
- Site Search Search Posts Find A Forum Thread Number Threads by Name Search FAQs
- ENGINEERING.com
- Eng-Tips Forums
- Tek-Tips Forums


Join Eng-Tips ® Today!
Join your peers on the Internet's largest technical engineering professional community. It's easy to join and it's free.
Here's Why Members Love Eng-Tips Forums:
- Notification Of Responses To Questions
- Favorite Forums One Click Access
- Keyword Search Of All Posts, And More...
Register now while it's still free!
Already a member? Close this window and log in.
Join Us Close
404 Not found

Protection from Electricity in Commercial Kitchen Installations
Nfpa code talk.
Since the release of the 2020 edition of NFPA 70®, National Electrical Code ® (NEC®), a lot of discussions have taken place around the many new or revised requirements that affect residential occupancies. Requirements like emergency disconnecting means, whole-house surge protection, and expanding GFCI requirements, to name just a few. However, I feel like while the lion’s share of attention gets placed on residential requirements, there is much more to know when it comes to commercial installations. After all, don’t commercial buildings share the same need for the safeguarding of persons and property from electrical hazards as dwelling units? According to fire report data, some of the leading causes of fire in a commercial setting involve cooking equipment, heating equipment, lighting, and other electrical equipment. All of which have a common denominator here, the use of electricity!
Let’s look at an area of a commercial building that has many of the components that cause a dangerous and potentially deadly event just lying in wait – a commercial kitchen. The NEC contains certain requirements aimed at protecting people and property from electrical dangers, but there are a few other documents that we will want to consult here as well. First, let us think about the direct danger of electrical hazards. Electrical shock remains the number one source of fatal workplace injuries due to electricity, and commercial kitchens have a host of reasons why protection from electricity must be a priority. Just about every surface in a commercial kitchen is conductive and bonded to the electrical system, either by direct contact to the equipment grounding conductor or by connection to another grounded surface such as the tile floor. Because of this, nearly any contact with an energized conductor has all the components needed for electrocution. To protect against this threat, the NEC relies on a time-tested approach that we know has a proven track record of saving lives from shock: the ground-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI).
Within a commercial kitchen, GFCI protection for personnel is going to be required on most receptacle outlets. This requirement applies to both single- and three-phase receptacles on branch circuits rated 150V to ground or less. On single-phase branch circuits, this applies to all receptacles up to 50A, and on three-phase circuits, the cut-off is 100A. There is also a requirement to protect certain appliances regardless of whether they are cord-and-plug connected. Dishwashers, vending machines, and drinking water coolers/bottle fill stations must all be GFCI protected when they are installed on branch circuits that are 150V to ground or less and that are 60A or less. New for the 2020 NEC is that they have also clarified that this protection is needed in areas that might only be used for food prep and don’t have the necessary cooking provisions to deem them a kitchen. Yet, they still have all of the same potential for electrical tragedy.
Another area of great concern in a commercial kitchen is the exhaust hood over major cooking appliances. It is this hood that keeps the smoke and fumes produced during the cooking process from entering the rest of the restaurant or whatever the building happens to be. There are also many other considerations that come along with this equipment that we must be aware of. Cooking equipment is a leading cause of fire in a commercial setting, so it stands to reason that there is a significant fire protection component to a commercial cooking hood. However, while the equipment needed to operate a kitchen hood might involve complex coordination, the premise is simple. The exhaust hood will pull a certain volume of air, smoke, and fumes out of the kitchen while running, and if the volume is large enough, this might require the use of a make-up air unit to pump fresh air back in. There will most likely be some form of automatic fire extinguishing system under the hood that is effective on grease fires. Lastly, any lighting within the hood must be able to withstand high heat and be easily wiped down to prevent a build-up of excess grease, which could potentially lead to grease fires if not kept in check.
The NEC contains many of the requirements to ensure that the electrical system does not contribute to kitchen fires when it comes to these exhaust hoods. However, we also need to look in NFPA 96, Standard for Ventilation Control and Fire Protection of Commercial Cooking Operations , which deals with ventilation control and fire protection of commercial cooking operations. This standard covers exactly how this system is intended to operate, both to minimize the fire hazard and to maximize the effort to extinguish any fire that might occur. This includes requirements for how the hood system will function, but it also contains requirements that the electrical system installer needs to know about as well. Chapter 9 contains sections that discuss what type of electrical equipment is permitted to be installed within these systems. Items like luminaires, motors, and other electrical devices are generally not permitted to be installed within hoods or in the direct path of travel for exhaust products. However, if this equipment is listed for this purpose, then it is acceptable. This means that any light, motor, sensor, switch, or other pieces of the electrical system of a hood must be specifically designed to handle the environment to which it will be exposed. The main thing here is that we don’t want the electrical system to be the cause of a grease fire within a kitchen exhaust hood.
In addition to requiring special light fixtures and motors for hood systems, there is another major component to the functionality of the associated equipment that we must be aware of. In the event of a fire, one that would activate the extinguishing system (not the kind from the fancy chefs as they flambé your steak), a few things need to happen. First, a fire needs fuel and air to burn, so when the extinguishing system is activated, it must be set up to immediately turn off all sources of fuel and electrical power that produces heat to all the cooking equipment under the protection of the hood. This means, most likely, the use of shunt-trip devices supplying the affected circuits. After all, no need to continue pumping heat into the fire that the system is trying to put out. Also, if there is a make-up air system, upon activation of the extinguishing system, the supply air must also shut down, and the exhaust must automatically ramp up to maximum capacity. This robs the oxygen from the fire to help maximize the effectiveness of the extinguishing efforts. This is usually accomplished within the programming of the kitchen hood control system. However, as an electrical contractor, I was often called in to work on kitchen equipment that was modified or added by individuals who were unaware of these requirements. Unfortunately, these kitchens were disasters waiting to happen.
Next time you find yourself enjoying a good meal at your favorite restaurant with the ones you love, take a minute to appreciate all the components that go into protecting them from the dangers lurking behind those swinging doors. It takes a lot of effort, planning, and execution to ensure that our night out on the town stays safe. Coordination between all trades involved in a kitchen is paramount for safe installations and the key to working together to achieve a safe environment. It’s like the mantra of NFPA says, “It’s a big world. Let’s protect it together!”
Air-Conditioning Equipment Installations

Basic three-phase power measurements explained

Safety in Marinas

Find Us on Socials
Electrically safe work practices — nfpa 70e basics.
Pre-Wired and Modular systems can save substantial time and money over traditional hard-wired methods.

Workforce Development and its Role in Electrical Safety
A change in overall workforce development will occur when more states make programs like these a requirement of licensure within their state.

EFCOG Best Practice #240 — Electrical Utility Risk Assessment
Electrical utility tasks involve high hazard activities where the risk is often undefined. This DOE best practice can be used as a guide for other type of projects.

- Forum Listing
- Marketplace
- Advanced Search
- General Electrical
- General Electrical Discussion
Kitchen Hood Fire Suppression System
- Add to quote
I usually do residental wiring and starting to get into commercial buildings when I can. I wired up a local grocery store and now the owner calls me back and asked if I can wire up the hood vent. I'm ok with the exhaust vent but the supply air has to be wired into the fire suppression system. So when theres a fire the system will cut the supply air feeding the fire. Anyone has any wiring diagram or directions? Thanks
No single wiring diagram exists because there's different ways to accomplish this. One way is to use several microswitches in the suppresion system to control the loads. Another method is to use one switch to control the coil of a contactor. And another is to use one microswitch to send power to shunt trip breakers. And you can always use hybrids of each of these methods as well. Keep in mind you may also need to do other things than just shut off the make-up (supply) air to the equipment. Fire codes vary, but you usually need to turn off ALL electrical power under the hood (to equipment and lighting), as well as turn on the exhaust fan. If the building contains a fire alarm, that as well may need to be triggered.
Talk to the company who is suppling fire suppresion system. They useually have a set of contacts that you have to wire to. this will cut the power to the fan or the control wiring.
The system should include a micro-form-C-switch for ya. Everything but the Exhaust fan must shut down. The gas-most likely has a mechanical shut down. Take the control ckt and hit this sw. first. same as a firematic application. Just don't shut off the exhaust.:thumbsup: NFPA-17A
- ?
- 94.4K members
Top Contributors this Month
- Semiconductors
- $2 for 1-8 layer PCBs
What Is A Shunt Trip Breaker & How Does It Work? Detailed Guide
Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will learn What Is A Shunt Trip Breaker & How Does It Work. Detailed Guide. There is electrical system safety is the main parameter for the power system/ The main element that ensures the safety of electrical installation is the shunt trip breaker. In this post, we will discuss the all details shunt trip breaker and other parameters. So let’s get started What is a shunt trip
Table of Contents
What is a Shunt Trip Breaker?
If the circuit breaker trips it finds faults condition and automatically shuts off the current flow to prevent the circuit from overheating. The shunt trip breaker is an optional device for a circuit breaker that helps to trip the breaker remotely in any instant or automatically in case of surge saving any damage and instrument damage.
There are 2 main types fo shunt trip breakers first one is manual and the second one is automatic.
Manual witches help to off the breaker externally with the use of the remote button. Automatic switch off power when detecting surges from the external power supply.
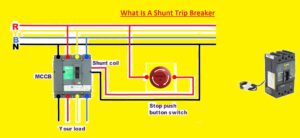
How Does a Shunt Trip Breaker Work?
Normally the current passes through the circuit breaker. But if these currents become high surges, the larger surge of power changes the electromagnet below the breaker switch, tripping the cutting power and switch.
The shunt trip breaker offers extra techniques to charge the electromagnet and trip switch, helping remote or automatic power shutoff. Some hunt trips are connected to an external power supply. When power surges get that source, signal flow from shunt trip to the breaker, mechanical cutting power.
The shunt trip can make a connection with the remote switch outside the building. Pushing the button on the switch sends a surge through shunt trip wiring and off the power.
Components of Shunt Trip Breaker
Read more Top Reasons Why Electric Outlet Stopped Working Breaker Not Tripped?
A shunt trip breaker comes with differnt components:
Main Contacts
This part of the shunt trip breaker is employed for carrying and interruption of current flow. Their main function s to control high current and make reliable connections
Shunt Coil
The shunt coil is an electromagnet that gets an electrical signal for breaker tripping. It produces a magentic field when gets energized releases the latch and starts the tripping process
Trip Mechanism
it helps to disconnect the mechanical circuit when the breaker trips. it has a latch that helps contact during normal working but releases due to trip signal.
Control Wiring
The control wiring triggers the device remotely or control panels. It works for remote activation of the shunt trip to provide the protection layers
Why Are Shunt Trip Breakers Important?
irrespective optional nature of the shunt trip breaker, it can be an important safety instrument in a power system. In a result, many engineers use this breaker as a layer of security since they save damage during power surges.
This breaker is good for many fonts but it’s commonly used during fire. By turning off power if a fire break out, the electrical hazard is no main risk. Some connections shunt trip to smoke alarm in homes, for power automatically off when detector trigger alarm. It not be good option, since in some conditions smoke alarm gets off due to steam from the shower of smoke from the kitchen
Applications of Shunt Trip Breakers
- Commercial buildings
- Hospitals and healthcare facilities
- Data centers
- Industrial facilities
- Laboratories
- Hotels and resorts
Advantages of Shunt Trip Breakers
- The main benefit of a shunt breaker is that it can remotely shut off in case of any fault. It quickly works and disconnects power in fire which helps to avoid damage in the home and protects people.
- These devices also increase safety levels and security by automating off power to the circuit if there is any fault. it helps to save electrical fires and any other damage.
- The shunt breaker is easily connected and confined with a power system, so it is easy to install the device in the building.
- The shunt breaker is a less cost solution for safety measures in buildings and industries. it is less costly to buy and connect and helps to save homes and buildings in the result of high fault.
- Shunt breakers support many electrical systems and devices so it is versatile devices that are used for the protection of circuits.
Troubleshooting of Shunt Trip Breakers
- Regular inspection of the breaker helps to find the symbols of damage or wear.
- Perform differnt electrical tests to check the it is working accurately or not
- Make sure there are no dust particles on the breaker so clean it regularly
- Make it properly lubricated
- After finding the faults solve it
Comparison with Other Circuit Protection Devices
Shunt trip breakers vs. standard circuit breakers, shunt trip breakers vs. ground fault circuit interrupters (gfcis), shunt trip breakers vs. arc fault circuit interrupters (afcis), how to choose right shunt trip breaker.
- Choose according to the voltage rating of your circuit
- it has compatibility with electrical panels and other protection devices used in circuitry
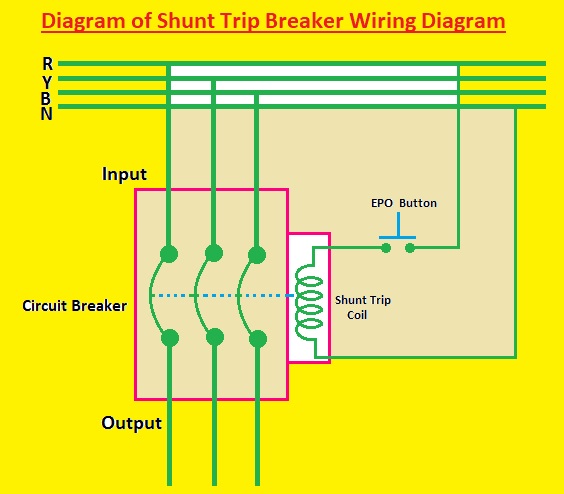
Shunt trip breaker wiring
Its wiring is very simple and easy. The shunt coil has two terminals one used for voltage supply and the other for neutral. The supply is about 120 volts AC and the neutral is connected to the neutral point of the breaker
The shunt coil is attached in a series combination with the push button. When we press the button it closes teh circuit to the shunt coil that trips the breaker. It is good to check that the shunt coil is rated for a similar voltage to the breaker. If the shunt coil does not have the same rating it can be damaged

Diagram of Shunt Trip Breaker Wiring Diagram
WHICH TYPE OF SHUNT TRIP BREAKER TO USE?
The manual breaker is best to use for small buildings or conditions where any technical staff is available to reset the breaker,. The automatic breaker can be best for larger-size buildings or conditions where there is no option for staff for breaker resetting.
it is also preferred for trigger shunt trip breakers at a distance or remotely. These relays are connected to fire alarm systems and can send a signal to the breaker for tripping if there is any fault.
Read more How Many Outlets on a 15 Amp Circuit Breaker?
How Many Outlets on a 15 Amp Circuit Breaker?
60 Amp Wire Size – Which AWG is Best for 60 Amp Breaker
Difference Between a Single and Double Pole Breaker
Where is the Doorbell Breaker Located? Easy Way to Findout
Difference Between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
How does a shunt trip breaker work?
A shunt trip breaker controlled by a small current from some distance. It is best for uses where it has the ability to off power to circuitry from distant points, like fire alarm systems
How is a shunt trip breaker wiring?
The shunt trip terminals are connected to the top and lower parts of the circuitry breaker. The small-size wire is used for wiring the shunt trip breaker between the shunt trip points and the remote source of supply. The power source can be battery relays
What is the purpose of a shunt with a relay?
The shut relay provided the remote tripping for the breaker. The shunt low resistance conductor is connected between the circuit breaker and relay. When current passes through the shunt, it makes a magnetic field that functions as the relay. The relay close contacts that trip the breaker.
What is shunt trip and under voltage?
Shunt trip and under voltage are differnt terms used for the differnt tripping methods of the breaker. Shunt trip use a shunt to have remote tripping. Under voltage is tripping off the circuit breaker when voltage loses less than a certain value
Where is shunt trip used?
- Fire alarm systems
- Security system
- Power distribution
- Industrial control systems
What is the difference between shunt and resistance?
The main difference between a resistor and a shunt is the temperature coefficient of thermal EMF . For resistors thermal EMF is not considered but for shunt resistors considered, based on temperature values two different conductive materials generate variable voltage
What is the purpose of a shunt breaker?
The shunt trip breaker is an optional device for a circuit breaker that helps to trip the breaker remotely or automatically when a surge exists, any damage, or emergencies.
Is the shunt resistor AC or DC?
Shunt resistors can be used for both AC and DC circuits. Though the value of the shunt resistor will be different from ac and DC circuits
Where are shunt trip breakers required?
If you are thinking that if shunt trip breaker is needed find that it is required in an electrical system where is a need for fast and easily shut-off power in case of a fault like fire.
Why is it called a shunt resistor?
The term shunt originated from the Latin word “scindere”, which means to split. A shunt resistor is used for spiting current in circuitry.
Why is low resistance called shunt?
When the resistor is connected with another resistor of low values then the equivalent resistance is lower than a single resistor that shunts the resistor.
What is another name for a shunt resistor?
it also called a shunt resistor is a current-dividing resistor.
What is unit of shunt resistance?
The unit of shunt resistance is ohm (Ω).
What is shunt resistance formula?
The shunt resistance formula is:
- Rs is the shunt resistance
- V is the voltage of the shunt resistor
- I is the current passing through the shunt resistor
What is shunt release in a circuit breaker?
The cut-off switch opens the solenoid coil electrical circuit if the breaker contact is opened. The solenoid coil so carries momentary current and is not rated for continuous duty. This process needs an external control supply or auxiliary supply for operation.
What is the difference between a shunt trip and series trip?
What are the different types of shunt trip breakers, does a shunt trip breaker need a neutral, what is the difference between shunt trip and shunt close, share this:.
Wholesale PCBs SMT Stencil & PCBA Service Provider
Special offer:$2 for 1-8 layer PCBs
Sign Up & Get 54$ Coupon
Author: Scott Spencer
I am professional content writer have professional degree in engineering. I have worked in different famous companies and also providing technical and seo based services clients all over the world. With that i am sharing my knowledge to engineering and technical students and new learners to enhance their learning and get new ideas in technical fields. Follow him on Twitter and Facebook .
Related Posts
Why Should Industries Choose Oil-Free Air Compressors? May 14, 2024
The 6 Critical Issues in the Construction Industry and Suggested Solutions in 2024 May 13, 2024

Writing Of Engineering Thesis and Dissertation: How to Ace it April 30, 2024
An Overview of the Assembly Line: The Technology that Transformed the Manufacturing Industry April 30, 2024

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post comment

- Circuit breakers
GE Shunt Trip Manual
- page of 4 Go / 4
Advertisement
Quick Links
Related manuals for ge shunt trip.

Summary of Contents for GE Shunt Trip
- Page 1 Lockout The catalog numbers for various voltage applications accessories, shown in Figures 1 and 2, can be installed are listed in Table 1 for the Shunt Trip and in Table 2 in 800-4000 ampere frame Power Break® II circuit for the Shunt Trip with Lockout.
- Page 2 Bell Alarm-Alarm Only or Bell A l a r m with Lockout accessories when a shunt trip occurs, The Shunt Trip accessory is installed in the accessory with the procedure described in the Accessory compartment through the front of the circuit breaker Configuration section.
- Page 3 Apply at least 55% of the rated ac voltage at least Lockout also change state. (The factory switch 75% of the rated de voltage to the Shunt Trip; the setting is disabled.) breaker should trip immediately. When an Undervoltage Release accessory causes...
- Page 4 Check that the accessory is Shunt Trip. completely inserted; reinsert if necessary. If a 1 2 Vdc Shunt Trip is installed, check that the polarity of the control power matches that shown on the label of the Shunt Trip accessory.
This manual is also suitable for:
Rename the bookmark, delete bookmark, delete from my manuals, upload manual.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Circuits serving equipments (electric consumed equipment, for example: grill, range, etc) under kitchen hood need to be protected by shunt-trip breakers. If the above equipments utilize gas instead of electricity and need only 120V circuits for control. Will these 120V control circuits need to...
1.) The breaker supplying the power to the trips themselves might get turned off (even with a lockon) and go unnoticed. 2.) Breaker space is usually at a premium in kitchens, never seems to be enough. The shunt trip needs an extra pole space. 3.) Contactor = less $$, and easier to get.
While it is not mentioned in the IFC, NFPA 17A does not require this for solid fueled burning operations such as barbeque pits or smokers (thank goodness). IBC 904.11.2 System interconnection. The actuation of the fire suppression system shall automatically shut down the fuel or electrical power supply to the cooking equipment.
Step 2: Gather the Necessary Tools and Materials. To wire a shunt trip circuit breaker, you will need a variety of tools and materials, including a voltage tester, wire strippers, wire connectors, and the shunt trip circuit breaker itself. Make sure you have everything you need before proceeding to the next step.
3) if there are "HEAT PRODUCING" electical items under the hood I disconnect ones with a shunt go breaker activated via the ANSUL system. Like an electric fryer, electric grill, more. 4) EGO do NOT disconnect general purpose receptacles that supply refrigeration power, timer power, or other non-heat generating electrical items which exist in ...
Within a commercial kitchen, GFCI protection for personnel is going to be required on most receptacle outlets. This requirement applies to both single- and three-phase receptacles on branch circuits rated 150V to ground or less. On single-phase branch circuits, this applies to all receptacles up to 50A, and on three-phase circuits, the cut-off ...
The shunt trip breaker is a combination of the shunt trip accessory and the main circuit breaker. This installs on the main breaker to add protection to your electrical system. This adds security to your electrical system as it manually or automatically cuts the electric supply in your circuit. This accessory can help prevent short circuits and ...
There was a kitchen remodel with all walls and receptacles new but the exhaust hood kept in place. Our mechanical engineer told them the integral fire suppression on the hood was fine to keep, but the GC tells me there is no way to tie in the shunt trip breakers I specified with the old hood that apparently lacks an ANSUL system?
One way is to use several microswitches in the suppresion system to control the loads. Another method is to use one switch to control the coil of a contactor. And another is to use one microswitch to send power to shunt trip breakers. And you can always use hybrids of each of these methods as well. Keep in mind you may also need to do other ...
CASService explains how to wire a shunt trip breaker or contactor to an exhaust hood control package. For questions, please contact CASService at 1-866-784-6...
Step-By-Step Guide to Wire a Shunt Trip Breaker Wiring Diagram. Step 1. Install Shunt Trip Accessory to the Circuit Breaker. Step 2. Installing Shunt Trip Circuit Breaker to the Panel Board. Step 3. Understanding the Shunt Trip Breaker Wiring Diagram. Step 4.
The shunt trip breaker is an optional device for a circuit breaker that helps to trip the breaker remotely in any instant or automatically in case of surge saving any damage and instrument damage. There are 2 main types fo shunt trip breakers first one is manual and the second one is automatic.
Overall, wiring a shunt trip breaker is quite simple and direct. Step 1: Get familiar with your shunt trip breaker's wiring schematic. It's crucial for a safe and correct installation. Step 2: Find the two screws on the shunt trip unit - these are where you'll connect your control circuit wires. Step 3: Attach the control circuit wires ...
2. Catalog numbers and voltages for the Shunt Trip with Lockout. Operation. Apply control voltage to terminals. terminal strip on the right side of the breaker to trip. the circuit breaker. The Shunt Trip will. circuit breaker to trip when. greater than 75% o f the rated de voltage or 55% of the.
Welcome to our tutorial on wiring a Shunt Trip on QO™ Circuit Breakers. In this step-by-step guide, we'll walk you through the process of wiring a Shunt Trip...
Shunt trip breakers have a simple yet genius job. They shut down electricity flow when an instant danger is detected. This isn't just any off switch, though—it's a complex dance between components that ensure your safety. Imagine an emergency switch, like the red button in a spy movie.
http://www.electricalindustrynetwork.com Kitchen Hood Wiring Shut down using a non-shunt trip system. This video is a brief description of how it works. I do...