

Voyager 2 Ephemeris Calculator
Compute the position of Voyager 2 for any date and time between 1 January 2013 and 30 December 2099 and display the results on an interactive star map.
Voyager 2 is an unmanned space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, just a few weeks before its sister craft Voyager 1. Its mission was to study the outer planets of our solar system, including Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. It was the first and only spacecraft to visit all four planets, and its observations revolutionized our understanding of these distant worlds. After completing its primary mission, Voyager 2 continued on its journey into interstellar space, where it is still sending back data on the interstellar medium and the heliosphere. Voyager 2 is currently the second most distant human-made object from Earth, after its sister craft Voyager 1, and continues to be in communication with NASA's Deep Space Network.
Voyager 2 is currently in the constellation of Pavo , at a distance of 20,367,509,289 kilometers from Earth.

Today's rise, transit and set times of Voyager 2 from Greenwich, United Kingdom edit_location_alt (all times relative to the local timezone Europe/London):
Today Voyager 2 is not visible from Greenwich, United Kingdom edit_location_alt
- Voyager 2 is below the horizon from Greenwich, United Kingdom edit_location_alt .
- Go to interactive sky chart
If you need to access this information frequently for your observations, you can create a simple customized Quick Access page , so that you can easily bookmark it in your browser favorites or add a shortcut to your mobile phones' home screen.
- Position and finder charts (see also Where is Voyager 2? )
- Distance from Earth (see also How far is Voyager 2 from Earth? )
- When does Voyager 2 rise and set?
- Interactive orbit visualization . 3d visualization showing the orbit of Voyager 2 with respect to the major Solar System objects.
- 15 days ephemerides . Table showing celestial coordinates and magnitude of Voyager 2 for the past and next 7 days.
- Interactive sky chart . An online planetarium application that shows where to locate Voyager 2 in the sky from your location.
- Live position tracker . A high precision sky chart that uses real deep sky imagery to help locate Voyager 2 with your telescope or on your astrophotographies.
Voyager 2 Position and Finder Charts

Higher precision deep sky finder chart, 60 arcmin wide, showing where Voyager 2 is right now. Click on the image to see a more detailed fullscreen tracker view .

Also check out Where is Voyager 2? , a page that provides all the information needed to find Voyager 2 in the sky and additional links to sky charts.
Voyager 2 Distance from Earth
The distance of Voyager 2 from Earth is currently 20,367,509,289 kilometers, equivalent to 136.148390 Astronomical Units . Light takes 18 hours, 52 minutes and 18.6981 seconds to travel from Voyager 2 and arrive to us.
The following chart shows the distance of Voyager 2 from Earth as a function of time. In the chart the distance data is measured in Astronomical Units and sampled with an interval of 1 day.
Closest Approach of Voyager 2 to Earth
NOTE: values for the closest approach are computed with a sampling interval of 1 day.
Visualization of Voyager 2 Orbit
This 3d orbit diagram is a feature of our 3D Solar System Simulator and shows the orbit of Voyager 2 with respect of the Sun and the orbits of the major planets . The position of Voyager 2 and the planets along their orbits in this diagram accurately represents the current configuration of the objects in the Solar System. This is an experimental feature and it requires a WebGL enabled browser. Please provide us feedback !
Voyager 2 15 Days Ephemeris
The following table lists the ephemerides of Voyager 2 computed for the past and next 7 days, with a 24 hours interval. Click on each row of the table to locate Voyager 2 in our Online Planetarium at the chosen date.

First to visit all four giant planets
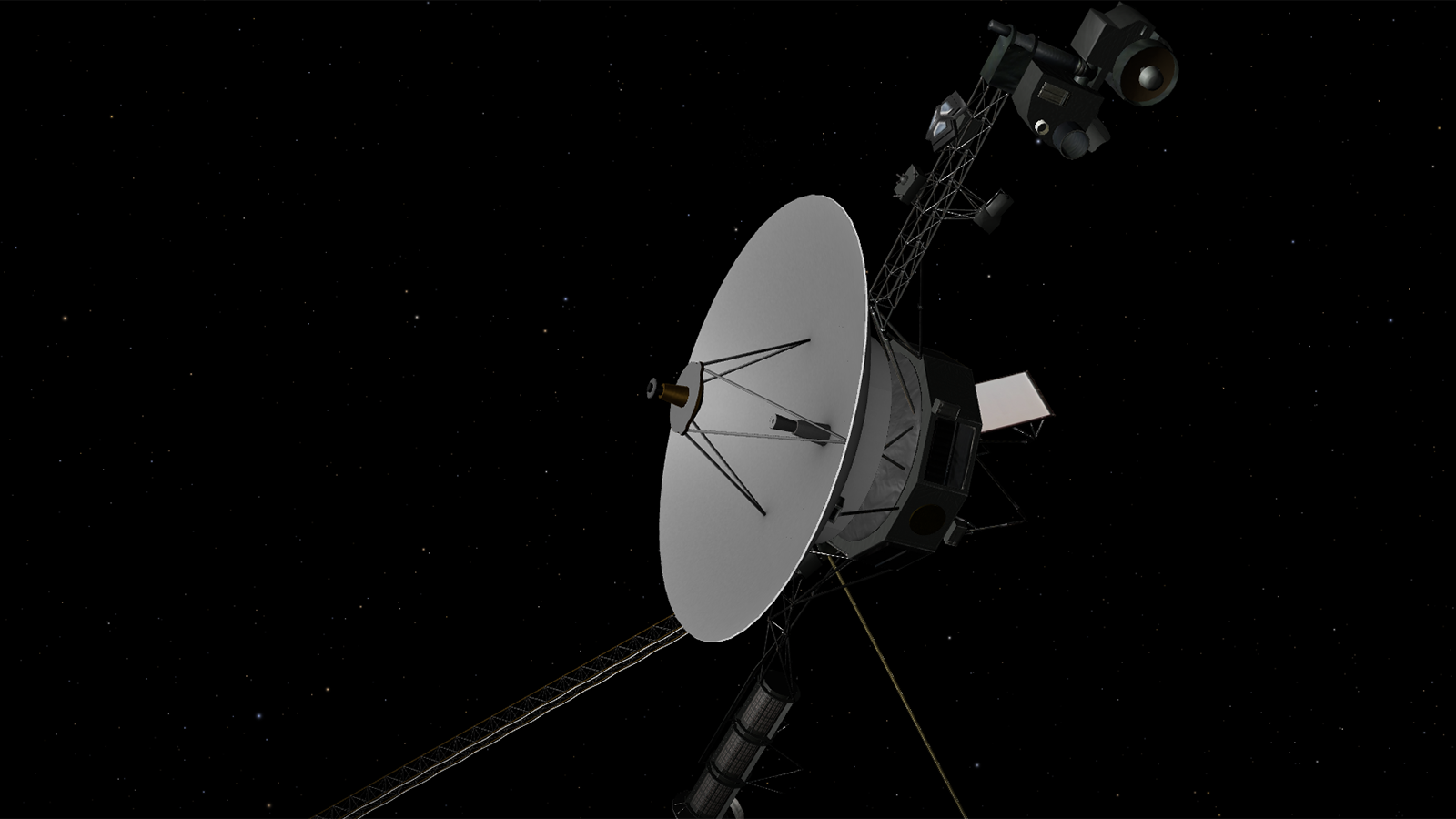

Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to visit Uranus and Neptune. The probe is now in interstellar space, the region outside the heliopause, or the bubble of energetic particles and magnetic fields from the Sun.
Mission Type
What is Voyager 2?
NASA's Voyager 2 is the second spacecraft to enter interstellar space. On Dec. 10, 2018, the spacecraft joined its twin – Voyager 1 – as the only human-made objects to enter the space between the stars.
- Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to study all four of the solar system's giant planets at close range.
- Voyager 2 discovered a 14th moon at Jupiter.
- Voyager 2 was the first human-made object to fly past Uranus.
- At Uranus, Voyager 2 discovered 10 new moons and two new rings.
- Voyager 2 was the first human-made object to fly by Neptune.
- At Neptune, Voyager 2 discovered five moons, four rings, and a "Great Dark Spot."
In Depth: Voyager 2
The two-spacecraft Voyager missions were designed to replace original plans for a “Grand Tour” of the planets that would have used four highly complex spacecraft to explore the five outer planets during the late 1970s.
NASA canceled the plan in January 1972 largely due to anticipated costs (projected at $1 billion) and instead proposed to launch only two spacecraft in 1977 to Jupiter and Saturn. The two spacecraft were designed to explore the two gas giants in more detail than the two Pioneers (Pioneers 10 and 11) that preceded them.
In 1974, mission planners proposed a mission in which, if the first Voyager was successful, the second one could be redirected to Uranus and then Neptune using gravity assist maneuvers.
Each of the two spacecraft was equipped with a slow-scan color TV camera to take images of the planets and their moons and each also carried an extensive suite of instruments to record magnetic, atmospheric, lunar, and other data about the planetary systems.
The design of the two spacecraft was based on the older Mariners, and they were known as Mariner 11 and Mariner 12 until March 7, 1977, when NASA Administrator James C. Fletcher (1919-1991) announced that they would be renamed Voyager.
Power was provided by three plutonium oxide radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) mounted at the end of a boom.
Voyager 2 at Jupiter
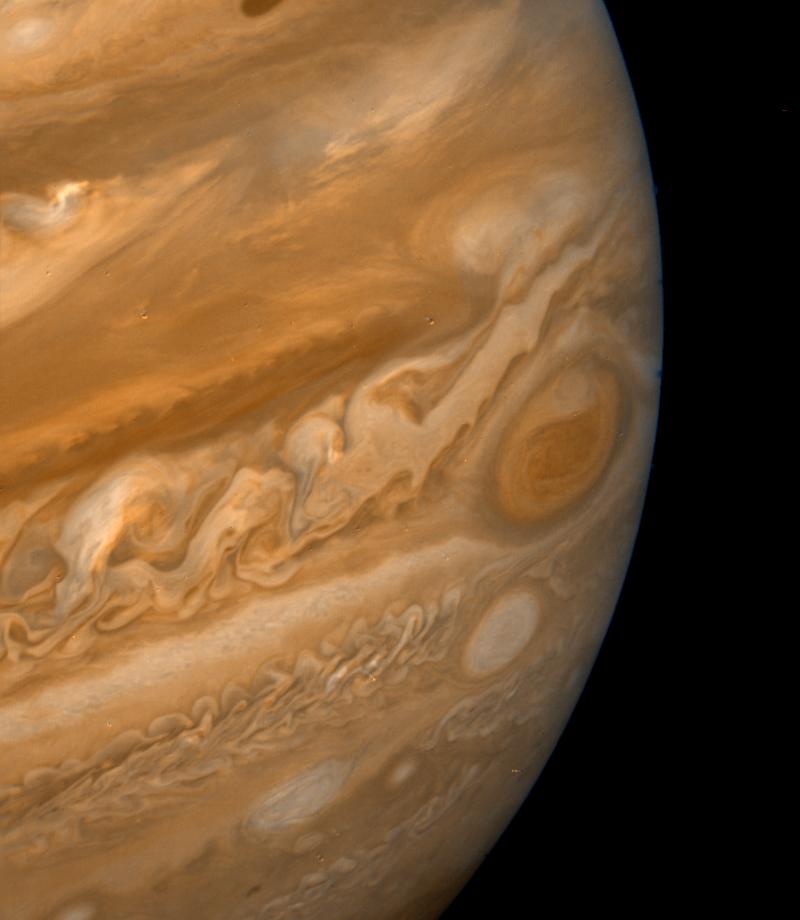

Voyager 2 began transmitting images of Jupiter April 24, 1979, for time-lapse movies of atmospheric circulation. Unlike Voyager 1, Voyager 2 made close passes to the Jovian moons on its way into the system, with scientists especially interested in more information from Europa and Io (which necessitated a 10 hour-long “volcano watch”).
During its encounter, it relayed back spectacular photos of the entire Jovian system, including its moons Callisto, Ganymede, Europa (at a range of about 127,830 miles or 205,720 kilometers, much closer than Voyager 1), Io, and Amalthea, all of which had already been surveyed by Voyager 1.
Voyager 2’s closest encounter to Jupiter was at 22:29 UT July 9, 1979, at a range of about 400,785 miles (645,000 kilometers). It transmitted new data on the planet’s clouds, its newly discovered four moons, and ring system as well as 17,000 new pictures.
When the earlier Pioneers flew by Jupiter, they detected few atmospheric changes from one encounter to the second, but Voyager 2 detected many significant changes, including a drift in the Great Red Spot as well as changes in its shape and color.
With the combined cameras of the two Voyagers, at least 80% of the surfaces of Ganymede and Callisto were mapped out to a resolution of about 3 miles (5 kilometers).
Voyager 2 at Saturn
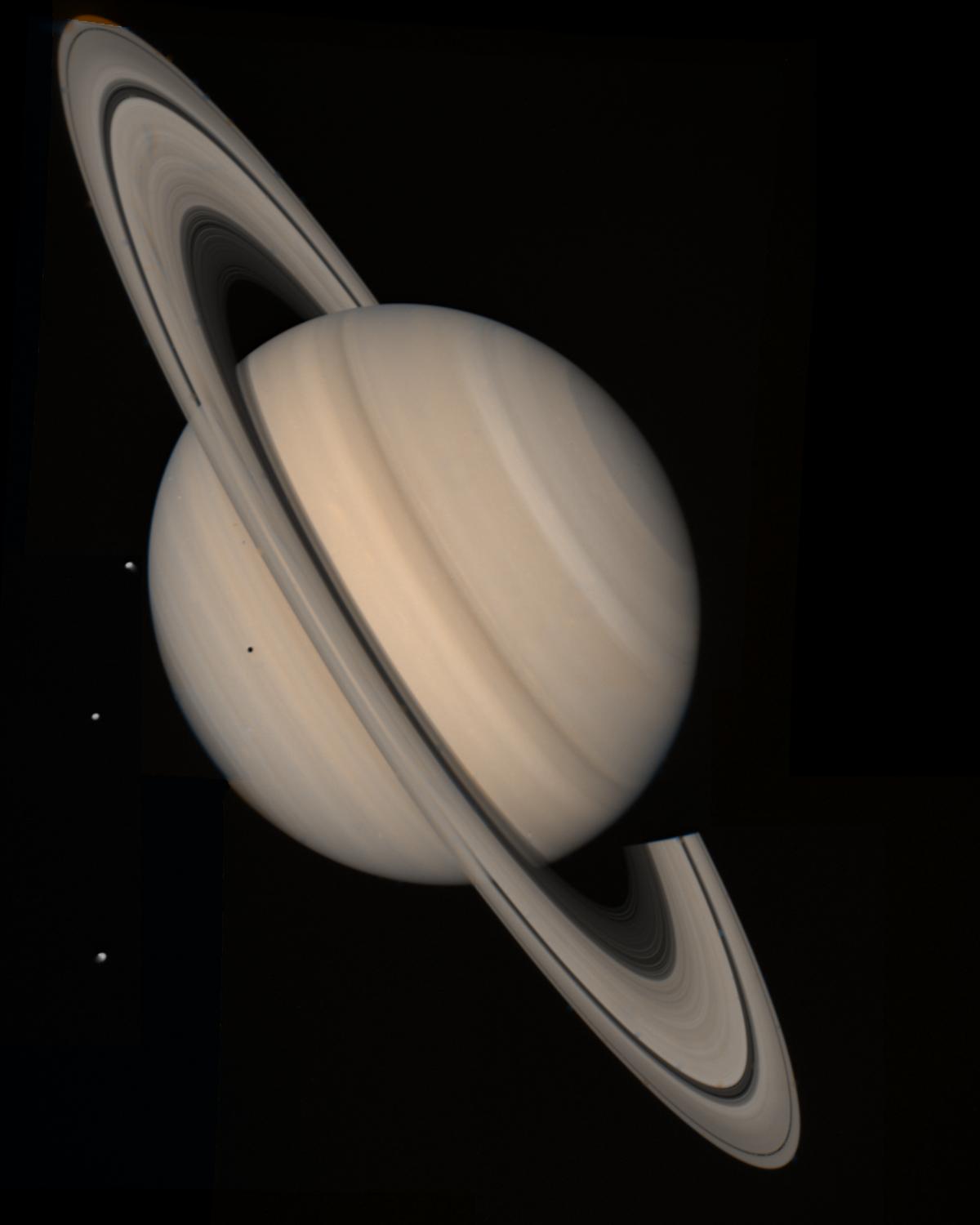

Following a course correction two hours after its closest approach to Jupiter, Voyager 2 sped to Saturn, its trajectory determined to a large degree by a decision made in January 1981, to try to send the spacecraft to Uranus and Neptune later in the decade.
Its encounter with the sixth planet began Aug. 22, 1981, two years after leaving the Jovian system, with imaging of the moon Iapetus. Once again, Voyager 2 repeated the photographic mission of its predecessor, although it actually flew about 14,290 miles (23,000 kilometers) closer to Saturn. The closest encounter to Saturn was at 01:21 UT Aug. 26, 1981, at a range of about 63,000 miles (101,000 kilometers).
The spacecraft provided more detailed images of the ring “spokes” and kinks, and also the F-ring and its shepherding moons, all found by Voyager 1. Voyager 2’s data suggested that Saturn’s A-ring was perhaps only about 980 feet (300 meters) thick.
As it flew behind and up past Saturn, the probe passed through the plane of Saturn’s rings at a speed of 8 miles per second (13 kilometers per second). For several minutes during this phase, the spacecraft was hit by thousands of micron-sized dust grains that created “puff” plasma as they were vaporized. Because the vehicle’s attitude was repeatedly shifted by the particles, attitude control jets automatically fired many times to stabilize the vehicle.
During the encounter, Voyager 2 also photographed the Saturn moons Hyperion (the “hamburger moon”), Enceladus, Tethys, and Phoebe as well as the more recently discovered Helene, Telesto and Calypso.
Voyager 2 at Uranus
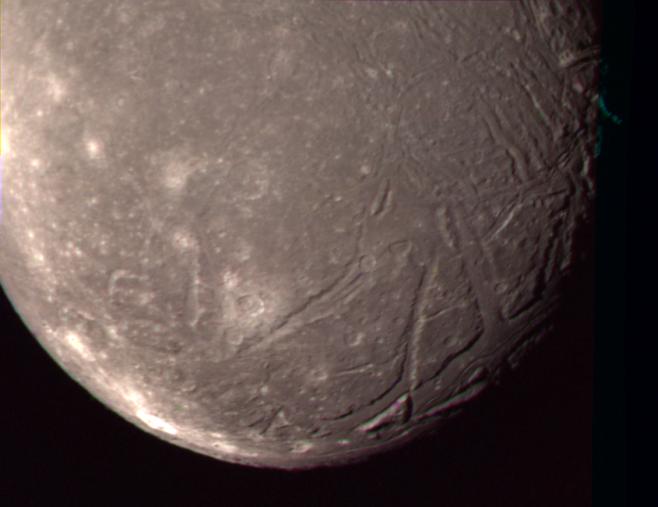

Although Voyager 2 had fulfilled its primary mission goals with the two planetary encounters, mission planners directed the veteran spacecraft to Uranus—a journey that would take about 4.5 years.
In fact, its encounter with Jupiter was optimized in part to ensure that future planetary flybys would be possible.
The Uranus encounter’s geometry was also defined by the possibility of a future encounter with Neptune: Voyager 2 had only 5.5 hours of close study during its flyby.
Voyager 2 was the first human-made object to fly past the planet Uranus.
Long-range observations of the planet began Nov. 4, 1985, when signals took approximately 2.5 hours to reach Earth. Light conditions were 400 times less than terrestrial conditions. Closest approach to Uranus took place at 17:59 UT Jan. 24, 1986, at a range of about 50,640 miles (81,500 kilometers).
During its flyby, Voyager 2 discovered 10 new moons (given such names as Puck, Portia, Juliet, Cressida, Rosalind, Belinda, Desdemona, Cordelia, Ophelia, and Bianca -- obvious allusions to Shakespeare), two new rings in addition to the “older” nine rings, and a magnetic field tilted at 55 degrees off-axis and off-center.
The spacecraft found wind speeds in Uranus’ atmosphere as high as 450 miles per hour (724 kilometers per hour) and found evidence of a boiling ocean of water some 497 miles (800 kilometers) below the top cloud surface. Its rings were found to be extremely variable in thickness and opacity.
Voyager 2 also returned spectacular photos of Miranda, Oberon, Ariel, Umbriel, and Titania, five of Uranus’ larger moons. In flying by Miranda at a range of only 17,560 miles (28,260 kilometers), the spacecraft came closest to any object so far in its nearly decade-long travels. Images of the moon showed a strange object whose surface was a mishmash of peculiar features that seemed to have no rhyme or reason. Uranus itself appeared generally featureless.
The spectacular news of the Uranus encounter was interrupted the same week by the tragic Challenger accident that killed seven astronauts during their space shuttle launch Jan. 28, 1986.
Voyager 2 at Neptune
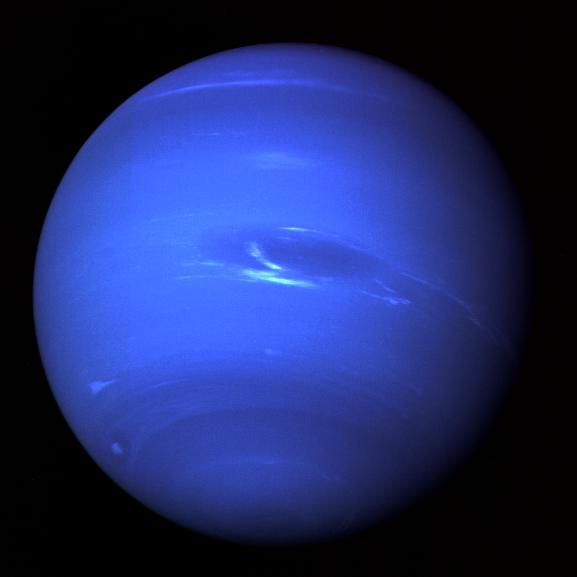

Following the Uranus encounter, the spacecraft performed a single midcourse correction Feb. 14, 1986—the largest ever made by Voyager 2—to set it on a precise course to Neptune.
Voyager 2’s encounter with Neptune capped a 4.3 billion-mile (7 billion-kilometer) journey when, on Aug. 25, 1989, at 03:56 UT, it flew about 2,980 miles (4,800 kilometers) over the cloud tops of the giant planet, the closest of its four flybys. It was the first human-made object to fly by the planet. Its 10 instruments were still in working order at the time.
During the encounter, the spacecraft discovered six new moons (Proteus, Larissa, Despina, Galatea, Thalassa, and Naiad) and four new rings.
The planet itself was found to be more active than previously believed, with 680-mile (1,100-kilometer) per hour winds. Hydrogen was found to be the most common atmospheric element, although the abundant methane gave the planet its blue appearance.
Images revealed details of the three major features in the planetary clouds—the Lesser Dark Spot, the Great Dark Spot, and Scooter.
Voyager photographed two-thirds of Neptune’s largest moon Triton, revealing the coldest known planetary body in the solar system and a nitrogen ice “volcano” on its surface. Spectacular images of its southern hemisphere showed a strange, pitted cantaloupe-type terrain.
The flyby of Neptune concluded Voyager 2’s planetary encounters, which spanned an amazing 12 years in deep space, virtually accomplishing the originally planned “Grand Tour” of the solar system, at least in terms of targets reached if not in science accomplished.
Voyager 2's Interstellar Mission
Once past the Neptune system, Voyager 2 followed a course below the ecliptic plane and out of the solar system. Approximately 35 million miles (56 million kilometers) past the encounter, Voyager 2’s instruments were put in low power mode to conserve energy.
After the Neptune encounter, NASA formally renamed the entire project the Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM).
Of the four spacecraft sent out to beyond the environs of the solar system in the 1970s, three of them -- Voyagers 1 and 2 and Pioneer 11 -- were all heading in the direction of the solar apex, i.e., the apparent direction of the Sun’s travel in the Milky Way galaxy, and thus would be expected to reach the heliopause earlier than Pioneer 10 which was headed in the direction of the heliospheric tail.
In November 1998, 21 years after launch, nonessential instruments were permanently turned off, leaving seven instruments still operating.
At 9.6 miles per second (15.4 kilometers per second) relative to the Sun, it will take about 19,390 years for Voyager 2 to traverse a single light year.

Asif Siddiqi
Beyond Earth: A Chronicle of Deep Space Exploration
Through the turn of the century, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) continued to receive ultraviolet and particle fields data. For example, on Jan. 12, 2001, an immense shock wave that had blasted out of the outer heliosphere on July 14, 2000, finally reached Voyager 2. During its six-month journey, the shock wave had plowed through the solar wind, sweeping up and accelerating charged particles. The spacecraft provided important information on high-energy shock-energized ions.
On Aug. 30, 2007, Voyager 2 passed the termination shock and then entered the heliosheath. By Nov. 5, 2017, the spacecraft was 116.167 AU (about 10.8 billion miles or about 17.378 billion kilometers) from Earth, moving at a velocity of 9.6 miles per second (15.4 kilometers per second) relative to the Sun, heading in the direction of the constellation Telescopium. At this velocity, it would take about 19,390 years to traverse a single light-year.
On July 8, 2019, Voyager 2 successfully fired up its trajectory correction maneuver thrusters and will be using them to control the pointing of the spacecraft for the foreseeable future. Voyager 2 last used those thrusters during its encounter with Neptune in 1989.
The spacecraft's aging attitude control thrusters have been experiencing degradation that required them to fire an increasing and untenable number of pulses to keep the spacecraft's antenna pointed at Earth. Voyager 1 had switched to its trajectory correction maneuver thrusters for the same reason in January 2018.
To ensure that both vintage robots continue to return the best scientific data possible from the frontiers of space, mission engineers are implementing a new plan to manage them. The plan involves making difficult choices, particularly about instruments and thrusters.

National Space Science Data Center: Voyager 2
A library of technical details and historic perspective.

A comprehensive history of missions sent to explore beyond Earth.
Discover More Topics From NASA


Voyager 1 and 2: The Interstellar Mission

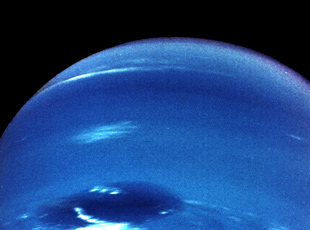
An image of Neptune taken by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
NASA has beautiful photos of every planet in our solar system. We even have images of faraway Neptune , as you can see in the photo above.
Neptune is much too distant for an astronaut to travel there with a camera. So, how do we have pictures from distant locations in our solar system? Our photographers were two spacecraft, called Voyager 1 and Voyager 2!

An artist’s rendering of one of the Voyager spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. Their mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn —and beyond to the outer planets of our solar system. This was a big task. No human-made object had ever attempted a journey like that before.
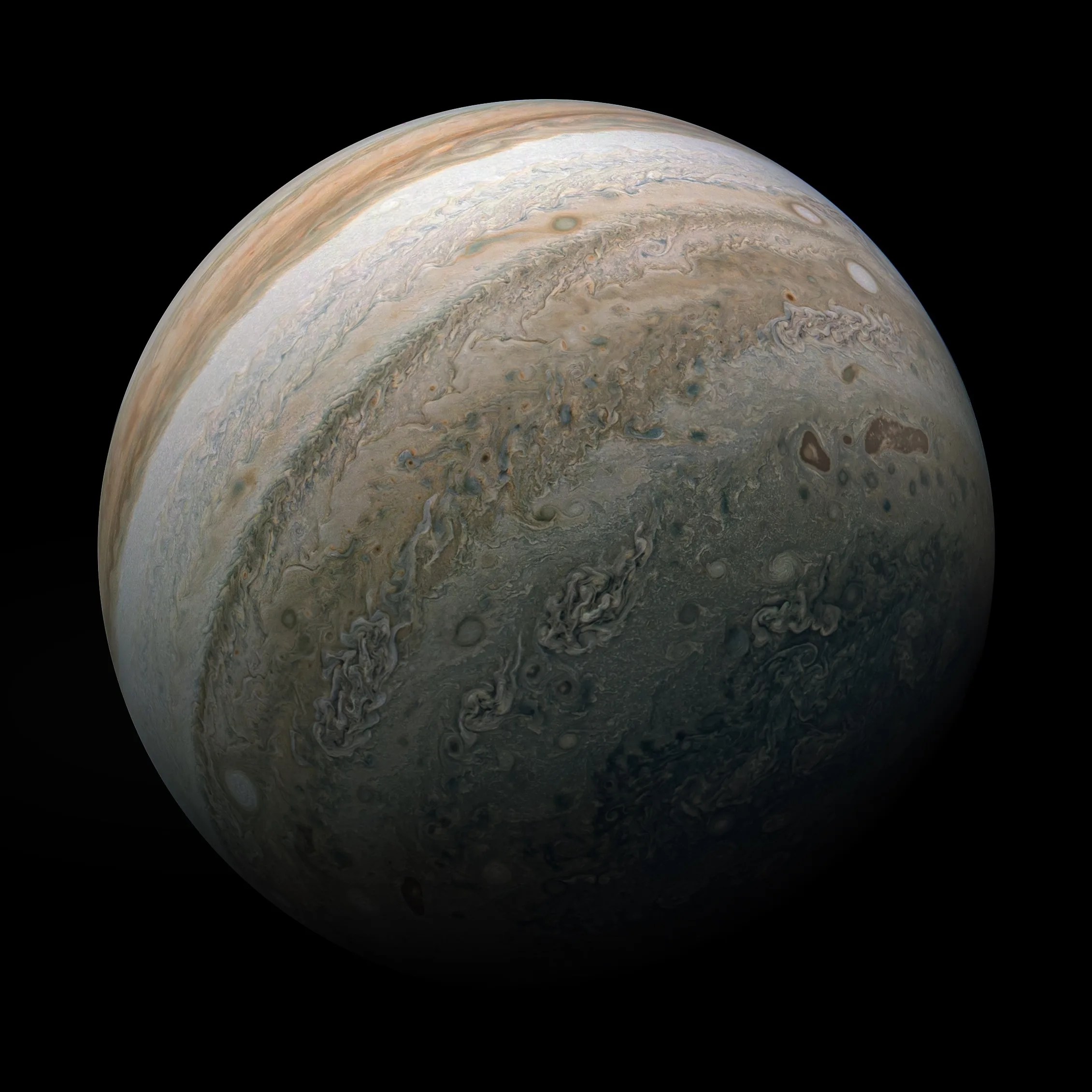
The two spacecraft took tens of thousands of pictures of Jupiter and Saturn and their moons. The pictures from Voyager 1 and 2 allowed us to see lots of things for the first time. For example, they captured detailed photos of Jupiter's clouds and storms, and the structure of Saturn's rings .

Image of storms on Jupiter taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
Voyager 1 and 2 also discovered active volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io , and much more. Voyager 2 also took pictures of Uranus and Neptune. Together, the Voyager missions discovered 22 moons.
Since then, these spacecraft have continued to travel farther away from us. Voyager 1 and 2 are now so far away that they are in interstellar space —the region between the stars. No other spacecraft have ever flown this far away.
Where will Voyager go next?
Watch this video to find out what's beyond our solar system!
Both spacecraft are still sending information back to Earth. This data will help us learn about conditions in the distant solar system and interstellar space.
The Voyagers have enough fuel and power to operate until 2025 and beyond. Sometime after this they will not be able to communicate with Earth anymore. Unless something stops them, they will continue to travel on and on, passing other stars after many thousands of years.
Each Voyager spacecraft also carries a message. Both spacecraft carry a golden record with scenes and sounds from Earth. The records also contain music and greetings in different languages. So, if intelligent life ever find these spacecraft, they may learn something about Earth and us as well!

A photo of the golden record that was sent into space on both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
More about our universe!

Where does interstellar space begin?

Searching for other planets like ours

Play Galactic Explorer!
If you liked this, you may like:
Voyager 2 Enters Final Planetary Encounter

NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft today entered the observatoryphase of its flyby of Neptune, signaling the beginning of its final planetary encounter after nearly 12 years of exploring the outer solar system.
Voyager mission controllers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., will now be tracking the spacecraft around the clock as Voyager begins taking systematic images of Neptune and sending back about 50 pictures day.
"Now that we've entered the observatory phase we'll be taking about six images every three hours to study changes in the atmosphere from rotation to rotation," said Dr. Ellis Miner, Voyager deputy project scientist.
Signals from Voyager 2 marking the beginning of the observatory phase were received at 3:40 a.m. Pacific Daylight Time. This official start of the Neptune encounter places Voyager at the top of the priority list of spacecraft being tracked by the NASA/JPL Deep Space Network. Before today, Voyager had to compete with other projects for DSN coverage. During the observatory phase, the spacecraft will be monitored at regular intervals by more than one antenna at each of the DSN sites in California, Spain and Australia.
In addition to taking images of the planet, Voyager 2 will also be making systematic ultraviolet observations of Neptune looking for any auroral activity and escaping gases. Calibrations of the spacecraft's instruments will also be done in preparation for critical near-encounter observations.
In observations of Neptune made by Voyager 2 in late 1988 and January of 1989, scientists saw bright spot in the southern hemisphere of the planet. Since January, that spot has dimmed and larger dark area has been seen in the images. Recently, the bright spot has begun to brighten again and other spots are becoming apparent. Neptune's atmosphere has also revealed regions of dark banding near its southern pole and similar banding has been seen north of the planet's equator.
Voyager's observatory phase ends and its far encounter phase starts on Aug. 6, 1989.
The near-encounter phase of the mission includes Voyager's closest approach to Neptune at 9 p.m. Pacific Daylight Time on Aug. 24, 1989, when the spacecraft passes just 4,850 kilometers (3,000 miles) from the planet's cloud tops. Five hours later, the spacecraft will fly about 39,000 kilometers (24,000 miles) from the planet's major moon Triton.
Voyager 2 is now 117 million kilometers (73 million miles) from Neptune. The Neptune flyby will be Voyager 2's fourth and final planetary encounter before the spacecraft heads out of the solar system to explore interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 2 and its twin Voyager 1 have encountered Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 went on to fly by Uranus in January 1986 while Voyager 1 continues its trek out of the solar system.
Now 4.271 billion kilometers (2.654 billion miles) from Earth, Voyager 2 is so far away that data radioed at the speed of light (186,000 miles per second) take nearly four hours to reach Earth. Voyager's images are being recorded on the spacecraft's tape recorders and will be played back to Earth beginning Tuesday morning.
The Voyager project is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications.
The remarkable twin Voyager spacecraft continue to explore the outer reaches of the solar system decades after they completed their surveys of the Outer Planets. Launched in 1977 (September 5 for Voyager 1 (V1) and August 20 for Voyager 2 (V2), whose trajectory took it past Jupiter after Voyager 1), the spacecraft pair made many fundamental discoveries as they flew past Jupiter (March 1979 for V1, July 1979 for V2) and Saturn (November 1980 for V1, August 1981 for V2). The path of Voyager 2 past Saturn was targeted so that it continued within the plane of the solar system, allowing it to become the first spacecraft to visit Uranus (January 1986) and Neptune (August 1989). Following the Neptune encounter, both spacecraft started a new phase of exploration under the intriguing title of the Voyager Interstellar Mission.

Five instruments continue to collect important measurements of magnetic fields, plasmas, and charged particles as both spacecraft explore different portions of the solar system beyond the orbits of the planets. Voyager 1 is now more than 118 astronomical units (one AU is equal to the average orbital distance of Earth from the Sun) distant from the sun, traveling at a speed (relative to the sun) of 17.1 kilometers per second (10.6 miles per second). Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s.

This processed color image of Jupiter was produced in 1990 by the U.S. Geological Survey from a Voyager image captured in 1979. The colors have been enhanced to bring out detail. Zones of light-colored, ascending clouds alternate with bands of dark, descending clouds. The clouds travel around the planet in alternating eastward and westward belts at speeds of up to 540 kilometers per hour. Tremendous storms as big as Earthly continents surge around the planet. The Great Red Spot (oval shape toward the lower-left) is an enormous anticyclonic storm that drifts along its belt, eventually circling the entire planet.
As seen in the night sky at Earth, Voyager 1 is within the confines of the constellation Ophiuchus, only slightly above the celestial equator; no telescope can see it, but radio contact is expected to be maintained for at least the next ten years. Voyager 2 is within the bounds of the constellation Telescopium (which somehow sounds quite appropriate) in the far southern night sky.

Both spacecraft have already passed something called the Termination Shock † (December 2004 for V1, August 2007 for V2), where the solar wind slows as it starts to interact with the particles and fields present between the stars. It is expected that both spacecraft will encounter the Heliopause, where the solar wind ceases as true interstellar space begins, from 10 to 20 years after crossing the Termination Shock. Theories exist for what should be present in interstellar space, but the Voyagers will become the first man-made objects to go beyond the influences of the Sun, hopefully returning the first measurements of what it is like out there. Each spacecraft is carrying a metal record with encoded sounds and sights from Earth, along with the needle needed to read the recordings, and simplified instructions for where the spacecraft came from, in case they are eventually discovered by intelligent extra-terrestrials.

Keep track of the Voyager spacecraft on the official Voyager Interstellar Mission website or follow @NASAVoyager2 on Twitter. † The sun ejects a continuous stream of charged particles (electrons, protons, etc) that is collectively termed the solar wind. The particles are traveling extremely fast and are dense enough to form a very tenuous atmosphere; the heliosphere represents the volume of space where the effects of the solar wind dominate over those of particles in interstellar space. The solar wind particles are moving very much faster than the local speed of sound represented by their low volume density. When the particles begin to interact with interstellar particles and fields (the interaction can be either physically running into other particles or experiencing an electromagnetic force resulting from a charged particle moving within a magnetic field), then they start to slow down. The point at which they become subsonic (rather than their normal hypersonic speed) is the Termination Shock.
We rely on the generous support of donors, sponsors, members, and other benefactors to share the history and impact of aviation and spaceflight, educate the public, and inspire future generations. With your help, we can continue to preserve and safeguard the world’s most comprehensive collection of artifacts representing the great achievements of flight and space exploration.
- Get Involved
- Host an Event
Thank you. You have successfully signed up for our newsletter.
Error message, sorry, there was a problem. please ensure your details are valid and try again..
- Free Timed-Entry Passes Required
- Terms of Use

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA-Led Study Provides New Global Accounting of Earth’s Rivers

NASA’s Hubble Pauses Science Due to Gyro Issue

NASA’s Optical Comms Demo Transmits Data Over 140 Million Miles
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Correction and Clarification of C.26 Rapid Mission Design Studies for Mars Sample Return

NASA’s Commercial Partners Deliver Cargo, Crew for Station Science

NASA Shares Lessons of Human Systems Integration with Industry

Work Underway on Large Cargo Landers for NASA’s Artemis Moon Missions

NASA’s ORCA, AirHARP Projects Paved Way for PACE to Reach Space
Amendment 11: Physical Oceanography not solicited in ROSES-2024

Why is Methane Seeping on Mars? NASA Scientists Have New Ideas

Mars Science Laboratory: Curiosity Rover

Hubble Spots a Magnificent Barred Galaxy

NASA’s Chandra Releases Doubleheader of Blockbuster Hits

Explore the Universe with the First E-Book from NASA’s Fermi

NASA Grant Brings Students at Underserved Institutions to the Stars

NASA Photographer Honored for Thrilling Inverted In-Flight Image

NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter Team Says Goodbye … for Now

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles

NASA Data Helps Beavers Build Back Streams

NASA’s Near Space Network Enables PACE Climate Mission to ‘Phone Home’

Washington State High Schooler Wins 2024 NASA Student Art Contest

NASA STEM Artemis Moon Trees

Kiyun Kim: From Intern to Accessibility Advocate

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
Nasa contacts voyager 2 using upgraded deep space network dish, jet propulsion laboratory.
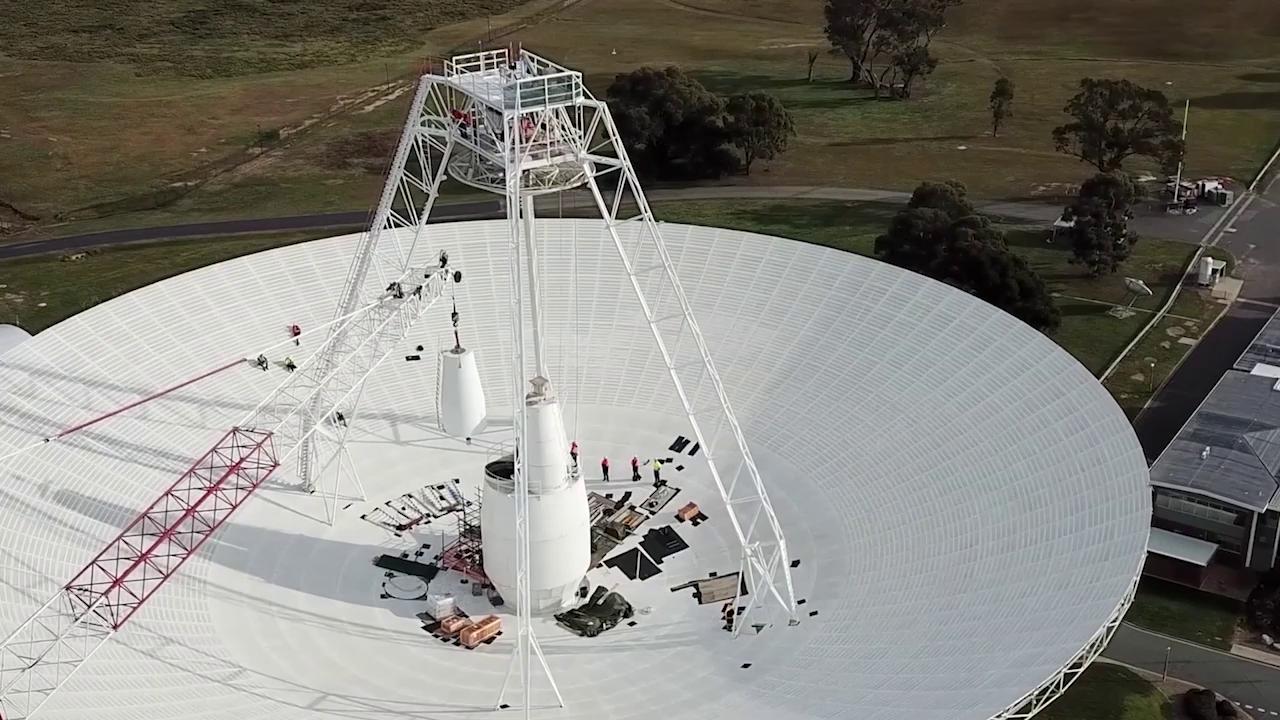

The only radio antenna that can command the 43-year-old spacecraft has been offline since March as it gets new hardware, but work is on track to wrap up in February.
On Oct. 29, mission operators sent a series of commands to NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft for the first time since mid-March. The spacecraft has been flying solo while the 70-meter-wide (230-foot-wide) radio antenna used to talk to it has been offline for repairs and upgrades. Voyager 2 returned a signal confirming it had received the “call” and executed the commands without issue.
The call to Voyager 2 was a test of new hardware recently installed on Deep Space Station 43, the only dish in the world that can send commands to Voyager 2. Located in Canberra, Australia, it is part of NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN), a collection of radio antennas around the world used primarily to communicate with spacecraft operating beyond the Moon. Since the dish went offline , mission operators have been able to receive health updates and science data from Voyager 2, but they haven’t been able to send commands to the far-flung probe, which has traveled billions of miles from Earth since its 1977 launch.
Among the upgrades to DSS43, as the dish is known, are two new radio transmitters. One of them, which is used to talk with Voyager 2, hasn’t been replaced in over 47 years. Engineers have also upgraded heating and cooling equipment, power supply equipment, and other electronics needed to run the new transmitters.
The successful call to Voyager 2 is just one indication that the dish will be back online in February 2021.
“What makes this task unique is that we’re doing work at all levels of the antenna, from the pedestal at ground level all the way up to the feedcones at the center of the dish that extend above the rim,” said Brad Arnold, the DSN project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California. “This test communication with Voyager 2 definitely tells us that things are on track with the work we’re doing.”
Worldwide Network
The Deep Space Network consist of radio antenna facilities spaced equally around the globe in Canberra; Goldstone, California; and Madrid, Spain. The positioning of the three facilities ensures that almost any spacecraft with a line of sight to Earth can communicate with at least one of the facilities at any time.
Voyager 2 is the rare exception. In order to make a close flyby of Neptune’s moon Triton in 1989, the probe flew over the planet’s north pole. That trajectory deflected it southward relative to the plane of the planets, and it has been heading in that direction ever since. Now more than 11.6 billion miles (18.8 billion kilometers) from Earth, the spacecraft is so far south that it doesn’t have a line of sight with radio antennas in the Northern Hemisphere.
Click on this interactive visualization of NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft and take it for a spin Launched in 1977, the spacecraft is now more than 11.6 billion miles (18.8 billion kilometers) from Earth. Trace its dramatic history through Eyes on the Solar System . Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
DSS43 is the only dish in the Southern Hemisphere that has a transmitter powerful enough and that broadcasts the right frequency to send commands to the distant spacecraft. Voyager 2’s faster-moving twin, Voyager 1, took a different path past Saturn and can communicate via antennas at the two DSN facilities in the Northern Hemisphere. The antennas must uplink commands to both Voyagers in a radio frequency range called S-band, and the antennas downlink data from the spacecraft in a range called X-band.
While mission operators haven’t been able to command Voyager 2 since DSS43 went offline, the three 34-meter-wide (111-foot-wide) radio antennas at the Canberra facility can be used together to capture the signals that Voyager 2 sends to Earth. The probe is sending back science data from interstellar space , or the region outside our Sun’s heliosphere – the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun that surrounds the planets and the Kuiper Belt (the collection of small, icy bodies beyond Neptune’s orbit).
DSS43 began operating in 1972 (five years before the launch of Voyager 2 and Voyager 1) and was only 64 meters (210 feet) wide at the time. It was expanded to 70 meters (230 feet) in 1987 and has received a variety of upgrades and repairs since then. But the engineers overseeing the current work say this is one of the most significant makeovers the dish has received and the longest it’s been offline in over 30 years.
“The DSS43 antenna is a highly specialized system; there are only two other similar antennas in the world, so having the antenna down for one year is not an ideal situation for Voyager or for many other NASA missions,” said Philip Baldwin, operations manager for NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) Program. “The agency made the decision to conduct these upgrades to ensure that the antenna can continue to be used for current and future missions. For an antenna that is almost 50 years old, it’s better to be proactive than reactive with critical maintenance.”
The repairs will benefit other missions, including the Mars Perseverance rover , which will land on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021. The network will also play a critical role in Moon to Mars exploration efforts, ensuring communication and navigation support for both the precursor Moon and Mars missions and the crewed Artemis missions .
The Deep Space Network is managed by JPL for the SCaN Program, located at NASA Headquarters within the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The Canberra station is managed on NASA’s behalf by Australia’s national science agency, the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation.
The Voyager spacecraft were built by JPL, which continues to operate both. JPL is a division of Caltech in Pasadena. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington. For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov
Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected] 2020-207
Subscribe or renew today
Every print subscription comes with full digital access
Science News
‘humanity’s spacecraft’ voyager 1 is back online and still exploring.
After five months of glitching, the spacecraft is talking to Earth again from interstellar space

The Voyager 1 spacecraft (illustrated) is back online after a few months of transmitting garbled data. It’s now poised to continue its exploration of interstellar space.
JPL-Caltech/NASA
Share this:
By Ramin Skibba
April 26, 2024 at 11:45 am
After months of challenging trouble-shooting and suspenseful waiting, Voyager 1 is once again talking to Earth.
The aging NASA spacecraft, about 24 billion kilometers from home, began transmitting garbled data in November. On April 20, NASA scientists got the probe back online after uploading new flight software to work around a chunk of onboard computer memory that had failed. They’re now receiving data about the spacecraft’s health and hope to hear from its science instruments again in a few weeks, says Suzanne Dodd, the mission’s project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
That means the iconic craft could be on a path to recovery — and to continue its exploration of interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 briefly visited Jupiter and Saturn before eventually departing the solar system. It and its twin, Voyager 2, are the longest-operating space probes, now tasked with studying far-flung solar particles and cosmic rays. In particular, the probes have been monitoring the changing of the sun’s magnetic field and the density of plasma beyond the solar system, yielding information about the farthest reaches of the sun’s influence .
“The spacecraft is really remarkable in its longevity. It’s incredible,” Dodd says. “We want to keep Voyager going as long as possible so we have this time record of these changes.”
Voyager 1 and 2, cruising along diverging paths, made history by crossing the heliopause in 2012 and 2018 , respectively ( SN: 9/12/13; SN: 12/10/18 ). At nearly 18 billion kilometers from the sun, that’s long been considered the outer extent of our star’s magnetic field and the solar wind, the boundary before interstellar space.
Since then, Dodd says, the science team has made some surprising findings ( SN: 11/4/19 ). For one, they’ve determined that the heliosphere, the huge bubble of space dominated by the solar wind, might not be spherical but have one or two tails, making it shaped like a comet or a croissant.
And thanks to Voyager, scientists now know that, despite expectations otherwise, the sun’s magnetic field and charged particles actually remain significant even beyond the heliopause, says David McComas, a Princeton University astrophysicist not involved in the mission.
Some theories predicted a serene environment in the distant oceans of interstellar space, but the Voyagers keep passing through waves of charged particles, indicating that the solar magnetic field still holds some sway there. What’s more, the probes’ data have shown how ripples in the field form bubbles at the edge of the solar system, which is more frothy and dynamic than expected.
Other missions have begun building on Voyager’s solar physics research. These include NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, and the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe, or IMAP, which is set to launch next year. Earth-orbiting IBEX has been measuring high-energy particles to map the heliosphere for 15 years, whereas IMAP will orbit between the sun and Earth, giving it an uninterrupted view of the sun as it monitors the galactic cosmic rays that manage to filter through the heliosphere.
“There’s a huge synergy between the Voyagers and both IBEX and IMAP,” says McComas, principal investigator of the latter two missions. “We were all really scared when Voyager 1 stopped phoning home.”
It will be decades until another mission could accomplish what the Voyagers have done. NASA’s New Horizons soared by Pluto in 2015 and kept going ( SN:8/9/18 ). It’s heading toward the edge of the solar system, but it’s cruising slowly and will run out of power before it can collect data beyond the heliopause.
The Voyagers can fly forever, but power for their instruments is waning. Over the next few years, NASA will shut some down to conserve energy for the rest.
That means Voyager 1’s days of collecting science data are numbered. “It’s a very beloved mission,” Dodd says. “It’s humanity’s spacecraft, and we need to take care of it.”
More Stories from Science News on Space

Separating science fact from fiction in Netflix’s ‘3 Body Problem’

Pluto’s heart-shaped basin might not hide an ocean after all

Our picture of habitability on Europa, a top contender for hosting life, is changing

Jupiter’s moon Io may have been volcanically active ever since it was born

50 years ago, scientists found a lunar rock nearly as old as the moon


How a sugar acid crucial for life could have formed in interstellar clouds

What Science News saw during the solar eclipse

During the awe of totality, scientists studied our planet’s reactions
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber? Become one now .
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Voyager 1 transmitting data again after Nasa remotely fixes 46-year-old probe
Engineers spent months working to repair link with Earth’s most distant spacecraft, says space agency
Earth’s most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.
Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), which makes and operates the agency’s robotic spacecraft, said in December that the probe – more than 15bn miles (24bn kilometres) away – was sending gibberish code back to Earth.
In an update released on Monday , JPL announced the mission team had managed “after some inventive sleuthing” to receive usable data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. “The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again,” JPL said. Despite the fault, Voyager 1 had operated normally throughout, it added.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was designed with the primary goal of conducting close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn in a five-year mission. However, its journey continued and the spacecraft is now approaching a half-century in operation.
Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012, making it the first human-made object to venture out of the solar system. It is currently travelling at 37,800mph (60,821km/h).
Hi, it's me. - V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe — NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
The recent problem was related to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, which are responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it is sent to Earth. Unable to repair a broken chip, the JPL team decided to move the corrupted code elsewhere, a tricky job considering the old technology.
The computers on Voyager 1 and its sister probe, Voyager 2, have less than 70 kilobytes of memory in total – the equivalent of a low-resolution computer image. They use old-fashioned digital tape to record data.
The fix was transmitted from Earth on 18 April but it took two days to assess if it had been successful as a radio signal takes about 22 and a half hours to reach Voyager 1 and another 22 and a half hours for a response to come back to Earth. “When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on 20 April, they saw that the modification worked,” JPL said.
Alongside its announcement, JPL posted a photo of members of the Voyager flight team cheering and clapping in a conference room after receiving usable data again, with laptops, notebooks and doughnuts on the table in front of them.
The Retired Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, who flew two space shuttle missions and acted as commander of the International Space Station, compared the JPL mission to long-distance maintenance on a vintage car.
“Imagine a computer chip fails in your 1977 vehicle. Now imagine it’s in interstellar space, 15bn miles away,” Hadfield wrote on X . “Nasa’s Voyager probe just got fixed by this team of brilliant software mechanics.
Voyager 1 and 2 have made numerous scientific discoveries , including taking detailed recordings of Saturn and revealing that Jupiter also has rings, as well as active volcanism on one of its moons, Io. The probes later discovered 23 new moons around the outer planets.
As their trajectory takes them so far from the sun, the Voyager probes are unable to use solar panels, instead converting the heat produced from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity to power the spacecraft’s systems.
Nasa hopes to continue to collect data from the two Voyager spacecraft for several more years but engineers expect the probes will be too far out of range to communicate in about a decade, depending on how much power they can generate. Voyager 2 is slightly behind its twin and is moving slightly slower.
In roughly 40,000 years, the probes will pass relatively close, in astronomical terms, to two stars. Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of a star in the constellation Ursa Minor, while Voyager 2 will come within a similar distance of a star called Ross 248 in the constellation of Andromeda.

Cosmic cleaners: the scientists scouring English cathedral roofs for space dust

Russia acknowledges continuing air leak from its segment of space station

Uncontrolled European satellite falls to Earth after 30 years in orbit

Cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko sets world record for most time spent in space

‘Old smokers’: astronomers discover giant ancient stars in Milky Way

Nasa postpones plans to send humans to moon

What happened to the Peregrine lander and what does it mean for moon missions?

Peregrine 1 has ‘no chance’ of landing on moon due to fuel leak
Most viewed.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Well, hello, Voyager 1! The venerable spacecraft is once again making sense

Nell Greenfieldboyce

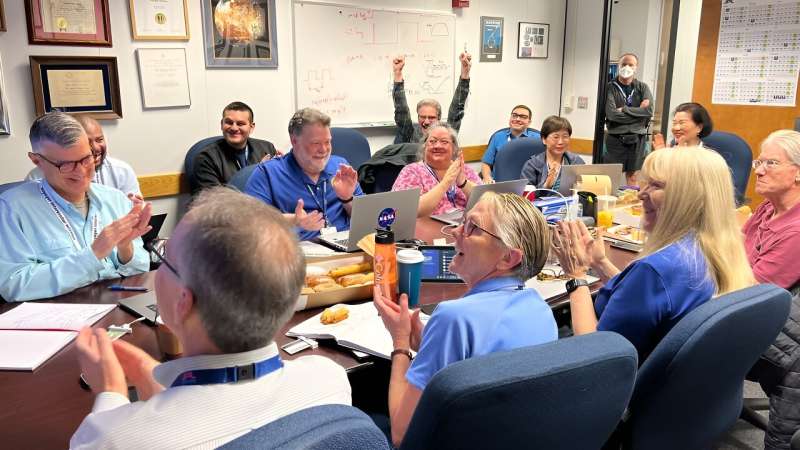
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months. NASA/JPL-Caltech hide caption
Members of the Voyager team celebrate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory after receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in months.
NASA says it is once again able to get meaningful information back from the Voyager 1 probe, after months of troubleshooting a glitch that had this venerable spacecraft sending home messages that made no sense.
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space, the previously unexplored region between the stars. (Its twin, traveling in a different direction, followed suit six years later.)
Voyager 1 had been faithfully sending back readings about this mysterious new environment for years — until November, when its messages suddenly became incoherent .

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is talking nonsense. Its friends on Earth are worried
It was a serious problem that had longtime Voyager scientists worried that this historic space mission wouldn't be able to recover. They'd hoped to be able to get precious readings from the spacecraft for at least a few more years, until its power ran out and its very last science instrument quit working.
For the last five months, a small team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California has been working to fix it. The team finally pinpointed the problem to a memory chip and figured out how to restore some essential software code.
"When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft," NASA stated in an update.
The usable data being returned so far concerns the workings of the spacecraft's engineering systems. In the coming weeks, the team will do more of this software repair work so that Voyager 1 will also be able to send science data, letting researchers once again see what the probe encounters as it journeys through interstellar space.

After a 12.3 billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
- interstellar mission
share this!
April 22, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
NASA's Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth

For the first time since November, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems. The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft's three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it's sent to Earth.
The team discovered that a single chip responsible for storing a portion of the FDS memory—including some of the FDS computer's software code—isn't working. The loss of that code rendered the science and engineering data unusable. Unable to repair the chip, the team decided to place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. But no single location is large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
So they devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS. To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole. Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated as well.

The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft's engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22.5 hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22.5 hours for a signal to come back to Earth. When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification had worked: For the first time in five months, they were able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago, the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history. Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
Provided by NASA
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Global study shows a third more insects come out after dark
20 hours ago

Cicada-palooza! Billions of bugs to blanket America
22 hours ago

Getting dynamic information from static snapshots

Ancient Maya blessed their ballcourts: Researchers find evidence of ceremonial offerings in Mexico

Optical barcodes expand range of high-resolution sensor
Apr 26, 2024

Ridesourcing platforms thrive on socio-economic inequality, say researchers

Did Vesuvius bury the home of the first Roman emperor?

Florida dolphin found with highly pathogenic avian flu: Report

A new way to study and help prevent landslides

New algorithm cuts through 'noisy' data to better predict tipping points
Relevant physicsforums posts, black holes colliding exactly head on.
3 hours ago
Need help simplifying standard error formula for redshift
23 hours ago
Our Beautiful Universe - Photos and Videos
Apr 25, 2024
Solar Activity and Space Weather Update thread
'devil' comet visible tonight 21.04.24, waves in space.
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

Engineers working to resolve issue with Voyager 1 computer
Dec 13, 2023

NASA hears signal from Voyager 2 spacecraft after mistakenly cutting contact
Aug 1, 2023

NASA listens for Voyager 2 spacecraft after wrong command cuts contact
Jul 31, 2023

NASA's Voyager team focuses on software patch, thrusters
Oct 20, 2023

NASA's Voyager will do more science with new power strategy
Apr 27, 2023

Engineers investigating NASA's Voyager 1 telemetry data
May 18, 2022
Recommended for you

Japan's moon lander wasn't built to survive a weekslong lunar night. It's still going after 3
Apr 24, 2024

Simulated microgravity affects sleep and physiological rhythms, study finds
Apr 22, 2024

'Tube map' around planets and moons made possible by knot theory
Apr 17, 2024

NASA's Ingenuity Mars helicopter team says goodbye—for now

NASA confirms mystery object that crashed through roof of Florida home came from space station
Apr 16, 2024

NASA is seeking a faster, cheaper way to bring Mars samples to Earth
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
NASA hears from Voyager 1, the most distant spacecraft from Earth, after months of quiet
NASA has finally heard back from Voyager 1 in a way that makes sense
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA has finally heard back from Voyager 1 again in a way that makes sense.
The most distant spacecraft from Earth stopped sending back understandable data last November. Flight controllers traced the blank communication to a bad computer chip and rearranged the spacecraft’s coding to work around the trouble.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California declared success after receiving good engineering updates late last week. The team is still working to restore transmission of the science data.
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space. The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.
Contact was never lost, rather it was like making a phone call where you can’t hear the person on the other end, a JPL spokeswoman said Tuesday.
Launched in 1977 to study Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 1 has been exploring interstellar space — the space between star systems — since 2012. Its twin, Voyager 2, is 12.6 billion miles (20 billion kilometers) away and still working fine.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Top Stories

Golden retriever steals the show as wedding ring bearer
- Apr 26, 11:42 AM

Judge upholds disqualification of challenger to judge in Trump’s Georgia election interference case
- Apr 26, 2:43 PM

Planning for potential presidential transition underway as Biden administration kicks it off
- Apr 26, 4:03 PM

'Coat hanger' could unlock storage room where Trump stored classified docs: Witness
- Apr 27, 10:26 AM

Ex-official told investigators Trump had 'no standing declassification order'
- Apr 25, 6:55 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
NASA’s Voyager 1 resumes sending data to Earth after 5 months
- Published: Apr. 23, 2024, 5:53 p.m.
- Ryan Mancini | [email protected]
In the depths of space, the spacecraft Voyager 1 continued sending usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems back to Earth, according to a statement from NASA.
Voyager 1 , the most distant human-made object in existence, stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, the statement released on Monday read. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, confirmed the problem was “tied to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem,” NASA said.
This subsystem is critical in packaging the science and engineering data before all the data goes back to Earth, the space agency continued. The team at JPL found that one chip responsible for storing part of the subsystem’s memory did not work, which rendered all of the data unusable and the code was too large to place in one new location.
More weather
- 7 Massachusetts counties under a frost advisory until early Saturday morning
- The current freeze warning will be expiring at 5 a.m.
- 9 Massachusetts counties under a freeze warning until early Friday morning
- Update: Freeze watch for 6 Massachusetts counties until early Friday morning
- Update: Freeze watch issued for 3 Massachusetts counties until early Friday morning
The team chose to “divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the” subsystem,” NASA said. On April 18, the team moved the spacecraft’s engineering data to a new location within the subsystem.
“A radio signal takes about 22 and a half hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22 and a half hours for a signal to come back to Earth,” NASA said in its statement. “When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.”
In the weeks ahead, the team at JPL will relocate and adjust any other affected parts of the subsystem software, the agency said.
Voyager 1′s twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, continues to function normally, NASA said. Like its twin, Voyager 2 the only other spacecraft to fly into interstellar space. Both were launched in 1977.
Aboard both probes are phonograph records called The Golden Records that each carry time capsules “intended to communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials,” according to NASA. Material placed on the records was chosen for NASA by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan .
If you purchase a product or register for an account through a link on our site, we may receive compensation. By using this site, you consent to our User Agreement and agree that your clicks, interactions, and personal information may be collected, recorded, and/or stored by us and social media and other third-party partners in accordance with our Privacy Policy.

- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
Galleries of Images Voyager Took
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft explored Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune before starting their journey toward interstellar space. Here you'll find some of those iconic images, including "The Pale Blue Dot" - famously described by Carl Sagan - and what are still the only up-close images of Uranus and Neptune.

Photography of Jupiter began in January 1979, when images of the brightly banded planet already exceeded the best taken from Earth. Voyager 1 completed its Jupiter encounter in early April, after taking almost 19,000 pictures and many other scientific measurements. Voyager 2 picked up the baton in late April and its encounter continued into August. They took more than 33,000 pictures of Jupiter and its five major satellites.

The Voyager 1 and 2 Saturn encounters occurred nine months apart, in November 1980 and August 1981. Voyager 1 is leaving the solar system. Voyager 2 completed its encounter with Uranus in January 1986 and with Neptune in August 1989, and is now also en route out of the solar system.

NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft flew closely past distant Uranus, the seventh planet from the Sun, in January. At its closet, the spacecraft came within 81,800 kilometers (50,600 miles) of Uranus's cloudtops on Jan. 24, 1986. Voyager 2 radioed thousands of images and voluminous amounts of other scientific data on the planet, its moons, rings, atmosphere, interior and the magnetic environment surrounding Uranus.
In the summer of 1989, NASA's Voyager 2 became the first spacecraft to observe the planet Neptune, its final planetary target. Passing about 4,950 kilometers (3,000 miles) above Neptune's north pole, Voyager 2 made its closest approach to any planet since leaving Earth 12 years ago. Five hours later, Voyager 2 passed about 40,000 kilometers (25,000 miles) from Neptune's largest moon, Triton, the last solid body the spacecraft will have an opportunity to study.

This narrow-angle color image of the Earth, dubbed 'Pale Blue Dot', is a part of the first ever 'portrait' of the solar system taken by Voyager 1. The spacecraft acquired a total of 60 frames for a mosaic of the solar system from a distance of more than 4 billion miles from Earth and about 32 degrees above the ecliptic. From Voyager's great distance Earth is a mere point of light, less than the size of a picture element even in the narrow-angle camera. Earth was a crescent only 0.12 pixel in size. Coincidentally, Earth lies right in the center of one of the scattered light rays resulting from taking the image so close to the sun. This blown-up image of the Earth was taken through three color filters -- violet, blue and green -- and recombined to produce the color image. The background features in the image are artifacts resulting from the magnification.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Note: Because Earth moves around the Sun faster than Voyager 1 or Voyager 2 is traveling from Earth, the one-way light time between Earth and each spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of the year. Cosmic Ray Data: This meter depicts the dramatic changes in readings by Voyager's cosmic ray instrument. The instrument detected a dip in ...
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 2's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 2 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year. ...
Voyager 2 live position and data. This page shows Voyager 2 location and other relevant astronomical data in real time. The celestial coordinates, magnitude, distances and speed are updated in real time and are computed using high quality data sets provided by the JPL Horizons ephemeris service (see acknowledgements for details). The sky map shown in the background represents a rectangular ...
The value of the distance of Voyager 2 from Earth is also available as a real time updated value in the Live Position and Data Tracker. Closest Approach of Voyager 2 to Earth Between 1 January 2013 and 30 December 2099, the closest approach of Voyager 2 to Earth happens on Sun Jun 2 2013 at a distance of 101.162452 Astronomical Units, or ...
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. In NASA's Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the actual spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers updated every five minutes.
Voyager 2 also returned spectacular photos of Miranda, Oberon, Ariel, Umbriel, and Titania, five of Uranus' larger moons. In flying by Miranda at a range of only 17,560 miles (28,260 kilometers), the spacecraft came closest to any object so far in its nearly decade-long travels. Images of the moon showed a strange object whose surface was a ...
About the mission. The Voyager 2 spacecraft, which has been in operation since 1977 and is the only spacecraft to have ever visited Uranus and Neptune, has made its way to interstellar space, where its twin spacecraft, Voyager 1, has resided since August 2012. During its travels through the outer solar system, Voyager 2 visited all four gas ...
Voyager 2. Heliocentric positions of the five interstellar probes (squares) and other bodies (circles) until 2020, with launch and flyby dates. Markers denote positions on 1 January of each year, with every fifth year labelled. Plot 1 is viewed from the north ecliptic pole, to scale. Plots 2 to 4 are third-angle projections at 20% scale.
NASA's Voyager Spacecraft Still Reaching for the Stars After 40 Years. Humanity's farthest and longest-lived spacecraft, Voyager 1 and 2, achieve 40 years of operation and exploration this August and September. Despite their vast distance, they continue to communicate with NASA daily, still probing the final frontier.
News updates on Voyager 2's encounter with Neptune will be available to the public during late August on special telephone numbers from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Frequently updated reports on the spacecraft mission can be heard August 19-31 by phoning (900) 590-1234. Cost for each call on this 900 number is 45 cents for the first minute ...
Dec 10, 2018. RELEASE 18-115. This illustration shows the position of NASA's Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes, outside of the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun that extends well past the orbit of Pluto. Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech. For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars.
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. Their mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn —and beyond to the outer planets of our solar system. This was a big task. No human-made object had ever attempted a journey like that before. The two spacecraft took tens of thousands of pictures of Jupiter and Saturn and their moons.
Forty-one years after it launched into space, NASA's Voyager 2 probe has exited our solar bubble and entered the region between stars. Its twin, Voyager 1, m...
Explore the solar system with NASA's Eyes, an interactive web app that lets you simulate the orbits and movements of planets, moons, asteroids, and spacecraft. You can zoom in and out, change the speed and direction of time, and view the solar system from different perspectives. Learn about the missions that explore our cosmic neighborhood and discover the wonders of the sun, Earth, and other ...
The Voyager project is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications. 818-354-5011. 1989-1246. NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft today entered the observatoryphase of its flyby of Neptune, signaling the beginning of its final planetary encounter after nearly 12 years of exploring the outer solar system.
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 after mistakenly pointing its antenna 2 degrees away from Earth. On Friday, contact was fully restored. Talk about a long ...
Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s. This processed color image of Jupiter was ...
The call to Voyager 2 was a test of new hardware recently installed on Deep Space Station 43, the only dish in the world that can send commands to Voyager 2. Located in Canberra, Australia, it is part of NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN), a collection of radio antennas around the world used primarily to communicate with spacecraft operating ...
This visualization tracks the trajectory of the Voyager 2 spacecraft through the solar system. Launched on August 20, 1977, it was one of two spacecraft sent to visit the giant planets of the outer solar system. Like Voyager 1, Voyager 2 flew by Jupiter and Saturn, but the Voyager 2 mission was extended to fly by Uranus and Neptune before being directed out of the solar system.To fit the 40 ...
Voyager 2 entered interstellar space on November 5, 2018 and scientists hope to learn more about this region. Both spacecraft are still sending scientific information about their surroundings through the Deep Space Network, or DSN. The primary mission was the exploration of Jupiter and Saturn. After making a string of discoveries there — such ...
Voyager 1 and 2, cruising along diverging paths, made history by crossing the heliopause in 2012 and 2018, respectively (SN: 9/12/13; SN: 12/10/18). At nearly 18 billion kilometers from the sun ...
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, both launched in 1977, were built to last five years. They've now beamed back cosmic information for well over four decades , a feat made possible by hardy spacecraft and ...
Meanwhile, Voyager 2 continues to operate normally, they said. The twin Voyager spacecraft were launched in 1977 and remain the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in human history.
Voyager 2 is slightly behind its twin and is moving slightly slower. In roughly 40,000 years, the probes will pass relatively close, in astronomical terms, to two stars. Voyager 1 will come within ...
Live Sessions Podcasts & Shows ... The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes launched in 1977 on a mission to study Jupiter and Saturn but continued onward through the outer reaches of the solar system ...
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago, the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history.
It takes 22 1/2 hours to send a signal to Voyager 1, more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away in interstellar space. The signal travel time is double that for a round trip.
Voyager 1′s twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, continues to function normally, NASA said. Like its twin, Voyager 2 the only other spacecraft to fly into interstellar space. Both were launched in 1977.
Voyager 2 radioed thousands of images and voluminous amounts of other scientific data on the planet, its moons, rings, atmosphere, interior and the magnetic environment surrounding Uranus. Neptune In the summer of 1989, NASA's Voyager 2 became the first spacecraft to observe the planet Neptune, its final planetary target. Passing about 4,950 ...
For You Live TV. NOW PLAYING. We're Getting Whiffs of Stagflation, Sosnick Says. 01:50. Chanel Boss: I Want to Change the World But Look Good While Doing It. 46:49. Balance of Power 04/26/24.