You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP)
How to fill out an icvp, how to reissue an icvp, vaccine exemptions (medical waivers), contraindications to required vaccines, where to order icvp.
International Health Regulations (IHR) allow countries to require arriving travelers 1 to provide proof of vaccination against certain diseases. The International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), also referred to as the “yellow card,” is the official, internationally recognized document that travelers use to document proof of vaccination for diseases included under the IHR.
Currently, vaccination against yellow fever, and in some instances, polio, must be documented using the ICVP. Travelers should check CDC’s webpage for their destination to learn if vaccination is required before entry.
There are currently no requirements to use the ICVP to document vaccination(s) against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Yellow Fever Vaccine
Some countries require all travelers to show proof of yellow fever vaccination before entering the country. Other countries require proof of vaccination from travelers arriving from countries with a risk of yellow fever virus exposure; for people visiting multiple countries, the order of travel may be important. Travelers should check CDC’s webpage for their destination to learn if yellow fever vaccination is required or recommended before entry.
Yellow fever vaccination (travel) clinics administer yellow fever vaccine and issue ICVPs to vaccine recipients. The ICVP must be validated with the Uniform Stamp of the center where the vaccine was given. CDC does not issue ICVPs.
ICVPs are valid beginning 10 days after the date of vaccination. Travelers who do not provide a valid ICVP may be denied entry, quarantined, or asked to get revaccinated at the point of entry to a country.
Travelers who received the yellow fever vaccination after December 15, 2007, must provide proof of vaccination on the new ICVP. If a person received the vaccine before December 15, 2007, their original ICVP card is still valid as proof of vaccination against yellow fever.
For more information, visit the CDC Yellow Book chapter: Yellow Fever .
Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV)
Travelers should check CDC’s webpage for their destination to learn if polio vaccination is recommended before entry. Even previously vaccinated travelers might need a one-time booster shot before traveling to countries with a risk of infection with polio virus . Travelers visiting a country with a high risk for polio may be required to show proof of vaccination against polio on their ICVP when departing that country.
For more information, visit the CDC Yellow Book chapter Polio and the Polio Vaccine for International Travelers webpage.
Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine (MenACWY)
Some countries require travelers to provide proof of vaccination against meningococcal disease. Some people who received a previous dose of meningococcal vaccine might need a booster shot. It takes 7–10 days after a person has been vaccinated before they have maximum protection against the disease.
Travelers aged 2 years or older visiting Saudi Arabia for Hajj or Umrah are required to submit proof of vaccination against meningococcal disease administered no less than 10 days and no more than 5 years (or 3 years for polysaccharide vaccine) before their arrival. This proof of vaccination can be documented on an ICVP, but can also be documented elsewhere. For more information, visit CDC’s Yellow Book chapters: Meningococcal Disease and Saudi Arabia: Hajj/Umrah Pilgrimage .
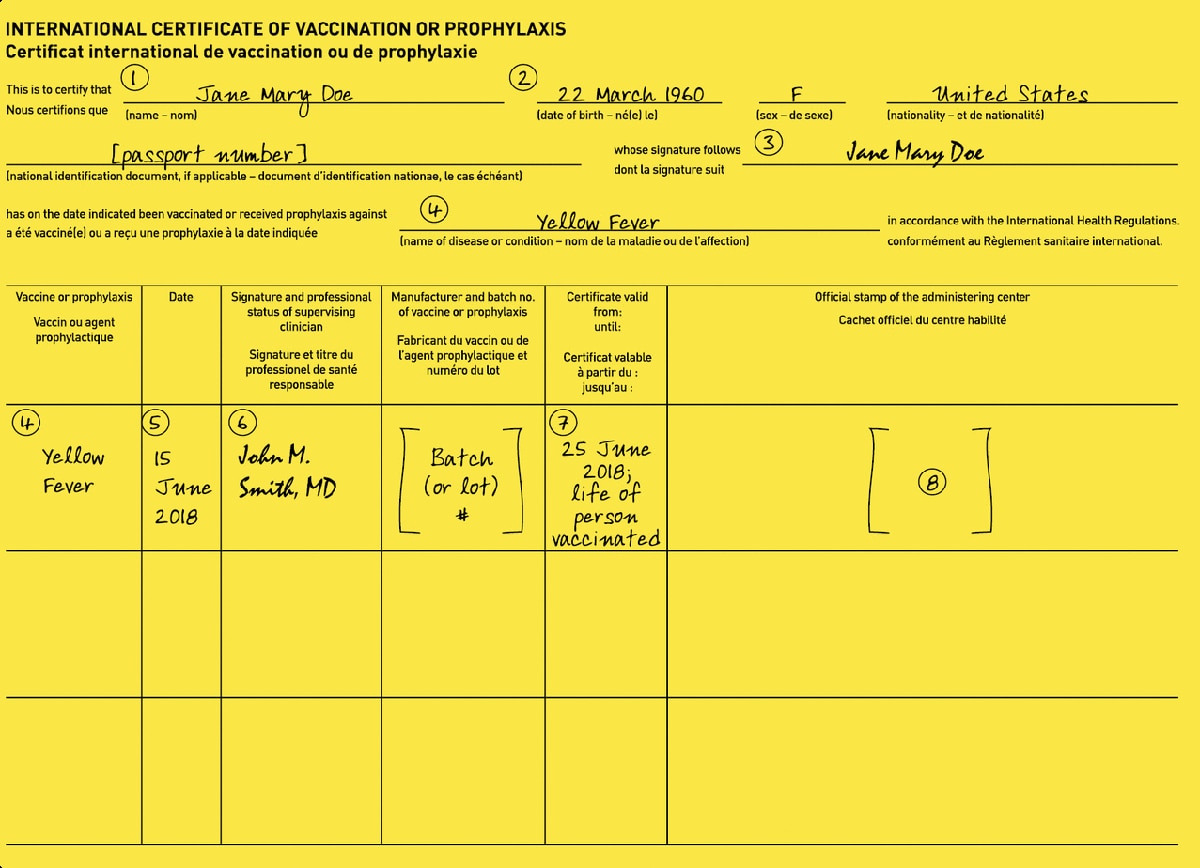
For all required vaccines
(1) Print the traveler’s name exactly as it appears on their passport.
(2), (5), (7) Enter all dates as shown: day (in numerals), month (in letters), year. In the example above, the traveler’s date of birth is correctly entered as 22 March 1960. Do not use DD/MM/YY or MM/DD/YY format.
(3) This space is reserved for the traveler’s signature.
(4) Write the name of the vaccine (yellow fever, polio, meningococcal) in this space. Other vaccinations can be listed on the other side of the ICVP card.
(5) Enter the date of vaccine administration, as shown.
(6) This space is reserved for the clinician’s handwritten signature. A signature stamp is not acceptable.
For Yellow Fever Vaccine
(4) Print “Yellow Fever” in both spaces.
(6) The clinician signing the ICVP can be the yellow fever vaccine Uniform Stamp owner, or another healthcare provider authorized by the stamp owner to administer or supervise the vaccine administration.
(7) The certificate of yellow fever vaccination is valid beginning 10 days after the date of primary vaccination. Add that date to this box along with the suggested wording “life of person vaccinated,” as shown.
(8) Imprint the Uniform Stamp of the vaccinating center in this box.
For Polio Vaccine
(4) Print “Polio” (or “Poliomyelitis”) in both spaces and the specific vaccine that the traveler received in the box.
(6) The clinician administering the polio vaccine should sign their name and indicate their professional status. If transcribing the record of a polio vaccine administered by another clinician in the past 12 months, the transcribing clinician should clearly record the administering clinician’s name and professional status and sign their own name.
(7) The certificate of polio vaccination is valid from the date of vaccination for 1 year.
For Meningococcal Vaccine
(4) Print “Meningococcal” in both spaces and the specific vaccine that the traveler received in the box.
(6) The clinician administering the meningococcal vaccine should sign their name and include their professional status. If transcribing the record of a meningococcal vaccine administered by another clinician in the past 5 years (3 years for polysaccharide vaccine), the transcribing clinician should clearly record the administering clinician’s name and professional status and sign their own name.
(7) For Hajj and Umrah pilgrims, the vaccine must have been administered between 10 days to 5 years (3 years for polysaccharide vaccine) before arrival to Saudi Arabia.
Clinicians may reissue a replacement ICVP to the traveler if they can confirm that the traveler’s vaccine information is accurate.
For All Vaccines
In addition to following all directions in the How to Fill Out an ICVP section, follow these steps to ensure certain sections of the replacement ICVP are correctly filled out
- Date: Enter the date of the original vaccination, not the date of reissuance.
- Signature and professional status of supervising clinician: The clinician who has confirmed the traveler’s information and is reissuing the ICVP should sign.
- Manufacturer and batch no. of vaccine or prophylaxis: Print manufacturer name and lot number.
- For Yellow Fever Vaccine Only: Official stamp of the administering center: The Uniform Stamp of the vaccinating center reissuing the ICVP card should appear in this box.
For international travelers with a medical contraindication to a required vaccine, it is up to the discretion of the clinician to provide them with a medical waiver. Advise the traveler that the destination country might not accept a medical waiver. Acceptance of the medical waiver is at the discretion of the destination country.
To improve the likelihood that border officials at a travelers’ destination will accept a medical waiver and approve entry, travelers should
- Obtain specific and authoritative advice from the embassy or consulate of the destination country or countries.
- Request documentation of requirements for waivers from embassies or consulates and present these, along with the completed Medical Contraindication to Vaccination section of the ICVP.
How to Fill Out an Exemption (Medical Waiver)
Complete and sign the “Medical Contraindications to Vaccination” section of the ICVP. Reasons other than medical contraindications are not acceptable for exemption from vaccination. Yellow fever vaccine providers should validate medical exemptions to yellow fever vaccine using the Uniform Stamp of the yellow fever vaccination center.
Clinicians should also provide the traveler with a signed and dated exemption letter on letterhead stationery, clearly stating the contraindications to vaccination (e.g., age, diagnosis of an immunocompromising condition, allergic reaction). For medical contraindications to yellow fever vaccine, include on the exemption letter an imprint of the Uniform Stamp used by the yellow fever vaccination center to validate the ICVP.
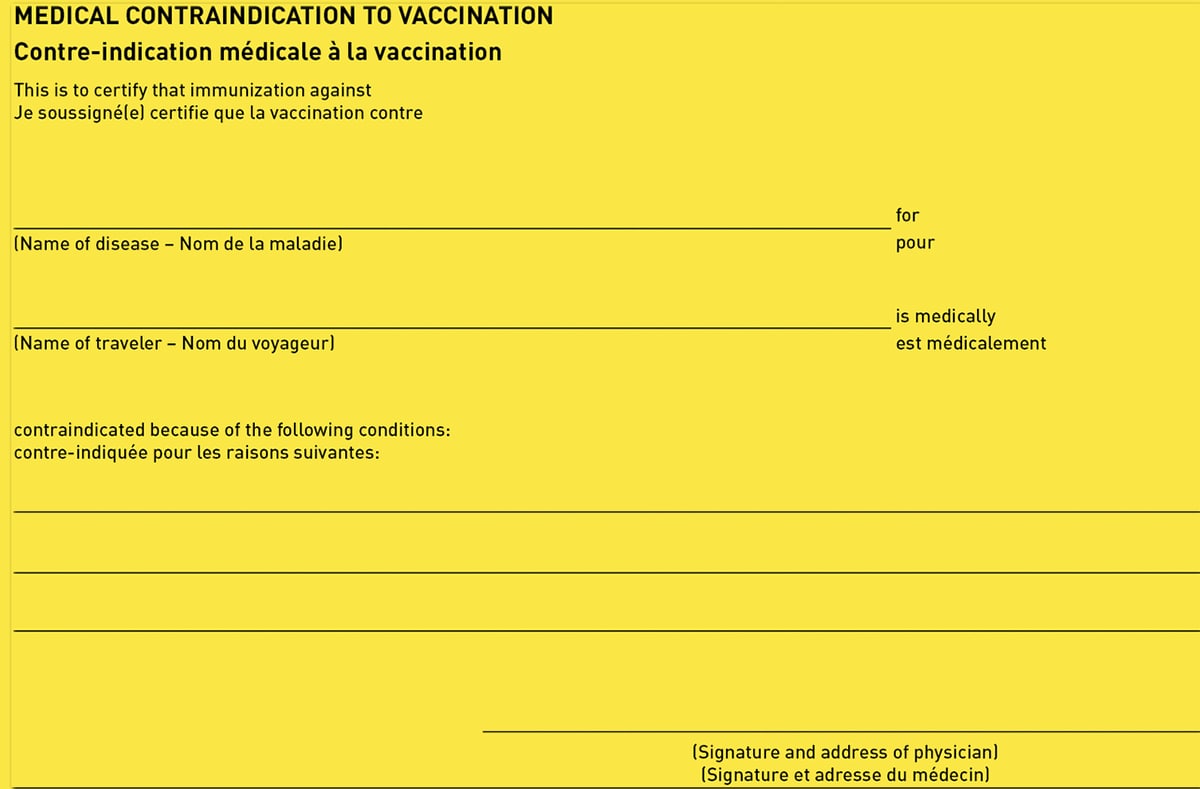
Yellow Fever
Yellow fever vaccine is contraindicated for people with certain underlying health conditions because of the increased risk for serious adverse events. Visit CDC’s Yellow Book chapter: Yellow Fever or the Yellow Fever Vaccine Recommendations webpage.
Do not administer IPV to people who have experienced a life-threatening allergic reaction after a dose of IPV or a severe allergy to any part of this vaccine. For moderately or severely ill people, delay vaccine administration until they recover. Visit the CDC Yellow Book chapter: Polio or the Polio Vaccination webpage for more information on who should not get the polio vaccination.
Meningococcal
MenACWY vaccines should not be administered to people who have experienced a life-threatening allergic reaction after a previous dose of the meningococcal vaccine or a severe allergy to any part of the vaccine. Pregnant people and people who are moderately or severely ill should talk with their healthcare provider before receiving the vaccine. Visit the CDC Yellow Book chapter: Meningococcal Disease or the Meningococcal Vaccine webpage for more information on who should not get the meningococcal vaccine.
ICVPs are available for purchase from the Government Printing Office bookstore. Individual copies are not available. To order, please visit U.S. Government Bookstore or call toll-free (866) 512-1800. Packages of 25 are available for $25 for the United States and $35 for international. Delivery time for orders varies based on shipping options. To have orders mailed via a shipping service, please place your order by phone.
1 Arriving travelers include people in transit on connecting flights.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Explore sell to government
- Ways you can sell to government
- How to access contract opportunities
- Conduct market research
- Register your business
- Certify as a small business
- Become a schedule holder
- Market your business
- Research active solicitations
- Respond to a solicitation
- What to expect during the award process
- Comply with contractual requirements
- Handle contract modifications
- Monitor past performance evaluations
- Explore real estate
- 3D-4D building information modeling
- Art in architecture | Fine arts
- Computer-aided design standards
- Commissioning
- Design excellence
- Engineering
- Project management information system
- Spatial data management
- Facilities operations
- Smart buildings
- Tenant services
- Utility services
- Water quality management
- Explore historic buildings
- Heritage tourism
- Historic preservation policy, tools and resources
- Historic building stewardship
- Videos, pictures, posters and more
- NEPA implementation
- Courthouse program
- Land ports of entry
- Prospectus library
- Regional buildings
- Renting property
- Visiting public buildings
- Real property disposal
- Reimbursable services (RWA)
- Rental policy and procedures
- Site selection and relocation
- For businesses seeking opportunities
- For federal customers
- For workers in federal buildings
- Explore policy and regulations
- Acquisition management policy
- Aviation management policy
- Information technology policy
- Real property management policy
- Relocation management policy
- Travel management policy
- Vehicle management policy
- Federal acquisition regulations
- Federal management regulations
- Federal travel regulations
- GSA acquisition manual
- Managing the federal rulemaking process
- Explore small business
- Explore business models
- Research the federal market
- Forecast of contracting opportunities
- Events and contacts
- Explore travel
- Per diem rates
- Transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.)
- State tax exemption
- Travel charge card
- Conferences and meetings
- E-gov travel service (ETS)
- Travel category schedule
- Federal travel regulation
- Travel policy
- Explore technology
- Cloud computing services
- Cybersecurity products and services
- Data center services
- Hardware products and services
- Professional IT services
- Software products and services
- Telecommunications and network services
- Work with small businesses
- Governmentwide acquisition contracts
- MAS information technology
- Software purchase agreements
- Cybersecurity
- Digital strategy
- Emerging citizen technology
- Federal identity, credentials, and access management
- Mobile government
- Technology modernization fund
- Explore about us
- Annual reports
- Mission and strategic goals
- Role in presidential transitions
- Get an internship
- Launch your career
- Elevate your professional career
- Discover special hiring paths
- Events and training
- Agency blog
- Congressional testimony
- GSA does that podcast
- News releases
- Leadership directory
- Staff directory
- Office of the administrator
- Federal Acquisition Service
- Public Buildings Service
- Staff offices
- Board of Contract Appeals
- Office of Inspector General
- Region 1 | New England
- Region 2 | Northeast and Caribbean
- Region 3 | Mid-Atlantic
- Region 4 | Southeast Sunbelt
- Region 5 | Great Lakes
- Region 6 | Heartland
- Region 7 | Greater Southwest
- Region 8 | Rocky Mountain
- Region 9 | Pacific Rim
- Region 10 | Northwest/Arctic
- Region 11 | National Capital Region
- Per Diem Lookup
United States Tax Exemption Form
- Title: United States Tax Exemption Form
- Form #: SF1094
- Current Revision Date: 04/2015
- Authority or Regulation: GSA-FAR (48 CFR) 53.229
PDF versions of forms use Adobe Reader ™ . Download Adobe Reader ™
PER DIEM LOOK-UP
1 choose a location.
Error, The Per Diem API is not responding. Please try again later.
No results could be found for the location you've entered.
Rates for Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. Territories and Possessions are set by the Department of Defense .
Rates for foreign countries are set by the State Department .
2 Choose a date
Rates are available between 10/1/2021 and 09/30/2024.
The End Date of your trip can not occur before the Start Date.
Traveler reimbursement is based on the location of the work activities and not the accommodations, unless lodging is not available at the work activity, then the agency may authorize the rate where lodging is obtained.
Unless otherwise specified, the per diem locality is defined as "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city, including independent entities located within those boundaries."
Per diem localities with county definitions shall include "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city as well as the boundaries of the listed counties, including independent entities located within the boundaries of the key city and the listed counties (unless otherwise listed separately)."
When a military installation or Government - related facility(whether or not specifically named) is located partially within more than one city or county boundary, the applicable per diem rate for the entire installation or facility is the higher of the rates which apply to the cities and / or counties, even though part(s) of such activities may be located outside the defined per diem locality.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets
Frequently Asked Questions: Guidance for Travelers to Enter the U.S.
Updated Date: April 21, 2022
Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request. On April 21, 2022, DHS announced that it would extend these requirements. In determining whether and when to rescind this order, DHS anticipates that it will take account of whether the vaccination requirement for non-U.S. air travelers remains in place.
These requirements apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for essential or non-essential reasons. They do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply. See CDC guidance for more details regarding air travel requirements.
Below is more information about what to know before you go, and answers to Frequently Asked Questions about cross-border travel.
Entering the U.S. Through a Land Port of Entry or Ferry Terminal
Q. what are the requirements for travelers entering the united states through land poes.
A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following:
- Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website.
- During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
- Bring a Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative compliant border crossing document, such as a valid passport (and visa if required), Trusted Traveler Program card, a Department of State-issued Border Crossing Card, Enhanced Driver’s License or Enhanced Tribal Card when entering the country. Travelers (including U.S. citizens) should be prepared to present the WHTI-compliant document and any other documents requested by the CBP officer.
Q. What are the requirements to enter the United States for children under the age of 18 who can't be vaccinated?
A: Children under 18 years of age are excepted from the vaccination requirement at land and ferry POEs.
Q: Which vaccines/combination of vaccines will be accepted?
A: Per CDC guidelines, all Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved and authorized vaccines, as well as all vaccines that have an Emergency Use Listing (EUL) from the World Health Organization (WHO), will be accepted.
Accepted Vaccines:
- More details are available in CDC guidance here .
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your dose of an accepted single-dose COVID-19 vaccine;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your second dose of an accepted 2-dose series;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received the full series of an accepted COVID-19 vaccine (not placebo) in a clinical trial;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received 2 doses of any “mix-and-match” combination of accepted COVID-19 vaccines administered at least 17 days apart.
Q. Is the United States requiring travelers to have a booster dose to be considered fully vaccinated for border entry purposes?
A: No. The CDC guidance for “full vaccination” can be found here.
Q: Do U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land POEs and ferry terminals?
A: No. Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or Lawful Permanent Residents (LPRs). Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: Is pre- or at-arrival COVID testing required to enter the United States via land POEs or ferry terminals?
A: No, there is no COVID testing requirement to enter the United States via land POE or ferry terminals. In this respect, the requirement for entering by a land POE or ferry terminal differs from arrival via air, where there is a requirement to have a negative test result before departure.
Processing Changes Announced on January 22, 2022
Q: new changes were recently announced. what changed on january 22.
A: Since January 22, 2022, non-citizens who are not U.S. nationals or Lawful Permanent Residents have been required to be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States at land ports of entry and ferry terminals, whether for essential or nonessential purposes. Previously, DHS required that non-U.S. persons be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States for nonessential purposes. Effective January 22, all non-U.S. individuals, to include essential travelers, must be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request. DHS announced an extension of this policy on April 21, 2022.
Q: Who is affected by the changes announced on January 22?
A: This requirement does not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. It applies to other noncitizens, such as a citizen of Mexico, Canada, or any other country seeking to enter the United States through a land port of entry or ferry terminal.
Q: Do U.S. citizens need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land port of entry or ferry terminals?
A: Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. Citizens, U.S. nationals or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: What is essential travel?
A: Under the prior policy, there was an exception from temporary travel restrictions for “essential travel.” Essential travel included travel to attend educational institutions, travel to work in the United States, travel for emergency response and public health purposes, and travel for lawful cross-border trade (e.g., commercial truckers). Under current policy, there is no exception for essential travel.
Q: Will there be any exemptions?
A: While most non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States will need to be vaccinated, there is a narrow list of exemptions consistent with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order in the air travel context.
- Certain categories of individuals on diplomatic or official foreign government travel as specified in the CDC Order
- Children under 18 years of age;
- Certain participants in certain COVID-19 vaccine trials as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals with medical contraindications to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals issued a humanitarian or emergency exception by the Secretary of Homeland Security;
- Individuals with valid nonimmigrant visas (excluding B-1 [business] or B-2 [tourism] visas) who are citizens of a country with limited COVID-19 vaccine availability, as specified in the CDC Order
- Members of the U.S. Armed Forces or their spouses or children (under 18 years of age) as specified in the CDC Order; and
- Individuals whose entry would be in the U.S. national interest, as determined by the Secretary of Homeland Security.
Q: What documentation will be required to show vaccination status?
A: Non-U.S. individuals are required to be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request regardless of the purpose of travel.
The current documentation requirement remains the same and is available on the CDC website . Documentation requirements for entry at land ports of entry and ferry terminals mirror those for entry by air.
Q: What happens if someone doesn’t have proof of vaccine status?
A: If non-U.S. individuals cannot present proof of vaccination upon request, they will not be admitted into the United States and will either be subject to removal or be allowed to withdraw their application for entry.
Q: Will incoming travelers be required to present COVID-19 test results?
A: There is no COVID-19 testing requirement for travelers at land border ports of entry, including ferry terminals.
Q: What does this mean for those who can't be vaccinated, either due to age or other health considerations?
A: See CDC guidance for additional information on this topic. Note that the vaccine requirement does not apply to children under 18 years of age.
Q: Does this requirement apply to amateur and professional athletes?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions.
Q: Are commercial truckers required to be vaccinated?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions. These requirements also apply to bus drivers as well as rail and ferry operators.
Q. Do you expect border wait times to increase?
A: As travelers navigate these new travel requirements, wait times may increase. Travelers should account for the possibility of longer than normal wait times and lines at U.S. land border crossings when planning their trip and are kindly encouraged to exercise patience.
To help reduce wait times and long lines, travelers can take advantage of innovative technology, such as facial biometrics and the CBP OneTM mobile application, which serves as a single portal for individuals to access CBP mobile applications and services.
Q: How is Customs and Border Protection staffing the ports of entry?
A: CBP’s current staffing levels at ports of entry throughout the United States are commensurate with pre-pandemic levels. CBP has continued to hire and train new employees throughout the pandemic. CBP expects some travelers to be non-compliant with the proof of vaccination requirements, which may at times lead to an increase in border wait times. Although trade and travel facilitation remain a priority, we cannot compromise national security, which is our primary mission. CBP Office of Field Operations will continue to dedicate its finite resources to the processing of arriving traffic with emphasis on trade facilitation to ensure economic recovery.
Q: What happens if a vaccinated individual is traveling with an unvaccinated individual?
A: The unvaccinated individual (if 18 or over) would not be eligible for admission.
Q: If I am traveling for an essential reason but am not vaccinated can I still enter?
A: No, if you are a non-U.S. individual. The policy announced on January 22, 2022 applies to both essential and non-essential travel by non-U.S. individual travelers. Since January 22, DHS has required that all inbound non-U.S. individuals crossing U.S. land or ferry POEs – whether for essential or non-essential reasons – be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request.
Q: Are sea crew members on vessels required to have a COVID vaccine to disembark?
A: Sea crew members traveling pursuant to a C-1 or D nonimmigrant visa are not excepted from COVID-19 vaccine requirements at the land border. This is a difference from the international air transportation context.
Entering the U.S. via Air Travel
Q: what are the covid vaccination requirements for air passengers to the united states .
A: According to CDC requirements [www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/noncitizens-US-air-travel.html | Link no longer valid], most noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily must be fully vaccinated prior to boarding a flight to the United States. These travelers are required to show proof of vaccination. A list of covered individuals is available on the CDC website.
Q: What are the COVID testing requirements for air passengers to the United States?
A: Effective Sunday, June 12 at 12:01 a.m. ET, CDC will no longer require pre-departure COVID-19 testing for U.S.-bound air travelers.
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Airport Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
- Skip to navigation
- Skip to main content

- ImmiAccount
- Visa Entitlement Verification Online (VEVO)
- Select language Language Unavailable English
Unvaccinated Australian citizens and permanent residents
travel exemption process to leave australia, need a hand, popular searches, your previous searches.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know

Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- For International Visitors
Types of Exemptions
$200 Exemption
If you cannot claim other exemptions because:
- You have been out of the country more than once in a 30-day period or because
- You have not been out of the country for at least 48 hours.
You may still bring back $200 worth of items free of duty and tax. As discussed earlier, these items must be for your personal or household use.
If you bring back more than $200 worth of dutiable items, or if any item is subject to duty or tax, the entire amount will be dutiable. For instance, you were out of the country for 36 hours and came back with a $300 piece of pottery. You could not deduct $200 from its value and pay duty on $100. The pottery would be dutiable for the full value of $300.
You may include with the $200 exemption your choice of the following: 50 cigarettes and 10 cigars and 150 milliliters (5 fl. oz.) of alcoholic beverages or 150 milliliters (5 fl. oz.) of perfume containing alcohol.
Note that unlike other exemptions, family members may not combine their individual $200 exemptions. Thus, if Mr. and Mrs. Smith spend a night in Canada, each may bring back up to $200 worth of goods, but they would not be allowed a collective family exemption of $400.
Also, duty on items you mail home to yourself will be waived if the value is $200 or less. See the Sending Items Back to the United States and Gifts pages.
$800 Exemption
If you are arriving from anywhere other than a U.S. insular possession (U.S. Virgin Islands, American Samoa, or Guam) you may bring back $800 worth of items duty free, as long as you bring them with you. This is called accompanied baggage.
For Caribbean Basin or Andean countries, your exemption is also $800. These countries include:
- Antigua and Barbuda
- British Virgin Islands
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Netherlands Antilles
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Trinidad and Tobago
You may include two liters of alcoholic beverages with this $800 exemption, as long as one of the liters was produced in one of the countries listed above. Please see the Sending Purchases from Insular Possessions and Caribbean Basin Countries- Duty-Free Shops page for more information.
Depending on what items you're bringing back from your trip, you could come home with more than $800 worth of gifts or purchases and still not be charged duty. For instance, say you received a $700 bracelet as a gift, and you bought a $40 hat and a $60 color print. Because these items total $800, you would not be charged duty, since you have not exceeded your duty-free exemption. If you had also bought a $500 painting on that trip, you could bring all $1,300 worth of merchandise home without having to pay duty, because fine art is duty-free.
$1,600 Exemption
If you return directly or indirectly from a U.S. insular possession (U.S. Virgin Islands, American Samoa, or Guam), you are allowed a $1,600 duty-free exemption.
As long as the amount does not exceed what that state considers a personal quantity*, Customs and Border Protection (CBP) will allow you to enter the U.S. with up to five liters of alcohol duty-free as part of your $1,600 exemption - as long as at least four liters were purchased in the insular possession, and at least one of them is a product of that insular possession. Additional bottles will be subject to a flat duty rate of 1.5% and subject to Internal Revenue Service taxes.
Please note, only one liter of alcohol purchased in a cruise ship's duty-free shop is eligible for a duty-free exemption, although if at least one bottle purchased on board is the product of an eligible Caribbean Basin country**, then you will be allowed two liters duty free. If you buy five liters of alcohol in - say - the U.S. Virgin Islands (USVI), and one of them is the product of the USVI, then you would have reached your duty-free limit. Any additional purchases made on board in a duty-free shop would be subject to CBP duty and IRS tax.
If you buy four bottles in the USVI, one of which is a product of the USVI, then you could purchase one additional bottle from the onboard duty-free, and it would be eligible for duty-free entry.
* Most States restrictions on the amount of alcohol that can be brought into that State apply only to residents of that State. Usually people transiting a state are not subject to those restrictions, but sometimes regulations change, and if this is a matter of utmost importance to you, you can check with the state Alcohol Beverage Control Board where you will be arriving to find out what their policies are.
** Most Caribbean Basin countries are considered beneficiary countries for purposes of this exemption. (Anguilla, Cayman Islands, Guadeloupe, Martinique and Turks and Caicos are not eligible)
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
TSA Cares provides information on security procedures aimed to help passengers with disabilities, medical conditions and individuals needing additional assistance to better prepare for the security screening process.
TSA has modified procedures to ensure that your screening experience is smooth and seamless. For information, please select a support category below.

Support Categories
Information and resources for passengers with disabilities and medical conditions
Information related to religious items or cultural beliefs.
Information for Tribal/Indigenous passengers regarding identification, religious items, and repatriation
Information for passengers who need assistance through the screening checkpoint.
Information for Military Members and DoD Civilians
Information for passengers traveling with children.
Information for passengers 75 years and older.
Federal regulations and training for law enforcement officers.
Information for transgender/non binary/gender nonconforming passengers.
Contact Center
(866) 289-9673 Weekdays: 8 a.m. to 11 p.m. ET Weekends/Holidays: 9 a.m. to 8 p.m. ET Contact TSA
To File a Complaint
If your screening experience did not meet your expectations, you may request to speak with a supervisor at the checkpoint. You may also submit your concern to the TSA Contact Center .
- Meet our partners
- Advertise with us
Canada reveals how extended family, compassionate travellers can apply for travel exemptions

Details have been released on Canada's definition of extended family members, requirements for compassionate travellers to get exempt, and how to get limited release from quarantine.
As of today, October 8, extended family members can now cross the border to Canada, provided they are staying for at least 15 days and meet existing eligibility and admissibility requirements . If you are extended family, you do not need a non-optional, non-discretionary reason to travel to Canada.
Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC)'s definition of extended family shifts depending on how the foreign traveller is related to the Canadian, or their spouse, common-law partner, or dating partner:
If you are directly connected to the Canadian citizen or permanent resident, you can be exempt if you:
- have been in an exclusive dating relationship , for at least one year and have spent time in the physical presence of that person at some point during the relationship;
- are a non-dependent child (adult child);
- are a grandchild (dependent child of a non-dependent adult child);
- are a sibling, half-sibling or step-sibling; or
- a grandparent.
If you are related to the Canadian's spouse or common-law partner you are considered extended family if you are:
- an adult child;
And if you are related to the Canadian's eligible dating partner, you are extended family if you are:
- a dependent child;
- an adult child; or
- a grandchild (dependent child of a non-dependent adult child).
Exempt extended family members will also need a signed declaration by the Canadian citizen or permanent resident that confirms your relationship. You will also need written authorization by IRCC.
Find out if you are eligible for Canadian immigration
Apply for travel exemption as extended family
There is a six-step process to apply for the travel exemption.
Step 1: Your family member fills out an application for authorization and statutory declaration
Your family member who is the Canadian citizen or permanent resident must fill out the application for authorization and statutory declaration form.
Step 2: You sign the declaration
Your family member in Canada sends you the application for authorization and statutory declaration that they filled out. You sign the form and send it back to your family member in Canada.
Step 3: Your family member signs the form by solemn declaration
Once you’ve sent the form back to your family member in Canada, they must sign the form by solemn declaration in front of any authorized official, such as a commissioner for oaths, justice of the peace, lawyer, or notary.
Step 4: Get a copy of the completed and signed form
Your family member in Canada must send you a copy of the completed and signed application for authorization and statutory declaration .
Step 5: Request written authorization to travel
Once you have a copy of the completed and signed application for authorization and statutory declaration use it as evidence of your relationship with your family member and request a written authorization from us.
You need written authorization from IRCC no matter where you’re travelling from.
How you request a written authorization depends on whether or not you already have a valid travel document, such as a Temporary Resident Visa (TRV) or electronic Travel Authorization (eTA).
You should not book a flight to Canada until you get your written authorization from IRCC.
Step 6: Bring your copy of the application for authorization and statutory declaration, as well as the written authorization with you when you travel.
You must have a copy of the application for authorization and statutory declaration as well as the written authorization with you when you travel. This is mandatory. If not, you won’t be allowed to board your flight or enter Canada.
Once the form is signed by solemn declaration, you have six months to travel to Canada. If you don't travel within six months, you’ll need a new statutory declaration.
Come to Canada for compassionate reasons
Friends and family can come visit Canadians, First Nations, permanent residents, temporary residents, and protected persons for compassionate reasons.
You can apply to be exempt from travel restrictions and limited release from quarantine if you are coming to Canada for one of the following reasons:
- to be present during the final moments of life for a loved one, or provide support or care to someone who is critically ill;
- to provide medical support to a person who needs it; and
- to attend a funeral, or end of life ceremony.
Before coming to Canada, you need advance approval for both the exemption to the border restrictions, and the limited release from quarantine. Otherwise, you won't be able to board a plane or enter Canada and you'll be subject to the mandatory quarantine requirements.
Each person making the trip to Canada must fill out their own application form . You need a Letter of Required Support or proof of death, as well as any necessary Site Visit Authorizations in order to submit an application.
Depending on your situation, you may not need all items in the following list:
- be present during the final moments of life for a loved one or to support someone who is critically ill; or
- provide care or support for someone who has a medical reason.
- a statement of death;
- a medical certificate of death;
- a burial permit; or
- a death certificate.
You may also need permission from the site you will be visiting, if you are going to a hospital or other location where you may come in contact with vulnerable people . Canada aims to process applications within seven business days, but notes that some cases will fall outside of the service standard.
Each province and territory may have additional requirements and processes for the limited release.
International travellers will also have to carry acceptable identification and a valid visa, such as a Temporary Resident Visa (TRV) or electronic Travel Authorization (eTA), when coming to Canada. IRCC has more information on what travel documents you will need to cross the border.
Border services officers have the final say on which individuals are allowed to enter the country. Along with your exemption, you will need a 14-day quarantine plan. If you will quarantine with a vulnerable person, you may be asked to provide proof that they consent to let you quarantine with them .
Canada also offers the ArriveCAN app , available on iOS , and Android , in an effort to speed up the arrival process. It allows travellers to submit their information before arrival.
PGP to open October 13
Last week, minister of immigration, Marco Mendicino, announced that students and families would be allowed to come to Canada . Shortly after, IRCC announced that the Parents and Grandparents Program (PGP) would open to expressions of interest from October 13 to November 3 .
Once all the Interest to Sponsor forms are in, IRCC will randomly select potential sponsors and invite them to submit an application. Once applicants receive this invitation, they have 60 days to formally apply to sponsor their parent or grandparent.
IRCC will accept up to 10,000 PGP applications for 2020. There will also be another intake period in 2021, when IRCC will accept up to 30,000 applications.
Are you eligible for PGP 2020? Complete our free eligibility tool!
© 2020 CIC News All Rights Reserved
- coronavirus
- travel restrictions
- Travel to Canada
- Do you need Canadian immigration assistance? Contact the Contact Cohen Immigration Law firm by completing our form
- Send us your feedback or your non-legal assistance questions by emailing us at [email protected]

- Express Entry

- Family Sponsorship
- Citizenship
- Life in Canada
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- International travel, immigration and repatriation during COVID-19
NHS COVID Pass
The NHS COVID Pass service has now closed.
This guidance was withdrawn on 8 March 2024
This content is now available at COVID-19: guidance and support .
Applies to England
- Guidance for Northern Ireland
- Guidance for Scotland
- Guidance for Wales
This page applies to England. See information about COVID certificates in Guernsey , Jersey and the Isle of Man .
There are no longer any domestic requirements to demonstrate your vaccination status.
The NHS COVID Pass is no longer required to travel abroad to any countries.
If you are travelling abroad, you should review travel entry requirements for the countries you will visit or travel through.
The NHS COVID Pass was developed at the height of the pandemic to let you share your COVID-19 vaccination status in a secure way. It was mainly used for international travel, as well as for some domestic purposes, such as entry to venues or events.
Updated guidance as the service has now closed.
Updated information on the XBB vaccine under COVID-19 booster vaccinations.
Updated information on previous medical exemptions – users can no longer view a record of these within the NHS COVID Pass.
Updated guidance.
From 21 July 2022, children aged 5 to 11 in England and the Isle of Man can get a digital NHS COVID Pass for international travel.
Updated to reflect that children aged 5 to 11 in England and Wales can also get a NHS COVID Pass letter for travel if they have evidence of a positive COVID-19 NHS PCR test within the last 180 days.
Updated to reflect that the domestic NHS COVID Pass is no longer available and the medical exemptions service is no longer accepting new applications.
Updated to tell users that from 12 May 2022 the domestic NHS COVID Pass will no longer be available and new medical exemption applications will not be accepted from this point.
NHS COVID Pass letters for international travel are now available for children aged 5 to 11 living in England, Wales and Isle of Man.
Updated to reflect that the domestic NHS COVID Pass letter is no longer available. Updated to no longer encourage high-risk events and venues to check COVID status as a condition of entry. Merged with guidance on medical exemptions and guidance for organisations wanting to use the NHS COVID Pass.
Removed information about the passenger locator form, as people entering the UK no longer need to complete it.
Children aged 5 and above can now have details of eligible COVID-19 vaccinations they have received overseas added to their NHS Record.
Updated to provide information on how to contact the Vaccination Data Resolution Service.
Updated to reflect new government guidance on self isolation policy if you test positive for COVID-19.
From 18 February, residents in England who have received one or more of the following vaccines can have them added to their NHS Record to generate an NHS COVID Pass: Sinopharm Beijing/BIBP, SinoVac-CoronaVac, Covishield (Institute of India) or Covaxin (Bharat Biotech).
Added details about the information that will be needed to prove the identity of children aged 12 and over to get a digital NHS COVID Pass for international travel (available from 3 February 2022).
Updated to reflect it is no longer a legal requirement for venues or events to check the COVID-19 status of attendees as a condition of entry.
From 3 February, children aged 12 and over will be able to get a digital NHS COVID Pass for international travel.
Updated video about the NHS COVID Pass letter for travel abroad in British Sign Language (BSL).
Updated 'What to do if you get a positive test result' section to reflect change in self-isolation rules - people who test positive can stop self-isolating on day 6 if they have negative rapid lateral flow test results on days 5 and 6. Added a reference to the change in rules on 27 January, when it will no longer be mandatory for venues to check the COVID-19 status of attendees as a condition of entry.
Added video about the NHS COVID Pass letter for domestic use in British Sign Language (BSL).
Updated the section 'What to do if you receive a positive test result' to reflect that from 11 January, asymptomatic people in England with a positive lateral flow test are no longer advised to take a confirmatory PCR test to confirm they have COVID-19.
Updated the section 'What the NHS COVID Pass letter tells you: translated versions and alternative formats' to reflect that there are 2 NHS COVID Pass letters (one for travel, one for domestic use). Updated the section 'How to use the NHS COVID Pass when travelling abroad' to add information about the passenger locator form.
Updated the section on how to use the NHS COVID Pass when travelling abroad to reflect that proof of prior infection cannot be used as evidence of your COVID-19 status when entering England.
Guidance updated to reflect changes to the self-isolation advice for people who have received a positive COVID-19 test result.
Added call-out to reflect the NHS COVID Pass digital service will be offline from 10pm on Tuesday 14 December due to planned maintenance.
Updated to correct guidance in the 'Residents in England who have taken part in COVID-19 vaccine clinical trials' section.
Added guidance on new mandatory certification rules on visiting certain venues and events coming into force on Wednesday 15 December if approved by Parliament.
Updated to reflect that fully vaccinated children aged 12 to 15 can request an NHS COVID Pass letter for international travel.
Updated to reflect that fully vaccinated children aged 12 to 15 can request an NHS COVID Pass letter for international travel from 9am on 13 December.
Updated to reflect that you can order an NHS COVID Pass letter to show proof of your booster vaccination for international travel.
Added the section 'Residents in England who have received COVID-19 vaccinations overseas'.
Updated information for residents in England who have taken part in COVID-19 vaccine clinical trials.
Added information about how to store your NHS COVID Pass in Google Pay Wallet.
Updated to reflect the latest information on how to obtain your NHS COVID Pass in digital or letter format via the NHS.UK website.
From 19 November, you can see details of your COVID-19 booster vaccination in your NHS COVID Pass.
Added information about COVID-19 booster vaccinations: The NHS COVID Pass for travel does not currently include COVID-19 booster vaccinations. You do not need a COVID-19 booster vaccination to get an NHS COVID Pass for domestic use in England. Also updated to reflect the UK linking with the EU Gateway. Your NHS COVID Pass can be scanned to check and validate your COVID-19 vaccination status in venues in over 40 countries, including those in the EU.
Updated content to reflect changes to international travel rules on 4 October 2021 (the red, amber, green traffic light system was replaced by a single red list of countries and simplified travel measures for arrivals from the rest of the world).
Added information on using the NHS COVID Pass if you're unable to get vaccinated and/or tested for medical reasons.
From 23 September, you will be able to store your NHS COVID Pass for international travel in Apple Wallet, even if your device is offline.
Updated the 'Children' section: children under 18 do not have to demonstrate their COVID-19 status for entry to domestic events or venues in England. Children aged 16 or over can get an NHS COVID Pass for travel but should follow the entry requirements of the country they are travelling to.
Added a link to information about COVID certificates in the Isle of Man.
Updated to clarify that if you've been vaccinated in Scotland, to obtain your NHS COVID Pass you must be resident in England and registered with a GP in England.
Updated to confirm that you can get NHS COVID Pass if you have been fully vaccinated in England, Wales or Scotland. Updated information for those participating in vaccination clinical trials. Added the phone number for contacting the NHS COVID Pass service from overseas.
Added: 'If you're in the UK armed forces, visit 'My health care hub' on the Defence Gateway (login required) to find out how to get your NHS COVID Pass.'
Updated the BSL guide (video) for people who have received an NHS COVID Pass letter.
Updated to add a link to guidance for people fully vaccinated by the USA or EU.
Updated to reflect that proof of natural immunity shown by a positive PCR test can be used to demonstrate COVID-19 status when travelling abroad; the NHS COVID Pass can be stored used the Apple Wallet when using an iPhone or iPad; and those who received the Novavax vaccine as part of a formally approved vaccine trial, can now obtain the NHS COVID Pass.
Updated to remove information on the Events Research Programme trials, which ended on 25 July 2021.
Updated to reflect that from Monday 19 July, you may be asked to demonstrate your COVID-19 status as a condition of entry to a venue or event in England. Added the conditions of obtaining an NHS COVID Pass for use at domestic events in England.
Added links to guidance about COVID-19 vaccine certification in Guernsey, Jersey and Northern Ireland.
Updated to reflect that the NHS COVID Pass letter has new branding, and that a full course of approved vaccinations now includes the single-dose Janssen vaccine.
Updated to reflect that from 21 June 2021, the NHS service to demonstrate your COVID-19 vaccination status is now called the NHS COVID Pass. Also added that people taking part in event trials as part of the Events Research Programme will also be requested to use the NHS COVID Pass.
Added video in British Sign Language about what to do if you cannot get a post-vaccination letter.
Added information about what to do if you cannot get a post-vaccination status letter.
You can now request a COVID-19 vaccination status letter to be posted to you via the NHS.UK website.
Added link to easy-read version of the COVID-19 post-vaccination confirmation letter.
Updated information on how to access your COVID-19 vaccination status on the NHS website and NHS app.
Updated to add a link to a video about the post-vaccination confimation letter in BSL.
This page has been updated to reflect the latest information on the COVID-19 vaccination status service and includes information on obtaining information in foreign languages and alternative formats.
Updated to reflect that if you call 119 to request a letter about your vaccination status, we expect the letter to take up to 7 working days to reach you.
Updated to reflect that you must wait at least 5 working days after you’ve completed your course of the vaccine before asking for a letter confirming your vaccination status to be posted to you. The letter can take up to 5 working days to reach you. It will be sent automatically to the address registered with your GP.
Updated to reflect that if you're aged 13 to 15, you'll need to contact your GP surgery to request access to GP online services before you can use the NHS App.
Updated to reflect that you should register with the NHS App before booking your international travel.
First published.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

Budget Letters
Budget and accounting policies and instructions are issued periodically, as needed, by the Department of Finance (DOF) as Budget Letters (BL), to supplement and revise the Budgeting Chapter (6000) and accounting chapters of the State Administrative Manual (SAM) . The Department of Finance offers an email subscription for Budget Letters and other budget or accounting related actions and notices. To subscribe, enroll via the Department of Finance Mailing Lists page .
- BL 24-06 Updated – Out-of-State Travel Requests-Approval by the Governor’s Office (issued 4/15/2024)
- BL 24-05 Year-End Financial Reporting Requirements (issued 4/8/2024)
- BL 24-04 The State Contract Act-Project Cost Threshold Adjustments (issued 2/1/2024)
- BL 24-03 Escalation of Construction Costs for State – Funded Capital Outlay Projects (issued 2/1/2024)
- BL 24-02 2024-25 Budget Change Letters (Spring Finance Letters) Update (issued 1/25/2024)
- BL 24-01 Current Year Expenditure Freeze Reporting Instructions and template (Attachment) (issued 1/22/2024)
- BL 23-27 Current Year Expenditure Freeze (issued 12/12/2023)
- BL 23-26 Submission of Final 2024-25 Governor’s Budget Materials (issued 12/4/2023)
- BL 23-25 2024-25 Governor’s Budget Supplementary Schedules (Attachment DF-301) (Attachment DF 302) (issued 11/28/2023)
- BL 23-24 Supplemental Language Report Request (issued 10/25/2023)
- BL 23-23 Employee Compensation Adjustments -Item 9800 (Attachment A) (Attachment B) (issued 10/4/2023)
- BL 23-22 2024-25 Price Letter (issued 9/20/2023)
- BL 23-21 Regulations Process (issued 8/31/2023)
- BL 23-20 Employer Retirement Contributions (Attachment) (issued 8/24/2023)
- BL 23-19 Position Control (issued 8/14/2023)
- BL 23-18 Budget Change Proposal Template and Instructions (issued 8/4/2023)
- BL 23-17 Budget Rollover in Hyperion for the 2024-25 Budget Cycle (issued 8/2/2023)
- BL 23-16 Capital Outlay Budget Proposals, Five Year Infrastructure Plans, Concept Papers, and Deferred Maintenance Submissions for 2024-25 (issued 7/27/2023)
- BL 23-15 Executive Orders and Budget Revisions (issued 7/27/2023)
- BL 23-14 2024-25 Budget Policy (issued 7/26/2023)
- BL 23-13 Expenditure Authorization Controls (issued 7/26/2023)
- BL 23-12 Information Technology Project Planning Budget Change Proposal Reporting Requirement (Attachment) (issued 7/25/2023)
- BL 23-11 Control Section 11.00 – IT Project Reporting Requirements Control Section 11.10 – Statewide Software License Agreements (Attachment) (issued 7/25/2023)
- BL 23-10 Late Payment Penalty Rates (issued 7/24/2023)
- BL 23-09 2024-25 General Administrative Costs and 2024-25 Statewide Cost Allocation Plan (Attachment I) (Attachment II) (issued 7/24/2023)
- BL 23-08 2024-25 Salaries and Wages Spreadsheet (Attachment C) (Attachment D) (issued 7/13/2023)
- BL 23-07 Past Year Budget Adjustments and Fund Balance Reconciliation for the 2024-25 Budget Cycle (Attachment) (issued 7/10/2023)
- BL 23-06 Baseline Budget Adjustments (issued 7/6/2023)
- BL 23-05 2024-25 Budget Preparation Guidelines (issued 6/19/2023)
- BL 23-04 COVID-19 Federal Funds Cost Tracking and Recovery (issued 5/2/2023)
- BL 23-03 Statewide Policies (issued 4/12/2023)
- BL 22-03 2022-23 Budget Change Letters (Spring Finance Letters) (issued 2/3/2022)
- BL 21-28 COVID-19 Federal Funds-Reporting, Monitoring and Auditing, Accounting, and Other Notification Requirements [ Attachment ] (issued 11/01/2021)
- BL 21-23 Ongoing Expenditure Reductions [ Attachment ] (8/18/2021)
- BL 21-17 Information Technology Project Planning Budget Change Proposal Reporting Requirement [ Attachment ] (7/27/2021)
- BL 21-07 2020 Wildfire Cost Reporting (6/16/2021)
- BL 21-02 Leases-New Accounting Policy (1/28/2021)
- BL 20-39 Submission of Final 2021-22 Governor’s Budget Materials (12/16/2020)
- BL 20-38 Governor’s Budget Supplementary Schedules (12/14/2020)
- BL 20-37 Current Year and Ongoing Expenditure Reductions [ Attachment ] (11/03/2020)
- BL 20-33 Employee Comp. Reductions [ Attachment ] (9/3/2020)
- BL 20-32 COVID-19 Cost Reporting [ Attachment ] (8/28/2020)
- BL 20-23 Fund Balance Reconciliation Responsibilities [ Attachment ] (7/20/2020)
- BL 20-12 Federal Stimulus-Accounting and Notification REQS [ Attachment ] (6/8/2020)
- BL 20-11 Current Year Expenditure Reductions [ Attachment ] (4/30/2020)
- BL 20-10 FEMA Reimbursements for COVID-19 Response (4/8/2020)
- BL 20-06 Employee Compensation Adjustments—Item 9800 [ Attachment ] (3/5/2020)
- BL 20-01 Wildfire and PuBLic Safety Power Shutoff Cost Reporting (1/31/2020)
- BL 19-30 Attorney Gen. Legal Services Rate Increases for Client Depts. [ Attachment ] (10/16/2019)
- BL 19-27 Enhancements in FI$CAL (Hyperion)(8/27/2019)
- BL 19-25 Budget Position Transparency [ Attachment ] (8/20/2019)
- BL 19-21 Changes to Certain General Statewide Sections (8/2/2019)
- BL 19-20 Wildfire Cost Reporting (8/01/2019)
- BL 19-02 Securities & Exchange Commission Rule 15c-12; Disclosure REQS Eff. February 27, 2019 (2/22/2019)
- BL 18-26 Control Section 6.10 of the Budget Act of 2018: Statewide Deferred Maintenance [ Attachment ] (8/15/2018)
- BL 16-31 Payment of Victim Comp Board Claims, Depart. of Justice Settlements and Judgments (10/24/2016)
- BL 16-11 Payee Data Record (STD. 204) REQS (7/5/2016)
- BL 16-03 The State Contract Act—Project Cost Threshold Adjustments (2/16/2016)
- BL 16-02 FI$Cal (Hyperion) Updates & Instructions for Spring Budget Process (1/29/2016)
- BL 15-26 U.S. Office of Management and Budget’s (OMB) Guidance for Federal Awards (11/6/2015)
- BL 14-29 Budget Bill Preparation/Process (11/12/2014)
- BL 14-17 Vacant Position Reestablishments (8/6/2014)
- BL 14-09 Budget Revision Instructions for All Multi-Funded Departments (BR-1 REQS) (6/27/2014)
- BL 14-08 Gov Budget Prep: Initial Upload Template—Financial Info System for CA (FI$Cal) (6/20/2014)
- BL 14-07 Implementation of Financial Info. System for California (FI$Cal) (4/29/2014)
- BL 13-30 Economic & Fiscal Impact Assessments/Regulatory Review [ Attachment I ] (12/26/2013)
- BL 13-29 Standardized Regulatory Impact Assessments [ Attachment I ] (12/26/2013)
- BL 13-21 Past, Current, and Budget Yr Schedule 10s (Supplemental Schedules of Appropriations) (8/26/2013)
- BL 13-16 Preparation of 2014-15 Governor’s Budget (8/6/2013)
- BL 13-13 Past Year Schedule 10Rs (Supplementary Schedules of Revenues and Transfers) (7/29/2013)
- BL12-21 Employee Compensation Reductions – Control Section 3.90 [ Attachment ] (8/29/2012)
- BL12-03 Adjust Budget Display Reflect Actual Exp./Eliminate Salary Savings [ Attachment , FAQs ] (3/12/2012)
- DOF DPA letter Personal Services Reduction and Layoff Plan
- MM01-24 Hiring Freeze Guidelines (12/27/2001)
- BL 01-47 Budget Letter Distribution (12/13/2001)
- BL 01-45 Proposed Reduction in 2001-02 Spending (11/19/2001)
- BL 01-39 Statewide Survey of Oracle Database Usage [ Survey , Executive Orders ] (11/5/2001)
- BL 01-35 CALFED Budget Change Proposals (9/7/2001)
- BL 01-07 Cesar Chavez Holiday (3/21/2001)
- BL 01-06 Employee Benefits in Specified Personal Services Contracts (2/26/2001)
- BL 01-04 Costs For Administration of Collective Bargaining, Litigation, and Arbitration (2/13/2001)
- MM02-20 Statewide Information Technology Policy, Instructions, and Guidelines (9/12/2002)
- MM02-12 Restrictions CMAS, Master Services Agreements, & Non-Competitively Bid Contracts
- BL 02-40 Additional 2002-03 Budget Reductions [ Attachment ] (11/21/2002)
- BL 02-39 Control Section 31.60 & 31.70/Government Code Section 12439 [ Attachment ] (11/15/2002)
- BL 02-33 Early Retirement Program [ Attachment ] (10/10/2002)
- BL 02-29 Information Security Controls [ Attachment ] (9/12/2002)
- BL 02-13 2002-03 Statewide Position and Dollar Reduction Plan [ Attachment ]
- BL 02-04 Oracle Enterprise License Agreement Cost Recovery (2/27/2002)
- BL 03-43 Contract, Equipment Acquisition, and Travel Ban [ Attachment , Exec Order S-4-03 ] (12/05/2003)
- BL 03-42 Hiring Freeze(11/26/2003)
- BL 03-41 Control Section 3.60 & Control Section 4.10, Budget Act of 2003 [ Attachment ] (11/17/2003)
- BL 03-37 Feasibility Email Consolidation Savings Attachment [ Attachment ] (9/26/2003)
- BL 03-33 2004-05 20-Percent Reduction/Elimination Proposals [ Attachment ] (9/5/2003)
- BL 03-32 Initial 2004-05 Budget Galley And Preparation Guidelines (8/26/2003)
- BL 03-25 2003-04 Automated Fund Condition Statement Budget Process (8/07/2003)
- BL 03-23 2003-04 Personal Services Reduction Plans [ Attachment ] (8/1/2003)
- BL 03-21 Personal Services Reduction Plans (Revised) (7/22/2003)
- BL 03-16 Updating Capital Outlay Fiscal Impact Worksheets for Legislative Changes (7/1/2003)
- BL 03-13 Assessment of Info. Technology Security Measures, Policies, & Practices (6/9/2003)
- BL 03-12 Cooperative Work Agreements (6/2/2003)
- BL 03-11 Safeguards for Firewalls and Servers (5/13/2003)
- BL 03-03 Notification of Information Technology Incidents and Computer Crimes (2/4/2003)
- BL 04-38 Annual meetings for state advisory boards and commissions (12/13/2008)
- BL 04-37 Attorney Rate Increases Depts w/Special or Non-gov. Cost Funds [ Attachment ] (11/22/2004)
- BL 04-35 Safeguarding Access to State Data (11/16/2004)
- BL 04-23 New Deficiency Funding Process [ Attachment ] (8/13/2004)
- BL 04-18 Major Changes In Deficiency Process May Result In Personal Liability for Directors (8/2/2004)
- BL 04-14 Surcharge For Statewide Costs [ Attachment ] (7/7/2004)
- BL 04-11 2005-06 Governor’s Budget (6/21/2004)
- BL 04-06 2004-05 3-Percent Reduction/Elimination Proposals [ Attachment ] (3/30/2004)
- BL 04-04 Modifications Implementation Statewide Info. Technology Project Framework (2/27/2004)
- BL 04-03 Control Section 4.10, Budget Act 2003, Effect of Program Reductions (2/24/2004)
- BL 04-01 IT Contract Exempt/Exempt Requests Contract/Equip Acq./Travel Ban (1/16/2004)
- BL 05-32 IT Security Policy – Encryption on PortaBLe Computing Devices (11/14/2005)
- BL 05-30 Deficiency Process Could Result Personal Liability Secretaries and Directors (10/17/2005)
- BL 05-17 2006-07 eBudget Process Overview (7/27/2005)
- BL 05-08 Information Technology Security Policy – Classification of Information (6/3/2005)
- BL 05-07 Capital Outlay Five-Year Infrastructure Plan and Budget Submission 2006-07 (5/23/2005)
- BL 05-03 Peer-to-Peer File Sharing (3/7/2005)
- BL 06-36 California Automated Travel Expense Reimbursement System (12/22/2006)
- BL 06-34 IT Security Policy- Info. Security Notification & Reporting (12/7/2006)
- BL 06-30 Methodology Change for General Administrative Costs (Pro Rata) (9/22/2006)
- BL 06-27 GS $Mart and Other Municipal Lease Financing (9/8/2006)
- BL 06-26 Adjustments to Statewide Surcharge [ Attachment ] (9/7/2006)
- BL 06-06 Full Compliance With Requirements To Utilize Authority To Revise Budgets (4/19/2006)
- BL 07-30 Budget Act of 2007, Section 28.00 and Budget Letter 07-25 [ Attachment ] (10/18/2007)
- BL 07-05 Use of Emergency Provision In Item 9840 Must Be Fully Justified (1/31/2007)
- BL 07-03 Policy Changes/Op Recovery/Modifications Designation Ltr /Op Recovery Plan (1/23/2007)
- BL 07-02 Control Section 4.04 for 2007-08—Price Increase Adjustments (1/19/2007)
- BL 08-33 Interim Loans For General OBLigation and Lease Revenue Bond Projects (12/18/2008)
- BL 08-20 Dept of Technology Svcs Rate Adjustments [ Attachment I , Attachment II ] (8/18/2008)
- BL 08-06 Transition IT Project Review, Approval/Oversight Office of State Chief Info (3/14/2008)
- BL 10-38 Sec.3.90: Reduction in Op Expenses/Equip Workforce Sec.15.30—IT Savings (11/30/2010)
- BL 10-28 Expanded Reporting on Federal Grants and Contracts (10/05/2010)
- BL 10-27 California Preschool, Transitional Kindergarten, and Full-Day Kindergarten Facilities Account
- BL 10-24 Automatic Increases Prohibition (9/01/2010)
- BL 10-13 Capitalization of IntangiBLe Assets [ Attachment I , Attachment II ] (6/18/2010)
- BL 10-12 Withholding Requirements On Nonresident Vendor Payments [ Attachment (5/24/2010)
- BL 10-09 General OBLigation Bond Funded Programs/Projects Attachment ] (4/27/2010)
- BL 10-06 Information Technology Expenditure Reporting and Cost Optimization [ Attachment ] (3/30/2010)
- BL 10-02 Architecture Revolving Fund (ARF) Deficit Recovery [ Attachment ] (1/21/2010)
- BL 11-35 Legislative Reports Inventory/ID of Reports No Longer of Value [ Attachment ] (12/21/2011)
- BL 11-33 Repeal of 3-percent Federal Withholding Requirements (12/12/2011)
- BL 11-29 Operational Efficiency Plans [ Attachment ] (9/20/2011)
- BL 11-08 Cellular Device Reduction and Related Savings [ Attachment ] (5/26/2011)
- BL 11-04 Hiring Freeze [ Attachment I , Attachment II ] (3/04/2011)
- BL 11-02 Cellular Phone Reductions [ Attachment I , Attachment II ] (1/28/2011)
- Moscow Tourism
- Moscow Hotels
- Moscow Bed and Breakfast
- Moscow Vacation Rentals
- Flights to Moscow
- Moscow Restaurants
- Things to Do in Moscow
- Moscow Travel Forum
- Moscow Photos
- All Moscow Hotels
- Moscow Hotel Deals
- Things to Do
- Restaurants
- Vacation Rentals
- Travel Stories
- Rental Cars
- Add a Place
- Travel Forum
- Travelers' Choice
- Help Center
Invitation letter-sky traveler-fake website!!! - Moscow Forum
- Europe
- Russia
- Central Russia
- Moscow
Invitation letter-sky traveler-fake website!!!
- United States Forums
- Europe Forums
- Canada Forums
- Asia Forums
- Central America Forums
- Africa Forums
- Caribbean Forums
- Mexico Forums
- South Pacific Forums
- South America Forums
- Middle East Forums
- Honeymoons and Romance
- Business Travel
- Train Travel
- Traveling With Disabilities
- Tripadvisor Support
- Solo Travel
- Bargain Travel
- Timeshares / Vacation Rentals
- Central Russia forums
- Moscow forum

Order on this website, for 2 days without any response, only got a PayPal email confirming take the money from my credit card. On third day, I lodged dispute with my Westpac bank, luckily, without much trouble-just done via bank app. I got my money back after 5 working days. Hope future travellers can avoid this website.

THANK YOU so much for warning folks...I do recall you had a lot of issues...glad you got your money back, but also am sure the delays and hassles were not fun either!
This topic has been closed to new posts due to inactivity.
- Train Booking Moscow to St. Peter Apr 24, 2024
- Planning trip to Russia Apr 09, 2024
- SIM card. Russian SIM cards, do they still work in the UK? Apr 09, 2024
- Union Pay debit card Mar 27, 2024
- Russian trying to book a hotel in Jerusalem Mar 14, 2024
- Dual Citizen Arrested in Russia Mar 12, 2024
- about clothes Feb 27, 2024
- NOTE - border crossing from Finland into Russia closed Feb 09, 2024
- Snow boots in Red Square Feb 04, 2024
- Travelling to Moscow & Murmansk with toddle in winter Feb 02, 2024
- Anyone traveling from London to Moscow this week ? Jan 27, 2024
- Booking accommodation Jan 11, 2024
- Traveling friends (Designers preferred) :) Jan 05, 2024
- Are shops and things closed during Christmas and New Week ? Dec 15, 2023
- Moscow to St Petersburg train or air?? 32 replies
- New Sapsan Express Train from Moscow to St Petersburg 18 replies
- New year's in moscow 8 replies
- Hop on Hop Off Bus Tour 5 replies
- How do you purchase Bolshoi Ballet tickets at a great price? 2 replies
- Select-a-room.com Are they legitimate? 3 replies
- Weather Moscow and St. petersburg in May 8 replies
- Night train to St Petersburg 3 replies
- ATM Access 12 replies
- Visa needed if on layover at Moscow Airport??????? 15 replies
- Where can I get initial answers to ANY question?
Expedia Rewards is now One Key™
Elektrostal, visit elektrostal, check elektrostal hotel availability, popular places to visit.
- Electrostal History and Art Museum
You can spend time exploring the galleries in Electrostal History and Art Museum in Elektrostal. Take in the museums while you're in the area.
- Cities near Elektrostal

- Places of interest
- Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center
- Peter the Great Military Academy
- Central Museum of the Air Forces at Monino
- History of Russian Scarfs and Shawls Museum
- Balashikha Arena
- Balashikha Museum of History and Local Lore
- Bykovo Manor
- Pekhorka Park
- Ramenskii History and Art Museum
- Malenky Puppet Theater
- Drama Theatre BOOM
- Likino Dulevo Museum of Local Lore
- Noginsk Museum and Exhibition Center
- Pavlovsky Posad Museum of Art and History
- Saturn Stadium
- Fairy Tale Children's Model Puppet Theater
- Fifth House Gallery
- Church of Vladimir
- Malakhovka Museum of History and Culture
- Orekhovo Zuevsky City Exhibition Hall

Preparing for the tidal wave of Canadian tax changes

2024 Canadian ESG Reporting Insights

Findings from the 2024 Global Digital Trust Insights

PwC Canada's Federal budget analysis

Canada’s Draft Sustainability Disclosure Standards

27th Annual Global CEO Survey—Canadian insights

2023 Canadian holiday outlook

Embracing the future of capital markets

Five opportunities facing Canadian government and public-sector organizations

How can Canadian family business founders and owners create the right outcomes

Managed Services

PwC Canada drives adoption of Generative AI with firmwide implementation of Copilot for Microsoft 365

Our purpose, vision and values

Inclusion and diversity

Apply today! Now hiring students and new graduates

We’re empowering women to thrive in tech

Why join our assurance practice?
Loading Results
No Match Found
2024 Federal Budget analysis
On April 16, 2024, the Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Finance, Chrystia Freeland, presented the government’s budget. The budget:
- increases the capital gains inclusion rate from 1/2 to 2/3, effective June 25, 2024 (up to $250,000 of annual gains for individuals will continue to benefit from the 1/2 inclusion rate)
- raises the lifetime capital gains exemption to $1.25 million and introduces a new 1/3 inclusion rate for up to $2 million of certain capital gains realized by entrepreneurs
- confirms previously announced alternative minimum tax proposals effective January 1, 2024, but softens the impact of these proposals on charitable donations
- provides design and implementation details for the clean electricity investment tax credit
- introduces accelerated capital cost allowance (CCA) for, and relief from interest deductibility limitations for debt incurred to fund the construction of, certain purpose-built rental housing
- provides immediate expensing for the cost of certain patents and computer equipment and software
- gives the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) additional information gathering powers
This Tax Insights discusses these and other tax initiatives proposed in the budget.
Tax measures
Capital gains inclusion rate.
- Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption
Canadian Entrepreneurs’ Incentive
- Alternative Minimum Tax
Employee Ownership Trust Tax Exemption
Volunteer firefighters tax credit and search and rescue volunteers tax credit, mineral exploration tax credit for flow-through share investors.
- Canada Child Benefit
Disability Supports Deduction
Charities and qualified donees.
- Home Buyers’ Plan
Qualified Investments for Registered Plans
Deduction for tradespeople’s travel expenses, indigenous child and family services settlement, clean electricity investment tax credit, ev supply chain investment tax credit, clean technology manufacturing investment tax credit.
- Accelerated Capital Cost Allowance
Interest Deductions and Purpose-Built Rental Housing
Taxing vacant lands to incentivize construction, confronting the financialization of housing, halal mortgages, non-compliance with information requests, synthetic equity arrangements, mutual fund corporations, canada carbon rebate for small business, avoidance of tax debts, reportable and notifiable transactions penalty, manipulation of bankrupt status.
- Scientific Research and Experimental Development
International
Crypto-asset reporting, withholding for non-resident service providers, international tax reform.
- Extending GST Relief to Student Residences
GST/HST on Face Masks and Face Shields
Previously announced, personal tax measures.
The budget proposes to increase the capital gains inclusion rate from 1/2 to:
- 2/3 for dispositions after June 24, 2024 for corporations and trusts, and
- 2/3 for the portion of capital gains realized after June 24, 2024 in excess of an annual $250,000 threshold for individuals
The $250,000 annual threshold would apply to capital gains realized by an individual, either directly or indirectly via a partnership or trust, net of:
- current year capital losses
- capital losses of other years applied to reduce current year capital gains, and
- capital gains in respect of which the Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption (LCGE), the proposed Employee Ownership Trust Exemption or the proposed Canadian Entrepreneurs’ Incentive is claimed
As a result, the following rates will apply to capital gains earned by individuals in excess of the $250,000 threshold who are subject to the top marginal income tax rate (i.e. on taxable income exceeding: $355,845 in Alberta, $252,752 in British Columbia, $1,103,478 in Newfoundland and Labrador, $500,000 in the Yukon and $246,752 in all other jurisdictions).
The budget also proposes to decrease the stock option deduction to 1/3 to align with the new capital gains inclusion rate. Individuals would continue to benefit from a deduction of 1/2 of the taxable benefit up to a combined $250,000 for both employee stock options and capital gains.
The inclusion rate for net capital losses carried forward and applied against capital gains will be adjusted to reflect the inclusion rate of the capital gains being offset.
Transitional rules will apply to taxation years that begin before June 25, 2024 and end after June 24, 2024 such that capital gains realized before June 25, 2024 would be subject to the 1/2 inclusion rate and capital gains realized after June 24, 2024 (net of any losses) would be subject to a 2/3 inclusion rate. The $250,000 threshold will not be prorated for individuals in 2024 and will apply only against capital gains incurred after June 24, 2024.
Additional details will be provided in the coming months.
Earning capital gains through a Canadian-controlled private corporation (CCPC)
In most jurisdictions, the increase in the capital gains inclusion rate makes it less attractive for individuals to earn capital gains in excess of $250,000 through a CCPC instead of directly. The Appendix shows the resulting income tax deferral (prepayment) and the tax cost for an individual who realizes capital gains in excess of $250,000 and pays tax at the top tax rate.
> Back to top
Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption (LCGE)
The budget proposes to increase the LCGE on eligible capital gains from $1,016,836 to $1,250,000 for dispositions that occur after June 24, 2024. The indexing of the LCGE to inflation will resume in 2026.
The budget introduces the Canadian Entrepreneurs’ Incentive, which will reduce the taxes on capital gains from the disposition of shares by eligible individuals which meet the following conditions:
- at the time of the sale the share was a share of a small business corporation owned directly by an individual
- used principally in an active business carried on primarily in Canada by the CCPC or a related corporation
- certain shares or debts of connected corporations, or
- a combination of these assets
- the individual was a founding investor and the individual held the share for a period of five years prior to the disposition
- at all times since the share subscription until the time immediately before the sale, the individual directly owned shares with a fair market value (FMV) of more than 10% of the FMV of all of the issued and outstanding shares of the corporation and shares entitling the individual to more than 10% of the votes
- throughout the five year period before the disposition the individual was actively engaged in a regular, continuous and substantial basis in the activities of the business
- the share does not represent a direct or indirect interest in a professional corporation, a corporation whose principal asset is the reputation or skill of one or more employees, or a corporation that carries on certain types of businesses including a business operating in the financial, insurance, real estate, food and accommodation, arts, recreation, or entertainment sector, or providing consulting or personal care services
- the share must have been obtained for fair market value consideration
The incentive would provide a capital gains inclusion rate of one half of the prevailing inclusion rate on up to $2 million in capital gains per individual during their lifetime. The $2 million limit will be phased in over 10 years by increments of $200,000 per year reaching $2 million by January 1, 2034.
Applying the proposed 2/3 inclusion rate would result in an inclusion rate of 1/3 for qualifying dispositions. This will apply in addition to the LCGE.
This measure would apply to dispositions that occur after December 31, 2024.
Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
The 2023 budget announced amendments to change the calculation of the AMT. Draft legislative proposals were released for consultation in the summer of 2023. (For more information, see our Tax Insights “ Proposed changes to the alternative minimum tax: How will it affect individuals and trusts ”.)
The budget proposes to revise the proposed charitable donation tax credit claim to allow individuals to claim 80% when calculating AMT (as opposed to the previously proposed 50%).
The budget also proposes additional amendments to the AMT proposals including:
- allowing deductions for the Guaranteed Income Supplement, social assistance and workers compensation payments
- fully exempting employee ownership trusts (EOTs) from the AMT, and
- allowing certain disallowed credits under the AMT to be eligible for the AMT carry-forward (i.e. the federal political contribution tax credit, investment tax credits (ITCs), and labour-sponsored funds tax credit)
The amendments would apply to taxation years that begin after December 31, 2023.
The budget also proposes certain technical amendments to the AMT legislative proposals to exempt certain trusts for the benefit of Indigenous groups.
The 2023 budget proposed tax rules to create EOTs. The 2023 Fall Economic Statement proposed to exempt $10 million of capital gains on the sale of a business to an EOT subject to certain conditions.
The budget introduces the conditions for this exemption. The exemption will be available to an individual (other than a trust) on the sale of a business to an EOT where the following conditions are met:
- the individual, a personal trust of which the individual is a beneficiary, or a partnership in which the individual is a member, disposes of shares of a corporation that is not a professional corporation
- the transaction is a qualifying business transfer (as defined in the proposed rules for EOTs) in which the trust acquiring the shares is not already an EOT or a similar trust with employee beneficiaries
- throughout the 24 months immediately prior to the qualifying business transfer, the transferred shares were exclusively owned by the individual claiming the exemption, a related person, or a partnership in which the individual is a member; and over 50% of the FMV of the corporation’s assets were used principally in an active business
- at any time prior to the qualifying business transfer, the individual (or their spouse or common-law partner) has been actively engaged in the qualifying business on a regular and continuous basis for a minimum period of 24 months
- immediately after the qualifying business transfer, at least 90% of the beneficiaries of the EOT are resident in Canada
Where multiple individuals dispose of shares to an EOT as part of a qualifying transfer and meet the conditions above, they may each claim an exemption, however the total exemption in respect of the sale cannot exceed $10 million. The individuals would have to agree on the allocation of the exemption.
If an EOT has a disqualifying event within 36 months of the transfer, the exemption claim will be retroactively denied. If this occurs more than 36 months after a transfer the EOT will be deemed to realize a capital gain equal to the total exempt capital gains. A disqualifying event would result where an EOT loses its status as an EOT or if less than 50% of the FMV of the qualifying business shares is attributable to assets used principally in an active business at the beginning of two consecutive years of the corporation.
The EOT, any corporation owned by the EOT that acquired the transferred shares, and the individual will need to elect to be jointly and severally, or solitarily liable for any tax payable by the individual as a result of an exemption being denied due to a disqualifying event occurring during the first 36 months.
For the purposes of the AMT calculation the capital gain on the transfer would be subject to an inclusion rate of 30% (consistent with the inclusion rate for capital gains eligible for the LCGE).
An individual’s normal reassessment period as it relates to this exemption is proposed to be extended by an additional three years.
The budget also proposes to expand qualifying business transfers to include the sale of shares to a workers cooperative corporation, provided it meets certain conditions.
These measures will apply to qualifying dispositions of shares that occur between January 1, 2024 through December 31, 2026.
The budget proposes to double the volunteer firefighters tax credit and the search and rescue volunteers tax credit to $6,000 for the 2024 and subsequent taxation years; this increases the maximum annual tax savings to $900.
The budget proposes to extend the eligibility for this credit for an additional year, so that it will apply to flow-through share agreements entered into before April 1, 2025.
Canada Child Benefit (CCB)
A CCB recipient is no longer eligible to claim the CCB in respect of a child in the month following the child’s death. The budget proposes to extend eligibility for the CCB to six months after the child’s death, provided the individual continued to be eligible for the CCB.
The budget proposes to extend the list of expenses recognized for the disability supports deduction.
It also provides that expenses for service animals, as defined under the medical expense tax credit (METC) rules, will be recognized under the disability supports deduction. The individual will choose whether to claim under the METC or the disability supports deduction.
A foreign charity may register as a qualified donee for a 24-month period where it received a gift from His Majesty in right of Canada and it is pursuing certain activities in the national interest of Canada. The budget proposes to extend the eligibility of a foreign charity to be considered a qualified donee from 24 months to 36 months. The foreign charity would also be required to submit an annual information return to the CRA that would be made publicly available. The extension will apply to foreign charities registered after April 16, 2024. The reporting requirements will apply to taxation years beginning after April 16, 2024.
The budget also proposes to simplify the issuance of official donation receipts by removing certain requirements.
Home Buyers’ Plan (HBP)
To help first-time home buyers, the budget proposes to:
- increase, from $35,000 to $60,000, the amount that an eligible home buyer can withdraw from their Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) under the HBP, without subjecting the withdrawal to tax, to buy or build a qualifying home (i.e. a first home or a home for a specified disabled individual), effective for the 2024 and subsequent calendar years, for withdrawals made after April 16, 2024
- temporarily extend the repayment grace period by three years, to five years, under the HBP, so that eligible home buyers who withdraw from their RRSP between January 1, 2022 and December 31, 2025 will have up to five years before they need to start repayments to their RRSP
Registered plans (RRSPs, Registered Retirement Income Funds, Tax-Free Savings Accounts, Registered Education Savings Plans, Registered Disability Savings Plans, First Home Savings Accounts, and Deferred Profit Sharing Plans) can invest only in qualified investments for those plans. Qualified investments include mutual funds, publicly traded securities, government and corporate bonds and guaranteed investment certificates. Over the years the qualified investment rules have been expanded to include additional investments for certain plans and to reflect the introduction of new types of plans, but there are inconsistencies and the qualified investment rules are difficult to understand in some cases.
Specific issues are currently under consideration. Stakeholders are invited to submit comments by July 15, 2024 as to how the qualified investment rules can be modernized on a prospective basis to improve the clarity and coherence of the registered plans regime.
Eligible tradespeople and apprentices in the construction industry are currently able to deduct up to $4,000 in eligible travel and relocation expenses per year by claiming the labour mobility deduction for tradespeople. A private member’s bill (Bill C-241) was introduced to enact an alternative deduction for certain travel expenses of tradespeople in the construction industry, with no cap on expenses, retroactive to the 2022 taxation year.
The budget announces that the government will consider bringing forward amendments to the Income Tax Act (ITA) to provide a single, harmonized deduction for tradespeople’s travel that respects the intent of Bill C-241.
The budget proposes to amend the ITA to exclude from taxation the income of the trusts established under the First Nations Child and Family Services, Jordan’s Principle, and Trout Class Settlement Agreement. This will also ensure that payments received by class members as beneficiaries of the trusts will not be included when computing income for federal income tax purposes.
This measure will apply to the 2024 and subsequent taxation years.
Business tax measures
The 2023 budget proposed a refundable ITC for clean electricity, equal to 15% of the capital cost of eligible property. The 2024 budget provides the design and implementation details of the ITC, including the eligibility criteria. It also includes special rules for property that generates electricity from natural gas with carbon capture and property used to transmit electrical energy between provinces or territories, as well as details of the compliance and recovery process.
The ITC will be available only to eligible Canadian corporations, which are defined as:
- taxable Canadian corporations and pension investment corporations
- provincial and territorial Crown corporations (subject to additional requirements)
- corporations owned by municipalities or Indigenous communities
Property eligible for the ITC includes equipment used to generate electricity from:
- solar, wind or water energy (certain class 43.1 property, but hydroelectric installations would not be subject to a capacity limit)
- concentrated solar energy (as defined for the purposes of the proposed clean technology ITC)
- nuclear fission, including heat generating equipment (as defined for the purposes of the proposed clean technology ITC, without the generating capacity limits and other certain requirements of that credit)
- geothermal energy, including heat generating equipment, if it is used exclusively for that purpose (excluding equipment that is part of a system that extracts fossil fuel for sale)
- specified waste materials, as part of a system
Eligible property also includes equipment that is:
- stationary electricity storage equipment and equipment used for pumped hydroelectric energy storage (excluding any that uses a fossil fuel in operation)
- part of an eligible natural gas energy system (special rules apply)
- used for transmission of electricity between provinces and territories (special rules apply)
Previously proposed labour requirements must be met to qualify for the 15% ITC, otherwise a 5% ITC is available. The ITC will be subject to potential repayment obligations, repayable in proportion to the FMV of the particular property when it has been converted to an ineligible use, exported from Canada, or disposed of.
The ITC will be available for new eligible property (i.e. has not been used for any purposes before its acquisition) that is acquired and becomes available for use after April 15, 2024 and before 2035 in respect of projects that did not begin construction before March 28, 2023.
The budget introduces the EV supply chain ITC, equal to 10% of the cost of buildings used in Canada in the following electric vehicle supply chain segments:
- electric vehicle assembly
- electric vehicle battery production
- cathode active material production
To qualify for the ITC, the taxpayer (or member of a group of related taxpayers) must claim the clean technology manufacturing ITC (CTMITC) in all three of the segments (or must claim the CTMITC in two of the three segments and hold at least a qualifying minority interest in an unrelated corporation that claims the CTMITC in the third segment – the building costs of the unrelated corporation would also qualify for the new ITC).
The ITC is effective for property that is acquired and becomes available for use after December 31, 2023. The ITC will be reduced to 5% for 2033 and 2034 and 0% after 2034. Design and implementation details of the ITC will be provided in the 2024 Fall Economic Statement.
The 2023 budget proposed a clean technology manufacturing ITC, and draft legislative proposals were released in December 2023. The 2024 budget proposes to update the clean technology manufacturing ITC for production of qualifying minerals (such as copper, nickel, cobalt, lithium, graphite and rate earth elements) that occur at polymetallic projects (i.e. projects engaged in the production of multiple minerals) by:
- clarifying that the value of qualifying materials will be used as the appropriate output metric when assessing the extent to which property is used (or expected to be used) for qualifying mineral activities producing qualifying materials
- modifying eligible expenditures to include investments in eligible property used in qualifying mineral activities that are expected to produce primarily qualifying materials at mine or well sites, including tailing ponds and mills located at these sites (50% or more of the financial value of the output comes from qualifying materials)
A safe harbour rule will apply to the recapture rule for all qualifying mineral activities, to mitigate against the effects of mineral price volatility on the potential recapture of the ITC, the details of which will be provided at a later date.
Accelerated Capital Cost Allowance (CCA)
Purpose-built rental housing.
The budget provides an accelerated CCA of 10% for new eligible purpose-built rental projects that begin construction after April 15, 2024 and before January 1, 2031, and are available for use before January 1, 2036.
Eligible property will be new purpose-built rental housing that is a residential complex:
- with at least four private apartment units, or 10 private rooms or suites, and
- in which at least 90% of residential units are held for long-term rental
The Accelerated Investment Incentive (AII), which suspends the half-year rule, will continue to apply to eligible property put in use before 2028. The accelerated CCA will not apply to renovations of existing residential complexes, but new additions to an existing structure will be eligible. Projects that convert existing non-residential real estate into a residential complex will be eligible.
Productivity-enhancing assets
The budget provides immediate expensing (i.e. a 100% first-year CCA deduction) for property that is acquired after April 15, 2024 and becomes available for use before January 1, 2027, for the following CCA classes of assets:
- class 44 (patents or rights to use patented information for a limited or unlimited period)
- class 46 (data network infrastructure equipment and related systems software)
- class 50 (general-purpose electronic data-processing equipment and systems software)
The accelerated CCA will be available only for the year in which the property becomes available for use. For a short taxation year, the accelerated CCA must be prorated and will not be available in the following taxation year. Property that becomes available for use after 2026 and before 2028 will continue to benefit from the AII.
Property that has been used (or acquired for use) for any purpose before it is acquired by the taxpayer will be eligible for the accelerated CCA only if both of the following conditions are met:
- neither the taxpayer nor a non-arm’s length person previously owned the property, and
- the property has not been transferred to the taxpayer on a tax-deferred “rollover” basis
The excessive interest and financing expenses limitation (EIFEL) rules restrict a Canadian taxpayer’s deductions for interest and financing expenses, based upon a percentage of its “tax-EBITDA” (i.e. its taxable income, adjusted for items such as interest expenses, depreciation and amortization). For a discussion of the EIFEL rules, see our Tax Insights “ Bill C-59 ─ Excessive interest and financing expenses limitation (EIFEL) regime .” The EIFEL rules currently include a single sector-specific exemption, for certain interest and financing expenses relating to public-private partnership (P3) infrastructure projects. The budget proposes to extend this election, on an elective basis, for certain interest and financing expenses relating to arm’s length financing that is used to build or acquire certain purpose-built rental housing located in Canada. This exemption will be effective for taxation years beginning after September 30, 2023, consistent with the EIFEL rules more generally. However, this exemption will be available only for expenses incurred before January 1, 2036.
The government is concerned that some landowners are holding residentially zoned vacant land as a speculative investment. The budget announces that the government will consider introducing a new tax on residentially zoned vacant land to spur development. The government will launch consultations later this year.
In March 2024, the government began consultations on how federal policies can better support the needs of all Canadians seeking to become homeowners. The government will provide an update in the 2024 Fall Economic Statement.
The budget announces the government’s intention to restrict the acquisition of existing single-family homes by very large corporate investors. The government will consult in the coming months and provide further details in the 2024 Fall Economic Statement.
The budget announces that the government is exploring new measures to expand access to alternative financing products for home purchasers, such as halal mortgages. These measures could include changes in the tax treatment of these products or a new regulatory regime for financial service providers, while ensuring adequate consumer protections are in place.
The budget proposes several amendments to the CRA’s information gathering provisions in the ITA, with the intent of enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of tax audits and facilitating the collection of tax revenues on a timelier basis. These changes include:
- allowing the CRA to issue a new type of notice, referred to as a “notice of non-compliance” and to levy a monetary penalty
- permitting the CRA to specify that any required information (oral or written) or documents be provided under oath or affirmation
- imposing a penalty when the CRA obtains a compliance order against a taxpayer, and
- extending the stop the clock rules (which suspend the counting of days in the assessment limitation period), so that these rules apply when a taxpayer seeks judicial review of any requirement or notice issued to the taxpayer by the CRA in relation to the audit and enforcement process, and during any period that a notice of non-compliance is outstanding
Analogous amendments are also proposed to other federal tax statutes administered by the CRA. The budget also proposes certain technical amendments to ensure the rules meet their policy objectives.
These amendments would come into force upon royal assent of the enacting legislation.
The ITA allows a corporation to deduct the amount of any dividends received on a share of a corporation resident in Canada, subject to certain limitations.
One of these limitations is an anti-avoidance rule that denies the dividend received deduction in connection with synthetic equity arrangements. Synthetic equity arrangements include arrangements in which a person receives a dividend on a share, but all or substantially all of the risk of loss and opportunity for gain or profit (the “economic exposure”) in respect of the share are provided to another person.
Where a taxpayer enters into a synthetic equity arrangement in respect of a share, the taxpayer is generally obligated to compensate the other person for the amount of any dividends paid on the share. This compensation payment may result in a tax deduction for the taxpayer in addition to the dividend received deduction. Unless the anti-avoidance rule applies to deny the dividend received deduction, a tax loss would generally arise as a result of the two deductions.
The anti-avoidance rule incorporates certain exceptions, including where the taxpayer establishes that no tax-indifferent investor has all or substantially all of the economic exposure in respect of the share. An associated exception is also available for synthetic equity arrangements traded on a derivatives exchange.
The budget proposes to remove the tax-indifferent investor exception (including the exchange traded exception) to the anti-avoidance rule. This measure would prevent taxpayers from claiming the dividend received deduction for dividends received on a share in respect of which there is a synthetic equity arrangement.
This measure would apply to dividends received after December 31, 2024.
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that allows investors to pool their money and invest in a portfolio of investments without purchasing the investments directly. A mutual fund corporation is a mutual fund organized as a corporation that meets certain conditions set out in the ITA.
The ITA includes special rules for mutual fund corporations that facilitate conduit treatment for investors (shareholders). For example, these rules generally allow capital gains realized by a mutual fund corporation to be treated as capital gains realized by its investors. In addition, a mutual fund corporation is not subject to mark-to-market taxation and can elect capital gains treatment on the disposition of Canadian securities.
To qualify as a mutual fund corporation under the ITA, a corporation must satisfy several conditions, including that it must be a “public corporation”. A corporation can meet this condition if a class of its shares is listed on a designated stock exchange in Canada. A corporation that is controlled by a corporate group may satisfy this condition, and qualify as a mutual fund corporation, even though it is not widely held. The government is concerned that this could allow a corporate group to use a mutual fund corporation to benefit from the special rules available to these corporations in an unintended manner.
Although the government believes this planning can be challenged based on existing rules in the ITA, the budget proposes specific amendments to the ITA to preclude a corporation from qualifying as a mutual fund corporation where it is controlled by or for the benefit of a corporate group (including a corporate group that consists of any combination of corporations, individuals, trusts, and partnerships that do not deal with each other at arm’s length). Exceptions would be provided to ensure that the measure does not adversely affect mutual fund corporations that are widely held pooled investment vehicles.
This measure would apply to taxation years that begin after 2024.
The budget introduces the Canada Carbon Rebate for Small Business, to return a portion of the federal backstop pollution pricing fuel charge proceeds collected from a province. This will be an automatic refundable tax credit for CCPCs with less than 500 employees in Canada in the calendar year in which the fuel charge begins. The tax credit in respect of the 2019-20 to 2023-24 fuel charge years will be available to a CCPC that files a tax return for its 2023 taxation year by July 15, 2024 (with similar timelines for future fuel charge years).
The tax credit amount:
- is determined for each applicable province in which the eligible corporation had employees in the calendar year in which the fuel charge year begins; and
- is equal to the number of persons employed by the eligible corporation in the province in that calendar year multiplied by a payment rate specified by the Minister of Finance for the province for the corresponding fuel charge year
The ITA includes an anti-avoidance rule that is intended to prevent taxpayers from avoiding payment of their tax liabilities by transferring their assets to non-arm’s length persons. The effect of this tax debt avoidance rule is to make the transferee jointly and severally, or solidarily, liable with the transferor for the transferor’s tax debts, to the extent that the value of the property transferred exceeds the amount of consideration given by the transferee for the property.
The ITA contains a number of rules that address various planning techniques employed by taxpayers attempting to circumvent the tax debt avoidance rule, as well as a penalty for those who engage in, participate in, assent to, or acquiesce in planning activity that they know, or would reasonably be expected to know, is tax debt avoidance planning.
The budget includes a new specific measure to address tax debt avoidance planning (although the government believes this planning can also be challenged based on existing rules in the ITA). The measure would apply in the following circumstances:
- there has been a transfer of property from a tax debtor to another person
- as part of the same transaction or series of transactions, there has been a separate transfer of property from a person other than the tax debtor to a transferee that does not deal at arm’s length with the tax debtor, and
- one of the purposes of the transaction or series is to avoid joint and several, or solidary, liability
Where these conditions are met, the property transferred by the tax debtor would be deemed to have been transferred to the transferee for the purposes of the tax debt avoidance rule. This would ensure that the tax debt avoidance rule applies in situations where property has been transferred from a tax debtor to a person and, as part of the same transaction or series, property has been received by a non-arm’s length person. The penalty applicable to those who participate in tax debt avoidance planning would also be extended to this proposed new rule.
In many cases, tax debt avoidance planning is facilitated by a planner who receives a significant fee, which is effectively funded by a portion of the avoided tax debt. The courts have held that a taxpayer who engages in tax debt avoidance planning is normally not jointly and severally, or solidarily, liable for the portion of the tax debt that has effectively been retained by the planner as a fee. The budget proposes that taxpayers who participate in tax debt avoidance planning be jointly and severally, or solidarily, liable for the full amount of the avoided tax debt, including any portion that has effectively been retained by the planner.
Similar amendments would be made to comparable provisions in other federal statutes.
These measures would apply to transactions or series of transactions that occur after April 15, 2024.
The ITA includes a general rule providing that a person who fails to file or make a return or comply with certain specified rules is guilty of an offence, and liable to penalties of up to $25,000 and imprisonment for up to a year. The mandatory disclosure rules in the ITA also include specific penalties that apply in these circumstances, making the application of this general penalty provision unnecessary.
The budget therefore proposes to remove from the scope of the general penalty provision the failure to file an information return in respect of a reportable or notifiable transaction under the mandatory disclosure rules.
This amendment would be deemed to have come into force on June 22, 2023, which is the day the enhanced mandatory disclosure rules received royal assent.
Under the ITA, losses and other tax attributes that arise from expenditures for which a taxpayer did not ultimately bear the cost are generally not recognized. The ITA contains a set of debt forgiveness rules that apply where a commercial debt is settled for less than its principal amount. These rules generally reduce tax attributes by the amount of debt that is forgiven and, where tax attributes have been fully reduced, the rules cause an income inclusion equal to half of the remaining forgiven amount. The ITA also contains a rule that entitles an insolvent corporation to a corresponding deduction to offset all or part of an income inclusion from the debt forgiveness rules.
Bankrupt taxpayers are generally excluded from these debt forgiveness rules. Instead, a separate loss restriction rule applies to extinguish the losses of bankrupt corporations that have received an absolute order of discharge.
The government is concerned that some taxpayers have sought to manipulate the bankrupt status of an insolvent corporation, with a view to benefiting from the exception in the debt forgiveness rules while also avoiding the loss restriction rule applicable to bankrupt corporations. This planning seeks to preserve the losses and other tax attributes of the insolvent corporation (which would otherwise be eliminated upon the forgiveness of its debts), so that these attributes can be acquired and used by a profitable corporation. This planning is the subject of a designated transaction under the notifiable transactions element of the mandatory disclosure rules.
Although the government believes that manipulation of bankrupt status can be challenged based on existing rules in the ITA, the budget proposes a specific legislative measure to address this issue: repealing the exception to the debt forgiveness rules for bankrupt corporations and the loss restriction rule applicable to bankrupt corporations. This change would subject bankrupt corporations to the general rules that apply to other corporations whose commercial debts are forgiven. The bankruptcy exception to the debt forgiveness rules would remain in place for individuals. While bankrupt corporations would be subject to the reduction of their loss carryforward balances and other tax attributes upon debt forgiveness, as insolvent corporations they could qualify for relief from the debt forgiveness income inclusion rule provided under the existing deduction for insolvent corporations.
These proposals would apply to bankruptcy proceedings that are commenced on or after April 16, 2024.
Scientific Research and Experimental Development (SR&ED)
The government launched a consultation on the existing SR&ED tax incentives on January 31, 2024, which closed on April 15, 2024. The budget announces a second phase of consultations, to focus on specific policy parameters, explore how Canadian public companies could become eligible for the enhanced SR&ED ITC and inform how additional funding announced by the budget can support future enhancements to the SR&ED program. Further details of the consultation will be released on the Department of Finance Canada website at a later date.
International tax measures
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed a framework for the automatic exchange of tax information relating to transactions in crypto-assets, the Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF). The budget proposes to implement the CARF in Canada. The new reporting rules will apply to crypto-asset service providers that are resident in Canada, or carry on business in Canada, and that provide services effectuating exchange transactions in crypto-assets. These service providers will need to report certain information regarding their customers and crypto-asset transactions. The budget also includes proposed amendments to the Canadian rules implementing the OECD’s Common Reporting Standard, including changes relating to electronic money products and central bank digital currencies. These measures will apply to 2026 and subsequent calendar years.
A person who makes a payment to a non-resident for services rendered in Canada is currently required to withhold 15% of the payment and remit that amount to the CRA. This is intended to serve as a prepayment of tax that the non-resident may ultimately owe in Canada. Certain non-residents do not owe Canadian tax for these services, e.g. due to exemptions in tax treaties, or exemptions for specific activities like international shipping. In these circumstances, the CRA may provide an advance waiver from the withholding obligation for specific transactions, or the non-residents may apply for refunds of amounts that have already been withheld. The budget proposes to give the CRA legislative authority to grant single waivers that cover multiple transactions occurring over a specific time period, where certain conditions are satisfied. This measure will take effect upon royal assent of the enacting legislation.
The OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on Base Erosion and Profit Shifting has developed a two-pillar plan to reform the international tax system, as part of the “BEPS 2.0” initiative. On October 8, 2021, Canada and 135 other countries in the Inclusive Framework committed to adopt this plan (for a discussion on that commitment, see our Tax Insights “ The new international tax framework and Canada’s digital services tax ”). The budget provides an update on the two pillars of this international tax reform initiative.
Pillar One will introduce new rules for allocating taxing rights between countries to address challenges raised by the digital economy. These rules will generally apply to multinational enterprises (MNEs) with annual revenue above €20 billion and profit margins above 10%. The right to tax a portion of these MNEs’ profits will be reallocated to market countries (i.e. the countries where the MNEs’ users and customers are located).
The budget reaffirms Canada’s commitment to bringing Pillar One into effect as soon as a critical mass of countries is willing to participate. In the meantime, Canada is moving ahead with its plan to enact the Digital Services Tax (DST). Implementing legislation for the DST is currently before Parliament in Bill C-59. The DST will take effect beginning in calendar year 2024, with the first year covering taxable revenues earned since January 1, 2022. (For a discussion of the DST, see our Tax Insights “ Digital Services Tax: One step closer to becoming a reality .”)
Pillar Two will introduce a 15% global minimum tax. This tax will generally apply to MNEs with global revenues of at least €750 million. These MNEs will be required to compute their effective tax rate (ETR) in each country where they operate. If the ETR for a particular country is below 15%, a top-up tax will be imposed, to raise that ETR to 15% (this top-up tax may be reduced by a substance-based income exclusion, which is computed based on the payroll costs and net book value of tangible assets located in the jurisdiction). Draft legislative proposals for a Global Minimum Tax Act to implement the Pillar Two regime in Canada were released for public comment in August 2023 (for a discussion of those proposals, see our Tax Insights “ Canada releases draft Global Minimum Tax Act ”). The budget states that Canada is moving forward with this implementing legislation and intends to introduce it in Parliament soon.
Sales tax measures
Extending goods and services tax (gst) relief to student residences.
On September 14, 2023, the government announced that it would temporarily remove the GST from new purpose-built rental housing projects (i.e. apartment buildings, student housing and senior residences built specifically for long-term rental accommodation) by implementing an Enhanced (100%) GST Rental Rebate for new qualifying purpose-built rental housing projects (for more information, see our Tax Insights “ Enhanced GST rental rebate for rental apartments that begin construction after September 13, 2023 ").
To ensure that universities, public colleges and school authorities can also claim the Enhanced (100%) GST Rental Rebate for student residences that are built for short-term use, the budget proposes to amend the Excise Tax Act to allow them to apply the normal GST/Harmonized sales tax (HST) rules that apply to other builders (i.e. paying GST/HST on the final value of the building) in respect of new student housing projects.
The budget also proposes to relax the rebate conditions so that universities, public colleges and school authorities that operate on a not-for-profit basis (i.e. those that would currently qualify for the Public Service Body rebates under the GST/HST) can claim the 100% rebate in respect of any new student residence that they acquire or construct provided it is primarily for the purpose of providing a place of residence for their students.
The proposed measures would apply to student residences that begin construction after September 13, 2023 and before 2031, and that complete construction before 2036.
The budget proposes to repeal the temporary zero rating of certain face masks or respirators and certain face shields under the GST/HST for supplies made after April 30, 2024.
Previously Announced Measures
The budget confirms that the government will proceed with the following previously announced measures, as modified to take into account consultations, deliberations and legislative developments since their announcement or release:
- legislative proposals released on December 20, 2023, which include measures relating to the clean hydrogen ITC, the clean technology manufacturing ITC, concessional loans and short-term rentals
- legislative and regulatory proposals announced in the 2023 Fall Economic Statement, which include measures relating to the Canadian journalism labour tax credit, the expansion of eligibility for the clean technology and clean electricity ITC, the GST/HST joint venture election rules and the Underused Housing Tax
- legislative and regulatory amendments to implement the Enhanced (100%) GST Rental Rebate for purpose-built rental housing announced on September 14, 2023
- the carbon capture, utilization and storage and the clean technology ITCs and labour requirements related to certain “clean economy” ITCs
- enhancing the reduced tax rates for zero-emission technology manufacturers
- flow-through shares and the critical mineral exploration tax credit – lithium from brines
- Retirement Compensation Arrangements
- strengthening the Intergenerational Business Transfer framework
- the income tax and GST/HST treatment of credit unions
- a tax on repurchases of equity
- modernizing the General Anti-Avoidance Rule
- global minimum tax and DST
- technical amendments to GST/HST rules for financial institutions
- providing relief in relation to the GST/HST treatment of payment card clearing services
- extending the quarterly duty remittance option to all licensed cannabis producers
- revised Luxury Tax draft regulations to provide greater clarity on the tax treatment of luxury items
- technical tax amendments to the ITA and the Income Tax Regulations
- legislative amendments to implement changes discussed in the transfer pricing consultation paper released on June 6, 2023
- tax measures announced in the 2023 budget, including the dividend received deduction by financial institutions
- substantive CCPCs
- technical amendments to the ITA and Income Tax Regulations
- legislative amendments to implement the hybrid mismatch arrangements rules announced in the 2021 budget
The budget also reaffirms the government’s commitment to move forward, as required, with technical amendments to improve the certainty and integrity of the tax system.
Integration – Capital gains ($)
(taxation year ended December 31, 2024, and $10,000 of capital gains earned after June 24, 2024)
This table shows:
- the income tax deferral (prepayment) if capital gains in excess of $250,000 are earned and retained in a corporation as opposed to being earned directly by an individual
- the tax (cost) if the after-tax corporate income is paid out as a dividend to the shareholder in 2024
The table assumes:
- the individual is in the top marginal tax rate
- no capital gains deductions are available
- the non-taxable portion of the capital gain is distributed as a tax-free capital dividend
- the taxable dividend paid is sufficient to generate a full refund of refundable tax
Download a PDF
Tax Insights: 2024 Federal budget ─ Supporting housing, raising taxes

Dean Landry
National Tax Leader, PwC Canada
Tel: +1 416 815 5090

© 2018 - 2024 PwC. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the PwC network and/or one or more of its member firms, each of which is a separate legal entity. Please see www.pwc.com/structure for further details.
- Cookies info
- Terms & Conditions
- Site Provider
- Accessibility

IMAGES
COMMENTS
International Health Regulations (IHR) allow countries to require arriving travelers 1 to provide proof of vaccination against certain diseases. The International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), also referred to as the "yellow card," is the official, internationally recognized document that travelers use to document proof of vaccination for diseases included under the IHR.
Title: United States Tax Exemption Form. Form #: SF1094. Current Revision Date: 04/2015. Authority or Regulation: GSA-FAR (48 CFR) 53.229. PDF versions of forms use Adobe Reader ™ . Download Adobe Reader ™.
Under current policy, there is no exception for essential travel. Q: Will there be any exemptions? A: While most non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States will need to be vaccinated, there is a narrow list of exemptions consistent with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order in the air travel context.
It must state you are making an application for travel exemption on the basis that you intend to be absent from Australia for more than three months. Depending on your circumstances, your suitable evidence may also include the following: travel itinerary. marriage, birth, death certificate/s.
Dear Name*: This letter responds to your request for an opinion on whether the travel time of non-exempt foremen and laborers is compensable worktime under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) in three different scenarios. This opinion is based exclusively on the facts you have presented. You represent that you do not seek this opinion for any ...
Types of Exemptions. $200 Exemption. If you cannot claim other exemptions because: You have been out of the country more than once in a 30-day period or because. You have not been out of the country for at least 48 hours. You may still bring back $200 worth of items free of duty and tax. As discussed earlier, these items must be for your ...
Travel code (flight/train number, vessel name) _____ E. Exemption Letters/Medical Notes If the person has a Provincial/Territorial exemption letter, please complete box E, but not F. Does the person possess a medical exemption letter or credential from a Province or Territory, or from a medical doctor or nurse practitioner licenced to practice ...
TSA Cares. TSA Cares provides information on security procedures aimed to help passengers with disabilities, medical conditions and individuals needing additional assistance to better prepare for the security screening process. TSA has modified procedures to ensure that your screening experience is smooth and seamless.
Complete this worksheet to apply for a waiver of Beneficiary Travel deductibles. Unless you are in receipt of VA Pension, Aid and Attendance or Housebound Benefits, provide your projected gross household income and allowable deductible expenses for the current calendar year. The calculator will apply the appropriate threshold to determine your ...
Apply for travel exemption as extended family. There is a six-step process to apply for the travel exemption. Step 1: Your family member fills out an application for authorization and statutory declaration. Your family member who is the Canadian citizen or permanent resident must fill out the application for authorization and statutory ...
No travel ban exemptions are in effect. Français; Español; Русский; عربي; 中文; Facebook; Twitter; YouTube; Flickr; UN Social Media
The letter of authorization for the high-performance amateur athletes exemption will be issued solely by the Deputy Minister of Canadian Heritage (PCH). Foreign nationals in possession of a letter of authorization for the travel exemption must also obtain all other required authorizations needed to travel to Canada seamlessly.
FRMS-8 Recruitment Travel Expense; Certification of In State Travel Expenses; Expense Reimbursement Forms. FRMS-6 In State Travel Per Diem Expense Form (CY 2023) FRMS-6 In State Travel Per Diem Expense Form (CY 2024) FRMS-6D In State Travel Actual Expense Form (CY 2023) FRMS-6D In State Travel Actual Expense Form (CY2023) effective 8.1.2023
The NHS COVID Pass was developed at the height of the pandemic to let you share your COVID-19 vaccination status in a secure way. It was mainly used for international travel, as well as for some ...
The information displayed is based on the available information from the state taxation authority about sales tax and does not include other taxes assessed by county or local governments. As a card/account holder, you are responsible for working with the merchant to meet the requirements of the state. If the merchant has questions, they should ...
Provide completed certificate to hotel to claim exemption from hotel tax. Hotel operators should request a photo ID, business card or other document to verify a guest's afiliation with the exempt entity. Employees of exempt entities traveling on oficial business can pay in any manner. For non-employees to be exempt, the exempt entity must ...
Budget and accounting policies and instructions are issued periodically, as needed, by the Department of Finance (DOF) as Budget Letters (BL), to supplement and revise the Budgeting Chapter (6000) and accounting chapters of the State Administrative Manual (SAM).The Department of Finance offers an email subscription for Budget Letters and other budget or accounting related actions and notices.
This exemption endorsement is a form of stamp affixed to the applicant's travel document, either a Restricted Travel Document (DPT) or an International Malaysian Passport (PMA), which exempts the holder from obtaining a pass or permit to live or work in the State of Sabah. ... Letter of Exchange / Service Placement in the State of Sabah ...
Pre- Interview Checklist For employment-based visa applications: Letter from your U.S. employer dated less than one month ago. If you have ever been convicted of a crime: Court and criminal records, English translation and a photocopy. If you have served in any country's military: Military records and a photocopy. English translations are required only
Subject: Request for Pandemic Exemption. Pursuant to 10 CFR 50.12, [license holder] hereby requests [cite the specific regulation(s) that warrants exemption, and include a brief summary of the supporting evaluation.] Approval of the proposed exemption is requested by [need date, including justification]. [If regulatory commitments are made in ...
1. Travel passport. 2. Ticket booking (vehicle documents).Application form with a photograph stuck on it. 3. Copy of travel passport first page. 4. Documents confirming purpose of travel 5. Medical insurance. 6. 7. Documents for minors. 8. Additional documents After you prepare all the supporting documents please check the rules of submission ...
Planning trip to Russia Apr 09, 2024; SIM card. Russian SIM cards, do they still work in the UK? Apr 09, 2024; Train Booking Moscow to St. Peter Mar 29, 2024; Union Pay debit card Mar 27, 2024; Russian trying to book a hotel in Jerusalem Mar 14, 2024; Dual Citizen Arrested in Russia Mar 12, 2024; about clothes Feb 27, 2024; NOTE - border crossing from Finland into Russia closed Feb 09, 2024
Travel Guide. Check-in. Check-out. Guests. Search. Explore map. Visit Elektrostal. Things to do. Check Elektrostal hotel availability. Check prices in Elektrostal for tonight, Apr 20 - Apr 21. Tonight. Apr 20 - Apr 21. Check prices in Elektrostal for tomorrow night, Apr 21 - Apr 22. Tomorrow night.
The 2023 Fall Economic Statement proposed to exempt $10 million of capital gains on the sale of a business to an EOT subject to certain conditions. The budget introduces the conditions for this exemption. The exemption will be available to an individual (other than a trust) on the sale of a business to an EOT where the following conditions are met: