

Travel Past Tense
Commonwealth travelled, US traveled past tense of travel is Commonwealth travelled, US traveled.
Travel verb forms
Conjugation of travel.
- What is the past tense of tup in English?
- What is the second form of verb TUPE?
- What is the third form of verb turbanize in English?
- What is the conjugation of turbinate in English?
- Conjugate turbocharge in English?
- turkey-trot
PastTenses is a database of English verbs. One can check verbs forms in different tenses. Use our search box to check present tense, present participle tense, past tense and past participle tense of desired verb.
Past Tense of Travel: Conjugations in Past and Present Participles

What is the past tense of “travel?” Most commonly, the past tense of the word “travel” is “traveled.” Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it’s used. For example, referencing “travel” in the present participle form will change it to “traveling,” but in the infinitive form, will be “travel.”
What is the past tense of the word "travel"
The past tense (past participle) form of “travel” is “traveled.” The infinitive of the word form is “travel.” The present participle form is “traveling.” The past tense form is “traveled” and past participle form is “traveled.”
Understanding verb tenses
The general grammar rules that govern past tenses are as follows. The simple past tense form is created by adding a -ed or -d affix to the root word of the verb. Some verbs use a -t variation where they end in a -t. For example, when "dream" turns into "dreamt."
The past perfect tense is formed for regular verbs (ending in -ed, -d, or -t) by adding "had" followed by the verb. For example, "I had finished ."
The past continuous tense is formed by the verb "be" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, " we were having dinner."
Lastly, the past perfect continuous tense is formed by adding "had been" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, "I had been building a castle with my sister."
For more information on forming all past tenses, visit our " understanding verb tenses " resource.
Sentence examples for the past tense of the word "travel"
- Infinitive: I travel.
- Present participle: She is traveling.
- Past tense: I traveled.
- Past particle: I have traveled.
Verb forms of the word "travel"
Example sentences in all verb forms:
Indefinite present tense
Present continuous tense.
She/he/it is traveling.
Present perfect continuous tense
She/he/it has/had traveled.
Present perfect tense
She/he/it has/had been traveling.
Simple past tense
She/he/it traveled.
Past continuous tense
She/he/it were traveling.
Past perfect tense
Perfect continuous tense.
She/he/it will/shall travel.
Simple future tense
She/he/it will/shall be traveling.
Future perfect tense
She/he/it will/shall have traveled.
Future perfect continuous tense
She/he/it will/shall have been traveling.
Sentence examples in all forms
Sentence examples in all participles and parts of speech :
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
Conjugation verb travel
Model : cancel
Auxiliary : have , be
Other forms: travel oneself / not travel
Contractions
in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings
The verb has several variants of conjugation, which may correspond to different meanings. Please use the menu to select one or all variants.
- he/she/it travels
- they travel
- I travelled/traveled
- you travelled/traveled
- he/she/it travelled/traveled
- we travelled/traveled
- they travelled/traveled
Present continuous
- I am travelling/traveling
- you are travelling/traveling
- he/she/it is travelling/traveling
- we are travelling/traveling
- they are travelling/traveling
Present perfect
- I have travelled/traveled
- you have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it has travelled/traveled
- we have travelled/traveled
- they have travelled/traveled
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he/she/it will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Future perfect
- I will have travelled/traveled
- you will have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it will have travelled/traveled
- we will have travelled/traveled
- they will have travelled/traveled
Past continous
- I was travelling/traveling
- you were travelling/traveling
- he/she/it was travelling/traveling
- we were travelling/traveling
- they were travelling/traveling
Past perfect
- I had travelled/traveled
- you had travelled/traveled
- he/she/it had travelled/traveled
- we had travelled/traveled
- they had travelled/traveled
Future continuous
- I will be travelling/traveling
- you will be travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will be travelling/traveling
- we will be travelling/traveling
- they will be travelling/traveling
Present perfect continuous
- I have been travelling/traveling
- you have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it has been travelling/traveling
- we have been travelling/traveling
- they have been travelling/traveling
Past perfect continuous
- I had been travelling/traveling
- you had been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it had been travelling/traveling
- we had been travelling/traveling
- they had been travelling/traveling
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been travelling/traveling
- you will have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will have been travelling/traveling
- we will have been travelling/traveling
- they will have been travelling/traveling
- let's travel
- travelling/traveling
- travelled/traveled
Perfect participle
- having travelled/traveled
Helping millions of people and large organizations communicate more efficiently and precisely in all languages.
Online Language Dictionaries
Perfect tenses, continuous (progressive) and emphatic tenses, compound continuous (progressive) tenses, conditional, subjunctive.
*Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. ( example ) *Red letters in conjugations are exceptions to the model. ( example )
Report a problem.
To support our work, we invite you to accept cookies or to subscribe.
You have chosen not to accept cookies when visiting our site.
The content available on our site is the result of the daily efforts of our editors. They all work towards a single goal: to provide you with rich, high-quality content. All this is possible thanks to the income generated by advertising and subscriptions.
By giving your consent or subscribing, you are supporting the work of our editorial team and ensuring the long-term future of our site.
If you already have purchased a subscription, please log in
How to conjugate "to travel" in English?
English "to travel" conjugation.
- traveled; travelled
Full conjugation of "to travel"
Translations for "to travel", present continuous, simple past, past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, conditional present, conditional present progressive, conditional perfect, conditional perfect progressive, subjunctive, present subjunctive, past subjunctive, past perfect subjunctive, present participle, past participle.
Translations for "to travel" in our English dictionaries
Popular English verbs
Find out the most frequently used verbs in English.
Social Login
- Slovenščina
- FAQ Technical Questions
- Text Translation
- Vocabulary Trainer
- Online Dictionary
- Login
- Online dictionary
- Products & Shop
- Conjugation
- Vocabulary trainer
- Dictionary API
- Add to home screen
- Browse the dictionaries
- Terms and conditions of use
- Supply chain
- Data Protection Declaration
- Legal notice
- Privacy Settings
- EN');"> English
- FR');"> French
- DE');"> German
- LA');"> Latin
- ES');"> Spanish
Verb Table for travel
- Simple tenses
- Continuous tenses
Conditional
Simple tenses • continuous tenses • conditional • imperative • impersonal, present perfect, past perfect, will -future, going to -future, future perfect, conditional past, past participle, browse the conjugations (verb tables), look up "travel" in other languages, links to further information.
You can suggest improvements to this PONS entry here:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
My search history
- Most popular
- English ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ French
- German ⇄ Greek
- German ⇄ Polish
- Arabic ⇄ English
- Arabic ⇄ German
- Bulgarian ⇄ English
- Bulgarian ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ English
- Chinese ⇄ French
- Chinese ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ Spanish
- Croatian ⇄ German
- Czech ⇄ German
- Danish ⇄ German
- Dutch ⇄ German
- Elvish ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Arabic
- English ⇄ Bulgarian
- English ⇄ Chinese
- English ⇄ French
- English ⇄ Italian
- English ⇄ Polish
- English ⇄ Portuguese
- English ⇄ Russian
- English → Serbian
- English ⇄ Spanish
- Finnish ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Chinese
- French ⇄ English
- French ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Italian
- French ⇄ Polish
- French ⇄ Slovenian
- French ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ Arabic
- German ⇄ Bulgarian
- German ⇄ Chinese
- German ⇄ Croatian
- German ⇄ Czech
- German ⇄ Danish
- German ⇄ Dutch
- German ⇄ Elvish
- German ⇄ English
- German ⇄ Finnish
- German ⇄ Hungarian
- German → Icelandic
- German ⇄ Italian
- German ⇄ Japanese
- German ⇄ Latin
- German ⇄ Norwegian
- German ⇄ Persian
- German ⇄ Portuguese
- German ⇄ Romanian
- German ⇄ Russian
- German → Serbian
- German ⇄ Slovakian
- German ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Swedish
- German ⇄ Turkish
- Dictionary of German Spelling
- Greek ⇄ German
- Hungarian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ English
- Italian ⇄ French
- Italian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ Polish
- Italian ⇄ Slovenian
- Italian ⇄ Spanish
- Japanese ⇄ German
- Latin ⇄ German
- Norwegian ⇄ German
- Persian ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ English
- Polish ⇄ French
- Polish ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ Italian
- Polish ⇄ Russian
- Polish ⇄ Spanish
- Portuguese ⇄ English
- Portuguese ⇄ German
- Portuguese ⇄ Spanish
- Romanian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ English
- Russian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ Polish
- Slovakian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ English
- Slovenian ⇄ French
- Slovenian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ Italian
- Slovenian ⇄ Spanish
- Spanish ⇄ Chinese
- Spanish ⇄ English
- Spanish ⇄ French
- Spanish ⇄ German
- Spanish ⇄ Italian
- Spanish ⇄ Polish
- Spanish ⇄ Portuguese
- Spanish ⇄ Slovenian
- Swedish ⇄ German
- Turkish ⇄ German
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->
Verb "travel"
For the settings to take effect, you must restart the trainer Restart
Conjugation
Simple tense.
Present Simple
- he, she travels
- they travel
Past Simple
- I traveled ; travelled
- you traveled ; travelled
- he, she traveled ; travelled
- we traveled ; travelled
- they traveled ; travelled
Future Simple
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he, she will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Continuous Tense
Present Simple Continuous
- I am traveling ; travelling
- you are traveling ; travelling
- he, she is traveling ; travelling
- we are traveling ; travelling
- they are traveling ; travelling
Past Simple Continuous
- I was traveling ; travelling
- you were traveling ; travelling
- he, she was traveling ; travelling
- we were traveling ; travelling
- they were traveling ; travelling
Future Simple Continuous
- I will be traveling ; travelling
- you will be traveling ; travelling
- he, she will be traveling ; travelling
- we will be traveling ; travelling
- they will be traveling ; travelling
Perfect Tense
Present Perfect
- I have traveled ; travelled
- you have traveled ; travelled
- he, she has traveled ; travelled
- we have traveled ; travelled
- they have traveled ; travelled
Past Perfect
- I had traveled ; travelled
- you had traveled ; travelled
- he, she had traveled ; travelled
- we had traveled ; travelled
- they had traveled ; travelled
Future Perfect
- I will have traveled ; travelled
- you will have traveled ; travelled
- he, she will have traveled ; travelled
- we will have traveled ; travelled
- they will have traveled ; travelled
Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous
- I have been traveling ; travelling
- you have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she has been traveling ; travelling
- we have been traveling ; travelling
- they have been traveling ; travelling
Past Perfect Continuous
- I had been traveling ; travelling
- you had been traveling ; travelling
- he, she had been traveling ; travelling
- we had been traveling ; travelling
- they had been traveling ; travelling
Future Perfect Continuous
- I will have been traveling ; travelling
- you will have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she will have been traveling ; travelling
- we will have been traveling ; travelling
- they will have been traveling ; travelling
Conditional
- I would travel
- you would travel
- he, she would travel
- we would travel
- they would travel
- I would have traveled ; travelled
- you would have traveled ; travelled
- he, she would have traveled ; travelled
- we would have traveled ; travelled
- they would have traveled ; travelled
Present Continuous
- I would be traveling ; travelling
- you would be traveling ; travelling
- he, she would be traveling ; travelling
- we would be traveling ; travelling
- they would be traveling ; travelling
Perfect Continuous
- I would have been traveling ; travelling
- you would have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she would have been traveling ; travelling
- we would have been traveling ; travelling
- they would have been traveling ; travelling
- we Let's travel
Other verbs
Be the first to comment.
Add comment
Here are the past tense forms of the verb travel
👉 Forms of verb travel in future and past simple and past participle. ❓ What is the past tense of travel.
Travel: Past, Present, and Participle Forms
What are the 2nd and 3rd forms of the verb travel.
🎓 What are the past simple, future simple, present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect forms of the base form (infinitive) ' travel '? 👉 It's quite simple -->
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'
- the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses.
- the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense.
- the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
What are the past tense and past participle of travel?
What is the past tense of travel.
The past tense of the verb "travel" is "travelled (BrE)", or "traveled (AmE)", and the past participle is "travelled (BrE)" or "traveled (AmE)".
Verb Tenses
Past simple — travel in past simple travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (V2) . Future simple — travel in future simple is travel (will + V1) . Present Perfect — travel in present perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (have/has + V3) . Past Perfect — travel in past perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (had + V3) .
travel regular or irregular verb?
👉 Is 'travel' a regular or irregular verb? The verb 'travel' is regular verb .
Examples of Verb travel in Sentences
- These days we travelled 1400 km (Past Simple)
- We didn't travel that long (Past Simple)
- She has travelled extensively in the Philippines (Present Perfect)
- I can't travel without you (Present Simple)
- We usually travel to work by bus (Present Simple)
- A plane travels faster than a train (Present Simple)
- They are travelling together since 2018 (Present Continuous)
- You can travel by foot, why not? (Present Simple)
- Unfortunately you can't travel without a ticket, so please proceed to the ticket office (Present Simple)
- How many countries have you travelled to? (Present Perfect)
Along with travel, words are popular give and tell .
Verbs by letter: r , d , u , c , m , p , b , w , h , a , e , g , s , q , j , l , t , f , o , n , k , i , v , y , z .
English verbs
- 318 Irregular verbs
- 904 Regular verbs
- 5 Modal verbs
- 407 Phrasal verb
Online verb dictionary
We are currently working to add new verbs and examples to our website, along with detailed descriptions. Please send us a message if you have any requests or suggestions, and we will add them as quickly as we can. Thank you for your interest in our website!
our editor - Peter (Certified TEFL Tutor with over 8 years experience)
Have a question or find mistake?

Select your English level
To personalize your experience.
- To Travel Conjugation
In the US the spelling 'traveling' and 'traveled' are preferred.
Continuous Perfect
Conditional.
We notice you're using an ad blocker.
Linguasorb is free and ad supported, without ad revenue we can't exist. Certain features such as audio, directly cost us money and so are disabled for ad block users.
Please disable your ad blocker for this site if you wish to use the premium features.
Alternatively you can become a supporter and remove the ads completely .
Conjugation of verb (past tense) travel
Past simple, traveled; travelled, past participle.
- ⭐Conjugation
- Podmínkové věty
- Frázová slovesa
- ⭐Conditional
- ⭐Subjunktiv
- ⭐Participle
Conjugation of the regular verb [travel]
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking.
The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is known as declension). Also it is often restricted to denoting the formation of finite forms of a verb – these may be referred to as conjugated forms, as opposed to non-finite forms, such as the infinitive or gerund, which tend not to be marked for most of the grammatical categories.
Conjugation is also the traditional name for a group of verbs that share a similar conjugation pattern in a particular language (a verb class). A verb that does not follow all of the standard conjugation patterns of the language is said to be an irregular verb .
Present Continuous
Past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional of the regular verb [travel].
Causality (also referred to as causation or cause and effect ) is influence by which one event, process, state or object (a cause) contributes to the production of another event, process, state or object (an effect) where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be causal factors for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future.
The conditional mood (abbreviated cond) is a grammatical mood used in conditional sentences to express a proposition whose validity is dependent on some condition, possibly counterfactual.
English does not have an inflective (morphological) conditional mood, except in as much as the modal verbs could, might, should and would may in some contexts be regarded as conditional forms of can, may, shall and will respectively. What is called the English conditional mood (or just the conditional) is formed periphrastically using the modal verb would in combination with the bare infinitive of the following verb. (Occasionally should is used in place of would with a first person subject – see shall and will. Also the aforementioned modal verbs could, might and should may replace would in order to express appropriate modality in addition to conditionality.)
Conditional present -->
Conditional present progressive -->, conditional perfect -->, conditional perfect progressive -->, subjunktiv of the regular verb [travel].
The subjunctive is a grammatical mood, a feature of the utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude toward it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality such as: wish, emotion, possibility, judgement, opinion, obligation, or action that has not yet occurred; the precise situations in which they are used vary from language to language. The subjunctive is one of the irrealis moods, which refer to what is not necessarily real. It is often contrasted with the indicative, a realis mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact.
Subjunctives occur most often, although not exclusively, in subordinate clauses, particularly that-clauses. Examples of the subjunctive in English are found in the sentences "I suggest that you be careful" and "It is important that she stay by your side."
The subjunctive mood in English is a clause type used in some contexts which describe non-actual possibilities, e.g. "It's crucial that you be here" and "It's crucial that he arrive early." In English, the subjunctive is syntactic rather than inflectional, since there is no specifically subjunctive verb form. Rather, subjunctive clauses recruit the bare form of the verb which is also used in a variety of other constructions.
Present subjunctive -->
Past subjunctive -->, past perfect subjunctive -->, imperativ of the regular verb [travel].
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request.
An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (you), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive).
Imperativ -->
Participle of the regular verb [travel].
The past participle is one of the most important parts of English grammar. It’s used to express perfect tenses and to form the passive voice. It’s also a useful tool for writing sentences that describe actions that started in the past and are still happening today. The past participles of irregular verbs don’t follow a specific pattern and can have numerous endings.
Present participle -->
Past participle -->, recent articles.
- Differences: past simple and past continuous
- Past simple sentences
- Past continuous structure
- Adverbs of past continuous tense
- Past continuous verbs
Start with any verb and browse through irregular verbs in alphabetical order
Use the button "Random choice"
Looking for a specific irregular verb?
regular verbs & Irregular verbs

'travel' conjugation table in English
Past participle, present participle, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All ENGLISH words that begin with 'T'
Example: eat, ate, eaten
Past Perfect
Future perfect, present - conditional, perfect - conditional.
bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250]
Daftar Kursus
Kebijakan privasi, syarat dan ketentuan, pertanyaan umum, contoh cerita pengalaman liburan dalam bahasa inggris.
Jan 05, 2023

Liburan akhir tahun sudah selesai! Waktunya kita kembali ke realita dan memulai aktivitas lagi seperti biasa. Biasanya setelah liburan gini kita sering sharing ke teman sekolah atau teman kantor tentang pengalaman atau cerita liburan kita masing-masing.
Kalau kamu masih bingung gimana caranya menceritakan pengalaman liburan pakai bahasa Inggris, ini penjelasan caranya!
Tense untuk Menceritakan Pengalaman Liburan
Untuk menceritakan pengalaman liburan dalam bahasa Inggris, kamu harus menggunakan rumus simple past tense . Simple past tense adalah bentuk kalimat bahasa Inggris yang digunakan untuk menyatakan peristiwa atau kejadian yang sudah selesai terjadi di masa lalu .
Ciri-ciri utama dari kalimat simple past tense adalah penggunaan V2 atau past simple. Berikut adalah rumus membuat kalimat simple past tense .
Pengen bisa bikin cerita sendiri pakai bahasa Inggris? Yuk, ikutan kelas English for Basic. Kamu akan belajar bahasa Inggris dari NOL sampai BISA dengan metode langsung praktik . Dijamin setelah ikut kelas ini kamu bisa praktik s peaking, listening, reading, dan writing sendiri di rumah. Klik DI SINI untuk konsutasi GRATIS dengan admin.
Rumus kalimat verbal simple past tense:
Contoh kalimat:
- I went to Gembira Loka Zoo last week.
(Aku pergi ke Kebun Binatang Gembira Loka minggu lalu.)
- We also visited many monuments.
(Kami juga mengunjungi banyak monumen.)
- My parents booked a hotel near the beach.
(Orang tuaku memesan hotel di dekat pantai.)
Rumus kalimat nominal simple past tense:
- We were in Universal Studio at that time.
(Kami menonton acara Pirates di Universal Studio.)
- The beach was very beautiful.
(Pantai itu sangat indah.)
- I was so happy when we were in Kuala Lumpur.
(Aku sangat senang ketika kami sedang di Kuala Lumpur.)
Selain itu, ada beberapa keterangan waktu ( adverbs of time ) yang sering dipakai dalam simple past tense , seperti kata:
- Last holiday = Liburan yang lalu
- Last month = Bulan lalu
- Last Sunday = Hari Minggu lalu
- Last two weeks = Dua minggu yang lalu
- Last week = Minggu lalu
- One week ago = Seminggu yang lalu
- This morning = Pagi tadi
- Two days ago = Dua hari yang lalu
- Yesterday = Kemarin
Setelah tahu tense yang seharusnya dipakai untuk menceritakan pengalaman, yuk kita lanjut dengan contoh cerita pengalaman liburan pakai bahasa Inggris. Check it out !
Contoh Cerita Liburan Sekolah Bahasa Inggris
Cerita pengalaman liburan di rumah saja dalam bahasa Inggris
My worst holiday ever happened on the last semester break. I stayed at home for the entire two weeks. I had the same schedule every day as well.
The first thing that I did after I got up was praying. After that, I ate breakfast right away. Right after I had my breakfast, I fed and played with my cats. They all are so cute.
In the afternoon, I ate lunch and then napped on the couch until almost in the evening. Then, I had dinner and watched my favorite TV series with my parents and siblings.
Those were the activities that I did last holiday for two weeks. Nothing special happened during that holiday. I believed it was the worst semester break I had ever experienced.
Baca juga: Menceritakan Pengalaman Kerja dalam Bahasa Inggris
Liburan terburukku terjadi di liburan semester lalu. Aku cuma di rumah selama dua minggu penuh. Aku juga melakukan hal yang sama setiap harinya.
Hal pertama yang aku lakukan setelah bangun tidur adalah salat. Setelah itu, aku langsung sarapan. Setelah aku sarapan, aku memberi makan dan bermain dengan kucing-kucingku. Mereka semua sangat lucu.
Di siang hari, aku makan siang lalu tidur siang di sofa sampai hampir malam. Kemudian, aku makan malam dan nonton serial TV favorit ku dengan orang tua dan saudaraku.
Itulah kegiatan-kegiatan yang aku lakukan pada liburan yang lalu selama dua minggu. Tidak ada hal istimewa terjadi selama liburan. Sepertinya liburan lalu adalah liburan semester terburuk yang pernah ku alami.
Cerita pengalaman liburan ke Yogyakarta dalam bahasa Inggris
During the last school holiday, my family and I went on a vacation to Yogyakarta to visit my grandparents. We traveled from Jakarta using a car driven by my father. After eight hours of driving, we finally arrived in Yogyakarta.
I was so happy I could finally meet my grandparents again after two years. We planned on spending new years in Yogyakarta.
On our first day in Yogyakarta, we visited the Prambanan temple. It was my third time visiting that temple since I was a child, but I never got bored with the beauty of it.
The next day, we visited Parangtritis Beach and Depok Beach to eat some seafood. It was my first time visiting those beaches.
On new year's eve, we went to Malioboro Street to see the fireworks and it was the best fireworks I have ever seen. I experienced a lot of new things during this visit in Yogyakarta. I hope I can visit my grandparents again this year.
Pada liburan sekolah yang lalu, aku dan keluargaku pergi berlibur ke Yogyakarta untuk mengunjungi kakek dan nenekku. Kita berangkat dari Jakarta menggunakan mobil yang dikendarai oleh ayahku. Setelah delapan jam perjalanan, akhirnya kita sampai di Yogyakarta.
Aku senang sekali akhirnya bisa bertemu kakek-nenek lagi setelah dua tahun. Aku dan keluarga berencana menghabiskan tahun baru di Yogyakarta.
Pada hari pertama di Yogyakarta, kita mengunjungi candi Prambanan. Ini ketiga kalinya aku mengunjungi candi itu sejak kecil, tetapi aku nggak pernah bosan dengan keindahannya.
Keesokan harinya, kita mengunjungi Pantai Parangtritis dan Pantai Depok untuk makan seafood. Ini adalah pertama kalinya aku mengunjungi pantai-pantai itu.
Pada malam tahun baru, kita pergi ke Jalan Malioboro untuk melihat kembang api dan itu adalah kembang api terbaik yang pernah ku lihat. Banyak hal baru yang aku alami selama di Yogyakarta. Aku berharap aku bisa mengunjungi kakek-nenek lagi tahun ini.
Cerita pengalaman liburan ke luar negeri dalam bahasa Inggris
My parents and I spent the holiday in Singapore. It was my first visit to Singapore, but my parents had been there several times for work.
The first place we visited was Universal Studios. I rode all of the rides there. It was the best theme park I had ever visited. My parents also bought me some of their merchandise. I was so happy on that day.
On the second day, we went to Merlion Park which is the symbol to welcome all visitors to Singapore. After we finished taking pictures there, my parents took me to Singapore Zoo.
I really enjoyed my holiday in Singapore. Even though it was only a short holiday, I think it was the best holiday of my life. I cannot wait to go there again .
Orang tuaku dan aku menghabiskan liburan di Singapura. Itu adalah kunjungan pertamaku ke Singapura, tetapi orang tuaku sudah beberapa kali ke sana untuk bekerja.
Tempat pertama yang kami kunjungi adalah Universal Studios. Aku menaiki semua wahana di sana. Tempat itu adalah taman hiburan terbaik yang pernah aku kunjungi. Orang tuaku juga membelikan aku beberapa suvenir dari sana. Aku senang sekali hari itu.
Di hari kedua, kami pergi ke Merlion Park yang merupakan simbol untuk menyambut semua pengunjung di Singapura. Setelah selesai berfoto disana, orang tuaku mengajakku ke Singapore Zoo.
Aku sangat menikmati liburanku di Singapura. Meskipun hanya liburan singkat, menurutku itu adalah liburan terbaik dalam hidupku. Aku nggak sabar kembali lagi ke sana.
Nah, itulah tense yang biasanya dipakai untuk menceritakan pengalaman liburan dalam bahasa Inggris beserta beberapa contoh cerita liburan dalam bahasa Inggris. Apapun pengalamannya kalau itu sudah terjadi di masa lalu, wajib pakai simple past tense ya!
Kamu pengen bisa bikin cerita sendiri pakai bahasa Inggris? Yuk, ikutan kelas English for Basic di Englishvit! Di kelas English for Basic kamu akan belajar bahasa Inggris dari NOL sampai BISA . Metode belajarnya akan fokus langsung praktik .
Dijamin setelah ikut kelas ini kamu bisa praktik speaking, listening, reading , dan writing sendiri di rumah. Menarik, kan? Yuk, tunggu apa lagi? Langsung aja klik DI SINI buat daftar kelasnya!

Budwining Anggraeni Tiyastuti

Yuk konsultasi tentang kursus bahasa Inggris!
Related post.

Teks Prosedur dalam Bahasa Inggris Singkat dan Lengkap
Oct 20, 2022

Cara Membuat dan Contoh Undangan Ulang Tahun Bahasa Inggris
Sep 15, 2022

Macam-Macam Kartu Ucapan Bahasa Inggris dan Contohnya
Sep 09, 2022

Fakta Unik Tentang Bahasa Inggris yang Jarang Orang Tahu!
Jul 05, 2022

Cara Menulis Tanggal dalam Bahasa Inggris Yang Benar dan Contohnya
Jun 27, 2022

Aturan Penggunaan Huruf Kapital dalam Bahasa Inggris + Contohnya
Jun 20, 2022
Improve your English

Intermediate Complete Grammar
Cara mudah jadi jago GRAMMAR!!
Basic Complete Grammar
Panduan komplit belajar grammar dari dasar!

Starter Plan
1x Test TOEFL Online Bersertifikat

Grammar for Speaking
Bantu kamu memperbaiki Grammar dalam speaking
English for Basic
Paket lengkap belajar bahasa Inggris dari NOL sampai BISA
Kembali terkoneksi dengan komunitas belajar bahasa Inggris terbaikmu.
Don’t have an account yet? Sign up
Ciptakan pengalaman baru belajar bahasa Inggris aktif bersama Englishvit.
Sudah punya akun? Login

- Mode Terang
- Gabung Kompas.com+
- Konten yang disimpan
- Konten yang disukai
- Berikan Masukanmu

- Megapolitan
- Surat Pembaca
- Kilas Daerah
- Kilas Korporasi
- Kilas Kementerian
- Sorot Politik
- Kilas Badan Negara
- Kelana Indonesia
- Kalbe Health Corner
- Kilas Parlemen
- Konsultasi Hukum
- Infrastructure
- Apps & OS
- Tech Innovation
- Kilas Internet
- Elektrifikasi
- Timnas Indonesia
- Liga Indonesia
- Liga Italia
- Liga Champions
- Liga Inggris
- Liga Spanyol
- Internasional
- Sadar Stunting
- Spend Smart
- Smartpreneur
- Kilas Badan
- Kilas Transportasi
- Kilas Fintech
- Kilas Perbankan
- Tanya Pajak
- Sorot Properti
- Tips Kuliner
- Tempat Makan
- Panduan Kuliner Yogyakarta
- Beranda UMKM
- Jagoan Lokal
- Perguruan Tinggi
- Pendidikan Khusus
- Kilas Pendidikan
- Jalan Jalan
- Travel Tips
- Hotel Story
- Travel Update
- Nawa Cahaya
- Ohayo Jepang
- Kehidupan sehat dan sejahtera
- Air bersih dan sanitasi layak
- Pendidikan Berkualitas
- Energi Bersih dan Terjangkau
- Penanganan Perubahan Iklim
- Ekosistem Lautan
- Ekosistem Daratan
- Tanpa Kemiskinan
- Tanpa Kelaparan
- Kesetaraan Gender
- Pekerjaan Layak dan Pertumbuhan ekonomi
- Industri, Inovasi & Infrastruktur
- Berkurangnya Kesenjangan
- Kota & Pemukiman yang Berkelanjutan
- Konsumsi & Produksi yang bertanggungjawab

5 Jenis Past Tense Beserta Rumus dan Contohnya
Kompas.com skola, serafica gischa.

KOMPAS.com - Tenses dibagi menjadi empat berdasarkan pembagian waktu, yaitu present, past, future, dan past future.
Masing-masing pembagian waktu tersebut menentukan bentuk kalimat untuk menjelaskan suatu peristiwa.
Dalam buku Kuasai Materi Bahasa Inggris (2015) karya Sinta Sasika Novel, past artinya masa lampau. Sehingga past tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu peristiwa di masa lampau atau sudah terjadi di masa lalu.
Dalam penggunaannya, past tense terbagi menjadi beberapa bagian atau rumus kalimat, yaitu:
Simple Past Tense
Simple past tense digunkaan untuk menyatakan suatu peristiwa yang terjadi di waktu lampau.
Rumus dari Simple Past Tense , yaitu:
Keterangan waktu (adverb) yang digunakan, antara lain:
- yesterday = kemarin
- just now = tadi, baru saja
- this morning = tadi pagi
- a year ago = satu tahun yang lalu
- last day/week/year = kemarin/minggu lalu/tahun lalu
Baca juga: Penggunaan To Be: Is, Am, dan Are
Contoh penggunaan kalimat:
(+) I wrote an essay yesterday (-) I did not/didn't write an essay yesterday (?) Did you write an essay yesterday?
Past Continuous Tense
Past Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu peristiwa yang sedang berlangsung di waktu lampau.
Rumus Past Continuous Tense
Contoh keterangan waktu yang sering digunakan adalah:
- when, while = ketika
- at 5 o'clock at last Monday = waktu tertentu di masa lampau
Baca juga: Apa Itu Present Tense?
(+) I was writing a novel when it happened (-) I wasn't writing a novel when it happened (?) Were you writing a novel when it happened?
Past Perfect Tense
Past Perfect Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu peristiwa yang terjadi sebelum peristiwa lain pada masa lampau untuk menyatakan dua peristiwa yang terjadi berurutan.
Rumus Past Perfect Tense:
Keterangan waktu yang iugunakan, antara lain:
- before = sebelum
- after = sesudah
- when = ketika
(+) I had written a novel before Vina came (-) I had not written a novel before Vina came (?) Had you written a novel before Vina came?
Baca juga: Penggunaan To Be: Was dan Were
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu peristiwa yang telah berlangsung beberapa waktu hingga peristiwa lain terjadi atau peristiwa kedua terjadi.
Keterangan waktu yang sering digunakan, adalah:
- For..... before
- For.... when......
- After....... for.....
Rumus Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
Contoh kalimat:
(+) I had been writing my homework for 3 hours when Juna came. (-) I had not been writing my homework for 3 hours when Juna came. (?) Had you been writing you homework for 3 hours when Juna came?
Buku Kuasai Materi Bahasa Inggris (2015) karya Sinta Sasika Novel bisa dibeli di Gramedia.com
Tag past tense Simple Past Tense Past Continuous Tense Past Perfect Tense materi bahasa Inggris kelas 10 past tense contoh

Narrative Text: Pengertian, Struktur dan Karakteristiknya

Bahasa Iklan: Sifat, Unsur, dan Syaratnya

Macam-Macam Tenses yang Paling Umum Digunakan

Pentingnya Sistem Ejaan pada Bahasa Indonesia


Empat Tonggak Ejaan Bahasa Indonesia

TTS Eps 137: Yuk Lebaran

TTS Eps 136: Takjil Khas di Indonesia

TTS Eps 135: Serba Serbi Ramadhan

Games Permainan Kata Bahasa Indonesia

TTS - Serba serbi Demokrasi

TTS Eps 130 - Tebak-tebakan Garing

TTS - Musik Yang Paling Mengguncang
Berita terkait.

Terkini Lainnya
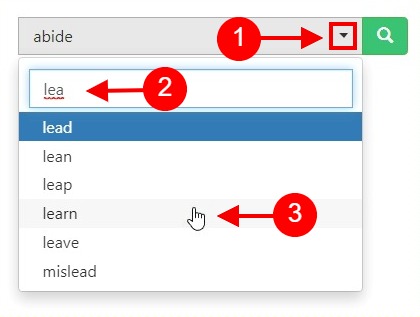
Apa yang Dimaksud dengan Sel Haploid?

Hewan Ternak: Pengertian dan Contohnya

Mengapa Air Termasuk Senyawa Anorganik?
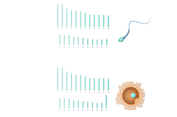
Apa yang Dimaksud dengan Mikoriza?

Jawaban dari Soal "Muatan Listrik 120 C Berpindah"

Interrogative Pronouns: Pengertian, Jenis, dan Contoh Kalimatnya
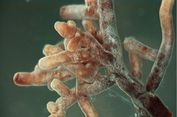
Senyawa yang Diperlukan dalam Reaksi Glikolisis

Mengapa Merkuri Berbahaya?

Mengapa Tulang Burung Berongga?

20 Cara Menghemat Listrik agar Tagihan Tidak Membengkak

Cara Menghitung Besarnya Energi Listrik yang Dipakai

Pengertian Korsleting dan 9 Cara Mencegahnya

4 Peran Listrik dalam Membantu Kehidupan Kita

Pengertian dan Manfaat Personal Branding

6 Jenis Instrumen Investasi dan Risikonya
Dua kali rosan roeslani kubu prabowo datangi megawati, pulang dibekali pesan perjuangan, hasil psg vs barcelona 2-3: dibobol mantan, barca menang, eks kiper milan sebut timnas indonesia maju usai ukir sejarah di piala asia, bukan karena magnet, ini penyebab mesin kendaraan mati di rel kereta, ketika jadi kiper ac milan adalah pekerjaan termudah di dunia..., now trending.

Puncak Arus Balik 14-15 April 2024, Pemudik Diimbau Atur Waktu Kepulangan

Kecelakaan Bus Rosalia Indah di Tol Batang, Sopir Alami "Microsleep" karena Kelelahan

Berebutan Ambil Sembako, Warga di "Open House" Jokowi sampai Terluka dan Pingsan

Waspada, Contraflow Arah Cikampek Diberlakukan di Tol Japek

Mungkin Anda melewatkan ini

Bahaya Ilmu Biologi dan Bioetika

Mendaratnya Pasukan AFNEI Inggris di Surabaya

Penetapan Hari Keluarga Nasional 29 Juni

Fungsi Lembaga Sosial

Apa Itu Reshuffle?
- Entertainment
- Pesona Indonesia
- Artikel Terpopuler
- Artikel Terkini
- Topik Pilihan
- Artikel Headline
- Harian KOMPAS
- Kompasiana.com
- Pasangiklan.com
- Gramedia.com
- Gramedia Digital
- Gridoto.com
- Bolasport.com
- Kontan.co.id
- Kabar Palmerah
- Kebijakan Data Pribadi
- Pedoman Media Siber
Copyright 2008 - 2023 PT. Kompas Cyber Media (Kompas Gramedia Digital Group). All Rights Reserved.
english is easy.
Cerita Liburan Akhir Pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris: How was your weekend?

EnglishCoo – Cerita Liburan Akhir Pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris beserta artinya tentang kegiatan pada saat Weekend. Sabtu & Minggu adalah hari paling ditunggu. Cerita liburan jadi berkesan dan menyenangkan. Apalagi jika liburnya beberapa hari atau sering disebut a long weekend . Wah, enak banget ya libur lama-lama.
“How was your weekend?” adalah topik kita kali ini. Bagi kebanyakan pelajar pemula mungkin masih agak asing dengan pertanyaan tersebut. Bagi penulis pun, ungkapan ini adalah hal baru. Nah, sambil membahasnya, kita belajar bersama. Asyik juga ya.
Sebelum lanjut, EnglishCoo ingin menyampaikan bahwa cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris ini adalah hasil karya dari seorang penulis lepas (lihat tentang penulis di akhir ya). Bagi kamu yang suka berbagi pengetahuan bahasa Inggris plus ingin dapat honor juga, simak kriteria dalam postingan: Yuk Menulis untuk EnglishCoo dan Berpenghasilan Online .

Yuk lanjut.
1. Waktu yang tepat bertanya “How was your weekend?” untuk mengupas cerita liburan akhir pekan
Mengapa memilih topik ini? Saat bertemu dengan seseorang, kita memberi pertanyaan Bahasa Inggris seperti “How are you?”, “How’s it going?” dan “How was your day?” Yap, setelah salam biasanya diikuti dengan pertanyaan seputar kabar. Jenis pertanyaan dalam Bahasa Inggris tersebut tak mengenal hari.
Sedangkan, untuk pertanyaan “How was your weekend?” hanya bisa dilontarkan setelah liburan akhir pekan saja. Kapan itu? Ya, hari Senin dong. Pokoknya setelah hari Sabtu dan Minggu atau habis akhir pekan panjang.
So, kalimat tanya dalam Bahasa Inggris “How was your weekend?” ini akan kita dengar pada waktu tertentu saja (misalnya hari Senin). Bisa juga saat kita bertemu dengan teman atau guru di sekolah atau rekan kerja di kantor. Ingat ya, pertanyaan menggunakan WAS dan WERE adalah untuk masa lalu (Simple Past Tense).
Jangan lewatkan pengetahuan luar biasa lengkap tentang Simple Past Tense, terutama Penggunaan Was dan Were dalam Kalimat Past Tense Sederhana .
2. Cara menjawab “How was your weekend?” untuk cerita liburan akhir pekan menyenangkan

Ada banyak cara menjawab pertanyaan tentang cerita liburan akhir pekan lalu. Kita bisa memberi jawaban singkat. Apabila ada waktu yang cukup dan dituntut menjelaskan, ya jawab dengan cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris.
Bagaimana cara singkat menjawab atau merespon pertanyaan tersebut? Pada kesempatan ini, saya akan membahas bagaimana respon saat ada teman atau orang lain bertanya tentang cerita liburan akhir pekan alias weekend.
Question: How was your weekend? Answer: My last weekend was good.
Gitu saja? Tenang, masih ada beberapa respon untuk merespon dengan cerita liburan akhir pekan menyenangkan. Berikut ini jawaban singkat untuk pertanyaan “How was your weekend?”
- It was awesome.
- It was really fun.
- It was great.
- It was wonderful.
- It was okay.
Tak berhenti sampai di sana saja. Kita pun harus siap dengan pertanyaan selanjutnya, yaitu “What did you do?” Nah, hal ini dapat menjadi awal sebuah cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris.
Question: So, what did you do? Answer: I went shopping with my Mom.
Percakapan di atas adalah contoh sederhana yaitu aku pergi berbelanja dengan Ibu. Setiap orang tentu memiliki kegiatan berbeda pada hari Sabtu dan Minggu. Cerita liburan akhir pekan menyenangkan seperti apa yang pernah kamu jalani?
Berikut adalah beberapa kegiatan menyenangkan dalam Bahasa Inggris yang mungkin dilakukan saat weekend.
- went shopping
- visited friends
- had a party
- saw a movie
- stayed at cousin’s house
- went for a walk
- watched a DVD
- went to the cinema
- stayed in a hotel
- visited many places
- went camping
- went to theatre
- spent time with family
- went to concerts
- had coffee with friends
Begitu banyak pilihan kegiatan bisa kita lakukan saat akhir pekan (Weekend) ya. Selain beberapa kegiatan di atas kamu juga bisa membuat cerita tentang kegiatan luar biasa lainnya dilakukan saat liburan akhir pekan lalu.
Baca juga: 23 Contoh Dialog Bahasa Inggris 2 Orang Percakapan Sehari Hari
3. Cara menjawab “How was your weekend?” untuk cerita liburan akhir pekan kurang menyenangkan

Dari pembahasan sebelumnya kita tahu cara merespon pertanyaan “How was your weekend?” untuk akhir pekan menyenangkan. Tapi nggak semua liburan akhir pekan itu menyenangkan. Setuju?
Bagaimana bila cerita liburan akhir pekan kita membosankan? Respon apa yang sesuai untuk pernyataan tersebut? Berikut cara merespon apabila cerita liburan akhir pekan yang kamu miliki kurang menyenangkan.
Question: How was your weekend? Answer: My last weekend was bad.
Bukan itu saja. Ada juga beberapa cara lain untuk mengawali cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris yang biasa saja atau bahkan kurang menyenangkan. Yuk simak contoh dalam Bahasa Inggris berikut ini.
- It was bad.
- It was a terrible weekend.
- My last weekend was awful.
- It was boring.
Untuk menjelaskan akhir pekan, kamu bisa gunakan kata sifat lainnya serta pelajari makna kata-kata membingungkan: Ribuan Daftar Kata Sifat dalam Bahasa Inggris Super Lengkap A sampai Z Confusing Words dalam Bahasa Inggris Penting Kamu Tahu
Apabila ada teman memberi jawaban tersebut, apa ya kira-kira respon yang cocok? Tentu saja bertanya-tanya apa yang membuat cerita liburan akhir pekannya kurang menyenangkan. Dan kalimat tanya yang bisa kita gunakan untuk meresponnya kembali yaitu:
Question: What was wrong? Answer: I worked all Sunday.
Ya, siapa juga yang suka bekerja pada saat libur terutama hari Minggu. Tentu saja liburan akhir pekan menjadi kurang menyenangkan. Apalagi pekerjaan yang dilakukan membosankan. Waduh!
Selain bekerja, berikut ini hal kurang menyenangkan dalam Bahasa Inggris yang dapat terjadi saat liburan akhir pekan.
- had a bad cold
- was ill on Saturday
- checked emails
- did homework
- stayed at home all Saturday
- finished the report
- worked half a day
- worked on Sunday
- worked at the weekend
- cleaned my house
- cleaned the car
- did the washing
- finished Math assignments
Yuk temukan tips untuk meningkatkan keterampilan Speaking: Belajar Speaking dan Listening Lewat Film dengan Cara Santai Ngomong Bahasa Inggris kayak Bule? Baca 4 Jurus Jitu Ini
4. Contoh cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris

Terakhir, saya akan memberi contoh paragraf atau cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris. Jangan lupa ya, di sini jenis kalimatnya menggunakan Simple Past Tense.
Sebagai pengingat, Simple Past Tense merupakan bentuk tense yang menceritakan atau menggambarkan kejadian di masa lampau (Past) dan menggunakan kata kerja bentuk kedua (Verb 2).
OK. Check it out now…
Artinya: Akhir pekan terakhirku baik-baik saja. Pacarku mengirimkan pesan. Ia mengajakku bertemu untuk sarapan. Kemudian, kami bermain bulu tangkis bersama. Pukul 11.00 dia dan aku pergi ke sebuah kafe dan minum secangkir kopi. Kami juga makan. Kami mendengarkan musik, mengobrol cukup banyak dan menikmati waktu bersama. Setelah itu, kami berjalan-jalan di sekitar Central Park. Jam 2 siang aku pulang ke rumah dan mendengarkan (lagu) Beyonce dan Selena Gomez selama satu jam. Setelah itu, aku masak makan malam untuk keluargaku. Setelah makan malam, sepupuku datang berkunjung dan membawa 2 buah tiket konser, jadi kami pergi ke konser malam itu. Kami tiba disana pukul 07:30. Kami duduk di tempat yang cukup tinggi, tapi pemandangannya begitu luar biasa. Pukul 10.00 malam kami pulang ke rumah. Hari yang begitu panjang dan aku sangat menikmatinya.
Ingin membaca & menulis contoh descriptive text dan narrative text? Nih ada beberapa contoh teks dalam Bahasa Inggris. Check them out! Contoh Descriptive Text about Someone, 7 Orang Sukses di Dunia 5 Contoh Descriptive Text Tentang Hewan Yang Diserbu Ribuan Orang 7 Contoh Descriptive Text tentang Tempat Keajaiban Dunia Populer Contoh Narrative Text Pendek dan Unik dari 7 Negara di Dunia
Kita bisa melihat bahwa kata kerja bentuk kedua (Verb 2) dari cerita liburan dalam Bahasa Inggris di atas yaitu texted, asked, played, went, had, ate, listened, talked, enjoyed, taken, cooked dan lain-lain.
Eemmm, buat para pembaca yang punya ketelitian cukup tinggi, kalian akan menemukan salah satu kata kerja Bahasa Inggris yang tidak mengikuti pola Simple Past Tense, verb manakah itu???
Pada contoh cerita liburan akhir pekan di atas, ada kalimat Bahasa Inggris tidak menggunakan verb 2 ( He asked me to meet him for breakfast ) yaitu kata kerja meet . Di sini meet tidak dirubah menjadi met (verb 2) karena merupakan infinitive. Dalam kalimat ini, setelah to harus diikuti kata kerja Verb 1.
Penjelasan infinitive bisa kita diskusikan pada kesempatan selanjutnya ya, karena di sini kita hanya fokus pada cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris menggunakan Simple Past Tense.
Selain itu, untuk membuat cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris menjadi lebih menarik, kamu bisa tambahkan beberapa kata keterangan (adverb) atau lainnya. Misalnya menambahkan “at the end of…” sebagai kalimat terakhir atau penutup.
“…We were sitting pretty high up, but the view was amazing. At the end of the concert, there was an accident …” atau “…We were sitting pretty high up, but the view was amazing. At the end of the concert, there was big applause …”
Ingin membaca contoh paragraf atau cerita dalam Bahasa Inggris? Nih ada beberapa artikel membahas contoh paragraf dengan tenses berbeda. Check them out. Contoh Paragraf Simple Present Tense, Cerita Diri, Orang Lain & Liburan Contoh Paragraf Simple Future Tense Cerita Masa Depan Contoh Paragraf Simple Past Tense, Cerita Seru Masa Lalu
Cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris berbeda antara satu orang dengan orang lainnya. Walaupun akhir pekan adalah waktu bersantai, tak semua orang memiliki cerita liburan akhir pekan menyenangkan. Ada yang membosankan dan bahkan menyedihkan. Bagaimana dengan akhir pekanmu yang telah berlalu?
Sekilas tentang penulis: AZZA SUNDUS ANTARTIKA Namanya Azza Sundus Antartika, perempuan yang lahir di kota Temanggung, dari keluarga sederhana. Sejak kecil dia selalu dinasehati ayah dan ibunya untuk selalu bekerja keras. Ia memiliki gelar sarjana Sains dari Universitas Gadjah Mada.
Website: www.englishcoo.com Facebook: englishcoocom Instagram: englishcoocom Youtube: EnglishCoo
3 thoughts on “ Cerita Liburan Akhir Pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris: How was your weekend? ”
thanks alot of information keren
terima kasih kakak, sangat membantu utk belajar anak-anak.
Hai Dwi, Sama-sama. Terimakasih sudah berkunjung dan menulis komentar di blog EnglishCoo 😉
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
About EnglishCoo
Belajar bahasa inggris, recent posts.
- Kalimat Bahasa Inggris Sehari Hari Paling Sering Digunakan
- Cara Membaca Jam dalam Bahasa Inggris dengan Mudah
- Ungkapan Sehari Hari dalam Bahasa Inggris dan Artinya
- 23 Contoh Dialog Bahasa Inggris 2 Orang Percakapan Sehari Hari
- 99 Contoh Kalimat Simple Present Tense, Rumus, dan Penjelasan
- 101 Contoh Kalimat Noun Clause dan Artinya Terlengkap
- 101 Contoh Noun Clause dan Artinya yang Paling Lengkap
- Noun Clause: Pengertian, Contoh, Fungsi, Soal Lengkap
- Contoh Kalimat Aktif dan Pasif Bahasa Inggris 16 Tenses
- Contoh Kalimat Passive Voice dalam Bahasa Inggris
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Past Continuous
- Past Future
- Past Future Continuous
- Past Future Perfect
- Past Future Perfect Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Simple Future
- Simple Past
- Simple Present

- Ramadhan Promo
- Anak Online
- Anak On Campus
- Remaja Online
- Remaja On Campus
- Dewasa Online
- Dewasa On Campus
- TOEFL Paper Based
- Kelas Online
- Tentang Kami
Past Tense: Pengertian, rumus, dan contoh
Hello English learners!
Masih semangat kan, belajar Bahasa Inggrisnya?
Harus semangat dong! Ingin kan, bisa punya karir cemerlang dan dapat beasiswa ke luar negeri ? Kalau iya, harus lancar Bahasa Inggris dong!
Tentu, belajar Bahasa Inggris membutuhkan waktu dan konsistensi, jadi, let’s learn it together step by step!
Hari ini, kita belajar tenses yuk!
Specifically, kita akan belajar tentang past tense!
Apa itu past tense?
Simpelnya, past tense digunakan untuk mendeskripsikan aktivitas atau situasi yang terjadi di masa lampau. Perhatikan contoh berikut:
- I wrote a letter to my friend (ini menunjukkan aktivitas di masa lampau)
- I was hungry (ini adalah situasi di masa lampau)
Past tense dibedakan menjadi beberapa jenis. Mari kita pelajari bersama!
Simple past tense
Sebelum kita mulai, coba deh, perhatikan contoh di bawah ini:
Victoria was the Queen of the United Kingdom, she reigned for 63 years, from 1837-1901. She was born in 1819 and died in 1901. She had 9 children.

Setiap kata dalam tulisan tebal adalah contoh dari past tense.
Jadi, bisakah kamu menebak dalam situasi apa past tense digunakan?
Yak, benar! Past tense digunakan untuk mendeskripsikan aktivitas yang dimulai dan juga telah berakhir di masa lampau.
Penggunaan Simple Past Tense
Untuk penggunaan past tense yang benar, kalian bisa simak penjelasan berikut dibawah ini ya :
- Untuk menerangkan kejadian di masa lampau dalam waktu yang pasti
- Untuk menyatakan kejadian di masa lampau yang telah selesai saat itu juga
- Digunakan pada kejadian yang berulang kali atau menjadi kebiasaan di masa lalu
- Untuk menyatakan perasaan atau emosi yang terjadi di masa lampau
- Untuk kejadian yang menjadi kebiasaan pada masa lampau namun sudah tidak lagi dilakukan. Kata kerja yang digunakan adalah used to
Ciri-ciri simple past tense
Simak ciri – ciri simple past tense pada penjelasan berikut :
- Menunjukkan aktivitas yang terjadi di masa lampau, atau menggunakan to be was/were, verb yang digunakan selalu bentuk ke dua
- Menggunakan time signal bentuk lampau seperti last night, yesterday, dan sebagainya
- Memakai kata kerja regular dan irregular
Rumus simple past tense
1. Nominal simple past tense Di bawah merupakan rumus dari nominal simple past tense : (+) Subject + to be (was/were) + complement (-) Subject +to be (was/were) + not + complement (?) To be (was/were) + Subject + complement
2. Verbal simple past tense Berikut ini merupakan rumus verbal simple past tense : (+) Subject + verb 2 + complement (-) Subject + did + not + verb 1 (?) Did + subject + verb 1
Regular verb & Irregular verb
Banyak verb dari simple past tense yang berakhiran -ed, ini dinamakan regular verb. Berikut beberapa contoh penggunaan regular verb :
- The Johnsons invited me to their dinner party
- She danced all night long
- Emma passed her exam because she studied hard for it
Namun, ada juga irregular verb. Perhatikan beberapa contoh berikut:
- Drink → drank Josh drank two cans of coke
- Pay → paid I paid for her taxi fare
- Send → sent She sent the invitation last week
Pada kalimat tanya dan kalimat negatif, kita menggunakan did/didn’t + infinitive (basic form of a verb: walk, drive, study, etc).
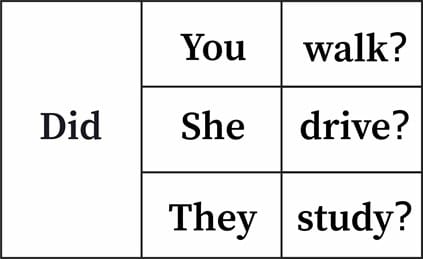
Perhatikan contoh-contoh berikut:
- I didn’t buy anything because I didn’t have enough money
- I didn’t drive to my grandma’s house. I took the bus.
- Did you study for the exam?
Bentuk past tense dari to be (am, is) adalah was, were.
Contoh:
- He was hungry so he ate a burger
- The water was too cold for me to swim
- They weren’t happy about the service
Gampang kan?
Oke deh, mari kita lanjut ke…
Past continuous tense
Sama seperti sebelumnya, yuk kita mulai dengan melihat contoh kalimat di bawah ini:
Yesterday, Holly and Daniel studied together. They started at 3 pm and finished at 5 pm. So, at 4 pm, they were studying together.

Kalimat they were studying mengindikasikan bahwa mereka sedang berada dalam proses belajar, jadi, belajarnya belum selesai.
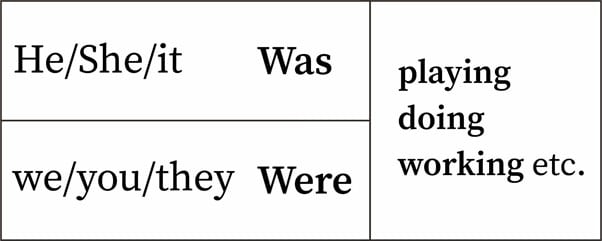
Rumus past continuous tense
Dapat dilihat dari contoh di atas, rumus past continuous tense itu mudah kok!
Kamu cukup menulis subject+was/were+ing
Ciri-ciri Past Continuous Tense
- Karena waktu terjadinya adalah di masa lampau (past), maka past continuous tense selalu diikuti auxiliary verb ‘be’, berupa was atau were
- Was digunakan untuk subjects he, she, it, atau singular (subjek tunggal)
- Were digunakan untuk subjects I, you, they, we, atau plural (subjek jamak)
- Verb yang digunakan adalah present participle atau V1, karena termasuk progressive tense
- Present participle yang digunakan dalam past continuous tense adalah verb -ing atau gerund
Penggunaan past continuous tense
Jadi, past continuous tense digunakan untuk mendeskripsikan aktivitas yang sedang berlangsung di masa lampau. Seringkali (tapi tidak selalu) past continuous tense digunakan sebagai latar situasi untuk kalimat past tense .
- We were playing dungeons and dragons when it started raining
Kita juga bisa menggunakan past continuous tense dalam kalimat yang sama dengan simple past tense untuk menjelaskan bahwa ada suatu kejadian yang berlangsung setelah kejadian lain. Contohnya:
- As I was walking down the street, I saw Sophie. So I stopped and we talked.
Sekarang, coba bandingkan 2 kalimat berikut:
Coba tebak, apa sih perbedaan dua kalimat tersebut?
Yak, benar!
Di kalimat pertama, aku sudah mulai bermain gitar ketika Kevin datang. Sedangkan di kalimat kedua, aku baru mulai bermain gitar setelah Kevin datang.
Gampang kan? Oke, mari kita lanjutkan ke…
Present perfect tense
Ha? Gimana?
Mungkin kamu berpikir, jelas-jelas namanya PRESENT perfect…
Tapi baca aja dulu! Seperti biasa, kita mulai dengan contoh bacaan ya!
Mrs. Greta lives in Norfolk, UK. Her children live in the US. She has not seen them in 3 years. However, Mrs. Greta has talked to her children on the phone many times. She has also seen pictures of her grandchildren . They have grown a lot since the last time Mrs. Greta met them three years ago.
Nah, sekarang paham kan kenapa present perfect masuk dalam bagian past tense?
Present perfect tense penting karena present perfect tense menunjukkan bahwa kejadian di masa lampau memiliki efek hingga masa sekarang.
Penggunaan present perfect tense
Present perfect tense dapat digunakan dalam berbagai konteks atau situasi, contohnya:
- Untuk mendeskripsikan aktivitas yang dilakukan berulang di masa lampau dan sekarang.
Contoh: She has gone to Japan many times (Dia sudah pernah pergi ke Jepang berulang kali)
- Untuk mendeskripsikan suatu kejadian di masa lampau yang masih berlanjut sampai sekarang
Contoh: I have lived in Australia since 2008 (Aku telah tinggal di Australia sejak tahun 2008)
- Untuk mendeskripsikan suatu kejadian yang belum selesai
Contoh: It has been raining a lot this month (satu bulan terakhir ini sering sekali hujan)
- Untuk mendeskripsikan suatu kejadian yang tidak terlalu lama ini telah usai
Contoh: She has just completed her bachelor’s degree (Dia baru saja menyelesaikan studi S1 nya)
- Untuk mendeskripsikan suatu kejadian dimana waktu bukanlah aspek yang penting
Contoh: He has lost his passport (Dia kehilangan paspornya)
Ciri – ciri present perfect tense
- Predikat kalimat dalam bentuk tense ini selalu terdiri dari: Have/Has + Past Participle
- Untuk subjek yang terdiri dari orang ketiga tunggal misalnya: Donna, Andy, She, He, It dsb, selalu menggunakan kata kerja bantu has, Sedangkan subjek yang terdiri dari I, you, they, we, dengan kata kerja bantu have
- Kalimat tanya dibentuk dengan memindahkan kata kerja bantu Has/Have ke depan subjek atau pokok kalimat, sedangkan negatifnya dengan menambahkan kata not di belakang Has/Have atau diletakkan setelah subjek
Rumus present perfect tense
Seperti bisa dilihat di contoh-contoh di atas, rumus untuk present perfect tense adalah subject+have/has + past participle
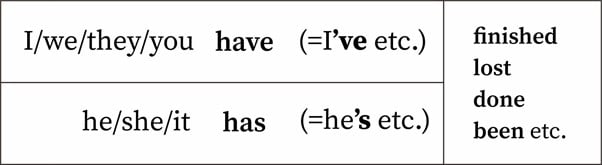
Okay, let’s do a little review!
Masih ingat tentang simple past tense bukan? Apakah kamu tahu perbedaannya dengan present perfect?
Bandingkan contoh berikut ini:
Sudah paham kan dengan perbedaannya?
Kalau sudah paham, mari lanjut ke…
Past perfect tense
Seperti biasa, mari kita mulai dengan membaca contoh paragraf di bawah:
Last night, Alexandra danced in a ballet dancing competition. She had practiced for nearly a year before the competition. She was mesmerizing. Alexandra’s family were in the audience. Before that night, they had never seen Alexandra dance.
After everyone had danced , the judges announced the winner. Alexandra won! She was the best dancer in the competition. Alexandra said she had never practiced so hard before! She was glad they had practised a lot.

Penggunaan past perfect tense
Jadi, dari contoh di atas, bisa tebak tidak kira-kira past perfect tense digunakan untuk apa?
Past perfect tense digunakan untuk menjelaskan hal yang terjadi sebelum hal lainnya yang juga terjadi masa lampau. Mengamati contoh di atas, kita bisa lihat bahwa contoh tersebut membicarakan suatu kejadian yang terjadi di masa lampau:
- Alexandra won the ballet competition last night.
Sebelum hal itu terjadi…
- She had practised for nearly a year.
Kapan kita harus menggunakan past perfect tense?
Apabila kamu sedang membicarakan suatu kejadian di masa lampau (mari kita sebut event A) dan kamu ingin menceritakan kejadian yang terjadi sebelum event A, kamu bisa menggunakan past perfect tense. Past perfect tense membantu kita menceritakan suatu kejadian secara berurutan dengan jelas dan spesifik.
Ciri – Ciri past perfect tense
- Mengungkapkan suatu kejadian yang telah terjadi atau selesai di masa lampau
- Lebih terpaku pada kejadian daripada waktu
- Pada past perfect tense predikatnya menggunakan Had + past participle
- Keterangan waktu digunakan dalam bentuk past perfect tense → after, before, just, two month ago, as soon as
Rumus past perfect tense
Mudah kok! Rumusnya adalah subject + had + past participle
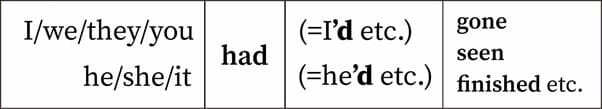
Yak, benar!
Kalimat pertama menggunakan simple past tense sedangkan kalimat kedua menggunakan past perfect tense. Di kalimat kedua, Daniel sudah tiba di rumah ketika aku menelepon. Sebelumnya, dia sedang berada di mall.
Oke, mari kita lanjut! Sekarang, saatnya bahas…
Past perfect continuous
Pasti sekarang sudah hafal dong, apa yang akan kita lakukan?
Yak, kita mulai dengan membaca contoh paragraf!
Tom and Sarah had been driving to church before they stopped. They had been driving down a dirt road when they heard a strange noise. Tom stopped the car then they exited the car.
Tom looked at the car. It had been going for half an hour or so. He knew how to fix cars. He had been working as a mechanic for nearly a decade before he moved to the country. Tom got his tools and looked under the hood. It seemed that the engine had been heating up .
Tom was able to fix the car and after that, they continued driving. By the time Tom and Sarah arrived at the church, they had been driving for 2 hours.

Penggunaan past perfect continuous
Dari contoh di atas, bisakah kamu menebak apa itu past perfect continuous tense dan kapan kita bisa menggunakannya?
Past perfect continuous digunakan untuk menjelaskan situasi yang berlangsung tapi kemudian sudah selesai di masa lampau.
Ciri – ciri past perfect continuous
Ciri – ciri dari past perfect continuous adalah predikat kalimat yang sering digunakan dalam bentuk tense ini berupa: Had + Been + Present Participle.
Rumus past perfect continuous
Rumusnya? Mudah saja! Subject+had been+verb ing

Ringkasan singkat past tenses

Selamat telah menyelesaikan hingga sejauh ini!
Sekarang, kamu sudah ahli di bidang past tense!
….or have you? 👀
Yuk, cek pemahamanmu melalui latihan di bawah!
A. Complete the sentences using the following verbs in the correct form
- Queen Victoria …. for 63 years.
- What … you do yesterday? I … at the lake because it was hot.
- Who … your biology class last semester? Mrs. Byrne.
- Agatha Christie …. 66 detective novels during her lifetime.
- When …. to choose between a holiday to Bangkok or Bali, she … the latter.

B. Put the verbs into the correct form, past continuous or past simple
- Jane …. (wait) for me when I … (arrive).
- ‘What… (you / do) at this time yesterday? ‘I was still at school’.
- ‘…. (you / go) out last night? ‘No, I was too tired.’
- I haven’t seen Kevin for ages. When I last … (see) him, he … (try) to find a job.
- I … (walk) along the street when suddenly I …. (hear) something behind me. Somebody … (follow) me. I was scared and I …. (start) to run.
C. Put the verb into the correct form, past perfect or past simple
- Regina wasn’t at the party when I arrived. … (she / go) home.
- I felt very tired when I got home, so …. (I / go) straight to bed.
- Dan travels a lot. When I first met him …. (he / already / visit) 34 countries.
- Sorry I’m late. The car … (break) down on my way here.
- We were driving along the road when … (we / see) a car which …. (break) down, so… (we / stop) to help.
D. Which is right?
- It was noisy last night. Our neighbours were having / had been having a party
- Owen was sitting on the ground. He was out of breath. He was running / he’d been running.
- I am entering a dance competition next month. I’ve been training / I’d been training for it every day.
- I had arranged to meet Lily, but I was late. When I finally arrived, she was waiting / she’d been waiting for me. She was annoyed because she was waiting / she’d been waiting such a long time.
- Henry and I work for the same company. He joined the company before me. When I started working here two years ago, he was already working / he’d already been working there.
Akhir kata
Ingin lancar berbahasa Inggris?
Kebanyakan orang di Indonesia malu bicara Bahasa Inggris di depan publik. Mereka takut salah dan tidak percaya diri saat harus bicara dalam Bahasa Inggris.
Ini akibat dari pengajaran Bahasa Inggris yang salah!
Mereka tidak hanya kehilangan waktu dan uang, lebih parah lagi mereka mendapat dasar Bahasa yang salah yang susah diperbaiki. Akhirnya, mereka menjadi bosan dan kehilangan percaya diri.
Ini adalah kesalahan yang fatal!
Kursus Bahasa Inggris #1 di Indonesia
Di IELC, kami mengajarkan Bahasa Inggris dengan cara yang benar supaya kamu dapat cepat berbicara dengan percaya diri dan lancar. Inilah keahlian yang kamu butuhkan untuk untuk memaksimalkan potensi dan meraih impian di masa depan.
Di lingkungan belajar modern kami, kamu akan merasa nyaman dan bebas untuk mengekspresikan diri.
Jangan khawatir, guru kami akan membimbingmu di setiap langkah proses pembelajaran untuk memastikan kamu mendapat hasil pembelajaran yang terbaik.
IELC adalah Kampus Bahasa Inggris #1 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan kursus Bahasa Inggris untuk anak, remaja, dan dewasa sebagai berikut:
- Kelas online anak
- Kelas online remaja
- Kelas online dewasa
- Kelas on campus anak
- Kelas on campus remaja
- Kelas on campus dewasa
- Kelas online dan on campus IELTS
- Kelas online dan on campus TOEFL PBT
- Kelas online dan on campus TOEFL iBT
Baik secara online maupun on campus, kami akan memberimu keahlian yang kamu butuhkan di masa depan. Hubungi kami hari ini dan ambil langkah pertama untuk menjadi lancar dan percaya diri.
Salam,
Anthony McCormick
IELC Managing Director
- Bahasa Inggris Online
- Bahasa Inggris untuk Anak
- Bahasa Inggris untuk Dewasa
- Bahasa Inggris untuk Remaja
- Grammar Tips
- Mengajar Bahasa Inggris
Intan Aulia Husnunnisa
February 28, 2024 • 10 minutes read

Past continuous tense ternyata tak hanya berfungsi untuk menceritakan kejadian yang sedang berlangsung di masa lampau, lo . Yuk, temukan penjelasan lengkapnya di artikel ini! —
Hai guys ! Hehe , kita bakal bahas tense s lagi nih . Soalnya, dengan belajar grammar yang satu ini akan membuat kita mengetahui bagaimana cara membuat kalimat. Jadi, materi paling dasar dalam bahasa Inggris ini nggak boleh kita lewatkan.
Anyway , di artikel-artikel sebelumnya, kita sudah mempelajari tiga simple tense. Mulai dari simple present tense , simple past tense , hingga simple future tense . Apakah kamu masih ingat? Pasti masih dong ?
Nah, kali ini kita akan mengupas tuntas tentang past continuous tense. But wait, sebelum lanjut scroll down , apakah sebelumnya kamu sudah memahami simple past tense dan present continuous tense ? Soalnya, kamu akan dapat mempelajari past continuous tense dengan lebih mudah kalau sudah punya bekal pemahaman tentang dua tenses tersebut. Hmm , kalau sudah, yuk, kita bahas mengenai past continuous tense di artikel ini!
Pengertian/Definisi P ast Continuous Tense
Kalau present continuous tense membahas tentang kejadian yang sedang berlangsung di masa sekarang , maka past continuous tense adalah tenses untuk menyatakan suatu peristiwa atau kejadian yang sedang terjadi di masa lalu ( past ) selama waktu tertentu .
Ingat-ingat ya, pokoknya kalau present berkaitan dengan masa sekarang, kalau past itu ada kaitannya dengan masa lalu .
Bentuk tenses ini menunjukkan bahwa suatu aksi dapat terjadi sebelum ( began before ), selama (was in progress during) , dan mungkin berlanjut setelah (continued after) ada aksi lainnya di masa lampau.
Jadi, past continuous tense adalah bentuk kalimat yang disela oleh kejadian lain dan juga dapat digabungkan dengan kejadian lainnya pada waktu yang bersamaan . Oke, jangan pusing dulu ya . Kita coba lihat rumus dan contohnya di bawah!
Rumus P ast Continuous Tense
Yak , bertambah lagi deh satu rumus yang harus kamu ingat dalam dunia tenses ini. Tapi biasanya, kalau ingat continuous , maka ingat penambahan – ing pada akhir kata kerja.
Eits eits , sayangnya formula yang satu ini nggak sesederhana itu guys . Yuk, kita lihat rumus past continuous tense pada setiap jenis/pola kalimat melalui tabel di bawah ini!

Dari rumus di atas, ada beberapa hal atau poin-poin penting yang menjadi ciri khas dari past continuous tense , catat ya!
- Past continuous tense dibentuk dengan auxiliary verb “be” , berupa was atau were , karena waktu terjadinya adalah di masa lampau ( past ).
- Past continuous tense termasuk progressive tense , maka verb atau kata kerja yang tepat adalah present participle .
- Present participle disebut juga dengan verb -ing .
- Present participle dikenal juga dengan gerund , dia adalah suatu bentuk kata kerja dalam bahasa Inggris . Untuk menyusun sebuah present participle , kita dapat menggunakan bentuk dasar dari kata kerjanya lalu menambahkan imbuhan – ing . Bentuk ini digunakan untuk menunjukkan aktivitas yang sedang berlangsung.
- “Be (was) ” digunakan untuk singular subject berupa singular noun (seperti: Doni, pen, dan dog) , serta singular pronoun (seperti: I, she, he, dan it) kecuali “you”.
- Sebaliknya, “ be (were) ” digunakan untuk plural subject berupa plural noun (seperti: dogs , people, pens ) dan plural pronoun (seperti: you, they, dan we).
Baca Juga: Future Continuous Tense: Pengertian, Rumus, Fungsi, dan Contoh Kalimat
Contoh kalimat P ast Continuous Tense
Sebelum lanjut ke berbagai fungsi past continuous tense yang cukup complicated , yuk, lihat beberapa contoh kalimat sederhananya terlebih dahulu!
(+) He was traveling to Venice. (Dia dulu sedang berlibur ke Venice.)
(+) She was eating a burger. (Dia dulu sedang makan burger.)
(-) He wasn’t sleeping . (Dia dulu tidak sedang tidur.)
(-) The people weren’t waiting . (Mereka dulu tidak sedang menunggu.)
(?) Was he buying a book? (Apakah dia dulu sedang membeli sebuah buku?)
(?) Were the people playing tennis? (Apakah orang-orang dulu sedang bermain tenis?)
Adverb of Time Past Continuous Tense
Kata keterangan waktu yang digunakan dalam past continuous tense sebetulnya hanya ada dua. Namun, keterangan waktu tersebut bisa bertambah sesuai dengan konteks pembahasan dan juga fungsi kalimat yang dipakai.
Seperti yang sudah kita bahas di bagian pengertian/definisi, karena tenses ini dapat disela oleh kejadian lain dan juga dapat digabungkan dengan peristiwa lainnya dalam waktu bersamaan, maka ada dua keterangan waktu yang menjadi ciri khas past continuous tense , yaitu:

P enggunaan dan Contoh Kalimat Past Continuous Tense
Seperti biasa, setiap tense memiliki fungsi dan kegunaannya masing-masing. Dalam hal ini, past continuous tense memiliki beberapa fungsi baik untuk speaking ataupun writing .
1. To express actions that were ongoing in past (menyatakan kejadian yang berlangsung di masa lampau)
Nah, inilah fungsi yang paling familiar dalam past continuous tense , yaitu menyatakan suatu aksi yang berlangsung di masa lampau seperti contoh yang sudah kita bahas sebelumnya.
Untuk fungsi kalimat ini, kamu dapat menggunakannya jika ingin menceritakan sesuatu yang nggak dibarengi dengan kejadian lain, jadi nggak pakai while atau when . Agar keterangan waktunya lebih jelas, berikut keterangan waktu atau time expression yang dapat digunakan, yaitu: at this time yesterday, at 5 am this morning, all day yesterday, in July, two years ago, last night, and so on. Contoh kalimatnya adalah :
- Two years ago, I was working at a bar in New York City. (Dua tahun lalu, saya sedang bekerja di sebuah bar di New York City.)
- They were making a toast at this time last night. (Mereka sedang membuat roti panggang pada jam ini kemarin malam.)
2. Two events that happened simultaneously in the past (menunjukkan dua kejadian yang terjadi secara bersamaan di waktu lampau)
Past continuous tense digunakan untuk menjelaskan peristiwa yang terjadi atau berlangsung secara bersamaan di masa lampau . Maka dari itu, di sini diperlukan keterangan waktu while atau when . Lihat contoh berikut:
I was eating while my brother was studying. (Saya sedang makan ketika adik saya sedang belajar.)
Diane was watching TV while Andy was taking a nap. (Diane sedang menonton tv sementara Andy sedang tidur siang.)
3. Before and after another action or event happened (sebelum dan sesudah tindakan atau peristiwa lain)
Yuk , perhatikan contoh berikut terlebih dahulu:
We were busy working on our assignment when our parents came home . (Kami sedang sibuk mengerjakan tugas kami ketika orang tua kami pulang.)
I was watching the lovely sunset as a flock of birds soared by. (Saya sedang menyaksikan matahari terbenam yang indah saat sekawanan burung terbang melintas.)
Mari kita coba pahami contoh pertama. Pada kalimat tersebut, berarti kami sedang mengerjakan tugas sebelum orang tua pulang, masih mengerjakan tugas ketika orang tua pulang, dan mungkin masih mengerjakan tugas setelah orang tua pulang. Kejadian tersebut terjadi pada suatu waktu di masa lampau dan tidak terjadi pada saat ini.
4. Interrupted by another action or event (suatu aktivitas terganggu oleh tindakan atau persitiwa lain)
Kamu dapat menggunakan past continuous tense jika saat ini kamu bercerita tentang kejadian berlangsung di masa lalu yang tiba-tiba terganggu oleh tindakan lain. Contohnya adalah sebagai berikut :
Mark was having the most wonderful time on the beach when the weather suddenly turned awful . (Mark sedang bersenang-senang di pantai ketika cuaca tiba-tiba berubah menjadi buruk.)
As they were leaving , the phone rang . (Ketika mereka pergi, telepon berdering.)
5. For a length of time ( whether specific or undefined – untuk jangka waktu yang lama apakah spesifik atau tidak ditentukan)
Kamu juga dapat menjadikan past continuous tense untuk menceritakan suatu aksi berlangsung di masa lalu dalam waktu yang spesifik, atau bahkan dalam waktu yang tidak ditentukan sama sekali a.k.a waktu yang nggak jelas. Contoh kalimatnya:
- My head was throbbing . ( undefined length of time ) (Kepalaku (dulu) berdenyut-denyut.)
- You were eating that sandwich for an hour ! ( specific length of time ) (Kamu (dulu) sedang makan sandwich itu selama satu jam!)
6. Repeatedly and frequently (membahas sesuatu yang berulang-ulang)
Past continuous tense digunakan juga untuk membahas sesuatu yang terjadi berulang-ulang. Meskipun interval kejadiannya acak, tapi sebetulnya kalimat ini menunjukkan kebiasaan alami. Contoh:
I was repeatedly checking things. (Saya dulu berulang kali memeriksa sesuatu.)
- My parents were fighting all the time when I decided to leave. (Orang tua saya bertengkar sepanjang waktu ketika saya memutuskan untuk pergi.)
7. A source of irritation (menunjukkan keburukan seseorang)
Pada penggunaan yang satu ini, kamu dapat menunjukkan keburukan seseorang di masa lalu melalui past continuous. Dalam hal ini, keterangan waktu yang dipakai adalah adverb of time dari simple present tense untuk menunjukkan frekuensi berulang-ulang, seperti always dan constantly . Contoh:
- My ex-husband was always leaving dirty dishes in the sink. (Mantan suami saya selalu meninggalkan piring kotor di wastafel.)
- The old boss was constantly berating employees over silly issues. (Bos lama terus-menerus mencaci-maki karyawan karena masalah konyol.)
9. To show development, growth, or other change(s) over time (untuk menunjukkan perkembangan, pertumbuhan, atau perubahan lain dari waktu ke waktu)
Tense ini juga bisa digunakan bersamaan dengan verb yang menunjukkan perubahan (change) atau perkembangan (growth), seperti: grow up, improve, go, dan change. Contoh kalimat:
- My life was changing rapidly. (Hidup saya berubah dengan cepat.)
- I thought her condition was improving , but I guess not. (Saya pikir kondisinya membaik, tapi saya rasa tidak.)
10. Narrating a story or describing an atmosphere (menceritakan sebuah kisah atau menggambarkan suasana)
Kalau fungsi yang satu ini pasti cukup mudah untuk kamu pahami. Yup, kamu dapat menceritakan suasana yang terjadi di waktu lampau menggunakan past continuous tense . Berikut ini contohnya:
As they walked into the sunshine, the birds were singing and the breeze was softly blowing . (Saat mereka berjalan di bawah sinar matahari, burung-burung bernyanyi dan angin sepoi-sepoi bertiup lembut.)
I was working in a New York City bar when all of this took place. (Saya sedang bekerja di bar Kota New York ketika semua ini terjadi.)
11. Shows an action with two durations at the same time (menunjukkan aksi dalam dua durasi berbeda di waktu bersamaan)
Past continuous juga dapat digunakan pada saat menyatakan bahwa ada aksi berdurasi pendek ( simple past tense ) yang terjadi ketika suatu aksi berdurasi panjang (past continuous tense ) sedang berlangsung.
Jadi, while dan when dapat digunakan dengan formula simple past tense + while + past continuous tense dan past continuous tense + when + simple past tense. Bagaimana jika kita ingin menggunakannya dalam sebuah kalimat? Please, take a look at the example below!
- The door was knocked while I was reading a book. (Pintu diketuk ketika saya sedang membaca buku.)
- Rio was sleeping when you called her. (Rio sedang tidur ketika kamu meneleponnya.)
Itulah dia fungsi dan kegunaan past continuous tense dalam beberapa jenis kalimat. Oke, tarik napas dulu jangan lupa. Anyway, setelah membaca sepuluh fungsi past continuous tense di atas, mungkin kamu perlu waktu untuk memahami keseluruhan materi secara mendalam. Kamu pasti banyak menemukan contoh yang nggak sama dengan rumus awal, kan? Yup, soalnya kalimat dalam tenses itu harus menyesuaikan juga dengan konteks kalimatnya. Nggak apa-apa, kita belajar pelan-pelan ya!
Kalau kamu merasa kesulitan saat belajar tenses sendiri dan butuh tutor untuk mendampingimu, maka English Academy siap untuk membantu. Di setiap sesi kelas English Academy , kamu akan mendapat kesempatan berdiskusi langsung dengan teman-teman dan tutor profesional, lo . Jadi, selain menambah teman, tentunya kamu juga akan mendapat study experience yang menyenangkan. Yuk, cari tahu informasi lebih lanjutnya sekarang!

The Free Dictionary. Past Continuous Tense. Online. Available at https://www.thefreedictionary.com/Past-Continuous-Tense.htm. [Accessed 09 February 2022]

Intan Aulia Husnunnisa, biasa dipanggil Intan. Menikmati dunia SEO Content Writing sejak 2020. Semoga tulisanku bermanfaat!
Bagikan artikel ini:

Artikel Lainnya

Quantifiers: Definisi, Jenis-jenis, dan Contoh Kalimatnya

61 Kosakata Bahasa Inggris Tentang Komputer Beserta Penjelasannya

Cara Menolak Tawaran Kerja dalam Bahasa Inggris Beserta Contohnya


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Conjugation of Travel. Simple / Indefinite Present Tense. He/She/It travels . I travel. You/We/They travel. Present Continuous Tense. He/She/It is Commonwealth travelling, US traveling. I am Commonwealth travelling, US traveling. You/We/They are Commonwealth travelling, US traveling.
Most commonly, the past tense of the word "travel" is "traveled.". Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it's used. For example, referencing "travel" in the present participle form will change it to "traveling," but in the infinitive form, will be "travel.".
Conjugate the English verb travel: indicative, past tense, participle, present perfect, gerund, conjugation models and irregular verbs. Translate travel in context, with examples of use and definition.
travel. 'travel' is the model of its conjugation. In British English, the final consonant is doubled before -ing and -ed. infinitive: present participle: past participle: (to) travel. trave ll ing. trave ll ed.
The correct answer would be "went.". Matching: In this exercise, you will be given a list of past tense verbs and a list of travel-related words. Your task is to match the past tense verb with the correct travel-related word. For example, "flew" would match with "airplane.". Written Exercises.
to do. to say. to love. to eat. to make. to like. to tell. to drive. 'to travel' conjugation - English verbs conjugated in all tenses with the bab.la verb conjugator.
Conjugate the verb travel in all tenses: present, past, participle, present perfect, gerund, etc.
Conjugation of the verb Travel in all tenses: future, present and past. 🎮 Conjugation trainer for memorizing forms. ... Present Perfect Continuous Past Perfect Continuous Future Perfect Continuous. Conditional . Present Perfect Present Continuous Perfect Continuous. Imperative . Imperative. For the settings to take effect, you must restart ...
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'. the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses. the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense. the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
To Travel Conjugation; To Travel Infinitive: to travel Gerund: travelling Past participle: travelled Simple past: travelled. Note. In the US the spelling 'traveling' and 'traveled' are preferred. Irregular forms Auxilliary verb Spelling change Use contractions. Positive Negative. Indicative.
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking. The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is ...
Present Continuous. I am travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling he/she/it is travelling or traveling we are travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling they are travelling or traveling.
Look up English verb forms - over 5000 verbs! Excellent resource for students and teachers.
Answer. The past tense of travel is travelled UK or traveled US (US) . The third-person singular simple present indicative form of travel is travels . The present participle of travel is travelling UK or traveling US . The past participle of travel is travelled UK or traveled US (US) .
Travelled is the past tense and past participle form of the verb "travel." It refers to the act of going from one place to another, typically over a distance. The term "travelled" is commonly used in British English and other English-speaking countries that follow British English conventions. Define Traveled
1. Nominal simple past tense. Kalau sebelumnya sudah membaca artikel Simple Present Tense: Pengertian, Kegunaan, Rumus, dan Contoh Kalimat dan memahaminya dengan baik, pasti kamu masih ingat dong, bahwa predikat dalam kalimat tenses terbagi menjadi dua, yaitu bentuk nominal dan verbal. Pada kalimat nominal, bagian predikat akan diisi oleh to be ...
Untuk menceritakan pengalaman liburan dalam bahasa Inggris, kamu harus menggunakan rumus simple past tense. Simple past tense adalah bentuk kalimat bahasa Inggris yang digunakan untuk menyatakan peristiwa atau kejadian yang sudah selesai terjadi di masa lalu. Ciri-ciri utama dari kalimat simple past tense adalah penggunaan V2 atau past simple.
Biar lebih paham, kita pelajari pola Simple Past Tense dan contohnya secara lebih detail, ya! 1. Rumus Simple Past Tense untuk Kalimat Verbal. Untuk pola atau rumus Simple Past Tense pada kalimat verbal beserta contohnya, berikut adalah detailnya. Kalimat Positif: Subject + Verb 2.
KOMPAS.com - Tenses dibagi menjadi empat berdasarkan pembagian waktu, yaitu present, past, future, dan past future.. Masing-masing pembagian waktu tersebut menentukan bentuk kalimat untuk menjelaskan suatu peristiwa. Dalam buku Kuasai Materi Bahasa Inggris (2015) karya Sinta Sasika Novel, past artinya masa lampau. Sehingga past tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu peristiwa di masa lampau ...
Konjugiere das Verb travel in allen Zeitformen: Present, Past, Participle, Present Perfect, Gerund, etc.
Terakhir, saya akan memberi contoh paragraf atau cerita liburan akhir pekan dalam Bahasa Inggris. Jangan lupa ya, di sini jenis kalimatnya menggunakan Simple Past Tense. Sebagai pengingat, Simple Past Tense merupakan bentuk tense yang menceritakan atau menggambarkan kejadian di masa lampau (Past) dan menggunakan kata kerja bentuk kedua (Verb 2 ...
Past tense dibedakan menjadi beberapa jenis. Mari kita pelajari bersama! Simple past tense. Sebelum kita mulai, coba deh, perhatikan contoh di bawah ini: Victoria was the Queen of the United Kingdom, she reigned for 63 years, from 1837-1901. She was born in 1819 and died in 1901. She had 9 children.
Past continuous tense ternyata tak hanya berfungsi untuk menceritakan kejadian yang sedang berlangsung di masa lampau, lo.Yuk, temukan penjelasan lengkapnya di artikel ini! — Hai guys!Hehe, kita bakal bahas tenses lagi nih.Soalnya, dengan belajar grammar yang satu ini akan membuat kita mengetahui bagaimana cara membuat kalimat. Jadi, materi paling dasar dalam bahasa Inggris ini nggak boleh ...