NASA Voyager Status Update on Voyager 1 Location

The consensus of the Voyager science team is that Voyager 1 has not yet reached interstellar space.

News Media Contact
Jia-Rui Cook
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-354-0724

Ephemeris Calculator
Compute Voyager 1 ephemerides for any date and time between 01 Jan 1970 and 01 Jan 1970 and display the predicted position in an interactive sky map.
- Where is Voyager 1?
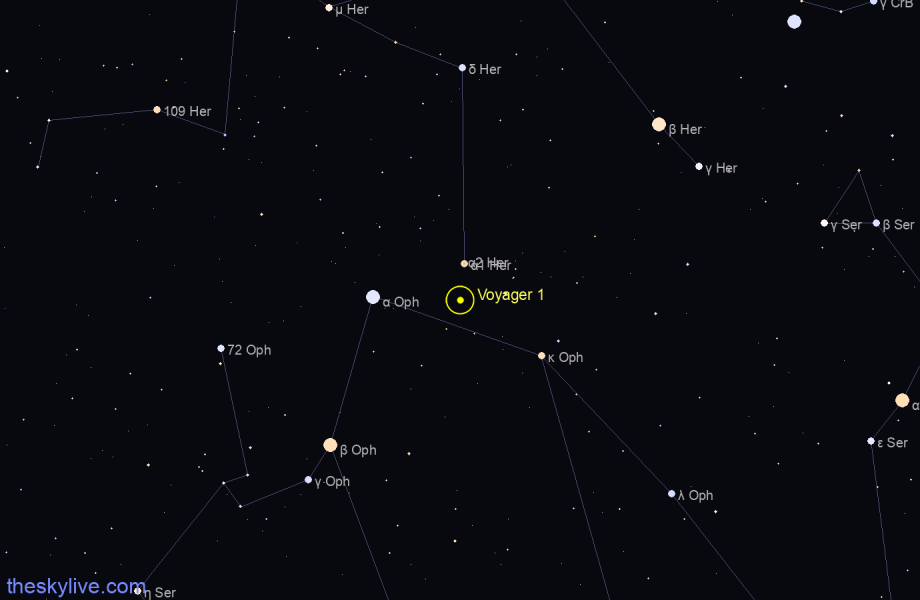
Voyager 1 is currently in the constellation of Ophiucus . The current Right Ascension is 17h 16m 05s and the Declination is +12° 20’ 23”.
Right now, from the selected location (Greenwich, United Kingdom edit_location_alt ), Voyager 1 is not visible because it is below the horizon . You can check Voyager 1 Rise and Set Times to know when Voyager 1 will rise from your location.
emoji_objects If you access this data frequently and would like to have a more synthetic view, you can create a Quick Access Page for this object and bookmark it or add it to your Home Screen.
See also the following additional resources about Voyager 1
- Voyager 1 Information on TheSkyLive.com
- How far is Voyager 1 from Earth?
- When does Voyager 1 rise and set?
- Interactive sky map
- Live position tracker

The remarkable twin Voyager spacecraft continue to explore the outer reaches of the solar system decades after they completed their surveys of the Outer Planets. Launched in 1977 (September 5 for Voyager 1 (V1) and August 20 for Voyager 2 (V2), whose trajectory took it past Jupiter after Voyager 1), the spacecraft pair made many fundamental discoveries as they flew past Jupiter (March 1979 for V1, July 1979 for V2) and Saturn (November 1980 for V1, August 1981 for V2). The path of Voyager 2 past Saturn was targeted so that it continued within the plane of the solar system, allowing it to become the first spacecraft to visit Uranus (January 1986) and Neptune (August 1989). Following the Neptune encounter, both spacecraft started a new phase of exploration under the intriguing title of the Voyager Interstellar Mission.

Five instruments continue to collect important measurements of magnetic fields, plasmas, and charged particles as both spacecraft explore different portions of the solar system beyond the orbits of the planets. Voyager 1 is now more than 118 astronomical units (one AU is equal to the average orbital distance of Earth from the Sun) distant from the sun, traveling at a speed (relative to the sun) of 17.1 kilometers per second (10.6 miles per second). Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s.

This processed color image of Jupiter was produced in 1990 by the U.S. Geological Survey from a Voyager image captured in 1979. The colors have been enhanced to bring out detail. Zones of light-colored, ascending clouds alternate with bands of dark, descending clouds. The clouds travel around the planet in alternating eastward and westward belts at speeds of up to 540 kilometers per hour. Tremendous storms as big as Earthly continents surge around the planet. The Great Red Spot (oval shape toward the lower-left) is an enormous anticyclonic storm that drifts along its belt, eventually circling the entire planet.
As seen in the night sky at Earth, Voyager 1 is within the confines of the constellation Ophiuchus, only slightly above the celestial equator; no telescope can see it, but radio contact is expected to be maintained for at least the next ten years. Voyager 2 is within the bounds of the constellation Telescopium (which somehow sounds quite appropriate) in the far southern night sky.

Both spacecraft have already passed something called the Termination Shock † (December 2004 for V1, August 2007 for V2), where the solar wind slows as it starts to interact with the particles and fields present between the stars. It is expected that both spacecraft will encounter the Heliopause, where the solar wind ceases as true interstellar space begins, from 10 to 20 years after crossing the Termination Shock. Theories exist for what should be present in interstellar space, but the Voyagers will become the first man-made objects to go beyond the influences of the Sun, hopefully returning the first measurements of what it is like out there. Each spacecraft is carrying a metal record with encoded sounds and sights from Earth, along with the needle needed to read the recordings, and simplified instructions for where the spacecraft came from, in case they are eventually discovered by intelligent extra-terrestrials.

Keep track of the Voyager spacecraft on the official Voyager Interstellar Mission website or follow @NASAVoyager2 on Twitter. † The sun ejects a continuous stream of charged particles (electrons, protons, etc) that is collectively termed the solar wind. The particles are traveling extremely fast and are dense enough to form a very tenuous atmosphere; the heliosphere represents the volume of space where the effects of the solar wind dominate over those of particles in interstellar space. The solar wind particles are moving very much faster than the local speed of sound represented by their low volume density. When the particles begin to interact with interstellar particles and fields (the interaction can be either physically running into other particles or experiencing an electromagnetic force resulting from a charged particle moving within a magnetic field), then they start to slow down. The point at which they become subsonic (rather than their normal hypersonic speed) is the Termination Shock.
We rely on the generous support of donors, sponsors, members, and other benefactors to share the history and impact of aviation and spaceflight, educate the public, and inspire future generations. With your help, we can continue to preserve and safeguard the world’s most comprehensive collection of artifacts representing the great achievements of flight and space exploration.
- Get Involved
- Host an Event
Thank you. You have successfully signed up for our newsletter.
Error message, sorry, there was a problem. please ensure your details are valid and try again..
- Free Timed-Entry Passes Required
- Terms of Use
The most distant spacecraft in the solar system — Where are they now?

Humans have been flinging things into deep space for 50 years now, since the 1972 launch of Pioneer 10. We now have five spacecraft that have either reached the edges of our solar system or are fast approaching it: Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and New Horizons.
Most of these probes have defied their expected deaths and are still operating long beyond their original mission plans. These spacecraft were originally planned to explore our neighboring planets, but now they're blazing a trail out of the solar system , providing astronomers with unique vantage points in space — and they've been up to a lot in 2022.
Voyagers 1 and 2
The Voyager missions celebrated a very special anniversary this year: 45 years of operations . From close fly-bys of the outer planets to exploring humans' furthest reach in space, these two spacecraft have contributed immensely to astronomers' understanding of the solar system.
Related : Voyager: 15 incredible images of our solar system captured by the twin probes (gallery)
Their main project now is exploring where the sun 's influence ends, and other stars' influences begin. Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause, the boundary where the sun's flow of particles ceases to be the most important influence, in 2012 with Voyager 2 following close after, in 2018.
"Voyager 1 has now been in interstellar space for a decade…and it's still going, still going strong," Linda Spilker, Voyager project scientist and a planetary scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in California, told Space.com.
The mission team hit one major hiccup this year, when the spacecraft began sending home garbled information about its location. The engineers found the cause — the spacecraft was using a bad piece of computer hardware when it shouldn't have — and restored operations.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
These kinds of incidents are to be expected with an aging spacecraft, though. The team is also actively managing the power supply onboard each spacecraft, which is dwindling each year as the probes' radioactive generators grow increasingly inefficient. This year, mission personnel turned off heaters keeping a number of scientific instruments on board warm in the harsh, cold environment of space — and, much to everyone's surprise, those instruments are still working perfectly well.
The cameras may have been turned off decades ago, but the spacecrafts' other instruments are collecting data on the plasma and magnetic fields from the sun at a great distance away from the star itself. Because particles of the solar wind — the constant stream of charged particles flowing off the sun — take time to travel such a long way, distant observations allow scientists to see how changes from the sun propagate throughout our cosmic neighborhood.
The edges of the solar system have been full of surprises, too. It would make sense that plasma from the sun becomes more sparse and spread out as you move away from the center of the solar system, but in fact, the Voyagers have encountered much denser plasma after crossing the heliopause. Astronomers are still puzzled about that one.
"It's just so amazing that even after all this time we continue to see the sun's influence in interstellar space," Spilker said. "I'm looking forward to Voyager continuing to operate, perhaps reaching the 50th anniversary."
Pioneers 10 and 11
The Pioneer spacecraft hold a special place in space history because of their role as, you guessed it, pioneers. Unfortunately, these milestone 50-year-old spacecraft are non-functional — Pioneer 10 lost communications back in 2003, and Pioneer 11 has been silent since its last contact in 1995.
But both these spacecraft are marks of humanity's presence in the solar system, and they are still continuing on their journeys, even if we're not sending them commands or firing their rockets anymore. Once a spacecraft is set on a trajectory out of the solar system, according to the laws of physics, it won't stop unless something changes its course.
New Horizons
New Horizons is by far the youngest sibling of these groundbreaking missions, having just launched in 2006 . After completing its famous flyby of dwarf planet Pluto in 2015 , this probe has been zooming out of the solar system at record speed, set to reach the heliopause around 2040.
Not only has it completed its primary mission, but it successfully completed a flyby of the smaller Kuiper Belt object, Arrokoth , in 2019 as its first mission extension. Earlier this year, the spacecraft was put into hibernation mode because an extended mission hadn't yet been approved. But now, the team is excitedly moving into New Horizons' 2nd Kuiper Belt Extended Mission, or KEM2 for short. KEM2 began on Oct. 1 , although the spacecraft will hibernate until March 1, 2023.
In the meantime, the mission team is preparing for exciting new observations. With cutting-edge instruments — far more advanced than what the Voyagers carried in the 1970s — the team is prepared to use New Horizons as a powerhouse observatory in the distant solar system, providing a viewpoint we can't achieve here on Earth .
Bonnie Burrati, planetary scientist at JPL and member of the New Horizons team, is particularly looking forward to new views of Kuiper Belt objects (KBOs), the chunks of ice and rock beyond Neptune . New Horizons' unique position in the outer solar system provides new angles of looking at these KBOs, she said. Different views can tell astronomers about how rough the objects' surfaces are, among other things, based on how light scatters and creates shadows on them.
Another planetary scientist on the team from Southwest Research Institute in Colorado, Leslie Young, wants to use the spacecraft for a new look at something closer to home: the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune. New Horizons’ unique viewpoint provides scientists with information about how light scatters through the planets’ atmospheres—information we can’t get from here on Earth, since we can’t see Uranus and Neptune from that angle. Planetary scientists are eager for more information about these planets, especially as NASA begins planning for a new mission to visit Uranus.
— The icy 'space snowman' Arrokoth in deep space just got names for its best features — Pale Blue Dot at 30: Voyager 1's iconic photo of Earth from space reveals our place in the universe — Destination Pluto: NASA's New Horizons mission in pictures
When the spacecraft wakes from hibernation, it will be past the so-called "Kuiper cliff," where scientists currently think there are far fewer large KBOs. "When we look at other star systems, we see debris disks extending to much larger distances from their host stars," Bryan Holler, an astronomer at Baltimore's Space Telescope Science Institute, told Space.com. "If ET were to look at our solar system, would they see the same thing?"
This next extended mission will even venture beyond New Horizons' original domain of planetary science. Now, the spacecraft will provide better-than-ever measurements of the background of light and cosmic rays in space, trace the distributions of dust throughout our solar system, and obtain crucial information on the sun's influence, complimentary to the Voyagers. Since the three functional far out spacecraft are heading in separate directions, they allow astronomers to map out irregularities in the solar system's structure.
Luckily for New Horizons, signs indicate that the spacecraft will have enough power to last through the 2040s and possibly beyond — each year, moving 300 million miles (480 million kilometers) farther into uncharted territory.
Follow the author at @ briles_34 on Twitter. Follow us on Twitter @ Spacedotcom and on Facebook .
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Briley Lewis (she/her) is a freelance science writer and Ph.D. Candidate/NSF Fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles studying Astronomy & Astrophysics. Follow her on Twitter @briles_34 or visit her website www.briley-lewis.com .
Car-size asteroid gives Earth a super-close shave with flyby closer than some satellites
SpaceX launches advanced weather satellite for US Space Force (video)
Cosmonaut Muhammed Faris, first Syrian in space, dies at 72
- bolide I wonder if the JWST could see any of these satellites, if it aimed in their direction. Reply
bolide said: I wonder if the JWST could see any of these satellites, if it aimed in their direction.
- View All 2 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 This Week In Space podcast: Episode 107 — Mars Sample Return Blues
- 3 Lego Star Wars Millennium Falcon (2024) review
- 4 Those magic minutes during April 8's solar eclipse brought me to tears
- 5 Everything we know about 'The Fantastic Four'
Mon 22 Apr 2024
2024 newspaper of the year
@ Contact us
Your newsletters
Where is Voyager 1? Location of Nasa space probe explained after it sends mysterious ‘impossible data’
Scientists will continue to monitor the probe to try and work out the source of the problem.

Nasa Voyager 1 probe, which was launched in 1977, is sending back data that are baffling scientists.
Experts are trying to get to the bottom of the problem.
Here is what we know so far.
What is the background to Nasa Voyager 1’s mission?
On 5 September, 1977, the Nasa Voyager 1 was launched. It was part of a programme to analyse the outer Solar System and the interstellar space beyond the Sun’s heliosphere. The heliosphere is a bubble around the planets – it is caused by the sun sending out solar wind.
Voyager 1 is14.5 billion miles away from Earth (as of January 2022). (You can keep tabs on its distance on the Nasa website ).
Over the past 45 years it has been sending data back to scientists.
The probe has made fl-ybys of Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn’s largest moon, Titan .
In 2012 Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause and entered interstellar space making it the first spacecraft to do so.
It takes light 20 hours and 33 minutes to travel that difference which means it takes around two days to send a message to Voyager 1 and get a response – something the mission team is well accustomed to.
What is the problem now with Nasa Voyager 1?
According to a statement from Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in California which built the probe: “The interstellar explorer is operating normally, receiving and executing commands from Earth, along with gathering and returning science data.
“But readouts from the probe’s attitude articulation and control system (AACS) don’t reflect what’s actually happening onboard.”
It adds that “the data may appear to be randomly generated, or does not reflect any possible state the AACS could be in.”
Voyager 1’s twin, Voyager 2 (currently 12.1 billion miles from Earth and also launched in 1977) continues to operate normally.
What could be causing this?
Both Voyagers have operated far longer than mission planners expected, and they are the only spacecraft to collect data in interstellar space.
Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager 1 and its twin, Voyager 2, at Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory said that it could be down to old age and the harsh environment.
“A mystery like this is sort of par for the course at this stage of the Voyager mission,” she explained. “The spacecraft are both almost 45 years old, which is far beyond what the mission planners anticipated.
“We’re also in interstellar space — a high-radiation environment that no spacecraft have flown in before.”
What next for the probe?
Nasa says that it will “continue to monitor the signal closely as they continue to determine whether the invalid data is coming directly from the AACS or another system involved in producing and sending telemetry data.”
The team may not find the source of the problem and will instead adapt to it, Dodd said.
If they are able to work out the problem, they may be able to solve the issue through software changes or by “using one of the spacecraft’s redundant hardware systems”.
It said until it can discover the nature of the issue it will not be able to anticipate how long the spacecraft “can collect and transmit science data”.
Most Read By Subscribers
- AAC Clyde Space
- Alaska Space
- Alba Orbital
- Anders Povlsen
- Astra Space
- Black Arrow
- Blue Origin
- Catriona Francis
- Chris Larmour
- Climate Change
- Copenhagen Suborbitals
- Craig Clark
- Elecnor Deimos
- Electron Rocket
- European Space Agency
- Frank Strang
- Firefly Aerospace
- Gilmour Space Technologies
- Highlands & Islands Enterprise
- Horizontal Launch
- ISAR Aerospace
- Kodiak rocket Launch
- Kristian Von Bengtson
- Laura Edison
- Llandebr Space Centre
- Lockheed Martin
- New Shepard
- Orbex Space
- Peter Guthrie
- Peter Madsen
- Prestwick Spaceport
- Proton Rocket
- Richard Branson
- Rocket Explosion
- Rocket Factory Augsburg
- Rocket Launch
- Satellite Launches
- Scottish Spaceport
- Shetland Space Centre (SaxaVord)
- Skylark Nano
- Small Satellites
- Snowdonia spaceport
- Space Apprenticeship
- Space Careers
- Space Debris
- Space Scholarship
- Space Tech Expo
- Space Tourism
- Spaceport Cornwall
- Sutherland Spaceport
- UK Space Agency
- UK Space Conference
- UK Space Race
- UK Spaceport
- Vertical Launch
- Virgin Galactic
- Virgin Orbit
- Volodymyr Levykin
Voyager 1 Loses Contact With Earth – Where Is Voyager 1 Now In 2024

2022 marks the 45th anniversary of NASA launching one of its most successful projects, the automatic spacecraft Voyager 1. The probe not only coped with the interplanetary mission brilliantly but also provided scientists with a large amount of valuable information about the heliosphere and interstellar space. Soon spacecraft may fail, but even after that, it will continue to serve for the benefit of humanity, carrying out a diplomatic mission. And while NASA knows the Voyager 1 location and what is happening to the probe, the interest in Voyager persists. Let’s find out more about this spacecraft.
Voyager 1 Loses Contact: What causes the communication breakdown?
Voyager 1 has been suffering a communication malfunction since 14 November 2023. The legendary spacecraft hasn’t responded in 3 months. The mission team is increasingly worried about the possibility of the distant spacecraft being unable to recover.
The engineering team is actively working to resolve the issue. However, the challenges lie in both software limitations and the vast distance between Voyager 1 and its terrestrial controllers, making the resolution of the problem a complex undertaking.
Voyager 1 has started to experience a disruption in communication with its mission team on Earth due to a computer malfunction. On 14 November 2023, the NASA team noticed the issue. The spacecraft possesses three onboard computers. One of them collects data from scientific instruments and combines it with engineering data about Voyager 1’s current health status. This information is transmitted to Earth in binary code. However, the flight data system is currently stuck in a loop, sending a repetitive pattern of ones and zeroes.
While Voyager 1 can receive and execute commands sent by the mission team, there is a problem with the telecommunications unit. It hinders the transmission of any scientific or engineering data from Voyager 1 back to Earth.
Moreover, the transmission of commands takes approximately 22.5 hours to reach the spacecraft. Also, there is an additional waiting period of 45 hours to receive a response from Voyager. This significant time delay poses a challenge for the team in managing and troubleshooting the current communication issue.
How much time will it take to resolve the problem?
Over a three-month period, the Voyager team attempted to restart the flight data system through commands. But as of now, they received no usable data. The further investigative process might extend over the course of several weeks.
Where did Voyager 1 go?
The primary mission was to fly around Saturn and Jupiter to study their satellite rings, magnetic fields, and weather. Voyager did an excellent job with this task, providing detailed images of the planets. At the time, no one could boast of such results, not even the USA’s main competitor, the USSR.
The second part of the mission was to search for and explore the boundaries of near-solar space and measure particles in the solar wind. Then, upon successful completion of the task, the probe had to move further and begin studying the interstellar medium. Skipping ahead, let’s say that the spacecraft exceeded all expectations, both in achieving the tasks set by the scientists and in the duration of work in deep space.
When did Voyager 1 launch?
Voyager 1 was launched on a Titan IIIE rocket from Cape Canaveral on September 5, 1977. Interestingly, there were two missions, Voyager 1 and 2. And the second Voyager was launched 16 days earlier than the first, on August 20.
It would be more logical to number the spacecraft in reverse, but the numbering order was defined by which spacecraft would be the first to meet Jupiter. So, Voyager 1 was supposed to reach Jupiter on March 5, 1979, and Voyager 2 — four months later, on July 9 of the same year.
How big is Voyager 1?
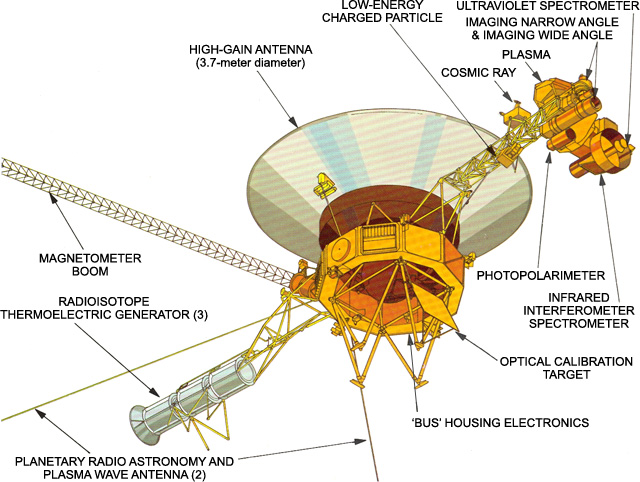
The spacecraft had a launch weight of 798 kg, a length of 2.5 m, and a payload mass of 86 kg. The body is a ten-facet prism, equipped with two antennas, a rod for electric generators, a rod with scientific instruments, and a separate rod for a magnetometer. The casing and equipment are supplemented by thermal insulation, heat shields, and plastic hoods.
Considering that the probe would operate far from the Sun, using solar panels would be pointless. Power is provided by three radioisotope thermoelectric generators operating on plutonium-238 oxide.
How fast is it travelling?
The speed of Voyager-1 at launch was 17 km/s, so it quickly reached Jupiter and began surveying the planet in January 1979. It approached Saturn in November 1980.
In August 2012, the probe became the first spacecraft to reach interstellar space. This fact was confirmed when the sensors recorded the influence of coronal mass ejections from the Sun in the form of a “tsunami wave”.
In 2017, the probe was recognized as the fastest spacecraft to leave our solar system. Even though the New Horizons probe, with a higher launch speed, was sent to Pluto in January 2006, Voyager 1 has beaten it in speed thanks to carefully calculated gravity manoeuvres. NASA claims that the spacecraft travels an average of 523 million kilometres a year.
How far away is it?
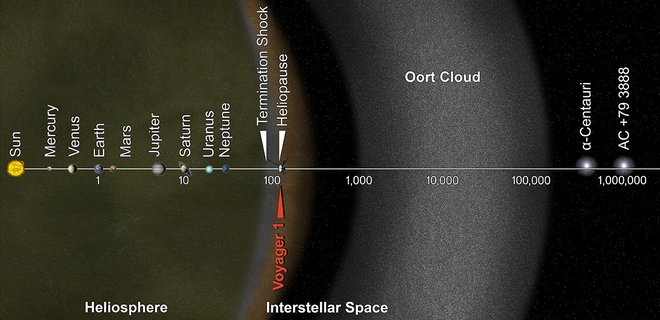
Voyager 1 is the most distant spacecraft ever launched by a man from Earth into space. We don’t really know exactly where the craft is now. According to NASA official data, as of February 17, 1998, the probe moved 10.4 billion km away from our planet.
In 2013, some media sources wrote that Voyager 1 will be leaving the solar system. However, this information was wrong. In fact, the probe only went beyond the solar wind. It will leave the solar system in about 30,000 years.

How far has Voyager 1 gone as of today?
Voyager 1 is currently zipping through space at around 38,000 mph (17 kilometers per second), according to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. It is currently the farthest human-made object from Earth. As of February 2024, Voyager 1 is more than 24 billion km away from Earth. The distance between Voyager and the Earth differs in different periods of the year. This is because the speed of the planet in its orbit around the Sun exceeds the speed of the spacecraft moving away from it.
Will Voyager 1 ever leave the Milky Way?
The Milky Way is a vast galaxy with a diameter of about 100,000 light-years. With Voyager 1’s current speed, it would take tens of thousands of years to travel even a small fraction of the Milky Way’s distance.
As of now, Voyager 1 is not on a trajectory that will take it out of the Milky Way. Its path is primarily influenced by the Sun’s gravitational field, and its velocity is not sufficient to overcome the gravitational pull of the Milky Way’s stars and dark matter. So, it’s unlikely that Voyager 1 will ever leave the Milky Way in the foreseeable future.
Is Voyager 1 still transmitting?
Many people ask this reasonable question: Did we lose contact with Voyager 1 because it has been ploughing the expanses of space for almost half a century! The probe made its last image of the Earth in 1990. The picture was called A Pale Blue Dot . Voyager 1 was about 4 billion miles from Earth when it captured its portrait. Caught in the centre of scattered light rays (the result of shooting so close to the Sun), the Earth appears as a tiny dot of light, a crescent moon only 0.12 pixels in size. After that, the ship’s cameras were turned off in order to save energy for the operation of other equipment and continue with the interstellar space exploration.
Is Voyager 1 still active in 2023?
So is Voyager 1 still active? Yes! In 2021, the probe transmitted data on the detection of interstellar sounds and the measurement of the matter density in space. As long as Voyager 1 remains healthy, it’s likely the probe will continue its record-breaking missions for years to come.
Can Voyager 1 still take pictures?
Voyager 1 is equipped with several instruments, including cameras, that were used to capture images of planets and other celestial bodies during its mission within the solar system. However, as Voyager 1 has moved beyond the outer planets and into interstellar space, the distance from Earth and the limited power available to the spacecraft have significantly impacted its ability to take pictures. This has led to the shutdown of certain instruments and systems to conserve power for the primary communications and scientific instruments.
When will Voyager 1 die?
Voyager’s energy sources are constantly cooling and depleted, so today, they can no longer properly maintain the static temperature of the hardware. There are still four devices operating on board. However, when the power runs out, the probe will stop transmitting signals to the ground station.
NASA engineers claim that the spacecraft retains around 70% of its fuel is left on the ship, which should keep it operational until 2025. However, no one knows what other factors may affect the probe’s functionality in outer space.
How long will Voyager 1 battery last?
By 2025, the probe’s batteries are expected to be fully depleted. To conserve energy and prolong its operational life, NASA has been deactivating the spacecraft’s onboard systems. Currently, Voyager 1 retains four functioning instruments, all powered by Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RITEGs), nuclear batteries that convert plutonium’s decay heat into electricity. However, due to a decline in power output over 44 years, NASA has shifted them into an economy mode. Engineers disabled the cosmic ray detector’s heater two years ago, a critical component for identifying the heliopause crossing.
Where will Voyager 1 be in 300 years?
Predicting Voyager 1’s exact location 300 years into the future is extremely challenging due to the complex interactions of gravitational forces and the dynamic nature of space. However, based on its current trajectory and velocity, it’s reasonable to assume that Voyager 1 will continue its journey through interstellar space within our Milky Way galaxy.
According to NASA, in about 300 years from now, Voyager 1 will enter the Oort Cloud, a spherical band far beyond Pluto’s orbit that’s full of billions of frozen comets. It will take another 30,000 years to reach the end of it.
Interesting facts about Voyager 1
Even after Voyager 1 cuts its cord with humanity it will continue to carry out an important diplomatic mission. The spacecraft has a gilded plate, called Voyager Golden Record , attached to its body. It contains a message for aliens in fifty different languages. The recording also carries music, sounds of nature, photographs of people, the Earth, cars, and aircraft. It carries the coordinates of the Earth so that another civilization can discover its location. In other words, Voyager 1 can still serve the benefit of mankind even outside of the Solar system.
How has Voyager 1 not hit anything?
Voyager 1’s remarkable avoidance of collisions during its journey through space can be attributed to a combination of factors. The vast expanse of the universe plays a significant role, as the immense distances between celestial bodies in the Milky Way mean that the likelihood of Voyager 1 encountering anything substantial is extraordinarily low. Additionally, the sparse distribution of matter in interstellar space further decreases the chances of collision. Meticulous trajectory planning by NASA’s experts has also been crucial. By utilizing intricate calculations and simulations, they’ve navigated the spacecraft through safe paths that circumvent known objects.
What happened to Voyager-1 in May 2022?
In May 2022, NASA recorded strange signals from Voyager-1. Mission specialists managed to find out that the device is still operating normally, but the readings of the articulation and attitude control system of the probe (AACS) do not reflect the real situation on board.
The AACS module is responsible for pointing the Voyager-1 antenna exactly at Earth, allowing the probe to send telemetry data. However, suddenly this data started to display incorrectly. Subsequent diagnostics revealed that, for some reason, AACS switched to another computer that stopped working several years ago, which distorted newly transmitted data. In August, NASA reported fixing this problem. A command was sent to AACS to switch to the correct computer, and it began to transmit correct telemetry data again. NASA suggests that AACS received an erroneous command from another computer (there are three of them on board Voyager-1), which may indicate that the main cause of the failure is somewhere else on the ship.
“We are happy that telemetry is back,” said the head of the mission, Suzanne Dodd. “Our team will perform a full read of the AACS memory and analyse its operation, which will help determine the exact cause that led to the distortion of the telemetry data.” At the same time, Dodd added that mission engineers do not see the incident as a long-term threat to Voyager-1 and are generally cautiously optimistic, although they still have to do more research.
Voyager 1 timeline
- 1977 – Launch year of Voyager 1.
- 1979 – The first detailed images of Jupiter, evidence of the first active volcanoes outside the Earth present on the Io satellite.
- 1981 – Discovery of three of Saturn’s satellites – Pandora, Prometheus and Atlas.
- 1982 – Correction of the engines operation to maximize the probe’s distance from Earth to put it outside the solar system.
- 1990 – The first “family portrait” of the solar system, including the Earth.
- 1998 – Voyager became the furthest from Earth human-made object.
- 2005 – It overcame the last shock wave, which was formed when the interstellar wind collided with the solar one. After that, no terrestrial computer can read his data.
- 2012 – Became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space. Measured the plasma readings in interstellar space with maximum accuracy.
- 2017 – NASA engineers activated the probe’s thrusters to correct the spacecraft’s course and extend its lifespan.
- 2021 – Voyager 1 recent discoveries confirmed the scientists’ guess that there is more activity in the interstellar gas than in the solar wind.
- 2022 – In May, Voyager began sending incorrect telemetry data back to Earth, allegedly due to a computer system malfunction. Three months later, NASA reported that the problem had been fixed.
Richard is an established commentator with a strong political background and a career that has spanned across the energy sector (oil, gas & renewable energy) as well as the space industry (satellites, launch & telemetry). He is a self-proclaimed environmental campaigner and is particularly enthusiastic about the role that the Scottish space industry will play in tackling the climate emergency that is happening around the world.
Cancel reply
Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.
Related Articles

We Asked Women What Inspired Them to Pursue Careers in the Space Sector. Here’s What They Told Us

Firefly Alpha rocket launch dates, history and schedule

UFO Sightings now a Topic for NASA Research
Explore orbital today.

April Rocket Launch Schedule 2022: Completed & Upcoming Launches

Northern Lights – Solar Weather Conditions Make Aurora Borealis More Visible

How far is Venus from the Earth and the Sun?
By continuing to use orbitaltoday.com you will be agreeing to the website Terms and Conditions and the Use of Cookies while using the website and our services. Please also read our Privacy Policy under which, to the extent stated, you consent to the processing of your personal data.

Hubble Provides Interstellar Road Map for Voyagers’ Galactic Trek
NASA’s two Voyager spacecraft are hurtling through unexplored territory on their road trip beyond our solar system. Along the way, they are measuring the interstellar medium, the mysterious environment between stars. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope is providing the road map – by measuring the material along the probes’ future trajectories. Even after the Voyagers run out of electrical power and are unable to send back new data, which may happen in about a decade, astronomers can use Hubble observations to characterize the environment through which these silent ambassadors will glide.
A preliminary analysis of the Hubble observations reveals a rich, complex interstellar ecology, containing multiple clouds of hydrogen laced with other elements. Hubble data, combined with the Voyagers, have also provided new insights into how our sun travels through interstellar space.
“This is a great opportunity to compare data from in situ measurements of the space environment by the Voyager spacecraft and telescopic measurements by Hubble,” said study leader Seth Redfield of Wesleyan University in Middletown, Connecticut. “The Voyagers are sampling tiny regions as they plow through space at roughly 38,000 miles per hour. But we have no idea if these small areas are typical or rare. The Hubble observations give us a broader view because the telescope is looking along a longer and wider path. So Hubble gives context to what each Voyager is passing through.”
The astronomers hope that the Hubble observations will help them characterize the physical properties of the local interstellar medium. “Ideally, synthesizing these insights with in situ measurements from Voyager would provide an unprecedented overview of the local interstellar environment,” said Hubble team member Julia Zachary of Wesleyan University.
The team’s results will be presented Jan. 6 at the winter meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Grapevine, Texas.
NASA launched the twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft in 1977. Both explored the outer planets Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 went on to visit Uranus and Neptune.
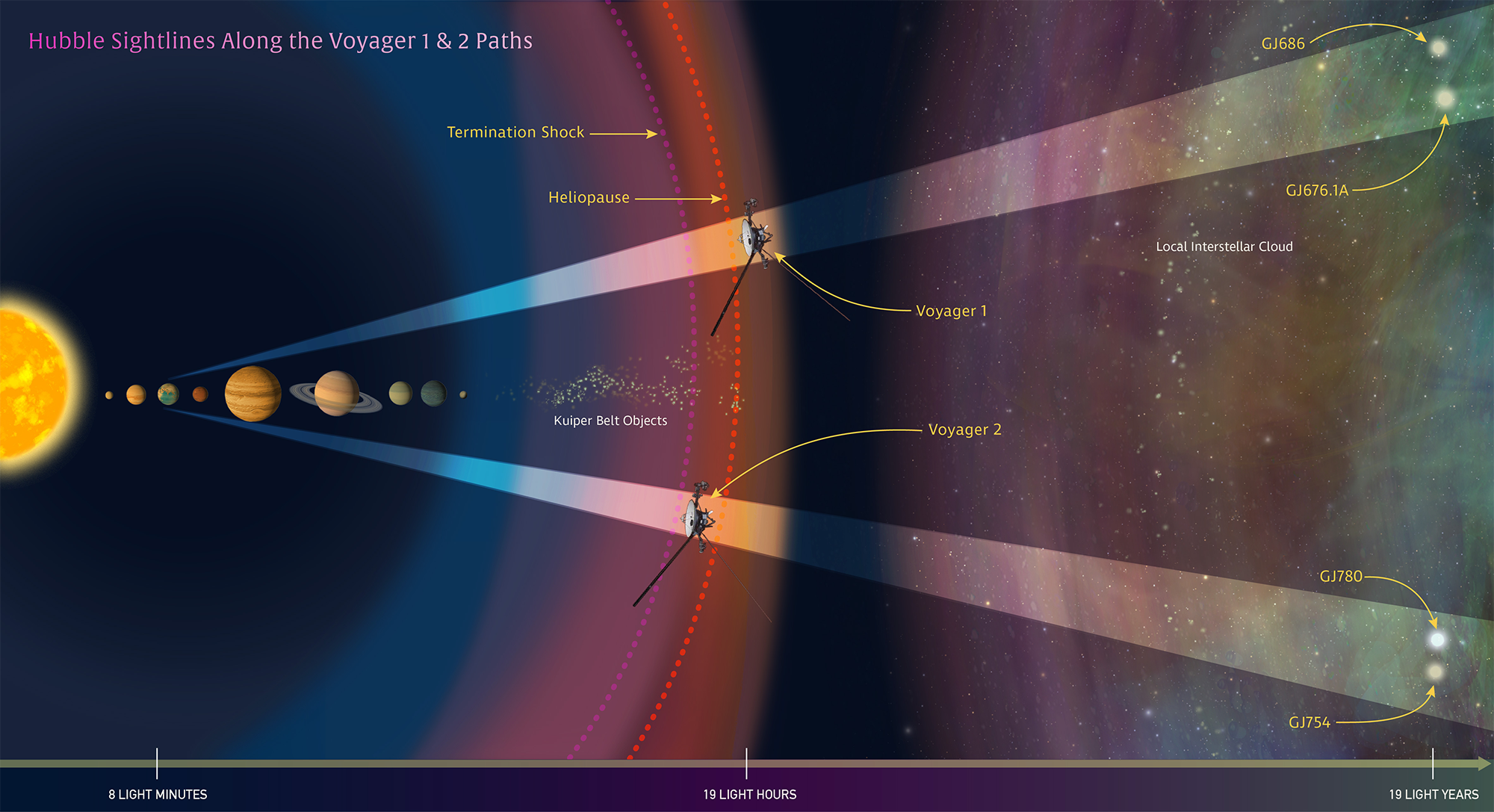
The pioneering Voyager spacecraft are currently exploring the outermost edge of the sun’s domain . Voyager 1 is now zooming through interstellar space, the region between the stars that is filled with gas, dust, and material recycled from dying stars.
Voyager 1 is 13 billion miles from Earth, making it the farthest human-made object ever built. In about 40,000 years, after the spacecraft will no longer be operational and will not be able to gather new data, it will pass within 1.6 light-years of the star Gliese 445, in the constellation Camelopardalis. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 10.5 billion miles from Earth, and will pass 1.7 light-years from the star Ross 248 in about 40,000 years.
For the next 10 years, the Voyagers will be making measurements of interstellar material, magnetic fields and cosmic rays along their trajectories. Hubble complements the Voyagers’ observations by gazing at two sight lines along each spacecraft’s path to map interstellar structure along their star-bound routes. Each sight line stretches several light-years to nearby stars. Sampling the light from those stars, Hubble’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph measures how interstellar material absorbs some of the starlight, leaving telltale spectral fingerprints.
Hubble found that Voyager 2 will move out of the interstellar cloud that surrounds the solar system in a couple thousand years. The astronomers, based on Hubble data, predict that the spacecraft will spend 90,000 years in a second cloud and pass into a third interstellar cloud.
An inventory of the clouds’ composition reveals slight variations in the abundances of the chemical elements contained in the structures. “These variations could mean the clouds formed in different ways, or from different areas, and then came together,” Redfield said.
An initial look at the Hubble data also suggests that the sun is passing through clumpier material in nearby space, which may affect the heliosphere, the large bubble containing our solar system that is produced by our sun’s powerful solar wind. At its boundary, called the heliopause, the solar wind pushes outward against the interstellar medium. Hubble and Voyager 1 made measurements of the interstellar environment beyond this boundary, where the wind comes from stars other than our sun.
“I’m really intrigued by the interaction between stars and the interstellar environment,” Redfield said. “These kinds of interactions are happening around most stars, and it is a dynamic process.”
The heliosphere is compressed when the sun moves through dense material, but it expands back out when the star passes through low-density matter. This expansion and contraction is caused by the interaction between the outward pressure of the stellar wind, composed of a stream of charged particles, and the pressure of the interstellar material surrounding a star.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. The Voyagers were built by JPL, which continues to operate both spacecraft. JPL is a division of Caltech.
For images and more information about the local interstellar medium and Hubble, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/hubble
For more information about the Voyager mission, visit: www.nasa.gov/voyager
For additional information, contact:
Felicia Chou NASA Headquarters, Washington, D.C. 202-358-0257 [email protected]
Donna Weaver / Ray Villard Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, Maryland 410-338-4493 / 410-338-4514 [email protected] / [email protected]
Elizabeth Landau Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 818-354-6425 [email protected]
Seth Redfield Wesleyan University, Middletown, Connecticut 860-685-3669 [email protected]
Related Terms
- Astrophysics
- Goddard Space Flight Center
- Hubble Space Telescope
Explore More
Nasa data helps beavers build back streams.
Humans aren’t the only mammals working to mitigate the effects of climate change in the Western United States. People there are also enlisting the aid of nature’s most prolific engineers – beavers. Using NASA-provided grants, two open-source programs from Boise State University in Idaho and Utah State University in Logan are making it possible for […]

Hubble Captures a Bright Galactic and Stellar Duo

Hubble Goes Hunting for Small Main Belt Asteroids
Discover more topics from nasa.
James Webb Space Telescope

Perseverance Rover

Parker Solar Probe


NASA Decodes the Reason Behind Voyager 1's Garbled Transmissions
For months, NASA's Voyager team has been struggling to translate garbled messages from beyond our solar system. Voyager 1 has been responding to NASA's data requests with tangles of 1s and 0s, none of which have made sense to anyone at the agency. But now, thanks to a "poke command" issued in March, the spacecraft seems to have helped scientists identify the error behind its wonky transmissions.
NASA had just managed to solve an issue with Voyager 1's attitude articulation and control system (AACS) in 2022 when a new glitch arose, jumbling the probe's flight data. This raw data is supposed to convey information about what Voyager 1's various scientific instruments have gleaned from remote regions of the Milky Way, but instead, it was just a mysterious stream of unintelligible numbers. Getting the spacecraft to return to its original "language" has been a challenge ever since, in part because most of the folks who originally worked on Voyager 1 are no longer alive .
In March, NASA sent Voyager 1 a poke command, or a command that directly modifies a system's memory addresses. Though poke commands are a fairly antiquated concept, they're occasionally useful for low-level memory control—a stone the Voyager team couldn't leave unturned. Their command prompted Voyager 1's system into using a different readout sequence for its software package than it typically defaults to, and about 22 hours later, NASA found itself with a new clue.
According to a Voyager mission blog post , activity from one portion of Voyager 1's flight data system (FDS) stood out from the probe's previous unreadable transmissions. A single engineer involved in NASA's Deep Space Network saw that the data contained a readout of Voyager 1's full FDS memory. This, the engineer noticed, offered the team an opportunity to compare and contrast Voyager 1's previous FDS readout with the latest snapshot of its inner workings.
NASA has since used the decoded readout to determine that roughly 3 percent of the probe's memory is corrupted. This may explain why restarting the FDS didn't resolve the issue back in November: If a system's memory has degraded, turning that system off and back on again won't do anything to bring it back. Luckily, engineers at the Voyager mission think the corruption is confined to just one chip, which could make the issue easier to circumvent or resolve.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "Interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey through the Universe. In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. ... 2022 Tracking Schedule 22_01_06-22_01_24 22_01_13-22_01_31 22_01_20-22_02_07 ...
Voyager 1 live position and data. This page shows Voyager 1 location and other relevant astronomical data in real time. The celestial coordinates, magnitude, distances and speed are updated in real time and are computed using high quality data sets provided by the JPL Horizons ephemeris service (see acknowledgements for details). The sky map shown in the background represents a rectangular ...
Voyager 1 is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, to study the outer Solar System and beyond. It is currently the most distant human-made object from Earth, having traveled over 14 billion miles (23 billion kilometers) from the Sun. Voyager 1's mission has included flybys of Jupiter and Saturn, with the goal of studying their moons, rings, and magnetic fields.
Voyager 2 Present Position. This simulated view of the solar system allows you to explore the planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and spacecraft exploring our solar system. You can also fast-forward and rewind in real-time. NASA/JPL-Caltech.
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
2022-07-14 Voyager 1 has reached a distance of 23.381 ... Voyager 1 was commanded to change its orientation to measure the sideways motion of the solar wind at that location in space in March 2011 (~33yr 6mo from launch). A test roll done in February had confirmed the spacecraft's ability to maneuver and reorient itself. The course of the ...
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
At approximately 2:10 p.m. Pacific time on February 17, 1998, Voyager 1, launched more than two decades ago, will cruise beyond the Pioneer 10 spacecraft and become the most distant human-created object in space at 10.4 billion kilometers (6.5 billion miles.) The two are headed in almost opposite directions away from the Sun.
Sept. 1, 2022 5 September 2021 marks the 45th anniversary of the Voyager 1 launch! Formerly known as Mariner Jupiter-Saturn 1977 or MJS77, Voyager is the most distant artificial object from Earth. ... Voyagers 1 and 2 were specifically designed to take advantage of a rare planetary alignment that occurs only once very ~176 years, and remains ...
In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between stars, filled with material ejected by the death of nearby stars millions of years ago. Voyager 2 entered interstellar space on November 5, 2018 and scientists hope to learn more about this region. Both spacecraft are still sending scientific ...
The consensus of the Voyager science team is that Voyager 1 has not yet reached interstellar space. "The Voyager team is aware of reports today that NASA's Voyager 1 has left the solar system," said Edward Stone, Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif. "It is the consensus of the Voyager ...
The probe launched on Sept. 5, 1977 — about two weeks after its twin Voyager 2 — and as of August 2022 is approximately 14.6 billion miles (23.5 billion kilometers) away from our planet ...
Voyager 1 is currently in the constellation of Ophiucus.The current Right Ascension is 17h 16m 11s and the Declination is +12° 19' 04".. Right now, from the selected location (Greenwich, United Kingdom edit_location_alt), Voyager 1 can be observed looking in the South-West direction at an altitude of 45° degrees above the horizon (view Voyager 1 position on a interactive sky map).
Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s. This processed color image of Jupiter was ...
We now have five spacecraft that have either reached the edges of our solar system or are fast approaching it: Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and New Horizons. Most of these probes ...
Jamie Rankin is the new deputy project scientist for Voyager (shown behind her), NASA's longest-running mission and deepest exploration into space. The twin Voyager spacecraft captured the public imagination in the 1970s and '80s as Earth's first ambassadors to the outer planets, providing close-up images of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and ...
Voyager 1 is14.5 billion miles away from Earth (as of January 2022). (You can keep tabs on its distance on the Nasa website ). Over the past 45 years it has been sending data back to scientists.
We don't really know exactly where the craft is now. According to NASA official data, as of February 17, 1998, the probe moved 10.4 billion km away from our planet. In 2013, some media sources wrote that Voyager 1 will be leaving the solar system. However, this information was wrong.
The 45-year-old probe has been a model of endurance, continuing to send back data using decades-old technology. But on May 18, 2022, NASA announced that Voyager 1 has been sending back mysterious ...
In about 40,000 years, after the spacecraft will no longer be operational and will not be able to gather new data, it will pass within 1.6 light-years of the star Gliese 445, in the constellation Camelopardalis. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 10.5 billion miles from Earth, and will pass 1.7 light-years from the star Ross 248 in about 40,000 years.
NASA Voyager Status Update on Voyager 1 Location. Artist concept of NASA's Voyager spacecraft. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech › larger image. "The Voyager team is aware of reports today that NASA's Voyager 1 has left the solar system," said Edward Stone, Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif.
NASA had just managed to solve an issue with Voyager 1's attitude articulation and control system (AACS) in 2022 when a new glitch arose, jumbling the probe's flight data. This raw data is ...