The Eight Character Archetypes of the Hero’s Journey

Classic trickster.
In The Hero of a Thousand Faces , Joseph Campbell demonstrated that many of the most popular stories, even over thousands of years and across cultures, shared a specific formula. That formula is now commonly referred to as mythic structure, or the hero’s journey . Even if you’ve never heard of it before, you’ve consumed this “ monomyth ” in works like Star Wars and Harry Potter.
Along with a specific plot structure, the hero’s journey has a repeating cast of characters, known as character archetypes. An archetype doesn’t specify a character’s age, race, or gender. In fact, it’s best to avoid stereotyping by steering clear of the demographics people associate with them. What archetypes really do is tell us the role a character plays in the story. Thinking about your characters in terms of their archetype will allow you to see whether they’re pulling their weight, or if they’re useless extras.
There are many way to categorize the cast of the hero’s journey, but most central characters fall into one of these eight roles:

The hero is the audience’s personal tour guide on the adventure that is the story. It’s critical that the audience can relate to them, because they experience the story through their eyes. During the journey, the hero will leave the world they are familiar with and enter a new one. This new world will be so different that whatever skills the hero used previously will no longer be sufficient. Together, the hero and the audience will master the rules of the new world, and save the day.
J is the heroic tour guide in Men in Black . A cop at the top of his beat, he is suddenly taken behind the masquerade of everyday life. Waiting for him is a world where aliens are hiding among everyday people, and a galaxy can be as small as a marble. While he’s still a cop in essence, his adversaries – and the tools he must wield against them – are nothing like he’s previously known.
Other heroes: any protagonist fits the hero role. Some heroes from stories that stick closely to the hero’s journey are Dorothy from The Wizard of Oz, Alice from Alice in Wonderland, and Luke Skywalker from Star Wars.

The hero has to learn how to survive in the new world incredibly fast, so the mentor appears to give them a fighting chance. This mentor will describe how the new world operates, and instruct the hero in using any innate abilities they possess. The mentor will also gift the hero with equipment, because a level one hero never has any decent weapons or armor.
Glinda the Good Witch from The Wizard of Oz appears soon after Dorothy enters Oz. She describes where Dorothy is, and explains that she’s just killed the Wicked Witch of the East. Then, before the Wicked Witch of the West can claim the ruby slippers, Glinda gifts them to the hero instead.
Often, the mentor will perform another important task – getting the plot moving. Heros can be reluctant to leave the world they know for one they don’t. Glinda tells Dorothy to seek the Wizard, and shows her the yellow brick road.
Once the hero is on the right path and has what they need to survive, the mentor disappears. Heroes must fight without their help.
Other mentors: Morpheus from the Matrix, Dumbledore from Harry Potter, and Tia Dalma from Pirates of the Caribbean 2 and 3.

The hero will have some great challenges ahead; too great for one person to face them alone. They’ll need someone to distract the guards, hack into the mainframe, or carry their gear. Plus, the journey could get a little dull without another character to interact with.
Like many allies, Samwise looks up to Frodo in The Lord of the Rings . He starts the story as a gardener, joining the group almost by accident. He feels it’s his job to keep Frodo safe. But not all allies start that way. They can be more like Han Solo, disagreeable at first, then friendly once the hero earns their respect. Either way, the loyalty and admiration allies have for the hero tells the audience that they are worthy of the trials ahead.
Other allies: Robin from Batman, Ron and Hermione from Harry Potter, and the Tin Man from The Wizard of Oz.

The herald appears near the beginning to announce the need for change in the hero’s life. They are the catalyst that sets the whole adventure in motion. While they often bring news of a threat in a distant land, they can also simply show a dissatisfied hero a tempting glimpse of a new life. Occasionally they single the hero out, picking them for a journey they wouldn’t otherwise take.
The great boar demon that appears at the beginning of Princess Mononoke is a herald bearing the scars of a faraway war. Ashitaka defeats him, but not without receiving a mark that sends him into banishment. This gets the hero moving and foreshadows the challenges he will face.
Heralds that do not fill another role will appear only briefly. Often, the herald isn’t a character at all, but a letter or invitation.
Other heralds: Effie from the Hunger Games, R2D2 from Star Wars, and the invitation to the ball in Cinderella.

5. Trickster

The trickster adds fun and humor to the story. When times are gloomy or emotionally tense, the trickster gives the audience a welcome break. Often, the trickster has another job: challenging the status quo. A good trickster offers an outside perspective and opens up important questions. They’re also great for lampshading the story or the actions of the other characters.
Dobby from Harry Potter is an ideal trickster. He means well, but his efforts to help Harry Potter do more harm than good. And every time he appears in person, his behavior is ridiculous. However, underlying the humorous exterior is a serious issue – Dobby is a slave, and he wants to be free of his masters.
Other tricksters: Luna Lovegood (also from Harry Potter), Crewman #6 from Galaxy Quest, and Merry and Pippin from LoTR.
6. Shapeshifter

The shapeshifter blurs the line between ally and enemy. Often they begin as an ally, then betray the hero at a critical moment. Other times, their loyalty is in question as they waver back and forth. Regardless, they provide a tantalizing combination of appeal and possible danger. Shapeshifters benefit stories by creating interesting relationships among the characters, and by adding tension to scenes filled with allies.
Dr. Elsa Schneider, from Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade , is a very effective shapeshifter. Even after she reveals she is working for the enemy, she and the hero still have feelings for each other. She allows him to steal an item back without getting caught, and he allows her to discover the McGuffin with him. But the distrust between them remains.
Other shapeshifters: Gollum from LoTR, Catwoman from Batman, and Gilderoy Lockhart from Harry Potter.
7. Guardian

The guardian, or threshold guardian, tests the hero before they face great challenges. They can appear at any stage of the story, but they always block an entrance or border of some kind. Their message to the hero is clear: “go home and forget your quest.” They also have a message for the audience: “this way lies danger.” Then the hero must prove their worth by answering a riddle, sneaking past, or defeating the guardian in combat.
The Wall Guard in Stardust is as classic as guardians get. He stands alone at a broken section of stone wall between real world England and the fairy realm of Stormhold. The guard is friendly when Tristan tries to pass into the fairy realm to start his adventure, but he carries a big stick and he’s not afraid to use it.
Other guardians: The Doorknob from Alice in Wonderland, the Black Knight from Monty Python and the Holy Grail, Heimdall from Thor.

Shadows are villains in the story. They exist to create threat and conflict, and to give the hero something to struggle against. Like many of the other archetypes, shadows do not have to be characters specifically – the dark side of the force is just as much a shadow for Luke as Darth Vader is.
The shadow is especially effective if it mirrors the hero in some way. It shows the audience the twisted person the hero could become if they head down the wrong path, and highlights the hero’s internal struggle. This, in turn, makes the hero’s success more meaningful. The reveal that Darth Vader is Luke’s father, right after Luke had ignored Yoda’s advice, makes the dark side feel more threatening.
Other shadows: Voldemort from Harry Potter, Sauron from LoTR, and Maleficent from Sleeping Beauty.
It’s unusual for stories to have exactly one character per archetype. Because archetypes are simply roles a character can take, Obi Won and Yoda can both be mentors, J can be a hero and a trickster, and Effie Trinket can be first a herald, then later an ally. While you shouldn’t rush to add archetypes that are missing, any character that fits more than one is probably important to the story. If you have a character that doesn’t fit any, make sure they are strengthening, and not detracting from, your plot.
Learn More About These Archetypes

P.S. Our bills are paid by our wonderful patrons. Could you chip in?
More in Character Archetypes
Episode 459: chosen ones: classic or cliché.

Six Character Archetypes for Villains

Four Supporting Characters Your Hero Can Learn From

Six Character Archetypes for Sidekicks

Five Arab and Muslim Stereotypes to Avoid
Kathy Ferguson Professor of Political Theory in Star Trek.
Your patronage keeps this site running. Become a patron.
Recent Articles in Storytelling

Finding Your Story’s Throughline

Why Nothing Good Ever Happens in an Interlude

How to Write Barbs and Banter That Aren’t Mean

Explaining Your Hero’s Secret Parentage

How Much Character Development Is Enough?
Recent comments.
Love Mythcreants?
Be our patron.
Join our community for special perks.
Comments on The Eight Character Archetypes of the Hero’s Journey
Thanks for this great guide!!
Thank you, very informative. Gives a better understanding on how to create a story and “important” NPCs.
Like your name. :)
I like your name
I have a question. In Disney’s/ABC’s Once Upon a Time would you consider Rumplestiltskin/The Dark One to be a Trickster or a Shapeshifter? He’s not a ‘true’ villain though the writer’s class him as a villain. He’s way too complicated to just be a villain!!! He does evil things, bad things, neutral things and sometimes good things, but he keeps changing back and forth. He has the ability to love (his son and his wife Belle) but he ALWAYS puts power above them (it’s more important to him than his son or wife). I always thought of him as ‘the Trickster’ but when I read your description of the Shapeshifter it started me thinking again! hmmmmmm
I haven’t watched enough Once Upon a Time to tell you for sure based on my personal knowledge of Rumplestiltskin, but if he is often working together with the good guys but is liable to betray them or do other bad things, he’s probably a shapeshifter. Tricksters almost always provide comic relief. In the few episodes I watched, it did not look like Rumplestiltskin was a comical character.
However, because the archetypes are roles, characters can have more than one or change what they are. It sounds like sometimes when he is doing especially bad things, he might be a Shadow temporarily.
Shapeshifter
Dianne its a very good question but its really what you think he is.he is apart of many difrent grous and some arnt on this site . The most common thing ppl think he is is a villan but it really isnt like that at all but its up to you. hope i help . sincerely wesh
Would I be right in saying that Magneto in X-Men would be considered a shapeshifter?
Based on my very crude knowledge of X-Men, Magneto is mostly a shadow. Like a good shadow, he is a dark reflection of Professor X. However, he also takes on the role of shapeshifter during their temporary alliances.
No no, the shapeshifter is Mystique. ;)
HA! Good one :D
She can turn into other people, too, so, in literal sense, she is one. I think Chris was talking figuratively.
You’re Welcome!!!!!!!!!!
Msytique es da best chicka in da world mahhh boi
dont do drugs kids
bahahahahah
The description of the shadow is a little misleading. He is not the antagonist, and not evil. He mirrors the side of the hero that he/she is not aware of, but must acknowledge in order to continue and be sucessful on his/her journey.
The Star Wars example with the cave sets it: Yes, Darth Vader is evil (he is antagonist and shadow all in one), but he is also Lukes father. Therefore, he wasn´t always evil. Luke knows this.
A great example for a shadow in film are the two girls in American Beauty. Angela is Janes Shadow. She represents everything that Jane must leave behind in order to get on with her life, find her destiny etc. But Angela is not evil. She is a rather normal teenager. She is Janes friend.
Interesting approach :) (I’m not being ironic)
Usually, shadows are antagonists.
I’m not super familiar with American Beauty, so I could be totally wrong on this, but it sounds like the character dynamic you are describing is the use of a foil. A foil is character who starkly contrasts with attributes of a character (nearly always the main character) in order to highlight certain attributes of a character.
The Shadow is most definitely the opposing force in a literary work. It is true that the shadow – when it is a character – is most effective if it is also a foil of the protagonist as this helps to illustrate how the hero’s conflict is as much internal as external, but existing expressly to mirror the hero in some way is not a defining feature of the shadow.
The villain of American Beauty is societal pressure to be “normal” and the havoc it wreaks on people who are unique and special.
All the characters in the movie in some way rebel against that pressure, some prevail and others are destroyed.
It would be interesting to think up ways to realign quest stories to make different figures the protagonist. Like, say, in the Matrix, they really had me going that Neo wasn’t the one – I thought it would turn out to be Morpheus. Which would mean we were seeing Morpheus’s Hero journey through the eyes of one of his last Guardians (the obstacle preventing Morpheus seeing the Hero he sought was himself).
That would have been really cool. Nobody thinks of themselves as the hero (no competent person anyway). And it would fit perfectly with the Oracle telling Trinity that she would love The One, because love can also be fraternal.
I have only a secondary knowledge of Science Fiction and mythical creatures, gleaned from sitting with my husband and son when they watch shows in the same room with me. I found your page very informative, interesting, and helpful so that I may understand what I am watching Sci-Fi shows or shows about mythology with my family. Thank you.
Thanks for this article! I am actually a sculptor building a portfolio for character modeling. I was told by an industry recruiter to include different archetypes. For the longest time I only vaguely knew what he meant until I read your post. Currently reading the recommended book – excellent by the way! – which I see is the industry bible on this subject. I now have a much clearer picture on what direction to take my work! I also am now starting to see the types as I watch and read things. Great article :-)
I actually feel like Snape is a better example of the shapeshifter than Lockhart.
Good point. He’s always portrayed as evil … up until the end, when you see he was on the other side the whole time.
Zuko from Avatar the Last Airbender seems to be a perfect shapeshifter to me.
Yes. The most common form of the shapeshifter is one who begins as Ally and betrays the hero, but a character taking the inverse course of action is also an example of a shapeshifter. What defines the shapeshifter is that there is at least a key moment where the audience is left to wonder for themselves if the character is friend or foe. Zuko is also a wonderfully written character who undergoes a Heroes quest of his own with Iroh serving as his mentor and Azula taking on the role of shadow. He can be viewed as many roles in series depending on which part of the series you are thinking about.
Sir Didimus (sp?) from Labyrinth would be a penultimate Guardian.
Welcome to the Mythcreants comment section, Jemma Caffyn!
p.s. You have the same name as my favorite scientist (a made-up spec fic scientist, of course)
what about a villian that goes from bad to good?
Unless somehow showing up as the shadow, redeemed villains are not part of Joseph Campbell’s monomyth. The overwhelming majority of myths and stories written before the romantic period had clear villains and heroes. Nietschze explained this by saying that all myths are morality tales; if people believe that there is a definite good and evil then it will be easier for them to accept anything their leaders do so long as their is a greater enemy. It is no coincidence that so many mythical heroes are of noble birth. It has even be argued that morally ambiguous characters are a feature of democracy ( https://www.theatlantic.com/entertainment/archive/2017/03/whats-so-american-about-john-miltons-lucifer/519624/ ).
If you are interested in redeemed villains, this blog has an article and a podcast about them: https://mythcreants.com/blog/creating-your-villains-journey/ https://mythcreants.com/blog/122-redeeming-a-villain/
Can the Drayo State feasibly be attained by a character who doesn’t just confront his or her shadow but cannibalises it and therefore digests the darker side of his or her own nature? Asking for a friend.
Well, first of all, what is the “Drayo State”?
Fantastically useful site & not just for sf & fantasy writers. I’ve learned such a lot. Thanks!
i agree, very useful.
Thanks for helping me do my homework!
Archetypes are kind of like personas in life in general.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Email * (will not be made public)

8 Key Archetypes of the Hero’s Journey
by Lewis / July 14, 2018 / Character Development
Archetypes are something we experience every day…
An older coworker passing along important tips at your new job or a friend turns out to be talking behind your back. Most of us can recognize these as archetypes, but can we apply these familiar patterns to our fictional worlds and characters? The answer is a resounding yes!
Just as we see these character archetypes mirrored in our own lives, they’ll show up in our storytelling as well. Not only do they provide guidelines for making our characters feel like real people, but they can add a whole new layer of complexity and depth to our stories too.
What Is an Archetype?
- 1 What Is an Archetype?
- 2 Our Case Study: Solo
- 3.1 The Hero:
- 3.2 The Shadow:
- 3.3 The Mentor:
- 3.4 The Ally:
- 3.5 The Threshold Guardian:
- 3.6 The Herald:
- 3.7 The Trickster:
- 3.8 The Shapeshifter:
- 4 Repeat Archetypes and How They Work
- 5 Using Archetypes in Your Own Novel

An archetype is a repeated motif or trait found in storytelling.
Based on that definition, you might initially think of the classic “damsel in distress” or “knight in shining armor” from European fairy tales. Both of these do fall under the umbrella of archetypes, however, these aren’t the archetypes we’ll be exploring here.
Instead, the character archetypes of the Hero’s Journey are universal archetypes, roles all characters can fill at different points along their journey. These archetypes help you flesh out your story with a complete cast, while ensuring no character exists without a purpose.
“The archetypes are part of the universal language of storytelling, and a command of their energy is as essential to the writer as breathing.” – Christopher Vogler, The Writer’s Journey
While most of these ideas originated with Joseph Campbell’s Monomyth and the Hero’s Journey, these eight universal archetypes are actually based on Christopher Vogler’s The Writer’s Journey. This book is beyond excellent, and breaks down the ideas of Campbell into a more usable storytelling guide—versus the highly academic The Hero With a Thousand Faces .
Both books are well worth your time, but we’ll be covering Vogler’s description of character archetypes here.
Of course, throughout this article I’ll assume you have at least a basic understanding of the Hero’s Journey. If you’re not familiar with this story structure, then check out my breakdown of the Hero’s Journey here.
Our Case Study: Solo

Rather, Solo is great for studying universal archetypes because each of its characters exhibits archetypal roles in interesting ways. Far from being stereotypes, Solo proves that these universal archetypes are the building blocks for forming unique characters.
For those unfamiliar with the movie, Solo is the origin story of Han Solo from the original Star Wars trilogy—and there will be major spoilers for Solo in this article.
Please enter at your own risk.
If you wish to continue but need a refresher on the plot, check out the Movie Structure Archives entry for Solo. It’ll give you a full breakdown of all the plot points I’ll be referencing here.
The 8 Universal Character Archetypes
You’re likely already familiar with the basics of the Hero archetype. After all, your protagonist will fill this role for most of your story as they overcome their flaws, drive your plot forward, and make important sacrifices.
Ultimately, their decisions will determine the outcome of the Climax .
However, other characters can also wear the Hero archetype at different points in your story. An Ally may become the Hero while your protagonist is incapacitated, or a Trickster may face a sudden change of heart. This dynamic allows other characters to temporarily take the spotlight and fulfill important story functions or resolve subplots.
In our case study, Han Solo fills the role of the Hero, though various Allies such as Val also fill it under special circumstances.
This makes sense because—beyond being on all the posters—this is Han’s journey. He grows the most from beginning to end, and is the catalyst for the movie’s progression. When the cast gets into a tight spot with Dryden Vos, it’s Han’s choices that propel them into the conflict. Not only that, but he is who the audience identifies with the most, meaning he checks all the boxes of the Hero archetype.
Of course, because the Hero is such a central archetype, it also has a whole host of specific traits and trials that go along with it. For more on the Hero’s character arc, check out this article.
The Shadow:
Just as the Hero archetype aligns with your protagonist, the Shadow is linked to your antagonist. This archetype seeks the antithesis of your Hero’s goals, often the destruction of what the Hero wishes to preserve.
Essentially, the Shadow embodies the dark aspects of the Hero.
The Shadow is meant to personify the suppressed wounds and inner struggles that the Hero will need to overcome—and this is why antagonists are often called “foil characters.” They’re a warning about what your protagonist will become if they fail to learn.
Of course, just like many characters can act as the Hero, many characters take on aspects of the Shadow. Your Hero may behave like the Shadow in moments. Allies, Heralds, and Threshold Guardians may do so as well, allowing you to create depth in characters that have thus far served only one purpose.
In Solo, Dryden Vos—from his name to his appearance and demeanor—screams antagonist. Because of this, it’s fairly obvious that Vos serves as the Shadow for most of the story.
However, he’s not the only character who plays this role.
While it’s easy to see Vos as the Shadow, Qi’ra actually fills this archetype in an even more crucial way. You see, Qi’ra’s role as a Shadow is intrinsically tied to Han’s character arc. Both begin from the same place and both are seeking to escape to a better life, but where Han’s journey molds him into a Hero, Qi’ra becomes a Shadow. This is a powerful contrast, and one we’ll be returning to later in the article.
The Mentor:
Acting as the Hero’s main guidance throughout their journey, the Mentor comes in many forms, but they always serve a critical purpose.
An elderly woman giving a soon-to-be bride a magic mirror to see the true face of her new husband or a veteran sports coach training young players both embody the Mentor archetype. This archetype is there to equip the Hero through knowledge, encouragement, and skills that allow them to overcome the conflict of the story and eventually surpass their flaws.
Of course, Mentors are a great opportunity to add depth to a story.
Because of this, Mentors often take on aspects of Threshold Guardians as Heroes prove their worth in exchange for help. Meanwhile, Shadow Mentors may seem to guide the Hero while actually misleading them—sometimes maliciously, sometimes mistakenly.
For example, while Han works under the guidance of a variety of Mentors throughout Solo , Tobias Beckett fills this role most often. He guides Han in how to deal with Vos, he teaches Han about this new world of crime, and he encourages Han at every step to leave it. Tobias clearly wears the mask of the Mentor archetype, but we’ll be coming back to him soon, as that isn’t the only archetype he wears.
The third of the well-known archetypes, Allies are seen in every story.
After all, Heroes need a friend to lean on, someone to lighten the load of the journey or to practice their growing skills with. That’s the role of the Ally, seen through characters like Samwise Gamgee in The Lord of the Rings , or Toto in The Wizard of Oz .
Because of how broad this archetype is, it serves many functions and can take on the aspects of many other archetypes. An Ally might act as a Mentor or may descend into a period of being a Shadow or Trickster. Thanks to this complexity, Allies are a great tool for humanizing your Hero, relieving tension, and furthering explore your story’s themes through subplots.
Fortunately, Ally archetypes are usually easy to identify, and primary Ally for Han is Chewbacca.
Audiences knew Chewie well before the story of Solo began, and he has served the same Ally role throughout the Star Wars series. Chewie is someone for Han to banter with and rely on, and he ends the movie as Han’s only lasting companion. While other characters such as Lando and Qi’ra wear the Ally archetype for only a short period of time, Chewie remains an Ally archetype for the entirety of Han’s life.
The Threshold Guardian:
Often an aspect of the Shadow, Threshold Guardians are there to represent the fears of your Hero and to challenge them as they progress along their journey. Of course, much like the midterm exams you may have had in school, Threshold Guardians aren’t the final test. Still, without your Hero proving they’ve mastered their new skills, these Guardians will prevent them from reaching their final test at all.
While Threshold Guardians are often henchmen of the Shadow, Mentors and Allies can also fulfill this role. For example, an Ally who has second thoughts about their quest might challenge the resolve of your Hero, forcing them to overcome their own doubts to convince their uncertain ally.
One of the primary Threshold Guardians on Han’s journey—though there are many—is a familiar character: Tobias Beckett.
Beckett’s role as a Threshold Guardian cannot go understated, and he actually embodies this role before he takes on the mantle of Mentor. When Han is struggling to get out of the Imperial Army, Tobias refuses to allow him into his gang and even gives him up to Imperial forces as a traitor. Fortunately, Han is persistent, and proves his value to the gang through his quick thinking. Only after he proves himself does Tobias allow him to join, fulfilling the role of the Threshold Guardian.
The Herald:
The Herald’s name gives away much of its function—your story’s Herald is there to give the Call to Adventure, to foreshadow the coming conflict, and to warn the audience that your Hero’s Ordinary World will soon fall away.
Based on this description, the Herald may sound like another aspect of the Shadow, and it certainly can be. However, it can also be a positive force, such as the spitfire young girl who coaxes the lonely bounty hunter out of his shell in, True Grit .
In Solo , the Herald is a character we’ve mentioned before.
From the start of Han’s journey, his mission has been the same—go back for Qi’ra. When he gets caught up with Beckett and his gang, this is still his focus. However, when he finally finds Qi’ra again, she’s not the scrappy child he remembers. This Qi’ra is powerful, elegant, respected, and under the frightening control of Vos.
Suddenly the dynamics of Han’s journey have shifted, and he can no longer live with the “one-day” mentality he had previously been had. His goal becomes urgent and firmly focused on the present, all thanks to Qi’ra’s role as the Herald.
The Trickster:
Next up, we’ll be looking at the Trickster archetype. A classic comedy character seen in sidekicks from a variety of genres, Tricksters are a great way to manage the pace your story. These moments of comedy relieve the tension built up by more action-packed moments, letting your readers take a moment to breathe.
Used in reverse, Tricksters are also great at increasing the weight of key scenes.
A character that’s been light-hearted throughout your story can suddenly turn serious as they approach the Climax. Your readers will take notice, and will soon find themselves anxiously wondering about what’s to come. If this previously comedic character is suddenly changing their tune, then the stakes of the adventure must be rising.
Serving as the Trickster in Solo , we have another repeat character from the original Star Wars trilogy: Lando Calrissian, along with his droid L3-37.
They provide the audience with plenty of antics and absurdities, lightening the mood between darker segments. For periods of the story Lando also serves as an Ally, but his true alliance is always with himself. Fortunately this isn’t malicious and is instead played for laughs, making him a strong Trickster character.
The Shapeshifter:
If you like to fill your stories with suspense you likely have one—if not many—important Shapeshifter characters.
Like the example of the traitorous friend we talked about at the start of this article, the Shapeshifter shows a different face when looked at from different angles. Seductresses, both sexually and in other ways, work to trick the Hero by presenting an alluring offer to their problems while seeking to trap or defeat them when they aren’t looking.
Shapeshifters aren’t always Shadows either.
For instance, the Hero may believe they have an Ally only to find a Shadow, leaving them betrayed and confused. Other times the Shapeshifter may start out as a Shadow, before becoming an Ally later on. This flexibility lets you layer the Shapeshifter archetype into existing characters to create suspense and tension in your story.
Unfortunately for Han, one of his key allies and his Mentor both embody the Shapeshifter archetype, causing suffering on two fronts. For starters, Beckett spends much of the movie acting as a pseudo father-figure, only to betray Han to Vos. This forces Han to kill Beckett to save himself and Chewie, robbing him of his Mentor figure.
Qi’ra engages in a similar betrayal after killing Vos. Han believes he has achieved his goal and that the pair can finally be together, but Qi’ra reveals her allegiance to the Sith and abandons Han. Her betrayal is arguably even more painful for Han than Beckett’s, as it robs him of everything he’s worked towards on his journey.
Repeat Archetypes and How They Work
By this point in the article, you may be wondering…
Why does Qi’ra show up in so many of these archetypes?
Well, to a large extent, this is a sign of how complex her character is. At its core, Solo is about Han and Qi’ra’s shared journey. While Han takes the traditional Hero’s path, Qi’ra represents the failed Hero.
In Qi’ra’s desperation to improve her life, she accepts the horrible actions committed by herself and other to gain power in exchange for using that power to protect herself. While the Climax sees Han letting go of his past and adhering to his moral compass, Qi’ra gives into her inner struggle, choosing security at the expense of happiness.
Ultimately, her archetypal roles reflect her struggle against herself. In the end, power and safety are more important than anything else—she’s suffered too much to make any other choice.
Using Archetypes in Your Own Novel
Like many other aspects of story structure , the archetypes of the Hero’s Journey are a guide—and as you’ve seen, they can be combined to create an infinite cast of characters. To help manage this complexity, I would recommend thinking of these archetypes in terms of primary and secondary archetypes.
- Primary Archetype: the main role the character embodies for the majority of their story.
- Secondary Archetype: the other, smaller archetypal roles they play during specific moments.
Each character has a primary archetype, such as the Mentor, and at different stages of the journey will wear secondary archetypes, such as the Trickster.
From there, if you feel someone is missing from your cast of characters, look at what archetypes aren’t represented. Likewise, if your cast feels bloated, look for characters with repeated archetypes you can remove or combine into one. As we’ve seen, individual characters can serve many archetypal roles, making extraneous characters often unnecessary.
Above all, I would recommend reading up on both the work of Joseph Campbell and Christopher Vogler. Each of them have a lot to offer, and they go into much more detail than I can here.
How do these archetypes appear in your own story? Let me know in the comments!
Thoughts on 8 key archetypes of the hero’s journey.
I’ve always thought that Qi’ra chooses safety in the end, yes, but is also a hero because she saves Han. She takes all eyes off of him and buys his freedom by absorbing responsibility.
Thanks for this.
I loved how detailed these descriptions are. I can see I need to learn more about shapeshifters and my first thought is going to be taking one of the antagonists in my story and shifting them over to being an ally character. This is going to be interesting.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Holiday Savings

cui:common.components.upgradeModal.offerHeader_undefined
The hero's journey: a story structure as old as time, the hero's journey offers a powerful framework for creating quest-based stories emphasizing self-transformation..

Table of Contents
Holding out for a hero to take your story to the next level?
The Hero’s Journey might be just what you’ve been looking for. Created by Joseph Campbell, this narrative framework packs mythic storytelling into a series of steps across three acts, each representing a crucial phase in a character's transformative journey.
Challenge . Growth . Triumph .
Whether you're penning a novel, screenplay, or video game, The Hero’s Journey is a tried-and-tested blueprint for crafting epic stories that transcend time and culture. Let’s explore the steps together and kickstart your next masterpiece.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey is a famous template for storytelling, mapping a hero's adventurous quest through trials and tribulations to ultimate transformation.
What are the Origins of the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey was invented by Campbell in his seminal 1949 work, The Hero with a Thousand Faces , where he introduces the concept of the "monomyth."
A comparative mythologist by trade, Campbell studied myths from cultures around the world and identified a common pattern in their narratives. He proposed that all mythic narratives are variations of a single, universal story, structured around a hero's adventure, trials, and eventual triumph.
His work unveiled the archetypal hero’s path as a mirror to humanity’s commonly shared experiences and aspirations. It was subsequently named one of the All-Time 100 Nonfiction Books by TIME in 2011.
How are the Hero’s and Heroine’s Journeys Different?
While both the Hero's and Heroine's Journeys share the theme of transformation, they diverge in their focus and execution.
The Hero’s Journey, as outlined by Campbell, emphasizes external challenges and a quest for physical or metaphorical treasures. In contrast, Murdock's Heroine’s Journey, explores internal landscapes, focusing on personal reconciliation, emotional growth, and the path to self-actualization.
In short, heroes seek to conquer the world, while heroines seek to transform their own lives; but…
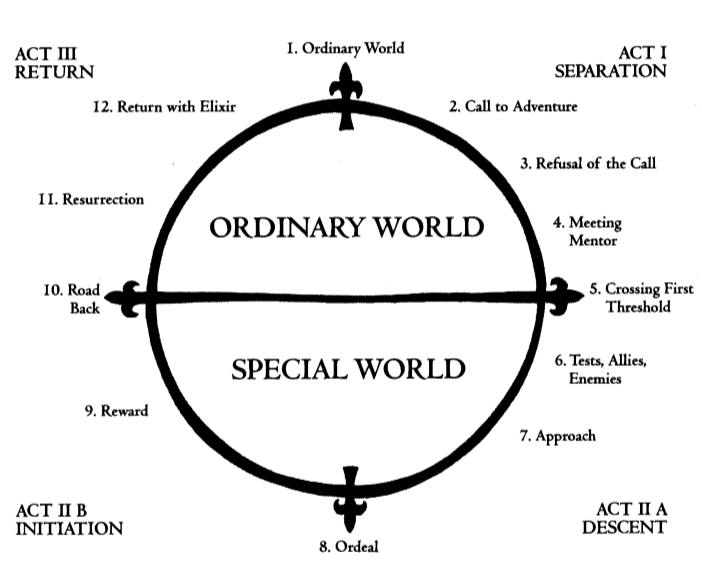
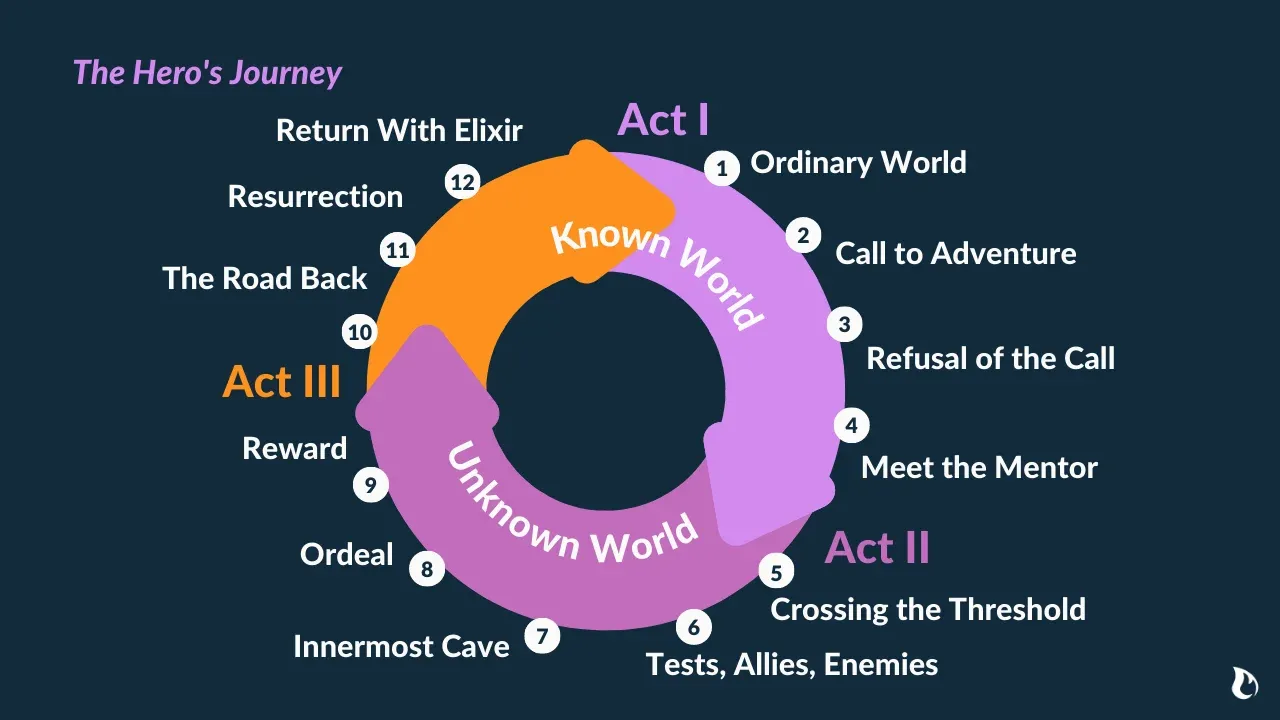
Twelve Steps of the Hero’s Journey
So influential was Campbell’s monomyth theory that it's been used as the basis for some of the largest franchises of our generation: The Lord of the Rings , Harry Potter ...and George Lucas even cited it as a direct influence on Star Wars .
There are, in fact, several variations of the Hero's Journey, which we discuss further below. But for this breakdown, we'll use the twelve-step version outlined by Christopher Vogler in his book, The Writer's Journey (seemingly now out of print, unfortunately).

You probably already know the above stories pretty well so we’ll unpack the twelve steps of the Hero's Journey using Ben Gates’ journey in National Treasure as a case study—because what is more heroic than saving the Declaration of Independence from a bunch of goons?
Ye be warned: Spoilers ahead!
Act One: Departure
Step 1. the ordinary world.
The journey begins with the status quo—business as usual. We meet the hero and are introduced to the Known World they live in. In other words, this is your exposition, the starting stuff that establishes the story to come.
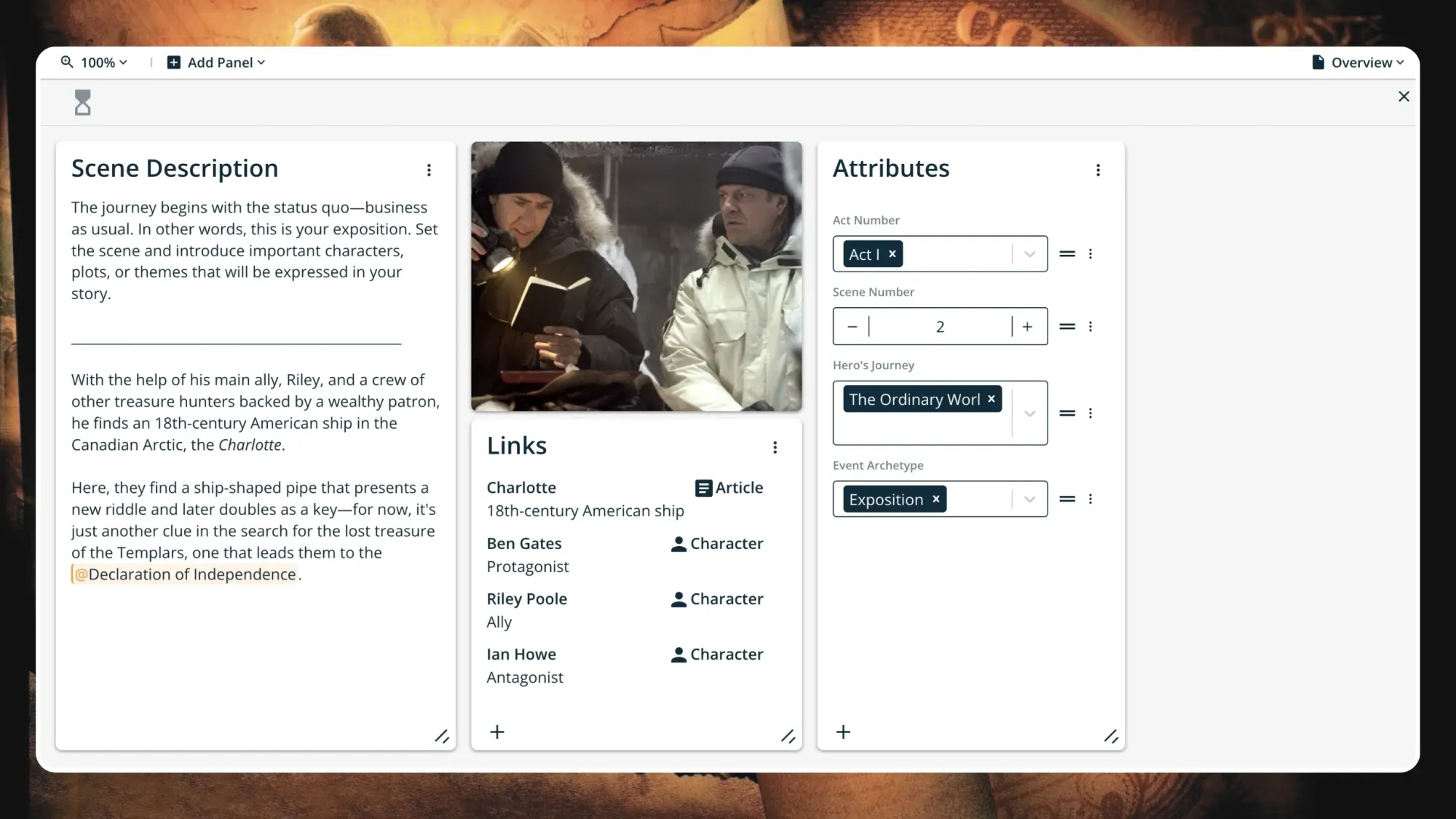
National Treasure begins in media res (preceded only by a short prologue), where we are given key information that introduces us to Ben Gates' world, who he is (a historian from a notorious family), what he does (treasure hunts), and why he's doing it (restoring his family's name).
With the help of his main ally, Riley, and a crew of other treasure hunters backed by a wealthy patron, he finds an 18th-century American ship in the Canadian Arctic, the Charlotte . Here, they find a ship-shaped pipe that presents a new riddle and later doubles as a key—for now, it's just another clue in the search for the lost treasure of the Templars, one that leads them to the Declaration of Independence.
Step 2. The Call to Adventure
The inciting incident takes place and the hero is called to act upon it. While they're still firmly in the Known World, the story kicks off and leaves the hero feeling out of balance. In other words, they are placed at a crossroads.
Ian (the wealthy patron of the Charlotte operation) steals the pipe from Ben and Riley and leaves them stranded. This is a key moment: Ian becomes the villain, Ben has now sufficiently lost his funding for this expedition, and if he decides to pursue the chase, he'll be up against extreme odds.
Step 3. Refusal of the Call
The hero hesitates and instead refuses their call to action. Following the call would mean making a conscious decision to break away from the status quo. Ahead lies danger, risk, and the unknown; but here and now, the hero is still in the safety and comfort of what they know.
Ben debates continuing the hunt for the Templar treasure. Before taking any action, he decides to try and warn the authorities: the FBI, Homeland Security, and the staff of the National Archives, where the Declaration of Independence is housed and monitored. Nobody will listen to him, and his family's notoriety doesn't help matters.
Step 4. Meeting the Mentor
The protagonist receives knowledge or motivation from a powerful or influential figure. This is a tactical move on the hero's part—remember that it was only the previous step in which they debated whether or not to jump headfirst into the unknown. By Meeting the Mentor, they can gain new information or insight, and better equip themselves for the journey they might to embark on.
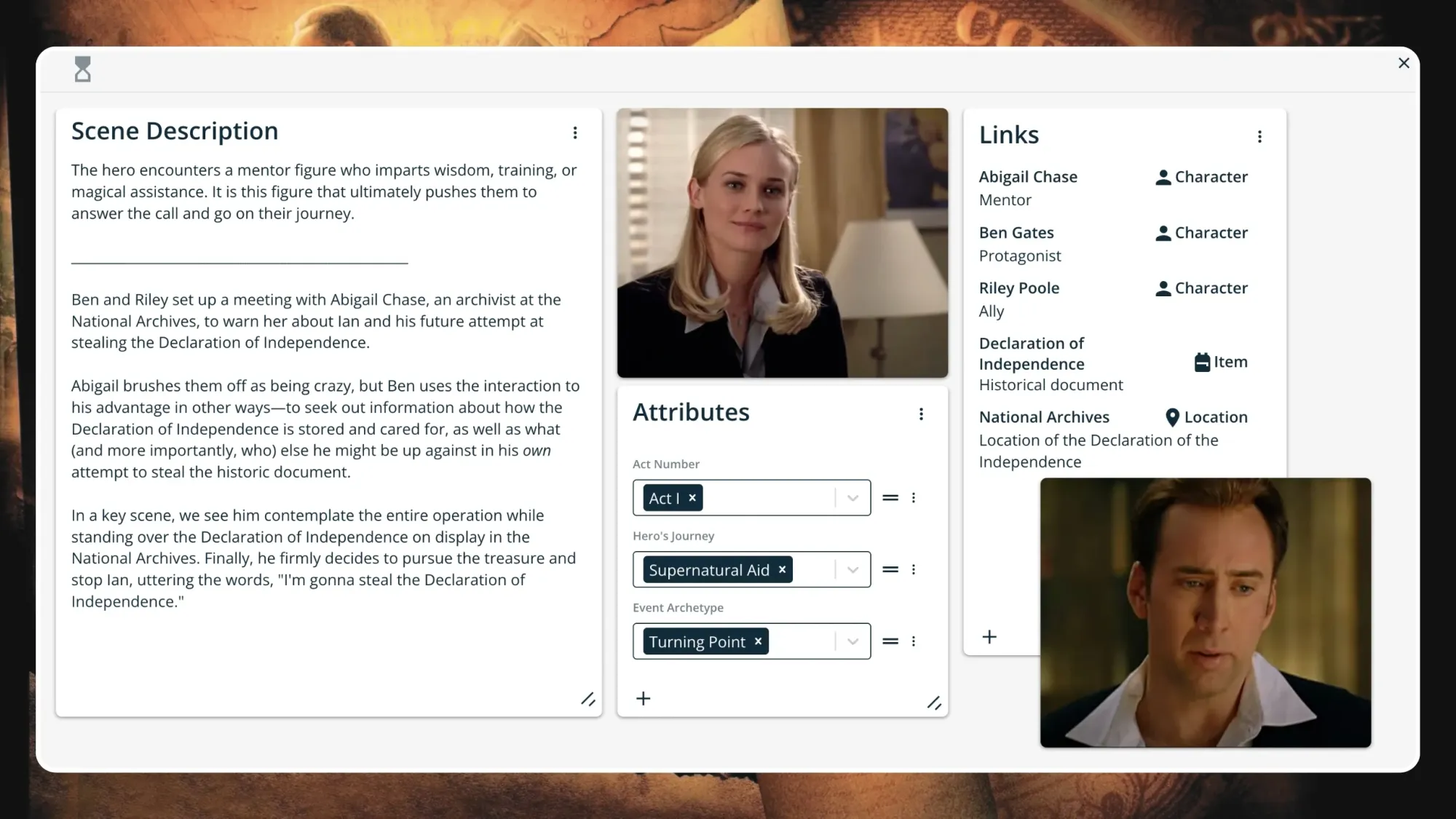
Abigail, an archivist at the National Archives, brushes Ben and Riley off as being crazy, but Ben uses the interaction to his advantage in other ways—to seek out information about how the Declaration of Independence is stored and cared for, as well as what (and more importantly, who) else he might be up against in his own attempt to steal it.
In a key scene, we see him contemplate the entire operation while standing over the glass-encased Declaration of Independence. Finally, he firmly decides to pursue the treasure and stop Ian, uttering the famous line, "I'm gonna steal the Declaration of Independence."
Act Two: Initiation
Step 5. crossing the threshold.
The hero leaves the Known World to face the Unknown World. They are fully committed to the journey, with no way to turn back now. There may be a confrontation of some sort, and the stakes will be raised.
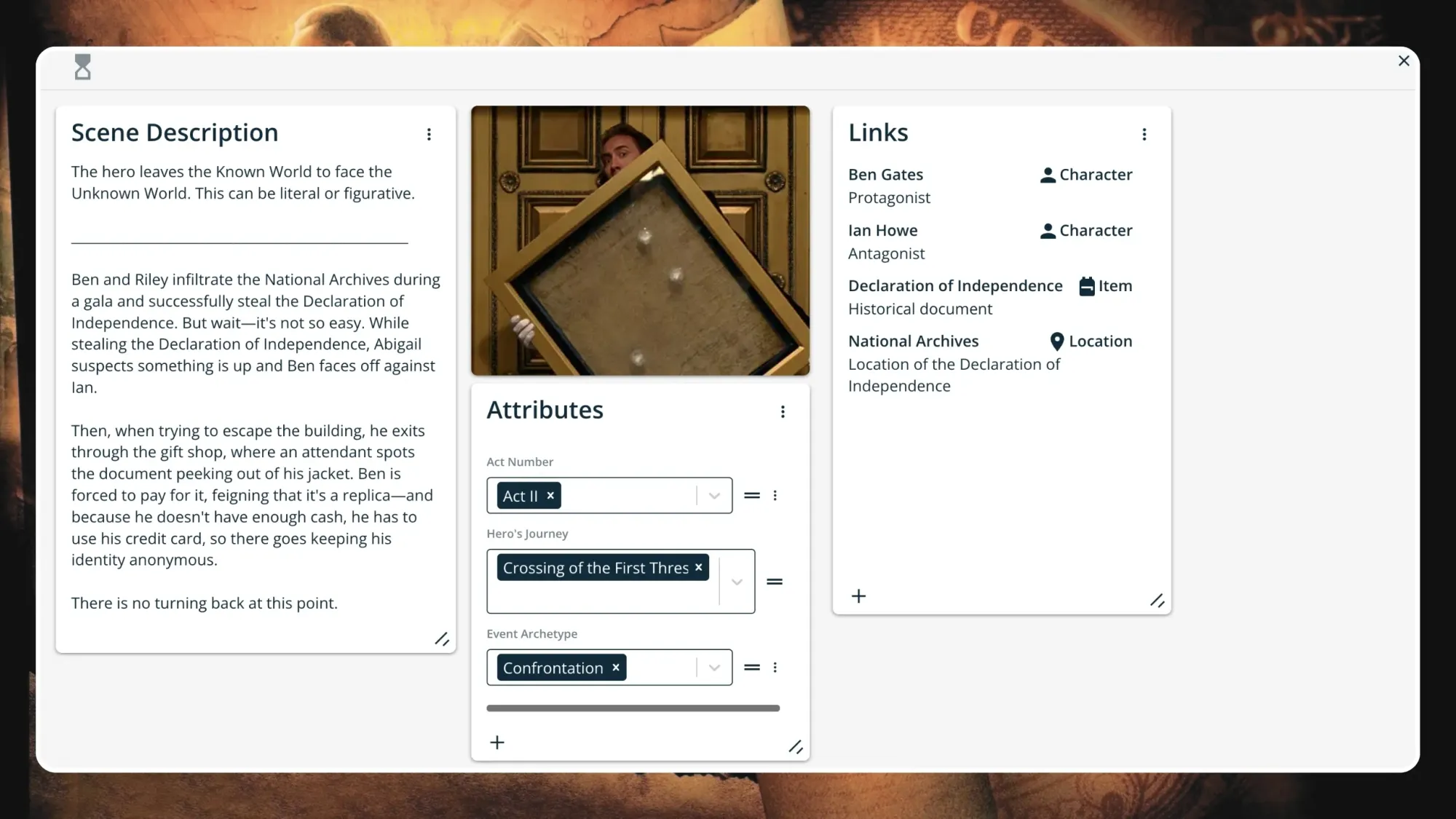
Ben and Riley infiltrate the National Archives during a gala and successfully steal the Declaration of Independence. But wait—it's not so easy. While stealing the Declaration of Independence, Abigail suspects something is up and Ben faces off against Ian.
Then, when trying to escape the building, Ben exits through the gift shop, where an attendant spots the document peeking out of his jacket. He is forced to pay for it, feigning that it's a replica—and because he doesn't have enough cash, he has to use his credit card, so there goes keeping his identity anonymous.
The game is afoot.
Step 6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
The hero explores the Unknown World. Now that they have firmly crossed the threshold from the Known World, the hero will face new challenges and possibly meet new enemies. They'll have to call upon their allies, new and old, in order to keep moving forward.
Abigail reluctantly joins the team under the agreement that she'll help handle the Declaration of Independence, given her background in document archiving and restoration. Ben and co. seek the aid of Ben's father, Patrick Gates, whom Ben has a strained relationship with thanks to years of failed treasure hunting that has created a rift between grandfather, father, and son. Finally, they travel around Philadelphia deciphering clues while avoiding both Ian and the FBI.
Step 7. Approach the Innermost Cave
The hero nears the goal of their quest, the reason they crossed the threshold in the first place. Here, they could be making plans, having new revelations, or gaining new skills. To put it in other familiar terms, this step would mark the moment just before the story's climax.
Ben uncovers a pivotal clue—or rather, he finds an essential item—a pair of bifocals with interchangeable lenses made by Benjamin Franklin. It is revealed that by switching through the various lenses, different messages will be revealed on the back of the Declaration of Independence. He's forced to split from Abigail and Riley, but Ben has never been closer to the treasure.
Step 8. The Ordeal
The hero faces a dire situation that changes how they view the world. All threads of the story come together at this pinnacle, the central crisis from which the hero will emerge unscathed or otherwise. The stakes will be at their absolute highest here.
Vogler details that in this stage, the hero will experience a "death," though it need not be literal. In your story, this could signify the end of something and the beginning of another, which could itself be figurative or literal. For example, a certain relationship could come to an end, or it could mean someone "stuck in their ways" opens up to a new perspective.
In National Treasure , The FBI captures Ben and Ian makes off with the Declaration of Independence—all hope feels lost. To add to it, Ian reveals that he's kidnapped Ben's father and threatens to take further action if Ben doesn't help solve the final clues and lead Ian to the treasure.
Ben escapes the FBI with Ian's help, reunites with Abigail and Riley, and leads everyone to an underground structure built below Trinity Church in New York City. Here, they manage to split from Ian once more, sending him on a goose chase to Boston with a false clue, and proceed further into the underground structure.
Though they haven't found the treasure just yet, being this far into the hunt proves to Ben's father, Patrick, that it's real enough. The two men share an emotional moment that validates what their family has been trying to do for generations.
Step 9. Reward
This is it, the moment the hero has been waiting for. They've survived "death," weathered the crisis of The Ordeal, and earned the Reward for which they went on this journey.
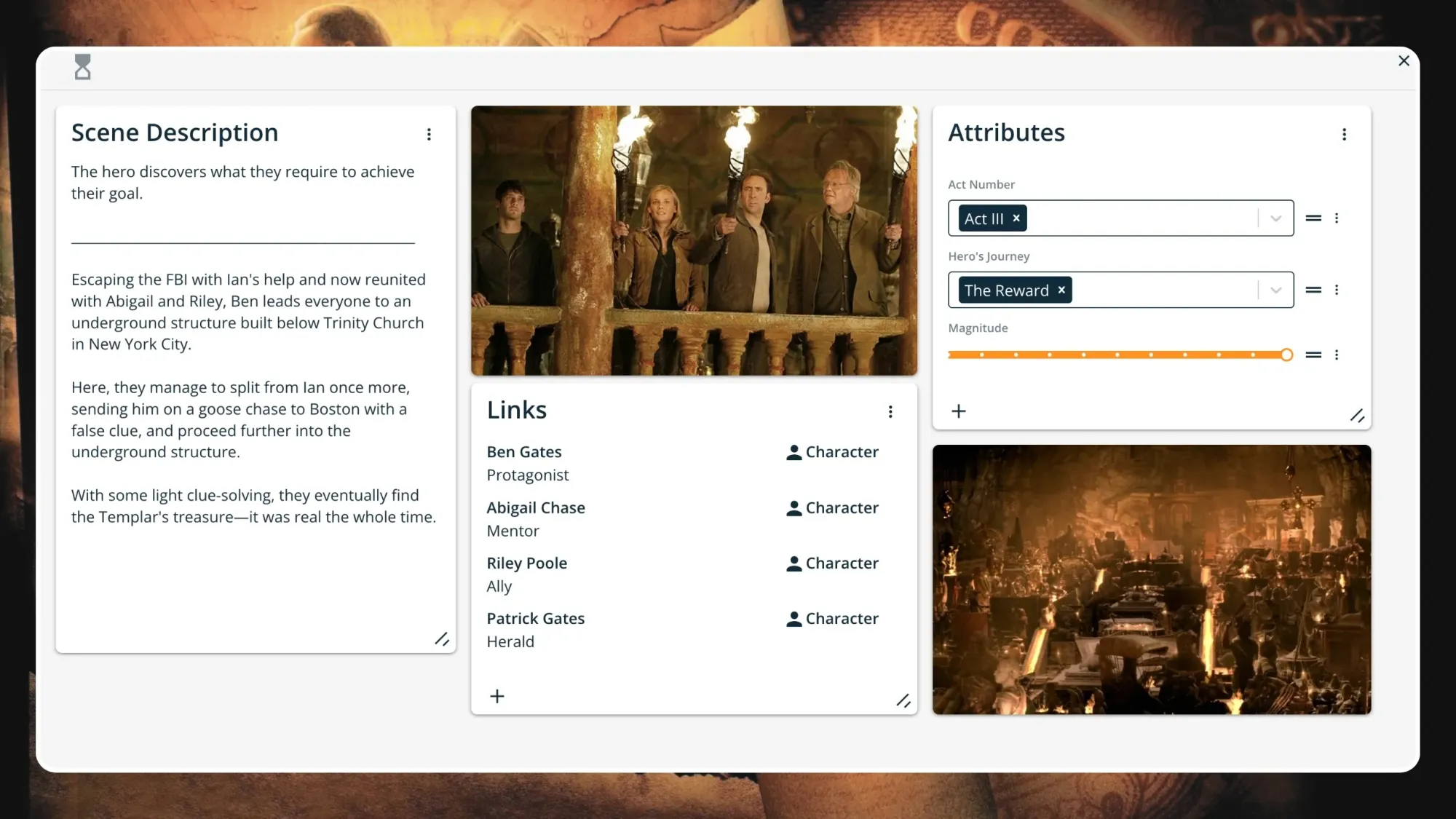
Now, free of Ian's clutches and with some light clue-solving, Ben, Abigail, Riley, and Patrick keep progressing through the underground structure and eventually find the Templar's treasure—it's real and more massive than they could have imagined. Everyone revels in their discovery while simultaneously looking for a way back out.
Act Three: Return
Step 10. the road back.
It's time for the journey to head towards its conclusion. The hero begins their return to the Known World and may face unexpected challenges. Whatever happens, the "why" remains paramount here (i.e. why the hero ultimately chose to embark on their journey).
This step marks a final turning point where they'll have to take action or make a decision to keep moving forward and be "reborn" back into the Known World.
Act Three of National Treasure is admittedly quite short. After finding the treasure, Ben and co. emerge from underground to face the FBI once more. Not much of a road to travel back here so much as a tunnel to scale in a crypt.
Step 11. Resurrection
The hero faces their ultimate challenge and emerges victorious, but forever changed. This step often requires a sacrifice of some sort, and having stepped into the role of The Hero™, they must answer to this.
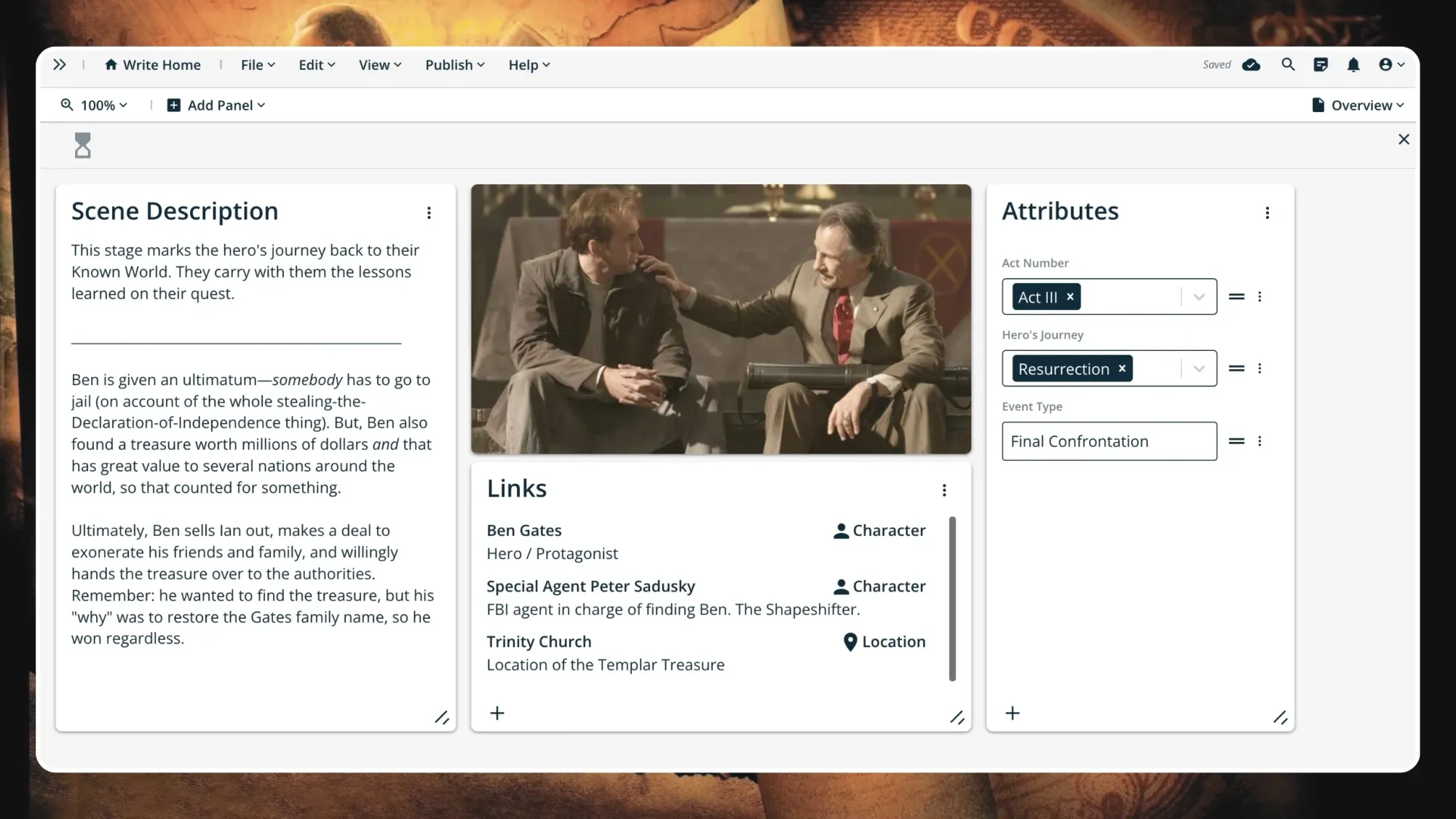
Ben is given an ultimatum— somebody has to go to jail (on account of the whole stealing-the-Declaration-of-Independence thing). But, Ben also found a treasure worth millions of dollars and that has great value to several nations around the world, so that counts for something.
Ultimately, Ben sells Ian out, makes a deal to exonerate his friends and family, and willingly hands the treasure over to the authorities. Remember: he wanted to find the treasure, but his "why" was to restore the Gates family name, so he won regardless.
Step 12. Return With the Elixir
Finally, the hero returns home as a new version of themself, the elixir is shared amongst the people, and the journey is completed full circle.
The elixir, like many other elements of the hero's journey, can be literal or figurative. It can be a tangible thing, such as an actual elixir meant for some specific purpose, or it could be represented by an abstract concept such as hope, wisdom, or love.
Vogler notes that if the Hero's Journey results in a tragedy, the elixir can instead have an effect external to the story—meaning that it could be something meant to affect the audience and/or increase their awareness of the world.
In the final scene of National Treasure , we see Ben and Abigail walking the grounds of a massive estate. Riley pulls up in a fancy sports car and comments on how they could have gotten more money. They all chat about attending a museum exhibit in Cairo (Egypt).
In one scene, we're given a lot of closure: Ben and co. received a hefty payout for finding the treasure, Ben and Abigail are a couple now, and the treasure was rightfully spread to those it benefitted most—in this case, countries who were able to reunite with significant pieces of their history. Everyone's happy, none of them went to jail despite the serious crimes committed, and they're all a whole lot wealthier. Oh, Hollywood.
Variations of the Hero's Journey
Plot structure is important, but you don't need to follow it exactly; and, in fact, your story probably won't. Your version of the Hero's Journey might require more or fewer steps, or you might simply go off the beaten path for a few steps—and that's okay!
What follows are three additional versions of the Hero's Journey, which you may be more familiar with than Vogler's version presented above.
Dan Harmon's Story Circle (or, The Eight-Step Hero's Journey)
Screenwriter Dan Harmon has riffed on the Hero's Journey by creating a more compact version, the Story Circle —and it works especially well for shorter-format stories such as television episodes, which happens to be what Harmon writes.
The Story Circle comprises eight simple steps with a heavy emphasis on the hero's character arc:
- The hero is in a zone of comfort...
- But they want something.
- They enter an unfamiliar situation...
- And adapt to it by facing trials.
- They get what they want...
- But they pay a heavy price for it.
- They return to their familiar situation...
- Having changed.
You may have noticed, but there is a sort of rhythm here. The eight steps work well in four pairs, simplifying the core of the Hero's Journey even further:
- The hero is in a zone of comfort, but they want something.
- They enter an unfamiliar situation and have to adapt via new trials.
- They get what they want, but they pay a price for it.
- They return to their zone of comfort, forever changed.
If you're writing shorter fiction, such as a short story or novella, definitely check out the Story Circle. It's the Hero's Journey minus all the extraneous bells & whistles.
Ten-Step Hero's Journey
The ten-step Hero's Journey is similar to the twelve-step version we presented above. It includes most of the same steps except for Refusal of the Call and Meeting the Mentor, arguing that these steps aren't as essential to include; and, it moves Crossing the Threshold to the end of Act One and Reward to the end of Act Two.
- The Ordinary World
- The Call to Adventure
- Crossing the Threshold
- Tests, Allies, Enemies
- Approach the Innermost Cave
- The Road Back
- Resurrection
- Return with Elixir
We've previously written about the ten-step hero's journey in a series of essays separated by act: Act One (with a prologue), Act Two , and Act Three .
Twelve-Step Hero's Journey: Version Two
Again, the second version of the twelve-step hero's journey is very similar to the one above, save for a few changes, including in which story act certain steps appear.
This version skips The Ordinary World exposition and starts right at The Call to Adventure; then, the story ends with two new steps in place of Return With Elixir: The Return and The Freedom to Live.
- The Refusal of the Call
- Meeting the Mentor
- Test, Allies, Enemies
- Approaching the Innermost Cave
- The Resurrection
- The Return*
- The Freedom to Live*
In the final act of this version, there is more of a focus on an internal transformation for the hero. They experience a metamorphosis on their journey back to the Known World, return home changed, and go on to live a new life, uninhibited.
Seventeen-Step Hero's Journey
Finally, the granddaddy of heroic journeys: the seventeen-step Hero's Journey. This version includes a slew of extra steps your hero might face out in the expanse.
- Refusal of the Call
- Supernatural Aid (aka Meeting the Mentor)
- Belly of the Whale*: This added stage marks the hero's immediate descent into danger once they've crossed the threshold.
- Road of Trials (...with Allies, Tests, and Enemies)
- Meeting with the Goddess/God*: In this stage, the hero meets with a new advisor or powerful figure, who equips them with the knowledge or insight needed to keep progressing forward.
- Woman as Temptress (or simply, Temptation)*: Here, the hero is tempted, against their better judgment, to question themselves and their reason for being on the journey. They may feel insecure about something specific or have an exposed weakness that momentarily holds them back.
- Atonement with the Father (or, Catharthis)*: The hero faces their Temptation and moves beyond it, shedding free from all that holds them back.
- Apotheosis (aka The Ordeal)
- The Ultimate Boon (aka the Reward)
- Refusal of the Return*: The hero wonders if they even want to go back to their old life now that they've been forever changed.
- The Magic Flight*: Having decided to return to the Known World, the hero needs to actually find a way back.
- Rescue From Without*: Allies may come to the hero's rescue, helping them escape this bold, new world and return home.
- Crossing of the Return Threshold (aka The Return)
- Master of Two Worlds*: Very closely resembling The Resurrection stage in other variations, this stage signifies that the hero is quite literally a master of two worlds—The Known World and the Unknown World—having conquered each.
- Freedom to Live
Again, we skip the Ordinary World opening here. Additionally, Acts Two and Three look pretty different from what we've seen so far, although, the bones of the Hero's Journey structure remain.
The Eight Hero’s Journey Archetypes
The Hero is, understandably, the cornerstone of the Hero’s Journey, but they’re just one of eight key archetypes that make up this narrative framework.
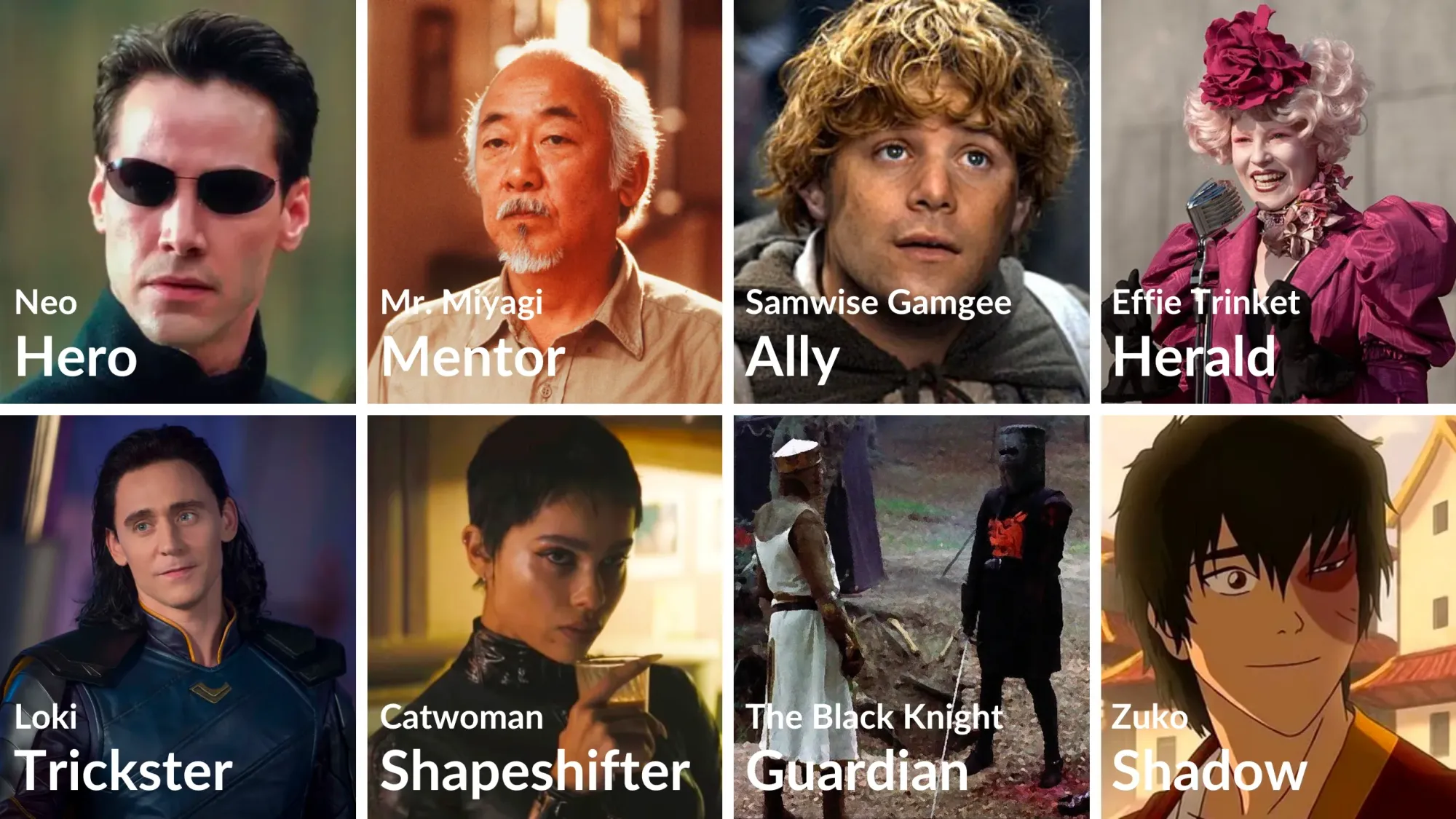

In The Writer's Journey , Vogler outlined seven of these archetypes, only excluding the Ally, which we've included below. Here’s a breakdown of all eight with examples:
1. The Hero
As outlined, the Hero is the protagonist who embarks on a transformative quest or journey. The challenges they overcome represent universal human struggles and triumphs.
Vogler assigned a "primary function" to each archetype—helpful for establishing their role in a story. The Hero's primary function is "to service and sacrifice."
Example: Neo from The Matrix , who evolves from a regular individual into the prophesied savior of humanity.
2. The Mentor
A wise guide offering knowledge, tools, and advice, Mentors help the Hero navigate the journey and discover their potential. Their primary function is "to guide."
Example: Mr. Miyagi from The Karate Kid imparts not only martial arts skills but invaluable life lessons to Daniel.
3. The Ally
Companions who support the Hero, Allies provide assistance, friendship, and moral support throughout the journey. They may also become a friends-to-lovers romantic partner.
Not included in Vogler's list is the Ally, though we'd argue they are essential nonetheless. Let's say their primary function is "to aid and support."
Example: Samwise Gamgee from Lord of the Rings , a loyal friend and steadfast supporter of Frodo.
4. The Herald
The Herald acts as a catalyst to initiate the Hero's Journey, often presenting a challenge or calling the hero to adventure. Their primary function is "to warn or challenge."
Example: Effie Trinket from The Hunger Games , whose selection at the Reaping sets Katniss’s journey into motion.
5. The Trickster
A character who brings humor and unpredictability, challenges conventions, and offers alternative perspectives or solutions. Their primary function is "to disrupt."
Example: Loki from Norse mythology exemplifies the trickster, with his cunning and chaotic influence.
6. The Shapeshifter
Ambiguous figures whose allegiance and intentions are uncertain. They may be a friend one moment and a foe the next. Their primary function is "to question and deceive."
Example: Catwoman from the Batman universe often blurs the line between ally and adversary, slinking between both roles with glee.
7. The Guardian
Protectors of important thresholds, Guardians challenge or test the Hero, serving as obstacles to overcome or lessons to be learned. Their primary function is "to test."
Example: The Black Knight in Monty Python and the Holy Grail literally bellows “None shall pass!”—a quintessential ( but not very effective ) Guardian.
8. The Shadow
Represents the Hero's inner conflict or an antagonist, often embodying the darker aspects of the hero or their opposition. Their primary function is "to destroy."
Example: Zuko from Avatar: The Last Airbender; initially an adversary, his journey parallels the Hero’s path of transformation.
While your story does not have to use all of the archetypes, they can help you develop your characters and visualize how they interact with one another—especially the Hero.
For example, take your hero and place them in the center of a blank worksheet, then write down your other major characters in a circle around them and determine who best fits into which archetype. Who challenges your hero? Who tricks them? Who guides them? And so on...
Stories that Use the Hero’s Journey
Not a fan of saving the Declaration of Independence? Check out these alternative examples of the Hero’s Journey to get inspired:
- Epic of Gilgamesh : An ancient Mesopotamian epic poem thought to be one of the earliest examples of the Hero’s Journey (and one of the oldest recorded stories).
- The Lion King (1994): Simba's exile and return depict a tale of growth, responsibility, and reclaiming his rightful place as king.
- The Alchemist by Paolo Coehlo: Santiago's quest for treasure transforms into a journey of self-discovery and personal enlightenment.
- Coraline by Neil Gaiman: A young girl's adventure in a parallel world teaches her about courage, family, and appreciating her own reality.
- Kung Fu Panda (2008): Po's transformation from a clumsy panda to a skilled warrior perfectly exemplifies the Hero's Journey. Skadoosh!
The Hero's Journey is so generalized that it's ubiquitous. You can plop the plot of just about any quest-style narrative into its framework and say that the story follows the Hero's Journey. Try it out for yourself as an exercise in getting familiar with the method.
Will the Hero's Journey Work For You?
As renowned as it is, the Hero's Journey works best for the kinds of tales that inspired it: mythic stories.
Writers of speculative fiction may gravitate towards this method over others, especially those writing epic fantasy and science fiction (big, bold fantasy quests and grand space operas come to mind).
The stories we tell today are vast and varied, and they stretch far beyond the dealings of deities, saving kingdoms, or acquiring some fabled "elixir." While that may have worked for Gilgamesh a few thousand years ago, it's not always representative of our lived experiences here and now.
If you decide to give the Hero's Journey a go, we encourage you to make it your own! The pieces of your plot don't have to neatly fit into the structure, but you can certainly make a strong start on mapping out your story.
Hero's Journey Campfire Template
The Timeline Module in Campfire offers a versatile canvas to plot out each basic component of your story while featuring nested "notebooks."
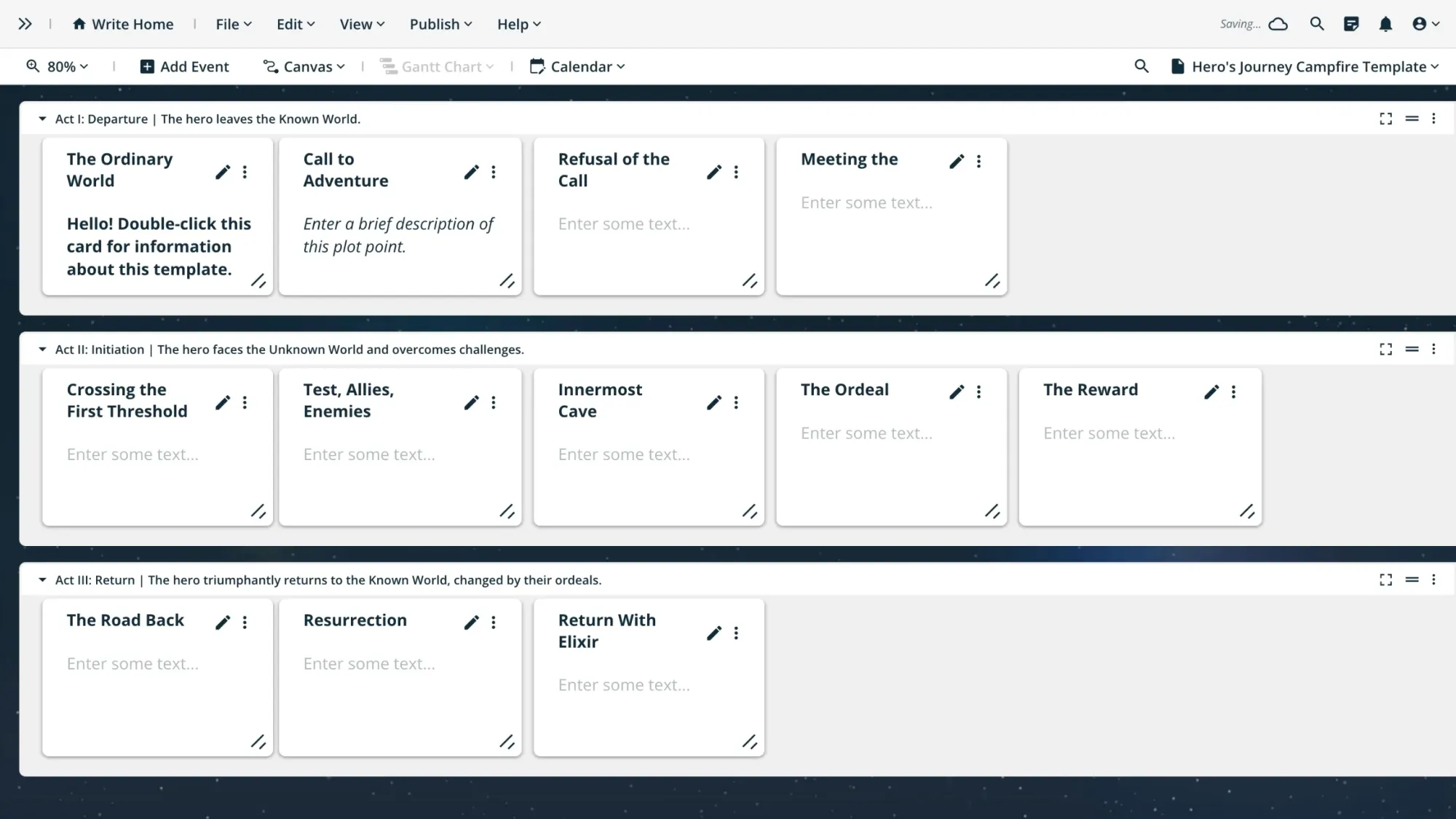
Simply double-click on each event card in your timeline to open up a canvas specific to that card. This allows you to look at your plot at the highest level, while also adding as much detail for each plot element as needed!
If you're just hearing about Campfire for the first time, it's free to sign up—forever! Let's plot the most epic of hero's journeys 👇
Lessons From the Hero’s Journey
The Hero's Journey offers a powerful framework for creating stories centered around growth, adventure, and transformation.
If you want to develop compelling characters, spin out engaging plots, and write books that express themes of valor and courage, consider The Hero’s Journey your blueprint. So stop holding out for a hero, and start writing!
Does your story mirror the Hero's Journey? Let us know in the comments below.

The Role of Archetypes in Literature
Christopher Vogler's work on archetypes helps us understand literature
- Tips For Adult Students
- Getting Your Ged
- The Hero's Journey
The Job of the Herald
The purpose of the mentor, overcoming the threshold guardian, meeting ourselves in shapeshifters, confronting the shadow, changes brought about by the trickster.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Deb-Nov2015-5895870e3df78caebc88766f.jpg)
- B.A., English, St. Olaf College
Carl Jung called archetypes the ancient patterns of personality that are the shared heritage of the human race. Archetypes are amazingly constant throughout all times and cultures in the collective unconscious, and you'll find them in all of the most satisfying literature. An understanding of these forces is one of the most powerful elements in the storyteller’s toolbox.
Understanding these ancient patterns can help you better understand literature and become a better writer yourself. You'll also be able to identify archetypes in your life experience and bring that wealth to your work.
When you grasp the function of the archetype a character expresses, you will know his or her purpose in the story.
Christopher Vogler, author of The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure , writes about how every good story reflects the total human story. In other words, the hero's journey represents the universal human condition of being born into this world, growing, learning, struggling to become an individual, and dying. The next time you watch a movie, TV program, even a commercial, identify the following archetypes. I guarantee you'll see some or all of them.
The Hero's Journey
The word "hero" comes from a Greek root that means to protect and serve. The hero is connected with self-sacrifice. He or she is the person who transcends ego, but at first, the hero is all ego.
The hero’s job is to incorporate all the separate parts of himself to become a true Self, which he then recognizes as part of the whole, Vogler says. The reader is usually invited to identify with the hero. You admire the hero's qualities and want to be like him or her, but the hero also has flaws. Weaknesses, quirks, and vices make a hero more appealing. The hero also has one or more inner conflicts. For example, he or she may struggle over the conflicts of love versus duty, trust versus suspicion, or hope versus despair.
In The Wizard of Oz Dorothy is the story's hero, a girl trying to find her place in the world.
Heralds issue challenges and announce the coming of significant change. Something changes the hero’s situation, and nothing is the same ever again.
The herald often delivers the Call to Adventure, sometimes in the form of a letter, a phone call, an accident.
Heralds provide the important psychological function of announcing the need for change, Vogler says.
Miss Gulch, at the beginning of the film version of The Wizard of Oz , makes a visit to Dorothy's house to complain that Toto is trouble. Toto is taken away, and the adventure begins.
Mentors provide heroes with motivation , inspiration , guidance, training, and gifts for the journey. Their gifts often come in the form of information or gadgets that come in handy later. Mentors seem inspired by divine wisdom; they are the voice of a god. They stand for the hero’s highest aspirations, Vogler says.
The gift or help given by the mentor should be earned by learning, sacrifice, or commitment.
Yoda is a classic mentor. So is Q from the James Bond series. Glinda, the Good Witch, is Dorothy's mentor in The Wizard of O z.
At each gateway on the journey, there are powerful guardians placed to keep the unworthy from entering. If properly understood, these guardians can be overcome, bypassed, or turned into allies. These characters are not the journey's main villain but are often lieutenants of the villain. They are the naysayers, doorkeepers, bouncers, bodyguards, and gunslingers, according to Vogler.
On a deeper psychological level, threshold guardians represent our internal demons. Their function is not necessarily to stop the hero but to test if he or she is really determined to accept the challenge of change.
Heroes learn to recognize resistance as a source of strength. Threshold Guardians are not to be defeated but incorporated into the self. The message: those who are put off by outward appearances cannot enter the Special World, but those who can see past surface impressions to the inner reality are welcome, according to Vogler.
The Doorman at the Emerald City, who attempts to stop Dorothy and her friends from seeing the wizard, is one threshold guardian. Another is the group of flying monkeys who attack the group. Finally, the Winkie Guards are literal threshold guardians who are enslaved by the Wicked Witch.
Shapeshifters express the energy of the animus (the male element in the female consciousness) and anima (the female element in the male consciousness). Vogler says we often recognize a resemblance of our own anima or animus in a person, project the full image onto him or her, enter a relationship with this ideal fantasy, and commence trying to force the partner to match our projection.
The shapeshifter is a catalyst for change, a symbol of the psychological urge to transform. The role serves the dramatic function of bringing doubt and suspense into a story. It is a mask that may be worn by any character in the story, and is often expressed by a character whose loyalty and true nature are always in question, Vogler says.
Think Scarecrow, Tin Man, Lion.
The shadow represents the energy of the dark side, the unexpressed, unrealized, or rejected aspects of something. The negative face of the shadow is the villain, antagonist, or enemy. It may also be an ally who is after the same goal but who disagrees with the hero’s tactics.
Vogler says the function of the shadow is to challenge the hero and give her a worthy opponent in the struggle. Femmes Fatale are lovers who shift shapes to such a degree they become the shadow. The best shadows have some admirable quality that humanizes them. Most shadows do not see themselves as villains, but merely as heroes of their own myths.
Internal shadows may be deeply repressed parts of the hero, according to Vogler. External shadows must be destroyed by the hero or redeemed and turned into a positive force. Shadows may also represent unexplored potentials, such as affection, creativity, or psychic ability that goes unexpressed.
The Wicked Witch is the obvious shadow in the Wizard of Oz.
The trickster embodies the energies of mischief and the desire for change. He cuts big egos down to size and brings heroes and readers down to earth, Vogler says. He brings change by drawing attention to the imbalance or absurdity of a stagnant situation and often provokes laughter. Tricksters are catalyst characters who affect the lives of others but are unchanged themselves.
The Wizard himself is both a shapeshifter and a trickster.
- The Approach to the Inmost Cave in the Hero's Journey
- The Hero's Journey: Crossing the Threshold
- An Introduction to The Hero's Journey
- The Hero's Journey: Refusing The Call to Adventure
- The Ordeal in the Hero's Journey
- The Reward and the Road Back
- The Hero's Journey: Meeting with the Mentor
- The Ordinary World in the Hero's Journey
- Therapeutic Metaphor
- The Resurrection and Return With the Elixir
- "The Wonderful Wizard of Oz" Study Guide
- Direct Question in Grammar
- Object of a Preposition Definition and Examples
- Ice Breaker Game: The Movie of Your Life
- May Writing Prompts
- Das Nibelungenlied: Epic German Classic
Improve your writing in one of the largest and most successful writing groups online
Join our writing community!
The Hero’s Journey Ultimate Writing Guide with Examples

by Alex Cabal
What do Star Wars , The Hobbit , and Harry Potter have in common? They’re all examples of a story archetype as old as time. You’ll see this universal narrative structure in books, films, and even video games.
This ultimate Hero’s Journey writing guide will define and explore all quintessential elements of the Hero’s Journey—character archetypes, themes, symbolism, the three act structure, as well as 12 stages of the Hero’s Journey. We’ll even provide a downloadable plot template, tips for writing the Hero’s Journey, and writing prompts to get the creative juices flowing.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey is a universal story structure that follows the personal metamorphosis and psychological development of a protagonist on a heroic adventure. The protagonist goes through a series of stages to overcome adversity and complete a quest to attain an ultimate reward—whether that’s something tangible, like the holy grail, or something internal, like self confidence.
In the process of self-discovery, the archetypal Hero’s Journey is typically cyclical; it begins and ends in the same place (Think Frodo leaving and then returning to the Shire). After the epic quest or adventure has been completed by overcoming adversity and conflict—both physical and mental—the hero arrives where they once began, changed in some as they rose to meet the ultimate conflict or ordeal of the quest.
Joseph Campbell and Christopher Vogler
The Hero’s Journey has a long history of conversation around the form and its uses, with notable contributors including Joseph Campbell and the screenwriter Christopher Vogler , who later revised the steps of the Hero’s Journey.
Joseph Campbell’s “monomyth” framework is the traditional story structure of the Hero’s Journey archetype. Campbell developed it through analysis of ancient myths, folktales, and religious stories. It generally follows three acts in a cyclical, rather than a linear, way: a hero embarks on a journey, faces a crisis, and then returns home transformed and victorious.
Campbell’s ideation of the monomyth in his book The Hero With a Thousand Faces was influenced by Carl Jung’s perspective of psychology and models of self-transformation , where the Hero’s Journey is a path of transformation to a higher self, psychological healing, and spiritual growth.
While Campbell’s original take on the monomyth included 17 steps within the three acts, Christopher Vogler, in his book The Writer’s Journey , refined those 17 steps into 12 stages—the common formula for the modern structure many writers use today.
It’s also worth checking out Maureen Murdock’s work on the archetype, “The Heroine’s Journey.” This takes a look at the female Hero’s Journey, which examines the traditionally masculine journey through a feminist lens.
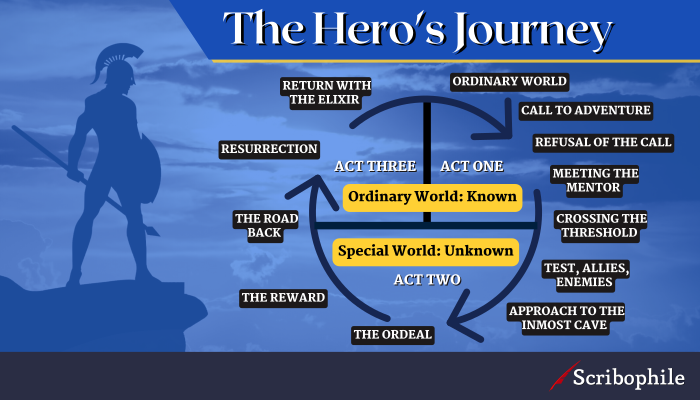
Hero’s Journey diagram: acts, steps, and stages
Below, you can see the way Volger’s Hero’s Journey is broken into twelve story beats across three acts.
Why is the Hero’s Journey so popular?
The structure of the Hero’s Journey appears in many of our most beloved classic stories, and it continues to resonate over time because it explores the concept of personal transformation and growth through both physical and mental trials and tribulations. In some sense, every individual in this mythic structure experiences rites of passage, the search for home and the true authentic self, which is mirrored in a protagonist’s journey of overcoming obstacles while seeking to fulfill a goal.
Additionally, the Hero’s Journey typically includes commonly shared symbols and aspects of the human psyche—the trickster, the mother, the child, etc. These archetypes play a role in creating a story that the reader can recognize from similar dynamics in their own relationships, experiences, and familiar world. Archetypes allow the writer to use these “metaphorical truths”—a playful deceiver, a maternal bond, a person of innocence and purity—to deeply and empathetically connect with the reader through symbolism. That’s why they continue to appear in countless stories all around the world.
Hero’s Journey character archetypes
Character archetypes are literary devices based on a set of qualities that are easy for a reader to identify, empathize with, and understand, as these qualities and traits are common to the human experience.
It should be noted that character archetypes are not stereotypes . While stereotypes are oversimplifications of demographics or personality traits, an archetype is a symbol of a universal type of character that can be recognized either in one’s self or in others in real life.
The following archetypes are commonly used in a Hero’s Journey:
The hero is typically the protagonist or principal point-of-view character within a story. The hero transforms—internally, externally, often both—while on their journey as they experience tests and trials and are aided or hindered by the other archetypes they encounter. In general, the hero must rise to the challenge and at some point make an act of sacrifice for the ultimate greater good. In this way, the Hero’s Journey represents the reader’s own everyday battles and their power to overcome them.
Heroes may be willing or unwilling. Some can be downright unheroic to begin with. Antiheroes are notably flawed characters that must grow significantly before they achieve the status of true hero.
The mentor often possesses divine wisdom or direct experience with the special world, and has faith in the hero. They often give the hero a gift or supernatural aid, which is usually something important for the quest: either a weapon to destroy a monster, or a talisman to enlighten the hero. The mentor may also directly aid the hero or present challenges to them that force internal or external growth. After their meeting, the hero leaves stronger and better prepared for the road ahead.
The herald is the “call to adventure.” They announce the coming of significant change and become the reason the hero ventures out onto a mysterious adventure. The herald is a catalyst that enters the story and makes it impossible for the hero to remain in status quo. Existing in the form of a person or an event, or sometimes just as information, they shift the hero’s balance and change their world.
The Threshold Guardian
This archetype guards the first threshold—the major turning point of the story where the hero must make the true commitment of the journey and embark on their quest to achieve their destiny. Threshold guardians spice up the story by providing obstacles the hero must overcome, but they’re usually not the main antagonist.
The role of the threshold guardian is to help round out the hero along their journey. The threshold guardian will test the hero’s determination and commitment and will drive them forward as the hero enters the next stage of their journey, assisting the development of the hero’s character arc within the plot. The threshold guardian can be a friend who doesn’t believe in the hero’s quest, or a foe that makes the hero question themselves, their desires, or motives in an attempt to deter the hero from their journey. Ultimately, the role of the threshold guardian is to test the hero’s resolve on their quest.
The Shape Shifter
The shape shifter adds dramatic tension to the story and provides the hero with a puzzle to solve. They can seem to be one thing, but in fact be something else. They bring doubt and suspense to the story and test the hero’s ability to discern their path. The shape shifter may be a lover, friend, ally, or enemy that somehow reveals their true self from the hero’s preconceived notion. This often causes the hero internal turmoil, or creates additional challenges and tests to overcome.
The shadow is the “monster under the bed,” and could be repressed feelings, deep trauma, or festering guilt. These all possess the dark energy of the shadow. It is the dark force of the unexpressed, unrealized, rejected, feared aspects of the hero and is often, but not necessarily, represented by the main antagonist or villain.
However, other characters may take the form of the shadow at different stages of the story as “foil characters” that contrast against the hero. They might also represent what could happen if the hero fails to learn, transform, and grow to complete their quest. At times, a hero may even succumb to the shadow, from which they will need to make sacrifices to be redeemed to continue on their overall quest.
The Trickster
The trickster is the jester or fool of the story that not only provides comic relief, but may also act as a commentator as the events of the plot unfold. Tricksters are typically witty, clever, spontaneous, and sometimes even ridiculous. The trickster within a story can bring a light-hearted element to a challenge, or find a clever way to overcome an obstacle.

Hero’s Journey themes and symbols
Alongside character archetypes, there are also archetypes for settings, situations, and symbolic items that can offer meaning to the world within the story or support your story’s theme.
Archetypes of themes, symbols, and situations represent shared patterns of human existence. This familiarity can provide the reader insight into the deeper meaning of a story without the writer needing to explicitly tell them. There are a great number of archetypes and symbols that can be used to reinforce a theme. Some that are common to the Hero’s Journey include:
Situational archetypes
Light vs. dark and the battle of good vs. evil
Death, rebirth, and transformation in the cycle of life
Nature vs. technology, and the evolution of humanity
Rags to riches or vice versa, as commentary on the material world and social status
Wisdom vs. knowledge and innocence vs. experience, in the understanding of intuition and learned experience
Setting archetypes
Gardens may represent the taming of nature, or living in harmony with nature.
Forests may represent reconnection with nature or wildness, or the fear of the unknown.
Cities or small towns may represent humanity at its best and at its worst. A small town may offer comfort and rest, while simultaneously offering judgment; a city may represent danger while simultaneously championing diversity of ideas, beings, and cultures.
Water and fire within a landscape may represent danger, change, purification, and cleansing.
Symbolic items
Items of the past self. These items are generally tokens from home that remind the hero of where they came from and who or what they’re fighting for.
Gifts to the hero. These items may be given to the hero from a mentor, ally, or even a minor character they meet along the way. These items are typically hero talismans, and may or may not be magical, but will aid the hero on their journey.
Found items. These items are typically found along the journey and represent some sort of growth or change within the hero. After all, the hero would never have found the item had they not left their everyday life behind. These items may immediately seem unimportant, but often carry great significance.
Earned rewards. These items are generally earned by overcoming a test or trial, and often represent growth, or give aid in future trials, tests, and conflicts.
The three act structure of the Hero’s Journey
The structure of the Hero’s Journey, including all 12 steps, can be grouped into three stages that encompass each phase of the journey. These acts follow the the external and internal arc of the hero—the beginning, the initiation and transformation, and the return home.
Act One: Departure (Steps 1—5)
The first act introduces the hero within the ordinary world, as they are—original and untransformed. The first act will typically include the first five steps of the Hero’s Journey.
This section allows the writer to set the stage with details that show who the hero is before their metamorphosis—what is the environment of the ordinary world? What’s important to the hero? Why do they first refuse the call, and then, why do they ultimately accept and embark on the journey to meet with the conflict?
This stage introduces the first major plot point of the story, explores the conflict the hero confronts, and provides the opportunity for characterization for the hero and their companions.
The end of the first act generally occurs when the hero has fully committed to the journey and crossed the threshold of the ordinary world—where there is no turning back.
Act Two: Initiation (Steps 6—9)
Once the hero begins their journey, the second act marks the beginning of their true initiation into the unfamiliar world—they have crossed the threshold, and through this choice, have undergone their first transformation.
The second act is generally the longest of the three and includes steps six through nine.
In this act, the hero meets most of the characters that will be pivotal to the plot, including friends, enemies, and allies. It offers the rising action and other minor plot points related to the overarching conflict. The hero will overcome various trials, grow and transform, and navigate subplots—the additional and unforeseen complexity of the conflict.
This act generally ends when the hero has risen to the challenge to overcome the ordeal and receives their reward. At the end of this act, it’s common for the theme and moral of the story to be fully unveiled.
Act Three: Return (Steps 10—12)
The final stage typically includes steps 10—12, generally beginning with the road back—the point in the story where the hero must recommit to the journey and use all of the growth, transformation, gifts and tools acquired along the journey to bring a decisive victory against their final conflict.
From this event, the hero will also be “reborn,” either literally or metaphorically, and then beginning anew as a self-actualized being, equipped with internal knowledge about themselves, external knowledge about the world, and experience.
At the end of the third act, the hero returns home to the ordinary world, bringing back the gifts they earned on their journey. In the final passages, both the hero and their perception of the ordinary world are compared with what they once were.
The 12 steps of the Hero’s Journey
The following guide outlines the 12 steps of the Hero’s Journey and represents a framework for the creation of a Hero’s Journey story template. You don’t necessarily need to follow the explicit cadence of these steps in your own writing, but they should act as checkpoints to the overall story.
We’ll also use JRR Tolkien’s The Hobbit as a literary example for each of these steps. The Hobbit does an exemplary job of following the Hero’s Journey, and it’s also an example of how checkpoints can exist in more than one place in a story, or how they may deviate from the typical 12-step process of the Hero’s Journey.

1. The Ordinary World
This stage in the Hero’s Journey is all about exposition. This introduces the hero’s backstory—who the hero is, where they come from, their worldview, culture, and so on. This offers the reader a chance to relate to the character in their untransformed form.
As the story and character arc develop, the reader is brought along the journey of transformation. By starting at the beginning, a reader has a basic understanding of what drives the hero, so they can understand why the hero makes the choices they do. The ordinary world shows the protagonist in their comfort zone, with their worldview being limited to the perspective of their everyday life.
Characters in the ordinary world may or may not be fully comfortable or satisfied, but they don’t have a point of reference to compare—they have yet to leave the ordinary world to gain the knowledge to do so.
Step One example
The Hobbit begins by introducing Bilbo in the Shire as a respectable and well-to-do member of the community. His ordinary world is utopian and comfortable. Yet, even within a village that is largely uninterested in the concerns of the world outside, the reader is provided a backstory: even though Bilbo buys into the comforts and normalcy of the Shire, he still yearns for adventure—something his neighbors frown upon. This ordinary world of the Shire is disrupted with the introduction of Gandalf—the “mentor”—who is somewhat uncomfortably invited to tea.
2. Call to Adventure
The call to adventure in the Hero’s Journey structure is the initial internal conflict that the protagonist hero faces, that drives them to the true conflict that they must overcome by the end of their journey.
The call occurs within the known world of the character. Here the writer can build on the characterization of the protagonist by detailing how they respond to the initial call. Are they hesitant, eager, excited, refusing, or willing to take a risk?
Step Two example
Bilbo’s call to adventure takes place at tea as the dwarves leisurely enter his home, followed by Gandalf, who identifies Bilbo as the group’s missing element—the burglar, and the lucky 14th member.
Bilbo and his ordinary world are emphasized by his discomfort with his rambunctious and careless guests. Yet as the dwarves sing stories of old adventures, caverns, and lineages, which introduce and foreshadow the conflict to come, a yearning for adventure is stirred. Though he still clings to his ordinary world and his life in the Shire, he’s conflicted. Should he leave the shire and experience the world, or stay in his comfortable home? Bilbo continues to refuse the call, but with mixed feelings.

3. Refusal of the Call
The refusal of the call in the Hero’s Journey showcases a “clinging” to one’s original self or world view. The initial refusal of the call represents a fear of change, as well as a resistance to the internal transformation that will occur after the adventure has begun.
The refusal reveals the risks that the protagonist faces if they were to answer the call, and shows what they’ll leave behind in the ordinary world once they accept.
The refusal of the call creates tension in the story, and should show the personal reasons why the hero is refusing—inner conflict, fear of change, hesitation, insecurity, etc. This helps make their character clearer for the reader.
These are all emotions a reader can relate to, and in presenting them through the hero, the writer deepens the reader’s relationship with them and helps the reader sympathize with the hero’s internal plight as they take the first step of transformation.
Step Three example
Bilbo refuses the call in his first encounter with Gandalf, and in his reaction to the dwarves during tea. Even though Bilbo’s “Tookish” tendencies make him yearn for adventure, he goes to bed that night still refusing the call. The next morning, as Bilbo awakes to an empty and almost fully clean hobbit home, he feels a slight disappointment for not joining the party, but quickly soothes his concerns by enjoying the comfort of his home—i.e. the ordinary world. Bilbo explores his hesitation to disembark from the ordinary world, questioning why a hobbit would become mixed up in the adventures of others, and choosing not to meet the dwarves at the designated location.
4. Meeting the Mentor
Meeting the mentor in the Hero’s Journey is the stage that provides the hero protagonist with a guide, relationship, and/or informational asset that has experience outside the ordinary world. The mentor offers confidence, advice, wisdom, training, insight, tools, items, or gifts of supernatural wonder that the hero will use along the journey and in overcoming the ultimate conflict.
The mentor often represents someone who has attempted to overcome, or actually has overcome, an obstacle, and encourages the hero to pursue their calling, regardless of the hero’s weaknesses or insecurities. The mentor may also explicitly point out the hero’s weaknesses, forcing them to reckon with and accept them, which is the first step to their personal transformation.
Note that not all mentors need to be a character . They can also be objects or knowledge that has been instilled in the hero somehow—cultural ethics, spiritual guidance, training of a particular skill, a map, book, diary, or object that illuminates the path forward, etc. In essence, the mentor character or object has a role in offering the protagonist outside help and guidance along the Hero’s Journey, and plays a key role in the protagonist’s transition from normalcy to heroism.
The mentor figure also offers the writer the opportunity to incorporate new information by expanding upon the story, plot, or backstory in unique ways. They do this by giving the hero information that would otherwise be difficult for the writer to convey naturally.
The mentor may accompany the hero throughout most of the story, or they may only periodically be included to facilitate changes and transformation within them.
Step Four example
The mentor, Gandalf, is introduced almost immediately. Gandalf is shown to be the mentor, firstly through his arrival from—and wisdom of—the outside world; and secondly, through his selection of Bilbo for the dwarven party by identifying the unique characteristics Bilbo has that are essential to overcoming the challenges in the journey. Gandalf doesn’t accompany Bilbo and the company through all of the trials and tribulations of the plot, but he does play a key role in offering guidance and assistance, and saves the group in times of dire peril.

5. Crossing the Threshold
As the hero crosses the first threshold, they begin their personal quest toward self-transformation. Crossing the threshold means that the character has committed to the journey, and has stepped outside of the ordinary world in the pursuit of their goal. This typically marks the conclusion of the first act.
The threshold lies between the ordinary world and the special world, and marks the point of the story where the hero fully commits to the road ahead. It’s a crucial stage in the Hero’s Journey, as the hero wouldn’t be able to grow and transform by staying in the ordinary world where they’re comfortable and their world view can’t change.
The threshold isn’t necessarily a specific place within the world of the story, though a place can symbolize the threshold—for example a border, gateway, or crossroads that separate what is safe and “known” from what is potentially dangerous. It can also be a moment or experience that causes the hero to recognize that the comforts and routine of their world no longer apply—like the loss of someone or something close to the hero, for example. The purpose of the threshold is to take the hero out of their element and force them, and the reader, to adapt from the known to the unknown.
This moment is crucial to the story’s tension. It marks the first true shift in the character arc and the moment the adventure has truly begun. The threshold commonly forces the hero into a situation where there’s no turning back. This is sometimes called the initiation stage or the departure stage.
Step Five example
The threshold moment in The Hobbit occurs when the party experiences true danger as a group for the first time. Bilbo, voted as scout by the party and eager to prove his burglar abilities, sneaks upon a lone fire in the forest where he finds three large trolls. Rather than turn back empty-handed—as he initially wants to—Bilbo chooses to prove himself, plucking up the courage to pickpocket the trolls—but is caught in the process. The dwarves are also captured and fortunately, Gandalf, the mentor, comes to save the party.
Bilbo’s character arc is solidified in this threshold moment. He experiences his first transformation when he casts aside fear and seeks to prove himself as a burglar, and as an official member of the party. This moment also provides further characterization of the party as a whole, proving the loyalty of the group in seeking out their captured member.
Gandalf’s position as the mentor is also firmly established as he returns to ultimately save all of the members of the party from being eaten by trolls. The chapter ends with Bilbo taking ownership of his first hero talisman—the sword that will accompany him through the rest of the adventure.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
Once the hero has crossed the threshold, they must now encounter tests of courage, make allies, and inevitably confront enemies. All these elements force the hero to learn the new ways of the special world and how it differs from the hero’s ordinary world—i.e. how the rules have changed, the conditions of the special world vs. the ordinary world, and the various beings and places within it.
All these elements spark stages of transformation within the hero—learning who they can trust and who they can’t, learning new skills, seeking training from the mentor, and overcoming challenges that force and drive them to grow and transform.
The hero may both succeed and fail at various points of this stage, which will test their commitment to the journey. The writer can create tension by making it clear that the hero may or may not succeed at the critical moment of crisis. These crises can be external or internal.
External conflicts are issues that the character must face and overcome within the plot—e.g. the enemy has a sword drawn and the hero must fight to survive.
Internal conflicts occur inside the hero. For example, the hero has reached safety, but their ally is in peril; will they step outside their comfort zone and rise to the occasion and save their friend? Or will they return home to their old life and the safety of the ordinary world?
Tests are conflicts and threats that the hero must face before they reach the true conflict, or ordeal, of the story. These tests set the stage and prime the hero to meet and achieve the ultimate goal. They provide the writer the opportunity to further the character development of the hero through their actions, inactions, and reactions to what they encounter. The various challenges they face will teach them valuable lessons, as well as keep the story compelling and the reader engaged.
Allies represent the characters that offer support to the protagonist along the journey. Some allies may be introduced from the beginning, while others may be gained along the journey. Secondary characters and allies provide additional nuance for the hero, through interactions, events, and relationships that further show who the hero is at heart, what they believe in, and what they’re willing to fight for. The role of the allies is to bring hope, inspiration, and further drive the hero to do what needs to be done.
Enemies represent a foil to the allies. While allies bring hope and inspiration, enemies will provide challenges, conflicts, tests, and challenges. Both allies and enemies may instigate transformative growth, but enemies do so in a way that fosters conflict and struggle.
Characterization of enemies can also enhance the development of the hero through how they interact and the lessons learned through those interactions. Is the hero easily duped, forgiving, empathetic, merciful? Do they hold a grudge and seek revenge? Who is the hero now that they have been harmed, faced an enemy, and lost pieces of their innocent worldview? To answer that, the hero is still transforming and gestating with every lesson, test, and enemy faced along the way.
Step Six example
As the plot of The Hobbit carries on, Bilbo encounters many tests, allies, and enemies that all drive complexity in the story. A few examples include:
The first major obstacle that Bilbo faces occurs within the dark and damp cave hidden in the goblin town. All alone, Bilbo must pluck up the wit and courage to outriddle a creature named Gollum. In doing so, Bilbo discovers the secret power of a golden ring (another hero talisman) that will aid him and the party through the rest of the journey.
The elves encountered after Bilbo “crosses the threshold” are presented as allies in the story. The hero receives gifts of food, a safe place to rest, and insight and guidance that allows the party to continue on their journey. While the party doesn’t dwell long with the elves, the elves also provide further character development for the party at large: the serious dwarf personalities are juxtaposed against the playful elvish ones, and the elves offer valuable historical insight with backstory to the weapons the party gathered from the troll encounter.
Goblins are a recurring enemy within the story that the hero and party must continue to face, fight, and run from. The goblins present consistent challenges that force Bilbo to face fear and learn and adapt, not only to survive but to save his friends.

7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
The approach to the inmost cave of the Hero’s Journey is the tense quiet before the storm; it’s the part of the story right before the hero faces their greatest fear, and it can be positioned in a few different ways. By now, the hero has overcome obstacles, setbacks, and tests, gained and lost allies and enemies, and has transformed in some way from the original protagonist first introduced in the ordinary world.
The moment when the hero approaches the inmost cave can be a moment of reflection, reorganization, and rekindling of morale. It presents an opportunity for the main characters of the story to come together in a moment of empathy for losses along the journey; a moment of planning and plotting next steps; an opportunity for the mentor to teach a final lesson to the hero; or a moment for the hero to sit quietly and reflect upon surmounting the challenge they have been journeying toward for the length of their adventure.
The “cave” may or may not be a physical place where the ultimate ordeal and conflict will occur. The approach represents the momentary period where the hero assumes their final preparation for the overall challenge that must be overcome. It’s a time for the hero and their allies, as well as the reader, to pause and reflect on the events of the story that have already occurred, and to consider the internal and external growth and transformation of the hero.
Having gained physical and/or emotional strength and fortitude through their trials and tests, learned more rules about the special world, found and lost allies and friends, is the hero prepared to face danger and their ultimate foe? Reflection, tension, and anticipation are the key elements of crafting the approach to the cave.
Step Seven example
The approach to the cave in The Hobbit occurs as the party enters the tunnel of the Lonely Mountain. The tunnel is the access point to the ultimate goal—Thorin’s familial treasure, as well as the ultimate test—the formidable dragon Smaug. During this part of the story, the party must hide, plot, and plan their approach to the final conflict. It’s at this time that Bilbo realizes he must go alone to scout out and face the dragon.
8. The Ordeal
The ordeal is the foreshadowed conflict that the hero must face, and represents the midpoint of the story. While the ordeal is the ultimate conflict that the hero knows they must overcome, it’s a false climax to the complete story—there’s still much ground to cover in the journey, and the hero will still be tested after completing this, the greatest challenge. In writing the ordeal phase of the Hero’s Journey, the writer should craft this as if it actually were the climax to the tale, even though it isn’t.
The first act, and the beginning of the second act, have built up to the ordeal with characterization and the transformation of the hero through their overcoming tests and trials. This growth—both internal and external—has all occurred to set the hero up to handle this major ordeal.
As this stage commences, the hero is typically faced with fresh challenges to make the ordeal even more difficult than they previously conceived. This may include additional setbacks for the hero, the hero’s realization that they were misinformed about the gravity of the situation, or additional conflicts that make the ordeal seem insurmountable.
These setbacks cause the hero to confront their greatest fears and build tension for both the hero and the reader, as they both question if the hero will ultimately succeed or fail. In an epic fantasy tale, this may mean a life-or-death moment for the hero, or experiencing death through the loss of an important ally or the mentor. In a romance, it may be the moment of crisis where a relationship ends or a partner reveals their dark side or true self, causing the hero great strife.
This is the rock-bottom moment for the hero, where they lose hope, courage, and faith. At this point, even though the hero has already crossed the threshold, this part of the story shows how the hero has changed in such a way that they can never return to their original self: even if they return to the ordinary world, they’ll never be the same; their perception of the world has been modified forever.
Choosing to endure against all odds and costs to face the ordeal represents the loss of the hero’s original self from the ordinary world, and a huge internal transformation occurs within the hero as they must rise and continue forth to complete their journey and do what they set out to do from the beginning.
The ordeal may also be positioned as an introduction to the greater villain through a trial with a shadow villain, where the hero realizes that the greatest conflict is unveiled as something else, still yet to come. In these instances, the hero may fail, or barely succeed, but must learn a crucial lesson and be metaphorically resurrected through their failure to rise again and overcome the greater challenge.
Step Eight example
Bilbo must now face his ultimate challenge: burgle the treasure from the dragon. This is the challenge that was set forth from the beginning, as it’s his purpose as the party’s 14th member, the burglar, anointed by Gandalf, the mentor. Additional conflicts arise as Bilbo realizes that he must face the dragon alone, and in doing so, must rely on all of the skills and gifts in the form of talismans and tokens he has gained throughout the adventure.
During the ordeal, Bilbo uses the courage he has gained by surmounting the story’s previous trials; he’s bolstered by his loyalty to the group and relies upon the skills and tools he has earned in previous trials. Much as he outwitted Gollum in the cave, Bilbo now uses his wit as well as his magical ring to defeat Smaug in a game of riddles, which ultimately leads Smaug out of the lair so that Bilbo can complete what he was set out to do—steal the treasure.

The reward of the Hero’s Journey is a moment of triumph, celebration, or change as the hero achieves their first major victory. This is a moment of reflection for both the reader and the hero, to take a breath to contemplate and acknowledge the growth, development, and transformation that has occurred so far.
The reward is the boon that the hero learns, is granted, or steals, that will be crucial to facing the true climax of the story that is yet to come. The reward may be a physical object, special knowledge, or reconciliation of some sort, but it’s always a thing that allows for some form of celebration or replenishment and provides the drive to succeed before the journey continues.
Note that the reward may not always be overtly positive—it may also be a double-edged sword that could harm them physically or spiritually. This type of reward typically triggers yet another internal transformation within the hero, one that grants them the knowledge and personal drive to complete the journey and face their remaining challenges.
From the reward, the hero is no longer externally driven to complete the journey, but has evolved to take on the onus of doing so.
Examples of rewards may include:
A weapon, elixir, or object that will be necessary to complete the quest.
Special knowledge, or a personal transformation to use against a foe.
An eye-opening experience that provides deep insight and fundamentally changes the hero and their position within the story and world.
Reconciliation with another character, or with themselves.
No matter what the reward is, the hero should experience some emotional or spiritual revelation and a semblance of inner peace or personal resolve to continue the journey. Even if the reward is not overtly positive, the hero and the reader deserve a moment of celebration for facing the great challenge they set out to overcome.
Step Nine example
Bilbo defeats the dragon at a battle of wits and riddles, and now receives his reward. He keeps the gifts he has earned, both the dagger and the gold ring. He is also granted his slice of the treasure, and the Lonely Mountain is returned to Thorin. The party at large is rewarded for completing the quest and challenge they set out to do.
However, Tolkien writes the reward to be more complex than it first appears. The party remains trapped and hungry within the Mountain as events unfold outside of it. Laketown has been attacked by Smaug, and the defenders will want compensation for the damage to their homes and for their having to kill the dragon. Bilbo discovers, and then hides, the Arkenstone (a symbolic double edged reward) to protect it from Thorin’s selfishness and greed.

10. The Road Back
The road back in the Hero’s Journey is the beginning of the third act, and represents a turning point within the story. The hero must recommit to the journey, alongside the new stakes and challenges that have arisen from the completion of the original goal.
The road back presents roadblocks—new and unforeseen challenges to the hero that they must now face on their journey back to the ordinary world. The trials aren’t over yet, and the stakes are raised just enough to keep the story compelling before the final and ultimate conflict—the hero’s resurrection—is revealed in the middle of the third act.
The hero has overcome their greatest challenge in the Ordeal and they aren’t the same person they were when they started. This stage of the story often sees the hero making a choice, or reflecting on their transformed state compared to their state at the start of the journey.
The writer’s purpose in the third act is not to eclipse the upcoming and final conflict, but to up the stakes, show the true risk of the final climax, and to reflect on what it will take for the hero to ultimately prevail. The road back should offer a glimmer of hope—the light at the end of the tunnel—and should let the reader know the dramatic finale is about to arrive.
Step Ten example
What was once a journey to steal treasure and slay a dragon has developed new complications. Our hero, Bilbo, must now use all of the powers granted in his personal transformation, as well as the gifts and rewards he earned on the quest, to complete the final stages of the journey.
This is the crisis moment of The Hobbit ; the armies of Laketown are prepared for battle to claim their reward for killing Smaug; the fearless leader of their party, Thorin, has lost reason and succumbed to greed; and Bilbo makes a crucial choice based his personal growth: he gives the Arkenstone to the king as a bargaining chip for peace. Bilbo also briefly reconnects with the mentor, Gandalf, who warns him of the unpleasant times ahead, but comforts Bilbo by saying that things may yet turn out for the best. Bilbo then loyally returns to his friends, the party of dwarves, to stand alongside them in the final battle.
11. Resurrection
The resurrection stage of the Hero’s Journey is the final climax of the story, and the heart of the third act. By now the hero has experienced internal and external transformation and a loss of innocence, coming out with newfound knowledge. They’re fully rooted in the special world, know its rules, and have made choices that underline this new understanding.
The hero must now overcome the final crisis of their external quest. In an epic fantasy tale, this may be the last battle of light versus darkness, good versus evil, a cumulation of fabulous forces. In a thriller, the hero might ultimately face their own morality as they approach the killer. In a drama or romance, the final and pivotal encounter in a relationship occurs and the hero puts their morality ahead of their immediate desires.
The stakes are the highest they’ve ever been, and the hero must often choose to make a sacrifice. The sacrifice may occur as a metaphoric or symbolic death of the self in some way; letting go of a relationship, title, or mental/emotional image of the self that a hero once used as a critical aspect of their identity, or perhaps even a metaphoric physical death—getting knocked out or incapacitated, losing a limb, etc.
Through whatever the great sacrifice is, be it loss or a metaphoric death, the hero will experience a form of resurrection, purification, or internal cleansing that is their final internal transformation.
In this stage, the hero’s character arc comes to an end, and balance is restored to the world. The theme of the story is fully fleshed out and the hero, having reached some form of self-actualization, is forever changed. Both the reader and the hero experience catharsis—the relief, insight, peace, closure, and purging of fear that had once held the hero back from their final transformation.
Step Eleven example
All the armies have gathered, and the final battle takes place. Just before the battle commences, Bilbo tells Thorin that it was he who gave the Arkenstone to the city of men and offers to sacrifice his reward of gold for taking the stone. Gandalf, the mentor, arrives, standing beside Bilbo and his decision. Bilbo is shunned by Thorin and is asked to leave the party for his betrayal.
Bilbo experiences a symbolic death when he’s knocked out by a stone. Upon awakening, Bilbo is brought to a dying Thorin, who forgives him of his betrayal, and acknowledges that Bilbo’s actions were truly the right thing to do. The theme of the story is fully unveiled: that bravery and courage comes in all sizes and forms, and that greed and gold are less worthy than a life rich in experiences and relationships.

12. Return with the Elixir
The elixir in the Hero’s Journey is the final reward the hero brings with them on their return, bridging their two worlds. It’s a reward hard earned through the various relationships, tests, and growth the hero has experienced along their journey. The “elixir” can be a magical potion, treasure, or object, but it can also be intangible—love, wisdom, knowledge, or experience.
The return is key to the circular nature of the Hero’s Journey. It offers a resolution to both the reader and the hero, and a comparison of their growth from when the journey began.
Without the return, the story would have a linear nature, a beginning and an end. In bringing the self-actualized hero home to the ordinary world, the character arc is completed, and the changes they’ve undergone through the journey are solidified. They’ve overcome the unknown, and though they’re returning home, they can no longer resume their old life because of their new insight and experiences.
Step Twelve example
The small yet mighty hero Bilbo is accompanied on his journey home by his mentor Gandalf, as well as the allies he gathered along his journey. He returns with many rewards—his dagger, his golden ring, and his 1/14th split of the treasure—yet his greatest rewards are his experience and the friends he has made along the way. Upon entering the Shire Bilbo sings a song of adventure, and the mentor Gandalf remarks, “My dear Bilbo! Something is the matter with you, you are not the hobbit you were.”
The final pages of The Hobbit explore Bilbo’s new self in the Shire, and how the community now sees him as a changed hobbit—no longer quite as respectable as he once was, with odd guests who visit from time to time. Bilbo also composes his story “There and Back Again,” a tale of his experiences, underlining his greatest reward—stepping outside of the Shire and into the unknown, then returning home, a changed hobbit.
Books that follow the Hero’s Journey
One of the best ways to become familiar with the plot structure of the Hero’s Journey is to read stories and books that successfully use it to tell a powerful tale. Maybe they’ll inspire you to use the hero’s journey in your own writing!
The Lord of the Rings trilogy by J. R. R. Tolkien.
The Harry Potter series by J. K. Rowling.
The Earthsea series by Ursula K. Le Guin.
The Odyssey by Homer.
Siddhartha by Herman Hesse.
Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen.
Writing tips for the Hero’s Journey
Writing a Hero’s Journey story often requires planning beforehand to organize the plot, structure, and events of the story. Here are some tips to use the hero’s journey archetype in a story:
Use a template or note cards to organize and store your ideas. This can assist in ensuring that you tie up any loose ends in the plot, and that the cadence of your story is already outlined before you begin writing.
Use word count goals for writing different sections of your story. This can help you keep pace while you plan and write the first draft. You can always revise, edit, and add in detail at later stages of development, but getting the ideas written without bogging them down with details can assist in preparing your outline, and may perhaps provide additional inspiration and guidance along the way.
Lean into creativity and be flexible with the 12 steps. They don’t need to occur in the exact order we’ve listed above, but that ordering can offer great checkpoint moments for your story.
Invest in characterization and ensure that your main character is balanced with credible strengths and weaknesses. A perfect, pure hero has no room to grow. A one-dimensional villain who relies on the trope of “pure evil” without any motivations for their actions is boring and predictable.
Ensure tension and urgency is woven into the story. An epic tale to the grocery store for baby formula may still be fraught with danger, and the price of failure is a hungry child. Without urgency, tension, and risk, a Hero’s Journey will fall flat.
Be hard on your characters. Give them deep conflicts that truly test their nature, and their mental, physical, and spiritual selves. An easy journey isn’t a memorable one.
Have a balance of scenes that play on both positive and negative emotions and outcomes for the hero to create a compelling plot line that continues to engage your reader. A story that’s relentlessly positive doesn’t provide a pathway for the hero to transform. Likewise, a story that’s nothing but doom, strife, and turmoil, without a light at the end of the tunnel or an opportunity for growth, can make a story feel stagnant and unengaging.
Reward your characters and your reader. Personal transformation and the road to the authentic self may be grueling, but there’s peace or joy at the end of the tunnel. Even if your character doesn’t fully saved the world, they—and the reader—should be rewarded with catharsis, a new perspective, or personal insight at the end of the tale.
Hero’s Journey templates
Download these free templates to help you plan out your Hero’s Journey:
Download the Hero’s Journey template template (docx) Download the Hero’s Journey template template (pdf)
Prompts and practices to help you write your own Hero’s Journey
Use the downloadable template listed below for the following exercises:
Read a book or watch a movie that follows the Hero’s Journey. Use the template to fill in when each step occurs or is completed. Make note of themes and symbols, character arcs, the main plot, and the subplots that drive complexity in the story.
When writing, use a timer set to 2—5 minutes per section to facilitate bursts of creativity. Brainstorm ideas for cadence, plot, and characters within the story. The outline you create can always be modified, but the timer ensures you can get ideas on paper without a commitment; you’re simply jotting down ideas as quickly as you can.
Use the downloadable template above to generate outlines based on the following prompts.
A woman’s estranged mother has died. A friend of the mother arrives at the woman’s home to tell her that her mother has left all her belongings to her daughter, and hands her a letter. The letter details the mother’s life, and the daughter must visit certain places and people to find her mother’s house and all the belongings in it—learning more about her mother’s life, and herself, along the way.
The last tree on earth has fallen, and technology can no longer sustain human life on Earth. An engineer, having long ago received alien radio signals from a tower in their backyard, has dedicated their life to building a spaceship in their garage. The time has come to launch, and the engineer must select a group of allies to bring with them to the stars, on a search for a new life, a new home, and “the others” out there in the universe.
A detective is given a new case: to find a much-talked-about murderer. The twist is, the murderer has sent a letter to the detective agency, quietly outing a homicidal politician who is up for re-election and is a major financial contributor to the police. In the letter, the murderer states that if the politician doesn’t come clean about their crimes, the murderer will kill the politician on the night of the election. The detective must solve the case before the election, and come to terms with their own feelings of justice and morality.
Get feedback on your writing today!
Scribophile is a community of hundreds of thousands of writers from all over the world. Meet beta readers, get feedback on your writing, and become a better writer!
Join now for free

Related articles

Freytag’s Pyramid: Definitions and Examples of Dramatic Structure

How to End a Story: 7 Different Kinds of Endings

Worldbuilding: The Ultimate Guide (Plus a Template!)

Story Archetypes: 50+ Plot Archetypes to Craft Your Narrative

What are the Elements of a Story? 12 Central Story Elements

Writing the Rebel Archetype: Fictional Characters Who Make Their Own Rules (with Examples)
There is NO AI content on this website. All content on TeachWithMovies.org has been written by human beings.

- FOR TEACHERS
- FOR PARENTS
- FOR HOME SCHOOL
- TESTIMONIALS
- SOCIAL MEDIA
- DMCA COMPLIANCE
- GRATUITOUS VIOLENCE
- MOVIES IN THE CLASSROOM
- PRIVACY POLICY
- U.S. HISTORY
- WORLD HISTORY
- SUBJECT MATTER
- APPROPRIATE AGE LEVEL
- MORAL/ETHICAL EMPHASIS
- SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL LEARNING
- SNIPPETS & SHORT SUBJECTS
- MOVIES BY THE CALENDAR
- DOCUMENTARIES & NON-FICTION
- TALKING AND PLAYING WITH MOVIES: AGES 3-8
- TWM’S BEST TEACHING FILMS
- TALKING AND PLAYING WITH MOVIES
- SET-UP-THE-SUB
- ARTICLES & STUDENT HANDOUTS
- MOVIE PERMISSION SLIP
- MOVIE & TELEVISION WORKSHEETS
- MATHEMATICS
- EARTH SCIENCE
- ANY FILM THAT IS A WORK OF FICTION
- FILM ADAPTATIONS OF NOVELS, SHORT STORIES, OR PLAYS
- ANY FILM THAT IS A DOCUMENTARY
- ANY FILM THAT EXPLORES ETHICAL ISSUES
- ADAPTATION OF A NOVEL
- DOCUMENTARIES
- HERO’S JOURNEY
- SCIENCE FICTION
- WORK OF FICTION
- WORK OF HISTORICAL FICTION
- PERSUASIVE DOCUMENTARY
- FICTION (SOAPS, DRAMAS, AND REALITY/SURVIVAL SHOW)
- HISTORICAL FICTION
- INFORMATIONAL DOCUMENTARY
- NEWS AND CURRENT EVENTS
- SEARCH [Custom]
STAGES AND ARCHETYPES OF THE HERO’S JOURNEY
Introducing the monomyth.
The Hero’s Journey is a fundamental paradigm of human experience that is frequently the basis for written stories, drama, and film. It was initially described by mythologist Joseph Campbell, who relied in part on the insights of psychologist Carl Jung. The stages and archetypes of the Journey have been developed and applied to film by Christopher Vogler. The writings of these men demonstrate that the Journey is helpful in understanding both fiction and reality.
What follows may be modified and used as a handout or serve as the basis for direct instruction. It is designed to be used with TWM’s Lesson plans on the Hero’s Journey which are listed in the English Language Arts Subject Index .
Most films recommended by TWM for the study of the Journey are not action/adventure movies. This will allow teachers to demonstrate that this structure can be found in any important quest and in all types of stories.
The Hero’s Journey in Life and Art
The human condition requires purposeful effort for any achievement and often for survival. Myths and stories in all cultures contain tales of successful quests through which great achievements have been made. Some are efforts to save an individual or a group; others are missions to protect or transform a community; many are stories of personal growth and development. The protagonists of these successful quests are often called heroes and the tale of their efforts has come to be known as “the Hero’s Journey.” Mythologist Joseph Campbell, who pioneered the study of the Hero’s Journey, referred to it as “the Monomyth” because it appears in all cultures and is basic to what it means to be human.
The origins of the Hero’s Journey/Monomyth are in the earliest beginnings of the human race. Undoubtedly, tales of struggle and triumph were heard around campfires of tribes long forgotten. When starvation had stalked the community, there would be a celebration when hunters returned from the first successful effort after many failures. The hunters would have told the story of the difficulties they had overcome and their eventual triumph. When tribes had been locked in mortal combat and the resolution had been in doubt, the victors would have delighted in recalling the tale of the battle and how they had vanquished the enemy. Those best at telling stories, people who had a way with words or music, would be asked to repeat the tale, again and again, praising those who had saved the community.
When people started to put stories into writing, the first epic poem was The Odyssey, which describes the Hero’s Journey of Odysseus on his quest to return home from the Trojan War. Since that time, stories of the Monomyth have appeared in countless variations, not only in epic poems, but also in novels, comic books, and plays. Movie plots frequently employ versions of the Hero’s Journey.
Joseph Campbell describes the mythical quest in its simplest form:
A hero ventures forth from the world of the common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won; the hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow man.
In life and in fiction, certain stages can be identified in most Hero’s Journeys. These include a starting place, an ordinary world that is somehow deficient or inadequate; a call to action; first steps on the journey; meeting with a mentor; the crisis, a reward, and a return with the result or a prize that corrects the deficiency or inadequacy that launched the quest. Each journey has its unique aspects and not all stories of the Monomyth contain all of the stages of the classic Hero’s Journey. In many situations, some of the stages are combined or occur simultaneously. The order of the steps usually follow in a certain sequence, but not always. Different scholars have described the stages in slightly different ways, but in countless myths and stories, the outline of the Hero’s Journey can be clearly seen.
In addition, stories that manifest the Monomyth contain certain types of characters whose functions relate to the hero’s progress on the Journey. These include not only the hero and the mentor, but also the threshold guardian, the shadow, the trickster, and the shapeshifter. In similar fashion to the stages of the Journey, not all of these characters appear in every Hero’s Journey and in some Journeys functions of different character types are combined in one individual. Because these character types have a structural relationship to the Hero’s Journey and they are parts of the human experience that appear in generation after generation and in story after story, they are called the archetypes of the Hero’s Journey.
The Monomyth can appear in many different types of stories. Adventure tales describe the experiences of heroes as they overcome villains who threaten certain individuals or endanger an entire community. In a romance, one of the characters, or the couple acting together, are on a quest to requite their love and live happily ever after. Sports stories involve the effort of one team or one contestant to triumph over all the others. In tales of personal transformation and growth, people examine their own lives, muster the courage to change, and accept the challenges presented on the path to fulfillment. Each of these types of stories often employ the stages of the Hero’s Journey.
One reason that the Monomyth has endured is that it matches the way in which many events actually occur: it illustrates how human beings on an important quest interact with their environment and with other people. Each person will at certain times in life perform different versions of the Hero’s Journey or they will see others do it. Some people will go on a quest to make a difference in society; most people will, at times, serve as the hero for a quest that is important to their family, their school, a friend, or themselves. One example of the Hero’s Journey, which has been undertaken by millions of people will be explored in detail in detail in this essay. It is the journey of an alcoholic or a drug addict who decides to take control of life and stop using drugs.
Stages of the Hero’s Journey
Set out below is a description of the stages of the Hero’s Journey developed for screenwriters by Hollywood story consultant Christopher Vogler in his book, The Writer’s Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers, 3rd Edition. Vogler’s work is based on the stages of the Monomyth developed by Joseph Campbell.
Note that: Vogler’s formulation of the Hero’s Journey is not the classic mythical journey in which there is repeated divine intervention and a meeting with the goddess. Vogler’s version is updated for modern sensibilities and reflects the contemporary view of life. It has been adopted by TWM because it has direct relevance to the stories told in film and, quite often, to quests undertaken by people living in modern times. Note also that while Vogler’s work has been in movie-making, the insights in his book apply to any work of fiction.
The stages of the Hero’s Journey can be separated into three sections. The first consists of the expository phase of the story. The second unfolds the complications and the crisis which describe the Hero’s struggle and provide the action in the story. The third section concludes the journey with resolution and denouement.
SECTION ONE — Introduction to Setting, Characters, and Conflict
1. The Ordinary World: This is the setting with which the protagonist is familiar, the life experienced before the quest. There will probably be many loved ones and the comfort of familiarity in the Ordinary World. However, in some way it is unstable or dissatisfying for the protagonist of the mission described in the story; either the Ordinary World has changed or the hero-to-be comes to feel the need for change due to some internal conflict or realization. In some tales that express the Monomyth, the Ordinary World has been destroyed or made uninhabitable by an outside force and the protagonist has no choice but to start on the journey to find a new life. In other stories, the Ordinary World still exists and often exerts a strong influence pulling the protagonist back from the challenges of the quest. In the classic Hero’s Journey, a victorious hero returns to the Ordinary World bringing back objects: the hunter brings food and the victor brings the spoils of war. In other Journeys there is no return to the Ordinary World and the successful hero lives in a new world that is better than the old. This also occurs in quests of personal growth in which a character seeks to resolve contradictions in his or her personality or overcome an emotional challenge, such as grief from the loss of a loved one.
The journey of an alcoholic/addict from addiction to sobriety is an example of a Hero’s Journey. Like all examples of the Monomyth, in life or in fiction, it has its unique aspects. For example, the journey of the recovering alcoholic/addict continues through the life of the individual and has no final conclusion. This contrasts sharply with most Hero’s Journeys, such as those of a hunt to bring food back to the starving clan or the tale of an athlete who wins a medal at the Olympics. However, most stages of the Monomyth are clearly evident in an alcoholic/addict’s road to recovery.
The Ordinary World of alcoholics and drug users are the days, months and years before they decide to quit. For an alcoholic/addict the ordinary world is one in which the drug controls most actions. It is a time of lying, cheating and stealing to support the habit. It is a time in which the alcoholic/addict manipulates loved ones to support the habit or avoid the consequences of an intoxicated life. It is a time of failing to meet responsibilities and in a fundamental way, it is a time of being isolated and alone. For many heroes the comfort and familiarity of the Ordinary World calls to them during their journey, and that is certainly true for alcoholics/addicts. Many recovering alcoholics and drug abusers never lose the urge for their intoxicant of choice.
2. The Call to Adventure: The call to adventure can take many forms, but it always pulls the protagonist away from the Ordinary World into a new situation. The Call to Adventure may be something that the hero-to-be voluntarily accepts or it may be an event which compels the journey, leaving the protagonist no choice but to embark on the journey.
For many heroes there is one call to adventure that sets them on the Journey. For alcoholics/addicts, there are usually many calls to change their lifestyle. For those who become the heroes of their own journey to sobriety, there is a Call to Adventure that finally sends them on their journey. Recovering alcoholics/addicts call this “hitting bottom.” That’s the time when the alcoholic/addict realizes that to continue drink alcohol or use drugs is intolerable. Some come to understand that they will actually die unless they stop. Some, who drive drunk, realize that they will probably kill someone else as well. For others, it’s the knowledge that continuing as an alcoholic/addict will destroy their relationship with their children or other people whom they love.
3. Refusing the Call: At one point (or on many occasions) the potential hero feels the pull of the familiar comforts of the Ordinary World and resists going on the adventure. After all, every quest carries with it the risk of failure and some Journeys are downright dangerous.
There are many alcoholics/addicts who relapse and after hitting bottom, start to use alcohol or drugs again. This is the equivalent of Refusing the Call to the adventure of their personal Hero’s Journey to sobriety. Some of them can rebound from this set back and continue on with their quest; others are lost.
4. Meeting with the Mentor: A Mentor is a guide or a teacher who will help the hero-to-be gather the courage, find the right path, or pass the tests required for successful completion of their mission. The meeting with the Mentor can come at any point in the Hero’s Journey.
Mentorship is so important for recovering alcoholics/addicts that everyone who enrolls in Alcoholics Anonymous is assigned a sponsor, a person to whom they can go for support and who will answer questions about the process of recovery. The same is true in many treatment programs for alcohol or drug addiction. The sponsor is the mentor for the recovering alcoholic/addict. Of course, alcoholics/addicts can also find people outside of AA or their treatment program to serve as mentors.
5. Crossing the First Threshold: This is the point at which there is no turning back without an admission that the protagonist is not to be a hero. Crossing the first threshold can be a voluntary, considered action or it can be an external event which launches the protagonist on the quest.
For most alcoholic/addicts, Crossing the First Threshold is entering treatment or attending the first AA meeting and committing themselves to join the program. For the very few people who can rid themselves of addiction without AA or a treatment program, Crossing the First Threshold is the first time they put down a drink or a syringe, the first time they reject a line of cocaine, with a personal commitment to stop using drugs and reform their life. However, alcoholics/addicts can always start their quest again, and in this way, the turning back is not a permanent admission that they will not be a hero. In this way, the journey of an alcoholic/addict to sobriety differs from the classic Hero’s Journey.
SECTION TWO — Action, Climax, Triumph
6. Tests, Allies, and Enemies: In most important quests there will be obstacles to overcome and challenges to meet; on most, there will be allies to assist the protagonist toward the goal. There may also be enemies seeking to obstruct the way. Enemies may also be aspects of nature or a part of the protagonist’s psyche. In both film and literature, these elements of the Journey provide the action, provoke interest, and serve as complications on the path to the goal.
Many alcoholic/addicts never lose the desire for intoxication; every day they must resist the urge to relapse. In AA there is a saying that recovery occurs one day at a time; every day is a test for the heroes of their own journeys to sobriety. There are also special challenges, as when, at a party, someone mistakenly hands a drink with alcohol to the person in recovery. Another test may occur during a time of emotional distress when the desire to escape and numb reality becomes especially strong. There are allies on the road of recovery, such as family and friends who provide support as well as other members of AA. There are also enemies, such as friends who still drink or use drugs and who want to include the recovering alcoholic/addict in their intoxicated experiences.
7. Approach to the Inmost Cave: This is the turning point, the moment in which the protagonist seems to realize completely what must be done and to accept all accompanied risks including the possibility of failure. In some stories, failure means death. The Approach to the Inmost Cave is an essential element in most stories describing a quest. It reveals the fact that the hero-to-be is operating with full awareness of the consequences of failure.
There comes a time when the alcoholic/addict is well launched on sobriety and realizes the extent to which their life has changed and will change forever. This occurs when people in recovery fully accept that they will never again enjoy the intoxication of the drug, something that is desperately desired and physically craved. It comes when they understand that all aspects of the intoxicated life are being left behind. But there are also the benefits of recovery which beckon and the alcoholic/addict must choose. In recovery from alcoholism/addiction, this stage may come after the Ordeal, while in most Hero’s Journeys in which there is a specific challenge that has to be overcome, this stage comes just before the Ordeal. “Hitting bottom” could also be seen as the Approach to the Inmost cave, but this occurs early in the process and is more like the Call to Action.
8. Ordeal: The climax, or the peak experience in the adventure, appears in virtually all stories. The hero-to-be faces the moment of truth: will he or she prevail in the struggle with the enemy?
For a person entering recovery from alcoholism/addiction, the most intense times often occur early on, when the body’s physical desire for the drug is the most intense. However, given the nature of recovery from alcoholism and drug addiction, the moment of truth can be said to reoccur occasionally throughout the life of an alcoholic/addict, or even every day. As they say, for many alcoholic/addicts it’s one day at a time.
9. Reward: The payoff for the protagonist’s struggle may be as simple as survival or it may involve fantastic riches or symbolic prizes that make the experience worthwhile. The Reward may be personal growth, self-knowledge, or the reconciliation of conflicting parts of the personality.
The payoff for a recovering alcoholic/addict is a life without addiction and all that this means for a better quality existence. For many, it means avoiding death, because the alcoholism/drug addiction would have killed them. Many alcoholics stopped maturing emotionally on the day they started to drink, usually as a teenager. When they had a problem in life, instead of dealing with it and learning what was necessary for growth and development, they just took several drinks or a hit from the drug. Many alcoholics/addicts report that when they went into recovery, they were back at the age when they began their intoxicated lifestyle. Recovery allows them to experience growth to maturity, with all of its challenges and rewards.
SECTION THREE — Resolution and Denouement
10. The Road Back: Returning to the ordinary world can be a difficult journey in itself and may offer additional risks for the adventuring protagonist, who is still not yet a hero. Some will be able to negotiate the Road Back and some will not: the hunter bringing the kill back to the village may be set upon by a pack of wolves who steal the hard won prey. For those protagonists who do not successfully pass this stage, the quest ends in failure; they never become heroes.
The road back for a recovering alcoholic/addict can be seen as the rest of their life. In the alternative, it can be said that this stage is absent in this version of the Hero’s Journey.
11. Resurrection: At this point, the protagonist, now a Hero, becomes transformed by the experience of the quest into a new, or at least a better, person.
An alcoholic/addict committed to recovery is a transformed person.
12. Return with the Elixir: In stories in which the Ordinary World still exists, upon re-entering that world, the Hero shares with those who stayed behind the prize won on the adventure. The Elixir shared can be abstract, such as love, or it can be concrete, such as something the group needs in order to survive or prosper. When the Ordinary World no longer exists or the Hero cannot, for some reason, return to the Ordinary World, the Hero will share the Elixir with those who accompanied him or her on the quest or those who inhabit the new world in which the victorious Hero will live. In journeys of personal growth and development, the Elixir is the new realization that the Hero has about life or about the self. The last two or three stages are often combined, especially in journeys of personal growth and development.
The Elixir for the recovering alcoholic/addict is the understanding that a sober life is better than an intoxicated life.
Archetypes in Life and Art
Certain character types and their structural relationships with others in family and community are parts of the human experience that repeat again and again. The functions of the father, the mother, the child, the hero, the mentor, and the trickster are found in most cultures and are timeless. People can take on different roles multiple times during their lives and they will change roles depending upon the situations in which they find themselves. For example, a person may be on a quest in one aspect of life and therefore take on the function of the hero, while at another time or in a different set of circumstances, the same person may function as a mentor for someone else’s quest. People can take on different roles in different situations and at different times. People are children in relation to their parents and later they are parents to their own children. As parents age, they become more child-like and their children take on the role of parent. People can take on more than one function at the same time. For example, every parent takes on different aspects of the mother (nurturing) and of the father (stern and judging); that is, aspects of both the mother and the father usually exist in varying degrees in any parent; and the relative strength of the different roles changes over time and as the situation changes.
Character types which have persisted over centuries and across cultures are called archetypes. The concept of archetypes is derived from the work of Swiss psychologist Carl Jung who theorized that people are born with a psychic inheritance, a collective unconscious, which affects all of human experience. Jung believed that this knowledge lies in our unconscious mind and can only be accessed indirectly through dreams, myths, forms of religious belief, and the arts, such as written fiction, movies, visual arts, music, and dance. It may be the Jung was correct or it may be that people learn about archetypes as children because there are certain basic ways in which human beings relate to each other in societies, in families, and in personal relationships. Whatever the source of the knowledge, the concept of archetype helps to organize and clarify human experience. As such, archetypes are an important part of understanding life and telling a story, whether in written form or presented on stage or screen.
Another way to look at archetypes is that they embody energies in the psyche that seek to fulfill a function in life and in story. Thus, one character can provide the energy to nurture, another the impetus to quest, a third the desire to the mentor, while a fourth provides the force of a leader, etc. The mother archetype nurtures, the father archetype judges, and the mentor archetype gives sage advice, etc. A person functions as a hero when engaging in purposeful effort, for example, putting a man on the moon or a journey of personal growth. The effort could be as simple as going on a trip and as mundane as learning to fit in when starting at a new school or asking a girl to go out on a date.
Every school contains character types that have existed for as long as we have had schools and which can be considered archetypes. The bully, the sports jock, the nerd, the class clown, and the teacher’s pet are examples. Centuries ago, the bully pattern of personality would have been evident in the powerful hunter or warrior who used his strength to dominate and hurt others. The characteristics of a bully contrast with those of a true leader, another archetype, who uses intelligence, knowledge, or the power of personality to take care of his people. And although math or science as fields of study are rather new in the long history of mankind, certainly there were members of ancient societies who involved themselves with numbers and were devoted to the accuracy of exchange, the measurement of distances, and even the passage of time. There have always been court jesters and comedians, and, of course, an individual favored by a person with power. Each of these functional types have recognizable expressions in school society.
While each archetype has its own constellation of attributes which most people recognize, everyone who functions as an archetypal character, in life and in story, will also have unique characteristics depending upon their culture, their own personality, and the situation. Dorothy Gale of The Wizard of Oz is a true heroine who defeats formidable adversaries on her journey. However, Dorothy, as required of a female by her culture, her time and her story, is always kind and considerate. While she kills the wicked witches of the East and the West as thoroughly as any action/adventure hero vanquishes a villain, Dorothy always kills by accident and without an intent to harm.
Joseph Campbell, the mythologist, refers to archetypes as elementary ideas and asserts that anthropologists and archeologists can account for the differences in the archetypes in mythologies across the globe as responses to environmental factors. In stories, the use of archetypes builds an empathic reaction as each reader or viewer sees many familiar aspects of characters who take on the archetypal roles. There is universal appeal when protagonists, antagonists, and ancillary characters exhibit aspects of various archetypes.
Archetypes of the Hero’s Journey – Characters of the Monomyth
There are certain archetypes which are often associated with the Hero’s Journey; their functions relate to the conduct of a quest. The following description of the archetypes of the Hero’s Journey are brief summaries derived from Christopher Vogler’s book. Mr. Vogler based his analysis on the ideas of psychologist Carl Jung and mythologist Joseph Campbell. Note that these summaries are an attempt to briefly describe complex personality patterns; they are necessarily incomplete.
1. The Hero is the person who embarks on the quest seeking to correct an imbalance in community, family, or psyche. For journeys of internal growth or reformation, the hero searches for the true self in its wholeness. The Hero can be willing or unwilling and can be acting on a matter which concerns society as a whole, relates to a specific group of people, or is personal to the Hero. The Hero can act alone or as the leader of a group.
2. A Mentor is an important individual, who transmits encouragement, understanding and wisdom to the Hero. The Mentor can simply give helpful advice or the mentor may also intervene and help the Hero surmount the challenges of the particular quest.
3. Threshold Guardians are characters who serve to challenge or obstruct the Hero’s progress from one stage of the Journey to another. They stand at the gateways to new experiences; their role is to keep the unworthy from continuing on the Journey. The Hero must prove his or her worthiness in some way, often by defeating and killing the Threshold Guardian or by passing some test.
4. A Herald issues challenges and announces the coming of significant change. The Herald is the voice demanding change and providing motivation for the protagonist to get on with the journey.
5. Shapeshifters , as seen from the Hero’s point of view, appear to change their form. The change may be in appearance, in mood, or in function with respect to the quest. For example, the Hero may have a romantic interest in a person who is fickle or two-faced. That person is a Shapeshifter.
6. The Shadow is a character who reflects or represents the dark, unexpressed, or rejected aspects of something, often a part of the Hero’s personality. A shadow character has the function of presenting the allure of qualities that a person must renounce and root out in order to successfully complete the quest.
7. The Trickster who sometimes supplies comic relief in a story, is nonetheless important as a catalyst for change and can sometimes be a Hero in his or her own right. Tricksters are also often Shapeshifters.
Some Other Important Literary Archetypes
Some of the archetypes identified by Carl Jung that are frequently found in the literature are summarized below.
1. The Father: Jung saw the authority figure as a powerful, serious-minded father, stern and judging. Usually, a character manifesting this archetype is male, but not always.
2. The mother: The individual who represents nurturing and caregiving is the Mother archetype. Often a character manifesting this archetype is female, but not always. Mentors often nurture and they are often male.
3. The Child: This archetype represents the innocence and potential for growth of children, who, with their honesty, pure-mindedness, and drive for growth and development offer salvation to errant adults. The Child Savior is a subset of this archetype. See TWM’s The Child Savior: An Example of a Literary Archetype.
4. The Maiden: Like the child, the maiden represents innocence and pure intention but has the added element of female sexual possibility and transition to another female archetype such as the Mother.
These archetypes may be found in many stories, including stories of the quest. They differ from the archetypes of the Hero’s Journey only because their function does not necessarily assist in reaching the resolution of a story of purposeful effort.
The Hero’s Journey/Monomyth is basic to the human experience. Jung, Campbell, and Vogler have shown that the stages of the Hero’s Journey correspond to what actually occurs in life. They have demonstrated that archetypes, assembled and reassembled in life and in stories, remain faithful to truths about human existence throughout time. The Hero’s Journey analysis assists in discovering the elemental messages of myth, drama, literature, and film. The Journey assists in understanding inner meaning and clarifying theme. In life, knowledge of the stages and archetypes of the successful quest will help people organize and understand their own experience.
Bibliography
- The Writer’s Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers, 3rd Edition, by Christopher Vogler;
- The Power of Myth by Joseph Campbell with Bill Moyers;
- The Hero with a Thousand Faces by Joseph Campbell; The quotation beginning “The hero ventures forth . . . ” is from page 23;
- The Archetypes and The Collective Unconscious (Collected Works of C.G. Jung Vol.9 Part 1).
This article was written by Mary RedClay and James Frieden for TeachWithMovies.org.
September C. Fawkes - Editor & Writer
Write better with an editor.
- The Triarchy Method of Story
- Editing Services
- Writing Tip Index
- Recommended Books
- Testimonials
- Glossary of Writing Terms
- Lifestyle Tools
- Conferences & Conventions
Writing Tips
My philosophy, monday, september 14, 2020, 8 archetypes of the hero's journey.

Today we are covering the eight character archetypes of The Hero's Journey .
Archetypes are recurring patterns and figures in storytelling (well, to put in simplified terms). Often a story won't feel "complete" without the proper archetypes .
But keep in mind that archetypes don't have to manifest exactly like this in your manuscript--it's not necessarily a character-for-character thing. In fact, these work more as functions , especially today. You can mix and match and combine them in your cast of characters. Or sometimes the functions may be like masks that different characters wear at different times.

Threshold Guardian

Shapeshifter

Remember, often today we don't use characters that fit archetypes exactly , but rather these are different character functions to bring into the story. Feel free to mix them up or bring something new to your character.
Why does this matter? Well, there is a reason these figures appear and reappear throughout human history. They represent different parts of the human experience : encouragement to do right, feelings of doubt, resistance, motivation, imbalance, repressed or unrealized desires. . . .
Including the different parts, makes a story feel more complete or whole, because it mimics life .
To learn more about this or other archetypes, check out and compare The Hero's Journey's list to Dramatica's list .
3 Quick Announcements:
This Wednesday at 6 p.m. MDT, I will be participating in a virtual Hamilton panel through FanX. We will be talking about the film recording and everything Hamilton . Visit the FanX website on Wednesday to watch.
I've recently added another editing service to my offerings: manuscript evaluation . This is similar to my content editing, but lighter. Basically, I read right through the manuscript and write up an editorial letter where I talk about how the manuscript can be taken to the next level or how the writer can improve, in general. I've done this as a "slimmer" version of my content editing in the past, but haven't advertised this approach lately because I personally think most manuscripts deserve a deeper edit. However, I understand that many people (especially now thanks to covid) are on a tighter budget. This approach is faster and therefore cheaper (but again, not as detailed). For now, I intend to have it listed only temporarily. For everything about my editing services, visit FawksEditing.com .
QueryLetter.com is holding a writing competition . This contest is all about book blurbs. The winner will receive $500 . Learn about the contest here . It looks like submissions must be sent by the 15th--so act quick if you want to enter!
0 comments:
Post a comment.
I love comments :)

Popular Writing Tips

Helpful Links
Search articles, september c. fawkes.

Let's be Social
Get writing tips by email:

Editing Testimonials

Recommended for Writers!

Find more of my tips on ...

- Recommended Reading
- Conferences & Conventions
- Icon Credit
Receive Big Ideas to Your Inbox
The hero’s journey archetype: a call to adventure.
- February 26, 2020
- TEDxMileHigh Admin
- Art & Design
Think of the last movie you watched. Think of everything that happens in this film. Think about the characters, plot, conflict, and ending. Now think of a different movie or even a book. Think about the same elements. Do you notice a trend? Yes, all stories are different and have different characters and outcomes, but have you noticed how most characters in a story follow a similar path? This path— this overlaying arc— is called the Hero’s Journey. Joseph Campbell first introduced this term in 1949, but the hero’s journey archetype has a longstanding place in storytelling.
Essentially, every character, whether in a book or a film, follows the same path and encounters three fundamental experiences along the way— separation, initiation, and return.
This is the beginning of our Hero’s Journey series where we will explore the archetype and how it shows up in our everyday lives.
As we lead up to TEDxMileHigh’s Summer 2020 event, Journey , discover that this journey is more relatable than you think—and that you may be the hero or heroine of your own journey.
The Hero’s Journey Archetype
So what exactly are we talking about here? We are diving into and dissecting the most basic form of storytelling, the arc that can be laid over any plotline and match it exactly, more or less. We’re talking about how Harry Potter receives his Hogwarts letter and goes on this massive quest to ultimately defeat Lord Voldemort and save the wizarding world. Marlin travels the entire Pacific Ocean, meets Dori and some sharks along the way, and finds Nemo. Luke Skywalker trains with Master Yoda, discovers who his father is, and blows up the Death Star.
All of these stories, every story, follow this hero’s journey archetype. It is the ultimate narrative archetype. And, you can break them all down into three basic points.
Whether they ask for it or not, something happens to the protagonist, or hero, that separates them from their ‘normal’ mundane world. This event, also termed the “call to adventure,” is the start of their journey, and it can manifest in different ways.
In the hero’s journey, drawn out by Campbell in The Hero with a Thousand Faces , there are several sub-points that occur along the hero’s journey that accompany the three main encounters. In the separation stage, the hero receives some kind of aid to push them to the threshold of their adventure. This aid can be the discovery of supernatural powers or the hero’s realization that they are not totally who they think they are.
For example, Harry Potter’s call to adventure came bursting through the door on his 13th birthday in the form of Rubeus Hagrid and his acceptance letter from Hogwarts. Harry discovers and fully embraces his wizarding powers and thus is pushed to the threshold of the next part of his hero’s journey: the initiation.
This stage of the hero’s journey archetype takes up the bulk of the journey. Throughout this stage, the hero meets several sub-points along the way including the introduction of a helper, a mentor, and the trials and temptations that eventually lead to a major conflict.
A classic example of this stage is Dorothy’s yellow-brick road journey to find the Wizard of Oz. Glenda, her mentor that she meets when she first lands in Oz, provides Dorothy with an answer to her problem (i.e., getting back home to Kansas) and aids her along the way. She meets helpers like the Scarecrow, the Tin Man, and the Lion. On her journey, Dorothy also runs into conflict with the Wicked Witch of the West.
A few flying monkeys and a conveniently placed water bucket later, Dorothy resolves, or melts, her conflict and is set to embark on the final part of her journey: the return.
This is the end of the hero’s journey. *Spoiler alert* Lord Voldemort dies, the Death Star blows up, and Dorothy makes it back to her family in Kansas. However, this resolution goes deeper than just a happy homecoming. In this stage, the hero returns but has changed. They have learned valuable information about themselves and the world around them.
In some cases, the hero’s journey is not complete unless this knowledge is shared. For example, Luke Skywalker defeats the Dark Side but is also left with the responsibility to continue to teach and share the ways of the Jedi. Dorothy’s lesson is more personal. She learns that there is adventure out there over the rainbow, but she shouldn’t take her current life or family for granted.
The Hero’s Versus the Heroine’s Journey
The hero’s journey archetype is similar across seemingly every example. However, how does the journey differ for a female character?
Author Maureen Murdock has examined and written about a key difference in her work The Heroine’s Journey: A Woman’s Quest for Wholeness . In her response to Campbell’s initial publication of the hero’s journey, Murdock outlined the separate experience the contemporary women embark on in their own heroine’s journey.
The three points along the journey are still the same. However, each stage consists of a deeper level of overcoming the expectations assumed by society. Essentially the journey “ involves the healing of the wounding of the feminine that exists deep within her and the culture,” says Murdock.
Returning to our Wizard of Oz example, Dorothy embarks on the quintessential heroine’s journey. During the separation stage, she has to overcome the expectations that the rest of her life will be spent on her family’s farm. Society’s expectations are that she will continue to support her uncles and follow in her aunt’s footsteps. When she finally receives the adventure she is longing for, Dorothy has to overcome the notion that she can’t complete this journey on her own. She meets helpers along the way, but rather than depending on them, they depend on her to help, thus reversing society’s view of women .
Upon her return, Dorothy learns that her life can be different and that she does not need to depend on her uncles. She can live her own life and have her own adventure all while still appreciating her family.
Are You a Hero or Heroine?
So, maybe you’ve read through these stages and are thinking ‘ That’s great! Why should I care? ’ Or maybe you’ve heard of the hero’s journey archetype before or you’ve at least noticed the trend in your favorites books or movies, but you don’t really see why it’s important.
The hero’s journey is important because it’s personal.
We are all the heroes of our own lives. That is, we are the protagonist in our own story— we are the main character. We are all on our own hero’s journey. Fictional characters are based on human experiences, and this time, that experience is ours. It’s our lives.
We are all in different stages of this journey but are on it, or will be on it soon. It’s important to understand where you are in your life in order to see where you are going. Maybe you’re in the midst of massive conflict and it seems endless and impossible. The hero’s journey tells us that this stage of your life is temporary and the next stage will be one of learning and resolution.
Maybe you’re hearing that call to adventure or an opportunity has presented itself and you’re unsure of what to do. The hero’s journey tells you to take that leap. Cross that threshold and discover your path, but be prepared for some conflict along the way.
The hero’s journey is important because it is a map, a cheat sheet, to life. Whether you wield a lightsaber or not, we are all on this same journey. And knowing where you are will give you a glimpse into where you are headed.
The hero’s journey is relatable and personal. We all find ourselves on some part of the path eventually. But what happens when you deviate from that path? Where are you on your path and who are the important characters in your journey? Stay tuned. We will explore the details of the hero’s journey archetype and discover just how relatable it is.
TEDxMileHigh is gearing up for its next event: Journey . This summer, we will explore the individual journeys that form societies, advance technologies, and inspire movements. If this article sparked your interest, and if you’re looking to dive deeper into your own personal life journey, join us on June 27th.
Get our most powerful and mind-blowing talks sent directly to your inbox.
Browse by category.
- Health & Science
- Social Issues
- Social Science
- TEDxMileHigh
- Volunteering
Related Posts

Hemangiosarcoma: What Every Dog Owner Needs to Know
As one of the most aggressive cancers seen in dogs, hemangiosarcoma grows and spreads rapidly, often without showing clear signs until it’s quite advanced. What

Cognitive Decline in Dogs and Cats: Managing Pet Brain Health
As our beloved furry companions age, some cognitive decline is to be expected. But when pets begin to exhibit signs of accelerated cognitive decline, they

Pet Dental Care: What You Need To Know
When it comes to taking care of our pets, dental care is usually the last thing we think of. Why is that? Well, there are
TED x Milehigh presented by:

HOSPITALITY

Follow Us On Instagram @tedxmilehigh
Join the milehigh conversation..
- Svg Vector Icons : http://www.onlinewebfonts.com/icon

Stay Connected
Spark your curiosity with talks and inside event updates sent directly to your inbox..
The Art of Narrative
Learn to write.

A Complete Guide to The Hero’s Journey (or The Monomyth)
Learn how to use the 12 steps of the Hero’s Journey to structure plot, develop characters, and write riveting stories that will keep readers engaged!
Before I start this post I would like to acknowledged the tragedy that occurred in my country this past month. George Floyd, an innocent man, was murdered by a police officer while three other officers witnessed that murder and remained silent.
To remain silent, in the face of injustice, violen ce, and murder is to be complicit . I acknowledge that as a white man I have benefited from a centuries old system of privilege and abuse against black people, women, American Indians, immigrants, and many, many more.
This systemic abuse is what lead to the murder of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, Sandra Bland, Eric Garner, Treyvon Martin, Philando Castile, Freddie Gray, Walter Scott, Tamir Rice and many more. Too many.
Whether I like it or not I’ve been complicit in this injustice. We can’t afford to be silent anymore. If you’re disturbed by the violence we’ve wit nessed over, and over again please vote this November, hold your local governments accountable, peacefully protest, and listen. Hopefully, together we can bring positive change. And, together, we can heal .
In this post, we’ll go over the stages of Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey, also known as the Monomyth. We’ll talk about how to use it to structure your story. You’ll also find some guided questions for each section of the Hero’s Journey. These questions are designed to help guide your thinking during the writing process. Finally, we’ll go through an example of the Hero’s Journey from 1997’s Men In Black.
Down at the bottom, we’ll go over reasons you shouldn’t rely on the Monomyth. And we’ll talk about a few alternatives for you to consider if the Hero’s Journey isn’t right for your story.
But, before we do all that let’s answer the obvious question-
What is the Hero’s Journey?

The Hero’s Journey was first described by Joseph Campbell. Campbell was an American professor of literature at Sarah Lawrence College. He wrote about the Hero’s Journey in his book The Hero with a Thousand Faces . More than a guide, this book was a study on the fundamental structure of myths throughout history.
Through his study, Campbell identified seventeen stages that make up what he called the Monomyth or Hero’s Journey. We’ll go over these stages in the next section. Here’s how Campbell describes the Monomyth in his book:
“A hero ventures forth from the world of common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won: the hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow man.”
Something important to note is that the Monomyth was not conceived as a tool for writers to develop a plot. Rather, Campbell identified it as a narrative pattern that was common in mythology.
George Lucas used Campbell’s Monomyth to structure his original Star Wars film. Thanks to Star Wars ’ success, filmmakers have adopted the Hero’s Journey as a common plot structure in movies.
We see it in films like The Matrix , Spider-man , The Lion King , and many more. But, keep in mind, this is not the only way to structure a story. We’ll talk about some alternatives at the end of this post.
With that out of the way, let’s go over the twelve stages of the Hero’s Journey, or Monomyth. We’ll use the original Men In Black film as an example (because why not?). And, we’ll look at some questions to help guide your thinking, as a writer, at each stage.
Quick note – The original Hero’s Journey is seventeen stages. But, Christopher Vogler, an executive working for Disney, condensed Campbell’s work. Vogler’s version has twelve stages, and it’s the version we’re talking about today. Vogler wrote a guide to use the Monomyth and I’ll link to it at the bottom.)
The 12 Stages of The Hero’s Journey
The ordinary world .

This is where the hero’s story begins. We meet our hero in a down-to-earth, or humble setting. We establish the hero as an ordinary citizen in this world, not necessarily “special” in any way.
Think exposition .
We get to know our hero at this stage of the story. We learn about the hero’s life, struggles, inner or outer demons. This an opportunity for readers to identify with the hero. A good idea since the story will be told from the hero’s perspective.
Read more about perspective and POV here.
In Men In Black, we meet our hero, James, who will become Agent J, chasing someone down the streets of a large city. The story reveals some important details through the action of the plo t. Let’s go over these details and how they’re shown through action.
Agent J’s job: He’s a cop. We know this because he’s chasing a criminal. He waves a badge and yells, “NYPD! Stop!”
The setting: The line “NYPD!” tells us that J is a New York City cop. The chase sequence also culminates on the roof of the Guggenheim Museum. Another clue to the setting.
J’s Personality: J is a dedicated cop. We know this because of his relentless pursuit of the suspect he’s chasing. J is also brave. He jumps off a bridge onto a moving bus. He also chases a man after witnessing him climb vertically, several stories, up a wall. This is an inhuman feat that would have most people noping out of there. J continues his pursuit, though.
Guided Questions
- What is your story’s ordinary world setting?
- How is this ordinary world different from the special world that your hero will enter later in the story?
- What action in this story will reveal the setting?
- Describe your hero and their personality.
- What action in the story will reveal details about your hero?
The Call of Adventure

The Call of Adventure is an event in the story that forces the hero to take action. The hero will move out of their comfort zone, aka the ordinary world. Does this sound familiar? It should, because, in practice, The Call of Adventure is an Inciting Event.
Read more about Inciting Events here.
The Call of Adventure can take many forms. It can mean a literal call like one character asking another to go with them on a journey or to help solve a problem. It can also be an event in the story that forces the character to act.
The Call of Adventure can include things like the arrival of a new character, a violent act of nature, or a traumatizing event. The Call can also be a series of events like what we see in our example from Men In Black.
The first Call of Adventure comes from the alien that Agent J chases to the roof of the Guggenheim. Before leaping from the roof, the alien says to J, “Your world’s going to end.” This pique’s the hero’s interest and hints at future conflict.
The second Call of Adventure comes after Agent K shows up to question J about the alien. K wipes J’s memory after the interaction, but he gives J a card with an address and a time. At this point, J has no idea what’s happened. All he knows is that K has asked him to show up at a specific place the next morning.
The final and most important Call comes after K has revealed the truth to J while the two sit on a park bench together. Agent K tells J that aliens exist. K reveals that there is a secret organization that controls alien activity on Earth. And the Call- Agent K wants J to come to work for this organization.
- What event (or events) happen to incite your character to act?
- How are these events disruptive to your character’s life?
- What aspects of your story’s special world will be revealed and how? (think action)
- What other characters will you introduce as part of this special world?
Refusal of the Call

This is an important stage in the Monomyth. It communicates with the audience the risks that come with Call to Adventure. Every Hero’s Journey should include risks to the main characters and a conflict. This is the stage where your hero contemplates those risks. They will be tempted to remain in the safety of the ordinary world.
In Men in Black, the Refusal of the Call is subtle. It consists of a single scene. Agent K offers J membership to the Men In Black. With that comes a life of secret knowledge and adventure. But, J will sever all ties to his former life. No one anywhere will ever know that J existed. Agent K tells J that he has until sunrise to make his decision.
J does not immediately say, “I’m in,” or “When’s our first mission.” Instead, he sits on the park bench all night contemplating his decision. In this scene, the audience understands that this is not an easy choice for him. Again, this is an excellent use of action to demonstrate a plot point.
It’s also important to note that J only asks K one question before he makes his decision, “is it worth it?” K responds that it is, but only, “if you’re strong enough.” This line of dialogue becomes one of two dramatic questions in the movie. Is J strong enough to be a man in black?
- What will your character have to sacrifice to answer the call of adventure?
- What fears does your character have about leaving the ordinary world?
- What risks or dangers await them in the special world?
Meeting the Mentor

At this point in the story, the hero is seeking wisdom after initially refusing the call of adventure. The mentor fulfills this need for your hero.
The mentor is usually a character who has been to the special world and knows how to navigate it. Mentor’s provides your hero with tools and resources to aid them in their journey. It’s important to note that the mentor doesn’t always have to be a character. The mentor could be a guide, map, or sacred texts.
If you’ve seen Men In Black then you can guess who acts as J’s mentor. Agent K, who recruited J, steps into the mentor role once J accepts the call to adventure.
Agent K gives J a tour of the MIB headquarters. He introduces him to key characters and explains to him how the special world of the MIB works. Agent K also gives J his signature weapon, the Noisy Cricket.
- Who is your hero’s mentor?
- How will your character find and encounter with their mentor?
- What tools and resources will your mentor provide?
- Why/how does your mentor know the special world?
Crossing the Threshold

This is the point where your hero finally crosses over from the ordinary world into the special one. At this point, there is no turning back for your hero.
Your hero may not cross into the special world on their own. Or, they may need a dramatic event that forces them to act.
At this point, you’ll want to establish the dramatic question of your story. This is the question will your reader wants to answer by the end of your story. A dramatic question is what will keep your audience reading.
Once J decides to commit to the MIB Agent K starts the process of deleting J’s identity. The filmmakers do a great job communicating the drastic nature of J’s decision. This is done through, again, action and an effective voice-over. J’s social security number is deleted, and his fingerprints are burned off. He dons a nondescript black suit, sunglasses, and a sick-ass Hamilton watch .
This scene is immediately followed by a threatening message sent by aliens called the Arquillians. They tell the MIB they will destroy the Earth unless J and K can deliver a galaxy. The only problem is no one knows what the galaxy is. So, we get our story question. Can J and K find and deliver the MacGuffin before the Earth is destroyed?
Read more about MacGuffins here.
- What event will push your hero into the special world?
- Once they enter the special world, what keeps them from turning back?
- What is the dramatic question you will introduce?
- How will your hero’s life change once they’ve entered the special world?
Tests, Allies, Enemies

This is stage is exactly what it sounds like. Once they’ve entered the special world, your hero will be tested. They will learn the rules of this new world. Your hero’s mentor may have to further teach your hero.
The hero will also begin collecting allies. Characters whose goals align with those of your hero’s. People who will help your hero achieve their goal. These characters may even join your hero on their quest.
And this is also the point where your hero’s enemy will reveal themselves. Now, you’ve may have hinted at, or even introduced the villain in the earlier stages. But, this is where the audience discovers how much of a threat this villain is to your hero.
Read more about creating villains here.
J and K arrive at the city morgue to investigate the body of a slain member of Arquillian royalty. While there, J encounters the villain of the film. He is lured into a standoff with Edgar. Edgar isn’t Edgar. He’s a 10 foot tall, alien cockroach wearing an “Edgar suit.”
J doesn’t know that yet, though.
Edgar has also taken a hostage. He threatens the life of Dr. Laurel Weaver who has discovered the truth about aliens living on Earth. Dr. Weaver becomes an ally of J’s as he continues his search for the Arquillian’s galaxy.
J is faced with a new test as well. Just before he dies, the Arquillian alien tells J that the galaxy is on Orion’s Belt. J must discover the meaning behind this cryptic message if he hopes to save Earth.
- Who is the villain of your story, and what is their goal?
- Who are your hero’s allies?
- How will your hero meet them? And, How do everyone’s goals align?
- How will your hero be tested? Through battle? A puzzle? An emotional trauma?
Approach to the Inmost Cave

The inmost cave is the path towards the central conflict of your story. In this section, your hero is preparing for battle. They may be regrouping with allies, going over important information, or taking a needed rest. This is also a part of the story where you may want to inject some humor.
The approach is also a moment for your audience to regroup. This is an important aspect of pacing. A fast-paced story can be very exciting for the audience, but at some point, the writer needs to tap the breaks.
This approach section gives your audience time to process the plot and consider the stakes of your conflict. This is also a good time to introduce a ticking clock, and it’s perfect for character development.
In Men, In Black the Approach the Inmost Cave involves an interview with a character called Frank the Pug. Frank is a Pug breed of dog. He’s an alien in disguise.
Frank knows important details about the conflict between the Arquillians and Edgar. This is one of the funnier scenes in an overall funny film.
Read more about alliteration here… jk.
Frank also gives J a vital clue to determine the location of the Arquillian’s galaxy. They also discover that the galaxy is an energy source and not an actual galaxy.
Finally, we have the arrival of the Arquillian battleship come to destroy Earth. They give the MIB a warning. If the galaxy is not returned in one hour the will fire on the planet. So, we have a literal ticking clock.
- Where and how will your hero slow down and regroup?
- What information or resources will they need to go into the final battle?
- How can you introduce some humor or character development into this section?
- What kind of “ticking clock” will you introduce to increase the stakes of your final act?
The Ordeal

The Ordeal is about one thing, and that’s death. Your hero must go through a life-altering challenge. This will be a conflict where the hero faces their greatest fears.
It’s essential that your audience feels as if the hero is really in danger. Make the audience question whether the hero will make it out alive. But, your story’s stakes may not be life or death, such as in a comedy or romance.
In that case the death your character experiences will be symbolic. And, your audience will believe that there’s a chance the hero won’t achieve their goal.
Through the ordeal, your hero will experience death whether that be real or symbolic. With this death, the hero will be reborn with greater powers or insight. Overall, the ordeal should be the point in which your character hits rock bottom.
The Ordeal in Men In Black comes the moment when J and K confront Edgar at the site of the World’s Fair. In the confrontation with Edgar, K is eaten alive by Edgar. At this moment J is left alone to confront death. The audience is left to wonder if J can defeat Edgar on his own.
Guided Questions
- What death will your hero confront?
- What does “rock bottom” mean for your character?
- How will your hero be changed on the other side of this death event?
Reward or Seizing the Sword

At this point in the story, your hero will earn some tangible treasure for all their trouble. This can be a physical treasure. In the context of the monomyth, this is often referred to as the elixir or sword.
However, the reward can be inwardly focused. Your hero might discover hidden knowledge or insight that helps them vanquish their foe. Or, your hero can find their confidence or some self-actualization. This reward, whatever it is, is the thing that they will take with them. It is what they earn from all their hard-fought struggles.
Once K is eaten J seems to be on his own with a massive alien cockroach. This is a pretty bad spot for the rookie agent. What’s worse is the Arquillian clock is still ticking. Edgar, the cockroach, is about to escape Earth, with the galaxy, sealing the planet’s fate.
All seems lost until J claims his reward. In this case, that reward comes in the form of an insight J has about Edgar. Being a giant cockroach, J realizes that Edgar may have a weakness for his Earth-bound counterparts. So, J kicks out a dumpster and starts to smash all the scurrying bugs under his foot.
J guesses correctly, and Edgar is momentarily distracted by J’s actions. Edgar climbs down from his ship to confront J. Agent K, who is still alive in Edgar’s stomach, can activate a gun, and blow Edgar in two. J’s reward is the knowledge that he is no longer a rookie, and he is strong enough for this job. J also captures a physical treasure. After Edgar has exploded, J finds the galaxy which Edgar had swallowed earlier in the film. In this scene, both dramatic questions are answered. The MIB can save the world. And, J is strong enough for the MIB.
- What reward will your hero win?
- A physical treasure, hidden knowledge, inner wisdom, or all of the above?
The Road Back
At this point, your hero has had some success in their quest and is close to returning to the ordinary world. Your hero has experienced a change from their time in the special world. This change might make your hero’s return difficult. Similar to when your hero crossed the threshold, your hero may need an event that forces them to return.
The road back must be a dramatic turning point that heightens stakes and changes the direction of your story. This event will also re-establish the dramatic question of your story. This act may present a final challenge for your hero before they can return home.
In Men In Black, the road backstage gets a little tricky. The film establishes that when J crosses the threshold he is not able to go back to the ordinary world. His entire identity is erased. Having J go back to his life as a detective would also undo his character growth and leave the audience feeling cheated. Luckily, the filmmakers work around this by having K return to the ordinary world rather than J.
After Edgar is defeated, K tells J that he is retiring from the MIB and that J will step in as K’s replacement. The movie establishes early that agents can retire, but only after having their memory wiped. So, K asks J to wipe his memory so that he can return to a normal life. Once again, J has to grapple with the question of whether he is strong enough for this job. Can he bring himself to wipe K’s memory and lose his mentor forever? Can he fill K’s shoes as an MIB agent?
- How will your hero have to recommit to their journey?
- What event will push your hero through their final test?
- What final test will your hero face before they return to the ordinary world?
Resurrection

This is the final act of your story. The hero will have one last glorious encounter with the forces that are set against them. This is the culminating event for your hero. Everything that has happened to your hero has prepared them for this moment.
This can also be thought of as a rebirth for your hero. A moment when they shed all the things that have held them back throughout the story. The resurrection is when your hero applies all the things they’ve learned through their journey.
The final moment can be a physical battle, or again, it can be metaphorical. This is also a moment when allies return to lend a last-minute hand. But, as with any ending of a story, you need to make sure your hero is the one who saves the day.
So, here’s where things start to get a little clumsy. There are a couple of moments that could be a resurrection for our hero J. It could be the moment he faces off with Edgar. This is right before Edgar is killed. But, it’s K that pulls the trigger and kills Edgar. Based on our explanation J needs to be the one who saves the day. Maybe by stalling for time J is the one responsible for saving the day? It’s hard to say what the filmmakers’ intention was here.
The second moment that could represent a resurrection for J might be when he wipes K’s memory. It is the final dramatic hurdle that J faces before he can become a true Man in Black. But, this moment doesn’t resolve the conflict of the film.
Notice that the Hero’s Journey framework isn’t always followed to the letter by all storytellers. We’ll get back to this point at the end of the article.
- What final challenge will your hero face?
- How will your hero use the skills they’ve used to overcome their last challenge?
- How will your hero’s allies help save the day?
Return with the Elixir

The ending of your story. Your hero returns to the ordinary world, but this time they carry with them the rewards earned during their journey. They may share these rewards with others who inhabit the ordinary world. But most important, is that you show that your hero has changed for the better.
The elixir represents whatever your hero gained on their journey. Remember, the elixir can be an actual physical reward like a treasure. But, the elixir can also be a metaphorical prize like knowledge or a feeling of fulfillment. This is a moment where your hero will return some sort of balance to the ordinary world.
Be sure to show that the journey has had a permanent effect on your hero.
In the final scene of the movie, we see that J has taken on a mentor role for Dr. Weaver, an MIB recruit now. He has physically changed- his clothes are more representative of his personality. This physical transformation is meant to show that J has fully embraced his new life and journey. No longer a rookie, J has stepped into his mentor, K’s, role.
- How will you show that your character has changed from their journey?
- What reward will they bring back to the ordinary world?
- In what way will they change the ordinary world when they return?

Should I Use the Hero’s Journey for My Story?
This is a question you should ask yourself before embarking on your journey. The Monomyth works well as a framework. This is pretty obvious when you realize how many films have used it as a plotting device.
But there’s a downside to the popularity of the Monomyth. And that’s that audiences are very familiar with the beats of this kind of story. Sure, they may not be able to describe each of the twelve sections in detail. But, audiences know, intuitively, what is going to happen in these stories. At the very least, audiences, or readers, know how these stories are going to end.
This isn’t necessarily a bad thing. If your story is exciting, well-paced, and the stakes are high, people aren’t going to mind some predictability. But, if you want to shock your readers-
(And if you’re interested in how to shock readers with a plot twist, click here. )
this might not be the best story structure. And, despite how popular it is, the hero’s journey ain’t the only game in town when it comes to story structure. And, you can always take artistic liberty with the Hero’s Journey. The fact that audiences are expecting certain beats means you have an opportunity to subvert expectations.
You can skip parts of the hero’s journey if they don’t fit your plot. With my example, Men In Black it was difficult to fit the story neatly into the hero’s journey framework. This is because aspects of the movie, like the fact that it’s a buddy comedy, don’t always jive with a hero’s journey. Agent K has an important character arch, and so he ends up killing the villain rather than J. But, K’s arch isn’t at all a hero’s journey.
The point is, don’t feel locked in by any single structure. Allow yourself some freedom to tell your story. If there’s no purpose to a resurrection stage in your story then skip it! No one is going to deduct your points.
With that said, here are a few resources on the Hero’s Journey, and some alternate plot structures you’ll want to check out!
This post contains affiliate links to products. We may receive a commission for purchases made through these links
Further Reading on Plot Structure and the Hero’s Journey

If you’d like to learn more about the Hero’s Journey, or Monomyth, why not go straight to the source? The Hero With 1000 Faces is a collection of work written by Joseph Campbell. His version of the hero’s journey has 17 stages. This is less of a writing manual and more of an exploration of the evolution of myth and storytelling through the ages.

The Seven Basic Plots , by Christopher Booker, is another academic study of storytelling by Christopher Booker. Booker identifies seven basic plots that all stories fit into. They are:
- Overcoming the Monster
- Rags to Riches
- Voyage and Return

The Snowflake Method is a teaching tool designed by Randy Ingermanson that will take you through a step-by-step process of writing a novel. The Snowflake Method boils down the novel-writing process six-step process. You will start with a single sentence and with each step you build on that sentence until you have a full-fledged novel! If you’re love processes then pick up a copy of this book today.

In The Writer’s Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers, Hollywood consultant, Christopher Vogler teaches writers how to use the Hero’s Journey to write riveting stories.
Resources:
Wikipedia- Joseph Campbell
Wikipedia- Hero With 1000 Faces
Published by John
View all posts by John
6 comments on “A Complete Guide to The Hero’s Journey (or The Monomyth)”
- Pingback: How to Create Stories with the Three-Act Structure - The Art of Narrative
- Pingback: Kishōtenketsu: Exploring The Four Act Story Structure - The Art of Narrative
- Pingback: A Definitive Guide to the Seven-Point Story Structure - The Art of Narrative
- Pingback: What are Character Archetypes? 25 Character Archetypes Explained - The Art of Narrative
- Pingback: How to use the 27 Chapter Plot Structure - The Art of Narrative
I don’t understand the use of all those pictures/graphics you threw in as I was reading. They were extremely distracting and seriously detracted from whatever message you were trying to convey.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Copy and paste this code to display the image on your site
Discover more from The Art of Narrative
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Archetypes in The Hero’s Journey
In this article you will learn about the archetypes in The Hero’s Journey , a theory about the narrative structure of stories in literature throughout the ages and how they all share common archetypal features.

Quick Navigation
What are the Archetypes The Hero’s Journey?
Author Joseph Campbell claimed in his writings that almost all stories follow essentially the same archetypal narrative pattern, something which he termed ‘the hero’s journey’.
This archetypal journey has three stages , as follows:
Stage 1: Departure
In this stage the hero is preparing for the quest to come. In this stage the hero receives an archetypal ‘call to adventure’ but often initially refuses the call. However, they usually then meet with an archetypal mentor who helps them understand why they need to heed the call.
Stage 2: Initiation
The archetypal hero of the story crosses the archetypal threshold, often having to overcome attempts by an archetypal ‘threshold guardian’ to prevent them from doing so, and commences their journey. They meet archetypal sidekicks and allies, but are tested often, usually by an archetypal villain. They usually have to overcome a life or death crisis, for which they receive an archetypal reward.
Stage 3: Return
The hero completes their journey, having passed the final test where everything is risk and begins their redemption/road back to normality
The Hero’s Journey Book Summary
Many books and movies follow the archetypal hero’s journey structure.
For example, the structure can be seen in The Lion King.
The story commences with Simba as heir to Pride Rock until his Uncle Scar kills his father Mufasa.
Scar tricks Simba into believing Mufasa’s death was his fault, telling him to flee Pride Rock. Simbaa flees alone into the desert, where he wanders until he meets Timon, a meerkat, and Pumbaa, a warthog, who introduce him to a new life in the jungle – the completion of stage one.
Simbaa embraces his new life with his sidekicks, Timon and Pumbaa.
However, childhood friend Nala finds him and they fall in love. She asks Simba to return home and take his rightful throne from Scar, telling him of the state their land had fallen into with villainous Scar in charge.
Simbaa is forced to choose between his new and old lives. The ghost of his father appears and urges him to go home.
He does so and faces Scar, learning the truth that Scar killed Mufasa. He kills Scar, the end of stage two. Simba reclaims his throne and restores Pride Rock to its former glory in stage three.
The Hero’s Journey Archetype Examples
- The hero’s journey
- Call to adventure
- Threshold guardians
Want more literary archetypes?
Go check out our extensive list of archetypes in literature to find out more about the characters seen in literature throughout the ages.
You might also like:
What Are The Hero’s Journey Archetypes?
Storytellers have used hero’s journey archetypes in the greatest stories, novels modern films. Learn what they are.
You may not think you know anything about the hero’s journey archetypes – but you’re actually way more familiar with these character types than you think! Hero’s journey archetypes permeate literary and popular culture and have done for time out of mind. They appear, in different forms, in cultures from around the world, and without them, the scaffolding behind the narrative structures of works from Indiana Jones to King Lear would likely collapse.
But who exactly, then, are these hero’s journey archetypes? Come along with us on a deep dive into these enigmatic, charismatic figures, their role, and why they’re so important – plus, we’ll give you some getting-started tips on how to use them in your own stories.
What’s an Archetype?
The hero’s journey explained, the warrior, the innocent, the creative, the romantic, the researcher, a mentor figure, the shadow: the hero’s dark reflection, developing your hero’s journey archetype’s character, combining hero archetypes, fulfilling expectations.
In the early 1900s, the psychiatrist and psychoanalyst Carl Jung started writing about archetypes. He termed them ancient personality patterns that are the shared heritage of humanity. Archetypes have characteristics that mark them as a typical example of a certain person (or thing). The word comes from the ancient Greek verb ‘archein’, which translates as ‘to begin’ or ‘to rule.’
The hero’s journey story involves the hero setting off on an adventure, often leaving their familiar world behind. This stage is typically described as The Departure. During the next stage, the Initiation, the character learns a lesson and usually wins some form of victory due to this new knowledge.
Next comes The Return, in which the hero returns to his/her familiar world, transformed. In this guide, we also explain how the hero’s journey works , but for context, let’s put some flesh on those conceptual monomyth bones, shall we?
Harry Potter is a classic hero archetype (more on the different versions of the hero archetype in a bit). In the first film and book, Potter sets off to Hogwarts, leaving the world of the muggles behind to begin an exciting new adventure (The Departure). Among the various trials inherent in settling into an enchanted boarding school, Potter and his friends discover the hidden location of the Philosopher’s Stone and triumph over many obstacles to recover it.
Along the way, they learn the true meaning of courage and friendship. Quirrell, who has been harboring Voldemort, then attempts to kill the boy wizard – unsuccessfully (The Initiation). Finally, after recovering in the school’s infirmary, Potter returns to the muggles’ world for the summer vacation, happy with the knowledge that his wizarding journey has just begun (The Return).
This pattern can be discerned in many stories, from The Lord of the Rings to The Wizard of Oz – and now you know about it, you’ll be spotting it in the most unlikely of places! The renowned scholar and professor of literature Joseph Campbell broke down the stages of the hero’s journey even further in his 1949 book The Hero with a Thousand Faces . Story doctor Christopher Vogler has also written extensively about this topic.
The Hero’s Journey Archetypes
So, now we’ve established the hero’s journey trope and how to recognize it, let’s move on to the archetypal characters we’ll meet in these stories. Whether you’re watching a TV series or a movie that follows the hero’s journey , these are the archetypes that you’ll come across.

Probably the archetype that most people would most easily identify as ‘heroic’ is The Warrior. Think Jason Bourne, Superman, Wonder Woman, and Luke Skywalker in Star Wars. These characters, as part of their journey, might find themselves confronted by a ‘dark night of the soul’ moment: the point right before the storm, the very edge of the precipice, beyond which is chaos and mayhem.
For Clark Kent/Superman, this is the bit in the movie when he knows he’s got to face an adversary who has kryptonite – or when he’s building up to telling Lois Lane his secret. For other Warrior hero archetypes, it could be the moment they discover the villain’s abducted someone they care about or that the baddie has got hold of a world-obliterating weapon.
The character archetypes offer room for flex, which can add interest or tension to the story. For example, how might The Warrior fare in a world or situation where his skills have become redundant?
One of the most common archetypes of the hero’s journey, this character, often a child and/or an orphan, finds themselves thrust into a dangerous world they’d previously not imagined existed. This is Dorothy finding herself a long way from Kansas, or Luke Skywalker suddenly whisked from his ordinary life on a moisture farm in Tatooine to become a key part in the fight to disarm Darth Vader’s Death Star. It’s Frodo Baggins swept away on that treacherous road to Mordor in The Lord of the Rings trilogy.
The Innocent often has an optimistic outlook and is loyal, honest, and sincere. They’re able to see the good in others and may be prone to be tricked by characters with fewer scruples.
Fundamentally, The Innocent archetype discovers a strength, resolve, tenacity, or skill they didn’t know they had. Dorothy realizes she can navigate the world independently. Luke learns how to use the Force, while Frodo, a hobbit from the Shire, finds he has the courage to journey to Mordor. For more examples, read our guide to movies that follow the hero’s journey .

Usually plagued by self-doubt, on the verge of obsession, and caught in an unconscious spiral of self-neglect. Characters in the mold of The Creative Archetype aren’t usually the most relaxed of folk.
This archetype often faces staunch resistance from the status quo, who reject or are fearful of their innovations, inventions, or new ways of thinking, which could herald the start of a new world. They have great powers of flair, imagination, and innovation but also tend towards perfectionism and even neuroticism.
As a result, they are often depicted as having a hard time navigating relationships and forming connections. Examples of The Creative hero archetype include Viktor Frankenstein, and Ed Wood, in the Tim Burton-directed movie of the same name. Being a Creative type usually comes at a great cost.
An essential part of The Creative’s story arc is the struggle to bring their vision to physical reality. In the course of the story, they’ll usually succeed, but things don’t pan out, often with disastrous consequences. Interestingly, many of fiction’s greatest villains start on the path of The Creative archetype: Voldemort and Professor Moriarty are just a few examples.
This archetype is prepared to live and die in the service of others; while they’re often cast as the main character, they also frequently appear as a sidekick or foil, adding balance to the narrative and a little comic relief.
Empathy, compassion, and the ability to nurture are traits typically found in The Carer. The drive to protect or heal is often the motivating force behind their actions, and they’re prepared to sublimate their own needs to accomplish these things. These characters often possess a strong sense of intuition – even a sixth sense that tells them when others are in need.
Sandra Bullock’s Leigh Anne Tuohy in Blindside and Denzel Washington’s character in The Equalizer are both caregiver hero archetypes. Woody from the movie Toy Story also falls into this category: his role is to take care of Andy’s toys, arranging their activities in such a way as to bring benefits to the whole group.
However, the Caregiver archetype needs to be wary of their shadow side. Many stories in which they appear as a hero find them confronting this darker reflection. Caring for someone may easily segue into becoming overbearing, even controlling.
Alternatively, they could have trouble finding their path if specific caring duties are no longer required. If you’re interested in using The Caregiver archetype in your own story, introducing these elements is a great way to ratchet up narrative tension and drive the plot.
It’s not enough for a hero to fall in love for his or her character to be categorized as a Romantic archetype. After all, James Bond might fall in love (multiple times) during the course of a movie, but finding love isn’t ever his main goal, so he doesn’t count as one of The Romantic archetypes.
This archetype often appears in literature and film as a Byronic hero . These characters have a set of traits codified by the English Romantic poet Lord Byron: a little aloof, even sullen, but with a rich inner life beneath that prickly surface.
The Romantic hero often also crosses into the neighboring territory of the Tragic Hero, a sub-category of hero archetypes. These characters labor under a single fatal flaw or make one catastrophic error in judgment in the course of the story that ultimately dooms them. As the audience, we can only watch their sad downfall, knowing all too well what will happen.
Romeo Montague is, of course, the epitome of this hero archetype – all his other goals and motivations are secondary to his pursuit of romantic love. The inimitable Mr. Darcy from Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice is also a great example of a romantic, Byronic hero.
Whereas The Warrior may overcome his/her enemies with physical strength, skill, and tenacity, The Researcher relies on his wits and his superior mind to succeed.
Character traits of this archetype include persistence, dependability, and curiosity. You can rely on them to come up with the goods. Their minds can make connections that others simply can’t, and a moment of insight is likely to lead to victory.
The Researcher often likes to spend time alone and isn’t afraid to move outside of social ‘norms’ – they’re more concerned with their work and ideas than fitting in. They’re self-sufficient, and this hero archetype may have problems (initially) working with others.
This archetype often manifests as a detective in stories and movies, most notably, Sherlock Holmes and in the tales of the many cases solved by Hercule Poirot. Indiana Jones is another example, using his intellect and exceptional research chops to overcome his adversaries.
Many hero’s journey books and stories include a mentor figure of some description. For example, Obi-Wan Kenobi forms this archetype in Star Wars. At first, he’s reluctant to train Luke in the ways of the force. Later, we discover he’s been looking out for and protecting Luke for years.
He becomes a type of mentor to Luke until his untimely death. He assists Luke in crossing over from an ordinary world into a special world: that of a Jedi Knight! In the subsequent films, Yoda fills this trope.
This hero archetype regularly appears in stories from fairy tales (Jack in Jack and the Beanstalk ) to contemporary movies. All five main characters from The Breakfast Club belong to The Rebel class for different reasons. Katniss Everdeen from The Hunger Games falls in this category, as does Prometheus from ancient Greek mythology, who did some serious sneaking about in a bid to give fire to humanity. For more, read our guide to popular hero’s journey books .
The Rebel figure connects with audiences as this character is usually an underdog: a small cog in a huge machine, apparently powerless to make a difference. Everyone knows the frustration of wanting but feeling unable to change things – of not being heard and seen.
Winston Smith, the protagonist in George Orwell’s 1984, is The Rebel hero archetype. In a world where one’s every move and thought is watched and controlled by the state, he still finds a way to express personal freedom. To learn more, read our guide to the best dystopian novels .
What motivates The Rebel character is to seek out their oppressor, or the root cause of their oppression, and overthrow him/her/them/it. In a nutshell, this archetype wants nothing more than to stick it to The Man – and as an audience, we’re usually right there behind them.
The Ruler archetype frequently takes the form of a king or queen. Throughout the story, they need to negotiate threats to their power. Often, the story begins with this archetype at the peak of their powers and then follows their decline. Needless to say, these tales usually take the form of a tragedy. Mafia or crime stories like Scarface tend to feature these character types and follow this overarching structure. And King Lear follows a similar template, too.
This archetype’s key traits include responsibility and extremely strong leadership skills. They’re usually organized and analytical and are driven by success, prosperity, and the importance of safeguarding their community. The Ruler usually fears a loss of control or influence and chaos.
As a hero archetype, The Ruler is motivated by a desire to provide stability and direction, especially during difficult times. These characters are good at looking at the big picture, aren’t afraid to make tough decisions, and are great at handling stress.
King Theoden, leader of the Rohan people in The Lord of the Rings, is a great example of The Ruler archetype. He is fearless in mounting a defense of his kingdom and committed to protecting all citizens under his care.
The Shadow is one of the most common versions of the villain archetype. This archetype is the hero’s reflection.
The Shadow character isn’t ‘pure evil’. They often believe that they’re the piece’s hero. And while their background is similar to that of the hero, they tend to foster a selfish, indifferent attitude toward others. They may take the form of the trickster: such as The Riddler in Batman or Puck-type figures in folklore.
George Lucas understood this: Anakin and Luke Skywalker’s early stories are similar, and both are inspired, ultimately, to hope and believe in the power of good eventually – even if it takes one of them much longer to get there than the other.
The connections don’t end there; the characters share many of the same associations, and Darth Sidious attempts to recruit both Luke (unsuccessfully) and Anakin (successfully). When it comes to The Shadow, the reader always gets the impression that this incarnation could easily have been the hero’s own destiny but for a twist or two of fate.
Typically, The Shadow will have started out pursuing a moral goal or design to create a better new world, but they end up pushing too far or going too fast and losing sight of their original noble vision. For The Shadow archetype, whatever the ends, they always justify the means, no matter the destruction that will result. And it’s this that most fundamentally differentiates them from the hero.
Choosing Your Own Hero’s Journey Archetype
If you’d like to write your own story and are wondering which of the hero archetypes to choose for your main character, think about the kind of tale you’re telling. Genre is an important consideration.
For example, The Creative will likely work well in a political thriller, while The Warrior will fit neatly into an action-adventure story. If you’ve narrowed it down but are struggling to make a decision, then pick the hero archetype that you’d feel most excited to write about – or how about creating an archetype hybrid?
So now what? The next stage of planning your story is giving your hero a mission or a reason for them to go on a quest. Ideally, this takes the form of a physical goal (taking the ring to Mordor) and a nonphysical imperative (a wistful longing to experience life beyond The Shire). As well as this, you’ll need to ensure you give your hero certain key character traits that will allow your readers or audience to relate to him or her. Inspiring empathy is crucial.
A consistent element of the hero’s journey is the fact that, at some point in the story, what they need isn’t necessarily the same as what they want, and there’ll be a conflict. For example, the hero may have an opportunity to achieve their goals…but at the expense of their values. Think about how you could incorporate this into your own story and how it will drive your narrative. It can make for neat dichotomies and the chance to get stuck into psychological drama.
Want to create a hybrid hero archetype? Go for it! In the film of the same title, Erin Brockovich is both The Researcher and The Rebel, while Simba, in The Lion King, is simultaneously The Innocent and The King. Consider different fusions of archetypes and how each would affect the tone and direction of the story you want to tell.
Finally, to captivate your readers and engage them thoroughly with your story, you need your hero archetype to fulfill audience expectations. They might not know why or even realize it’s happening, but folk love a recognizable archetype.
So if you’ve gone with The Creative hero archetype, be sure to show your readers clearly just how obsessed this character is with their invention or their concept that they’re convinced is going to improve…whatever it is. Let us see them still awake in the early hours, scribbling notes about tweaks they need to make to their plans or knocking on the door of patent offices and getting consistently turned away.
And once you’ve fulfilled your readers’ expectations? Now it’s time to innovate. Don’t be afraid to throw a literary cat in amongst the pigeons. Reimagine the archetype, keeping his/her key tropes intact but adding a large dollop of your own imagination. Your Creative hero? How about having him as someone in their eighties who’s lived a normal life until this point, when he suddenly woke up this morning with the tech idea of the century that could herald the dawn of a whole new world?
Combining fulfillment and innovation makes for the perfect blend, allowing you to create a fresh version of a hero archetype that’ll have your audience rooting for them throughout.

Melanie Smith is a freelance content and creative writer from Gloucestershire, UK, where she lives with her daughter, long-suffering partner, and cat, The Magical Mr. Bobo. Her blog posts and articles feature regularly in magazines and websites around the world.
View all posts

Mastering The Hero's Journey: A Comprehensive Guide To Storytelling Success
Table of Contents
Origins of the Hero's Journey
The three-act structure, the 12 stages of the hero's journey, key archetypes in the hero's journey, the inner and outer journey, applying the hero's journey to your story, adaptations and variations of the hero's journey, case studies: the hero's journey in popular fiction, common mistakes and how to avoid them, writing tips for crafting a compelling hero's journey, frequently asked questions, further reading.
The concept of the Hero's Journey can be traced back to the work of renowned mythologist Joseph Campbell . In his seminal book, The Hero with a Thousand Faces (1949), Campbell examined myths and stories from various cultures around the world and identified a common narrative pattern that he dubbed the "monomyth."
According to Campbell, the monomyth is a universal story template that transcends time, culture, and geography. It consists of a series of stages that a hero must go through in order to fulfill their destiny or complete their quest. Campbell drew inspiration for this concept from the works of prominent scholars such as Carl Jung , whose theories on archetypes and the collective unconscious greatly influenced his thinking.
Another significant influence on Campbell's work was James Frazer , who studied comparative mythology and religion in his groundbreaking book, The Golden Bough (1890). Frazer's work helped Campbell recognize the similarities between myths from different cultures and formulate the idea of a shared, underlying narrative structure.
In The Hero with a Thousand Faces , Campbell outlined the basic structure of the monomyth, which he divided into three main stages: Departure, Initiation, and Return. These stages encompass various sub-stages that the hero encounters on their journey, creating a blueprint for the Hero's Journey that can be applied to countless stories.
While Campbell's work focused primarily on myths and legends, the Hero's Journey has been widely adopted by writers and filmmakers in crafting their narratives. Some of the most successful books and movies, such as Star Wars and The Lord of the Rings , have followed the basic structure of the monomyth, proving the enduring appeal of this timeless narrative framework.
Over the years, the Hero's Journey has been refined and expanded upon by other scholars and writers, most notably Christopher Vogler , who adapted Campbell's ideas for use in modern storytelling in his book The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers (1992). Vogler's work has made the Hero's Journey more accessible to contemporary writers, ensuring its continued relevance in the world of storytelling.
The Three-Act Structure is a widely-used storytelling model that divides a narrative into three distinct parts or "acts": Setup, Confrontation, and Resolution. This model has its roots in classical drama and has been adapted for use in modern storytelling, particularly in the realms of screenwriting and novel writing. The Three-Act Structure provides a framework for pacing and plot development, helping writers create a well-structured and engaging narrative.
Act One: Setup
The first act of a story serves to introduce the main characters, establish the setting, and provide important background information. During this act, the protagonist is typically confronted with an inciting incident that sets the story in motion and propels them into the main conflict. This act ends with a turning point or "plot point" that pushes the protagonist into the second act.
In the context of the Hero's Journey, Act One corresponds to the Departure stage, which includes elements such as the Call to Adventure, Refusal of the Call, and the Meeting with the Mentor. These events set the stage for the hero's transformation and the challenges they will face throughout their journey.
Act Two: Confrontation
The second act, often referred to as the "rising action," sees the protagonist facing a series of obstacles and challenges as they pursue their goal. This is the longest part of the story, as it delves into the hero's struggles, their growth, and their relationships with other characters. The second act also features a turning point or "midpoint" that raises the stakes and heightens the tension. This act concludes with another major plot point, often involving a crisis or setback for the protagonist, propelling them into the final act.
In the Hero's Journey, Act Two encompasses the Initiation stage, with events such as the Road of Trials, the Approach to the Inmost Cave, and the Ordeal. These challenges test the hero's mettle, forcing them to confront their fears, learn important lessons, and acquire the skills they need to succeed in their quest.
Act Three: Resolution
The third and final act of a story focuses on the resolution of the conflict and the protagonist's ultimate transformation. The climax of the story typically occurs near the beginning of this act, as the hero faces their final challenge or confrontation with the antagonist. After the climax, the story moves into the "falling action," where loose ends are tied up, and the consequences of the protagonist's actions are revealed. The story concludes with the "denouement," which provides closure and shows how the characters have been affected by the events of the story.
In the context of the Hero's Journey, Act Three corresponds to the Return stage, featuring events such as the Resurrection, the Atonement with the Father, and the Freedom to Live. These elements signify the hero's completion of their quest, their reconciliation with their past, and their newfound ability to live a more fulfilled and authentic life.
By following the Three-Act Structure, writers can effectively pace their stories and ensure that the narrative remains engaging and satisfying for their audience. When combined with the stages and elements of the Hero's Journey, this structure provides a powerful blueprint for crafting compelling and resonant tales.
While the Hero's Journey can be broken down into the Three-Act Structure, it is often further divided into 12 distinct stages that the hero must go through during their quest. These stages, as described by Joseph Campbell and adapted by Christopher Vogler, provide a more detailed roadmap for writers seeking to create a compelling Hero's Journey narrative. The 12 stages are as follows:
- The Ordinary World : This stage establishes the protagonist's normal life before their adventure begins. It provides important context and allows the audience to become familiar with the hero's circumstances, values, and motivations. ( source )
- The Call to Adventure : The hero is confronted with an event or challenge that disrupts their ordinary world and sets the stage for their adventure. This call can take many forms, such as a threat, a discovery, or a personal loss. ( source )
- Refusal of the Call : Initially, the hero may be hesitant or resistant to embark on their journey, often due to fear, doubt, or a sense of obligation to their ordinary world. This stage highlights the hero's internal conflict and the stakes involved in their decision. ( source )
- Meeting the Mentor : The hero encounters a wise figure or guide who provides advice, guidance, or magical assistance to help them on their journey. This mentor figure can take various forms, such as a teacher, a parent, or even a supernatural being. ( source )
- Crossing the Threshold : The hero makes the decision to leave their ordinary world and fully commit to their adventure. This stage signifies the hero's acceptance of the call to adventure and their willingness to face the unknown. ( source )
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies : As the hero embarks on their journey, they encounter a series of obstacles, challenges, and antagonistic forces. They must also forge alliances with other characters who can help them along the way. This stage serves to develop the hero's character, test their resolve, and teach them valuable lessons. ( source )
- Approach to the Inmost Cave : The hero prepares for the central crisis or ordeal of their journey, often involving a confrontation with their greatest fear or the story's main antagonist. This stage often involves a period of introspection and reflection, as the hero gathers their strength and resources for the upcoming challenge. ( source )
- The Ordeal : The hero faces their most difficult challenge, which often involves a life-or-death situation or a confrontation with their greatest fear. This stage serves as the climax of the story and represents the hero's transformation, as they must overcome their inner and outer demons to succeed. ( source )
- Reward (Seizing the Sword) : After overcoming the ordeal, the hero receives a reward, which could be a physical object, a piece of knowledge, or personal growth. This stage signifies the hero's victory and the attainment of their goal. ( source )
- The Road Back : The hero begins their journey back to the ordinary world, often with a renewed sense of purpose and the knowledge or reward they gained during their adventure. This stage can involve additional challenges, as the hero's transformation may be met with resistance from their ordinary world. ( source )
- Resurrection : The hero faces a final test or confrontation that represents the culmination of their character growth and the ultimate resolution of the story's conflict. This stage often involves a symbolic "death" and "rebirth" for the hero, signifying their transformation and newfound wisdom. ( source )
- Return with the Elixir : The hero returns to their ordinary world, having been transformed by their experiences and armed with the knowledge or reward they gained during their journey. This stage signifies the completion of the Hero's Journey and the hero's newfound ability to make a positive impact on their world. ( source )
By incorporating these 12 stages into their narrative, writers can craft a rich and satisfying Hero's Journey that resonates with audiences and follows a time-tested pattern of storytelling.
In addition to the 12 stages, the Hero's Journey also features several key archetypes that frequently appear in these narratives. These archetypes, derived from the work of Carl Jung and popularized by Joseph Campbell, represent universal symbols and character types that resonate with audiences across cultures and time periods. By incorporating these archetypes into their story, writers can create a rich and engaging narrative that taps into the human psyche. Some of the most common archetypes in the Hero's Journey include:
- The Hero : The protagonist of the story, who embarks on a journey to achieve a goal or resolve a conflict. The hero undergoes a transformation, often involving personal growth, self-discovery, and the acquisition of new skills or knowledge. ( source )
- The Mentor : A wise and experienced figure who provides guidance, support, and knowledge to the hero. The mentor often possesses valuable information or abilities that the hero needs to complete their journey. ( source )
- The Threshold Guardian : A character or obstacle that tests the hero's resolve and commitment to their journey. Threshold guardians often appear at the beginning of the adventure, forcing the hero to prove their worth and overcome their initial fears or doubts. ( source )
- The Herald : A character or event that signals the beginning of the hero's journey and delivers the Call to Adventure. The herald may also appear later in the story to announce important events or changes. ( source )
- The Shapeshifter : A character whose allegiance, motives, or appearance are uncertain or subject to change. The shapeshifter often serves to create tension and intrigue within the story, as the hero and the audience are left unsure of their true intentions. ( source )
- The Shadow : The antagonist or opposing force in the story, often representing the hero's greatest fears, flaws, or challenges. The shadow serves as a foil to the hero, highlighting their weaknesses and forcing them to confront their inner demons. ( source )
- The Ally : A character who aids and supports the hero on their journey, often providing companionship, advice, or practical assistance. Allies can take many forms, from loyal friends to unlikely partners, and help the hero overcome the obstacles they face. ( source )
- The Trickster : A character who uses wit, cunning, or humor to challenge the status quo and disrupt the established order. The trickster often serves as comic relief, but can also play a more significant role in the hero's journey by introducing new perspectives or forcing the hero to question their assumptions. ( source )
Understanding these key archetypes can help writers create well-rounded characters and engaging narratives that resonate with their audience. By incorporating these archetypes into their Hero's Journey, writers can tap into universal themes and symbols that have captivated readers and viewers for generations.
The Hero's Journey is not just a physical quest but also a psychological one, often referred to as the Inner and Outer Journey. The Outer Journey represents the hero's external actions and experiences, while the Inner Journey delves into their emotional growth, personal development, and the transformation of their beliefs and values. Understanding these two aspects of the Hero's Journey can help writers create a more nuanced and emotionally resonant narrative. Here is an overview of the Inner and Outer Journey in relation to the Hero's Journey:
The Outer Journey
The Outer Journey focuses on the hero's physical actions, experiences, and obstacles they encounter throughout their adventure. This journey is primarily plot-driven and involves the hero's progression through the various stages of the Hero's Journey, such as the Call to Adventure, the Ordeal, and the Return with the Elixir. The Outer Journey often includes the following elements:
- Action and adventure
- Conflict and resolution
- Settings and world-building
- Interaction with other characters
Writers can use the Outer Journey to create engaging and dynamic narratives that keep the audience invested in the hero's plight and the outcome of their quest. ( source )
The Inner Journey
The Inner Journey delves into the hero's psychological and emotional transformation, which is often closely intertwined with the events of the Outer Journey. This journey is primarily character-driven and explores the hero's internal struggles, personal growth, and the evolution of their beliefs and values. The Inner Journey often includes the following elements:
- Character development and growth
- Emotional arcs and conflicts
- Inner demons and fears
- Moral dilemmas and choices
By incorporating the Inner Journey into their narrative, writers can create complex and relatable characters that resonate with their audience on a deeper, more personal level. ( source )
Both the Inner and Outer Journey are integral components of the Hero's Journey, and a successful narrative will weave these two aspects together to create a compelling and emotionally satisfying story. By understanding the interplay between the hero's external actions and their internal growth, writers can create a more nuanced and engaging Hero's Journey that resonates with their audience.
Now that you have a thorough understanding of the Hero's Journey and its various components, it's time to apply this framework to your own story. By incorporating the 12 stages, key archetypes, and the Inner and Outer Journey into your narrative, you can create a rich and engaging story that resonates with your audience. Here are some practical tips and guidelines for applying the Hero's Journey to your story:
1. Identify your hero
Start by identifying your protagonist or hero, the character who will embark on the journey and undergo a transformation. Consider their background, motivations, and personal flaws, as these elements will shape their journey and influence their character development. ( source )
2. Define the Call to Adventure
Determine the inciting incident or Call to Adventure that will propel your hero into their journey. This event should create a sense of urgency, challenge the hero's status quo, and set the stage for their transformation. ( source )
3. Outline the stages of the journey
Using the 12 stages of the Hero's Journey as a guide, outline the key events and turning points in your story. Consider how each stage contributes to the hero's growth and transformation, and ensure that your narrative follows a logical and satisfying arc. ( source )
4. Develop your archetypes
Introduce the key archetypes that will populate your story, such as the Mentor, the Threshold Guardian, and the Shadow. Consider how each archetype can contribute to the hero's journey and help to shape their character development. ( source )
5. Balance the Inner and Outer Journey
Ensure that your story effectively balances the hero's Inner and Outer Journey, weaving together their emotional growth and external experiences into a cohesive narrative. Consider how the events of the Outer Journey influence the hero's Inner Journey and vice versa, and use this interplay to create a compelling and emotionally resonant story. ( source )
6. Revise and refine your story
Once you have applied the Hero's Journey framework to your story, review and revise your narrative to ensure that it adheres to the principles of the Hero's Journey while remaining true to your unique vision and voice. Consider seeking feedback from others, such as critique partners, beta readers, or professional editors, to help you refine your story and bring it to its full potential. ( source )
By following these guidelines and incorporating the Hero's Journey into your narrative, you can create a rich and engaging story that resonates with your audience and follows a time-tested pattern of storytelling success.
While the Hero's Journey provides a useful framework for storytelling, it's important to recognize that not all stories will follow this structure exactly. Over time, various adaptations and variations of the Hero's Journey have emerged, offering different perspectives and approaches to storytelling. By exploring these adaptations, writers can gain a broader understanding of the narrative possibilities and apply these insights to their own work. Here are some notable adaptations and variations of the Hero's Journey:
1. The Heroine's Journey
The Heroine's Journey, first proposed by Maureen Murdock in her book "The Heroine's Journey: Woman's Quest for Wholeness," offers a gendered perspective on the Hero's Journey, focusing on the unique challenges and experiences faced by female protagonists. The Heroine's Journey emphasizes the importance of relationships, self-discovery, and the integration of masculine and feminine qualities within the individual. ( source )
2. The Writer's Journey
Christopher Vogler's "The Writer's Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers" adapts the Hero's Journey for screenwriters and novelists, condensing Campbell's 17 stages into a more streamlined 12-stage structure. Vogler's adaptation has been widely embraced by the writing community and is particularly influential in the world of screenwriting. ( source )
3. The Virgin's Promise
Kim Hudson's "The Virgin's Promise" offers an alternative narrative structure that focuses on the protagonist's journey towards self-fulfillment and personal empowerment, rather than a quest to save others or restore balance to the world. The Virgin's Promise is particularly relevant to stories featuring female protagonists and themes of personal growth and transformation. ( source )
4. The Anti-Hero's Journey
The Anti-Hero's Journey explores the narrative arc of protagonists who do not possess traditional heroic qualities, such as moral integrity, courage, or selflessness. The Anti-Hero's Journey may involve a more morally ambiguous or complex character, who may not ultimately achieve redemption or success in the conventional sense.
5. The Collective Journey
The Collective Journey, as proposed by Jeff Gomez, focuses on the interconnected and collaborative nature of modern storytelling, particularly in transmedia narratives and shared storyworlds. In the Collective Journey, the focus shifts from the individual hero to a diverse ensemble of characters, each contributing to the narrative in unique and meaningful ways. ( source )
By exploring these adaptations and variations of the Hero's Journey, writers can gain a broader understanding of the possibilities for storytelling and create narratives that reflect their unique perspective and voice. Remember that the Hero's Journey is not a rigid formula, but rather a flexible framework that can be adapted and modified to suit the needs of your story and your characters.
To further illustrate the power and versatility of the Hero's Journey, let's examine some case studies of popular fiction that employ this narrative structure. By analyzing these examples, you can gain a deeper understanding of how the Hero's Journey can be applied to various genres, mediums, and story types.
1. The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien
Tolkien's epic fantasy trilogy is a prime example of the Hero's Journey, with its protagonist Frodo Baggins embarking on a quest to destroy the One Ring and save Middle-earth. The story follows the classic stages of the Hero's Journey, with Frodo facing numerous trials, allies, and enemies along the way, ultimately transforming from a humble Hobbit into a hero capable of great courage and sacrifice. ( source )
2. The Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling
Rowling's beloved fantasy series follows the young wizard Harry Potter as he embarks on a journey to defeat the dark wizard Voldemort. Over the course of the series, Harry undergoes the stages of the Hero's Journey, from the Call to Adventure (receiving his Hogwarts letter) to the Ordeal (battling Voldemort) and the Return with the Elixir (restoring peace to the wizarding world). The series also features a rich cast of archetypal characters, such as the Mentor (Dumbledore), the Shadow (Voldemort), and the Shapeshifter (Snape). ( source )
3. The Hunger Games trilogy by Suzanne Collins
Collins' dystopian series follows the journey of Katniss Everdeen, a young woman who becomes the symbol of rebellion against a tyrannical government. Katniss' journey reflects the Hero's Journey, as she faces trials in the Hunger Games arena, encounters allies and enemies, and ultimately leads a revolution to overthrow the Capitol. The series also incorporates elements of the Heroine's Journey, exploring themes of personal growth, relationships, and the integration of masculine and feminine qualities. ( source )
4. Star Wars by George Lucas
George Lucas' iconic space opera is heavily influenced by Joseph Campbell's work on the Hero's Journey, with its protagonist Luke Skywalker embarking on a quest to become a Jedi and defeat the evil Empire. The original Star Wars trilogy follows the stages of the Hero's Journey, with Luke undergoing a transformation from a simple farm boy to a powerful Jedi Knight. The series also features a cast of archetypal characters, such as the Mentor (Obi-Wan Kenobi), the Shadow (Darth Vader), and the Trickster (Han Solo). ( source )
These case studies demonstrate the enduring appeal and versatility of the Hero's Journey as a narrative structure. By applying the principles of the Hero's Journey to your own work, you can create compelling stories that resonate with audiences across genres, mediums, and cultures.
While the Hero's Journey can be a powerful tool for storytelling, it's essential to avoid some common mistakes when applying this framework to your work. By recognizing these pitfalls and taking steps to avoid them, you can create a more engaging and original story that stands out in today's competitive market. Here are some common mistakes and tips for avoiding them:
1. Rigid adherence to the Hero's Journey
One of the most common mistakes writers make is treating the Hero's Journey as a rigid formula rather than a flexible framework. It's important to remember that not every story will follow the Hero's Journey exactly, and forcing your narrative to adhere to this structure can result in a predictable and uninspired story. Instead, use the Hero's Journey as a guide and adapt it to suit your unique vision and characters. ( source )
2. Stereotypical characters and archetypes
While the Hero's Journey relies on certain archetypal characters, it's essential to avoid creating one-dimensional, stereotypical characters that lack depth and complexity. Instead, strive to develop nuanced and multifaceted characters that challenge audience expectations and engage their emotions. This will result in a richer and more satisfying story. ( source )
3. Neglecting the Inner Journey
Another common mistake is focusing solely on the external events of the Hero's Journey and neglecting the protagonist's emotional growth and transformation. To create a truly compelling story, it's essential to balance the Inner and Outer Journey, ensuring that your hero's emotional development is intertwined with their external experiences. This will result in a more emotionally resonant and satisfying narrative. ( source )
4. Overemphasis on action and spectacle
While the Hero's Journey often involves high-stakes action and conflict, it's essential not to let these elements overshadow the emotional core of your story. Instead, focus on your characters' relationships, motivations, and personal growth, ensuring that the action and spectacle serve to enhance the emotional stakes and drive the narrative forward. ( source )
5. Ignoring cultural context and diversity
Finally, it's important to recognize that the Hero's Journey is rooted in a specific cultural context and may not apply universally to all stories and cultures. When crafting your narrative, be mindful of cultural diversity and strive to create stories that reflect and celebrate the rich tapestry of human experience. This will result in a more inclusive and engaging story that resonates with a broader audience. ( source )
By avoiding these common mistakes and applying the principles of the Hero's Journey thoughtfully and creatively, you can craft a powerful and engaging story that stands out in today's competitive market and resonates with your audience.
Creating a compelling Hero's Journey requires a thoughtful approach to storytelling, character development, and narrative structure. To help you craft a memorable and engaging story, consider these writing tips:
1. Understand the foundation of the Hero's Journey
Before attempting to write a Hero's Journey, familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts, stages, and archetypes outlined by Joseph Campbell and other scholars. This will provide a solid foundation for crafting your narrative and help you identify the essential elements of your story. ( source )
2. Develop compelling characters
Creating engaging, multidimensional characters is essential for a successful Hero's Journey. Focus on developing your protagonist, as well as the supporting cast of allies, enemies, and mentors, ensuring that each character is unique, relatable, and serves a purpose within the narrative.
3. Focus on emotional stakes
The emotional stakes of your story are crucial to maintaining reader engagement and investment in the Hero's Journey. Strive to create a narrative with high emotional stakes, where the protagonist's personal growth and relationships are intertwined with their external quest. ( source )
4. Use the Hero's Journey as a guide, not a template
While the Hero's Journey provides a useful framework for crafting your story, avoid treating it as a rigid formula. Instead, use the Hero's Journey as a starting point and adapt it to suit your unique vision, characters, and genre. This will result in a more original and engaging narrative. ( source )
To create a satisfying and well-rounded narrative, it's essential to balance the Inner Journey (the protagonist's emotional growth) with the Outer Journey (their external quest). Ensure that both aspects of the Hero's Journey are interconnected and contribute to the protagonist's overall transformation. ( source )
6. Embrace diversity and cultural context
When crafting your Hero's Journey, be mindful of cultural diversity and consider incorporating elements from various myths, legends, and cultural traditions. This will enrich your narrative and help it resonate with a broader audience. ( source )
7. Revise, revise, revise
Finally, remember that writing a compelling Hero's Journey is an iterative process that requires multiple drafts and revisions. Be prepared to revise your work, seeking feedback from beta readers, editors, and writing groups to refine your narrative and ensure that it effectively communicates your vision. ( source )
By applying these writing tips and maintaining a thoughtful, creative approach to storytelling, you can craft a compelling Hero's Journey that engages your audience and leaves a lasting impact.
Below are some frequently asked questions that will provide you with more information.
How can I adapt the Hero's Journey framework to my unique story?
Adapting the Hero's Journey to your unique story involves understanding its core principles and using them as a guide rather than a rigid template. Be creative and flexible, allowing your story's characters and themes to drive the narrative. Don't be afraid to deviate from the traditional Hero's Journey if it better serves your story's vision and purpose.
What are the key components of a compelling Hero's Journey narrative?
The key components of a compelling Hero's Journey narrative include a well-developed protagonist, a clear and meaningful quest, engaging character archetypes, high emotional stakes, and a balance between the Inner and Outer Journeys. Additionally, focusing on character growth and transformation can create a more emotionally resonant and satisfying story.
How can I avoid common mistakes when writing a Hero's Journey story?
Avoid common mistakes by not treating the Hero's Journey as a rigid formula, developing nuanced characters instead of stereotypes, focusing on emotional stakes, and considering cultural diversity. Also, be mindful of the balance between the Inner and Outer Journeys, ensuring that your protagonist's emotional growth is intertwined with their external quest.
What are some writing tips for crafting a compelling Hero's Journey?
Writing tips for crafting a compelling Hero's Journey include understanding the foundation of the Hero's Journey, developing compelling characters, focusing on emotional stakes, using the Hero's Journey as a guide rather than a template, balancing the Inner and Outer Journeys, embracing diversity and cultural context, and revising your work iteratively.
If you're interested in exploring the Hero's Journey further, here are three non-fiction books that delve into the topic and provide valuable insights:
In conclusion, mastering the Hero's Journey is a crucial skill for any writer seeking to create a compelling and resonant narrative. By understanding the origins of the Hero's Journey and its connections to myth, legend, and the human psyche, you can tap into a powerful framework for storytelling success.
The Hero's Journey provides a structure that can guide your narrative, helping you craft a story that engages readers and speaks to universal themes of personal growth, transformation, and triumph over adversity. By carefully studying the Three-Act Structure , the 12 Stages of the Hero's Journey , and the key archetypes that populate this narrative structure, you'll be better equipped to create a story that resonates with your audience.
Remember that while the Hero's Journey offers a valuable blueprint for storytelling, it's essential to adapt and personalize this framework to suit your unique vision and narrative goals. Be open to deviating from the traditional structure, incorporating diverse cultural elements, and exploring new ways to tell your story.
Finally, embrace the iterative nature of the writing process, seeking feedback from others and revising your work to ensure that your Hero's Journey effectively communicates your intended message and themes. By dedicating time and effort to mastering the Hero's Journey, you'll be well on your way to crafting a captivating and successful story.
Claim your free eBook today and join over 25,000 writers who have read and benefited from this ebook.
'It is probably one of the best books on writing I've read so far.' Miz Bent

- Story Writing Guides
12 Hero’s Journey Stages Explained (+ Free Templates)
From zero to hero, the hero’s journey is a popular character development arc used in many stories. In today’s post, we will explain the 12 hero’s journey stages, along with the simple example of Cinderella.
The Hero’s Journey was originally formulated by American writer Joseph Campbell to describe the typical character arc of many classic stories, particularly in the context of mythology and folklore. The original hero’s journey contained 17 steps. Although the hero’s journey has been adapted since then for use in modern fiction, the concept is not limited to literature. It can be applied to any story, video game, film or even music that features an archetypal hero who undergoes a transformation. Common examples of the hero’s journey in popular works include Star Wars, Lord of the Rings, The Hunger Games and Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s Stone.
- What is the hero's journey?
Stage 1: The Ordinary World
Stage 2: call of adventure, stage 3: refusal of the call, stage 4: meeting the mentor, stage 5: crossing the threshold, stage 6: tests, allies, enemies, stage 7: the approach, stage 8: the ordeal, stage 9: reward, stage 10: the road back, stage 11: resurrection, stage 12: return with the elixir, cinderella example, campbell’s 17-step journey, leeming’s 8-step journey, cousineau’s 8-step journey.
- Free Hero's Journey Templates
What is the hero’s journey?
The hero’s journey, also known as the monomyth, is a character arc used in many stories. The idea behind it is that heroes undergo a journey that leads them to find their true selves. This is often represented in a series of stages. There are typically 12 stages to the hero’s journey. Each stage represents a change in the hero’s mindset or attitude, which is triggered by an external or internal event. These events cause the hero to overcome a challenge, reach a threshold, and then return to a normal life.
The hero’s journey is a powerful tool for understanding your characters. It can help you decide who they are, what they want, where they came from, and how they will change over time. It can be used to
- Understand the challenges your characters will face
- Understand how your characters react to those challenges
- Help develop your characters’ traits and relationships
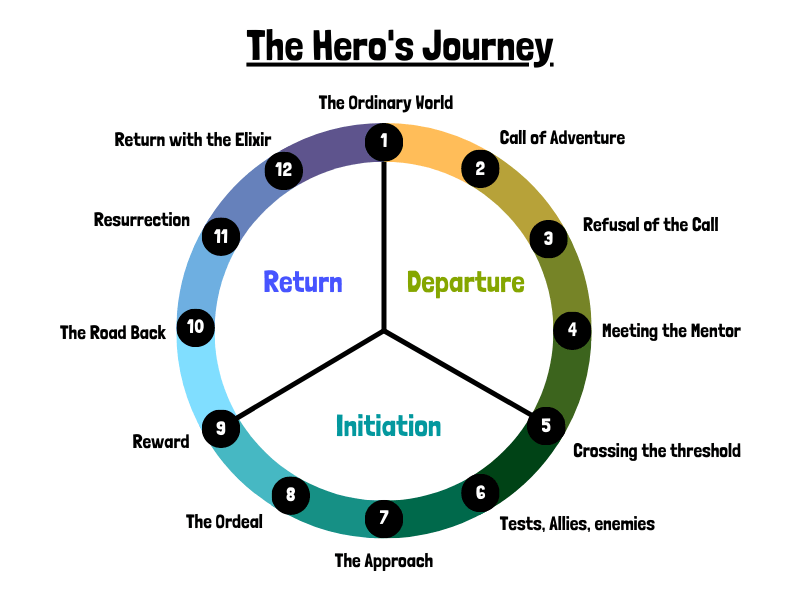
In this post, we will explain each stage of the hero’s journey, using the example of Cinderella.
You might also be interested in our post on the story mountain or this guide on how to outline a book .
12 Hero’s Journey Stages
The archetypal hero’s journey contains 12 stages and was created by Christopher Vogler. These steps take your main character through an epic struggle that leads to their ultimate triumph or demise. While these steps may seem formulaic at first glance, they actually form a very flexible structure. The hero’s journey is about transformation, not perfection.
Your hero starts out in the ordinary world. He or she is just like every other person in their environment, doing things that are normal for them and experiencing the same struggles and challenges as everyone else. In the ordinary world, the hero feels stuck and confused, so he or she goes on a quest to find a way out of this predicament.
Example: Cinderella’s father passes away and she is now stuck doing chores and taking abuse from her stepsisters and stepmother.
The hero gets his or her first taste of adventure when the call comes. This could be in the form of an encounter with a stranger or someone they know who encourages them to take a leap of faith. This encounter is typically an accident, a series of coincidences that put the hero in the right place at the right time.
Example: An invite arrives inviting the family to a royal ball where the Prince will choose a wife.
Some people will refuse to leave their safe surroundings and live by their own rules. The hero has to overcome the negative influences in order to hear the call again. They also have to deal with any personal doubts that arise from thinking too much about the potential dangers involved in the quest. It is common for the hero to deny their own abilities in this stage and to lack confidence in themselves.
Example: Cinderella accepts the call by making her own dress for the ball. However, her stepmother refuses the call for her by not letting her go to the ball. And her step-sisters ruin her dress, so she can not go.
After hearing the call, the hero begins a relationship with a mentor who helps them learn about themselves and the world. In some cases, the mentor may be someone the hero already knows. The mentor is usually someone who is well-versed in the knowledge that the hero needs to acquire, but who does not judge the hero for their lack of experience.
Example: Cinderella meets her fairy godmother who equips her with everything she needs for the ball, including a dress and a carriage.
The hero leaves their old life behind and enters the unfamiliar new world. The crossing of the threshold symbolises leaving their old self behind and becoming a new person. Sometimes this can include learning a new skill or changing their physical appearance. It can also include a time of wandering, which is an essential part of the hero’s journey.
Example: Cinderella hops into the carriage and heads off to the ball. She has transformed from a servant into an elegant young lady.
As the hero goes on this journey, they will meet both allies (people who help the hero) and enemies (people who try to stop the hero). There will also be tests, where the hero is tempted to quit, turn back, or become discouraged. The hero must be persistent and resilient to overcome challenges.
Example: At the ball, Cinderella meets the prince, and even see’s her stepmother and stepsister. She dances with Prince all night long making her step-sisters extremely jealous.
The hero now reaches the destination of their journey, in some cases, this is a literal location, such as a cave or castle. It could also be metaphorical, such as the hero having an internal conflict or having to make a difficult decision. In either case, the hero has to confront their deepest fears in this stage with bravery. In some ways, this stage can mark the end of the hero’s journey because the hero must now face their darkest fears and bring them under control. If they do not do this, the hero could be defeated in the final battle and will fail the story.
Example: Cinderella is having a great time at the ball and nearly forgets about the midnight rule. As she runs away in a hurry, her glass slipper falls off outside the palace.
The hero has made it to the final challenge of their journey and now must face all odds and defeat their greatest adversary. Consider this the climax of the story. This could be in the form of a physical battle, a moral dilemma or even an emotional challenge. The hero will look to their allies or mentor for further support and guidance in this ordeal. Whatever happens in this stage could change the rest of the story, either for good or bad.
Example: Prince Charming looks all over the kingdom for the mysterious girl he met at the ball. He finally visits Cinderella’s house and tries the slippers on the step-sisters. The prince is about to leave and then he sees Cinderella in the corner cleaning.
When the hero has defeated the most powerful and dangerous of adversaries, they will receive their reward. This reward could be an object, a new relationship or even a new piece of knowledge. The reward, which typically comes as a result of the hero’s perseverance and hard work, signifies the end of their journey. Given that the hero has accomplished their goal and served their purpose, it is a time of great success and accomplishment.
Example: The prince tries the glass slipper on Cinderella. The glass slipper fits Cinderella perfectly, and they fall in love.
The journey is now complete, and the hero is now heading back home. As the hero considers their journey and reflects on the lessons they learned along the way, the road back is sometimes marked by a sense of nostalgia or even regret. As they must find their way back to the normal world and reintegrate into their former life, the hero may encounter additional difficulties or tests along the way. It is common for the hero to run into previous adversaries or challenges they believed they had overcome.
Example: Cinderella and Prince Charming head back to the Prince’s castle to get married.
The hero has one final battle to face. At this stage, the hero might have to fight to the death against a much more powerful foe. The hero might even be confronted with their own mortality or their greatest fear. This is usually when the hero’s true personality emerges. This stage is normally symbolised by the hero rising from the dark place and fighting back. This dark place could again be a physical location, such as the underground or a dark cave. It might even be a dark, mental state, such as depression. As the hero rises again, they might change physically or even experience an emotional transformation.
Example: Cinderella is reborn as a princess. She once again feels the love and happiness that she felt when she was a little girl living with her father.
At the end of the story, the hero returns to the ordinary world and shares the knowledge gained in their journey with their fellow man. This can be done by imparting some form of wisdom, an object of great value or by bringing about a social revolution. In all cases, the hero returns changed and often wiser.
Example: Cinderella and Prince Charming live happily ever after. She uses her new role to punish her stepmother and stepsisters and to revitalise the kingdom.
We have used the example of Cinderella in Vogler’s hero’s journey model below:

Below we have briefly explained the other variations of the hero’s journey arc.
The very first hero’s journey arc was created by Joseph Campbell in 1949. It contained the following 17 steps:
- The Call to Adventure: The hero receives a call or a reason to go on a journey.
- Refusal of the Call: The hero does not accept the quest. They worry about their own abilities or fear the journey itself.
- Supernatural Aid: Someone (the mentor) comes to help the hero and they have supernatural powers, which are usually magical.
- The Crossing of the First Threshold: A symbolic boundary is crossed by the hero, often after a test.
- Belly of the Whale: The point where the hero has the most difficulty making it through.
- The Road of Trials: In this step, the hero will be tempted and tested by the outside world, with a number of negative experiences.
- The Meeting with the Goddess: The hero meets someone who can give them the knowledge, power or even items for the journey ahead.
- Woman as the Temptress: The hero is tempted to go back home or return to their old ways.
- Atonement with the Father: The hero has to make amends for any wrongdoings they may have done in the past. They need to confront whatever holds them back.
- Apotheosis: The hero gains some powerful knowledge or grows to a higher level.
- The Ultimate Boon: The ultimate boon is the reward for completing all the trials of the quest. The hero achieves their ultimate goal and feels powerful.
- Refusal of the Return: After collecting their reward, the hero refuses to return to normal life. They want to continue living like gods.
- The Magic Flight: The hero escapes with the reward in hand.
- Rescue from Without: The hero has been hurt and needs help from their allies or guides.
- The Crossing of the Return Threshold: The hero must come back and learn to integrate with the ordinary world once again.
- Master of the Two Worlds: The hero shares their wisdom or gifts with the ordinary world. Learning to live in both worlds.
- Freedom to Live: The hero accepts the new version of themselves and lives happily without fear.
David Adams Leeming later adapted the hero’s journey based on his research of legendary heroes found in mythology. He noted the following steps as a pattern that all heroes in stories follow:
- Miraculous conception and birth: This is the first trauma that the hero has to deal with. The Hero is often an orphan or abandoned child and therefore faces many hardships early on in life.
- Initiation of the hero-child: The child faces their first major challenge. At this point, the challenge is normally won with assistance from someone else.
- Withdrawal from family or community: The hero runs away and is tempted by negative forces.
- Trial and quest: A quest finds the hero giving them an opportunity to prove themselves.
- Death: The hero fails and is left near death or actually does die.
- Descent into the underworld: The hero rises again from death or their near-death experience.
- Resurrection and rebirth: The hero learns from the errors of their way and is reborn into a better, wiser being.
- Ascension, apotheosis, and atonement: The hero gains some powerful knowledge or grows to a higher level (sometimes a god-like level).
In 1990, Phil Cousineau further adapted the hero’s journey by simplifying the steps from Campbell’s model and rearranging them slightly to suit his own findings of heroes in literature. Again Cousineau’s hero’s journey included 8 steps:
- The call to adventure: The hero must have a reason to go on an adventure.
- The road of trials: The hero undergoes a number of tests that help them to transform.
- The vision quest: Through the quest, the hero learns the errors of their ways and has a realisation of something.
- The meeting with the goddess: To help the hero someone helps them by giving them some knowledge, power or even items for the journey ahead.
- The boon: This is the reward for completing the journey.
- The magic flight: The hero must escape, as the reward is attached to something terrible.
- The return threshold: The hero must learn to live back in the ordinary world.
- The master of two worlds: The hero shares their knowledge with the ordinary world and learns to live in both worlds.
As you can see, every version of the hero’s journey is about the main character showing great levels of transformation. Their journey may start and end at the same location, but they have personally evolved as a character in your story. Once a weakling, they now possess the knowledge and skill set to protect their world if needed.
Free Hero’s Journey Templates
Use the free Hero’s journey templates below to practice the skills you learned in this guide! You can either draw or write notes in each of the scene boxes. Once the template is complete, you will have a better idea of how your main character or the hero of your story develops over time:
The storyboard template below is a great way to develop your main character and organise your story:

Did you find this guide on the hero’s journey stages useful? Let us know in the comments below.

Marty the wizard is the master of Imagine Forest. When he's not reading a ton of books or writing some of his own tales, he loves to be surrounded by the magical creatures that live in Imagine Forest. While living in his tree house he has devoted his time to helping children around the world with their writing skills and creativity.
Related Posts

Comments loading...

Mastering the Hero’s Journey and Archetypes: Essential Guide

This lesson dissects the age-old narrative structure that underpins countless stories, from Homer’s Odyssey to today’s cinematic epics. Understanding this journey and the roles that populate it is not just about analyzing literature; it’s about recognizing the patterns that shape our understanding of heroism, challenge, and transformation across cultures and ages. It’s a tool to engage students with the universal truths woven into the fabric of the stories they love, and it’s a testament to the timeless relevance of storytelling in human experience.
Learning Goals
- I will be able to identify and explain the stages of the Hero’s Journey, including the Call to Adventure, the Initiation, and the Return.
- I will be able to distinguish between different archetypes, such as the Mentor, Ally, Herald, Trickster, Shapeshifter, Guardian, and Shadow, within various narratives.
- Either present and have students take down the hero’s journey note or distribute it as a handout.
- Distribute the archetypes handout.
- Have students read and summarize the handout on the worksheet.
Either take up the worksheet together or collect and mark it.
12 Stages of a Hero's Journey

1. Ordinary World
- The hero is a normal person or member of society
- The hero’s surroundings are common, comfortable, mundane, or even boring
2. Call to Adventure
- The call establishes the stakes of the game and makes clear the hero’s goals
- The hero learns what is at stake The hero is expected to leave the Ordinary World
- The call is usually made by a herald
3. Refusal of the Call
- Hero expresses his, her, or their reluctance
- Hero does not wish to commit to the journey
4. Meeting the Mentor
- Mentor serves as a motivator or teacher to the hero
- He, she, or they helps the hero prepare for the unknown
- Old hero passes the torch However, the mentor can only go so far…
5. Crossing the First Threshold
- Hero finally agrees to face the conflict
- Hero is willing to accept the consequences of entering the special world
- Adventure gets moving!
6. The Special World
- The hero is tested.
- We meet new allies.
- We discover new enemies.
7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
- Cave may symbolize where a secret object may be found
- Cave may be where the enemy is hiding or the edge of some dangerous place
- Many heroes pause before entering to prepare a plan to outwit the enemy
8. The Supreme Ordeal
- Hero is forced to confront his, her, or their greatest fear!
- Hero faces a possibility of death Audience or reader is held in suspense
- Hero overcomes his, her, or their obstacle and takes possession of the reward
- The reward can be an object, person, knowledge, sword, secret, etc.
10. The Road Back
- This stage marks the hero’s return to the Ordinary World
- However, hostile forces still rage after the hero…he’ not out of the woods yet
11. The Resurrection
- This state marks a second life and death moment for the hero.
- He cannot quite reach the Ordinary World just yet.
12. Return with Elixir
- Hero returns to the Ordinary World with new treasure, knowledge, or lesson from the special world.
- Hero takes his, her, or their new experiences from the Special World home.
Archetypes in The Hero’s Journey
An archetype is a very typical example of a certain person or thing, or an original that has been imitated. In the context of literature, art, and psychology, the term has specific nuances:
Both of the following definitions are important to us:
Literature and Art: An archetype can refer to a character, a theme, a symbol, or even a setting that represents universal patterns of human nature. It is also commonly used in mythology, where certain figures or themes recur across various cultures and are considered archetypal because they are imbued with a certain universal significance. For example, the “hero” archetype is seen in characters that embody courage and adventure; the “mentor” archetype is a figure that guides or aids the hero.
Psychology: The term was adopted by Carl Jung, who used it to describe his theory of the human psyche. He believed archetypes are innate, universal prototypes for ideas and may be used to interpret observations. In Jungian psychology, archetypes are thought of as universal, archaic symbols and images that derive from the collective unconscious and are the psychic counterpart of instinct. They are inherited potentials that are actualized when they enter consciousness as images or manifest in behavior on interaction with the external world.
Fill out the archetypes worksheet, using the following information:

The archetype of the Hero represents the protagonist of a story who is often called to leave their ordinary world and enter into a new, challenging environment where they must face a series of trials. The Hero is usually portrayed as a character who seeks something of great value, whether it be a physical object, knowledge, wisdom, or peace. The journey they undertake is as much an external adventure as it is an internal transformation, with the Hero often experiencing significant personal growth and development.
Characteristics of the Hero archetype include courage, perseverance, sacrifice, and the willingness to face the unknown. The Hero is often, but not always, destined for greatness or has an inherent nobility, either in their character or their lineage. They typically possess a strong moral compass, and their actions are usually driven by a sense of duty, love, or honor.
Harry Potter, from J.K. Rowling’s “Harry Potter” series, is an exemplary literary Hero. Luke Skywalker from “Star Wars” is a classic cinematic Hero.

The archetype of the Mentor represents the guide or teacher who assists the Hero on their journey. This figure often possesses wisdom and experience and serves to motivate, inspire, or educate the Hero, helping them to overcome doubts and prepare for the challenges ahead. The Mentor can be a protective presence, offering gifts of knowledge or tools, crucial advice, or even magical support to the Hero. They are a source of spiritual and moral guidance and often embody the Hero’s aspirations.
Characteristics of the Mentor archetype include wisdom, knowledge, insight, and often a certain degree of patience and compassion. They are usually portrayed as a benevolent figure, though their methods of teaching may sometimes seem harsh or challenging. Mentors are critical in helping the Hero to build the necessary skills or acquire the knowledge needed to overcome impending trials. Their influence is pivotal to the Hero’s development and in shaping the path that will lead to maturity or fulfillment of the quest.
In literature, Gandalf from J.R.R. Tolkien’s “The Lord of the Rings” series is a quintessential Mentor. As a wise wizard, Gandalf guides the young hobbit, Frodo Baggins, on his perilous journey to destroy the One Ring. Gandalf offers wisdom, support, and guidance, not only to Frodo but to the entire Fellowship, steering them through their darkest moments.
In cinema, Mr. Miyagi from “The Karate Kid” is an iconic Mentor. He teaches Daniel LaRusso not just the physical skills of karate but also valuable life lessons about balance, patience, and respect, transforming Daniel not just into a skilled martial artist but into a more confident and resilient individual.

The archetype of the Ally represents a companion or supporter of the Hero on their journey, playing a crucial role in the Hero’s adventure. Allies come in many forms, sometimes as friends, lovers, or family members, and they often complement the Hero’s strengths or compensate for their weaknesses. An Ally may also provide emotional support, encouragement, and camaraderie, which are essential as the Hero faces the unknown. These characters can also inject humor, provide a sounding board for ideas, and assist in problem-solving throughout the narrative.
Characteristics of the Ally archetype include loyalty, devotion, and the willingness to face shared risks. While the Hero may be the primary focus of the narrative, Allies are often well-developed characters with their own quirks, backgrounds, and arcs. They contribute significantly to the plot, aid in the development of the Hero, and sometimes undergo their own growth and transformation. Allies may challenge the Hero’s ideas and actions, fostering critical growth and change.
In literature, Samwise Gamgee from J.R.R. Tolkien’s “The Lord of the Rings” series epitomizes the Ally archetype. Sam is the steadfast companion of Frodo Baggins, offering unwavering loyalty, physical assistance, and emotional support. His down-to-earth wisdom, courage, and dedication play a pivotal role in the success of Frodo’s mission to destroy the One Ring.
In movies, Ron Weasley and Hermione Granger from the “Harry Potter” series are exemplary Allies. They support Harry in various ways: Ron provides loyalty and relief from the weight of Harry’s destiny, while Hermione offers intelligence, resourcefulness, and a voice of reason. Both characters contribute significantly to Harry’s journey and to the triumph over the challenges they face together.

The archetype of the Herald is the character or force in a story that initiates the call to adventure, signaling the beginning of the Hero’s journey and the impending change in their life. The Herald often appears at the outset of the story to challenge the status quo and to push or invite the Hero out of their comfortable existence into the realm of the unknown. This call to adventure can be a direct challenge, an invitation, a threat, or simply a piece of news that shakes the Hero’s ordinary world.
Characteristics of the Herald archetype include the delivery of significant news, the triggering of action, and often serving as a catalyst for change. The Herald may not necessarily be a person; it can be an event, an object, or a message that compels the Hero to act. Heralds often appear briefly, but their impact on the plot is profound as they set the narrative in motion.
In literature, the White Rabbit from Lewis Carroll’s “Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland” serves as the Herald. The White Rabbit’s appearance and subsequent dash down the rabbit hole beckon Alice to follow, leading her away from her mundane, everyday life into the fantastical world of Wonderland, where her incredible journey begins.
The Trickster

The archetype of the Trickster is a character in a story known for their cunning, mischievous nature, and tendency to break the rules and conventional behavior. The Trickster is often a catalyst for change and a disruptor of the status quo. They challenge other characters and can alter the course of the narrative through unpredictable behavior. Tricksters are shapeshifters in the metaphorical sense, navigating the story with a fluidity that both aids and complicates the Hero’s journey.
Characteristics of the Trickster archetype include a propensity for humor, wit, and the ability to cross boundaries. They often serve as a comic relief in the story but their role is much deeper—they question and mock authority, expose hypocrisy, and can bring to light uncomfortable truths that others are not willing to confront. The Trickster can be both a creator and a destroyer, a figure who provides critical insight or necessary distraction that forces characters to look at situations in new ways.
In literature, Puck from William Shakespeare’s “A Midsummer Night’s Dream” exemplifies the Trickster archetype. As a mischievous fairy, Puck’s antics and errors with a love potion create chaos and confusion among the play’s couples, leading to a series of comedic and unforeseen events that propel the various subplots of the play.
Shapeshifter

The archetype of the Shapeshifter in storytelling is a character whose motives, loyalty, or intentions are unclear, creating suspense and intrigue within the narrative. This archetype is named for their ability to “shape-shift” — metaphorically changing their demeanor, appearance, or side in the conflict as it suits their purposes. Shapeshifters are often complex, multidimensional characters who play a pivotal role in the Hero’s journey by providing tests or trials.
Characteristics of the Shapeshifter archetype include ambiguity, unpredictability, and transformation. They often contribute to the theme of appearance vs. reality in a story, as they can present one thing while being another. The uncertainty surrounding a Shapeshifter can serve to mirror the Hero’s insecurities, challenge their trust, and force the Hero to question their perceptions and beliefs.
In literature, Severus Snape from J.K. Rowling’s “Harry Potter” series is an iconic Shapeshifter. Throughout the series, Snape’s true intentions are questionable. He appears to serve the dark antagonist, Voldemort, while also showing moments of protecting Harry. The complexity of his character keeps his true allegiance hidden until the very end, revealing a depth of character that is both surprising and fitting to the narrative.
The Guardian

The archetype of the Guardian, also known as the Threshold Guardian, represents a challenge or obstacle the Hero must overcome to enter into a new phase of life or embark further on their journey. The Guardian stands at the precipice of important change or at critical gateways the Hero must pass through. These characters, creatures, or even situations are tests that the Hero must confront and overcome, usually to prove their worthiness, resolve, or commitment to the journey.
Characteristics of the Guardian archetype include the role of protector or keeper of a particular passage or knowledge. They are not necessarily enemies; rather, they serve as a form of quality control for the Hero’s progress and can even become allies once their challenge is met or understood. The Guardian can embody fear, doubt, or any other form of inner conflict the Hero must face and conquer in order to continue on their journey.
In literature, the Sphinx from Greek mythology, famously encountered by Oedipus, is a classic example of a Guardian. It poses a riddle that Oedipus must solve to pass and save the city of Thebes, symbolizing a gatekeeper to his own destiny and the destiny of the city.

The archetype of the Shadow in storytelling embodies the darker side of humanity and often represents the antagonist or the Hero’s nemesis. This figure can be a character, group of characters, or even an inner darkness within the Hero themselves. The Shadow exists to oppose the Hero and create conflict within the story. It often represents the qualities that the Hero has rejected or prefers not to acknowledge within themselves, serving as a reflection of their greatest fears and challenges.
Characteristics of the Shadow archetype include the projection of the Hero’s inner fears, moral weakness, or flaws. The Shadow can reveal the Hero’s repressed desires or unresolved conflicts. It is not necessarily evil, though it is commonly depicted that way; rather, it represents the unexpressed or underdeveloped aspects of the Hero’s personality or the chaos and disorder challenging the Hero’s world.
In literature, the character of Voldemort in J.K. Rowling’s “Harry Potter” series is a prime example of a Shadow. He is the dark counterpart to Harry Potter, embodying the fear, power, and aggression that Harry must confront and overcome both within himself and in the external world.
In movies, Darth Vader from the “Star Wars” saga epitomizes the Shadow archetype. Representing the darkness and fear that Luke Skywalker must face, Darth Vader is not only a physical threat but also a psychological one, as he is revealed to be Luke’s father, thus embodying the darkness within the Hero’s own lineage and potential future.
Join our Community!
Sign up for our weekly roundup of new content on The Teachers' Blog. We don’t spam! Read our privacy policy for more info.
Check your inbox or spam folder to confirm your subscription.

Click Here to see more from the Greek Mythology Unit Plan
Archetypes vs. Stereotypes: A New Look At The Hero’s Journey
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Subscribe: RSS
Archetypes are one of the most valuable and also most challenging concepts in screenwriting.
To understand how to use archetypes effectively, we have to go back all the way to the source, Carl Jung (famously not a screenwriter).
We have to understand where the concept of archetypes comes from, and how it connects to a larger concept called the Collective Unconscious.
And we have to learn how to tap into archetypes intuitively, rather than just intellectually.
If you are trying to tap into archetypes from a purely intellectual perspective in your screenwriting, there’s a good chance that you’re not actually writing archetypes. You’re actually writing stereotypes.
So what is an archetype? How do they work? How do you write them? How do you connect to the archetypes that live inside of you?
That’s what we’re going to be talking about in this podcast.
As I mentioned, archetypes begin with Carl Jung, and his idea of the Collective Unconscious. To vastly oversimplify this very complicated concept:
The idea of the Collective Unconscious is that there’s a fabric that ties all human experience together. That even though in my waking life, I think I am Jake, and you are you, and we think that we are different and separated, in our dreams we can actually tap into a collective fabric, a shared experience, that makes us human.
Jung believed that there were certain metaphors, certain elements, certain aspects of our dreams that actually mean the same thing to everyone who experiences them.
And by using our subconscious mind, by using the power of our dreams, we can tap into the Collective Unconscious and step into experiences that we’ve never yet had, and parts of ourselves we have never yet met.
In doing so, he believed that we could find the universal tie that binds us all together.
A brilliant professor named Joseph Campbell came along and took Jung’s beautiful concept of the Collective Unconscious to the next level for writers, by creating something called The Hero’s Journey
To vastly oversimplify Campbell in the same way we just did Jung, Campbell essentially realized that if there’s such a thing as a Collective Unconscious, there must also be such a thing as a Collective Story, a universal story.
And if we could learn to tell that universal story, that universal story would speak to everyone. Everyone could go on that same journey together; it would mean the same thing for everyone.
And in that way, it could move us all to a place of catharsis, of meaning, of growth, of connecting to who we are as human beings.
He called this The Hero’s Journey.
You’ve probably heard of The Hero’s Journey if you’ve been studying screenwriting, or any kind of writing. In fact, Campbell’s work spawned hundreds of disciples, from really incredible theorists like James Bonnet and Christopher Vogler, to more surfacy Save the Cat! kinds of approaches.
Almost every screenwriting book, and almost every screenwriting teacher, teaches archetypes in some way, and they’re all tracking back to Campbell, who’s tracking back to Jung.
Sounds like a pretty good idea, right?
There are 21 steps of The Hero’s Journey, and a host of specific archetypal character types, and these theorists suggest that if we simply find those steps and find these characters, then we’ve got a structure and the characters of a screenplay that will have universal appeal.
In other words, if there are certain kinds of archetypal roles in every life, there must also be certain kinds of archetypal characters in every screenplay: The Terrible Father, The Emotional Mother, The Spiritual Father, The Anima or Animus, The Threshold Guardian, etc. ( to use some Hero’s Journey parlance ) .
And if there are certain kinds of archetypal events that exist in every life, then there must be certain archetypal events that happen in every screenplay: The Refusal of the Call, The Journey To The Innermost Cave, The Return With Boon, etc .
If there are certain kinds of characters and events that exist in every story, then it stands to reason that all we have to do is reach out, grab one of those characters, grab one of those archetypal events, throw it in our story, and we will connect to the universal and tell a story that everyone can connect to.
Wouldn’t that be awesome? Well, sometimes it is awesome.
The archetypes of The Hero’s Journey gave birth to some of the best movies of all time: The Matrix, Apocalypse Now, Star Wars . But the same Hero’s Journey archetypes also gave birth to Jar Jar Binks, Star Wars Episodes 1-3 and countless other boring and predictable movies and TV shows.
So how did the same archetypal elements that led to so many incredible movies also lead to such stereotypical, predictable, formulaic and untruthful writing– sometimes even in the hands of the same writers?
These archetypal elements were supposed to help the writer connect to the Universal Story, the Collective Unconscious, but in many cases seemed to do the opposite. Instead of connecting us to the Collective Unconscious and taking us all on a journey where we could see the fabric that ties us together, where we could experience catharsis by watching somebody else’s journey, where we could feel on some level, “ That’s me up there! I know what that feels like,” even as we watched a character that was ostensibly different from us– these lesser Hero’s Journey screenplays in fact did the opposite! They alienated us. They reminded us that what we were watching was fake, that we were disconnected, that we were bored.
They came between us and our connection to the Collective Unconscious, that feeling of “ That’s me up there! I know what that feels like!” and instead made us feel “What I’m seeing is something completely separate from me. That’s not a person up there. There is something disconnected from the fabric of humanity in what I’m seeing right now.”
If you’re a screenwriter, you know what that feels like in your writing. You know what it feels like to write something and know it’s a bunch of B.S. Even if everybody loves it, you can feel it: This is not connected. This is not truthful. I know there’s something off. I feel like there’s a wall between me and my character. I feel that there’s a wall between me and my structure. We all know what it’s like to feel that.
The good news is that archetypes can actually help you transcend that feeling of disconnection. But archetypes used in the wrong way can get in the way of that connection.
The problem with archetypes is that archetypes are labels.
And the reason that archetypes are labels is because brilliant professors, who like to study things like archetypes, also like to put labels on things; that is their job.
They need to put labels on things so that we can discuss them. They need to say, “Yoda is a Threshold Guardian,” so that somebody else can argue, “Yoda is not a Threshold Guardian. Yoda is a Spiritual Father.” “That moment is the Return With Boon.” “No, that moment isn’t the Return with Boon !”
(if you get on Reddit, you can watch people fight about this kind of stuff– and you’ll quickly realize none of it has any value to screenwriters).
PhD’s label archetypes so that we can talk about them, argue about them, understand them with our intellect. Writers step into archetypes intuitively, so that we can feel them.
You know intuitively that as soon as you label anybody, a character, another human being, even yourself– as soon as you put a label on somebody or something, you are also putting them in a box, You are by nature stereotyping.
When we put a label on somebody based on their skin color, we call that racism.
When we put a label on somebody based on their gender, we call that sexism.
When we put a label on somebody based on their economic status, we call that elitism .
We know that this is bad. And we know that this is limiting.
We know that when we judge somebody by a box that we put them in, rather than wondering,” hmm, I’m curious about them ,” it limits our ability to understand them, connect with them, empathize with them or even see them clearly!
We even know that that limits our ability to do the same thing with ourselves.
If we tell ourselves. “ Well, you know, I’m just not that bright .” Well, guess what? We won’t see the possibility in ourselves to actually be that bright. If we tell ourselves “ well, you know, I just never pursue the things I really want,” and start to identify with that label, we never will pursue the things we really want.
If you stick yourself or anybody else in a box, you stop seeing the human being, and you start seeing the label. You stop seeing the person and you start seeing the stereotype.
In fact, what you’re really doing when you put a label on another human being is disconnecting from your intuitive connection to the Collective Unconscious!
It would make an incredibly boring book to simply say the truth: that if there is such a thing as a Collective Unconscious, and if you want to connect to it, all you have to do is close your eyes.
All you have to do is use your senses to transcend your inner censor and your own expectations and prejudices. All you have to do is just notice what you see, feel and hear. And write down exactly that. And look with specificity until you see that thing for real, until you get past your expectations of what that element or person or object or metaphor is supposed to be, is supposed to act, is supposed to look like, is supposed to sound like, is you’re supposed to feel like– and instead just allow yourself to be surprised by the specificity of what is.
And in that specificity, you will find the universal, because you will be connected to the Collective Unconscious through your subconscious mind.
As helpful and as true as that book would be, that would be a pretty short book, and it’s probably not going to get you published, and it’s probably not going to get you your PhD.
But if you are a screenwriter, that simple advice actually might be more valuable than trying to break down The Hero’s Journey into 21 rigid steps, or trying to write an Emotional Mother or a Terrible Father for your character.
(By the way, those are not my terms. I’m not judging mothers or fathers. Those are archetypal terms used by Hero’s Journey people).
So remember: it’s not that the labels are always wrong, it’s that the labels are always limiting. And when we approach our screenwriting through labels, we stop seeing characters and we end up writing stereotypes.
For example, if you think of Billy Elliot , it’s a wonderful movie, a total romp. Billy Elliot himself is a great character. He is not a stereotype. He, like any great character (to paraphrase Walt Whitman) is large and contains multitudes. Which is to say, he’s tapped into the Collective Unconscious.
But if you think of Billy Elliot’s father, you’ll soon realize Billy Elliot’s father is not a full blown character. Billy Elliot’s father is a cartoon character, who exists only to play the role of Terrible Father in the movie. The man’s entire existence in the script is simply to make sure his son doesn’t become a “poof.”
He does not have a life outside of that; he does not contain multitudes. He is nothing more than the role that he was playing.
In fact, he’s so stereotypical that later Ben Stiller will parody him in creating Derek Zoolander’s father in Zoolander .
This is not a full blown character. This is not a man with clear wants, deep emotional needs, a unique how , who happens to be a homophobe, who happens to be a Terrible Father .
This is, rather, simply a stereotype, a character who exists to demonstrate the box that the writer has put him in.
On the other hand, look at a film like Terrence Malick’s The Tree of Life (check out my series of articles about The Tree of Life ).
In The Tree of Life , we see a character in Brad Pitt who happens to be a Terrible Father in the archetypal way but does not come off as a stereotype.
By the way, by Terrible Father , when we talk about it archetypally, we don’t mean a “bad” father, we mean a father who inflicts harm on his children. And because it’s an archetypal role, it means we recognize that alll fathers (and all people), in some way contain the Terrible Father archetype.
Just like all fathers (and all people) also contain the Emotional Mother archetype. Just like all fathers (and all people) also contain the Threshold Guardian archetype and every other archetype. Because by their very nature, archetypes are elements of character that are contained collectively in all of us.
Some of us just tend to express more of one part of ourselves than another.
If you really believe in the concept of the Collective Unconscious, it means we are all large. We all contain multitudes. Because if such a thing as a Collective Unconscious exists, it is the collective unconscious. It’s the thing that we all share.
As writers, what we’re really doing when we create archetypes is going into ourselves and pulling some piece that already exists, out of ourselves.
We’re blooming life, not by making up something from out there , but by connecting to something that already exists in here .
It might be a part of you that you know really well and love. It might be a part of you that you don’t normally invite to the table. It might be a part of you that you feel shame about. It might be part of you that you are afraid you might become. It might be a part of you that gives you confidence that there’s something good about you or the world. It might be a part of you that you aspire to be.
It could be anything. Your anger might be a way of accessing an archetype. Or your love. Or your confidence. Or your bravery. Or your fear, right? These are all pieces of you that are actually pieces of your characters as well.
So what we do is reach into ourselves, look extremely closely at one part of ourselves, and ask ourselves: what’s this? In Write Your Screenplay and in my Master Class , (for those of you who have taken those classes), we talk in depth about how to connect to these archetypes through meditative writing, and how to reach them through a concept called the emotional need.
But there are many ways to reach into ourselves, find these archetypal characters that reside there, and blow life into them.
If it’s helpful to you, you can start by using an archetypal term. But don’t try to make your character be that term. Instead, you can ask yourself “ what is the Terrible Father in him ?” “What is the Emotional Mother in him ?”
Or you can ask “what are the unexpressed parts of the character? What are the parts of them that they are not showing?” And we can blow life into those parts– either by finding situations in which those aspects of your character can be expressed, or by allowing them to be embodied by other characters in your screenplay, with whom your main character will interact.
If we go back to Malick’s The Tree of Life , Brad Pitt’s character happens to embody the archetype of the Terrible Father at multiple points in the film; he happens to inflict harm on his children.
Brad Pitt’s character in The Tree of Life happens to be a Terrible Father . But he’s not there in the script for the purpose of being a Terrible Father. He’s actually trying to be a good father.
His goal in life is to make sure that his children get the choices that he didn’t get to have.
He’s not like the coal miner father in Billy Elliot who doesn’t want his son to be a “poof.” He wants his children to be artists! He wants them to get to do the things that he didn’t get to do.
It’s the how – the way that he goes about that– which ends up making him a Terrible Father, who unintentionally inflicts psychological and emotional harm on his children.
So we have Brad Pitt playing this incredible character, who is not playing a stereotypical role. He is large. He contains multitudes. He just happens to be a Terrible Father .
In fact, one of the most painful moments in The Tree of Life, for me, is the scene in which Brad Pitt is simply trying to get his children to kiss him goodnight. That’s all he wants! But in the process of trying to get a kiss goodnight, he ends up inflicting so much emotional harm on those kids.
When you realize your characters are large and contain multitudes– when rather than using the archetype as the limiting belief about the character, you allow the archetype to shimmer and reveal itself.
You tell yourself “I realize this is a big part of the character, but I’m not going to make them the archetype. Rather, I’m going to use the archetype to connect to them.”
Again, you can go through many different doors to achieve that. For example, in Write Your Screenplay , we talk about five different doors that help us connect to archetypes, all without giving a single label.
There are so many ways you can connect. But the goal is not to make something up or to demonstrate that a person is a certain way.
The goal is to simply go inside and focus on what you find there.
Just watch your character. What do you notice them doing that surprises you? What kinds of choices do they make? How do they do it in a way that’s slightly different than any other character? How do you look, listen and feel as you write them with such specificity that you get past the container, the stereotype, of who youI expect them to be, and start to find the specific how of who they really are?
This is the incredible thing about archetypes. When we get specific, we tap into the Collective Unconscious. When we get specific, that’s actually how we get universal.
And when we get general, when we put our characters in a box, when we think more about the label than the how of the character– when we do this to anybody, whether it’s a character that exists in us, another person that we pass in the street or even to ourselves– we don’t just limit who they can be, we also we can be. We limit what we can see. We limit our own creativity. We limit our own ability to be surprised.
If you are a writer, if your focus is on the label, rather than the archetype, if your focus is on the intellectual, rather than the intuitive, if your focus is on trying to demonstrate a 21 step formula, instead of getting curious about the kinds of things that might happen to this specific character, who wants this specific thing in this specific situation– if you get too intellectual, there’s a good chance that what you’re going to write is a bunch of clichés.
Tapping into the Collective Unconscious does not happen, as Jung points out, at the Conscious Level.
The analysis can happen on the Conscious level, just as, in screenwriting, the revision can happen on a Conscious Level. But the process of connecting happens on the Subconscious Level.
It happens by going inside. It happens by setting aside your expectations, your stereotypes, your prejudices.
It starts by letting go of what you desire for the character to do for you and your screenplay, and instead getting curious.
Who are they? What do they want? What do they need? How are they? What are the obstacles they’re facing? What are the choices that they’re making?
When you approach archetypes like this, it puts you back in the intuitive driver’s seat and allows both you and your character to break out of the cliche.
It allows you to see them clearly. And then, seeing them clearly, to tap into the Collective Unconscious in a way that just might let you see yourself more clearly, as well.
If you’re enjoying what you’re seeing here , like and follow .
And if you want to study with me then check out Thursday Night Writes . It is free! Every Thursday night at writeyourscreenplay.com/thursday .
*Edited for length and clarity
Email: [email protected]
Call: 917.464.3594
Login / My Account
NEWSLETTER SIGN UP
Join us to receive screenwriting tips, informative newsletters, and discounts on writing classes.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
© 2014 - 2024 jacob krueger studio, llc | privacy & terms of use, course participant agreement.
By registering for the course, you are agreeing to the following terms, which form a legal contract between you and Jacob Krueger Studio, LLC (“ Company ”) and govern your attendance at and/or participation in Company’s course (the “ Course ”).
- Admittance. Your registration entitles you to admittance to the Course. Any and all other costs associated with your attendance (including, without limitation, any travel or accommodation expenses) shall be borne solely by you and Company shall not be liable for any such costs.
- Media. For good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which are hereby acknowledged, you grant Company the right to record, film, photograph or capture your likeness in connection with the Course, in any media now available and hereafter developed (“ Course Footage ”). You further grant to Company in perpetuity the rights to use, license, edit, copy, distribute, publicly display and make derivative works of the Course Footage, including exploitation for marketing, advertising or merchandising related to the Course, throughout the universe. You hereby waive any and all approval rights you may have over Company’s use of the Course Footage and acknowledge these rights are granted without any payment, including royalties or residuals, to you.
- Conduct . You acknowledge that Company reserves the right to request your removal from the Course if Company, in its sole discretion, considers your presence or behavior to create a disruption or to hinder the Course or the enjoyment of the Course by other attendees or speakers.
- Payment. The payment of the applicable fee(s) for the Course is due upon registration or per your payment plan. If such payment is insufficient or declined for any reason, you acknowledge that Company has the right and sole discretion to refuse your admission to the Course.
- Taxes. The fee(s) may be subject sales tax, value added tax, or any other taxes and duties which, if applicable, will be charged to you in addition to the fee(s).
- Intellectual Property. All intellectual property rights, including trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets and patents, in and to the Course, the Course content and all materials distributed at or in connection with the Course (the “ Course Materials ”) are owned by Company. You may not use, license, copy, display, or make derivative works of the Course Materials without the prior written permission of Company. For the avoidance of doubt, nothing in this agreement shall be deemed to vest in you any legal or beneficial right in or to any trademarks or other intellectual property rights owned or used under license by Company or grant to you any right or license to any other intellectual property rights of Company, all of which shall at all times remain the exclusive property of Company.
- Other than to the extent required as a matter of law: (i) neither Company nor its employees, agents or affiliates (“ Company Parties ”) shall be liable for any direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential costs, damages or losses arising directly or indirectly from the Course or other aspect related thereto or in connection with this agreement. The maximum aggregate liability of Company Parties for any claim in any way connected with therewith or this agreement whether in contract, tort or otherwise (including any negligent act or omission) shall be limited to the amount paid by you to Company under this agreement to attend the Course.
- You represent and warrant that you have the full right and authority to grant Company the rights provided in this agreement and that you have made no commitments which conflict with this agreement or the rights granted herein. You agree that your participation in the Course is entirely at your own risk and accept full responsibility for your decision to participate in the Course. In no event shall you have the right to enjoin the development, production, exploitation or use of the Course and/or your Contributions to it.
- Governing Law and Venue. This agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of New York without regard to its conflict of laws provisions. The parties hereto agree to submit to personal and subject matter jurisdiction in the federal or state courts located in the City and State of New York, United States of America.
- Dispute Resolution. All claims and disputes arising under or relating to this agreement are to be settled by binding arbitration in the state of New York or another location mutually agreeable to the parties. The arbitration shall be conducted on a confidential basis pursuant to the Commercial Arbitration Rules of the American Arbitration Association. Any decision or award as a result of any such arbitration proceeding shall be in writing and shall provide an explanation for all conclusions of law and fact and shall include the assessment of costs, expenses, and reasonable attorneys’ fees by the winner against the loser. Any such arbitration shall include a written record of the arbitration hearing. An award of arbitration may be confirmed in a court of competent jurisdiction.
- Miscellaneous. Company may transfer and assign this agreement or all or any of its rights or privileges hereunder to any entity or individual without restriction. This agreement shall be binding on all of your successors-in-interest, heirs and assigns. This agreement sets forth the entire agreement between you and the Company in relation to the Course, and you acknowledge that in entering into it, you are not relying upon any promises or statements made by anyone about the nature of the Course or your Contributions or the identity of any other participants or persons involved with the Course. This agreement may not be altered or amended except in writing signed by both parties.
Prevention of “Zoom-Bomber” Disruptions; Unauthorized Publication of Class Videos. Company will record each class session, including your participation in the session, entitled “The Videos” . To prevent disruptions by “zoom-bombers” and provide Company and
participants the legal standing to remove unauthorized content from platforms such as YouTube and social media sites, you agree that
(1) you are prohibited from recording any portion of the Course;
(2) in exchange for the opportunity to participate in the Course, you assign to Company your verbal contributions to the session discussions.
To be clear, you assign to Company only your oral statements during recorded Course sessions. You retain all copyright to any and all written materials you submit to the class and the right to use them in any way you choose without permission from or compensation to the Company.
Welcom Back!
Log in to access your account
Our website uses cookies to provide a better user experience. By using our site, you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about cookies and how you can refuse them.
We will see you this Thursday! 7pm ET / 4pm PT
Check Your Email For The Link
(Don’t see it? Check your spam folder)
Donate To Our Scholarship Fund
We match every donation we receive dollar for dollar, and use the funds to offset the cost of our programs for students who otherwise could not afford to attend.
We have given away over 140,000 of scholarships in the past year.
Thank you for your support!
Other Amount? CONTACT US
Get Your Video Seminar
Where should we send it?
" * " indicates required fields
Need A Payment Plan?
We like working with artists and strive not to leave writers behind over money..
If you need a payment plan or another arrangement to participate in our programs, we are happy to help.
Chat us or give us a call at 917-464-3594 and we will figure out a plan that fits your budget.
Join the waitlist!
Fill in the form below to be placed on the waitlist. We'll let you know once a slot opens up!
- Name * First Last
5 Essential Hero’s Journey Symbolic Archetypes (And 4 Bonus Archetypes)
by David Safford | 0 comments
Symbols enrich your story's meaning by connecting what's literally happening with overarching themes. Does your story include symbols? And what symbols should you include? In this article, we'll look at symbolic archetypes that will help you create powerful symbols in your story.

The Hero's Journey is a beloved storytelling style. One of the reasons why audiences love it so much is that it uses familiar storytelling elements that are familiar and creating a feeling of connectedness between the audience and storyteller.
This begins with character . And while stories are essentially about great characters, a powerful Hero's Journey also includes a number of other objects or symbolic elements.
These are called Symbolic Archetypes.
If character archetypes are the steak, symbolic archetypes are the delicious seasonings that bring out the meat's flavor (sorry to all you vegans/vegetarians out there!).
These storytelling elements are often subtle details that the reader may not consciously notice, but work to great effect in telling your heroic story in a way that establishes a deep and meaningful theme.
Here's how to weave them into your story and create a wonderful reading experience for your audience.
Symbolic Archetypes of the Hero's Journey
Is this post going to be another boring lesson from high school English class?
Of course not! We're about to discover how to put symbols in your story, often hiding them in plain sight.
Here's what a symbolic archetype is and how it works.
Symbolic Archetype Definition
A symbolic archetype is an object, location, or image in a story that contains more than one functional meaning. It has both a physical meaning in the story world and a thematic meaning for the reader to interpret.
First, the object, location, or image “is what it is” in the world of the story. A dungeon is a dungeon. A river is a river. And a sunrise is a sunrise.
But second, the object, location, or image also contains an additional function or meaning connected to eternal themes of human existence. A dungeon represents captivity. A river represents a journey or growth. And a sunrise represents rebirth or a new opportunity.
The Power of Symbols
Joseph Campbell's “monomyth” theory, also known as the Hero's Journey , is the idea that all characters, situations, and symbols in any story (regardless of culture, genre, or time period) are incredibly similar. This means that stories are the product of human psychology, not just a specific culture or generation.
Symbols form the physical fabric of meaning in society. We use them all the time, often without thinking of their meaning.
Companies use them by creating logos, and then fill our world with that symbol everywhere they can. Religions use them, and followers wear those symbols as jewelry and tattoos. We even notice them when certain situations seem ironic, as when a red light stops us in our tracks and we are forced to wait when we'd much rather hurry onward.
In stories, symbols do the same thing. Symbolic Archetypes connect the physical world your characters live in to the nonphysical world of Theme.
That being said, it's important to make a distinction before going forward: Not all symbols are the same.
A better way to say this is that while archetypes are universal, their implementation and interpretation is not. Here's an example.
In the West, black clothing is symbolic of death and mourning. In many other cultures, however, the color for death and mourning is white. If you're from Europe or America, it may seem absurd to wear white clothing to a funeral! Yet this is exactly what one would find in many other cultures and religious sects.
However, the colors “black” and “white” are not archetypes. They are simply colors.
What is universal and archetypal is the association of color with grief. It is a symbol (an image) that functions as it is, clothing, and as a thematic message, grief.
How you choose to implement this in your story is up to you. What if characters in your world used a different color for grief? This is one way to consider innovating an established symbolic archetype.
So as you consider texturing your world with Symbolic Archetypes, remember that the archetype is a way that humans connect the physical world to the nonphysical, not necessarily the specific way that connection is made (in various cultures, perhaps).
The 5 Essential Symbolic Archetypes of the Hero's Journey
What are the most common symbolic bridges in the Heroic Journey stories that readers love? Let's discuss five essential symbols you can use to add meaning to your story and help establish its themes!
1. Light vs. Darkness
The dichotomy between light and darkness is a straightforward way to show contrast. Usually, light means purity, truth, hope, or holiness. Darkness and shadows, to the contrary, represents guilt, deceit, despair, and being cursed or damned.
This dichotomy works as an archetype for a number of reasons. Humans tend to fear the dark and all the unknowns within it. But when light is thrown upon that darkness, revealing all to see, healing can occur and hope is restored. To see this in effect, simply turn on the bedroom lights for a child who thinks there's a monster in his closet.
How to Use It
In your story, consider how this dichotomy can occur. Remember that the colors, or shades of light, don't have to mean what I've written above. What's primary is the functional fear of darkness that lives inside your reader, and the peace that comes when light shines into that darkness.
2. The Magic Weapon
Heroes are heroic because of their ultimately selfless actions.
However, they may exhibit physical heroism through mastery of some kind of weapon, known in Campbell's theory as the Magic Weapon. Just look at Marvel's superheroes to see this in action.
Iron Man's weapon is his suit. Captain America's weapon is his shield. Black Widow doesn't have a tool as her weapon; her weapon is her body and the martial arts skills she possesses (though she shoots a lot of guns in the Marvel movies, too).
If you're going to give your hero a Magic Weapon, then you do consign yourself to at least one “obligatory” scene : the loss of the Weapon.
Since it is ultimately the hero's heart, not his weapons, that make him a hero, there is almost always a scene where the hero's weapon is lost, damaged, or stolen, rendering the hero vulnerable for a period of time. It is in this time of testing that his true nature is revealed and he becomes “worthy,” at least in the narrative, of wielding the weapon once more.
3. The Underworld
This archetype is so common that it was spoofed in the Austin Powers films: the villainous underground “lair.”
This archetype is derived from classic epics like Beowulf and Dante's Inferno, where the hero must descend into the depths of a cave or underwater cavern to slay a beast. In medieval tales, it evolved into dungeons, tunnels, crypts, and more.
But the reason why your story needs a symbolic Underground is because as humans, we know what “going underground” really means: Dying. As is spoken at many a funeral, “From dust you came, and to dust you shall return.” In our guts, we know that the Underground or Underworld is a place of death, darkness, and evil.
That's why so many climactic scenes take place underground. It could be a confrontation with the Shadow or Devil Figure character(s); it could be an escape scene, where the hero(es) must pass through a tunnel or flooded area.
One of the earliest examples of this step is the famous “Red Sea” scene in the story of the Hebrew Exodus. Fleeing from Pharaoh's army, the Hebrews pass through the parted Red Sea, a place where no human should logically be. At any moment, God could release the waters and every single man, woman, and child would be destroyed.
But instead, the Hebrews pass through unscathed, a symbolic resurrection and baptismal washing from their previous slavery status.
Indeed, it is not uncommon for the Resurrection step of the Hero's Journey to take place in a symbolic Underground or Underworld!
There are a lot of ways to craft an Underground or Underworld: cellars and basements, caves, tunnels, ditches, underwater areas, and so on. Regardless of your story's genre, there are ways to craft your darkest and highest-stakes scenes in a place that is underground or near to it.
How can you put your characters in a position of symbolic death while they wrestle with the death of their hopes and dreams as well?
4. The Castle
Just as every human instinctually associates the Underground with death, humans connect castles and fortresses with power. There is something overwhelming about a massive structure of reinforced stone, wood, and steel. Even visiting a crumbling castle from the ancient past, one can easily imagine its ramparts manned by innumerable soldiers and archers ready to repel any attack.
This is why your Shadow character needs a Castle.
Of course it doesn't need to be an actual European castle. Remember, symbols are physical representations of nonphysical truths. And the nonphysical truth of a castle is power.
To fashion your Shadow's Castle, consider: What is the type of power that the Shadow wields in your story?
Is it political power? Then perhaps the Shadow should be hidden behind the facade of a massive government building, like the Kremlin.
Perhaps the power in your story is military. In that case, the Shadow should lurk inside the fenced, heavily patrolled walls of a base or compound.
If the power in your world is financial, put your Shadow in a mansion or skyscraper.
Even a film like Elf uses this archetype when Buddy first attempts to connect with his father, Walter Hobbs, who works in the upper floors of the Empire State Building. Buddy doesn't realize that his father is the Shadow of the story, a man who hides in his office, surrounded by secretaries and security staff, doing little-to-nothing as he produces crappy children's books.
Yet Buddy, through his kindness and perseverance, is able to penetrate the defenses of Walter's Castle (for awhile) until the story no longer needs the archetype anymore.
So consider what goal your hero is pursuing, and what the Shadow would logically do to thwart the hero. What kind of fortress would the Shadow erect for himself in the world of your story? What defenses would the Shadow put in place?
Remember, the Castle is symbolic, evoking the idea of great defensive power gathered into one impressive place. How would your Shadow bring this about in his or her world?
5. The Unhealable Wound
Injuries are a part of life. Thankfully most of them heal within a few days or weeks.
However, sometimes life brings an injury that never fully heals. The victim is forever scarred, perhaps unable to walk without a limp, use an arm, or live a functional life like before.
While these types of injuries are physical and not symbolic, the emotions that come from them are. With an Unhealable Wound comes feelings of brokenness, mortality, and an inability to let go of the past. That's why this archetype is a subtle-yet-powerful element to include in your story.
As an example, think of Frodo Baggins's wounding by the Witch King of the Nazgul. Trapped on the hilltop at Weathertop, Frodo puts on the Ring of Power to avoid being seen. Instead, however, he sees his attackers in the spiritual realm and one of them stabs Frodo in the shoulder with a Morgul blade.
While he is healed of the wound's immediate danger by the elves, it continues to hobble and hurt him throughout his life. Even at the end of the lengthy novel, Frodo complains of its pain as he nears the time when he will have to choose between staying in the Shire or taking the boats to the Undying Lands (which is, conversely, a symbolic death).
Consider a way that your Hero can be injured or wounded, even nonphysically, in pursuit of their goal.
How can this wound hamper the Hero throughout the journey? How can learning to live with it be a part of the Hero pursuing their internal needs, rather than just external wants? Also, how can this process help the Hero become more selfless (and therefore heroic) in a way that benefits the entire community of your story?
4 Additional Symbolic Archetypes of the Hero's Journey
There are a lot of ways to add meaning and depth to your story using other sources of symbolism. An internet search for “symbolic archetypes” will take you to a long list of Western-centric colors, shapes, and numbers, along with their “meanings.”
But it's important to remember that these are often culturally specific and only reflect how one particular group of people link the physical world to nonphysical meaning. How will you innovate the following four tropes for your story?
1. The Significance of Color
Physical colors bear nonphysical meanings in various cultures. In the United States, for example, red is often associated with love and passion; however, it is also associated with violence, blood, and death. Green, on the other hand, represents a wide variety of things: nature, money, and greed, to name a few.
You are welcome to incorporate these interpretations into your own story. But be aware that all readers might not make the same symbolic connections that you intend.
That is why I encourage you to forge ahead with your own use of symbolic color.
J. R. R. Tolkien did this, making the color “white” differ based on regions in his world of Middle Earth. In Gondor, “the White Tower” was a symbol of hope against the black smoke and ash of Mordor. But in Rohan, “the white hand of Saruman” was a symbol of terror and evil, as a “white wizard” attempted to eradicate an entire race of men.
2. The Significance of Numbers
Numerical symbology is heavily dependent on cultural context. In Judeo-Christian societies, the numbers three, seven, and twelve are very symbolic and used in countless ways. This is connected to the Trinity, the holiness of the number seven, and the twelve disciplines and months of the year.
But in other cultures, especially ones that don't embrace Judeo-Christian heritage, the number four is deeply symbolic. It is tied to cycles of nature: the four cardinal directions, the four seasons, and the four classic elements of earth, wind, fire, and water.
So what numbers will be significant in your world? What mythology or history will they be based on?
If your genre is more realistic, like a contemporary romance, then you'd be wise to adopt the numeric symbolism of your story's setting or your character's backgrounds. This could be especially interesting in a story about two people from vastly different cultures falling in love.
But if your genre is more fantastical and open to creative world-building, feel free to conjure a few symbolic numbers. Just make sure they are tied to mythology or history that is relevant to your hero's pursuit of the goal.
3. The Significance of Shapes
Shapes are like the bones of many symbols. For more on this, see anything by Dan Brown about the Catholic Church!
Essentially there are four shapes used to establish physical symbols: circle, triangle, square, and diamond. Animators often use these simple shapes as the building blocks for characters. Pixar's Inside Out features five main characters each based on a simple shape.
Another example of this symbology put to use is that of the “deathly hallows” in J.K. Rowling's final Harry Potter novel. Even today you can see this symbol on people's car windows and flesh.
A guiding principle for this is to limit the number of shapes you use in your story's symbolic world. Don't overwhelm your reader with ten symbols when one will capture the ideas you're presenting.
Think of it this way: Use the symbol to establish or illustrate your story's primary theme. Make it simple, memorable, and easy to draw (even in one's mind). One can see this principle embodied perfectly in Rowling's “deathly hallows.”
4. The Significance of Seasons
Finally, human beings who live in any latitude with seasons have gut-level feelings that associate seaons with nonphysical realities of life (sorry, Floridians).
In a nutshell, Spring symbolizes birth (hence the festival of eggs and rabbits that we now connect with the resurrection of Jesus, called “Easter”). Summer represents the vibrancy of youth and adulthood.
Autumn symbolizes advanced age and the slow decay of the body (consider how the image of slowly-falling discolored leaves makes you feel); and Winter undeniably represents death, as all life ceases to thrive and succumbs to a long, quiet sleep under the cruel, cold snow.
As with color and numbers, you are free to co-opt these commonly understood associations of the seasons. However, these associations are specifically Western and may not reflect the values of your story's culture, or the culture you are creating for your story.
What does each season mean? Why? How can the passage of time and seasons provide a meaningful backdrop for your Hero's transformation into a truly sacrificial source of hope and redemption?
Bring Meaning With Symbols
The great news about Symbolic Archetypes is that you don't need a ton of them to succeed. You also don't need to use them throughout the entire story. If it serves your story well, you may use an archetype in only a small number of scenes, as Elf does with the Empire State Building (the Castle).
So how will you build the bridge of meaning between your story's physical world and the nonphysical feelings, sensations, and beliefs we all experience?
Because this is what separates “good” stories from truly great stories. The truly great stories that we love and talk about are layered with symbolic meaning that seem to say something important about how we live our lives.
And these great stories do so with carefully crafted subtlety. Finding the balance between a story with no meaning and a story that bashes readers over the head with preachy symbolism is a tough, time-tested challenge. You will need to rewrite scenes and chapters several times to find the right balance.
You'll also need to share your drafts with your writing community, asking its members to let you know if the symbolism and themes were clear without being too heavy-handed.
After some focused and insightful feedback comes your way, you'll be able to sharpen your symbols like chef's knives so they make a precise impact on your story, and its readers, all the way through.
What symbols can you think of from stories you love? Let us know in the comments .
Think about the Hero's Journey story you've been planning throughout this series. (Want to start from the beginning? Kick off your own Hero's Journey here. )
How might these Symbolic Archetypes appear in your story? Take fifteen minutes to journal about one of the five Essential Symbolic Archetypes, brainstorming ways to craft a physical object, location, or image that could have nonphysical meaning.
Share your writing in the comments , and then leave some constructive feedback on another writer's post!
David Safford
You deserve a great book. That's why David Safford writes adventure stories that you won't be able to put down. Read his latest story at his website. David is a Language Arts teacher, novelist, blogger, hiker, Legend of Zelda fanatic, puzzle-doer, husband, and father of two awesome children.

Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- 5 Essential Hero’s Journey Symbolic Archetypes (And 4 Bonus Archetypes) – Books, Literature & Writing - […] “Symbols are a bridge between the physical world and our nonphysical feelings about the world. They connect what we…
- Hit the like button if you love this info! - […] “ Symbols are a bridge between the physical world and our nonphysical feelings about the world. They connect what…
- Drop a site below if you’ve found anything cool for writers! - […] “ Symbols are a bridge between the physical world and our nonphysical feelings about the world. They connect what…
- 5 Essential Hero’s Journey Symbolic Archetypes (And 4 Bonus Archetypes) – Av7groups - […] “Symbols are a bridge between the physical world and our nonphysical feelings about the nations of the world. They…
- Hit the like button if you like this info! - […] Learn more: Here’s how to utilize deep and meaningful Hero’s Journey symbols! […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.

- 15 aug. 2023
- 5 minuten om te lezen
The Hero’s Journey: The Archetypes Series, Part 1 – The Hero
Bijgewerkt op: 1 sep. 2023
That’s right; I’m gonna do a series of posts on the Hero’s Journey . More specifically, I will focus on the archetypes. We start this series with The Hero.
The Hero’s Journey is probably one of the most popular frameworks and was first brought into this world by Joseph Campbell. The information you’ll find in this post will come from the book called The Writer’s Journey by Christopher Vogler.
If you don’t know it, I’d definitely recommend you get the book. It has a lot of useful information that will help with your writing without a doubt.
What are archetypes?
The hero archetype, story function, types of heroes.

It’s a nice word, archetypes, but what exactly are they? In short, they’re the kind of characters that exist in pretty much any story, such as heroes, heralds, the wise old man, villains, tricksters, etc.
These characters are certain aspects of a person’s personality, meaning that we all have parts of these archetypes within us. We all have a ‘dark’ side, we all become the wise old person, and we can have a hero within our hearts.
So, consistent with this idea, a character doesn’t have to be just one archetype. They can be fluid, at one point functioning as the mentor, and at the other time as a herald or a trickster.
Similarly, an archetype is not constricted to just one character. Multiple characters can be mentors, heralds, and villains.
So, in this series, I will discuss the most common archetype, as also mentioned in the book by Christopher Vogler. These are:
the Threshold Guardian
the Shapeshifter
the Trickster
Related: How to create a fictional character
In its essence, the Hero is someone who ends up sacrificing their own needs on behalf of others. Self-sacrifice is the keyword here.
Psychologically speaking, the hero represents the Ego . This is a Freudian concept, quite famous in psychology.
The idea is that personality consists of three parts: the Id, the Ego, and the SuperEgo. The Id is our most primal part, the one that drives our urges. It’s the part that says, “I want to eat that entire chocolate bar.”
Then there’s the Ego, which suppresses our desires from the Id. It makes sure whatever we want happens in a socially acceptable manner. This is the part that would say, “I will eat just the one piece.”
Then there’s the SuperEgo, which incorporates our morals and social norms. Meaning, what we consider to be acceptable behavior, which is dependent on what we learn from society and our closest relations (most often your parents).
This part would make you consider whether eating the chocolate fits with your ideals. If you’re ideal is to look skinny and eat healthily, you might not eat any chocolate at all.
After that bit of psychology, you probably wonder what it has to do with the Hero. At the beginning of the story, the Hero is all Ego—they’ll act in a socially acceptable manner, but don’t consider what is good for society, or whether it falls under their morals and ideals. They consider themselves to be separate from the system. By the end, they will transcend these bounds and become more like the SuperEgo, which does incorporate our morals and ideals. Hence, self-sacrifice comes into play for the benefit of a group or society as a whole. The Hero needs to sacrifice something of themselves in order to become truly heroic.
The Hero is often the POV character in a story. The readers identify with the Hero and see the story through their eyes. For this reason, Heroes often have a mix of personality characteristics that are both universal and unique so that the readers can relate.
They also usually have universal drives, like the desire to be loved, to succeed, to survive, to be free, to get revenge, or seek self-expression. Readers project themselves on the Hero and experience the story and all the emotions that come with it. That’s why the Hero is such a powerful archetype.
It makes sense, then, that the Hero should show growth. They should overcome difficult obstacles by learning and gaining new knowledge. And importantly, heroes should be active . They need to make decisions that impact the story; otherwise, they’re just passive participants in their lives. And that’s not all that interesting to read about. Readers want to feel inspired, like if the Hero can achieve these things, so can they.
While it’s quite common that Heroes in the story are powerful and brave, they don’t have to be. These aren’t the qualities that make the Hero. What is necessary is that they deal with a kind of death . This might be literal death stakes, but it can also be symbolic, such as a romantic death, a professional death, or a psychological death, for instance. The Hero teaches the readers how to cope with such situations.
The role of Hero doesn’t just have to be manifested in the protagonist. It can show in other characters when they act heroically. It can even be another archetype character who is striving to be a Hero. Consider Obi-Wan Kenobi. He’s a clear mentor archetype, yet he acts heroically and, thus, wears the mask of the Hero when he sacrifices himself by facing Darth Vader so that Luke can escape.
There are many varieties of the Hero archetype, such as a willing and unwilling Hero , the anti-Hero , and the tragic Hero, to name a few.
A willing Hero is active, committed to the adventure, has no doubts, and goes ahead bravely.
On the other hand, an unwilling Hero is full of doubts and needs to be pushed into the adventure by outside forces. If you go for an unwilling Hero, it’s best to change them at some point, because a whole story with a passive Hero can become quite dull.
The anti-Hero is not the opposite of a Hero, but rather a Hero who is an outlaw or villain according to society. But the readers still identify with this outlaw. They can behave much like conventional Heroes, but with a lot of cynicism, or they can be tragic Heroes . These are figures who aren’t even likable and whose actions the readers might even condemn.
There are also Heroes who are group-oriented . This has to do with their orientation to society. Their journey takes them to an unknown land, and they are part of a clan, tribe, or town.
They experience separation from the group, a lone adventure in the wilderness away from the group, and usually an eventual reintegration with the group. But they might also choose to stay in the new world they discovered.
Opposite of the group-oriented Hero is the Loner Hero . This type is used often in Westerns: the lone cowboy riding through the towns. Here, the Hero is estranged from society. They experience a re-entry into the group, an adventure within the group, and then a return to isolation.
Then, finally, there’s also a type of Hero who doesn’t change much but brings transformation in others. These are Catalyst Heroes .
Wrapping Up
That’s it for this first part about the Hero archetype. I hope it was informative, and that it will help you develop and write your characters.
Go to the next part: the Mentor archetype.
Do you use the framework of the Hero’s Journey in your writing? Have you ever looked at the archetypes and tried to find them in your own work or others?
Recente blogposts
How do You Start Writing an Epic Fantasy Story? Part 1: Hero’s Journey
How to Develop a Fictional Character Readers Won’t Forget
The Hero’s Journey: The Archetype Series, Part 2 – The Mentor
Commentaires
ARCHETYPES OF THE ‘HERO’S JOURNEY’

What is Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey or the Monomyth is a template for storytelling that contains the elements of mythical narrations. Mostly studied through works of Joseph Campbell and Carl Jung, Hero’s Journey or Monomyth shows that the narration techniques and character archetypes have numerous similarities throughout the history of narration/storytelling. Hero’s Journey starts with an opportunity presenting itself to the hero to go on an adventure and ends with him/her being changed or transformed. Within this type of narration there are 8 common character archetypes. All 8 of these archetypes serve a different purpose and enrich the story in their own way.
What are 8 Common Character Archetypes?
They are, in order they’re commonly listed; Hero, Mentor, Ally, Herald, Trickster, Shapeshifter, Guardian and Shadow. It is important to keep in mind that these archetypes are not specific in gender, race or age.
Let’s take a look at each character archetype’s characteristics and purpose. In order to understand the archetype’s role better and provide continuity in explanation, examples will be provided for each archetype from Harry Potter Series (J.K Rowling, 1997-2007).
HERO: Hero is the audience’s way into the story. We go along on the same journey the hero is set out to and we see everything from Hero’s point of view. It is important for Hero to be relatable because when the opportunity to go on the adventure arises, Hero will have to make choices that he/she has never encountered before. During the adventure audience must trust them and root for their future success. Hero isn’t always the protagonist, it is the central character in the story. Harry Potter is one of the most recent and fitting examples for The Hero.
MENTOR: As soon as Hero decides to take on the adventure, everything will change. They have to adapt quickly to the new environment and circumstances. Here Mentor comes to aid. Mentor helps Hero by giving them advice, support and gifts. In this stage generally, Hero doesn’t have the necessary tools to confront what’s coming so Mentor provides them with whatever’s necessary. Mentor is also the one who keeps the story moving. At first, Hero can be reluctant to accept the task and continue but Mentor convinces them to keep going. Professor Dumbledore is the Mentor for Harry Potter.
ALLY: The dangers of the chosen path are often almost impossible to face alone. Ally accompanies Hero on their journey providing them with whatever help they need. Sometimes they distract, sometimes they offer knowledge and sometimes they prove their worth by extreme acts of loyalty. Hermione Granger and Ron Weasley are the Allies for Harry Potter.
HERALD: Herald is the messenger of the new world, new adventure. They inform the hero of the possibility of a new world; a world Hero has never known existed. Without Herald’s invitation Hero wouldn’t have chosen to go to the adventure in the first place. Since he is the one informed Harry about a new world with the famous line “You are a wizard Harry.” , Hagrid is the Herald in the story.
TRICKSTER: Trickster adds humor to the story. When things are dark and intense, Trickster provides a much-needed comedic relief but most importantly Trickster challenges the existing condition. They are the ones who provide a new way of looking at the situation and offer a different point of view often causing conflict/confusion for the Hero. Dobby, the Elf is a perfect example of Trickster archetype.
SHAPESHIFTER: Shapeshifter is the character constantly moves between ally and enemy throughout the story. They may start off as an enemy and then shift to Hero’s side or vice versa. We can never be sure of their loyalty until the end, maybe ever. They are often charismatic, add complications and appeal to the story. They provide the story with interesting elements to play with. Severus Snape is the Shapeshifter of Harry Potter series, which is revealed to us in the very end. Just like this example, the threat he represents and certain charisma he has can be emphasized over and over again causing uncertainty for the Hero and the audience.
GUARDIAN (THRESHOLD GUARDIAN): Right before Hero takes on the adventure, Guardian is the one that tests them. They are the obstacle. They inform Hero on the possible dangers of the path they’re about to choose and advise them not to go through that path. They are not necessarily enemies, but they are there to stop the Hero from fulfilling their fate. Hero would have to trick or defeat them to continue. Harry Potter’s relatives Vernon and Petunia Dursley serve as Guardians for the series’ story development.
SHADOW: They are usually the villain of the story. They give Hero something to fight against, something to overcome. They create conflict, challenge the Hero and give them a reason to improve and change. This change may not always be positive because in a way Shadow portrays a possible version of the Hero. If Hero goes down the wrong way, makes wrong decisions, they can become the very thing they’re fighting against. This is generally a dramatic reveal that adds dimension to the story by showing Hero’s internal struggle. Harry Potter’s Shadow is Lord Voldemort. Harry Potter was literally a piece of him that he didn’t mean to create.
OTHER ARTICLES

HOW TO WRITE A STRONG DIALOGUE WHICH IS MEMORABLE & REALISTIC

HOW TO OVERCOME A WRITER’S BLOCK

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Along with a specific plot structure, the hero's journey has a repeating cast of characters, known as character archetypes. An archetype doesn't specify a character's age, race, or gender. In fact, it's best to avoid stereotyping by steering clear of the demographics people associate with them. What archetypes really do is tell us the ...
While most of these ideas originated with Joseph Campbell's Monomyth and the Hero's Journey, these eight universal archetypes are actually based on Christopher Vogler's The Writer's Journey. This book is beyond excellent, and breaks down the ideas of Campbell into a more usable storytelling guide—versus the highly academic The Hero ...
The Hero's Journey was invented by Campbell in his seminal 1949 work, The Hero with a Thousand Faces, where he introduces the concept of the "monomyth." A comparative mythologist by trade, Campbell studied myths from cultures around the world and identified a common pattern in their narratives.
Updated on July 03, 2019. Carl Jung called archetypes the ancient patterns of personality that are the shared heritage of the human race. Archetypes are amazingly constant throughout all times and cultures in the collective unconscious, and you'll find them in all of the most satisfying literature. An understanding of these forces is one of the ...
This ultimate Hero's Journey writing guide will define and explore all quintessential elements of the Hero's Journey—character archetypes, themes, symbolism, the three act structure, as well as 12 stages of the Hero's Journey. We'll even provide a downloadable plot template, tips for writing the Hero's Journey, and writing prompts ...
Star Wars is all about rebellion, particularly the kind that stands up to evil fascist dictatorships and blow up anything called a "Death Star.". Find Rebel hero archetypes in one of these plot types: Action, Adventure, Political Thriller, Sci-fi, Fantasy, Western.
The Hero's Journey is a fundamental paradigm of human experience that is frequently the basis for written stories, drama, and film. It was initially described by mythologist Joseph Campbell, who relied in part on the insights of psychologist Carl Jung. The stages and archetypes of the Journey have been developed and applied to film by ...
Traditionally, the Mentor is a positive figure who trains the Hero. Both Dramatica and The Hero's Journey touch on the idea that this archetype is similar to God or the conscience or a higher self, in the sense that it encourages the Hero to do what is right. This figure often functions like a parent. In addition to teaching, the Mentor often ...
Learn more: Hero's Journey Character archetypes that will make your story awesome. 5 Hero's Journey Symbols to Use. A Hero's Journey Symbol, also known as a symbolic archetype, is an object, location, or image in a story that contains more than one functional meaning. It has both a physical meaning in the story world and a thematic meaning for ...
Illustration of the hero's journey. In narratology and comparative mythology, the hero's journey, also known as the monomyth, is the common template of stories that involve a hero who goes on an adventure, is victorious in a decisive crisis, and comes home changed or transformed.. Earlier figures had proposed similar concepts, including psychoanalyst Otto Rank and amateur anthropologist Lord ...
This stage of the hero's journey archetype takes up the bulk of the journey. Throughout this stage, the hero meets several sub-points along the way including the introduction of a helper, a mentor, and the trials and temptations that eventually lead to a major conflict. A classic example of this stage is Dorothy's yellow-brick road journey ...
What is the Hero's Journey? The Hero's Journey was first described by Joseph Campbell. Campbell was an American professor of literature at Sarah Lawrence College. He wrote about the Hero's Journey in his book The Hero with a Thousand Faces. More than a guide, this book was a study on the fundamental structure of myths throughout history.
Many books and movies follow the archetypal hero's journey structure. For example, the structure can be seen in The Lion King. The story commences with Simba as heir to Pride Rock until his Uncle Scar kills his father Mufasa. Scar tricks Simba into believing Mufasa's death was his fault, telling him to flee Pride Rock. Simbaa flees alone ...
Joseph Campbell. & the Hero's Journey. A hero ventures forth from the world of common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won: the hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow men. The Hero With A Thousand Faces 23.
Within the hero's journey, there is a recurring pattern of characters with extraordinary exploits and characteristics known as the hero archetype. Campbell, in his book, identified several common ...
The Hero's Journey Archetypes. So, now we've established the hero's journey trope and how to recognize it, let's move on to the archetypal characters we'll meet in these stories. Whether you're watching a TV series or a movie that follows the hero's journey, these are the archetypes that you'll come across. The Warrior
Key Archetypes in the Hero's Journey. In addition to the 12 stages, the Hero's Journey also features several key archetypes that frequently appear in these narratives. These archetypes, derived from the work of Carl Jung and popularized by Joseph Campbell, represent universal symbols and character types that resonate with audiences across ...
The archetypal hero's journey contains 12 stages and was created by Christopher Vogler. These steps take your main character through an epic struggle that leads to their ultimate triumph or demise. While these steps may seem formulaic at first glance, they actually form a very flexible structure. The hero's journey is about transformation ...
The archetype of the Herald is the character or force in a story that initiates the call to adventure, signaling the beginning of the Hero's journey and the impending change in their life. The Herald often appears at the outset of the story to challenge the status quo and to push or invite the Hero out of their comfortable existence into the ...
The archetypes of The Hero's Journey gave birth to some of the best movies of all time: The Matrix, Apocalypse Now, Star Wars. But the same Hero's Journey archetypes also gave birth to Jar Jar Binks, Star Wars Episodes 1-3 and countless other boring and predictable movies and TV shows.
4 Additional Symbolic Archetypes of the Hero's Journey. There are a lot of ways to add meaning and depth to your story using other sources of symbolism. An internet search for "symbolic archetypes" will take you to a long list of Western-centric colors, shapes, and numbers, along with their "meanings."
Psychologically speaking, the hero represents the Ego. This is a Freudian concept, quite famous in psychology. The idea is that personality consists of three parts: the Id, the Ego, and the SuperEgo. The Id is our most primal part, the one that drives our urges. It's the part that says, "I want to eat that entire chocolate bar.".
The Heroine/Hero is the archetype who sets out on an adventurous journey, in pursuit of her or his call for transformation. Rebillot based on Campbell's (1949) mythological work, The Hero with a Thousand Faces created an experiential approach in the form of a one-week workshop, which utilizes methods from theatre and Gestalt therapy.
In order to understand the archetype's role better and provide continuity in explanation, examples will be provided for each archetype from Harry Potter Series (J.K Rowling, 1997-2007). HERO: Hero is the audience's way into the story. We go along on the same journey the hero is set out to and we see everything from Hero's point of view.