

Voyager 1 and Voyager 2
Where are they now.
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. In NASA's Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the actual spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers updated every five minutes.
Mission Status
Instrument status.
Voyager 1 Present Position
Voyager 2 present position, voyager's grand tour: 1977 - today.
Voyager 1: 'The Spacecraft That Could' Hits New Milestone

Voyager 1, already the most distant human-made object in the cosmos, reaches 100 astronomical units from the sun on Tuesday, August 15 at 5:13 p.m. Eastern time (2:13 p.m. Pacific time).
News Media Contact
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-354-0880
Subscribe or renew today
Every print subscription comes with full digital access
Science News
‘humanity’s spacecraft’ voyager 1 is back online and still exploring.
After five months of glitching, the spacecraft is talking to Earth again from interstellar space

The Voyager 1 spacecraft (illustrated) is back online after a few months of transmitting garbled data. It’s now poised to continue its exploration of interstellar space.
JPL-Caltech/NASA
Share this:
By Ramin Skibba
April 26, 2024 at 11:45 am
After months of challenging trouble-shooting and suspenseful waiting, Voyager 1 is once again talking to Earth.
The aging NASA spacecraft, about 24 billion kilometers from home, began transmitting garbled data in November. On April 20, NASA scientists got the probe back online after uploading new flight software to work around a chunk of onboard computer memory that had failed. They’re now receiving data about the spacecraft’s health and hope to hear from its science instruments again in a few weeks, says Suzanne Dodd, the mission’s project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
That means the iconic craft could be on a path to recovery — and to continue its exploration of interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 briefly visited Jupiter and Saturn before eventually departing the solar system. It and its twin, Voyager 2, are the longest-operating space probes, now tasked with studying far-flung solar particles and cosmic rays. In particular, the probes have been monitoring the changing of the sun’s magnetic field and the density of plasma beyond the solar system, yielding information about the farthest reaches of the sun’s influence .
“The spacecraft is really remarkable in its longevity. It’s incredible,” Dodd says. “We want to keep Voyager going as long as possible so we have this time record of these changes.”
Voyager 1 and 2, cruising along diverging paths, made history by crossing the heliopause in 2012 and 2018 , respectively ( SN: 9/12/13; SN: 12/10/18 ). At nearly 18 billion kilometers from the sun, that’s long been considered the outer extent of our star’s magnetic field and the solar wind, the boundary before interstellar space.
Since then, Dodd says, the science team has made some surprising findings ( SN: 11/4/19 ). For one, they’ve determined that the heliosphere, the huge bubble of space dominated by the solar wind, might not be spherical but have one or two tails, making it shaped like a comet or a croissant.
And thanks to Voyager, scientists now know that, despite expectations otherwise, the sun’s magnetic field and charged particles actually remain significant even beyond the heliopause, says David McComas, a Princeton University astrophysicist not involved in the mission.
Some theories predicted a serene environment in the distant oceans of interstellar space, but the Voyagers keep passing through waves of charged particles, indicating that the solar magnetic field still holds some sway there. What’s more, the probes’ data have shown how ripples in the field form bubbles at the edge of the solar system, which is more frothy and dynamic than expected.
Other missions have begun building on Voyager’s solar physics research. These include NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, and the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe, or IMAP, which is set to launch next year. Earth-orbiting IBEX has been measuring high-energy particles to map the heliosphere for 15 years, whereas IMAP will orbit between the sun and Earth, giving it an uninterrupted view of the sun as it monitors the galactic cosmic rays that manage to filter through the heliosphere.
“There’s a huge synergy between the Voyagers and both IBEX and IMAP,” says McComas, principal investigator of the latter two missions. “We were all really scared when Voyager 1 stopped phoning home.”
It will be decades until another mission could accomplish what the Voyagers have done. NASA’s New Horizons soared by Pluto in 2015 and kept going ( SN:8/9/18 ). It’s heading toward the edge of the solar system, but it’s cruising slowly and will run out of power before it can collect data beyond the heliopause.
The Voyagers can fly forever, but power for their instruments is waning. Over the next few years, NASA will shut some down to conserve energy for the rest.
That means Voyager 1’s days of collecting science data are numbered. “It’s a very beloved mission,” Dodd says. “It’s humanity’s spacecraft, and we need to take care of it.”
More Stories from Science News on Space

Separating science fact from fiction in Netflix’s ‘3 Body Problem’

Pluto’s heart-shaped basin might not hide an ocean after all

Our picture of habitability on Europa, a top contender for hosting life, is changing

Jupiter’s moon Io may have been volcanically active ever since it was born

50 years ago, scientists found a lunar rock nearly as old as the moon

How a sugar acid crucial for life could have formed in interstellar clouds

What Science News saw during the solar eclipse

During the awe of totality, scientists studied our planet’s reactions
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber? Become one now .
Inside NASA's 5-month fight to save the Voyager 1 mission in interstellar space

After working for five months to re-establish communication with the farthest-flung human-made object in existence, NASA announced this week that the Voyager 1 probe had finally phoned home.
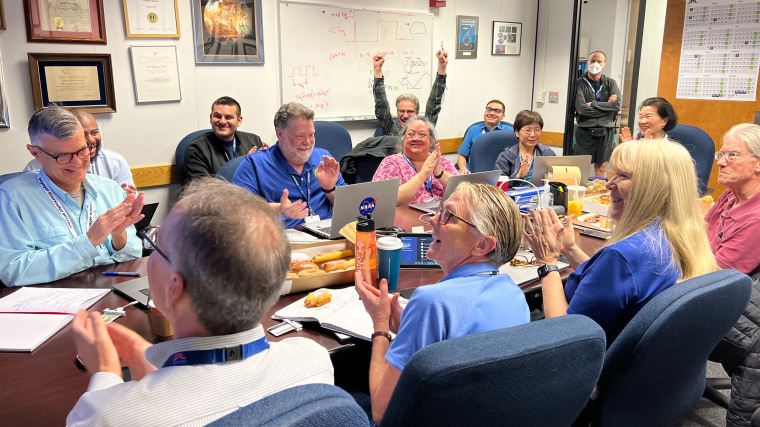
For the engineers and scientists who work on NASA’s longest-operating mission in space, it was a moment of joy and intense relief.
“That Saturday morning, we all came in, we’re sitting around boxes of doughnuts and waiting for the data to come back from Voyager,” said Linda Spilker, the project scientist for the Voyager 1 mission at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “We knew exactly what time it was going to happen, and it got really quiet and everybody just sat there and they’re looking at the screen.”
When at long last the spacecraft returned the agency’s call, Spilker said the room erupted in celebration.
“There were cheers, people raising their hands,” she said. “And a sense of relief, too — that OK, after all this hard work and going from barely being able to have a signal coming from Voyager to being in communication again, that was a tremendous relief and a great feeling.”

The problem with Voyager 1 was first detected in November . At the time, NASA said it was still in contact with the spacecraft and could see that it was receiving signals from Earth. But what was being relayed back to mission controllers — including science data and information about the health of the probe and its various systems — was garbled and unreadable.
That kicked off a monthslong push to identify what had gone wrong and try to save the Voyager 1 mission.
Spilker said she and her colleagues stayed hopeful and optimistic, but the team faced enormous challenges. For one, engineers were trying to troubleshoot a spacecraft traveling in interstellar space , more than 15 billion miles away — the ultimate long-distance call.
“With Voyager 1, it takes 22 1/2 hours to get the signal up and 22 1/2 hours to get the signal back, so we’d get the commands ready, send them up, and then like two days later, you’d get the answer if it had worked or not,” Spilker said.

The team eventually determined that the issue stemmed from one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers. Spilker said a hardware failure, perhaps as a result of age or because it was hit by radiation, likely messed up a small section of code in the memory of the computer. The glitch meant Voyager 1 was unable to send coherent updates about its health and science observations.
NASA engineers determined that they would not be able to repair the chip where the mangled software is stored. And the bad code was also too large for Voyager 1's computer to store both it and any newly uploaded instructions. Because the technology aboard Voyager 1 dates back to the 1960s and 1970s, the computer’s memory pales in comparison to any modern smartphone. Spilker said it’s roughly equivalent to the amount of memory in an electronic car key.
The team found a workaround, however: They could divide up the code into smaller parts and store them in different areas of the computer’s memory. Then, they could reprogram the section that needed fixing while ensuring that the entire system still worked cohesively.
That was a feat, because the longevity of the Voyager mission means there are no working test beds or simulators here on Earth to test the new bits of code before they are sent to the spacecraft.
“There were three different people looking through line by line of the patch of the code we were going to send up, looking for anything that they had missed,” Spilker said. “And so it was sort of an eyes-only check of the software that we sent up.”
The hard work paid off.
NASA reported the happy development Monday, writing in a post on X : “Sounding a little more like yourself, #Voyager1.” The spacecraft’s own social media account responded , saying, “Hi, it’s me.”
So far, the team has determined that Voyager 1 is healthy and operating normally. Spilker said the probe’s scientific instruments are on and appear to be working, but it will take some time for Voyager 1 to resume sending back science data.
Voyager 1 and its twin, the Voyager 2 probe, each launched in 1977 on missions to study the outer solar system. As it sped through the cosmos, Voyager 1 flew by Jupiter and Saturn, studying the planets’ moons up close and snapping images along the way.
Voyager 2, which is 12.6 billion miles away, had close encounters with Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune and continues to operate as normal.
In 2012, Voyager 1 ventured beyond the solar system , becoming the first human-made object to enter interstellar space, or the space between stars. Voyager 2 followed suit in 2018.
Spilker, who first began working on the Voyager missions when she graduated college in 1977, said the missions could last into the 2030s. Eventually, though, the probes will run out of power or their components will simply be too old to continue operating.
Spilker said it will be tough to finally close out the missions someday, but Voyager 1 and 2 will live on as “our silent ambassadors.”
Both probes carry time capsules with them — messages on gold-plated copper disks that are collectively known as The Golden Record . The disks contain images and sounds that represent life on Earth and humanity’s culture, including snippets of music, animal sounds, laughter and recorded greetings in different languages. The idea is for the probes to carry the messages until they are possibly found by spacefarers in the distant future.
“Maybe in 40,000 years or so, they will be getting relatively close to another star,” Spilker said, “and they could be found at that point.”
Denise Chow is a reporter for NBC News Science focused on general science and climate change.
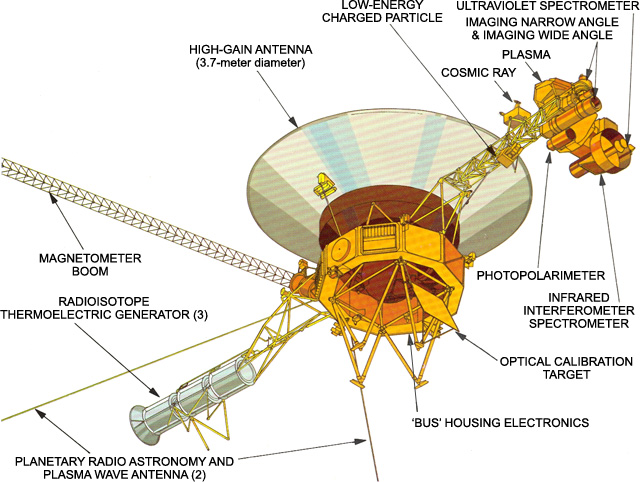
The remarkable twin Voyager spacecraft continue to explore the outer reaches of the solar system decades after they completed their surveys of the Outer Planets. Launched in 1977 (September 5 for Voyager 1 (V1) and August 20 for Voyager 2 (V2), whose trajectory took it past Jupiter after Voyager 1), the spacecraft pair made many fundamental discoveries as they flew past Jupiter (March 1979 for V1, July 1979 for V2) and Saturn (November 1980 for V1, August 1981 for V2). The path of Voyager 2 past Saturn was targeted so that it continued within the plane of the solar system, allowing it to become the first spacecraft to visit Uranus (January 1986) and Neptune (August 1989). Following the Neptune encounter, both spacecraft started a new phase of exploration under the intriguing title of the Voyager Interstellar Mission.

Five instruments continue to collect important measurements of magnetic fields, plasmas, and charged particles as both spacecraft explore different portions of the solar system beyond the orbits of the planets. Voyager 1 is now more than 118 astronomical units (one AU is equal to the average orbital distance of Earth from the Sun) distant from the sun, traveling at a speed (relative to the sun) of 17.1 kilometers per second (10.6 miles per second). Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s.

This processed color image of Jupiter was produced in 1990 by the U.S. Geological Survey from a Voyager image captured in 1979. The colors have been enhanced to bring out detail. Zones of light-colored, ascending clouds alternate with bands of dark, descending clouds. The clouds travel around the planet in alternating eastward and westward belts at speeds of up to 540 kilometers per hour. Tremendous storms as big as Earthly continents surge around the planet. The Great Red Spot (oval shape toward the lower-left) is an enormous anticyclonic storm that drifts along its belt, eventually circling the entire planet.
As seen in the night sky at Earth, Voyager 1 is within the confines of the constellation Ophiuchus, only slightly above the celestial equator; no telescope can see it, but radio contact is expected to be maintained for at least the next ten years. Voyager 2 is within the bounds of the constellation Telescopium (which somehow sounds quite appropriate) in the far southern night sky.

Both spacecraft have already passed something called the Termination Shock † (December 2004 for V1, August 2007 for V2), where the solar wind slows as it starts to interact with the particles and fields present between the stars. It is expected that both spacecraft will encounter the Heliopause, where the solar wind ceases as true interstellar space begins, from 10 to 20 years after crossing the Termination Shock. Theories exist for what should be present in interstellar space, but the Voyagers will become the first man-made objects to go beyond the influences of the Sun, hopefully returning the first measurements of what it is like out there. Each spacecraft is carrying a metal record with encoded sounds and sights from Earth, along with the needle needed to read the recordings, and simplified instructions for where the spacecraft came from, in case they are eventually discovered by intelligent extra-terrestrials.

Keep track of the Voyager spacecraft on the official Voyager Interstellar Mission website or follow @NASAVoyager2 on Twitter. † The sun ejects a continuous stream of charged particles (electrons, protons, etc) that is collectively termed the solar wind. The particles are traveling extremely fast and are dense enough to form a very tenuous atmosphere; the heliosphere represents the volume of space where the effects of the solar wind dominate over those of particles in interstellar space. The solar wind particles are moving very much faster than the local speed of sound represented by their low volume density. When the particles begin to interact with interstellar particles and fields (the interaction can be either physically running into other particles or experiencing an electromagnetic force resulting from a charged particle moving within a magnetic field), then they start to slow down. The point at which they become subsonic (rather than their normal hypersonic speed) is the Termination Shock.
We rely on the generous support of donors, sponsors, members, and other benefactors to share the history and impact of aviation and spaceflight, educate the public, and inspire future generations. With your help, we can continue to preserve and safeguard the world’s most comprehensive collection of artifacts representing the great achievements of flight and space exploration.
- Get Involved
- Host an Event
Thank you. You have successfully signed up for our newsletter.
Error message, sorry, there was a problem. please ensure your details are valid and try again..
- Free Timed-Entry Passes Required
- Terms of Use
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Voyager 1, First Craft in Interstellar Space, May Have Gone Dark
The 46-year-old probe, which flew by Jupiter and Saturn in its youth and inspired earthlings with images of the planet as a “Pale Blue Dot,” hasn’t sent usable data from interstellar space in months.

By Orlando Mayorquin
When Voyager 1 launched in 1977, scientists hoped it could do what it was built to do and take up-close images of Jupiter and Saturn. It did that — and much more.
Voyager 1 discovered active volcanoes, moons and planetary rings, proving along the way that Earth and all of humanity could be squished into a single pixel in a photograph, a “ pale blue dot, ” as the astronomer Carl Sagan called it. It stretched a four-year mission into the present day, embarking on the deepest journey ever into space.
Now, it may have bid its final farewell to that faraway dot.
Voyager 1 , the farthest man-made object in space, hasn’t sent coherent data to Earth since November. NASA has been trying to diagnose what the Voyager mission’s project manager, Suzanne Dodd, called the “most serious issue” the robotic probe has faced since she took the job in 2010.
The spacecraft encountered a glitch in one of its computers that has eliminated its ability to send engineering and science data back to Earth.
The loss of Voyager 1 would cap decades of scientific breakthroughs and signal the beginning of the end for a mission that has given shape to humanity’s most distant ambition and inspired generations to look to the skies.
“Scientifically, it’s a big loss,” Ms. Dodd said. “I think — emotionally — it’s maybe even a bigger loss.”
Voyager 1 is one half of the Voyager mission. It has a twin spacecraft, Voyager 2.
Launched in 1977, they were primarily built for a four-year trip to Jupiter and Saturn , expanding on earlier flybys by the Pioneer 10 and 11 probes.
The Voyager mission capitalized on a rare alignment of the outer planets — once every 175 years — allowing the probes to visit all four.
Using the gravity of each planet, the Voyager spacecraft could swing onto the next, according to NASA .
The mission to Jupiter and Saturn was a success.
The 1980s flybys yielded several new discoveries, including new insights about the so-called great red spot on Jupiter, the rings around Saturn and the many moons of each planet.
Voyager 2 also explored Uranus and Neptune , becoming in 1989 the only spacecraft to explore all four outer planets.

Voyager 1, meanwhile, had set a course for deep space, using its camera to photograph the planets it was leaving behind along the way. Voyager 2 would later begin its own trek into deep space.
“Anybody who is interested in space is interested in the things Voyager discovered about the outer planets and their moons,” said Kate Howells, the public education specialist at the Planetary Society, an organization co-founded by Dr. Sagan to promote space exploration.
“But I think the pale blue dot was one of those things that was sort of more poetic and touching,” she added.
On Valentine’s Day 1990, Voyager 1, darting 3.7 billion miles away from the sun toward the outer reaches of the solar system, turned around and snapped a photo of Earth that Dr. Sagan and others understood to be a humbling self-portrait of humanity.
“It’s known the world over, and it does connect humanity to the stars,” Ms. Dodd said of the mission.
She added: “I’ve had many, many many people come up to me and say: ‘Wow, I love Voyager. It’s what got me excited about space. It’s what got me thinking about our place here on Earth and what that means.’”
Ms. Howells, 35, counts herself among those people.
About 10 years ago, to celebrate the beginning of her space career, Ms. Howells spent her first paycheck from the Planetary Society to get a Voyager tattoo.
Though spacecraft “all kind of look the same,” she said, more people recognize the tattoo than she anticipated.
“I think that speaks to how famous Voyager is,” she said.
The Voyagers made their mark on popular culture , inspiring a highly intelligent “Voyager 6” in “Star Trek: The Motion Picture” and references on “The X Files” and “The West Wing.”
Even as more advanced probes were launched from Earth, Voyager 1 continued to reliably enrich our understanding of space.
In 2012, it became the first man-made object to exit the heliosphere, the space around the solar system directly influenced by the sun. There is a technical debate among scientists around whether Voyager 1 has actually left the solar system, but, nonetheless, it became interstellar — traversing the space between stars.
That charted a new path for heliophysics, which looks at how the sun influences the space around it. In 2018, Voyager 2 followed its twin between the stars.
Before Voyager 1, scientific data on the sun’s gases and material came only from within the heliosphere’s confines, according to Dr. Jamie Rankin, Voyager’s deputy project scientist.
“And so now we can for the first time kind of connect the inside-out view from the outside-in,” Dr. Rankin said, “That’s a big part of it,” she added. “But the other half is simply that a lot of this material can’t be measured any other way than sending a spacecraft out there.”
Voyager 1 and 2 are the only such spacecraft. Before it went offline, Voyager 1 had been studying an anomalous disturbance in the magnetic field and plasma particles in interstellar space.
“Nothing else is getting launched to go out there,” Ms. Dodd said. “So that’s why we’re spending the time and being careful about trying to recover this spacecraft — because the science is so valuable.”
But recovery means getting under the hood of an aging spacecraft more than 15 billion miles away, equipped with the technology of yesteryear. It takes 45 hours to exchange information with the craft.
It has been repeated over the years that a smartphone has hundreds of thousands of times Voyager 1’s memory — and that the radio transmitter emits as many watts as a refrigerator lightbulb.
“There was one analogy given that is it’s like trying to figure out where your cursor is on your laptop screen when your laptop screen doesn’t work,” Ms. Dodd said.
Her team is still holding out hope, she said, especially as the tantalizing 50th launch anniversary in 2027 approaches. Voyager 1 has survived glitches before, though none as serious.
Voyager 2 is still operational, but aging. It has faced its own technical difficulties too.
NASA had already estimated that the nuclear-powered generators of both spacecrafts would likely die around 2025.
Even if the Voyager interstellar mission is near its end, the voyage still has far to go.
Voyager 1 and its twin, each 40,000 years away from the next closest star, will arguably remain on an indefinite mission.
“If Voyager should sometime in its distant future encounter beings from some other civilization in space, it bears a message,” Dr. Sagan said in a 1980 interview .
Each spacecraft carries a gold-plated phonograph record loaded with an array of sound recordings and images representing humanity’s richness, its diverse cultures and life on Earth.
“A gift across the cosmic ocean from one island of civilization to another,” Dr. Sagan said.
Orlando Mayorquin is a general assignment and breaking news reporter based in New York. More about Orlando Mayorquin

What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
Scientists may have discovered a major flaw in their understanding of dark energy, a mysterious cosmic force . That could be good news for the fate of the universe.
A new set of computer simulations, which take into account the effects of stars moving past our solar system, has effectively made it harder to predict Earth’s future and reconstruct its past.
Dante Lauretta, the planetary scientist who led the OSIRIS-REx mission to retrieve a handful of space dust , discusses his next final frontier.
A nova named T Coronae Borealis lit up the night about 80 years ago. Astronomers say it’s expected to put on another show in the coming months.
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .
April 22, 2024
After Months of Gibberish, Voyager 1 Is Communicating Well Again
NASA scientists spent months coaxing the 46-year-old Voyager 1 spacecraft back into healthy communication
By Meghan Bartels

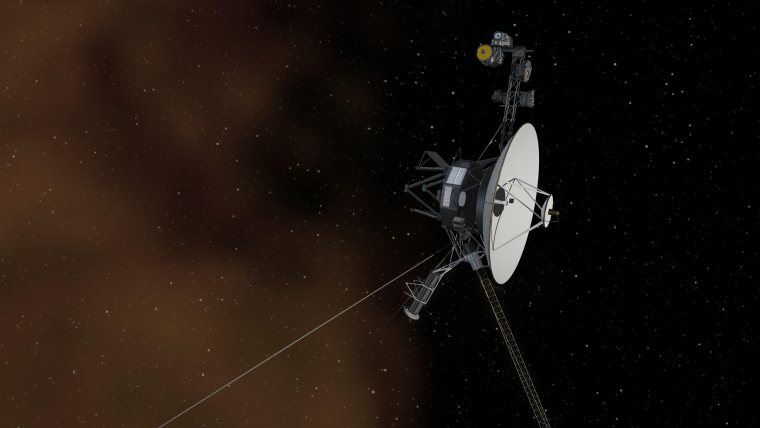
NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is depicted in this artist’s concept traveling through interstellar space, or the space between stars, which it entered in 2012.
NASA/JPL-Caltech
After months of nonsensical transmissions from humanity’s most distant emissary, NASA’s iconic Voyager 1 spacecraft is finally communicating intelligibly with Earth again.
Voyager 1 launched in 1977 , zipped past Jupiter and Saturn within just a few years and has been trekking farther from our sun ever since; the craft crossed into interstellar space in 2012. But in mid-November 2023 Voyager 1’s data transmissions became garbled , sending NASA engineers on a slow quest to troubleshoot the distant spacecraft. Finally, that work has paid off, and NASA has clear information on the probe’s health and status, the agency announced on April 22.
“It’s the most serious issue we’ve had since I’ve been the project manager, and it’s scary because you lose communication with the spacecraft,” said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in an interview with Scientific American when the team was still tracking down the issue.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
The Voyager 1 spacecraft is a scientific legend : It discovered that Jupiter’s moon Io, far from being a dead world like our own companion, is instead a supervolcanic world . The craft’s data suggested that Saturn’s moon Titan might have liquid on its surface. And for more than a decade, Voyager 1 has given scientists a glimpse at what space looks like beyond the influence of our sun.
Yet its long years in the harsh environment of space have done a number on the probe, which was designed to last just four years. In particular, degraded performance and low power supplies have forced NASA to turn off six of its 10 instruments, and its communication has gotten even spottier than can be explained by the fact that cosmic mechanics mean a signal takes nearly one Earth day to travel between humans and the probe.
When the latest communications glitch occurred last fall, scientists could still send signals to the distant probe, and they could tell that the spacecraft was operating. But all they got from Voyager 1 was gibberish—what NASA described in December 2023 as “a repeating pattern of ones and zeros.” The team was able to trace the issue back to a part of the spacecraft’s computer system called the flight data subsystem, or FDS, and identified that a particular chip within that system had failed.
Mission personnel couldn’t repair the chip. They were, however, able to break the code held on the failed chip into pieces they could tuck into spare corners of the FDS’s memory, according to NASA. The first such fix was transmitted to Voyager 1 on April 18. With a total distance of 30 billion miles to cross from Earth to the spacecraft and back, the team had to wait nearly two full days for a response from the probe. But on April 20 NASA got confirmation that the initial fix worked. Additional commands to rewrite the rest of the FDS system’s lost code are scheduled for the coming weeks, according to the space agency, including commands that will restore the spacecraft’s ability to send home science data.
Although, for now, Voyager 1 appears to be on the mend, NASA scientists know it won’t last forever. Sooner or later, a glitch they can’t fix will occur, or the spacecraft’s ever dwindling fuel supply will run out for good. Until then NASA is determined to get as much data as possible out of the venerable spacecraft—and its twin, Voyager 2, which experienced its own communications glitch earlier in 2023 .
How the most distant object ever made by humans is spending its dying days
Voyager 1 continues to observe the farthest corners of the solar system—but it may not for long.
By Rahul Rao | Published Apr 28, 2021 4:00 PM EDT

The eyes of the world might be fixed upon Mars, where last week alone, the Ingenuity helicopter took flight and the Perseverance rover made oxygen . But farther—much farther—Voyager 1, one of the oldest space probes and the most distant human-made object from Earth, is still doing science.
The probe is well into the fourth decade of its mission, and it hasn’t come near a planet since it flew past Saturn in 1980. But even as it drifts farther and farther from a dimming sun, it’s still sending information back to Earth, as scientists recently reported in The Astrophysical Journal.
For decades, Voyager has been sailing away at around 11 miles (17 kilometers) every second. Each year, it travels another 3.5 AU (the distance between Earth and the sun) away from us. Now, it’s sending messages home even as it prepares to leave this solar system behind.
There are multiple ways to think about the “edge of the solar system.” One is a boundary region called the heliopause. That’s the frontier where the solar wind (the soup of charged particles continually thrown off by the sun) is too weak to hold off the interstellar medium—the plasma, dust, and radiation that fill the bulk of space.
When Voyager 1 left Earth in 1977, nobody was certain where the heliopause was, according to Bill Kurth , an astrophysicist at the University of Iowa who has been working with Voyager 1 since before it launched. Some scientists then even thought the heliopause was as close as 10 or even 5 AU—around the orbits of Jupiter, which Voyager 1 passed in 1979, or Saturn.
In reality, the heliopause is around 120 AU away. We know this partly because Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause in August 2012, a whole three and a half decades after it departed Earth. That puts the probe well and truly in interstellar space.
[Related: Voyager 2 can finally probe the rarified plasma surrounding our solar system ]
Out here, space is filled with interstellar medium—but you’ll not see very much of it. A cube of air at sea level on Earth contains more than a trillion times as many molecules as an equal-sized cube of even the interstellar medium’s densest parts. The region that Voyager 1 is traversing is sparser still. And for the most part, it’s quiet.
But every few years, as Voyager 1 records more data about the plasma and dust out here, it finds something . For instance, in 2012 and again in 2014, Voyager 1 felt a shock. According to Kurth, what Voyager 1 recorded was a magnetic spike, accompanied by a burst of energetic electrons that caused intense, oscillating electric fields. These shocks are the most distant effects of the sun, rippling outwards even past the heliopause.
What Voyager 1 encountered in 2020 was another jump in magnetic field strength, but without those intense electrical oscillations. Scientists instead think it’s a pressure front, a much more subtle disturbance moving out into the interstellar medium. Voyager 1 previously encountered something like it in 2017.
According to Jon Richardson , an astrophysicist at MIT who wasn’t an author on the paper, this latest finding shows that Voyager 1 is still capable of surprising scientists. Normally, he says, the probe would need to experience a shock in the surrounding plasma to measure its density. But with observations like this one, scientists have found a way to use Voyager 1 to continually monitor that density—over 13 billion miles away from us.
Richardson also says the findings show that Voyager 1 continues to feel the sun’s tendrils, billions of miles past the heliopause. “The sun is still having a major effect,” he says, “far outside the heliosphere.”
Meanwhile, Voyager 1 is still within the sun’s gravitational influence. In about 300 years, scientists expect, Voyager 1 will start to enter the inner edge of the Oort cloud, that shroud of comets which stretches as far as several light-years away.
We’ve never actually seen evidence of the Oort cloud, but sadly, Voyager 1 likely won’t be the one to reveal it. The probe is quite literally living on borrowed time. Plutonium-238, the radioisotope that powers the probe’s generator, has a half-life of about 88 years.
[Related: Ask Us Anything: What happens to your body when you die in space? ]
As a result, Voyager 1 is starting to lose fuel. Scientists are already having to make choices about which parts of the probe they should keep functional. By the mid-2020s, it’s likely that the probe won’t be able to power even a single instrument.
Still, scientists like Kurth hope they can eke the probe’s life out to 2027, the 50th anniversary of its launch. That, Kurth says, is a milestone that none of Voyager 1’s designers could ever have foreseen.

Rahul Rao is a former intern and contributing science writer for Popular Science since early 2021. He covers physics, space, technology, and their intersections with each other and everything else. Contact the author here.
Like science, tech, and DIY projects?
Sign up to receive Popular Science's emails and get the highlights.
NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft finally phones home after 5 months of no contact
On Saturday, April 5, Voyager 1 finally "phoned home" and updated its NASA operating team about its health.

NASA's interstellar explorer Voyager 1 is finally communicating with ground control in an understandable way again. On Saturday (April 20), Voyager 1 updated ground control about its health status for the first time in 5 months. While the Voyager 1 spacecraft still isn't sending valid science data back to Earth, it is now returning usable information about the health and operating status of its onboard engineering systems.
Thirty-five years after its launch in 1977, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to leave the solar system and enter interstellar space . It was followed out of our cosmic quarters by its space-faring sibling, Voyager 2 , six years later in 2018. Voyager 2, thankfully, is still operational and communicating well with Earth.
The two spacecraft remain the only human-made objects exploring space beyond the influence of the sun. However, on Nov. 14, 2023, after 11 years of exploring interstellar space and while sitting a staggering 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, Voyager 1's binary code — computer language composed of 0s and 1s that it uses to communicate with its flight team at NASA — stopped making sense.
Related: We finally know why NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft stopped communicating — scientists are working on a fix
In March, NASA's Voyager 1 operating team sent a digital "poke" to the spacecraft, prompting its flight data subsystem (FDS) to send a full memory readout back home.
This memory dump revealed to scientists and engineers that the "glitch" is the result of a corrupted code contained on a single chip representing around 3% of the FDS memory. The loss of this code rendered Voyager 1's science and engineering data unusable.

The NASA team can't physically repair or replace this chip, of course, but what they can do is remotely place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. Though no single section of the memory is large enough to hold this code entirely, the team can slice it into sections and store these chunks separately. To do this, they will also have to adjust the relevant storage sections to ensure the addition of this corrupted code won't cause those areas to stop operating individually, or working together as a whole. In addition to this, NASA staff will also have to ensure any references to the corrupted code's location are updated.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
— Voyager 2: An iconic spacecraft that's still exploring 45 years on
— NASA's interstellar Voyager probes get software updates beamed from 12 billion miles away
— NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft extends its interstellar science mission for 3 more years
On April 18, 2024, the team began sending the code to its new location in the FDS memory. This was a painstaking process, as a radio signal takes 22.5 hours to traverse the distance between Earth and Voyager 1, and it then takes another 22.5 hours to get a signal back from the craft.
By Saturday (April 20), however, the team confirmed their modification had worked. For the first time in five months, the scientists were able to communicate with Voyager 1 and check its health. Over the next few weeks, the team will work on adjusting the rest of the FDS software and aim to recover the regions of the system that are responsible for packaging and returning vital science data from beyond the limits of the solar system.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
SpaceX launching Falcon 9 rocket on record-tying 20th mission today
Boeing Starliner 1st astronaut flight: Live updates
Russia vetoes UN resolution against nuclear weapons in space
- Robb62 'V'ger must contact the creator. Reply
- Holy HannaH! Couldn't help but think that "repair" sounded extremely similar to the mechanics of DNA and the evolution of life. Reply
- Torbjorn Larsson *Applause* indeed, thanks to the Voyager teams for the hard work! Reply
- SpaceSpinner I notice that the article says that it has been in space for 35 years. Either I have gone back in time 10 years, or their AI is off by 10 years. V-*ger has been captured! Reply
Admin said: On Saturday, April 5, Voyager 1 finally "phoned home" and updated its NASA operating team about its health. The interstellar explorer is back in touch after five months of sending back nonsense data. NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft finally phones home after 5 months of no contact : Read more
evw said: I'm incredibly grateful for the persistence and dedication of the Voyagers' teams and for the amazing accomplishments that have kept these two spacecrafts operational so many years beyond their expected lifetimes. V-1 was launched when I was 25 years young; I was nearly delirious with joy. Exploring the physical universe captivated my attention while I was in elementary school and has kept me mesmerized since. I'm very emotional writing this note, thinking about what amounts to a miracle of technology and longevity in my eyes. BRAVO!!! THANK YOU EVERYONE PAST & PRESENT!!!
- EBairead I presume it's Fortran. Well done all. Reply
SpaceSpinner said: I notice that the article says that it has been in space for 35 years. Either I have gone back in time 10 years, or their AI is off by 10 years. V-*ger has been captured!
EBairead said: I presume it's Fortran. Well done all.
- View All 11 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 Beavers are helping fight climate change, satellite data shows
- 3 Astronomers just discovered a comet that could be brighter than most stars when we see it next year. Or will it?
- 4 This Week In Space podcast: Episode 108 — Starliner: Better Late Than Never?
- 5 Boeing's Starliner spacecraft will not fly private missions yet, officials say
Voyager 1 talking to Earth again after NASA engineers 24 billion kilometres away devise software fix
NASA's Voyager 1 probe — the most distant man-made object in the universe — is returning usable information to ground control following months of spouting gibberish, the US space agency says.
The spaceship stopped sending readable data back to Earth on November 14, 2023, even though controllers could tell it was still receiving their commands.
In March, teams working at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered that a single malfunctioning chip was to blame.
They then had to devise a clever coding fix that worked within the tight memory constraints of its 46-year-old computer system.
"There was a section of the computer memory no longer working," project leader Dr Linda Spilker told the ABC.
"So we had to reprogram what was in that memory, move it to a different location, link everything back together and send everything up in a patch.
"And then on Saturday morning, we watched as Voyager 1 sent its first commands back and we knew we were back in communication once again."
Dr Spilker said they were receiving engineering data, so they knew the health and safety of the spacecraft.
"The next step is going to be to develop a patch so we can send back the science data," she said.
"That will really be exciting, to once again learn about interstellar space and what has been going on there that we've missed since November."
Dr Spilker said Voyager sent back data in real time, so the team had no facility to retrieve data covering the time since transmission was lost.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was mankind's first spacecraft to enter the interstellar medium , in 2012, and is currently more than 24 billion kilometres from Earth.
Messages sent from Earth take about 22.5 hours to reach the spacecraft.
Its twin, Voyager 2, also left the solar system in 2018 as it was tracked by Australia's Parkes radio telescope.
Australia was also vital to a 2023 search for Voyager 2 after signals were lost, with Canberra's Deep Space Communication Complex monitoring for signals and then sending a successful command to shift the spacecraft's antenna 2 degrees .
Both Voyager spacecraft carry " Golden Records ": 12-inch, gold-plated copper disks intended to convey the story of our world to extraterrestrials.
These include a map of our solar system, a piece of uranium that serves as a radioactive clock allowing recipients to date the spaceship's launch, and symbolic instructions that convey how to play the record.
The contents of the record, selected for NASA by a committee chaired by legendary astronomer Carl Sagan, include encoded images of life on Earth, as well as music and sounds that can be played using an included stylus.
Their power banks were expected to be depleted sometime after 2025, but Dr Spilker said several systems had been turned off, so they were hopeful the two spacecraft would function into the 2030s.
They will then continue to wander the Milky Way, potentially for eternity, in silence.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Nasa restores contact with missing voyager 2 spacecraft after weeks of silence.
How songs from tiny villages in the Pacific are now floating in outer space
Voyager 1 spacecraft enters interstellar space
- Astronomy (Space)
- Computer Science
- Space Exploration
- United States
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Well, hello, Voyager 1! The venerable spacecraft is once again making sense

Nell Greenfieldboyce

Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months. NASA/JPL-Caltech hide caption
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months.
NASA says it is once again able to get meaningful information back from the Voyager 1 probe, after months of troubleshooting a glitch that had this venerable spacecraft sending home messages that made no sense.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space, the previously unexplored region between the stars. (Its twin, traveling in a different direction, followed suit six years later.)
Voyager 1 had been faithfully sending back readings about this mysterious new environment for years — until November, when its messages suddenly became incoherent .

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is talking nonsense. Its friends on Earth are worried
It was a serious problem that had longtime Voyager scientists worried that this historic space mission wouldn't be able to recover. They'd hoped to be able to get precious readings from the spacecraft for at least a few more years, until its power ran out and its very last science instrument quit working.
For the last five months, a small team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California has been working to fix it. The team finally pinpointed the problem to a memory chip and figured out how to restore some essential software code.
"When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft," NASA stated in an update.
The usable data being returned so far concerns the workings of the spacecraft's engineering systems. In the coming weeks, the team will do more of this software repair work so that Voyager 1 will also be able to send science data, letting researchers once again see what the probe encounters as it journeys through interstellar space.

After a 12.3 billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
- interstellar mission
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Become an FT subscriber
Try unlimited access Only $1 for 4 weeks
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- Videos & Podcasts
- FT App on Android & iOS
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Premium newsletters
- Weekday Print Edition
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Premium Digital
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Everything in Print
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition

- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
The Golden Record
Pioneers 10 and 11, which preceded Voyager, both carried small metal plaques identifying their time and place of origin for the benefit of any other spacefarers that might find them in the distant future. With this example before them, NASA placed a more ambitious message aboard Voyager 1 and 2, a kind of time capsule, intended to communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials. The Voyager message is carried by a phonograph record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year. Distance from Sun: This is a real-time indicator of Voyagers' straight-line distance from the sun in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi ...
Voyager 1 is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and the interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. It was launched 16 days after its twin Voyager 2.
For the first time since November, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems.The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. In NASA's Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the actual spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers updated every five minutes.
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
Voyager 1 is the first spacecraft to travel beyond the solar system and reach interstellar space . The probe launched on Sept. 5, 1977 — about two weeks after its twin Voyager 2 — and as of ...
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system. ...
Voyager 1, robotic U.S. interplanetary probe launched in 1977 that visited Jupiter and Saturn and was the first spacecraft to reach interstellar space. Voyager 1 swung by Jupiter on March 5, 1979, and then headed for Saturn, which it reached on November 12, 1980.
Voyager 1 is literally venturing into the great unknown and is approaching interstellar space. Traveling at a speed of about one million miles per day, Voyager 1 could cross into interstellar space within the next 10 years. "Interstellar space is filled with material ejected by explosions of nearby stars," Stone said.
Voyager 1 flew within 64,200 kilometers (40,000 miles) of the cloud tops, while Voyager 2 came within 41,000 kilometers (26,000 miles). Saturn is the second largest planet in the solar system. It takes 29.5 Earth years to complete one orbit of the Sun, and its day was clocked at 10 hours, 39 minutes. Saturn is known to have at least 17 moons ...
Today, 45 years after its launch and 14.6 billion miles from Earth, four of Voyager 1's 11 instruments continue to return useful data, having now spent 10 years in interstellar space. Signals from the spacecraft take nearly 22 hours to reach Earth, and 22 hours for Earth-based signals to reach the spacecraft.
Voyager 1 and 2, cruising along diverging paths, made history by crossing the heliopause in 2012 and 2018, respectively (SN: 9/12/13; SN: 12/10/18). At nearly 18 billion kilometers from the sun ...
The Voyager 1 probe is the most distant human-made object in existence. After a major effort to restore communication with it, NASA announced success this week.
Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s. This processed color image of Jupiter was ...
The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA's Voyager 1 at a distance of 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) from the Sun. NASA/JPL-Caltech. Voyager 1, meanwhile ...
The first such fix was transmitted to Voyager 1 on April 18. With a total distance of 30 billion miles to cross from Earth to the spacecraft and back, the team had to wait nearly two full days for ...
Voyager 1 previously encountered something like it in 2017. According to Jon Richardson, an astrophysicist at MIT who wasn't an author on the paper, this latest finding shows that Voyager 1 is ...
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
On Saturday, April 5, Voyager 1 finally "phoned home" and updated its NASA operating team about its health. The interstellar explorer is back in touch after five months of sending back nonsense data.
Because Voyager 1 is more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach the spacecraft. And then it's another 22.5 hours for the probe ...
NASA's Voyager 1 probe — the most distant man-made object in the universe — is returning usable information to ground control following months of spouting gibberish, the US space agency says.
Voyager 1 has been traveling through space since 1977, and some scientists hoped it could keep sending back science data for 50 years. But a serious glitch has put that milestone in jeopardy.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first ...
Voyager 1 was the first-ever object to reach interstellar space on August 25, 2012 when it passed beyond the sun's realm of plasma influence (the heliosphere) and it is the most distant human-made object. But it will take about 300 years for Voyager 1 to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud and possibly about 30,000 years to fly beyond it ...
Voyager 1, now outside the solar system and the most distant man-made object at 24bn km away, has begun sending meaningful signals once again. The news feels both uplifting and bittersweet.
Voyager 1 is currently about 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away, and at 46 years old, the probe has shown multiple quirks and signs of aging in recent years.
The Golden Record. Pioneers 10 and 11, which preceded Voyager, both carried small metal plaques identifying their time and place of origin for the benefit of any other spacefarers that might find them in the distant future. With this example before them, NASA placed a more ambitious message aboard Voyager 1 and 2, a kind of time capsule ...
NASA's Voyager craft have ventured where no other human machines have ever gone — the space between the stars. But that comes with a cost. At some 15 and 12 billion miles away, Voyager 1 and 2 ...