An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

Vaccines for Travelers
Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places.
Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you’re traveling. It will also help make sure that you don’t bring any serious diseases home to your family, friends, and community.
On this page, you'll find answers to common questions about vaccines for travelers.
Which vaccines do I need before traveling?
The vaccines you need to get before traveling will depend on few things, including:
- Where you plan to travel . Some countries require proof of vaccination for certain diseases, like yellow fever or polio. And traveling in developing countries and rural areas may bring you into contact with more diseases, which means you might need more vaccines before you visit.
- Your health . If you’re pregnant or have an ongoing illness or weakened immune system, you may need additional vaccines.
- The vaccinations you’ve already had . It’s important to be up to date on your routine vaccinations. While diseases like measles are rare in the United States, they are more common in other countries. Learn more about routine vaccines for specific age groups .
How far in advance should I get vaccinated before traveling?
It’s important to get vaccinated at least 4 to 6 weeks before you travel. This will give the vaccines time to start working, so you’re protected while you’re traveling. It will also usually make sure there’s enough time for you to get vaccines that require more than 1 dose.
Where can I go to get travel vaccines?
Start by finding a:
- Travel clinic
- Health department
- Yellow fever vaccination clinic
Learn more about where you can get vaccines .
What resources can I use to prepare for my trip?
Here are some resources that may come in handy as you’re planning your trip:
- Visit CDC’s travel website to find out which vaccines you may need based on where you plan to travel, what you’ll be doing, and any health conditions you have.
- Download CDC's TravWell app to get recommended vaccines, a checklist to help prepare for travel, and a personalized packing list. You can also use it to store travel documents and keep a record of your medicines and vaccinations.
- Read the current travel notices to learn about any new disease outbreaks in or vaccine recommendations for the areas where you plan to travel.
- Visit the State Department’s website to learn about vaccinations, insurance, and medical emergencies while traveling.
Traveling with a child? Make sure they get the measles vaccine.
Measles is still common in some countries. Getting your child vaccinated will protect them from getting measles — and from bringing it back to the United States where it can spread to others. Learn more about the measles vaccine.
Find out which vaccines you need
CDC’s Adult Vaccine Quiz helps you create a list of vaccines you may need based on your age, health conditions, and more.
Take the quiz now !
Get Immunized
Getting immunized is easy. Vaccines and preventive antibodies are available at the doctor’s office or pharmacies — and are usually covered by insurance.
Find out how to get protected .
Get Vaccinated Before You Travel
It’s important to plan ahead to get the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit.

Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by:
- Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip
- Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines
- Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family’s travel plans
Avoid getting sick or coming back home and spreading the disease to others.
Vaccinate at least a month before you travel
See your doctor when you start to plan your trip abroad. It’s important to do this well in advance.
- Your body needs time to build up immunity.
- You may need several weeks to get all the doses of the vaccine.
- Your primary doctor may not stock travel vaccines. Visit a travel medical clinic .
- You’ll need time to prepare for your pre-travel appointment .
- If the country you visit requires a yellow fever vaccine , only a limited number of clinics have the vaccine and will probably be some distance from where you live. You must get it at least 10 days before travel.
Find out which vaccines are recommended or required for the countries you plan to visit .
TIP : Save time by getting routine vaccines during the same doctor visit. Use the Vaccine Self-Assessment Tool and discuss the results with your doctor. It tells you which U.S. recommended vaccines you (19 years and older) or your child (birth – 18 years) might need.
Last-minute travelers
When traveling to another country be aware your doctor may not carry a travel vaccine and you may have to visit a medical clinic.
Many travel vaccines require multiple shots or take time to become fully effective. But some multiple-dose vaccines (like hepatitis A) can still give you partial protection after just one dose. Some can also be given on an “accelerated schedule,” meaning doses are given in a shorter period of time.
- Discover and learn about specific diseases that can affect you while traveling
- What to do if you get sick after traveling
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Which Vaccinations Are Required for Travel?
By Cassie Shortsleeve

A trip abroad requires you to be up-to-date on a whole checklist of things these days: travel insurance, airline policies, visas, passports , and, as far as your health is concerned, vaccines. Yet while the COVID-19 pandemic has made us acutely aware of the importance of staying healthy on the road, travel vaccines have always been a mainstay of safe travel—a crucial tool in avoiding the (often expensive) headaches of getting sick , and treating sicknesses, abroad.
Whether you have travel on the horizon or want to be prepared for 2023 trips and beyond, this guide will get you up to speed on the vaccinations required for travel depending on your destination, itinerary, and health status. Follow the below steps to protect your immune system in another country.
Make sure you’re current with routine vaccines
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends all travelers be up to date on routine vaccines before travel. Routine vaccines include shots like COVID-19; chickenpox; Hepatitis A and B; Influenza; Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR); Polio; and more. The CDC has a full list of routine vaccines here .
“‘Routinely recommended vaccines’ are vaccines that have been considered very important to prevent common diseases in the population to start,” says Lin H. Chen , M.D. director of the Travel Medicine Center at Mount Auburn Hospital in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and the former president of the International Society of Travel Medicine (ISTM).
Routine vaccines protect against disease that exists at low levels (chickenpox) or barely exists at all (measles) in the U.S. They also protect against severe disease from diseases that are still present in the United States (influenza or COVID-19). Generally, they’re given in childhood or adolescence—though some are given through adulthood—so it’s always a good idea to double-check your vaccination records.
When traveling, routine shots are especially important because international travel increases your chances of both contracting and spreading diseases that aren’t common in the U.S. A good example of this is measles. While it’s practically non-existent in the U.S., international travel increases your risk of exposure and popular destinations including Europe still have measles outbreaks.
It’s worth double checking your status even if you think you’re up to date: “During the pandemic, some routine vaccination programs may have suffered lapses, so there is concern that diseases may become more common,” says Dr. Chen.
The routine vaccination recommendations have also changed over the years (the addition of the COVID-19 vaccine to the list is an example) and it’s easy to let vaccines like tetanus ( generally needed every 10 years ) lapse.
“It is even recommended at this time that certain adults who are traveling who have not had a polio vaccine for many years and are traveling to a risk area get an additional dose of the polio vaccine,” says Elizabeth D. Barnett , M.D., a professor at Boston University Medical School and a leader in the field of travel and tropical Medicine.
If you’re traveling with a child , talk to your pediatrician: Rules around vaccination can be different for babies traveling internationally. A baby who is not leaving the U.S., for example, gets their first dose of the MMR vaccine at 12 months; if they will be leaving the country, they get the first dose at six months .
Utilize official resources to learn more about vaccination recommendations around the world
“Understanding the epidemiology of where diseases are circulating is really important,” says Dr. Chen.
That’s why, generally, she sends travelers to the CDC’s website , which outlines exactly what additional vaccines you may need for essentially every country in the world. All you have to do is plug in your destination and you’ll find information about vaccines and medications, health travel notices, COVID-19 travel information, and more.
Start a conversation with your primary care doctor—then consider seeing a travel medicine specialist
It’s always good to start a conversation with your primary care doctor about vaccines before you travel, but if your itinerary is complex, involving multiple countries, being in rural areas, areas without good hygiene, or areas where you may not be able to protect yourself from mosquito- or food-borne illnesses, or if you have questions based on what you found on the CDC website or your own personal health history, consider asking your physician for a referral to a travel medicine specialist or travel clinic.
After all, when it comes to vaccinations required for travel, it’s not just about where you travel, but how you travel.
“The art of travel medicine is listening to where the person is going, what they're going to be doing, and making a decision based on the risk-benefit ratio,” says Dr. Barnett. A travel medicine doctor will be able to analyze disease trends and trip details such as how long you’ll be traveling or how well you’ll be able to protect yourself against mosquitoes. “You have to really dig into those things,” she says.

Harrison Pierce

María Casbas

CNT Editors

Take a vaccine called the Japanese encephalitis vaccine, which prevents a type of encephalitis (inflammation of the brain). “We can't just say the risk is present in a specific country, because the risk depends on the time of year, whether the disease is being transmitted at that time, the exact location—rural areas, especially farming regions are associated with much higher risk — whether there's a local outbreak situation going on, and more.”
You may not be able to get every shot you need at your primary care doctor’s office either. The yellow fever vaccine, for example (which you may need if you’re traveling somewhere like Sub-Saharan Africa or specific parts of South America), is only available at special travel clinics or public health settings, says Dr. Barnett. You can find a list of travel medicine clinics on the CDC’s website.
Your health background (what diseases you’ve had in the past, whether or not you’re immune-suppressed, and if you’re more predisposed to a certain condition) also play a role in what vaccines to consider. (A very small subset of people vaccinated against yellow fever, for example, experience severe adverse events, says Dr. Barnett.)
The bottom line
For many people and many trips, discussing travel plans with your primary care doctor and using the CDC’s destination feature for vaccine guidance will suffice. Other, more complex trips require a visit to a travel clinic. If you’re aiming to get into one, start the process at least a month before your departure date—appointments can be hard to get and your body needs time to build up immunity from any additional vaccines you may require.
By signing up you agree to our User Agreement (including the class action waiver and arbitration provisions ), our Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement and to receive marketing and account-related emails from Traveller. You can unsubscribe at any time. This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Thanks for visiting! GoodRx is not available outside of the United States. If you are trying to access this site from the United States and believe you have received this message in error, please reach out to [email protected] and let us know.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets
Frequently Asked Questions: Guidance for Travelers to Enter the U.S.
Updated Date: April 21, 2022
Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request. On April 21, 2022, DHS announced that it would extend these requirements. In determining whether and when to rescind this order, DHS anticipates that it will take account of whether the vaccination requirement for non-U.S. air travelers remains in place.
These requirements apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for essential or non-essential reasons. They do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply. See CDC guidance for more details regarding air travel requirements.
Below is more information about what to know before you go, and answers to Frequently Asked Questions about cross-border travel.
Entering the U.S. Through a Land Port of Entry or Ferry Terminal
Q. what are the requirements for travelers entering the united states through land poes.
A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following:
- Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website.
- During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
- Bring a Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative compliant border crossing document, such as a valid passport (and visa if required), Trusted Traveler Program card, a Department of State-issued Border Crossing Card, Enhanced Driver’s License or Enhanced Tribal Card when entering the country. Travelers (including U.S. citizens) should be prepared to present the WHTI-compliant document and any other documents requested by the CBP officer.
Q. What are the requirements to enter the United States for children under the age of 18 who can't be vaccinated?
A: Children under 18 years of age are excepted from the vaccination requirement at land and ferry POEs.
Q: Which vaccines/combination of vaccines will be accepted?
A: Per CDC guidelines, all Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved and authorized vaccines, as well as all vaccines that have an Emergency Use Listing (EUL) from the World Health Organization (WHO), will be accepted.
Accepted Vaccines:
- More details are available in CDC guidance here .
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your dose of an accepted single-dose COVID-19 vaccine;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your second dose of an accepted 2-dose series;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received the full series of an accepted COVID-19 vaccine (not placebo) in a clinical trial;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received 2 doses of any “mix-and-match” combination of accepted COVID-19 vaccines administered at least 17 days apart.
Q. Is the United States requiring travelers to have a booster dose to be considered fully vaccinated for border entry purposes?
A: No. The CDC guidance for “full vaccination” can be found here.
Q: Do U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land POEs and ferry terminals?
A: No. Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or Lawful Permanent Residents (LPRs). Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: Is pre- or at-arrival COVID testing required to enter the United States via land POEs or ferry terminals?
A: No, there is no COVID testing requirement to enter the United States via land POE or ferry terminals. In this respect, the requirement for entering by a land POE or ferry terminal differs from arrival via air, where there is a requirement to have a negative test result before departure.
Processing Changes Announced on January 22, 2022
Q: new changes were recently announced. what changed on january 22.
A: Since January 22, 2022, non-citizens who are not U.S. nationals or Lawful Permanent Residents have been required to be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States at land ports of entry and ferry terminals, whether for essential or nonessential purposes. Previously, DHS required that non-U.S. persons be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States for nonessential purposes. Effective January 22, all non-U.S. individuals, to include essential travelers, must be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request. DHS announced an extension of this policy on April 21, 2022.
Q: Who is affected by the changes announced on January 22?
A: This requirement does not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. It applies to other noncitizens, such as a citizen of Mexico, Canada, or any other country seeking to enter the United States through a land port of entry or ferry terminal.
Q: Do U.S. citizens need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land port of entry or ferry terminals?
A: Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. Citizens, U.S. nationals or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: What is essential travel?
A: Under the prior policy, there was an exception from temporary travel restrictions for “essential travel.” Essential travel included travel to attend educational institutions, travel to work in the United States, travel for emergency response and public health purposes, and travel for lawful cross-border trade (e.g., commercial truckers). Under current policy, there is no exception for essential travel.
Q: Will there be any exemptions?
A: While most non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States will need to be vaccinated, there is a narrow list of exemptions consistent with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order in the air travel context.
- Certain categories of individuals on diplomatic or official foreign government travel as specified in the CDC Order
- Children under 18 years of age;
- Certain participants in certain COVID-19 vaccine trials as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals with medical contraindications to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals issued a humanitarian or emergency exception by the Secretary of Homeland Security;
- Individuals with valid nonimmigrant visas (excluding B-1 [business] or B-2 [tourism] visas) who are citizens of a country with limited COVID-19 vaccine availability, as specified in the CDC Order
- Members of the U.S. Armed Forces or their spouses or children (under 18 years of age) as specified in the CDC Order; and
- Individuals whose entry would be in the U.S. national interest, as determined by the Secretary of Homeland Security.
Q: What documentation will be required to show vaccination status?
A: Non-U.S. individuals are required to be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request regardless of the purpose of travel.
The current documentation requirement remains the same and is available on the CDC website . Documentation requirements for entry at land ports of entry and ferry terminals mirror those for entry by air.
Q: What happens if someone doesn’t have proof of vaccine status?
A: If non-U.S. individuals cannot present proof of vaccination upon request, they will not be admitted into the United States and will either be subject to removal or be allowed to withdraw their application for entry.
Q: Will incoming travelers be required to present COVID-19 test results?
A: There is no COVID-19 testing requirement for travelers at land border ports of entry, including ferry terminals.
Q: What does this mean for those who can't be vaccinated, either due to age or other health considerations?
A: See CDC guidance for additional information on this topic. Note that the vaccine requirement does not apply to children under 18 years of age.
Q: Does this requirement apply to amateur and professional athletes?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions.
Q: Are commercial truckers required to be vaccinated?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions. These requirements also apply to bus drivers as well as rail and ferry operators.
Q. Do you expect border wait times to increase?
A: As travelers navigate these new travel requirements, wait times may increase. Travelers should account for the possibility of longer than normal wait times and lines at U.S. land border crossings when planning their trip and are kindly encouraged to exercise patience.
To help reduce wait times and long lines, travelers can take advantage of innovative technology, such as facial biometrics and the CBP OneTM mobile application, which serves as a single portal for individuals to access CBP mobile applications and services.
Q: How is Customs and Border Protection staffing the ports of entry?
A: CBP’s current staffing levels at ports of entry throughout the United States are commensurate with pre-pandemic levels. CBP has continued to hire and train new employees throughout the pandemic. CBP expects some travelers to be non-compliant with the proof of vaccination requirements, which may at times lead to an increase in border wait times. Although trade and travel facilitation remain a priority, we cannot compromise national security, which is our primary mission. CBP Office of Field Operations will continue to dedicate its finite resources to the processing of arriving traffic with emphasis on trade facilitation to ensure economic recovery.
Q: What happens if a vaccinated individual is traveling with an unvaccinated individual?
A: The unvaccinated individual (if 18 or over) would not be eligible for admission.
Q: If I am traveling for an essential reason but am not vaccinated can I still enter?
A: No, if you are a non-U.S. individual. The policy announced on January 22, 2022 applies to both essential and non-essential travel by non-U.S. individual travelers. Since January 22, DHS has required that all inbound non-U.S. individuals crossing U.S. land or ferry POEs – whether for essential or non-essential reasons – be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request.
Q: Are sea crew members on vessels required to have a COVID vaccine to disembark?
A: Sea crew members traveling pursuant to a C-1 or D nonimmigrant visa are not excepted from COVID-19 vaccine requirements at the land border. This is a difference from the international air transportation context.
Entering the U.S. via Air Travel
Q: what are the covid vaccination requirements for air passengers to the united states .
A: According to CDC requirements [www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/noncitizens-US-air-travel.html | Link no longer valid], most noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily must be fully vaccinated prior to boarding a flight to the United States. These travelers are required to show proof of vaccination. A list of covered individuals is available on the CDC website.
Q: What are the COVID testing requirements for air passengers to the United States?
A: Effective Sunday, June 12 at 12:01 a.m. ET, CDC will no longer require pre-departure COVID-19 testing for U.S.-bound air travelers.
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Airport Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Travel.State.Gov Newsroom
U.S. Passports News
International Travel News
U.S. Visas News
Intercountry Adoption News and Notices
Share this page:
Update on Change to U.S. Travel Policy Requiring COVID-19 Vaccination for nonimmigrant travel
Worldwide Visa Operations: Update
Employment-Based Fourth Preference (EB-4) Announcement
Suspension of Visa Services in Sudan
Diversity Visa 2024 Update
Nonimmigrant Visa Fee Increases to Take Effect June 17, 2023
India EB-3 Retrogression
Expiration of Covid-Era Visa Application Fee Receipts
Digital Visa Authorization (DVA) Proof of Concept
Final Rule Governing Public Charge Grounds of Visa Ineligibility
Visa Waiver Travel for Israeli Citizens
Important Update on Waivers of the Interview Requirement for Certain Nonimmigrant Visa Applicants
Department of State to Process Domestic Visa Renewals in Limited Pilot Program
Visa Information for Nationals of Haiti
Department of State/AILA Liaison Committee Meeting March 20, 2024
The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with an accepted COVID-19 vaccine to board a flight to the United States. CDC’s Amended Order Implementing Presidential Proclamation on Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic will no longer be in effect when the Presidential Proclamation Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic is revoked .
Please see: https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2023/05/01/the-biden-administration-will-end-covid-19-vaccination-requirements-for-federal-employees-contractors-international-travelers-head-start-educators-and-cms-certified-facilities/
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Travelers' Health Most Frequently Asked Questions
On this page, travel vaccines and medications, yellow fever vaccine.
CDC Travelers’ Health Branch provides health advice to international travelers, including advice about medications and vaccines. On this page, you’ll find some of our most frequently asked questions and responses.
1. What vaccines or medicines should I get before traveling to my destination?
A: It depends on where you are going and what you will be doing. Use our destination tool to find the vaccines and medications you need for your next trip, and schedule an appointment with your doctor or a travel medicine specialist at least a month before traveling to get recommended or required vaccines and medicines.
2. If I am going on a cruise that will stop in several countries, which vaccines should I get for each country?

A: You should be up-to-date on routine vaccines, such as measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), tetanus, and flu. Depending on where you’re going and what activities you plan, other vaccines may be recommended. More cruise information .
3. What is the difference between routine, recommended, and required vaccines?
A: Routine vaccines are those that are recommended for everyone in the United States based on their age, health condition, or other risk factors. You may think of these as the childhood vaccines you got before starting school, but some are routinely recommended for adults, like the adult pertussis booster Tdap, and some every year (like the flu vaccine) or every 10 years (like the tetanus booster for adults).
A required vaccine is one that travelers must have in order to enter a country, based on that country’s regulations. Yellow fever , meningococcal, and polio vaccines may be required by certain countries.
Recommended vaccines are those that CDC recommends travelers get to protect their health, even if they aren't required for entry by the government of the country you are visiting. They protect travelers from illnesses that are usually travel-related. For example, a typhoid vaccine can prevent typhoid , a serious disease spread by contaminated food and water, which is not usually found in the United States. The vaccines recommended for a traveler depend on several things, including age, health, and itinerary.
Find out more about travel vaccines . Clinicians: Use our 2-page Quick Guide to Travel Vaccination Recommendations .
4. What are the prices of vaccines needed for travel outside the United States?
A: Prices vary by provider and insurance coverage. You should be able to get routine vaccines from your primary health care provider, health clinic, or health department. Travel clinics and yellow fever vaccine clinics should be able to give you any vaccines that your health care provider cannot.
5. How long do travel vaccines last (when do I need to get a booster dose)?
A: How long travel vaccines last depends on the vaccine. If you're traveling outside the United States, you should see a health care provider who is familiar with travel medicine at least a month before your trip. They can give you advice about any vaccines and vaccine boosters based on where you are going and your previous vaccinations. Be sure to bring your vaccine records to your appointment!
6. Which medications can I travel with?
A: When packing for trips abroad, don’t forget there may be special considerations for bringing your prescriptions and other medicines with you. Some medicines that are commonly prescribed or available over-the-counter in the United States can be illegal in other countries. Check with the embassy or consulate in the country you will be visiting to make sure your medicines are permitted in that country.
See your health care provider at least a month before you go to get any needed or extra medications, and pack medications in your carry-on in case your luggage is lost.

7. Which countries require yellow fever vaccine for travel?
A: Some countries in South America and Africa require you to provide proof that you have been vaccinated against yellow fever by presenting an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis when entering the country. However, there are other popular travel destinations where the threat of infection with yellow fever virus is very real, and there is no requirement for you to be vaccinated to enter the country.
If you only get the yellow fever vaccine before going to countries that require it, you could be putting your health at risk. Since yellow fever disease can be serious or even fatal, CDC recommends that individuals be vaccinated when traveling to any areas where there is a risk of acquiring infection with yellow fever virus. Use our destination tool to find out which vaccines the CDC recommends you have for anywhere you travel around the world and talk to a travel medicine provider for more details.
Yellow fever vaccine is only available at yellow fever vaccine clinic , so call ahead (well in advance of travel) and book your appointment.
Even if you get the yellow fever vaccine, you can still get other diseases from mosquito bites, like malaria, dengue, and Zika. The best ways to prevent mosquito-borne diseases are to use insect repellent while outdoors, wear long pants and long sleeves, and choose accommodations with air conditioning or mosquito nets. For travel to areas where malaria is a risk , taking medicine that can prevent malaria may also be advised.
8. How far in advance of my trip do I need to get the yellow fever vaccine?
A: For most people, it takes up to 10 days after the vaccine is given to be protected against the yellow fever virus . If your destination requires yellow fever vaccine, the proof of vaccination does not become valid until 10 days after the vaccine is given.
9. Where can I get a yellow fever vaccine in my area?
A: The nearest yellow fever vaccination clinic may be far away from where you live, and appointments may be limited. Be sure to contact the clinic ahead of time.
10. Who should not get the yellow fever vaccine?
A: Some people should not get the yellow fever vaccine : infants younger than 6 months, or people with a history of a bad reaction to the vaccine should not receive yellow fever vaccine. If you have a thymus disorder associated with abnormal immune cell function (such as a thymoma or myasthenia gravis) you should not receive yellow fever vaccine. If cancer, or the drugs or radiation used to treat cancer, has weakened your immune system, you should not receive yellow fever vaccine. If you received an organ transplant and take medicines to prevent rejection of that transplant, you should not receive yellow fever vaccine. Other conditions and medicines can also affect your immune system and could be a reason not to receive yellow fever vaccine. Check with your doctor to find out more.
If you are older than 60 years old, pregnant, or breastfeeding, talk to your doctor before getting a yellow fever vaccine. There are potential risks to your health from the vaccine. If you are infected with HIV, talk to your doctor; you may still be able to get yellow fever vaccine, depending on your CD4 cell count and immune function. Infants 6–8 months old can receive yellow fever vaccine, although it is less risky to postpone travel to areas with yellow fever until the baby is 9 months of age or older. After the age of 9 months, the health risks from the vaccine are considerably lower.

11. Is Zika a risk in my next destination?
A: Check our world map of areas with risk of Zika for the most up-to-date information before you make international travel plans. Please be advised: CDC does not track the number of Zika cases outside the United States.
It is difficult to determine the risk of Zika in other countries. Zika frequently causes only mild symptoms, and people with Zika might not go to the doctor. If they go to a doctor, the doctor might not test for Zika or report cases to the government. A lack of reported cases does not mean a lack of risk. CDC considers any country that has ever had Zika cases to have possible risk, but we cannot say how high or low that risk is.
CDC now recommends pregnant women and couples trying to become pregnant within the next 3 months first talk to their healthcare providers and carefully consider the risks and possible consequences of Zika infection before traveling to areas that report past or current spread of Zika but no current outbreak. Pregnant women: avoid mosquito bites and sexual exposure during travel. If partner travels, avoid sex or use condoms for remainder of pregnancy. Women planning to conceive may wish to delay pregnancy,
CDC continues to recommend that pregnant women not travel to areas where a Zika outbreak is occurring.
12. How can I contact the local US embassy?

A: 1. Enroll with the nearest US embassy or consulate through the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) . It’s a FREE service that allows US citizens traveling or living abroad to receive the latest security updates for their location. 2. If you need to contact a US embassy or consulate, call 1-888-407-4747 (from the US or Canada) OR 00-1-202-501-4444 (from other countries).
Travel healthy, from CDC’s Travelers’ Health!
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
AITC Immunization & Travel Clinic
We provide travel health visits, vaccinations, TB testing, and blood tests. Appointment only.
Attention! starting April 15, 2024
Our new website address is SF.GOV/AITC

AITC Services, Price, and Forms
Book an appointment on line and get clinic forms
See our services and prices
Donate to AITC
Welcome to AITC
AITC is a non-profit clinic that is part of the San Francisco Department of Public Health (SFDPH). As public health providers, our mission is to prevent disease and protect the health of all.
We are open to the public, and serve all members of the community, including:
- Teens and adults seeking recommended vaccinations
- School age children needing vaccines required for school
- Adults who need vaccines for work or school
- Immigrants to the US requiring vaccines for Change of Status
- Individuals and families planning international travel
Our services are by appointment only.
AITC is unable to accept insurance. Fees must be paid at the time of service. Low-cost or free services are available to those who qualify.
Message about our MPOX vaccine (JYNNEOS) supply
Mpox vaccine at AITC is still supplied free of charge by the government. Later in 2024 we may need to purchase the vaccine and charge a fee for it. We will post more information when it becomes available.
Getting here
Metered street parking or Civic Center Garage
Public transportation
Southwest corner, Civic Center Plaza Across from City Hall BART / MUNI : Civic Center Station
Make an appointment online by clicking the left link. It is highly recommended; it is simpler and faster.
If you need assistance, please call us.
AITC Immunization & Travel Clinic
Mon to Fri, 9:00 am to 4:00 pm Closed for lunch 12 pm - 1pm
We are closed weekends and holidays .
Find more information about how to get to our clinic .
Departments
Advertisement
Supported by
What to Know About Testing and Vaccine Requirements for Travel
Do you need to be vaccinated or have a negative Covid-19 test for your next trip? Check this guide before traveling domestically or abroad.
- Share full article

By Concepción de León
As vaccinations ramp up and regulations loosen for people in the United States, many are planning travel for summer and beyond, with experts predicting that July 4 will be the biggest travel weekend since the beginning of the pandemic.
But with regulations shifting, people might have questions about testing or vaccination requirements for their trips. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently eased travel recommendations to more than 100 countries. On June 18, the European Union added the United States to its “safe list” of countries , meaning that both vaccinated and unvaccinated American travelers should now be able to visit the 27 member countries, but these member states are allowed to set their own requirements and restrictions for travelers.
In the United States, the C.D.C. has advised that vaccinated people no longer need to wear masks in most places and released new travel guidelines that said domestic travel is safe for them. But travelers must take note of local advice and regulations, as these can vary state by state.
Here’s everything you need to consider about testing and vaccinations before you travel within the U.S. or internationally.
Are there testing and vaccination requirements for domestic travel?
For most places, no. You do not need to be vaccinated for any domestic travel. Hawaii is the only state that requires a negative test for travel.
In Hawaii, the test must be administered within 72 hours of arrival and the results uploaded to its Safe Travel platform to avoid a mandatory quarantine when entering the state.
Alternatively in Hawaii, you can also provide proof that you’ve recovered from Covid-19 in the past 90 days, including both a positive test result and a letter from a doctor clearing you to travel.
The state’s governor, David Ige, said this month that people who received their vaccination in the state of Hawaii may bypass testing and quarantine requirements starting on June 15, and that anyone vaccinated in the U.S. will be able to enter Hawaii without testing once the state has reached a 60 percent vaccination rate.
If you are unvaccinated, you should continue to adhere to social distancing and mask-wearing protocols while traveling domestically, the C.D.C. said . You can use the C.D.C.’s Travel Planner to check guidelines by state.
What are the testing and vaccination rules for international travel?
While testing and vaccination requirements vary by destination country, everyone arriving in the U.S. — even vaccinated Americans — must present a negative test result upon entry .
Many nations are still closed to American travelers. Those that are open may require a negative test, proof of vaccination or evidence of recovery (or a combination of these) to enter.
The United Kingdom , for instance, requires that American travelers, regardless of vaccination status, provide proof of a negative test taken within 72 hours of departure, quarantine upon arrival and take two additional tests during their stay. Children under 11 are exempt from these requirements, as are some other people depending on their reason for travel.
Some European countries have been allowing in Americans who are vaccinated or who can show a negative test. Americans are on the European Union’s “safe list” of countries, but while the bloc aims to take a coordinated approach to travel this summer, member states will be allowed to set their own requirements for travelers from individual countries, which could include testing and vaccination.
The E.U. “safe list” also applies to Europe’s border-free Schengen Zone, which includes non-E.U. countries such as Norway, Switzerland, Iceland and Lichtenstein.
Canada is still closed to Americans , with few exceptions, and will remain so until at least early July, said Patty Hajdu, the country’s minister of health, in a news conference in June.
The U.S.-Mexico land border is closed for nonessential travel until at least June 21, but air travel is allowed and the country does not require a negative test for entry. Because of its high risk level, the C.D.C. recommends that travelers be fully vaccinated before traveling to Mexico.
Consult the C.D.C.’s inventory of international travel health notices for more information on regulations by country.
“Travelers should always check with their airline and the embassy of the country they are visiting to ensure they have the proper documentation required to enter the country,” said Perry Flint, a spokesman for The International Air Transport Association, a global airline industry group.
What test should I take, and where and when?
To enter the U.S., travelers must show a negative result to a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) — PCR is a type of NAAT test — or an antigen test, also known as a rapid test, taken in the three days before departure, according to the C.D.C .
Some airports offer on-site testing, such as Heathrow Airport in England, or Rome’s Fiumicino International Airport in Italy.
Josh Alexander, a New York-based luxury travel agent for Protravel International, said that many international hotels, including most Four Seasons hotels and resorts , are offering on-site rapid tests for free or at a nominal cost.
Testing at local clinics is also available in many places, though you should check availability at your destination ahead of time and book if you can. It may also come at a high cost. Mr. Alexander said that PCR tests abroad can range from $50 to $150.
The C.D.C. said that it allows for a three-day time frame rather than 72 hours to allow flexibility in the time of day the test can be taken. For instance, if you are flying out on a Friday, the test may be taken at any time on Tuesday.
But, when it comes to international destinations, Mr. Alexander recommends erring on the side of caution when timing your test by calculating it based on time of arrival at your destination.
“Rules are constantly changing,” he said, “so we’re just trying to always tell people they should always be as conservative as possible to eliminate any gray area.”

What are the requirements for minors?
The C.D.C. testing recommendations apply to all children 2 years and older, which means your toddler also needs to deliver a negative Covid-19 test to enter the U.S. from abroad. When traveling, children should wear masks, practice social distancing and wash hands often, the C.D.C. said .
“If the kids are age 12 and older, get ’em vaccinated,” said William Schaffner, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, in an email.
If you’re traveling to a country within the European Union that is open to travelers from the U.S., children who cannot be vaccinated should have a negative PCR test taken no more than 72 hours before arrival at your destination, and additional testing may be required upon arrival.
Travelers should check with their airline or destination country website for relevant requirements.
What if I want to go on a cruise?
Rules vary from one cruise line to another, with some planning to require that all passengers and crew be vaccinated, and others adopting a hybrid model.
But recent laws passed in Florida and Texas banning businesses from requiring proof of vaccination to use their services may complicate this plan.
Celebrity Cruises, set to be the first U.S. cruise ship to restart operations on June 26 from Fort Lauderdale, Fla., said it’s optimistic that a resolution would be reached in time . It is requiring that guests 16 years and older be vaccinated, while children will be tested at the terminal.
Carnival Cruises said on Monday that its first ship would set sail from the Port of Galveston, in Texas, on July 3 and would be available only for vaccinated passengers. Norwegian, which will begin to operate cruises from Miami in August, said it will require the same through October 31 and has threatened to skip Florida ports if the state does not allow cruise lines an exemption from the law banning vaccine requirements.
Christine Duffy, the president of Carnival Cruise Line, said in a statement on June 7 that “the current CDC requirements for cruising with a guest base that is unvaccinated will make it very difficult to deliver the experience our guests expect, especially given the large number of families with younger children who sail with us.”
“As a result, our alternative is to operate our ships from the U.S. during the month of July with vaccinated guests,” she said.
But even if you are vaccinated, you must also consider the requirements of the country where the cruise is disembarking. The Caribbean island of St. Maarten, for instance, where Celebrity Cruises started sailing on June 5, requires a negative test in addition to proof of vaccination.
What documents should I bring with me if I travel?
This will also depend on where you’re going, but a good rule of thumb is to carry your physical vaccine card, if you have it, and proof of a negative test, if it is required.
Mr. Alexander, the travel agent, recommends people bring the original documents. While a number of digital health certificates — which show vaccine status and test results — are in the works, he said, they are not yet widely accepted. You should check, also, that your document is in the correct language. The United Kingdom , for instance, requires that test results be in English, Spanish or French.
CommonPass , from the Geneva-based nonprofit the Commons Project Foundation, and the I.A.T.A. Travel Pass are two apps providing digital access to vaccine and testing records for travel. The European Union will be releasing its own digital Covid certificate for E.U. citizens by July 1, though it is unclear whether Americans will be able to use it.
You should check with your airline to see if the app you want to use will be accepted at your destination. Both the CommonPass and I.A.T.A. websites list destinations and airline partners accepting the digital health certificates.
Mr. Alexander added that some countries, such as Croatia, may also require proof of a return flight or confirmation of your hotel booking or other accommodation, though this is rare. In South Africa, which has implemented a curfew, travelers may need to show their flight ticket to law enforcement officers to show they are allowed to be in transit.
But these shifting regulations should not dissuade people from traveling, Mr. Alexander said.
“If you’re vaccinated and you’re following safe precautions, you can still have a great experience,” he said.
Concepción de León is a travel reporter based in New York. More about Concepción de León

- About the Handbook
Vaccination for international travellers
Ensure that travellers are up to date with routine vaccines. Also consider other vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and risk of disease exposure.
Recently added
This page was added on 09 June 2018 .
Updates made
This page was updated on 23 October 2023 . View history of updates
Millions of Australians travel overseas every year. More than half of these trips are to destinations other than New Zealand, North America and Europe. 1
This page helps with making decisions about travel vaccines. Also check the disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for details about specific vaccines.
See also Infographic. Vaccination for international travellers .
Health risks of overseas travel
Health risks associated with international travel include exposure to:
- infective agents
- altitude and temperature extremes
- other physical, psychological and environmental hazards
- poor-quality or limited access to clean water, shelter, hygiene and sanitation facilities, and health and medical care
The level of health risks depends on factors such as:
- the traveller’s underlying physical and mental health and physiological state
- the itinerary and activities undertaken
- the duration of exposure to various hazards during travel
Travellers at increased risk of serious travel-associated infections include:
- young children and infants
- pregnant women
- people with underlying medical conditions, especially immunocompromising conditions due to disease or medical treatment
- people spending extended periods in multiple regions with poor resources or in remote areas
- people participating in events where large numbers of people will gather, such as major sporting, cultural, social or religious events
- migrant families travelling back to their region of origin to visit friends and relatives
Those travelling to visit friends and relatives are more likely to: 2
- have closer contact with local populations
- stay in remote or rural areas
- consume higher-risk food and beverages
Those travelling to visit friends and relatives are less likely to: 2,3
- recognise the health risks associated with travelling
- seek pre-travel health advice
- obtain the recommended vaccines or prophylaxis
Common infections acquired by travellers
Exposure to infectious diseases is one of the many health hazards of international travel. Some of these diseases are vaccine preventable. Although some of these diseases are present in Australia, the risk of acquiring them overseas may be higher because of:
- higher disease incidence in other countries
- increased risk of exposure from participating in certain activities while travelling
Foodborne and waterborne infections
It is common for travellers to ingest contaminated food or beverages, resulting in an illness. 4-6 Practicing safe eating and drinking habits is essential to minimise the risk of contracting food and waterborne diseases while travelling. These include treating water or only drinking bottled water, avoiding undercooked meat, and avoiding raw fruit and vegetables (unless they can be peeled or washed in safe water prior to eating). Most infections are diarrhoeal diseases due to enteric pathogens, but some are due to extra-intestinal microorganisms, such as hepatitis A virus and Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi (causing typhoid).
Vaccines are available against hepatitis A, typhoid and cholera.
Vector-borne infections
Insect-borne — especially mosquito-borne — infections, such as malaria and dengue, are important causes of fever in Australian travellers returning from endemic areas, particularly Southeast Asia and Oceania. 4,6
A dengue vaccine (Dengvaxia) is available for the prevention of secondary dengue infections (not primary prevention of initial dengue infection ) in select individuals. See Clinical advice: ATAGI statement on use of Dengvaxia® for Australians .
Japanese encephalitis occurs throughout much of Asia and the Western Pacific region, including eastern Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. 7 Yellow fever occurs only in parts of Africa and South America, 8 and tick-borne encephalitis occurs in parts of Europe and Asia. 9
Vaccines are available against Japanese encephalitis , yellow fever and tick-borne encephalitis .
Some other vector-borne diseases and parasitic (including protozoal and helminthic) diseases are also important for international travellers. Some are preventable through appropriate barrier precautions and chemoprophylaxis (for example, malaria). 9
Aerosol-borne infections
Vaccine-preventable infections transmitted by aerosols and/or droplets include: 9
- influenza (the most common vaccine-preventable infection among travellers) 10
- meningococcal disease
- varicella (chickenpox)
The incidence of measles and mumps is higher in many overseas countries, including some developed countries, than in Australia.
Tuberculosis is a rare infection in travellers. 11 Expatriates who live in endemic areas for a long time are more likely to acquire tuberculosis than short-term visitors. 12
Vaccines are available against all of these diseases.
Bloodborne and sexually transmitted infections
Some Australian travellers may be at risk from bloodborne and sexually transmissible infections, such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV. In some areas, healthcare workers using non-sterile medical equipment or other poor infection control practices may transmit these viruses and other bloodborne agents.
Vaccines are available against hepatitis B.
Exotic infectious agents
Travellers may be exposed to a variety of other exotic infections, such as:
- rabies from bites or scratches from rabid dogs, bats and other mammals in many countries
- schistosomiasis from exposure to water infested with the parasites, especially in Africa
- leptospirosis through activities such as rafting or wading in contaminated streams
Of these diseases, vaccines are available only against rabies.
Recommending travel vaccines
Although recommending appropriate vaccines is important, it is not the only part of a pre-travel medical consultation. Travel vaccines — those relevant for travelling — include all relevant vaccines, not just the ones that prevent diseases that most commonly occur overseas.
Do not recommend a vaccine based only on the destination country, because there is no single ‘correct’ list of vaccines for travel to any particular country.
There are 3 categories of travel vaccines:
- routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas)
- selected vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure
- vaccines required by the International Health Regulations 2005 (IHR) or for entry into specific countries
Questions for a pre-travel medical consultation
During a pre-travel medical consultation, ask questions about the traveller’s:
- personal information, including age and whether they are pregnant or planning pregnancy
- underlying medical conditions, particularly immunocompromising conditions, and current medicines
- vaccination history (including adverse events following immunisation) and allergy history
- purpose of travel and intended activities, especially those associated with various environmental risks and hazards
- plans for travel insurance
Also ask about their itinerary in detail, including:
- date of departure and time available for vaccinations
- specific localities and routes
- rural versus urban stay
- duration of stay
- likely access to health care and other services
- likelihood of changing the planned itinerary
This information helps to tailor recommendations about preventive vaccination or chemoprophylaxis for exposure risks during the proposed trip. It also allows the clinician to advise about other appropriate preventive health measures (for example, food and water precautions, avoiding bites from mosquitoes or other arthropods) and about managing possible health conditions during travel.
Organisational requirements for vaccination
Some overseas organisations, such as schools, colleges and universities, require evidence of vaccination or immunity against some vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles and meningococcal disease. Consider these requirements when planning and scheduling vaccines before departure.
Routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas)
Vaccinate all prospective travellers according to the recommended vaccination schedule appropriate for their age, underlying health conditions, occupation and lifestyle. Vaccines might include, for example, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for an older person, or hepatitis B vaccine for a first aid officer.
Also ensure that all children are vaccinated according to the National Immunisation Program schedule. In exceptional circumstances, give the National Immunisation Program vaccines at the minimum age rather than the recommended age (see Table. Minimum acceptable age for the 1st dose of scheduled vaccines in infants in special circumstances ). Children vaccinated using the minimum age rather than the recommended age may need extra vaccine doses to ensure adequate protection. Observe the minimum interval requirements between doses (see Table. Minimum acceptable dose intervals for children <10 years of age ). The chances of being exposed to some diseases, such as measles and mumps, may be greater during overseas travel, even to other developed countries.
For some itineraries, it may be appropriate for the traveller to receive some booster doses earlier than the routine recommended time. An example may be diphtheria-tetanus booster.
Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis
Vaccinate adult travellers against tetanus before departure, particularly if:
- their risk of sustaining a tetanus-prone wound is high
- there could be delays in accessing health services where they can receive tetanus toxoid boosters safely, if required
Offer dTpa vaccine during a pre-travel consultation if the traveller has never received a dose of dTpa . This provides protection against pertussis (see Pertussis ).
For high-risk travel, consider giving a booster dose of either dTpa or dT vaccine if more than 5 years have passed (see Tetanus ).
Hepatitis B
Most Australian children born since 2000 have been vaccinated against hepatitis B under the National Immunisation Program or state and territory school-based vaccination programs.
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for long-term or frequent travellers to regions of intermediate or high endemicity of hepatitis B, including:
- Central and South America
This is because travellers may be exposed to hepatitis B virus through bloodborne routes (including during emergency medical or dental procedures) or sexual routes. According to 1 survey, about half of Australian travellers who spent at least 3 nights in Southeast or East Asia participated in at least 1 activity that had a risk of hepatitis B transmission. 13
See also Hepatitis B .
Influenza and pneumococcal disease
Older travellers and those with any relevant underlying medical or behavioural risk factors should receive pneumococcal vaccine. See Pneumococcal disease for more details.
Consider influenza vaccine for all travellers, especially if they are travelling to a region during its influenza season. Influenza vaccine is particularly relevant if:
- there is an influenza epidemic at the traveller’s destination
- the person is travelling in a large tourist group, especially one that includes older people
- the person is travelling on cruises, where people are relatively confined for days to weeks
See also Influenza.
Measles, mumps and rubella
Inadequately vaccinated young adult travellers are responsible for most current measles outbreaks in Australia. This occurs when they acquire the infection overseas and bring it back to Australia. Some countries, regions or communities — including developed countries — have a higher incidence of measles and mumps than Australia. 9
Australians born during or since 1966 who have not received the recommended 2 doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella)–containing vaccines are recommended to receive MMR vaccine before travelling. This also applies to infants 6–12 months old travelling to areas with measles outbreaks or where measles is endemic . The exception is for pregnant women, because MMR is a live vaccine and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
People born before 1966 do not need to receive measles-containing vaccine (unless serological evidence indicates that they are not immune). This is because circulating measles virus and disease were prevalent before 1966, so most people would have acquired immunity from natural infection .
However, confirmed cases of measles have occurred in people born before 1966. 14 If in doubt about a person’s immunity, it may be faster and easier to vaccinate the person than conduct serological testing . See Serological testing for immunity to measles .
See also Measles .
Unvaccinated travellers are recommended to receive varicella vaccine if they either:
- have not had clinical disease, or
- have an uncertain history of clinical disease and serology shows a lack of immunity
The exception is for pregnant women, because varicella vaccine is a live vaccine and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
See also Varicella .
Meningococcal disease
Vaccination against meningococcal serogroups A, C, W-135, Y and B is recommended for certain age and population groups who are at increased risk of meningococcal disease.
In addition, MenACWY (quadrivalent meningococcal) vaccine is recommended for people who are:
- planning travel to, or living in, parts of the world where epidemics of serogroup A, C, W-135 or Y meningococcal disease occur, particularly the ‘meningitis belt’ of sub-Saharan Africa 15
- planning travel to mass gatherings, such as pilgrims travelling to the Hajj in Saudi Arabia
Seek up-to-date epidemiological information to determine whether a traveller needs meningococcal vaccination. See Accessing up-to-date travel information.
The Saudi Arabian authorities require that all pilgrims travelling to Mecca (for the Hajj or Umra) have evidence of recent vaccination with the quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine. 16 See Requirements for travellers to Mecca and Accessing up-to-date travel information .
See also Meningococcal disease .
Poliomyelitis
Ensure that all travellers are age-appropriately vaccinated against polio (see Poliomyelitis ).
If the person is travelling to a country where wild poliovirus is still circulating, they should receive inactivated poliovirus ( IPV ) vaccine if they have not completed a 3-dose primary course of any polio vaccine. Travellers who have completed the primary course should receive a single booster dose.
The World Health Organization (WHO) Global Polio Eradication Initiative website website has an up-to-date list of polio-affected countries.
Documented evidence of polio vaccination is not routinely required for travellers under the International Health Regulations. However, documented evidence of vaccination may be temporarily required according to WHO recommendations in response to new evidence of the spread of wild poliovirus (see Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries and Documentation and certificates ).
International polio epidemiology and associated travel requirements can change. Check the Australian Government Department of Health website for current recommendations for Australian travellers .
Ensure that all travellers are age-appropriately vaccinated against COVID-19. Foreign governments may require evidence of COVID-19 vaccination before a traveller is allowed to enter. The Australian-issued International COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate is a secure way to prove COVID-19 vaccination history that has been developed to meet agreed international travel standards. Parents and carers of children <14 years of age, adolescents ≥14 years of age and adults can get a copy of their COVID-19 vaccination certificate at any time:
- using their Medicare online account through myGov
- through the Medicare Express Plus mobile app
- by calling 1800 653 809 (free call)
See also COVID-19 .
Vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure
Use a risk assessment approach when recommending travel vaccines. Weigh the potential risks of disease exposure and protective benefits from vaccination against potential adverse effects, and the non-financial and financial costs of vaccination.
Prioritise vaccines for diseases that are:
- common and of significant impact, such as influenza and hepatitis A
- less common, but have severe potential adverse outcomes, such as Japanese encephalitis and rabies
Consider booster doses, where appropriate (see disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for recommendations). If the person is departing for travel soon, consider an accelerated schedule, if appropriate, such as for hepatitis B vaccine or the combination hepatitis A-hepatitis B vaccine (see Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B ). Although immunity may be established sooner with the accelerated schedule, people who receive an accelerated schedule need another dose about a year later to complete the course and ensure long-term protection.
Most travellers do not need cholera vaccine. 16,17 The risk of a traveller acquiring cholera is very low if they avoid contaminated food and water.
No country requires travellers to have certification of cholera vaccination. No country has official entry requirements for cholera vaccination
See also Cholera .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for all travellers ≥1 year of age travelling to moderately or highly endemic countries (including all developing countries). The exceptions are people who have evidence of natural immunity after previous infection .
Normal human immunoglobulin is no longer used to protect travellers against hepatitis A.
See also Hepatitis A .
Japanese encephalitis
While now considered an emerging disease in Australia, Japanese Encephalitis is more likely in travellers to endemic regions overseas. 18 Japanese encephalitis ( JE ) vaccine is recommended for travellers spending a month or more in endemic areas in Asia, Papua New Guinea or the outer islands of Torres Strait during the JE virus transmission season.
Consider JE vaccination for shorter-term travellers, particularly if:
- travel is during the wet season
- travel may be repeated
- the person will spend a lot of time outdoors
- the person’s accommodation has no air-conditioning, screens or bed nets
Check a reputable source before travel for information about JE virus activity — for example, Health Information for International Travel (the ‘Yellow Book’) . 19
A traveller’s overall risk of acquiring JE in these JE - endemic countries is likely to be low (<1 case per 1 million travellers). Determine the specific risk according to the: 17
- season of travel
- regions visited
- duration of travel
- extent of outdoor activity
- extent to which the person avoids mosquito bites
See also Japanese encephalitis .
Before travel to rabies- endemic regions, advise people about:
- the risk of rabies infection
- avoiding close contact with wild, stray and domestic animals — especially dogs, cats, monkeys and bats
- the importance of appropriate immediate wound care of all animal bites and scratches
See also Rabies and other lyssaviruses, including Australian bat lyssavirus .
Recommendations for rabies vaccination as pre-exposure prophylaxis
When deciding whether to give a pre-travel prophylactic rabies vaccination, assess the:
- likelihood of exposure to potentially rabid animals
- access to appropriate health care and availability of post-exposure prophylaxis , including rabies immunoglobulin , should there be an at-risk exposure
- timeliness of access to health care after exposure
Use a lower threshold for recommending rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis for children travelling to endemic areas.
Benefits of vaccination as pre-exposure prophylaxis
Pre-travel rabies vaccination:
- ensures that the traveller has received a safe and efficacious vaccine
- simplifies the management of a subsequent exposure because the person will need fewer doses of vaccine
- means that rabies immunoglobulin — which is often extremely expensive, and difficult or even impossible to obtain in many developing countries — is not needed
- reduces the urgency of post-exposure prophylaxis
Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is caused by a tick-borne RNA flavivirus. The disease may involve the central nervous system. TBE is prevalent in parts of central and northern European temperate regions, and across northern Asia. Travellers are at risk when hiking or camping in forested areas in endemic regions during the summer months.
Safe and effective vaccines are available. Vaccination is recommended only for people with a high risk of exposure.
TBE vaccine is not registered in Australia, but a small stock of vaccine may be available for use under the Special Access Scheme .
Tuberculosis
Vaccination with BCG (bacille Calmette–Guérin) vaccine is generally recommended for tuberculin-negative children <5 years of age who will be staying in high-risk countries for an extended period (3 months or longer).
Vaccinating older children and adults appears to be less beneficial. However, consider vaccinating tuberculin-negative children aged ≥5 years but <16 years who may be living or travelling for long periods in high-risk countries.
A high-risk country is one that has a tuberculosis incidence of >40 per 100,000 population.
For travellers who need BCG vaccine, consider the following precautions when scheduling their vaccination visits:
- If possible, give BCG vaccine at least 3 months before the person will arrive in an endemic area.
- Give other live viral vaccines (for example, MMR , varicella, yellow fever) at the same time or with a minimum 4-week interval after BCG vaccination.
- A tuberculin skin test (TST; Mantoux), performed by trained and accredited healthcare practitioners, is recommended before receiving BCG vaccine for all individuals (except infants aged <6 months).
- People may suppress reactions to tuberculin for 4–6 weeks after viral infections or live viral vaccines, particularly measles infection and measles-containing vaccines.
State and territory tuberculosis services can provide tuberculin skin tests and BCG vaccine.
See also Tuberculosis .
Typhoid vaccine may be recommended for travellers ≥2 years of age travelling to endemic regions, including:
- the Indian subcontinent
- most Southeast Asian countries
- several South Pacific nations, including Papua New Guinea
This advice is also relevant for those travelling to endemic regions to visit friends and relatives.
Inactivated parenteral and live oral typhoid vaccine formulations are available.
See also Typhoid fever .
Yellow fever
Yellow fever vaccine is recommended for all people ≥9 months of age travelling to, or living in, an area with a risk of yellow fever virus transmission. 20
To minimise the risk of introducing yellow fever, some countries require documented evidence of yellow fever vaccination for entry, in line with the International Health Regulations (see Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries ).
When assessing the need for yellow fever vaccination, consider:
- the risk of the person being infected with yellow fever virus
- country entry requirements
- individual factors such as age, pregnancy and underlying medical conditions
Vaccination is generally not recommended for travel to areas with a low probability of yellow fever virus exposure — that is:
- where human yellow fever cases have never been reported
- where evidence suggests only low levels of yellow fever virus transmission in the past
However, consider vaccination for a small subset of travellers to lower-risk areas who are at increased risk of exposure to mosquitoes or who are unable to avoid mosquito bites. 20
People aged ≥60 years are at increased risk of severe adverse events after primary yellow fever vaccination. Weigh the adverse effects of vaccinating people in this age group against the potential for yellow fever virus exposure and, in turn, the benefits of vaccination. 17
See also Yellow fever .
Booster doses
Most people do not need a booster dose of yellow fever vaccine. A single dose induces protective antibody levels that last for many decades. However, certain people are recommended to receive a booster if their last dose was more than 10 years ago and they are at ongoing risk of yellow fever virus infection . See Yellow fever .
Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries
Yellow fever requirements.
The International Health Regulations require yellow fever vaccination for travelling in certain circumstances. This is to:
- protect travellers who are likely to be exposed to yellow fever
- stop importation of the virus into countries that have the relevant vectors (see Yellow fever ).
Some countries may require documented evidence of yellow fever vaccination as a condition of entry or exit (see Planning and documenting vaccines ). This includes countries that do not currently have yellow fever circulating.
Australia’s yellow fever travel requirements are detailed in the Australian Government Department of Health’s yellow fever fact sheet .
Contact the relevant embassies or consulates in Australia to confirm the entry requirements for yellow fever vaccination for the countries a traveller intends to enter or transit through.
Requirements for travellers to Mecca
Each year, Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Health publishes the requirements and recommendations for entry visas for travellers on pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj and Umra). 16
For pilgrims travelling directly from Australia, only evidence of MenACWY vaccination is currently mandatory. However, check the current requirements when advising prospective Hajj and Umra pilgrims (see Meningococcal disease and Accessing up-to-date travel information ).
Temporary requirements
The International Health Regulations may temporarily introduce requirements for other vaccine-preventable diseases in response to changes in disease epidemiology that are of international health concern. An example is for polio vaccination.
Because country vaccination requirements are subject to change at any time, confirm all current vaccination requirements for the countries a traveller intends to enter or transit through before travel. See Poliomyelitis and Accessing up-to-date travel information .
Planning and documenting vaccines
Ideally, start vaccination courses early enough before departure to allow:
- monitoring of any possible adverse events
- time for adequate immunity to develop
Requirements for multiple vaccines
A traveller may need multiple vaccines before they depart. Apply the standard recommendations and precautions when giving multiple vaccines (see Administration of vaccines ).
A traveller may need more than 1 clinic visit if they need multiple vaccines or doses (for example, rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis or hepatitis B vaccine). Pay special attention to scheduling of these visits, and consider:
- dose interval precautions (for example, for multiple live vaccines)
- requirements for pre-vaccination tests (for example, tuberculin skin test)
- potential interference by some antimalarials, if relevant (for example, rabies vaccine)
Documentation and certificates
It is important to document travel vaccines:
- in the clinic’s record
- in the traveller’s record that they can carry with them
- on the Australian Immunisation Register
The record should also include all the other routinely recommended vaccines that the traveller has ever received.
For yellow fever vaccination, a traveller needs to have an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), which only Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres can provide under the International Health Regulations (see Yellow fever ).
Travellers may also need an ICVP for other vaccine-preventable diseases, such as polio, based on temporary recommendations.
See also Accessing up-to-date travel information .
Vaccinating travellers with special risk factors
See Vaccination for women who are planning pregnancy, pregnant or breastfeeding , Vaccination for people who are immunocompromised and the disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for recommendations for travellers who are pregnant or immunocompromised.
Accessing up-to-date travel information
International travellers’ health risks constantly change. Up-to-date information, and knowledge of the changing epidemiology and current outbreaks of infectious and emerging diseases are essential. Reliable online information sources include:
- World Health Organization (WHO) for disease outbreak news, and its Travel and health section for specific advice on travel and health, including travel vaccination recommendations
- Travelers’ health , United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Travel health information , Australian Government Department of Health
- Smartraveller , the Australian Government’s travel advisory and consular information service, which provides up-to-date advice about health, safety and other risks of specific destinations for Australian travellers
The following resources have comprehensive technical advice on international travel and health, including vaccination:
- the latest edition of WHO’s International travel and health
- the CDC’s Health Information for International Travel (the ‘Yellow Book’)
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 3401.0 – Overseas arrivals and departures, Australia, Mar 2018 (accessed May 2018).
- Paudel P, Raina C, Zwar N, et al. Risk activities and pre-travel health seeking practices of notified cases of imported infectious diseases in Australia. Journal of Travel Medicine 2017;24(5):tax044.
- Heywood AE, Watkins RE, Iamsirithaworn S, Nilvarangkul K, MacIntyre CR. A cross-sectional study of pre-travel health-seeking practices among travelers departing Sydney and Bangkok airports. BMC Public Health 2012;12:321.
- Chen LH, Leder K, Barbre KA, et al. Business travel-associated illness: a GeoSentinel analysis. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018;25.
- Angelo KM, Kozarsky PE, Ryan ET, Chen LH, Sotir MJ. What proportion of international travellers acquire a travel-related illness? A review of the literature. Journal of Travel Medicine 2017;24.
- Freedman DO, Weld LH, Kozarsky PE, et al. Spectrum of disease and relation to place of exposure among ill returned travelers. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354:119-30.
- Halstead SB, Hills SL, Dubischar K. Japanese encephalitis vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin's vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
- Staples JE , Monath TP, Gershman MD, Barrett AD. Yellow fever vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin's vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Chapter 6: Vaccine-preventable diseases and vaccines . In: International travel and health. Geneva: WHO; 2017.
- Steffen R. Travel vaccine preventable diseases-updated logarithmic scale with monthly incidence rates. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018;25.
- Denholm JT, Thevarajan I. Tuberculosis and the traveller: evaluating and reducing risk through travel consultation. Journal of Travel Medicine 2016;23.
- Lachish T, Tenenboim S, Schwartz E. 35 - Humanitarian Aid Workers. In: Keystone JS, Kozarsky PE, Connor BA, et al., eds. Travel Medicine (Fourth Edition). London: Elsevier; 2019. (Accessed 6 July 2023). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323546966000355
- Leggat PA, Zwar NA, Hudson BJ. Hepatitis B risks and immunisation coverage amongst Australians travelling to Southeast Asia and East Asia. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease 2009;7:344-9.
- Winkler NE, Dey A, Quinn HE, et al. Australian vaccine preventable disease epidemiological review series: measles, 2012-2019. Commun Dis Intell (2018) 2022;46.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Epidemic meningitis control in countries of the African meningitis belt, 2017. Weekly Epidemiological Record 2018;93:173-84.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International travel and health: health conditions for travellers to Saudi Arabia for the pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) . 2017 (accessed May 2018).
- Freedman DO, Chen LH. Vaccines for International Travel. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2019;94:2314-39.
- Furuya-Kanamori L, Gyawali N, Mills DJ, et al. The Emergence of Japanese Encephalitis in Australia and the Implications for a Vaccination Strategy. Trop Med Infect Dis 2022;7.
- Hills SL, Rabe IB, Fischer M. Infectious diseases related to travel: Japanese encephalitis . In: CDC yellow book 2018: health information for international travel. New York: Oxford University Press; 2017.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International travel and health (accessed Apr 2018).
Page history
Minor updates to clinical guidance around routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas), including the addition of advice regarding COVID-19.
Editorial update to reflect changes to pneumococcal vaccine recommendations for older adults and people with medical risk factors.
Guidance on vaccination of travellers against measles, mumps and rubella updated to reflect advice in the Measles chapter.
Help us improve the Australian Immunisation Handbook
Printed content may be out of date. For up to date information, always refer to the digital version:
Subscribe to receive notifications regarding updates to the Australian Immunisation Handbook and changes to immunisation policy.
Help us improve
We are always looking for ways to improve our website, the NICC and mobile app.
Provide feedback
Acknowledgement
The Department of Health and Aged Care acknowledges First Nations peoples as the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia, and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to them and their cultures, and to all Elders both past and present.
© Commonwealth of Australia | Department of Health and Aged Care
Link , share or bookmark directly to this section of the page.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Americans who have traveled internationally stand out in their views and knowledge of foreign affairs

Do people who travel think differently about the world? A new Pew Research Center survey suggests they do.
Americans who have traveled internationally are more interested in and knowledgeable about foreign affairs, feel closer to others around the world, and favor a more active foreign policy, according to the survey of 3,576 U.S. adults conducted in spring 2023. We also surveyed people in 23 other countries about their international travel habits.
This analysis examines international travel with a focus on Americans’ travel, including which Americans travel abroad and how their interest in the world and views of international affairs differ from others.
For this analysis, we surveyed 3,576 U.S. adults from March 20 to March 26, 2023; 3,581 U.S. adults from March 21 to March 27, 2022; and 10,606 U.S. adults from June 14 to June 27, 2021. Everyone who took part in these surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
For non-U.S. data, this report draws on nationally representative surveys of 27,285 adults conducted from Feb. 20 to May 22, 2023. All surveys were conducted over the phone with adults in Canada, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, South Korea, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Surveys were conducted face-to-face in Hungary, Poland, India, Indonesia, Israel, Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa, Argentina, Brazil and Mexico. In Australia, we used a mixed-mode probability-based online panel.
Here are the June 2021 survey questions and responses used in this analysis. Those for the March 2022 survey may be found here , as well as those for the March 2023 survey .
How many Americans have traveled internationally?
Roughly three-quarters of Americans (76%) have visited at least one other country, including 26% who have been to five or more. About a quarter (23%) have not traveled internationally, though most in this group say they would if they had the opportunity.
Related: How experience with international travel varies across 24 countries
To analyze how Americans’ travel experiences relate to their attitudes on other questions, we placed people into three categories:
- Globe-trotters have traveled to at least five other countries. About a quarter of the U.S. public (26%) falls into this category.
- Casual travelers have traveled to between one and four other countries. Half of Americans fall into this category.
- Nontravelers have never left the United States. This category includes 23% of Americans.
Compared with Americans, people in many European nations are more likely to have traveled to five or more other countries. For instance, 88% of Swedes have done so.
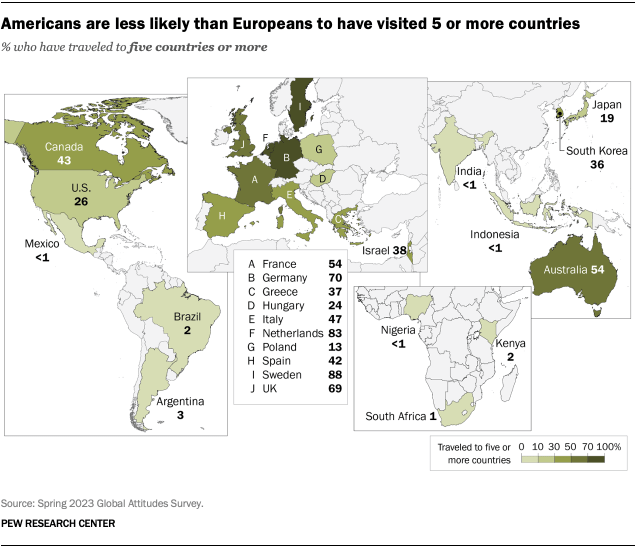
However, international travel is much less common in many middle-income nations. It is strongly correlated with a nation’s gross domestic product per capita. (For more on international travel and views about global engagement, read “Attitudes on an Interconnected World.” )
Who travels internationally?

Perhaps unsurprisingly, older people are more likely than younger people to have traveled internationally. Americans ages 65 and older are more than twice as likely as adults under 30 to fall into our globe-trotter category (37% vs. 17%).
Income is even more strongly related to travel than age. Two-thirds of upper-income Americans have traveled to at least five countries, compared with 9% of Americans with lower incomes.
Similarly, Americans with a postgraduate degree are far more likely to be globe-trotters than those with a high school education or less (59% vs. 10%).
Residents of suburban and urban areas generally have more international travel experience than people who live in rural areas.
There are no significant partisan differences when it comes to international travel: 26% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents qualify as globe-trotters, as do 28% of Republicans and GOP leaners.
Do travelers know more about the world?
Globe-trotters are especially likely to say they are interested in foreign affairs and follow international news. Casual travelers, in turn, are more likely than nontravelers to do so.
Globe-trotters are also the most knowledgeable about international affairs. In 2022, we conducted an international affairs quiz , asking Americans 12 questions related to international news. On average, globe-trotters got 8.2 of the 12 questions correct, compared with 6.4 for casual travelers and 4.2 for nontravelers.
Is international travel related to views of global engagement?

International travel experience is also linked to Americans’ views about international affairs and their feelings of connection to other people around the world.
When asked which comes closest to their view, 57% of globe-trotters say the U.S. should be active in world affairs, while 43% say the U.S. should pay less attention to problems in other countries and concentrate on problems at home. In contrast, most casual travelers and nontravelers say the U.S. should focus on problems at home.
In all three groups, at least half of respondents say that when the U.S. is making foreign policy, it should take other countries’ interests into account – even if that means making compromises. But globe-trotters are especially likely to hold that view.
Globe-trotters are also particularly likely to say they feel close to people around the world, with 42% saying so. By comparison, 34% of casual travelers and 30% of nontravelers say this.
- International Affairs

Richard Wike is director of global attitudes research at Pew Research Center

Janell Fetterolf is a senior researcher focusing on global attitudes at Pew Research Center
A growing share of Americans have little or no confidence in Netanyahu
Fewer americans view the united nations favorably than in 2023, what are americans’ top foreign policy priorities, rising numbers of americans say jews and muslims face a lot of discrimination, younger americans stand out in their views of the israel-hamas war, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
Where Americans Are Traveling in 2024: By the Numbers

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Americans are traveling abroad in droves.
The number of U.S. citizens flying to international destinations reached nearly 6.5 million passengers in March, according to the International Trade Administration. That’s the highest March total in over five years and shows that the post-pandemic “revenge travel” trend is the new normal.
It wasn’t just March, which usually sees a spike in international departures for spring break. In every month of 2024 so far, more Americans left the country than last year and 2019. These trends point to a blockbuster summer for overseas travel.
Nearly half of Americans (45%) plan to travel by air and/or stay in a hotel this summer and expect to spend $3,594 on average, on these expenses, according to a survey of 2,000 U.S. adults, conducted online by The Harris Poll and commissioned by NerdWallet.
That's despite rising travel prices that have caused some hesitancy among would-be travelers. About 22% of those choosing not to travel this summer cite inflation making travel too expensive as a reason for staying home, according to the poll.
So where are traveling Americans going? And what does it mean for those looking to avoid crowds of tourists and higher travel prices?
New travel patterns
Nearly every region in the world saw an increase in U.S. visitors in March 2024 compared with March 2023, according to International Trade Administration data. Only the Middle East saw a decline of 9%. Yet not every region saw the same year-over-year bump. U.S. visitors to Asia saw a 33% jump, while Oceania and Central America each saw a 30% increase.
Comparing 2024 with 2023 only tells part of the story, however. The new patterns really emerge when comparing international travel trends to 2019. For example, Central America received 50% more U.S. visitors in March 2024 compared with March 2019. Nearly 1.5 million Americans visited Mexico, up 39% compared with before the pandemic. That’s almost as many visitors as the entire continent of Europe, which has seen a more modest 10% increase since 2019.
Only Canada and Oceania saw fewer visitors in March 2024 than in 2019, suggesting that interest in these locations has not rebounded. Indeed, the trends indicate a kind of tourism inertia from COVID-19 pandemic-era lockdowns: Those destinations that were more open to U.S. visitors during the pandemic, such as Mexico, have remained popular, while those that were closed, such as Australia, have fallen off travelers’ radars.
Price pressures
How these trends play out throughout the rest of the year will depend on a host of factors. Yet, none will likely prove more important than affordability. After months of steadiness, the cost of travel, including airfare, hotels and rental cars, has begun to sneak up again.
About 45% of U.S. travelers say cost is their main consideration when planning their summer vacation, according to a survey of 2,000 Americans by the travel booking platform Skyscanner.
That’s likely to weigh further on U.S. travelers’ appetite for visiting expensive destinations such as Europe, while encouraging travel to budget-friendly countries. It could also depress overall international travel as well, yet so far, Americans seem to be traveling more.
For those looking to avoid crowds while maintaining a budget, Skyscanner travel trends expert Laura Lindsay offered a recommendation many of us might need help finding on a map.
“Albania has been on the radar of travelers looking for something different,” Lindsay said. "Most people have yet to discover it, but flights and tourism infrastructure are in place, and there are fewer crowds in comparison to trending European destinations like Italy, Greece, or Portugal.”
On the flip side, American travelers looking to avoid crowds of compatriots would do well to avoid Japan, which has seen a staggering 50% increase in U.S. tourists between March 2019 and 2024.
How to maximize your rewards
You want a travel credit card that prioritizes what’s important to you. Here are our picks for the best travel credit cards of 2024 , including those best for:
Flexibility, point transfers and a large bonus: Chase Sapphire Preferred® Card
No annual fee: Bank of America® Travel Rewards credit card
Flat-rate travel rewards: Capital One Venture Rewards Credit Card
Bonus travel rewards and high-end perks: Chase Sapphire Reserve®
Luxury perks: The Platinum Card® from American Express
Business travelers: Ink Business Preferred® Credit Card
On a similar note...


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
International travel increases your chances of getting and spreading diseases that are rare or not found in United States. Find out which travel vaccines you may need to help you stay healthy on your trip. Before Travel. Make sure you are up-to-date on all of your routine vaccines.
Prevention modalities: vaccination, medication, consultation. Hepatitis A. Contaminated food & water. Vaccination (2-dose vaccine): Recommended for most travelers. --Administer 2 doses, at least 6 months apart. --At least 1 dose should be given before travel. Consultation: Advise patient to wash hands frequently and avoid unsafe food and water.
Vaccines for Travelers. Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places. Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you're ...
Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by: Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip. Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines. Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family's ...
Before you embark on your journey, he suggests making sure you're up to date with routine vaccinations, including vaccines for: COVID-19. Flu. Hepatitis A. Hepatitis B. Tetanus. "People don ...
CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide guidance to the clinicians who serve them. ... Routine Vaccines. It's important to be up to date on recommended routine vaccines prior to travel, including Flu, RSV and COVID-19. ...
Travel vaccines, also called travel immunizations, are shots travelers can get before visiting certain areas of the world that help protect them from serious illnesses. Vaccinations work by ...
A trip abroad requires you to be up-to-date on a whole checklist of things these days: travel insurance, airline policies, visas, passports, and, as far as your health is concerned, vaccines.Yet ...
The vaccines you should get depend on where you're going. No matter where you're going, check to make sure you're up to date on all routine vaccines: measles-mumps-rubella, diphtheria-tetanus ...
Vaccines. Vaccination is the administration of agent-specific, but safe, antigenic components that in vaccinated individuals can induce protective immunity against the corresponding infectious agent. Before departure, travelers should have a medical consultation to learn about the risk of disease in the country or countries they plan to visit ...
Even though you can't get sick from travel vaccines, side effects are possible. The most common side effects of injectable vaccines are pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site. These are often mild and go away quickly. Other possible side effects include: Tiredness. Headache.
So as of November the 8th, nonimmigrant foreign national air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of vaccination status prior to boarding an airplane to the United States. I'll let Dr. Friedman speak to the specific vaccines that will be accepted.
Vaccination requirements for international travel are the aspect of vaccination policy that concerns the movement of people across borders.Countries around the world require travellers departing to other countries, or arriving from other countries, to be vaccinated against certain infectious diseases in order to prevent epidemics.At border checks, these travellers are required to show proof of ...
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply.
Last Updated: May 4, 2023. The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with ...
Ned Price, Department Spokesperson. October 25, 2021. Today, the White House and CDC announced details of the new vaccination policy that will go into effect for international travelers on November 8. As of that date, foreign national air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of vaccination ...
If you need to contact a US embassy or consulate, call 1-888-407-4747 (from the US or Canada) OR 00-1-202-501-4444 (from other countries). Travel healthy, from CDC's Travelers' Health! CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides health advice to international travelers, including advice about medications and vaccines.
Teens and adults seeking recommended vaccinations; School age children needing vaccines required for school; Adults who need vaccines for work or school; Immigrants to the US requiring vaccines for Change of Status; Individuals and families planning international travel; Our services are by appointment only. AITC is unable to accept insurance.
You do not need to be vaccinated for any domestic travel. Hawaii is the only state that requires a negative test for travel. In Hawaii, the test must be administered within 72 hours of arrival and ...
Vaccinations for International Travel. Routine vaccines should be up to date prior to travel. The following vaccines are recommended before international travel depending on your age, health, vaccine history and destination. COVID-19 - one or more doses of the updated vaccine. Chickenpox (Varicella) - Schedule: 2 shots. Recommended: Yes.
There are 3 categories of travel vaccines: routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas) selected vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure; vaccines required by the International Health Regulations 2005 (IHR) or for entry into specific countries
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19. As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
This analysis examines international travel with a focus on Americans' travel, including which Americans travel abroad and how their interest in the world and views of international affairs differ from others. For this analysis, we surveyed 3,576 U.S. adults from March 20 to March 26, 2023; 3,581 U.S. adults from March 21 to March 27, 2022 ...
The new patterns really emerge when comparing international travel trends to 2019. For example, Central America received 50% more U.S. visitors in March 2024 compared with March 2019.