Note: Your browser does not support JavaScript, Press Continue to proceed...

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION A Message from Our Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer...............................................i Our Values........................................................................1 LEAD WITH INTEGRITY Uphold the Code...............................................................2 Report Violations..............................................................3 Participate in Training......................................................4 Take Action.......................................................................5 RESPECT OTHERS Zero Tolerance for Harassment.......................................6 Zero Tolerance for Discrimination...................................7 Do Not Retaliate...............................................................8 Respect Privacy................................................................9 DEMONSTRATE ACCOUNTABILITY Use Assets Responsibly.................................................10 Keep Accurate Business Records and Accurately Communicate to the Public.........................11 Protect Sensitive Information........................................12 Accurately Charge Labor and Other Costs....................13 Avoid Individual Conflicts of Interest.............................14 Avoid Conflicts of Interest with Government Employees.................................................15 Avoid Organizational Conflicts of Interest.....................16

Do Not Engage in Insider Trading..................................17 Ensure the Quality and Safety of Our Products and Services........................................18 Use Artificial Intelligence Responsibly..........................19 CONDUCT BUSINESS FAIRLY Fair Competition.............................................................20 Abide by Trade Guidelines..............................................21 Actions of Third Parties..................................................22 Corruption and Kickbacks Will Not be Tolerated......................................................23 Strictly Adhere to All Antitrust Laws..............................24 Accept and Provide Only Appropriate Business Courtesies.......................................................25 OUR WORK ENVIRONMENT Safe and Healthy Work Environment..............................26 Maintain a Drug-Free Workplace....................................27 Security............................................................................28 GOOD CORPORATE CITIZENSHIP Sustainability and Responsible Corporate Citizenship.....................................................29 Respect and Appreciate Human Rights.........................30 Political Process.............................................................31 Questions or Concerns...................................................32 Receipt and Acknowledgement......................................33

A video message from our Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer
Click here to view the transcript of this video.

At Lockheed Martin, our core values – to do what’s right, respect others, and perform with excellence – unite us as a team and define how we operate every day. Building trust with our colleagues, customers, and communities depends on the integrity and high standards we share. That’s why I encourage you to read and understand Lockheed Martin’s “Code of Ethics and Business Conduct,” which provides guidance when we act on behalf of our organization. We hold every team member to the same standards, policies, and procedures. Many of these standards are higher than local laws or customs may require. We also expect and encourage you to step forward and speak up if you witness actions or behaviors that are inconsistent with our standards. You can do so with confidence – knowing that our Code of Conduct clearly states our zero-tolerance policy for retaliation, harassment, discrimination, or corruption. Lockheed Martin’s reputation depends on every one of our team members. So thank you for your commitment to upholding our core values. Together as OneLM, we can ensure our integrity and reputation for excellence continues to guide us. Jim Taiclet Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer
Video Transcript

Introduction
Lead with Integrity
Respect Others
Demonstrate Accountability
Conduct Business Fairly
Our Work Environment
Good Corporate Citizenship
Receipt and Acknowledgement
Lockheed Martin Code of Conduct

DO WHAT’S RIGHT We are committed to the highest standards of ethical conduct in all that we do. RESPECT OTHERS We recognize that our success depends on the talent, skills and expertise of our people. PERFORM WITH EXCELLENCE We understand the importance of our missions and the trust our customers place in us.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
We Promote Good Corporate Citizenship
We Lead with Integrity

We Respect Others

We Demonstrate Accountability

We Conduct Business Fairly

We Care About Our Work Environment

• CPS-001 Ethics and Business Conduct
Uphold the Code

• CPS-001 Ethics and Business Conduct • CPS-718 Disclosures to the United States Government • CRX-021 Internal Investigations

WE SET THE STANDARD
• Our Code establishes the principles by which we maintain our commitment to ethical business practices, which often go beyond what the law requires. • Follow both the letter and the spirit of the laws and regulations that govern our business and the countries in which we operate. • Cooperate in investigations. • Our Code applies to Lockheed Martin employees, our Board of Directors, consultants, contract laborers and others representing or acting for our Corporation. • Any waiver of the Code for executive officers or members of the Board of Directors may be made only by the Board or a Board committee and must be promptly disclosed to our stockholders on our website.
Why It Matters
• Maintaining the trust of employees, our customers and stakeholders is essential to ensuring sustainable success.
What to Watch Out For
• Violations of the Code may result in disciplinary action up to and including termination. • Leaders are accountable for actions that could influence employees to violate our Code.
Investigations
You must notify the Legal Department, Ethics Office or Security if you learn that a government agency or any third party is conducting an investigation or asking for information pertaining to a suspected violation of law. We must never destroy or alter any documents or electronic records, lie to or mislead an investigator or obstruct the collection of information relating to an investigation or any legal action brought on behalf of, or against, the Corporation. To the greatest extent possible, we will cooperate with government agencies responsible for investigating suspected violations of the law. If requested by Lockheed Martin, we will cooperate with investigations conducted by any government.
This prevents waivers of the Code from being hidden from the public and complies with New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) requirements and similar rules under the Securities and Exchange Commission and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
• CRX-021 Internal Investigations
Report Violations

• We take prompt action to report violations of the Code, policy or a contract provision.
• Any one of us may be the only person to see or suspect a potential violation. If we don’t report it, who will? • Timely reporting may allow issues to be resolved before they become larger issues.
• Failure to report may itself be a violation of this Code.
Ethics is here for you for guidance. You’ll receive information and resources to help address your concern: Call: 1-800-LM ETHIC (1-800-563-8442) When calling from outside the U.S., first dial the origin country’s exit code Email: [email protected] Mail: Corporate Ethics Office Lockheed Martin Corporation 6801 Rockledge Drive, MP-211 Bethesda, MD 20817
If you have reason to believe that questionable or illicit conduct exists, report suspected violations to your supervisor, manager, Human Resources Business Partner, Ethics Officer, Legal, Security, EEO Investigations, Global Diversity and Inclusion, Environment, Safety & Health, Sustainability, Internal Audit or the Audit Committee.
Employees may transmit concerns about accounting, internal controls or auditing matters and confidential or anonymous submission of questionable accounting or auditing matters to the Audit Committee of the Lockheed Martin Board of Directors. If you wish to raise a concern to the Audit Committee, you may do so by contacting the Corporate Ethics Office and your concern will be communicated to the Chair of the Audit Committee of the Board.
Audit Committee
Participate in Training

• Complete all required Business Conduct Compliance Training and annual Ethics Awareness Training.
• Training prepares us to recognize and effectively react to situations requiring ethical decision making.
• Be sure to complete your required training by the due date.
- Addresses the consequences of compliance violations. - Helps improve our understanding of topics in this Code.
Take Action
• Act with integrity, ask tough questions and understand how our words and actions affect our colleagues and the Corporation. • Use, and encourage others to use, the Voicing Our Values techniques to help take action and put our values into practice.
• Challenges to our values may be a normal occurrence in the work environment, but you must resolve them.
• Warning signs help you identify and correct potential problems before they become larger issues. • Assumptions and inferences can impact your impartiality and hinder ethical decision-making.
Voicing Our Values Techniques

• CPS-003 Nondiscrimination and Equal Employment Opportunity • CPS-564 Harassment-Free Workplace • CPS-734 Combating Trafficking in Persons • CRX-053 Workplace Security - Maintaining a Safe and Respectful Workplace Free from Threats and Violence
Zero Tolerance for Harassment

• Verbal or physical conduct that offends, abuses, intimidates, torments, degrades or threatens another person is prohibited. • You will help maintain a work environment that is free of physical, psychological, and verbal harassment or other abusive conduct.
• Success depends on the talent, skills and expertise of all employees. • Targets, as well as witnesses, of harassment may struggle to contribute to their full potential.
• Be knowledgeable of prohibited conduct by reviewing policy. • Be mindful of your own behavior and how your actions, words and deeds could impact someone else.
EXAMPLES OF SEXUAL HARASSMENT INCLUDE:
• Unwanted sexual advances, including verbal sexual advances and propositions. • Offering employment benefits in exchange for sexual favors. • Making or threatening reprisals after a negative response to sexual advances. • Leering or making sexual gestures. • Displaying pornographic or sexually suggestive objects, pictures, cartoons, or posters. • Using inappropriate terms of endearment. • Verbal abuse of a sexual nature. • Graphic verbal commentaries about an individual’s body. • Sexually degrading words used to describe an individual. • Suggestive or obscene letters, notes, or invitations.
• Harassment can occur in many forms, inside and outside of the workplace. • Be an Upstander and intervene when you witness, or become aware of, harassing or discriminatory behavior.

• CPS-003 Nondiscrimination and Equal Employment Opportunity • CPS-564 Harassment-Free Workplace • CPS-734 Combating Trafficking in Persons • CRX-515 Business Resource Groups and Employee Networks • CRX-537 Military Leave
Zero Tolerance for Discrimination
• Do not discriminate against employees or applicants on the basis of characteristics protected by applicable law or Lockheed Martin policy. • Follow all policies and laws that relate to recruitment, selection, and other aspects of employment such as promotion, demotion, transfer, layoff, termination, compensation, education, training and disciplinary action.
• Excluding someone based on protected characteristics - simply by virtue of who they are - is against the law.
• Perpetuating stereotypes is a form of discrimination that can damage the culture and the performance of the Corporation.

• CPS-001 Ethics and Business Conduct • CPS-003 Nondiscrimination and Equal Employment Opportunity • CPS-564 Harassment-Free Workplace • CPS-575 Providing Reasonable Accommodations in the Workplace and for Applicants
Do Not Retaliate
• Lockheed Martin does not tolerate retaliation against anyone who, in good faith, makes an inquiry, participates in an investigation or reports misconduct. Contacting Ethics in “Good Faith” does not mean you have to be right, but it does mean you believe the information provided is truthful.
Retaliation is the unfair or inappropriate treatment against an employee for reporting misconduct, filing a complaint, assisting another in making a complaint, participating in a company internal investigation, or making an ethics-related inquiry.

• Fear of retaliation is one of the most common reasons why employees won’t speak up or take action. • Retaliation destroys trust.
• If someone tries to stop you from reporting an issue, that person can be subject to disciplinary action up to and including termination. • Retaliation can be subtle, including changes in work assignments or casual work-related interactions, or it can be overt at times. You are legally protected from reprisals for reporting fraud, waste or abuse on government programs.
U.S. law also entitles each Lockheed Martin employee to certain rights and protections against reprisals if the employee discloses, to certain governmental officials or to the Legal Department or Ethics Office, information that the employee reasonably believes is evidence of gross waste, mismanagement, abuse of authority, or violations of law related to U.S. government contracts, grants, or funds; or evidence of a substantial and specific danger to public health and safety.

• CRX-015 Protection of Sensitive Information • CRX-016 Privacy - United States • CRX-017 Personal Data Protection - Non-U.S.
Respect Privacy
• Do not collect, store or access Personal Information / Personal Data (PI / PD) unless there is a legitimate business purpose and you have the proper authorization. • Respect the privacy and dignity of all individuals and safeguard the confidentiality of employee records and information.
• Safeguarding PI / PD builds trust with employees and customers.
• Be sure to use the appropriate Personal Information / Personal Data legend in the subject line of email messages. • Ensure that you do not share Personal Information / Personal Data on social media or collaborative workspaces. • Data disclosed to third parties should be limited to only the information necessary to fulfill contractual agreements.

Personal Information (PI) and Personal Data (PD) at Lockheed Martin is defined as any information that permits the identity of an individual to be determined. PI includes identifiable information for persons in the US; PD for persons in non-US countries.
PERSONAL INFORMATION / PERSONAL DATA
• When transmitting PI / PD outside the LM network (LMI), use approved secure e-mail and file transfer methods.
• Privacy regulations differ by country.
This includes electronic communication systems, information resources, materials, facilities and equipment.

• CPS-007 Personal Use of Lockheed Martin Assets • CPS-037 Proper Use of Computing and Information Resources • CRX-014 Individual Conflict of Interest • CRX-156 Purchasing Cards (P-Cards) • CRX-253 Social Media • CRX-303 Electronic Messaging • CRX-325 Business Travel • CRX-327 Commercial Cards • TVL-001 Business Travel Handbook
Use Assets Responsibly

• You are responsible for properly using and protecting our Corporation’s, and our customers’, property and assets, and ensuring their efficient use. • Do not waste nor abuse company and customer assets.
• Our customers expect us to protect resources that they entrust to us. • Unauthorized use of company assets, as well as third-party information entrusted to the Corporation, can create risks to the Corporation and impact our financial obligations. • Improper use of assets could result in violations of law and failure to meet contractual obligations and / or deviations from company policies; all of which can have unintended impacts to the corporation and individuals.
• Misuse of U.S. Government assets can constitute a federal crime. • Activities of concern include:
- Using customer assets for anything that is not specifically or contractually allowed / authorized. - Sending / storing / handling sensitive information on a personal computing device. - Sending company information to personal email addresses. - Using unapproved electronic items to store data in company / customer assets. - Personal use of company assets. - Personal use of your corporate credit card.
Keep Accurate Business Records and Accurately Communicate to the Public

• You will honestly and accurately prepare all business and financial records. • Conduct business transparently while not compromising proprietary or confidential information. • Never misrepresent facts or falsify records. • Promptly and accurately enter all business transactions in our books and business records. • You have an obligation to make accurate disclosures to the public and our stockholders.
• Customers, regulators and investors expect us to maintain the integrity of our records. • Complex business processes demand that each of us be able to rely on the accuracy of the data we provide each other to serve our customers.
• Every business record you provide helps us provide accurate disclosures to all government and regulatory agencies. • Be mindful of any proprietary or confidential information included in any type of public disclosure / external communication.
• Properly account for all costs, including labor, travel, material and any other expenses. • If you prepare business or financial records or public communications on behalf of the Corporation, ensure that they contain comprehensive, fair, timely, accurate and understandable information. • Inaccurate pricing information submitted in proposals, reporting of business travel expenses, or labor charging, violates policy and may also be illegal.
• CPS-011 Internal Control and Enterprise Risk Management • CPS-020 Fair Disclosure of Material Information and Financial Information to the Investment Community and Public • CPS-201 Release of Information • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CRX-011 International Business Development Consultants
Public disclosures: Include reports or documents filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and other regulatory authorities as well as other public communications made by the Corporation, including external presentations.
Public Disclosures
• Keeping accurate records is critical to accurately recording and reporting financial transactions and meeting our legal and regulatory obligations. • Our investors rely on accurate public disclosures.
Protect Sensitive Information

• Use, store and protect Sensitive Information in accordance with applicable requirements. • Obtain proper authorization before disclosing or receiving any Sensitive Information. • Do not share Sensitive Information in unapproved forums.
• We generate, acquire, and access large amounts of valuable information every day. This information provides us and our customers with business, technological, and economic advantage; and can also impact national security interests.
• Obtain proper approval before publishing or making external presentations about Lockheed Martin or its customers or partners. • Wherever we do business there are countryspecific laws and regulations governing import / export issues and unique information handling and safeguarding requirements. • Use social media responsibly and take extra care to protect information about the Corporation, your colleagues, customers and yourself. • Information protection requirements stay in effect even if your employment or engagement with the Corporation ends.
To obtain approval, U.S. employees should visit the PIRA tool (Public Information Release Authorization System - https://pira.us.lmco.com/pira/). Non-U.S. employees should contact Communications for the appropriate point of contact to review their materials.
Proper Approval
• CPS-022 Ethical Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence • CPS-201 Release of Information • CPS-310 International Trade Controls and Compliance • CPS-569 Security • CRX-002 Intellectual Property • CRX-013 Government and Competitor Information • CRX-015 Protection of Sensitive Information • CRX-016 Privacy - United States • CRX-017 Personal Data Protection - Non-U.S. • CRX-253 Social Media • CRX-303 Electronic Messaging
Information in any or all of these categories: Personal Information (U.S.), Personal Data (Non-U.S.), Export Controlled Information, Lockheed Martin Proprietary Information, Third-Party Proprietary Information, Attorney-Client Privileged Information and / or Attorney Work Product and Protected Information.
Sensitive Information
Accurately Charge Labor and Other Costs

• Follow the business-specific labor recording policies and procedures where you work. • Properly account for all costs including labor, travel, material and other costs.
• You will be held accountable for ensuring that your labor charges are accurate. • Excessive use of online collaboration tools / Internet for non-work purposes could lead to labor mischarging. • Inaccurate labor charging or leaders approving / directing mischarging may violate policy and may be illegal.
These costs include, but are not limited to, normal contract work, work related to normal contract research and development and bid and proposal activities. This means that transactions between the Corporation and outside individuals and the organizations are accounted for and executed in accordance with generally accepted accounting practices and principles in the United States, and in the countries where we do business.
• CMS-505 Recording and Verification of Direct Labor Costs • CPS-441 Cost Estimating/Pricing • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CRX-325 Business Travel • CRX-327 Commercial Cards
• The violation of labor charging practices is one of the most frequent case allegations atLockheed Martin. • Improperly charging time on customer contracts could be considered fraud.
• CPS-008 Gifts, Hospitality, Other Business Courtesies, and Sponsorships • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CRX-010 U.S. Business Development Consultants • CRX-011 International Business Development Consultants • CRX-013 Government and Competitor Information • CRX-014 Individual Conflict of Interest
Avoid Individual Conflicts of Interest

• Be fair and impartial in all business dealings. • Place the interest of Lockheed Martin over personal interests in matters relating to the Corporation’s business. • Avoid actual conflicts of interest as well as activities that create the appearance of one. • Do not use our contacts or position in the Corporation to advance outside or personal interests. • Our Corporation’s property, information or opportunities will not be used for personal gain. • We will provide immediate written disclosure of actual or potential conflicts of interest.
• You may think you can balance multiple interests at the same time and not realize when your loyalties are divided.
• Disclose all potential conflicts of interest to get an independent, objective assessment and take appropriate mitigating actions.
Avoid Conflicts of Interest with Government Employees

NOTE: U.S. Government employees should have their government ethics official review their background before applying for work.

• Comply with all conflicts of interest laws and regulations covering employing or acquiring the services of government employees, which includes military personnel.
• Our success and ability to compete depends on ensuring that we do not hire or work with current or former government employees in a manner that creates a real or perceived conflict of interest. • The nature of the information and the competitive advantage and / or detail of information that the individual possesses may itself create a conflict.
• There are rules for contacting or negotiating with current government employees to discuss their potential future employment or their service as consultants or subcontractors. • There may be restrictions regarding roles or responsibilities that former government employees may perform.
• CPS-008 Gifts, Hospitality, Other Business Courtesies, and Sponsorships • CRX-014A Conflict of Interest - Government Employment
U.S. Government employees should have their government ethics official review their background before applying for work. This process may result in a recusal letter (also called a disqualification letter) and an ethics opinion letter which would explain any restrictions or bans on their potential post-government employment.
Review Their Background
• CRX-014E People with Organizational Conflict of Interest Restrictions • CRX-600 Organizational Conflict of Interest

Avoid Organizational Conflicts of Interest
• Avoid, neutralize, or mitigate Organizational Conflicts of Interest (OCI). • Prevent unfair competitive advantage or conflicting roles that might impair objectivity.
• You may have worked with multiple customer representatives across different programs. • A conflict on one government contract could compromise our ability to work on another. • Failure to properly screen new business opportunities could result in disqualification or loss of business. • Policies are intended to prevent unfair competitive advantage and conflicting roles that might bias the Corporation’s judgment.
• Be sure to report and maintain the disclosure of any OCI restrictions.
Visit CRX-600 for the process regarding preparing a screening letter and distributing it through the OCI Reporting System.
OCI Reporting System

Do Not Engage in Insider Trading
• You must comply with all applicable securities laws and avoid even the appearance of impropriety. • You must not engage in insider trading, which means you must not:
• Investors’ trust in us and the public’s trust in financial markets depend on confidence that trades in securities are based on publicly available information.
• If you learn of important information related to Lockheed Martin or a third party before the general public knows, there’s a possibility it could be considered material nonpublic information. Communicating such information to others may violate the law, even if you personally do not trade any securities based on such information.
Securities include stock (common and preferred), restricted stock units, employee stock options, bonds, notes, debentures, put or call options, or similar instruments.
[CEROS OBJECT]Lockheed Martin Code of Conduct
• CPS-016 Mergers, Acquisitions, Divestitures, Business Ventures, and Investments • CPS-020 Fair Disclosure of Material Information and Financial Information to the Investment Community and Public • CPS-722 Compliance with United States Securities Laws
- trade in the securities of any company (including Lockheed Martin) when you possess material, nonpublic information (MNPI) about that company, - suggest (or “tip”) that others engage in such trading, or - share MNPI with others (including other employees of Lockheed Martin) unless authorized to do so.
Trading includes all transactions in securities, including fund transfers or fund reallocations into or out of the Lockheed Martin stock fund in your savings, benefit or deferred compensation plans; any purchase or sale of common stock (including the sale of shares received from vested restricted stock units); gifts of Lockheed Martin securities if the value of the gift is established for tax purposes at the time the gift is made; and the exercise of employee stock options. It also includes trades executed pursuant to limit orders, even if these were placed prior to your coming into possession of material, nonpublic information.
Information is “material” if there is a substantial likelihood that a reasonable investor would consider it important in deciding whether to trade a security. Both positive and negative information can be “material.”
Information is considered “nonpublic” until it is widely disseminated. This means it has been in the news or released in the form of an official announcement and enough time has passed in the open market, privately or in company plans for the information to be assimilated by the general public (typically the next business day).
• You are responsible for making sure that you do not share MNPI with your family and that you do not share MNPI with other employees of Lockheed Martin or third parties without express authorization. You can be held liable for the actions of others with whom you share MNPI.
• Each of the terms “securities,” “trading,” “material” and “nonpublic” have extensive and complicated legal definitions..

Ensure the Quality and Safety of Our Products and Services
• Be committed to meeting customer and company expectations by identifying and adhering to policies and procedures that ensure Quality, Mission Success, and System Safety Engineering throughout the product or service lifecycle. • Develop and deliver high-quality products and services that meet all applicable quality and safety standards for their intended use. • Implement and follow disciplined systems to measure performance and consistency.
• Quality assurance processes detect and correct defects to ensure delivery of safe products and services that meet all contractual, legal and regulatory requirements.
• All quality concerns will be taken seriously, whether from inside or outside the company, and addressed appropriately.
• CPS-002 Quality, Mission Success, and System Safety
• Seek to continuously advance safety and quality in the design and manufacture of our products and services. • If something does not appear to conform to the standards expected, use a “See Something, Say Something” approach and notify your leader.
• CPS-022 Ethical Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence
Use Artificial Intelligence Responsibly

• The benefits of Artificial Intelligence (AI) will be pursued while ensuring the procurement, development and our internal use are in accordance with our values.
• We have established an Artificial Intelligence Ethics Advisory Committee to develop further guidance and to adjudicate concerns related to the above principles. Employees who have concerns about adherence to our Ethical AI principles should contact Ethics or a member of the Artificial Intelligence Ethics Advisory Committee. • Practice the ethical development of AI capabilities and follow our principles in areas related to AI such as machine learning, data analytics, and data mining.
• We recognize that AI holds tremendous potential benefits for our customers and our operations, and we intend to be an industry leader in this revolutionary technology. • Increased access to data and high- performance computing has unleashed unprecedented opportunities in AI that are changing the way companies operate in all industry sectors. • As a rapidly evolving discipline, there may be risks that must be considered and addressed in the design and implementation of AI systems. • There are significant potential legal risks associated with the use of third party AI models, tools and data sets as well as associated with reliance on AI to perform tasks and generate content.

Lockheed Martin subscribes to the following ethics principles in our AI design, development, deployment, and internal use: - Responsible - Equitable - Traceable - Reliable - Governable See CPS-022 for details.
• Contact our Artificial Intelligence Ethics Advisory Committee to adjudicate concerns or receive guidance related to our AI principles.
Fair Competition

• Be fair when dealing with customers, suppliers, competitors and employees. • Ensure all communications and representations to prospective customers, suppliers and partners are accurate and truthful. • Perform all contracts in compliance with laws, specifications, requirements, and contract terms and conditions. • Never request, accept, use, copy or distribute any information to which Lockheed Martin is not legitimately entitled.
• These activities not only violate policy, but also may be illegal:
- Discussing, using, copying or distributing any unauthorized information (especially pricing, bid strategy or customer information obtained during bids or negotiations or in connection with attendance at trade shows, industry groups or training) without seeking guidance from the Legal Department or Ethics Office.
• Maintaining the highest standards of integrity in our procurement processes, and in bidding or negotiating contracts, is essential to performing on current and future contracts, products and services. • If you receive unauthorized information, or are uncertain as to the Corporation’s legal right to use or share the information, do not copy, distribute or use it until guidance from the Legal Department has been provided.

• CPS-009 New Business Opportunity Management • CPS-441 Cost Estimating/Pricing • CPS-729 Compliance with United States Antiboycott Laws • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CRX-011 International Business Development Consultants • CRX-013 Government and Competitor Information • CRX-015 Protection of Sensitive Information
• Report any inquiries made to us in connection with our bid or negotiation activities to the Legal Department.
Abide by International Trade Laws

• Comply with all export and import laws and regulations that cover the transfer of certain technical data, equipment and technology between countries. • Do not engage in or support restrictive international trade practices or boycotts not sanctioned by the U.S. Government. • Comply with U.S. law and the laws of the countries where we do business.
• Any written or oral request request in bids and proposals to comply with boycotts not sanctioned by the U.S Government is a boycott red flag and must be immediately reported to your Element Legal Counsel, even if Lockheed Martin decides not to proceed with the bid / proposal.
• Export and import violations, and illegal boycotts, damage the trust and transparency needed to transact legitimate and long-term business. • Customers expect fair and open competition in how we do business worldwide with our competitors, suppliers and customers.
This includes explicit or more subtle contract language such as, “The Seller agrees to fully comply with the Israeli Boycott rules and certifies that the equipment to be supplied under this contract will not be of Israeli origin…” or, “The Seller’s specialists shall abide by all rules and laws of Country X.”
Written or Oral Requests
• CPS-310 International Trade Controls and Compliance • CPS-729 Compliance with United States Antiboycott Laws • CRX-015 Protection of Sensitive Information
• The U.S. maintains sanctions or embargoes that prohibit engaging in certain business activities in specified countries, as well as with specified individuals and entities. For example, U.S. law prohibits interaction with identified terrorist states and organizations.
Actions of Third Parties

• Do not engage with third parties to conduct business in a manner that is contrary to law or to our policies or that would circumvent our values and principles. • Provide training to certain third parties on our ethical values, policies and compliance requirements.
• Be certain that all third parties, including business development consultants and independent contractors, understand and comply with their obligations to act in accordance with applicable laws and regulations and the Corporation's requirements for doing business.
• Be certain that consultants, representatives and third parties certify that they will comply, and are acting in compliance with, the Corporation’s requirements for doing business on its behalf.
• The actions of third parties who conduct business on our behalf can impact our reputation. • Improper actions conducted on our behalf could result in criminal or civil liability for the Corporation or for the employee(s) responsible for the third party. • We may be accountable for the actions of anyone conducting business on our behalf.
• CPS-008 Gifts, Hospitality, Other Business Courtesies, and Sponsorships • CPS-113 Acquisition of Goods and Services • CPS-716 Compliance with the Anti-Kickback Act of 1986 • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CPS-734 Combating Trafficking in Persons • CRX-010 U.S. Business Development Consultants • CRX-011 International Business Development Consultants • CRX-025 Teaming Agreements • CRX-106 Managing Major Subcontracts • CRX-126 Counterfeit Prevention
Corruption and Kickbacks will not be Tolerated

• Do not offer, give, solicit or receive any form of bribe or kickback. • Walk away from any business engagement that would violate any anticorruption law or our Code of Conduct, or that would create even a perception of impropriety.
• A party’s poor reputation, ties to government and public officials, questionable or unusual circumstances, unusual compensation and questionable accounting or invoicing, or insufficient capabilities are red flags. • Expressions such as; ‘that’s the way business is done here’, ‘everyone does it’, ‘that is what is expected to win the contract’, or ‘this is normal in this country’ are also red flags.
• Corruption creates unfair competition, increases cost and jeopardizes the quality and capability of our products and services. • Bribery, including even the attempt to corrupt, is illegal and may be enough to be prosecuted under U.S. and other countries’ laws. • Conducting business where there is even a hint of impropriety could cause irreparable reputational harm, in addition to legal harm to our business such as,
• CPS-008 Gifts, Hospitality, Other Business Courtesies, and Sponsorships • CPS-021 Good Corporate Citizenship and Respect for Human Rights • CPS-310 International Trade Controls and Compliance • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CRX-011 International Business Development Consultants • CRX-015 Protection of Sensitive Information
Bribery is directly or indirectly paying, promising, giving, offering or authorizing to give anything of value to anyone for the purpose of influencing that person to misuse his or her position.
A “red flag” is a fact, event, or set of circumstances, or other information that may indicate a potential legal compliance concern for illegal or unethical business conduct, particularly with regard to corrupt practices and non-compliance with anti-corruption laws.
Corruption is any unlawful, illegitimate or improper behavior intended to gain an advantage and includes bribery, fraud, extortion, theft, abuse of power and money laundering.
A kickback is any money, fee, commission, credit, gift, gratuity, thing of value, loan, entertainment, service or compensation of any kind that is provided, directly or indirectly, to any prime contractor, prime contractor employee, subcontractor or subcontractor employee for the purpose of improperly obtaining or rewarding favorable treatment in connection with a prime contract with the U.S., or a subcontract in connection with a prime contract with the U.S.
• CPS-720 Compliance with the Antitrust Laws
Strictly Adhere to all Antitrust Laws

• Do not enter into business arrangements that eliminate or discourage competition or that give us an improper competitive advantage.
• Discussion or agreement with competitors or partners to allocate bids, contracts, customers, markets or territories, or coordinate pricing or limit supply of products or services.
• Antitrust laws apply world-wide and protect trade and commerce from unlawful restraints and monopolies, or unfair business practices, protecting customers, Lockheed Martin and our business partners.
Antitrust rules apply to more than you might think. They require that you avoid engaging in certain activities and business discussions. Examples from the policy include:
• Price fixing. • Boycotting suppliers or customers. • Pricing intended to run a competitor out of business. • Disparaging, misrepresenting or harassing a competitor. • Teaming with companies to create less competitive outcomes for customers or blocking competitors to prevent market entry.
• Restricting the hiring or salaries of employees with competitors or suppliers. • Entering into agreements with competitors to divide the market by allocating bids, contracts, territories or markets or restricting the production or sale of products or product lines. • Conditioning the sale of one product or service on the sale of another product or service. • Conditioning the sale or purchase of product or services on the requirement that the seller or purchaser not do business with competitors of the Corporation.

• CPS-008 Gifts, Hospitality, Other Business Courtesies, and Sponsorships • CPS-716 Compliance with the Anti-Kickback Act of 1986 • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CRX-010 U.S. Business Development Consultants • CRX-011 International Business Development Consultants
Accept and Provide Only Appropriate Business Courtesies
• Avoid even the perception that favorable treatment is being sought, received or given. • Ensure that any business courtesy offered or accepted is permitted by law and policy.
• Complex rules and monetary limits apply when dealing with Public Officials. Consult policy and obtain guidance if you are uncertain if an action is inappropriate or within the allowable limits. • Understand that a business relation is any individual or group with whom we do business or we seek to do business or who seeks to do business with us. • We have established country-specific, permissible thresholds which may not be exceeded without prior approvals. • It is not only the value of the business courtesy that matters. The simple act of offering, giving or receiving any business courtesy, or the perception of an intent to gain an improper business advantage, may be illegal or unethical. • No sponsorship may be undertaken to directly or indirectly procure future business or with the intent to obtain or retain business, secure an improper advantage or induce anyone to act improperly. • Global Supply Chain Operations employees and those who are involved in the process of directing business or funds are held to a higher standard. • Giving cash, cash equivalents or gift cards to business relations is prohibited.
• When people exchange gifts or business courtesies, it can create the perception that favors were granted in order to improperly influence business judgment. • You will compete on the merits of our products and services and not give business courtesies to gain an unfair competitive advantage. • Source products and services fairly to avoid accepting business courtesies that may cause even the perception of an inappropriate business relationship.

A business courtesy is any tangible or intangible thing of value for which fair market value is not paid by the recipient.
Business Courtesies

• CPS-015 Environment, Safety and Health (ESH)
Safe and Healthy Work Environment

• Provide a safe and healthy work environment and operate in a manner that protects the environment, conserves natural resources and prevents pollution. • Stop immediately if something that is unsafe or can harm the environment is identified.
• Report any non-compliance to posted warnings, procedures and regulations. • Any accident, injury or close call sustained on the job, or any environment, safety or health concern you may have must be reported immediately.
• Whether working on-site or at home, it is important that our workplace is safe and beneficial to our personal welfare and the environment.

• ID (Identify): assess the situation to identify safety risk • E (Evaluate): determine the best course of action to address the risk
• A (Act): communicate or report your safety concerns to colleagues and your leader, and mitigate the risk
• CRX-525 Tobacco- and Smoke-Free Environment • CRX-545 Drug-Free Workplace
Maintain a Drug-Free Workplace

• The possession, use, sale, manufacture, transfer, trafficking in, or being under the influence of illegal drugs, or the abusive use of legal drugs, in the workplace or in the performance of company business, is prohibited. • Being under the influence of alcohol in the workplace or in any other location where we perform business on behalf of the Company is prohibited. • Complying with the Drug-Free Workplace Act of 1988 and federal, state, and local laws and regulations concerning violations of criminal drug statutes in the workplace is a requirement. • We will not knowingly hire or rehire individuals who possess, use, sell, manufacture, transfer, or traffic in illegal drugs.
• State and local initiatives legalizing the use of marijuana for medical and / or recreational purposes do not alter Lockheed Martin’s obligation as a federal contractor to maintain a drug-free workplace. • Being “under the influence” doesn’t necessarily mean being above the legal limit. • If you or a colleague has a drug or alcohol dependency issue, take advantage of company resources for help.
• Using an illegal substance can negatively impact your ability to perform safely, be productive and obtain or maintain a security clearance or continued employment.

• Protect our people, operations and assets. • Take action to mitigate threats to employee safety. • Properly safeguard all classified material and other information entrusted to us. • Comply with and seek to exceed customer and national security policy requirements. • Maintain dedicated counterintelligence and insider threat detection programs. • Use a thorough and objective security investigative process.
information from external sources regarding company people, facilities, operations, programs or products. It’s up to you to report it. • Ensure that any unauthorized access to information or assets is reported. • An email security threat can contain references that may appear to be legitimate in order to trick you into thinking it’s coming from a legitimate source.
• Security compliance benefits our Corporation, customers, national security and global stability. • Adherence to security requirements supports contract performance and enables our products and services to be delivered uncompromised.
• CPS-569 Security • CRX-052 Crisis Management • CRX-053 Workplace Security - Maintaining a Safe and Respectful Workplace Free from Threats and Violence • CRX-055 Travel or Assignment to Elevated Risk Locations • CRX-056 International Security Operations • CRX-057 LMSecurity Procedures • CRX-059 Insider Threat Detection Program
• A strong security program fosters a safe environment for our workforce. • We are a prime target for a number of threat actors seeking to gain information or to damage / destroy our capabilities.
• You may be the first person to notice concerning changes in a colleague’s behavior, or suspicious or unusual activity, such as inquiries or requests for

• CPS-021 Good Corporate Citizenship and Respect for Human Rights • CPS-803 Sustainability • CRX-202 Restrictions on the Use of Chemical Substances in Products and Processes • CRX-350 Energy
Sustainability and Responsible Corporate Citizenship

• Fosters innovation, integrity and security across our platforms and services. • Maximizes the positive contributions of our products and services on the environment, the economy, community development and infrastructure resilience. • Seeks to avoid and minimize negative consequences of business activities across the full value chain. • Operates in a manner that protects the environment, as well as people, by conserving natural resources, preventing pollution an ensuring ethical business conduct.
• Drives affordability, risk mitigation and innovation throughout our business strategy and our value chain.
• Ensures long-term competitiveness of our business and health of our communities and planet. • Improves customer and stakeholder collaboration.
• Signifies commitment and fosters a sense of purpose that align with employee values.
Respect and Appreciate Human Rights

• Respect for human rights is an essential element of being a good corporate citizen. • The importance of human rights across the globe, includes:
• Protecting and advancing human rights:
• CPS-001 Ethics and Business Conduct • CPS-003 Nondiscrimination and Equal Employment Opportunity • CPS-021 Good Corporate Citizenship and Respect for Human Rights • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CPS-734 Combating Trafficking in Persons • CPS-803 Sustainability • CRX-515 Business Resource Groups and Employee Networks
- Treating employees with respect, championing diversity and inclusion. - Promoting fair responsible employment and wage & hour practices. - Providing fair and competitive wages. - Prohibiting harassment, bullying, discrimination, use of child or forced labor, or trafficking in persons for any purpose.
• Trafficking in persons and slavery are issues around the world, and if we are not mindful, we could unwittingly engage with third parties who violate these principles.
• Suspicious behavior or activities may indicate the presence of human rights violations.
- Maintains our commitment to integrity and our core values. - Promotes employee satisfaction and productivity. - Enhances competitiveness of our business.
• Employees can exercise their right of free association and to choose or not choose collective bargaining representation. • Employees and suppliers must take the appropriate steps to ensure respect for human rights in our business. • We adhere to human rights precepts in our relations with stakeholders and through our products and services.
Political Process

• Follow corporate policy and the law concerning the political process in all countries where we do business. • Uphold the spirit and letter of all laws relating to our participation in the political process.
• Laws governing political contributions and lobbying are complex. • Even unintended violations can result in loss of business opportunities, damage to our reputation and civil and criminal penalties.
• CPS-004 Political Activity • CPS-005 International Operations • CPS-008 Gifts, Hospitality, Other Business Courtesies, and Sponsorships • CPS-045 Government Affairs • CPS-730 Compliance with Anti-Corruption Laws • CRX-251 Charitable Contributions
• Prohibited • We Support the Political Process • Require Caution • Permitted
You are encouraged to: • Participate in the Lockheed Martin Employees’ Political Action Committee, if eligible. • Participate personally in civic affairs and the political process on your own time, and at your own expense. • Support the political parties and candidates of your choice.
• Using any Lockheed Martin funds, assets or facilities for the benefit of political parties or candidates anywhere in the world without obtaining prior written approval.
• Public Office - Conflicts of interest can arise if you seek or hold public office or serve on commissions or advisory groups. • Lobbying - Lobbying can be direct or indirect, but either way, it is highly scrutinized and must follow policy. • U.S. Congressional and Executive Branch - It is important that Lockheed Martin present a single, consistent business message to our U.S.-based customer community. Government Affairs works with business areas to develop a united approach to the Corporation’s U.S.- based marketing initiatives and policy, regulatory and legislative strategies. To this end, Government Affairs must authorize any interaction with U.S. Congressional members or Executive Branch officials in Washington, D.C. or their employees and staff. • State and Local Governments - Government Affairs must authorize any interaction with state and local government officials on behalf of Lockheed Martin. • Non-U.S. Governments - Follow policy when engaging with Non-U.S. Government Officials to assure that their activities are permitted and within local laws and regulations. • Individual Political Contributions - Some state and local laws may restrict, limit or require disclosure of personal political contributions made by individual employees or their immediate family members.
Require Caution
• Many countries, in addition to the United States, may prohibit corporate political contributions. This may include donating corporate funds, goods or services, directly or indirectly, to political candidates, including through consultants or employee work time. • Local and state laws may limit corporate political contributions and activities.
We Support the Political Process

Who should I contact if I have a problem, question or concern?

In general, start by discussing the situation with your supervisor or manager. If that is not practical or if your manager is not able to help you resolve the matter, it is your responsibility to continue to speak up and seek resolution. For more information, please visit the Corporate Ethics and Business Conduct website to review our “How the Ethics Process Works” brochure.
800-LM ETHIC (800-563-8442) International: Dial the United States access code 01 and 800-563-8442 For the Hearing or Speech Impaired: 800-441-7457
Office of Ethics and Business Conduct Lockheed Martin Corporation 6801 Rockledge Drive Bethesda, MD 20817
Audit Committee:

You acknowledge that you have read and will abide by Setting the Standard, the Lockheed Martin Code of Ethics and Business Conduct (the Code). You are acknowledging that you understand that each Lockheed Martin employee, member of the Board of Directors, consultant, contract laborer or other agent representing or acting for the Corporation is responsible for knowing and adhering to the principles and standards of the Code. You are also acknowledging that you understand that violations of the Code are cause for corrective action, which may result in disciplinary action up to and including discharge. To take credit in Atlas Learning, click here and complete "TAKE CREDIT (STEP 2)".
SETTING THE STANDARD Updated October 2023. Lockheed Martin Corporation 6801 Rockledge Drive Bethesda, MD 20817 ©1995-2023. Lockheed Martin Corporation. All rights reserved.
1-800-LM ETHIC (1-800-563-8442) [email protected] Corporate Ethics Office Lockheed Martin Corporation 6801 Rockledge Drive, MP-211 Bethesda, MD 20817

Keyword Search
Type a keyword in the box below:.
- A Message from Our Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer Jim Taiclet Chairman President Chief Executive Officer CEO
- Our Values standard integrity stakeholders customers right respect perform
- Uphold the Code principles ethical business practices employees board of directors consultants contract laborers others laws regulations investigations violations trust stakeholders customers violations disciplinary action termination accountable report question concern waiver board committee Legal Department Ethics Office Security government agency third party conducting investigation suspected violation law destroy alter documents electronic records lie mislead investigator obstruct information legal action agencies investigating violations Code public New York Stock Exchange NYSE Securities and Exchange Commission Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
- Report Violations action report reporting violations policy contract provision potential violation violations timely reporting failure suspected questionable conduct supervisor human resources ethics legal security EEO Investigations environment safety and health global diversity and inclusion internal Audit Committee guidance information resources concern illicit contact manager Human Resources Business Partner Ethics Officer Security Global Diversity Inclusion employees concerns accounting internal controls auditing matters confidential anonymous Corporate Ethics Office Chair Board
- Participate in Training training values real-life scenarios workplace violations violation required training compliance ethics awareness training individual employees application
- Take Action integrity questions actions colleagues corporation values conflicts potential violations law policy leadership personnel voicing our values identify correct problems issues unconscious bias ethical decision-making questions data talk reframe issue techniques
- Zero Tolerance for Harassment tolerance harassment verbal physical conduct abuses intimidates torments degrades threatens person environment psychological verbal harassment abusive conduct team witnesses unwelcome touching assault impeding movements blocking movements accessing transmitting displaying offensive messages images cartoons derogatory comments epithets slurs jokes objects sexual harassment behavior words deeds electronic communication online collaboration tools outside workplace policies conduct off-premises work U.S. law employee rights protections reprisals governmental officials Legal Department Ethics Office gross waste mismanagement abuse authority violations government contracts public health safety
- Zero Tolerance for Discrimination discrimination employees applicants characteristics protected law laws policy policies recruitment selection promotion demotion transfer layoff termination compensation education training disciplinary action diverse talents perspectives solutions value virtue unconscious bias culture performance harassment overt race ethnicity religion color sex pregnancy age veteran status ancestry sexual orientation gender identity expression marital status family structure genetic information mental physical disability legally protected characteristic
- Do Not Retaliate zero tolerate retaliation good faith inquiry participates investigation reports misconduct fear employee employees trust reporting termination interactions legally protected reprisals fraud waste abuse government programs inappropriate treatment complaint participating internal investigation ethics-related inquiry truthful
- Respect Privacy personal information data business purpose authorization privacy dignity individuals safeguard confidentiality employee records externally file transfer trust employees customers protections appropriate email messages social media collaborative workspaces third parties necessary contractual agreements
- Use Assets Responsibly responsible protecting customers property assets use waste abuse customer company resources entrust entrusted unauthorized third-party information risks financial obligations improper violations violation laws law failure contractual obligations deviations policies unintended individuals misuse U.S. Government federal crime concern using customer contractually allowed authorized sending storing handling sensitive information personal computing device email addresses unapproved electronic items memory sticks data corporate credit card care guard borrow remove permission communication systems resources materials facilities equipment
- Keep Accurate Business Records and Accurately Communicate to the Public honestly accurately business financial records conduct business transparently compromising proprietary confidential information misrepresent fact falsify records promptly transactions books obligation public stockholders accurate disclosures customers investors maintain processes data accurate records legal regulatory obligations public company trust confidence public disclosures inputs government agencies external communications account costs labor travel material expenses behalf ensure comprehensive fair timely accurate understandable violate policy illegal inaccurate pricing submitted proposals reporting travel expenses labor charging U.S. Federal Acquisition Regulatory Council defense contractor reports documents U.S. Securities and Exchange Committee regulatory authorities presentations
- Protect Sensitive Information use store protect sensitive information applicable requirements obtain authorization disclosing receiving recipients security clearance need to know social media responsibly conscious share unapproved generate acquire access valuable customers business technological economic advantages national security interests incident mishandling information damage reputation partners countries proper approval publishing making external presentations country-specific laws regulations import/export issues handling safeguarding requirements data security sensitivity safe colleagues protection engagement ends facilities customer locations working home public remotely Personal Information U.S. Personal Data Non-U.S. Export Controlled Information Proprietary Information Third Party PIRA employees Public Information Release Authorization tool point of contact Communications
- Accurately Charge Labor and Other Costs business-specific labor recording policies procedures account costs labor travel material improperly charging time customer contracts fraud accountable labor charges accurate recording time excessive online collaboration tools internet non-work purposes labor mischarging violate policy illegal falsifying timekeeping records incorrectly objective approving shifting costs improper accounts appropriately violation ethics case allegation contract work independent research development bid proposal transactions outside individuals organizations generally accepted accounting practices principles United States countries
- Avoid Individual Conflicts of Interest fair impartial business dealings personal interests interest corporation's business conflicts of interest activities appearance contacts position advance outside personal interests property information opportunities personal gain written disclosure action potential conflicts aware multiple loyalties disclosing potential independent objective assessment mitigating action owning substantial interest customer competitor supplier firm owned controlled employee family relationships persons accepting gifts payments consultant subordinate Conflict of Interest Network Tool COIN
- Avoid Conflicts of Interest with Government Employees conflicts of interest conflict connection employing acquiring services current former government employees military personnel comply laws regulations success ability compete marketplace hire work current former creates real perceived information competitive advantage individual possesses conflict contacting negotiating potential future employment service consultants subcontractors restrict roles responsibilities perform behalf complex advice legal Human Resources Department U.S. Government government ethics official background
- Avoid Organizational Conflicts of Interest actively work avoid neutralize mitigate Organizational Conflicts of Interest OCI prevent unfair competitive advantage conflicting roles impair objectivity products services limited government customers employees multiple customer representatives programs conflict government contract compromise failure screen business opportunities disqualification opportunity policies prevent bias judgment report disclosure restrictions supervisors notify prospective relationships impartial assistance advice objectivity screening letter OCI Reporting System
- Do Not Engage in Insider Trading comply applicable securities laws avoid appearance impropriety possession material nonpublic information company trade company's share tip underlying investor's trust public's trust financial markets depend confidence trades publicly available security trading material nonpublic terms legal definitions contact Legal Department question important related third party general public possibility communicating violate law stock Insider Trading learned stock common preferred restricted units employee options bonds notes debentures options call options instruments transactions securities fund transfers reallocations stock fund savings benefit deferred compensation plans purchase sale of common stock sale shares vested restricted stock units gifts gift tax trades limit orders prior possession material disseminated news official announcement open market privately company plans assimilated general public reasonable investor
- Ensure the Quality and Safety of Our Products and Services quality systems safety products product safety services expectations mission success engineering product service lifecycle standards discipline disciplined performance consistency defects safe product contractual legal regulatory requirements concerns design manufacture see something say something
- Use Artificial Intelligence Responsibly Artificial Intelligence AI benefits advisory committee responsible equitable traceable reliable governable procurement development use values potential customers operations industry leader revolutionary technology access valuable data high-performance computing unleashed unprecedented opportunities changing companies sectors evolving discipline risks addressed design implementation systems principles concepts Ethical Development Use of Artificial Intelligence U.S. Department of Defense guidance
- Fair Competition fair dealings customers suppliers competitors employees communications representations prospective customer supplier partners accurate truthful contracts compliance laws specifications requirements contract terms conditions request accept use copy distribute information legitimately entitled highest standards integrity procurement processes bidding negotiating contracts essential current future products services activities violate policy illegal discussing using copying distributing unauthorized information pricing bid strategy bids negotiations connection attendance trade industry groups training guidance legal department ethics office discussion agreement competitors markets territories products services report inquiries Legal Department government prosecutors price-fixing bid-rigging written expressed agreement circumstantial evidence suspicious bid patterns travel expense reports prosecute competitor unauthorized legal right copy distribute
- Abide by International Trade Laws comply export import laws regulations transfer technical data equipment technology countries support restrictive international trade practices boycotts sanctioned U.S. Government U.S. law business violations illegal damage trust transparency transact legitimate long-term customers fair open competition worldwide competitors suppliers written oral request bids proposals red flag reported Element Legal Counsel restrictions sanctions embargoes prohibit activities prohibits interaction identified terrorist states organizations international trade careful inadvertent violations explicit contract language
- Actions of Third Parties engage third parties third party conduct business contrary law policies values principles training ethical compliance requirements actions behalf impact reputation improper actions conducted criminal civil liability employee employees accountable conducting business development consultants independent contractors obligations applicable laws regulations acting consultants representatives comply trained clear responsibilities action adherence policies international
- Corruption and Kickbacks will not be Tolerated tolerance bribery corruption offer give solicit receive bribe kickback business engagement violate anti-corruption law laws Code of Conduct perception impropriety unfair competition cost jeopardizes products services attempt corrupt illegal prosecuted U.S. countries conducting reputational legal harm financial penalties debarment reputation government public officials unusual circumstances questionable compensation accounting invoicing capabilities red flags expressions red flag Legal directly indirectly paying promising giving offering authorizing value influencing person misuse position unlawful illegitimate improper behavior gain advantage bribery fraud extortion theft abuse power money laundering money fee commission credit gift gratuity thing of value loan entertainment service compensation prime contractor employee subcontractor improperly obtaining rewarding favorable treatment prime contract subcontract fact event circumstances information legal compliance illegal unethical conduct corrupt practices non-compliance anti-corruption laws international
- Strictly Adhere to all Antitrust Laws knowingly business arrangements eliminate discourage competition improper competitive advantage antitrust laws law world-wide protect trade commerce unlawful restraints monopolies unfair business practices protecting partners proposed activity complies Legal department rules engaging activities discussions price fixing boycotting suppliers customers pricing competitor disparaging misrepresenting harassing competitor teaming companies outcomes blocking competitors market entry bribery kickbacks stealing trade secrets agreements market allocating bids contacts territories restricting production sale products lines product service conditioning purchase services requirement seller purchaser
- Accept and Provide Only Appropriate Business Courtesies favorable treatment received given exchange business courtesies courtesy offered accepted law policy gifts perception favors improperly influence judgment compete merits products services unfair competitive advantage fairly avoid inappropriate relationship rules monetary limits Public Officials guidance Ethics uncertain allowable limits guidelines country value offering giving receiving intent gain illegal unethical fair market value employees Supply Chain Management relations Gifts Decision Tree tangible intangible fair market value recipient international
- Safe and Healthy Work Environment safe healthy work environment operating protects conserves natural resources prevents pollution speak up culture encourage identify unsafe harm home trust workplace company cares welfare report violations posted warnings procedures regulations management accident injury job environmental safety health concern IDEA identify evaluate act
- Maintain a Drug-Free Workplace hire rehire individuals possess use sell manufacture transfer trafficking under the influence illegal drugs abusive use legal drugs workplace company business prohibit alcohol location behalf comply Drug-Free Workplace Act of 1988 federal state local laws regulations violations criminal drug statutes substance perform ability safely productive security clearance employment U.S. federal contactor drug-free United States state local initiatives legalizing marijuana medical recreational requirement colleague dependency issue advantage resources help risk damage morale productivity public image limit
- Security protect people operations assets mitigate threats employee safety safeguard classified material information entrusted comply exceed customer national security policy requirements dedicated counterintelligence insider threat detection programs objective security investigative process security compliance benefits customers national global stability contract performance products services uncompromised target threat actors gain damage destroy capabilities colleague's behavior suspicious unusual activity inquires request external sources facilities operations programs products report unauthorized assets reported email security threat trick legitimate source partners
- Sustainability and Responsible Corporate Citizenship positive impacts products services environment economy community development infrastructure resilience avoid minimize negative consequences business activities society employees protects conserves natural resources prevents pollution commitments long-term competitiveness sustainability cost risk innovation global policies procedures practices commitment corporate citizenship mission choices
- Respect and Appreciate Human Rights respect human rights element corporate citizen globe championing diversity inclusion promoting fair responsible employment wage hour practices fair competitive wages prohibiting harassment bullying discrimination child labor forced labor trafficking persons purpose employees suppliers steps supply chain relations stakeholders product services protecting advancing integrity core values satisfaction productivity competitiveness slavery world engage third parties violate principles suspicious behavior violations global history criminal
- Political Process policy law political processes countries business spirit letter laws participation process contributions gifts lobbying unintended violations opportunities damage reputation civil criminal penalties employees aware action prohibited require caution permitted personal best interests shareholders funds assets facilities benefit political parties candidates world written approval Government Affairs International activities United States countries prohibit corporate contributions donating goods services directly indirectly consultants employee work local state laws
- Who should I contact if I have a problem, question or concern? contact problem question concern situation manager supervisor resolution ethics and business conduct website how the ethics process works brochure
- Receipt and Acknowledgement acknowledge acknowledgement credit receipt receive know adhere principles standards violations
Popular Keywords
How to Address Business Travel in Your Employee Handbook
Business travel can be an essential component of a company’s operations, enabling employees to attend conferences, meet clients, secure deals, or expand into new markets. However, it also comes with logistical challenges, financial considerations, and potential risks. To ensure a smooth and successful experience for both the employee and the company, it’s crucial to address business travel comprehensively in your employee handbook.
This in-depth guide will walk you through the key aspects to cover, offering explanations, examples, and best practices to create a robust and informative travel policy.
Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, business travel has become increasingly common for companies of all sizes. Whether it’s attending industry conferences, meeting with clients, or exploring new markets, employees often find themselves traveling for work-related purposes. While business travel can be exciting and rewarding, it’s important to establish clear guidelines and expectations to ensure a safe and efficient experience for everyone involved.
The employee handbook serves as a comprehensive resource for employees, outlining company policies, procedures, and expectations. When it comes to business travel, a well-defined section in the handbook can provide employees with the necessary information to navigate the process smoothly. This guide will delve into the key elements to include in your employee handbook’s business travel section, offering explanations, examples, and best practices to create a robust and informative policy.
Why Address Business Travel in Your Employee Handbook?
Before we dive into the specifics, let’s explore why it’s crucial to address business travel in your employee handbook:
- Clarity and Consistency: A well-defined travel policy ensures that all employees are aware of the company’s expectations regarding travel arrangements, expenses, and reimbursement procedures. This promotes consistency across the organization and prevents misunderstandings.
- Risk Mitigation: Business travel can expose employees to various risks, including health issues, accidents, and security concerns. By outlining safety protocols, insurance coverage, and emergency procedures, you can help mitigate these risks and protect your employees.
Cost Control: Business travel expenses can quickly add up. A clear travel policy helps manage costs by establishing guidelines for booking flights and accommodations, setting per diem rates for meals and incidentals, and outlining the approval process for travel requests.
Compliance: Depending on your industry and location, there may be legal or regulatory requirements related to business travel. Addressing these requirements in your handbook ensures compliance and avoids potential penalties.
Employee Satisfaction: A transparent and comprehensive travel policy can enhance employee satisfaction by providing clarity, support, and resources for a positive travel experience.
Key Elements to Include in Your Business Travel Policy
Now that we understand the importance of addressing business travel in your employee handbook, let’s explore the key elements to include in your policy:
1. Purpose and Scope:
Clearly define the purpose of the business travel policy. Explain that it aims to provide guidelines for employees who travel for work-related purposes, ensuring a safe, efficient, and cost-effective experience. Additionally, specify the scope of the policy, indicating which types of travel it covers (domestic, international, overnight stays, etc.) and which employees it applies to.
“The purpose of this policy is to establish guidelines and procedures for employees who travel on behalf of the company for work-related purposes. This policy applies to all full-time and part-time employees who are authorized to travel for business.”
2. Travel Authorization and Approval Process:
Outline the process for requesting and obtaining authorization for business travel. Explain who needs to approve travel requests, what information is required in the request, and the timeframe for obtaining approval. Consider using a standardized travel request form to streamline the process.
“All business travel requests must be submitted through the company’s online travel request system at least two weeks before the intended travel date. The request should include the purpose of the trip, the destination, the dates of travel, the estimated cost, and any supporting documentation. Travel requests must be approved by the employee’s direct supervisor and the department head.”
3. Booking Travel Arrangements:
Provide guidance on booking flights, accommodations, and ground transportation. Specify whether employees should use a designated travel agency or corporate booking tool, or if they have the flexibility to make their own arrangements. If applicable, set preferred vendors or airlines to leverage negotiated rates.
“Employees are encouraged to book their travel arrangements through the company’s preferred travel agency, XYZ Travel. This agency has negotiated discounted rates with several airlines and hotels, which can help reduce travel costs. If employees choose to book their arrangements independently, they must ensure that the costs fall within the company’s travel budget and guidelines.”
4. Travel Expenses and Reimbursement:
Clearly outline the types of expenses that are eligible for reimbursement, such as airfare, hotel accommodations, meals, ground transportation, and incidentals. Specify any limits or per diem rates for meals and incidentals, and explain the process for submitting expense reports and obtaining reimbursement. Consider using a standardized expense report form and setting a deadline for submission.
“The following expenses are eligible for reimbursement:
- Airfare (economy class)
Hotel accommodations (up to $200 per night)
Meals (up to $50 per day)
Ground transportation (taxi, rideshare, public transportation)
Incidentals (tips, Wi-Fi, parking)
Employees must submit their expense reports within 30 days of completing their trip. The expense report should include itemized receipts for all expenses and a brief explanation of the purpose of each expense.”
5. Travel Advances:
Explain whether the company provides travel advances to cover expenses before the trip. Specify the amount of the advance, the conditions for obtaining it, and the repayment process. If applicable, outline any penalties for failing to repay the advance.
“The company offers travel advances of up to $500 to cover expenses before the trip. To obtain a travel advance, employees must submit a completed travel request form and a signed travel advance agreement. The advance will be deducted from the employee’s final expense reimbursement.”
6. Travel Insurance:
Address the company’s policy on travel insurance. Explain whether the company provides travel insurance for employees on business trips, or if employees are responsible for obtaining their own coverage. If the company provides insurance, outline the coverage details and claim procedures. If employees must obtain their own insurance, provide recommendations or resources.
“The company provides comprehensive travel insurance for all employees who travel on business. The insurance covers medical expenses, trip cancellation or interruption, lost or delayed baggage, and emergency evacuation. Employees should familiarize themselves with the insurance coverage details and carry a copy of the insurance card during their trip.”
7. Safety and Security:
Emphasize the importance of safety and security during business travel. Provide general safety tips, such as being aware of surroundings, avoiding traveling alone at night, and keeping valuables secure. Additionally, address specific concerns related to the destination, such as health risks, political instability, or natural disasters. Encourage employees to register their travel plans with the company’s travel management provider or the relevant embassy or consulate.
“The company prioritizes the safety and security of its employees during business travel. We encourage employees to follow these safety tips:
- Be aware of your surroundings at all times.
Avoid traveling alone at night.
Keep valuables secure in a hotel safe or locked luggage.
Register your travel plans with the company’s travel management provider or the relevant embassy or consulate.
Familiarize yourself with the local laws and customs of the destination.
Carry a copy of your passport and itinerary with you at all times.
Stay informed about any travel advisories or warnings issued by the government.”
8. International Travel Considerations:
If employees travel internationally, address additional considerations specific to international travel. These may include obtaining visas or work permits, understanding cultural differences, exchanging currency, using international roaming for mobile phones, and adhering to local laws and regulations.
“For international travel, employees must obtain the necessary visas or work permits before their trip. The company will provide assistance with the visa application process. Employees should also research the cultural differences and customs of the destination to avoid misunderstandings. It’s advisable to exchange currency before the trip and to inform your bank or credit card company about your travel plans to avoid any issues with using your cards abroad.”
9. Business Conduct While Traveling:
Outline expectations for professional conduct while traveling on behalf of the company. This may include adhering to the company’s dress code, maintaining a professional demeanor in all interactions, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and representing the company in a positive light.
“Employees are expected to maintain a professional demeanor at all times while traveling on behalf of the company. This includes adhering to the company’s dress code, being punctual for meetings and appointments, and treating clients, colleagues, and service providers with respect. Employees should avoid excessive alcohol consumption and any behavior that could reflect negatively on the company.”
10. Emergency Procedures:
Provide clear instructions on what to do in case of an emergency during business travel. This may include contacting the company’s travel management provider, the local embassy or consulate, or emergency services. Specify the contact information for each of these resources.
“In case of an emergency during business travel, employees should immediately contact the company’s travel management provider, XYZ Travel, at [phone number]. If unable to reach XYZ Travel, employees should contact the local embassy or consulate for assistance. In the event of a medical emergency, employees should seek immediate medical attention and inform the company as soon as possible.”
Additional Considerations
In addition to the key elements
Share this:

The complete guide to corporate travel policies
The business travel policy guide you’ve been waiting for .
Creating a business travel policy for employees can feel really daunting. You don’t want to just throw something together and hope for the best, but it feels impossible to anticipate every possible scenario. The truth is your policy serves as more than a rule book; it's a guide to better decision-making about your corporate travel program and can save you a world of headaches down the road.
Introduction
What is a travel policy .
- Why do you need a travel policy?
- How to create a travel policy
What to include in a travel policy
- Travel policy best practices
- How to promote travel policy compliance
- How to market your travel policy
When to review and update your travel policy
- Final thoughts
When it comes to company travel, a travel policy brings it all to one place. It acts as an influencer for travelers to make the most cost-effective choices, an important visibility tool for your managers and HR department, and it protects your people if it’s done right.
If you’re new to business travel or haven’t looked at your travel policy in a while, we’ll start with the basics and then move into the nitty gritty of corporate travel policies. We’ll touch on a few best practices for writing a travel policy, what to include, and offer plenty of resources along the way.
Ready to get cracking? Let’s go!
A travel policy is a guide for business travelers to follow that outlines:
- How, where, and when to book
- Approved technology for travel management
- Preferred suppliers for air travel, land travel, and accommodations
- Approvals process for out-of-policy bookings
- Trip extensions and personal travel
- Expenses and what is covered or not covered
- Reimbursement processes
- Business travel insurance information
- Emergency procedures and contacts
Your company’s travel policy should reflect your company culture and values, be supportive of your travelers and their needs, and protect your company from unforeseen circumstances. It acts as a central document that guides your team to the processes of embarking on company business travel, from start to finish!
While you might hear a few grumbles and groans around the words “policy” or “process,” don’t worry! A travel policy does not need to be rigid and inflexible.
Do your travelers prefer to book on their own? Don’t take away their autonomy. They can still self-book, you’ll just provide them with a better tool and way to do it more efficiently.
Do your people feel prepared for any event that can cause a travel hiccup? With a travel policy, you can give them clarity and help them feel more prepared when traveling for business purposes.
Why do you need a travel policy?
Your travel policy is an extension of your travel program and company culture. It’s the glue that holds your travel program together – from approvals, expenses, booking processes, and emergency contacts.
Having a travel policy helps you:
- Control travel costs
- Determine how reimbursement works
- Compile a list of trusted and approved travel vendors
- Manage an employee’s travel experience and safety
- Cut rogue bookings – and simplify approvals
- Budget, report on travel expenses and activity and reconcile bookings
It’s a roadmap or guidebook that your travelers can reference when they’re booking their own travel if they run into a tricky situation abroad, and it helps provide clarity around processes.
As a company though, your travel policy helps centralize your travel program, makes data and tracking more accurate and easier to navigate, and it saves time and money (including on expense management). Plus, if you take the time to craft your policy in an intentional and inclusive way, you’ll have a policy your travelers are happier to follow.
How to create a travel policy for employees
- Determine business travel guidelines
- Create a travel policy that puts your people first
- Set reasonable budget limits
- Simplify the process of expense claims
- Adopt a user-friendly all-in-one travel platform
Once you’ve read through our tips, be sure to download our free travel policy template so you can get started on creating a travel policy of your own!
1) Determine corporate travel guidelines
When you take the time to create a policy that meets the needs of your business, you are making sure that your travelers are safe, costs are controlled, and you’ve made every business trip count.
Start by looking at what types of travel are allowed and the reason for each trip.
If you have team members traveling all over the globe, you might want to set some extra safety measures. You should also decide if there will be restrictions on the type of ground transportation used or where employees can stay.
Create a process for booking flights, hotels, and other ground transportation needs. How far in advance should they be booking? Do different rules apply based on the traveler’s position? Who is the point of contact for bookings and other travel questions?
Making sure to include your company’s travel insurance info is also important. Make sure to note if your policy covers medical expenses and/or any losses due to cancellations or delays in transportation services due to factors outside an employee’s control.
Do you have a policy for reporting and documenting expenses? This includes having a system in place for claims (like meal expenses) and a reimbursement process, so your team can easily get their money!
2) Create a travel policy that puts your people first
You’ve heard the term “duty of care” before, so it’s important to create a corporate travel policy that puts traveler safety and accessibility needs first. You’ll need to define and assign the roles and responsibilities of everyone involved, including a travel manager, if you have one.
Set up an emergency plan and provide access to traveler safety information. Determine who is the emergency contact (your TMC?) and how to get in touch. Do they have 24/7 emergency support available by phone or chat? What about email support?
Invite your HR department, the travelers themselves, and your DE&I manager into a discussion to find out what needs your team has as individuals, what hiccups they face when traveling, and what holes exist in your travel program that make it difficult to navigate.
Working with a TMC is a great way to ensure travelers are kept safe before and during their trip.
3) Set reasonable budget limits for business travel
You have a budget you need to adhere to, but is it realistic? Setting reasonable budget limits is key to an effective policy.
Your budget should account for all travel-related expenses, including airfare, accommodation, meals, and ground transportation. And once you’ve set your budget, you can determine reasonable costs for hotels and accommodation, ground transport, flights, and more. Build these caps into your travel booking software to help travelers stay within the set parameters, which will later help with accountability.
It's important to set clear rules on what the company can pay back and what types of expenses are out-of-pocket.
If you’ve set a maximum daily rate for meals on work trips, it's crucial that travelers understand the limit before racking up additional charges. Requiring receipts can also help keep track of employee spending and make sure they're not going over budget.
By working with a travel management company like Corporate Traveler, you can review your previous year’s expenses and find where you can optimize or make changes based on market changes.
4) Simplify the process of expense claims
If you're unfamiliar with how to write a travel expense policy, creating a simple process for claiming expenses is key to getting your team on the same page. Do you have access to a payment system that pays for the majority of expenses at the time of booking? This could be a good way to save time and stress down the road.
The more you can pay for before your travelers get to their destination, the easier everything is to reconcile after they get home.
If you have a person in charge of reviewing expense reports and watching pre-trip approvals, make sure to set criteria for claim approvals and look at automating processes to make approvals simple!
5) Adopt a user-friendly all-in-one travel platform
Finding the right corporate travel platform is essential. The right booking platform can provide travelers with an easy-to-use experience, giving them access to the best fares and availability.
For example, at Corporate Traveler, we use Melon . It’s a booking tool, reporting suite, travel policy pusher, traveler profile manager, and so much more. Melon features a “recommended spend” function, which helps keep travelers booking in policy. Hello, visual guilt!
Melon’s simple user interface, combined with dedicated travel consultants and expert 24/7 support, makes it simple to book, manage, and keep track of your business travel. You’ll be able to access Melon-exclusive deals and perks (alongside many negotiated contracts and online deals) and take care of all your travel needs from one place.
From the get-go, you’ll be able to work closely with our team to ensure that all of your needs are met. We'll help you customize your travel program to meet specific business needs, build your travel policy into the platform, and offer training to staff to help them along the way.
Putting it all together
Wow! You’ve reached the end and should have a better idea of how to write a corporate travel policy. High five! Now it’s time to put it all together and get it on paper.
Maybe you already have something in place that needs some work or an entire overhaul. Check out our easy-to-use template and start checking those boxes!
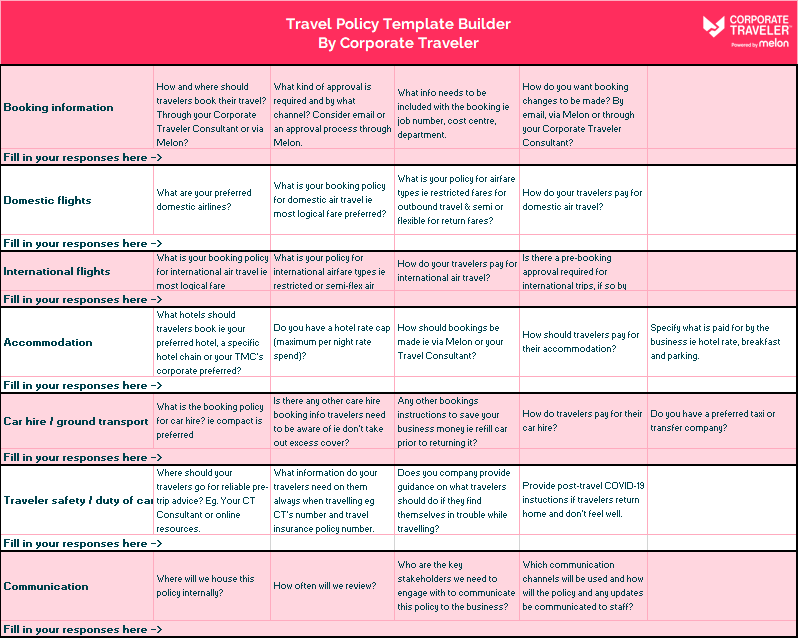
Grab our corporate travel policy template builder
Not sure where to start? No worries! We’ve got you. Here’s how to streamline your process with a travel policy template!
While there’s no one-size-fits-all travel policy for every company, following the set guidelines helps you nail a perfect-for-you policy that can see you through an ever-changing travel climate.
Travel policy template
When you’re crafting your business travel policy, there are so many considerations to be made. Things might come up that you never even thought of, but not to worry. We have loads of resources to help you see this through.
Starting out, it might be looking a little drab and wordy, but depending on your travel program size, a visual travel policy might be just what you need. You can search for examples online or take a look at an example of a visual travel policy we’ve created.
When building your policy, it’s important to include:
1. International or foreign travel policies
When you’ve got travelers all over the globe, you need to build out a policy for international or foreign travel. This is a protects them (and you) on anything from travel safety, to expenses, and everywhere in between.
Whether your travelers are individuals or entire teams, your international travel policy needs to cover:
- How and where to book – is that with a travel manager, online booking tool, a travel management company (TMC) ?
- Travel insurance coverages and contact info – international numbers and policy information
- Emergency contacts – how to reach them and the process of in-destination emergencies
- Travel expenses – limits and how to file for reimbursement
- Travel documentation – who to contact with questions
- Advance booking timelines – when should they be booking for international travel?
- Travel extensions – are these allowed and what are travelers expected to cover if they choose to extend their trip for leisure?
By outlining all of this information in your policy, you’ll streamline the process for your finance teams, travel managers, and your travelers. And really, who doesn’t want to make travel a smoother experience?
2. Corporate travel policy for business class travel
Does your corporate travel program have different rules, limits, or allowances for different levels of seniority? Are some junior members expected to travel in economy class, while some executives are allowed to book in business class?
If some certain exceptions and situations might allow for an employee to book business class, regardless of their position, you should include that in your policy as well.
Making this as clear as possible will avoid an approvals nightmare down the road.
3. Corporate meal allowance policy
It’s great if you’ve already centralized most of your business travel expenses like flights, accommodation, transportation, and car rentals, but your people gotta eat! It’s super important to include a meal allowance policy that clearly outlines which meals (and how much) you’ll cover.
Some of your team might be traveling with corporate credit cards, while others might need to be reimbursed. The guidelines and procedures for submitting expenses or asking for reimbursement need to be crystal clear!
Make sure to outline if you have a corporate travel policy for alcohol, too! You don’t want murky policies when it comes to footing the bill for drinks.
Some things to consider for your meal allowance and alcohol travel policy:
- Which meals are covered and for how much?
- Who is footing the bill for an alcoholic beverage with dinner?
- If entertaining clients, what is the budget, and how flexible is it?
- What is the process of submitting company card expenses?
- What is the process for requesting reimbursement?
Your team will always have questions about the policy on food and drinks, so make sure they can find the info easily and have a point of contact for whoever can offer more clarity.
4. Executive travel policy
We briefly touched on executive travel when we talked about traveling in business class, but there is certainly more to the top dogs traveling.
Executive travel can be a touchy subject if there are more lenient policies in place than there is for less senior team members. Your executives also may need to know the guidelines in place for their own travel, so they don’t accidently go overboard, which could be an accounting nightmare!
You’ll need to make sure you deliver a guide for approvals, procedures, booking deadlines, meals, accommodation, basically everything.
Lay it all out. Make your policy as digestible as possible, and for a busy exec, consider bullet points and titles in bold so they can easily skim to the areas they need to know.
5. Natural disaster or COVID-19 business travel policy
We can all agree that COVID-19 caused business travel to come to a screeching halt. Across most industries, the pandemic impacted client relationships, the ability to gain new clients and caused budgets to get slashed pretty dramatically.
While this was only one event, many businesses have begun to consider the “what-ifs” of their travel programs should another outbreak of COVID or something else happen. Crossing our fingers and toes doesn’t cut it, unfortunately.
There is also the chance of their travel being impacted by a natural disaster. We’ve seen it before – earthquakes, tsunamis, volcano eruptions, hurricanes. Do you have a plan or policy to aid your team and guide them through the unthinkable?
In 2022, we surveyed 120 employees across various industries and businesses. More than half, 51% of respondents said their companies didn’t provide resources or tips for safety on their trips. Duty of care isn’t something to put on the back burner, it’s your legal obligation to make sure your team is informed.
So, what’s the solution, you ask?
Working with a TMC gives you the backup you need if anything ever happens and you have people traveling abroad. At Corporate Traveler, our travel management software, Melon, is a central place to house your policy for quick and easy access. Plus, our travel experts can help you paint the big picture of what to do, who to call, and how to get your team home safely as quickly as possible.
Is there anything missing from your travel policy?
Let’s break it down. If you think of your policy like a sandwich, it should include:
The bread and butter
- Where and why: Are there any restrictions on who travels domestically or internationally? Or guidelines around reasons for travel?
- When: Are there any restrictions on when business travel is a no-no, like during an auditing period or financial downturn?
- How? How should travel arrangements be booked? Through your corporate travel booking software or with a preferred Travel Management Company (TMC)? How far in advance should domestic and international trips be booked?
- Preferred suppliers: Do you have preferred partners for air travel, accommodation, ground transport or travel insurance?
- Approvals: Who’s responsible for giving the green light on trips?
- Show me the money: What’s the process for managing/submitting expenses, paying for travel and reimbursements?
- Uh-oh: How will you prevent or deal with non-compliance to the travel policy?
- Noise level: Getting loads of ‘noise’ and questions about things in your policy? This means it’s not clear and it’s time to review why and where the stumbling block is for travelers (or your finance team!)
The filling
- Classy, baby: Who gets to fly business class, book 5-star properties or order UberLUX? And how does your business handle upgrades or airport lounge access for long-haul flights?
- All work, some play: What are the conditions if someone wants to extend their business trip to take personal leave? Are you happy for them to enjoy a bleisure trip, and if so, who foots the bill and for what?
- Loyalty: Are there any travel rewards or business loyalty programs that can be used during booking?
- Spending money: Do your business travelers have a daily allowance for meals, snacks, and drinks? How much is it, what does it include – and what’s not covered? Can they order room service, drink from the mini-bar, or use the in-house laundry service?
The not-so-secret sauce
- Safety first: your policy should support air, accommodation and ground transport suppliers that have been safety and security vetted. Guidelines or information on travel insurance for work trips is also helpful.
- Now what: What’s the plan of action in the case of Acts of God or Force Majeure events? Does your team know who to call for help?
- What’s next: Who is responsible for updating and reviewing your travel policy, and how often?
Corporate travel policy best practices
- Write for skim readers
- Guide travelers to the right resources
- Automate your policies
- Stipulate a timeframe for expense claims
- Be prepared for the unexpected
1. Write for skim readers
One of the first steps towards writing a people-first travel policy is understanding how your travelers will read it. And the truth is…
They probably won’t.
Research has shown that adults get distracted every 47 seconds . So if a business traveler is looking at your policy, they’re most likely just searching for a specific answer – and they want it fast. So what can you do?
First, make sure the document is easy to navigate. That means including things like:
- A table of contents
- Visual elements to help guide the eye toward crucial information, like flow charts and tables
- Clear headings and important details in bold
- Bulleted lists (see what we did here?)
And even though it’s a technical document, don’t make it sound like one. An effective travel policy should be clear, concise, and easily comprehended. So skip the long, complex sentence structures and technical jargon, and write in plain, simple English. It helps to pretend like you’re writing it so an eighth-grader can understand it.
2. Guide travelers to the right resources
Remember when we said travelers will only read your policy to find a solution for a specific need? Whether it’s a link, a phone number, or a step-by-step tutorial – a well-managed travel policy should provide them with the right resources.
Instead of treating a travel policy as a list of rules, treat it like a resource sheet. Here are some key pieces of information travelers might need to pull up easily:
Your approved online booking tool (and steps on how to use it)
- QR codes to download your mobile travel app
- Preferred airlines, including class, budgets, and other limits
- Permissible hotels, including guidelines on star-class and incidental expenses
- Guidelines on ground transportation (trains, ride-sharing services, rental cars, and personal car usage)
- How to get travel support
- Travel insurance carrier
- Clarification on the reimbursement process (more on this later)
You can also include other factors specific to your company, but this should at least be the necessary groundwork to help employees make the right choices on their own.
3. Automate your policies
Let’s face it: even with the best communication efforts, there’s always a chance that an employee may violate policy, even unintentionally. So, what can you do?
Build policy into booking.
By building your travel policy into your travel management software, it becomes unavoidably embedded in the booking process, so even the most easily confused employees end up following by default.
Automation tools can sound the alarm on out-of-policy bookings and even provide an audit trail. This can be especially helpful for employees who may struggle to remember procedures and policies, especially after big changes to your travel program.
4. Stipulate a timeframe for expense claims
No one wants to get stuck waiting on the money they’re owed – or worse – find out they’re not getting reimbursed for an expenditure they thought would be covered.
Having a clear and well-defined expense claim process is critical in any travel policy. Employees need to know how to claim their travel expenses, how soon they need to submit an expense report, and when to expect reimbursement.
The policy should also be clear about what expenses are and are not reimbursable, including any limits or exceptions. For example, if an employee needs to book a different seat class to accommodate a disability , the policy should include the process for requesting and approving this expense.
Plus, a submission deadline reduces cash flow issues and provides more accurate and complete expense data for that period (your finance team will thank you later).
5. Be prepared for the unexpected
As a company, you have a duty-of-care responsibility. When it comes to business trips, you need to be prepared for the unexpected. No matter how much effort you put into planning, there will always be a few hiccups along the way.
For instance, lost luggage, canceled or delayed flights, and sudden weather or political emergencies in unfamiliar destinations could all leave your employee stranded.
“Companies need to be prepared to plan for the particular, not just the universal. Every aspect of the travel program needs to be able to fit each of your travelers like a glove, from adaptable plans and experts on call, to technology that makes the journey seamless.” - Emese Graham, DE&I Manager @ FCTG
Don’t let unexpected situations blindside you. Have processes in place to ensure travel safety and security. Make sure they know what to do, where to go, and who to get a hold of if something goes wrong. Taking a proactive and prepared approach to your policy can minimize the impact of emergencies and take care of your team’s well-being while they’re on the road.
BONUS TIP: Update your policy regularly
Here’s a free business travel policy best practice just for you! It isn’t just a “one and done” deal – it’s a living document.
What’s that mean? As your company grows and travel conditions change, so should your travel policy. Revisit your expense policy at least once a year to keep it relevant and effective – and lead you towards new cost-saving solutions.
Data is going to be your best friend here. Here are a few key factors you should look into when updating your travel policy:
- Analyze travel spend patterns – are you throwing a lot of company money at certain suppliers? You might want to see if you can negotiate a new deal or find better rates elsewhere.
- Identify areas of overspending or inefficiency – are employees accruing high parking or travel costs? See if you can get season tickets or other accommodations.
- Evaluate the overall performance of your policy – are you still compliant with any new regulations that have come into play since the policy was established? How can traveler experience be improved?
You may even want to consider enlisting the help of professionals, such as a travel management company with experience in expense management, to give advice on how to optimize your travel policy to better meet the needs of your employees and your business as a whole.
Building a travel policy that's good for business and travelers and meets their needs is no small feat. But whether you're looking to retain your team, attract new talent, or make life a little easier for your travelers, investing in a well-designed travel policy is definitely worth the effort and great for company culture.
By following these travel policy best practices and ensuring your policy meets all travelers' needs, you’ll be on your way to smoother, safer, and more enjoyable travel experiences for all.
How to promote travel policy compliance
Whether compliance is a big or small issue in your company, it takes a little bit of investigating to figure out why it’s an issue at all.
Maybe your policy meets the needs of only a few of your team members. Maybe it’s too difficult to navigate your policy. Or maybe, your policy is written in legalese and makes your travelers vision blur before they go rogue and book how they want.
It could be that your travelers prefer a bit of freedom in booking and would rather do it on their own. Or, maybe they have specific needs that aren’t being met by the options provided.
Whatever their reasons, it’s your job to figure out why they aren’t following and what you can do to build better compliance.
Here are a few tips to improve travel policy compliance:
- Make your policy easy to navigate, understand, and find
- Use an online booking tool (OBT) for travelers who prefer to self-book
- Allow a bit of flexibility so travelers feel they have some autonomy
- Include a category for last-minute bookings so it doesn’t mess up your data
- Understand your traveler needs and build an inclusive policy

Read the full guide:
You've researched, gathered the necessary resources, and communicated your travel and expense (T&E) policy to your employees. But now, you're not so sure they're actually following it.
Read the full guide: How to Improve Corporate Travel Policy Compliance
How to market your corporate travel policy internally?
Corporate travel might be off the radar for most employees, especially those outside of customer-facing positions. The first step in promoting successful corporate travel policies is awareness.
Do employees know about the policy? Where can they find information and updates on business travel? Clear communication at pivotal points and frequent intervals can help keep everyone aware.
Review common and expected challenges
Business trip policies might be ineffective if they don't meet the needs of some business travellers. You can get ahead of challenges by understanding that last-minute travel can be necessary or that different travellers have unique needs.
Inclusive policies plan for employee safety and comfort on a range of business trips, paying attention to details such as arrival and departure times, car rentals, ground transportation, and noise levels.
Communicate business travel policies effectively
Travel managers can use best practices to ensure all employees are aware of and understand travel programs. Visual policies, internal documents, and guides all work well. People learn differently, so it’s a good idea to have key information in both visual and text formats.
A yearly update is also beneficial, as well as communication on any major changes, like new technology or changes in the approval process or submitting expenses. An internal FAQ page can increase understanding of corporate travel guidelines, as well as prompt new questions.
Book a demo of Melon , the all-in-one travel platform.
Increase employee engagement
Highlight areas of company travel that offer flexibility, to show what’s possible for different preferences. Talk about benefits like an online booking tool vs. working directly with a TCM.
Developing interactive content, like employee surveys, can show if traveller satisfaction is achieved. It also helps identify travel arrangements that are unnecessary for cost savings.
Find internal champions for the business travel program
Travel policies cross paths with a lot of different departments, from sales to the finance team. Identifying key people and keeping them involved in developing the travel program means getting buy-in and internal support.
Corporate Traveler has a long history of travel management and is ready to join forces as an external member of your travel planning team. Let’s make booking a breeze , together.
Case studies: effectively marketing your corporate travel program
A travel manager should match your company culture for the best fit. Find out how these companies successfully targeted the right mix of technology and service to meet employee expectations and business goals.

Flipp Travel Case Study

Streamlining global travel for Eliquent Life Sciences

Beyond Energy Case Study
If the last time you reviewed or upgraded your travel policy was more than a year ago, it’s outdated and needs a refresher. If your company is small and has low turnover, you could probably get away with making small tweaks and optimizations.
But if you have a larger company with multiple departments and higher turnover, you probably need to do an overhaul and review it more regularly. We’re not saying you have to change it every time someone is hired or leaves the company, but making sure it’s relevant to the people who are there and are traveling matters!
Corporate Traveler conducted a survey in 2022, which showed that 48% of respondents didn’t know if their company had resources for specific traveler profiles, while 41% said their company didn’t provide resources for specific traveler profiles. This really goes to show that there’s room for improvement in how policies are built to support their people and their businesses.
A people-first travel program and policy have become necessary as the world grows and begins to understand neurodiversity, disabilities, and cultural differences. When we learn about our team members’ diverse needs, we can better understand how to support them when they venture abroad for our businesses.
GUIDE: Download the How to design a people-first travel program guide
We recommend policy reviews every 3-6 months, but at the minimum, once per year.
Final thoughts
Business travel is so unpredictable, as we’ve seen in recent years. There will always be circumstances you can’t avoid as a company, but making sure that you have the necessary checks and balances in place can help to make things just a little easier. If you have groups traveling, VIPS, or people heading to high-risk destinations, it’s important that your policy is relevant.
Don’t forget that travel policies shouldn’t be written and forgotten about – these are living documents that must be regularly updated to make sure they best protect your people.
Remember these best practices when writing your travel policy:
- Keep it simple and make it pop with visuals, bullet points, and bold headings.
- Answer any and every question possible – think of all the eventualities
- Always put your people first
- Implement a quick and simple approval process
- Automate as much as you can
- Use technology that’s supports your policy
- Be flexible with due reason
- Be clear about what’s not allowed
- Update your travel policy at least once a year
- Keep it somewhere easy to find
And finally, it doesn’t hurt to have a couple of different formats. Consider a visual version and an extended version so the message is delivered best depending on the person reading. For some, it might be easier to digest one over the other.
Looking for a policy review? We’d be happy to work with you.
Let’s chat .

7 Step Guide to Writing a Business Travel Policy
Download the PDF eBook version
It’s common to assume that you might not need a business travel policy. Maybe your company is only just starting out, still in its early growth stage, or just doesn’t do much business travel.
That line of thinking couldn’t be more wrong, though.
A company travel policy isn’t something exclusive only to large businesses. Even small startups whose employees only travel twice a year can really benefit from having a solid corporate travel policy.
Corporate travel policies reduce time-wasting, repetitive, and redundant questions. It’s a place to turn to for convenient answers and guidance to ensure everything is on the up and up with the company.
Having a business travel policy in place helps foster fairness and transparency. It also provides employees with greater freedom and autonomy while maintaining corporate authority and management.
Most importantly, it also serves as a way to ensure the safety of your travellers, especially in today’s post-COVID world.
Now that we’ve established the need for a travel policy, how do you go about building one that employees would follow?
Creating, maintaining, and enforcing a company travel policy doesn’t mean micromanaging every last detail of your employee’s business trip. Instead, it means providing them with the tools and information they need to feel safe, comfortable, and supported by the company.
Moreover, many travel policies today centre around flexibility and providing employees with greater freedom to arrange their business travel.
Our guide will give you everything to do exactly that — we’ll discuss various travel management styles, provide tips for creating modern travel policies, and offer techniques to help increase compliance.
The Downside of Travel Policies
Anything connected to the word “policy” is often instantly deemed complicated and overwhelming. Company travel policies are no different. Travel arrangements and requirements can already be time-consuming and challenging to take in without adding company rules into the mix.
When we know what employees don’t like about their current business travel policy or what keeps them from fully using them, we can create policies that specifically avoid those issues.
4 Common Problems with Travel Policies
- The policies are too technical or difficult to understand.
- Almost no one bothers to read the policies due to their length.
- No one remembers the content of the policies.
- Companies don’t automatically enforce travel policies.
These issues contribute to a low policy compliance rate. A 2018 survey by Skift and Turkish Airlines showed that only 60% of business travellers follow their company’s travel policy, particularly when booking their accommodations.
Understanding the common problems with travel policies can help guide us in creating one that employees would want to use and appreciate.
Failure to heed these common problems can easily make all the effort we put into creating a great corporate travel policy to waste.
Don't have time to finish this guide now? Download the PDF eBook version

Why Build a Corporate Travel Policy?
The difficulty in creating and ensuring compliance with business travel policies might turn you away from putting any policy in place. You wouldn’t be the only one to think this way, either.
Sixty percent of companies in the U.S. don’t have a corporate travel policy in place.
However, in doing so, you can miss out on several important benefits — not just for employees but for your company.
Travel Policy Benefits for Travellers
- Clear rules and regulations
- Less hassle when making travel arrangements
- Fairness amongst the team
- Ensure safety and wellness
- Better flexibility and autonomy
Travel Policy Benefits for the Company
- Lessen travel cost spikes.
- Improve management over company travel expenses.
- Streamlined reimbursement protocol.
- Increased fairness helps foster better employee sentiment.
- Positive company culture.
Creating a business travel policy provides you and your company with clear guidelines. This, in turn, helps ensure fairness and equality for everyone.
A Step by Step Guide to Writing a Business Travel Policy
Now that we’ve had a better perspective on travel policy dos, don’ts, and the benefits, it’s time to focus on writing one.
Here is a quick look at our seven-step, fool-proof process for writing a modern business travel policy:
1. Review existing or previous travel policies
Similar to how we took a look at the dos, don’ts, and benefits, it is also important to review old or existing policies.
2. Outline policy goals and identify stakeholders
In any project or undertaking, it is best to start with clear goals and priorities. Regardless of whether you choose to focus on reducing confusion or limiting travel expenses, you and your team should be clear on what the policy’s focus should be.
During this stage, it's important to involve all of the right people. This will help ensure the fairness and appropriateness of your travel policy.
3. Ensure it’s easy for everyone to use the policy
As early as now, think of a way to make using your travel policy convenient for everyone who may need it — whether they are rank and file employees, supervisors, or executives.
This will help ensure that everyone is aware of the new policy, where they may access it, and how to use it.
4. Decide on the travel management style or strictness
Before you can create the travel policy’s rough draft, it is important to choose your travel management style. Along with this, you also need to determine your level of strictness.
These two factors will help ensure that all parts of your policy are in line with each other. They will help when making decisions regarding individual rules, tools, and more.
5. List down what to include in the travel policy
After working through your travel management style and strictness, start brainstorming what you want to include in the document. You can use an old travel policy or a successful one from a competitor as a reference for what to and not to include.
6. Create the first draft
Finalise the list of things your travel policy needs to have, then start writing the first draft. There are templates available online that may help make finishing this stage easier and faster.
7. Implement the travel policy
Expect your first draft to go through several revisions. However, once the final version has been approved by the management, make sure to share it with the whole company.
Immediate, company-wide implementation and briefing on how any travel management tool you use is necessary to encourage adoption and full compliance.
A Detailed Dive into the Writing Process
The outline we provided is only a brief look into what you should expect to do for each step. In the following sections, we will dive deeper into what each step would entail.
Review Your Current Travel Practices
What travel policy do you currently have in place? If you don’t have one, what are your employees’ travel practices? Answering these questions will help you get a better idea of what works, what employees prefer to do, and what to avoid.
It is best to do this with your company's major stakeholders, including the HR department, finance, and upper management. Having a few frequent business travellers join in the meeting would also prove helpful. If not, then asking your employees to answer a survey regarding your travel rules or practices may be a suitable alternative.
Set Your Policy Goals and Identify Stakeholders
A smart travel policy requires clear priorities and goals. These will give your writing purpose and steer you in the right direction. Additionally, it’s important to define the accepted business travel purposes so that all employees understand why it’s necessary and when they may be expected to go.
It’s also important to identify and notify your stakeholders. Ask yourself, who are the people whose input is necessary for the project? Who are the people whom your travel policy would affect?
Here is a list of people who should be involved in the creation of any travel policy:
- Human resource department
- The finance department (specifically the CFO and controller)
- CEO and COO
- Travel manager
- Office manager
- Frequent business travellers
These people are the most important ones to include in the discussions. They can either help write the document or be involved in its approval. After holding a kick-off meeting to establish priorities and goals, you can simply reach out to the stakeholders individually to minimise any disruptions in their regular duties.
A 3-Step Guide to Setting Future-Proof Priorities
Referring to your old travel policy (or your competitors’ if you don’t have one) will help you determine your priorities.
Step 1: List down what works in your teference travel program. This can be as simple as “travel expenses are exceptionally high in X city” or “employees still book flights or accommodations out of policy.”
Step 2: Set clear core goals. We recommend having two to three core goals for updating or creating a corporate travel policy. An example of a core goal could be “to meet the needs of a growing company or team.” Under each core goal, you can list down secondary or specific priorities.
Here are several basic travel policy priorities that most businesses share:
- Limit unnecessary travel expenses
- Improve transparency and visibility
- Boost employees’ travel autonomy
- Increase overall efficiency and satisfaction of business trips
- Reduce employee confusion
- Streamline manual work for the HR and administrative departments
- Improve traveler safety and duty of care
- Boost travel policy compliance
- Improve convenience in making travel arrangements
Step 3: Discuss upcoming changes in the business. Doing so will help you future-proof your travel policy, at least to a certain extent. Important changes to take note of include office consolidations, expanding to new locations or offices, hiring more people, and any potential long-distance business partners.
Ensure Every Employee Can Use the Travel Policy
There are two ways you can create your company travel policy. These are:
- Classic or traditional method: Providing employees with a hard copy or a PDF document of the policy handbook, a link to an intranet page, or publishing it on the company’s internal wiki page.
- Automated or in-app method: Customising a travel management platform according to your policies and providing access to the employees. This allows the company to automate business travel booking arrangements in real-time.
We also recommend combining these two methods. Having an easily accessible app automates the process but having a classic corporate policy document gives employees something to refer to in case they have questions.
Aside from publishing it internally through a company wiki page or intranet page, it’s also common to provide employees with a link to a shared file folder or PDF via cloud data services, like Google Drive for example.
Additionally, it is a good idea to provide new employees with either a hardcopy or digital file during the onboarding process.
All About Travel Management Platforms
One way to make sure that everyone in the company can use the travel policy you create is by using a travel management platform.
A travel management platform or system, also called corporate travel management software, helps improve travel coordination and booking processes. It is one of the most convenient ways to manage travel arrangements internally.
Instead of spending more time manually planning trips across different websites or platforms, you and your employees can simply use one system to manage everything. This includes finding the most affordable flights, the best accommodation locations, and even arranging reimbursements for canceled or missed flights.
We highly recommend choosing a travel management tool like Locomote (shameless plug) that allows you to incorporate and or create your travel policy in its system. This helps ensure automatic policy compliance.
Decide on the Travel Management Style and Strictness
It’s crucial to determine your travel management style and level of strictness before listing down what you want and need to include in the document.
Travel management style refers to how you want to structure your corporate travel arrangements. This essentially means deciding on whether to have a hands-on or hands-off approach.
Will an administrator or manager handle all the bookings? Or will you give employees the freedom and autonomy to choose their travel arrangements? Will the employees be allowed to extend official business trips to mix it with personal or leisurely travel?
As for the level of strictness, this mainly refers to the restrictions set on your chosen booking tool or travel management software.
For example, will the system still allow employees to make bookings outside of your set policies? Will they need a manager’s approval to do so? Will you require approval for all travel arrangements they make, even those that follow the company’s policies?
In deciding the style and strictness level, it’s crucial to seek the opinions of your stakeholders. The company executives, HR department, and Finance teams have the most say in this case.
Figure Out What to Include in the Travel Policy
So, what exactly goes into a corporate travel policy? It’s simple: anything and everything employees might want or need to know about traveling — both domestically and internationally.
Remember, the goal in building a business travel policy is to provide employees with a helpful reference in case they have questions. Here is an overview of some basic rules and modern guidelines:
Booking and Approval Process
- Who makes the airline and hotel bookings?
- What are the requirements for travel approval?
- What tools or platforms should employees use?
Travel Safety
- What type of travel insurance do employees get?
- Who is your duty of care vendors?
- What are your emergency procedures?
- Who is your employees’ point of contact in the company in case of travel emergencies?
Accommodation Expenses
- What is the maximum allowable spend per night?
- Are there different budgets for different cities?
- How can employees get corporate hotel rates when booking by themselves?
- Are employees allowed to book alternative accommodation, such as AirBnB?
- What types of alternative accommodation are allowed?
- Are there circumstances where alternative accommodation is not reimbursable?
Airline Travel Expenses
- What is the maximum allowable spend per domestic flight?
- What is the maximum allowable spend per international flight?
- Can employees book flights without approval?
- What is the required minimum amount of time to book in advance?
Ground Travel Expenses
- What are employees’ options for ground transportation?
- What are the company’s preferred modes of ground transportation?
- Is there a maximum cost per train ticket?
- What are the rules for renting vehicles?
- What are the rules for using personal vehicles?
- Are employees entitled to fuel and accommodation reimbursements for multi-day drives?
Food and Daily Allowance
- Will daily allowance be provided?
- What will it include and not include?
- What are the daily allowance limits?
Entertaining Clients
- What counts as client entertainment?
- What is the maximum cost per entertainment ticket?
- How much can employees spend without needing approval?
- What is the maximum spend per meal for clients?
Reimbursement Processes
- Until when can employees file for reimbursements?
- What purchases or expenses count as non-reimbursable?
- Who approves reimbursement claims?
- How should the reimbursement claims be submitted?
- How do employees submit expense reports?
Leisure Trip Extensions
- Does the company allow “bleisure” or business leisure travels?
- What counts as business leisure trip extensions?
- Will the company shoulder accommodation extensions?
- Will employees continue to receive an allowance during leisure trip extensions?
Create Your First Business Travel Policy Draft
The key to creating a business travel policy that employees would find helpful and gladly follow is to always put the employees’ needs first.
Moreover, make sure you take into account the current size of the company and its expected growth in the following years. Although the company may be limited to business trips to neighboring cities or states, for now, a fast-paced growth may require international travel in the following year or two.
As such, it’s important to try to include policies for everything the employees may experience in the future. Future-proofing your business travel policy allows you to keep it for a longer time and avoid rewriting it each year.
Get feedback from different people after finishing the first draft. If there are points that need to be revised, do so before submitting the first draft for management approval.
It’s normal for travel policy drafts to go through several rounds of revisions. Don’t be disheartened by these. Instead, use it as an opportunity to improve the policies and get actionable feedback from the people who would eventually use them.
Implement the Business Travel Policy
Once the travel policy is approved by the company executives and other stakeholders, you can start to share it with all the employees. We recommend having a town hall meeting to introduce the new policies and brief employees on the most important points.
Another way to improve policy implementation and compliance rates is by providing all employees with a copy of the document. You can do this through a company wiki page, an intranet page, a shared folder or file on the company cloud platform, or a printed booklet.
But how can you ensure employees will read the document?
The best tip we can give to boost policy read-through rates is to include the reimbursement information in the travel policy document. Everyone loves free stuff — and reimbursements count!
Including information that employees genuinely care about in your business travel policy increases the chances of them reading through the whole document.
How to Create an Automated Travel Policy in Locomote
After creating or updating your travel policy document, make sure to create an automated version, too. This is what will boost your travel policy’s compliance rate and further improve employee freedom and autonomy.
Locomote is one of the best business travel management platforms in the market. Our award-winning technology allowed us to help large and small companies streamline their travel programs.
Using our system, travel managers and employees can book, manage, track, and report in one convenient platform, globally.
Now that we’ve guided you on how to build a travel policy document, you can use it to set up an automated travel policy using the Locomote.
Benefits of Using Locomote
Locomote offers a wide variety of benefits for both businesses and employees, including the following:
- Clean and modern user interface
- Easy to navigate mobile app
- Transparent pricing
- Offers group booking
- Dedicated 24/7 travel support at no extra charge
- Allows employees to book their trips
- Real-time data reporting
- Per department budget limits
- Integrates with expenses or finance management tools
- Accepts multiple payment methods
In today’s post-pandemic world, business and leisure travel can still be quite tedious. As infection rates go up and down, and cities and states react accordingly, responding as fast as possible are necessary.
That is exactly what Locomote provides.
Using our platform, travel managers can easily make adjustments based on new travel restrictions and pandemic rates.
You can also adjust the settings based on the data our platform collects from all the travel bookings and costs reported.
How To Cut Travel Expenses Using Automated Travel Platforms
Thanks to our clients and their thousands of employees that use Locomote, we were able to gather enough data and find more ways to help businesses like yours cut down on travel costs.
- Booking flights at least a month or farther in advance if possible
- Providing access to low-cost airlines or carriers, such as Jetstar, EasyJet, Spirit Airlines, and more
- Offering flexible booking rates for easy cancellation or changes
- Setting caps for hotel costs and daily allowances
- Providing options for streamlined account reconciliation
All of these are possible through Locomote. Together with our per-trip pricing setup, exclusive rates, and discounts, companies can save up to 34% in total business travel costs.
Improving Your Corporate Travel Experience
Better business travel management equals a smoother overall travel experience. Help your employee travellers feel more empowered by giving them freedom while also optimising your travel policy.
See how we can optimise your travel program and make your company more efficient.
Click here to get a free, in-depth product demonstration and walkthrough.
BTN's 2021 Business Travel Buyer's Handbook is for travel managers who may be new to the practice or those who may be expanding their responsibility sets. It includes chapter-by-chapter introductory articles covering the ongoing trends and pressures occurring in the travel industry as it recovers from the Covid-19 pandemic.
Chapters Include :
- Structuring a Managed Travel Program
- Establishing A Travel & Expense Policy
- Setting Up A Corporate Lodging Program
- Working With Airlines
- Taking on Travel Risk Management
Download Your Copy Today!
Which of the following statements reflect your involvement with business travel? (select all that apply)
I accept the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy
Course Descriptions
Tvl 101 - introduction to travel and tourism.
This course offers an insightful look into the fields of travel, tourism and hospitality. Students will explore the many exciting career opportunities that await them in an industry that has propelled to the forefront of world business. The economic role of travel and tourism is assessed with regard to its impact on public policy and destination development. Domestic and international air travel, car rentals, rail and the world of lodging are just a few of the topics that will be examined.
Course Learning Outcomes 1. Compare and contrast the hub-and-spoke versus point to point travel systems. 2. Describe the differences in air transportation practices and procedures prior to deregulation versus after deregulation. 3. Explain differences among domestic airline overbooking, denied boarding compensation, and bumping of passengers. 4. Research and compare ancillary fees charged by domestic carriers. 5. Differentiate between domestic and international services. 6. Contrast train service in the United States with that of other countries. 7. Explain the customer qualifications necessary to rent a car both domestically and internationally. 8. Describe various types of hotels and the markets they serve. 9. List the variables that affect hotel room rates. 10. List the benefits of the train travel pass system. 11. Describe various hotel industry procedures using appropriate terminology. 12. Describe the role of a destination marketing organization or tourism board.
Course Offered Fall, Spring
T.V.L. Global Logistics Co., Ltd.

- T.V.L. BUSINESS GROUP

Introduction


In light of the trend of corporate globalization, TVL has noticed that traditional freight forwarding service can not match customer’s need for global supply chain management anymore. To respond the needs for globalization, international purchasing, manufacturing, and marketing from our customers, TVL Business Group set up TVL Global Logistics in 2005 to provide logistics service for customers who require exquisite and integrated service. Our mission is to help our clients save cost and increase revenue by providing supply chain management planning and total logistics solution, and expect the enterprises can keep the leading positions under the globalized competition.
Address:4F., No.217, Sec. 3, Nanjing E. Rd., Zhongshan Dist., Taipei City 104, Taiwan (R.O.C.) Reg. No.:97478872 TEL:+886 2 2514-8388 FAX:+886 2 2778-5681


- Kindle Store
- Kindle eBooks
- Business & Money
Promotions apply when you purchase
These promotions will be applied to this item:
Some promotions may be combined; others are not eligible to be combined with other offers. For details, please see the Terms & Conditions associated with these promotions.
Buy for others
Buying and sending ebooks to others.
- Select quantity
- Buy and send eBooks
- Recipients can read on any device
These ebooks can only be redeemed by recipients in the US. Redemption links and eBooks cannot be resold.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
The Business Travel Handbook Kindle Edition
If you read this book cover to cover before your next business trip, you will be set up for success before you even step onto the plane. The Business Travel Handbook is packed with more than twenty-five years of practical experience from an international business expert who’s worked in sixteen countries and surpassed his millionth mile traveling.
Written for novices and experienced business travelers alike, the guide is organized in a straightforward manner so that veteran travelers can easily find the areas that can help them quickly. Meanwhile, for novice travelers, the book begins with a helpful explanation of how to build a personal brand and how to adapt your mindset to any travel or business situation. From there, the text takes readers on a business trip—from the planning all the way through the return trip home. You’ll learn what to pack, tips on working trade shows, how to travel well with colleagues, the art of balancing work and personal time, as well as the latest info on helpful smartphone apps and gadgets for business travel.
Business travel doesn’t have to be exhausting or overly complicated. Learn how to make business travel enrich your career and your life.
- Print length 202 pages
- Language English
- Sticky notes On Kindle Scribe
- Publication date December 7, 2014
- File size 1216 KB
- Page Flip Enabled
- Word Wise Enabled
- Enhanced typesetting Enabled
- See all details
Editorial Reviews
About the author.
Technology industry executive Bill Butler is a million-mile business traveler based in the San Francisco area who holds both United States and Canadian citizenship. Over his career, he's lived and worked in three countries and has done business in sixteen countries. Having made an art of international business, Butler decided to write The Business Travel Handbook to share the tips and tricks he's learned doing business around the world.
Product details
- ASIN : B00QQO3LEG
- Publication date : December 7, 2014
- Language : English
- File size : 1216 KB
- Text-to-Speech : Enabled
- Screen Reader : Supported
- Enhanced typesetting : Enabled
- X-Ray : Not Enabled
- Word Wise : Enabled
- Sticky notes : On Kindle Scribe
- Print length : 202 pages
- Page numbers source ISBN : 0692239898
Customer reviews
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 5 star 82% 18% 0% 0% 0% 82%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 4 star 82% 18% 0% 0% 0% 18%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 3 star 82% 18% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 2 star 82% 18% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 1 star 82% 18% 0% 0% 0% 0%
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
Report an issue
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Registry & Gift List
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
- South Africa
- Czech Republic
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- Guest Posts
- Travel Ramblings
Russia: One Week Itinerary
Russia , the largest country in the world has been on my bucketlist for the longest time. This is where the first ‘women only’ tour of Ticking the Bucketlist is headed. We are off tomorrow and would be spending one week in this enchanting land!
Here is what our ‘one week in Russia’ itinerary looks like….
Day 1: Moscow – Izmailovsky Flea Market and ‘Moscow by Night’
We start our trip from Delhi on an Aeroflot flight and reach Moscow at about 0835 in the morning. We head straight to our hotel to stretch our legs and get some shut-eye. We need to charge our batteries for the Russian sojourn. We are staying in the Best Western Vega at the Izmailovsky area, which is very famous for its local flea market. The Izmailovsky Market is the best place in Moscow for souvenir shopping …dolls, porcelain, jewelry boxes…we will buy them all from here.
Day 2: Moscow – Moscow City Tour and Kremlin Tour
A red building at the Red Square of the Kremlin
Having seen the city’s light the previous night, it is time to see the city’s colours this morning. We will set off on the Moscow City Tour shows us the highlights of city, starting with the Red Square. This is our day to click a 1000 pictures in front of all the monuments that represent Moscow…St Basil’s Cathedral, the Bolshoi theatre, the Olympic Stadium and the Sparrow Hills.
Exploring the Kremlin
Today is also the day to visit and learn more about the most famous monument in Russia. Kremlin, literally means a fort inside a city. Dynasties built on the site, one century after another and the site came to known as the Kremlin in the 14the century. The walled structure of the Kremlin includes palaces and cathedrals… and a historical past!
Later in the evening, we will enjoy the Russian circus that many of us have seen to television ever so often. Acrobats, clowns and animals….its is time to let the little girl in you come out and clap her hands!
Day 3: Moscow – Metro Stations and Arbat Street followed by the Bolshoi Ballet
Mosaics on the walls of the metro station
Today, we set out to explore the metro stations of Moscow, each of which is a stellar work of art. Stunning frescos and chandeliers in marble surroundings… it’s a work of art! We will then walk along the Arbat street, which is the city’s only pedestrian street, lined with shops and cafes.
As the night unfolds, I intend to don a classy dress and get set to watch one of the finest shows on earth at the Bolshoi Theatre. I have always been awestruck by the art form and would love to see some of the best performers in the world move gracefully. A performance that is rated as one of the best in the world has to be ticked off my bucketlist!
Day 4: Moscow – Day Tour to Sergiev Posad followed by a crazy bar hopping night!
Sergiev Posad is one the strongest spiritual centres in Russia. Home to stunning churches, Sergiev Posad will give us a flavour of the famous ‘Golden Ring’ of Russia. The tour will take 5-7 hours and we will be back at the hotel in second half.
Exploring Sergiev Posad
This will be our last night in Moscow, and we are not going to leave the city without sampling some fine Russian vodka. So, this night is dedicated to bar hopping and pub crawling. Hope to meet some travellers and make new friends.
Day 5: Saint Petersburg – Sapsan train experience to Saint Petersburg and Matryoshka Doll painting class
Saint Petersburg , our next destination, is at least 700 km away from Moscow… and we will zip zap zoom on the Sapsan (the high speed train) to get there in about four hours! The high speed trains are engineering marvels, worth experiencing and we ride this iron horse in the afternoon, reaching St Peterburg in the evening.
As a group, we also join a masterclass to paint our own nested Matryoshka dolls… our own little souvenir to carry and remind us of a fun week in Russia.
With our very own Matryoshka dolls!
Day 6: Saint Petersburg – City Tour and Peterhof Palace
The day starts with a city tour of Saint Petersburg that will give us a peek into what this city has… many bridges, stunning castles, colourful cathedrals and fortresses.
Post lunch, we will head to the Peterhof Palace, also called the Russian Versailles. With spring having set in, the gardens would be green and the fountains will put up a show…I am excited!
Peterhof Palace
Day 7: Saint Petersburg – Hermitage Museum and Shopping
The highlights tour on the previous day will surely make us want to see more of Saint Petersburg…and we will do so by visiting the Hermitage Museum, which is also called the ‘Louvre of Russia’. The Hermitage complex itself is of architectural delight … and the collections have stories to speak which will hopefully, spike our interest enough to make to go back read our history textbooks.
The Hermitage Museum
The rest of the day is totally free to visit any of the other monuments or simply shop … it’s every girl’s favourite sport, isn’t it?
Our last night Russia… Oh Russia!!!! Tonight we will explore the party scene in SPB … or maybe … pack for the next day?
Day 8: Saint Petersburg …Bye Bye Russia
Memories, souvenirs and new friendships… it’s time take them all back to India! We check out of our hotel and take the flight from SPB to Delhi, via Moscow.
Farewell Russia!
You may also like
About post author, 11 responses.
Your photos are beautiful! I have always wanted to visit Russia, especially after seeing Anastasia (the Disney movie) 🙂 I can’t believe those mosaics are on the walls at the METRO STATION! How unreal. Great stuff, thanks for sharing.
Wow that is quite an awesome itinerary. I mean… huge Russia in 1 week. I am still dreaming of St. Petersbourg. So many people told me that it is gorgeous. And I would die to see the Ballet
You know I have never considered Russia but this itinerary looks amazing. St. Petersburg looks beautiful. I will certainly consider a trip there now
I’ve only been to St Petersburg so far, and did a few tours in the city and around. But I have a good friend in Moscow, so the incentive is definitely there to go back. I enjoy doing those by night experiences and see how cities transform in different times of day – especially if it’s topped with a circus visit, amazing 🙂
We are thinking of heading to Russia next Summer so will deffo use this itinerary, looks amazing! Would love to visit the Kremlin in Moscow! Thanks for sharing!
I have always been fascinated by Russia. I like the colourful rounds domes on the Palaces just like an Aladin’s Palace. FIFA Football World will be held in Russia next year and I will try my best to visit this beautiful country and will follow your itinerary and contact you. 🙂
Moscow and Kremlin city tour looks amazing. Your one week itinerary is helpful and complete tour of Russian delights. St.Petersburg city tour is also enchanting and splendid. I really want to have Russian vacation now after seeing your pictures
Wow, this is awesome. Well weaved itinerary! We had always dreamed of taking pictures of those onion-domed palaces and those colors on the palaces are just mind blowing. We didn’t know that there is a Versailles in Russia the exterior paint and the colors look much similar. We had loved it in France and would love to visit it in Russia too.
The Peterhof Palace is a delight to visit. Highly recommend it if you are in SPB
I haven’t visited Russia, but it’s definitely on the list! This a great itinerary, I love how you included things to do but also gave some leeway to do things on your own as well (like shopping haha). Beautiful pictures, the buildings and Russian dolls are stunning! I wonder if they’re all hand painted.
The dolls are all hand painted. The cost increases depending on the quality of work and the artist.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Currently you have JavaScript disabled. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your browser.
Let’s Travel
Your Name (required)
Your Email (required)
Your Message

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This system is the property of Lockheed Martin and its subsidiaries and affiliates ("LM") and is intended for the use of authorized users only. Employees and users of these computing and information resources should have no expectation of privacy with regard to the use of these resources, except where the employees or users are located in a ...
OLICY TVL 1-1PURPOSEThese policies and procedures are designed to act as a guideline for business travel and entertainment expense and miscellaneous expense c. arges/reimbursements. They are intended to keep pace with industry best practices while balancing concern for traveler s. fety and convenience. It is the Company's intent that travel ...
• CPS-001 Ethics and Business Conduct Policies. Uphold the Code. Page 2. ... • CRX-253 Social Media • CRX-303 Electronic Messaging • CRX-325 Business Travel • CRX-327 Commercial Cards • TVL-001 Business Travel Handbook.
Visit LMPeople > Security, Safety, and Travel > International Security > Traveler's Suitcase > Travel Reporting > Initiate A New Trip Note: Reporting international personal and business travel (travel outside of the United States, U.S. possessions and territories) to the U.S. government is a requirement for all personnel who maintain a U.S ...
When it comes to business travel, a well-defined section in the handbook can provide employees with the necessary information to navigate the process smoothly. This guide will delve into the key elements to include in your employee handbook's business travel section, offering explanations, examples, and best practices to create a robust and ...
Having a travel policy helps you: Control travel costs. Determine how reimbursement works. Compile a list of trusted and approved travel vendors. Manage an employee's travel experience and safety. Cut rogue bookings - and simplify approvals. Budget, report on travel expenses and activity and reconcile bookings.
The company estimates its U.S.-booked air volume will decline by $2.6 million in 2018 to $201 million. Of the company's 2017 U.S.-booked dollar volume, 52 percent was for international travel. The percentage of airline tickets that were made through the organization's approved online tools was 85 percent, and 98 percent of those were transacted ...
Anyone wanting to reach the Office of Ethics and Business Conduct may do so by any of the following methods: Call: 800-LM ETHIC Domestic or International: 800-563-8442 For the Hearing or Speech Impaired: 800-441-7457. Write: Ethics Office Lockheed Martin Corporation 6801 Rockledge Drive Bethesda, MD 20817.
BUSINESS TRAVEL BUYERS HANDBOOK 2018 TCT www.businesstravelnews.com MANAGING TRAVEL TODAY IS AN EXERCISE IN BALANCE. A WELL-MANAGED program must balance cost containment with traveler satisfaction, traveler compliance with traveler productivity on the road, and traveler comfort and convenience with safety and security.
The travel policy guide also highlights areas where you can introduce cost-saving measures and support risk management. This guide will help you with: Understanding the importance of a travel policy. Booking travel and expense processes. Air and rail policies. Lodging policy. Car rental policy. "Before at NTTS, there were a lot of policies ...
A Step by Step Guide to Writing a Business Travel Policy. Now that we've had a better perspective on travel policy dos, don'ts, and the benefits, it's time to focus on writing one. Here is a quick look at our seven-step, fool-proof process for writing a modern business travel policy: 1. Review existing or previous travel policies
Travel Policy Workbook 2. The Global Business Travel Association (GBTA) advises that an organization can reduce travel costs by creating and enforcing a clear travel and expense policy. Your travel policy is the engine that powers everything related to your travel management process. A corporate travel and expense policy is key to establishing ...
This document outlines Lockheed Martin's policy on gifts, hospitality, business courtesies, and sponsorships. It defines key terms like bribes, business courtesies, public officials, and nominal value. The policy applies to Lockheed Martin employees and representatives. It prohibits bribery and kickbacks. Business courtesies and sponsorships must avoid even the perception of favoritism and ...
Travel Management Handbooks. Travel Policy Related Documents. Explore. Budget Operation and Execution. Financial Reporting. Internal Controls. Travel. Useful Links. CFO/ASA Home.
BTN's 2021 Business Travel Buyer's Handbook is for travel managers who may be new to the practice or those who may be expanding their responsibility sets. It includes chapter-by-chapter introductory articles covering the ongoing trends and pressures occurring in the travel industry as it recovers from the Covid-19 pandemic. Chapters Include ...
The Financial Services Center offers a professional, courteous help desk that provides assistance regarding entitlements and usage of the Web-based travel system. Phone Number: 1 (866) 533-0188.
TVL Business Group has been set up for more than 30 years. We earn very good reputation in the transportation service industry and were selected as one of the top 500 companies in service industry in Taiwan by Common Wealth Magazine for many years as well. Our services include ocean freight, air freight, customs brokerage, warehouse, and inland ...
Adhering to the motto of "preserving legacy for next generations by loyalty; achieving worldwide reputation through diligence," two founders Kenneth Lee and Frank Roan established the first company of T.V.L.BUSINESS GROUP in 1980 as an international multi-modal transportation provider. Its major core businesses include ships management and ...
Toggle navigation Menu Monroe Community College. Academics. Majors & Programs; Class Schedule; Academic Departments; Corporate College
To respond the needs for globalization, international purchasing, manufacturing, and marketing from our customers, TVL Business Group set up TVL Global Logistics in 2005 to provide logistics service for customers who require exquisite and integrated service. Our mission is to help our clients save cost and increase revenue by providing supply ...
The Business Travel Handbook is packed with more than twenty-five years of practical experience from an international business expert who's worked in sixteen countries and surpassed his millionth mile traveling. Written for novices and experienced business travelers alike, the guide is organized in a straightforward manner so that veteran ...
The Business Travel Handbook is packed with more than twenty-five years of practical experience from an international business expert who's worked in sixteen countries and surpassed his millionth mile traveling. Written for novices and experienced business travelers alike, the guide is organized in a straightforward manner so that veteran ...
Having seen the city's light the previous night, it is time to see the city's colours this morning. We will set off on the Moscow City Tour shows us the highlights of city, starting with the Red Square. This is our day to click a 1000 pictures in front of all the monuments that represent Moscow…St Basil's Cathedral, the Bolshoi theatre, the Olympic Stadium and the Sparrow Hills.