- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides

Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest news
- Stock market
- Premium news
- Biden economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash-back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Car insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
2024 state of the cruise industry report shows cruise tourism has surpassed historical levels, demonstrates its significant economic contribution and leadership in environmental sustainability and responsible tourism.
New Oceans of Opportunities publication highlights the global cruise workforce and the growth of careers in cruising.
WASHINGTON , April 9, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Today, Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA), the leading voice of the global cruise community, has released its annual State of the Cruise Industry report and a new publication, Oceans of Opportunities workforce skills report.
The annual state of the industry report includes the release of 2023 passenger volume, which reached 31.7 million— surpassing 2019 by 7%. The report also shows continued demand for cruise holidays, noting intent to cruise at 82%. The forecast for cruise capacity shows an increase of 10% from 2024 through 2028, as cruise lines make ongoing, concrete progress in pursuit of net- zero emissions by 2050.
"Cruise continues to be one of the fastest-growing and most resilient sectors of tourism— rebounding faster than international tourist arrivals—and a strong contributor to local and national economies. In 2022, cruise tourism cruise generated 90% of economic impact compared to 2019, despite passenger volumes that year at 70% of 2019 levels. Over the past 50 years, cruise tourism has demonstrated its leadership in managed tourism and is an industry that has plenty of room for continued responsible growth given cruise travel comprises just 2% of overall travel and tourism," said Kelly Craighead , president and CEO of CLIA. "The industry also continues to lead the way in environmental sustainability and destination stewardship, with cruise lines making advancements in technology, infrastructure and operations, and in green skills training for crew."
Highlights from CLIA's 2024 State of the Industry report include:
Cruise is Thriving:
Cruise tourism reached 107% of 2019 levels in 2023, with 31.7 million passengers sailing – almost two million more than 2019.
2024 is forecast to see 35.7 cruise passengers sailing.
Intent to cruise is 6% higher than 2019, with Millennials being the most enthusiastic cruise travelers of the future.
Global cruise capacity is forecast to grow from 677K lower berths in 2024 to 745K lower berths in 2028.
Each year, the fleet becomes more efficient, as cruise lines invest in propulsion technologies with conversion capabilities for future alternative fuels and utilize a range of technologies and innovations to advance their sustainability initiatives.
2022 Global Economic Impact . In 2022, cruise generated:
$138 billion to the global economy
1.2 million jobs – up 4% compared to 2019.
$43 billion in wages
63% of those who have taken a cruise say that they have returned to a destination that they first visited via cruise ship for a longer stay, extending the economic impact.
For 2023, the economic impact is forecast to be even greater given the 50% increase in the number of passengers sailing in 2023 compared to 2022.
Trends in Cruise:
The number of new-to-cruise is increasing – 27% of cruisers over the past two years are new-to-cruise, an increase of 12% over the past year.
Cruises are a top choice for multi-generational travel – with more than 30% of families traveling by cruise with at least two generations and 28% of cruise travelers traveling with three to five generations.
Expedition and exploration are the fastest-growing sectors of cruise tourism, with a 71% increase in passengers traveling on expedition itineraries from 2019 to 2023.
Accessible tour excursions are on the rise—with 45% of cruise passengers booking an accessible tour for their most recent cruise.
73% of cruise travelers say that travel advisors have a meaningful influence on their decision to cruise.
"Cruise is the best vacation value there is, with incredible guest experiences delivered by a talented and dedicated multinational workforce of nearly 300,000 seafarers. To highlight the tremendous employment opportunities that cruise tourism supports around the world, CLIA has published a new skills and workforce publication, Oceans of Opportunity . With at least 56 new ships coming online between 2024 and 2028, there are vast opportunities for careers in cruise, which boasts an impressive employee retention rate upwards of 80%," said Craighead.
Highlights from CLIA's Oceans of Opportunities workforce report include:
In 2024, cruise lines will employ a multinational workforce of nearly 300,000 seafarers representing more than 150 countries, as well as tens of thousands of employees on land.
94% of women seafarers work in the cruise industry.
Around 40% of senior leadership roles at cruise companies are held by women.
Among current and future workforce needs are green skills.
To view the full 2024 State of the Cruise Industry Outlook report, see here . To view the full Oceans of Opportunities publication, see here .
About the Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA)
CLIA is the world's largest cruise industry trade association, providing a unified voice for the industry as the leading authority of the global cruise community. On behalf of its members, affiliates and partners, the organization supports policies and practices that foster a secure, healthy, and sustainable cruise ship environment, promoting positive travel experiences for millions of travelers who cruise annually. This year, CLIA forecasts that annual the number of passengers will reach 34.7 million passengers. The CLIA community includes the world's most prestigious ocean, river, and specialty cruise lines; a widespread network of stakeholders, including ports and destinations, ship development, suppliers, and business services; and a highly trained and certified travel agent members that represent the largest network of travel professionals specializing in cruise travel. The organization's global headquarters are in Washington, DC , with regional offices located in North and South America , Europe , and Australasia.
For more information, please visit cruising.org or follow us on Facebook , Instagram, Twitter , and YouTube with our handle @CLIAGlobal—or on LinkedIn .
View original content to download multimedia: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/2024-state-of-the-cruise-industry-report-shows-cruise-tourism-has-surpassed-historical-levels-demonstrates-its-significant-economic-contribution-and-leadership-in-environmental-sustainability-and-responsible-tourism-302111983.html
SOURCE CRUISE LINES INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Cruise Industry Stages a Comeback
After watching thousands of passengers get ill and more than a year of devastating financial losses, the global cruise industry is coming back to life. And it says it knows how to deal with the coronavirus.

By Ceylan Yeginsu and Niraj Chokshi
Nothing quite demonstrated the horrors of the coronavirus contagion in the early stages of the pandemic like the major outbreaks onboard cruise ships , when vacation selfies and videos abruptly turned into grim journals of endless days spent confined to cabins as the virus raged through the behemoth vessels, eventually infecting thousands of people, and killing more than 100.
Passengers on the Diamond Princess and Grand Princess, two of the worst-hit ships, were forced to quarantine inside their small staterooms — some without windows — as infections on board spiraled out of control. Every day anxiety and fear mounted as the captains of the ships announced new cases, which continued to spread rapidly through ventilation systems and among crew members, who slept in shared quarters and worked tirelessly throughout the day to deliver food to guests.
At the time, it was difficult to imagine how the ships, which carry millions of passengers around the world each year, would be able to sail safely again. Even after the vaccination rollout gained momentum in the United States in April, allowing most travel sectors to restart operations, cruise ships remained docked in ports, costing the industry billions of dollars in losses each month.
Together, Carnival , the world’s largest cruise company, and the two other biggest cruise operators, Royal Caribbean and Norwegian Cruise Line , lost nearly $900 million each month during the pandemic, according to Moody’s, the credit rating agency. The industry carried 80 percent fewer passengers last year compared to 2019, according to the Cruise Lines International Association, a trade group. Third-quarter revenues for Carnival showed a year-to-year decline of 99.5 percent — to $31 million in 2020, down from $6.5 billion in 2019.
And yet in June, Richard D. Fain, chairman and chief executive of Royal Caribbean Cruises, was beaming with excitement as he sat sipping his morning coffee onboard Celebrity Edge, which became the first major cruise ship to restart U.S. operations, with a sailing out of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. “At the beginning we didn’t have testing capabilities, treatments, vaccines or a real understanding of how the virus spread, so we were forced to shut down because we didn’t know how to prevent it,” he said.
Several epidemiologists questioned whether cruise ships, with their high capacities, close quarters and forced physical proximity, could restart during the pandemic, or whether they would be able to win back the trust of travelers traumatized from the initial outbreaks.
Now, said Mr. Fain, the opposite has proved true. “The ship environment is no longer a disadvantage, it’s an advantage because unlike anywhere else, we are able to control our environment, which eliminates the risks of a big outbreak.”
Cruise companies restarted operations in Europe and Asia late last year, and, after months of preparations to meet stringent health and safety guidelines set by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, cruise lines have started to welcome back passengers for U.S. sailings, where demand is outweighing supply, with many itineraries fully booked throughout the summer.
Carnival said bookings for upcoming cruises soared by 45 percent during March, April and May as compared to the three previous months, while Royal Caribbean recently announced that all sailings from Florida in July and August are fully booked.
Several coronavirus cases have been identified on cruise ships since U.S. operations restarted in June, including six passengers who tested positive on Royal Caribbean’s Adventure of the Seas recently, testing the cruise lines’ new Covid-19 protocols, which include isolating, contact tracing and testing passengers to prevent the virus from spreading. Most ships were able to complete their itineraries without issues, but American Cruise Lines, a small ship company, cut short an Alaska sailing earlier this month after three people tested positive for the virus.
The industry’s turnaround is far from guaranteed. The highly contagious Delta variant, which is causing surges of the virus around the world, could stymie the industry’s recovery, especially if large outbreaks occur on board. But analysts are generally optimistic about its prospects and the potential for passenger numbers to recover to prepandemic levels, perhaps as soon as next year. That optimism is fueled by what may be the industry’s best asset: an unshakably loyal customer base.
Even during the pandemic, huge numbers of people who had booked opted against taking refunds , instead converting payments already made into credit for future travel, which the companies often offered at a higher value as an incentive. Last fall, Carnival reported that about 45 percent of customers with canceled trips had opted for credit instead of cash back. About half of customers in a similar position with Royal Caribbean Cruises did the same by the end of last year, the company said at the time.
“The demand is there,” said Jaime Katz, an analyst with Morningstar. “You know that there have been 15 months of people who have had cruises booked that have been canceled.”
No U.S. bailout for the cruise companies
By April 2020, the industry was in crisis. Cruises were halted around the world after the alarming outbreaks on ships, leading to sailing bans from the C.D.C. and other global authorities.
While they employ many Americans, the major cruise companies are all incorporated abroad and were ultimately left out of the $2 trillion federal stimulus known as the CARES Act, with lawmakers chafing at the prospect of bailing out foreign corporations largely exempt from income taxes. Environmentalists lobbied against the aid, citing the industry’s poor track record on climate issues. And criticism over how the companies handled early virus outbreaks on board ships sapped any remaining political will to help. Huge losses mounted as questions swirled about whether cruise lines could avoid bankruptcy.
“All our conversations here were, ‘At this cash burn rate for each of these companies, how long can they survive?’” said Pete Trombetta, an analyst focused on lodging and cruises at Moody’s.
Cruise lines were forced to send most cruise workers home, keeping small skeleton crews on board to maintain their ships. After months without work or an income, many of the workers, who are frequently drawn from countries like the Philippines, Bangladesh and India, fell into debt and struggled to provide for their families.
The timing couldn’t have been worse for Virgin Voyages , the new cruise company founded by the British billionaire Richard Branson, which had planned to launch its inaugural ship, Scarlet Lady, with a sailing from Miami in March 2020. The ship’s official U.S. debut has been delayed until October, but a series of short sailings will take place in August out of Portsmouth, England, for British residents.
“It’s been a very difficult 15 months and we had to make some very tough cuts along the way like the rest of the industry,” said Tom McAlpin, president and chief officer of Virgin Voyages.
In the end, most cruise companies made it through the pandemic intact, but only after receiving help. That came in the form of assistance from governments abroad or money raised from investors emboldened by efforts to backstop the economy from the Federal Reserve and others. The cash wasn’t cheap, though. When Carnival Corp. sold $4 billion in bonds in April 2020, it agreed to interest on those bonds of 11.5 percent — more than half of which it recently refinanced at a more reasonable rate of 4 percent.
Carnival, which operates under nine brands globally, has lost more than $13 billion since the pandemic began and said in a securities filing last month that it expects those losses to continue at least through August. The company amassed more than $9 billion in cash and short-term investments as of the end of May — enough, it said last month, to pay its obligations for at least another year. It says it expects to have at least 42 ships carrying passengers by the end of November, representing just over half of its global fleet.
The industry faces a long road back to normal. Moodys downgraded ratings for each of the big three cruise companies during the pandemic and says it will probably take until 2023 for the major cruise operators to start substantially reducing their debt, which had nearly doubled during the pandemic.
The companies have also been caught up in a series of legal battles in Florida, the biggest base of operations in the United States, that has them sometimes allied with the administration of Gov. Ron DeSantis, and sometimes opposing it.
In June, Florida sued the C.D.C., saying the agency’s guidelines for how cruising could restart were burdensome and harmed the multi-billion-dollar industry that provides about 159,000 jobs for the state. The C.D.C. guidelines require 98 percent of crew and 95 percent of passengers to be fully vaccinated before a cruise ship can set sail, otherwise the cruise company must carry out test voyages and wait for approval.
So far, the state has prevailed in the courts, with a ruling from a federal judge that prevented the C.D.C.’s vaccine requirements from going into effect after July 18. A federal appeals court upheld that ruling on July 23.
Despite the court’s decision, Cruise Lines International Association, the trade group, said cruise companies will continue to operate in accordance with the C.D.C. requirements. The cruise lines found the C.D.C.’s initial guidance too onerous, but once the agency made revisions to factor in the U.S. immunization program, the companies agreed to comply and said they preferred passengers to be vaccinated, because it simplifies the onboard experience.
As that suit was making its way through the courts, Norwegian filed suit on July 13 against the state of Florida, saying that a law banning business from requiring proof of immunization from people seeking to use their services prevented the company from “safely and soundly resuming passenger cruise operations.”
There has yet to be a ruling in the case.
Hurdles remain
Several other hurdles could also derail the rebound of the industry. While cruising has resumed, operators still have to contend with a patchwork of domestic and international rules, some of which impose strict conditions on passengers who go on shore excursions. A serious and widespread outbreak aboard a ship, or a broader communitywide surge in virus infections, could drive away potential customers and stall the momentum of the cruise comeback.
But despite the delays and potential for further disruptions, Virgin Voyages is hopeful for a successful launch of its new brand. Virgin’s Scarlet Lady adult-only ship, which was inspired by a superyacht design, aims to attract a hip and younger crowd, offering 20 different buffet-free dining options and a range of entertainment, including D.J. sets and immersive experiences.
“We have a fantastic set of investors behind us, and I think we are well positioned to make a big comeback because people are ready to travel and cruise again and we are launching a very attractive new onboard product right in the middle of it all,” Mr. McAlpin said.
Two new cruise ships, Carnival’s Mardi Gras and Royal Caribbean’s Odyssey of the Seas are set to launch in the U.S. this week.
And cruise workers, many of whom burned through savings and went into debt during their enforced layoff, are thrilled to be back. “I can’t believe the day has come when I have been called back to work,” said Alvin Villorente, a wine steward for Norwegian Cruise Line, who spent the last year at home in the Philippines, carrying out odd jobs to pay his bills.
“It felt too good to be true,” he continued. “I made my wife read the email to make sure I understood correctly and when I saw her smile everything suddenly went from black to bright colors. I could look after my family again.”
At a time when airports are busy and chaotic and hotels and holiday rentals are expensive and booked up, cruise companies hope to appeal to people who wouldn’t normally consider a cruise vacation.
“I’m still on the fence about booking any travel because of the constantly changing rules around the world, but an adult-only cruise with some friends could be fun, especially if it meant not having to fly anywhere,” said Crystal Marks, a 37-year-old personal trainer from Miami who went on a cruise once as a child and has been looking at Virgin sailings for early next year after a friend sent her a promotional video.
“Yoga classes at sunrise, fitness throughout the day, city-style restaurants, spa treatments, it sounds pretty perfect to me,” she added with a laugh. “If everyone on board is vaccinated and tested regularly it’s probably one of the safer options for international travel.”
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places list for 2021 .
Ceylan Yeginsu is a London-based reporter. She joined The Times in 2013, and was previously a correspondent in Turkey covering politics, the migrant crisis, the Kurdish conflict, and the rise of Islamic State extremism in Syria and the region. More about Ceylan Yeginsu
Niraj Chokshi covers the business of transportation, with a focus on autonomous vehicles, airlines and logistics. More about Niraj Chokshi
Come Sail Away
Love them or hate them, cruises can provide a unique perspective on travel..
Cruise Ship Surprises: Here are five unexpected features on ships , some of which you hopefully won’t discover on your own.
Icon of the Seas: Our reporter joined thousands of passengers on the inaugural sailing of Royal Caribbean’s Icon of the Seas . The most surprising thing she found? Some actual peace and quiet .
Th ree-Year Cruise, Unraveled: The Life at Sea cruise was supposed to be the ultimate bucket-list experience : 382 port calls over 1,095 days. Here’s why those who signed up are seeking fraud charges instead.
TikTok’s Favorite New ‘Reality Show’: People on social media have turned the unwitting passengers of a nine-month world cruise into “cast members” overnight.
Dipping Their Toes: Younger generations of travelers are venturing onto ships for the first time . Many are saving money.
Cult Cruisers: These devoted cruise fanatics, most of them retirees, have one main goal: to almost never touch dry land .
Switch language:

Cruise in 2022: the state of the industry
Using the latest thematic insights from GlobalData, Peter Nilson looks at the state of the cruise industry.
- Share on Linkedin
- Share on Facebook

At the beginning of the year, many companies, governments, and travel authorities had predicted a stronger recovery for the cruise market in 2021. Unfortunately, that was not the case.
The pandemic has proven unpredictable, with many cruise destinations going into second and third lockdowns during 2021 after a global surge in Covid-19 cases .
Go deeper with GlobalData

Innovation in Ship: Anti-fouling Ship Hull Coatings
Environmental sustainability in ship: bio-fuel propulsion marine ve..., premium insights.
The gold standard of business intelligence.
Find out more
Related Company Profiles
The walt disney co, carnival corporation & plc, expedia group inc, norwegian cruise line holdings ltd.
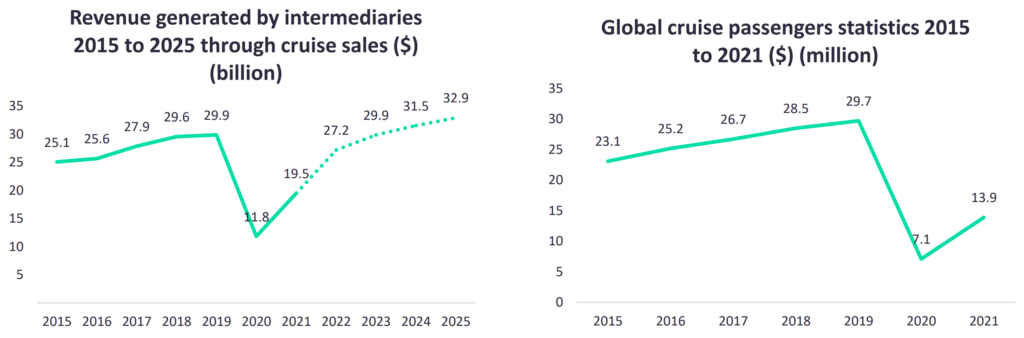
While the cruise industry has experienced a 96% Year-on-Year (YoY) increase of passengers, reaching 13.9 million, it still does not compare to the pre-pandemic levels of 2019, where there were 29.7 million passengers globally. It has been an even worse year for travel intermediaries specializing in cruise holidays.
These companies are the primary selling points for cruise trips and are often responsible for selling upgrades, premium drinks packages and excursions. Global spending across 60 major cruise markets increased by 65% YoY, resulting in total revenues of $19.4bn. Nevertheless, this was still far from pre-pandemic levels in 2019, which were approximately $29.8bn, 35% higher than 2021’s figure.
To reduce costs, many ships were retired between 2019 and 2021. Cruise ships are the most expensive assets, making this practice a necessity for many firms to stay afloat.
However, more optimistic times lie ahead for the sector. During the pandemic, the cruise industry has witnessed new innovative cruise ships and a brand-new competitor in the form of Virgin Voyages . Many cruise liners have come good with orders for new cruise ships built before the pandemic, resulting in an exciting time for loyal cruise holidaymakers to try new ships, services, and onboard experiences.
How well do you really know your competitors?
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Your download email will arrive shortly
Not ready to buy yet? Download a free sample
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
Global cruise passengers and revenue
2021 provided a tough lesson for the cruise industry, with businesses aiming to make a swifter recovery from the latest round of lockdowns.
The cruise industry’s recovery rate was modest in 2021. Although a 96% YoY increase sounds positive, it is still nowhere near pre-pandemic levels. In 2021, only 13.9 million passengers went on a cruise, 53% lower than the pre-pandemic levels of 2019.
With the fluctuations of global passengers, revenues will generally follow a similar pattern unless there is a substantial shift in consumer behaviour. Usually, the most significant impacts on a travel company’s revenues, aside from passenger flows, are an economic recession, foreign exchange, or a change in booking trends.
During the pandemic, it has become clear that the latter affected cruise intermediary revenues. In 2021, revenue generated for cruises from intermediaries reached $19.5bn, a 65% YoY increase from $11.8bn. However, cruise passenger flows increased by 95% YoY, which is a significantly higher rate of improvement.
According to the CEO of the Royal Caribbean Group, Richard Fain, this was not unexpected. The world’s fourth-largest cruise company has seen intermediaries such as online travel agencies (OTAs) and high street agencies lose a proportion of their market share, with customers opting to book directly with the cruise operator rather than a third party.
The same sentiment was echoed by Norwegian Cruise Lines CEO Frank Del Rio, who said the company had witnessed a similar booking pattern. The result is not surprising. Many agencies have had to cut back on their workforce due to poor revenue performance in 2020, resulting in fewer sales agents to capture the rising demand in 2021. This has led to more customers booking directly with cruise companies.
Research from GlobalData also supports this, when comparing two consumer surveys from 2019 and 2021. In 2019, 44% of respondents said they typically book via an OTA. However, in a Q4 2021 survey, only 24% of respondents said they booked their last holiday via this booking method. In addition, respondents who said they booked directly increased from 32% to 36%.
New cruise ships and trends for 2022
There are many new cruise ships scheduled to set sail in 2022. Many of these boast a more contemporary feel to their décor and interior, moving away from the traditional looks of the past cruise ships and moving to a more fashionable boutique hotel design.
The motivation for this stems from the fact that cruise operators need to attract a younger market. This evolution is necessary for making cruise businesses more resilient in the future by drawing the next generation of cruise tourists.
According to a 2020 GlobalData survey, 37% of Gen Z and Millennials said that they ‘strongly’ or ‘slightly’ agreed with the notion that they would book an international trip this year. In comparison, only 22% of those older than 35 responded with the same sentiment, highlighting that the younger generation may be more likely to travel in today’s travel climate.
Furthermore, cruising has also become more popular with younger adults. In GlobalData’s Q3 2019 and 2021 global consumer surveys, the percentage of Gen Z and Millennial respondents who typically take a cruise holiday increased from 17% to 21%, indicating changes in consumer tastes.
The importance of Covid-19 safety protocols on cruise ships has never been more critical. According to GlobalData, there is a demand from consumers to receive information about Covid-19 initiatives. This data shows that consumers need substantial levels of communication from cruise providers, and that cruise companies will need to develop robust communication strategies, which need to be scaled over the next few years.
Many travellers are opting to book directly with the operator rather than via an intermediary such as an OTA. According to a Q3 2019 GlobalData survey, 44% of consumers said they typically book via an OTA.
However, this has fallen substantially over the last two years. In a Q4 2021 survey, only 24% of respondents said they booked their previous holiday via an OTA.
In addition, respondents who said they booked directly with a travel supplier increased from 32% to 36%, showing that booking directly with the supplier is becoming more trustworthy and popular.
Nevertheless, this booking behaviour could well be a temporary result, with some cruise operators expecting intermediary trade to pick up again in 2022.
Sign up for our daily news round-up!
Give your business an edge with our leading industry insights.
More Relevant
Orient Express adds Brunvoll propulsion to Silenseas sailing cruise ship
Leading robotics companies in the shipping industry, bunker fuels, lubricants and fluids for the shipping industry, ship corrosion prevention: cathodic protection, coatings and insulation for the shipping industry, sign up to the newsletter: in brief, your corporate email address, i would also like to subscribe to:.
Ship Technology In Brief
Ship Technology Global : Ship Technology Focus (monthly)
I consent to Verdict Media Limited collecting my details provided via this form in accordance with Privacy Policy
Thank you for subscribing
View all newsletters from across the GlobalData Media network.

Growth of the Ocean Cruise Line Industry
Worldwide, the ocean cruise industry experienced an annual passenger compound annual growth rate of 5.9% from 1990 to 2024.
While the COVID-19 pandemic brought the ocean passenger cruise industry to a standstill for nearly two years, it also prompted the accelerated retirement of numerous older ships. Simultaneously, new additions to fleets adopted a more modern and environmentally friendly approach. In 2024, passenger numbers are expected to surpass the pre-COVID levels of 2019.
Between 2023 and 2024, a total of 10 new ships, with a combined passenger capacity of 25,450, are set to be added (refer to the tables below). This influx will bring the worldwide ocean cruise passenger capacity to 673,000, spread across 360 ships. These vessels are projected to carry a total of 30.0 million passengers by the end of 2024, representing a 4.2% increase over 2023 and a 9.2% increase over 2019.

Shipbuilding Summary
Sources: Royal Caribbean Cruises, Ltd., Carnival Corporation and plc, NCL Corporation Ltd., Thomson/First Call, Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA) , The Florida-Caribbean Cruise Association (FCCA) , DVB Bank and proprietary Cruise Market Watch Cruise Pulse data.
Royal Caribbean lifts profit view again on cruise boom, higher prices
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Juveria Tabassum in Bengaluru and Doyinsola Oladipo in New York; Editing by Devika Syamnath and Shounak Dasgupta
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

Ex-McKinsey partner sues firm, claims he was made opioids 'scapegoat'
A former McKinsey & Co partner sued the global consulting firm on Friday and accused it of defaming him and making him a "scapegoat" to distract attention from its work advising OxyContin maker Purdue Pharma and other manufacturers of opioid pain medications.

- CLIA Cruise Lines
- CLIA Global Executive Committee
- Mercy Ships
- Explore Topics
- Join or Renew
- Professional Development
- Travel Agent Cruise News
- Verify a Member
- Eligibility
- Marketing Partners
- Refund Policy
- Executive Partners
- Fact Sheets
- News and Media Room
- Australasia
- North America
- North West and Canada
- UK & Ireland
- My Certifications
- My Training
- Find a Travel Agent

- Cruising Home
- News and Research
- News Releases and Statements
- Cruise Industry Contribution to U.S. Economy Grew to 55.5 Billion in 2019, Generating More Than 436,000 American Jobs
Press Release | November 19, 2020
Cruise Industry Contribution to U.S. Economy Grew to $55.5 Billion in 2019, Generating More Than 436,000 American Jobs (USA)
Pre-pandemic industry output grew 5.3% in 2019 compared to 2018, fueled by rising popularity of cruise vacations and nearly 14 million passenger embarkations from u.s. ports.
NOVEMBER 17, 2020 (Washington, DC) —Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA), the leading voice of the global cruise industry, announced new economic impact data from its annual report on the contributions of the cruise industry to the U.S. economy. The newly released 2019 U.S. Economic Impact Analysis underscores the tremendous growth of the cruise industry and the corresponding growth of the industry’s contributions to the U.S. economy prior to the global health emergency.
In 2019, the cruise industry generated a total of $55.5 billion in economic activity in the United States, a 5.3% increase from 2018. Moreover, growth in economic activity was accompanied by an increase in industry-supported jobs. According to the report, the cruise industry supported 436,600 American jobs paying $24.4 billion in wages in 2019—a 3.5% and 5.4% increase from 2018, respectively.
The latest figures follow nearly ten years of continued growth in the cruise industry, fueled by the rising popularity of cruise vacations. Over 13.7 million passengers embarked on cruise ships from U.S. ports in 2019, up nearly 8% from 2018 and 26% from just five years ago.
“The pre-pandemic trends clearly demonstrate that cruising has emerged as one of the fastest growing sectors of travel and tourism,” said Kelly Craighead, president and CEO of CLIA. “The cruise industry is proud to play an important role in the creation of jobs and economic opportunity for nearly half a million Americans throughout the country. At the same time, we recognize the devastating impact that COVID-19 has had on our community. A resumption of cruising in the United States in 2021, with stringent measures in place and with the support of health authorities, will be critical to putting people back to work and fueling the greater economic recovery from the pandemic.”
The report highlights the cruise industry’s economic contributions across multiple sectors, from transportation and aviation, to food and beverage, lodging, manufacturing, agriculture, travel agencies and a robust supply chain that stretches across the United States. The top ten states benefitting economically from the contributions of the cruise industry include:
The full report is available here , along with corresponding infographics and fact sheets.
Media Inquiries
Please send media inquiries to - [email protected]
Don’t yet have a login? Create a new account
Forgot Password
If you have forgotten your Password, complete the information requested below and click the submit button.
You will receive an email with a reset token to change your password.
Please allow at least 10 minutes to receive the email before requesting another password reset. Please be sure to check your Spam folder for the password reset email.
Please note: the Email you provide must be the one that is associated with your profile.
If you have difficulty resetting your password please email [email protected] .
Create a New CLIA Account
Set or change password.
Please use the form below to set or change your password. Passwords must be at least 8 characters.
We are sorry. An error has occurred.
Please confirm, select your region to be directed to the correct website.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

The global cruise industry: Financial performance evaluation
The global cruise industry has experienced persistent growth dynamics over the last two decades, with an impressive rebound after the 2008 financial crisis, unlike commercial shipping. Globalization, restructurings, mergers and a diverse bundle of travel and tourism services to cater for different passenger profiles have boosted robust revenue and profitability growth. Major cruise companies deploy ambitious investment plans to expand and renew their expensive fleet with larger modern vessels of high value. The mix of funding sources to finance these capital-intensive projects is critical and exerts a direct impact on the cost of capital. The paper contributes a rigorous corporate financial performance evaluation in the cruise sector and attempts to shed light on managerial financial efficiency, capital structure options, solvency conditions and corporate value dynamics. A sample of leading cruise companies, jointly holding a dominant market position, is incorporated to empirically investigate and assess their financial, accounting and stock market performance, based on convenient financial ratios and established market metrics. The detrimental impact of the recent coronavirus pandemic on the cruise sector is also discussed. This original study attempts to bridge the relevant research gap, as past literature remains surprisingly thin on this critical topic. A set of challenging and innovative contributions is delivered for the financial performance of major cruise companies, for the first time to the authors' knowledge, in support of efficient managerial implications and recommendations.
1. Introduction
Cruise tourism business is a form of traveling for leisure purposes that involves an all-inclusive holiday on a cruise ship. According to UNWTO, cruise tourism includes ‘a wide range of activities for travelers in addition to its traditional function of providing transport and accommodation’. The cruise industry is the fastest growing sector of the travel industry, with demand estimated to grow at 7.0% per annum over the past decade, and cruise passenger surpassing the threshold of 30 mln. in 2019 ( CLIA, 2020 ; Wondirad, 2019 ). At the same time, the business is seen to be extremely volatile and ever more highly capital-intensive. Newbuilt cruise vessels can cost multiples in value compared with commercial ocean ships, estimated at $1.3 bln. per vessel, accommodating up to 6000 passengers, albeit at lower operating unit costs ( Dowling, 2006 ; Lester & Weeden, 2004 ; Wood, 2004 ). Nevertheless, in the 1990s, the cruise industry has experienced extensive restructuring, following a wave of failures and consolidations. Larger holding cruise companies acquired smaller peers that continued operating as ‘brands’ withing the new business ventures though, serving repeat customer loyalty and offering diverse quality and service levels.
Financial empirical research on cruise shipping remains surprisingly thin. Few earlier studies investigate, selectively, topics such as, the translational partnership organization of the industry ( Hall & Braithwaite, 1990 ); cruise impact on and implications for regional and local market development ( Hobson, 1993 ); cruise market globalization trends ( Wood, 2000 ); cruise strategic capacity investments ( Byung-Wook, 2005 ; Wie, 2005 ); cruise line and passenger challenges ( Veronneau & Roy, 2012 ); cruise line supply chains and logistics ( Daly & Fernandez-Stark, 2017 ; Veronneau and Roy, 2009 , Veronneau and Roy, 2011 ; Veronneau, Roy, & Beaulieu, 2015 ); fund raising approaches for newbuilding cruise ships ( Kiziellewicz, 2017 ; OECD, 2007 ); and mergers, acquisitions and restructurings ( Charlier, 2004 ; Hobson, 1994 ); inter alia.
This study focuses on the financial performance evaluation of the global cruise business and attempts to fill this research gap in the field by contributing a set of challenging and innovative findings, as well as managerial implications and recommendations. To the authors’ best knowledge, this appears to be the first attempt to investigate in depth the critical issues of managerial efficiency, profitability, and growth prospects, financing sources and capital structure, leverage, solvency, and value creation dynamics in the context of the global cruise industry. Initially, a concise overview of prevailing key developments and trends in the cruise business over recent years is provided. Subsequently, critical key financial metrics and performance indicators are estimated and evaluated over time and against major peer competitors for a sample of leading cruise players.
The theoretical framework and the stream of literature that the paper is grounded on relates to critical investment and financing decisions and their financial implications for managerial performance, corporate profitability, value creation, and firm growth. To this end, in a broader context, a core set of seminal reference papers investigate key managerial decisions on funding source options (debt and/or equity), capital structure mix priorities, (weighted average) cost of capital (WACC) shifts, and share price volatility, inter alia, as well as their interrelated implications for investment decisions and overall corporate financial performance (e.g., Baker & Wurgler, 2002 ; Donaldson, 1961 ; Hovakimian, 2006 ; Kisgen, 2006 ; Modigliani and Miller, 1958 , Modigliani and Miller, 1963 ; Myers, 1984 , Myers, 2001 ; Myers & Majluf, 1984 ). It remains an innovative, challenging and fruitful empirical task to investigate the financial implications of these decisions and evaluate the managerial efficiency and financial performance of major global cruise companies, as depicted and reflected on the evolution of critical and widely established financial ratios and metrics. Indeed, these issues are not seen to have been investigated yet in the relevant empirical literature. Nevertheless, they remain important for a highly capital-intensive sector, such as the cruise industry, taking, indicatively, into consideration that the cost of a newbuild cruise vessel can now surpass the $1.0 bln. threshold ( CLIA, 2020 ).
The empirical approach is based on a blended financial methodology, including preliminary data mining and collection, financial statement analysis and comparative assessment and evaluation of critical cruise financial ratios and indices. Based on that, a set of focal policy recommendations is finally provided. The information input is obtained from financial statements and annual reports, stock market datasets and company financial analysis reports, over a recent five-year horizon.
The paper is structured as follows. Section 2 provides a concise summary of recent developments in cruise demand and supply sides, identifying critical growth drivers, economic implications, and prospects ahead. Section 3 overviews major cruise company investment decisions; and Section 4 analyses the complex topic of financing decisions and fund-raising approaches, based on alternative capital structure options that eventually shape the critical cost of capital indicator. Section 5 investigates, analyses, and evaluates a set of key financial ratios, metrics, and indicators to assess cruise company financial performance and value creation dynamics. Finally, Section 6 concludes.
2. Cruise business growth drivers
2.1. demand for cruise services and economic impact.
Cruise shipping business offers a bundle of combined global shipping and tourism services to cruise passengers, as it caters for vacation services on board and ashore, with a full package of diverse recreational tourism-related services. However, a fundamental strategic shift is seen in global cruise business over time ( Garin, 2005 ). Whereas in earlier days, cruise shipping services were mainly targeting higher net-worth luxury customers at substantial price cost, the industry has gradually diversified to demonstrate market segmentation and to attract massively average-income cruise passengers of different age and social profiles. This trend has been supported by attractive cruise service packages at reasonable prices, as massive newbuilt vessel capacity has resulted to extensive economies of scale benefits. Broadly, cruise shipping is perceived as a ‘customer's market’, shaped by shifting consumer tastes and trends. Cruise passengers appear to increasingly prefer ‘paying more for experiences than for possessions’.
Cruise shipping is the fastest-growing segment in the leisure travel market with high capacity utilization rates. The prime cruise business actors include more than 55 cruise line companies, offering ocean, river, and specialty cruise services, and covering more than 95% of global cruise capacity. Business members include also more than 340 executive partners that are key suppliers and cruise line partners, including ports and destinations, ship development suppliers and business services; around 15,000 travel agencies, including the largest players, hosts, franchises and consortia; and, 25,000 travel agent members worldwide ( CLIA, 2019 ).
Contrary to commercial ocean shipping, the global cruise business has shown robust growth rates and persistent recovery, after the 2008 financial crisis. In terms of total revenue, the cruise industry generated $46.6 bln. in 2018, exhibiting a spectacular rebound since revenue had declined abruptly below $25 bln., due to the recession spread after 2008 ( CLIA, 2020 ). The economic output generated by the global cruise industry is estimated at $150 bln. in 2018 against $126 bln. in 2016 (+20%, 2018/2016), with 28.5 mln. cruise passengers, offering 1.17 mln. jobs (full-time equivalent employees; +6.2%, 2018/2017), and distributing $50.2 bln. in wages and salaries ( CLIA, 2018 , CLIA, 2019 ). In view of global passenger spending capacity, estimates indicate aggregate direct purchases of $7.97 bln. (+11.4%, 2018/2017), corresponding to $376 average passenger spending before boarding a cruise and to $101 in port visiting during a cruise. Furthermore, 65% of cruise passengers is seen to spend a few extra days at embarkation or debarkation ports. Cruise business is seen to develop around Caribbean, Australasia, Brazil, Europe, North America, Asia, Canada, UK, and Ireland. The worldwide income multiplier effects of the cruise industry have wider economic implications, as these disseminate to a wide spectrum of related business sectors and activities.
Over 2008–2018, the global cruise business has experienced an unprecedented 10-year average growth above 45% in sourced cruise passengers ( CLIA, 2019 ; Florida Caribbean Cruise Association, 2019 ). This performance is attributable predominantly to the spectacular passenger growth from European markets (60.4%), followed by North American markets (39.4%). This figure raises up to nearly 75% if passenger growth of the rest of the world is also counted ( Table 1 ). The number of total cruise passengers came up to 30 mln. in 2019 from 16.3 mln. in 2008 (+84%). A steady cumulative annual passenger growth rate (CAGR) at 7% is estimated over 1990–2020.
International demand for cruises (sourced passengers, mln).
Source: CLIA (2019) .
Initial estimates on the number of annualized worldwide cruise passengers carried indicate 32.0 mln. passengers for 2020 against 3.6 mln. passengers back in 1990 (+790%, 2020/1990) ( Fig. 1 ).

Global cruise passengers carried (mln.)
Cruise passengers originate from a diversity of geographic regions and source markets ( Table 2 ). North America remains by far the largest source region of cruise passengers, contributing more than half of global cruise passenger flows (50.2%); its share, though, has dropped compared with 2007 (66%). Europe follows at a distance (23.7%) and has also seen its share slightly on the decline. Asia, on the other hand, is a robustly upcoming cruise passenger source region (15.0% in 2019, up from 9.2% in 2018).
Worldwide cruise passenger by source region (%).
Europe: Benelux, France, Germany, Italy, Scandinavia, Spain, Portugal, UK. Source: CLIA (2020) .
The breakdown of preferred destinations, as depicted by cruise line deployment by region is presented for 2018 and 2019 in Table 3 . The Caribbean remains by far the prime cruise destination of high demand (32%) with the Mediterranean (17%) and Europe (excluding Mediterranean; 11%) following at a distance ( Table 3 ).
Cruise line deployment by region (%).
Source: CLIA (2020) .
The cruise market share distribution among major cruise players is presented below ( Table 4 ). Three leading players are seen to dominate the global cruise market. Carnival Corporation holds a dominant position with passenger and revenue market shares at 47.4% and 39.4%, respectively. Royal Caribbean Cruise ranks second with passenger and revenue shares at 23.0% and 20.2%, respectively. Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings follows at a distance with passenger and revenue shares at 9.5% and 12.6%, respectively. These three major players control a global cruise market share of 80% in passenger terms and 72.2% in revenue terms, respectively.
Cruise line market share.
Source: Authors' compilation; www.cruisemarketwatch.com .
2.2. Growth drivers and prospects
Cruise shipping growth is driven by consistent efforts of all parties involved to explore alternative approaches towards increasing business efficiencies. These include further newbuilding investments to expand and modernize cruise fleet, adding new vessels of larger capacity, diversifying the destination choices offered, increasing penetration in core North American and Latin American markets, attracting more passengers from new source markets and enriching on-board and on-shore activities to meet cruise passenger demands. Furthermore, the inclusion of more local ports has been treated responsibly, based on collaboration with cruise destinations and local communities. The cruise industry is seen to become more conscientious, paying attention towards preservation of local cultures and landmarks and minimization of environmental footprints; exploring alternative creative ways to manage visitors' flows; and, implementing higher standards of responsible tourism. The latter include partnerships with local governments, staggered arrivals and departures, local excursion diversification, shoreside power, and local passenger spending, as more travelers are spending time in and near cruise ports (e.g., Klein, 2011 ).
Broadly, the cruise industry demonstrates promising growth dynamics ahead. This is supported by a global shift in consumer tastes and habits around cruise services, irrespective of passenger generation. For instance, more than 66% of generation ‘X', 71% of millennials, and expanding percentages of generation ‘Z', originating predominantly from the vital US market, are seen to have an increasingly positive attitude towards cruise travel and tourism services compared with earlier years. Generation ‘Z' is anticipated to become the largest consumer generation by 2020 outpacing even millennials. This generation, like the one before, prefers experiences over material items. They appear to prefer cruise travels, including multiple destinations and targeted specialized services (such as music festivals at sea, for instance; CLIA, 2020 ).
Cruise passenger numbers originating from major emerging markets, such as China, India, and Latin America, are anticipated to increase further, supported by improving global disposable income and economic growth conditions. In addition, social demographic shifts indicate that, as global marriage rates are on a decline, increasing numbers of single adults are seen to pursue lone cruise services with a ‘traveling alone’ focus. Cruise lines respond to this upcoming clientele by offering, targeted ‘solo travel’ services, such as studio cabins, solo-lounges, and single-friendly activities. Another upcoming cruise clientele sub-group is female travelers, as their numbers are seen growing. Many tourism and travel companies are creating female-centered cruise itineraries, based on focused interests, and facilitating building women community bonds ( CLIA, 2020 ). Relevant references investigating these issues further include Teye and Leclerc (2003) , Chen, Neuts, Nijkamp, and Liu (2016) , Satta, Parola, Penco, Persico, and Musso (2016) , inter alia.
What is more, cruise travelers are now seen to set sights on destinations that were previously out of reach and some only accessible by cruise ships from the Galapagos Islands to Antarctica. Demand for off-peak season cruise packages also exhibits rising popularity, as travelers may prefer to visit tropical destinations to escape a domestic cold season. The number of modern ‘digital nomads’, that is travelers combining work with leisure time, is also on the rise. This target group can enjoy cruise vacation services in conjunction with remote e-work, cutting down on time-off and still earning an income. On the other hand, micro travel cruise services exhibit upward demand trends as well, as many travelers are interested in quick recreational trips of varied and flexible trip duration alternatives. In response to that, cruise companies offer bite-sized cruise options of three-to-five-days, scheduling shorter itineraries to a variety of destinations.
3. Investment decisions in the cruise business
The cruise companies promote consistently a set of ambitious and capital-intensive strategies to sustain business growth. Newbuilding investment projects target to expand and modernize the existing fleet with vessels of larger capacity. Total cruise industry capacity reached 537 thous. passengers and 314 ships, with about 55 active cruise companies at the end of 2018 ( CLIA, 2020 ). The brand diversification of operations is summarized in Table 5 .
Cruise passenger capacity.
Source: Authors' compilation; CLIA (2020) .
Most cruise players have large investment plans under deployment, scheduled over 2019–2025. For instance, Carnival, Royal Caribbean, and Norwegian plan to invest $4.2 bln., $7.2 bln., and $4.5. bln., respectively, in newbuilding vessels, aggregating to $16 bln. in investments. With total cruise sector investments adding up to $70.3 bln., the joint investment share of these three major players corresponds to 23% of total cruise investment budget ( Table 6 ).
Newbuilding investments – capital requirements (USD bln.), 2019–2025.
Source: Authors' compilation; www.cruisemarketwatch.com (2020).
Broadly, an impressive newbuilding cruise vessel orderbook is under execution over 2019–2025 ( Table 7 ; more details in Table 7A in the Appendix; ( WAC, 2019 )). It is worth noting that the large vessel size in several cases can accommodate more than 6000 cruise passengers. Recent feedback on cruise investment plans indicates that 278 vessels are projected in operation by the end of 2020 and 19 vessels are scheduled to debut in 2020. The average age of cruise fleet is seen at 14.1 years, improved from 14.6 years in 2018.
Cruise ship newbuilding orders, 2019–2025.
A broader issue of concern for cruise investments relates to the environmental sustainability commitment. While cruise ships comprise less than 1% of global maritime fleet, the entire shipping industry benefits from the adoption of new technologies and practices that were not in play earlier. The development of new technologies and cleaner fuels remains a high priority for the cruise industry. Estimates indicate that the cruise companies have invested over $22 bln. in new energy-efficient ships and technologies to minimize the environmental impact, supporting the goal of reducing carbon emission rates by 40% by 2030 compared to 2008 ( CLIA, 2020 ). As per new emission standards, sulfur in the fuel is limited to 0.5% from January 2020. The cruise industry is also seen to be consistently committed to responsible tourism practices, with a focus on destination stewardship, setting-up partnerships with local governments in key destinations. A complementary concern relates inevitably to cruise hosting port constraints, including market segmentation, vessel size service capacities, seasonality effects and congestion bottlenecks at peak periods. To that end, cruise players are anticipated to invest further into port facilities and related infrastructure.
Having said that, the compliance of cruise companies to environmental protection is associated with high investment costs for the construction of new generation cruise ships. Vessel manufacturing costs also rise as ships incorporate innovative advanced technologies. Although cruise vessel prices are seen, on average, at around half a billion dollars, updated estimates indicate this figure to now surpass the one billion dollars threshold ( CLIA, 2020 ). To that end, the critical questions as to how these massive investments are to be financed and at what capital cost remain to be tackled. Following the global financial crisis, several leading international banks specialized in ship credit, such as RBS and DVB, have decided to exit ship lending entirely, liquidating their ship loan portfolios. On the other hand, an emerging global trend relates to private entry strategies, partnerships, and internationalization patterns of cruise companies entering cruise terminal operations in major destinations, such as the Mediterranean Sea ( Pallis, Parola, Satta, & Notteboom, 2018 ). Plausibly, the deployment of such strategies is anticipated to bring about considerable financial implications for cruise lines and cruise terminals, both in terms of spending patterns as well as of income.
4. Financing decisions in the cruise business
4.1. capital funding priorities.
The financing approach a cruise company is to follow to fund its investments and the contribution of alternative capital source options are of fundamental managerial importance. Obviously, this should have direct implications for this cruise company's optimal capital structure mix and its cost of funding. The investigation of these issues in the context of cruise companies remains a challenging and innovative task. To the authors' knowledge, this appears to be the first empirical study tackling these issues in the cruise industry. This research interest is further reinforced and justified considering that the global cruise industry is a highly capital-intensive business with consistent investment expansion plans under development over the last decades, associated with substantial funding requirements. As noted earlier, most cruise companies plan to expand and upgrade their fleet and have already placed a massive newbuilding orderbook under play. The incorporation of luxury facilities and high-end technological advances and services drive unit vessel prices even higher than $1.3 bln. ( CLIA, 2020 ).
Managerial financing decisions have direct implications for the cruise company's capital structure mix, its cost of capital and, eventually, shareholder value creation and growth prospects. The capital structure mix refers to the percentage weights of equity and debt, reflecting the respective capital source contribution to form the company's total invested capital. As the cost of equity and cost of debt differ, modifications in the capital structure mix also affect the company's overall cost of capital. These focal issues have generated steaming debate among academics and market practitioners over time. A summary of major finance theories on capital structure is now provided and subsequently explored briefly in the context of the cruise business.
Modigliani and Miller (1958) , first, postulate the capital structure irrelevance approach. Assuming perfect markets and absence of taxes and bankruptcy costs, the capital structure mix is irrelevant because firm market value is determined by the company's earning power and the risk of its underlying assets. Modigliani and Miller (1963) incorporate, subsequently, the tax effect on capital cost and firm value. In this case, firm value increases with leverage due to tax shield benefits. Interest on debt capital is an acceptable deduction from the firm's income and thus decreases the firm's net tax payment. Assuming potential tax benefits, debt financing can result to lower cost of capital.
Trade-off theory, furthermore, argues that the optimal level of debt is where the marginal debt benefit is equal to its marginal cost ( Myers, 1984 ). Debt financing up to a certain level contributes interest tax shield benefits, offsetting financial distress costs. A firm can attain an optimal capital structure by adjusting debt and equity weights, thereby balancing tax shield benefits and financial distress costs. Myers and Majluf (1984) postulate the pecking order theory, based on earlier research by Donaldson (1961) , and argue that (assuming perfect capital markets) management prefers internally generated funds rather than raising external funds. A company should prefer internal funding first, then issue debt, and finally, as a last resort, issue equity capital. Firms with higher profit and growth opportunities would use less debt capital ( Myers, 2001 ). If a firm has no investment opportunities available, profits are retained to avoid future external financing. Information asymmetry between insiders and outsiders and separation of ownership can explain why firms avoid capital markets.
Market timing theory of capital structure maintains that companies are more likely to issue equity when their market value is high, relative to book and past market values, and to repurchase equity when their market value is low ( Baker & Wurgler, 2002 ). Share price volatility affects corporate financing decisions, and eventually the firm's capital structure. As the resulting effects on capital structure are persistent, this indicates that current capital structure is strongly related to historical market values. Capital structure is perceived to be the cumulative outcome of past attempts to time the equity market. It is argued though, that market timing does not exert material effects on the firms' capital structure in the long run ( Hovakimian, 2006 ). The credit rating-capital structure (CR-CS) hypothesis is proposed as an extension of the existing trade-off theory of capital structure ( Kisgen, 2006 ). Capital structure decisions are expected to adjust along the relevant benefits and costs associated with shifts between different credit rating levels. When a firm is closer to a rating shift, it may issue less debt compared to the alternative of being far from a credit rating shift.
To sum up, debt financing can offer a lower cost of capital, due to tax deductibility advantages. A company with positive prospects can proceed to raise capital using primarily debt rather than equity, so to avoid ownership dilution (transmitting negative signals to market players). Debt signaling (company announcements of funding with debt) is typically seen as positive news. However, a high debt exposure bears enhanced bankruptcy risks, and increases shareholders' financial risks, thus a higher return on equity is required. To conclude, companies must assess their optimal funding mix at which the marginal benefits of debt equal the marginal costs incurred. The optimal capital structure mix is associated with that combination of equity and debt financing that results to a lower cost of capital, supporting robust value creation prospects.
4.2. Capital structure mix and WACC
Based on 2019 figures, all three major cruise companies have seen their long-term debt exposure increased against 2018, by 22.8% at $9.7 bln. for Carnival, by 8.4% at $9.0 bln. for Royal Caribbean, and, by 5.2% at $6.1 bln. for Norwegian ( Table 8 ). This reflects a debt weight reallocation in the capital structure mix for Carnival and Norwegian, though this remained stable for Royal Caribbean. Over 2016–2019, debt funding contribution increased from 41.9% to 43.7% for Carnival and from 59.2% to 59.9% for Royal Caribbean but declined overall from 65.1% to 61.1% for Norwegian. On average, Carnival is seen to rely more on equity funding (equity/debt mix: 60/40), contrary to Royal Caribbean and Norwegian that are seen to be more dependent on debt (equity/debt mix: 40/60) ( Table 9 ; Fig. 2 ).
Capital sources (USD bln.).
Source: Authors' calculation based on cruise company financial statements.
Cruise company capital structure mix (%).

Capital structure mix components.
As the capital structure of major cruise companies indicates, the funding mix is relatively balanced with a reasonable exposure to debt risk. This comes in contrast to global commercial shipping business that is seen to be typically financed predominantly by bank lending ( Drobetz, Gounopoulos, Merikas, & Schroder, 2013 ; Syriopoulos, 2007 , Syriopoulos, 2010 ).
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is a critical metric for a company's aggregate cost of funding from all potential capital sources. It is calculated as the weighted average cost of equity and cost of debt (weighted contribution of equity and debt (plus of any other capital source) in total invested capital), that is:
where: k e = cost of equity; E = Equity; k d = pre-tax cost of debt; t = corporate tax rate; D = Debt; E/(E + D) and D/(E + D) = weights of equity and debt in the company's capital structure, respectively.
Hence, WACC is a key indicator of the minimum after-tax required rate of return which the cruise company must earn for all its investors (capital suppliers, i.e. shareholders and debtholders). At the same time, the company's cost of capital is the expected return to both stakeholders (owners and lenders) and represents investors' opportunity cost of taking on the risk of investing their funds into the company. More specifically, cost of equity is the required rate of return on common stock of the company. It is the minimum rate of return which a company must earn to keep its common stock price from declining. Cost of equity is estimated using alternative models (including, dividend discount model (DDM) and capital asset pricing model (CAPM)). After-tax cost of debt represents the after-tax rate of return debtholders require to earn until debt maturity. Cost of debt is calculated by assessing the yield to maturity of the company's bonds and other loan instruments. If no yield to maturity is available, the cost of debt can be estimated using the instrument's current yield. After-tax cost of debt is included in WACC calculation because debt offers a tax shield (i.e., interest expense on debt reduces taxes and this is incorporated in the cost of debt calculation). The WACC factor for major cruise companies in 2019 is summarized below ( Table 10 ).
Cruise company cost of capital, WACC (%).
WACC: Weighted Average Cost of Capital. Year: 2019.
Source: Authors' calculation based on cruise company financial statements and Bloomberg database.
The next section focuses on the core research objectives and develops the empirical methodology on the financial performance evaluation of major cruise companies to contribute a set of fruitful managerial recommendations, and conclusions.
Fig. 3 illustrates the underlying logical nexus and summarizes the earlier key points, interrelating cruise company investment and financing decisions with critical corporate financial performance ratios and metrics to follow in the next section and highlights the paper's contributions to the topic at hand.

Nexus of investment and financing decisions to cruise company financial performance.
Source: Authors' compilation.
5. Financial performance evaluation: Methodology and key findings
This section deals with a solid quantitative assessment of corporate financial performance dynamics, and trends shaped in the cruise industry, over the period 2016–2019. As mentioned, this topic remains surprisingly unresearched in the relevant academic literature (e.g., Clancy, 2017 ). To explicitly state the research objectives and innovative contributions of this study, the following critical issues are investigated for leading global cruise companies: the ambitious investment plans under deployment; the capital funding priorities and sources, based on the decomposition of the capital structure mix; and, the assessment and evolution of the WACC metric over time. To assess, subsequently, the profitability robustness, value creation dynamics and growth prospects of the sample cruise companies, an integrated financial performance evaluation approach is undertaken, based on a widely applicable, financial ratio analysis, focusing on the following key issues: revenue and profit growth; managerial efficiency, as depicted by ROE, ROA, ROIC ratios; the ROIC-WACC interrelationship and its growth and value dynamics implications; financial leverage exposure and solvency assessment; and earnings per share ratios and share price performance over time.
To serve these research objectives, the empirical methodology is based on a solid corporate financial analysis, assessment, and evaluation of critical financial ratios and established metrics on key cruise market players, built on financial statement, accounting, and stock market inputs. This applied approach can then produce useful empirical findings and policy recommendations for efficient managerial decisions of the cruise companies. Though this methodological framework is standard in different business sectors, to the authors' best knowledge, this appears to be the first empirical application to global cruise corporate players.
A case study company sample is selected, consisting of the major cruise players, namely Carnival, Royal Caribbean, and Norwegian cruise lines. As discussed earlier, these cruise companies hold an undoubtedly dominant market share, as they jointly control more than 80% of the global cruise market in terms of revenue and passengers and set the financial tune in the sector ( CLIA, 2020 ). Hence, by focusing on these companies, a solid, reliable, and sufficiently representative feedback can be gained for the overall cruise sector. Furthermore, these leading cruise companies have their shares listed and traded on international stock exchanges (New York, London); thus, useful empirical reflections can be gained by their stock market behavior, performance, and market value. The consolidated financial statements of the sample cruise companies have been incorporated for the empirical financial analysis. These cruise companies own several subsidiaries (e.g., Carnival Corporation & PLC owns Costa Crociere, and Aida Cruise, through Costa Group; as well as it owns P&O Cruises and Cunard, through Carnival UK, etc.), and the strategies of the parent companies are realized also by their own brands.
As a point of clarification, MSC Cruise is also an important cruise market player, though it holds a relatively lower market share compared with the other sample companies. MSC was initially included in the preliminary sample compilation under study. However, it was eventually excluded from the final sample, to preserve data consistency and convergence, as MSC Cruise is not listed on a stock exchange and a part of the research interest is in the stock market behavior of the listed cruise companies. Due to the dominant market share and economic importance of the sample cruise companies, the empirical analysis and findings are not expected to be affected materially by the exclusion of MSC Cruise. In any case, a relevant follow-up study could enrich and expand on the current sample to include more cruise players.
A brief corporate profile of each sample cruise company now follows.
5.1. Cruise company profile
Carnival Corporation & Plc (CCL) offers cruise services under the Carnival Cruise Lines, Holland America Line, Princess Cruises, and Seabourn brand names in North America; and AIDA Cruises, Costa Cruises, Cunard, and P&O Cruises names in Europe, Australia, and Asia. Carnival runs 100 cruise ships and is a sole dominant cruise market player, as it controls a market share at 48%. This is the only cruise group with its shares traded on dual listing (S&P500 and FTSE100 indices). The company was founded in 1972 and is headquartered in Miami, Florida.
Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd. (RCL) operates as a global cruise vacation company the cruise brands Royal Caribbean International, Celebrity Cruises, Azamara and Silversea Cruises. The firm also holds interest in TUI Cruises, Pullmantur and SkySea Cruises brands. Royal Caribbean runs 60 ships and holds a significant cruise market share at 23%. The company plans to launch 11 new cruise ships of average vessel capacity over 4500 passengers by 2025. The company was founded in 1968 and is headquartered in Miami, Florida.
Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings Ltd. (NCLH) is a global cruise company and operates the Norwegian Cruise Line, Oceania Cruises and Regent Seven Seas Cruises brands, offering itineraries to more than 490 destinations worldwide. With a combined fleet of 28 ships, and nine ships to be added by 2027 with an average capacity of 3000 passengers per vessel it holds a cruise market share at 10%. The company was founded in 2010 and is headquartered in Miami, Florida.
5.2. Revenue and profit growth
Cruise revenues exhibit consistently robust growth trends for the leading cruise players, over 2016–2019 ( Table 11 ). Contrary to most commercial shipping market segments that experienced abrupt and persistent revenue declines since the outbreak of 2008 global financial crisis, cruise shipping has seen a robust resistance and relatively rapid recovery. In 2019, Carnival recorded cruise revenue at $20.8 bln. (+10.3%, 2019/2018). Similarly, Royal Caribbean also gained robust revenues at $10.9 bln. (+15.3%, 2019/2018). Norwegian Cruise Line, on the other hand, saw comparatively modest revenue growth at $6.5 bln. (+6.6%, 2019/2018).
Cruise company revenue and profits.
EBITDA: Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation and Amortization.
Source: Authors' calculations; cruise company financial statements; www.macrotrends.net .
Gross profits exhibit an upward trend for all three cruise players, especially for the market leaders, Carnival, and Royal Caribbean. Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) is considered as a critical indicator of operational profitability and is defined as income after operating expenses have been deducted and before interest payments, taxes, depreciation, and amortization have been deducted. This profit component is to compensate subsequently for debtholder claims (interest payments), State claims (taxes) and, lastly, shareholder claims (dividends), with the latter ones perceived as residual claimants, bearing highest risk levels. The leading cruise companies exhibit modest EBITDA and Net Income shifts over 2016–2019.
According to a market motto, ‘if gross profit is not there, there will be no net profit’ as well. Gross profit margin is calculated as the ratio of gross profits to revenue. Assuming a cruise company investing in a sector that exhibits a high gross profit margin but not making bottom-line net profits may be a striking indication of a mismanaged case. Corporate restructuring and operational tuning may be required to turn the business into a profitable venture. Broadly, the level of gross profit margin depends directly on how a business is organized and the other costs it must support. For instance, after gross profit calculation, a cruise company still must pay operating expenses, financial, tax and other expenses. Subsequently, a cruise company must have robust net profits to distribute an attractive return (dividend) to shareholders. In case a cruise company can effectively control operating expenses, it can remain profitable with a lower gross margin ratio. Broadly, a higher gross profit margin is preferred, as it indicates efficient processes and offers flexibility to have money left over to spend on other business operations.
The net profit margin is calculated as the ratio of net profits to revenue. Net profit is calculated as the gross profit (revenue minus cost of goods sold) minus operating expenses, interest paid on debt, taxes and all other expenses. The net profit margin is a far more definitive profitability metric for investors and analysts and indicates how much of each dollar received as revenue translates to corporate profit. This is critical since revenue increases do not necessarily translate into increased profitability. A higher profit margin is desirable since it means the company generates more profits from its revenue. A careful assessment of both cruise company gross profit margin and net profit margin reveals managerial efficiency in earning profits relative to the costs involved in producing cruise services.
The operating profit margin, on the other hand, is calculated as Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) to revenue. EBIT is revenue minus all operating costs, before interest paid, taxes and dividends. A highly variable EBIT can indicate a risky business, whereas a stable EBIT a well-managed and predictable one. Hence, the operating profit margin ratio indicates the net operating profitability and points to a successful management at generating income from the core business operations (per dollar of revenue), controlling costs effectively and/or increasing revenues faster than operating costs.
The profit margin ratios for all three sample cruise companies remain consistently high over 2016–2019 ( Table 12 ). The 2019 net profit margin for Royal Caribbean, for instance, at 17.4% indicates that, for $100 of revenue, $17.4 have remained as net profit in the company. The joint evaluation of gross, operating, and net profit margins for the leading cruise companies indicates a broadly stable, efficient, and successful financial management.
Cruise management financial efficiency.
GPM: Gross Profit Margin; OPM: Operating Profit Margin; NPM: Net Profit Margin.
When examining the per day figures, cruise revenue and profits per day are seen at $51.7 mln. and $8.6 mln., for Carnival; $ 26.0 mln. and $5.0 mln., for Royal Caribbean; and $16.6 mln. and $2.6 mln., for Norwegian, respectively, for 2018. Average cruise revenue and expense per passenger are estimated at $1791 and $1562, respectively. This corresponds to a profit at $227 per passenger, forming a net profit margin at 12.7%. A breakdown of the estimated average cruise revenue and expense per passenger is summarized in Table 13 .
Average cruise revenue and expense breakdown per passenger.
2018 figures; financial breakdown of typical cruiser worldwide (across all cruise lines). Average cruise duration: 8.0 days; median duration: 7.0 days.
Source: Carnival Corporation & Plc., Royal Caribbean Cruises, Norwegian Cruise Lines, Thomson/First Call, Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA), Florida Caribbean Cruise Association (FCCA), DVB Bank, Cruise Pulse; www.cruisemarketwatch.com .
5.3. Managerial efficiency ratios
A set of critical and widely employed diagnostics tools to evaluate managerial efficiency on cruise company financial performance include the Return on Equity (ROE), Return of Assets (ROA) and Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) ratios. These metrics permit comparative performance evaluation of each sample cruise company over time as well as against its competitors. They can also reveal critical drivers of growth and provide explanation for the stock market behavior of the cruise companies' share trading patterns at higher/lower valuation levels.
ROE is defined as net income to equity and indicates the equity required to generate a certain amount of net income; or, how well the company is using equity (owners' capital). ROA is calculated as net income to assets and indicates the assets required to generate a certain amount of net income; or how effectively the management utilizes the company's fixed and current assets (how dependent it is on them). ROIC is defined as EBIT (earnings before interest and tax) to total invested capital (equity plus debt) and indicates the operational profit generated by the total capital employed in the company; or, how efficiently the company allocates all its capital to profitable investments; or, how much capital is required to grow its business. ROE attracts investors' attention as it a critical indicator of how effectively a company's management uses shareholders' capital and reveals whether management is growing the company's value at an attractive and competitive rate. ROE, ROA and ROIC ratios are calculated as in the forms below ( Table 14 ).
ROE – ROA – ROIC ratios.
ROE: Return on Equity; ROA: Return on Assets; ROIC: Return of Invested Capital.
EAT = Earnings After Tax (Net Income); EBIT = Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (Operating Profit); Invested Capital = Equity + Debt.
A key factor distinguishing ROE and ROA is financial leverage or debt, since the fundamental balance sheet equation holds that assets equal equity plus debt. Plausibly, in case a company carries no debt, its equity and total assets will be the same, hence, ROE and ROA would also be the same. However, if that company takes on financial leverage, ROE will rise above ROA; this relates to the balance sheet equation, since equity equals assets minus liabilities. Thus, by taking on debt, a company increases its assets, due to the cash that comes in. But since equity equals assets minus debt, a company decreases its equity by increasing debt. In other words, when debt increases, equity shrinks; since equity is ROE's denominator, then ROE, in turn, gets a boost. At the same time, when a company takes on debt, total assets (ROA denominator) increase; hence, debt amplifies ROE in relation to ROA. ROE, however, weights net income only against owners' equity and does not provide any feedback on how well the management uses funding from borrowing and issuing bonds. If ROA is sound and debt levels are reasonable, a strong ROE is a solid signal that management is efficient at generating returns from shareholders' capital. On the other hand, if ROA is low or the company bears a heavy debt, a high ROE may be misleading as to the company's growth prospects.
ROIC overcomes certain ROE and ROA limitations and is a better measure of profitability than ROA and ROE, as it removes the debt related distortion that can make highly leveraged companies look highly profitable when using ROE. Unlike ROE and ROA that incorporate net income, ROIC is based on EBIT (earnings before interest expenses and taxes), arguably a critical operating profitability indicator that takes total invested capital into account. This can offer a closer focus on the core operating performance, removing financing decision effects (that is, regardless of the capital source, equity, or debt).
The joint evaluation of ROE ROA and ROIC ratios for the leading cruise companies indicates a persistently robust financial performance and efficient use of each company's equity, debt, and assets in all cases ( Table 15 ). ROE ratios run from 12.1% (Carnival) to 14.9% (Norwegian) to 16.0% (Royal Caribbean), respectively, reflecting a satisfactory return on shareholders' equity. Carnival is seen to attain the best performance of its assets (ROA: 6.7%), with the other cruise companies following closely (Royal Caribbean: 6.3%; Norwegian: 5.8%). ROIC ratios are seen also to be very close for all three cruise companies (Carnival: 9.6%, Royal Caribbean: 10%, Norwegian: 9.8%), indicating a solid operational performance with efficient use of shareholder and debtholder capital, and supporting robust growth dynamics and value creation.
WACC: Weighted Average Cost of Capital. Year: 2019. Source: Bloomberg database.
5.4. ROIC versus WACC: Growth and value dynamics
When comparing a company's return on invested capital (ROIC) against its cost of capital (WACC), ROIC should stand higher than WACC to support robust growth prospects, value creation and share price trading at a premium. ROIC also can be used as a benchmark to compare a firm's value against competitors. A common market benchmark spread in support of value creation is a ROIC higher than WACC by at least +2%. A ROIC lower that WACC (or a spread of less than 2%) is considered as a value destroying condition. Some companies run at a zero-return level, and, while they may not be destroying value, they have no excess capital to invest in future growth ( Koller, Goedhart, & Wessels, 2020 ). The cruise companies under evaluation exhibit a ROIC higher than WACC in all cases. However, the ROIC-WACC spread is seen lower than 2% in all sample cruise cases, raising concerns about their solid growth prospects and value creation potential.
The ROIC ratio can be adjusted on a per unit basis to be equivalently recalculated as:
This implies that superior ROIC ratios can be attained from either a) a ‘price premium’ relative to peers; b) a lower ‘cost of capital’ per unit, improving cost and capital efficiency; or, c) a combination of both, a) and b). A company can create value by investing its capital into profitable investment projects to attain attractive ROICs. Robust revenue growth rates, ROIC higher than WACC and operating cash flows are core drivers to corporate value creation.
In the longer-term, a company can sustain strong revenue growth and high ROIC only in case it possesses and preserves a well-defined ‘competitive advantage’ against its peers. However, as competition erodes ROICs and competitive advantages, management should consistently seek new sources of competitive advantage to create sustainable value. Empirical evidence indicates that, of alternative growth models to value creation, launching new products or services typically creates more value for shareholders ( Koller et al., 2020 ). In this context, a challenging strategic option for cruise companies remains as to how effectively they can respond towards their competitive advantages, by developing, for instance, alternative diversified bundles of cruise products and services to contain intensified global competition.
5.5. Financial leverage – Solvency
Cruise companies, in line with commercial shipping counterparts, have typically relied mainly on debt (bank lending and bond issuing) to finance their capital-intensive investment projects ( Syriopoulos, 2007 , Syriopoulos, 2010 ). The financial leverage, or debt-to-equity ratio (or debt ratio), is a widely used financial debt burden metric that compares a company's total debt (creditors' financing) to shareholder equity (owners' financing). Based on that, management and investors can evaluate debt contribution into invested capital, signal equity or asset adequacy to fulfill obligations to creditors (particularly under distress conditions), and assess the borrower's credit risk profile.
A debt ratio of 0.5, for instance, means that there are half as many liabilities than there is equity. In other words, shareholder funding is twice as high as creditors funding, implying shareholders and creditors own 66.6% and 33.3% of company assets, respectively. A lower debt-to-equity ratio usually implies a more financially stable business. On the other hand, a high debt-to-equity ratio indicates an aggressively debt-financed business. Companies with a higher debt component must repay their credit obligations to lenders (debt servicing with regular interest payments); hence, debt financing can turn more expensive than equity financing. Highly leveraged companies, furthermore, may run at risk of being unable to adequately service a high debt exposure. As a result, prospective investors may assume a higher risk exposure, refraining from investing their funds on this company. At the same time, financial leverage should not decline excessively, as companies raising equity (by issuing stock) are exposed to high stock market volatility and ownership dilution implications.
Financial leverage contributes to a better understanding of the debt impact on the overall cruise company profitability and growth. It is important to investigate whether debt is high because it supports healthy business expansion and growth. This can eventually generate higher earnings than it would have without this debt financing. If leverage increases earnings by a greater amount than debt's cost (interest payment), then the business and its shareholders should expect to benefit by value creation. On the contrary, high leverage associated with a weak financial performance may result to additional debt financing, as shareholders should be reluctant to contribute additional equity financing. In this case, share prices and corporate value may decline.
The interest coverage or times interest earned (TIE) ratio is another widely popular debt metric. It indicates how many times a company's annual debt obligations (interest and debt service expenses) are covered by the net operating income (income before interest and tax). It is a long-term solvency ratio, expressed in times, to assess a company's long-term solvency ability to pay its debt liabilities as they become due. TIE reveals also whether a prospective borrower can afford to take on any additional debt.
Higher TIE ratios are considered more favorable than lower ones. A TIE at 4.0, for instance, indicates that operating income is four times higher than yearly interest expense liabilities; hence, the company can comfortably meet its debt obligations. On the contrary, a TIE less than 1.0 reflects a company that cannot meet its interest obligations on its debt. Companies with weak TIE ratios may face difficulties in raising funds for their operations. A better TIE ratio implies the company has enough cash after paying its debt to continue investing in the business. However, management should be careful to avoid a very high TIE ratio in case this is due to an unnecessarily conservative stance towards debt and/or absence of policies to take full advantages of debt facilities. Plausibly, a company's capital structure mix has a critical direct impact on TIE ratio.
The leading cruise companies are seen to follow a careful approach towards debt financing and to maintain robust solvency positions over 2016–2019 ( Table 16 ). Carnival exhibits a consistently attractive and stable debt-to-equity ratio, at 0.78 in 2019. This is obviously in line with the higher equity component apparent in its capital structure mix. The same holds for Carnival's solvency position, displaying a comfortable operating profitability position to meet its interest payment obligations, with TIE ratio at 14.4 in 2019. Royal Caribbean and Norwegian are exposed to higher debt financing with a debt-to-equity ratio at 1.49 and 1.57, respectively in 2019. Whereas TIE ratios for Royal Caribbean and Norwegian are well above 1.0, at 5.3 and 4.3, respectively in 2019, these ratios still lag considerably behind Carnival. Broadly, the debt-to-equity and TIE ratios of leading cruise companies reflect balanced financing strategies with manageable debt exposures and adequate solvency positions. This comes in contrast to the typically heavily indebted commercial shipping companies ( Syriopoulos, 2007 , Syriopoulos, 2010 ).
Financial leverage – solvency ratios.
5.6. Earnings per share ratios
Earnings per share (eps) growth is an important financial indicator to measure managerial performance as it reflects a company's growth prospect dynamics. If revenue shows how much money is flowing into the company, eps depicts how much of that money is flowing down to shareholders, as profits per every outstanding share of stock. In other words, eps shows the net earnings contribution generated per share to shareholders, not simply because of changes in earnings but also after accounting for the effects of issuance of new shares. This may be particularly important in case the growth comes because of acquisitions, a strategic path of growth preferred by several cruise companies over the last decades.
A comparison of eps growth for major cruise companies, over 2016–2019, reveals that Norwegian has attained the best performance (eps growth: 56%), and Royal Caribbean follows closely (eps growth: 50%), whereas Carnival is lagging behind at a distance (eps growth: 12%). Broadly, the leading cruise companies exhibit robust profitability and promising growth prospects, rendering cruise company shares a broadly challenging investment choice ( Table 17 ).
Cruise company eps ratios.
6. Managerial implications and conclusion
6.1. a note on the covid-19 impact.
As this study was about to close, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the COVID-19 outbreak as a global pandemic on March 11, 2020. Most countries around the world introduced restrictions to international travel and imposed bans on non-essential travel to contain the virus spread. To that end, recent UNWTO estimates indicate that the near-complete global lockdown has abruptly halted economic growth, exerting an unprecedented impact on most business sectors, and especially on the travel, tourism, and cruise industries. In fact, these dramatic circumstances resulted eventually to the cruise ship business shutting, inevitably, entirely down. Current forecasts estimate the total industry revenues for 2020 to be 35% lower than in 2019 (from $685 bln. in 2019 down to $447 bln. for 2020; UNWTO, 2020 ; Richter, 2020 ). This translates into a fall of 300 mln. tourists and $320 bln. losses in international tourism receipts, more than three times the losses during the 2008 global financial crisis.
With a focus on the global cruise business, the virus spread led many countries to close their borders, resulting to thousands of cruise passengers kept at sea and vessels seeking a port to dock. Canada, for instance, banned all ships with more than 500 people from docking in its ports (mid-March). Australia, New Zealand, and the US banned all ships arriving from foreign ports and directed all foreign flagged ships to leave the country. Cruise passengers and crew members were quarantined on board and cruise liners had to struggle hard to attain delayed repatriation ( Giese, 2020 ; Ito, Hanaoka, & Kawasaki, 2020 ; Moussali & Tsekoura, 2020 ).
The following points highlight a set of critical implications for the cruise industry due to the coronavirus pandemic ( Giese, 2020 ; Research and Markets, 2020 ):
- most operators have had to suspend all voyages and others have cancelled most cruises;
- cruise companies have experienced detrimental financial implications, in terms of revenue and profits and at the same time of upward additional costs (for instance, costs associated with substantial refunds for cancellations, costs associated with docking ships at ports where ships were quarantined, costs of maintenance even when not sailing for utilizing cruise ship engines to provide power to maintain onboard services, air conditioning, desalination and propulsion);
- the defensive reaction to coronavirus spread has exerted domino effects and provoked far reaching implications for many cruise-linked companies, and cruise destinations, as many small island nations and other local economies rely heavily on the jobs, income cashflows and value chain effects generated by cruise ships and related business; for instance, the cruise industry is estimated to contribute about $2.0 bln. to the Caribbean each year; this results in a 5.9% contribution to some nations' entire GDP, as is the case with St. Kitts and Nevis ( Ship Technology, 2020 );
- it is highly doubtful whether the cruise companies will remain in a position to sustain their robust financial performance, as discussed in the previous sections; liquidity constraints are expected to eventually drug cruise companies into additional debt (with global investors' stock market sentiment remaining low); hence, further deterioration in their funding costs is anticipated ( McKinsey, 2020a ; Syriopoulos & Bakos, 2019 );
- to elaborate the deterioration in financial terms and capital costs, Carnival Cruise Line, the world's largest cruise operator, has lost its investment-grade status in June 2020, after S&P downgraded its rating at BB- (dropped from BBB-); S&P analysts perceive a ‘high level of uncertainty’ for the cruise operator's return to normal services and its ultimate recovery path; furthermore, the firm's credit measures are expected to ‘remain very weak through 2021 because of its plans for a gradual reintroduction of capacity’; the weak demand may eventually force Carnival to speed up removal of older ships and delay new ship deliveries ( Nagarajan, 2020 );
- in sum, the cruise industry faces a long struggle to ensure its survival as a widespread sentiment of concern, uncertainty, and instability has prevailed in the sector ( McKinsey, 2020b );
- these adverse circumstances are vividly reflected on the abrupt share price and market value decline of leading listed cruise companies ( Fig. 4 ).

Cruise share returns (%) – Post COVID-19 impact.
The detrimental COVID-19 financial implications for cruise revenue, profits and the gloomy business prospects (risk of closure for several cruise companies) are underlined indeed by the highly volatile and dramatic collapse of share prices for the largest listed cruise groups (even by −130% on average in few days; Fig. 4 ). Indicatively, Carnival, Royal Caribbean and Norwegian cruise share prices declined sharply at $7.97, $24.36, and $8.40, respectively, as the virus burst (April 2), recording losses by 70–80% from the beginning of the year (share prices at $51.31, $134.65, and $58.83, respectively, on January 2). Cruise share prices, nevertheless, rebounded impressively recently, returning up at $14.33, $50.83, and $14.22, respectively (July 28), partly mitigating the earlier heavy losses.

6.2. Key managerial implications and recommendations
This study has undertaken a concise, focused, and updated financial performance evaluation of the cruise sector, based on a sample of leading cruise players. Surprisingly, to the authors' best knowledge, relevant studies remain extremely thin on this topic. This paper intends to partially fill this research gap and to offer a set of innovative contributions and managerial recommendations. Cruise companies have shown a consistently dynamic growth performance over recent years, rebounding impressively after the 2008 financial crisis impact. Cruise revenue and profitability are seen on a solid upward trend, diverging from commercial shipping companies. Critical financial performance indicators, such a ROE, ROA and ROIC ratios, are consistently high, reflecting efficient managerial investing, operating, and financing decisions. The leading cruise companies have ambitious and highly capital-intensive investment plans under development, with active newbuilding orderbooks for vessels of larger carrying capacity, expensive technological advances, and modern facilities to cater for diversified cruise passenger needs, complying at the same time with strict environmental conditions. As major international banks are seen to exit ship lending, a critical question remains as of potential alternative capital sources to finance these investments, assuming that cruise vessel construction costs typically range from $0.5 bln. to over $1.5 bln. The capital structure of the leading cruise companies demonstrates a balanced and healthy debt-equity mix, with dept-to-equity ratios and solvency ratios performing impressively.
The global pandemic has hit the cruise sector severely with destabilizing effects to many corporate players as well as to cruise-related businesses even at risk of fatal default. These fragile financial circumstances generate a set of critical managerial implications, recommendations, and potential actions for the cruise companies under pressure to support their business overcome the virus crisis, including the following:
- robust cash liquidity positions supported by the earlier impressive profitability are to benefit the most prudent, well prepared, and forward-looking cruise companies;
- in fact, heavy pressure on cruise revenue and profits is already apparent, as cruise cancellations, customer refunds, additional operational costs and widespread uncertainty have been escalating;
- cruise managers must inevitably proceed towards an extensive reassessment of their investment, financing, and operating plans with a view to curtail the earlier ambitious projects for larger costly newbuild cruise vessels;
- as the pandemic implications affect nearly all business sectors and liquidity turns scarce and expensive, financing strategies have to be redesigned, conveniently tailored under these adverse circumstances;
- the relatively attractive cruise company WACCs, estimated earlier in this study, are hard to maintain further, as funding is turning more expensive, typically in favor of the largest and best reputed players;
- the optimal capital structure mix remains of critical concern, as different capital sources bear different funding costs, diversified among competing cruise companies;
- as a result, the earlier robust and promising financial performance of the cruise companies, as depicted by the ROE, ROA, ROIC, WACC ratios, leverage exposure, solvency, earning per share and stock market performance, is highly unlikely to remain unaffected under the prevailing gloomy market circumstances;
- a vital short-term goal for cruise business is undoubtedly survival; this comes at a severe cost, as government intervention and extensive lending is seen to become imperative to keep cruise companies afloat;
- long term objectives of cruise companies should include the restoration of the disastrous reputational damage that has been caused by the virus effects on the broader cruise business.
Having said that, cruise business has in fact faced hard times and global crises in the past but managed to recover convincingly, demonstrating tough resilience, adaptability, and flexibility. This virus crisis, however, appears to be quite different. The critical question remains as to when the cruise industry is going to return into business operations again ( Calder, 2020 ). Unfortunately, there is no clear answer to that yet, as there are many uncertainties to make rational forecasts for the entire 2020. Fears are that this crisis will affect cruise revenues for a long time, particularly in the Asian region, as this is a dynamic market of growing importance for the cruise industry in recent years ( Moussali & Tsekoura, 2020 ; OMR Global, 2020 ). Obviously, these adverse implications are anticipated to have a tremendous financial impact on all cruise players, inducing downward adjustments in investment, financing, and profitability projections. However, it is for small cruise players that the implications are expected to be even more painful, forcing inevitably several of them to exit the market or to be taken over.
According to a recent KPMG report ( Giese, 2020 ), a set of direct responsive actions is under play by the cruise industry to keep future business intact, including bonus credit offers (110–125% of booking amount) instead of cash refunds, as an option to cruise passengers whose trips have been cancelled due to the pandemic, providing flexibility for future bookings. Based on recent UBS bank estimates ( Panetta, 2020 ), around 76% of the passengers whose cruises were cancelled due to pandemic have opted for a credit for future trips instead of a refund. Furthermore, based on a recent CLIA survey, 82% of cruisers indicate their interest in booking a cruise for their next vacation. Despite multiple outbreaks of COVID-19 and uncertainty over when sailing will reconvene, several reports record increased bookings for 2021 in comparison to 2019. This reflects a persisting interest of cruise passengers in continuing pursuing cruise travel and tourism services in the future, though it may be harder to convince first-time cruisers ( Giese, 2020 ; Panetta, 2020 ). At the same time, as most countries continue to fight against COVID-19 effects, the virus impact is anticipated to challenge the business model of several industries ( McKinsey, 2020c ). For the time being, there does not seem to be a clear timeline for the restart of cruise operations. To gain customer support after travel restrictions will have been lifted, companies consider promotion campaigns at reduced cruise package prices for 2021, to compete and revitalize cruise demand. In any case, the assessment of the post-COVID-19 impact on the global cruise business can be more accurately evaluated after the pandemic is over. This could well lead to a challenging follow-up empirical study.
Appendix A.
Source: Authors ‘compilation; www.cruiseindustrynews.com ( Cruiseindustrynews, 2020 ). A summary version is presented in Table 7 .
Author's statement
The authors confirm that their paper entitled ‘The Global Cruise Industry: Financial Performance Evaluation’ (RTMB-D-20-00143R1_R2) is the output of original research and it has not been published elsewhere, nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhere.
To the authors' view this manuscript is appropriate for publication in the Research in Transportation Business and Management – Special Issue on Cruise Shipping, Ports and Destinations (Cartagena 2020 Conference) because it covers an unresearched topic and contributes innovative empirical findings and useful policy recommendations.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
- Baker M., Wurgler J. Market timing and capital structure. Journal of Finance. 2002; 57 (1):1–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- Byung-Wook W. A dynamic game model of strategic capacity investment in the cruise line industry. Tourism Management. 2005; 26 (2):203–217. [ Google Scholar ]
- Calder S. 2020. Coronavirus: When will cruises start again and should I book?, The independent (April 16) [ Google Scholar ]
- Charlier J. The cruise shipping industry in the corporate mergers and overpanamax eras. A comparison with the container shipping industry. Revue Belge de Géographie. 2004;(4):433–460. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen J., Neuts B., Nijkamp P., Liu J. Demand determinants of cruise tourists in competitive markets: Motivation, preference and intention. Tourism Economics. 2016; 22 (2):227–253. [ Google Scholar ]
- Clancy M. In: Cruise ship tourism (2nd ed.) Dowling R., Weeden C., editors. CAB International; 2017. Power and profits in the global cruise industry (Ch. 2) pp. 43–56. [ Google Scholar ]
- CLIA . 2018. The contribution of the international cruise industry to the global economy in 2018, report, cruise line international association, Miami, Florida. [ Google Scholar ]
- CLIA . 2019. Cruise trends industry outlook, report, cruise line international association, Miami, Florida. [ Google Scholar ]
- CLIA . 2020. State of the cruise industry outlook, report, cruise line international association, Miami, Florida. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cruiseindustrynews Cruise Ship Order Book 2019–2027. 2020. http://www.cruiseindustrynews.com/cruisenews/cruise-ship-orderbook.html Cruise Industry News, posted on May 15.
- Daly J., Fernandez-Stark K. Duke University; 2017. Barbados in the cruise tourism global value chain, technical report, global value chains Centre. [ Google Scholar ]
- Donaldson G. 1961. Corporate debt capacity: A study of corporate debt policy and the determination of corporate debt capacity, Boston, Harvard. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dowling R. CAB International; Cambridge: 2006. Cruise ship tourism. [ Google Scholar ]
- Drobetz W., Gounopoulos D., Merikas A., Schroder H. Capital structure decisions of globally-listed shipping companies. Transportation Research – Part E. 2013; 52 :49–76. [ Google Scholar ]
- Florida Caribbean Cruise Association . 2019. Cruise industry overview 2018, industry report, Miami, Florida. [ Google Scholar ]
- Garin K.A. 2005. Devils on the deep Blue Sea: The dreams, schemes, and showdowns that built America’s cruise-ship empires, New York, Plume. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giese M. COVID-19 impacts on global cruise industry: How is the cruise industry coping with the COVID −19 crisis? KPMG Report, posted on July 23. 2020. https://home.kpmg/xx/en/blogs/home/posts/2020/07/covid-19-impacts-on-global-cruise-industry.html
- Hall A., Braithwaite R. Caribbean cruise tourism: A business of transnational partnerships. Tourism Management. 1990; 11 (4):339–347. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hobson P. Analysis of the US cruise line industry. Tourism Management. 1993; 14 (6):453–462. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hobson P. Increasing consolidation within the cruise line industry. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing. 1994; 2 (4):91–96. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hovakimian A. Are observed capital structures determined by equity market timing? Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis. 2006; 41 (1):221–243. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ito H., Hanaoka S., Kawasaki T. The cruise industry and the COVID-19 outbreak. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives. 2020; 5 :100–136. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kisgen D. Credit ratings and capital structure. Journal of Finance. 2006; 61 (3):1035–1072. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kiziellewicz J. Methods of raising funds for purchasing of new cruise ships by international corporations. International Journal of Management and Economics. 2017; 53 (2):69–83. [ Google Scholar ]
- Klein R.A. Responsible cruise tourism: Issues of cruise tourism and sustainability. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management. 2011; 18 (1):107–116. [ Google Scholar ]
- Koller T., Goedhart M., Wessels D. 7th ed. McKinsey & Company Inc; 2020. Valuation: Measuring and managing the value of companies. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lester J., Weeden C. Stakeholders, the natural environment and the future of Caribbean cruise tourism. International Journal of Tourism Research. 2004; 6 :39–50. [ Google Scholar ]
- McKinsey Managing and monitoring credit risk after the COVID-19 pandemic, Article, posted on July 31. 2020. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/risk/our-insights/managing-and-monitoring-credit-risk-after-the-covid-19-pandemic?cid=other-eml-alt-mip-mck&hlkid=d3dc5ab195164ab19954a2c7203a037a&hctky=2577872&hdpid=cbb80600-b563-4c85-9556-10e61d36411a
- McKinsey Consumer sentiment and behavior continue to reflect the uncertainty of the COVID-19 crisis, article, posted on July 8. 2020. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/marketing-and-sales/our-insights/a-global-view-of-how-consumer-behavior-is-changing-amid-covid-19
- McKinsey Banking models after COVID-19: Taking model-risk management to the next level, article, May 5. 2020. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/risk/our-insights/banking-models-after-covid-19-taking-model-risk-management-to-the-next-level?cid=other-eml-alt-mip-mck&hlkid=2784fd8611e24462b62cacb72c4afccb&hctky=2577872&hdpid=cbb80600-b563-4c85-9556-10e61d36411a#
- Modigliani F., Miller M. The cost of capital, corporation finance, and the theory of investment. American Economic Review. 1958; 48 :161–197. [ Google Scholar ]
- Modigliani F., Miller M. Corporate income taxes and the cost of capital: A correction. American Εconomic Review. 1963; 53 :433–443. [ Google Scholar ]
- Moussali M.A., Tsekoura I. COVID-19 marine: Cruise industry impact from coronavirus, Clyde and co report, posted on May 10. 2020. https://www.clydeco.com/insight/article/coronavirus-and-the-impact-on-the-cruise-industry
- Myers S. The capital structure puzzle. Journal of Finance. 1984; 39 (3):574–592. [ Google Scholar ]
- Myers S. Capital structure. Journal of Economic Perspectives. 2001; 15 (2):81–102. [ Google Scholar ]
- Myers S., Majluf N. Corporate financing and investment decisions when firms have information those investors do not have. Journal of Financial Economics. 1984; 13 :187–221. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nagarajan S. Carnival has its credit rating slashed as its return to the seas is likely crippled by an uptick in COVID-19 cases, business insider article, posted on June 24. 2020. https://markets.businessinsider.com/news/stocks/carnival-loses-investment-grade-rating-after-uptick-covid19-cases-2020-6-1029336911
- OECD . Working Party on Shipbuilding; Paris: 2007. Report on ship financing, organisation for economic cooperation and development. [ Google Scholar ]
- OMR Global Impact of COVID-19 on global cruise industry, and forecasts: 2019–2025, report. 2020. https://www.omrglobal.com/industry-reports/impact-of-covid-19-on-global-cruise-industry (April)
- Pallis A., Parola F., Satta G., Notteboom T. Private entry in cruise terminal operations in the Mediterranean Sea. Maritime Economics & Logistics. 2018; 20 (1):1–28. [ Google Scholar ]
- Panetta G. Cruise ship bookings for 2021 are already on the rise despite multiple COVID-19 outbreaks, business insider article, posted on April 12. 2020. https://www.businessinsider.com/cruise-ship-bookings-are-increasing-for-2021-despite-coronavirus-2020-4
- Research and Markets Impact of COVID-19 on the global cruise industry, market report, June. 2020. https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5017152/impact-of-covid-19-on-the-global-cruise-industry#rela0-5010882
- Richter H. Cruising post-COVID-19: Lessons and challenges for the cruise ship industry, report, Sustainalytics, a Morningstar Company, posted on June 24. 2020. https://www.sustainalytics.com/esg-blog/cruising-post-covid-19-lessons-and-challenges-for-the-cruise-ship-industry/
- Satta G., Parola F., Penco L., Persico L., Musso E. Motivation-based segmentation in the cruise industry: An exploratory study. International Journal of Transport Economics. 2016; 43 (1–2):155–184. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ship Technology The cruise industry will struggle to cope with the effects of Covid-1, report, posted on March 18. 2020. https://www.ship-technology.com/comment/cruise-industry-effects-covid-19/
- Syriopoulos T. In: Maritime transport: The Greek Paradigm, research in transportation economics, 21. Pallis A., editor. 2007. Financing Greek shipping: Modern instruments, methods and markets (Ch. 6) pp. 171–219. [ Google Scholar ]
- Syriopoulos T. In: The handbook of maritime economics and business. 2nd ed. Grammenos C.T., editor. Routledge; Informa Law: 2010. Shipping finance and international capital markets (Ch. 28) pp. 811–849. [ Google Scholar ]
- Syriopoulos T., Bakos G. Investor herding behaviour in globally listed shipping stock returns. Maritime Policy & Management. 2019; 46 (5):545–564. [ Google Scholar ]
- Teye V., Leclerc D. The white Caucasian and ethnic minority cruise markets: Some motivational perspectives. Journal of Vacation Marketing. 2003; 9 (3):227–242. [ Google Scholar ]
- UNWTO Impact of COVID-19 on global tourism made clear as UNWTO counts the cost of standstill, UNWTO Report, posted on July 28. 2020. https://www.unwto.org/news/impact-of-covid-19-on-global-tourism-made-clear-as-unwto-counts-the-cost-of-standstill
- Veronneau S., Roy J. Global service supply chains: An empirical study of current practices and challenges of a cruise line corporation. Tourism Management. 2009; 30 (1):128–139. [ Google Scholar ]
- Veronneau S., Roy J. In: The business and Management of Ocean Cruises. Vogel M., Papathanassis A., Wolber B., editors. CAB International; 2011. Cruise Lines’ purchasing and logistics management (Ch. 7) pp. 90–100. [ Google Scholar ]
- Veronneau S., Roy J. In: The Blackwell companion to maritime economics. Wayne T.K., editor. Blackwell; 2012. Cruise lines and passengers (Ch. 8) pp. 138–160. [ Google Scholar ]
- Veronneau S., Roy J., Beaulieu M. Cruise ship suppliers: A field study of the supplier relationship characteristics in a service supply chain. Tourism Management Perspectives. 2015; 16 :76–84. [ Google Scholar ]
- WAC Cruise ships on order 2017–2025 (10th revision), Amem communication. 2019. www.amem.at
- Wie B. A dynamic game model of strategic capacity investment in the cruise line industry. Tourism Management. 2005; 26 (2):203–217. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wondirad A. Retracing the past, comprehending the present and contemplating the future of cruise tourism through a meta-analysis of journal publications. Marine Policy. 2019; 108 doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2019.103618. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wood R. Caribbean cruise tourism: Globalization at sea. Annals of Tourism Research. 2000; 27 (2):345–370. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wood R. In: Tourism and transport: Issues and agenda for the new millennium. Lumsdom L., Page S., editors. Elsevier; 2004. Cruise ships: Deterritorialized destinations (Ch. 10) pp. 133–146. [ Google Scholar ]
Cruise Industry: 100+ Statistics, Facts, and Trends [2023]
Over 32M passengers were expected to go cruising in 2020.
Only a handful of 400 cruise ships ready to hit the water could take passengers onboard due to COVID-19.
The result? Over $60B in losses.
So if you’d like to learn more about the cruise industry, you’ve come to the right place.
In this data-driven roundup, we’ve compiled the most relevant and up-to-date stats and facts on the topic to help you catch the essence.
Let’s dive right in:
Top 10 Cruise Industry Stats and Facts to Know in 2023
General cruise industry statistics & facts, wonder of the seas, working onboard a cruise ship, cruise ships: a general overview, cruise industry demographics, cruise ships pollute but are good at recycling, covid-19 impact on cruise tourism.
- The cruise industry made $18B in revenue in 2022.
- The total number of cruise ship passengers stood at 13M+ as of 2021.
- The cruise industry is expected to reach $25.1B in revenue by the end of 2023.
- The cruise industry supports over 1M jobs.
- A cruise costs an average of $214 per passenger daily.
- The world’s fleet of cruise ships totals 430.
- US nationals made up the majority (43%) of all cruise passengers in 2021.
- US nationals made up 43% of all cruise passengers in 2021.
- The cruise industry seeks to reduce carbon emissions by 40% by 2030.
- A cruise ship emits more greenhouse gasses daily than 13M cars.
- The global revenue of cruises is set to reach $30B by 2024.
- Only 22% of cruise tickets are purchased online. Instead, 78% of the sales come from offline channels (e.g., ticket offices).
- Wonder of the Seas, owned by Royal Caribbean Group., is the world’s largest cruise ship.
- 1.7M passengers cruised to the Caribbean region in 2021.
- The US, Canada, and Mexico make up half of all cruise passengers.
- Crime rates on cruise ships are 95% lower than on land.
- Wonder of the Seas is the largest cruise ship in the world. It’s 1,188 feet long and 209 feet wide (362 x 64m).
- Wonder of the Seas can take up to 7K passengers and 2.3K crew members onboard.
- The Wonder of the Seas ship was ordered in 2016 and completed in 2022, with a construction cost of $1.3B.
- Wonder of the Seas has a Central Park (the first ever park at sea) with over 20K natural plants.
- The Wonder of the Seas ship has four thrusters with 7.5K horsepower each, which help it reach the cruising speed of 22 knots (25 mph).
- Wonder of the Seas has 24 bars and dining facilities.
- There are eight specially designed neighborhoods on the Wonder of the Seas ship.

Looking for passport photos? Discover more information:
- Take Baby Passport Photo at Home
- Passport Size Photos Maker
- Take Green Card Photo
- The cruise industry provided 1.7M jobs in 2019.
- It takes 24 passengers to support one full-time job on a cruise ship.
- The cruise industry has average employee turnover rates: 25–35%.
- A cruise ship may require over 2K crew members.
- Cruise ships have a strict, military-like chain of command: officers > staff > crew members.
- 70% of cruise ship crew work in the hotel division.
- Most cruise companies (70%) hire employees via foreign agencies.
- A typical cruise ship employment form is a 6-month-long contract.
- Cruise ship crew are on call around the clock.
- An average cruise ship member in the US makes $29K annually.
- 72 new ships were manufactured in 2021.
- The average cost of building a cruise ship is $600M.
- There were 65 ocean cruise lines as of 2022.
- The three leading cruise companies made 85% of the global revenue in 2021.
- Only 11% of cruise ships can accommodate more than 4K passengers.
- Most cruise ships (32%) can take 2–3K tourists onboard.
- 371 out of 430 cruise ships operated in 2022.
- Here’s a look at the highest-rated cruise lines:
- The cruise ship’s passenger capacity is projected to reach over 38M in 2027.
- The average age of a cruise ship is 14.
- The world’s longest cruise ship (~1,188 ft or 362m) is just 6.5 ft (2m) longer than the fifth longest ship (853 ft or 260m).
- Royal Caribbean has all five longest cruise ships in its fleet.
- The most expensive cruise ships are Oasis of the Seas and Allure of the Seas. The former cost 1.5B to build, and the latter’s price tag was 1.4B.
- Here’s a breakdown of the world’s largest cruise ships:
- 57% of cruisers are college graduates.
- 83% of cruise passengers are married.
- Cruisers spend around $385 in the port city before boarding a ship.
- During a typical cruise, passengers spend an average of $750 per person in port cities.
- Cruise passengers are 47 years old, on average.
- 85% of Millennials plan to cruise in the future, compared to 82% of Gen Xers and 79% of Gen Zers.
- Eight in 10 cruisers are likely to book their next vacation on a cruise ship.
- ~70% of cruisers are willing to board a cruise ship next year.
- Almost 60% of people who have never cruised say they are likely to cruise in the next few years.
- 70% of cruisers have an annual household income greater than $80K.
- 17% of Americans have cruised at least once.
- Most cruisers (77%) travel with a spouse.
- 30% of cruise passengers travel mainly with under-aged children.
- A quarter of cruisers generally travel with friends.
- A 3K-person cruise ship generates an average of 150K gallons (567 liters) of sewage per week.
- Cruise ships dump as much as 1B gallons (3.7B liters) of bacteria, heavy metals, and nutrients into the sea yearly.
- Here’s an overview of the waste produced by a 3K-passenger cruise ship during one week voyage:
- The cruise line industry dumps 285K gallons (1M liters) of wastewater into the sea every day.
- 75% of solid waste is incinerated on cruise ships, and the ash is typically discharged at sea.
- 24% of the solid waste generated by all ships comes from cruise ships.
- Cruise ships recycle 60% more waste daily than people on land.
- Cruise lines recycle 80K tons of paper, plastic, aluminum, and glass each year.
- The global revenue from cruises dropped by 88% in 2020.
- The cruise industry made just $3B in 2020 compared to 27B in 2019.
- The revenue growth in the cruise market is expected to plateau at 3% by 2026.
- The number of cruise passengers globally dropped by 84% in 2020.
- The cruise industry expected to carry 32M passengers in 2020.
- The number of ocean cruise passengers stood at 7M in 2020.
- Only 5M people went ocean cruising in 2021.
- The number of cruise passengers from North America dropped from 15M in 2019 to 3M in 2020.
- In 2021, the cruise industry declined by 25% compared to 2020.
- In the Middle East, the number of cruise passengers declined by 92% in 2020, followed by a 160% increase in 2021.
- In North America, the number of cruise passengers dropped by 80% in 2020 and continued to decline by another 25% in 2021.
- Leading cruise companies saw a 90% drop in revenue in 2021 compared to 2019.
- Here’s a look at the net income of the largest cruise companies between 2019 and 2021:
- The cruise industry’s economic contribution in 2019 was $154B.
- In 2020, the economic contribution of the cruise industry dropped by 59% to $63B.
- Due to the COVID-19 outbreak, cruise industry-supported jobs shrank by 50%.
- The number of cruise passengers will surpass the 2019 levels by 2024.
Stacking It All Up
There you have it.
A comprehensive list of cruise industry statistics, facts, and trends to help you better understand the market and its direction.
Was there a statistic you found particularly surprising? Or maybe there are other cruising stats you’d like to see?
Let us know in the comments.
Is the cruise industry growing?
Before 2019, the cruise industry had a 3–5% yearly growth, but in 2020, the market saw a drop of over 80% due to COVID. In 2021, the market got back on track, seeing a 300% increase in revenue and 50% in passenger numbers.
How big is the cruise line industry?
There are over 60 ocean cruise lines, operating a total of 430 ships. In 2019 (before coronavirus), these cruises brought $27B in revenue. By the end of 2023, that number is expected to reach $25B.
Who are the biggest players in the cruise industry?
Three companies made 85% of the total revenue in the cruise industry in 2021. These are Carnival Cruise ( 45%) , Royal Caribbean Group ( 25% ), and Norwegian Cruise Line ( 15% ).
What’s the #1 cruise line in the world?
Carnival Cruise Lines is the #1 cruise line in the world in terms of revenue ( $12.168B ). However, Royal Caribbean has five of the world’s largest cruise ships in its fleet.
How much money does the cruise industry make?
The cruise industry made $18B in revenue in 2022. It’s also set to reach $30B by 2024.
Fair Use Statement
Did you like our infographics? If so, feel free to share them with your audience. Just remember to mention the source and link back to this page.
- Bureau of Transportation Statistics, “Summary of Cruise Ship Waste Streams”
- Comparably, “Cruise Ship Salary”
- Condé Nast Traveler, “Top Cruise Lines: Readers’ Choice Awards 2022”
- Cruise Industry News , “Cruise Ships in Service (Oct 2022)”
- Cruise Industry News, “31.7 Million Cruise Passengers Possible in 2022”
- Cruise Lines International Association, “Environmental Stewardship”
- Cruise Lines International Association, “Security At Sea”
- Cruise Lines International Association, “State Of The Cruise Industry Outlook 2019”
- Cruise Lines International Association, “State Of The Cruise Industry Outlook 2020”
- Cruise Lines International Association, “State Of The Cruise Industry Outlook 2021”
- Cruise Lines International Association, “State Of The Cruise Industry Outlook 2022”
- Cruise Market Watch, “Financial Breakdown of Typical Cruiser”
- Cruise Market Watch, “Passenger Origins”
- Friends of the Earth, “ 2022 Cruise Ship Report Card”
- Grand View Research, “Cruise Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Type (Ocean Cruises, River Cruises), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2022 – 2028”
- Indeed, “How Much Do Cruise Ship Workers Make?”
- Scherb M., “Improving Employee Retention Rates in Cruise Industry by Assessing Living and Working Conditions”
- Ship Technology, “Wonder of the Seas Cruise Ship”
- Statista, “Cruise Passenger Volume Index Worldwide in 2019 and 2020, with a Forecast until 2026, by Scenario”
- Statista, “Gross Tonnage of Cruise Ships in the Global Order Book In 2021, by Region”
- Statista, “Largest Cruise Ships Worldwide as of February 2022, by Length”
- Statista, “Leading Countries in the Cruise Industry Revenue Worldwide from 2019 to 2022”
- Statista, “Most Expensive Cruise Ships Worldwide in 2022, by Building Cost”
- Statista, “Net Income of Carnival Corporation & Plc Worldwide from 2008 to 2021”
- Statista, “Net Income of Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings Ltd. Worldwide from 2011 to 2021”
- Statista, “Net Income of Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd. Worldwide from 2007 to 2021”
- Statista, “Number of Ocean Cruise Passengers Worldwide from 2009 to 2021”
- Statista, “Number of Ocean Cruise Passengers Worldwide from 2019 to 2021, by Region”
- Statista, “Percentage Change in Revenue of Leading Cruise Companies Worldwide during the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic in 2020 and 2021”
- Statista, “Revenue Growth of the Cruise Industry Worldwide from 2018 to 2026”
- Statista, “Revenue of the Cruise Industry Worldwide from 2017 to 2026”
- Statista, “Revenue Share of Sales Channels of the Global Cruise Industry from 2017 to 2026”
- Statista, “Worldwide Market Share of Leading Cruise Companies in 2021”
- Statista, “Year-Over-Year Percentage Change in Cruise Passengers during the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic Worldwide in 2020 and 2021, by Source Region”
- Wander Eat Write, “What Working on Cruise Ships Is Really Like: Pros & Cons”
- Wikipedia, “Environmental Effects of Shipping”
- Wikipedia, “List of Cruise Lines”
- Wikipedia, “List of Largest Cruise Ships”
- Wikipedia, “Wonder of the Seas”

Adam is an SEO & Digital PR writer with a child’s curiosity about the surrounding world. His superpower to dig out juicy facts got him citations in Forbes, Social Media Today, and 90+ other news outlets. Adam enjoys snapping pictures and won the national Huawei Next Image Award.

Cruise ship industry is booming despite spate of high-seas deaths
I t’s full steam ahead for the cruise ship industry after Royal Caribbean hiked its full-year profit guidance on Thursday, saying it expects 60% growth from last year following record bookings during the first quarter.
Travelers are paying “record ticket prices,” according to Royal Caribbean — despite a recent spate of high-sea deaths and missing passengers reports, including a Florida 20-year-old who jumped off a Royal Caribbean cruise this month.
Soaring demand for vacations at sea has given cruise operators ample room to raise ticket prices as the industry looks to close the pricing gap between more expensive land-based holidays and give their profits a lift.
Royal Caribbean, which operates the Celebrity Cruises, now expects annual profits of between $10.70 and $10.90 per share, compared with its earlier forecast of $9.90 to $10.10.
“Our existing fleet along with our new ships continue to perform exceptionally well, highlighted by the market response to the launch of Icon of the Seas,” CEO Jason Liberty said.
Royal Caribbean’s shares — which have spiked 126% in the past year, were up 2% on Thursday morning, to $139.32.
“I remember owning the stock in 2022 and every client was giving me grief about it,” said Peter Ahluwalia, manager at Belinvest Global Equity Fund that holds Royal Caribbean stocks and chief investment officer at Swiss Partners Group. “We’re turning almost 45% return on equity at the moment, which is quite incredible.”
Overall, the industry which was among the hardest hit during the pandemic, is expected to grow to 39.4 million passengers in 2027 from 31.7 million last year, according to Statista.
The surge in demand comes amid major publicity blows from incidents at sea involving passengers who have gone missing, including the Florida man who jumped overboard on April 4 in front of his brother and father after a night of drinking.
Last December, a 41-year-old Royal Caribbean passenger went overboard on a cruise to the Bahamas. That followed an incident last August involving a 64 year-old woman sailing from Singapore to Malaysia on Royal Caribbean who is presumed to have jumped to her death .
On average, 19 people go overboard on cruise ships every year — and of those, only about four are rescued, according to a 2020 study commissioned by the industry trade group Cruise Lines International Association.


Royal Caribbean and Celebrity: Strategic Deployment Approach
“The general strength of the Caribbean has been a factor,” said Marc Miller, director, deployment and itinerary planning, Royal Caribbean Group, pointing to more capacity in the region for both the Royal Caribbean International and Celebrity Cruises brands. “For Royal Caribbean we have added more hardware year-round and we also
CRUISE NEWS

Carnival Pride Repositions to the East Coast
After completing its winter 2023-24 program in Tampa, the Carnival Pride recently repositioned to the East Coast. The Carnival Cruise Line vessel is now offering a series of seven- to 14-night cruises departing from Norfolk. The itineraries were initially scheduled to depart from the Port of Baltimore, which remains closed

Spectrum of the Seas Marks Royal Caribbean’s Return to China
Marking Royal Caribbean International’s return to China after a four-year hiatus, the Spectrum of the Seas arrived in Shanghai today. Ending an eight-night repositioning cruise that started in Singapore, the 2019-built vessel docked at the Shanghai Baoshan International Cruise Terminal after visits to Vietnam and Hong Kong. The Spectrum of
Royal Caribbean Reports 2024 Q1; Increases Guidance
Royal Caribbean Group today reported first quarter Earnings per Share (“EPS”) of $1.35 and Adjusted EPS of $1.7, according to a press release. These results were better than the company’s guidance due to stronger pricing on close-in demand, strength in onboard revenue and favorable timing of expenses. As a result

Crystal Offering ‘Unique Brand’ in Luxury Market
“Crystal is truly unique in the market, epitomizing the unparalleled sophistication we offer with award-winning service, exquisite culinary experiences and remarkable innovative entertainment. But what truly sets us apart is how we are rethinking, repositioning and elevating the brand to make it a lifestyle brand at sea,” said Jacqueline Barney,

Former Braemar Sails from Scotland Ahead of Villa Vie Debut
The former Braemar has sailed from Scotland ahead of debuting for Villa Vie Residences. After spending almost four years docked in Rosyth, the 1993-built vessel left the port under its own power on Tuesday morning. Set to be renamed Villa Vie Odyssey, the cruise ship is now on its way

New Norwegian Aqua Floats Out At Fincantieri
Norwegian Cruise Line and its partners at Fincantieri celebrated the float out of the Norwegian Aqua from the drydock at the shipyard in Marghera (Venice), Italy. This marks the completion of the external work on the ship ahead of its April 2025 debut. As per maritime tradition, two ceremonial coins

Carnival Sunrise Conversion Marks Five Years
The Carnival Sunrise conversion is marking five years this month. The $200-million project took place in Spain and saw the Carnival Cruise Line ship essentially being rebuilt. As part of the bow-to-stern makeover project, the former Carnival Triumph received all-new public areas, as well as additional cabins and new features.

Princess Cruises: 2024 Capacity Breakdown
Princess Cruises continues to invest in its core markets in 2024. According to the 2024 Cruise Industry News Annual Report, the Carnival Corporation brand will see most of its capacity concentrated in North America. The premium brand is set to offer strong programs in the Caribbean and Alaska, which account

Azamara: Diversifying Itineraries More
Highlights of 2025 will include an extended Greenland program and the addition of a series of Canada and New England sailings, according to Michael Pawlus, head of itinerary planning. “For 2025 and 2026 we are also diversifying more. We have had all our eggs in Europe (in the summer), but

Carnival: Introducing Celebration Key
The big news for Carnival Cruise Line for 2025 will be the July opening of Celebration Key. Eighteen ships sailing from 10 different homeports will be calling at Carnival’s new destination in the Bahamas, Fred Stein, vice president of planning and deployment, told Cruise Industry News. “Our regular itinerary cycles

Silver Ray Completes Conveyance
Silversea Cruises’ newest addition to the fleet, the Silver Ray, has completed conveyance on the River Ems its according to Meyer Werft. The ship is expected to moor in the Dutch port of Eemshaven for final outfitting ahead of its technical and nautical sea trials on the North Sea. The

Carnival Spirit Completes First Winter Program in Mobile
The Carnival Spirit recently wrapped up its first winter program out of Mobile. After completing a final sailing from its Alabama homeport earlier this month, the Carnival Cruise Line vessel deadheaded to Tampa to embark on a repositioning cruise to the West Coast. Set to spend the upcoming cruise season

Cunard Officially Welcomes Queen Anne with Ceremony at Fincantieri Shipyard
The Queen Anne has officially joined Cunard’s fleet during a handover ceremony at the Fincantieri Marghera shipyard in Venice, according to a press release. The event was attended by Italian Minister of Enterprises and Made in Italy, Adolfo Urso, and Italian Minister for Relations with Parliament, Luca Ciriani. Also present

Atlas Ocean Voyages Announces 2025-26 Antarctic Season
Atlas Ocean Voyages announced that its 2025-26 Antarctica expeditions are now available for bookings. Running from October 2025 to March 2026, the new Antarctica season offers 37 departures aboard the World Voyager, World Navigator and World Traveller, according to a press release. “Antarctica continues to be the most popular and

Fincantieri: ‘Covering All Brands’ with Eye on Future Fuels
Coming off a big newbuild order from Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings, Daniele Fanara, director newbuilding and after-sales at Fincantieri, is positive on the future. “We are serving all segments of the market, from small luxury vessels to mega-size vessels to upper premium,” said Fanara, speaking to Cruise Industry News. “This
Get the latest breaking cruise news . Sign up.
54 Ships | 122,002 Berths | $36 Billion | View

Highlights:
- Mkt. Overview
- Record Year
- Refit Schedule
- PDF Download
- Order Today

- 2033 Industry Outlook
- All Operators
- Easy to Use
- Pre-Order Offer
- Advertising
- Cruise News
- Magazine Articles
- Quarterly Magazine
- Annual Report
- Email Newsletter
- Executive Guide
- Digital Reports
Privacy Overview
Cruise Line Industry Statistics
- Author: Alexander Eser
- Last updated: April 25, 2024
Highlights: The Most Important Statistics
In 2019, the global ocean cruise line industry was valued at $150.6 billion.
The number of ocean cruise passengers worldwide in 2019 was approximately 29.7 million.
Cruise industry spending generated $55.5 billion in total U.S. economic impact in 2019.
The industry contributed to over 436,600 U.S. jobs in 2019.
- Florida's ports accommodated roughly 59.9% of all U.S. cruise embarkations in 2019.
As of 2021, Carnival Corporation was the leading cruise line by annual passenger capacity, with capacity for over 12 million passengers.
The Caribbean is the largest cruising market, with over 11.3 million passengers in 2019.
The average cost of a cruise trip per person per day was $214.25 in 2019.
The average cruise passenger is 47 years old.
Nearly 30% of cruise vacationers are first timers.
Europe represented 26.3% of the global cruise market in 2019.
Asian cruisers spent an average of 4.9 days at sea in 2019.
Female cruisers outnumbered males in the cruise line industry, with 66% of passengers being female in 2017.
Seniors (65+ years old) constituted the largest portion of cruise passengers, encompassing 30.48% of all travelers in 2017.
Royal Caribbean International had the biggest Instagram following among cruise lines, with over 1.7 million followers in 2021.
As of 2020, over 270 ocean cruise ships were operating worldwide.
There were 537,000 cruise passengers from the UK in the first half of 2019, a rise of 3% over the previous year.
- In 2016, the cruise industry's expenditure in the UK reached 2.58 billion GBP.
In 2018, the revenue from the Norwegian cruise liner amounted to approximately 6.1 billion U.S. dollars.
The cruise industry contributed 53 billion euros to the European economy in 2017.
With the growth of the global tourism industry, the cruise line sector has become a significant player in the travel market. Understanding the latest statistics and trends in the cruise line industry is crucial for stakeholders, investors, and travelers alike. In this blog post, we will delve into key statistics and insights that shed light on the dynamics of the cruise line industry. From market size and revenue to passenger demographics and popular destinations, we will explore the data that shapes this vibrant sector. Join us as we set sail into the world of cruise line industry statistics.
The Latest Cruise Line Industry Statistics Explained
The statistic that the global ocean cruise line industry was valued at $150.6 billion in 2019 indicates the total revenue generated by companies operating ocean cruise ships worldwide during that year. This figure encompasses the combined value of ticket sales, onboard spending, and other associated revenues earned by cruise lines. It highlights the significant economic impact of the ocean cruise industry on a global scale, emphasizing the industry’s size and importance within the broader travel and tourism sector. The statistic reflects the growing popularity of cruise vacations among travelers and signals the industry’s substantial contribution to the overall economy.
The statistic “The number of ocean cruise passengers worldwide in 2019 was approximately 29.7 million” indicates the total number of individuals who took ocean cruises around the world in the year 2019. This figure suggests a significant level of global interest and participation in cruise travel during that particular year. The statistic is useful for understanding the scale and impact of the cruise industry on tourism and the economy, as well as for analyzing trends and patterns in consumer behavior related to vacation preferences and travel choices. Additionally, this statistic may be valuable for businesses, policymakers, and researchers seeking to assess the growth and market demand for ocean cruise experiences.
The statistic indicates that the cruise industry had a significant economic impact on the United States in 2019, contributing a total of $55.5 billion to the economy. This figure includes direct spending by cruise lines as well as secondary effects such as spending by passengers on goods and services in ports of call and related industries. The economic impact of the cruise industry goes beyond just the cruise lines themselves and also supports businesses in various sectors including hospitality, transportation, and tourism. This statistic highlights the substantial contribution that the cruise industry makes to the overall economy by creating jobs, generating revenue, and stimulating economic growth.
The statistic that the industry contributed to over 436,600 U.S. jobs in 2019 indicates the significant impact that the industry had on employment in the United States during that year. This number represents the total number of jobs directly supported by the industry, including roles in manufacturing, production, distribution, sales, and related services. The industry’s contribution to job creation highlights its importance as a major driver of economic growth and employment opportunities in the U.S. The data suggests that the industry played a crucial role in providing livelihoods for a large number of individuals and supporting the broader economy in 2019.
Florida’s ports accommodated roughly 59.9% of all U.S. cruise embarkations in 2019.
This statistic indicates that Florida’s ports played a significant role in the U.S. cruise industry in 2019, accounting for approximately 59.9% of all cruise embarkations in the country. This means that a large majority of cruise passengers in the U.S. chose Florida’s ports as their starting point for their cruise vacations during that year. Florida’s popularity among cruise passengers could be attributed to various factors such as its strategic geographic location, availability of diverse cruise itineraries, and excellent port infrastructure. This statistic highlights the importance of Florida as a key player in the U.S. cruise industry and underscores its significant contribution to the overall cruise market in the country.
The statistic stating that Carnival Corporation was the leading cruise line by annual passenger capacity as of 2021 signifies that Carnival Corporation had the highest passenger-carrying capability among all cruise lines in that year, accommodating more than 12 million passengers. This indicates that Carnival Corporation’s fleet of cruise ships had the largest collective capacity to serve passengers compared to its competitors in the cruise line industry. The high passenger capacity suggests that Carnival Corporation was a major player in the cruise industry, attracting a significant number of passengers annually and potentially generating substantial revenue from ticket sales, onboard spending, and other associated services.
The statistic that the Caribbean is the largest cruising market with over 11.3 million passengers in 2019 highlights the significant popularity of cruising in this region. This statistic represents the total number of passengers who embarked on cruises departing from or visiting Caribbean ports in 2019. The large number of passengers reflects the appeal of the Caribbean as a top destination for cruises due to its beautiful beaches, vibrant cultures, and variety of attractions. The robust cruise industry in the Caribbean not only provides economic benefits to the region but also offers travelers a diverse range of experiences and itineraries to choose from.
The statistic indicates that the average cost per person per day for a cruise trip in 2019 was $214.25. This figure represents the average amount spent by a single individual for each day of their cruise vacation, encompassing expenses such as accommodation, food, entertainment, and other onboard activities. Understanding this average cost provides valuable insight for consumers planning a cruise trip, allowing them to budget and make informed decisions based on typical expenditure patterns within the industry during the specified time period.
The statistic “The average cruise passenger is 47 years old” summarizes the central tendency of the age distribution for passengers on cruises. This means that if you were to take the total ages of all cruise passengers and divide it by the total number of passengers, the resulting average age would be 47 years old. It is important to note that while the average age may provide a general understanding of the typical age of cruise passengers, it does not provide information about the spread or variability of ages within the population. Additionally, factors such as the cruise line, destination, and time of year may influence the age composition of passengers on a particular cruise.
The statistic that nearly 30% of cruise vacationers are first timers indicates that a significant portion of individuals embarking on cruise vacations are doing so for the first time. This suggests that the cruise industry is attracting a notable number of new customers, possibly due to increased marketing efforts, affordability, or changing consumer preferences. For cruise companies, this statistic highlights the importance of catering to the needs and expectations of first-time cruisers to ensure a positive experience and potentially cultivate long-term customer loyalty. Additionally, this information could be valuable for marketing strategies and product development aimed at capturing this segment of the market.
The statistic “Europe represented 26.3% of the global cruise market in 2019” signifies that of all cruise passengers worldwide in 2019, 26.3% of them sailed in or from European ports. This information highlights Europe’s significant presence and influence in the global cruise industry during that year, showcasing the popularity of cruises among Europeans and travelers visiting European destinations. The statistic suggests that Europe is a key player in the cruise market, attracting a substantial share of cruise passengers compared to other regions around the world.
The statistic “Asian cruisers spent an average of 4.9 days at sea in 2019” indicates the average amount of time Asian individuals spent on cruise ships during the year 2019. This statistic provides valuable insight into the behaviors and preferences of Asian cruise passengers, demonstrating that they tend to enjoy spending nearly 5 days at sea when embarking on cruise vacations. Understanding the average duration of stay at sea for Asian cruisers can help cruise companies in tailoring their offerings to better meet the needs and desires of this particular demographic, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and potentially increasing business opportunities.
In the cruise line industry in 2017, females represented the majority of passengers, as 66% of all cruisers were female. This statistic indicates that there were more female passengers than male passengers taking cruises during that year. The cruise line industry’s demographics skew towards females, suggesting that they are more likely to participate in cruise vacations. This information is valuable for cruise companies in terms of marketing strategies, service offerings, and understanding their customer base to cater to the preferences and needs of their predominantly female clientele.
The statistic highlights that seniors aged 65 years and older made up the highest proportion of individuals who went on cruises in 2017, accounting for 30.48% of all travelers. This indicates that senior citizens were the most prevalent age group among cruise passengers during that year. The data suggests that seniors have a significant interest in cruise travel, possibly due to factors such as retirement, disposable income, or leisure preferences. Understanding the demographic composition of cruise passengers can help cruise companies tailor their services and marketing strategies to better cater to the preferences and needs of this key demographic group.
The statistic indicates that Royal Caribbean International, a popular cruise line company, had the largest Instagram following among all cruise lines in 2021, with the number of followers exceeding 1.7 million. This suggests that Royal Caribbean International has effectively leveraged the social media platform to reach a wide audience and engage with potential customers. With a large following on Instagram, the company is likely to have a strong online presence and brand visibility in the competitive cruise industry. This statistic highlights the importance of social media marketing for businesses in the travel and hospitality sector, demonstrating Royal Caribbean International’s success in building a sizable and engaged digital community.
The statistic that as of 2020, over 270 ocean cruise ships were operating worldwide highlights the significant presence and popularity of ocean cruises as a mode of travel and leisure. This statistic indicates a large number of cruising options available to consumers across various regions globally. The cruise industry has been expanding over the years, attracting a growing number of passengers seeking unique experiences and relaxation on board these floating resorts. The high number of operating cruise ships reflects the competitive nature of the industry as companies strive to offer diverse itineraries and amenities to attract passengers. Additionally, this statistic also underscores the economic impact of the cruise sector, as it generates revenue and creates employment opportunities in various ports and destinations around the world.
The statistic indicates that there were a total of 537,000 cruise passengers from the UK in the first half of 2019, representing a 3% increase compared to the same period in the previous year. This rise in the number of cruise passengers suggests a growing interest in cruise travel among UK residents. The 3% increase signifies a modest but positive trend in the cruise industry and reflects potential growth and demand for cruise vacations. This data could be valuable for cruise companies, travel agencies, and policymakers in understanding consumer behavior and making informed decisions regarding marketing strategies, capacity planning, and overall industry trends.
In 2016, the cruise industry’s expenditure in the UK reached 2.58 billion GBP.
The statistic ‘In 2016, the cruise industry’s expenditure in the UK reached 2.58 billion GBP’ indicates the total amount of money spent by the cruise industry in the UK during that year. This expenditure figure encompasses various costs incurred by the industry, such as port fees, fuel, supplies, wages, and marketing expenses. The substantial investment made by the cruise industry highlights its significant economic impact on the UK, including contributions to the tourism sector, employment opportunities, and infrastructure development. This statistic serves as a valuable indicator of the industry’s financial footprint and underscores its importance in the UK’s economy.
The statistic indicates that in 2018, the Norwegian cruise liner generated revenue totaling around 6.1 billion U.S. dollars. This figure represents the total amount of money earned by the Norwegian cruise liner company through its operations such as ticket sales, onboard purchases, and other services. The revenue is a key indicator of the company’s financial performance and reflects its ability to attract customers and generate profits. The high revenue figure suggests that the Norwegian cruise liner had a successful year in 2018, likely due to factors such as increased demand for cruise vacations, effective marketing strategies, and strong customer satisfaction.
The statistic that the cruise industry contributed 53 billion euros to the European economy in 2017 indicates the significant economic impact of this sector on the region. This figure represents the total value generated by the cruise industry through various operations, including cruise ship activities, passenger spending, port fees, and employment opportunities. The substantial economic contribution highlights the industry’s role in driving growth, creating jobs, and supporting local businesses across Europe. Policymakers, stakeholders, and investors can use this statistic to recognize the importance of the cruise industry and make informed decisions to further support and develop this sector for continued economic benefits.
0. – https://cruising.org
1. – https://www.cruisemarketwatch.com
2. – https://www.statista.com
3. – https://www.fdot.gov
Try Our Meeting Notes Software
We’ve developed ZipDo to solve our own meeting issues. Now we want to share it with you.
- Connect your Google Calendar
- Automatically create a note for every meeting
- Organize your meetings and meeting notes in a channel like Slack
EXPLORE MORE
Related Statistic Reports
Music education industry statistics.

Read Article
Private tutoring industry statistics, u.s. edtech industry statistics, china education industry statistics, online language learning industry statistics, us equity industry statistics.
StarTribune
Land o'lakes delivers a profit for its dairy unit that, like the industry, has been strained.
Paying more for butter? Land O'Lakes and its farmer-owners may be benefiting.
Price increases helped the Arden Hills-based cooperative earn a $254 million profit and return $175 million of that to owners in 2023, a boost from the year before.
"Land O'Lakes helped position our members for their own individual and organizational success," CEO Beth Ford and board chair Rick Brand wrote in the company's annual report released this spring.
Land O'Lakes saw revenue slip 12%, to $16.8 billion, after hitting a record $19.2 billion in 2022. But profits climbed 5% due in part to charging higher prices for butter and other dairy products even as the cost to make them fell, the company reported.
It's a welcome reprieve for those in the business. The dairy industry is known for tight margins and high volatility that have proven especially difficult in recent years. Land O'Lakes' dairy foods segment overall claimed a $48 million pre-tax profit last year after a $56 million loss in 2022.
Sales of crop inputs like seeds, fertilizers, pesticides and agronomy services took in $232 million for the WinField United business, a decline from a record segment profit the year before.
"Dairy foods earnings showed significant improvement, as business returned to more pre-pandemic rhythms," Ford and Brand wrote. "WinField United has consistently been responsible for growth and support across our enterprise."
The Purina animal nutrition arm, meanwhile, lost $3 million and was hurt by higher prices as the company sold less feed. It's a business "in transition."
"Animal nutrition is investing in one of the most significant business transformations in its history," the company said.
Fitch Ratings anticipates a turnaround for animal nutrition this year. After a recent restructuring and major software upgrade, Land O'Lakes "could right-size or close some plants to help stabilize the business," the ratings agency said.
Fitch predicts continued growth for dairy as the cooperative focuses on its more-profitable branded products.
Overall, Land O'Lakes earnings in 2024 should look similar to last year, though Fitch expects cash paid to members to decline.
Nationwide, farm income is expected to fall for a second consecutive year in 2024 after hitting records in 2022, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, but it is not expected to sink below the 20-year average.
For now, the outlook for dairy producers is improving.
"Milk prices are expected to be higher in 2024," the USDA predicts, "as modest increases in production, coupled with robust demand for dairy products from both domestic and global markets, support the values of most dairy products."
Brooks Johnson is a business reporter covering Minnesota’s food industry, 3M and manufacturing trends.
- Patrick Reusse on the dominance of the Timberwolves
- Why late-night options have dwindled in Minneapolis
- Edwards puts in 40 points; Wolves knock out Suns in playoff sweep
- Yuen: The bizarre and relatable case of Minnesota state Sen. Nicole Mitchell
- Souhan: Experts made two mistakes when they panned Gobert trade
- Supporters rally at courthouse as Minnesota state trooper appears for murder hearing
Tractor-trailers with no one aboard? The future is near for self-driving trucks on US roads
Japan's currency falls to its weakest since 1990 against the dollar as the yen keeps yelping, house and senate negotiate bill to help faa add more air traffic controllers and safety inspectors, stock market today: wall street drifts ahead of a week full of earnings reports and a fed meeting, tesla, domino's pizza rise; amc entertainment, sofi technologies fall, monday, 4/29/2024.

- Democratic Sen. Nicole Mitchell returns to work at Minnesota Capitol after burglary charge 11 minutes ago
- Broadway actor quits CTC's 'A Year With Frog and Toad' 2 days before opening night Apr. 28
- What commission changes mean for Minnesota homebuyers, sellers and agents • Business
- General Mills could sell $2B-plus North American yogurt business, including Yoplait • Business
- After ATF ruling, bottom falls out for St. Cloud firearms maker • Business
- Ramstad: Minnesota demographer takes deeper look at migration, workforce pressure • Business
- Friends split a mortgage, share a home to beat high housing costs • Business
© 2024 StarTribune. All rights reserved.
- Travel, Tourism & Hospitality ›
Leisure Travel
Industry-specific and extensively researched technical data (partially from exclusive partnerships). A paid subscription is required for full access.
Revenue of the cruise industry worldwide 2007-2027
Revenue of the cruise industry worldwide from 2007 to 2027 (in billion u.s. dollars).
- Immediate access to 1m+ statistics
- Incl. source references
- Download as PNG, PDF, XLS, PPT
Additional Information
Show sources information Show publisher information Use Ask Statista Research Service
August 2017
2007 to 2016
* Estimated figure. ** Forecasted figure.
Other statistics on the topic
Largest cruise ships worldwide 2023, by gross tonnage
Number of global ocean cruise passengers 2009-2027
Shipbuilding
Most expensive cruise ships worldwide by building cost 2022
- Number of passengers carried by Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2007-2023
To download this statistic in XLS format you need a Statista Account
To download this statistic in PNG format you need a Statista Account
To download this statistic in PDF format you need a Statista Account
To download this statistic in PPT format you need a Statista Account
As a Premium user you get access to the detailed source references and background information about this statistic.
As a Premium user you get access to background information and details about the release of this statistic.
As soon as this statistic is updated, you will immediately be notified via e-mail.
… to incorporate the statistic into your presentation at any time.
You need at least a Starter Account to use this feature.
- Immediate access to statistics, forecasts & reports
- Usage and publication rights
- Download in various formats
You only have access to basic statistics. This statistic is not included in your account.
- Instant access to 1m statistics
- Download in XLS, PDF & PNG format
- Detailed references
Business Solutions including all features.
Other statistics that may interest you
- Operating expenses of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide 2008-2023, by segment
- Market size of the global cruise industry in 2014, by region
- Cruise passenger movements at selected Mediterranean ports 2019-2022
- Transit cruise passengers at selected Mediterranean ports 2019-2022
- Number of Royal Caribbean Cruises passenger cruise days worldwide 2007-2023
- Number of Royal Caribbean Cruises employees 2011-2023
- Revenue of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2009-2023, by segment
- Revenue of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 1988-2023
- Phoenix Reisen river cruise revenue in Germany 2009-2021
- Number of cruise passengers from Europe 2012-2022
- Number of passengers carried by MSC Cruises worldwide 2015-2021
- Passenger capacity of the cruise industry worldwide 2017, by cruise line
- New cruise ships planned worldwide from 2015 to 2017, by passenger capacity
- Revenue of Norwegian Cruise Line worldwide 2011-2023
- Operating income of Norwegian Cruise Line worldwide 2011-2023
- Net income of Norwegian Cruise Line worldwide 2011-2023
- Total assets of Norwegian Cruise Line worldwide 2011-2023
- Operating expenses of Norwegian Cruise Line cruises worldwide 2013-2023
- Number of Royal Caribbean Cruises ships 2011-2023, by brand
- Total assets of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2007-2023
- Number of Royal Caribbean Cruises available passenger cruise days worldwide 2007-2023
- Operating income of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2007-2023
- Number of cruises and voyages in Asia 2013-2019
- Number of cruise ships active in Asia 2013-2019, by size category
- Cruise sector: direct expenditures in Europe 2017, by country
- Leading European cruise passenger markets 2011-2022
- Cruise revenue passengers at major European ports 2011-2017
- Growth rate of the European cruise passenger volume 2011-2022
- Number of fly cruise passengers in the UK 2010-2016
- Number of cruise ship vacation tourists in Germany 2012-2016
- South & Central America: leading source countries for cruise tourism 2019
- Number of passengers of Color Line 2013-2020
- Passenger capacity of the Asian cruise market 2013-2019 by type
- Ocean cruise passengers in Spain 2019, by travel route
- Number of ocean cruise passengers in Austria 2011-2018
- Number of ocean cruise passengers from Switzerland 2011-2021
- Cruise sector: cost of ships built in Europe 2018-2021, by country of build
- European cruise market: cruise passenger distribution 2017, by source country
- Cruise sector: top 10 Northern European ports in 2017, by passenger numbers
- Cruise sector: leading Northern European ports of call in 2017, by passenger numbers
- Cruise sector: number of passengers embarking in Europe in 2017, by country
- Cruise sector: number of new ships planned in Europe 2018-2021, by country of build
- Occupancy rate of Royal Caribbean Cruises 2007-2023
- Net income of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2007-2023
- Revenue of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide 2008-2023, by segment
- Net income of Carnival Corporation & plc 2008-2023
Other statistics that may interest you Statistics on
About the industry
- Premium Statistic Operating expenses of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide 2008-2023, by segment
- Premium Statistic Market size of the global cruise industry in 2014, by region
- Basic Statistic Cruise passenger movements at selected Mediterranean ports 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Transit cruise passengers at selected Mediterranean ports 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Number of Royal Caribbean Cruises passenger cruise days worldwide 2007-2023
- Premium Statistic Number of Royal Caribbean Cruises employees 2011-2023
- Premium Statistic Revenue of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2009-2023, by segment
- Premium Statistic Revenue of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 1988-2023
- Premium Statistic Phoenix Reisen river cruise revenue in Germany 2009-2021
- Premium Statistic Number of cruise passengers from Europe 2012-2022
About the region
- Premium Statistic Number of passengers carried by MSC Cruises worldwide 2015-2021
- Premium Statistic Passenger capacity of the cruise industry worldwide 2017, by cruise line
- Basic Statistic New cruise ships planned worldwide from 2015 to 2017, by passenger capacity
- Premium Statistic Revenue of Norwegian Cruise Line worldwide 2011-2023
- Premium Statistic Operating income of Norwegian Cruise Line worldwide 2011-2023
- Premium Statistic Net income of Norwegian Cruise Line worldwide 2011-2023
- Premium Statistic Total assets of Norwegian Cruise Line worldwide 2011-2023
- Premium Statistic Operating expenses of Norwegian Cruise Line cruises worldwide 2013-2023
- Premium Statistic Number of Royal Caribbean Cruises ships 2011-2023, by brand
- Premium Statistic Number of passengers carried by Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2007-2023
Selected statistics
- Premium Statistic Total assets of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2007-2023
- Premium Statistic Number of Royal Caribbean Cruises available passenger cruise days worldwide 2007-2023
- Premium Statistic Operating income of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2007-2023
- Premium Statistic Number of cruises and voyages in Asia 2013-2019
- Premium Statistic Number of cruise ships active in Asia 2013-2019, by size category
- Premium Statistic Cruise sector: direct expenditures in Europe 2017, by country
- Premium Statistic Leading European cruise passenger markets 2011-2022
- Basic Statistic Cruise revenue passengers at major European ports 2011-2017
Other regions
- Premium Statistic Growth rate of the European cruise passenger volume 2011-2022
- Premium Statistic Number of fly cruise passengers in the UK 2010-2016
- Premium Statistic Number of cruise ship vacation tourists in Germany 2012-2016
- Premium Statistic South & Central America: leading source countries for cruise tourism 2019
- Basic Statistic Number of passengers of Color Line 2013-2020
- Premium Statistic Passenger capacity of the Asian cruise market 2013-2019 by type
- Premium Statistic Ocean cruise passengers in Spain 2019, by travel route
- Premium Statistic Number of ocean cruise passengers in Austria 2011-2018
- Premium Statistic Number of ocean cruise passengers from Switzerland 2011-2021
Related statistics
- Premium Statistic Cruise sector: cost of ships built in Europe 2018-2021, by country of build
- Premium Statistic European cruise market: cruise passenger distribution 2017, by source country
- Basic Statistic Cruise sector: top 10 Northern European ports in 2017, by passenger numbers
- Basic Statistic Cruise sector: leading Northern European ports of call in 2017, by passenger numbers
- Basic Statistic Cruise sector: number of passengers embarking in Europe in 2017, by country
- Premium Statistic Cruise sector: number of new ships planned in Europe 2018-2021, by country of build
- Premium Statistic Occupancy rate of Royal Caribbean Cruises 2007-2023
- Premium Statistic Net income of Royal Caribbean Cruises worldwide 2007-2023
- Premium Statistic Revenue of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide 2008-2023, by segment
- Premium Statistic Net income of Carnival Corporation & plc 2008-2023
Further related statistics
- Premium Statistic Countries with the highest outbound tourism expenditure worldwide 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Factors affecting accommodation booking worldwide as of July 2016
- Premium Statistic Travelers trusting family & friends as travel resources worldwide in 2013, by region
- Premium Statistic Travelers completing feedback surveys worldwide in 2013, by region
- Premium Statistic International tourist arrivals in Europe 2006-2023
- Premium Statistic Annual revenue of China Tourism Group Duty Free 2013-2023
- Basic Statistic Revenue of Booking Holdings worldwide 2007-2023
- Basic Statistic Number of Marriott International hotels worldwide 2009-2023
- Basic Statistic Number of Marriott International hotel rooms worldwide 2009-2023
- Premium Statistic Countries with the highest number of inbound tourist arrivals worldwide 2019-2022
Further Content: You might find this interesting as well
- Countries with the highest outbound tourism expenditure worldwide 2019-2022
- Factors affecting accommodation booking worldwide as of July 2016
- Travelers trusting family & friends as travel resources worldwide in 2013, by region
- Travelers completing feedback surveys worldwide in 2013, by region
- International tourist arrivals in Europe 2006-2023
- Annual revenue of China Tourism Group Duty Free 2013-2023
- Revenue of Booking Holdings worldwide 2007-2023
- Number of Marriott International hotels worldwide 2009-2023
- Number of Marriott International hotel rooms worldwide 2009-2023
- Countries with the highest number of inbound tourist arrivals worldwide 2019-2022

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Leading countries in the cruise industry revenue worldwide from 2025 to 2028 (in million U.S. dollars) Premium Statistic Share of sales channels of the global cruise industry revenue 2018-2028
The ocean cruise segment accounted for above 80.0% of its revenue share in 2022. Strong players offering services in the ocean cruises segment for the intercontinental trips at a large number is attributed to the higher market revenue share. ... Due to the government initiatives to develop the tourism industry to increase the economic output ...
THE STATE OF THE CRUISE INDUSTRY 2023 CRUISE UPDATE & FORECAST Cruise tourism is rebounding faster than international tourism arrivals Source: CLIA Cruise Forecast/Tourism Economics (December 2022) Projected global cruise passenger volume (numbers represent an index of volume relative to 2019 (2019=100)) Projected global cruise passenger volume
The annual state of the industry report includes the release of 2023 passenger volume, which reached 31.7 million— surpassing 2019 by 7%. The report also shows continued demand for cruise ...
The reality of 2020 sits in stark contrast to the year that immediately preceded it. In 2019, the global cruise industry welcomed nearly 30 million passengers, creating jobs for 1.8 million people around the world and contributing over $154 billion to the global economy. With this growth came increased recognition of cruising as one of the best ...
WASHINGTON, DC (27 January 2022) - Cruise Lines International Association, the leading voice of the global cruise community, today released the 2022 State of the Cruise Industry Outlook report. The annual report shows how the industry has continued to resume responsibly with proven protocols that are leading the way, underscores the value of ...
The Cruise Industry News Annual Report 2022 is the only information resource of its kind — presenting the entire worldwide cruise industry in 400 pages with cruise industry analytics and statistics, in print and PDF formats. Click here to order. About the Annual Report: The 400-page report covers everything from new ships on order to supply-and-demand scenarios from the early 1990s through ...
Together, Carnival, the world's largest cruise company, and the two other biggest cruise operators, Royal Caribbean and Norwegian Cruise Line, lost nearly $900 million each month during the ...
Based on sentiment data from travelers across the globe, a significant number plan to book a future cruise. In fact, over one-third of respondents (35%) are already looking to book a future cruise ...
Global cruise passengers and revenue. 2021 provided a tough lesson for the cruise industry, with businesses aiming to make a swifter recovery from the latest round of lockdowns. The cruise industry's recovery rate was modest in 2021. Although a 96% YoY increase sounds positive, it is still nowhere near pre-pandemic levels.
Growth of the Ocean Cruise Line Industry. Worldwide, the ocean cruise industry experienced an annual passenger compound annual growth rate of 5.9% from 1990 to 2024. While the COVID-19 pandemic brought the ocean passenger cruise industry to a standstill for nearly two years, it also prompted the accelerated retirement of numerous older ships.
The cruise industry generated more than $40 billion in revenue worldwide in 2019. In 2009, the global ocean cruise industry carried about 17.8 million passengers. In 2019, this figure peaked at 29 ...
The Cruise Industry News Annual Report is the only information resource of its kind — presenting the entire worldwide cruise industry in 400 pages with cruise industry analytics and statistics, in print and PDF formats.. The 2024 Annual Report is available for order in both print and PDF formats.. About the Annual Report: The 400-page report covers everything from new ships on order to ...
Royal Caribbean's Icon of the Seas, the largest cruise ship in the world, is docked at Costa Maya Cruise Port, in the village town of Mahahual, Quintana Roo state, Mexico, February 6, 2024.
According to the report, the cruise industry supported 436,600 American jobs paying $24.4 billion in wages in 2019—a 3.5% and 5.4% increase from 2018, respectively. The latest figures follow nearly ten years of continued growth in the cruise industry, fueled by the rising popularity of cruise vacations.
The global cruise industry has experienced persistent growth dynamics over the last two decades, with an impressive rebound after the 2008 financial crisis, unlike commercial shipping. ... In terms of total revenue, the cruise industry generated $46.6 bln. in 2018, exhibiting a spectacular rebound since revenue had declined abruptly below $25 ...
The cruise industry is expected to reach $25.1B in revenue by the end of 2023. The cruise industry supports over 1M jobs. A cruise costs an average of $214 per passenger daily. The world's fleet of cruise ships totals 430. US nationals made up the majority (43%) of all cruise passengers in 2021. US nationals made up 43% of all cruise ...
Overall, the industry which was among the hardest hit during the pandemic, is expected to grow to 39.4 million passengers in 2027 from 31.7 million last year, according to Statista.
April 22, 2024. The big news for Carnival Cruise Line for 2025 will be the July opening of Celebration Key. Eighteen ships sailing from 10 different homeports will be calling at Carnival's new destination in the Bahamas, Fred Stein, vice president of planning and deployment, told Cruise Industry News. "Our regular itinerary cycles.
In 2016, the cruise industry's expenditure in the UK reached 2.58 billion GBP. In 2018, the revenue from the Norwegian cruise liner amounted to approximately 6.1 billion U.S. dollars. The cruise industry contributed 53 billion euros to the European economy in 2017.
Cruise industry purchases in Europe in 2017, by industry; Leading cruise line companies worldwide in 2016, by revenue; Cruise sector: output generated by cruise industry expenditures in Europe ...
Viking Holdings Ltd. said Monday it plans to offer 44 million shares priced up to $25 each in an initial public offering that could raise up to $1.1 billion for the cruise line company. Viking ...
For one, these two countries are reporting record bookings and revenues as the cruise industry rebounds. Carnival's annual revenue jumped from $12.1 billion in 2022 to over $21.59 billion in 2023.
Land O'Lakes saw revenue slip 12%, to $16.8 billion, after hitting a record $19.2 billion in 2022. ... The dairy industry is known for tight margins and high volatility that have proven especially ...
Revenue of the cruise industry worldwide 2007-2027. Published by Statista Research Department , Dec 16, 2021. This statistic shows the revenue of the cruise industry worldwide from 2008 to 2016 ...