How Much Do Travel Nurses Make?


Average Pay for Travel Nurses
Travel nursing pay explained, highest and lowest paying states for travel nurses.
- Highest Paying Travel Nurse Specialties
- Ways to Increase Pay
Are you ready to earn your online nursing degree?

Travel nursing offers a unique work experience with the opportunity to earn above-average hourly wages. These wages may even exceed those of other registered nurses (RNs) with the same education and credentials.
Travel nurses are typically employed by travel nursing agencies and work assignments across the country wherever nurses are needed. Because each assignment is different, the total annual income for travel nurses can vary significantly. Factors include the details of the pay package, where the assignment is located, and nursing specialty.
On this page you will find the most recent information about travel RN salaries, benefits, specialties, and the states with a high demand for travel nurses.
Fast Facts About Travel Nurses
- Travel nurses generally earn as much or more than staff nurses with the same experience and qualifications.
- Lodging reimbursement and tax advantages impact travel nursing salaries.
- The most in-demand travel nursing specialties include labor and delivery, emergency room, and medical-surgical/telemetry.
The average travel nurse salary varies greatly depending on the work assignment. Depending on travel location, these practitioners can earn between $3,000 and $7,000 per week, averaging a 36-hour work week. According to Vivian , a healthcare jobs marketplace, and the U.S. Bureau of Labor and Statistics (BLS), travel nurses earn jan average of $2,183 per week, while RNs earn a mean hourly wage of $42.80. However, aspiring travel nurses should note that living on the road leads to additional personal expenses, so the increase in pay accounts for living accommodations.
Max Weekly Pay
Average Total Weekly Pay
Source: Vivian , September 2023
Travel nurse pay differs from full-time nursing positions because agencies offer hourly rates for each assignment, meaning RNs can shop around and find opportunities with ideal pay. In contrast, RNs working full time at hospitals, physicians’ offices, and other facilities usually rely on raises or additional education to increase their earning potential.
Practitioners considering this role also need to explore what take-home pay looks like for travel nurses . Nursing agencies set their own conditions, so pay packages vary. For instance, organizations may offer an hourly base pay with additional stipends to cover housing or meals, while other companies may offer a higher hourly rate to account for additional expenses.
Travel nurse salaries vary by state and region. Locations in need of RNs typically offer more competitive wages. In fact, the popularity of a particular region can influence travel nurses’ earning potential. Less popular locations may pay more, while desirable locations may pay less. Likewise, states with a higher cost of living offer higher wages relative to living costs.
According to 2023 data from Vivian, the top-paying states for travel RNs included New Jersey , California, and Alaska. Practitioners also want to consider the highest-paying specialties to determine earning potential which may vary by state. The following section includes the top specialties in demand.
Highest Paying Travel Nurse Specialities
Typically, nursing specialties that lack licensed practitioners offer more pay than other specialties, which further increases earning potential for travel nurses. Higher acuity facilities also offer higher pay, as they need skilled practitioners who can meet their patients’ needs. Here are five in-demand specialties for travel nurses.
Labor and Delivery
Emergency room, medical-surgical/telemetry, critical care – intensive care unit, operating room registered nurse, 4 ways to increase pay as a travel nurse.
While travel nurse pay may exceed traditional full-time RN salaries, travel nurses can additionally increase their earning potential by considering factors like demand for specialties, understaffed or unpopular shifts, and locations in need of skilled RNs.
Travel nurses should examine the full benefits package to determine if jobs can provide sufficient take-home pay. For instance, regions with a high cost of living may impact how much practitioners actually earn if stipends do not cover all costs.
Frequently Asked Questions: Travel Nursing Salaries
How much does a traveling nurse make per year.
Travel nurse salaries vary significantly, especially since the outbreak of COVID-19. Factors that can influence earning potential include geographic location and specialty. However, travel RNs should anticipate working 46 weeks a year and earning about $2,183 on a weekly basis .
Do travel nurses get paid more?
Travel nurses typically earn more than full-time salaried RNs because they often take job assignments where there is a nursing shortage. Travel nurse agencies also pay practitioners by the hour and offer additional benefits, including housing and meal stipends.
Is travel nursing worth the money?
Travel nurses generally earn more than salaried RNs. However, practitioners should consider their lifestyle as well. For instance, an RN with a family may not feel the additional pay outweighs time at home, while another practitioner may find the pay suitable and enjoy the travel opportunities.
Do travel nurses get time off?
Travel nurses often do not receive time off since they work hourly and take temporary job assignments. While assignments vary, travel nurses should plan to work for 8-26 weeks at a time. Most travel nurses schedule time off between job assignments.
Learn More About Travel Nurses
Are you ready to earn your online nursing degree.
Whether you’re looking to get your pre-licensure degree or taking the next step in your career, the education you need could be more affordable than you think. Find the right nursing program for you.

AI in Healthcare: Fundamentals for Nurse Educators
Artificial intelligence in nursing education is lagging. Find out recommendations and applications for nurse educators to utilize AI in the nursing curriculum.

Nurse Practitioner Ranked Top Healthcare Job for 2024

Social Media and the Nurse Educator: How Nursing Educators Can Use Social Platforms More Effectively
How to Make the Most Money as a Travel Nurse
What is a travel nurse.
- How to Become
- Travel Nurse Salary
- Salary by State
- Travel Nurse vs Staff Nurse Salary
- Salary Factors
- Making the Most Money
- Highest Paying Assignments

A travel nurse is a registered nurse (RN) who works in short-term roles at hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities worldwide. Daily travel nurse duties are often similar to traditional RN roles, but their flexibility allows them to fill gaps in areas with nursing shortages. As a result, the average travel nurse's salary can be quite high!
>> Click here to see available high-paying travel nurse opportunities!
During the COVID-19 pandemic, travel nurses were seeing some of the highest pay packages ever because of the overwhelming need for nurses, especially in hot spots like New York, Florida, and California. While pay packages might not be as high as they were a few years ago, there is still significant money to be made for those interested in pursuing travel nursing.
But, there are still a number of factors you need to consider when it comes to your travel nurse salary. Here's what you need to know to navigate pay as a travel nurse.

How to Become a Travel Nurse
Travel nurses do need a few requirements before being considered, including being a registered nurse with a license in good standing, and typically 2 years of nursing experience. They don't need any additional certifications or credentials other than the ones they need for their specific specialty.
While a BSN is not required to become a travel nurse, it will open more opportunities to nurses such as Magnet hospitals and Level 1 trauma centers. Without a BSN, your options might be more limited.
How Much Money Do Travel Nurses Make?
Under normal circumstances, many travel nurses have the potential to earn over $3,000 per week. Travel nurses can bring in over $50 per hour, plus company-paid housing accommodations. Making it entirely possible for travel nurses to make well over $100K per year.
Travel Nurse Salary by State
Source: Ziprecruiter
>> Show Me Online Nursing Programs
How Does Travel Nurse Pay Differ From Staff Nurse Pay?
Staff nurses in a hospital are usually paid a set salary based on education and experience. They typically receive incremental pay increases at various time frames. Staff nurses can also see pay increases with overall cost of living increases.
Travel nurse pay is totally different and can be a bit of a gray area. Typical pay packages are composed of various components, including hourly pay, non-taxed travel nurse housing stipends, non-taxed per diems, travel reimbursements, and more. It’s important to speak to your recruiter about specific pay package breakdowns.
>> Related: Top 10 Six-Figure Nursing Jobs
What Factors Impact Your Pay as a Travel Nurse?
There are a number of factors that can influence how much you can expect to make as a travel nurse. These include:
Location - The specific location of the assignment most heavily influences travel nurse pay. Simply put, pay rates often reflect the cost of living in the area and also regional trends.
Which states pay the most for travel nurses? Historically speaking, the highest-paying states for travel nurses include California, Texas, Massachusetts, Washington, and New York.
Southern states tend to have lower living costs and, in turn, lower travel nurse pay.
Areas that are considered “destination locations” (like, Hawaii and Florida) may pay lower. Though, with rapid-response assignments, this isn’t always the case.
Specialty - The travel nurse’s specialty also impacts pay. Non-specialty nurses, such as the medical/surgical and psychiatric specialties, are typically paid a lower rate than specialized nurses. Furthermore, specialized nurses with highly sought-after skills and credentials have the ability to earn more lucrative pay with seemingly endless opportunities.
- Shift - If you haven’t noticed, night shift assignments are more prevalent in the world of travel nursing. The good news is that many hospitals offer higher rates for their night shift assignments. If you want to make the most money, flexibility is key. A word of caution, if the night shift is not your thing, no amount of money is worth your safety, happiness, or license. If you provide better patient care during the day shift, stick to that. Your patients will thank you.
- Practice level/Education - Travel RNs make more money than stationary RNs. But those who also pursue advanced practice nursing credentials stand to earn even more. For example, the average travel nurse practitioner's salary is around $131,543 per year but can go up to $218,000.

>> Show Me Online Nursing Programs
How To Make The Most Money As A Travel Nurse
While the factors listed above do influence travel nurse pay, the following types of assignments almost always pay exceptionally well. Oftentimes, these types of assignments are not influenced by location, specialty or shift.
Everything else aside, if you’re looking to make the most money as a travel nurse, seek out these specific assignments:
1. Rapid Response and “Crisis” Assignments
These assignments boast some of the highest rates in the travel nursing industry due to their urgent requirements. As the name suggests, these assignments require nurses to arrive at work fast -- usually within 2 weeks.
Nurses working in these assignments may have limited options in terms of location. They are also typically shorter than the general 13-week assignment - if you're ready to go, you can get started right away in areas that need you the most.
Assignments range from 36 to 48 hours per week but are certainly more lucrative for the nurse working 48, particularly given overtime pay rates.
Crisis Examples
- A crisis assignment is not always because of a natural or man-made disaster. However, in some cases they are. For example, one agency was able to send nurses within 48 hours to provide support to hospitals treating patients in the aftermath of Hurricane Harvey.
- More often, though, facilities in need of rapid response solutions include those managing unexpected census spikes, unit openings, emergency responses, EMR upgrades, and more.
- However, some facilities may leverage flexible-length assignment options to manage patient care during short-term staff shortages.
- Crisis assignments might also occur if a large number of nurses on the unit are on maternity leave at the same time, or can occur if there is an outbreak on the unit (GI illness) and the hospital needs staff immediately.
This type of assignment may be appealing to hospitals because they do not require the 13-week commitment that many other travel companies require. This means that agencies offering these types of assignments have the ability to offer travelers a larger selection of shorter and higher-paying assignments. A great option especially if you’re looking for a position to better fit your lifestyle.
So, what's the catch?
As mentioned, rapid response assignments require a quick turnaround. Therefore, it is absolutely crucial for nurses to have their paperwork in order if they want to reap the benefits of top pay. Credentials, tests, licenses, and other documents should be submitted to the agency as quickly as possible. Frequently, there are a limited number of positions available for these types of assignments and some agencies will be first-come, first-serve.
What Travel Nurse Agencies Say About Rapid-Response Assignments
We reached out to travel nursing agencies for more information about their rapid-response assignments. They said that most agencies will occasionally help nurses acquire licenses and certifications, including paying for new state licenses for nurses who complete an assignment with the company there.
Agencies also offer the option to cover housing costs if the nurse stays in one of their preferred hotels. Alternatively, many travel nursing agencies provide a housing stipend calculated to cover the cost of a nurse acquiring his or her own housing during the assignment. Lastly, they also cover the travel costs nurses incur at the start and end of an assignment.
Hospital vs Agency Bonuses
Hospital bonuses are paid separately from the bill rate, are usually offered as completion bonuses. This means they are not paid until after you complete your assignment. These bonuses usually range from $250-$5000.
Agency bonuses may be taken out of the bill rate and affect your overall pay. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing, especially if you enjoy getting a large amount of money as a lump sum.
How do you know the difference between hospital and agency bonuses? For starters, you can ask your recruiter where the bonus comes from -- hospital or agency?
- Retention Bonus
Some agencies will pay nurses bonuses once they end up working with that agency for multiple assignments. This is commonly referred to as a retention bonus and each agency will have its own requirements. These bonuses usually range from $100-$2,000 or more.
- Referral Bonus
A referral bonus is a fee the agency pays to travel nurses who refer other nurses to work for their agency. The funds often come out of a separate budget allocated to referral fees and should not affect the travel nurse’s pay package.
Referral bonuses typically range from $500-$4,000 per nurse referral. Some of the best agencies in the industry pay nurses lucrative referrals bonuses once their referral completes an assignment.
Strikes occur when a labor contract or bargaining agreement between a hospital and a union is up for renewal. When the two sides aren’t able to come up with an acceptable compromise, the union may strike.
In such a case, patients still need care. Therefore, hospitals will usually hire travel nurses to fill the temporary need. Due to the urgency, travel nurses who work strikes make much more money than they do when working on typical travel nurse assignments.
How to Find the Highest-Paying Travel Nurse Assignments
First of all, you can always ask recruiters directly about their highest-paying assignments. Let them know that money is a motivator and that you are not interested in assignments that pay less than a certain amount. The best travel nurse recruiters will be honest with you about pay while giving you their best pay packages from the beginning.
We suggest working with agencies that are known to pay high rates and who specialize in rapid-response and strike nursing. Hospitals pay these agencies higher rates to urgently provide highly specialized staff on a short-term basis. Those high rates are passed along to their travel nurses.
Top 11 Tips For Travel Nurses (From a Travel Nurse Recruiter!)
1. crisis contracts.
Crisis contracts were extremely popular during the pandemic. Travel nurses were able to garner premium pay and had the opportunity to make significant amounts in a short period of time. While these specific types of crisis contracts are not readily available, healthcare companies around the country still need to fill gaps, especially for short periods of time.
2. Find Your Own Housing
We suggest taking a housing stipend and securing your own housing. This will give you the freedom to choose your price point. Agencies will often house nurses in pricier accommodations (they have a reputation to uphold.) Additionally, agencies sign corporate leases -- leases that come with a “corporate” price tag. Some agencies are able to offer free housing if you stay in one of their preferred hotels. Most other agencies do not cover this cost outright, though, they’ll help you set it up.
3. Be Flexible
If money is your motivation, flexibility is key. Sometimes the highest paying assignments pay higher because they are not the most ideal. They may be in a less-than-desirable location or on a hard-to-fill time shift, such as nights or variables. Though it’s not always the case, nights, variables and weekends may come with higher pay or shift differentials.
4. Work With Agencies Who are Known for Their High Pay and Transparency
Every agency is different and will structure its pay packages differently as well. Transparency is key. The most trustworthy agencies will publish their compensation packages publicly and will disclose take-home pay. This focus on transparency allows nurses to skip the negotiating or fact-finding step and rapidly decide if the position is right for them.
Industry jargon and terms like “blended rates” get confusing. Negotiations can increase confusion and lead to mistrust between nurses and recruiters. That’s why working with agencies that do not allow for negotiations may prove to be the best agencies to work for. They likely give the nurse their best rate from the “get-go” and therefore actually have no room left for negotiations. If you’re able to negotiate with a recruiter, why weren’t they offering you their best rate from the beginning? Something to consider.
5. Make Sure Your Profile is Up-to-Date
Top-paying travel nursing assignments come with a timestamp -- they are in high demand and competition is fierce. Truth is, agencies can’t simply submit you for a job just because you want to be considered. They literally have to “sell” your skills to the hospital.
How do they do this? Through your paperwork, commonly referred to as your “profile” -- resume, references, skills checklists, license, etc. Having organized paperwork that can quickly (and easily) be submitted to a new agency will increase your chances of landing high-paying assignments. The quicker you get your paperwork to your recruiter, the faster they can submit you to a top-paying job.
Side note, many nurse managers hire travel nurses on a "first come, first serve" basis. Why? Because your agency has already vetted you, the hospital doesn’t need to do more research to determine if you’re qualified. The hospital needs your skills to fill a temporary staffing need. If you treat every high-paying job with extreme urgency your chances of landing the job will increase. We recommend keeping your paperwork up to date and storing it online on the cloud using something like Dropbox or Google Drive. This will make it easy to simply share your paperwork folder with your recruiter.
Another tip, if you don’t have a scanner, download a scanning app -- works like a charm and you don’t have to lug around a bulky machine. Many agencies are getting tech-savvy and developing mobile apps that allow nurses to directly upload documents to their profile with the company, where they can be stored and updated when the app notifies nurses of their expirations, etc.
6. Work With Multiple Agencies
The truth is, no agency will have assignments available in every location in the US. More truth, some hospitals pay each agency at a different rate and local agencies may have better relationships with the hospitals in their area. Bottom line, it’s a good idea to work with multiple agencies, this will increase your opportunities.
Word of advice -- if you work with multiple recruiters, don’t be shady. Be honest with them about each other. Don’t "pit" them against each other. And, by all means, keep in touch with them even if you don’t choose their assignment (this time). Chances are they’ll want to work with you again in the future. Who knows, you might even make a new friend!
7. Maintain Multiple State Licenses
Did you know that many hospitals will not even look at your professional profile if you are not licensed in their state? It’s true. You’ll increase your chances of continuously landing high-paying jobs by maintaining active licenses in multiple states.
For example, rates in northern states usually increase during the winter months -- so, a license in Massachusetts is a must! If you want to work in a certain state, you need to have a license. Period. Even better – have a compact nursing license? This will automatically set you up for success.
If you don’t have a license in that state, and you want to travel there soon, apply now! Some states have quick licensure turnaround of just 48 hours. Other states, like California, can take up to 6 months to process licensure paperwork. Some agencies do assist or reimburse for licensing fees.
8. Work Agency Per Diem and Pick Up Extra Shifts
Travel nurses who want to make even more money will often work local agencies’ per diem shifts. They’ll also volunteer to work extra shifts during their assignments.
9. Communicate With Your Recruiter
Recruiters are the connection between you and the highest-paying travel nursing assignments. It’s important to communicate with them about your compensation needs. Looking for a high-paying assignment? Ask. Need a sign-on or completion bonus? Ask. Can’t live happily with an income below a certain amount? Tell them. Remember, a closed mouth doesn’t get fed.
10. Ask for Sign-On, Completion, and Retention Bonuses
Some travel companies may offer bonuses. Bonuses are paid either on day #1 of your assignment, upon completion of the assignment, or when you work multiple assignments with your agency. Inquire about bonuses.
11. Refer Your Friends to Agencies
In the travel nursing industry, referrals are golden. Nurses are much more likely to trust their friend’s opinion of an agency they’ve actually worked for than they are an advertisement or recruiter. This is why agencies pay nurses referral bonuses to refer their friends. Referral fees differ but some agencies pay as high as $4,000 per nurse referral!

Find Nursing Programs
Travel nurse faqs, what does a travel nurse do.
- A travel nurse is employed by a temporary staffing agency to work a contract with a healthcare facility for a short amount of time, usually around 13 weeks.
What is the highest paid travel nurse?
- Any specialty area travel nurse, such as OR, ICU, MICU/SICU will have a higher earning potential. Additionally, APRNs such as a CRNA, will earn the highest wages.
Is travel nursing worth the money?
- Travel nursing can be highly profitable, but you’ll want to consider all of the factors involved with the job, such as short-term contracts, inconsistent benefits and pay, new environments, and sometimes, high stress.
What do you need to be a travel nurse?
- In addition to being a Registered Nurse, typically, you need at least one year of experience on the floor to become a travel nurse.
Is it hard to become a travel nurse?
- Travel nursing can be competitive, but if you want to become a travel nurse, there are endless opportunities. You can increase your appeal by earning certifications in specialty areas.
How much money do travel nurses make?
- The take-home pay for travel nurses can vary widely based on the area’s need, the nurse’s specialty and any certifications, and other factors, but most travel nurses make well over six figures.
Why do hospitals hire travel nurses?
- Hospitals and other healthcare facilities may hire travel nurses when they are lacking their own staff, when the patient census becomes too high for their current staffing, or when a medical crisis, like COVID-19, or an emergency occurs.

Angelina has her finger on the pulse of everything nursing. Whether it's a trending news topic, valuable resource or, heartfelt story, Angelina is an expert at producing content that nurses love to read. She specializes in warmly engaging with the nursing community and exponentially growing our social presence.

Plus, get exclusive access to discounts for nurses, stay informed on the latest nurse news, and learn how to take the next steps in your career.
By clicking “Join Now”, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org. We will not sell or distribute your email address to any third party, and you may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.


Travel Nurse Pay Breakdown | Expenses & Tax 2022
I was originally drawn to the travel nursing field for the opportunity to travel the country while getting paid at the same time. I knew travel nurses were paid fairly well and had been bombarded with various emails advertising travel nursing pay scales as high as $40 an hour.
Find available positions here!
I am typically not the type of person to do something just for the money. I tend to be more interested in the experience, but I also realize that I have bills to pay too. I didn’t really pay attention to the breakdown of my travel nursing pay, all I cared about was whether or not I had enough money to live and to get from point A to point B.
Fortunately, I had a wonderful travel experience but wish I took the time to really understand travel nursing pay scales, expenses and how to deal with taxes. Many of your recruiters don’t take the time to break these topics down for you so it is ultimately your responsibility to seek out the information and educate yourself.
Non-Taxable Travel Nurse Pay
The most alluring advertisement travel nursing agencies use to get you in the door is the infamous “tax advantage plan”. This can also be referred to as per-diem, stipends, reimbursements or a combination of all three. What this basically means is that if you are traveling away from your home for work, there are certain expenses that are tax deductible and certain reimbursements that are non-taxable.
The most common types of stipends or reimbursements that you will hear about in the travel nursing world are referred to as meals and incidentals (incidentals include taxi/bus fares, parking, and tips), lodging or housing stipends, and travel reimbursements which cover your expenses to and from each assignment; other non-taxable items can include retirement plans, license reimbursements and health insurance. When travel nursing companies advertise pay rates, they will often tell you a blended rate. A blended rate combines an hourly taxable wage such as $20 an hour with your non-taxable reimbursements and stipends to give you a higher hourly rate. Here is an example of a typical pay package:
- $20 per hour – taxable base rate that is reported to the IRS
- $250 per week for meals and incidentals – non-taxable
- $2,000 a month for lodging – non-taxable
- $500 for travel reimbursement – non-taxable
Your blended rate is calculated by breaking down your non-taxable stipends into an hourly rate and adding it to your taxable base rate. For instance, if you worked 36 hours per week on a 13 week assignment, your hourly rate would look something like this based on the above scenario:
Flex Pay and Rigid Pay
There are two different types of pay packages: flex pay and rigid pay.
Flex pay packages allow you to mix and match, add or subtract various non-taxable stipends such as healthcare, retirement, and license reimbursements to your pay package, while rigid pay packages are non-negotiable. The benefit of flex pay is that you can decrease your hourly taxable base rate and increase your non-taxable earnings by adding more benefits such as 401K. Many travel agencies have to be careful not to enter the illegal realm of wage re-characterization when dealing with flex pay packages. To learn more about wage re-characterization visit traveltax.com .
Travel Nurse Overtime
There are some travel contracts offering overtime; for example, some agencies will ask you if you want to work 4 days a week instead of 3 days a week. Overtime by law has to be paid time and a half of your taxable base rate. So, if you make $20 and hour, then your overtime pay will be $30 an hour. In the world of nursing, $30 an hour isn’t really that much extra money for an extra shift; however, over the long run it does add up. If this is something you are considering doing than make sure you negotiate a higher taxable rate for lower non-taxable stipends if possible so that you really get more bang for your buck. I have never heard of a part-time travel contract so if you are looking to work part-time than it would be better to consider an agency job in your desired destination.
Discover available travel nursing positions today!
Disadvantages of Non-taxable Stipend Pay

We also have to take into consideration retirement. I know many of you aren’t necessarily thinking about your social security check right now, but it is important to take into consideration that the social security payments are based on 35 of your highest income earning years. Non-taxable money is not considered income.
Last but not least, if you get injured on the job, you only receive 2/3 of your hourly taxable base rate. These are some scenarios to take into consideration when thinking about a travel nursing pay package.
Travel Nursing Pay: Things to Consider
With all things considered, a travel nurses pay rate, is very comparable to a staff nurse’s pay rate. However, there are some out of pocket expenses travel nurses have to be aware of that regular staff nurses don’t have to consider;
- Most travel nursing agencies do not offer paid time off. If you are thinking of taking a vacation or are taking time off in between assignments then you will not be paid
- Most travel nurses have to pay for their own certifications such as BLS and ACLS
- Sometimes travel nursing agencies will not pay for your annual physical and TB tests
- If you want to take an assignment that is across the country, your travel reimbursement might not cover the entire cost
Just like any of other profession, it is important to budget and prepare for the unknown. Take care of yourself make sure you are well organized.
What is an “IRS Tax Home”?
In order to qualify for these non-taxable stipends or reimbursements, one must maintain what the IRS calls a tax home. A tax home is your place of residence that you maintain and pay for while you are out on your travel assignment. Ideally, the IRS would like a travel nurse to take an assignment somewhere and then return to their tax home where they maintain a PRN or full-time nursing job.
Most travel nursing agencies will have you sign a form stating that you do have a tax home. If you do not have a residence that you are planning on maintaining when you are traveling, you will be referred to as an itinerant worker. As an itinerant worker, you will be required to pay taxes on all income earned including stipends and reimbursements. When applying with different travel agencies, make sure they are aware of your itinerant status. You can get more information about tax homes here .
Ready to start travel nursing? Start here!
Tips to Make Traveling a Snap
All of this talk about taxes and the IRS can be a little scary. Here are a few easy tips to follow to make your traveling experience a little less complicated:
- Maintain a mileage log. You will have to write down you odometer reading the beginning of the year on January 1 and again at the end of the year on Dec 31. If you start traveling in the middle of the year you can look back at your maintenance records for previous odometer readings. You must also document your mileage to and from your place of employment. Click here to print a mileage log.
- Return to your tax home in between assignments if possible or at a minimum of once per year. Document when you travel back to your tax home. Here is a travel log for your trips back home .
- Maintain a PRN or agency job in the same vicinity as your tax home. The IRS would like to know that you do business on a regular basis where you live.
- There is no need to keep track of meal or grocery receipts. The IRS gives you a set stipend for meals. If you exceed the stipend you are considered to be living above your means and will not be reimbursed.
- Keep a copy of all of your travel contracts. Make sure they have a beginning and ending date on them. This proves that you were really working on a temporary basis.
- Don’t work in a city more than 12 months in a 24 month period. The IRS will think you abandoned your tax home.
- There are tax people who specialize specifically in travel nursing. I recommend getting in contact with these people prior to starting your assignment. If you want to tackle this on your own then I recommend getting organized. Here is an organizer that helps you keep track of all your tax information;
Don’t let the IRS or financial aspects of travel nursing scare you. Travel nursing should be an enjoyable experience not an accounting nightmare.
As with any tax issues, you should seek advice from a licensed tax professional before filing. This article only offers suggestions and isn’t meant to be tax advice. We leave that to the pros.
Professionals can help you through this experience in combination with educating yourself about nursing pay packages. It sounds complicated in the beginning, but the more you learn the lingo, the more prepared you will be to negotiate your next travel contract.
Start your travel nursing adventure here!
You may also like

8 Best Places For Travel Nursing In The Summer

Current Nursing Compact States 2023

Travel Nurse Insurance Guide

10 Ways To Earn Rewards For Travel Nurses

Join the many nurses already traveling.
Don't miss out on your adventure..
Contract Nurse Agencies Are Making Big Money in the Age of COVID-19. Are They ‘Exploiting’ the Pandemic?

I n the 40 years that Jennie Kahn has worked as a registered nurse, the last two have been by far the most grueling.
A lot of that is due to COVID-19, which transformed health care facilities, including Thomas Health’s hospital system in Charleston, West Virginia, where Kahn works, into triage centers and forced nurses to take on an extraordinary amount of personal risk and heartache. It’s no mystery why some 18% of health care workers quit their jobs between Feb 2020 and Sept 2021, according to a Morning Consult poll.
But another reason these past two years have been so punishing, Kahn says, is that hospital nursing staffs have been subject to extraordinary churn as thousands of nurses have quit their staff positions to become contract travel nurses, where the pay is often two to four times higher. This rapid turnover has triggered a costly feedback loop: hospital administrators, facing shortages in staff nurses, spend a mint hiring contract nurses, which makes them less able or willing to increase their staff nurses’ pay. So more staff nurses quit to become contract nurses, thus further lowering nurse supply and driving demand for contract nurses. “It is a vicious cycle,” says Kahn, the hospital system’s chief nursing officer.
Meanwhile, contract nursing agencies have increased their prices. The advertised pay rate for travel nurses has surged 67% from January 2020 to January 2022, according to Prolucent Health, a workforce management tool for healthcare companies, while some staffing agencies such as AMN Healthcare, told TIME that pay rates for travel nurses at facilities they work with rose by 164% from the fourth quarter of 2019 to the fourth quarter of 2021. Some of these agencies’ profit margins top 20%.
Some hospital administrators, many of which saw their facilities’ profits shrivel during COVID, say they’ve reached a crisis point and are calling on Congress and the Biden Administration to step in. They argue that contract nursing agencies are exploiting circumstances resulting from COVID-19 to pad their own pockets. The agencies say their prices are merely a reflection of growing demand. Nurses, meanwhile, argue that hospital administrators, who are somehow finding a way to pay premium rates for contract nurses, could have avoided the mass nurse exodus by paying their staff nurses better and improving working conditions from the start, and that a fragmented nursing force with quick turnover is bad for patients’ health.
The solution is not straight-forward. Health care facilities, desperate to keep nurses on staff, may have to improve salaries and working conditions, but at many facilities, that’s easier said than done. At long-term care centers, bottom lines are dictated by Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement, and at many small and medium-sized hospitals, the cost of personal protective equipment and patient loads have fluctuated dramatically since March 2020.
“This is not anything that any health system can sustain for a long period of time,” says Kahn. “If the rates do not decrease or if travel nursing is not reduced somewhat, hospital systems are going to have to find alternative ways to provide patient care.”
An explosion of temporary staffing
Travel nurses have been around for decades and became more widespread in the 1980s, as nursing shortages grew, but it’s really the pandemic that changed the landscape of the profession. In some healthcare settings, contract nurses are now almost as prevalent as staff nurses.
Jeffrey Tieman, president and CEO of Vermont Association of Hospitals and Health Systems (VAHHS), says that prior to COVID-19, his system used travel nurses “as a stop gap”; now he says they’re “in every department of the hospital every day of the week.” The same is true of Thomas Health, Kahn says. When she first became the hospital system’s chief nursing officer in 2019, the acute care team didn’t rely on traveling nurses at all; these days, about 40% of her acute care nurses are on temporary contracts.
The financial fallout of this trend for hospitals’ and nursing homes is staggering. Due largely to the increase in contract nurses, Thomas Health is now roughly 100% over its previous staffing budget, the hospital system tells TIME. Between Fiscal Years 2020 and 2021, VAHHS’s outlay for contract nurses increased $29 million, or 35%, the group says. “As the pandemic picked up and dragged on, the need for nurses intensified when the supply of nurses diminished,” Tieman says.
Depending on contract nurses also creates logistical problems, says Deb Snell, a registered nurse and the president of the Vermont Federation of Nurses & Health Professionals. “It is difficult when you have new people coming in every 12-13 weeks, and orienting them to your floor, making sure they know where equipment is, where meds are, who to call for a problem,” she says. “It’s constant turnover.”
Struggling to fill empty roles and way over budget on staffing, VAHHS reached out to Vermont Congressman Peter Welch for help coming up with a solution, and on Jan. 24, Welch and Morgan Griffith of Virginia wrote a letter to the White House, cosigned by nearly 200 other members of Congress. The letter urges the Biden Administration to investigate the extent to which contract nursing agencies are exploiting the pandemic to drive their profits by engaging in anticompetitive activity. “We are writing because of our concerns that certain nurse-staffing agencies are taking advantage of these difficult circumstances to increase their profits at the expense of patients and the hospitals that treat them,” the letter says.
Days later, the American Hospital Association and the American Health Care Association/National Center for Assisted Living, the major nursing home trade group, threw their support behind Welch and Griffith, calling on the Administration to help prevent the travel agencies “from exploiting our organizations’ desperate need for health care personnel.”
Travel nurses, meanwhile, were incensed. On social media and message boards, they begged supporters to call their members of Congress to defend them and their pay schedules. “Wait, what? They want to cap travel nurse pay but they won’t cap CEO and executive pay? Well… I guess they know who their true masters are, and it sure as hell ain’t the voters,” wrote one Reddit user.
“It’s just because they can get away with it”
Welch says capping contract nurses’ take-home pay was never the intention of his letter. “I never have and never would propose a cap on nursing pay,” he says. “Nurses are the frontline, and they’re overworked, they’re underpaid, and they legitimately point out how the executives get fat salaries while they have to do all this work.”
Instead, he says, one big reason for the financial burden on hospitals is the fees that nurse staffing agencies charge to assign travel nurses to health care settings that need them. Proculent Health, the workforce management tool used by healthcare companies, estimates that hospitals and other healthcare facilities are billed an additional 28% to 32% above the wages the agencies pay contract nurses.
Welch argues these agencies may be exploiting the pandemic’s circumstances at the expense of hospitals, health centers, and the patients who seek care at them. “The fee that the agency charges is not related to any additional work they do, or any value added,” Welch tells TIME. “It’s just because they can get away with it.”
AMN Healthcare Services reported its gross profits were $434 million in the fourth quarter of 2021, up 109% from a year prior, according to an annual earnings report . Its net income, which takes into account all business related expenses and taxes it had to pay, was $116 million, an 1100% increase. Another healthcare staffing agency, Cross Country Healthcare, saw its revenue increase 93% between the third quarters of 2020 and 2021. It also reached $1 billion in annual revenue for the first time in the company’s history in 2021.
In recent months, private equity firms have begun acquiring contract healthcare staff agencies at a rapid clip, signaling to Welch that investors believe there is even more money to be made off the travel nurse industry in years to come—which would put hospitals under even greater strain. One of the largest healthcare staffing agencies, Medical Solutions, was purchased by two private investment firms in August. Favorite Healthcare, another large staffing group, was bought by a private equity-owned staffing firm in January.
“Three of the 10 largest staffing agencies—and probably more—were purchased by private equity right around the time that the pandemic began,” Welch says.
Staffing agencies argue that the higher prices health care facilities are paying are driven primarily by the higher wages the agencies pay nurses to meet the demand. In 2020, 75% of revenue nurse staffing agencies made went to wages and the costs of employing nurses, including payroll taxes, worker’s compensation and unemployment insurance payments, and other benefits, says Toby Malara, vice president of government relations for the American Staffing Association (ASA), a trade group for the staffing industry. He adds that most of the association’s nurse staffing agencies have seen their profits remain “relatively stable” during the pandemic.
Nurses worry about pay cuts — for good reason
Many nurses are worried that heightened government scrutiny will result in lower take-home pay for them — and that anxiety is not necessarily unfounded. Some states already cap nurse pay under certain situations, or are considering legislative action to do so. Minnesota, for example, caps contract nurses who work in nursing homes. The most that an RN can earn per hour during non-holidays is $62.36, according to documentation provided by the state’s Department of Health. Massachusetts caps pay for RNs at hospitals around $120 per hour. At nursing home facilities, the state caps an RN’s pay around $79 per hour, the state’s Executive Office of Health and Human Services says .
Other states including Kansas, Ohio, Oregon, Illinois and Pennsylvania are now considering legislation to cap nurse pay in some cases. Pennsylvania state Rep. Timothy Bonner has introduced a bill to establish maximum rates for employees of travel nursing agencies in his state that would be no higher than 150% of the average statewide pay rate for similar jobs. “[Staffing] agencies have seized on the pandemic and the critical need for workers,” he wrote in a letter to his statehouse colleagues, according to the Lewistown Sentinel , “and have raised their hourly rates to 100 percent, 200 percent or even 400 percent above the current median wage rate.”
The White House referred TIME’s questions about how regulatory action against the contract nursing industry would work to the Federal Trade Commission, which did not return a request for comment.
Many nurses say arbitrary pay caps are unfair. The problem is not high pay, they say; it is that there aren’t enough nurses to do an increasingly challenging job for relatively low wages. And while the pandemic exacerbated nurse shortages nationwide, the problem long preceded COVID-19’s added pressures. “Things were already getting tight even prior to the pandemic,” says Snell in Vermont. “Nurses have known and seen this coming for a while. We just couldn’t get people to listen.”
Part of the issue is demographics. The median age of RNs in 2020 was 52, according to a recent survey from the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, and with baby boomers retiring, more nurses will need replacing. But there’s no lack of interest. Enrollment in baccalaureate and higher-degree nursing programs increased in 2020, according to the American Association of Colleges of Nursing, and nurse practitioner graduates have swelled in recent years too. Nursing schools could be training even more graduates, experts say, but the cost of nursing school can be a barrier for students, and schools are also experiencing a shortage of nursing instructors.
But the largest factor, according to nurses unions and professional groups, is how low the pay is compared to how difficult the work environment is. “There is no nursing shortage in the United States. There is a shortage of nurses who are willing to work in these conditions,” says Michelle Mahon, a registered nurse who is assistant director of nursing practice at National Nurses United (NNU), the largest nurses union in the country. “This is something that’s been created by health care employers over a very long period of time.”
NNU has frequently criticized hospitals for adopting what it says are policies of chronic understaffing in order to help their bottom line. High patient-to-nurse ratios deteriorated patient care and put nurses at increased risk of workplace injuries and infections before COVID-19, Mahon says. Then when the pandemic swept in, hospitals that had prioritized cutting costs were unprepared.
Health care doesn’t operate like a free market
While some nurse unions have been able to demand raises from large hospital systems during the pandemic, health facilities that see primarily patients who have government health insurance are often more limited in what they can pay. Nursing homes are overwhelmingly paid by Medicaid and Medicare, so they say the rates they can pay nursing staff are largely determined by how much the government programs reimburse per patient, and hospitals in low-income areas can face similar situations.
About 70% of the costs of operating a nursing home are related to labor, according to Clif Porter, senior vice president of government relations at AHCA/NCAL. But even as facilities have had to pay two to three times normal wages to hire temporary nurses during the pandemic, their reimbursement rates have not kept pace. “I can’t pass on inflation to my customer,” he says. “This creates a situation where our expenses exceed our revenue. It’s just that simple. And that’s just not sustainable.”
Porter says that he doesn’t want maximums for what nurses can make, but floats the idea of a cap on agency profits or regulations that stipulate how much of what a staffing agency charges it must pass on to its workers.
“If the legislation were to directly impact the [agency] overhead, we don’t believe that nurses salaries would be impacted,” says Ernest Grant, president of the American Nurses Association. But the ANA does not support any effort to lower nurse wages, and Grant added that the concern over price gouging has “become quite a distraction.”
Mahon agrees, saying the idea of investigating these staffing agencies will not solve the staffing crisis. Even if the health care facilities are not happy about the rates these staffing agencies are charging, she notes, they have found the money to pay them. “If there was serious reflection and introspection and desire to solve [the nursing shortage], it would be focused inward by this industry,” Mahon says.
More nurses, better treatment
Nurses groups’ say there are other solutions that could retain and attract a larger workforce. NNU would like to see minimum staffing ratios, enhanced workplace safety measures, and increased funding for nursing education, for example. The ANA has also promoted ideas including improving nurse hours and mental health support, adjusting the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services payment methods, and removing barriers that make it difficult for nurses to practice. “We really need to address it once and for all, and not just cap it off at this particular time,” Grant says.
Desperate to retain staff, Thomas Health, where Jennie Kahn works, has increased bonus pay, instituted recruitment bonuses, expanded its tuition repayment programs and started offering its staff free meals at hospital cafeterias.
The University of Vermont Medical Center, meanwhile, just agreed to raise its nurse’s wages by 20% over two years, with 10% being implemented now and an additional 5% coming in October 2022 and an additional 5% coming in October 2023.
Though Snell says the raises are a positive step toward retaining staff, she’s not certain it is sufficient to stop the bleeding. A study released in October by the American Nurses Foundation reports 21% of nurses nationwide said they planned to resign from their jobs within the next six months. Another 29% said they were considering leaving. University of Vermont Medical Center is not immune.
“We have a lot of nurses leaving our hospital to go travel,” she says. “I’m hoping the 10% right now will be enough to maybe keep some of them in place.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- The Revolution of Yulia Navalnaya
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- What's the Deal With the Bitcoin Halving?
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Abby Vesoulis at [email protected] and Abigail Abrams at [email protected]
TravelNursing
Travel Nurse Salary: How Much Do They Make?
By Aaron Moore, MSN, RN-BC, travel nurse blogger
Money can be a huge driver for many to enter the field of travel nursing. Personally, I was more driven by the adventure of seeing new places, but I’ll admit that the money ain’t bad either!
But what can you really expect as far as a travel nurse’s salary and overall compensation?
Dispelling 4 myths about your travel nurse salary
Here are some common misconceptions and myths about the salaries of travel nurses:
“I’m gonna get rich in travel nursing.”
You can earn a lot of money, certainly! But there truly is no average travel nurse pay. Travel nursing jobs and salaries really vary. Most of my travel assignments did pay higher than most of my staff positions, especially when you include the free housing, daily allowances and reimbursements.
Your financial gains will depend on things like:
- Location of your travel nursing jobs, since salary rates vary by region
- Your nursing specialty
- Type of assignment; for instance, rapid response/critical staffing jobs often pay more
- Your flexibility regarding available assignments
- Your personal situation, such as if you travel alone, if you maintain a tax home, etc.
“This assignment pay is low; it won’t be worth it.”
Not necessarily, my friend. Many factors go into how much a travel nursing assignment pays and whether you might deem it worthwhile.
Some places pay a lower travel nurse salary, but also have a lower cost of living, so you’ll be able to live well during your assignment and possibly stash money away for the future. (Remember: free housing, reimbursements, etc.)
RELATED : Where Do RNs Earn Top Dollar ?
You may also gain important skills for future nursing jobs that will raise your earning potential.
There may be other reasons to take a lower travel nurse salary, too, such as for a dream location. For years I wanted to get a travel job in Hawaii, hoping for a crazy island adventure. I even interviewed for a few positions on the islands but thought the pay was too low. Now I wish I would have gone for it!
“This travel nursing pay is super high, it must be a horrible place to work.”
Again, this one is a myth. I’ve had several high-paying travel RN jobs and most of them were great.
Pay is often a result of demand/need, cost of living and some of the other factors mentioned above.
My best paying travel nurse job was in Southern California working night shift. Off shifts, holiday seasons and weekend jobs typically offer a differential in pay, so be aware of this when shopping for your next travel gig.
“Travel nurse contracts really limit your pay.”
Travel nurse salaries are set by contract, but there are several ways to earn more than just your hourly rate. Certain travel jobs offer sign-on bonuses, completion bonuses and extra money if you work a certain shift or days (such as every holiday during your assignment). Overtime pay is also a possibility.
How much travel nurses make is usually a combination of taxable pay and nontaxable reimbursements, as well, so be sure you understand the ins and outs.
In fact, be sure to go over all the details about pay and benefits with your recruiter before accepting any travel nursing job. There are usually specifics that need to be followed to earn bonuses and such, so I’d hate to see anyone lose out on money because you didn’t understand the fine print.
Again, there’s a lot of variation when it comes to travel nursing salaries, and factors like location, housing and career opportunity can all trump money in my book.
You’ll need to weigh all these factors for yourself.
READ MORE of Aaron’s travel nursing blogs or FIND ANSWERS to travel nursing questions with TravelNursing.com.
- Share full article

The Future of Work Issue
‘Nurses Have Finally Learned What They’re Worth’
As the coronavirus spread, demand for nurses came from every corner. Some jobs for travelers paid more than $10,000 a week. Will the boom last?
Chris Detten earned enough as a traveling nurse to make a down payment on a home in Lubbock, Texas. Credit... George Etheredge for The New York Times
Supported by
By Lauren Hilgers
- Published Feb. 15, 2022 Updated June 15, 2023
Listen to This Article
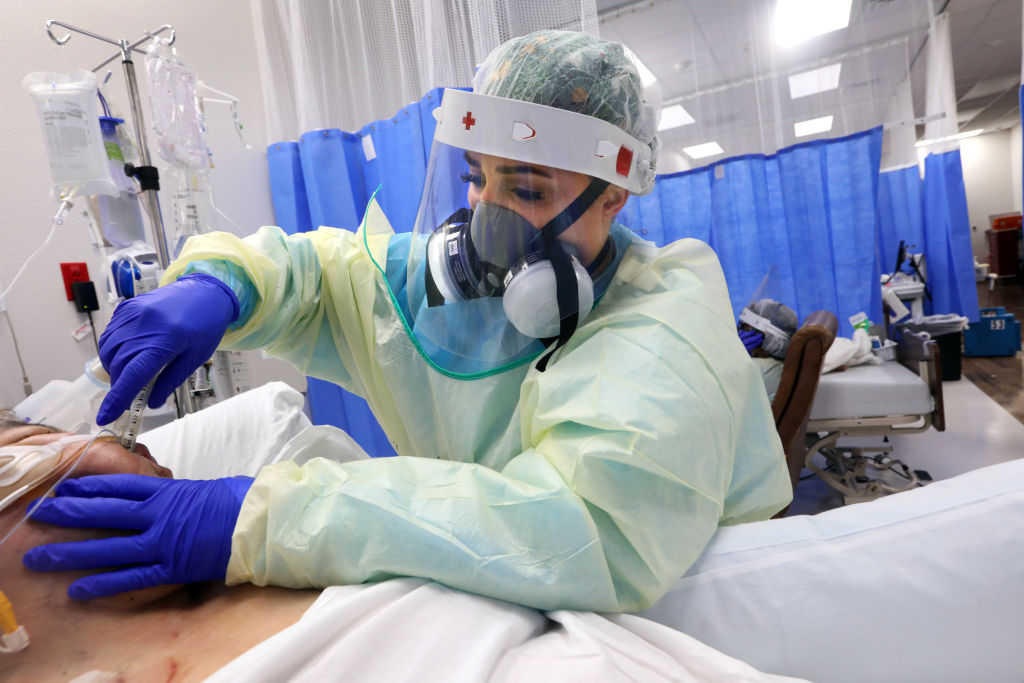
In the early morning on Mother’s Day in 2020, Solomon Barraza walked into an intensive-care unit in Amarillo, Texas, and, with the fluorescent lights clicking on above him after the night shift, flipped through the stack of papers attached to a gray clipboard — his roster of patients and nurses for the day. Barraza, who was 30 at the time, had only recently become a charge nurse at Northwest Texas Healthcare System hospital. He was technically still a “baby nurse”: Just over a year earlier, he started working his first shifts in the I.C.U. Now he was responsible for overseeing the care of everyone there, making sure his nurses and patients had whatever they needed, answering questions and directing care in case of an emergency. As he looked through his roster, he saw that there were 11 patients on his floor; eight had Covid-19, and five of those were intubated. Then he looked at the other sheet of paper. There would be four nurses working for the next 12 hours. He needed at least six.
He could see the day play out: a cascade of emergencies, a cacophony of beeping alarms and running feet, disasters that ended with overwhelmed nurses and patients crashing alone. And so for the first time, Barraza made the decision to call for “safe harbor” under a Texas law that can be invoked to protect nurses’ licenses while working in conditions that are potentially unsafe for patients. Barraza grabbed a form from the nurses’ station, and one by one, they all signed it.
Almost immediately, the emergencies began. “You need to get over to 18!” someone shouted. Barraza grabbed his mask and ran. He started hand-pumping air into the patient’s lungs with a ventilation bag while two other nurses hooked the bag up to oxygen. They stabilized that patient, and Barraza jogged down the hallways to check on the other seven. One person’s blood pressure was dropping precipitously, and Barraza was preparing to go inside the room when he thought to check on another patient, one door down. That patient’s blood-oxygen level had dropped into the 40s, far below the normal range of 95 to 100. “So what do I do?” Barraza said. “Who do I help first? There are multiple people’s lives at stake at the same time. What if I pick wrong and someone dies?”
A year and a half later, Barraza was sitting on the desk in the middle of the cardiac-intensive-care unit, or C.I.C.U. — which handles both coronary and Covid patients — looking around the group of nurses, remembering those first months of an ongoing crisis. “There were some funky things going on with staffing back then,” he told the group. Nurses were leaving the hospital to take traveling jobs in New York. The rest of the hospital was shut down, so the I.C.U. floor was the chaotic heart of a ghost town. The hospital had yet to hire traveling nurses to pad its local staff, and Mother’s Day felt like a turning point. It was the day Barraza recognized that the pandemic would be defined by twin emergencies, two figures that he would watch anxiously as they rose and fell: the waves of patients on ventilators in his I.C.U., and the number of nurses available to take care of them.
In 2020 alone, Northwest lost 185 nurses — nearly 20 percent of its nursing staff. In the I.C.U., that number was closer to 80 percent. Many of those nurses left to take jobs with travel-nursing agencies, which placed them, on a temporary and highly lucrative basis, in hospitals throughout the country. When the nurses at Northwest quit, the hospital eventually hired its own travelers, who flowed onto Barraza’s floor to work for weeks or months at a time. There have been days when the unit was barely staffed and days when 20 travelers showed up unexpectedly. Barraza has watched friends burn out and retire. He has watched nurses leave for better pay or less stressful jobs. He has welcomed the strangers who have come to take their place — befriending them, folding them into his I.C.U. team and then watching them leave all over again.
Bedside nursing has always been, as one hospital chief executive put it, a “burnout profession.” The work is hard. It is physical and emotional. And hospitals have built shortages into their business model, keeping their staffs lean and their labor costs down. When the pandemic hit, shortages only increased, pushing hospitals to the breaking point. Nationwide, the tally of nurses with both the skills and the willingness to endure the punishing routines of Covid nursing — the isolation rooms, the angry families and the unceasing drumbeat of death — is dwindling. In a survey of critical-care nurses last year, 66 percent of respondents said they were considering retirement.
Sitting on the desk that day, Barraza didn’t know why he kept reflecting on May 2020. He had stabilized those two patients that morning, but that would not always be the case. For the most part, he said, the days bleed together in his mind. Sometimes it felt as if he had spent the last two years running the world’s longest marathon, his adrenaline pushing him from patient to patient, watching people die and trying his best to pause for a moment, just enough time to recognize each as an individual without being overwhelmed by emotion.
“That was the first time we called for safe harbor,” said Matt Melvyn, a veteran nurse who has stayed with Barraza throughout the pandemic. “But it was definitely not the last.”
In the flood of resignations, retirements and shortages that have redefined workplaces across industries these past two years, nothing has been as dramatic or as consequential as the shifts taking place in nursing. The scramble for bedside nurses is tied to everything from how we run our hospitals to the way we value the work of caring for others to our understanding of public health and medicine. And if our health care system has faltered under the weight of the pandemic, it will need hundreds of thousands more nurses to build itself back up.
For at least three decades, hospitals across the United States have followed a model that aims to match nurses precisely to the number of occupied beds. It’s a guessing game that has charge nurses performing daily tallies and hospital administrators anticipating the seasonal movements of illness and people — winter flus and migrating retirees. Many hospitals don’t offer nurses clear paths toward career advancement or pay increases. Depending on demand, they may trade nurses between units. When there are shortages throughout the hospital, they will send out emails and text messages asking nurses to come in and take an extra 12-hour shift. And when the shortages are too great, hospitals turn to travelers.
Even before the pandemic, there were many reasons to hire travelers. Nurses would be brought in for a season, a maternity leave or the opening of a new department. This kind of gig work grew increasingly common, and from 2009 to 2019, according to data from Staffing Industry Analysts, revenue in the travel industry tripled, reflecting a work force that was already in flux. There are hundreds of staffing agencies in the United States — national agencies, regional agencies, agencies that specialize in bringing in nurses from other countries, agencies that send American nurses abroad. In mid-March 2020, there were over 12,000 job opportunities for traveling nurses, more than twice the number in 2019.
Then, as the coronavirus spread, demand came from every corner. By December 2020, there were more than 30,000 open positions for travelers. And with the help of federal dollars — from the CARES Act Provider-Relief Funds and the American Rescue Plan — their salaries started climbing. Job listings in Fargo, N.D., advertised positions for $8,000 a week. In New York, travelers could make $10,000 or more. The average salary of a staff nurse in Texas is about $75,000; a traveler could make that in months.
Nurses often refer to their jobs as a calling — a vocation that is not, at its core, about money. At the same time, nurses have spent years protesting their long hours and nurse-to-patient ratios. In 2018 alone, there were protests in California, Michigan, New York, Pennsylvania and several other states. When the pandemic hit and travel positions opened up in hospitals all over the country, nurses suddenly had more options than ever. They could continue serving patients, continue working grueling hours in frantic conditions, but they would be paid well for it. Travelers were valued. Their work was in demand. The money would be enough that after a few weeks or months on the job, they could go home and recover.
Hospital associations were already beginning to see the steep costs of these workers, but they had little choice in the matter. The shortages were too severe, and they would only get worse. In July 2020, Texas established a statewide emergency staffing system, coordinated by select regional advisory councils. The state has put $7 billion in relief funds toward supplementing staffing, which has allowed hospitals like Northwest to attract travel nurses without shouldering the full cost. “The problem is that their salaries were so much higher than our employee salaries,” said Brian Weis, the chief medical officer at Northwest. “Our employed nurses were doing the same job, but they’re saying, ‘Why are we getting paid a fraction of what these nurses are?’”
The following year, the demand for travel nursing broke loose from Covid. In April and May 2021, as case counts dipped, hospital requests for travel nurses only grew exponentially. “They now know what pent-up demand does to a health care system, and it’s not healthy,” said April Hansen, the group president at Aya Healthcare, one of the largest providers of travel nurses in the country. “If you look at our demand today, it looks like our demand pre-Covid in terms of specialties: med surge, telemetry, I.C.U., emergency room, surgical. It’s just the volume that is being asked for in every specialty.”
It isn’t the traveling-nurse boom alone that has transformed the market. There are also more job opportunities beyond the bedside than ever. Nurse practitioners treat patients in doctors’ offices; insurance companies employ thousands of nurses; Microsoft and Amazon have hundreds of open nursing jobs. Today, only 54 percent of the country’s registered nurses work in hospitals. “There was competition for talent before the pandemic,” Hansen said. “But the pandemic took a small crack and made it as wide as the Grand Canyon.”
To make things worse, the nursing shortage is part of a worker shortfall that spans the entire health care industry. “This is labor across the hospital,” said Rose O. Sherman, an emeritus professor of nursing at Florida Atlantic University. “This is respiratory therapy. This is lab. This is dietary, environmental services. They have not been immune to having an Amazon warehouse open up and losing a significant chunk of their staff.” If labs are backed up, patients have to wait for a diagnosis. If rooms aren’t cleaned, nurses step in to do the work themselves. Barraza has been known to empty bedpans when the housekeeper is too busy.
Even as hospitals have scrambled to hire travel nurses, many have been chafing at the rising price tag. A number of states are exploring the option to cap travel-nursing pay, and the American Hospital Association is pushing for a congressional inquiry into the pricing practices of travel-nursing agencies. Sherman, however, believes that the problem will not be solved until hospitals start considering how to make bedside jobs more desirable.
After two years, nurses have borne witness to hundreds of thousands of deaths. They have found themselves in the middle of a politicized illness and faced countless angry, grieving family members. Many, now, are moving on. They are looking for jobs outside the hospital. Others are simply uprooting themselves — leaving their homes and their families and continuing to do their jobs for a higher salary. “Nurses have finally learned what they’re worth,” Nora Shadix, one I.C.U. nurse, told me. “I don’t think they’re going to go back to the way it was before. I don’t think they’re going to settle.”

One of the nurses who has cycled through Barraza’s staff is Kulule Kenea, who was furloughed from her job as a nurse practitioner in Minneapolis in March 2020 as part of the city’s initial lockdown. She spent her early years working in I.C.U.s and trauma wards. Her uncle was a registered nurse, as was her cousin. It was something she had always wanted to do. Kenea, who is 33, liked her job. She never had that itch to travel or move. Even before starting her furlough, she got text messages from travel agencies looking for nurses willing to fly to New York. She wasn’t sure how the agencies got her number, but the offers kept coming. “I saw and heard other nurses too,” she said, “just getting mass texts out of nowhere.”
Many nurses like Kenea started traveling in the early months of the pandemic. They were nurses who had also been furloughed, nurses whose personal circumstances allowed them to travel, nurses who felt the call to help people in an emergency and nurses who were drawn by the salaries. Ivette Palomeque, who lives in Texas, traveled to Florida during her divorce. Shadix, who was working at BSA Health System in Amarillo, the hospital across the street from Northwest, decided to travel for six months starting in the summer of 2020 after her boyfriend at the time gave her the number for a staffing agency. Susie Scott, a charge nurse in Abilene, Texas, left her job in the fall of 2020, after 19 years at the same hospital; it had become so short-staffed that Scott was doing the jobs of two or three people. Traveling was an escape. “Now, what I do,” Scott told me, “I go in, I take care of my patients and that is it.”
“People were so desperate for this particular skill,” Kenea told me. “My only responsibility at home is to water my plants. I don’t have kids. I don’t have any other responsibilities. It felt wrong. It felt unfair to be able to just sit at home in the comfort of my house when other people are suffering.” Kenea took a contract to travel to New York and was on an airplane within days — there were only a handful of other people on her flight. She spent a night in a hotel, woke up the next morning and boarded a bus heading to a hospital in Harlem. She was assigned to a medical surgical unit and, on her first shift, was given 11 patients, compared with the typical four or five. It was, Kenea said, unreal. “It did not feel like America.” She worked 14 days in a row, 12-hour shifts, compared with the three-day-a-week standard before the pandemic. She did chest compressions on one patient while another was in the room, watching her, terrified.
Kenea’s father sent her text messages daily, asking her to come home and to stop risking her health. “He would send me all these statistics,” she said. “And I would be like: ‘I’m in the hospital. I know.’” A few months later, in July 2020, Kenea contracted with a traveling agency called Krucial Staffing, which specializes in emergency disaster response. She knew her assignment would be in Texas but had to call in to learn which city — the agency was working primarily with nurses who were willing to go anywhere at a moment’s notice. Kenea would have about a day to get her bearings, taking quick tours of I.C.U.s, notebook in hand. The alarms in each I.C.U. have their own sounds. The charting systems change from place to place. “You need to know the pins for certain doors and a telephone number or email for a manager or somebody who can make stuff happen for you quickly,” Kenea said. “You need to get those things down pat first within the first couple of hours: eyes wide open, ears listening sharp, constantly aware of things.”
Kenea was sent to Corpus Christi and assigned to an older part of the hospital that had been reopened to help accommodate the influx of Covid patients. Not long afterward, she was transferred to another ward, where many of the nurses were younger than she was. Kenea worked a relatively manageable five days each week, although the job was still grueling. “I am not afraid of running toward the fire,” she told me. And the staff nurses were welcoming. Some stopped to ask Kenea for advice on how to start traveling themselves.
Barraza’s unit sits on the fourth floor of a tower on the north side of Northwest. It is brightly lit and wide, and most doors have a yellow sign alerting everyone to the need for personal protective equipment. The medical intensive-care unit, or M.I.C.U., where Shadix has been working as a staff nurse after her stint as a traveler, is separated from the C.I.C.U. by a bank of elevators. There, the lights are dim, and most of the patients have been medically paralyzed so the ventilators can work without resistance. Alarms beep, and monitors are facing the glass, the oxygen levels of each patient blinking toward the hallways.
I.C.U. nursing demands a particular set of skills. Nurses here monitor life-support equipment, track patients’ reactions to medications and respond quickly in an emergency. It can be physical work — it takes multiple people, for example, to turn a patient without unhooking any equipment. I.C.U. nurses are trained to titrate several medications and drips. Good nurses can anticipate when a patient is about to crash. They’re expected to handle situations that are unpredictable and patients who are unstable. “If you don’t use those skills,” Kenea said, “you lose it.”
In December 2020, Kenea arrived in Amarillo for an assignment on Barraza’s team. By that time, the hospital had already seen waves of travelers come and go. Before the pandemic, potential travel nurses were carefully vetted by agencies for expertise and good standing. They were required to have clocked at least a year in their specialty, sometimes two or three. Kenea, for her part, had eight years of nursing experience under her belt. During the early days of the pandemic, however, with hospital staffs suffering from shortages and looking for immediate relief, many local nurses and administrators had doubts about the level of experience of some of the travelers who were landing in their I.C.U.s.
When groups of travel nurses started arriving in Amarillo, Barraza barely had time to connect with them before they disappeared. Their contracts didn’t stipulate how long they needed to stay in any particular hospital, and some would be gone within weeks. Barraza worked shifts in which he was the only member of the core staff, unsure of who had the experience to handle an emergency. “There were some travelers that came, and they were amazing,” he told me. “They were some of the best nurses I’ve worked with. But then there were the ones who shouldn’t have been there.”
If the challenge for travelers, before and during the pandemic, has been to do their job in an unfamiliar environment, the challenge for the nurses who stayed was to offer consistency amid the chaos. Barraza knew early in the pandemic that he would stay. He took on the job of keeping up morale and arrived at his shifts with the energy of a favorite aunt. He started taking in baskets of candy and snacks. He knew the moods of his nurses and which patients were feeling scared and in need of company. He knew who needed a break and who could keep going.
As time went on, the work of boosting morale became more difficult as nurses found themselves facing an unprecedented level of hostility from the outside world. A majority of Covid patients now in the I.C.U. at Northwest are unvaccinated — the region hovers below a 50 percent vaccination rate — and restaurants and malls are filled with unmasked people. Melvyn, the veteran on Barraza’s team, said that one of the most difficult parts of the job is walking outside the hospital into a world where it seems that the pandemic is already over. “You are here and it’s a war zone, and you walk outside and there’s no war,” he said. “My whole life we’ve been preparing for a pandemic, but in none of those meetings, in none of those drills, did anyone say, ‘What if there’s a pandemic, and nobody believes it’s a pandemic?’”
Families of patients now yell at staff daily, asking for unproven treatments or accusing nurses of doing harm. They oppose intubation or refuse to wear masks. Shadix still remembers the time a family blamed her for the death of their loved one. “I will always have compassion for my patients,” she said. “But I’m running out of compassion for the families.”
Nurses have compassion fatigue, fatigue fatigue and alarm fatigue, becoming desensitized to the beeps of monitors. Nurses at Northwest have nightmares about crashing patients, nightmares that they’re being intubated themselves, nightmares that wake them up doing chest compressions on their mattresses. Shadix turns on cartoons while she falls asleep to drown out the soundtrack of alarms that plays in her head. A lot of nurses are stoic, she said. They hold it in. They make jokes. “Surely the Lord is going to bless me for putting up with all of this crap,” one nurse told me.
On bad days, Barraza holds the nurses’ hands while they cry. “We have a pretty well versed nurse that has been a nurse for a long time,” he told me. “But there was a day when her patient was going to be intubated, and she was in the hallway crying, saying that this isn’t fair and she couldn’t do it. I hugged her, and I said: ‘It sucks that it is this hard, but you’re here for a reason. I am here for you, and you’re here for me, and we’re here for these people.’” He went on: “I’m still trying to keep holding on to that aspect of my personality and who I am. If I start losing that part of me, then I need to get out.”
When Shadix was traveling, she left her daughter in the care of her mother and ex-husband and struggled to leave her work at work, she said. For months she took it back to her hotel rooms and Airbnbs — the faces of the patients she lost, the feeling of doing chest compressions, the fear in people’s eyes when they came in. Now when she loses someone, she counts to 10 and allows herself to feel all her emotions. Then she takes a breath and does her best to put them aside.
But for many other travelers, the exhaustion and the hostility they regularly face is blunted by their ability to do something staff nurses can’t: leave. Kenea thinks that moving around has helped her navigate the emotional toll of the pandemic without losing hope — she has witnessed death firsthand, but in episodes, each hospital providing a change of scenery. And when she “decommissions” from an assignment, she allows herself a break before she takes a new job. She feels overwhelmed at times but never burned out. At the end of each shift, she assesses her day, and if she feels she has done everything she can, she lets go of it as soon as she leaves the parking lot.
Then, of course, there’s the pay. Kenea has made enough money to help cover the tuition to become a nurse anesthetist. Shadix’s six-month stint as a traveler allowed her to put a down payment on a house. Chris Detten, a traveler at Northwest, was also able to afford a down payment. Adrian Chavira, Detten’s friend and another traveler at Northwest, said the money has made it possible for his partner to stay at home with their new baby. “Money is a very good motivator,” Detten said. There’s a sense that all the hard work is being rewarded. “You don’t have to worry about the politics of the hospital you’re in.” The power plays, the interoffice dramas, the personalities you can’t escape — the travelers are insulated from it all.
“I appreciate that they’re here,” said Karen Hammett, a longtime charge nurse at Northwest. “Am I a little salty that they’re making more than me? Yes.” Hammett was a veteran of the hospital. She had made it through every wave of the pandemic. But last year was her hardest. “It’s having to deal with the secondary stuff that gets to me — the hate is what sucks. And it’s the worst it’s ever been.” She had her last shift at Northwest on Nov. 21. After nearly 20 years at the hospital, she quit.
As I.C.U. beds in city hospitals filled up and staff nurses started leaving in droves, another story of a precariously overextended health care system was unfolding in smaller hospitals across the country. Rural hospitals, which have long sent their most acute cases to larger hospitals, were left with patients they were ill equipped to handle. Many of these hospitals, with lower profits and wages, struggled to retain nurses and compete with the enormous salaries offered by travel agencies. With no padding, entire departments shut down. Only 40 percent of rural hospitals in Texas offer labor-and-delivery services, and with staffing shortages, many deliver babies only a few days a week. There are 71 counties in the state with no hospitals at all. Across the country, 22 rural hospitals have shuttered in the past two years. According to one 2020 study, 453 more are in danger of closing.
Hereford Regional Medical Center is roughly 50 miles southwest of Amarillo. Shortly before Christmas, hospital officials there declared an internal state of disaster — all the travelers had gone home for the holidays, leaving the remaining staff and administrators struggling to keep the doors open. Administrative staff took shifts over Christmas and New Year’s to avoid a complete shutdown. Nursing teachers from Amarillo drove in to help bridge the gap between the departing and arriving traveling nurses. The hospital had stopped performing surgeries and was sending its labor-and-delivery patients to other hospitals. It could no longer take referrals — serving only the people who showed up in the emergency room — and none of the larger hospitals nearby were able to take its acute cases.
Other rural hospitals are reeling from similar shortages. In Missouri, one rural hospital was unable to transfer a patient with acute pneumonia after contacting 19 different hospitals. A nurse saved the woman’s life by staying up all night, loosening the mucus in the patient’s lungs with a hand-held massager. Rural hospitals in New Mexico have reported calling 40 or 50 hospitals in order to find a bed for acute patients. Candice Smith, the chief nursing officer at Hereford Regional, said: “We need staff, we need supplies, we need medicines. We have spent multiple hours on the phone to try to get patients out of here. If they’ve had a stroke or a heart attack or a traumatic brain injury, we’ve been getting them to Dallas or Oklahoma.” Smith sent a request to its regional advisory council asking for more travelers, but she was unsure of when, or whether, they might show up. “As a rural hospital, we can’t pay for them forever,” she told me. “It will cripple the health care industry.”
“There has been an evolution in the travelers,” Smith continued. “Now they don’t come here or to any facility and say: ‘What can I do? I’m willing to work any day you tell me to.’ Now they say: ‘I’m only going to work Sunday, Monday, Tuesday. I’m going to take off for Christmas.’” When I asked Smith if there was anything else she wanted to share, she said simply, “Just tell people to pray for us.”
In light of the grim staffing numbers, both city and rural hospitals have tried to focus on retention efforts, in some cases mirroring the benefits of the travel-nursing industry. Northwest now offers higher overtime rates for nurses who take extra shifts, and BSA started offering better pay overall. In Florida, hospitals are hiring recent nursing graduates and placing them in nursing teams with more experienced personnel. UAMS Medical Center at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences is offering a signing bonus of $25,000 to qualified nurses willing to stay for three years. At Parkland Health and Hospital System in Dallas, doctors have been helping ease the burden on nurses by performing some of their duties.
Ronda Crow is the chief nursing officer at Moore County Hospital District, a nonprofit that serves Dumas, Texas, and the surrounding rural areas. She has spent nearly 10 years working on hiring and retaining nurses, including implementing scholarship programs to help local students through nursing school. Everyone was paid a full salary throughout the pandemic whether they were scheduled to work or not — an incentive, Crow hoped, to stay. “We’re lucky here in Dumas,” she told me. The hospital has the backing of a foundation that helps with funding. During the pandemic, Crow has managed to increase her staff and now has the ability to open every bed in the hospital. “By staffing up, it gives me the opportunity to grow nurse leaders,” Crow said. “Is it an expensive gamble? Yes. Will it pay off in the end? Yes.”
Other rural hospitals, however, will continue to struggle. Without state support, many can’t afford to pay the higher wages that nurses are commanding. Fewer patients are insured, and many are older, their illnesses more severe. And experienced nurses are continuing to leave for other, lower-stress jobs. There are around 153,000 new nurses being licensed every year, but based on projected demand, it will not be enough.
For Barraza, each new spike in Covid patients seems to happen overnight. He may know a surge is coming. He may worry about families gathering for the holidays, but the influx always feels sudden. In the fall, Covid cases in Amarillo dropped, and the hospital was assigned fewer state-subsidized nurses. But the moment the travelers started to leave, a wave of new Covid cases began to fill the hospital’s beds. Northwest scrambled to bring in travelers again. Then the Omicron variant arrived. The hospital’s exhausted nurses went into overdrive. In late December, Shadix texted me a GIF of an exploding house.
“It’s bad,” she said. “But it’s fine. We’re fine.” There were new nurses in the medical intensive-care unit, people who had just graduated, and Shadix was watching them flounder. “It’s a sink-or-swim situation,” she said. “And you learn to swim really quickly, because otherwise, people die.” She had taken on many of the hard conversations with families — telling them that their loved ones would probably not make it. “They started calling me the hospice queen,” she said grimly. Families were allowed to enter the I.C.U.s, and Shadix let them, hoping that once they saw how bad things were — how low the quality of life was for their family members — they would start to let them go. Early in the pandemic, Shadix told me, nurses in the M.I.C.U. tried to stay positive, to offer family members a ray of hope until the end. Now they are more realistic. They need to set expectations.
By January, Northwest had made appeals to the regional advisory council and FEMA for more nurses. Covid patients were filling up the emergency room and surgical floor. At one point, Brian Weis, the chief medical officer, knew of 43 patients in rural hospitals waiting for a transfer. Around 75 staff members at Northwest were in quarantine. While travel and military nurses began arriving, core staff continued leaving. Dellani Spradling, a charge nurse in the M.I.C.U. who never anticipated leaving, abruptly resigned in early February. Another Northwest nurse took a traveling job that moved him to the hospital across the street.
Shadix hopes to be a traveler again. She loves the physicians she works with at Northwest — she knows what labs they need and what questions they’re going to ask. But staying doesn’t make sense. “Here you are, killing yourself for five days making pennies,” she said, “versus working four days or three days making three times what you’re making right now.” Once Shadix goes, some of the longest-serving nurses in the M.I.C.U. will be travelers.
Many nurses are hoping to move on from the I.C.U. entirely. Kenea is starting the nurse-anesthetist program in May. Shadix is taking classes toward her nurse practitioner’s license. “Maybe once this is all over and done with, I’ll come back to the I.C.U. and take my normal patients,” she told me. “But if I never have to see another N95 mask in my life, I will not be sad.”
Barraza is hanging on for now, providing as much continuity as he can. In December, he was working six days a week. The C.I.C.U. was so full of Covid patients that it couldn’t take transfers from the emergency room. “We have beds; we just don’t have the ability to staff them,” he told me. “If we do bring them in, we just overwhelm people even more and possibly push them out the door.”
Barraza has begun taking patients himself in addition to overseeing all the nurses in his unit. He tries to take his candy cart down to the nurses in the emergency room now — he knows they are tired, too. Emergency-department doctors are in such huge demand in smaller hospitals that Weis recalled at least one at Northwest who was contacted and told to name his price.
As the new year started, however, even Barraza was beginning to fray at the edges. He has been having trouble falling asleep. He passes out on his couch most nights. “I lay there, and I see the people that I saw all day and the people that I saw before. I try to keep myself centered and not dwell on it too long, because it puts me in a low place.” He thinks, instead, of his staff. He thinks of the nurses who have made it out. He thinks of a patient who recently recovered. He tries to relax, but sometimes his body won’t let him forget.
Lately, as he tries to fall asleep, he has been feeling the phantom pressure of a hand in his — the feeling of a patient about to be intubated, another frightened person on the edge of life and death. “You get all these sensations and feelings,” he told me. “Feeling them grasp you, and feeling their grasp letting go when the medication hits them.”
Lauren Hilgers is a writer based in New York. She is the author of “Patriot Number One: A Chinese Rebel Comes to America.” George Etheredge is a New York City based photographer raised in North Carolina. He was recognized as one of “The 30: New and Emerging Photographers to Watch in 2020.”
Explore The New York Times Magazine
A Playwright Reimagines America: In her new play, “Sally & Tom,” Suzan-Lori Parks brings exuberant provocation to the gravest historical questions.
The New Mood Music: The Texan trio Khruangbin’s vibes have spawned countless imitators, but their magic isn’t so easy to replicate.
Inside a Media-Fighting Law Firm: Tensions had been brewing for years inside Clare Locke, a top defamation law firm. Then came the biggest defamation case of them all : a case against Fox News.
Is Corporate America in Denial?: Despite Donald Trump’s populist promises , many bigwigs are keeping the faith that it couldn’t really happen here.
Larry David’s Rule Book: He’s a wild, monomaniacal jerk . He’s also our greatest interpreter of American manners since Emily Post.
Inside The National Enquirer : An ex-editor at the tabloid reveals the story of the notorious “catch and kill” campaign that now stands at the heart of Donald Trump’s’s legal trial.
Advertisement
Travel nurses' gold rush is over. Now, some are joining other nurses in leaving the profession altogether.

Working as a travel nurse in the early days of the Covid pandemic was emotionally exhausting for Reese Brown — she was forced to leave her young daughter with her family as she moved from one gig to the next, and she watched too many of her intensive care patients die.
“It was a lot of loneliness,” Brown, 30, said. “I’m a single mom, I just wanted to have my daughter, her hugs, and see her face and not just through FaceTime.”
But the money was too good to say no. In July 2020, she had started earning $5,000 or more a week, almost triple her pre-pandemic pay. That was the year the money was so enticing that thousands of hospital staffers quit their jobs and hit the road as travel nurses as the pandemic raged.

Two years later, the gold rush is over. Brown is home in Louisiana with her daughter and turning down work. The highest paid travel gigs she’s offered are $2,200 weekly, a rate that would have thrilled her pre-pandemic. But after two "traumatic" years of tending to Covid patients, she said, it doesn’t feel worth it.
“I think it’s disgusting because we went from being praised to literally, two years later, our rates dropped,” she said. “People are still sick, and people are still dying.”
The drop in pay doesn’t mean, however, that travel nurses are going to head back to staff jobs. The short-lived travel nurse boom was a temporary fix for a long-term decline in the profession that predates the pandemic. According to a report from McKinsey & Co., the United States may see a shortage of up to 450,000 registered nurses within three years barring aggressive action by health care providers and the government to recruit new people. Nurses are quitting, and hospitals are struggling to field enough staff to cover shifts.
Nine nurses around the country, including Brown, told NBC News they are considering alternate career paths, studying for advanced degrees or exiting the profession altogether.
“We’re burned out, tired nurses working for $2,200 a week,” Brown said. People are leaving the field, she said, “because there’s no point in staying in nursing if we’re expendable.”
$124.96 an hour
Travel nursing seems to have started as a profession, industry experts say, in the late 1970s in New Orleans, where hospitals needed to add temporary staff to care for sick tourists during Mardi Gras. In the 1980s and the 1990s, travel nurses were often covering for staff nurses who were on maternity leave, meaning that 13-week contracts become common.
By 2000, over a hundred agencies provided travel contracts, a number that quadrupled by the end of the decade. It had become a lucrative business for the agencies, given the generous commissions that hospitals pay them. A fee of 40 percent on top of the nurse’s contracted salary is not unheard of, according to a spokesperson for the American Health Care Association , which represents long-term care providers.
Just before the pandemic, in January 2020, there were about 50,000 travel nurses in the U.S., or about 1.5 percent of the nation's registered nurses, according to Timothy Landhuis, vice president of research at Staffing Industry Analysts, an industry research firm. That pool doubled in size to at least 100,000 as Covid spread, and he says the actual number at the peak of the pandemic may have far exceeded that estimate.
By 2021, travel nurses were earning an average of $124.96 an hour, according to the research firm — three times the hourly rate of staff nurses, according to federal statistics.
That year, according to the 2022 National Health Care Retention & RN Staffing Report from Nursing Solutions Inc., a nurse recruiting firm, the travel pay available to registered nurses contributed to 2.47% of them leaving hospital staff jobs.
But then, as the rate of deaths and hospitalizations from Covid waned, the demand for travel nurses fell hard, according to industry statistics, as did the pay.
Demand dropped 42 percent from January to July this year, according to Aya Healthcare, one of the largest staffing firms in the country.
That doesn’t mean the travel nurses are going back to staff jobs.
Brown said she’s now thinking about leaving the nursing field altogether and has started her own business. Natalie Smith of Michigan, who became a travel nurse during the pandemic, says she intends to pursue an advanced degree in nursing but possibly outside of bedside nursing.
Pamela Esmond of northern Illinois, who also became a travel nurse during the pandemic, said she’ll keep working as a travel nurse, but only because she needs the money to retire by 65. She’s now 59.

“The reality is they don’t pay staff nurses enough, and if they would pay staff nurses enough, we wouldn’t have this problem,” she said. “I would love to go back to staff nursing, but on my staff job, I would never be able to retire.”
The coronavirus exacerbated issues that were already driving health care workers out of their professions, Landhuis said. “A nursing shortage was on the horizon before the pandemic,” he said.
According to this year’s Nursing Solutions staffing report, nurses are exiting the bedside at “an alarming rate” because of rising patient ratios, and their own fatigue and burnout. The average hospital has turned over 100.5% of its workforce in the past five years, according to the report, and the annual turnover rate has now hit 25.9%, exceeding every previous survey.
There are now more than 203,000 open registered nurse positions nationwide, more than twice the number just before the pandemic in January 2020, according to Aya Healthcare.
An obvious short-term solution would be to keep using travel nurses. Even with salaries falling, however, the cost of hiring them is punishing.
LaNelle Weems, executive director of Mississippi Hospital Association’s Center for Quality and Workforce, said hospitals can’t keep spending like they did during the peak of the pandemic.
“Hospitals cannot sustain paying these exorbitant labor costs,” Weems said. “One nuance that I want to make sure you understand is that what a travel agency charges the hospitals is not what is paid to the nurse.”
Ultimately, it’s the patients who will suffer from the shortage of nurses, whether they are staff or gig workers.
“Each patient added to a hospital nurse’s workload is associated with a 7%-12% increase in hospital mortality,” said Linda Aiken, founding director of the University of Pennsylvania’s Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research.
Nurses across the country told NBC News that they chose the profession because they cared about patient safety and wanted to be at the bedside in the first line of care.
“People say it’s burnout but it’s not,” Esmond said about why nurses are quitting. “It’s the moral injury of watching patients not being taken care of on a day-to-day basis. You just can’t take it anymore.”
Jean Lee is an associate reporter with NBC News’ Social Newsgathering team in Los Angeles. She previously reported for the NBC News consumer investigative unit.
13 Pros and Cons of Being a Travel Nurse

So, if you have found yourself here, then you must be considering a career as a travel nurse. For starters, having a job as a travel nurse will enable you to see the country and all that it has to offer. This may sound like a dream to some people, but as with any job, you will find pros and cons, and travel nursing is no different. Mapping out the pros and cons of being a travel nurse can be a tedious endeavor, but rest assured I am here to help you out with that feat. If you keep reading below, you will find the top 13 pros and cons of being a travel nurse. This article will surely help you decide if this is the right career choice for you.
TOP CONS OF BEING A TRAVEL NURSE
1. you will always find yourself in an unfamiliar environment., 2. you will always be the new guy., 3. varying pay rates, 4. what do you do when your contract has ended, 5. not the best work assignments, 6. license issues, 7. floating, 8. your contract can be canceled., 9. you may not have your dream schedule., 10. you may become homesick., 11. where are you going to live, 12. your taxes could be a nightmare., 13. you may not have paid time off., top pros of being a travel nurse, 1. great pay., 2. you will have a tax-free living stipend., 3. you get the chance to travel., 4. you will make new friends., 5. you can avoid all the politics at work., 6. you will gain experience., 7. flexibility, 8. you can try before you dive all in., 9. travel nursing can be a networking event., 10. you can choose your adventure., 11. you will learn life skills., 12. job security, 13. reimbursement, the bottomline.


What Travel Nurses Should Know About Paid Time Off and Vacation Benefits

Paid Time Off (PTO) and Paid Vacation Time are tricky issues when it comes to travel nursing pay packages. Some travel nursing agencies offer such benefits while others don’t. However, just as with all benefits offered as part of a travel nursing pay package, the fact that an agency offers the benefit doesn’t necessarily make their pay packages better. Moreover, there are issues unique to travel healthcare that all travelers should consider when evaluating these benefits.
Does Paid Time Off Come out of the Travel Nurse’s Rate?
As we regularly mention on this blog, nothing is free when it comes to travel nursing pay. This is because an agency has one source of revenue, the rate that they’re able to bill for the travelers’ time at the hospital. This is why you commonly hear people say, “everything comes out of the rate.”
Now, you will find many recruiters defend their “free benefits” and make it sound as though the cost of these benefits are not coming out of the rate. These recruiters aren’t lying. They just have a different understanding of the issue; one that travelers should not make the mistake of relying on.
Find your next travel healthcare job on BluePipes!
For example, during a discussion on this topic in a popular travel nursing forum, one recruiter had this to say about his company’s PTO policy:
I placed two nurses at the same hospital, same bill rate different units, last October. They had the exact same pay package as each other. One took a perm position after the assignment, and the other has been with me for over a year and has earned 40 hours of PTO. I paid each of them the maximum amount that I could. I can account/budget for things such as per-diem, housing, travel, etc. But I cannot individually budget for PTO as I will never know who will work one assignment for me and who will be with me for years.
The recruiter is arguing that the PTO benefit his agency offers does not come out of the rate. On the surface, this explanation seems plausible. However, it misses two key points for travelers intent on properly evaluating and comparing pay packages .
First, note how the recruiter says, “I paid each of them the maximum amount that I could.” How does he determine the “maximum amount” that he can pay? The maximum amount is most likely based on a minimum profit margin that his agency has determined they are willing to accept. They decide the minimum profit margin by analyzing their costs. PTO is a cost so it’s part of the analysis. For all intents and purposes, the agency could just as easily lower the minimum profit margin they are willing to accept and do away with their PTO benefit.
Of course, this particular recruiter’s response is, “I cannot individually budget for PTO as I will never know who will work one assignment for me and who will be with me for years.” However, the fact of the matter is that no business knows how long it’s employees will stay with them, yet all businesses budget for their PTO expenses. The recruiter may not budget for it when determining the pay rate, but rest assured it’s being budgeted for. Agencies track the results of their benefits and rely on historical data to budget. In fact, the agency’s top management most likely knows exactly how many hours of PTO get accumulated per hour worked and they most certainly consider this cost when determining how to set their maximum pay rates.
Second, notice that this recruiter is comparing two different travel nurses to prove his point. The problem is that they’re both with the same company. Therefore, this comparison only holds true for his company. Again, if you were to compare his pay rate with another company’s pay rate for the same exact assignment, you may find that the other company pays more, but does not offer the PTO benefit. Of course, you may also find that the agency with the PTO benefit pays more. This is why we always say it’s so important to compare travel healthcare compensation packages in their entirety .
Now, you maybe wondering if it’s really that important to go through the hassle of scrutinizing pay packages if all we’re talking about is a few days of PTO per year. However, each day of PTO is worth anywhere from $450 to $600 depending on the rate it’s paid at. So three days of PTO per year is worth $1,350 to $1,800. We think that amount is worth the brief amount of time it will take to investigate pay packages.
Moreover, that’s just the value of the PTO benefit. There may be many similar benefits that an agency offers in addition to a PTO benefit, all of which could potentially be lowering the agency’s pay rates in lieu of providing the benefit. Therefore, if you really want these benefits, you need to make sure that you will indeed qualify to receive them.Because if you don’t receive the benefit, then you’re essentially leaving money on the table and in the agency’s pocket.
In order to accomplish this, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the issues at play with travel nursing PTO and Vacation benefits. First, it’s important to understand the difference between PTO and paid Vacation. Second, it’s important to understand the unique circumstances that travel companies are faced with when it comes to Vacation and PTO. Third, it’s important to understand the specifics of the PTO policies for any agency you’re considering working with. Finally, it’s good to know the potential motivations driving agencies to offer PTO or paid Vacation time.
Paid Vacation VS PTO
In the permanent employment market, the distinction between paid vacation time and PTO is distinct. The traditional approach is for companies to offer both paid sick leave and paid vacation days. Many companies still do this and the policies vary from company to company. In general, an employee builds up paid sick days and paid vacation on a per hour basis. In some companies, the time can build up over the years but may be capped at a specified number of hours for each category. At other companies employees may lose their time if they don’t use it by a certain date. The main idea is that you’re only supposed to use sick days when you’re sick and vacation days when you’re taking a vacation.
The original Universal Job Application and Credential Management for travelers.
In recent years, many companies decided that they wanted to give their employees more flexibility, so they lumped paid sick days with paid vacation and called it Paid Time Off. One of the main factors driving this policy was that employers wanted to reward employees who didn’t use their sick days with the ability to have extra vacation days.
This is an important distinction, especially when it comes to travel healthcare. You see, an employee should be able to use PTO whenever they want. If you’re sick, then you’re sick and you should be able to call off from work and get paid for the time. When it comes to extended vacation, the employer may still want employees to schedule the time off, but the employer is expected to be flexible with their approvals. Otherwise, the employee could just call in sick and not be violating any policies.
Unique Circumstances for Travel Nursing Companies and PTO / Vacation
Why is this important in travel healthcare? In travel healthcare, the agency is just as much a middle-man as they are an employer. It’s true that for all intents and purposes, the traveler is the employee of the agency. However, the hospital expects the traveler to be there for all scheduled shifts. In theory, the hospital is in dire need of the healthcare professional. They would not have them there otherwise. So even sick days are frowned upon. And the hospital definitely expects to have the final say on approving any vacation time. In fact, this typically happens prior to the traveler being offered an assignment.
So as long as a hospital is given final say approving vacation time, they shouldn’t really have a problem with an agency offering paid vacation because the hospital could always deny the request. However, hospitals may not like it very much if the agencies they work with offer paid sick leave. They may view it as incentivizing their supplemental staff to call off shifts. Sad, but true.
Another unique circumstance that both agencies and travelers are faced with is the inherently short-term nature of employment engagements in travel healthcare. The standard contract is for 13 weeks. Many travel healthcare professionals want to travel and work in different parts of the country. That’s one of the main appeals of travel nursing as a career choice. The problem for most agencies is that they may not have contracts available in the locations that their travelers want to go next. This is one of the many reasons that travelers tend to work with multiple agencies.
The problem for travelers is that short-term stints hinder the ability to accumulate meaningful PTO or Vacation benefits. This is because PTO and Paid vacation benefits typically accumulate over time.
Another unique circumstance is that travelers routinely leave an agency only to return at some point in the future. Often, this happens sooner than later. For example a travel nurse may leave an agency for a contract and then return once that contract is complete. This type of intermittent employment is quite rare in the permanent employment market.
Finally, travelers tend to receive compensation packages that vary greatly from assignment to assignment. For example, the total value of compensation packages can vary based on the bill rates for the assignments in question. Or, the traveler may take company housing on one assignment and provide their own housing on another assignment. This is much different than permanent pay packages that remain relatively stable over time. Of course, the value of your paid time off is typically based on your pay rate.
Know the The Travel Nursing Company’s PTO/Vacation Policy
As a result of these unique circumstances, agencies have developed unique policies for their PTO and paid vacation benefits. Therefore, travel nurses shouldn’t assume that these benefits are going to behave the same as those provided by permanent employers.
One big difference between travel and permanent vacation and PTO benefits is that there is a blurring of the lines between PTO and Vacation in travel healthcare. You see many agencies advertise PTO but when you dive into the details of their policy, you find that it’s pretty much vacation time and not PTO. Why? Because many agencies won’t pay for sick days. As mentioned above, sick days are supposed to part of PTO. You’ll also find many agencies that only allow the PTO to be used in between assignments. Both of these policies are designed to ensure that travelers don’t miss time while on assignment.
Many agencies will not pay out for unused PTO if a traveler leaves the company. However, many agencies that employ this policy will bank the PTO so it can be used if the traveler returns to the agency for another contract.
Agencies will also utilize expiration policies that are much more strict than their permanent counterparts. For example, they may expire all accrued hours on an annual basis which effectively means that all travelers start the new year with zero accumulated hours.
Some agencies will offer PTO for doing things other than working. The most common example is to give PTO for referring travelers to the agency. Typically, the PTO is paid when the referral completes a contract and is offered in addition to the agency’s standard referral bonus.
There are some agencies that have developed entirely unique vacation programs. For example, we’ve seen agencies that award points for various actions including hours worked over the course of year. The points are given a monetary value that can be applied to the agency’s annual trip to some exotic destination. If a traveler doesn’t accumulate enough points to pay for the entire cost of the trip, then they can pay the difference and take the trip anyway.
Free eBook: How To Negotiate Travel Nursing Pay
It’s also important to note that different agencies value their PTO in different ways. For example, an agency may value your PTO based on the total blended rate for the contract you’re working at the time you use the PTO. Others may value the PTO at only the taxable base rate for the contract you’re working.
Finally, agencies maintain policies that allow them to cancel PTO hours at their own discretion. We have a difficult time speculating on the circumstances that would lead an agency to take such an action, but the policies exist nonetheless.
What Motivates Agencies to Offer PTO and Vacation Benefits?
With that in mind, there are several motivating factors driving agencies to offer these benefits and utilize these polices. First, agencies are looking to retain travelers. Retention is a major cost cutting factor for agencies. It’s quite expensive to recruit new candidates when all the manpower and advertising costs are considered. The fact that it’s so easy for travelers to jump ship to a new agency is one of the reasons that many agencies don’t pay out their PTO benefits in cash when a traveler leaves the company.
Second, agencies are looking to attract travelers with these incentives. This is why you’ll find coordinated vacations masquerading as Vacation time. These agencies are appealing to travelers’ sense of adventure.
Finally, many agencies are motivated to provide these incentives for the simple fact that their competitors offer them as well. You see, it’s more difficult to explain why you don’t offer an incentive, than it is to explain why you do offer an incentive. This is particularly true when it comes to working with new travel healthcare candidates. Seasoned pros tend to understand the travel compensation game quite a bit better and have an easier time evaluating pay packages and understanding the nuances.
Newcomers on the other hand are understandably perplexed by the compensation packages. And because a significant percentage of travelers engage in travel healthcare for a short period of time, there are a lot of newcomers. So agencies must design their programs to be newcomer friendly.
Create your free Travel Healthcare Resume on BluePipes!
In any case, the most important thing to remember is that you must evaluate compensation packages in their entirety in order to determine how competitive an offer is. Be sure to scrutinize PTO and Vacation policies to make sure you’ll even qualify to receive the benefits. In the end, you may find that you’re simply taking less money now in order to have a chance at obtaining a future PTO benefit. As a result, you’ll run the risk of not receiving the money at all.
As always, we’d love hear your questions, comments and experiences with this topic. Please post in the comments section below!

Related posts:
- Travel Nursing Pay – The Company’s Perspective: Part 1 Perhaps the most complex and least understood aspect of travel...
- Travel Nursing Pay – Qualifying for Tax-Free Stipends and Tax Deductions: Part 2: Maintaining Temporary Status In our previous blog post we laid out the criteria under...
- 4 Ways That Time Impacts Travel Nursing Pay Travel nursing pay packages are complex. There are many more...
PTO doesn’t sound like a great incentive but why don’t agencies give loyalty pay as they need to less with us than a new hire?
Comments are closed.
Popular on bluepipes blog.
Discover Jobs
- Travel Nursing Jobs
- Travel Therapy and Tech Jobs
© Copyright 2012-2022 BluePipes, Inc


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Been a nurse for 9 years traveling on and off for 5 years. Current contract is $1247/shift. Which is above average. I can work 7 days a week if I want and make whatever that is. Or 3 and still make 3k/week or easily 130k+/year. Go to 4 or 5 days/week and you are looking at real good money (if you work 52weeks/year).
Depending on travel location, these practitioners can earn between $3,000 and $7,000 per week, averaging a 36-hour work week. According to Vivian, a healthcare jobs marketplace, and the U.S. Bureau of Labor and Statistics (BLS), travel nurses earn jan average of $2,183 per week, while RNs earn a mean hourly wage of $42.80.
Under normal circumstances, many travel nurses have the potential to earn over $3,000 per week. Travel nurses can bring in over $50 per hour, plus company-paid housing accommodations. Making it entirely possible for travel nurses to make well over $100K per year.
The amount of money a travel nurse can make varies depending on several factors, including the specialty, location, part-time or full-time status, and years of experience. According to ZipRecruiter, as of February 2023, travel nurses earn a median salary of $105,818 annually or $51 an hour.
ZipRecruiter.com reports the national average for travel nurses is $118,400 per year. The highest-paying states are New York, California, and Idaho while the lowest reported salaries are in Louisiana and North Carolina. Even though North Carolina has the lowest travel nurse salary, the annual travel nurse salary is still more than the $77,600 ...
Here is an example of a typical pay package: $20 per hour - taxable base rate that is reported to the IRS. $250 per week for meals and incidentals - non-taxable. $2,000 a month for lodging - non-taxable. $500 for travel reimbursement - non-taxable. Your blended rate is calculated by breaking down your non-taxable stipends into an hourly ...
The advertised pay rate for travel nurses has surged 67% from January 2020 to January 2022, according to Prolucent Health, a workforce management tool for healthcare companies, while some staffing ...
During the second week of January 2023, the average weekly travel nurse salary on Vivian was $2,557 based on active jobs posted over the previous week. This weekly salary breaks down to about $63.93 hourly in a standard 40-hour workweek. In comparison, RNs in permanent positions earned an average of $37.24 per hour, according to Vivian's ...
Dispelling 4 myths about your travel nurse salary. Here are some common misconceptions and myths about the salaries of travel nurses: "I'm gonna get rich in travel nursing.". You can earn a lot of money, certainly! But there truly is no average travel nurse pay. Travel nursing jobs and salaries really vary. Most of my travel assignments ...
Hourly: The average hourly rate for a travel nurse is $59.66. However, recently-licensed travel nurses tend to earn a much lower starting salary of $39.83 while their more experienced counterparts earn an average of $86.68. Some of this may include overtime hours, though the availability and demand for overtime will vary from one assignment to ...
Job listings in Fargo, N.D., advertised positions for $8,000 a week. In New York, travelers could make $10,000 or more. The average salary of a staff nurse in Texas is about $75,000; a traveler ...
That year, according to the 2022 National Health Care Retention & RN Staffing Report from Nursing Solutions Inc., a nurse recruiting firm, the travel pay available to registered nurses contributed ...
The "50 Mile Rule" is one of the most common fallacies pertaining to tax-free reimbursements for travel nurses. It's prominent among both travel nurses and travel nursing recruiters. Purveyors of this "rule" claim that it allows travel nurses to accept tax-free reimbursements as long as the travel assignment is 50 miles or more from ...
Calculating net pay. As mentioned above, we simply subtract the estimated weekly taxes from the weekly taxable wage and add the remainder to the total weekly tax-free stipends to calculate weekly net pay for a contract. For Sample #1 we're looking at $720 - $167.59 = $552.41 + $688.46 = $1240.87 net weekly pay.
3. You get the chance to travel. A travel nurse does precisely what is in their name; they travel! When weighing the pros and cons of being a travel nurse, being able to travel the country is definitely one of the advantages of being a travel nurse. You will have the opportunity to see and visit many different places.
Just be sure that you're comparing the pay quotes accurately. 17. Leverage Social Proof when Negotiating as a Travel Nurse. In the book Negotiation Genius, Harvard Professors Deeepak Malhotra and Max Bazerman discuss ways that negotiators can generate "social proof" in order to increase their negotiating power.
Now, you maybe wondering if it's really that important to go through the hassle of scrutinizing pay packages if all we're talking about is a few days of PTO per year. However, each day of PTO is worth anywhere from $450 to $600 depending on the rate it's paid at. So three days of PTO per year is worth $1,350 to $1,800.