however, they tend to do this as part of an organised group. This type of tourist seeks the familiar over novelty every time and they are often found with tour guides and undertaking group tours. The Organised Mass Tourist will generally have an itinerary or a plan and they will stick to it.
Whilst we can easily criticise this theory for being too generalised and for accounting for the specific and the individual, there is no questioning that it does have real-world value. By better understanding the different types of tourists tourism businesses and tourism industry stakeholders can better provide for the tourists- they can tailor their products and services better, they can understand the tourist demands and desires and they can help to improve the overall quality of the tourism provision that is offered to particular tourists.
There are many academic studies which utilise Cohen’s tourist typology as a means to understanding particular issues within the tourism industry, you can see one example here .
If you have found this article helpful, you may also enjoy these-
- Butler’s Tourism Area Life Cycle Model: A simple explanation
- Leiper’s Tourism System: A simple explanation
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism Glossary
- The mass tourism industry EXPLAINED
Liked this article? Click to share!
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Classification Of Various Forms Of Tourism
- Author & abstract
- Related works & more
Corrections
- Ghete Ana-Maria
Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
The Impact of High-Speed Traffic on the Tourism Economy of Urban Agglomerations: A Joint Effect and Heterogeneous Classification
- Conference paper
- First Online: 30 April 2024
- Cite this conference paper

- Chuntao Wu 2 &
Part of the book series: Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics ((SPBE))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Workshop on HSR Socioeconomic Impacts
This article focuses on the impact of high-speed transportation systems formed by vehicles with speeds above 200 km/h (i.e. high-speed rail and aviation) on the tourism industry in urban agglomerations. A multi-phase DID model is used to verify the positive role of high-speed rail and aviation construction in the development of the tourism industry, and a fixed effects model is used to classify the comprehensive impact of high-speed transportation system operation on the tourism industry. The results show that there is a three stage lag of the driving effect of high-speed transportation on the tourism industry, and there is significant heterogeneity of the impact on urban agglomerations of different economic levels. Specifically, 19 urban agglomerations can be divided into six bilateral impact types, five unilateral high-speed rail impact types, five unilateral civil aviation impact types, and three bilateral no impact types. The economic development and policy factors that form this phenomenon are summarized. This study provides a theoretical basis and guiding significance for the planning and construction of urban agglomerations in China, the coordinated construction of urban high-speed rail and air transportation networks, and the rapid development of the tourism industry in the future.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Albalate, D., Campos, J., & Jiménez, J. (2017). Tourism and high speed rail in Spain: Does the AVE increase local visitors?. Annals of Tourism Research, 65 (Jul.), 71–82.
Google Scholar
Banister, D., & Berechman, Y. ( 2005). Transport investment and the promotion of economic growth [J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 9 (3), 209–18.
Bieger, T., & Wittmer, A. (2006). Air transport and tourism—Perspectives and challenges for destinations, airines and governments. Journal of Air Transport Management, 12 (1), 40–46.
Article Google Scholar
Chen, Z., Haynes, K. E. (2012). Tourism industry and high speed rail—Is there a linkage: Evidence from china's high speed rail development . Social Science Electronic Publishing.
Chen, S. Y., Yang, B., & Tang, X. W. A. (2006). Research of competitive situation and strategy of air transport opening between China and USA. Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Management Science & Engineering (Vol. 1–3, pp. 1871–1876).
Civil Aviation Administration of China Subject Group. (2009). Impact of high-speed railway on civil aviation development and policy recommendations (I). Civil Aviation Administration of China, 8 , 15–9.
Gutiérrez, J. (2001). Location, economic potential and daily accessibility: an analysis of the accessibility impact of the high-speed line Madrid–Barcelona–French border. Journal of Transport Geography, 9 (4), 229–242.
Huang, M., Yang, X. J., Liu, D. P., & Fang, H. D. (2022). Effects of perceived change of urban destination on destination attachment. Frontiers in Psychology, 13 , 22.
Khadaroo, J., & Seetanah, B. (2008). The role of transport infrastructure in international tourism development: A gravity model approach. Tourism Management, 29 (5), 831–840.
Liu, Y., & Yang, W. (2019). Impact of high-speed rail on air transportation market in the context of transportation power in the new era [J]. Value Engineering, 38 (31), 97–100.
Lundgren, J. O. J. (2013). The tourist frontier of Nouveau Quebec: Functions and regional linkages. Tourism Review, 37 (2), 10–16.
Masson, S., & Petiot, R. (2009). Can the high speed rail reinforce tourism attractiveness? The case of the high speed rail between Perpignan (France) and Barcelona (Spain). Technovation, 29 (9), 611–617.
Page, S. J., & Duignan, M. (2023). Progress in tourism management: Is urban tourism a paradoxical research domain? Progress since 2011 and prospects for the future. Tourism Management, 98 (4), 532–546.
Pan, H., Luan, X., Liu, Q., & Li, Z. (2019). A study on the impact of built environment along high-speed railways on passenger transfer time consumption. Urban Development Research, 26 (4), 17–21.
Prideaux, B. (2000a). The resort development spectrum—A new approach to modeling resort development. Tourism Management, 21 (3), 225–240.
Prideaux, B. (2000b). The role of the transport system in destination development. Tourism Management, 21 (1), 53–63.
Wang, D. G., Niu, Y., & Qian, J. (2018). Evolution and optimization of China's urban tourism spatial structure: A high speed rail perspective. Tourism Management, 64 , 218–232.
Wang, J., Jing, Y., & Yang, H. (2019). Measurement of substitution effect of high-speed railroad on domestic civil passenger transportation. Journal of Natural Resources, 34 (9), 1933–1944.
Wu, M. (2019). Analysis of airline-high-speed railway competitive relationship [J]. Civil Aviation Management, 10 , 11–5.
Yunxia, L., & Weina, Y. (2019). Impact of high-speed rail on air transportation market in the context of a strong transportation country in the new era. Value Engineering, 38 (31), 97–100.
Zhong, L. S., Deng, J. Y., Song, Z. W., & Ding, P. Y. (2011). Research on environmental impacts of tourism in China: Progress and prospect. Journal of Environmental Management, 92 (11), 2972–2983.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065, China
Chuntao Wu & Yan Li
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yan Li .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Civil, Architecture and Environment Engineering, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy
Francesca Pagliara
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Wu, C., Li, Y. (2024). The Impact of High-Speed Traffic on the Tourism Economy of Urban Agglomerations: A Joint Effect and Heterogeneous Classification. In: Pagliara, F. (eds) Socioeconomic Impacts of High-Speed Rail Systems. IW-HSR 2023. Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53684-7_21
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53684-7_21
Published : 30 April 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-53683-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-53684-7
eBook Packages : Economics and Finance Economics and Finance (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Types/ Classification of Tourism

Tourism was only restricted to certain people in the past. But, now with the development of infrastructures, has helped to spread atechnology around the world.
Now tourism is not only the privilege of the rich and wealthy but also normal people middle class people. It has been possible with the development of technology that everyone has access to travel if they wish to.
Also, with the development of jet travel, communication, new technology, tourism, and tourism has became one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing industry.
Travel and tourism also has emerged as a dominant economic force on the global scene. It now accounts for almost 15% of world’s total trade and is growing at a rapid Pace.
Types/ Categories of Tourism
Tourism can be categorized into various forms but is usually is categorized on the following basis:
On the basis of destination
Tourism is classified into tow types on the basis of destination namely: International and domestic tourism. International Tourism is further classified as Outbound Tourism and Inbound Tourism.
International Tourism:
Travel or tourism in which one person visits a foreign country living his residence either permanently or temporarily is called International tourism. In order to travel to a foreign country, one must follow a certain set of rules and laws.
For example, when travelling to another foreign country, tourist must have a valid id passport, visa, health documents, foreign exchange, etc.
International tourism is further classified into two types: Inbound Tourism and Outbound Tourism.
Inbound Tourism
When tourists of outside origin enter a particular country, it is called Inbound tourism. When people travel outside their host/native country to another country, then it is called inbound tourism for that country where he/she is traveling. For example when a tourist from Nepali origin travels to Japan then it is Inbound tourism for Japan because foreign tourist comes to Japan.
Outbound Tourism
When a tourist/ traveler travels from their origin of the country to another country, it is called Outbound tourism. For example, when a tourist from Nepal travels to Japan then it is outbound tourism for Nepal and Inbound tourism for Japan.
Domestic Tourism
Tourism activities done within a residing country by its residents are called domestic tourism. This is an easy form of tourism where a tourist doesn’t have to have any legal requirements to travel. He/she can travel or visit any place within the country whenever they want.
Also, in domestic tourism, the tourist doesn’t have to face problems that he/she has to face when they are visiting a foreign country. International tourists usually have to face the problems of Language barrier, monetary exchange, and understanding rules and regulations, etc.
On the basis of Size
On the basis of size, tourism is divided into the following three types:
Mass tourism:
Mass tourism is when, a large group of people move together for a visit or travel. These types of tourism or travel are generally conducted by institutions, colleges, etc. for different purposes.
Controlled Tourism:
This is another type of tourism on the basis of size in which their area limited a number of individuals traveling to different parts. This type of tourism is mainly when a family or a group of close friends travels.
This, controlled type of tourism is what happens most because people mainly like to travel in a small group.
Elite Tourism/ Tourist:
This is another form or type of tourism where there is only one individual who travels through different parts, be it domestic or international. These type of tourists have an individual mindset and can be considered powerful mentally.

On the basis of Purpose
On the basis of purpose, there are different types of tourism and the list is extensive. Here are some of the popular types of tourism on the basis of purpose:
Tourism for Visiting Friends and Family
This is one of the major reasons why most people travel to different places during their free/ leisure time. constitutes the act of traveling to home or friends and family or to a place of mutual convenience. VFR is particularly popular in areas that have been subjected to high immigration such as Pakistan, Mexico, and Poland.
Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism is another type of tourism that involves experiencing your destination through physically participating in activities. This can involve a variety of actions such as; hiking, snorkeling, sky diving, and much more.
It mainly appeals to those seeking adrenaline and thrill. It involves removing oneself from the everyday routine and inserting into something unfamiliar. Adventure tourism locations are often referred to as ¨bucket list¨ destinations.
Medical Tourism
The process of traveling to different nations or parts of the same nation for the purpose of receiving medical care is called medical tourism . It is now in a growing trend.
People from developing countries tend to move to developed or better countries in order to receive the medical facilities that are not available in their residence.
Virtual Tourism
With the development of new technology, this type of tourism is getting more traction. Basically, virtual tourism is the act of using technology to simulate traveling experiences and their features.
Although virtual tourism will not replace physical visits or visits to destination, it has seen a lot of traction since the ongoing corona pandemic.
It has also been used as a marketing tool by different agencies to enhance the user experience.
Village Tourism
Village Tourism is the process of participating in a village/ rural lifestyle without disturbing the natural environment. This type of tour gives you the chance to explore the real villages unlike having spent a short time in different villages on the trek.
You have the chance to eat the traditional local food prepared in the neat and clean kitchen, which are delicious and are hygienic.
Urban Tourism
Urban tourism is a type of tourism activity that takes place in an urban space with its inherent attributes characterized by a non-agricultural-based economy such as administration, manufacturing, trade, and services and by being nodal points of transport. Urban/city destinations offer a broad and heterogeneous range of cultural, architectural, technological, social, and natural experiences and products for leisure and business.
Agritourism
Agritourism is another type of tourism where a tourist or a traveler involves in any agriculturally based operation or activity that brings him/ her to a farm or an agricultural land in different places.
Business Tourism
Business tourism is the provision of facilities and services to the millions of delegates who annually attend meetings, congresses, exhibitions, business events, incentive travel and corporate hospitality.
And there are many more types of tourism on the basis of purpose of travel or visit, some more types are listed below:
- Geo-tourism
- Wildlife tourism
- Water tourism
- Recreational tourism
- Religious tourism
- Sex tourism
- Space tourism
- Wellness tourism
- Educational tourism

The 5 Phases of tourism & reacreation
Difference between tourist, tourism and recreation
Forestry Bloq
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
I accept the Privacy Policy
Post Comment
Javascript est desactivé dans votre navigateur.
République Française
Service-Public.fr
Le site officiel de l’administration française
- Se connecter
- Accéder au site pour les entreprises
This page has been automatically translated. Please refer to the page in French if needed.
Share the page
Link copied
Le lien vers cette page a été envoyé avec succès aux destinataires.
Rent your second home (furnished tourist).
Verified 01 January 2022 - Directorate for Legal and Administrative Information (Prime Minister)
It is possible to make your second home a furnished tourist , that is, you can rent it for a transient clientele, for its exclusive use and for short periods. Several steps need to be taken. It is possible to ask for its classification, as a hotelier would do.
For what accommodation?
The furnished tourist is an individual accommodation type villa, apartment, furnished studio offered for rent. The following 3 conditions must be met:
- The dwelling is for the exclusive use of the tenant, i.e. the owner is not present
- The tenant does not take up residence there, it is a transient clientele
- The tenant resides there for a short period (rental by the day, week or month) and for a maximum cumulative duration of 90 days
To qualify as furnished, the accommodation must include the following equipment:
- Gas stove or hot plates
- Refrigerator
- Kitchen utensils
if the dwelling is part of a condominium, it must be checked beforehand that the condominium regulation does not prohibit the making of a furnished apartment. This prohibition generally concerns buildings for exclusively bourgeois residential use, that is to say, where all professional activity is prohibited.
Representations to the City Hall
It is mandatory to declare your furnished tourist in town hall.
The procedure for doing so depends on the municipality in which your secondary residence is located.
3 procedures exist:
- Some very large cities require the owner to request a change-of-use authorization First of all. These include Paris, Annecy, Aix-en-Provence, Biarritz, Bordeaux, Cannes, Lyon, Nice, Strasbourg, Toulouse and Tours.
- The others large cities (municipalities of more than 200,000 inhabitants and municipalities located in the Hauts-de-Seine, the Seine-Saint-Denis and the Val-de-Marne) require the owner to make a declaration and then request a change-of-use authorization . However, any other municipality may decide to apply this procedure.
- In all other cities , the owner must make a declaration.
Ask your city council about the procedure in effect.
Who shall I contact
Very big city, application for authorization to change use.
You must obtain authorization from the City Hall to change the use of your accommodation in furnished tourism (transition in furnished tourism).
Failure to comply with this obligation shall be punished by a civil fine of up to €50,000 . The restoration of the dwelling to its original condition and a periodic penalty payment of €1,000 per day per m 2 may be ordered.
obtaining such authorization may be subject to compliance with a rule known as of compensation . This rule requires you to purchase an equivalent area from a commercial space that you will have to convert into a living space. Ask your local council for more information.
If the authorization is granted, you must then proceed to change the destination of the premises into hotel accommodation.
Declaration of the furniture
You must declare the property to the City Hall in order to obtain a declaration number.
Contact your city hall to find out how to proceed.
Upon receipt of your declaration, the City Hall will immediately issue you an acknowledgement of receipt including a declaration number. This number will have to be indicated in each of the advertisements for the rental offer of this accommodation.
failure to declare your accommodation in the city hall is punishable by a civil fine of up to €5,000 .
You will need to include this number in all rental listings for your accommodation.
You have to declare the housing in town hall. Failure to comply with this obligation is punishable by a fine of up to €450 .
You must use the following online service:
Declare in town hall a furnished tourist
You must obtain authorization from the City Hall to change the use of your accommodation as a tourist furniture.
Failure to comply with this obligation is punishable by a civil fine of up to €50,000 . In the event of a conviction, the housing must be restored to its original condition and a penalty payment of €1,000 per day per m 2 may be ordered.
Proceedings against taxes
You must declare your start of business within 15 days.
To do this, you must use the following online service:
This approach allows you to obtain a SIRET number .
This number allows tax authorities to identify you when:
- Supplementary income tax return . In fact, income from the rental, as a non-professional lessor, is subject to income tax .
- Payment of social contributions, beyond of a certain amount of rental income
- Payment of the companies' property levy according to the housing municipality
Please note
if you use an internet platform, it must provide you in january with a document showing the gross amount of transactions from the previous year.
Request for classification (optional)
Benefits of filing.
The classification of a piece of furniture allows to indicate its level of comfort and equipment to the customer. There are 5 categories (from 1 to 5 stars).
classification sometimes allows you to benefit from tax advantages (exemption from housing tax and property tax) in ZRR , flat-rate allowance on rental income for micro-enterprises). In addition, it avoids the application of an increased tourist tax.
To do this, you must use these forms:
Request the exemption from the housing tax for bed and breakfasts and tourist furniture located in rural revitalization areas (RRZs)
Property Tax Exemption on Built-up Property (TFPB): Hotels, Tourist Furnished or Bed & Breakfast in Rural Revitalization Areas (RRZs)
The forms are to be sent to the public finance center.
- Department in charge of taxes (treasury, tax department...)
How do I get the ranking?
You can ask for the classification of your piece of tourist furniture to the accredited or approved evaluating body of your choice (listed on the lists on the Atout France website ) using a form:
Request for classification of a piece of furniture for tourism
The evaluating body shall carry out a classification visit of the accommodation. Within one month of your visit, you will receive a certificate of inspection that includes the following:
- Report and Control Grid
- Proposal for a decision to classify your furniture for the category mentioned in the inspection report
You have 15 days from the receipt of the certificate of inspection to refuse the classification proposal. After this period and in the absence of a refusal, the classification is acquired.
The decision is valid for 5 years. It shall indicate the following:
- Your name (and possibly the name of your representative)
- Address of the tourist furniture, capacity expressed in number of persons that can be accommodated and category of its classification
You have the obligation to display the classification decision visibly inside the furniture.
In case of absence or serious insufficiency of maintenance of your furnished furniture, the prefect can delete it from the list of classified furnished.
If the advertised description or the ranking displayed does not correspond to the characteristics of your furnished apartment, the tenant can apply to the Departmental Directorate for the Protection of Populations (DDPP or DDCSPP) for deceptive commercial practice:
- Departmental Directorate for the Protection of Populations (DDPP)
Rental Listing
If you use an intermediary (intermediary or negotiator, or digital platform provider), they must inform you of your obligations (declaration, application for authorization).
Prior to the publication of the rental advertisement, you must provide this intermediary with an attestation on honor. Your honor must certify that you have fulfilled the prior obligations (declaration, or even authorization for change of use) and that the dwelling is not your principal residence. If you have been assigned a housing declaration number by the City Hall, you must also provide this number.
You can help yourself with this model of attestation on honor:
Attestation on honor
Furnished rental ads can be found in the city hall, in a tourist office and on online booking sites.
To report a deceptive commercial practice on a furnished rental, you can contact the Departmental Directorate for the Protection of Populations (DDPP or DDCSPP).
Other rules to follow
You must comply with the other rules applicable to tourist furniture:
- Lease Agreement
- Income taxes
- Social contributions
In some municipalities, you will have to collect the tourist tax with the holidaymaker and return it to the municipality. Since 2019, if you use an internet platform as a payment intermediary, it is up to them to collect the real tourist tax .
You can use an online service to find out how much city tax your municipality charges.
Tourist tax rates per municipality
Statute and miscellaneous references
Code of Tourism: Articles L324-1 to L324-2-1
Ranking and declaration in town hall of furnished tourist
Code of Tourism: Articles D324-1 to R324-8
Definition and declaration in the town hall of the furnished tourist
Construction and housing code: articles L631-7 to L631-10
Authorization to change the use of immovable property
Construction and housing code: article L651-2
Civil penalty for unauthorized change of use
Construction and housing code: article L651-3
Criminal penalty in the case of concealment of premises subject to authorization for change of use
Order of 2 August 2010 laying down the standards and procedure for classifying furnished tourist products
Order of 6 December 2010 on inspection bodies for tourist furniture
Online services and forms
Online service
Supplementary declaration of income from self-employed occupations
Search tools
Document template
Do you have to pay social security contributions for renting a furnished apartment?
Tourist tax: what are the rates?
Additional topics
Income tax - Income from furnished rentals
Rent your main residence (furnished tourist)
Owner's Guide: Renting Furnished Tourists (PDF - 3.2 MB)
Ministry of the Environment
Regulation of Tourist Furniture
Ministry of Economy
Classification of tourist accommodation: general principles
Atout France - Tourist development agency of France
Accredited inspection body for the classification of tourist accommodation
Perimeter of Rural Revitalization Areas (RRZs)
National Agency for Territorial Cohesion (ANCT)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Classification of tourism trips according to the main purpose refers to nine categories: this typology allows the identification of different subsets of visitors (business visitors, transit visitors, etc.) See also destination of a tourism trip (IRTS 2008, 3.14).
Classification of Tourism. Tourism can be classified into six distinct categories according to the purpose of travel. These are the following: 1) Recreational: Recreational or leisure tourism takes a person away from the humdrum of everyday life. In this case, people spend their leisure time in the hills, sea beaches, etc.
Contents hide 1 Introduction 2 Types of Tourism 2.1 Adventure Tourism 2.2 Cultural Tourism 2.3 Eco-Tourism 2.4 Medical Tourism 2.5 Beach Tourism 2.6 Religious Tourism 2.7 Business Tourism 2.8 Sports Tourism 2.9 Educational Tourism 2.10 Heritage Tourism 2.11 Culinary Tourism 3 Other Types of Tourism 3.1 Annual Holiday Tourism 3.2 Pleasure Tourism 3.3 Relaxation; Rest […]
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
Beyond the ones we listed, there are plenty of other types of tourism, such as medical tourism, religious tourism, wellness tourism, dark tourism, and more. Broadly speaking, however, we could consider leisure and business tourism to be among the two main categories based on travelers' motivation. Categories.
The preparation of international tourism recommendations is a part of the efforts of UNWTO and the United Nations Statistics Division to strengthen countries in the methodological and operational foundations of tourism statistics in an integrated manner, including enhancement of the coherence of tourism statistics with other offi-
In Chapter 3, the main concepts and definitions with respect to tourism are presented and discussed. Special attention is given to the concepts of international tourism, domestic tourism, and same-day visits. Finally, Chapter 4 starts with a brief inventory of the key characteristics of tourism. Variables and classifications are presented and ...
UNWTO Tourism Definitions is a comprehensive and authoritative source of tourism-related terms and concepts, covering different aspects of the tourism sector and its impacts. The publication provides definitions of tourism, tourist, visitor, excursionist, domestic tourism, inbound tourism, outbound tourism, and many more, in English, French and Spanish. It also includes a glossary of acronyms ...
In this case, the classification of tourism types is generally considered to be common knowledge, without need for an explanation. Currently, systematic studies on the classification of tourism types are not available. 2.5. Tourism naming. The literature on tourism naming focuses mainly on the naming of tourism places and attractions.
Classification of Tourism. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism involves the movement of people in the country's natural environment or outside the country for personal or other purposes. These different purposes classified the tourism industry in many ways.
Tourism security is a subdiscipline of tourist studies that explores the factors that affect the ontological security of tourists. Risks are evaluated by their impact and nature. Tourism security includes methodologies, theories and techniques oriented to protect the organic image of tourist destinations.
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities ...
The UNWTO Statistics Department is committed to developing tourism measurement for furthering knowledge of the sector, monitoring progress, evaluating impact, promoting results-focused management, and highlighting strategic issues for policy objectives.. The department works towards advancing the methodological frameworks for measuring tourism and expanding its analytical potential, designs ...
Towns and cities. Examples of tourist cities: Paris, Rome, London, New York, Sydney, Shanghai, Cape Town, Rio de Janeiro. Towns and cities are popular types of tourist destinations. One of the reasons for this popularity is accessibility. Typically, large towns and cities are well connected.
MAIN PURPOSE OF A TOURISM TRIP. This is defined as the purpose for which for which the trip was taken. In the absence of this main purpose the trip would not have been taken. Where more than one parties travel and have different individual purposes, the main purpose is the one central to the decision to take the trip.
Tourism essentially refers to the activities undertaken by visitors, also known as the visitor economy. The tourism industry encompasses all activity that takes place within the visitor economy. This includes activities that are directly related to the tourist, such as staying in a hotel, ordering a meal or visiting a tourist attraction.
Tourism Statistics. Get the latest and most up-to-date tourism statistics for all the countries and regions around the world. Data on inbound, domestic and outbound tourism is available, as well as on tourism industries, employment and complementary indicators. All statistical tables available are displayed and can be accessed individually ...
Multiple and varied types of tourism can be differentiated depending on the topic it addresses. There is film tourism, childbirth tourism, business tourism, etc. From the point of view of the number of people: Individual tourism. It is the type of tourism that is done alone or without company. Sometimes family tourism or with a small group of ...
Second, for tourist classification, certain preliminaries and previous knowledge (i.e., circular reasoning) are made in relation to "known" tourism behavior, such as the presumed visited locations. Finally, most tourist classification approaches lack a holistic basis that addresses both tourist behaviors and destination characteristics ...
Cohen breaks down his tourist typology further, suggesting that there are four main types of tourists: The Drifter. The Explorer. The Individual Mass Tourist. The Organised Mass Tourist. The first two types of tourists (the Drifter and the Explorer) are deemed noninstitutionalised tourists and the latter two (The Individual Mass Tourist and the ...
Depending on the means of transport used distinguish the following forms of tourism: hiking, tourism, rail, road, sea and air. Tourism travel motivations of tourists divided in the following forms: leisure tourism, leisure and recreation, spa treatments or cures, sports, shopping, technical or scientific or religious.
This is the first classification of the degree of tourism development in urban agglomerations under the influence of the high-speed transportation system, and has a pioneering role in subsequent research on the integration of transportation and tourism development. The contribution of this article is twofold.
Mass tourism is when, a large group of people move together for a visit or travel. These types of tourism or travel are generally conducted by institutions, colleges, etc. for different purposes. Controlled Tourism: This is another type of tourism on the basis of size in which their area limited a number of individuals traveling to different parts.
Classification of tourist accommodation: general principles. Atout France - Tourist development agency of France. Accredited inspection body for the classification of tourist accommodation.