UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Competitiveness.
- Market Intelligence
- Policy and Destination Management

Product Development
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
As defined by UN Tourism, a Tourism Product is "a combination of tangible and intangible elements, such as natural, cultural and man-made resources, attractions, facilities, services and activities around a specific center of interest which represents the core of the destination marketing mix and creates an overall visitor experience including emotional aspects for the potential customers. A tourism product is priced and sold through distribution channels and it has a life-cycle".
Rural tourism
UN Tourism understands Rural Tourism as "a type of tourism activity in which the visitor’s experience is related to a wide range of products generally linked to nature-based activities, agriculture, rural lifestyle / culture, angling and sightseeing.
Gastronomy and Wine Tourism
As global tourism is on the rise and competition between destinations increases, unique local and regional intangible cultural heritage become increasingly the discerning factor for the attraction of tourists.
Mountain Tourism
Mountain Tourism is a type of "tourism activity which takes place in a defined and limited geographical space such as hills or mountains with distinctive characteristics and attributes that are inherent to a specific landscape, topography, climate, biodiversity (flora and fauna) and local community. It encompasses a broad range of outdoor leisure and sports activities".
Urban Tourism
According to UN Tourism, Urban Tourism is "a type of tourism activity which takes place in an urban space with its inherent attributes characterized by non-agricultural based economy such as administration, manufacturing, trade and services and by being nodal points of transport. Urban/city destinations offer a broad and heterogeneous range of cultural, architectural, technological, social and natural experiences and products for leisure and business".
Sports Tourism
Tourism and sports are interrelated and complementary. Sports – as a professional, amateur or leisure activity – involves a considerable amount of traveling to play and compete in different destinations and countries. Major sporting events, such as the Olympic Games, football and rugby championships have become powerful tourism attractions in themselves – making a very positive contribution to the tourism image of the host destination.
Shopping Tourism
Shopping Tourism is becoming an increasingly relevant component of the tourism value chain. Shopping has converted into a determinant factor affecting destination choice, an important component of the overall travel experience and, in some cases the prime travel motivation.

What is Tourism Product? Definition, Types, Characteristics
- Post last modified: 3 October 2021
- Reading time: 14 mins read
- Post category: Uncategorized
What is Tourism Product?
Tourism Products are a combination of goods and services demanded by a tourist during travel to and stay at a destination. These include natural, cultural and manmade attractions and facilities such as hotels, transport and ancillary services.
In this process, tourists derive an experience which varies from individual to individual. From a broader perspective, the sum total of experiences derived by the tourists during the entire trip can be considered as the product.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Tourism Product?
- 2 Definition of Tourism Product
- 3.1 Natural Tourism Product
- 3.2 Man-Made Tourism Product
- 3.3 Symbiotic Tourism Product
- 3.4 Event Based Tourism
- 3.5 Site Based Tourism Product
- 4.1 Intangibility
- 4.2 Inseperatability
- 4.3 Perishability
- 4.4 Heterogeneity
- 4.5 Essentially of Users Presence
- 4.6 Complexity in Marketing
- 4.7 Absence of Ownership
Definition of Tourism Product
Burkat and Medlik say tourism products to an array of integrated products, which consist of objects and attractions, transportation, accommodation and entertainment, where each element of the tourism product is prepared by individual companies and are offered separately to consumers (tourist/tourist).
The tourism “product” is not the destination, but it is about the experiences of that place and what happens there. – Chris Ryan
Economist M. Sinclair and Mike Stabler define the tourism product as a “composite product involving transport, accommodation, catering, natural resources, entertainment and other facilities and services, such as shops and banks, travel agents and tour operators.”
According to Suswantoro (2007:75) on substantially the understanding of tourism products “is obtained and the overall service felt or enjoyed by tourists since he left his residence to the tourist destination of his choice and to return home where she originally departed”.
Types of Tourism Products
Following figure describes the classification of Tourism Product:
Natural Tourism Product
Man-made tourism product, symbiotic tourism product, event based tourism, site based tourism product.
These are the products connected to the natural environment. Natural environment that constitutes natural resources which is related to area, climate and its settings, and the landscapes. These natural resources are the most important elements in a destination’s attraction. Such as countryside, climate, natural beauty, water, flora and fauna, wildlife, beaches, deserts, islands or any scenic attraction.
Some examples of natural tourism products in India are Marina beach- Chennai, Darjeeling hill station-West Bengal, Islands of Andaman & Nicobar- Andaman & Nicobar, Deserts of Thar-Rajasthan, etc
Something which is not natural, found in the destinations to attract the tourists. These are man-made creations. As per the tourism point of view they are made for pleasure, leisure or business.
Man-made tourism products are further divided into three subtypes:
- Sites and areas of archaeological interest
- Historical buildings and monuments
- Places of historical significance l museums and art galleries
- Political and educational institutions
- Religious institutions
- Fairs and festivals
- Arts and handicrafts
- Folklore l native life and customs
- Amusement and recreation parks
- Sporting events
- Zoos and oceanariums
- Cinemas and theatres
- Night life l cuisines
Examples of Man-made tourism products are Ajanta and Ellora cave-Maharashtra (Cultural), Surajkund Craft Mela-Haryana (Traditional), Essel World-Mumbai, etc
This type of tourism product do not fall in any particular category because they are a blend of nature and man but the core attraction is nature. These are the natural resource that has been converted into a tourism product by maintaining and managing them.
In other words man has taken initiative to preserve the natural aspects of earth and also managed in a way to provide best possible services to the tourists who come for the visit, for example, accommodation, parking facilities, etc. Some examples are National Park or Wildlife Sanctuaries, Flower Festival, Marine Park, Aero and Water Sports, Botanical Garden etc.
In India, there are many national parks like Ranthambhore-Rajasthan, where tigers and many animals are preserved and tourists are given facilities like a jungle safari.
Product Here event is the main source of attraction. Tourist comes to observe and participate in the events. Events are temporary in nature and are often mounted in order to increase the number of tourists to a particular destination.
Some events are for a short time scale while other last for longer days. Sometimes events are mounted in those places where the tourist’s eye usually don’t reach such as unusual exhibitions.
Some examples of event-based tourism product include Camel Polo at Jaisalmer- Rajasthan, Kite flying in Ahmedabad-Gujarat, where tourists also participate and observes. In Snake boat race-Kerela, one can enjoy witnessing it. Short time scale event includes Republic day parade-New Delhi and long days event include Khajuraho dance festival-Madhya Pradesh.
It is a particular site or a place, permanent in nature which is the main source of attraction for the tourists. In India examples are like Taj Mahal, Beaches of Goa, Sunset at Kanyakumari, Temples of Khajuraho, etc.
Characteristics of Tourism Product
Following are the main characteristics of tourism products:
Intangibility
Inseperatability, perishability, heterogeneity, essentially of users presence, complexity in marketing, absence of ownership.
As discussed earlier in this chapter, tourism products are actually the services that are being sold to the tourists, and it’s not the goods. Services can’t be seen, smelled, felt or touched, it can only be experienced. What can be seen is their effect.
For example, a guide’s comments can be heard. A travel agents books a ticket from place A to B. The ticket is just a piece of paper, an entry pass for using the service. An airline provides the service of transportation, comfort and leisure. A thorough evaluation of the service before buying it is therefore impossible and leads customers to use other cues to help them assess the service like the interior of the restaurant, the appearance of the hotel entrance or the behaviour of the receptionist.
A service of a tourism product cannot be separated from the provider of the service. For most services, the producer and the seller are the same people. Services are manufactured and consumed at the same time. In the case of products, consumption takes place after production and often far away from the factory.
In the case of tourism products for example a guide has to be present to explain the attraction. A pilot has to be present to fly a plane. Both service providers and the service user have to be physically present for mutually satisfying the exchange of service. The visitor to a national park cannot experience counter service if the receptionist is not present, nor can the receptionist render the service is the visitor is absent.
The tourism product is highly perishable, which means it cannot be stored. For example, a hotel room or an aeroplane seat that is not sold on a particular day, is a lost sale. If the tourists don’t visit a particular place, the opportunity is lost. If the opportunity is lost, the moment is lost. This adversely affects the tourism business.
The demand has to be managed by the marketer in such a way as to ensure that as little capacity as possible is lost. The problem is unique for the tourism industry. Due to these reason sometimes heavy discount is offered by hotels or transport generating organization.
Services offered by most people are never the same. There is some degree of variability present in almost all types of services. This may be due to the extensive involvement of people in the production of service. This issue is not present when a machine dominates. Depending on the mood, behaviour, working style, efficiency and knowledge of the people variability exist.
For example, all air hostesses cannot provide the same quality service like the other. Yet again the same individual air hostess may not perform the same uniform service both in the morning as well as in the evening.
Even the tour package and the aircraft can’t be consistent of equal standards because an aircraft can de-shape the travelling pleasure into a nightmare and a holiday seaside is ruined by the prolonged rainy spell.
Another reason for variability of service is the involvement of customers in the process of product delivery and consumption system. For example, a musician performing at a program may not perform with uniformity. His performance will depend on the response and appreciation of the audience. Hence service varies from person to person, time to time and from situation to situation.
In travel and tourism businesses, service quality depends on uncontrollable factors and there is no sure way of knowing whether the service delivered matched what was planned or promoted, or what was expected by the customer.
Presence of the user is necessary to avail the service. The customer or the guest has to be personally present on the spot. It can’t be brought to the user. As in the case of other tangible goods, the buyer can avail the service from anywhere or from his home. But in the case of tourism products, it is not at all possible. The tourist has to go to the tourist attraction to experience the tour.
However the marketers here need an in-depth study of users behaviour, tastes, preferences, likes and dislikes so that expectations and realities coincide and satisfaction is made possible.
Tourism product involves complexity in marketing. It requires a lot of effort to convince a buyer. As in the case of travel agents. In order to sell their tour package they need to convince the customer by introducing various facilities, discounts and services. Product demonstration is bit difficult in the case of tourism product.
As in the case of tangible goods like television. As soon as we buy it, we become the owner of it. But this is not the case with tourism products. A tourism product when sold to the customer or tourist, he can only avail the service but can’t be its owner.
For example, while buying a hotel room, while buying a seat in an aircraft or a luxurious train, you can only take the facilities of the service for a certain time. You can’t be its owner for lifelong.
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window X
- Opens in a new window Facebook
- Opens in a new window Pinterest
- Opens in a new window LinkedIn
- Opens in a new window Reddit
- Opens in a new window WhatsApp
You Might Also Like
What is travel itinerary types, steps in planning, do & don’t, what is tour cost components, types of tour costs, what is ice cream types, serving, storing, customer retention: in marketing, measures of customer, recruitment, styles of service in restaurant | techniques, order to serving meals, handling service dishes and utensils, most popular monuments in pondicherry, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION
Home | About WTO | News & events | Trade topics | WTO membership | Documents & resources | External relations
Contact us | Site map | A-Z | Search
español français
- trade topics
- sector-by-sector
- tourism and travel-related services
SERVICES: SECTOR BY SECTOR
Tourism and travel-related services
Tourism plays an important role for nearly all WTO members, especially in terms of its contribution to employment, GDP, and the generation of foreign exchange. Tourism-related services are typically labour-intensive, with numerous links to other major segments of the economy, such as transport, cultural and creative services, or financial and insurance services.
Tourism and travel-related services include services provided by hotels and restaurants (including catering), travel agencies and tour operator services, tourist guide services and other related services.
A crucial aspect of trade in tourism services is the cross-border movement of consumers (mode 2). This permits a variety of workers, including those in remote areas, to become services exporters — for instance, by guiding tourists, performing in local events, or working in tourist accommodation. While digitalisation offers great potential for many aspects of tourism services, the sector continues to depend highly on the cross-border movement of both customers and employees, and remains strongly linked to transport services.
Current commitments and exemptions
Tourism commitments have been undertaken by over 133 WTO members, more than in any other service sector. This indicates the desire of most members to expand their tourism sectors and to increase inward foreign direct investment (FDI) as part of their efforts to promote economic growth.
The level of commitments by sub-sector varies widely for tourism and travel-related services. Commitments on services provided by hotels and restaurants are the most frequent, with a significantly smaller number of WTO members making commitments on travel agencies and tour operator services. Only about half of members with commitments on tourism have included tourist guide services, and only a few members have made commitments for the “other” tourism services category.
- Schedules of WTO Members with Specific Commitments on Tourism Services
Treatment of the sector in negotiations
Tourism services, like other services covered by the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS), were included in the services negotiations that began in 2000.
One of the earliest documents was a proposal for a GATS Annex on Tourism, originally sponsored by the Dominican Republic, El Salvador and Honduras ( S/C/W/127 and S/C/W/127/Corr.1 ). The proposal had two main aspects: more comprehensive treatment of the tourism sector (with respect to classification issues), and the prevention of anti-competitive practices. As part of the plurilateral process, a joint request was made by a group of developing countries, asking for improved tourism commitments for all modes of supply.
- Proposals and related negotiating documents on tourism services
Additional information
Search Documents Online These links open a new window: allow a moment for the results to appear.
- Secretariat background notes on tourism services (Document code S/C/W/* and keyword “tourism and Background Note”) > search > help
- Tourism services (Document code S/CSS/W/* or TN/S/W/* and Title Tourism) > search
You can perform more sophisticated searches from the Documents Online search facility by defining multiple search criteria such as document symbol (i.e. code number), full text search or document date.
Some useful links
- World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
- World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC)
- OECD Tourism Unit (Centre for Entrepreneurship, SMEs, Regions and Cities)
Problems viewing this page? If so, please contact [email protected] giving details of the operating system and web browser you are using.
Market Design for Sustainable Tourism Products and Services
- First Online: 17 March 2021
Cite this chapter

- Md. Nekmahmud 2 , 3 ,
- Ahmad Daragmeh 2 , 3 ,
- Betgilu Oshora 2 , 3 &
- Hunar Jabar Mohammed 2 , 3
438 Accesses
2 Citations
In a rapidly changing, advanced, and globalized world, tourism considers one of the evidential economic growth factors. The chapter shed light on the value of tourism marketing and explore the tourism industry’s marketing mix. Furthermore, it investigates tourism products and services deeply in terms of their nature (e.g. accommodation, transportation, food & beverage, and ancillary services), elements of tourism products and the current state, and the imprtance of investment in developing the tourism products and services. The chapter also discusses sustainability in tourism products from three different aspects; environmental, economic, and social-cultural. The latter part argues for tourism products’ role in supporting economies without disrupting local cultures and the ecological foundation. Since all industries, included the tourism industry, have a distinct market design to promote products and services. Therefore, the investigation outlines a market design with a wide range of marketing tools, techniques, and strategies that Bangladesh can use to promote the tourism industry in terms of quantity and quality. The chapter also analyzes the current state of the tourism market, the attraction level of tourism products and services in Bangladesh, and the tourism markets potentiality from global perspective. The methodology part used secondary data to develop the conceptual analyses of the theoretical aspects of sustainable tourism products and services. This study’s findings would help academicians, students, policymakers, marketers, tourist agencies to identify a combination of marketing tools and strategies that can help them to make acceptable resource utilization policy for maximum return with achieving SDGs. This qualitative chapter boils down much of the previous discussion into a concise summary of some key marketing points for promoting potential tourism products and services. Finally, it recommends how to promote potential tourism products and services more effectively and efficiently with sustainable ways to attract both domestic and foreign tourists and ultimately contribute to the economic growth of the country.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
https://www.wttc.org/economic-impact/country-analysis/country-data/
Lonely Planet’s Best in Travel 2011. Lonely Planet, 2011.
Top 10 best value destinations for 2011. Lonely Planet.
https://www.icao.int/sustainability/Documents/AVIATION-BENEFITS-2019-web.pdf
https://traveltips.usatoday.com/meaning-sustainable-tourism-2297.html (accessed: the 24th March, 2020).
Ahmmed, M. (2014). An analysis on tourism marketing in Bangladesh. AlmaTourism Journal of Tourism, Culture and Territorial Development, 5 (10), 162–168.
Google Scholar
Booms, B. H., & Bitner, M. J. (1981). Marketing strategies and organisation structures for service firms. In J. Donnelly & W. R. George (Eds.), Marketing of services (pp. 51–67). Chicago, IL: American Marketing Association.
Boyne, S., & Hall, D. (2004). Place promotion through food and tourism: Rural branding and the role of websites. Place Branding, 1 (1), 80–92.
Article Google Scholar
Chowdhury, T., Fahim, S. T., & Dooty, E. N. (2013). Promoting public private partnership for development of tourism industryof Bangladesh: An exploratory study. European Journal of Business Management, 5 , 194–202.
Cooper, C. (2008). Tourism: Principles and practice . London: Pearson education.
Cristina, S. (2017). New perspectives of the tourism and air travel relationship. Cactus Tourism Journal, 15 (2), 24–32.
Dolnicar, S., & Ring, A. (2014). Tourism marketing research: Past, present and future. Annals of Tourism Research, 47 , 31–47.
Font, X. (2005). Marketing sustainable tourism products . United Nations Environment Programme.
Hall, C. M., & Sharples, L. (2004). The consumption of experiences or the experience of consumption? An introduction to the tourism of taste. In Food tourism around the world (pp. 13–36). Routledge.
Hall, C. M., Sharples, L., Mitchell, R., Macionis, N., & Cambourne, B. (Eds.). (2004). Food tourism around the world . Oxon: Routledge.
Hasan, M. M., Nekmahmud, M., Yajuan, L., & Patwary, M. A. (2019). Green business value chain: A systematic review. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 20 , 326–339.
Henderson, I. L., Avis, M., & Tsui, W. H. K. (2018). Testing discontinuous innovations in the tourism industry: The case of scenic airship services. Tourism Management, 66 , 167–179.
Henderson, J. C. (2004). Food as a tourism resource: A view from Singapore. Tourism Recreation Research, 29 (3), 69–74.
Hjalager, A. M. (2010). A review of innovation research in tourism. Tourism Management, 31 (1), 1–12.
Hossain, M. A. (2002). Foreign tourists’ attitude towards marketing mix elements of the tourism industry in Bangladesh. Journal of Business Studies, 23 (1), 85–95.
Hossain, M. A., & Nazmin, S. (2006). Development of tourism industry in Bangladesh-an empirical study on its problems and prospects . Dhaka: Centre for Tourism and Hotel Management Research, University of Dhaka.
Hossain, M. A., Rahman, M. M., & Khan, M. M. H. (2005). Potentials of tourism development in Bangladesh-an empirical study. Journal of Business Studies, 26 (1), 67–85.
Jovičić, Ž. (1988). A plea for tourismological theory and methodology. Revue de Tourisme, 43 (3), 2–5.
Khan, M. S., & Kemal, A. R. (1996). Government investment and economic growth in the developing world [with comments]. The Pakistan Development Review, 35 (4), 419–439.
Lee, C. C., & Chang, C. P. (2008). Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tourism Management, 29 (1), 180–192.
Lee, S. Y., Reynolds, J. S., & Kennon, L. R. (2003). Bed and breakfast industries: Successful marketing strategies. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 14 (1), 37–53.
Lickorish, L. J., & Jefferson, A. (1988). Marketing tourism: A practical guide . Harlow: Longman.
Nekmahmud, M., & Rahman, S. (2018). Measuring the competitiveness factors in telecommunication markets. In Competitiveness in emerging markets (pp. 339–372). Cham: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Nekmahmud, M. (2020). Environmental marketing: Tourists’ purchase behaviour response on green products. In Hassan, A. (Ed.) Tourism Marketing in Bangladesh: An introduction (pp. 273–295). London, UK: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003007241-26 .
Nekmahmud, M., & Fekete-Farkas, M. (2020). Why not green marketing? Determinates of consumers’ intention to green purchase decision in a new developing nation. Sustainability, 12 (19), 7880. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12197880 .
Nekmahmud, M., Fekete-Farkas, M., & Hassan, A. (2020). Tourism marketing in Bangladesh. In Hassan, A. (Ed.) Tourism Marketing in Bangladesh: An introduction (pp. 12–27). London, UK: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003007241-3
Okumus, B., Okumus, F., & McKercher, B. (2007). Incorporating local and international cuisines in the marketing of tourism destinations: The cases of Hong Kong and Turkey. Tourism Management, 28 (1), 253–261.
Poudel, S. (2013). The influence of the accommodation sector on tourism development and its sustainability: Case Study: Strand Camping, Larsmo . Retrieved from: https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/61014/Thesis_Final_SP.pdf?sequence=1 . Accessed 24 Mar 2020.
Quddus, M. A. (1998). Opportunities & facilities of tourism industry in Bangladesh: Applied Marketing in Bangladesh (some case studies) (pp. 01–04). Dhaka: Department of Marketing, University of Dhaka.
Read, J. (2020). What is the meaning of sustainable tourism? Retrieved from: https://traveltips.usatoday.com/meaning-sustainable-tourism-2297.html . Accessed 24 Mar 2020.
Rosentraub, M. S., & Joo, M. (2009). Tourism and economic development: Which investments produce gains for regions? Tourism Management, 30 (5), 759–770.
Saco, R. M., & Goncalves, A. P. (2008). Service design: An appraisal. Design Management Review, 19 (1), 10–19.
Sims, R. (2010). Putting place on the menu: The negotiation of locality in UK food tourism, from production to consumption. Journal of Rural Studies, 26 (2), 105–115.
Sinitsyn, M. (2015). Nature-based tourism product and its development: Case Safartica . Retrived from: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/6a9e/b7b8b171ec0fbf26082cf989403e2d0c57f3.pdf . Aaccessed 24 Mar 2020.
Smith, S. L. (1994). The tourism product. Annals of Tourism Research, 21 (3), 582–595.
Sofronov, B. (2018). The development of quality management in the tourism industry. Annals of Spiru Haret University Economic Series, 18 (4), 123–137.
Stickdorn, M., & Zehrer, A. (2009). Service design in tourism: Customer experience driven destination management. In Proceedings of the First Nordic conference on service design and service innovation. Oslo: the 24th–26th November, pp. 7–23.
Tang, C. F., & Tan, E. C. (2015). Does tourism effectively stimulate Malaysia's economic growth? Tourism Management, 46 , 158–163.
Tribe, J. (1999). The concept of tourism: Framing a wide tourism world and broad tourism society. Tourism Recreation Research, 24 (2), 75–81.
United Nations (UN). (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 agenda for sustainable development .
Van Truong, N., & Shimizu, T. (2017). The effect of transportation on tourism promotion: Literature review on application of the Computable General Equilibrium (CGE) Model. Transportation Research Procedia, 25 , 3096–3115.
Wang, C., & Xu, H. (2011). Government intervention in investment by Chinese listed companies that have diversified into tourism. Tourism Management, 32 (6), 1371–1380.
World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED). (1987). Our common future , 17, pp. 1–91.
Wolf, E. (2006). Culinary tourism: The hidden harvest: A dozen hot and fresh reasons how culinary tourism creates economic and community development . Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt.
World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC). (2019). Bangladesh 2019 annual research: Key highlights . Retrieved from: https://www.wttc.org/economic-impact/country-analysis/country-data/ . Accessed 24 Mar 2020.
Xu, J. B. (2010). Perceptions of tourism products. Tourism Management, 31 (5), 607-610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2009.06.011 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Economic and Social Sciences, Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences, Gödöllo, Budapest, Hungary
Md. Nekmahmud, Ahmad Daragmeh, Betgilu Oshora & Hunar Jabar Mohammed
Doctoral School of Management and Business Administration, Szent Istvan University, Gödöllo, Budapest, Hungary
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Md. Nekmahmud .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Tourism Consultants Network, The Tourism Society, London, UK
Azizul Hassan
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Nekmahmud, M., Daragmeh, A., Oshora, B., Mohammed, H.J. (2021). Market Design for Sustainable Tourism Products and Services. In: Hassan, A. (eds) Tourism Products and Services in Bangladesh. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4279-8_17
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4279-8_17
Published : 17 March 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-33-4278-1
Online ISBN : 978-981-33-4279-8
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
What is a tourism product? Classification of tourism product services

Here at Hanami Hotel Danang , nestled in the heart of this vibrant coastal city, we have come to understand the true essence of what a tourism product is. It is more than just a service; it’s an experience—a tapestry of local culture, meticulous service, and memories waiting to be woven.
What is a tourism product? Classification of tourism product services. Venture with us as we explore the physical and emotional contours of these offerings, understanding their importance in the grand puzzle of travel and human connection.
This exploration is as much a journey for us as it is for you—arousing passion, expanding knowledge, and cementing our shared love for the world’s cultures and the adventures they hold.

What is a tourism product? Definition of tourism product
A tourism product is the elements and services created to meet the needs of tourists during their travels. These are the components and experiences that tourists can purchase or use to enjoy and make the most of their trip.
Tourism products include transportation means such as airplane tickets, train tickets, or bus tickets for tourists to reach their desired destinations. Additionally, there are accommodation services like hotels, resorts, guesthouses, or homestays, providing comfortable and convenient places for tourists to stay.
Tour packages are a popular tourism product, offering a service package for tourists to visit and explore destinations. They often include transportation, accommodation, tour guides, and related tourism activities. Tour guides are also an important service, accompanying tourists and providing information, guidance, and navigation throughout the trip.
Moreover, tourism products also include entertainment and sightseeing activities. Tourists can engage in activities such as nature exploration, historical site visits, enjoying the sea, and outdoor sports activities. Tourism products may also include culinary services, shopping, and visiting entertainment venues.
Components of a tourism product

Having grasped the concept of a tourism product, we will delve into its fundamental components. A tourism product is a complete experience from when a tourist leaves home until they finish their trip. From this, we can infer that the elements constituting a tourism product include:
Transportation
Transportation is an indispensable element of a tourism product. It ensures that tourists have the means to arrive at and move between different destinations during their trip.
The modes of transportation are diverse and varied, including airplanes, trains, buses, bicycles, motorcycles, and even other vehicles such as boats, cruise ships, cable cars, and horse-drawn carriages.
Airplanes are the primary mode of transportation for international or long-distance travel. They offer speed, convenience, and comfort to tourists. Airplanes also enable tourists to overcome long distances and access hard-to-reach destinations that might not be possible with other modes of transport.
Trains are a popular mode of transportation for domestic and international travel. Buses are a flexible and cost-effective option for city and regional travel. Bicycles and motorcycles help tourists save on transportation costs while also providing a more intimate experience with the environment and local community.
Additionally, in certain special cases, other modes of transportation such as boats, cruise ships, cable cars, and horse-drawn carriages may be used.
Boats and cruise ships are suitable for exploring seas, rivers, lakes, and islands. Cable cars offer thrilling sensations and stunning views from above. Horse-drawn carriages provide a traditional and environmentally friendly experience for tourists.
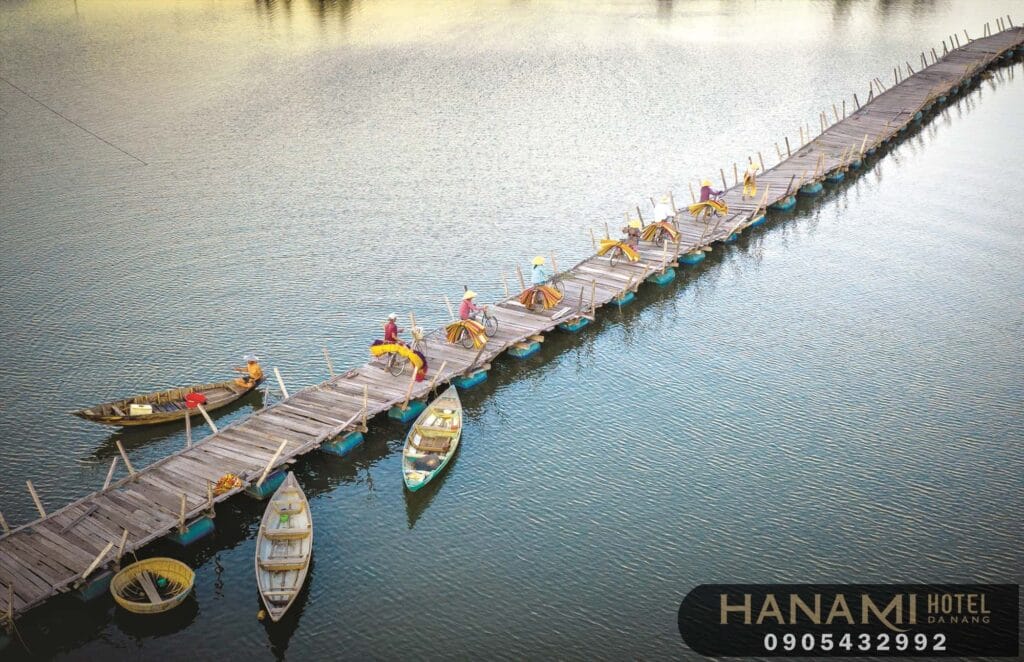

Accommodation Services
The provision of rest and lodging is a crucial part of a tourism product. When traveling, tourists need a safe and comfortable place to rest after their exploratory activities. Accommodations can include various types such as hotels, resorts, guesthouses, rental apartments, homestays, camping sites, and tents.
Hotels are a popular choice for tourists, especially in urban and developed tourist areas. Hotels typically offer a range of services and amenities such as comfortable bedrooms, restaurants, bars, fitness centers, and other facilities like spas and swimming pools.
Hotels can be categorized by star ratings to assess the level of comfort and quality of service. Whether it’s a hotel, resort, guesthouse, rental apartment, homestay, or camping site and tent, tourist accommodations must meet the basic needs of tourists for comfort, safety, and convenience.
Bedrooms should be fully equipped with necessary amenities such as beds, wardrobes, and lighting. Additionally, bathrooms must be clean and include facilities such as showers, bathtubs, sinks, and personal hygiene items.
Moreover, accommodations must also provide other amenities and services such as restaurants, bars, fitness centers, spas, swimming pools, cable TV, internet, and room service. The service staff should also be friendly, professional, and ready to assist tourists throughout their stay.
Activities and Experiences
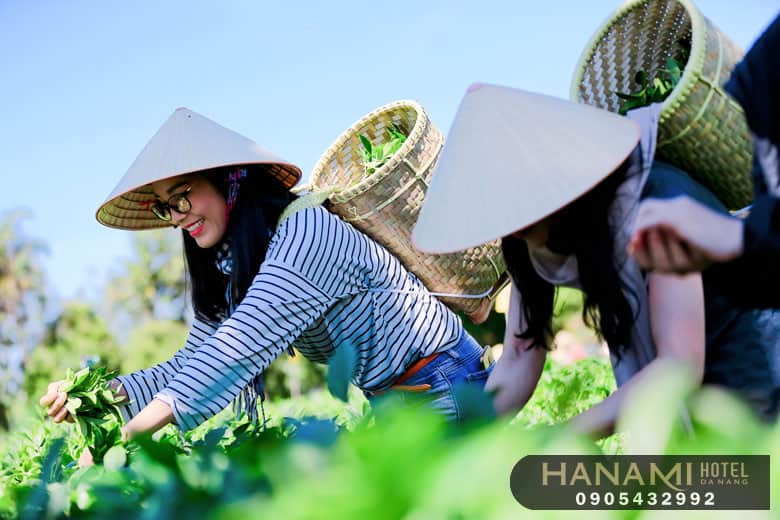

Travel is not just about moving to a new location, but it is also an adventure filled with experiences and exciting activities. As tourists embark on their journey, many activities and experiences await them.
One of the most significant experiences in travel is discovering famous tourist landmarks. Tourists can visit large cities and charming small towns, explore the unique architecture of temples, shrines, palaces, and churches, or admire the stunning scenery of dense forests, mountains, rivers, and seas.
Each destination has its own beauty and draws tourists into its historical and cultural story. Beyond exploration, tourists can also participate in entertaining activities.
With beautiful beaches, tourists can dive into the underwater world through activities like scuba diving, windsurfing, sailing, or surfing. Rivers and lakes also invite tourists to go kayaking or enjoy exciting boat trips.
If tourists want to challenge themselves, they can go mountain climbing, hiking, or exploring fascinating caves. These activities not only allow tourists to enjoy the incredible natural beauty but also bring a sense of excitement and satisfaction.
An indispensable part of travel is enjoying local cuisine. Tourists can embark on a culinary adventure, savoring specialty and traditional dishes at restaurants, eateries, and night markets.
Sampling unique foods and immersing oneself in local culinary culture is a wonderful way to gain a deeper understanding of the country and its people.
Guidance and Support Services

Services that provide information, guidance, and support for tourists during their travels are crucial to ensure they have a smooth and memorable trip. First, professional tour guides play an important role in providing information and guidance to tourists.
Customer support services also play a vital role in meeting the needs and requests of tourists. Customer support staff will advise and assist tourists in booking, ticket changes, itinerary information, and answering related queries.
Tourism information is also an essential service to help tourists get the necessary information before and during their trip. Tourist information centers provide tourists with information about tourist sites, destinations, schedules, and activities.
Tourists can learn about famous landmarks, local events, and available entertainment activities. Tourism information also includes tour packages, attraction tickets, and pricing information so tourists can choose and shape their trip.
Food and Culinary Services
In the field of tourism, elements related to culinary services and food play an important role in providing a unique and culturally rich experience for tourists. These services include a range of options such as restaurants, cafes, bars, hotel dining services, or on-site cooking services.
Restaurants are where tourists can enjoy a variety of local signature dishes. Restaurants may serve traditional dishes, local specialties, and international cuisine. By tasting local dishes, tourists have the opportunity to experience and discover the flavors, aromas, and cooking styles characteristic of the destination.
Restaurants can also create a unique space and environment for tourists to enjoy their meal and the culinary atmosphere.
Cafes and bars are also popular spots for tourists to enjoy drinks and light snacks. Cafes typically offer a variety of coffees, from traditional black coffee to special and blended types.
Additionally, cafes may serve other beverages such as tea, fruit juices, and light alcoholic drinks. Bars usually focus on serving alcoholic beverages and provide an entertainment space for tourists.
Classification of tourism products

There are many ways to classify tourism products based on various factors. Below is a common classification based on the main types of tourism products:
Cultural Tourism
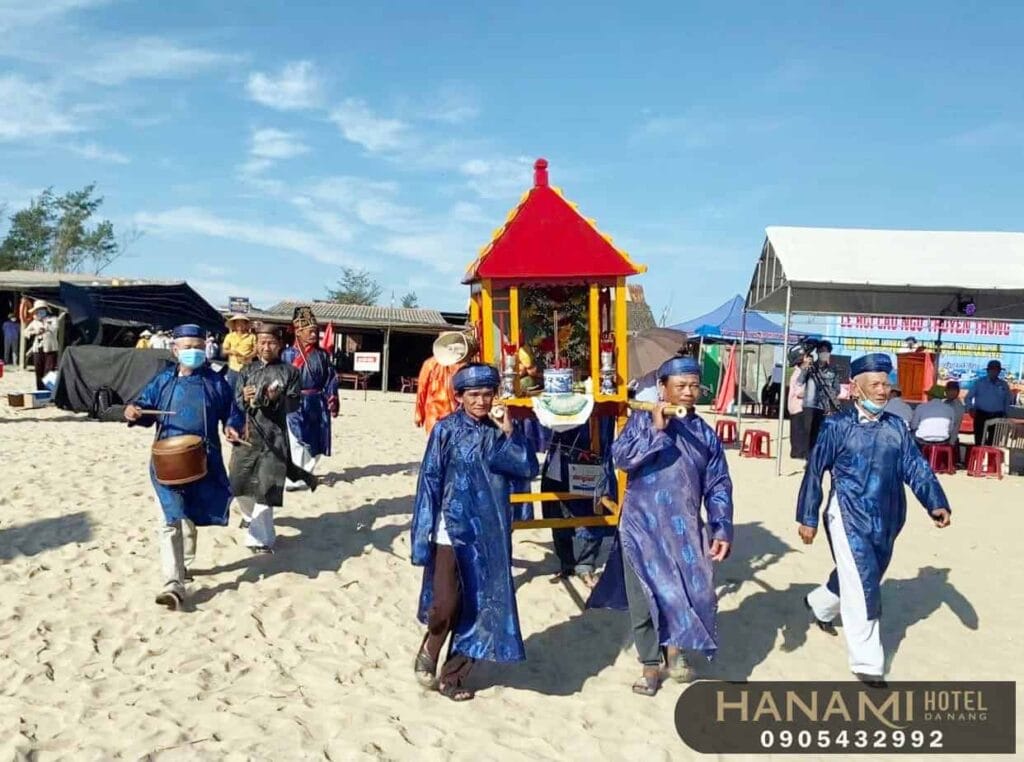
This includes exploring historical sites, scenic landmarks, unique architecture, and experiencing the culture of a place. This could involve visiting museums, touring historical sites, attending local cultural festivals and events, and learning about the culture, history, and traditions characteristic of a culture.
Exploring historical sites, scenic landmarks, unique architecture, and experiencing the culture of a place is an important part of the travel experience. Through visiting museums, touring historical sites, attending local cultural festivals and events, and learning about the culture, history, and traditions of a culture, tourists have the opportunity to access the profound and unique aspects of the place they visit.
This not only provides tourists with a great experience but also expands their knowledge and understanding of the world around us.

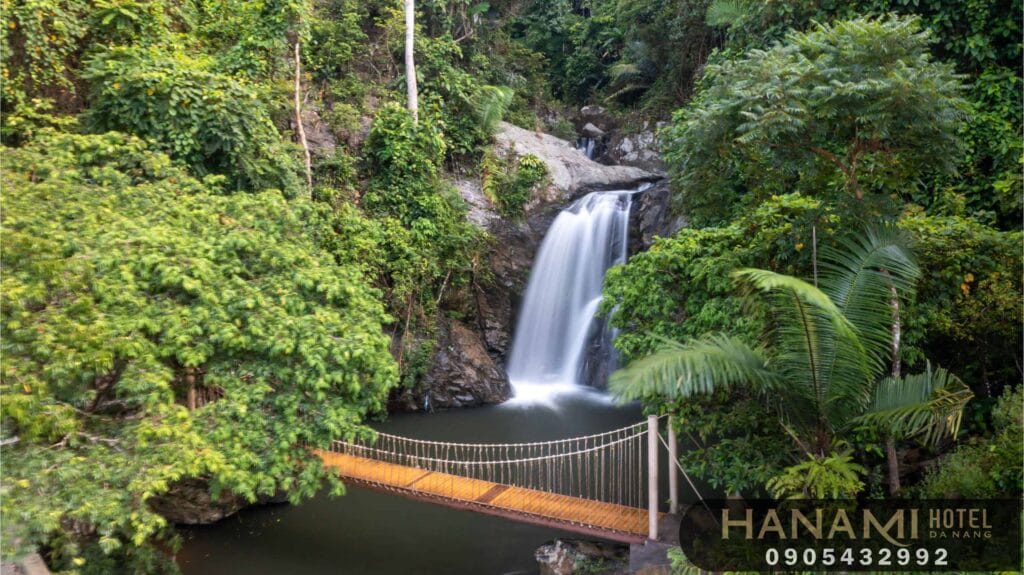
Nature Tourism
This includes exploring and discovering beautiful natural landmarks and areas such as forests, mountains, seas, lakes, streams, meadows, and national parks. Tourists can engage in activities such as mountain climbing, hiking, fishing, caving, scuba diving, or visiting and enjoying special natural landscapes. Exploring and enjoying beautiful natural landmarks and areas gives tourists unique and unforgettable experiences. Tourists can participate in many activities such as mountain climbing, hiking, fishing, caving, scuba diving, or visiting and enjoying special natural landscapes. Each landmark and area offers its own beauty and unique experience, contributing to making the trip interesting and memorable.
Recreational Tourism
This tourism includes visiting amusement parks, theme parks, zoos, playgrounds, stadiums, casinos, popular shopping venues, and other entertainment activities. Tourists can enjoy games, go on rides, watch performances, and participate in sports and entertainment activities at these locations.
Tourists can enjoy games, participate in sports and entertainment activities at places like amusement parks, theme parks, zoos, playgrounds, stadiums, casinos, and explore popular shopping venues. With the diversity and richness of these activities, tourists can create memorable moments during their trip.
Arts and Culture Tourism
This includes experiencing art and cultural events such as watching art performances, cinema, live music, opera, ballet, visiting art exhibitions, participating in art courses, or engaging in local cultural events.
These artistic and cultural experiences not only bring joy and relaxation but also help tourists discover and understand more about the local culture, history, and artistic development. At the same time, participating in these activities creates opportunities for interaction, connection, and sharing of artistic and cultural passions with other art lovers.
Sports and Adventure Tourism
Activities include mountain climbing, hiking, cycling, wall climbing, caving, surfing, scuba diving, swimming, exploring terrain, camping, and other adventurous activities.
These sports and adventure activities bring excitement, challenge, and discovery to tourists. However, before participating in any activity, tourists should check safety and comply with local regulations to ensure a safe and memorable experience.
Resort and Relaxation Tourism
Enjoy a relaxing holiday at resorts, villas, luxury hotels, or famous beach, mountain, or city destinations. Tourists can enjoy spa services, massages, yoga, swimming, golfing, and participate in recreational activities at the resort.
Enjoying a relaxing holiday at resorts, villas, luxury hotels, or famous destinations provides tourists with an enjoyable and serene experience. From enjoying spa services, yoga, and swimming to playing golf and participating in recreational activities, people can find relaxation and happiness in their vacation.

As we conclude this journey into the intricacies of tourism products, we hope you have gained a deeper appreciation for the myriad experiences and services that come together to create memorable travel moments. Here at Hanami Hotel Danang, our greatest reward is crafting unforgettable memories for our guests against the backdrop of this vibrant coastal city and the alluring Vietnamese culture.
We invite you to become part of this tapestry yourself—allow us to be your guide as you explore lantern-lit streets, discover local delicacies, and find sanctuary in the arms of gentle waves and cherry blossoms in bloom.
Our tailored experiences, meticulous service, and insider knowledge of Danang’s hidden gems await. Contact us at Hanami Hotel Danang or visit hanamihotel.com to begin your journey today.
CONTACT INFORMATION:
- Address: 61-63 Hoang Ke Viem, Bac My An, Ngu Hanh Son, Da Nang
- Phone: 0905432992
- Email: [email protected]
- Website: https://hanamihotel.com
- Google Map: https://g.page/hanamihotel
- Facebook : https://facebook.com/hanamihotel
Bài viết liên quan:
- Dong Dinh Musium – The Memory garden between Da Nang’s Mountains – Hot Spot for Tourism
- DA NANG TOURISM – THE TRANQUIL AND ANCIENT BEAUTY OF HOI AN
- TOP 7 BEST ECO-TOURISM SITES IN DA NANG
- Ngam Doi eco-tourism zone in Danang
- YEN RETREAT IN HOA BAC – DA NANG: BEST PLACE FOR EXPERIENCING ECO-TOURISM IN DA NANG
- CHILLING OUT AT SUOI MO ECO-TOURISM AREA IN DA NANG
- Hoa Bac tourism sector – Get back to nature in Danang
- Da Nang Beach Tourism Season 2023
- Things you don’t know about MICE tourism in Da Nang
- What’s special about the Da Nang Golf Tourism Festival?
About The Author
Lê Thị Kiều Trinh
Hanami đề xuất, bài viết mới nhất.
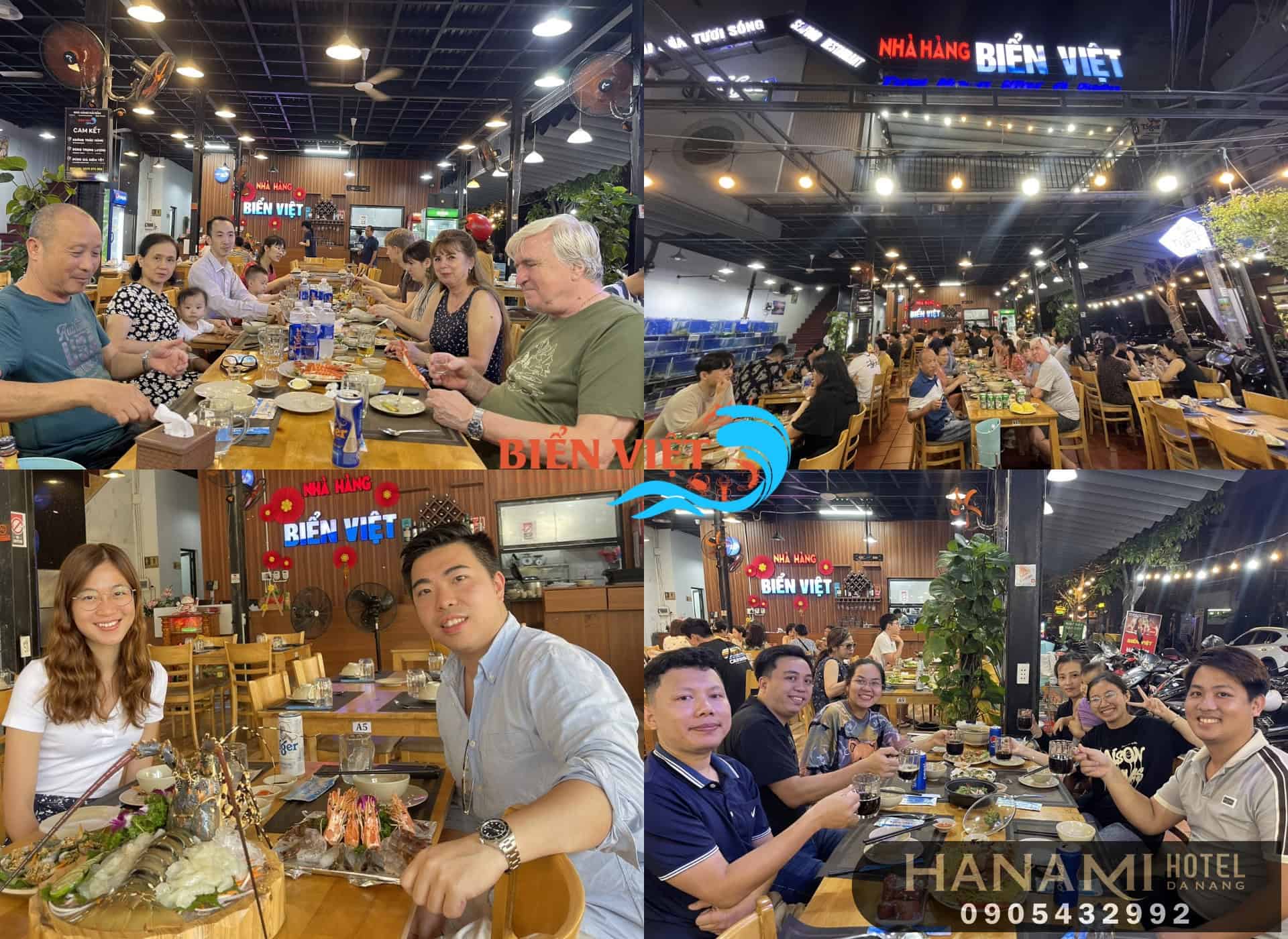


Discover Bien Viet Seafood Restaurant, Reviews by Hanami

Top 10 best jewelry stores in Da Nang, review by Hanami

TOP 11+ BEST IPHONE SCREEN REPLACEMENT ADDRESS IN DA NANG, REVIEWS BY HANAMI

Top 14 best bun mam eateries in Da Nang, review by Hanami

Top 10 best meat noodle eateries in Hoi An, review by Hanami

- Market information
- Develop your tourism product
- Share this on:
How to get started developing your tourism product
Whether you are offering guided tours, boat rentals, accommodation or provide river cruises, you are offering services to your customers. For today’s tourists, just a service is not enough. They seek experiences, often even experiences that contribute to their quality of life. This document offers you guidelines to identify your customers’ needs and to develop innovative products, services or experiences that really matter to them.
Contents of this page
- Why develop your product with this method?
- This is what you need before you start
- Get inspired by your (potential) customer (Step 1)
- Make a persona for each type of customer (Step 2)
- Identify the core needs of the customers and the key opportunity areas for your business (Step 3)
- Develop a multitude of ideas for solutions, or new products, services or experiences (Step 4)
- Turn your best ideas into prototypes that can be tested and improved step by step (Step 5)
- Test your prototypes in practice (Step 6)
1. Why develop your product with this method?
The needs of tourists from Europe have evolved over the past few decades. Current tourists are looking for quality service and experiences that really matter to them. To offer quality and experiences that matter to your customers, you need to know them very well, personally. What quality means for some may be different from what it means to others. And an experience that is life-changing for some, may be dull to others. This report teaches you how to get in touch with your customers, how to learn what they really need to boost their quality of life, and how you can design products, services or experiences that really matter. The nice thing is that if you succeed, your customers will share their experiences with their friends and followers, also on social media. In other words: they will promote your product to others. For free!
The current coronavirus crisis has put international travel under pressure . In many countries, tourist arrivals have nearly dropped to zero. It is likely that international tourism will be affected by the COVID-19 crisis for the next couple of years. Several scenarios are possible. The frequent holidays made by Europeans to faraway destinations may decrease and this may turn into less frequent and longer holidays closer to home. The battle for tourist visits may become fiercer. The attention for sustainability may also increase. Europeans might be willing to travel longer distances, but only for a very good reason. To tempt potential tourists from Europe to come to your country, your region or your business, you need to stand out, to understand the traveller well and be super-innovative – more than ever. Amazing stories and experiences may become even more important. As will issues of safety, security and assisting tourists in returning to their home countries.
- Read more on this in our study on how to respond to COVID-19 . This study offers insight into actions you should take immediately, while also providing guidance on long-term decisions.
The method described in this report is based on the principles of design thinking. It has been employed internationally in all kinds of businesses. To mention a few examples in tourism:
- Destinations like the Bahamas (an example is the One-Stop Online Booking and Immigration Card ).
- Design for All , also referred to as ‘universal design’, to allow access for people with disabilities. You can read more about this in this thesis .
- Hotels. For example Hyatt Hotels has developed various prototype hotels around the world, which are free from regulation. Another example is The next-generation hotel experience , getting the details right to improve travellers’ stays, and designing a modern work experience for business travellers .
- Visitor attractions, like improving the tourist experience of the Polar Bear Society , a visitor attraction in Norway, or bringing Tourists to a hidden coastal gem .
- Travel and transport. Examples are pioneering a car-sharing service and developing a customer strategy for public transport in Oslo.
- Restaurants, like creating a fresh and modern take on the Indian culinary experience .
- Organisation and development. An example is turning a historic music college into a collaborative learning platform .
- Tourism-related services. An example is the mobile visitor centre in Saint Paul, Minnesota. Another example is to ‘design of waste out of the food system’, taking place in a collaboration between hotels, food banks, foundations, and entrepreneurs to fight food waste .
2. This is what you need before you start
The procedure described below is not difficult. To follow the steps, it helps to have a few basic tools – but only if you already have them) – since it is the idea of how you are doing this that is important .
- Lots of sticky notes (Post-its)
- Sheets of flipchart paper
In product development, we try to find a match between the needs of the European market and any of your local situation and business resources that might entail certain limitations. The following tips are related to this.
- Where possible, engage your customers to build a personal relationship and to get to know them well.
- If you find it difficult to engage with customers from a different culture or find it difficult to understand them, try to work with local partners who can serve as intermediaries (such as tour operators in source countries) with the guests or act as interpreter.
- Involve others working in your business or in other businesses in the community where you live, people working in education, or other people with an open and positive mind. This will make it more fun and rewarding. It will also contribute to the quality of the work.
- To work through the process described below, you may want to ask support from a local CBI coach and or an intern from a university abroad, for example via SAVE tourism .
Below, the steps are described to help you to develop innovative products and services for new and existing customers. Staying tuned with the market is an ongoing process. The outcomes of each step are illustrated in Figure 1.
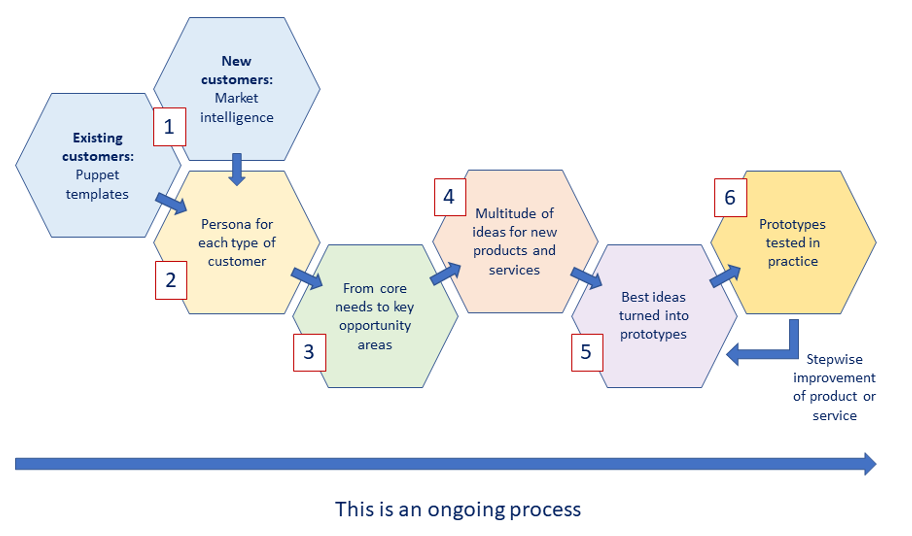
3. Get inspired by your (potential) customer (Step 1)
You can only create meaningful products, services and experiences for your customers if you truly understand them. So try to understand the situations and experiences that are or might be meaningful to them. If you do not have any customers yet, or are looking for new customers, you need to get your inspiration from existing market intelligence (step 1a). If you already have customers, you can use these customers as a source of inspiration (step 1b).
a. Get inspired by potential customers
The largest share of potential customers doesn’t know you or your product offering, or perhaps even the destination. So you have to draw their attention by offering products and services that matter. What do you need to do to make a start?
- Get access to market intelligence reports of the European market. Subscribe to free newsletters or blogs of market intelligence institutions, such as UNWTO , WTTC , Global Sustainable Tourism Council or IATA . Read the annual UNWTO publications , such as Tourism Highlights and World Tourism Barometer .
- Review and read the market intelligence information provided by CBI . This webpage gives access to a CBI trend report and promising market segments and target groups on the European market.
- These sources will help you to identify important (emerging) trends and markets in Europe on a regular basis.
- Try to identify a few target groups or niches that may feel attracted to your business.
b. Get inspired by existing customers
When customers make use of your service business they could also inspire you to make new products. This means that you would need to involve them in the development process. Do not ask them what they want (as they may not know) with a questionnaire, but try to get an idea of the needs they have in a different way.
There are three nice alternative methods you could use, although there are other methods available as well, such as the ones in Ideo’s free Human Centered Design Toolkit . The first time you do so, it might make you feel uneasy to approach a customer. However, always remember that communication with them is key in developing a better product or service.
- It is your duty as an entrepreneur to look after your customers. So you can see it as part of your job to observe your customers during different phases of their customer journey and to learn to understand this customer journey through their eyes. Such observation should be done discreetly and quietly, so as not to disturb or annoy them while enjoying their holiday or business trip. It gives you insights into what they think, what they do, how they interact with others, and what they dream and wish for. While you observe your customers, you can also make notes. Afterwards, you need to find a moment that suits your customer to share your observations in an informal setting, and ask questions about things you did not expect, did not understand, or what they found appropriate. Again, make notes!
- You may also ask your customers whether they would like to help you with improving your services. Ask your customers to take photographs . You could also ask your customers to document their customer journey with a camera and to take pictures of what they consider appropriate products or services. When they give you the pictures, ask them whether there is a suitable moment for them to share some thoughts about these. When you discuss them, do not forget to make notes. Do not insist if a person does not want to cooperate, but try others instead.
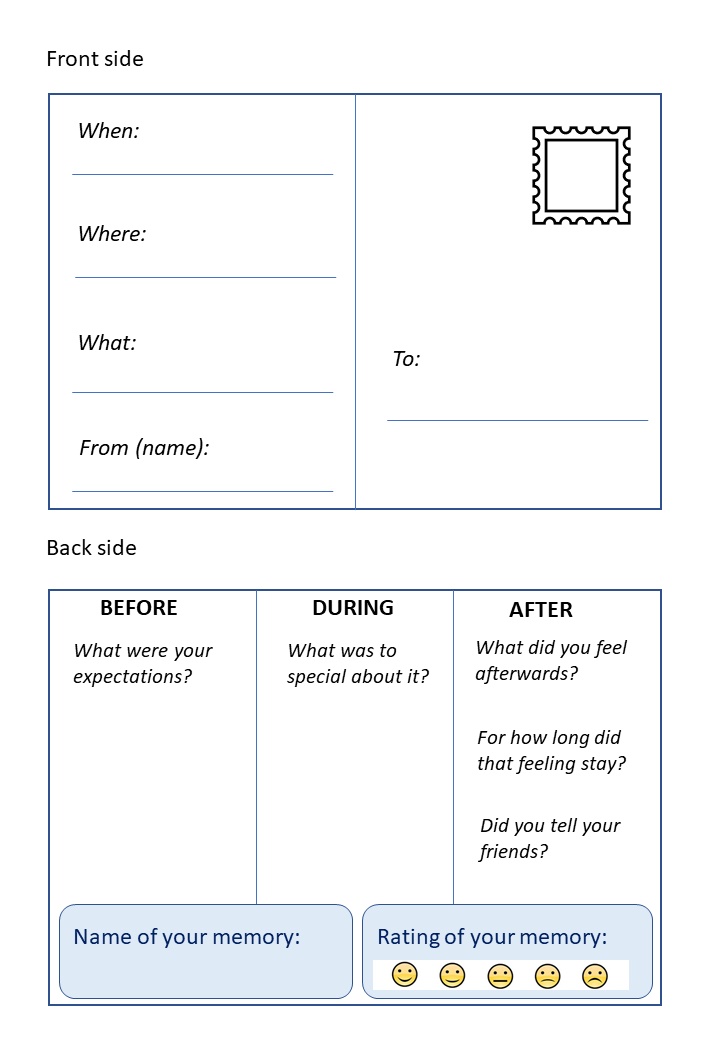
- The third approach also requires asking your customers for help in making your services more appealing to them. Ask your customers whether they are willing to take a number of ‘memory cards’ along with them while using your product or service. These cards have to be printed by you beforehand in a kind of postcard format (such as in Figure 2). Ask your customers to fill in a card each time they experience something they did not expect, or which they find very positive or negative. Ask them to return the cards to you by the end of each day or when they leave. If they are open to doing so, ask them whether they have time to share their thoughts with you. If so, be sure you make notes.
- Download and make use of the print version of the ‘memory card as shown in Figure 2.
A useful way to describe an individual customer is by using a puppet template. A puppet template is a simple picture of a single customer surrounded by clouds, words bubbles and icons, such as illustrated in Figure 3. Ideally you would make a puppet template together with a customer. This shows that you are open and willing to build a personal relationship with them. A good moment is when you have the chat about the observations, the photographs that they took, or the memory cards that they filled in. During this conversation you could also talk about the person’s age, where they come from, their work, what they do in their daily life, their main interests in life, their worries, their wishes and dreams, or their preferences in tourism. This generates a lot of relevant background information. Take notes! Each customer you talk with gets a separate puppet template.
You will end up with a number of puppet templates. Review the puppet templates and take a closer look at each one. What do you see? You will probably discover that some of the templates are similar to one another. This means that you have already started to understand your customers a little better! Now, group together the puppet templates that show similarities. Each group represents a type of tourist that makes use of your business .
- Involve people in your business or community to assist you with understanding the language or the culture of the customer.
- They may help you with making puppet templates and with grouping the templates into types of tourists.
- Download and use of the print version of the puppet template shown in Figure 3.

4. Make a persona for each type of customer (Step 2)
In the previous step, you grouped the puppet templates with similarities together. Each group represents a type of tourist who could be attracted to your business. Now the challenge is to turn each type of tourist into a market description. You will do this in the form of a so-called persona: one persona for each type of tourist. You might end up with 4-8 personas. You may need to go back to the market intelligence and the puppet templates in step 1 for detailed information. A persona describes each tourist profile, point for point. It would be nice to add a quote on each persona to bring them to life.
A persona includes:
- List of ages & countries or origin
- List of work and ambitions
- Details about personal lives
- List of main interests
- List of wishes, preferences and dreams
- You may want to add photographs (for example from magazines) and quotes that characterise the type of customer
- Key locations they went to
- Alone? Or with whom?
- What did they like and what not?
- Which emotions did they show?
- Key issues, needs, dilemma’s
Most organisations have their own template. The Interacting Design Foundation explains the use of personas in a video . In the figures below, you will find a few examples with different levels of detail and a different style. You can put each persona on a different flipchart sheet.

5. Identify the core needs of the customers and the key opportunity areas for your business (Step 3)
Now you need to identify the most prominent needs, hurdles, issues or disappointments of each type of customer (persona).
- What would be remarkable events and experiences for that persona? What were remarkable events and experiences for that persona?
- What would be stunning likes for that persona? What were stunning likes for that persona?
- What would be striking issues, hurdles, disappointments, wishes or needs for that persona? What were striking issues, hurdles, disappointments, wishes or needs for that persona?
- You may need to go back to the market intelligence and puppet templates in step 1 for possible answers.
- Write each possible answer on a separate sticky note no matter from which persona. Try to get at least 25 sticky notes in total. More would be even better.
- When you are finished, group the Post-its together into areas of which you think they could have a positive impact on your customers’ experiences. Label each grouping of Post-its with a short telegram-style sentence that identifies the impact area . You could write these labels on a Post-it. A label could be, for example: “customers need more personal attention during the excursion”, “customers like to enjoy local cuisine”, or “customers need to be able to connect online”.
- Finally, turn each label into a positive opportunity for your business, also known as an opportunity area , and write it on another Post-it that you put at the top of the label. The header could be for example: “much personal attention during excursion”, “provide local cuisine to the customer”, “adequate Wi-Fi network”.
- Try to do this step with your team or with people from the community.
Now you have created opportunity areas for your business! It would be great if you were able to end up with anywhere between two to five such opportunity areas.
6. Develop a multitude of ideas for solutions, or new products, services or experiences (Step 4)
During the previous steps you started with collecting a lot of information that, step by step, you worked into just a few opportunity areas for your business. Now we will try to generate ideas for new products, services or experiences that matter to your customers for each opportunity area. Ideally, you should take this step together with colleagues in your business (not just senior staff!). If you think it is outside the range of your core business, you may also want to involve other businesses in your community.
For a long-term benefit, you first need lots of ideas to get a single good one. This one idea should be innovative and really different from the others. It might be a completely new solution to a problem customers did not even know they had. Do not be satisfied with an obvious solution!
How does it work?
Brainstorm for each opportunity area
Write out each idea on separate Post-its
Sort and group/cluster the ideas that you wrote down
- Brainstorm for each opportunity area that you created in the previous step. Come up with as many ideas as possible. Try to think of weird solutions, products, services or experiences. Never worry whether ideas are right, wrong, absurd or obvious. That hampers your creative flow of thoughts. If you do it with your team you might end up with dozens of ideas.
- Write each idea on a separate Post-it . If it helps you to understand it better, you can make a drawing of what you have in mind.
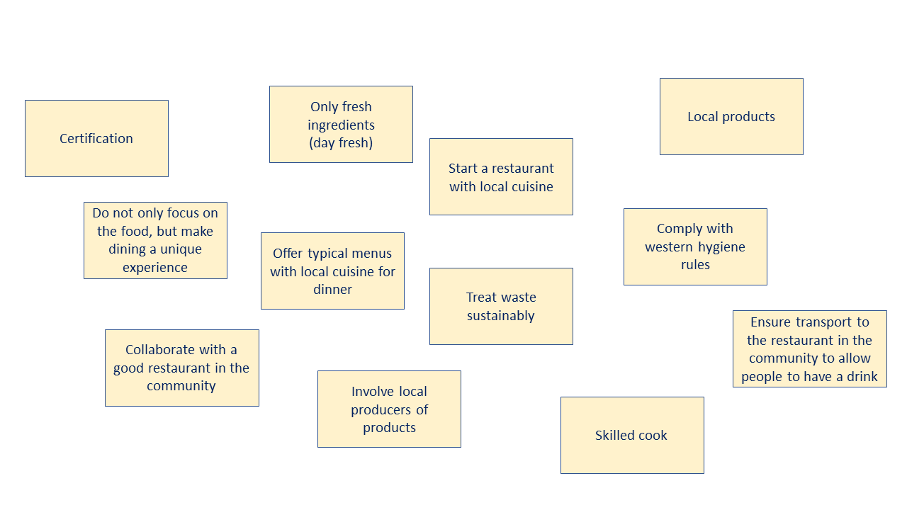
- Next, sort and group the ideas that you wrote down . Put the bad ideas to the side. Group the ideas that go well together into clusters. Give each cluster a label that tells you what the overarching idea is that the cluster is about. Brainstorming for the opportunity area “provide local cuisine to the customer” could lead to the following labels (Figure 5): start our own restaurant; authentic design of the restaurant; involve local farmers; kitchen staff recruitment and training programme; sustainable waste treatment.
- If you take a closer look at the clusters with the labels, you might get ideas about more details. You can write these down on additional Post-its. For example, once you have made a cluster with the label ‘waste treatment’, you may add other ideas: the name of a certification programme you would like to comply with; how you want to adhere to the certification programme; aspects of how you organise the waste flow in the restaurant and kitchen; communication of the certification with the customers, etc. So the labels give you inspiration to add to the clusters to make these more specific.
You will end up with a shortlist of your best ideas for solutions: new products, new services or new experiences. It is a good idea to show the ideas to some of your customers for feedback. In the case of Figure 6, you would end up with the following products and services: authentically designed restaurant (product); strengthened involvement with the community (service and products); collaboration with regional/national educational institutions to train qualified kitchen staff to be skilled at cooking, but to also always pay attention to hygiene rules; a certified waste treatment service.
7. Turn your best ideas into prototypes that can be tested and improved step by step (Step 5)
Now is the time to create a first design for the ideas for new products or services that you have created. We call this a prototype . If you make such a detailed design, this will help you to understand your idea better, but also to determine whether you have the resources to implement it, and whether there are any unforeseen challenges or consequences. These things are important for long-term success.
- Select the ideas that could upgrade one of your business’s current products or services or be integrated with such a product or service. These ideas will probably be the easiest to develop because they fit best with your everyday work.
- For each of the products or services that you selected, make a detailed description of how you want it to be designed. We call this a prototype of your product or service.
How do you make a prototype?
- Take a large piece of paper, such as a flipchart sheet, for each of your innovative ideas.
- Draw a cross on each sheet in order to divide it into four quarters. Each quarter is dedicated to one building block of your product or service idea, as illustrated in Figure 5.
- Describe and visualise what each building block would look like according to you. Put your description into a few sentences. Also use a few sketches, drawings and/or cartoons. You can use simple shapes, because the quality of the sketch is not so important at this stage.
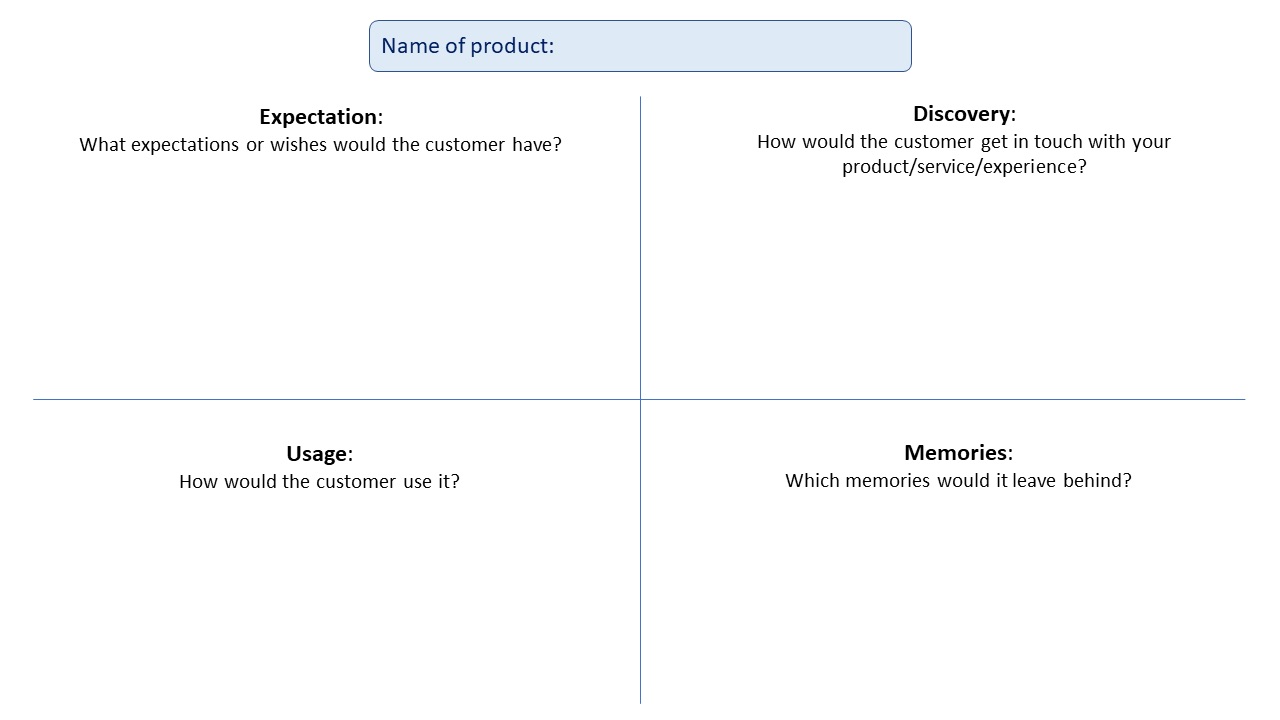
- Start with the name.
- Write down the persona(s) who would feel attracted to the product because it matches their needs. You need to go back to the steps you completed earlier.
- Write down an appealing story about your new product or service that can be communicated with the European market. If you have a website, you can put the name and story of your new product/service there.

Each sheet that you have finished is a prototype of the ideas that you have created for innovations for your business. These are ready to be tested, like the prototype of a new car or airplane that is tested in a wind tunnel.
Never worry that your prototype is incomplete or indistinguishable from the final product that you have in mind. This will be dealt with later in the process.
8. Test your prototypes in practice (Step 6)
The final step is to put your innovative idea into practice and offer it to your customers as you have described and visualised it in your prototype. It is a process of learning by doing. You get feedback from your customers on what worked and what did not. Based on this feedback, you then create a new and improved version of your product, service or experience. Then you once again get feedback and make more improvements. In this way, your product or service will improve step by step.
- Do not expect immediate success but accept that you can make mistakes now that otherwise would cost you a lot of money later on.
- See it as a learning process. Be open to the feedback and do not defend your prototype if the users are less positive than you expected. Try to get as much feedback and suggestions for improvement as possible.
- Try to put some speed and efficiency in this phase. This will help you with moving quickly from prototype to putting it to the test, to gathering feedback, and then to making a better version of your product or service.
- Never forget that new trends and new markets will arise. This means that your customer and the needs of your customers may change over the years. This is why you need to restart at step 1 every few years to stay tuned to the needs of the market.
This study was carried out on behalf of CBI by Molgo and ETFI .
Please review our market information disclaimer .
Enter search terms to find market research
Do you have questions about this research?
Ask your question
Webinar recording
29 September 2020
Related research
- What is the demand for outbound tourism on the European market?
- What trends offer opportunities or pose threats on the European outbound tourism market?
- What are the requirements for tourism services in the European market?
- (opens in a new tab) Twitter
- (opens in a new tab) Facebook
- (opens in a new tab) LinkedIn

- Tourism Management Tutorial
- Tourism Management - Home
- Tourism Basics
- Tourism Management - Introduction
- Tourism Management - Types
- Tourism Management - Terminology
- Tourism Management - Factors
- Tourism Management - Demand
- Tourism Mngmt - Motivation Factors
- Maslow's Pyramid of Motivation
- Consumer Behavior in Tourism
- Tourism Management - Plog's Model
- About Tourism Destinations
- Destination Awareness
- Tourism Management - Milieus
- Tourism Management Destination
- Tools for Destination Management
- Managing Tourism
- Tourism Management - Supply
- Tourism Functional Management
- Business Departments
- Market Segmentation
- Tourism Mngmt - Marketing Mix
- Tourism Mngmt - Products & Services
- Developing Product
- Product Development Phases
- Tourism Impacts, Trends, & Future
- Tourism Management - Impacts
- Tourism Mngmt - Trends & Future
- Tourism Management Resources
- Tourism Management - Quick Guide
- Tourism Management - Resources
- Tourism Management - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Products and Services
“Don’t give up and always keep on believing in your product. Because if you don’t, how can you make others believe in it?” − Niels Van Deuren, Founder, housinganywhere.com.
The tourism industry as a whole survives because of various tourism products and services. Tourism industry is flexible. The products of tourism cannot be easily standardized as they are created for the customers of varied interests and demands. As the tourism products are mainly the tourists’ experience, they can be stored only in the tourists’ memories.
Let us understand more about tourism products and services −
Types of Tourism Products
The tourism products are grouped into the following types −
Tourism Oriented Products (TOP)
These are the products and services created primarily for the tourists and also for the locals. These products need a great share of investments in private sector. A few of them are −
- Accommodations; For example, Taj, ITC Hotels.
- Transportation; For example, Owning taxis, luxury buses, and boats.
- Retail Travel Agents
- Tour Operators
- Shopping Centers such as malls
- Cinema Theatres such as PVR
- Restaurants for Food and Beverages
- Tourism Information Centers
- Souvenirs Outlets
- Museums, Temples, Gardens, and Theme parks
Residents Oriented Products (ROP)
Here, the products and services are created mainly for the local residents staying at a particular tourist destination. This category requires investment in public sectors more. Some of them are −
- Public Parks
- Banks and ATMs
- Petrol Pumps
- Postal Service
Intangible Products of Tourism
They include −
Bookings of accommodations, theatres, and at various sites.
Tourists’ experience by visiting a destination, eating at a restaurant, or performing an activity.
Tourists’ memory which is created by storing the details of events and experience on the tour. The high degree of satisfaction or dissatisfaction is often stored as a long term memory.
Transportation of tourists and their luggage from one place to another.
Tour Operator’s Products and Services
To realize the facilities and experience a tourism product offers, service is required by skilled and qualified staff. The tour operator provides the following typical products and services −
Accommodations
The tourist destinations are equipped with different types of accommodations. They cater for tourists’ stay at the destination.
Serviced − This type of accommodation is supported by skilled staff such as housekeepers, drivers, guides, and cooks.
Self-catering − This accommodation offers staying facilities but dining is required to be self-catered. It is equipped with cooking, fuel and facility, some basic supplies such as tea/coffee/sugar sachets, and a drinking water source.
Hotels − Budget rooms to 7* hotels with classy amenities. The hotels contribute a major share of imparting the experience to the tourists by providing best services and amenities.
Guest Houses − Owned by business or government organizations, which can be used by its staff and staff relatives.
Camping Sites − They are open sites often located in areas of lush greenery. They are equipped with clean place to pitch the personal tent, a water supply, and electric supply. Camp sites have common rest rooms.
Reservations
The tour operator is responsible for making reservations for special events or activities the tourists are interested in. At some places, the reservations are required to be done well in advance to avoid last minute hassles. The events or activities such as a music concert or a theatre show, visiting a theme park or a zoo, require people to secure seats or avail entry with prior reservations.
Guided Tours
The tour operators can arrange guided tours. Some qualified staff who can get access to the place, explain the importance of the place, support, and guide the participants through the entire visit. The guide is arranged to accompany the tour participants as a part of tour.
Transport Facilities
These facilities are for travelling from one place to another.
Surface Transport − It includes support of transport by road or water.
Air Transport − This is the support of transport by air, generally given for long distance travel. Many times the tours include a halt of a couple of hours at transit destinations. Today the airports are built and maintained as engaging tourist terminals by providing amenities such as spas, lounges, food joints, bars, and book shops, retail shops for selling authentic local food, clothes, and souvenirs.
Today the Airlines are no more backstage when it comes to caring for their customers. They offer loyalty programs to their customers under Frequent Flyer Program to encourage the customers to travel more and accumulate points and redeem them against travel or rewards.
Dining Facilities
The tour operators can book accommodation that provides dining facilities or it can tie up with the local restaurants which are ready to entertain groups. If the tour package is all inclusive, the tour operator pays for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. If not, the tourists need to pay from their own pocket.

Tourism Product Concept
Tourism Product Concept: Tourism product is usually as the amount of psychological and physical satisfaction it offers or delivers to the tourists when they are travelling to a new place or are on the way to a given destination it can be both domestic and international. Tourism products are more concerned towards services and facilities produced to fulfil the requirement of the consumers or the tourists.

Tourism product concept may be combined or amalgamated in nature i.e. the various attraction at a given destination, transportation facilities and other entertainment facilities result in full or 100% customer satisfaction. every element in tourism product is delivered by single supplier service or facilities like tour operator , airline companies, hotels and resorts etc. tourist products can be studied on the basis of four important elements viz. attraction, accessibility, accommodation and amenities.
Meaning of Tourism Product
Tourism product is a group of various components and elements which are combined together to satisfy the needs and wants of the consumers. The product in tourism industry is the complete experience of the tourist from the point of origin to the destination point and back to the origin point. The product in Tourism may be defined as the ‘sum total of physical and psychological satisfaction it provides to the tourist from the origin point to the destination and during their travelling route’.
Also read Tourism
The raw material in tourism industry is the natural beauty, Climate, History, Culture and people of the destination and some other important elements are the existing facilities or the infrastructure such as water supply, electricity, roads, transport , communication, services and other ancillary services. If any of these elements get missing, then it will completely destroy the whole experience of the tourist. Tourism products are offered in the market with some cost i.e. money. A Product could therefore be defined by its three characteristic:
- The product must be offered
- It should satisfy some need or needs of the customers
- It should be exchanged for some value
Also read more about Tourism Product Life Cycle
So, we can say that if the Tourism Product i.e. the sum total of a country’s tourist attractions, transport systems, hospitality , entertainment, and infrastructure is well designed and developed and then offered to the tourist this will ultimately result in consumer satisfaction. Tourism products are nothing but various services offered to the tourists, and falls under the category of service product. Tourism product is the prime reason for tourist to choose a destination. Tourism product helps in earning revenue for the destination. So all the tourism product should be properly preserved and promoted
A) Attraction
Attraction is the first and the most important element of tourism product, until unless there is an attraction, then only a tourist would be encouraged to visit a particular place. Attraction is a very important element as it determines the choice made by a tourist to travel to a particular place rather than another place or destination. An attraction can be of different types such as historical buildings and monuments, areas of archaeological interests, mountains, beaches, resorts, national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, Flora and Fauna, events like conferences, exhibitions, sports meet, world cups, music and art festivals etc.
You may may be interested to read about Aviation Industry
Demand for tourist products can be determined on the basis of upcoming trends in the market or current fashions. Present fashion in the market are helpful for analyzing and fulfilling the demand for different tourism products (which can include attractions, services and other amenities). Tourist visiting to hill stations for their natural beauty and panoramic views may choose to opt for some other destination due to current trends in the market and sometimes change in the fashion.
You may read History of Travel and Tourism
Peter has sketched up a list of the different attractions that are important in the tourism . Though, the attractions of tourism are, to a very large amount, geographical in character. Location and accessibility (whether a place or coastal or inland position and the ease with which a given place can be reached) are essential. Those who wish to seek wilderness and adventure may think of physical space at a destination.
Landscape or scenery is a mix of landforms; water and flora and has a beautiful and artistic value. Weather conditions, especially in relation to the amount of sunshine, temperature and precipitation (rain as well now), are of unique importance. Animal life might be a significant attraction, first in relation, to bird watching or viewing game in their natural habit and second, for sports purposes, e.g. hunting and fishing. Human’s influence on the natural landscape in the name of his settlements, archaeological remains and ancient monuments and is also a main attraction. Finally, a range of artistic elements folklore, artistic expressions, ways of life etc. offer valued attractions to large tourists.
B) Accessibility
Accessibility can be defined as means by which a person/tourist can travel or reach to particular place or destination. Tourist attractions can be of different types some may be accessible or some may be not by a mode of transportation . A tourist always looks up to a mode or means of transport in order to reach that particular place/attraction. Mode of transportation can be a coach, a car, an aeroplane, a ship or boat and a train that can enable or help a tourist to visit his desired destination. There are certain destinations which are not accessible by different modes of transport or inadequate transportation services, these destinations then turn into of a little value.
Generally the tourist attractions that are situated close to a tourist generating area or market and are connected by a proper network of effective modes of transportation, experience a large number of tourist visits. Distance between the places of origin to the desired destination plays a crucial role in the movement of tourists and effect their choices in destination selection, proper connectivity between places or destination can act as motivation factor for tourists to visit a particular destination or place. Long distance destination increases the cost of travel for the tourists which somehow restricts the limits of different tourists travelling across places.
Time constraint and cost play a crucial role in the movement of tourists across the globe. An instance can be that of India. Almost two and half million tourist visitors for a country of the size of India may seem to be rather insignificant. Though, we see at certain things like the country’s distance from the affluent tourist markets of the world such as Europe, United States, Japan, Canada and Australia, one may determine that the long distance is one of the reasons liable for low tourist visits. It costs a tourist from these nations, quite a large amount, to travel to India for a vacation. It has been listed before that North America and Europe last to be major markets creating and getting areas for international tourist arrivals, accounting for as much as 70% and 20% respectively, of inbound tourist arrivals. Easy-going accessibility, thus is a main aspect for the development and growth of tourist arrivals.
C) Accommodation
Lodging and other services balance the tourist attractions. Accommodation is very crucial and plays a central role and is very essential requirement of every tourist destination. As per the definition given by UNWTO, a person travelling to a new place from his place of origin must spend at least 24 hours at a particular destination so then only he/she would be considered a tourist. This tells about the importance of accommodation facilities at a different destination.
The demand for accommodation has always been there since ages. Therefore, the demand or the need for accommodation is met through variety of facilities. In the accommodation sector, the range and type of lodging is a bit wide-ranging and has experienced through different stages in the last couple of years. There is a decrease in the need for small hotels, boarding houses and other accommodation facilities. Large hotel chains have started to increase their share at famous tourist destinations and big metropolitans throughout the globe in more traditional holiday and sea- side resorts in Europe and elsewhere, large hotels are keeping their share of holiday resorts.
In the past few years, certain changes have arisen in the accommodation sector and the type of accommodation has totally transformed. The demand for non-traditional and informal types of lodging facilities have increased to a great extent. Holiday villages and concepts like home stays, condominiums and youth hostels are the current trends in the accommodation sector and popularity of these types of accommodations has increasing in the present times. Accommodation in itself has become an attraction in the modern times.
You can also read History of Travel and Tourism
In fact, a big group of travelers visit a specific town or destination simply since there is a first class luxury resort and hotel that offers outstanding facilities sand services for the entertainment of tourists. Few nations like Holland, France, Switzerland, Belgium and Austria have achieved a reputation for offering exceptional lodging with lavish food. Countless hotel companies away in different nations, specially the resort hotels have earned a status for their exceptional services, cuisines and other entertainment facilities. The French government for example, overlaid the way for tourist expansion of Corsica by introduction of a large hotel growth agenda.
D) Amenities
Every tourist travelling to a new destination desires for world class facilities and services. In order to fulfill their demand huge efforts are made by the industry. High quality facilities are important aid to every tourist destination or center. For a coastal resort, services like swimming, boating, yachting, surf-riding and other amenities like recreation, dancing and other entertainment and amusement services are very essential for each and every tourist destination/center. Facilities can be of 2 kind’s natural, i.e. sea-bathing, beaches, possibilities of fishing, opportunities for trekking, climbing or viewing etc. and man-made, i.e. different kinds of entertainment facilities that can cater to the unique requirements of the various tourists. Outstanding beaches, sheltered from sunshine with palm and coconut trees and providing good bathing conditions makes a very goo the tourist center. Various other natural facilities like large water for the purpose of cruising or the chances for hunting and fishing are equally very significant.
Characteristics of Tourism Product
Tourism products are mostly service goods that have different types or features. For instance, in business tourism management and planning are the services provided by different large convention centers and hotel chains. Various fair and festivals are the events that are provided for the entertainment and amusement only at a given time of the year and these are usually variable and perishable. In country like India numerous traditional/ancient attractions in the form of music and dance can be watched and experienced. There are different natural products which are been consumed by the tourist travelling to India like flora and fauna, wildlife. Following are some of the features and characteristics of tourism products:
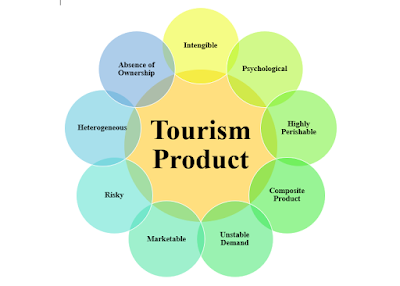
a) Intangibility of Tourism Product
Unlike a physical product, say, a train or television, there is no handover of ownership of products is included in tourism. The goods or products in tourism cannot be consumed or demonstrated before purchasing it. Instead, some installations, amenities, items of equipment are available for a certain or fixed period pf time and for a particular use. For instance, a hotel room is offered or provided for a given time frame or a seat in a train is provided for a couple of hours of the journey.
b) Psychological
A tourism product is offered to provide or offer certain level of satisfaction to the consumers or tourist. A person/tourist acquires experience with the consumption of different tourist products. Experiences derived while interacting to new places, people and environments helps in the encouragement of potential customers and helps in attracting them to consume the products offered to the market.
Read more about Hospitality
c) Highly Perishable
Usually a tour operator or a travel agent offer or sells various tourism products to the market, which are perishable in nature and cannot be stored or sustained for a longer time frame. Production of the products and services is only possible if there is a demand and the customers are actually present and if the customer buys the product it cannot be blocked, disturbed or customized. If the product is not consumed on time or is unused the chances are lost which means, if a tourist doesn’t buy the flight ticket on a given date, the chance at that time is lost or can say the validity of the seat is expired or is left unused. The reason can be heavy discounts or offers given by the airline company on the given date or during off season.
d) Composite nature of tourism Product
A tourism product is never offered or produced by a single enterprise there is an involvement of different parties (viz travel agent , hotels, airline company, tour guide etc.) when compared to a manufactured product. There is a involvement of various parties in providing or manufacturing a complete tourist product. The product shields broad experience of a holiday to a specific destination. And numerous suppliers and providers that supply to create this experience. For example, a hotel provides a food and rooms, travel agent makes booking for sightseeing and stay at different places, airline and rail provides seats etc.
e) Unstable Demand of Tourism Product
There is a problem or one can say a challenge for tourism products as tourism products are influenced by the seasonality, economic , political factors. For instance, there is a demand for the hill station in the summer season as people like to travel to cold places mostly places likes Manali, Shimla, Nainital, Mussorie etc. whereas the demand for coastal areas like Goa rises in the winters. There are different times of a year when there is a demand for a particular destination than other destinations. This is the time when there is a huge tension on the hotel bookings, transport system, the employment etc.
f) Fixed supply in the short run
Tourism product similarly as the factory-made products cannot be transported to the final consumers, the consumers have to go to the products offered to them. Product development is done on the basis of analysis of the taste and preferences, behavior, dislikes and likes of the consumers, so that the expectations and realities of the consumers. Therefore, the supply of the tourism product is limited in the short run and may be maximized on a long term basis depending upon the increasing demand pattern of the tourist product.
g) Absence of ownership in Tourism Product
Tourism products have absence of ownership. For instance, when you buy a product say a bike or a car, the possession of the same is reassigned to you, but when one rents a cab, he/she only buys the right to be transferred from one place to another, you neither own the driver nor the cab. Similarly, in case of tourism products like airline tickets, train tickets or a hotel room can be used for given time frame but not owned. Tourism products can only be purchased for using but the ownership of the same stays with the provider of the service or the product so, an Opera show can be watched but the performer cannot be kept.
h) Heterogeneous nature of Tourism Product
Tourism is not a uniform product. Similarly, tourism product is not same, since they tend to change or vary in terms of quality and standard with the passage of time, unlike a television set or any other factory-made product. A flight or a tour package cannot be the same at all times. The reason behind the changing nature of the tourism products is a service and services are customers/consumer oriented. So there is variability in tourism products as all humans are not the same and vary in terms of their behavior, taste and preferences. For example, all workers working in a hotel cannot give the same excellence of facility and the same worker might not perform equally in the morning and evening. Therefore, the services cannot be uniforms or homogeneous.
Tourism products are first purchased and later on consumed that is why there is a high level of risk involved in purchasing before the consumption of the products. An element of chance of risk is always there in the process. For instance, a movie might not be as entertaining as it promises to be or a summer vacation in Goa may be disappointing due to bad weather or heavy rains.
j) Marketable
Tourism products are marketable at different markets. Firstly, both the regional and national organizations involve themselves in catering the potential customers/tourists to travel to different region/destinations across the country. Secondly, the individual firms are trying to market their own tourism products in order to cater potential customers.
Read more on Aviation Industry in India
Read more on Tourism Economics
Tourism Product Concept Tourism Product Concept Tourism Product Concept Tourism Product Concept

You Might Also Like

Tourism in the 21st Century

Marketing of Tourism Product
This post has one comment.
Pingback: Which of the following is a characteristic of the tourism product? – AnswerParadise.net
Comments are closed.

- Government of india
- Skip to main content

- All matters related to creation and maintenance of Tourism Assets Bank and subsequent research and content collation.
- All matters related to overall strategy.
- All matters related to partnerships with private sector, start-ups, others for attractions and experiences creation.
- All matters related to inter-ministerial convergence across tourist touch points.
- All matters related to ‘Meet in India’ and development of MICE Tourism, ‘Heal in India’, development of AYUSH, Wellness, medical tourism, ‘India says I Do’, development of wedding tourism, eco-tourism, Vibrant Villages Program, Best Tourism Villages, Central Nodal Agencies for Sustainable Tourism and Rural Tourism & Rural Home stays, Mega Adventure Trails and other aspects related to tourism sub-sector ecosystem development.


COMMENTS
Product Development. As defined by UN Tourism, a Tourism Product is "a combination of tangible and intangible elements, such as natural, cultural and man-made resources, attractions, facilities, services and activities around a specific center of interest which represents the core of the destination marketing mix and creates an overall visitor experience including emotional aspects for the ...
Tourism Products are a combination of goods and services demanded by a tourist during travel to and stay at a destination. These include natural, cultural and manmade attractions and facilities such as hotels, transport and ancillary services. In this process, tourists derive an experience which varies from individual to individual.
Tourism and travel-related services include services provided by hotels and restaurants (including catering), travel agencies and tour operator services, tourist guide services and other related services. A crucial aspect of trade in tourism services is the cross-border movement of consumers (mode 2). This permits a variety of workers ...
1. Introduction. Destinations depend on their primary tourism products as key pull factors motivating tourists to visit them. The paper's analysis focuses on primary tourism products rather than on products which are less likely to provide a substantial tourist draw to specific destinations, such as accommodation, food services and transportation (Jansen-Verbeke, 1986).
Abstract. The aim of this paper is to propose a marketing-oriented definition of the tourist product as. well as a classification system of its components based on an extensive review and analysis ...
Product, tourism. In a marketing context, products are bundles of tangible and intangible elements conveying benefits to satisfy needs. They may take the form of goods, services, ideas, events, persons, places, or organizations (Kotler and Armstrong 2008 ), fulfilling two distinct tasks. First, each product satisfies a need through the benefit ...
2.2.1 The Core Product. The most basic level is the core product; which is the real core benefit or service (Baines, et al., 2019: 300).According to Levitt (), the generic or core product is a material or physical product.As Fig. 8.1 illustrates, the core product stands at the centre of the total product-offering. The core product, which is the real core benefit or service is intangible; it is ...
Handbook on Tourism Product Development. Published: 2011 Pages: 153. eISBN: 978-92-844-1395-9. Abstract: Tourism products are the basis for a destination's tourism sector operation: unless the tourism product meets the needs and expectations of tourists, the destination cannot realise its full potential. However, only few destinations focus ...
The UNWTO/ETC Handbook on Tourism Product Development outlines the essential elements in the process of tourism product development planning and implementation, e.g. coordination, consultation, collaboration - co-opetition. It illustrates these principles through a range of successful approaches and case studies from around the world and sets ...
Unlike financial or other services, tourism product development requires a physical stage in the form of mountains, beaches, or infrastructure created on purpose (e.g., theme parks). Tourism products are thus linked to specific locations, so customers have to travel physically to those places to enjoy these products. Tourism product development ...
Nevertheless, product design helps to create new benefits or improve the existing service to the expected level of the consumers. This market design for tourism products or services indicates a holistic way for a business to earn, harmony, and comprehensive service design of client needs (Saco and Goncalves 2008 ).
Based on the new services or products' concept, project managers identify tourism destinations' core resources, select the stakeholders, and design transformative tourism experiences. This framework can be applied to innovative tourism products or re-evaluations of existing products in order to maintain tourism destinations' competitiveness.
Classification of tourism product services. Venture with us as we explore the physical and emotional contours of these offerings, understanding their importance in the grand puzzle of travel and human connection. This exploration is as much a journey for us as it is for you—arousing passion, expanding knowledge, and cementing our shared love ...
Below, the steps are described to help you to develop innovative products and services for new and existing customers. Staying tuned with the market is an ongoing process. The outcomes of each step are illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1. From inspiration from your (potential) customers to innovative products and services. 3.
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
The tourism industry as a whole survives because of various tourism products and services. Tourism industry is flexible. The products of tourism cannot be easily standardized as they are created for the customers of varied interests and demands. As the tourism products are mainly the tourists' experience, they can be stored only in the ...
Tourism products are nothing but various services offered to the tourists, and falls under the category of service product. Tourism product is the prime reason for tourist to choose a destination. Tourism product helps in earning revenue for the destination. So all the tourism product should be properly preserved and promoted. A) Attraction
PERISHABILITY. Perishability plays the most significant characteristic in the tourism industry. The product or services in the tourism and travel industry are been availed as they are produced. Usually, the service can't be stored as they are highly perishable. When the room in the hotel is not reserved tonight, you can't take 'tonight ...
Tourist loyalty is created through good tourism service quality and the availability of tourism products. This study discussed the various attributes of tourism service quality, namely, tour ...
of the tourism product. Thanks to the emerging infrastructure, tourist resources are being developed, their attractiveness and accessibility for tourists are increasing, and the tourist capacity of the territory is growing.Thus, hotel services are the basis of the tourism offer, including that of the rural tourism.
component of the tourism infrastructu re, since the accommodatio n service is a key element of the tourism product. Thanks to the emerging infrastructure, tourist resources are being
The presence of a tourism village in Indonesia might be viewed as an opportunity to strengthen small, micro, and medium-sized businesses as a driving force in the local economy. The goal of Micro Small Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) development is to create a tourism village supported by MSMEs that combines natural and culture attractions, local gastronomic and artisan, and public service facilities.
additional hotel services in accommodation facilities of the city of Rostov-on-Don and to study their impact on the development of business tourism in the Rostov region. The increasing complexity and differentiation of human needs contributes to the expansion and improvement of the system of providing additional services in the hotel industry. The
All matters related to creation and maintenance of Tourism Assets Bank and subsequent research and content collation. All matters related to overall strategy. All matters related to partnerships with private sector, start-ups, others for attractions and experiences creation.
successful promotion of bleisure tourism. The organization of services for bleisure tourists can become a highly profitable area for business hotels. Keywords: bleisure tourist, bleisure tourism, hotel, hotel service, additional ... from the sale of the main product, and also help to distinguish the main product from competing products. The ...