02. We describe how the customer journey should look
Why you need the customer journey.
Using customer journeys guarantees that the design starts and finishes with customers and their experiences. You will therefore design an end product or service that maximizes customer satisfaction.

Our activities at this stage
- Mapping your clients' current customer journey and helping you identify the weaknesses (known as pain points ) of your products and services.
- Outlining ideas for preventing or eliminating pain points.
- Formulating an aspirational customer journey with you and defining the steps for reaching the destination.
- A map of the current customer journey
- A map of the aspirational customer journey, including suggestions for improvement
Useful tips
- Before starting, you should approve the level of detail. At some firms, a more basic approach is sufficient; at others, a detailed customer journey is a prerequisite for a good roadmap.
- So that you always keep the customer in mind, experience the customer journey through the individual's eyes, not through the company's eyes.
- First, consider the customer journey from a broad, company-wide perspective. Then, work out selected parts of the customer journey in the required level of detail.
- The customer journey is also appropriate for an internal solution, e.g. when the customer is an employee.
- KPMG Discovery

- Who We Serve
- Case Studies
- Experience Operating System (XOS)
- Customer Centricity
- Experience Transformation
- VoC and Measurement
- Journey Mapping
- Employee Experience
- Build CX+EX Management Capabilities
- Experience Strategy
- Experience Design
- Measurement and Analytics
- Training and Education
- VoC Management
- About McorpCX
- Our History
- Resource Center
- Book: Smart Customers
- Book: Experience Rules
How to Use Buyer Personas to Support Customer Journey Mapping
Buyer personas are a well-worn technique adopted by marketers to get under the skin of customers. But personas also have a crucial role to play in the increasingly important discipline of customer journey mapping.
A fictional but data-driven profile of your ideal or actual customers, buyer personas have long been used by the marketing department as a way to surface and document customer needs and wants, and help understand how customers make purchasing decisions.
And if accurate, these completed personas can then enable marketers to better segment their messaging, by targeting different personas with the most appropriate content and offers; develop new products/services based on the needs and wants of your key customers; and reach the right people, thereby pre-qualifying leads by attracting the right leads.
“Personas are the starting point,” says Michael Hinshaw, CX strategist and president of MCorpCX . “Because a journey map is the story of a customers’ experience – it explains what happens along the way, to whom, and how it happens –you need to know who is taking the journey to tell the story. Personas represent the customers whose journeys we’re mapping… in fact, we’ll often do persona workshops in advance of journey mapping workshops to make sure everyone is aligned on which customer they’re solving for.”
He continues: “Persona and journey maps together help shift companies focus from inside-out to outside-in. Personas describe in detail who your key customers are and why they feel the ways that they do. Customer journey maps show you what your customers do as they interact, including where things do and don’t meet their expectations, and places where an organisation can improve to serve customers better.”
Simon Spyer, cofounder and insight partner at Conduit Data Services , adds: “Personas are a tool that helps you take a customer-centric approach to journey mapping: they help you to really define the tasks that your customers or prospects want to complete and their needs and pain points in doing so across the customer journey. By understanding these needs and pain points, you can start to define the ‘moments of truth’ that really matter to your customers, where your business has a role to play and what you need to do to make this possible.”
So with buyer personas playing such an important role in the overall customer journey mapping process, it is vital that organisations create valuable personas that provide a robust platform upon which to build the maps. The question, then, is how to successfully generate these customer personas. And to answer that question we must first establish what constitutes a robust buyer persona.
Vicky Smith, executive advisor, customer experience design, at KPMG Nunwood, advises that a universal persona template should be used across the business. She recommends that the template should typically consist of:
A persona name, image or photo – depicting the customer segment that you are aiming to portray. “A name and photo helps to bring the customer segment ‘to life’ and means that stakeholders can more easily relate to the specific customer type,” says Smith.
Key characteristics and key information about them regarding the nature of the subject (e.g. ‘My finances’), using any ‘hard facts’ that you have collated on the relevant customer segment. “This includes demographic traits, as well as any insight into the type and value of any products held with the brand versus any competitor providers.”
Lifestyle characteristics and key rational and emotional needs, e.g. ‘What matters most to me?’ ‘My lifestyle’ and ‘My attitudes’. “This should use any additional information that you have on the segment, something likely to come from segment profiles or from more in-depth qualitative research.”
Spyer says that good personas typically consist of five parts:
- Needs and goals. What is your persona trying to do, why and by when?
- Motivations. What are their key triggers and barriers? What influences their thinking? And do they have an actual need or feeling pressure from elsewhere?
- Behaviours. Where do they find information? Is your persona spontaneous or do they research and plan every detail? What media channels do they like to use?
- Profile. Think about your persona’s demographics. It can also be useful to think about variables like price sensitivity, confidence with technology and amount of leisure time and whether your persona over- or under-indexes on them.
- Quotes and photos. Bring your personas to life. It’s important that they are stereotypes that feel real so give them a name, add comments captured through research and photos of what they look like.
Other information that should be accounted for in the template is transactional data, such as purchase histories and post-sale service records.
With the template in place, it’s now time to fill it out! While some buyer personas are built to be aspirational, if the personas in question are being used to support customer journey mapping, the profiles need to be built around real customers groups. Therefore, in order to fill out the template, you need to ensure you know all the information in question – and that means doing some deep customer research.
“If personas are created based on gut instinct rather than accurate data and defensible research, they’re not going to help you be more customer-centric,” warns Hinshaw. “In fact, the incorrect perceptions that these represent real customers or relevant (to your customer) situations can create significant issues.”
“You need to get away from your desk and computer, get out of your building and go! Talk to people, listen to them, meet your customers and stakeholders,” says Arne van Oosterom, senior partner and founder of DesignThinkers Group.
“Be curious, realise you are full of biases, let go and open your mind. Ask people about their lives, their goals, their frustration. Ask open questions and let people tell you stories. Write everything down and make picture and videos. Get together with your team and cluster all the things you heard and try to discover patterns. Then get some customers to help you map their customer journey to enrich your understanding. Keep doing this until you know enough to move on. That moment will come.”
But Spyer recommends that persona work should also incorporate data above and beyond customer interviews, including existing information and the knowledge that exists within your own four walls.
“You can't just make your personas up. They should be informed by your data and research. This may mean kicking off new research that’s specific to your objectives. But we often find that a lot can be gained from working with existing research,” he notes.
“Involve a wide team in the development of your personas. Harness the knowledge and insight of your whole team, particularly those who are customer-facing. Personas shouldn’t be the sole domain of the marketing department.”
Finally, with the research conducted and the persona templates completed and verified by stakeholders within the organisation and the customers themselves, there is one final consideration – design.
“Personas need to be well-designed,” recommends Hinshaw. “This means they need to look and feel professional, incorporate basic information design principles (easy to scan at a high level, or dive into the data in more depth). We also like them to align to an organisation’s visual brand, helping to reinforce the notion that these are created and owned by the company, for its customers - which they should be, regardless.”
It is important to remember, however, that persona work doesn’t end there. While it provides the catalyst to build customer journey maps that are appropriate to this particular moment in time, the reality is that with business objectives, markets, products, services and customers all continuing to change over time, personas can become outdated.
Hinshaw notes: “We encourage customer experience teams to conduct regular reviews of persona to ensure they’re accurate, as well as proactively engaging across the business to stay on top of initiatives that need customer insight.
“For most businesses, revisiting persona as part of annual business planning is sufficient, though changes can occur at any time – and to the degree those changes affect your customers, your persona may need to be reassessed as well.”
If you'd like to speak with someone at McorpCX, please reach out!
Other posts you might be interested in
Measuring customer loyalty as well as satisfaction, mcorpcx a “top 10” cx firm recognized by banking cio outlook, the customer experience (cx) and survival in the 21st century, subscribe to email updates..
Enter your email below to receive daily resources and updates.

McorpCX is independently recognized as a top customer experience services and solutions company, enabling and guiding leading organizations since 2002.
- Customer Experience Transformation
- Employee Experience Transformation
- Digital Experience Transformation
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Employee Journey Mapping
- Persona Mapping
- Customer Experience Management
- Voice of Customer Programs
- Voice of Customer Measurement
Touchpoint Mapping®, Touchpoint Metrics® and Loyalty Mapping® are registered trademarks of McorpCX, LLC
- Case studies
- Expert advice
How to create a customer journey map — a step-by-step guide with examples
Learning more about client experience is the best way to understand and improve it. As you are reading this article, you already know that 😉
Here, you will find a detailed step-by-step guide on making a customer journey map (CJM), examples, expert tips, templates, and a PDF guide to download and save for later.
- 1 What is a customer journey map?
- 2 Benefits of client journey mapping
- 3.1 Step 1: Define your persona
- 3.2 Step 2: Set customer journey stages
- 3.3 Step 3: Define journey map sections
- 3.4 Step 4: Set customer goals
- 3.5 Step 5: Define touchpoints
- 3.6 Step 6: Processes and channels
- 3.7 Step 7: Problems and ideas
- 3.8 Step 8: Emotional graph
- 3.9 Step ?: Be Creative!
- 4 Customer journey map examples
- 5 A customer journey mapping checklist
- 6 The free guide to download
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is the final output of the collaborative visualization process called customer journey mapping. This process lets you reveal typical experiences the customers have over time when interacting with your organization, service, or product. A finished map provides insights into their actions, processes, goals, needs, channels, emotions, and many other aspects shaping the customer experience.
Journey maps can be of different scopes. For example, a broad-scope map would include multiple customer journey stages like ‘Awareness’, ‘Decision’, ‘Purchase’, ‘Support’, and ‘Renewal’. In contrast, a map with a narrower focus would look at a few specific stages like ‘Decision’ and ‘Purchase’.

CJMs focusing on the current experience are AS-IS maps, while journey maps visualizing the future, desired, state of the experience are called TO-BE maps.
There’s also a similar technique, customer experience mapping, which is often used interchangeably with journey mapping. Experience maps are variations of CJMs, but they typically cover a wider range of interactions and contexts beyond a specific consumer-business relationship.
Benefits of client journey mapping
Why make journey mapping your tool of choice? There are plenty of reasons, the major of which include:
- Gaining a deeper understanding of your customers
For instance, a high-end fashion retailer may discover that its younger customers prefer online shopping, while older customers enjoy the in-store experience.
- Getting a single view of your customer within the organization
Journey mapping will help you turn a fragmented vision of the customer experience into a unified, organization-wide one. It will have a massive impact on the decision-making process, encouraging you to consider how your actions will affect your clients and become customer-focused.
- Breaking corporate and cross-department silos
To make the way toward delivering a great customer experience, you will need to collaborate with others. Understanding why this collaboration is essential, departments and employees will be more inclined to participate in conversations and collaborate.

- Improving customer experience, retention, and loyalty
While working on a map, you will discover customer pain points at different stages of their journey with you. Fixing the most crucial one as quickly as possible will do you a good turn by eliminating the reasons for leaving you. If fixes take much time, look for quick wins first.
For instance, adding details about your shipping policy on the website will take a developer half an hour, while it will set the right expectations among customers. They won’t be expecting the delivery the next day anymore, bombarding your customer support team with frustrated messages. Another example is a subscription-based video streaming service that can personalize content recommendations to keep subscribers engaged and less likely to cancel their subscriptions.
- Better conversion and targeting of your target customers
Sometimes, it makes sense to focus on a specific segment or, talking journey mapping terms, specific personas. Customer journey insights will help you with this endeavor by giving you a glimpse into these people’s minds and ensuring the higher effectiveness of your marketing.

How to build a customer journey map
Although there is no gold standard for creating a customer journey map, we’ll try to create a somewhat generalized map. So that you can use it as a reference when making maps of your own.
We’ll be using our CJM Online tool along the way for two reasons. Because it’s easy to use and lets you create a CJM fairly quickly without wasting time setting up the environment. Oh, and there's a Personas building tool that comes with it 😉

We’ll take a pizza restaurant as an example of business and learn how to make a customer journey map together.
Step 1: Define your persona
Creating personas is a crucial part of customer experience service and journey mapping in particular. We won’t go into details — you can find them in this post about defining personas .
Let’s just say that our persona’s name will be Eva Moline — 29, works as a journalist and loves pizza. Eva is not really tech-savvy, and she tries to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
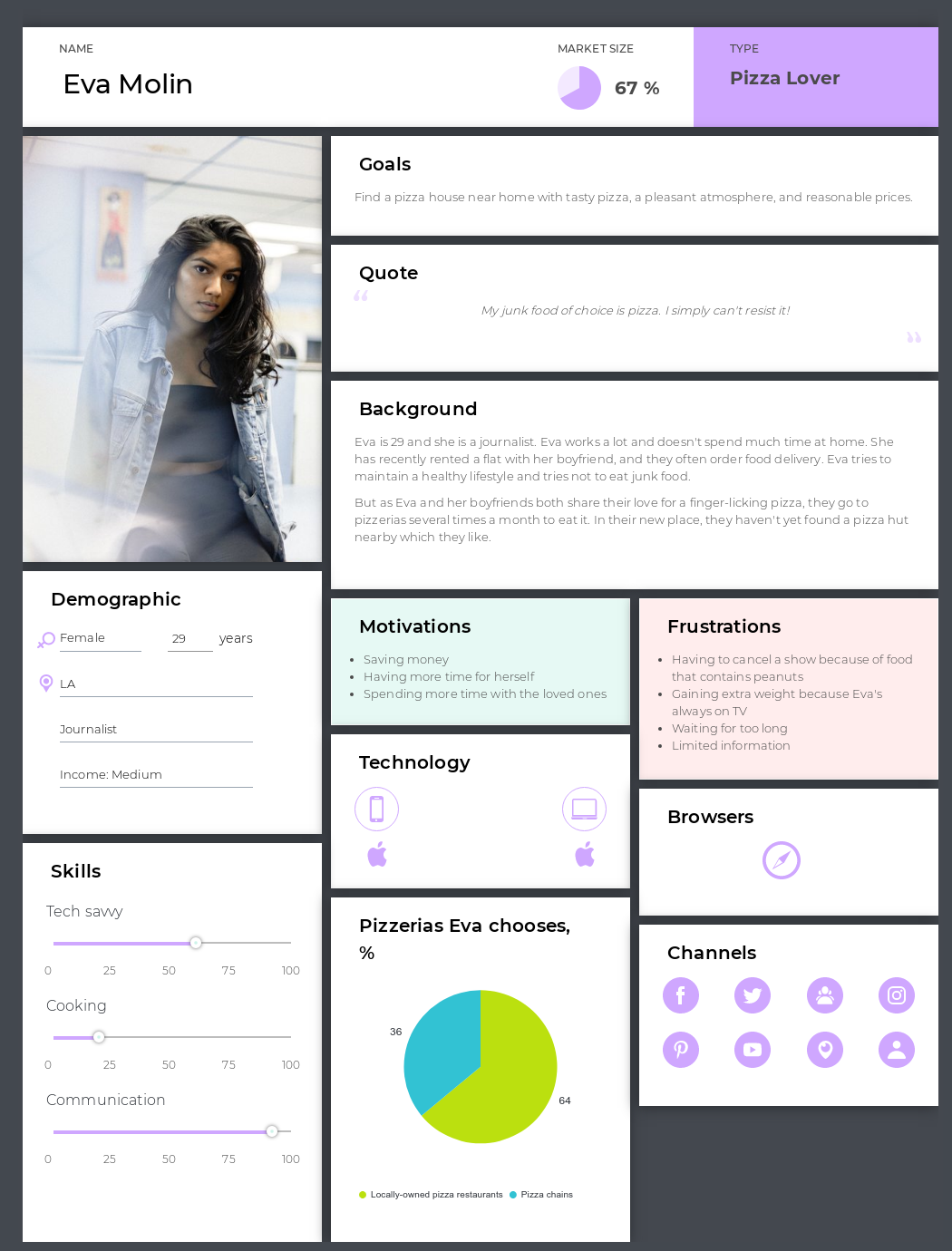
Step 2: Set customer journey stages
Stages are the steps customers take when interacting with a business. The easiest way to identify them is to think of all the actions the person has to take throughout their journey, organize them into logical groups, and name these groups. These will be your map stages.
The number of stages varies from business to business, but we’ll take 8 for this example:
💡 Expert tips:
- If you’re unsure about the order or names of the stages, don’t worry about that. You can change both at any time when working on the map.
- If your stages are complex, you can break them into smaller ones. Read this blog post about defining customer journey stages to learn more.
Step 3: Define journey map sections
Sections are horizontal rows with data that, together with the stages you defined, make up a customer journey map.
When picking sections for a map, your choice will depend on your journey’s type and purpose.
As for UXPressia’s Journey Map tool, it offers a set of more or less universal sections for all kinds of maps.
We’ll use some of the sections in the current example.
Step 4: Set customer goals
Setting customer goals at each stage is great for multiple reasons:
- It helps you understand how your business goals align with the goals of your customers.
- You can meet your customers’ needs better, gaining their loyalty by helping them achieve their goals at each stage.

Above, you can see some of the goals we set for Eva. They are self-explanatory, so there’s no need for extra details.
Step 5: Define touchpoints
Touchpoints are encounters that happen between your business and customers. In the pizza restaurant example, touchpoints happen:
- At the Awareness phase, when Eva is actively looking for a pizza place nearby. She is asking around, searching locations on Google Maps, etc.
- At the Research phase, when she is trying to find out what people say about the place by asking her friends and reading online reviews.
- At the Arrival stage, when Eva searches for a parking spot and enters the restaurant to get seated after parking the car.
- At the Order stage, when she makes an order and waits for it.
- Time to eat! At this stage, touchpoints occur when Eva is being served and when she is eating her meal.
- At the Leave stage, Eva interacts with the waiter, pays for the meal, etc.
- At the Feedback stage, she goes to the pizzeria’s website and drops a few lines on Instagram.
- At the last stage, Eva gets a promo email from the restaurant with discounts or other special offers.
Defining all the touchpoints is critical because each touchpoint leaves some impression, and your main goal is to keep it up to the mark.
You can also have a separate section to describe the actions your persona takes:
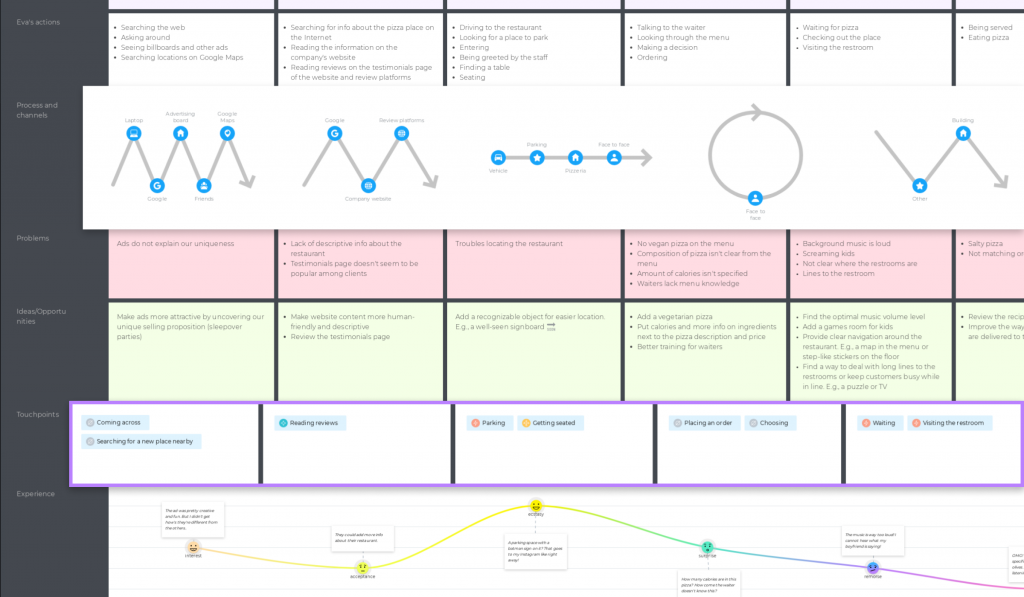
Step 6: Processes and channels
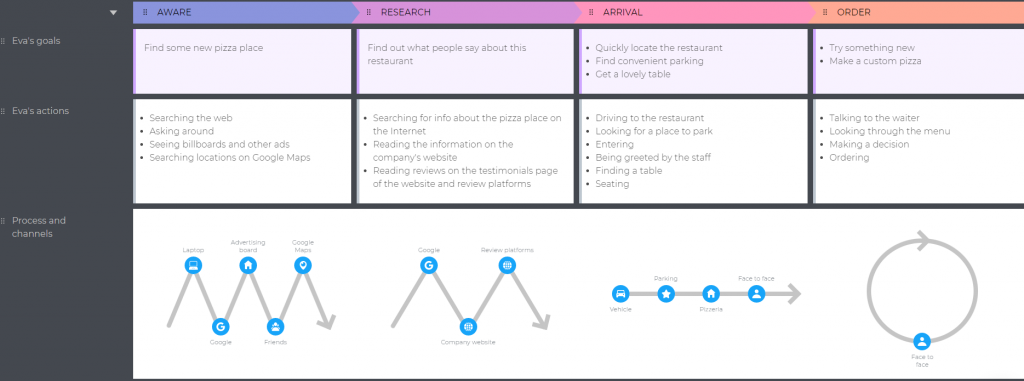
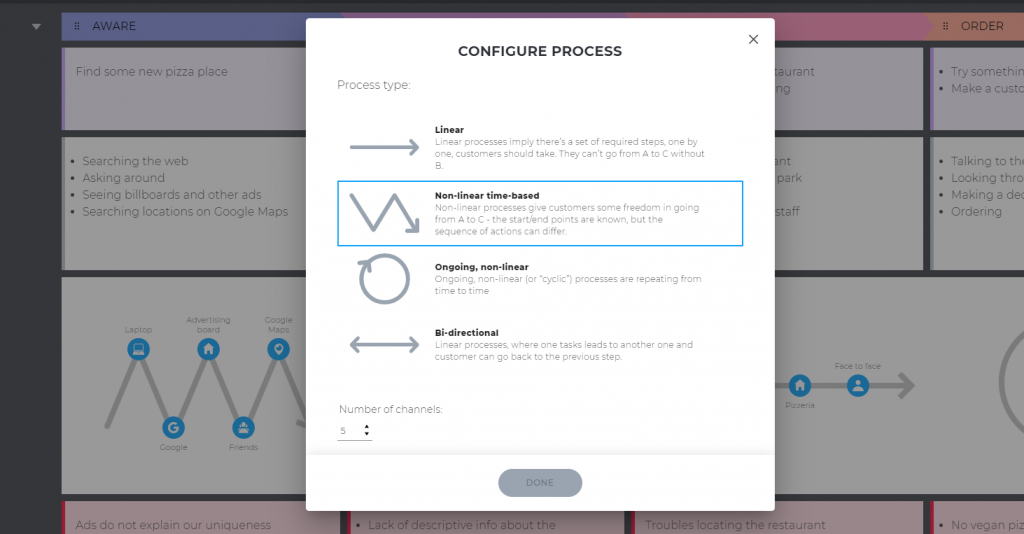
Now, you may want to add some processes and channels to the map. Just to see what channels your persona uses and what types of processes are in their journey. Luckily, our tool lets you do it in the most awesome way. Processes can be linear, non-linear & time-based, cyclic, or bi-directional. In UXPressia, you can specify up to 10 channels per process.
Step 7: Problems and ideas
It’s time to explore problems Eva might have when using our service. It could be a lack of info about the pizza house. Few reviews and ads do not show how our pizza differs from others.
Upon arriving, Eva may struggle with locating the place due to unclear information on signboards or just because of a hard-to-find location.
When making her order, Eva may look for detailed info on dish ingredients to learn whether it contains peanuts she’s allergic to. Descriptions may not be as detailed as she’d want them to be.
While waiting for the pizza, Eva may want to check out the place. Finding a restroom can turn into a nightmare if you don’t have clear signs showing what’s where in the restaurant.
Once you’re done with problems, it’s time to find solutions to these problems. Brainstorm for some ideas on how this or that problem can be solved. Here’s what we brainstormed for Eva’s case:

Step 8: Emotional graph
Never underestimate the power of visualization. And our Customer Journey tool is all about it. We added an emotional graph to see where our service example shines and where it stinks. Plus, we filled text boxes with Eva’s thoughts:
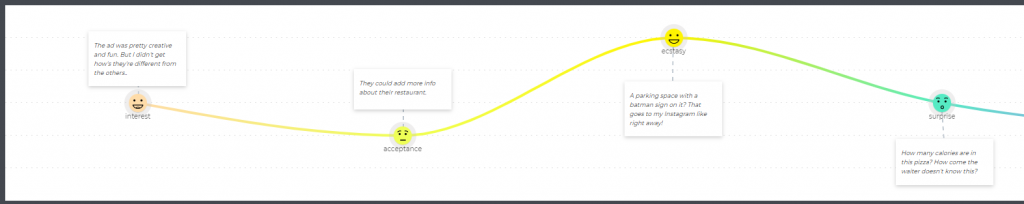
There’s also a special section ( “Think & feel” ) to put personas’ thoughts.
Step ?: Be Creative!
This is a good start, but the map is far from being complete. So, keep exploring Eva’s journey to find more insights and then add all of them to the map.
If you use our tool (which we highly recommend you to do), check out other CJM sections:
- Image section for screenshots, photos, or any other relevant imagery. You can even turn it into a storyboard , describing the journey from beginning to end with your images or those from our library.
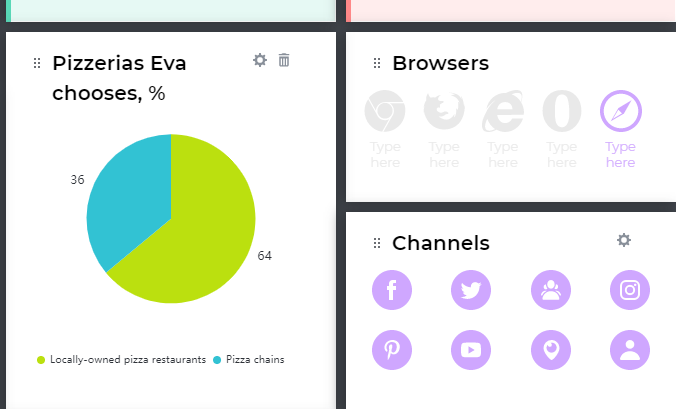
- Charts section for communicating data in a visual and meaningful way, just like we did it in the persona:
- Video and document sections for journey-related videos and documentation (e.g., an annual marketing report).
- Personas section for visualizing different personas’ interactions within the same journey.
💡 Expert tip: The section with the persona’s questions works like a charm for marketing and content purposes. So be sure to add one 😉
Customer journey map examples
There are also a whole lot of free CJM templates for all sorts of journeys in our library. Here are three examples we picked for you.
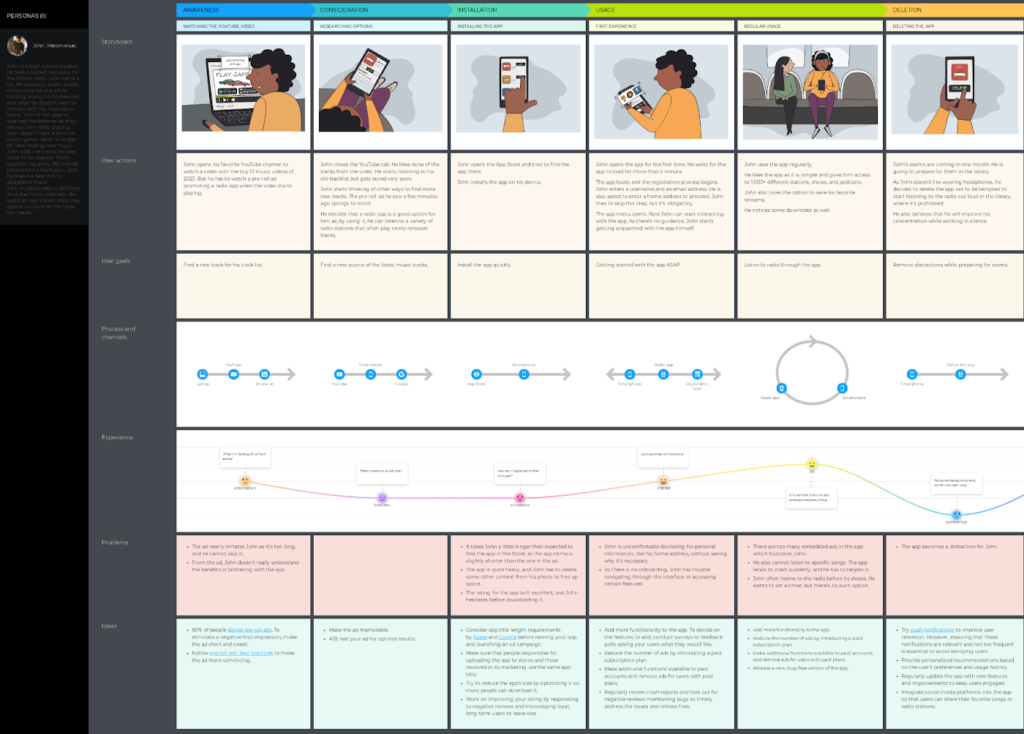
- Example 1: a mobile user journey
This user journey map template covers the digital experience of the persona who discovers a new mobile app, installs it, and uses the app for some time before deleting it.
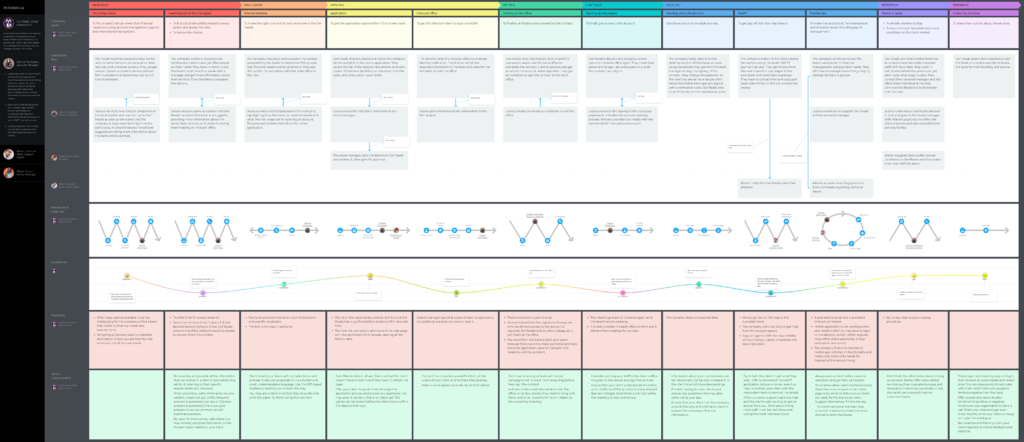
- Example 2: a client journey map for a corporate bank
This free template is an example of a multi-persona, B2B customer journey. The key persona is a newly opened company looking for a bank to run their business. The CJM also visualizes interactions between the personas involved.
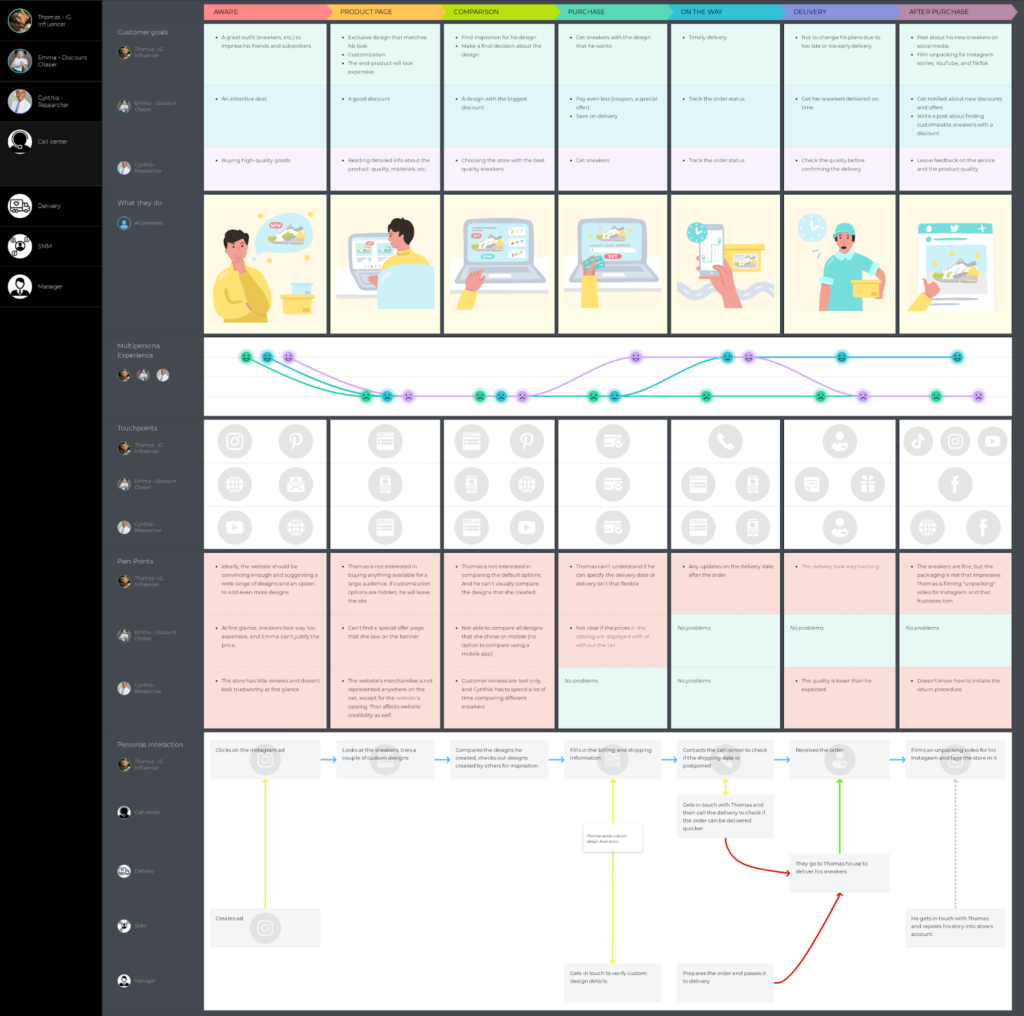
- Example 3: a digital customer journey
This customer journey map example shows the digital journey of three customer personas who want to buy a new pair of sneakers online. They go through the same stages, but if you look at the map, you will be able to see the differences in customer behavior, goals, and actions. It’s also a multi-persona journey map .
A customer journey mapping checklist
As a quick recap, here is a checklist with key steps to follow when creating a customer journey map:
- Do research
To represent real people, your real customers, and visualize their journeys, you must base your personas and journey maps upon actual data.
- Define your customer persona(s)
Identify your target personas. Create detailed profiles focusing on information relevant to your journey mapping initiative. Include such details as background, customer needs, motivations, channels, etc.
- Specify journey map stages
Determine the stages you want to have on your map and come up with their names.
- Decide on the map sections
Determine which sections to include in your map (e.g., actions, touchpoints, emotions, channels).
- Set customer goals for each stage
Make sure that it is your customers’ goals, not your business goals.
- Identify touchpoints between the persona(s) and your organization, product, or service
Consider both online and offline interactions.
- Map out processes and channels
Visualize the journey-specific processes and the channels your customers use at each stage. Include both digital and physical channels.
- Highlight problems and look for opportunities
Identify any pain points and issues customers might encounter. Brainstorm potential solutions and quick wins to improve the experience.
- Add details about the emotional experience
Visualize the persona’s emotional journey. Include thoughts and feelings where it’s relevant.
- Use more sections
Include illustrations, images, and charts to make the map visually engaging and easy to understand. Enrich your journey map with more data, like KPIs related to journey stages.
Feel free to tailor this checklist to the specific context of your business and your project's needs.
The free guide to download
As a bonus, download our free customer journey mapping guide. Fill in the form below to get a PDF file as an email.
Related posts
The post was originally written in 2017.
Rate this post
first of all, excellent example and I’m very happy to I could understand how to create user journey map, due to for a long time I can’t understand it and how, many thanks for your efforts 🙂 I have some question about ser journey map. I hope to open your chest for me,
1-no there are rules for user journey map? 2-I need another example ?(for example Uber)?further understand 3-have I create user journey map without customer?
Hello, Karim!
I am very glad that this article helped you understand customer journey mapping 🙂
In regards to your first question, I would say that journey maps differ from business to business. However, they tend to have the same structure give or take. So no matter what industry you make a CJM for, you will end up having several stages and a bunch of sections we mentioned in this post.
If you’re looking for CJM examples of Uber customers, here is one: https://www.mindomo.com/doc.htm?d=92be818b774d422bad7eab790957ebc0&m=7d286174ccf1450bbb77c921a609ff65 Plus we have a lot more on our template page: https://uxpressia.com/templates
As for your last question, yes. You may have a journey map without a customer (persona) and use target audience segments instead (or have a generic map without personas at all, though I don’t recommend the latter as in this case it will be hard to empathize with real people). So you will certainly have to introduce a customer down the road to gain a deeper understanding of the journey.
many thanks for your reply to me and again I have some questions
1-why you don’t use in your example? user experience, empathy maps such as use goal touch point, and how to create it 2-As for the previous example (Uber) very confuse for me not as your example
Could you please rephrase your first question? And as for the Uber map, well, that’s all I managed to find. 🙂 But again, here you can find a hundred of map examples of all stripes and colors: https://uxpressia.com/templates
welcome again, my question is? what’s different between Aware and Research
The differences come from the names.
At the aware stage your client realizes that there’s a need for a service/product. Or they find out that your company exists and offer a desired service.
While at the research stage they either do research on your business (e.g. visit your website or ask their friends if they used your service) or they research what is out there on the market that can help them.
Makes sense? 🙂
Thank you for this,
I am wondering , Have you done examples on B2B services. I work in Accreditation & Certification, this seems to be the least visited topic in marketing platforms and blog sites.
We have some B2B templates in our Template Library . Type B2B tag in the search placeholder and you will see all categories with the fitting templates. You can also explore the B2B mapping guide here .
Good luck and happy customers!
Great article, well articulated and detailed. I am starting off with service design and was wondering if I could get some advice mapping out a customer journey for a specific project. I was mapping out how do one approach to repair services?
Hi Shreya, glad you liked the article!
If you’re dealing with home repair, I might suggest our pre-filled template for an interior design agency customer journey: https://uxpressia.com/templates/real-estate . Templates can be a great starting point even if they’re not a 100% match to your use case.
Other than that, you will need to create a persona. If you don’t have any research data yet, do it based on your assumptions. Then, try to visualize what their experience across all stages and interactions with the repair service might be. Once you have the first draft, you can proceed with validating it and adding more data as it comes in.
If you have more context on the project, I can look into it and come up with specific tips 🙂
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Thank you for sharing, it was something I researched.
Hi Rok! Happy mapping 🙂

Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
The definitive 8-step customer journey mapping process
In business, as in life, it's the customer's journey that makes the company's destination worth all the trouble. No customer wants to jump through several different hoops to get to your product: they want it fast and they want it now.
Following certain customer journey mapping stages helps you improve your user's experience (UX) to create a product they love interacting with, ensures you stay ahead of key workflow tasks, and keeps stakeholders aligned. But a misaligned map can derail your plans—leading to dissatisfied users who don’t stick around long enough to convert or become loyal customers.
Last updated
Reading time.

This article walks you through the eight key stages of great customer journey mapping, and shows you how to adapt each to your unique business and product to optimize the customer experience from start to finish.
Learn how customers interact with your product and website
Hotjar's Observe and Ask tools let you go ‘behind the scenes’ to understand your users’ product experiences and improve their customer journey.
An 8-step process for effective customer journey mapping
A customer journey map is a visualization of every point of interaction a user has with your company and product.
Mapping out the customer journey gives you insights into your buyers’ behavior to help you make changes that improve your website and the user flow between touchpoints. This helps you increase online sales and turn users into loyal customers and brand advocates.
Follow these eight proven steps to understand—and enhance—the customer experience.
Note: every business is distinct, so be sure to adapt these steps to your particular user and business needs.
1. Define your purpose
The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won’t know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
To define your purpose, consider your company’s mission statement and incorporate your specific user pain points as much as possible.
Make your purpose specific to your company’s needs and goals—for example, the purpose of an ecommerce brand looking to help users navigate several different products and make multiple purchases will differ from that of a SaaS company selling subscriptions for one core product.
2. Make sure your team is aligned and roles are clear
Cross-functional collaboration is essential when mapping out your brand's or product’s user journey. Get insights from different teams within your organization to find out exactly how users engage with key touchpoints to derive a holistic sense of the user experience (UX), which will help you improve every aspect of the customer experience.
Lisa Schuck , marketing lead at Airship , emphasizes the importance of keeping “anybody that has a touchpoint with a customer” involved. She advises teams to “figure out how to align your external marketing and sales with your internal operations and service.”
Although sales, product, and marketing departments are often the key players in customer journey mapping, also involve your operations and design teams that are responsible for creating the user flow.
If you have a SaaS company, for example, marketing creatives, sales teams, product owners and designers, and your customer experience department all need to participate in the process. Clearly define who’s responsible for different aspects of the map, and regularly check in to make sure your final map isn’t missing any important perspectives.
Pro tip: use Hotjar's Highlights feature to collect and organize key product experience (PX) insights and data on user behavior from teams across your organization to help you build your customer journey map. Then use Hotjar’s Slack integration to quickly share learnings with your relevant stakeholders to get buy-in and ensure everyone is aligned.
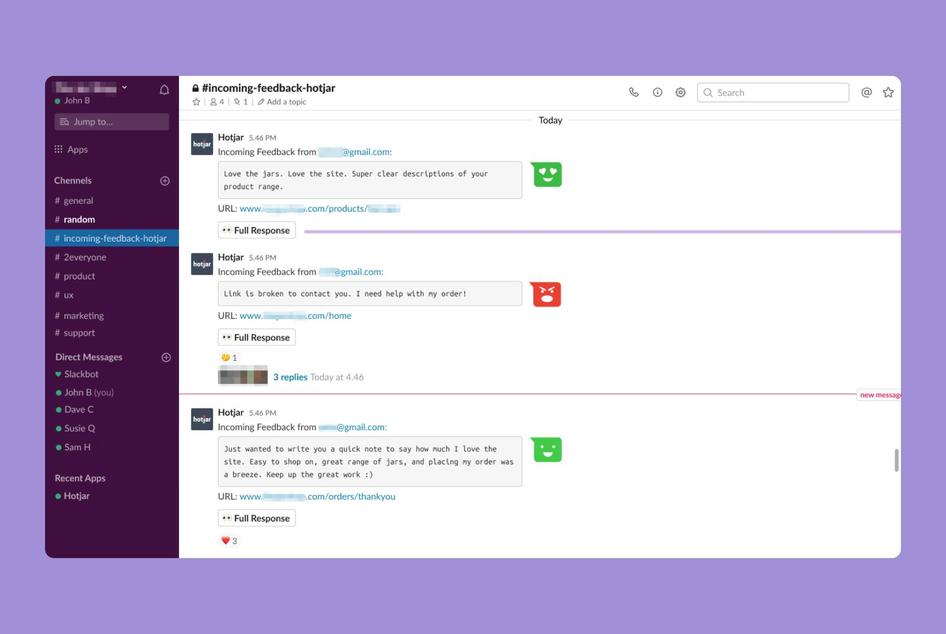
Hotjar’s Slack integration Slack lets teams discuss insights in the moment, so they’re up to date with critical issues
3. Create user personas
Once you’ve defined your purpose and involved all relevant stakeholders, it’s time to design your user personas . Use resources like UXPressia and HubSpot’s Make My Persona tool to help you design various product personas .
Create a range of user personas to understand what each type of buyer needs to curate a journey that’s easy and enjoyable for every customer. This is an important early step in the customer journey mapping process—because if you don’t understand your users, you won’t be able to fully comprehend how they interact with your brand to better it.
Create user personas for all your product’s possible buyers—for example, to map out a B2B customer journey for a company in the hospitality business means developing personas for a range of different customers, from large chain hotel managers to small vacation rental owners.
4. Understand your user goals
Once you’ve designed your user personas, it’s time to define their jobs to be done . What do your users hope to accomplish when they search for your product or service? What do they want to do when they click on your website? Address and answer these questions to build a deep understanding of your users’ goals and pain points to inform your customer journey.
In a SaaS customer journey , perhaps users are looking for helpful comparisons of product features on your website, or want to easily sign up for a trial account in the hopes that your product will solve their problems. But you won’t know until you ask .
Once you have users or test users, get direct insights from them with Hotjar's Feedback tools and Surveys to ask buyers exactly what their goals are as they browse different pages of your website or interact with product features.
Since user goals are at the center of your customer journey map, define them early on—but keep speaking to your users throughout the entire process to make sure you’re up to date with their needs.
5. Identify customer touchpoints
After you understand your users and what their goals are, it’s time to identify the ways they interact with your company and your product.
"Touchpoints are the moments the customer interacts with your brand, be it through social media channels, your product, or customer support. The quality of these experiences affects the overall customer experience, which is why it’s important to be aware of them. Consider what happens before, during, and after a customer makes a purchase or uses your product."
Key customer journey touchpoints for a website or product include your homepage, landing pages, product pages, CTA buttons, sign-up forms, social media accounts, and paid ads.
Collaboration is key to identifying touchpoints throughout the entire customer journey. Include insights from different teams and stakeholders —your marketing and sales teams will have a strong understanding of the touchpoints involved pre-purchase, while the customer experience department can shed light on post-purchase touchpoints.
Post-purchase touchpoints can help turn users into loyal customers and even advocates for your brand.
In the words of Lisa Schuck, "When you create a raving fan, or a brand advocate, who goes out and tells the world how wonderful you are, you get social credibility and validity. It’s becoming more and more important to have advocates."
Pro tip : speak with your users regularly to get direct voice-of-the-customer (VoC) insights on what they love and what frustrates them on their journey. Place Hotjar Feedback widgets and Surveys at key website touchpoints like your homepage and landing pages to get valuable user insights on what you can improve. Use Hotjar’s survey templates to get inspiration for your survey questions.
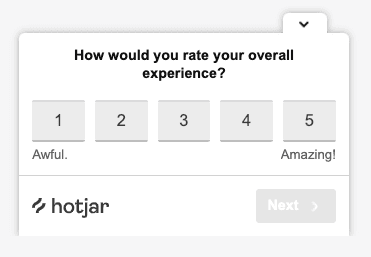
An example of an on-site Hotjar Survey
6. Map out the customer journey
Once your user and product research are complete and all roles are distributed, it’s time to map out the full customer journey.
First, map out an overarching customer journey by putting your key touchpoints in order and identifying how your various user personas interact with them. Then, home in on the details, looking at how customers engage with specific aspects of your website, product, or social media accounts.
Breaking down the mapping process into smaller phases will ensure you don’t miss any key interactions.
Here’s how an ecommerce brand could lay out general touchpoints, then narrow each down into more specific actions:
Pro tip : it’s helpful to think of the user journey in terms of different functions when mapping it out, like:
Connect: how are buyers connecting with your brand?
Attract: how are you convincing them to convert?
Serve: how are you serving customers when they want to purchase?
Retain: how are you promoting brand advocacy and customer retention ?
7. Test the customer journey
Once you’ve mapped out the customer journey, it’s time to take it for a spin. You can’t understand how your users move through customer touchpoints unless you test out the user flow yourself.
Start with an informational Google search, then visit your website, check out your social media pages, and simulate the purchase process. This will help you get a better sense of how users interact with each touchpoint and how easy it is to move between them.
Be sure to try out the journey from the standpoint of every relevant user persona. For an enterprise software company, this could mean looking at how decision-makers move through the user flow vs. the employees who’ll use your software day to day.
By walking through the customer journey yourself, you can identify issues and difficulties that users may have to address them proactively.
Try out the user flow with test users to get a realistic perspective of the user experience. Be sure to use focus groups that represent every one of your user personas.
8. Use continuous research to refine your map
Continuously map out, analyze, and evaluate the customer journey by observing users and getting their feedback. Hotjar Heatmaps and Recordings help you understand how your users are experiencing the customer journey on your website: create heatmaps to see whether users are clicking on CTAs or key buttons, and watch recordings to find out how they navigate once they reach your homepage.
Then, use Google Analytics to get an overview of your website traffic and understand how customers from different channels move through the user journey.
Finally, once you have these combined user insights, use them to make changes on your website and create a user journey that is more intuitive and enjoyable.
Pitfalls to avoid during the customer journey mapping stages
Jamie Irwin , director & search marketing expert at Straight Up Search , says companies should avoid these three common mistakes when mapping out the customer journey:
Don't map out the entire customer journey at once
Don't forget about the ‘hidden journeys’
Don't make assumptions about customer behavior
To sidestep these common pitfalls:
Start by mapping out the overall journey, and only drill down into more detail once you have a broader, higher-level overview of the customer journey
Factor in every way that customers interact with your brand, even the ones you don’t have as much visibility on, like ‘dark social’ communications about your brand shared in private channels. Talk to your users to find out what they’ve heard about your brand outside of public channels , and use sticky share buttons to keep track of when your content’s shared through email or social media messengers.
Take a data-informed approach: don’t assume you already know your users —test out your hypotheses with real users and qualitative and quantitative data.
Follow proven steps to successfully map out the customer journey
Take the time to understand your business goals and users, involve the right teams, and test frequently to consistently improve your customer journey and make the decisions that will help you map out an experience that will get you happy and loyal customers.
FAQs about customer journey mapping stages
What is the purpose of customer journey mapping.
Customer journey mapping helps you visualize how users interact with your business and product, from the moment they find it until long after they make their first purchase.
The purpose of customer journey mapping is to gain insights into the buyer's journey to create a more enjoyable, streamlined, and intuitive experience for your customers.
What are the benefits of following a customer journey mapping process?
The main benefits of a customer journey mapping process are: :
Building on tried-and-tested processes
Not missing any key steps
Considering all buyer personas
Keeping all relevant stakeholders involved
Creating a valuable customer journey map
Improving user experience
What happens if you don’t follow key steps in customer journey mapping?
If you don’t follow key steps when mapping out the customer journey, your map likely won’t give you the insights you need to enhance the experience users have with your most important touchpoints —like your homepage, landing pages, CTAs, and product pages.
This can result in high bounce rates, low conversion, and unsatisfied users who fail to become loyal customers.
CJM benefits
Previous chapter
CJM touchpoints
Next chapter
Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Updated: April 17, 2024
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2022? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map at the last second?

The thing is — understanding your customer base can be very challenging. Even when you think you’ve got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

While it isn’t possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a convenient tool for keeping track of critical milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I’ll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents
What is the customer journey?
What is a customer journey map, benefits of customer journey mapping, customer journey stages.
- What’s included in a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
Steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Customer Journey Design
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer’s journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I’ve worked with were confused about the differences between the customer’s journey and the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don’t wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process of considering, evaluating, and purchasing a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand’s place within the buyer’s journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer’s journey. When you create a customer journey map, you’re taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey instead of leaving it up to chance.
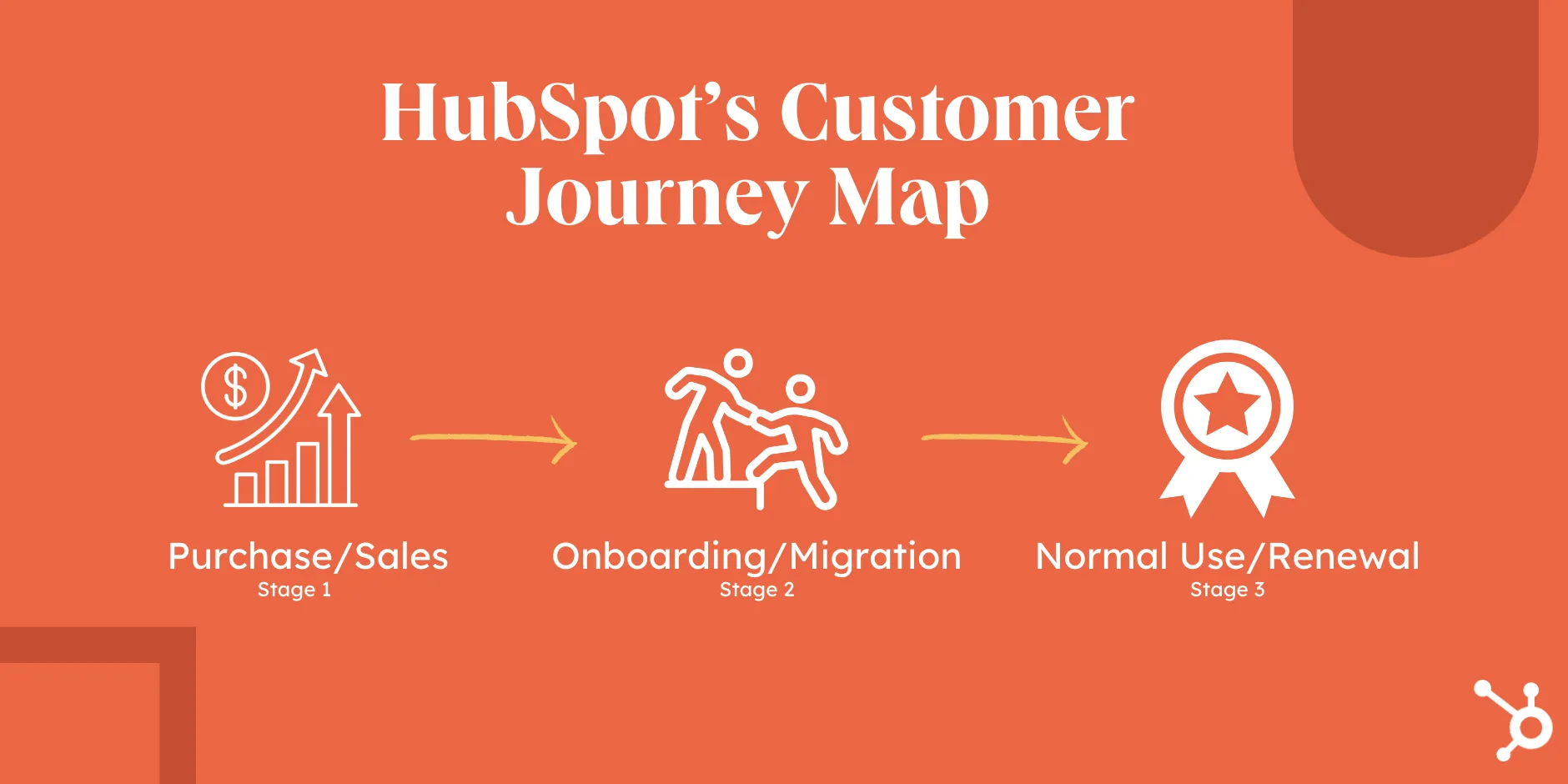
For example, at HubSpot, our customer’s journey is divided into three stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
1. Use customer journey map templates.
Why make a customer journey map from scratch when you can use a template? Save yourself some time by downloading HubSpot’s free customer journey map templates .
This has templates that map out a buyer’s journey, a day in your customer’s life, lead nurturing, and more.
These templates can help sales, marketing, and customer support teams learn more about your company’s buyer persona. This will improve your product and customer experience.
2. Set clear objectives for the map.
Before you dive into your customer journey map, you need to ask yourself why you’re creating one in the first place.
What goals are you directing this map towards? Who is it for? What experience is it based upon?
If you don’t have one, I recommend creating a buyer persona . This persona is a fictitious customer with all the demographics and psychographics of your average customer. This persona reminds you to direct every aspect of your customer journey map toward the right audience.
3. Profile your personas and define their goals.
Next, you should conduct research. This is where it helps to have customer journey analytics ready.
Don’t have them? No worries. You can check out HubSpot’s Customer Journey Analytics tool to get started.
Questionnaires and user testing are great ways to obtain valuable customer feedback. The important thing is to only contact actual customers or prospects.
You want feedback from people interested in purchasing your products and services who have either interacted with your company or plan to do so.
Some examples of good questions to ask are:
- How did you hear about our company?
- What first attracted you to our website?
- What are the goals you want to achieve with our company? In other words, what problems are you trying to solve?
- How long have you/do you typically spend on our website?
- Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, what was your deciding factor?
- Have you ever interacted with our website to make a purchase but decided not to? If so, what led you to this decision?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how easily can you navigate our website?
- Did you ever require customer support? If so, how helpful was it, on a scale of 1 to 10?
- Can we further support you to make your process easier?
You can use this buyer persona tool to fill in the details you procure from customer feedback.
4. Highlight your target customer personas.
Once you’ve learned about the customer personas that interact with your business, I recommend narrowing your focus to one or two.
Remember, a customer journey map tracks the experience of a customer taking a particular path with your company. If you group too many personas into one journey, your map won’t accurately reflect that experience.
When creating your first map, it’s best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
You can use a marketing dashboard to compare each and determine the best fit for your journey map. Don’t worry about the ones you leave out, as you can always go back and create a new map specific to those customer types.
5. List out all touchpoints.
Begin by listing the touchpoints on your website.
What is a touchpoint in a customer journey map?
A touchpoint in a customer journey map is an instance where your customer can form an opinion of your business. You can find touchpoints in places where your business comes in direct contact with a potential or existing customer.
For example, if I were to view a display ad, interact with an employee, reach a 404 error, or leave a Google review, all of those interactions would be considered a customer touchpoint.
Your brand exists beyond your website and marketing materials, so you must consider the different types of touchpoints in your customer journey map. These touchpoints can help uncover opportunities for improvement in the buying journey.
Based on your research, you should have a list of all the touchpoints your customers are currently using and the ones you believe they should be using if there’s no overlap.
This is essential in creating a customer journey map because it provides insight into your customers’ actions.
For instance, if they use fewer touchpoints than expected, does this mean they’re quickly getting turned away and leaving your site early? If they are using more than expected, does this mean your website is complicated and requires several steps to reach an end goal?
Whatever the case, understanding touchpoints help you understand the ease or difficulties of the customer journey.
Aside from your website, you must also look at how your customers might find you online. These channels might include:
- Social channels.
- Email marketing.
- Third-party review sites or mentions.
Run a quick Google search of your brand to see all the pages that mention you. Verify these by checking your Google Analytics to see where your traffic is coming from. Whittle your list down to those touchpoints that are the most common and will be most likely to see an action associated with it.
At HubSpot, we hosted workshops where employees from all over the company highlighted instances where our product, service, or brand impacted a customer. Those moments were recorded and logged as touchpoints. This showed us multiple areas of our customer journey where our communication was inconsistent.
The proof is in the pudding — you can see us literally mapping these touch points out with sticky notes in the image below.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![customer journey map kpmg How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![customer journey map kpmg How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![customer journey map kpmg Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)

Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2023
![customer journey map kpmg How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
![customer journey map kpmg Customer Experience vs. User Experience: What’s the Difference? [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-experience-vs-user-experience_2.webp)
Customer Experience vs. User Experience: What’s the Difference? [+ Examples]
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
What is customer journey mapping?
Customer journey map template, the customer journey mapping process, data inputs for your customer journey map, why should you use customer journey maps, the uses of customer journey mapping, how to improve a customer journey, tools to help you with your journey mapping, see how xm for customer frontlines works, customer journey mapping 101: definition, template & tips.
22 min read Find out about how to start customer journey mapping, and how to improve it for the benefit of your customers and the business.
If you want to improve your customer experience you need to be able to understand and adapt the customer journey you offer when someone interacts with your organization. Whether their journey is entirely online , offline, or a blend of both, there are multiple journeys a customer might undergo.
Understanding the customer journey in depth helps you identify and take action on customer pain points and repeat what’s working. By doing this, you will improve the overall experience that your customers have, which will have better outcomes for your business.
Outlining the potential customer journeys your audience might go through requires a process called customer journey mapping.
Free Course: Customer journey management & improvement
Creating a customer journey map is the process of forming a visual representation of customers’ processes, needs , and perceptions throughout their interactions and relationship with an organization. It helps you understand the steps customers take – the ones you see, and don’t – when they interact with your business.
It enables you to assess:
- Insights – from your existing customer journey, how to understand it better
- Impact – how to optimize budgets and effort for changes we want to make to the customer experiences
- Issues/opportunities – Diagnose the existing customer journey
- Innovation – where you might want to completely change the existing customer experience
A customer journey map gives you deeper insight into the customer, so you can go beyond what you already know. Many brands see the customer journey as something that is visible – where the customer interacts with the brand. But in reality, this is not true, and only accounts for a percentage of the entire customer journey. Creating a customer journey map gets you thinking about the aspects of the journey you don’t see, but have equal weight and importance to the entire experience.
When mapping out the customer journey, you are looking for the moments that matter – where there is the greatest emotional load.
If you’re buying a car, then the greatest moment of emotional load is when you go to pick the car up because it’s yours , after picking the color, choosing the model, and waiting for it to be ready.
Ensuring these moments match your customers’ expectations of your product, brand and service teams are key to helping you reach your business goals. But you can only do that by understanding the journey your customers go on in order to get there, what they’re thinking and needing from you at that time. Developing a customer journey map puts you in their shoes so you can understand them better than ever before.
Getting started when creating a customer journey map template doesn’t have to be difficult. However, your customer journey map template will need to cover several elements in order to be effective.
There are several ingredients that make up the anatomy of a customer journey, all of which should be looked at carefully so that you can find out where the customer journey runs smoothly and meets customer needs at that moment in time – and where the experience does not, and needs some improvement.
Understanding their behaviors and attitudes also means you can fix bad experiences more effectively too because you know why you haven’t met your customers’ expectations and what you need to do to make amends. There may be times when things go wrong, but it’s how you adapt and what you do to fix these experiences that separates the best. Knowing how the customer will be feeling makes taking that decisive action much easier.
When exploring and visualizing the customer journey we are assessing:
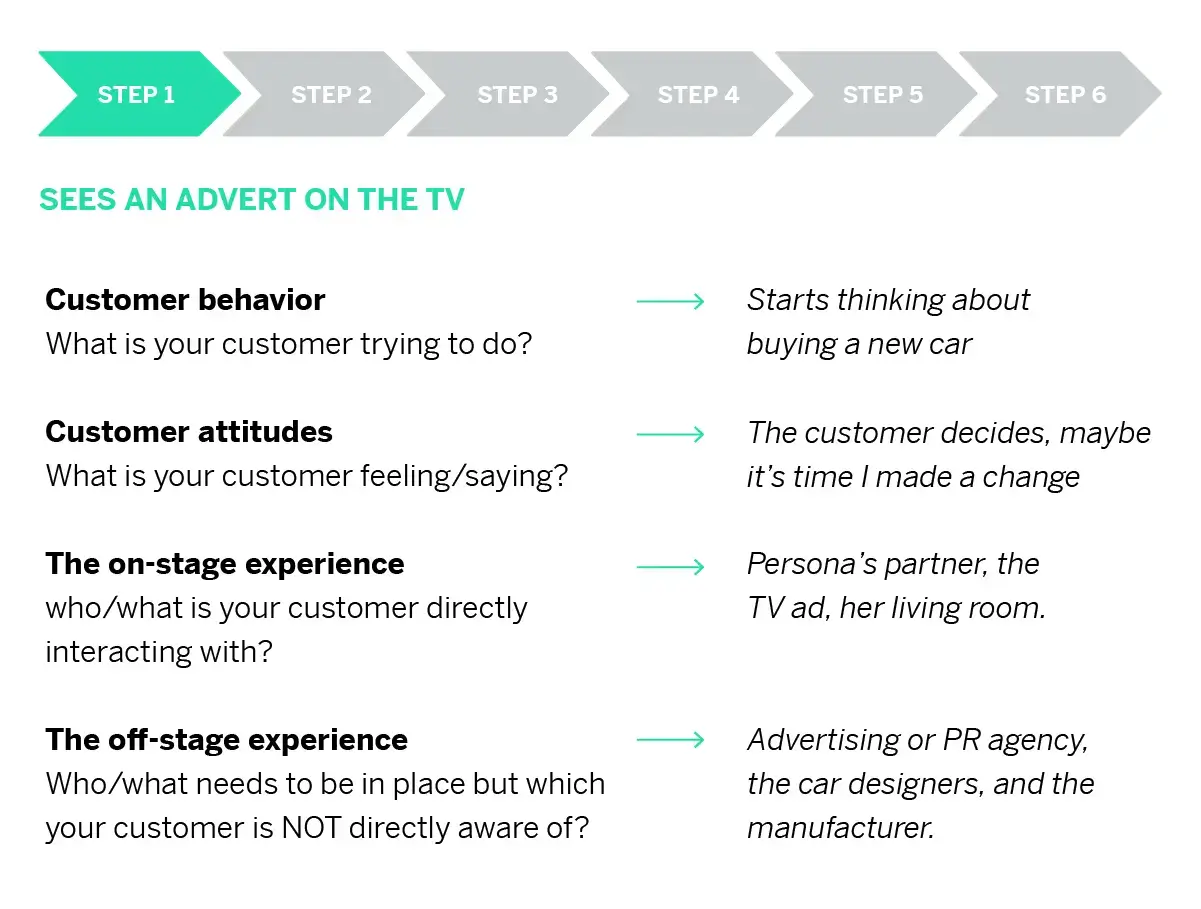
- Customer behavior What is your customer trying to do?
- Customer attitudes What is your customer feeling/saying?
- The on-stage experience Who/what is your customer directly interacting with? (This includes various channels, such as TV ads or social media)
- The off-stage experience Who/what needs to be in place but which your customer is NOT directly aware of?
So what could the customer journey map examples look like when starting the process of buying a car?
Customer journey vs process flow
Understanding customer perspective, behavior, attitudes, and the on-stage and off-stage is essential to successfully create a customer journey map – otherwise, all you have is a process flow. If you just write down the touchpoints where the customer is interacting with your brand, you’re typically missing up to 40% of the entire customer journey.
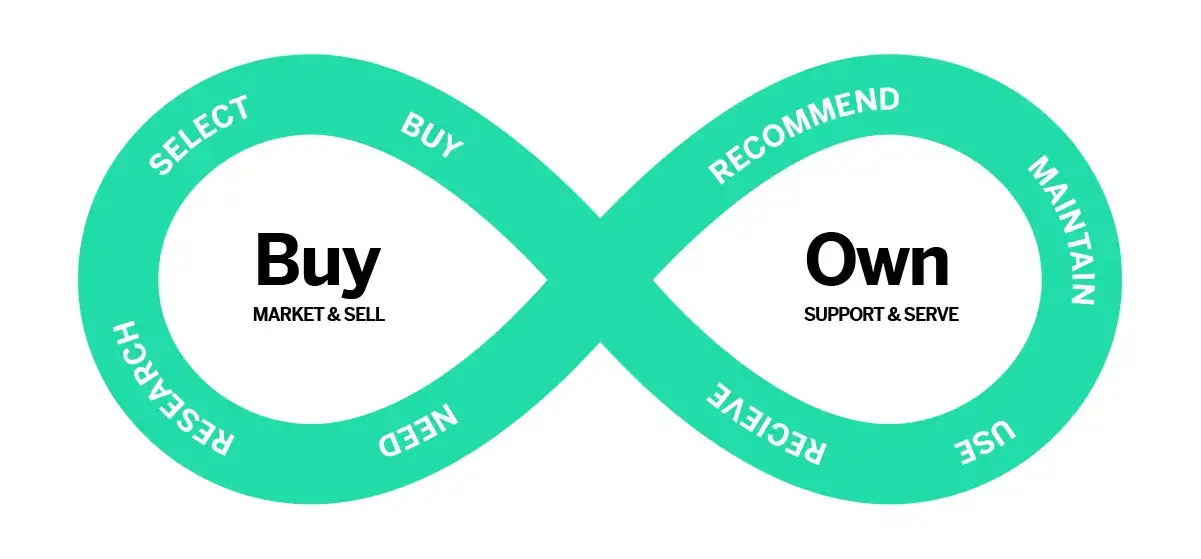
There is no single customer journey. In fact, there are multiple. The best experiences combine multiple journeys in a seamless way to create a continuous customer lifecycle as outlined below.
Getting started with customer journey map templates
To begin, start by choosing a journey that you would like to create a customer journey map for and outline the first step that customers will take.
You can use this customer journey map template below to work out the customer behaviors, attitudes, the on-stage and off-stage processes – and the KPIs attached to measuring the success of this experience.
Download our free journey mapping template here
The step-by-step process of mapping the customer journey begins with the buyer persona .
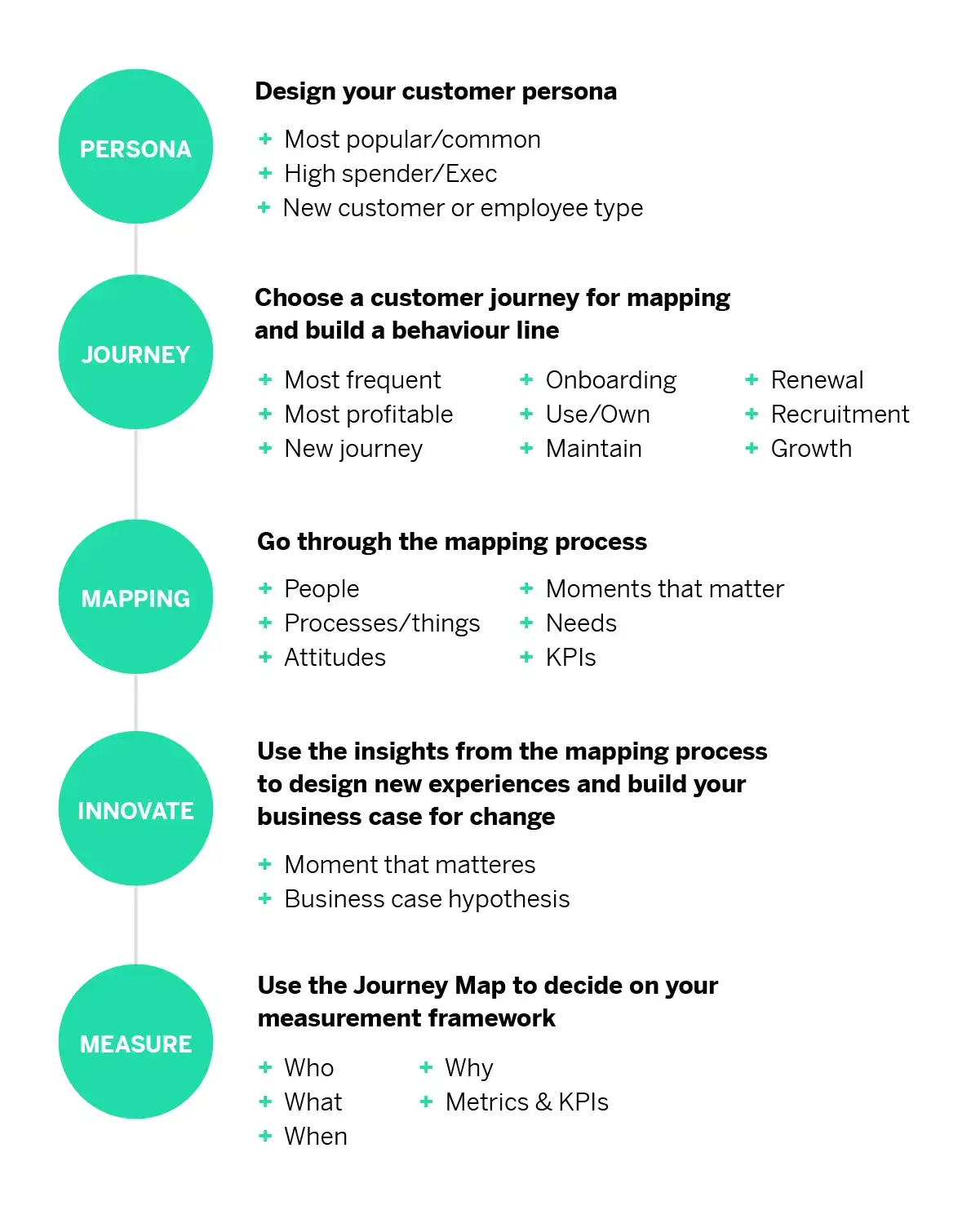
Step 1 – Create a customer persona to test
In order to effectively understand the customer journey, you need to understand the customer – and this is where creating a persona really helps. You may base this around the most common or regular customers, big spend, or new customers you haven’t worked with before. This persona is beyond a marketing segment , but that can be a great place to begin if you’re just starting out on the mapping process for your organization.
What do you include? Start with these characteristics.
- Family status
- Professional goals
- Personal goals
These personas help you gain a deeper understanding of your customers and can be derived from insights and demographic data , or even customer interviews . This works for both B2B and B2C business models, but in B2B especially you’ll have multiple customers for each opportunity so it’s recommended you build out multiple personas.
To begin, start with no more than three personas to keep things simple.
Create a diverse team
When creating a customer journey map, you also need to build out a diverse mapping team to represent the whole business. Include frontline staff , day-to-day management, corporate teams, HR, and business support functions. They will give you vital feedback, advice, and perspectives you hadn’t thought of.
Step 2 – Choose a customer journey for mapping
Select a customer journey map to construct, then build a behavior line. This might be a new customer journey, renewal, or fixing a product issue. You might also choose this based on the most frequent customer journeys taken, or the most profitable.
Step 3 – Work through the mapping process
Ask yourself the following:
- Who are the people involved in this journey? E.g. if you’re in a car dealership, that might be the customer, the sales rep, and front-of-house staff.
- What are the processes or the things that happen during this journey?
- What are the customer attitudes ? What are they feeling at this time? Go beyond excitement or frustration. Bring these feelings to life. This car is my dream come true!
- What is the moment that matters? Identify the greatest moment of emotional load. The make or break where everything could be good up until that point, but if you get that moment of maximum impact wrong, then all that’s good is forgotten. The best experience brands get this moment right and identifying it is an important first step to achieving that. In that moment, ask yourself what are the things/people/processes involved? Think about this for the whole business – across your product , brand , and service teams.
- But beyond identifying this moment, you need to establish what your customers’ needs are. What are they getting out of this moment? How do their needs change if this experience goes badly? Knowing the answer to these questions can help you deliver experiences that will resonate , and respond quickly to unforeseen circumstances or issues.
- And finally, how do you measure how effectively you are meeting customer needs throughout the journey? Set KPIs to put benchmarks in place for your customer journey map and customer experience and track your progress.
Step 4 – Innovate
When you are mapping out your customer journey, brainstorm ideas for how to improve that moment that really matters . These ideas don’t need to be practical, but by putting together a diverse mapping team from around the business you can begin to filter through these ideas.
Then, test it.
Ask yourself: Is it feasible? Is it viable? Is it desirable? Don’t ask can we do it, ask should we do it? Then you can start to differentiate yourself from your competitors.
Step 5 – Measure
Use the customer journey map to decide on your measurement framework.
Who are you measuring? What are you measuring? When on the journey are you measuring it? And why? And finally, what metrics and KPI’s are in place to measure this?
Your customer journey map process will require you to use several different data inputs to get an accurate picture of how your customers behave and where you can improve their experience.
A customer journey map is often developed using data gleaned from customer feedback you’ve requested . While this type of market research is useful, your research process needs to be deeper to gain a richer, more accurate understanding of your customer’s behavior.
To create a customer journey map that accurately reflects the truth of customer actions and intentions, you need to take into account both solicited and unsolicited data.
Use solicited data to understand the voice of the customer
Solicited data includes the customer feedback you gain when you conduct research through surveys such as Net Promoter Score (NPS) or ask customers for feedback on social media. This approach can be very useful for understanding your customer’s point of view , rather than just making assumptions about how they think and behave.
However, your target audiences won’t tell you everything about what they plan to do when undergoing their customer journey. Though they might tell you that they’ve had a great experience in a particular part of their customer journey, this type of feedback presents a few issues:
- You have to know when to ask for feedback : You might already have a customer journey in mind when asking for feedback – but do you know all the routes a customer might take in your customer journey map?
- It’s a snapshot: When you survey customers, you’ll likely only get insights into their experience at that particular moment about a specific touchpoint
- It’s what customers say they think/will do, not what they actually think/will do: You’re relying on your customers to accurately reflect their sentiment and intentions in their responses, which isn’t always the case. For your customer journey map to be effective, you need to find the truth
- Your sample size might be too small : If you’re trying to understand how a relatively niche customer journey is doing, you might find that the number of customers who have not only taken the customer journey but are willing to respond with feedback is very limited. You can’t risk survey fatigue by polling the same audience several times, so your insights are limited
- You’re only getting part of the picture : You will likely have several types of useful customer data on file, but these are often not considered as part of the process when creating a customer journey design because solicited data takes precedence
You’ll need to infer how customers feel to be able to accurately predict the actions a customer takes. To do so, you’ll need to look at unsolicited data.
Unsolicited data
Unsolicited data covers everything your customers aren’t telling you directly when you ask them and contextual data that you likely already collect on them, such as purchase history. It can be taken from various sources, such as your website and social channels, third-party sites, customer calls, chat transcripts, frontline employee feedback , operational sources, and more.
This type of data is nuanced, but it allows you to establish the truth of your customers’ experience. The ability to gather unsolicited customer feedback from every channel enables you to see more than just what a customer tells you directly. Using real-time feedback gathering and natural language understanding (NLU) models that can detect emotion, intent, and effort, you’ll be able to understand your customers’ actions in a more profound way. Unsolicited data offers you a 100% response rate that better indicates what your customers actually think of each step in their customer journey.
Rather than be limited to a small sample size of customers who respond to surveys, you’ll be able to build an accurate picture of the average customer on each step of the customer journey map by using this richer insight data with your own operational data.
Why using solicited and unsolicited data is important data
With solicited data, you don’t always see why a customer behaves or thinks as they do. For example, a customer might tell you that they would recommend you to a friend or family – but they don’t renew their subscription with you. A customer might be an ideal candidate for a particular journey, but they abandon their basket when prompted to give their personal details. Understanding the why behind customer actions is key for designing a great customer journey, and that’s why both solicited and unsolicited data collection and evaluation are necessary for creating great customer journey maps.
Of course, knowing how customers will actually respond to your customer touchpoints is only part of the process. You may need to develop more than one customer journey map and create sub-audiences for your customer personas to accurately see where you can rectify pain points and improve outcomes. You will need to collect and analyze contextual data across all customer journey touchpoints and develop a highly detailed journey map that can unveil routes your customers might be taking without your knowledge.
Qualtrics’ Experience ID platform can overlay solicited and unsolicited data to provide an all-encompassing picture of your customer journey map, no matter how complex. Creating an effective customer journey map is easier with all your data collated and analyzed together, with actionable insights created automatically.
A customer journey map creates a common understanding for the organization of how a customer interacts during different stages of the customer lifecycle, and the roles and responsibilities of the different teams in charge of fulfilling that experience.
It will also bring an organization together, and foster empathy and collaboration between teams because people will know what is required from everyone in the business to deliver the experiences that customers expect. This will help you to develop a shared sense of ownership of the customer relationship, which ultimately drives a customer-centric culture . With everyone working towards a common goal, communication of what you learn about the customer and the journey they go through is vital in order to drive best practices throughout the organization.
Creating an accurate customer journey map will help your customer service team to focus on more specific issues, rather than handling problems generated by a less-tailored customer journey. Your customer experience will be improved with a customer journey that’s personalized to the specific personas you have generated. You’ll have put yourself in your customer’s shoes and adapted your strategy to reflect your customer’s perspective – which in turn will create more memorable experiences.
Creating a customer journey map will influence your journey analytics across the business. So for example, it will determine what you ask, who you ask, when you ask, why you ask it and how you ask questions in your Voice of the Customer Program .
So when should you use customer journey mapping?
There are four main uses:
- Assess the current state of your customer journey Understand and diagnose the specific issues in current experiences
- Understand what the future state of your customer journey should look like Design, redesign and create new experiences
- Blueprints For implementing change
- Communication Bringing teams together to train and scale up best practices.
Take stock and take action
To improve the customer journey you need a clear vision of what you want to achieve and you need to make a distinction between the present and the future.
- What is your customer journey right now?
- What does the future state of your customer journey look like?
This is why organizations blueprint their customer journey because they can see what works and act accordingly. By understanding your customers’ attitudes and needs at critical times in the journey, you can make amends to better meet them – and develop contingencies to cope when these needs aren’t or can’t be met. For example, during a sudden, unexpected surge in demand.
Orchestrate your customer journey
To offer your customers truly optimized experiences, you’ll need to go further than just creating a customer journey map. You’ll also need to orchestrate journeys using real-time customer behavior to adapt your strategy as your customers make choices. Orchestrating a journey means taking dynamic action towards optimizing your customer’s experience, using real-time customer behavior as informative data.
Improve your employee experience
Use your diverse mapping team to come up with ideas that incorporate experience from all aspects of the business to improve the customer journey – and remember that this has a significant payoff for your employees too. Improving the employee journey – by giving teams the tools to make a difference – can have a positive knock-on effect for the customer and improve their experience in those key moments. This is because employees have the autonomy and motivation in their roles to help their customers, and realize their own potential.
Your customer journey map isn’t just designed to improve the customer experience. Creating an accurate customer journey map can help you to improve your business outcomes.
Being able to link operational data to key touchpoints in a customer journey is transformative for organizations. This is because improving segments of the customer journey will see a direct impact on your business. The Qualtrics Journey Optimizer helps you do just that. By analyzing areas for improvement as outlined by your customer journey map, organizations can take actions that will have maximum benefit for their customers, and the business too.
With Qualtrics CustomerXM , you’ll:
- Create a common understanding throughout your workforce of how a customer interacts with your organization, and you’ll know the roles and responsibilities of your different teams
- Develop empathy and collaboration between teams, working together to achieve the same outcome
- Develop a shared sense of ownership of the customer relationship which ultimately drives a customer-centric culture
Free course: Customer journey management & improvement
Related resources
Customer Journey
B2B Customer Journey 13 min read
Customer interactions 11 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, customer journey orchestration 12 min read, customer journey management 14 min read, customer journey stages 12 min read, buyer's journey 16 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Blog / Journey Measurement
Customer Journey KPIs: The Metrics and Magic of Journey Mapping
- November 15, 2023

Table of Contents
Key takeaways.
- Understanding customer journey metrics allows you to optimize the customer journey at every stage, leading to higher retention rates.
- Important metrics include traffic, impressions, leads, engagement, conversions, CPC, churn, CLV, and UGC.
- It’s vital to set goals that improve your customer journey along the way. Metrics can help you spot issues and drop-off points for customers.
Why should you measure customer journey metrics?
Which kpis should you track, 14 customer journey kpis to understand and improve customer experience (cx), customer journey metrics to track in the awareness stage, 1. website traffic and content views.
Get the guide to customer journey tracking
We outline the actionable strategies to track & optimize the customer journey at every stage of the funnel

2. SEO ranking
- Optimize your website for relevant keywords
- Create high-quality content that’s engaging, informative, and useful to the site visitor
- Improve your site speed; Google’s recommended site speed is less than two seconds
- Implement a backlink strategy to acquire relevant links from authoritative sources
- Work to decrease your bounce rate to between 26% and 40%.
3. Brand impressions
- Consistent and targeted marketing campaigns
- Creating engaging content
- Leveraging social media effectively
Customer journey KPIs to measure in the consideration stage
4. lead generation.
- Optimize your website for conversion
- Set up effective product sales funnels
- Create compelling lead generation content that speaks to your customer’s pain points
- Maintain consistent, helpful, and personalized communication
- Questionnaire-based signup forms

5. Engagement rate
- Creating compelling, shareable content
- Engaging with your audience and responding to comments promptly
- Running interactive campaigns and competitions
Customer journey metrics for the decision stage
6. conversion rate.
- Optimize your website for user-friendliness
- Create persuasive calls-to-action
- Refine your targeting strategies to ensure a seamless path from interest to action

7. Sales metrics
- Refine your sales strategies
- Streamline your sales funnel
- Provide an exceptional CX ( 73% of customers say CX is the most important thing they consider when deciding whether to purchase from a company)
Visualize your full customer journey with Funnelytics
Optimize every funnel type with our data-driven funnel mapping platform
8. Cost per conversion (CPC)
- Refine your audience targeting
- Use A/B testing to find the most effective ad creative
- Continuously monitor your campaigns to maximize results while minimizing costs
Customer journey KPIs to track in the retention stage
9. customer churn rate.
- Providing exceptional customer service
- Implementing retention strategies
- Seeking customer feedback to identify and address issues
10. Customer lifetime value (CLV)
- Prioritize offering excellent customer experiences
- Run loyalty programs
- Engage with your customers on an ongoing basis
11. Repeat purchase rate
- Launch and maintain a post-purchase marketing campaign in the form of emails, in-app messages, and texts. Include tips and tutorials for using and maximizing the benefits of purchased products.
- Offer a loyalty program, discounts, or free items for repeat customers.
- Use retargeting campaigns to reach out to dormant customers and maintain the relationship.
- Use surveys to improve customer satisfaction.
Customer journey metrics for the advocacy stage
12. referral rate or net promoter score (nps).
- Focus on providing top-notch experiences
- Implement referral programs
- Nurture your customer relationships to inspire customers to become enthusiastic brand advocates
13. Social media shares
- Create engaging, shareable content
- Encourage sharing by adding prominent social buttons on your website
- Interact with your audience by responding to comments and fostering conversations
- Implement a social media competition that offers a discount or prize for liking and sharing posts
14. User-generated content (UGC)
- Encourage and incentivize your audience to create and share content related to your brand
- Showcase user-generated content on your website and social media
- Engage with your customers by acknowledging and sharing their contributions
How to set goals to improve your customer journey
Choose the right customer journey analytics tool.
Start your free trial of Funnelytics Performance
Unleash the full potential of Funnelytics with a free 14-day trial and get access to the platform that will help you plan, measure and optimize your customer journeys.

Related resources

Sales Funnel vs. Customer Journey: What are the Differences?

Cracking the Code: Funnel Reporting for Marketers

The Customer Lifecycle Journey: What it is and How to Use it to Create Repeat Customers
9 Best Funnel Tracking Software Tools to Streamline Your Sales Success
Start your free trial.
Unleash the full potential of Funnelytics with a 14-day trial, no strings attached. Gain full access to the features that will propel your growth to new heights.
A customer-centric approach to sales and marketing goes a long way. According to a Salesforce survey, about 66% of customers
A marketing funnel is a critical way to discover the needs and wants of your customers by tracking their entire

Customer Journey Measurement: Charting the Path to Success
Customer experience (CX) is critical to a business’s success. In a recent study, customer-centric brands reported an 80% increase in
Seeing is believing.
Try funnelytics for free.
Sign up for your free 14-day trial today and experience all the benefits Funnelytics will bring to your business first-hand. No contracts. No commitments. Just full-on customer journey insights.
© Funnelytics Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Get a tour of Funnelytics
Prep for your call

Atlassian Presents: Unleash
Product updates, hands-on training, and technical demos – catch all that and more at our biggest agile & DevOps event.
- Atlassian.com
Customer Journey Mapping
Journey mapping helps you visualize how customers experience your product or service, and how they feel along the way. Scroll to step 6 for a real-life example from one of our product teams!
USE THIS PLAY TO...
Understand the customer journey from a specific persona's perspective so that you can design a better experience.

Running the play
Depending on how many touchpoints along the customer journey you're mapping, you might break the journey into stages and tackle each stage in pairs.
Sticky notes
Whiteboards.io Template
Define the map's scope (15 min)
Ideally, customer journey mapping focuses on the experience of a single persona in a single scenario with a single goal. Else, the journey map will be too generic, and you'll miss out on opportunities for new insights and questions. You may need to pause creating a customer journey map until you have defined your customer personas . Your personas should be informed by customer interviews , as well as data wherever possible.
Saying that, don't let perfect be the enemy of good! Sometimes a team just needs to get started, and you can agree to revisit with more rigor in a few months' time. Once scope is agreed on, check your invite list to make sure you've got people who know the details of what customers experience when using your product or service.
Set the stage (5 min)
It's really important that your group understands the user persona and the goal driving their journey. Decide on or recap with your group the target persona and the scope of the journey being explored in your session. Make sure to pre-share required reading with the team at least a week ahead of your session to make sure everyone understands the persona, scope of the journey, and has a chance to delve deeper into research and data where needed. Even better- invite the team to run or attend the customer interviews to hear from customers first hand!
E.g. "We're going to focus on the Alana persona. Alana's role is project manager, and her goal is to find a scalable way for her team to share their knowledge so they spend less time explaining things over email. We're going to map out what it's like for Alana to evaluate Confluence for this purpose, from the point where she clicks that TRY button, to the point where she decides to buy it – or not."
Build a customer back-story (10 min)
Have the group use sticky notes to post up reasons why your target persona would be on this journey in the first place. Odds are, you'll get a range of responses: everything from high-level goals, to pain points, to requested features or services. Group similar ideas and groom the stickies so you can design a story from them.
These narratives should be inspired by actual customer interviews. But each team member will also bring a different perspective to the table that helps to broaden the lens.
Take a look at the example provided in the call out of this section. This back story starts with the pain points – the reasons why Alana would be wanting something like Confluence in the first place.
- E.g., "Her team's knowledge is in silos"
Then it basically has a list of requirements – what Alana is looking for in a product to solve the bottom pain points. This is essentially a mental shopping list for the group to refer to when mapping out the customer journey.
- E.g., "Provide structure"
Then it has the outcomes – goals that Alana wants to achieve by using the product
- E.g., "To keep my team focused on their work instead of distracted by unnecessary emails and shoulder-taps"
And finally the highest-level goal for her and her team.
- E.g., "Improve team efficiency"
Round off the back story by getting someone to say out loud what they think the overall story so far is, highlighting the main goals the customer has. This ensures a shared understanding that will inform the journey mapping, and improve the chances that your team will map it from the persona's point of view (not their own).
- E.g., "Alana and her team are frustrated by having to spend so much time explaining their work to each other, and to stakeholders. They want a way to share their knowledge, and organize it so it's easy for people outside their team to find, so they can focus more energy on the tasks at hand."

For example...
Here's a backstory the Confluence team created.
Map what the customer thinks and feels (30-60 min)
With the target persona, back story, and destination in place, it's time to walk a mile in their shoes. Show participants how to get going by writing the first thing that the persona does on a sticky note. The whole group can then grab stickies and markers and continue plotting the journey one action at a time.
This can also include questions and decisions! If the journey branches based on the answers or choices, have one participant map out each path. Keep in mind that the purpose of this Play is to build empathy for, and a shared understanding of the customer for the team. In order to do this, we focus on mapping the current state of one discrete end to end journey, and looking for opportunities for improvement.
To do a more comprehensive discovery and inform strategy, you will need to go deeper on researching and designing these journey maps, which will need to split up over multiple sessions. Take a look at the variation below for tipes on how to design a completely new customer journey.
Use different color sticky notes for actions, questions, decisions, etc. so it's easier to see each element when you look at the whole map.
For each action on the customer journey, capture which channels are used for the interactions. Depending on your context, channels might include a website, phone, email, postal mail, face-to-face, and/or social media.
It might also help to visually split the mapping area in zones, such as "frontstage" (what the customer experiences) versus "backstage" (what systems and processes are active in the background).
Journey mapping can open up rich discussion, but try to avoid delving into the wrong sort of detail. The idea is to explore the journey and mine it for opportunities to improve the experience instead of coming up with solutions on the spot. It's important not only to keep the conversation on track, but also to create an artefact that can be easily referenced in the future. Use expands or footnotes in the Confluence template to capture any additional context while keeping the overview stable.
Try to be the commentator, not the critic. And remember: you're there to call out what’s going on for the persona, not explain what’s going on with internal systems and processes.
To get more granular on the 'backstage' processes required to provide the 'frontstage' customer value, consider using Confluence Whiteboard's Service Blueprint template as a next step to follow up on this Play.

ANTI-PATTERN
Your map has heaps of branches and loops.
Your scope is probably too high-level. Map a specific journey that focuses on a specific task, rather than mapping how a customer might explore for the first time.
Map the pain points (10-30 min)
"Ok, show me where it hurts." Go back over the map and jot down pain points on sticky notes. Place them underneath the corresponding touchpoints on the journey. Where is there frustration? Errors? Bottlenecks? Things not working as expected?
For added value, talk about the impact of each pain point. Is it trivial, or is it likely to necessitate some kind of hack or work-around. Even worse: does it cause the persona to abandon their journey entirely?
Chart a sentiment line (15 min)
(Optional, but totally worth it.) Plot the persona's sentiment in an area under your journey map, so that you can see how their emotional experience changes with each touchpoint. Look for things like:
- Areas of sawtooth sentiment – going up and down a lot is pretty common, but that doesn't mean it's not exhausting for the persona.
- Rapid drops – this indicates large gaps in expectations, and frustration.
- Troughs – these indicate opportunities for lifting overall sentiments.
- Positive peaks – can you design an experience that lifts them even higher? Can you delight the persona and inspire them to recommend you?
Remember that pain points don't always cause immediate drops in customer sentiment. Sometimes some friction may even buold trust (consider requiring verification for example). A pain point early in the journey might also result in negative feelings later on, as experiences accumulate.
Having customers in the session to help validate and challenge the journey map means you'll be more confident what comes out of this session.
Analyse the big picture (15 min)
As a group, stand back from the journey map and discuss trends and patterns in the experience.
- Where are the areas of greatest confusion/frustration?
- Where is the journey falling short of expectations?
- Are there any new un-met needs that have come up for the user type?
- Are there areas in the process being needlessly complicated or duplicated? Are there lots of emails being sent that aren’t actually useful?
Then, discuss areas of opportunity to improve the experience. E.g., are there areas in the process where seven steps could be reduced to three? Is that verification email actually needed?
You can use quantitative data to validate the impact of the various opportunity areas identified. A particular step may well be a customer experience that falls short, but how many of your customers are actually effected by that step? Might you be better off as a team focused on another higher impact opportunity?
Here's a user onboarding jouney map our Engaging First Impressions team created.
Be sure to run a full Health Monitor session or checkpoint with your team to see if you're improving.
MAP A FUTURE STATE
Instead of mapping the current experience, map out an experience you haven't delivered yet. You can map one that simply improves on existing pain points, or design an absolutely visionary amazeballs awesome experience!
Just make sure to always base your ideas on real customer interviews and data. When designing a totally new customer journey, it can also be interesting to map competitor or peer customer journeys to find inspiration. Working on a personalised service? How do they do it in grocery? What about fashion? Finance?
After the mapping session, create a stakeholder summary. What pain points have the highest impact to customers' evaluation, adoption and usage of our products? What opportunities are there, and which teams should know about them? What is your action plan to resolve these pain points? Keep it at a summary level for a fast share out of key takeaways.
For a broader audience, or to allow stakeholders to go deeper, you could also create a write-up of your analysis and recommendations you came up with, notes captured, photos of the group and the artefacts created on a Confluence page. A great way of sharing this information is in a video walk through of the journey map. Loom is a great tool for this as viewers can comment on specific stages of the journey. This can be a great way to inspire change in your organization and provide a model for customer-centric design practices.
KEEP IT REAL
Now that you have interviewed your customers and created your customer journey map, circle back to your customers and validate! And yes: you might learn that your entire map is invalid and have to start again from scratch. (Better to find that out now, versus after you've delivered the journey!) Major initiatives typically make multiple journey maps to capture the needs of multiple personas, and often iterate on each map. Remember not to set and forget. Journeys are rapidly disrupted, and keeping your finger on the pulse of your customer's reality will enable your team to pivot (and get results!) faster when needed.
Related Plays
Customer Interview
Project Poster
Want even more Playbook?
Drop your email below to be notified when we add new Health Monitors and plays.
Thanks! Now get back to work.
Got feedback?
Drop a question or comment on the Atlassian Community site.
Shared understanding
Different types of teams need to share an understanding of different things.
LEADERSHIP TEAMS
The team has a shared vision and collective purpose which they support, and confidence they have made the right strategic bets to achieve success.
Proof of concept
Project teams.
Some sort of demonstration has been created and tested, that demonstrates why this problem needs to be solved, and demonstrates its value.
Customer centricity
Service teams.
Team members are skilled at understanding , empathizing and resolving requests with an effective customer feedback loop in place that drives improvements and builds trust to improve service offerings.

Collaborative customer journey mapping tools
Easily plan and create customer journey maps in Miro. Exercise empathy, understand your user’s wants and needs, and build exceptional customer experiences.
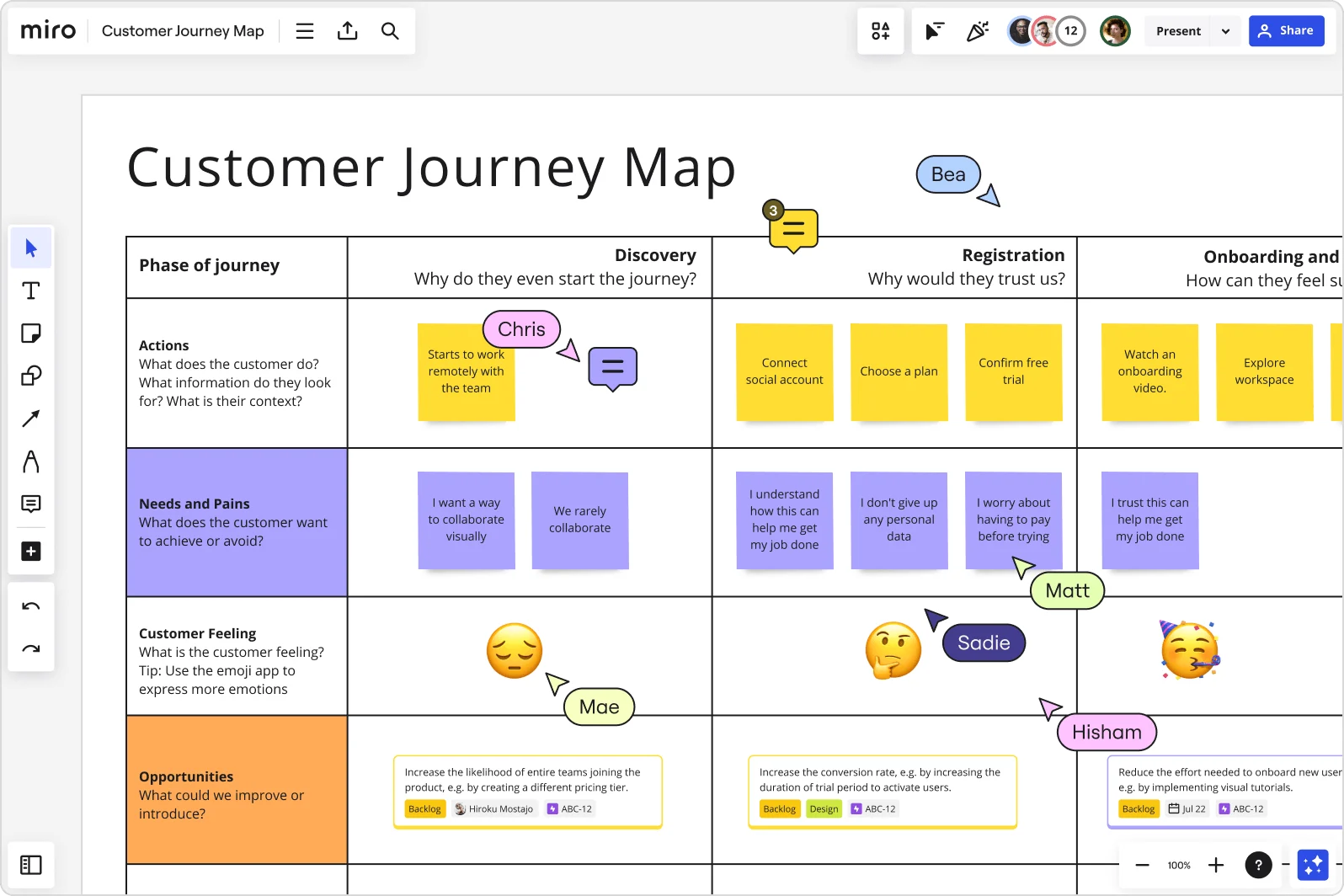
Over 60M users love Miro.
Ready-made customer journey map templates
Design transformative customer journeys with templates for persona building, touchpoint maps, service blueprints, and more. Help your team quickly visualize, collaborate, and iterate on your customer experience, bringing in data and research to make the best-informed decisions.
Create a shared understanding, faster
Build highly visual and accurate maps that bring a customer’s humanity and experience to life with dynamically populated input, feedback, and data from various sources, like Amplitude, Looker, Blossom, Loom, and UserTesting. Record interactive walkthroughs with Talktrack so everyone can engage on their own time, with all the context on the board.
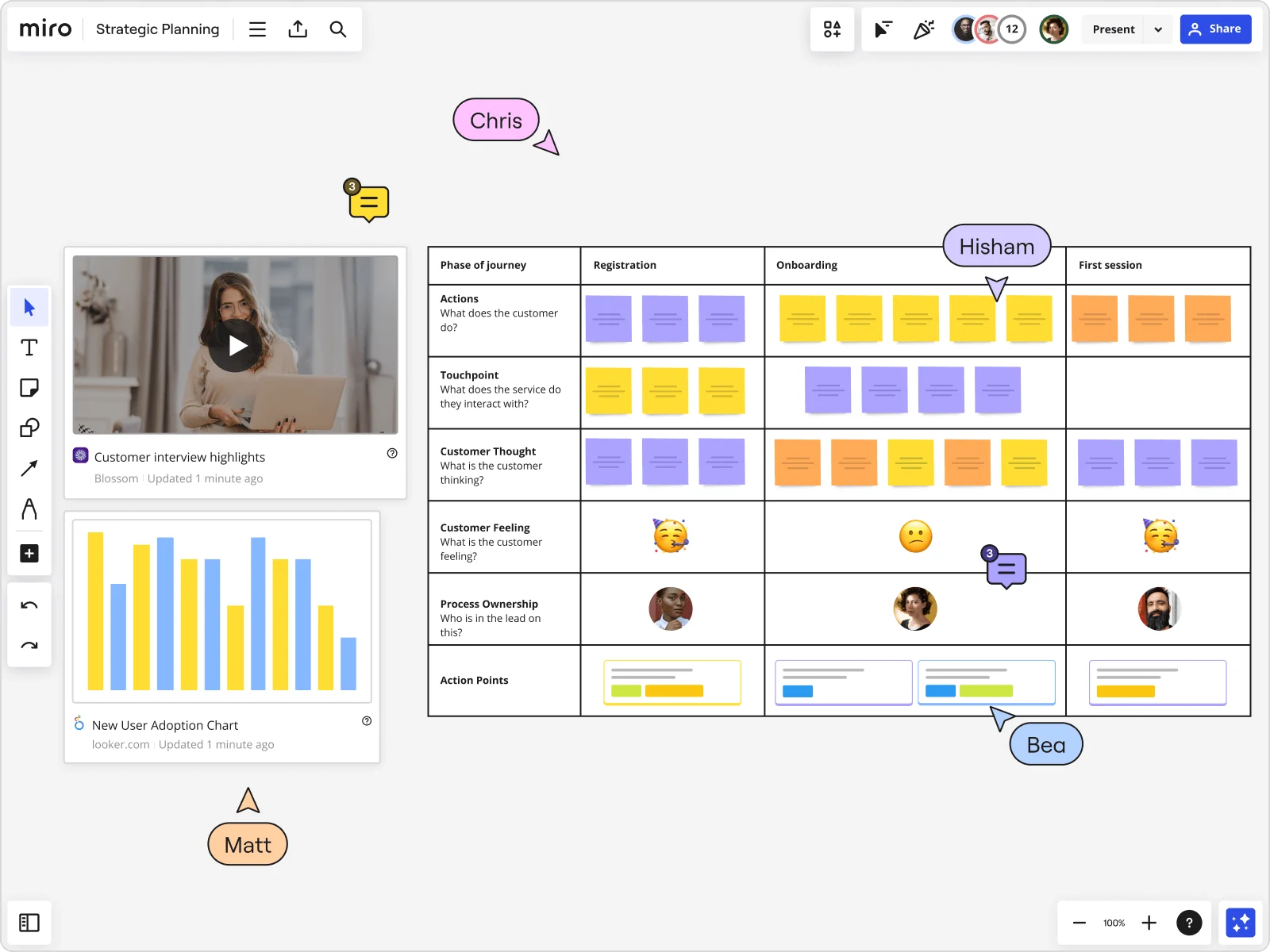
Easy to share and change
Give your team easy access to customer journey maps so they can leave feedback, ask questions, and make immediate changes as needed. Keep customer-centricity top of mind by embedding it everywhere your teams work (like Confluence) and it’ll always be synced to the latest version, or export your customer journey map as an image or PDF file for presentations.
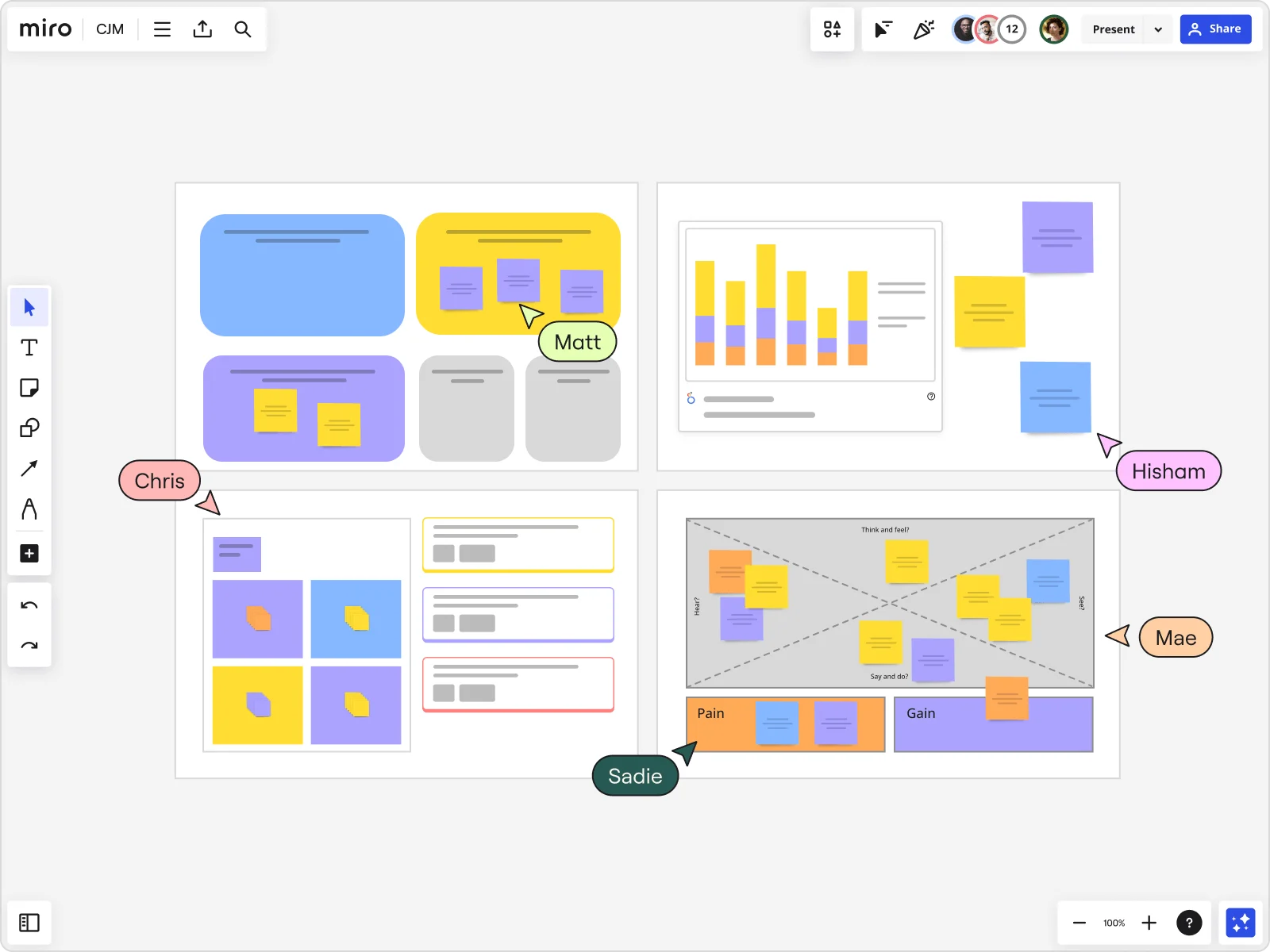
Why people love Miro for customer journey mapping
Uncover possibilities.
Miro’s infinite canvas gives you the ability to collaborate across product teams and cross-functional stakeholders on customer journeys. It serves as a team hub for mapping and research, where you can plot your customer’s paths, visualize their journey, and gather insights all in one tool.
Empathy made easy
Make sure all voices are heard and tap into your team’s collective imagination to identify customer pain points, cultivate empathy, wireframe solutions, and ship innovative products — all with Miro’s customer journey map tools.
Be the voice of the customer
Map your user journey step-by-step and truly understand the people using your product. Bring your team with you in this process and share your customer journey map across your organization. Become the customer advocate and ensure you add value to your product.
Quickly get started
Miro’s customer journey map tool helps accelerate your team’s processes by clearly visualizing journeys, touchpoints, personas, and more. Save time by crafting your customer journey map using one of our pre-made frameworks, or build one from scratch with our many editing tools.
Deliver better results
Make better-informed decisions by getting instant feedback and craft experiences that people will remember. Tag team members, receive comments, and gain more insights with Miro’s collaborative customer journey mapping tool.
Share it with everyone
Share your insights and be proactive by running customer workshops inside your organization. Use Miro’s collaborative features, such as the timer and voting, to help lead interactive sessions and engage your team. Offer the space and tools needed for blue-sky thinking.
Related templates
Customer Journey Map Template
Design the best product experience and meet your customer's needs.
Customer Touchpoint Map Template
Identify opportunities and gain a competitive advantage.
Customer Problem Statement Template
Create a problem statement to understand your customer's point of view.
Voice of the Customer Template
Create standards to understand and improve your customer experience.
Customer Journey Mapping Template Pack
Easily create customer journey maps for projects of all kinds.
Experience Mapping Template
Bring a customer-centric approach to product development and branding.
More than just a customer journey map
Customer journey mapping in Miro is the perfect blend of structure and flexibility, so your team can seamlessly visualize, collaborate, and iterate on your user journeys. From workshops with product teams to client presentations, focus on what matters and build great customer experiences.
UX & Design
From brainstorming with your cross-functional squad to gathering feedback for iteration and reiteration, create product experiences that people love.
Research and Design
Embrace design thinking and collaborate on design sprints, customer journey maps, wireframes, and more. Transform the way your team builds products.
Strategic planning
Propel your plans from strategy through execution. Run engaging remote planning sessions, build visual presentations, and manage and track progress collaboratively.
Bring teams together and create everything you need to develop campaigns that delight customers and drive business forward — all in one place.
Wireframing
Create quick app and website wireframes, ideate on sticky notes, map user flows, and collect references. Do it all in real time with your team on one board.
Bring teams closer together and execute faster in a hybrid, collaborative Obeya room.
How to create a customer journey map with Miro
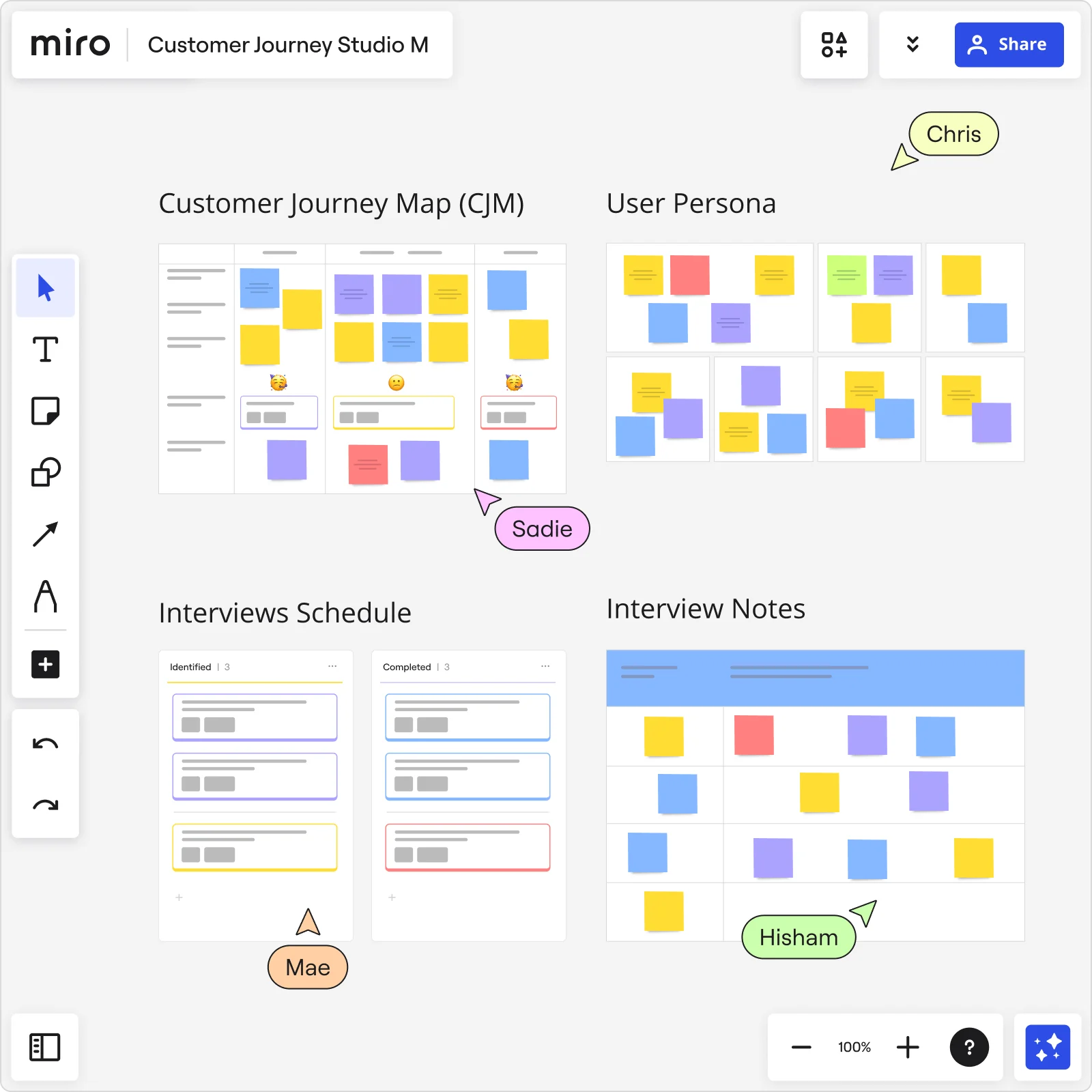
Define personas
Determine which specific customer segments or personas you want to focus on. Collect data and insights about their needs, behaviors, and preferences.
Identify touchpoints
Identify key stages of the customer journey listing the touchpoints. Detail the specific actions, emotions, and pain points customers experience at each stage.
Add context and insights
Integrate data from customer surveys, interviews, analytics, and other sources to enrich your understanding of customer behaviors and preferences.
Share and find opportunities
Identify opportunities to improve the customer experience. When ready, share with stakeholders for feedback and collaboratively draft an action plan to implement the findings.
Iterate and update
Embed the map where teams and stakeholders can easily find it. Regularly review and evolve the customer journey map as you gain more data, insights, and feedback.
Customer journey mapping tools FAQs
What makes a good customer journey.
To create a good customer journey map, make sure you add all the stages your user goes through by mapping every customer touchpoint and the phases they belong to. After you map out your customer journey, to know more about who they are, you can create a storyboard or dig deeper with an empathy map. Miro’s customer journey mapping software makes it easy to add other artifacts and maps to your board, so you can have a great overview of your customer journey and what influences your customer's experiences. It can get messy, and it’s ok! Once you have all the information you need in one shared space, it’s easier to craft your customer journey or create a new user journey map.
What are the components of a customer journey map?
In Miro’s customer journey mapping tool, you have the flexibility to add as many components as you’d like. In our template, we use the following: actions, touchpoints, customer thoughts, customer feelings, process ownership, and opportunities. Each component belongs to a customer journey stage and is added to the board. Some folks also add user research data and other tools, such as empathy maps or timelines.
Can I download or share my customer journey map?
Yes, you can download your customer journey map as an image or PDF file or share your board link with others. Embed the map everywhere your teams work, like Confluence or Notion and it'll always be synced to the latest version. The customer journey map can be treated as a living document, evolving according to your product evolution and need.
Discover more
The ultimate list of templates for understanding your customers
A field guide to customer journey mapping
3 steps to go from customer interviews to a customer journey map
Service blueprint vs. journey maps
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.

Using Customer Journey Maps to Create Effective Account Plans
How do you create your account plans? Do you start from scratch every time or have a template? Are they chronological with specific points along the journey, or do they read more like a checklist of goals? Whatever the case may be, if you’re creating account plans or at least want to make yours better along the way, you’re already on the right track, but lately, we’ve found that borrowing from the marketing matrix can help you better format your account plans.
Today, we’ll take a look at how you can use your customer experience journey, map it, and integrate it into your account plans for a more precise, accurate, and predictive plan. If you do it correctly, you can better predict what your customer might do next based on the actions of preview clients and even influence them at the right time for more premium services.
Why Map the Customer Experience?
If you don’t already have journey maps in place in your organization, you might wonder what they are in the first place. In many cases, marketing departments make use of the customer journey maps because they follow them from initial contact all the way through to their purchase. For marketing efforts, it’s crucial to understand the customer journey and set checkpoints along the way so they can consistently optimize their efforts and find new ways to make the buying process easier for the customer and the selling process easier for them.
It’s no secret that key account management and marketing are two entirely separate things. While marketing is concerned with reeling in new customers, you’re more concerned with keeping your clients happy and their goals moving forward. However, just because you two are working towards different goals doesn’t mean that you can’t borrow each other’s tools to help you get there.
A Customer Journey Map will help you create more streamlined account plans that realistically reflect the steps, pain points, goals, and needs of a customer as they develop a relationship. If you can get your art of relationship building down to a science with this new, revamped account plan, you’ll have better odds of repeating that success with future clients. Let’s take a look at some of the components of a typical customer journey map and how they can relate to your key account management efforts.
Components of a Typical Customer Journey Map
In a typical Customer Journey Map, you’re going to find a few of the following components:
First, you’ll have buyer personas, which are essentially a representation of your target customers (in your case, your current customers) that includes details about their demographics, age, job title, experience, etc. Depending on your services, you might want to track different demographic metrics, and things such as job title and experience will be more important than their age.
Second, you’ll have the most important component when related to key account management, and that’s the customer stages segment. Before you can map out the entire process from pre-sale to delivery, you’ll need to figure out the various stages that your customers go through to get to your brand in the first place. With a better understanding of all of the stages along the way, you can better influence the customer’s behavior, improve your services, and provide them with more value in your account management work.
Third, in order to create an account plan based around the customer journey map, you need an in-depth appreciation and understanding of your customer’s goals and how they relate to your products and services. Key account management is all about delivering the win-win outcomes that will practically guarantee success time and time again. With this in-depth understanding, you can create a winning game plan that you can use to replicate for success organization-wide.
Fourth, you should have a clear-cut timeframe in mind for the account plan. While nothing in life ever stays on schedule 100% of the time, having at least some way to measure the time that’s passed between each step will ensure that your customer is moving through the purchase cycle smoothly and you’re delivering the right results and the right advice at the right time.
Finally, you need to leave room in your customer journey map for your customer’s emotions. Key account management might be all about business on the outside, but in reality, it’s a very emotional experience on both ends. You need to make sure that you are keeping your customers satisfied and impressing them time and time again with your products and services. With these emotions, you also need a backup plan for the times they are upset with you, and if you have worked with clients before, you know they can get pretty upset from time to time.
With all of these components, let’s consider the actual stages that your customer goes through during the journey.
The Phases from Pre-Sale to Delivery
So, to fill out your new account plan, it’s best to fill in the top line with at least a few of the important phases that your customers go through from pre-sale to delivery and beyond. Typically, it all starts with awareness, but rather than thinking in the marketing sense where your customer is first becoming aware of your company, since they already work with you, it’s more related to their awareness of new products or services that your company is offering.
After awareness, they move into the consideration and decision stage. They’ll be weighing their options and deciding whether, based on their past experience with you, the new product or service is worth the extra investment. Before your client gets to this stage, you need to have a strong argument and a record to brag about to them to showcase their wins, growth, and how you have helped their organization become better.
The final stage is conversion and retention where they will agree to add these new services or products to their subscription, and you keep them on as a client, with just more revenue coming from them every month. With this final stage complete, you can then essentially start the entire journey over again and rinse and repeat.
Using a customer experience journey map for account planning can help you become more predictive of how your customers respond, but these phases are just a high-level view of how it all works. The reality is, there are still a few blanks that you need to fill in to ensure that your key account management team is a well-oiled, smooth-running machine.
What Are Your Customers’ Pain Points?
The first set of blanks that you want to fill in with your account plans are the pain points that your customers experience along the way. Every organization will have different customers, and these customers might have wildly different pain points as well. It’s crucial that you understand not only what makes your customers happy, but what their annoyances have been in the past. Whether they have complaints about you or other service providers, with a better understanding of their pain points, you can better target them and sell more effectively.
You should consider the pain points for every phase of the buyer journey and how you can capitalize on them and help your customers overcome them throughout the process. For example, during the initial awareness stage, your customers might have found in the past that they couldn’t ever learn about how a product or service directly relates to their organization and goals. Instead, they were met with a pushy salesperson that promised anything and everything it took to get them to sign up. To overcome this, you do what you do best, and come to them as their Trusted Advisor that knows about their business, goals, challenges, and hopes for the future, and you can present your premium services as the specific solution.
Understanding these pain points of your customer will enable you to speak their language and really reach out without having to push too hard. Your job is to listen, and if your account plan is tight and holds water, you can predict when if the best time to sell to them along with objections they might have, and what they are most worried about in the process.
How Could the Process be Easier for Your Team?
While your customers’ pain points are important to understand, you also want to consider the internal pain points of your team. How could their lives be easier? Being a key account manager is a pretty stressful job, and there are a ton of moving pieces. What snags do you always hit when trying to work with your clients? For some, it might be that they don’t have enough insight into their clients, for others it could be that their technology and tools aren’t up to date, leaving them to do their job the hard way.
Consult with other members of your team and listen to determine ways that your internal processes could be improved. Specifically, you want to know the pain points associated with account plans and how they improve their relationships. Whether it means you need to invest in a new account management package with included Account Plan Templates or it means that you need to reduce the time it takes to onboard a client, track all pain points and incorporate fallback plans into your account plans.
Make Your Account Plans Actionable
Along with laying out the phases of the customer journey and what you plan to do for your customer in each one, you need to make sure that your account plan is actionable. You should be able to jump to any point and see a clear set of instructions on what to do next. As you’re writing and building out your account plans , consider what would be a good step for you to take, no matter how big or small.
For every action item, you should list who is in charge along with ideal delivery dates to keep the entire process moving forward and on time. You want to set your sights high but also keep everything in perspective, so you aren’t overpromising your clients anything and setting yourself up for failure. Make everything actionable and more like a to-do list so you can ensure that you never miss your opportunity down the line to either bolster sales or grow the relationship at the minimum.
Continually Make Improvements
Finally, it’s important to remember that your account plans aren’t written in stone. You should always look for new opportunities for improvement and update them as your clients’ needs and wants change, and as they move through the buyer journey. This proactive approach will keep things fresh and prevent you from making the same mistake again and again.
If you at any point identify an area that isn’t quite working, don’t just keep doing it over and over again with hopes you’ll have different results and fix it! With that in mind, you also don’t need to reinvent the wheel whenever you onboard a new client or one moves through the customer journey. Using Kapta, you’ll be able to reuse old account plan templates and repeat your success with every client.
How Kapta Can Help
As an all-in-one enterprise key account management platform, Kapta allows you to do more for your organization’s biggest clients. By getting your account managers out of the spreadsheets and onto the phone, you can focus more on the relationship that you develop with your top 20% of clients rather than pushing digits around. Kapta features a selection of innovative account management tools like Voice of Customer (VOC) Insights , account health score, and account plan templates so you can generate more revenue, build relationships, and achieve your customer’s goals almost automatically. See where you stand with its visualization tools and streamline your workflow with Kapta.
Schedule a free demo of Kapta and see for yourself here .

You might also like


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
With KPMG Journey Mapping, companies have the means to provide the right experiences to the right person at the right time and in the right way, helping to change customer behavior in alignment with business objectives. A unique foundation for mapping the customer experience KPMG Journey Mapping is built on design thinking—a
The Key Principles of Customer Journey Mapping Based on far-reaching customer experience research and design work across numerous industries, KPMG Nunwood has identified five key principles to making customer journey mapping a success: Customer journey mapping must be aligned to and be a central part of a business'
So that you always keep the customer in mind, experience the customer journey through the individual's eyes, not through the company's eyes. First, consider the customer journey from a broad, company-wide perspective. Then, work out selected parts of the customer journey in the required level of detail. The customer journey is also appropriate ...
KPMG CYCLE is an easy-to-use, virtual design and collaboration tool for design process management that can significantly reduce the time and effort required to develop software assets, including KPMG Journey Mapping. Built for distributed and diverse teams of business users, KPMG CYCLE supports efficient online collaboration, enabling ...
A best practice guide providing marketers with overview of customer journey mapping and a simple starting point for anyone yet to map out their customer journeys. By Michelle Goodall January 2020. Content. Customer journey mapping is an essential piece of the puzzle when it comes to understanding and improving the customer experience.
A customer journey map helps you gain a better understanding of your customers so you can spot and avoid potential concerns, make better business decisions and improve customer retention. The map ...
Write everything down and make picture and videos. Get together with your team and cluster all the things you heard and try to discover patterns. Then get some customers to help you map their customer journey to enrich your understanding. Keep doing this until you know enough to move on. That moment will come.".
Example 2: a client journey map for a corporate bank. This free template is an example of a multi-persona, B2B customer journey. The key persona is a newly opened company looking for a bank to run their business. The CJM also visualizes interactions between the personas involved. Open a full-size image in a new tab.
1. Define your purpose. The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won't know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
The customer journey map template can also help you discover areas of improvement in your product, marketing, and support processes. Download a free, editable customer journey map template. Types of Customer Journey Maps and Examples. There are 4 types of customer journey maps, each with unique benefits. Pick the one that makes the most sense ...
Customer journey vs process flow. Understanding customer perspective, behavior, attitudes, and the on-stage and off-stage is essential to successfully create a customer journey map - otherwise, all you have is a process flow. If you just write down the touchpoints where the customer is interacting with your brand, you're typically missing up to 40% of the entire customer journey.
Customer journey KPIs offer invaluable insights and guide data-driven decisions for enhancing CX. Funnelytics simplifies this process, allowing you to effortlessly collect, measure, and interpret crucial metrics. It provides real-time visualizations on a single canvas, making it easy to pinpoint areas for improvement.
Define the map's scope (15 min) Ideally, customer journey mapping focuses on the experience of a single persona in a single scenario with a single goal. Else, the journey map will be too generic, and you'll miss out on opportunities for new insights and questions. You may need to pause creating a customer journey map until you have defined your ...
How to create a customer journey map with Miro. 1. Define personas. Determine which specific customer segments or personas you want to focus on. Collect data and insights about their needs, behaviors, and preferences. 2. Identify touchpoints. 3. Add context and insights.
A Customer Journey Map will help you create more streamlined account plans that realistically reflect the steps, pain points, goals, and needs of a customer as they develop a relationship. If you can get your art of relationship building down to a science with this new, revamped account plan, you'll have better odds of repeating that success ...