Space Tourism: Can A Civilian Go To Space?

2021 has been a busy year for private space tourism: overall, more than 15 civilians took a trip to space during this year. In this article, you will learn more about the space tourism industry, its history, and the companies that are most likely to make you a space tourist.

What is space tourism?
Brief history of space tourism, space tourism companies, orbital and suborbital space flights, how much does it cost for a person to go to space, is space tourism worth it, can i become a space tourist, why is space tourism bad for the environment.
Space tourism is human space travel for recreational or leisure purposes . It’s divided into different types, including orbital, suborbital, and lunar space tourism.
However, there are broader definitions for space tourism. According to the Space Tourism Guide , space tourism is a commercial activity related to space that includes going to space as a tourist, watching a rocket launch, going stargazing, or traveling to a space-focused destination.
The first space tourist was Dennis Tito, an American multimillionaire, who spent nearly eight days onboard the International Space Station in April 2001. This trip cost him $20 million and made Tito the first private citizen who purchased his space ticket. Over the next eight years, six more private citizens followed Tito to the International Space Station to become space tourists.
As space tourism became a real thing, dozens of companies entered this industry hoping to capitalize on renewed public interest in space, including Blue Origin in 2000 and Virgin Galactic in 2004. In the 2000s, space tourists were limited to launches aboard Russian Soyuz aircraft and only could go to the ISS. However, everything changed when the other players started to grow up on the market. There are now a variety of destinations and companies for travels to space.
There are now six major space companies that are arranging or planning to arrange touristic flights to space:
- Virgin Galactic;
- Blue Origin;
- Axiom Space;
- Space Perspective.
While the first two are focused on suborbital flights, Axiom and Boeing are working on orbital missions. SpaceX, in its turn, is prioritizing lunar tourism in the future. For now, Elon Musk’s company has allowed its Crew Dragon spacecraft to be chartered for orbital flights, as it happened with the Inspiration4 3-day mission . Space Perspective is developing a different balloon-based system to carry customers to the stratosphere and is planning to start its commercial flights in 2024.
Orbital and suborbital flights are very different. Taking an orbital flight means staying in orbit; in other words, going around the planet continually at a very high speed to not fall back to the Earth. Such a trip takes several days, even a week or more. A suborbital flight in its turn is more like a space hop — you blast off, make a huge arc, and eventually fall back to the Earth, never making it into orbit. A flight duration, in this case, ranges from 2 to 3 hours.
Here is an example: a spaceflight takes you to an altitude of 100 km above the Earth. To enter into orbit — make an orbital flight — you would have to gain a speed of about 28,000 km per hour (17,400 mph) or more. But to reach the given altitude and fall back to the Earth — make a suborbital flight — you would have to fly at only 6,000 km per hour (3,700 mph). This flight takes less energy, less fuel; therefore, it is less expensive.
- Virgin Galactic: $250,000 for a 2-hour suborbital flight at an altitude of 80 km;
- Blue Origin: approximately $300,000 for 12 minutes suborbital flight at an altitude of 100 km;
- Axiom Space: $55 million for a 10-day orbital flight;
- Space Perspective: $125,000 for a 6-hour flight to the edge of space (32 km above the Earth).
The price depends, but remember that suborbital space flights are always cheaper.
What exactly do you expect from a journey to space? Besides the awesome impressions, here is what you can experience during such a trip:
- Weightlessness . Keep in mind that during a suborbital flight you’ll get only a couple of minutes in weightlessness, but it will be truly fascinating .
- Space sickness . The symptoms include cold sweating, malaise, loss of appetite, nausea, fatigue, and vomiting. Even experienced astronauts are not immune from it!
- G-force . 1G is the acceleration we feel due to the force of gravity; a usual g-force astronauts experience during a rocket launch is around 3gs. To understand how a g-force influences people , watch this video.
For now, the most significant barrier for space tourism is price. But air travel was also once expensive; a one-way ticket cost more than half the price of a new car . Most likely, the price for space travel will reduce overtime as well. For now, you need to be either quite wealthy or win in a competition, as did Sian Proctor, a member of Inspiration4 mission . But before spending thousands of dollars on space travel, here is one more fact you might want to consider.
Rocket launches are harmful to the environment in general. During the burning of rocket fuels, rocket engines release harmful gases and soot particles (also known as black carbon) into the upper atmosphere, resulting in ozone depletion. Think about this: in 2018 black-carbon-producing rockets emitted about the same amount of black carbon as the global aviation industry emits annually.
However, not all space companies use black carbon for fuel. Blue Origin’s New Shepard rocket has a liquid hydrogen-fuelled engine: hydrogen doesn’t emit carbon but simply turns into water vapor when burning.
The main reason why space tourism could be harmful to the environment is its potential popularity. With the rising amount of rocket launches the carbon footprint will only increase — Virgin Galactic alone aims to launch 400 of these flights annually. Meanwhile, the soot released by 1,000 space tourism flights could warm Antarctica by nearly 1°C !
Would you want to become a space tourist? Let us know your opinion on social media and share the article with your friends, if you enjoyed it! Also, the Best Mobile App Awards 2021 is going on right now, and we would very much appreciate it if you would vote for our Sky Tonight app . Simply tap "Vote for this app" in the upper part of the screen. No registration is required!
Everything You Need to Know About Space Tourism Right Now
Your next travel splurge could be a flight to space
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/StefanieWaldek-38071ba574ea46c2ac94e15fa18dc581.jpg)
Virgin Galactic vehicle SpaceShipTwo on its first glide flight on October 10, 2010 over Mojave in California. (Virgin Galactic / Getty Images)
While 2020 has been an abysmal year on many counts, there’s one industry that’s thriving: space exploration. Within the first eight months of the year, we’ve seen the successful launches of three Mars missions, promising tests of new rockets, and the return of crewed spaceflight to U.S. soil—aboard a privately built spacecraft, no less! But we’re also getting much closer to the launch of the space tourism industry, meaning your dream of becoming an astronaut could become reality quite soon. We’re still a little ways away from regular flights into space for paying customers, but here are all the developments you need to know about.
The History of Space Tourism
Traveling to space has long been the domain of professional astronauts, not ordinary citizens. But that all changed when American entrepreneur Dennis Tito flew to space in 2001 with space tourism company Space Adventures, who organized the trip with Russian space agency Roscosmos. Tito was the first of only seven true “space tourists,” each of whom traveled to the International Space Station (ISS) via Roscosmos's Soyuz spacecraft for about a weeklong stay—or for two separate weeklong stays, in the case of one space traveler—for a reported cost between $20 million to $35 million per trip (plus months of training). The final space tourism excursion was made by Cirque du Soleil founder Guy Laliberté in 2009, after which Roscosmos had to end touristic flights: when NASA retired its space shuttle program in 2011, each seat on its Soyuz spacecraft needed to be reserved for crews heading to the ISS, not tourists. Since then, space tourism has been halted.
Nearly There: Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic
The issue with Space Adventure’s program is that it relies on other operators for transportation, which limits its access to space. But the next wave of private spaceflight companies have been developing their own vehicles to propel clients into weightlessness. The two frontrunners in the space tourism race are Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origin and Sir Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic, both of which are in advanced testing phases—Virgin Galactic has even opened ticket sales already, with more than 600 passengers booked. While both aerospace companies will provide their clients with suborbital trips into space, they’ll do so in entirely different fashions.
Blue Origin
Blue Origin plans to send tourists to space in its New Shepard vehicle, named after the first American in space, Alan Shepard, from its launch site in West Texas. New Shepard, which is an entirely autonomous craft that doesn’t need a human pilot, is similar to Roscosmos’s Soyuz and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon vehicles in that its six passengers will be housed in a capsule and vertically launched into space via a rocket.
After a day of training, passengers will get to experience a launch just as professional astronauts do: they’ll feel the intense G-forces pressing down on them as the rocket shuttles them to an altitude of approximately 62 miles, which is widely accepted as the boundary of space. When the engines cut off, passengers will be weightless, and they’re free to float about the capsule, taking in the views of the planet and of the darkness of space through the capsule’s large windows. After a few minutes, the capsule will fall back to Earth under parachutes. All in, the trip lasts just 11 minutes—it’s a pretty short flight considering tickets will likely cost about $250,000.
Blue Origin has successfully launched New Shepard on 12 un-crewed test flights since 2015, but it’ll need to get humans up into space before it’ll be certified to start carrying paying customers. The company originally hoped to launch a crewed test flight in 2019; however, it still has not done so, nor has it announced a new timeline for the test.
Virgin Galactic
Virgin Galactic, on the other hand, will fly passengers to space aboard a winged vehicle called SpaceShipTwo , which bears similarities to NASA’s space shuttle. But whereas the shuttle launched vertically via a rocket, SpaceShipTwo is launched horizontally. The vehicle, which seats six passengers plus two pilots, takes off from a runway like a regular plane via its carrier aircraft called WhiteKnightTwo. Virgin Galactic currently launches from the Mojave Air and Space Port in California, but it will also launch from Spaceport America in New Mexico.
After takeoff, WhiteKnightTwo ascends to 50,000 feet, after which SpaceShipTwo is released, and its rocket-powered engines kick in to bring it all the way to a maximum altitude of roughly 68 miles. As with Blue Origin’s New Shepard, passengers will enjoy a few minutes of weightlessness before returning to Earth, but instead of a parachute landing, SpaceShipTwo will land on a runway like a plane—which is also how the space shuttle landed. Total run time: between two and three hours in flight, plus two-and-a-half days of training, with a price tag of $250,000.
Virgin Galactic has been conducting test flights since 2010, but progress has been a bit slow—and deadly. In 2014, a test pilot was killed after a SpaceShipTwo vehicle broke apart during a flight, primarily due to pilot error. Testing resumed in 2016 and is ongoing, with no official word on when commercial operations will begin.
Other Companies Dreaming Big
Of all the space tourism operations out there, Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic are by far the closest to launching passengers. (Elon Musk's SpaceX, which has already successfully launched NASA astronauts into space, is not focusing on tourism, though it will provide lifts for third-party companies.) But coming in hot on their heels is Boeing, whose Starliner vehicle is being developed for NASA's Commercial Crew Program; its contract, however, allows for tourists to potentially join flights.
The other viable space tourism companies on the horizon are not developing their own vehicles, rather, they plan on hitching rides with other providers. Space Adventures is still in the game, having entered a partnership with SpaceX to fly passengers on Crew Dragon as soon as next year. It’s also revived its tourism operations with Roscosmos: two tourists are booked on a trip to the ISS in 2023. Another company, Axiom Space, plans on taking passengers to the ISS via SpaceX’s Crew Dragon as soon as 2021, before launching its own private space station by the end of the decade. Similarly, Orion Span has announced its intentions to launch its Aurora Space Station in 2021, though construction on the project has yet to begin.
Virgin Galactic Debuts the Interior of Its SpaceShipTwo Space Plane
You Can Now Book Your Flight to Space
Hotels.com Wants to Be the First Booking Platform to List Hotels in Space
The Complete Guide to Disney's Star Wars: Galaxy’s Edge
The 15 Tallest Roller Coasters in the World Will Take You to New Heights
I Spent Two Nights Aboard Star Wars: Galactic Starcruiser—Here's What It Was Like
The 8 Best Luggage Sets of 2024, Tested and Reviewed
Moscow - Russian Rivers and Waterways Port of Call
NASA Johnson Space Center and Space Center Houston: The Complete Guide
Is Thailand Ready to Reopen Its Borders to Tourists?
10 Air and Space Museums to Visit in the USA
What It’s Like to Fly Halfway Around the World During the Pandemic
The 13 Best Day Trips From Miami
Puerto Rico Airports
Driving in Paris, France
What to Expect If You’re Going on a Cruise This Winter
Leisure travel might be a little more exciting for the world’s wealthiest adventure seekers as space, long the exclusive domain of professional astronauts, is now accessible to tourists. In July 2021, Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin each successfully launched suborbital tourism programs from their spaceports in New Mexico and Texas, respectively (with Blue Origin completing its second launch in October 2021). In September 2021, SpaceX’s Inspiration4 mission kicked off the company’s orbital tourism program from the Kennedy Space Center’s historic Launch Complex 39A. Each of these companies hope to make space a popular destination by offering regular launch services to private citizens. Aspiring space tourists can expect to pay upwards of $250,000 for a seat on suborbital spacecrafts and an estimated $50 million for a ticket to orbit. Space enthusiasts on a budget can tour Spaceport America, where Virgin Galactic launches to space, for $50 or less.
These historic spaceflights represent the most recent chapter in a longer history of space tourism. More than 20 years ago, Dennis Tito, the first “space tourist” (also known as “spaceflight participant”), flew to the International Space Station aboard a Soyuz spacecraft for a six-day stay. Tito donated the Sokol pressure suit he wore in space to the Museum in 2003. Since his flight, only six other individuals scored self-funded travel to space (one of these intrepid travelers flew twice). Space Adventures, a US-based travel agency to the stars, facilitated these multi-million dollar, out-of-this-world experiences in partnership with the Russian space agency, Roscosmos.

Dennis Tito wore this suit when he launched to the International Space Station on April 28, 2001. (Smithsonian Institution)
Although space itself remained inaccessible to private citizens until the 21st century, other places where Earth and space meet—such as National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) centers—have long been popular destinations for a different kind of space tourist.
The Space Age dawned in the golden age of the family road trip. Thanks to the proliferation of private automobile ownership, an expanding interstate highway system, and the advent of more generous vacation policies in the workplace, Americans ventured from home in greater numbers in the 1960s than at any earlier time in the nation’s history. Millions of these travelers included on their itineraries NASA centers, particularly those with ties to the human spaceflight program: the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; the John F. Kennedy Space Center in Brevard County, Florida; and the Manned Spacecraft Center (known since 1973 as the Johnson Space Center) in Houston, Texas.
NASA centers were not prepared for the tourists who appeared en masse outside their gates. In the early 1960s, the centers operated much like—and were often physically adjacent to—secure military installations. For reasons of national security, the centers restricted access to official visitors only. In response to curious onlookers, the centers developed ad hoc visitor programs. At the same time, proactive civic leaders and enterprising business-people responded to the presence of space center tourists by developing their own space-themed attractions, including museums, halls of fame, and amusement parks, and amenities, such as motels, hotels, and restaurants.
At the Kennedy Space Center, for example, public affairs officers facilitated increasing access to NASA’s launch complex between 1964 and 1967. Their efforts began while the spaceport was under construction with a modest roadside trailer featuring wall-mounted exhibitions. They soon expanded visitor programming to include self-guided driving tours on weekends and holidays during breaks in construction activity. In 1966, the space center partnered with Trans World Airlines (TWA) to operate an escorted bus tour program.

Trans World Airlines (TWA) operated the bus tour program at the Kennedy Space Center in the 1960s. (NASA/KSC Spaceport News)
The following year, the Visitor Information Center opened to the public. It featured indoor exhibition and presentation facilities, an outdoor “rocket garden” that became a popular backdrop for family photos, and a depot for the bus tour program. The architect included all the amenities a traveler might need, such as restrooms, food concessions, a gift shop, and a pay phone, which is now on display at our Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center. Shaped like a Mercury capsule, the pay phone was painted in a playful tropical teal color, which was en vogue at other Florida attractions at the time. Since 1967, the Visitor Information Center has continued to evolve and expand, reflecting developments in spaceflight and the evolving expectations of 21st century vacationers. Some 1.5 million people visit annually.

This phonebooth was installed at the Visitor Information Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center during the 1960s. (Smithsonian Institution)
Whether venturing to space, visiting a spaceport, or engaging in space-related recreation, individuals and families are likely to continue the tradition of incorporating space activities as part of their leisure time. As we enter the next chapter in the history of space tourism, questions about the significance of these experiences endure: What do “space tourists” hope to gain from their encounter with space or space sites? What does their choice of vacation destination say about their individual identities and the cultural significance of space? Who has access to these experiences and who is left out? And how will space tourism reshape communities on Earth as the industry evolves?
We rely on the generous support of donors, sponsors, members, and other benefactors to share the history and impact of aviation and spaceflight, educate the public, and inspire future generations. With your help, we can continue to preserve and safeguard the world’s most comprehensive collection of artifacts representing the great achievements of flight and space exploration.
- Get Involved
- Host an Event
Thank you. You have successfully signed up for our newsletter.
Error message, sorry, there was a problem. please ensure your details are valid and try again..
- Free Timed-Entry Passes Required
- Terms of Use

Space tourism – 20 years in the making – is finally ready for launch
Professor of Strategy and Security Studies, Air University
Disclosure statement
Wendy Whitman Cobb is affiliated with the US Air Force School of Advanced Air and Space Studies. Her views are her own and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Department of Defense or any of its affiliates.
View all partners
For most people, getting to the stars is nothing more than a dream. On April 28, 2001, Dennis Tito achieved that lifelong goal – but he wasn’t a typical astronaut. Tito, a wealthy businessman, paid US$20 million for a seat on a Russian Soyuz spacecraft to be the first tourist to visit the International Space Station. Only seven people have followed suit in the 20 years since, but that number is poised to double in the next 12 months alone.
NASA has long been hesitant to play host to space tourists , so Russia – looking for sources of money post-Cold War in the 1990s and 2000s – has been the only option available for those looking for this kind of extreme adventure. However, it seems the rise of private space companies is going to make it easier for regular people to experience space.
From my perspective as a space policy analyst , I see the beginning of an era in which more people can experience space. With companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin hoping to build a future for humanity in space, space tourism is a way to demonstrate both the safety and reliability of space travel to the general public.

The development of space tourism
Flights to space like Dennis Tito’s are expensive for a reason. A rocket must burn a lot of costly fuel to travel high and fast enough to enter Earth’s orbit.
Another cheaper possibility is a suborbital launch, with the rocket going high enough to reach the edge of space and coming right back down. While passengers on a suborbital trip experience weightlessness and incredible views, these launches are more accessible.
The difficulty and expense of either option has meant that, traditionally, only nation-states have been able to explore space. This began to change in the 1990s as a series of entrepreneurs entered the space arena. Three companies led by billionaire CEOs have emerged as the major players: Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin and SpaceX. Though none have taken paying, private customers to space, all anticipate doing so in the very near future.
British billionaire Richard Branson has built his brand on not just business but also his love of adventure. In pursuing space tourism, Branson has brought both of those to bear. He established Virgin Galactic after buying SpaceShipOne - a company that won the Ansari X-Prize by building the first reusable spaceship. Since then, Virgin Galactic has sought to design, build and fly a larger SpaceShipTwo that can carry up to six passengers in a suborbital flight.

The going has been harder than anticipated. While Branson predicted opening the business to tourists in 2009, Virgin Galactic has encountered some significant hurdles – including the death of a pilot in a crash in 2014 . After the crash, engineers found significant problems with the design of the vehicle, which required modifications.
Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos, respective leaders of SpaceX and Blue Origin, began their own ventures in the early 2000s.
Musk, fearing that a catastrophe of some sort could leave Earth uninhabitable, was frustrated at the lack of progress in making humanity a multiplanetary species. He founded SpaceX in 2002 with the goal of first developing reusable launch technology to decrease the cost of getting to space. Since then, SpaceX has found success with its Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft. SpaceX’s ultimate goal is human settlement of Mars – sending paying customers to space is an intermediate step. Musk says he hopes to show that space travel can be done easily and that tourism might provide a revenue stream to support development of the larger, Mars-focused Starship system.
Bezos, inspired by the vision of physicist Gerard O’Neill , wants to expand humanity and industry not to Mars, but to space itself. Blue Origin , established in 2004, has proceeded slowly and quietly in also developing reusable rockets. Its New Shepard rocket, first successfully flown in 2015, will eventually offer tourists a suborbital trip to the edge of space, similar to Virgin Galactic’s. For Bezos, these launches represent an effort at making space travel routine, reliable and accessible to people as a first step to enabling further space exploration.

Outlook for the future
Now, SpaceX is the only option for someone looking to go into space and orbit the Earth. It currently has two tourist launches planned. The first is scheduled for as early as September 2021 , funded by billionaire businessman Jared Isaacman. The other trip, planned for 2022, is being organized by Axiom Space . These trips will be costly , at $55 million for the flight and a stay on the International Space Station. The high cost has led some to warn that space tourism – and private access to space more broadly – might reinforce inequality between rich and poor.
Blue Origin’s and Virgin Galactic’s suborbital trips are far more reasonable in cost, with both priced between $200,000 and $250,000 . Blue Origin appears to be the nearest to allowing paying customers on board, saying after a recent launch that crewed missions would be happening “soon.” Virgin Galactic continues to test SpaceShipTwo, but no specific timetable has been announced for tourist flights.
Though these prices are high, it is worth considering that Dennis Tito’s $20 million ticket in 2001 could pay for 100 flights on Blue Origin soon. The experience of viewing the Earth from space, though, may prove to be priceless for a whole new generation of space explorers.
[ Over 104,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletter to understand the world. Sign up today .]
An updated version of this article was published on May 7, 2021. Read it here .
- Space tourism
- International Space Station (ISS)
- Virgin Galactic
- Space industry
- Blue Origin
- Private spaceflight

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Regional Engagement Officer - Shepparton

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Social Media Producer
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Ramin Skibba
2021 Was the Year Space Tourism Opened Up. But for Whom?

In the early years of this century, executives at Virgin Galactic, founded by the irreverent Richard Branson, predicted that commercial flights to space for paying passengers were only a couple of years away. That turned out to be far too ambitious. Disaster struck the company twice in the next decade: In 2007 an explosion during pre-launch tests of SpaceShipTwo’s rocket systems killed three people. Then in 2014, a pilot was killed during a test flight when the space plane crashed in the Mojave desert.
Now, in 2021, everything looks different. On July 11, Branson and three crew members traveled to Spaceport America, Virgin Galactic’s human spaceflight headquarters in southern New Mexico, and clambered aboard VSS Unity , a much upgraded version of SpaceShipTwo. They blasted toward the edge of space , at an altitude of 54 miles above the Earth, allowing the passengers a panoramic view of the world as they excitedly floated in zero gravity for about four minutes of their hour-long journey.
Nine days later, Blue Origin’s founder, Jeff Bezos, and three others made a similar voyage aboard their New Shepard space vehicle, this time reaching an altitude of 63 miles, also staying aloft and weightless for a few minutes. And then in September, Elon Musk’s SpaceX launched the all-civilian Inspiration4 mission aboard a Crew Dragon spacecraft. They reached an orbit just above the International Space Station’s, flying for about three days before their capsule safely splashed down off the coast of Florida.
After decades of research, development, trial, error, and hype, the dream of commercial spaceflight had finally gotten off the ground. While private passengers have previously hitched rides on NASA shuttles and Russian Soyuz spacecraft, the three billionaire titans of the industry have made it possible to book a trip to space and back on a private spacecraft. With plenty more flights from these companies (and others) on the horizon, space tourism has surely arrived. In fact, the industry is now launching so many people into space that in January the FAA will end its Commercial Space Astronaut Wings program, which was originally designed to promote the industry. (The agency will continue to recognize space travelers on its website.)
“I honestly think that we are at the dawn of an incredible inflection point in history for human spaceflight. I truly believe that seeing Earth from space is transformative and will ultimately help humanity and the Earth in unknown ways,” says Beth Moses, Virgin Galactic’s chief astronaut instructor, who previously worked for NASA and who flew with Branson in July.
“Until this year, it’s predominantly been government-focused—NASA propelling astronauts to the space station. That's an achievement, but also a turning point where we’re noticing the effects of the democratization of space. You don’t need to be an astronaut to go to space,” says Danielle Bernstein, co-lead of the Aerospace Corporation’s Space Safety Institute.
But this access currently depends on the whims and largesse of a handful of billionaires. Despite some lofty rhetoric, the leaders of the industry still struggle to make the case that their rockets have more to offer than expensive trips for the rich and famous. “There’s a surface attempt to make them appear as commercial science vessels, but they’re much more like yachts or cruises,” says University of Chicago space historian Jordan Bimm.

Juliane Bergmann

Julian Chokkattu

Charlie Wood

David Gilbert
Others question the purpose of space tourism too. “These are technological achievements, there’s no doubt about that,” says Kathryn Denning, an anthropologist and space ethics researcher at York University in Toronto. But, she suggests, “their most significant achievement is the domination of the airwaves and television coverage.”
So far, tickets to the edge of space go for six figures—$200,000 or more—while booking an orbital expedition costs up to eight figures. A $200,000 price tag for a brief spaceflight tops the annual income of about 90 percent of Americans . It’s hard not to take note of that, especially at a time of climate crisis , a pandemic, and growing awareness of inequality. Each seat aboard a suborbital flight is like launching a home while there are more than half a million unhoused Americans, or like launching a family’s lifetime health care costs while tens of millions lack health care, or like launching college tuition when a majority of Americans don’t have access to higher education.
“Every time somebody flies for $250,000, while in that same country children aren’t eating and people are lined up along the borders, I have a hard time getting my head around it, to be honest,” Denning says.
But if the 20th-century aviation industry is any guide, while these flights will begin as luxuries, prices will drop, and access to space will broaden beyond ultra-rich people as the market opens up and technologies and infrastructure improve. “If you rewind to 100 years ago, it wasn’t your everyday person taking advantage of airlines that were just beginning to figure out how to fly routes around the world. But nowadays, for a very reasonable sum, anybody can hop on a plane, and they don’t think twice about it. It’s very safe. That’s probably the vision for space,” Bernstein says.
This also isn’t the first time that a handful of wealthy individuals have played an outsize role in US space activities. “It was actually billionaires like Andrew Carnegie and John D. Rockefeller who funded the largest astronomical telescopes in the country in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It was the Guggenheim family that was the primary source of funding for Robert Goddard, who was the first rocketry pioneer in the US,” says Alex MacDonald, chief economist at NASA.
And on the other hand, MacDonald points out, NASA has supported and invested in the burgeoning private space industry for decades, signing a variety of contracts for equipment and services, including with the once-fledgling SpaceX, which turns 20 next spring. NASA’s currently investing in Blue Origin and two other companies to develop designs for a commercial space station to follow the ISS. It’s part of a long-term plan to support the private sector in low Earth orbit, while reducing costs and freeing up more of the agency’s budget for long-distance exploration.
While the first six decades of spaceflight belonged to highly trained astronauts, now passengers can fly just for the spectacular view, or for fun, or for the challenge. And while the cost of a ticket is high, these early private flights did make room for a handful of people who would have never had the opportunity before. The commander of SpaceX’s Inspiration4 was Jared Isaacman, the billionaire CEO of the payment processing company Shift4Payments, and he funded the tickets that went to the three other travelers. Artist and scientist Sian Proctor won hers in a contest, Chris Sembroski got his ticket from a friend who won a lottery-like competition, and Hayley Arceneaux was offered her spot as an ambassador for the St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, an organization for which the mission raised $200 million—a charitable purpose that could become a model for some other private flights. Virgin Galactic announced on November 24 that Keisha Schahaff, a health and energy coach in Antigua, won two seats in a sweepstakes that raised $1.7 million for Space for Humanity, a Denver-based nonprofit that works to expand access to space with its Citizen Astronaut Program.
Passengers on other flights seem to have been chosen for their qualities as “goodwill ambassadors” for space travel. That includes pilot Wally Funk , who was one of the all-female Mercury 13 astronaut trainees in the 1960s, but wasn’t selected for a mission because of the sexism of her era, and William Shatner, aka Star Trek ’s Captain Kirk.
What people think of as an astronaut (or as a “spaceflight participant,” to use the FAA’s term ) has always been evolving. Early space exploration involved the military, in the context of the space race and the Cold War, and the first astronauts were mostly test pilots with “the right stuff.” After the successful Apollo program and moon landing, a greater emphasis on science led to sending more scientists. “As we go through those stages, it’s not an erasure of the previous one, but a layering on over them,” Bimm says. “Look at the Inspiration4 crew: While they’re civilians, they tried hard to look both like militarized astronauts, appearing in jets and flight suits , and as scientists, with performative science as part of their mission.” The crew collected their own biomedical data during their flight , but Bimm says it’s not clear how much that data will aid research on effects of low gravity on astronaut health, for example.
One of the most-touted benefits of sending people to space has always been that it’s awe-inspiring to do, generating feelings of optimism, wonder, and international cooperation. The sight of our little planet seen from far away moves many space fliers, as well, in what’s often called the “overview effect.” It’s a rare opportunity to witness how unique the Earth is, to see it without borders and in all of its vulnerability. Virgin Galactic’s Beth Moses calls it an “indescribable and magical experience.” And Shatner, who flew on Blue Origin’s second passenger flight in October, afterward called it a “ profound ” one that he hopes he’ll never recover from.
But some people question whether spaceflight is necessary to learn this existential and cosmological lesson. “I’m sure it’s beautiful to behold,” Denning says. But, she asks, “do you actually have to go to space to have an experience like that? And the answer for many thousands of years has been no. You can have a spiritual oneness with the Earth and a rise in enviro-consciousness without that.”
Similarly, Bimm doubts that space tourism inevitably spurs people to make the world a better place. “I worry that the very wealthy are going to start going to space, claiming they had the overview effect, and come back to Earth and use that claim of a ‘transformative experience’ to do pretty much anything they want,” he says. Bezos’ dubious project to move heavy industry into space, which he touted after his jaunt in July, is a prime example, Bimm says.
He also isn’t sold on the value of taking along passengers with compelling stories, like Shatner, Funk, Proctor, and Arceneaux, who is a cancer survivor and has a prosthetic body part. It almost serves as a deflection technique, Bimm says, since it distracts attention from the wealthy, lower-profile paying customers, as well as from Bezos’ and Musk’s problems on Earth, like complaints about the treatment of workers at Amazon and Tesla .
Fred Scharmen, author of the new book Space Forces , wonders how long these good feelings will last in an era of private flight. “That kind of feeling and vibe that the public agencies are able to tap into almost effortlessly—everybody loves NASA—it’ll be interesting to keep an eye on how long the private actors can invoke or connect to that kind of feeling of goodwill, hope, and overwhelmingly sublime awe that space travel inspires,” he says.
There are already signs that the private passenger space industry is beginning to expand beyond tourism, and it’s shaving down the price of getting there. The first mission of up-and-coming Houston-based company Axiom Space, dubbed Ax-1, will deliver four crew members to the ISS in February for an eight-day stay, where they’ll conduct research experiments involving the health impacts of space. “It is a pathfinder, pioneering mission for this new era of commercial human spaceflight to the ISS and in the future to commercial space stations. The long-term goal is to open up low Earth orbit to become its own marketplace,” says Michael López-Alegría, Ax-1’s commander, Axiom’s vice president of business development, and a former NASA astronaut. He anticipates a market that includes tourism and research as well as advertising and entertainment.
Axiom has also already signed NASA contracts to develop modules to attach to the ISS, which will later detach and become their own station . Other commercial space stations will become destinations as well, for astronauts, tourists, and a variety of businesses. There’s already a market for space wine , space beer , and movies filmed in space , Denning says.
A variety of other ventures will follow. That includes teardrop-shaped space balloons the size of football fields from the company Space Perspective, based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. “Rather than going to space at high g's on a rocket, you’re going to space very gently and comfortably at 12 miles an hour,” says Jane Poynter, the company’s co-CEO. The balloons carry a pressurized capsule and eight passengers aloft, nearly 20 miles above the Earth’s surface. They’re planning their first crewed flight in 2023 and their first commercial one the following year, with tickets going for around $125,000. It’s also a relatively safe way to fly to the edge of space, rather than strapping oneself to a rocket, Poynter points out. (Blue Origin and SpaceX use traditional vertical-launch rockets that are automated, with the crew sitting in a capsule on top, while Virgin makes use of a piloted space plane.)
As the industry matures, ideas for improving it can develop as well. Ariel Ekblaw, founder and director of the MIT Space Exploration Initiative and author of the book Into the Anthropocosmos , believes there should be more transparency in the way space fliers are chosen, because people around the world pay attention to these flights and to their crew. And Bimm argues that companies should be transparent about something else: whether the crew's flight plan is just to hang out and enjoy the spectacular view, rather than gathering scientific data.
Right now, private flights seem to encompass multiple things at once: They’re science missions, ecotourism expeditions, and yacht trips led by famous space barons. “We have yet to see what the hybrid role of these missions are,” says Ekblaw. “We’re at a cusp of a public grand opening of space.”
- 📩 The latest on tech, science, and more: Get our newsletters !
- Amazon's dark secret : It has failed to protect your data
- Humans have broken a fundamental law of the ocean
- What The Matrix got wrong about cities of the future
- The father of Web3 wants you to trust less
- Which streaming services are actually worth it?
- 👁️ Explore AI like never before with our new database
- 💻 Upgrade your work game with our Gear team’s favorite laptops , keyboards , typing alternatives , and noise-canceling headphones

David Kushner

Matt Reynolds

Victoria St. Martin

Rachel Lance

Jessica Rawnsley

You Won’t Hear Much About the Next Chapter of Space Travel
Space tourism is getting less transparent, and more like traveling by private jet.

Listen to this article
Listen to more stories on hark
Of all the high-flying tourism ventures spawned by space-obsessed billionaires, Virgin Galactic, founded by Richard Branson, offers perhaps the most unconventional approach. It doesn’t use big rockets or gumdrop-shaped capsules. Instead, an airplane takes off with a spacecraft strapped to its wing. The spacecraft, shaped like a plane itself, holds the paying customers and more pilots. When the airplane reaches a certain altitude, it releases the spacecraft. The spacecraft’s pilots then ignite its engine, and the vehicle soars straight up, to the fuzzy boundary that separates us from the rest of the universe, before gliding back down and landing on a runway.
The spaceplane experience is a stark contrast to Blue Origin’s suborbital jaunts and SpaceX’s orbital missions, but Virgin Galactic’s passengers still have a few surreal minutes of weightlessness, and they get to see the planet gleaming against the darkness of space. Those passengers have included the first former Olympian to reach space, as well as the first mother-daughter duo and, most recently, the first Pakistani .
In the midst of all that, Virgin Galactic clocked a first that raised some eyebrows: The company withheld the passenger list from the public before a takeoff last month, divulging the travelers’ names only after they had landed. The company never publicly explained its preflight secrecy. (Virgin Galactic did not respond to a request for comment.) Yesterday, Virgin Galactic announced its next flight, scheduled for November; the company kept one of the three listed passengers anonymous, saying only that the person is “of Franco-Italian nationality.”
Virgin is of course within its rights to withhold passenger names before takeoff. After all, airlines and railroads keep private the names of their customers. But Virgin Galactic’s choice to do so marks a subtle shift—the latest in U.S. spaceflight’s arc from a publicly funded national mission to private tourism. NASA, as a taxpayer-funded organization, has always had to provide the public with launch lists and livestreams. But the age of space tourism raises a host of questions: How much openness do space-tourism companies owe the public? How much privacy do they owe their customers? Before the Virgin flight returned home last month, it operated almost like a privately chartered plane, its movements known to relevant aviation agencies but its passengers’ names undisclosed to the public. Commercial spaceflight and air travel are still far from alike, but in this particular aspect, the space-tourism industry may be drifting toward its private-jet era.
Read: The new ‘right stuff’ is money and luck
In practice, the space-tourism industry is barely more than two years old, and it’s “still finding its norms,” says Carissa Christensen, a space consultant and the CEO of BryceTech, an analytics and engineering firm. The first passenger rosters were marquee news in 2021, when Branson and Jeff Bezos were racing to be the first to ride their own spacecraft , and Elon Musk’s SpaceX was working to send a quartet of private astronauts with zero spaceflight experience into orbit.
All three of their companies publicized, and even hyped, the passenger lists, in some cases months in advance. Wally Funk, an octogenarian aviator who had outperformed male candidates in astronaut tests during the 1960s but was kept out of the astronaut corps because she was a woman, flew alongside Bezos . Jared Isaacman, a billionaire businessman, paid for three other people to fly into orbit with him on SpaceX; all of them gave countless interviews before launch. And who can forget the hype ahead of William Shatner’s flight, and the Star Trek star’s unfiltered, emotional remarks after landing?
The rosters became less noteworthy as time went on: The customers were no longer memorable guests who got free rides, but simply very wealthy people who could afford the trips on their own. Last month’s temporarily secret Virgin Galactic fliers included a real-estate investor from Las Vegas, a South African entrepreneur, and a British engineer who founded a company that builds race cars. Michelle Hanlon, a space lawyer and the executive director of the University of Mississippi’s Center for Air and Space Law, told me that she was mildly surprised by Virgin Galactic’s decision to withhold the passengers’ identities before takeoff, but that the decision did not strike her as inappropriate.
“From a paparazzi standpoint, if it’s Ashton Kutcher, the world’s gonna care a little bit more than if it’s Michelle Hanlon,” Hanlon said. (Kutcher did, in fact, purchase a Virgin Galactic ticket in 2012, but he later sold it back to the company after his wife and fellow actor, Mila Kunis, talked him out of going.) And from a legal standpoint, nothing inappropriate occurred, Hanlon said; there are no existing requirements for a private company to disclose passenger names. Space travelers must sign waivers from the Federal Aviation Administration outlining the risks associated with the activity, she said, but the companies they’re flying with are not required to provide the agency with a passenger list.
Read: Jeff Bezos knows who paid for him to go to space
Passenger names aren’t the only details of commercial spaceflight that are becoming more opaque. When SpaceX launched its first set of private astronauts, the company shared significantly less live footage of their experience in orbit than they did when NASA astronauts test-drove the capsule a year earlier. During its last two flights, Virgin Galactic decided not to provide a livestream, giving updates on social media instead.
Because there are no regulations, it’s difficult to say when the companies’ right to privacy becomes a concerning level of secrecy. NASA overshares when it comes to its astronauts and their mission, because the public—which funds the agency—expects it. Americans might also expect a good look at SpaceX customers who visit the International Space Station, which relies on billions of dollars of taxpayer money, and where private visitors share meals with government astronauts. But what about other kinds of SpaceX missions, which go into orbit without disembarking at any government-owned facility? The company developed its crewed launch services with significant investment from NASA, so virtually every SpaceX trip indirectly involves government money. That doesn’t necessarily mean SpaceX is obligated to share as the space agency does, even if people on the ground feel that it should.
Another major difference between NASA missions and private ones, of course, is that astronauts are at work, whereas many space tourists are presumably just having fun. Caryn Schenewerk, a consultant who specializes in commercial spaceflight at her firm CS Consulting, told me that she thinks commercial spaceflight will adopt the practices of other forms of adventure tourism. Take skydiving, for example: Schenewerk said that she has signed paperwork granting the skydiving company permission to use footage of her experience for its own purposes. “There’s some expectation of privacy on the individual’s behalf that then has to be actively waived for the company’s benefit,” she said.
The once-anonymous Virgin Galactic passengers on the September flight have since publicly shared their stories , basking in the awe of their experience. Christensen told me that most future tourists will likely do the same. “A big part of the fun is other people knowing that you’ve done it,” she said. Flying to space isn’t exactly something to be modest about: Fewer than 700 people have done it since human beings first achieved the feat, in the early 1960s, and we know all of their names. If Virgin’s new mystery passenger doesn’t reveal their name, they really will make history.
Read: Seeing Earth from space will change you
Many spacefarers—the Soviet cosmonauts who inhabited the first space station, the American astronauts who shuttled their way into orbit, the Chinese astronauts living in space right now, all of the people who have flown commercial—have spoken about the transformational wonder of seeing Earth from space, a phenomenon known as the overview effect . They reported that they better understood the reality of our beautiful, fragile planet, and that they felt a duty to share their impressions with people on the ground. Gene Cernan, one of the dozen men who walked on the lunar surface, once said, “If only everyone could relate to the beauty and the purposefulness of it … It wouldn’t bring a utopia to this planet for people to understand it all, but it might make a difference.” In this sense, for a space traveler to remain unknown forever would be a sort of anti–overview effect: Just as they may have the right to request some privacy, they have no obligation to bring the transcendent power of their journey back to Earth.
Three years ago, two NASA astronauts made a historic flight on a new SpaceX astronaut capsule. Ahead of the mission, I asked NASA what Doug Hurley and Bob Behnken were going to have for breakfast on the morning of the launch. It was a question with a long tradition in spacefaring history: During the Apollo days, the public was privy to the final Earth-bound meals of history-making astronauts. NASA officials balked, saying they couldn’t divulge that information for privacy reasons. But on the day of the launch, Hurley, as if to sate the space press corps, posted a picture of his steak and eggs on Twitter (as it was still known then).
Hurley and Behnken’s preflight hours seemed like fair game; after all, these men were government employees, doing their job on their assigned mission. But future passengers may decide that we have no business knowing their breakfast order—or even their name.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Future of Space Tourism Is Now. Well, Not Quite.
From zero-pressure balloon trips to astronaut boot camps, reservations for getting off the planet — or pretending to — are skyrocketing. The prices, however, are still out of this world.

By Debra Kamin
Ilida Alvarez has dreamed of traveling to space since she was a child. But Ms. Alvarez, a legal-mediation firm owner, is afraid of flying, and she isn’t a billionaire — two facts that she was sure, until just a few weeks ago, would keep her fantasy as out of reach as the stars. She was wrong.
Ms. Alvarez, 46, and her husband, Rafael Landestoy, recently booked a flight on a 10-person pressurized capsule that — attached to a massive helium-filled balloon — will gently float to 100,000 feet while passengers sip champagne and recline in ergonomic chairs. The reservation required a $500 deposit; the flight itself will cost $50,000 and last six to 12 hours.
“I feel like it was tailor-made for the chickens like me who don’t want to get on a rocket,” said Ms. Alvarez, whose flight, organized by a company called World View , is scheduled to depart from the Grand Canyon in 2024.
Less than a year after Jeff Bezos and Richard Branson kicked off a commercial space race by blasting into the upper atmosphere within weeks of each other last summer, the global space tourism market is skyrocketing, with dozens of companies now offering reservations for everything from zero-pressure balloon trips to astronaut boot camps and simulated zero-gravity flights. But don’t don your spacesuit just yet. While the financial services company UBS estimates the space travel market will be worth $3 billion by 2030, the Federal Aviation Administration has yet to approve most out-of-this-world trips, and construction has not started on the first space hotel. And while access and options — not to mention launchpads — are burgeoning, space tourism remains astronomically expensive for most.
First, what counts as space travel?
Sixty miles (about 100 kilometers) above our heads lies the Kármán line, the widely accepted aeronautical boundary of the earth’s atmosphere. It’s the boundary used by the Féderátion Aéronautique Internationale, which certifies and controls global astronautical records. But many organizations in the United States, including the F.A.A. and NASA, define everything above 50 miles to be space.
Much of the attention has been focused on a trio of billionaire-led rocket companies: Mr. Bezos’ Blue Origin , whose passengers have included William Shatner; Mr. Branson’s Virgin Galactic , where tickets for a suborbital spaceflight start at $450,000; and Elon Musk’s SpaceX , which in September launched an all-civilian spaceflight, with no trained astronauts on board. Mr. Branson’s inaugural Virgin Galactic flight in 2021 reached about 53 miles, while Blue Origin flies above the 62-mile mark. Both are eclipsed by SpaceX, whose rockets charge far deeper in to the cosmos, reaching more than 120 miles above Earth.
Balloons, like those operated by World View, don’t go nearly as high. But even at their maximum altitude of 18 or 19 miles, operators say they float high enough to show travelers the curvature of the planet, and give them a chance to experience the overview effect — an intense perspective shift that many astronauts say kicks in when you view Earth from above.
Now, how to get there …
Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, which are both licensed for passenger space travel by the F.A.A., are open for ticket sales. (Blue Origin remains mum on pricing.) Both companies currently have hundreds or even thousands of earthlings on their wait lists for a whirl to the edge of space. SpaceX charges tens of millions of dollars for its further-reaching flights and is building a new facility in Texas that is currently under F.A.A. review.
Craig Curran is a major space enthusiast — he’s held a reserved seat on a Virgin Galactic flight since 2011 — and the owner of Deprez Travel in Rochester, N.Y. The travel agency has a special space travel arm, Galactic Experiences by Deprez , through which Mr. Curran sells everything from rocket launch tickets to astronaut training.
Sales in the space tourism space, Mr. Curran acknowledges, “are reasonably difficult to make,” and mostly come from peer-to-peer networking. “You can imagine that people who spend $450,000 to go to space probably operate in circles that are not the same as yours and mine,” he said.
Some of Mr. Curran’s most popular offerings include flights where you can experience the same stomach-dropping feeling of zero gravity that astronauts feel in space, which he arranges for clients via chartered, specialized Boeing 727s that are flown in parabolic arcs to mimic being in space. Operators including Zero G also offer the service; the cost is around $8,200.
You can almost count the number of completed space tourist launches on one hand — Blue Origin has had four; SpaceX, two. Virgin Galactic, meanwhile, on Thursday announced the launch of its commercial passenger service, previously scheduled for late 2022, was delayed until early 2023. Many of those on waiting lists are biding their time before blastoff by signing up for training. Axiom Space, which contracts with SpaceX, currently offers NASA-partnered training at Houston’s Johnson Space Center. Virgin Galactic, which already offers a “customized Future Astronaut Readiness program” at its Spaceport America facility in New Mexico, is also partnering with NASA to build a training program for private astronauts.
Would-be space tourists should not expect the rigor that NASA astronauts face. Training for Virgin Galactic’s three-hour trips is included in the cost of a ticket and lasts a handful of days; it includes pilot briefings and being “fitted for your bespoke Under Armour spacesuit and boots,” according to its website.
Not ready for a rocket? Balloon rides offer a less hair-raising celestial experience.
“We go to space at 12 miles an hour, which means that it’s very smooth and very gentle. You’re not rocketing away from earth,” said Jane Poynter, a co-founder and co-chief executive of Space Perspective , which is readying its own touristic balloon spaceship, Spaceship Neptune. If all goes according to plan, voyages are scheduled to begin departing from Florida in 2024, at a cost of $125,000 per person. That’s a fraction of the price tag for Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, but still more than double the average annual salary of an American worker.
Neither Space Perspective nor World View has the required approval yet from the F.A.A. to operate flights.
Unique implications
Whether a capsule or a rocket is your transport, the travel insurance company battleface launched a civilian space insurance plan in late 2021, a direct response, said chief executive Sasha Gainullin, to an increase in space tourism interest and infrastructure. Benefits include accidental death and permanent disablement in space and are valid for spaceflights on operators like SpaceX, Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, as well as on stratospheric balloon rides. They’ve had many inquiries, Mr. Gainullin said, but no purchases just yet.
“Right now it’s such high-net-worth individuals who are traveling to space, so they probably don’t need insurance,” he said. “But for quote-unquote regular travelers, I think we’ll see some takeups soon.”
And as the industry grows, so perhaps will space travel’s impact on the environment. Not only do rocket launches have immense carbon footprints, even some stratospheric balloon flights have potentially significant implications: World View’s balloons are powered by thousands of cubic meters of helium, which is a limited resource . But Ted Parson, a professor of environmental law at the University of California, Los Angeles, said that space travel’s environmental impact is still dwarfed by civil aviation. And because space travel is ultra-niche, he believes it’s likely to stay that way.
“Despite extensive projections, space tourism is likely to remain a tiny fraction of commercial space exploration,” he said. “It reminds me of tourism on Mt. Everest. It’s the indulgence of very rich people seeking a transcendent, once-in-a-lifetime experience, and the local environmental burden is intense.”
Stay a while?
In the future, space enthusiasts insist, travelers won’t be traveling to space just for the ride. They’ll want to stay a while. Orbital Assembly Corporation, a manufacturing company whose goal is to colonize space, is currently building the world’s first space hotels — two ring-shaped properties that will orbit Earth, called Pioneer Station and Voyager Station. The company, quite optimistically, projects an opening date of 2025 for Pioneer Station, with a capacity of 28 guests. The design for the larger Voyager Station , which they say will open in 2027, promises villas and suites, as well as a gym, restaurant and bar. Both provide the ultimate luxury: simulated gravity. Axiom Space , a space infrastructure company, is currently building the world’s first private space station; plans include Philippe Starck-designed accommodations for travelers to spend the night.
Joshua Bush, chief executive of travel agency Avenue Two Travel , has sold a handful of seats on upcoming Virgin Galactic flights to customers. The market for space travel (and the sky-high prices that come with it), he believes, will evolve much like civilian air travel did.
“In the beginning of the 20th century, only very affluent people could afford to fly,” he said. “Just as we have Spirit and Southwest Airlines today, there will be some sort of equivalent of that in space travel, too. Hopefully within my lifetime.”

52 Places for a Changed World
The 2022 list highlights places around the globe where travelers can be part of the solution.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places for a Changed World for 2022.
What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
A celestial image, an Impressionistic swirl of color in the center of the Milky Way, represents a first step toward understanding the role of magnetic fields in the cycle of stellar death and rebirth.
Scientists may have discovered a major flaw in their understanding of dark energy, a mysterious cosmic force . That could be good news for the fate of the universe.
A new set of computer simulations, which take into account the effects of stars moving past our solar system, has effectively made it harder to predict Earth’s future and reconstruct its past.
Dante Lauretta, the planetary scientist who led the OSIRIS-REx mission to retrieve a handful of space dust , discusses his next final frontier.
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .
Want to be a space tourist? Here are 6 things to consider first

The industry of space tourism could exist in the future. Image: Unsplash/NASA
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Steven Freeland

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Space is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
- In July 2021, entrepreneur Sir Richard Branson and Amazon founder Jeff Bezos went up into space, accompanied by fellow passengers.
- These trips created vast amounts of media coverage and brand recognition for Branson’s Virgin Galactic and Bezos’ Blue Origin.
- This could indicate that a commercial space tourism industry is on the horizon.
- Before space trips become commercially available, important factors such as environmental and safety laws need to be considered.
It’s been a momentous month for space-faring billionaires. On July 11, British entrepreneur Sir Richard Branson’s Unity “rocket-plane” flew him and five fellow passengers about 85 kilometres above Earth. And this week, Amazon founder Jeff Bezos’ New Shepard capsule reached an altitude of 106km , carrying Bezos, his brother, and the oldest and youngest people ever to reach such a height. Passengers on both flights experienced several minutes of weightlessness and took in breathtaking views of our beautiful and fragile Earth.
Both flights created an avalanche of media coverage and brand recognition for Branson’s Virgin Galactic and Bezos’s Blue Origin. There is renewed anticipation of a lucrative commercial space tourism industry that could eventually see thousands of paying passengers journey into space (or not quite into space, depending on your preferred level of pedantry).
This year marks 60 years since Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space. Since then, almost 600 trained astronauts have gone into outer space, but very few people have become space tourists.
The first, US engineer Dennis Tito, paid a reported US$20 million to spend six days orbiting Earth in the Russian section of the International Space Station in April 2001, after three months’ training at Russia’s Star City complex. He was followed by a handful of other very wealthy “orbital tourists”, most recently Cirque de Soleil founder Guy Laliberté in 2009, whose ticket reportedly cost US$35 million.
Unlike their predecessors, Branson’s and Bezos’ flights were suborbital – they didn’t reach the velocity needed to orbit Earth. Bezos’s entire flight lasted just over 10 minutes. Suborbital flights are much less technically complex, and in theory cheaper (although one seat on the New Shepard flight was auctioned for US$28 million ).

While they might quibble over billionaire bragging rights, there’s no denying that suborbital “space” flights have the potential to be less eye-wateringly expensive than going into orbital outer space and beyond.
But before you sign up – assuming you’re lucky enough to afford it – here are a few things to consider.
Where does space start, anyway?
Have you read, how many space launches does it take to have a serious climate impact, from space squid to saliva: what's inside nasa's cargo missions and why, the big space clean-up - and why it matters.
Despite assertions to the contrary , there is no legal definition of “outer space”, and thus no official boundary where airspace ends and outer space begins. In the past, the International Aeronautical Federation has looked to the von Karman line , but this does not coincide with the boundary of any of the atmosphere’s scientifically defined layers, and the UN Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space , which deals with such issues, has not yet resolved the question.
Conveniently for Branson, 80km has been proposed by some experts as an appropriate boundary.
Outer space is undeniably influenced by Earthly geopolitics. Essentially, the larger space-faring countries see no need to legally define a boundary that would clearly demarcate the upper limits of their sovereignty.
Will you be an ‘astronaut’?
The 1967 UN Outer Space Treaty designates astronauts as “envoys of (hu)mankind in outer space”. Certainly, that seemed to be the case as the world watched the historic Apollo 11 Moon landing and prayed for a safe return of the stricken Apollo 13 capsule. However, the 1968 UN Rescue Agreement refers to “personnel of a spacecraft”, which may imply not everyone on board should be considered a fully fledged astronaut.
Of course, these legal niceties won’t deter space tourism companies from awarding “astronaut wings” to their passengers.

What laws apply when things go wrong?
The 1986 Challenger and 2003 Columbia shuttle disasters are stark reminders of the dangers of space travel. Human space travel has always involved determining acceptable levels of risk for trained astronauts. But commercial space tourism is different to state-sponsored space programs, and will need the highest possible safety standards.
Commercial space travel will also require a system of responsibility and liability, for cases in which a space tourist suffers injury, loss or damage.
Space tourists (or their families) can’t claim for compensation under the 1972 UN Liability Convention which, in terms of space, applies only to collisions between space objects such as satellites and space debris. While there may be scope to take legal action under national laws, it is likely space tourists will be asked to sign carefully worded waivers of liability.
The same is probably true of international air law , which applies to “aircraft” — a designation space tourism operators will understandably be keen to avoid.
Ultimately, we may need to develop a system of “aerospace law” to govern these suborbital flights as well as “transorbital” transport such as the keenly envisaged flights that might one day take passengers from Sydney to London in just a few hours.
What activities should be allowed in space?
The advent of space tourism will give rise to some interesting ethical questions. Should there be advertising billboards in space? What about casinos, or brothels? On what legal basis should these things be restricted?
How does tourism fit with the underlying philosophy of space law: that the exploration and use of outer space “shall be carried out for the benefit and in the interests of all countries”?
Will space tourism harm the environment?
Space tourism will inevitably put pressure on Earth’s environment – there are claims that space vehicles may one day become the world’s biggest source of carbon dioxide emissions. We will need to manage space traffic carefully to avoid disastrous collisions and steer clear of space debris .
If tourists go to the Moon, they may cause pollution or damage the heritage of earlier exploration, such as Neil Armstrong’s footprints .

Will tourism workers have to live in space?
If space tourism does become truly widespread, it will need infrastructure and perhaps even staff. People may end up living permanently in space settlements, perhaps having children who will be born as “space citizens”. What legal rights would someone have if they were born at a Moon base? Would they be subject to terrestrial laws, or some version of current international legal rules for outer space?
The World Economic Forum was the first to draw the world’s attention to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the current period of unprecedented change driven by rapid technological advances. Policies, norms and regulations have not been able to keep up with the pace of innovation, creating a growing need to fill this gap.
The Forum established the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Network in 2017 to ensure that new and emerging technologies will help—not harm—humanity in the future. Headquartered in San Francisco, the network launched centres in China, India and Japan in 2018 and is rapidly establishing locally-run Affiliate Centres in many countries around the world.
The global network is working closely with partners from government, business, academia and civil society to co-design and pilot agile frameworks for governing new and emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) , autonomous vehicles , blockchain , data policy , digital trade , drones , internet of things (IoT) , precision medicine and environmental innovations .
Learn more about the groundbreaking work that the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Network is doing to prepare us for the future.
Want to help us shape the Fourth Industrial Revolution? Contact us to find out how you can become a member or partner.
These are obviously questions for the future. But given the excitement generated by the brief journeys of a couple of wealthy entrepreneurs, we should start contemplating them now. Outer space is the new frontier, but it is not — and must not — be a lawless one.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
- Travel, Tourism & Hospitality ›
Leisure Travel
Space tourism - statistics & facts
What is the public’s opinion on space tourism, do the public want to travel to space, key insights.
Detailed statistics
Global sub-orbital space tourism market size 2021-2031, by flight vehicle type
Amount invested globally into space companies by venture capitalists 2013-2022
Equity investments in space companies worldwide 2013-2022, by type
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Current statistics on this topic.
Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
Forecast revenue of orbital space travel and tourism worldwide 2021-2030
Share of U.S. adults who want to travel to space 2021
Related topics
Recommended.
- Space industry worldwide
- Space Mining
- Tourism worldwide
- Travel and tourism in the U.S.
- Aviation and aerospace industries in Germany
- European aerospace industry
- Aerospace industry in Japan
Recommended statistics
Market overview.
- Premium Statistic Global sub-orbital space tourism market size 2021-2031, by flight vehicle type
- Premium Statistic Forecast revenue of orbital space travel and tourism worldwide 2021-2030
- Premium Statistic Amount invested globally into space companies by venture capitalists 2013-2022
- Premium Statistic Equity investments in space companies worldwide 2013-2022, by type
- Premium Statistic Share of investment deals in space start-ups worldwide by company in 2020
- Premium Statistic Distribution of space start-up investors by type 2000-2020
Sub-orbital space tourism market size worldwide in 2021, with a forecast for 2031, by flight vehicle type (in million U.S. dollars)
Forecast revenue of the orbital space travel and tourism market worldwide from 2021 to 2030 (in million U.S. dollars)
Amount venture capitalists invested into space companies worldwide from 2013 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Cumulative equity investment in space companies worldwide from 2013 to 2022, by type (in billion U.S. dollars)
Share of investment deals in space start-ups worldwide by company in 2020
Distribution of investment deals on space start-ups worldwide in 2020, by company
Distribution of space start-up investors by type 2000-2020
Distribution of investor groups in space start-ups from 2000 to 2020, by investor type
Public opinion
- Premium Statistic U.S. public opinion on which private space companies are leading the space race 2021
- Premium Statistic U.S. opinion on which private space companies are leading the space race 2021, by age
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults that believe space travel should be accessible to everyone 2021
- Premium Statistic U.S. public opinion on profitability of space exploration companies in future 2021
- Premium Statistic U.S. adults that believe billionaires should spend money on space travel 2021
U.S. public opinion on which private space companies are leading the space race 2021
Public opinion on which space companies are leading the private sector's push into space in the United States as of December 2021
U.S. opinion on which private space companies are leading the space race 2021, by age
Public opinion on which space companies are leading the private sector's push into space in the United States as of December 2021, by generation
Share of U.S. adults that believe space travel should be accessible to everyone 2021
Share of adults that believe space travel should be accessible to everyone and not just those that can afford the costs in the United States as of September 2021
U.S. public opinion on profitability of space exploration companies in future 2021
Share of the public that believe private companies focused on space exploration will make a profit in the next 10 years in the United States as of December 2021
U.S. adults that believe billionaires should spend money on space travel 2021
Share of adults that believe billionaires should be spending money traveling to space in the United States as of September 2021
Traveler interest
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults who want to travel to space 2021
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults who want to travel to space 2021, by gender
- Premium Statistic Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon if money was not a factor 2021
- Premium Statistic Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon in 2021, by generation
- Premium Statistic Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon in 2021, by gender
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults who would travel to the moon 2021, by age
- Premium Statistic Share of U.S. adults who would spend over 100 thousand USD to travel to space 2021
Share of adults that would want to travel to space if money was not an issue in the United States as of September 2021
Share of U.S. adults who want to travel to space 2021, by gender
Share of adults that want to travel to space if money was not an issue in the United States as of September 2021, by gender
Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon if money was not a factor 2021
Share of the public that would go to the moon as a tourist if money was not a factor in the United States as of December 2021
Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon in 2021, by generation
Share of the public that would go to the moon as a tourist if money was not a factor in the United States as of December 2021, by generation
Share of the U.S. public who would go to the moon in 2021, by gender
Share of the public that would go to the moon as a tourist if money was not a factor in the United States as of December 2021, by gender
Share of U.S. adults who would travel to the moon 2021, by age
Share of adults that would travel to the moon in the United States as of May 2021, by age
Share of U.S. adults who would spend over 100 thousand USD to travel to space 2021
Share of adults that would spend more than 100 thousand U.S. dollars to travel to space in the United States as of September 2021
Further reports Get the best reports to understand your industry
Get the best reports to understand your industry.
- Space tourism
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
The space tourism we were promised is finally here—sort of
SpaceX’s first “all-civilian” mission into orbit could create a whole new service in the space economy. But not everyone will be able to participate.
- Neel V. Patel archive page

SpaceX weathered through the onset of the covid-19 pandemic last year to become the first private company to launch astronauts into space using a commercial spacecraft.
It’s poised to build on that success with another huge milestone before 2021 is over. On Monday, the company announced plans to launch the first “all-civilian” mission into orbit by the end of the year. Called Inspiration4, the mission will take billionaire Jared Isaacman, a trained pilot and the CEO of digital payments company Shift4Payments, plus three others into low Earth orbit via a Crew Dragon vehicle for two to four days, possibly longer.
Inspiration4 includes a charity element: Isaacman (the sole buyer of the mission and its “commander”) has donated $100 million to St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, in Memphis, and is attempting to raise at least $100 million more from public donors. One seat is going to a “St. Jude ambassador” that’s already been chosen. But the two others are still up for grabs: one will be raffled off to someone who donates at least $10 to St. Jude, while the other will be a business entrepreneur chosen through a competition held by Shift4Payments.
“This is an important milestone towards enabling access to space for everyone,” SpaceX CEO Elon Musk told reporters on Monday. “It is only through missions like this that we're able to bring the cost down over time and make space accessible to all."
Inspiration4 marks SpaceX’s fourth scheduled private mission in the next few years. The other three include a collaboration with Axiom Space to use Crew Dragon to take four people for an eight-day stay aboard the International Space Station (now scheduled for no earlier than January 2022); another Crew Dragon mission into orbit later that year for four private citizens through tourism company Space Adventures; and Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa’s #dearMoon mission around the moon in 2023 for himself plus seven to 10 others aboard the Starship spacecraft.
SpaceX has never really billed itself as a space tourism company as aggressively as Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic have. While Crew Dragon goes all the way into low-Earth orbit, Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo and Blue Origin’s New Shepard vehicles just go into suborbital space, offering a taste of microgravity and a view of the Earth from high above for just a few minutes—but for way less money. And yet, in building a business that goes even farther, with higher launch costs and the need for more powerful rockets, SpaceX already has four more private missions on the books than any other company does.
When Crew Dragon first took NASA astronauts into space last year, one of the biggest questions to come up was whether customers outside NASA would actually be interested in going .
“A lot of people believe there is a market for space tourism,” says Howard McCurdy, a space policy expert at American University in Washington, DC. “But right now it’s at the very high end. As transportation capabilities improve, the hope is that the costs will come down. That begs the question of whether or not you can sustain a new space company on space tourism alone. I think that’s questionable.”
So why has SpaceX’s expansion into the private mission scene gone so well so far? Part of it must be that it’s such an attractive brand to partner with at the moment. But even if a market does not materialize soon to make private missions a profitable venture, SpaceX doesn’t need to be concerned. It has plenty of other ways to make money.
“I’m not sure Elon Musk cares much if he makes money through this business,” says McCurdy. “But he’s very good at leveraging and financing his operations.” SpaceX launches satellites for government and commercial customers around the world; it’s got contracts with NASA for taking cargo and astronauts alike to the space station; it’s ramping up progress with building out the Starlink constellation and should start offering internet services to the public some time this year.
“It really reduces your risk when you can have multiple sources of revenue and business for an undertaking that’s based upon the single leap of rockets and space technologies,” says McCurdy. “The market for space tourism is not large enough to sustain a commercial space company. When combined with government contracts, private investments, and foreign sales it starts to become sustainable.”
Space tourism, especially to low-Earth orbit, will still remain incredibly expensive for the foreseeable future. And that underscores the issue of equity. “If we’re going into space, who’s the ‘we’?” asks McCurdy. “Is it just the top 1% of the top 1%?”
The lottery concept addresses this to some extent and offers opportunities to ordinary people, but it won’t be enough on its own. Space tourism, and the rest of the space industry, still needs a sustainable model that can invite more people to participate.
For now, SpaceX appears to be leading the drive to popularize space tourism. And competitors don’t necessarily need to emulate SpaceX’s business model precisely in order to catch up. Robert Goehlich, a German-based space tourism expert at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, notes that space tourism itself is already multifaceted, encompassing suborbital flights, orbital flights, space station flights, space hotel flights, and moon flights. The market for one, such as cheaper suborbital flights, is not necessarily faced with the same constraints as the others.
Amplifying space’s potential with quantum
How to safely watch and photograph the total solar eclipse.
The solar eclipse this Monday, April 8, will be visible to millions. Here’s how to make the most of your experience.
- Rhiannon Williams archive page
The great commercial takeover of low Earth orbit
Axiom Space and other companies are betting they can build private structures to replace the International Space Station.
- David W. Brown archive page
The race to fix space-weather forecasting before next big solar storm hits
Solar activity can knock satellites off track, raising the risk of collisions. Scientists are hoping improved atmospheric models will help.
- Tereza Pultarova archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.

Space tourism explained: What, why and where
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Space tourism is an exciting development in the travel and tourism industry. A futuristic type of tourism , the prospect of being able to spend leisure time in space is a daunting concept for many. But whilst some of us may have expected only have to be able to experience space tourism using virtual reality software, several companies are turning holidays in space into a reality.
What is space tourism?
Space tourism definitions, history of space tourism, rocket launches, space museums, space tourism holidays, virgin galactic, blue origin, is space tourism safe, the cost of space tourism holidays, space tourism: conclusion, further reading.
Space tourism is a type of tourism that involves an interest in space. Whilst most people associate space tourism solely with trips to space, the concept of space tourism is, in fact, broader than this.
Space tourism can include visiting space-focussed museums, watching rocket launches or travelling to destinations popular for stargazing, amongst other space-related activities.
Most recently, there has been a lot of commercial attention centred around the concept of travelling to space as a tourist; this is something that several companies are working to achieve in the near future, including Virgin Galactic and SpaceX.

If you Google the phrase ‘what is space tourism’ you will quickly be informed by Google, Wikipedia and a range of other sources that it is travelling to space for leisure or business purposes.
I, however, contest that space tourism is solely focussed upon the act of travelling to space. There is so much more to space tourism than this! Yes, this is an exciting prospect that has grabbed the attention of the media and the public, but hold on a minute…. what about all the other space-related activities that we can do without boarding a rocket and leaving the solar system?
The people over at The Space Tourism Guide have the right idea. They state that;
‘Space Tourism is not — and should not be — confined to space alone… While we can and should consider all of the activities from space tourism companies like Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin, Zero2Infinity, and others space tourism, we should not discredit the companies and destinations here on earth who meet the needs and desires for all of us who love to travel for space-related activities. These can vary widely, from cities and museums like Space Center Houston to hotels with space-themed rooms.’
Space tourism is so much more than taking a trip to space! In fact, I argue that space tourism should encompass all activities related to space and astrology!

To date, there is little academic research into space tourism. Yes, some people have looked into astrology and the like, but on the whole, there is a dearth of information. Most research that has been conducted has focussed on looking at potential demand and market demographics.
In light of the misleading definitions that you will find when asking your favourite search engine what is meant by the term space tourism, I have provided my own definition below.
‘Space tourism is the act of taking part in activities that involve or are related to space, either for business or leisure purposes.’
So there you have it- a definition of space tourism.
There are a total of 600 people that have been to space. The first man visited space in 1961, but it was actually long before this day that many people developed an interest in space. In fact, people have been star gazing as long as records go back. Heck, even the ancient pyramids of Egypt were built around the stars .
So, the concept of space tourism is not new.
The 1950s, 60s, 70s and 80s saw huge progress in space research. The Soviet Union and The United States were world leaders in this area; undertaking many trips to space, exploring our solar system, nearby planets and moons. Space travel became more affordable and we learnt a lot during this time.
It was only at the turn of the new millennium that commercial space tourism ,whereby a tourist could travel to space, started to become a reality. A handful of wealthy citizens from around the world embarked on their leisure outings to space between 2001-2009. Observing this demand, a number of space tourism operators began to emerge, namely Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic and Rocket Lab. Said companies have since become household names.

In recent years the commercial hype and excitement towards space tourism has died down. The public continue to eagerly await the days that they may be able to exchange their all-inclusive holiday in Benidorm for a week of zero-gravity in space, but for most, this is an unrealistic and unachievable prospect.
For now, it appears that travelling into space will be available only for the super-rich, and we do not yet know when this might be attainable. BUT the space tourism industry in all its other forms (museums, star gazing, rocket launches etc) remains to be obtainable to all.
Types of space tourism
We might not realistically be able to travel into space for our annual leave days just yet, but there are still ways that we can get involved with the space tourism industry. Here are some examples.

Stargazing is a popular space tourism pastime for many. There are many parts of the world that are renowned for their stargazing potential. These are usually remote areas, where the light pollution is reduced, enabling maximum visibility.
Some popular stargazing destinations have capitalised on the tourist market by organising stargazing tours or stargazing-focussed accommodation options, such as bubble hotels. This CNN article shows you some of the best bubble hotel spots around the world. Many people use this opportunity to visit the Northern Lights or the Southern Lights too.
Lots of these destinations are perfect for practicing your astrophotography too!

Whilst a rocket launch may not be an everyday occurrence, it is possible to spectate when they do happen. Once operated only by Governments, there are now a range of private companies that undertake rocket launches.
If you travel to a destination with the sole intention of watching a rocket launch, or if you watch a rocket launch alongside other business or leisure pursuits, you can be classified as a space tourist.
A prominent part of the space tourism industry are space museums.
There are many museums throughout the world that are focussed around the concept of space, although these are most numerous in the United States and Russia. Here are some of the most highly-rated space museums.
- Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum, Washington DC, US
- Canada Aviation and Space Museum, Ottawa, Canada
- Memorial Museum of Cosmonautics, Moscow, Russia
- Pima Air and Space Museum, Arizona , US
- Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum, New York City, US
- Le Bourget Air and Space Museum, Paris, France
- Kennedy Space Center, Florida , US
- Cité de l’espace, Toulouse, France

As I mentioned earlier, space tourism holidays are what many people think space tourism is all about. Whilst there are other activities that constitute space tourism, space tourism holidays have gained a lot of media attention in recent years, and rightly so. Who wouldn’t pick up the paper and read an article that tells them that they can swap their two weeks in the sun for two weeks in space?
OK, so it isn’t quite so simple. It will require some adjustment to spending time at zero gravity, you might get a little travel sick and you might not return home with quite the same tan lines, BUT space tourism holidays are set to become a reality.
There are a number of companies who have been developing their space tourism products for a number of years, although exactly when we can go on our next space tourism holiday, is yet to be determined.
Space tourism companies
There are several key players in the space tourism holiday market. See below for a brief summary of each.
Virgin Galactic is perhaps one of the best known space tourism holiday companies. It is part of the wider Virgin Group and therefore has the benefit of an already well-established brand and reputation. It is owned by Richard Branson.
The company plans to send range of tourists to space and already has an extensive waitlist for eager space travellers, including the likes of Brad Pitt, Angelina Jolie, Leonardo DiCaprio, Ashton Kutcher and Justin Bieber.
Virgin Galactic has, however, had some negative publicity in recent times, with multiple delays and the in-flight loss of its VSS Enterprise spaceplane in 2014.
Unlike Virgin Galactic, SpaceX are an experienced rocket launching company that are now extending their operations to the commercial space tourism holiday market.
SpaceX was founded by Elon Musk. Their first holiday was initially scheduled for 2018, but has since been delayed.
Blue Origin plans to offer similar space tourism holidays to that offered by Virgin Galactic. With a traditional, vertical take-off rocket, the company plans to begin operations soon, although there is not firm date set yet.
Blue Origin was founded in 2000 by Mr Bezos.
Orion Span plans to send tourists to space to stay in their ‘space hotel’. The space hotel would accommodate up to six tourists at a time and would be positioned the private commercial space station, Aurora Space Station.
The CEO of Orion Span is Frank Bunger who states that the company’s ‘goal is to make space accessible to all’. They plan to begin operations in 2021.
Better known for their aircraft that do not leave the hemisphere, Boeing have also branched out into the space tourism holiday market.
Boeing’s involvement emerged from their working arrangement with NASA, whereby they have been working on the Commercial Crew Development programme, aimed at increasing involvement from private sector companies in the production of crew vehicles to be launched into orbit.
Boeing have developed a crew capsule, called the Boeing CST-100 Starliner, providing them with the opportunity to sell seats to space tourists.
There have been some concerns over the safety of space tourism, particularly after the negative publicity surrounding the Virgin Galactic loss of aircraft in 2014.
Because it’s so early in development of the space tourism industry and the FAA can’t control how companies design and manufacture their aircraft , it’s hard to say how safe space tourism holidays will be.
There have been many critiques, however, who have suggested that there will be deaths amongst tourists who seek to holiday in space. The number of accidents that have occurred during the testing phases hasn’t done much to people’s minds at ease, either.
Space tourism holidays are for everyday folk, at least not yet anyway, because you need to have a hefty sum of money in your pocket to be able to afford the ticket.
Prices start from US$250,000 and range up to tens of millions of Dollars. Whilst each space tourism holiday company will differ slightly, prices will typically include pre-departure training and equipment. For now, space tourism trips are set to be short in duration, lasting only a few hours. The intention is, however, that trips can be extended in the future to allow for prolonged stays in space.
As you can see, the space tourism industry is a prominent part of the wider tourism industry. Whilst most attention typically goes to the exciting prospect of space tourism holidays, there are also a number of other leisure pursuits that constitute space tourism.
It is likely that we will see many developments in the space tourism industry in the coming years, as research and development continues to be undertaken by a number of commercial operators. Watch this space and maybe you will be the next person to spend your annual leave days in space!
If you want to read up on the space tourism industry a little more then I can recommend the following texts-
- The Market for Space Tourism: Early Indications by Geoffrey Crouch- An overview of the Space Tourism market and its future potential
- Endurance: A Year in Space, A Lifetime of Discovery by Scott Kelly- A diary account of NASA astronaut’s experiences in space.
- Space Tourism by Patrick Stakem- A textbook introducing the concept of space tourism.
Liked this article? Click to share!
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters

Everything you need to know about space travel (almost)
We're a long way from home...
Paul Parsons
When did we first start exploring space?
The first human-made object to go into space was a German V2 missile , launched on a test flight in 1942. Although uncrewed, it reached an altitude of 189km (117 miles).
Former Nazi rocket scientists were later recruited by both America and Russia (often at gunpoint in the latter case), where they were instrumental in developing Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) – rockets capable of carrying nuclear weapons from one side of the planet to the other.

It was these super-missiles that formed the basis for the space programmes of both post-war superpowers. As it happened, Russia was the first to reach Earth orbit, when it launched the uncrewed Sputnik 1 in October 1957, followed a month later by Sputnik 2, carrying the dog Laika – the first live animal in space.
The USA sent its first uncrewed satellite, Explorer 1, into orbit soon after, in January 1958. A slew of robotic spaceflights followed, from both sides of the Atlantic, before Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin piloted Vostok 1 into orbit on 12 April 1961, to become the first human being in space . And from there the space race proper began, culminating in Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin becoming the first people to walk on the Moon as part of NASA's Apollo programme .
Why is space travel important?
Space exploration is the future. It satisfies the human urge to explore and to travel, and in the years and decades to come it could even provide our species with new places to call home – especially relevant now, as Earth becomes increasingly crowded .
Extending our reach into space is also necessary for the advancement of science. Space telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope and probes to the distant worlds of the Solar System are continually updating, and occasionally revolutionising, our understanding of astronomy and physics.
- Subscribe to the Science Focus Podcast on these services: Acast , iTunes , Stitcher , RSS , Overcast
But there are also some very practical reasons, such as mining asteroids for materials that are extremely rare here on Earth.
One example is the huge reserve of the chemical isotope helium-3 thought to be locked away in the soil on the surface of the Moon . This isotope is a potential fuel for future nuclear fusion reactors – power stations that tap into the same source of energy as the Sun. Unlike other fusion fuels, helium-3 gives off no hard-to-contain and deadly neutron radiation.
However, for this to happen the first challenge to overcome is how to build a base on the Moon. In 2019, China's Chang’e 4 mission marked the beginning of a new space race to conquer the Moon, signalling their intent to build a permanent lunar base , while the NASA Artemis mission plans to build a space station, called Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway , providing a platform to ferry astronauts to the Moon's surface.
Could humans travel into interstellar space and how would we get there?
It’s entirely feasible that human explorers will visit the furthest reaches of our Solar System. The stars, however, are another matter. Interstellar space is so vast that it takes light – the fastest thing we know of in the Universe – years, centuries and millennia to traverse it. Faster-than-light travel may be possible one day, but is unlikely to become a reality in our lifetimes.
It’s not impossible that humans might one day cross this cosmic gulf, though it won’t be easy. The combustion-powered rocket engines of today certainly aren’t up to the job – they just don’t use fuel efficiently enough. Instead, interstellar spacecraft may create a rocket-like propulsion jet using electric and magnetic fields. This so-called ‘ ion drive ’ technology has already been tested aboard uncrewed Solar System probes.

Another possibility is to push spacecraft off towards the stars using the light from a high-powered laser . A consortium of scientists calling themselves Breakthrough Starshot is already planning to send a flotilla of tiny robotic probes to our nearest star, Proxima Centauri, using just this method.
Though whether human astronauts could survive such punishing acceleration, or the decades-long journey through deep space, remains to be seen.
How do we benefit from space exploration?
Pushing forward the frontiers of science is the stated goal of many space missions . But even the development of space travel technology itself can lead to unintended yet beneficial ‘spin-off’ technologies with some very down-to-earth applications.
Notable spin-offs from the US space programme, NASA, include memory foam mattresses, artificial hearts, and the lubricant spray WD-40. Doubtless, there are many more to come.
Read more about space exploration:
- The next giant leaps: The UK missions getting us to the Moon
- Move over, Mars: why we should look further afield for future human colonies
- Everything you need to know about the Voyager mission
- 6 out-of-this-world experiments recreating space on Earth
Space exploration also instils a sense of wonder, it reminds us that there are issues beyond our humdrum planet and its petty squabbles, and without doubt it helps to inspire each new generation of young scientists. It’s also an insurance policy. We’re now all too aware that global calamities can and do happen – for instance, climate change and the giant asteroid that smashed into the Earth 65 million years ago, leading to the total extinction of the dinosaurs .
The lesson for the human species is that we keep all our eggs in one basket at our peril. On the other hand, a healthy space programme, and the means to travel to other worlds, gives us an out.
Is space travel dangerous?
In short, yes – very. Reaching orbit means accelerating up to around 28,000kph (17,000mph, or 22 times the speed of sound ). If anything goes wrong at that speed, it’s seldom good news.
Then there’s the growing cloud of space junk to contend with in Earth's orbit – defunct satellites, discarded rocket stages and other detritus – all moving just as fast. A five-gram bolt hitting at orbital speed packs as much energy as a 200kg weight dropped from the top of an 18-storey building.

And getting to space is just the start of the danger. The principal hazard once there is cancer-producing radiation – the typical dose from one day in space is equivalent to what you’d receive over an entire year back on Earth, thanks to the planet’s atmosphere and protective magnetic field.
Add to that the icy cold airless vacuum , the need to bring all your own food and water, plus the effects of long-duration weightlessness on bone density, the brain and muscular condition – including that of the heart – and it soon becomes clear that venturing into space really isn’t for the faint-hearted.
When will space travel be available to everyone?
It’s already happening – that is, assuming your pockets are deep enough. The first self-funded ‘space tourist’ was US businessman Dennis Tito, who in 2001 spent a week aboard the International Space Station (ISS) for the cool sum of $20m (£15m).
Virgin Galactic has long been promising to take customers on short sub-orbital hops into space – where passengers get to experience rocket propulsion and several minutes of weightlessness, before gliding back to a runway landing on Earth, all for $250k (£190k). In late July 2020, the company unveiled the finished cabin in its SpaceShipTwo vehicle, suggesting that commercial spaceflights may begin shortly.
Meanwhile, Elon Musk’s SpaceX , which in May 2020 became the first private company to launch a human crew to Earth orbit aboard the Crew Dragon , plans to offer stays on the ISS for $35k (£27k) per night. SpaceX is now prototyping its huge Starship vehicle , which is designed to take 100 passengers from Earth to as far afield as Mars for around $20k (£15k) per head. Musk stated in January that he hoped to be operating 1,000 Starships by 2050.
10 Short Lessons in Space Travel by Paul Parsons is out now (£9.99, Michael O'Mara)
- Buy now from Amazon UK , Foyles , WH Smith and Wordery
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Sweepstakes
- Space Travel + Astronomy
13 Things Tourists Should Know Before Traveling to Space, According to Astronauts
We asked the pros for their best tips on handling a first trip to space.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Stefanie-Waldek-7eed18a8c9734cb28c5d887eb583f816.jpg)
For most of human spaceflight history, those lucky enough to reach the stars were professional astronauts hired and trained by government agencies around the world. But since the early 2000s, when seven intrepid travelers paid millions to spend a few days aboard the International Space Station (ISS), space tourism has begun to take off. We're now on the cusp of a new era of space exploration, with commercial companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin launching spacecraft capable of taking paying travelers beyond the Earth's surface.
We spoke with former NASA astronauts Leroy Chiao and Scott Parazynski to get their tips for first-time spaceflight participants. During his 15 years with NASA, Chiao participated in four missions — three aboard the space shuttle and one to the ISS, in which he served as commander. Parazynski worked at NASA for 17 years, flying five shuttle missions throughout his career. Read on to discover what they think aspiring space tourists need to know.
Your only job on the flight will be to kick back, relax, and enjoy the ride.
If you're taking a suborbital flight, which is what companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin have offered, your ride will be a quick up-and-down to reach space, rather than a full orbit of the Earth. The short journey is relatively easy compared to what professional astronauts experience. For starters, you won't need to worry about flying your spacecraft. That's all up to the spaceflight provider. "You won't have any responsibility other than to enjoy the experience — and not kick anyone else in the head," says Parazynski. "Their obligations on the flight are pretty straightforward."
As such, the training programs for suborbital space tourist experiences are relatively minimal, perhaps only a few days in length at most. "The downside of not having a lot of training is that you don't have the confidence that comes from lots of training," says Parazynski. "Contrast that with the training I had on the space shuttle, where we trained for hundreds and hundreds of hours for launching in space. If something were to go awry, we would know exactly what to do and our hearts wouldn't skip a beat."
So, other than learning to place your complete trust in your spaceflight provider, Parazynski recommends talking to people who have flown before in order to ease any nervousness. Chiao agrees: "The best advice I can give on launch — and it's easy to say, harder to do — is to try to relax and enjoy the whole process," he says. "Pay attention during your training, talk to other people who've been there if you can. And actually, you might be surprised — it's quite calm!"
Make sure you’re physically and mentally fit.
"I think people should treat this as their Olympics or Super Bowl. This is a really big life experience, and though you don't need to be an Olympic athlete or a Super Bowl champion to fly in space, it helps to be fit," says Parazynski. After all, your body will be experiencing quite a range of new sensations during your spaceflight."
But it's not just about physical fitness — mental fitness is key, too. "I think through fitness comes mental acuity as well," says Parazynski. "The more you can be engaged in the experience, the more you'll remember of it — it'll be more impactful to you."
The G-forces experienced on launch and reentry are not as intense as you might expect.
If you've ever watched a livestream of an astronaut launch, caught any Hollywood flick about space travel, or ridden Mission: Space at Walt Disney World's Epcot theme park, you know that during launch, astronauts get crushed back into their seats. (And, actually, during reentry, too!) They're experiencing strong G-forces, or a sensation of weight felt during acceleration. It's the same feeling you get when you speed up quickly in a car or zoom through a loop or a sharp curve on a roller coaster, but during a rocket launch, those forces are stronger and more sustained. While the experience might seem a little terrifying, the pros say it's quite manageable.
"The G-forces aren't nearly as bad as they show in the movies," says Chiao. "If you're good enough to be given medical approval to go on a trip like this, you're not going to have any problems handling the G-forces." He also notes that you'll likely go through centrifugal runs during your training to prep for the sensation — you'll be strapped into a spinning machine that lets you experience strong G-forces, just like that spinning amusement park ride where you're pressed against the wall and the floor drops.
But to make launch and reentry as comfortable on your body as possible, you'll want to physically relax your muscles so you don't fight against the G-forces. "If you relax and let your body sink into the launch couch, you're going to tolerate it much better," says Chiao. "If you're rigid, that's where you might hurt yourself. And make sure your limbs and arms are inside of the couch."
To prep for weightlessness, you should book a zero-gravity flight.
While it takes quite a bit of effort (and time and money) to get into space to experience weightlessness, you can actually experience the sensation right here on Earth — or rather, just slightly above it. All you need to do is book a zero-gravity flight , where a plane flies in a series of parabolas (or arch-like shapes) during which passengers experience simulated weightlessness through free fall.
It's physically the same as skydiving or even riding a roller coaster, but in those two instances, your senses tell you you're actually falling. "When you're in a zero-G airplane, the airplane is falling at the same rate you are, so you're floating inside the airplane," says Chiao. "That's what it's like in a spacecraft when you get up into space and the engines cut off."
Through commercial companies like the Zero Gravity Corporation , anyone who can spare the cost of a ticket can experience weightlessness — and anyone who's planning on making a trip to space should definitely give it a go. "If they have the means, they should get on a zero-G flight before they go on a suborbital flight," says Parazynski. "It would take some of the mystery out of 'what am I going to feel like?' and 'how do I move?'"
Learning how to scuba dive is good weightlessness training, too.
While being underwater isn't exactly like floating in space, it's a pretty good way to practice moving around in a weightless environment. In fact, NASA even has a life-sized replica of the ISS set inside a giant pool, so astronauts can train for spacewalks underwater.
"Moving in weightlessness comes to you very quickly when you spend some time underwater," says Parazynski. "Get neutrally buoyant underwater and very gently try and move yourself along the ocean floor or bottom of your pool. It doesn't take a lot of force, but it does take a lot of thought."
Come up with a game plan for your few minutes in space.
On suborbital flights, you're only going to have a few minutes in weightlessness, so you should plan exactly how you want to spend your time up there. Figure out if you'd like to bring a memento like a family photo or college pennant for a fun picture. (U.S. Naval Academy graduates and former astronauts Wally Schirra and Tom Stafford famously put a "Beat Army" sign in the window of their Gemini VI spacecraft, so there's a long tradition of this.) Decide in advance if you want to attempt what spaceflight veterans call "stupid astronaut tricks," like flips or spins. But most importantly, budget time to look out the window.
"The most important thing I would tell future astronauts is to savor the view out the window," says Parazynski. "It's, for lack of a better term, a God's-eye view, and so few people have ever had a chance to see it. It's really a beautiful thing to be hovering in space and looking down at your planet."
Don’t worry about taking your own photos.
"As far as taking photographs, I don't know that I would recommend it," says Chiao. "You're not going to be very good at it, first of all, because it takes a little bit of practice to get used to zero-G. Don't waste that time taking photos. Get your memories, look out those windows, and enjoy the whole experience of being weightless." Plus, given the price tag of these spaceflights, we're pretty sure that your operator will provide you with photos and videos of your journey anyway.
When you get into zero gravity, you might feel a little dizzy.
The body functions a bit differently when you remove gravity from the equation for a sustained period of time, and side effects may include dizziness and nausea. "You're going to feel full-headed because there's no longer gravity pulling fluid down into your legs," says Chiao. "And so all that fluid comes up into your torso, and you can feel it right away. It feels kind of like you're standing on your head."
But the good news is, on suborbital flights you might be able to avoid the worst of it. "The adrenaline and excitement are going to make you do OK at first, and by the time you might start feeling bad, it's time to strap back in and come back down," says Chiao.
If you’re spending a few days in space, be prepared for some bumps and bruises.
On a suborbital flight, you won't have a ton of time in space, so you won't really have to worry about acclimating to zero gravity. However, some private spaceflight companies are looking to send their clients up into orbit for longer stays and there are even talks of a space hotel within Voyager Station . If you're going to spend a few days or even a few weeks up in space, you're probably going to bump your head more than once, no matter how much you've trained for the experience.
"It's really funny watching rookie astronauts the first day or two up on a mission," says Parazynski. "We called them the bull in a china shop. They push off with full force and they crack their skull or bang their knee."
You’re also going to make a mess.
Doing routine tasks like brushing your teeth (you can't just spit your toothpaste into a sink), clipping your fingernails (you don't want them floating off into your space station), and going to the bathroom (have you ever thought about how to use a toilet without gravity?) are all very different experiences in weightlessness. Inevitably, you might have a few mishaps early on in your trip.
"Just sitting down for a meal, you put your fork down, and it's gone in 30 seconds," says Parazynski. "You may find it two days later in the cabin air cleaner because that's where the air currents have taken it." Luckily, a lost fork is an easy mess to clean up — and the situation can be prevented by tethering it down. Other messes are a different story.
"As far as using the restroom, that's what you need to pay attention to during your training. The toilet is not particularly simple and you have to be careful," says Chiao. (In case you were wondering, space toilets use airflow to guide things where they're supposed to go.) "But be prepared to make some messes," says Chiao. "And everybody has to clean up their own mess."
If you’re going to do a spacewalk, the stakes are much higher for you and your crew.
If you want to zip around space with a jetpack like George Clooney in "Gravity," sorry, but chances are that's not going to happen any time soon. Most private astronauts will be safely tucked inside their craft for the duration of their flight.
Unlike suborbital flights, future orbital flights with a spacewalk will require extensive training, given that spacewalks are inherently more dangerous than simply riding in a vessel. "If you're careless with your tethers and you float off into the void, there's not a whole lot anyone can come do for you," says Parazynski. It's possible that a crewmate may be able to head out to rescue you, but then you're endangering their life as well. "It's paramount for a spacewalker to think not just about their own health and well-being and their experience, but also that of their crewmates," he says.
If you’re in a capsule, be prepared for a bumpy landing.
While the only way up to space is by rocket, there are two ways to come back down: via a winged vehicle, like the space shuttle or Virgin Galactic's SpaceShipTwo, or a capsule, like Apollo, Soyuz, and Blue Origin's New Shepard. The experiences are quite different, as winged vehicles land like an airplane on a runway, whereas capsules descend beneath parachutes onto land or water. While both experience a range of G-forces during reentry, capsules have a bit of a rougher ride, particularly at the very end.
"When the parachute comes out, you can expect to get jostled around a fair amount, so that can be disorienting," says Chiao. "Then, whether you're hitting the water or the ground, you're gonna get a good bump. There are shock-absorbing mechanisms, of course, that make it not too big a deal. But on Soyuz, you smack the ground pretty darn hard. It was kind of surprising!"
It’ll be worth every penny.
Sure, it's going to cost a small fortune to go into space as a tourist — for now, that's somewhere in the ballpark of several hundred thousand dollars for a suborbital flight and millions of dollars for longer-duration orbital stays. But ask any astronaut, and they're sure to tell you it'll be worth the investment.
"What I would tell prospective astronauts is that it's going to change their lives forever," says Parazynski. "It's a perspective that can't be captured in emotion on film. Even in 3D IMAX, there's no way to capture the way it's going to make you feel, the connectedness you feel to planet Earth, and the awe you have when you look out into the universe."

Passing Thru Travel
Travel Beyond Earth: Exploring the Future of Space Tourism
Posted: March 22, 2024 | Last updated: March 22, 2024

Space tourism, once a mere figment of science fiction, rapidly evolves into a tangible reality, offering the most intrepid travelers an unprecedented opportunity to venture beyond Earth’s confines. This burgeoning industry promises to redefine the boundaries of exploration, providing experiences ranging from suborbital flights to extended stays in space stations. As private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic spearhead this new era, the dream of gazing upon Earth from the vastness of space is closer than ever. This guide explores the forefront of space tourism, presenting ideas that mark the future of extraterrestrial travel.

1. Suborbital Spaceflights
Image Credit: Shutterstock / Dima Zel
Suborbital spaceflights represent the threshold of human space exploration, offering a brief yet profound journey beyond the confines of Earth’s atmosphere. This experience allows you to witness the curvature of the Earth against the backdrop of the infinite cosmos, a sight that has transformed the perspective of many astronauts.
During the flight, you’ll experience a few minutes of weightlessness, floating freely within the cabin, an exhilarating and serene sensation. Companies leading this venture, such as Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, utilize cutting-edge spacecraft designed for safety, comfort, and the optimal viewing experience. The flights are meticulously planned, with each phase — from the rocket’s ascent to the silent glide back to Earth — maximizing the passenger’s experience of space.
Insider’s Tip: Opt for a comprehensive training program offered by these companies to prepare physically and mentally for the rigors and euphoria of space travel.

2. Orbital Spaceflights
Orbital spaceflights are the next frontier for private space tourism, offering an extended stay in low Earth orbit. This experience goes beyond the brief moments of weightlessness, allowing you to live and move in space, witnessing multiple sunrises and sunsets in a single day from the vantage point of a spacecraft. Currently, this level of space travel is offered by companies like SpaceX, which plans to use its Crew Dragon spacecraft to transport private citizens to orbit.
While aboard, you’ll experience life as modern astronauts, from sleeping in zero gravity to observing the Earth from a unique orbital perspective. The journey is about experiencing the day-to-day life of an astronaut, making it a profoundly transformative experience.
Insider’s Tip: Engage in a rigorous pre-flight conditioning regimen to ensure you can fully enjoy and participate in the activities and demands of living in space.

3. Space Hotels
Image Credit: Shutterstock / Alones
The concept of space hotels is set to revolutionize space tourism, offering a luxurious stay in orbit. These hotels, planned by companies like Axiom Space, aim to attach habitable modules to the International Space Station or even construct free-flying space stations designed for commercial use.
Guests can expect accommodations that combine the thrill of space with the comforts of Earth, including rooms with views of the planet below, space-grown food, and recreational activities adapted for microgravity. The development of space hotels highlights the growing accessibility of space travel, promising an extraordinary vacation destination that was once the realm of astronauts.
Insider’s Tip: Keep an eye on the development progress of these stations and plan for a longer training period to acclimate to extended periods in microgravity.

4. Lunar Flybys
Lunar flybys mark an ambitious step in space tourism, offering private citizens the chance to journey around the Moon. This mission, reminiscent of the Apollo missions of the 1960s and 70s, promises an unparalleled adventure, bringing you up close to the lunar surface before witnessing the Earth rising over the Moon’s horizon.
SpaceX’s Starship is one of the spacecraft intended to make such missions possible, providing a comfortable and safe journey for those aboard. The experience of seeing the Moon up close and the Earth in full view offers an extraordinary sense of our place in the universe and the interconnectedness of all life on our planet.
Insider’s Tip: Such a mission requires physical preparation and a deep commitment, as it represents one of the longer-duration space tourism experiences currently planned.

5. Zero-Gravity Flights
Image Credit: Shutterstock / Frame Stock Footage
Embarking on a zero-gravity flight offers an unparalleled introduction to the sensations of space without leaving Earth’s atmosphere. This experience simulates the weightlessness of outer space through parabolic flight patterns, creating moments where gravity’s pull is momentarily negated.
Inside a specially modified aircraft, you’ll float, flip, and soar as if in space, providing a unique taste of what astronauts experience aboard the International Space Station. The flights are meticulously planned and executed, involving a series of steep climbs and descents, with each parabola offering around 20 to 30 seconds of weightlessness.
For those dreaming of space travel, this adventure is an accessible and exhilarating preview, requiring minimal training compared to orbital missions. It’s a favorite among space enthusiasts, researchers, and educators for its educational value and the sheer joy of experiencing microgravity.
Insider’s Tip: Focus on mastering movements in microgravity during the flight to maximize the experience. Quick acclimation allows for more freedom and enjoyment during the brief periods of weightlessness.
6. Spacewalk Simulations
Image Credit: Shutterstock / vicspacewalker
Spacewalk simulations offer an immersive experience that closely mimics the extravehicular activities (EVAs) performed by astronauts in the vacuum of space. Utilizing advanced virtual reality (VR) technology and neutral buoyancy labs, these simulations give participants a realistic sense of the challenges and exhilaration of conducting a spacewalk.
In neutral buoyancy labs, participants are submerged in large pools equipped with full-scale models of spacecraft and space station modules, allowing them to practice tasks under conditions that simulate microgravity. VR simulations, on the other hand, use cutting-edge graphics and motion-sensing technology to create detailed, interactive environments where participants can explore and work on virtual spacecraft or satellites.
These experiences are designed not only for entertainment but also as educational tools, offering insights into the physics of space, the complexity of astronaut tasks, and the teamwork required to complete a mission outside the Earth’s atmosphere.
Insider’s Tip: Take the time to learn about the intricacies of real space missions to enhance the realism and immersion of the simulation experience.

7. Astronaut Training Experiences
Astronaut training experiences are comprehensive programs designed to simulate the physical and mental preparation required for space travel. These programs cover a wide range of activities, from high-G force centrifuge training to simulate rocket launches to underwater neutral buoyancy sessions that mimic the weightlessness of space.
Participants also engage in classroom sessions where they learn about spacecraft operations, navigation, and the science behind human spaceflight. Additionally, survival training exercises prepare participants for emergency scenarios, including how to safely return to Earth in unforeseen circumstances.
These experiences are offered by various space agencies and private companies, aiming to provide an authentic glimpse into the life of an astronaut and the rigorous training they undergo.
Insider’s Tip: Embrace every aspect of the training for a holistic understanding of the physical and psychological demands of space travel.

8. Visits to Space Launch Facilities
Image Credit: Shutterstock / Northfoto
Visits to space launch facilities offer a unique opportunity to witness the intersection of human ingenuity and cosmos exploration. Facilities like NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida and SpaceX’s launch site at Boca Chica, Texas, provide guided tours where visitors can see launch pads, vehicle assembly buildings, and control rooms.
These tours often include exhibits on the history of space exploration, showcasing spacecraft, satellites, and memorabilia from historic missions. For those interested in the future of space travel, some facilities also offer the chance to see the latest aerospace technology and spacecraft being prepared for upcoming missions.
Witnessing a live rocket launch is a highlight of visiting these facilities, offering a tangible sense of the power and potential of space exploration.
Insider’s Tip: Plan your visit to coincide with a live rocket launch for an unforgettable experience, but be prepared for schedule changes due to weather or technical delays.

9. Space Camps for Adults
Image Credit: Shutterstock / Mike_shots
Space camps designed for adults blend the thrill of space exploration with the rigor of astronaut training in an immersive, educational environment. These camps offer a comprehensive overview of space science, including hands-on activities like building and launching model rockets, simulating space missions, and navigating obstacle courses designed to mimic the physical challenges of space travel.
Beyond the physical activities, workshops, and lectures from experts in the field provide insights into the complexities of spaceflight, the history of space exploration, and the future of humanity in space. This experience is about fulfilling childhood dreams and understanding the teamwork, problem-solving, and technical knowledge required for space missions.
Whether you’re a space enthusiast looking to deepen your understanding or simply seeking an adventure out of this world, adult space camps offer an unforgettable journey into the final frontier.
Insider’s Tip: Engage fully in the camp activities and network with fellow space enthusiasts to enrich your experience and foster connections within the space tourism community.

10. Virtual Reality Space Exploration
Image Credit: Shutterstock / Gorodenkoff
Virtual reality (VR) space exploration represents the cutting edge of technology, allowing you to traverse the cosmos from the comfort of your own home. High-definition visuals and immersive audio transport you to other worlds, from the International Space Station to the rugged terrain of Mars. These experiences are crafted with attention to scientific accuracy, offering not just entertainment but an educational journey through space and time.
You can embark on guided tours of extraterrestrial landscapes, participate in simulated space missions, and learn about the cosmos in an engaging, interactive format. VR technology continues to evolve, promising ever more realistic and expansive explorations of the universe. For those fascinated by space but not ready to leave Earth, virtual reality offers a compelling window into what lies beyond our planet.
Insider’s Tip: Invest in a high-quality VR headset and explore the various space exploration programs available to maximize the realism and depth of your virtual space experience.

The Bottom Line
Image Credit: Shutterstock / Skreidzeleu
As space tourism evolves, these journeys become increasingly accessible to those who dream of the stars. Whether through a brief parabolic flight or an ambitious journey around the Moon, the opportunities for adventure beyond Earth’s atmosphere are expanding. Each of these experiences requires financial investment, a commitment to preparation, and a willingness to embrace the unknown.
As you contemplate your place in the cosmos, remember that the essence of space tourism lies in pushing the boundaries of human experience, offering a new perspective on our planet and our place within the universe. The future of travel beyond Earth promises new destinations and a new understanding of what it means to explore.
More Articles Like This…
Barcelona: Discover the Top 10 Beach Clubs
2024 Global City Travel Guide – Your Passport to the World’s Top Destination Cities
Exploring Khao Yai 2024 – A Hidden Gem of Thailand
The post Travel Beyond Earth: Exploring the Future of Space Tourism republished on Passing Thru with permission from The Green Voyage .
Featured Image Credit: Shutterstock / Andrei Armiagov.
For transparency, this content was partly developed with AI assistance and carefully curated by an experienced editor to be informative and ensure accuracy.
More for You
Jake Paul vs Mike Tyson rules finally revealed as ‘knockout’ decision is made
Popular Frozen Pizza Recalled for Potential Health Hazards
The lowest-earning college major in America, according to data—and the see runners-up
CBS makes major changes to 'NFL Today': Phil Simms and Boomer Esiason out
5 Types of Homes That Will Plummet in Value in 2024
17 Phrases Older People Use That No One Else Gets
Taco Bell Receives Massive Pushback on New Unpopular Menu Change
8 Netflix shows with a perfect Rotten Tomatoes score you need to watch
D.C. police just schooled a university on freedom of speech rights
Practical invention - How To Quickly Remove Rust
10 in-demand remote jobs companies are hiring for right now—many pay over $100,000
How Much You Take Home from the Average Salary in Each State
We Ordered 7 Fast-Food Breakfast Sandwiches to Find the Best One
Here is the true value of having a fully paid-off home in America — especially when you're heading into retirement
Russia Loses Control of Key Island
The films everyone should see at least once before they die, according to critics
Genshin Impact: Praetorian Golem Locations
7 weird jobs that are well-paying but nobody knows about, according to a viral Reddit thread
Netflix thriller dubbed ‘Irish Avengers’ welcomes Game of Thrones icon out of retirement
4 Hidden Money Traps New Parents Need To Avoid
HALO Space unveils capsule design for stratospheric space 'glamping'
A Spanish balloon company plans to begin flying paying space tourists in 2026

LONDON — Stratospheric balloon company HALO Space plans to offer aspiring space travelers the space tourism equivalent of glamping. Instead of tight space suits and stomach-churning G-forces typically attached to a rocket flight, the company's pressurized capsule, attached to a helium-filled balloon, will offer comfy swivel seats, giant windows and a selection of fine cuisine.
The Spanish-headquartered firm unveiled the design of the 3.9-ton (3.5 metric tonnes) Aurora capsule at an event in London on Wednesday, April 10, and said it hoped to begin commercial operations in 2026.
Unlike suborbital space tourism companies such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin , HALO Space won't be taking passengers high enough to experience weightlessness . The flight will be a rather leisurely affair lasting up to six hours, almost four of which will be spent hovering in the stratosphere some 22 miles (35 kilometers) above Earth's surface. There, high above the cloud tops, passengers will be able to admire the star-studded blackness of space above, as well as the curvature of the planet shrouded in the atmosphere beneath their feet.
Related: Space Perspective is nearly ready to fly tourists on luxury balloon rides near the edge of space (exclusive)
"When you talk to astronauts, they tell you that this experience of watching the planet from above is really something unique and extraordinary," HALO Space CEO Carlos Mira said in the press conference. "So far, only 650 humans have had the opportunity to experience this overview effect. But you don’t need to go all the way to space to have it. We hope to offer this experience to 1,000 people by 2030."
HALO Space is one of two companies currently readying its balloon technology to begin commercial operations in the next two years. The other is Florida-based Space Perspective, which revealed a completed test model of their Spaceship Neptune in February. HALO Space said they have conducted five test flights with a mockup and plan to take off for the first crewed test in 2025 before commencing flights with paying passengers a year later.

Both companies hope their propositions will attract a wider customer base than the jerky rocket rides of Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, which propel daredevil clients on short joy rides to the edge of space and back. Reaching an altitude nearly three times higher than stratospheric balloons, Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin's spacecraft experience several-minute-long spells of microgravity before falling back to Earth .
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
At $164,000 per seat, a trip with HALO Space will cost about a third of the price of a Virgin Galactic flight and won't require any advanced medical certifications.
"The take-off will be like being in an elevator," said Mira. "The ascent is soft and gentle, climbing at 12 miles per hour."
The 16-foot-wide (5 meters) and 11.5-foot-tall (3.5 m) capsule will be made of aluminum alloy and composite materials. With an internal space of 30.4 square feet (2.8 square meters), the spaceship could host eight paying passengers, plus a pilot. The internal atmosphere will be maintained by a life-support system similar to that of an aircraft. Yet despite this crammed interior and the extreme environment outside the capsule, passengers should still feel perfectly comfortable and able to relax.
"It's meant to be a sort of a glamping experience," Frank Stephenson, creative director and founder of Frank Stephenson Design who led the design work said at the conference. "It's a high-level experience for these people who are used to flying first class rather than economy."

Stephenson, who had previously worked for high-end car makers including BMW, Ferrari, Maserati and McLaren, said the biggest challenge was keeping the capsule light enough so that it can be safely lifted by the balloon while still making sure every aspect of the interior lives up to the expectations of passengers.
“It's very easy to add weight to things and make it super comfortable," Stephenson said. "It's more difficult to reduce weight, reduce material and still make it feel like a very unique experience."
When fully inflated, the stratospheric balloon will be 460 feet (140 meters) tall, towering over the gleaming space capsule. The balloon is designed to detach from the capsule during descent. The capsule will then be brought down to a landing under a steerable parachute. Mira said the balloon technology is inherently safer than rockets loaded with explosive fuels. It also produces no greenhouse gas emissions, making the experience 100 percent compliant with the most stringent environmental protection standards.
— Space Perspective wants to take tourists on balloon rides to the stratosphere
— Space Perspective partners with Exclusive Resorts for balloon rides to the stratosphere
— Space Perspective starts selling seats for balloon rides
"We are using mature technologies," said Mira. "Balloons in general have been around for more than 200 years. This type of balloon, stratospheric balloons, have been around for almost 100 years. The first human went to the stratosphere on a balloon in 1931."
HALO Space plans to fly from spaceports in the Mojave Desert in the U.S., Spain, Australia and Saudi Arabia. The company is currently working with the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration to receive a license before its first crewed flight next year.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Tereza is a London-based science and technology journalist, aspiring fiction writer and amateur gymnast. Originally from Prague, the Czech Republic, she spent the first seven years of her career working as a reporter, script-writer and presenter for various TV programmes of the Czech Public Service Television. She later took a career break to pursue further education and added a Master's in Science from the International Space University, France, to her Bachelor's in Journalism and Master's in Cultural Anthropology from Prague's Charles University. She worked as a reporter at the Engineering and Technology magazine, freelanced for a range of publications including Live Science, Space.com, Professional Engineering, Via Satellite and Space News and served as a maternity cover science editor at the European Space Agency.
Watch 2 gorgeous supernova remnants evolve over 20 years (timelapse video)
James Webb Space Telescope discovers some early universe galaxies grew up surprisingly fast
SpaceX's Starship could help this start-up beam clean energy from space. Here's how (video)
Most Popular
- 2 Evidence for Planet 9 found in icy bodies sneaking past Neptune
- 3 NASA crew announced for simulated Mars mission next month
- 4 NASA's Viper moon rover gets its 'neck' and 'head' installed for mission later this year
- 5 China releases world's most detailed moon atlas (video)

Life on Other Planets: What is Life and What Does It Need?
One day, perhaps in the not-too-distant future, a faraway planet could yield hints that it might host some form of life – but surrender its secrets reluctantly.
Our space telescopes might detect a mixture of gases in its atmosphere that resembles our own. Computer models would offer predictions about the planet’s life-bearing potential. Experts would debate whether the evidence made a strong case for the presence of life, or try to find still more evidence to support such a groundbreaking interpretation.
“We are in the beginning of a golden era right now,” said Ravi Kopparapu, a scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, who studies habitable planets. “For the first time in the history of civilization we might be able to answer the question: Is there life beyond Earth?”
For exoplanets – planets around other stars – that era opens with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Instruments aboard the spacecraft are detecting the composition of atmospheres on exoplanets. As the power of telescopes increases in the years ahead, future advanced instruments could capture possible signs of life – “biosignatures” – from a planet light-years away.
Within our solar system, the Perseverance rover on Mars is gathering rock samples for eventual return to Earth, so scientists can probe them for signs of life. And the coming Europa Clipper mission will visit an icy moon of Jupiter. Its goal: to determine whether conditions on that moon would allow life to thrive in its global ocean, buried beneath a global ice shell.
But any hints of life beyond Earth would come with another big question: How certain could any scientific conclusions really be?
“The challenge is deciding what is life – when to say, ‘I found it,’” said Laurie Barge of the Origins and Habitability Lab at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
With so much unknown about what even constitutes a “sign of life,” astrobiologists are working on a new framework to understand the strength of the evidence. A sample framework, proposed in 2021, includes a scale ranging from 1 to 7, with hints of other life at level 1, to increasingly substantial evidence, all the way to certainty of life elsewhere at level 7. This framework, which is being discussed and revised, acknowledges that scientific exploration in the search for life is a twisted, winding road, rather than a straightforward path.
And identifying definitive signs remains difficult enough for “life as we know it.” Even more uncertain would be finding evidence of life as we don’t know it, made of unfamiliar molecular combinations or based on a solvent other than water.
Still, as the search for life begins in earnest, among the planets in our own solar system as well as far distant systems known only by their light, NASA scientists and their partners around the world have some ideas that serve as starting points.
Life That Evolves
First, there’s NASA’s less-than-formal, non-binding but still helpful working definition of life: “A self-sustaining chemical system capable of Darwinian evolution.” Charles Darwin famously described evolution by natural selection, with characteristics preserved across generations leading to changes in organisms over time.
Derived in the 1990s by a NASA exobiology working group, the definition is not used to design missions or research projects. It does help to set expectations, and to focus debate on the critical issues around another thorny question: When does non-life become life?
“Biology is chemistry with history,” says Gerald Joyce, one of the members of the working group that helped create the NASA definition and now a research professor at the Salk Institute in La Jolla, California.
That means history recorded by the chemistry itself – in our case, inscribed in our DNA, which encodes genetic data that can be translated into the structures and physical processes that make up our bodies.
The DNA record must be robust, complex, self-replicating and open-ended, Joyce suggests, to endure and adapt over billions of years.
“That would be a smoking gun: evidence for information having been recorded in molecules,” Joyce said.
Such a molecule from another world in our solar system, whether DNA, RNA or something else, might turn up in a sample from Mars, say from the Mars sample-return mission now being planned by NASA.
Or it might be found among the “ocean worlds” in the outer solar system – Jupiter’s moon, Europa, Saturn’s Enceladus or one of the other moons of gas giants that hide vast oceans beneath shells of ice.
We can’t obtain samples of such information-bearing molecules from planets beyond our solar system, since they are so far away that it would take tens of thousands of years to travel there even in the fastest spaceships ever built. Instead, we’ll have to rely on remote detection of potential biosignatures, measuring the types and quantities of gases in exoplanet atmospheres to try to determine whether they were generated by life-forms. That likely will require deeper knowledge of what life needs to get its start – and to persist long enough to be detected.
A Place Where Life Emerges
There is no true consensus on a list of requirements for life, whether in our solar system or the stars beyond. But Joyce, who researches life’s origin and development, suggests a few likely “must-haves.”
Topping the list is liquid water. Despite a broad spectrum of environmental conditions inhabited by living things on Earth, all life on the planet seems to require it. Liquid water provides a medium for the chemical components of life to persist over time and come together for reactions, in a way that air or the surface of a rock don’t do as well.
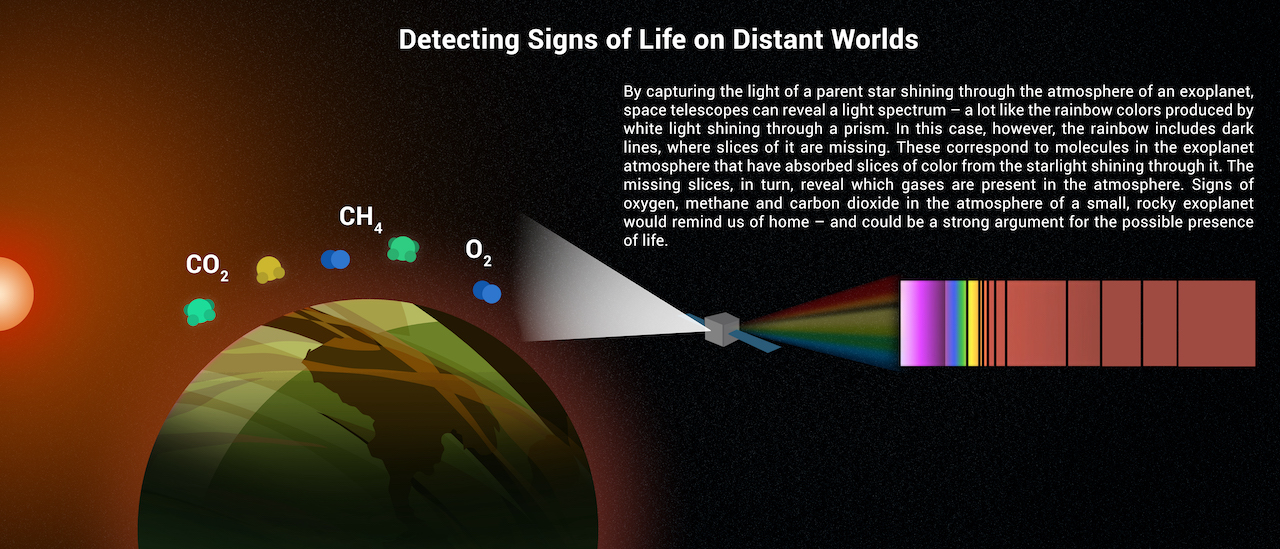
Also essential: an energy source, both for chemical reactions that produce structures and to create “order” against the universal tendency toward “disorder” – also known as entropy.
An imbalance in atmospheric gases also might offer a tell-tale sign of the presence of life.
“In Earth’s atmosphere, oxygen and methane are highly reactive with each other,” Kopparapu said. Left to themselves, they would quickly cancel each other out.
“They should not be seen together,” he said. “So why are we seeing methane, why are we seeing oxygen? Something must be constantly replenishing these compounds.”
On Earth, that “something” is life, pumping more of each into the atmosphere and keeping it out of balance. Such an imbalance, in these compounds or others, could be detected on a distant exoplanet, suggesting the presence of a living biosphere. But scientists also will have to rule out geological processes like volcanic or hydrothermal activity that could generate molecules that we might otherwise associate with life.
Careful laboratory work and precision modeling of possible exoplanet atmospheres will be needed to tell the difference.
Going Through Changes
Barge also places high on the list the idea of “gradients,” or changes that occur over time and distance, like wet to dry, hot to cold, and many other possible environments. Gradients create places for energy to go, changing along the way and generating molecules or chemical systems that later might be incorporated into life-forms.
Plate tectonics on Earth, and the cycling of gases like carbon dioxide – buried beneath Earth’s crust by subduction, perhaps, or released back into the atmosphere by volcanoes – represent one kind of gradient.
Barge’s specialty, the chemistry of hydrothermal vents on the ocean floor billions of years ago, is another. It’s one possible pathway to have created a kind of primitive metabolism – the translation of organic compounds into energy – as a potential precursor to true life-forms.
“What gradients existed before life?” she asks. “If life depends so much on gradients, could the origin of life also have benefited from these gradients?”
Clearer mapping of possible pathways to life ultimately could inform the design of future space telescopes, tasked with parsing the gases in the atmospheres of potentially habitable exoplanets.
“If we want to be sure it’s coming from biology, we have to not only look for gases; we have to look at how it’s being emitted from the planet, if it’s emitted in the right quantities, in the right way,” Kopparapu said. “With future telescopes, we’ll be more confident because they’ll be designed to look for life on other planets.”
Search for Life
This article is one in a series about how NASA is searching for life in the cosmos.
Beginnings: Life on Our World and Others
The Hunt for Life on Mars – and Elsewhere in the Solar System
'Life' in the Lab
Searching for Signs of Intelligent Life: Technosignatures
Finding Life Beyond Earth: What Comes Next?

Related Terms
- Terrestrial Exoplanets
- The Search for Life
Explore More

NASA-Led Study Provides New Global Accounting of Earth’s Rivers
The novel approach to estimating river water storage and discharge also identifies regions marked by ‘fingerprints’ of intense water use. A study led by NASA researchers provides new estimates of how much water courses through Earth’s rivers, the rates at which it’s flowing into the ocean, and how much both of those figures have fluctuated […]

NASA’s ORCA, AirHARP Projects Paved Way for PACE to Reach Space
It took the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission just 13 minutes to reach low-Earth orbit from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in February 2024. It took a network of scientists at NASA and research institutions around the world more than 20 years to carefully craft and test the novel instruments that allow PACE […]

NASA’s CloudSat Ends Mission Peering Into the Heart of Clouds
Over the course of nearly two decades, its powerful radar provided never-before-seen details of clouds and helped advance global weather and climate predictions. CloudSat, a NASA mission that peered into hurricanes, tallied global snowfall rates, and achieved other weather and climate firsts, has ended its operations. Originally proposed as a 22-month mission, the spacecraft was […]
Discover More Topics From NASA

Black Holes

Science | April 26, 2024
Ten Amazing Facts About Tornadoes, Explained
To prepare you for the movie “Twisters,” we’ve compiled some jaw-dropping details about the powerful phenomenon
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/33/dc/33dc6f79-65f4-47c2-b67f-8dd30d26e647/gettyimages-937849166_web.jpg)
Catherine Duncan
Staff Contributor
As looming thunderstorm clouds spit out baseball-sized hail and torrential rain, a narrow whirlwind of air stretches its way toward the ground, signaling the arrival of one of nature’s most violent phenomena: a tornado.
Also known as twisters, these violent cyclones can reach wind speeds of 300 miles per hour and blaze a path of destruction that can last from mere seconds to several hours . While most people flee or take shelter at the sight of these alarming conditions, others dive headfirst into them. Storm chasers, people who get dangerously close to extreme weather events, sometimes for scientific research, jump at the chance to pursue the ever-unpredictable tornado.
The 1996 disaster classic Twister follows a group of these daring storm chasers, a university professor and her team of students who rush toward an outbreak of severe twisters sweeping Oklahoma. Their goal: deploy a revolutionary weather alert device, aptly named “Dorothy,” within the heart of multiple tornado systems to track and possibly tame the forces of nature. After a series of disastrous attempts to deploy their invention within multiple cyclones, a final, massive tornado rips through the area. In the nick of time, the team successfully sets up their device in the twister’s center and collects crucial data.
The highly awaited sequel Twisters sees the continuation of this research nearly two decades later, with a new generation of storm chasers and technology. The story’s hesitant protagonist Kate Cooper, played by Daisy Edgar-Jones, joins forces with adrenaline junkie Tyler Owens, played by Glen Powell, as twin twisters ravage the plains of central Oklahoma. The pair races against a rival team and devastating weather conditions to conduct groundbreaking analysis. Though the film is fictionalized, its overarching circumstances—the treacherous nature of twisters and the difficulty of predicting their arrival—ring true.

In anticipation of the July 19 release of Twisters , we contacted three scientists to unravel some of the secrets wrapped within these catastrophic cyclones. Here are a few of the coolest finds we uncovered.
Supercell thunderstorms are responsible for creating tornadoes
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/05/8b/058bb8e8-210f-4339-9aa4-83fe134be1e4/supercell_thunderstorm_over_needmore_texas_may_4_2019_web.jpg)
Tornadoes are born within supercell thunderstorms , an anvil-shaped cloud with a rotating updraft called a mesocyclone. As an extremely rare weather event, only one in thousands of storms yields a supercell thunderstorm. One in five or six supercells , though, produces a tornado.
“To get a thunderstorm, we have to have an unstable atmosphere, and generally, for a tornado, we need the thunderstorms to rotate,” says William Gallus, a meteorologist at Iowa State University. “That happens if we have wind shear, which means that the wind speed and wind directions are changing as you go up.”
Warm air rises, cold air falls, rough winds whip within the storm system, and an updraft occurs. If this rotating updraft descends toward the ground, lowering itself below the storm, a tornado can emerge from the chaos.
The tornado forms as the mesocyclone accelerates from the bottom up—and the feature intensifies its rotation, in a way similar to an ice skater who pulls her arms into her body to spin faster, says Jana Houser , a supercell thunderstorm and tornado radar analysis expert at Ohio State University.
The strongest winds of the tornado are closest to the ground
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/b3/8d/b38dc04c-527b-4586-a357-66bfe4af2ca4/gettyimages-535057762_web.jpg)
In the atmosphere, the winds get stronger the higher up you go. Tornadoes reverse these conditions, with their strongest winds appearing at the lowest points. This powerful rotation starts at the ground and then floats its way upward to converge into the visible funnel cloud.
“This process happens very quickly,” says Houser, who, alongside her team and National Geographic cameras, captured the very tornadoes set to appear as background footage in the upcoming film Twisters . “In under a minute, you can go from a weak rotation to, all of a sudden, a full tornado.”
According to Gallus, computer models of tornadoes have shown that the strongest winds could lie just 15 feet above the ground—their most brutal region lining up with the height of homes and buildings.
“That’s pretty unfortunate for all of us who live on Earth, because that means that in a tornado, unlike any other weather system, the very worst winds are impacting buildings, people and trees down near the ground,” says Gallus.
Tornadoes can form anywhere, anytime
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/1f/f8/1ff86ef4-3453-48d8-9df0-a9425de1a083/tornadoalley_web.jpg)
Most tornadoes are formed in the Great Plains of the United States, in an area deemed “Tornado Alley.” Flat terrain combined with unstable conditions—warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico collides with dry winds drifting in from the Rocky Mountains—provides the ideal breeding ground for twisters to spawn. But tornadoes can happen almost anywhere. They have been reported in all 50 states and all continents except Antarctica, and they’ve struck major urban areas , such as Dallas, Miami and Minneapolis.
But cyclones don’t follow any sort of pattern or path, contrary to popular misconceptions. “It doesn’t matter if you’re in a downtown part of the city, in a hilly area or even a mountainous area,” says Houser. She adds that some terrain may reduce or increase the probability of tornadoes, but complete protection from the twisters can’t be guaranteed.
Similarly, while peak tornado season ranges from May to July depending on location, tornadoes can hit at any month and any time, both day and night.
Tornadoes have uniquely powerful upward motion

In most weather phenomena, the most aggressive winds blow horizontally, directing their potency outward toward the north, south, east and west, rather than upward and downward. Tornadoes defy these expectations. Things resting in the tornado’s path—the roofs of homes, cars, animals—can be suddenly whisked straight up and into the whirl of debris, victim to the sheer power of the tornado’s upward winds. According to Gallus, the strength of a tornado’s upward motion is comparable to the speed at which it moves along terrain, with 100- or 200-mile-an-hour winds shooting up toward the sky.
“That’s why the damage that a tornado does to buildings is very different than if you have the exact same mile-per-hour wind from just a thunderstorm,” says Gallus. “It’s also why you hear these stories of people or things getting picked up and seeming to levitate or fly up into the air—it’s because the tornado has such strong upward motion.”
The air pressure inside a tornado can cause just as much damage as the wind itself
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/76/8a/768a0468-e614-45f2-bfce-4fd9c9252dd6/gettyimages-545869429_web.jpg)
When visiting the site of a Missouri hospital ravaged by a tornado, Gallus recalls, a nurse he spoke with had to tilt her head a certain direction to hear. Due to the intense air pressure change caused by the tornado, her eardrum ruptured. The air pressure in the middle of a tornado can drop suddenly and strongly, as if you were riding on a plane flying up into the air extremely fast. Many people near tornadoes have reported their ears “popping” during the phenomenon. “That change in pressure is almost like nature’s way of giving you a very last warning by having your head experience this strange rapid adjustment and popping going on in your head,” says Gallus.
The change in air pressure can also create an additional force on buildings that, along with the strong winds, can intensify and quicken their destruction.
Terrain can change a tornado’s behavior
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/c0/15/c0152ae6-7858-4517-983b-82084c5eb34c/gettyimages-1321594650_web.jpg)
Researchers have a difficult time predicting when a tornado will form—and where it will go. Changing winds and differing terrain can make it hard for meteorologists chart the exact path of a twister.
“Tornadoes are incredibly susceptible to very small nuances in the land cover, in the environment, in the storm itself, and it’s very difficult, I would say impossible, to account for every single factor that could possibly go into changing what a tornado is doing,” says Houser. “They defy generalization.”
While predicating a storm is hard, meteorologists say that some features of terrain may enhance the conditions needed for a twister to form. For example, sprawling urban areas can affect thunderstorms, which, in turn, can affect tornadoes. Since cities have more precipitation on their downwind side because of the way water systems interact with urban structures, they produce more rain and more hail, and can be warmer, helping set up an environment that’s more likely for a tornado to form.
“Sometimes urban areas are warmer than rural areas due to the urban heat island. What happens if a tornado goes over a warmer city?” says Jason Naylor, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Louisville. “It looks like the urban heat island could potentially enhance the low-level updrafts in the storm and may help instigate tornadoes in a theoretical way.”
Tornadoes usually rotate counterclockwise, but they can switch directions
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/79/31/7931efbe-e744-46fb-a37a-8eb4687b8e5e/pl23_nssl0254_web.jpg)
In the Northern Hemisphere, about 98 percent of tornadoes spin counterclockwise , which meteorologists label as cyclonical. However, a clockwise-swirling tornado is not out of the question—just much less common.
The counterclockwise motion of most tornadoes has long been attributed to the Coriolis effect, the force caused by the Earth’s rotation. But, according to Houser, this is merely a myth. Tornadoes exist on “too small a space scale and time scale for the Coriolis force to affect it,” she says. Rather, the counterclockwise motion results from how vertical winds change in speed and height within the storm.
Meteorologists call clockwise tornadoes anti-cyclonic. “You get an anti-cyclonic tornado when you have a very strong surge of air within the storm,” says Houser.
Storms can produce more than one tornado at a time
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/18/b1/18b12ac6-1b65-4098-9350-f334ce1dea3b/pl23_con00002_web.jpg)
Twisters sees two groups of storm chasers unite as two different tornadoes converge over a small town in central Ohio. This event isn’t just movie magic: The same storm system can really eject multiple tornadoes at once. As winds change, the storm itself can begin to form a new tornado in a slightly different location from the original tornado—with the fledgling rotating updraft gaining power as the other twister slowly dies down. Or, if the original tornado is particularly violent , the level of agitation can churn out smaller whirlwinds that extend toward the ground.
And Houser says that other freak circumstances, such as extremely strong rotation along the edges of a storm, can also produce multiple tornadoes. A clockwise and counterclockwise tornado can even appear in the same storm system.
Tornadoes themselves can’t be forecast—only the conditions that produce them can
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/ea/d5/ead5205b-33f5-4305-b238-8714480a6bc4/may_4_0012_r_web.jpg)
The 1996 film Twister and its 2024 companion Twisters center around the same key issue: the frustrating impossibility of forecasting tornadoes. “We don’t even really try to forecast exactly when and where a tornado would hit, because we simply cannot do that ahead of time,” says Gallus.
Warnings for tornadoes are only issued when a twister is already forming and has been sighted—or indicated by weather radar—and the alerts cover an area that may be impacted.
Scientists are able to predict, however, the conditions favorable for supporting thunderstorms that spin and would be more likely to produce tornadoes. Up to a couple of hours ahead of time, when increased weather severity is detected, local television and radio news stations issue a tornado watch.
But a tornado’s intensity can’t be determined until after its wake. Scientists determine a tornado’s level of destruction by using the Enhanced Fujita Scale . The scale assesses the damage a tornado does to trees, buildings and homes. Scientists then use that information to calculate its probable wind speed. The rating system ranges from F0, the weakest cyclone, to F5, a vicious, deadly tornado, which a character in Twister deems the “finger of God.”
Climate change is affecting tornadoes

Tornado Alley is moving eastward . In the past decade, twisters have been inching their way into the Midwest and hitting states such as Missouri in record-breaking severity . Meteorologists attribute this shift to climate change.
“Now, with climate change, places that were normally too cold in the winter are finding themselves with days warm enough that you’re starting to see tornadoes at times of year, parts of the country, where they didn’t used to happen,” says Gallus.
This is caused by climate change’s impact on weather. Gallus says that climate change is making conditions warmer and more humid near the ground, which is increasing the level of instability that leads to stronger, tornado-producing storms.
According to Gallus, we may see more days that meteorologists call tornado outbreak days, where five to ten tornadoes crop up. But climate change could also decrease the frequency of days where one or two tornadoes crop up. Essentially, the number of tornadoes could be concentrated on fewer days.
“We can’t say that tornadoes are going to become stronger. We can’t say that we’re going to have less,” says Gallus. “But what we do know is, because of how the temperature is changing, we are going to start finding them in weird times of the year and places where it always used to be too cold to have a tornado.”
Get the latest Science stories in your inbox.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Catherine_Duncan_headshot.png)
Catherine Duncan | READ MORE
Catherine Duncan is an intern with Smithsonian magazine.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Spaceflight. Space tourism is human space travel for recreational purposes. [1] There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital, suborbital and lunar space tourism. Tourists are motivated by the possibility of viewing Earth from space, feeling weightlessness, experiencing extremely high speed and something unusual, and ...
The advent of space tourism occurred at the end of the 1990s with a deal between the Russian company MirCorp and the American company Space Adventures Ltd. MirCorp was a private venture in charge of the space station Mir. To generate income for maintenance of the aging space station, MirCorp decided to sell a trip to Mir, and Tito became its ...
As space tourism became a real thing, dozens of companies entered this industry hoping to capitalize on renewed public interest in space, including Blue Origin in 2000 and Virgin Galactic in 2004. In the 2000s, space tourists were limited to launches aboard Russian Soyuz aircraft and only could go to the ISS.
5) SpaceX stacks tallest booster ever with Starship. SpaceX's first orbital Starship SN20 is stacked atop its massive Super Heavy Booster 4 for the first time on Aug. 6, 2021 at the company's ...
The final space tourism excursion was made by Cirque du Soleil founder Guy Laliberté in 2009, after which Roscosmos had to end touristic flights: when NASA retired its space shuttle program in 2011, each seat on its Soyuz spacecraft needed to be reserved for crews heading to the ISS, not tourists. Since then, space tourism has been halted.
The US space agency has changed its tune on space tourism since Tito's historical trip, announcing back in 2019 plans to open the ISS to tourists. 2020 is when private spaceflight just got ...
More than 20 years ago, Dennis Tito, the first "space tourist" (also known as "spaceflight participant"), flew to the International Space Station aboard a Soyuz spacecraft for a six-day stay. Tito donated the Sokol pressure suit he wore in space to the Museum in 2003. Since his flight, only six other individuals scored self-funded ...
According to UBS, if even only 5% of the average 150 million passengers that travel on 10 hour or longer flights pay $2,500 per trip, then returns could skyrocket to $20 billion per year in today ...
NASA/WikimediaCommons. The VSS Unity spacecraft is one of the ships that Virgin Galactic plans to use for space tours. AP Photo/Matt Hartman. The first space tourist left Earth 20 years ago aboard ...
Virgin Galactic announced on November 24 that Keisha Schahaff, a health and energy coach in Antigua, won two seats in a sweepstakes that raised $1.7 million for Space for Humanity, a Denver-based ...
00:00. 09:13. Listen to more stories on hark. Of all the high-flying tourism ventures spawned by space-obsessed billionaires, Virgin Galactic, founded by Richard Branson, offers perhaps the most ...
Jason Lyon. By Debra Kamin. May 7, 2022. Ilida Alvarez has dreamed of traveling to space since she was a child. But Ms. Alvarez, a legal-mediation firm owner, is afraid of flying, and she isn't ...
She'll be only the fourth Black woman from the US to travel to orbit. Chris Sembroski, a 42-year-old Seattle-based Lockheed Martin employee and former camp counselor at Alabama's famed Space Camp.
The 1986 Challenger and 2003 Columbia shuttle disasters are stark reminders of the dangers of space travel. Human space travel has always involved determining acceptable levels of risk for trained astronauts. But commercial space tourism is different to state-sponsored space programs, and will need the highest possible safety standards.
The estimated revenue of the orbital space tourism market worldwide amounted to roughly 385 million U.S. dollars in 2021, and this figure was forecast to reach 555 million U.S. dollars by 2030 ...
The 1970s: The Birth of Space Tourism. The 1960s came to a close and the repeatability of human spaceflight was proven. The 1970s began with an idea that perhaps people other than highly-trained astronauts and cosmonauts could able to go to space. This is the first real chapter in the history of space tourism.
The space tourism we were promised is finally here—sort of. SpaceX's first "all-civilian" mission into orbit could create a whole new service in the space economy. But not everyone will be ...
CNN —. Virgin Galactic — the space tourism company founded by British billionaire Richard Branson — finally launched its first space tourists to the edge of the cosmos, a major step toward ...
Space tourism is an exciting development in the travel and tourism industry. A futuristic type of tourism, the prospect of being able to spend leisure time in space is a daunting concept for many. But. Everything you need to know about the space tourism industry including a definition of space tourism, types of space tourism activities and ...
Everything you need to know about space travel (almost) - BBC Science Focus Magazine.
Stefanie Waldek is a freelance space, travel, and design journalist with expertise in aviation, meteorology, and polar regions. She was a former editor at Architectural Digest, TripAdvisor, and ...
A space tourism boom has been forecast for more than a decade,2 but the current regulatory landscape is designed for a fledgling industry that is yet to fully emerge.3 Companies proposing to offer space tourism, which have stayed afloat financially with the help of investors who foresee
Space tourism, once a mere figment of science fiction, rapidly evolves into a tangible reality, offering the most intrepid travelers an unprecedented opportunity to venture beyond Earth's confines.
Unlike suborbital space tourism companies such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin, HALO Space won't be taking passengers high enough to experience weightlessness.The flight will be a rather ...
Our space telescopes might detect a mixture of gases in its atmosphere that resembles our own. Computer models would offer predictions about the planet's life-bearing potential. Experts would debate whether the evidence made a strong case for the presence of life, or try to find still more evidence to support such a groundbreaking interpretation.
Science | April 26, 2024. Ten Amazing Facts About Tornadoes, Explained. To prepare you for the movie "Twisters," we've compiled some jaw-dropping details about the powerful phenomenon