Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 07 October 2023

A ten-year review analysis of the impact of digitization on tourism development (2012–2022)
- Chunyu Jiang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6072-8365 1 &
- Seuk Wai Phoong ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9925-0901 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 665 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
5273 Accesses
1 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Development studies
- Science, technology and society
Many tourism-related activities have been suspended due to the nationally enforced lockdown to combat the Coronavirus pandemic. The tourism industry suffered immensely from the lockdown, and as a result of this, digital tourism began gaining traction and attracted public attention. This study analyses the impact of digitalization on the social and economic sustainability of the tourism industry via systematic literature network analysis. The findings indicated that digitalization impacts economic sustainability, encompassing economic benefits in tourism product development, tourism consumption, and industrial development. Moreover, digitalization fosters social development, cultural awareness, and tourism participation in digital technology and cultural heritage. This study identified publication trends and research hotspots using bibliometric analysis, and it was confirmed that Sustainability was the top journal in published digital and tourism sustainability-related articles, followed by the International Journal of Tourism Research, Tourism Management , and Current Issues in Tourism . This study resulted in two implications: identifying the knowledge gap and evidence-based decision-making based on the (previous) literature. Recommendation for future research is also discussed in this study, which is helpful to policymakers, tourism planners, and researchers to develop strategies grounded in research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Worldwide divergence of values
Joshua Conrad Jackson & Danila Medvedev
Persistent interaction patterns across social media platforms and over time
Michele Avalle, Niccolò Di Marco, … Walter Quattrociocchi
The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals
Ricardo Vinuesa, Hossein Azizpour, … Francesco Fuso Nerini
Introduction
From 2019 through 2022, the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) wreaked havoc on the world’s tourism business (Navarro-Drazich and Lorenzo, 2021 ). Tourism contributes to many nations’ gross domestic product (GDP) as it is intertwined with various industries (Gössling et al., 2017 ). Examples of tourism products include lodging options such as hotels and Airbnb. Food and drink, theme parks, museum visits, and fashion items such as clothes and bags are additional examples of tourism products that boost the economic health of the individual and the nation.
Tourism is regarded as a complex service-driven industry, one of the characteristics of which is that if external influences disrupt the tourism sector, other industries linked to it will also be directly affected. Tourism development refers to creating and maintaining the tourism industry in a particular location and is closely linked to economic and social progress (Telfer and Sharpley, 2015 ). Over the past four decades, global tourism development has reported intense growth performance and research on tourism development (Capocchi et al., 2019 ). Kreishan ( 2010 ) posited that the impact of tourism development on destination development is a commonly discussed issue, particularly in terms of tourism development improving economic efficiency and local competitiveness. The growth of tourism currently is significant not only from an economic perspective but also from a social perspective, as evidenced by the optimization of the local social structure (Yang et al., 2021 ), increased community participation (W. Li, 2006 ), participation of women (Ferguson, 2011 ), and increased cultural awareness (Carbone, 2017 ). Also, the development of the tourism industry benefits the environment by increasing environmental protection awareness and providing greater funding for initiatives to conserve resources and the environment (Zhao and Li, 2018 ).
However, unmanaged over-tourism can cause serious harm, according to Berselli et al. ( 2022 ). From an economic standpoint, excessive tourism can result in higher prices and imbalanced industrial structure development, which lowers industries’ overall resilience. Social issues arising from over-tourism include the commercialization of culture (Wang et al., 2019 ), the shift in locals’ attitudes from friendliness to hostility towards tourists (Kim and Kang, 2020 ), and the emergence of on-stage authenticity (Taylor, 2001 ). In terms of the environment, issues such as excessive carbon emissions causing global warming (Liu et al., 2022 ), damage to water and soil resources, destruction to flora and fauna (Gössling and Hall, 2006 ), and even harm to cultural heritage (Zhang et al., 2015 ) are some of the effects of over-tourism. Since the development of the tourism industry combines economic, social, and cultural phenomena, as well as the past COVID-19 disruptions, the industry’s suspension for several years presents a significant opportunity for all stakeholders to reposition tourism for sustainable development.
Some studies suggest the tourism industry will recover after COVID-19 (Zhong et al., 2021 ). However, given the abovementioned problems caused by over-tourism, what needs to be considered is the sustainability of the tourism industry post-COVID-19. Researchers and tourism stakeholders are becoming more aware of the importance of the concept of sustainable development (Miceli et al., 2021 ), especially since COVID-19, as the tourism or hospitality industry remains one of the least developed sectors in terms of sustainable tourism practices (Kim and Park, 2017 ). Korstanje and George ( 2020 ) noted that over-tourism is a chronic disease that mere temporary changes cannot treat; it can be minimized via education and training to raise awareness. The tourism industry needs to rethink how to develop in a sustainable and healthy direction (Higgins-Desbiolles et al., 2019 ), not only in terms of ecotourism or green tourism but also in terms of putting the concept of sustainability into practice at a deeper level as it faces multiple pressures and challenges of an overarching environment, economy, and society.
Sustainability is often cited as one of the reasons for improved competitiveness among different tourism destinations (Han et al., 2019 ). The United Nations 2030 (UN, 2030 ) Agenda for Sustainable Development has developed a Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) plan, defined as a set of global goals for fair and sustainable health at every level, from the planetary biosphere to the local community. The aim is to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that everyone enjoys peace and prosperity now and in the future. The basic concept is that productivity can be preserved for future generations. Due to the general emphasis of the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) on sustainable tourism and the industry’s economic importance, the SDGs and its associated millennium development goals (MDGs) have become critical elements for research into tourism’s contribution to sustainable development and overall sustainability (Saarinen et al., 2011 ; Saarinen and Rogerson, 2014 ). Winter et al. ( 2020 ) indicated that as sustainable tourism development needs to take complete account of the combined social, economic, and environmental impacts, stakeholders are expected to integrate scientific management and practice for future sustainability using updated and innovative technologies that can provide more tourism opportunities for groups unable to travel directly while enhancing environmentally-friendly behavior. Bramwell and Lane ( 2011 ) suggested that effective policy support is also crucial to implementing sustainable tourism development, as the path to sustainable development is guided and monitored by excellent and progressive policies. From a postmodernist perspective, social media and place brand authenticity in smart tourism are essential to place trust, place identity, and place brand image, while the development of this brand authenticity is one of the critical indicators of the visitor experience (Handayani and Korstanje, 2017 ). As a result, Korstanje et al. ( 2022 ) contended that new paradigms and strategies must be created to confront risks to tourism in the 21st century and satisfy the SDGs by 2030.
Several studies are underway to determine the impact of various programs and strategies on the environmental component of sustainability practices (Goralski and Tan, 2020 ). Yalina and Rozas ( 2020 ) suggested that a digital workplace can promote environmental sustainability. Although there have been studies on the digitalization of tourism and environmental sustainability, such as Loureiro and Nascimento ( 2021 ), who reviewed digital technology on the sustainability of tourism using bibliometric methods, there is a need for a thorough examination of the impact of digital transformation on sustainable tourism growth, particularly in terms of economic and social dimensions (Feroz et al., 2021 ). Therefore, the objective of this study is to review the impact of tourism digital technology development on the economic and social sustainability of tourism development to offer future research guidance.
With the growing literature and the emergence of cross-disciplinary research related to sustainability and digitalization in tourism development, it is critical to analyze the changes in its research, summarize the focus of previous research content, and predict future research prospects. As a result, this study will address the above research gaps by answering the following three questions.
RQ1: What are the prominent documents, authors, sources, organizations, and keywords in digitalization for the economic and social sustainability of tourism development?
RQ2: What are the linkages based on bibliographic coupling, co-authorship, co-occurrence, and citation in digitalization for the economic and social sustainability of tourism development?
RQ3: What is the future research agenda based on the results of this study?
Literature review
Several review papers on tourism research are now available and relevant to this study. Ülker et al. ( 2023 ) assumed that there are currently 136 bibliometric studies in the tourism and hospitality industry, of which the literature review studies on overall trends in the tourism and hospitality industry are continuously being updated (Chang and Katrichis, 2016 ; Wang et al., 2023 ). Also, economic development in the tourism industry (Comerio and Strozzi, 2019 ), tourism marketing (Mwinuka, 2017 ), tourism and education (Goh and King, 2020 ), hospitality (Manoharan and Singal, 2017 ), Airbnb (Andreu et al., 2020 ), and even COVID-19 review articles related to tourism development are available (Bhatia et al., 2022 ).
With the emergence of cross-disciplinary digital-related technologies, the link between tourism and digitalization has become one of the hot topics of research, and as a result, several literature review articles on digitalization and tourism have been published, such as on robotics (Buhalis and Cheng, 2020 ; Ivanov et al., 2019 ; Pizam et al., 2022 ), ICT (Buhalis and Law, 2008 ; Law et al., 2014 ), big data (Li et al., 2018 ; Stylos et al., 2021 ), smart tourism (Buhalis, 2020 ; Mehraliyev et al., 2020 ), social media (Buhalis and Inversini, 2014 ; Mirzaalian and Halpenny, 2019 ), eye-tracking (Muñoz-Leiva et al., 2019 ; Scott et al., 2019 ), AI (Buhalis and Moldavska, 2022 ; Doborjeh et al., 2022 ; Dwivedi et al., 2023 ), VR (Koohang et al., 2023 ; Wei, 2019 ), AR (Jingen Liang and Elliot, 2021 ; Tscheu and Buhalis, 2016 ; Yovcheva et al., 2012 ), MR (Buhalis and Karatay, 2022 ), and the Metaverse (Ahuja et al., 2023 ; Buhalis et al., 2022 , 2023 ; Go and Kang, 2023 ).
Due to the rise of sustainability research, the literature review on sustainability research in tourism has seen a stark increase (León-Gómez et al., 2021 ; Ruhanen et al., 2018 ; Streimikiene et al., 2021 ). The proliferation of studies related to digitalization and sustainable tourism development has led to a considerable number of review articles (Elkhwesky et al., 2022 ; Gössling, 2017 ; Loureiro and Nascimento, 2021 ; Nascimento and Loureiro, 2022 ; Rahmadian et al., 2022 ). Feroz et al. ( 2021 ) conducted a literature study on the environmental aspects of tourism sustainability and digitalization; however, there is a distinct lack of studies on the economic and social dimensions.
Therefore, the study’s unique value is that it presents the first literature review in the field of digitalization and social and tourism economic sustainability development using a novel method of systematic literature network analysis (SLNA), filling a gap in the literature review landscape and addressing the need for more comprehensive, detailed, and up-to-date research endeavor.
Methodology
Colicchia and Strozzi ( 2012 ) proposed a systematic literature review analysis (SLNA) to identify past research trends more sophisticatedly, integrated, and scientifically. This method is currently used in reviews of sustainable development research (Afeltra et al., 2021 ) but is rarely used in reviews of tourism sustainability; therefore, SLNA is used in this study.
Systematic literature review (SLR) and bibliographic network analysis (BNA) are the two phases of SLNA. These actions comprise the first phase of SLR, which includes choosing the study’s final selection, conducting a dialectical examination of the most pertinent articles, and evaluating the results. Next, citation analysis and bibliographic coupling of BNA are also included in this paper to investigate the relationship between the previous literature, assess the research trends, and aid in uncovering future research innovation opportunities. Bibliographic coupling is a scientific mapping technique regarding two articles with a common citation contentedly comparable. This technique permits the segmentation of publications into thematic clusters utilizing published references to understand the most recent developments in current research issues (Donthu et al., 2021 ). Citation analysis reveals which papers are influential and their authors and journals and aids in comprehending what past literature has contributed (Pilkington and Meredith, 2009 ).
First phase: systematic literature review (SLR)
Introduction of slr.
The most widely used and reputable databases are the Web of Science (WOS) and Scopus (Garrigos-Simon et al., 2018 ); thus, both were used in this study to eliminate data search omissions, broaden the search scope, and improve the accuracy of data outputs.
Figure 1 shows the flow diagram for systematic bibliometric analysis. Firstly, this paper takes “virtual reality or augmented reality or artificial intelligence or big data or mobile technology or internet of technology or social platform technology) and (sustainable tourism development or sustainability of tourism or green tourism or ecotourism” as keywords. The search process began by searching topics (including article titles, abstracts, and keywords). The language of the articles was set to English and had to be published between 2012 and 2022. The search process resulted in 91 articles. The data were extracted on February 15, 2022, per Fig. 2 .
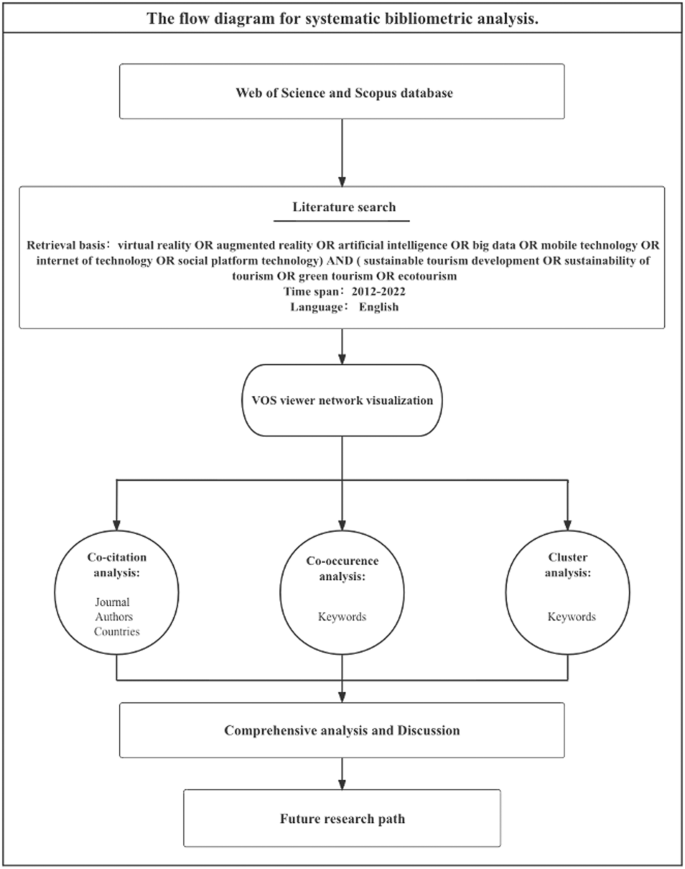
This figure shows the overall process of this study from database selection until suggestions for future research. Source: Own elaboration.
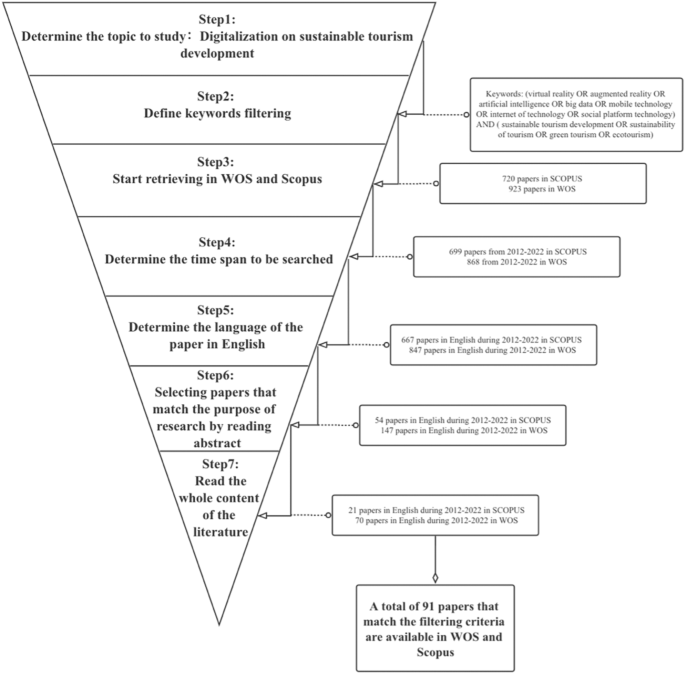
The criteria and steps used to identify the selected target literature are explained in this diagram. Source: Own elaboration.
A review article with scholarly worth and contribution is required to describe the literature’s links and contents and examine and critique it precisely (Hart, 2018 ). As seen in Fig. 3 , the following research topics are divided into two categories: economic sustainability (which includes topics such as economic benefit, industry development, and tourist consumption) and social sustainability (which includes topics such as tourist behavior, social development, cultural awareness, and participation).
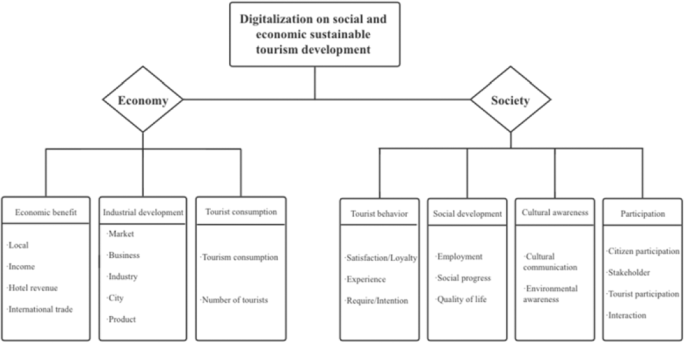
The research topics are divided into two categories: economic sustainability (which includes topics such as economic benefit, industry development, and tourist consumption) and social sustainability (which includes topics such as tourist behavior, social development, cultural awareness, and participation. Source: Own elaboration.
The SLRs are used to locate, appraise, and synthesize existing, completed, and documented work (Cocchia, 2014 ), facilitating classification and summarization, particularly for micro-profiling within macro-level fields of study.
Digitalization’s impact on economic sustainability
Digitalization’s impact on economic benefits.
Adequately improving the economic development of tourism is also one of the sustainable needs for developing tourism. At a time when tourism has been devastated by COVID-19, the tourism industry has almost ceased to exist. Therefore, one of the most popular research topics is maintaining substantial economic benefits while allowing the tourism industry to flourish sustainably.
Digital technology has piqued researchers’ interest due to its potential benefit to the tourism industry. Technologies that directly improve the economic situation are classed as economic benefits, and per many studies, digitization positively impacts local economic development and may bring objective revenue to tourism (Tables 1 – 7 ).
Digital technology promotes economic development. The growth of information communication technologies (ICT) positively impacts China’s tourism industry while promoting economic growth (Shehzad et al., 2019 ). As a rapidly evolving digital technology, mobile technology has significantly minimized asymmetric information, enhanced local GDP growth, and increased citizens’ financial capital through tourism (Kim and Kim, 2017 ; Phoong et al., 2022 ). Technologies such as 3D virtual, mixed reality (MR), virtual reality (VR), or augmented reality (AR) applied in heritage tourism can effectively increase local economic income and the added value of tourism (Manglis et al., 2021 ; Martinez-Grana et al., 2019 ). Furthermore, marketing tools such as small programs and network technologies confer several advantages to tourism stakeholders, such as the ability to help local communities contribute value and support the tourism economy (Caciora et al., 2021 ; Lin et al., 2020a , b ). Also, smart heritage city tourism technology tools can drive the tourism economy to inaccessible areas (Gomez-Oliva et al., 2019 ).
The increase in income is proportional to increased economic benefits. ICT is often used in the tourism industry, which has an essential impact on the tourism service industry, one of which is the improvement of tourism income (Gomez-Oliva et al., 2019 ; Koukopoulos and Koukopoulos, 2019 ). Virtual tourism technologies, such as AR and VR, are digital tools that can help overcome cultural heritage tourism challenges, such as reviving the tourism industry and resolving funding shortages (Lu et al., 2022 ). Mobile money, such as electronic traveler’s checks and credit cards, can assist low-income people in taking advantage of their marginal savings and encourage implementing a cashless economy for tourism sustainability (Singh, 2017 ).
Second, digital marketing technologies are frequently utilized by hotels to improve hotel performance, which increases profit (Theocharidis et al., 2020 ; Vitezic et al., 2015 ). Another example is Muslim-friendly apps promoting the international trade of products during the tourism process (Cuesta-Valiño et al., 2020 ),
Digitalization’s impact on tourism industrial development
Technological development has driven the tourism industry in local tourist cities, organizations, businesses, and governments. From the perspective of industrial market development, ICT, extensive data network marketing, and other virtual tourism technologies can create market development potential and improve market positioning for companies (Ammirato et al., 2021 ; Filipiak et al., 2020 ; Ma et al., 2021 ).
Adopting and applying information in the tourism industry are commonly regarded as a source of corporate innovation. The implementation of ICT can increase the profitability of tourism enterprises while also increasing organizational productivity (Croitoru and Manoliu, 2016 ; De Lucia et al., 2021 ; Duy et al., 2020 ; Obonyo et al., 2018 ). VR, AR, 3D digital technology, and mobile technology can all be used to improve a company’s performance and competitiveness in the tourism industry (Cranmer et al., 2021 ; Koukopoulos and Koukopoulos, 2018 ; Pavlidis et al., 2022 ; Yuce et al., 2020 ), and these technologies have made significant economic contribution to economic sustainability.
The application and implementation of ICT play an essential role in developing the tourism industry (Adeola and Evans, 2020 ; Tan et al., 2019 ; Zhou and Sotiriadis, 2021 ). Also, digital advanced technologies, such as MR technology adopted by museums, AR technology adopted by destinations, and smart tourism products and tourism ecological reservation systems have made significant contributions in the front-end development stage, providing opportunities to monitor the future development of tourism, as well as being beneficial to the formulation and implementation of tourism industry strategies at later stages (Graziano and Privitera, 2020 ; Tsai et al., 2018 ). The abovementioned electronic environment is an excellent lubricant for tourism’s active and healthy development (Maiorescu et al., 2016 ). Moreover, apps can help customers understand legacy cities more from the standpoint of heritage preservation and help cities promote tourist city development (Briciu et al., 2020 ).
From the perspective of products sold and variations in product types, online services in Muslim-friendly apps can be helpful for market segmentation and promotion of product positioning and sales (Cuesta-Valiño et al., 2020 ). Furthermore, virtual multi-sensory technologies can improve the company’s potential, increase public awareness, and sell products (Martins et al., 2017 ). Undeniably, the development of digitalization enriches the cultural service products of museums in developing heritage tourism (Palumbo, 2021 ), and AR technology also increases the diversification of products in water tourism (Kaźmierczak et al., 2021 ).
Digitalization’s impact on tourism consumption
Tourists’ spending power can reflect the overall economic development of the tourism industry as one of the contributing variables, and the number of tourists and the value of tourist flow are two measurement criteria of tourism consumer spending. Tourism apps, for example, can make traveling more convenient for tourists, increasing tourism consumption (Lin et al., 2020a , b ). Virtual tourism products or augmented reality technology allow tourists to spend more leisure time, increasing consumption (da Silva, 2021 ; Pehlivanides et al., 2020 ).
The application of virtual tourism technology is also helpful in improving the attractiveness of tourists (Cai et al., 2021 ; Manglis et al., 2021 ; Martins et al., 2017 ). Meanwhile, big data analytic tools, e-marketing (WOM), and mobile applications positively influence customers’ intention to travel and contribute to improving tourism sustainability (Gajdosik, 2019 ; Kim and Chang, 2020 ; Pica et al., 2018 ). With the application and construction of ICT, the demand for tourism has increased, and the number of tourists has also increased (Adeola and Evans, 2020 ; Kabassi, 2017 ; Kumar and Kumar, 2020 ). In addition to enhancing tourists’ imagination, virtual tourism technology and 3D digital technology can also be used as practical tools to further develop tourism and increase the number and flow of tourists (Bae et al., 2020 ; Graziano and Privitera, 2020 ; Pavlidis et al., 2022 ). Word-of-mouth marketing has increased the number of tourists (Fernandez-Lores et al., 2022 ; Wang et al., 2020 ).
Digitalization’s impact on social sustainability
Digitalization’s impact on tourist behavior.
Virtual tourism technology is gradually being implemented in the tourism industry, focusing on increasing the satisfaction of the elderly and disabled (Lu et al., 2022 ). Artificial intelligence and virtual reality are integrated into human-computer interaction system equipment, boosting service quality and increasing tourist satisfaction (Van et al., 2020 ). The mixed experience helps enrich tourists’ feelings about the surroundings, thereby boosting tourists’ contentment (Bae et al., 2020 ), and the succinct information and dependable system offered by VR can promote tourists’ satisfaction (Yuce et al., 2020 ). 3D digital technology to build innovative and appealing tourism items can help boost consumer satisfaction and positive feedback (Pavlidis et al., 2022 ).
Tourism stakeholders’ use of tourism apps is critical to increasing tourist satisfaction (Lin et al., 2020a , b ). For example, tourism management in Ho Chi Minh City’s use of Web 4.0 can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty in the long run (Duy et al., 2020 ). The mobile usability and ease of use of social media as a suitable medium directly impact satisfaction (Sharmin et al., 2021 ). It can also serve as a platform for tourists to communicate and contribute to increased satisfaction (Jamshidi et al., 2021 ). Simultaneously, tourism safety is an essential factor that influences tourist satisfaction, and the use of closed-circuit television (CCTV) and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can help to improve tourism safety (Ko and Song, 2021 ). The use of mobile technologies and payment mechanisms in the tourism process is also a fascinating study. Through electronic technology, two-dimensional code payment techniques improve tourists’ pleasure (Lou et al., 2017 ). Furthermore, incorporating digital innovation into hotel management structures increases hotel performance and client satisfaction (Vitezic et al., 2015 ).
Tourism satisfaction is directly related to tourism experience, and tourism experience is one of the most important criteria to measure in the tourism process. The findings suggest that using virtual immersion technologies such as AR, VR, and MR in the tourism process can significantly improve the tourist experience (Bae et al., 2020 ; Fernandez-Lores et al., 2022 ; Franco and Mota, 2021 ; Lee and Kim, 2021 ; Yin et al., 2021 ).
Additionally, the intention and motivation of tourism drive tourism behavior from the psychological aspect. Digital innovative technology can boost tourists’ interest in tourism products and locations, enrich their understanding of tourism culture, attract more tourists, enhance tourists’ preferences, and strengthen their desire to visit (Caciora et al., 2021 ; Cranmer et al., 2021 ; Gajdosik, 2019 ; Kang, 2020 ; Kaźmierczak et al., 2021 ; Manglis et al., 2021 ; Monterroso-Checa et al., 2020 ;). Digital marketing tools can ramp up customers’ desires and habits (Theocharidis et al., 2020 ), and digital mobile programs can increase tourists’ attention, influencing their overall view of the tourism experience (Wang et al., 2020 ). Big data can also be utilized to foresee client wants and expectations, allowing for a better understanding of customer needs (Del Vecchio et al., 2018 ). For example, Internet of Things technology can scientifically guide and divert tourists to alleviate the problem of local saturation and overload in scenic sites, thus improving the tourist experience (Xie and Zhang, 2021 ). It can also provide various cultural tourism content to enhance and support the experience of active tourists (Ammirato et al., 2021 ).
Digitalization’s impact on social development
Tourism planners and governments can use the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and geographic information system-remote sensing (GIS-RS) technology to accurately select sites, develop eco-tourism activities, relieve the burden of tourism in the region, and thus help the locals create new employment opportunities (Chaudhary et al., n.d. ). Virtual tourism technology, such as AR, can also aid in analyzing tourist flow and conditions, improve safety, and expand job chances (Franco and Mota, 2021 ). Advances and innovations in tourism ICT can benefit enterprises enough to increase job prospects (De Lucia et al., 2021 ). Virtual tourism, ICT, mobile technology, smart heritage tourism technology, and innovative marketing methods improve stakeholders’ quality of life, increasing the tourism system and community awareness (Lemmi and Deri, 2020 ).
Digitalization’s impact on cultural awareness
Virtual technologies, such as AR, VR, and mobile augmented reality (MAR), are now widely used in cultural heritage tourism, with the potential to protect cultural heritages and enhance the potential of heritage management, thereby contributing to cultural communication (Bec et al., 2019 ; Caciora et al., 2021 ; Graziano and Privitera, 2020 ). Some studies indicate that online engagement platforms, mobile application technologies, and smart tourism models can all support the socially sustainable growth of culture (Bonacini et al., 2018 ; Pica et al., 2018 ; Zubiaga et al., 2019 ).
AR, VR, and other techniques can promote tourists’ behavior in underwater cultural tourism and raise public awareness of natural heritage protection among tourists (Manglis et al., 2021 ). Research on low-carbon travel modes is frequently concerned with tourism sustainability, and big data marketing technology can supply tourists with more low-carbon transport schemes, thus increasing tourists’ environmental consciousness (Ma et al., 2021 ). As a common medium for cultural communication, social media can raise tourists’ awareness of environmental protection (Haque et al., 2021 ).
Digitalization’s impact on participation
Tourists’ active participation in cultural heritage can be enhanced by digital technology, as can people’s feeling of belonging and responsibility to society (Koukopoulos and Koukopoulos, 2019 ; Permatasari et al., 2020 ). Virtual technology can also encourage public participation in preserving and promoting cultural heritages (Caciora et al., 2021 ), while digital media can help tourism businesses improve public relations and social participation (Camilleri, 2018 ; Haque et al., 2021 ). Increased smart tourism destinations optimize the potential for these communities to involve the destinations’ residents and impact their lives due to the improved urban tourism experience.
Stakeholders are closely linked to the sustainable development of tourism. Innovative applications of digital technology can better manage destination stakeholders, strengthening their linkages (Camilleri, 2018 ), help promote their participation in the development of tourist destinations (del Vecchio et al., n.d. ; Gajdosik, 2019 ), and create a democratic and sustainable system when promoting cultural heritage, which balances the opinions of different stakeholders.
The interactive network platform empowers local communities and encourages local inhabitants and tourists to communicate, which promotes the healthy growth of resident-tourism relationships (Dionisio et al., 2019 ). Also, ICT tourism apps influence the ultimate perception of older tourists’ travel experiences, stimulate tourists’ interest in world cultural heritage sites (WCHS), and increase contact and understanding between tourists and destinations (Ramos-Soler et al., 2019 ). Social media can help tourists increase their knowledge of environmental protection, which increases the participation of tourists and citizens and helps formulate sustainable goals (Haque et al., 2021 ).
Second phase: bibliographic network analysis (BNA)
The VOSviewer is the analysis tool used in this work to visualize the impact of digital technology on sustainable tourism development in economic and social aspects. VOSviewer employs the visualization of similarities (VOS) mapping approach to create a map (Moya‐Anegón et al., 2007 ).
Bibliographic coupling network of sources
Bibliographic coupling analysis mainly measures the similarity of documents by the number of identical references cited by documents. Although co-citation refers to the appearance of two documents in the same reference list, bibliographic coupling refers to the number of references that a group of papers share; for example, paper A and paper B are coupled if they both cite document C (Garrigos-Simon et al., 2018 ). In other words, bibliographic coupling happens when two documents quote the same document (Phoong et al., 2022 ; Mulet-Forteza et al., 2018 ), demonstrating the power of one publication in comparison to a group of others (Cavalcante et al., 2021 ). It should be pointed out that the size of the sphere represents the number of similar citations. This paper analyzes the bibliographic coupling network of sources, and the findings are summarized in Fig. 4 . Per Fig. 4 , there are 9 clusters, and the journal source with the highest number of similar citations is Sustainability . It can, therefore, be concluded that this journal has the most citations and published articles on this subject.
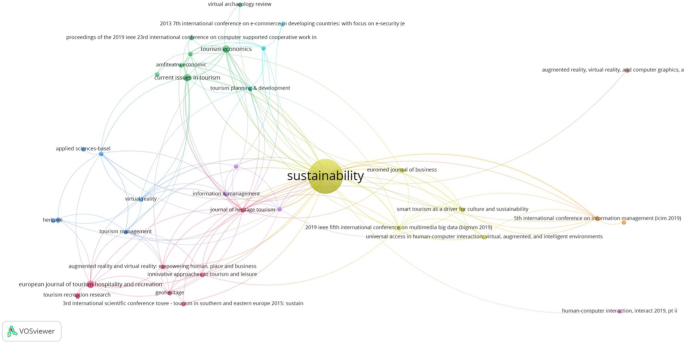
This figure refers to the number of references shared by a group of papers. Source: Own elaboration.
Citation network of documents
Citations are formed when two documents cite the same document and are used to illustrate the relation between documents and study fields. Figure 5 shows four clusters, each representing the degree of connection and the extent of influence in size. This study has the highest influence, according to the largest green group. It offers insight into the impact of reality and virtual reality on heritage tourism, stating that these technologies favorably impact tourists’ experiences (Bec et al., 2019 ).

Cluster size indicates the degree of connection and influence of the literature and research area. There are four groups, with the blue (Encalada et al., 2017 ) and green (Bec et al., 2019 ) groups representing the two articles that are relatively most influential. Source: Own elaboration.
This Blue Group study is also prominent, proposing that the widespread use of information and communication technologies, such as cloud computing, the Internet of Things, and data mining with high processing performance, are the key to tourism’s sustainability (Encalada et al., 2017 ).
The number of citations between documents is used in co-citation analysis to determine their relevance. Figure 6 shows which publications are cited most frequently, and it is clear that tourism management and sustainability are the two commanding the most attention. Generally, the closer two journals are located to each other, the stronger their relatedness. For example, according to an article published in Tourism Management , virtual reality has significantly increased tourism intention and consumption (Tussyadiah et al., 2018 ). Simultaneously, this article presents the finding, which illustrates that combining history with cutting-edge technology in immersive spaces can preserve and manage legacy and enrich the visitor experience and, as a result, engagement with history (Bec et al., 2019 ).
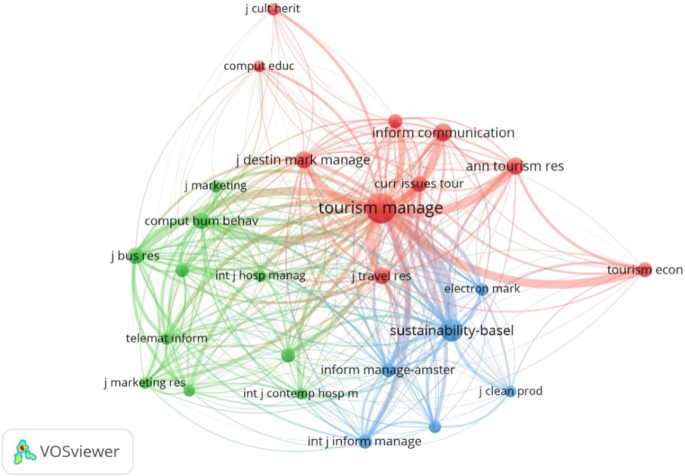
This figure represents the citation strength of publications. The circle distance represents relevance. Source: Own elaboration.
Co-occurrence network of Keywords and titles
The significance of keyword co-occurrence analysis in bibliometrics resides in an intuitive understanding of hot subjects in the study field through the frequency and relevance of terms (Phoong et al., 2022 ). Before that, the following considerations must be made.
To begin, each node in the network map indicates a keyword, and the size of the ball represents the number of keywords that appear. The larger the ball, for example, indicates the higher frequency of keywords occurring. Second, the larger the co-occurrence rate between terms, the thicker the curve between the second keywords. In the third, on the network map, different color groups reflect different theme collections, while the same color represents similar subjects (Loureiro and Nascimento, 2021 ).
Figures 7 and 8 illustrate overlay visualization (Fig. 8 ) and network visualization (Fig. 7 ). From Fig. 7 , the keywords of high frequency include tourism (37 occurrences), technology (35 occurrences), tourist (32 occurrences), experience (31 occurrences), information (25 occurrences), application (23 occurrences), data (22 occurrences), analysis (21 occurrences), impact (21 occurrences), sustainability (14 occurrences) and sustainable development (9 occurrences). Some of Red Network Group’s primary keywords are tourism, information, impact, communication technology, virtual reality, new technology, and cultural tourism. The study’s content focuses on the impact of the relationship between information technology and tourism. Yellow Network Group’s primary keywords are destination, tourism destination, environment, and AR, mainly concentrated on destination environment and AR application research. The green network group comprises tourists, analysis, process, big data, management, stakeholders, case studies, innovation, and other topics. This group has conducted more studies on the effect of digital technology on enterprise management from stakeholders’ perspectives. The Blue Network Group focuses on technology, experience, data, service, research, relationships, social media, sustainable development, tourist satisfaction, intention, and other related topics, and this group study is particularly interested in the influence of technology on tourist experience and satisfaction.
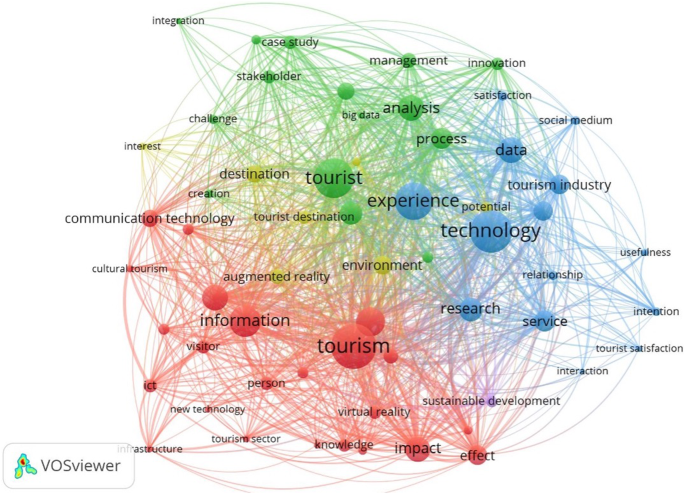
The same color indicates a close relationship between the keywords. The red network group focuses on tourism and information technology, the yellow network group concentrates on destinations and the environment, and the blue group emphasizes tourists and technology, the green group concerns tourists and analyses. Source: Own elaboration.
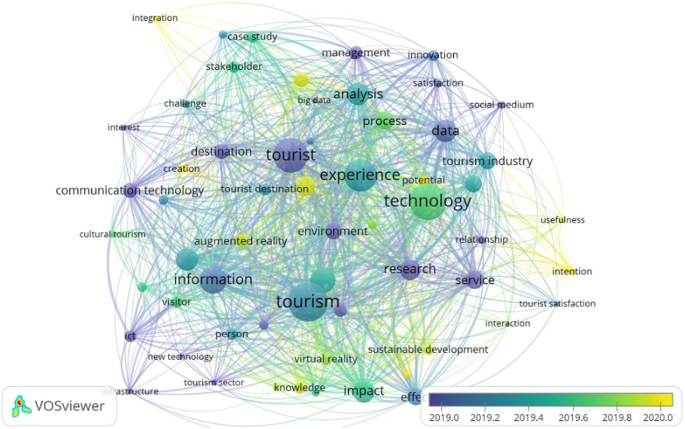
Darker colors indicate older keywords such as tourists, information, data, research, etc. and lighter colors show the recent hot keywords such as big data, AR, VR, sustainable development, etc. Source: Own elaboration.
After conducting a literature review on digital technology’s economic and social implications on sustainable tourism development over the last ten years and creating a density visualization network map, it can be concluded that tourist experience, information technology, augmented reality, and data are research hotspots. As a result, most studies on tourism sustainability in social and economic dimensions focus on the impact of digital technology on the tourist experience.
Even though they are all co-occurrence analyses of keywords in literature, the emphasis in each network map is different. Generally, overlay visualization and network visualization are comparable to a certain extent; however, the color differs in overlay visualization (Fig. 8 ). In the lower right corner, there is also a quantification table. Purple indicates that the keywords are older, while yellow indicates that they are more modern. For example, keywords such as big data, augmented reality, sustainable development, creation, and intention are yellow, indicating a recent research hotspot, but keywords such as communication technology, information, environment, and service are purple, indicating that these themes were formerly popular.
Results and discussion
The data were collected from 2012 until February 2022. Analysis of the published articles shows a significant increase in publications on digitalization and tourism sustainability development. In 2017, seven articles were published, 10 in 2018, 16 in 2019, and 23 in 2020 and 2021. Furthermore, there are 6 published in the first two months of 2022. These findings illustrate a rise in data availability for digitalization and sustainable tourism development research and suggest that researchers are considering this topic more seriously, demonstrating its value to academic research.
According to the findings, Sustainability was the top journal in published digital and tourism sustainability-related articles. This is followed by the International Journal of Tourism Research , Tourism Management , and Current Issues in Tourism . The number of publications on the relevant subject has increased steadily, particularly in recent years, indicating that this form of research is increasingly gaining attention. Research over the last decade has shown the existence of a certain number of empirical studies on the relationship between digitalization and tourism social and economic sustainability, and from the bibliometric analysis, it emerges that the current research direction on tourism social and economic sustainability has shifted from exploring ICT to AR and VR. Moreover, Tourism Management and Sustainability have the highest citation.
In summary, this study answers RQ1 using the bibliometric literature analysis, while a systematic literature review used to answer RQ2 and RQ3 is discussed in the conclusion and further recommendation sections.
The content of relevant articles published in WOS and Scopus in this research area over the last decade was visually analyzed through bibliometric and systematic literature analysis, and a total of 91 articles meeting the research criteria were selected to provide information on the status of the impact of digitalization on the social and economic aspects of sustainable tourism development, as well as to identify specific research fields and research topics. It can be concluded that the digitalization of the social dimension of tourism sustainability is more richly studied and explored from a more diverse perspective, considering not only the tourists’ but also the residents’ perspectives. There are two implications in the present study. The first is that this study pinpointed the knowledge gaps. Systematic literature review analysis is used in this study to identify the gaps in the existing body of research in tourism development. By reviewing the previous literature and synthesizing the findings, researchers can identify the areas receiving limited or much attention. This insight is valuable for policymakers, tourism planners, and researchers when dealing with specific areas where future research is warranted. Furthermore, the publication trend and popular research themes were also discussed in this study. This enables the policymaker and tourism planner to understand tourism development and the potential for improved policies and practices. The second implication is enabling evidence-based decision-making in tourism development. Researchers can identify patterns, trends, and best practices by synthesizing the findings from multiple studies. This evidence-based approach helps policymakers, destination managers, and tourism stakeholders make informed decisions and develop strategies grounded in research. However, there is a lack of a more comprehensive perspective to explore in an integrated manner. For example, social and economic sustainability development sometimes does not increase simultaneously, and perhaps there is a particular imbalance between the two when using certain digital technologies. Therefore, it can be observed from this study that there is a lack of research in the past ten years that has explored both the economic and social sustainability of tourism comprehensively and that future research could emphasize the integration of social and economic sustainability, even a synthesis study of three dimensions: environmental social, and economic.
Therefore, when considering future developments, several challenges were raised.
Lack of integration study of social and economic dimensions.
Lack of cooperative research among other disciplines.
Lack of suitable theory and conceptual model for sustainable development research in the tourism area.
Lack of universality in different regions based on proposed digital technology.
Lack of research from the perspective of subject education or particular population as the research object.
Based on this literature study, relatively few research topics about this research area are suggested, and the following research scope and questions can be referred to as a priority in the future research process so that research trends can be accurately grasped more quickly and efficiently.
What is the impact of digital technologies on the economic and social sustainability of destinations?
How do digital technologies used in cultural heritage tourism impact tourism sustainability?
What is the impact of digital technology on education?
How can tourism companies improve employee satisfaction, loyalty, and sustainable performance through digital technology?
How can we create a globally accessible and digital system for tourism destinations for sustainable development goals?
How does digitalization impact sustainable development from stakeholders’ perspectives?
The above suggestions and research direction recommendations can provide new research inspiration to researchers in the same field for future research, and this study is expected to help other researchers understand the current research trends related to the digitalization of sustainable tourism development.
Adeola O, Evans O (2020) ICT, infrastructure, and tourism development in Africa. Tour Econ 26(1):97–114
Google Scholar
Afeltra G, Alerasoul SA, Strozzi F (2021) The evolution of sustainable innovation: from the past to the future. Eur J Innov Manag 26(2):386–421. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJIM-02-2021-0113
Article Google Scholar
Ahuja AS, Polascik BW, Doddapaneni D, Byrnes ES, Sridhar J (2023) The digital metaverse: applications in artificial intelligence, medical education, and integrative health. Integr Med Res 12(1):100917
PubMed Google Scholar
Ammirato S, Felicetti AM, Linzalone R, Carlucci D (2021) Digital business models in cultural tourism. Int J Entrep Behav Res Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-01-2021-0070
Andreu L, Bigne E, Amaro S, Palomo J (2020) Airbnb research: an analysis in tourism and hospitality journals. Int J Cult Tour Hosp Res 14(1):2–20
Anser M, Adeleye B, Tabash M, Tiwari A (n.d.) Services trade–ICT–tourism nexus in selected Asian countries: new evidence from panel data techniques. Curr Issues Tour. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.1965554
Bae S, Jung T, Moorhouse N, Suh M, Kwon O (2020) The influence of mixed reality on satisfaction and brand loyalty in cultural heritage attractions: a brand equity perspective. Sustainability 12(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072956
Balakrishnan J, Dwivedi Y, Malik F, Baabdullah A (n.d.) Role of smart tourism technology in heritage tourism development. J Sustain Tour. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1995398
Bec A, Moyle B, Timms K, Schaffer V, Skavronskaya L, Little C (2019) Management of immersive heritage tourism experiences: a conceptual model. Tour Manag 72:117–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.10.033
Berselli C, Pereira LA, Pereira T, Limberger PF (2022) Overtourism: residents’ perceived impacts of tourism saturation. Tour Anal 27(2):161–172
Bhatia A, Roy B, Kumar A (2022) A review of tourism sustainability in the era of Covid-19. J Stat Manag Syst 25(8):1871–1888
Boboc R, Duguleana M, Voinea G, Postelnicu C, Popovici D, Carrozzino M (2019) Mobile augmented reality for cultural heritage: following the footsteps of ovid among different locations in Europe. Sustainability 11(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041167
Bonacini E, Tanasi D, Trapani P (2018) Digital heritage dissemination and the participatory storytelling project #iziTRAVELSicilia: the case of the Archaeological Museum of Syracuse (Italy). Acta IMEKO 7(3):31–41. https://doi.org/10.21014/acta_imeko.v7i3.584 . Scopus
Bramwell B, Lane B (2011) Critical research on the governance of tourism and sustainability. J Sustain Tour 19(4–5):411–421
Briciu A, Briciu V, Kavoura A (2020) Evaluating how “smart” Brasov, Romania can be virtually via a mobile application for cultural tourism. Sustainability 12(13). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135324
Bruno F, Ricca M, Lagudi A, Kalamara P, Manglis A, Fourkiotou A, Papadopoulou D, Veneti A (2020) Digital technologies for the sustainable development of the accessible underwater cultural heritage sites. J Mar Sci Eng 8(11):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8110955
Buhalis D (2020) Technology in tourism-from information communication technologies to eTourism and smart tourism towards ambient intelligence tourism: a perspective article. Tour Rev 75(1):267–272
Buhalis D, Cheng ESY (eds) (2020) Exploring the use of chatbots in hotels: technology providers’ perspective. In: Information and communication technologies in tourism 2020: proceedings of the international conference in Surrey, United Kingdom, January. Springer International Publishing, 8–10. pp. 231–242
Buhalis D, Inversini A (eds) (2014) Tourism branding, identity, reputation co-creation, and word-of-mouth in the age of social media. In: Tourism management, marketing, and development: vol I: the importance of networks and ICTs. pp. 15–40
Buhalis D, Karatay N (eds) (2022) Mixed reality (MR) for generation Z in cultural heritage tourism towards metaverse. In: Information and communication technologies in tourism 2022: Proceedings of the ENTER 2022 ETourism conference, Springer, Cham, January 11–14, 2022. pp. 16–27
Buhalis D, Law R (2008) Progress in information technology and tourism management: 20 years on and 10 years after the Internet—the state of eTourism research. Tour Manag 29(4):609–623
Buhalis D, Leung D, Lin M (2023) Metaverse as a disruptive technology revolutionising tourism management and marketing. Tour Manag 97:104724
Buhalis D, Lin MS, Leung D (2022) Metaverse as a driver for customer experience and value co-creation: implications for hospitality and tourism management and marketing. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 35(2):701–716
Buhalis D, Moldavska I (2022) Voice assistants in hospitality: using artificial intelligence for customer service. J Hosp Tour Technol 13(3):386–403
Caciora T, Herman GV, Ilieș A, Baias, Ștefan, Ilieș DC, Josan I, Hodor N (2021) The use of virtual reality to promote sustainable tourism: a case study of wooden churches historical monuments from Romania. Remote Sens 13(9):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091758
Article ADS Google Scholar
Cai Z, Fang C, Zhang Q, Chen F (2021) Joint development of cultural heritage protection and tourism: the case of Mount Lushan cultural landscape heritage site. Herit Sci 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-021-00558-5
Camilleri MA (2018) The promotion of responsible tourism management through digital media. Tour Plan Dev 15(6):653–671. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568316.2017.1393772
Capocchi A, Vallone C, Pierotti M, Amaduzzi A (2019) Overtourism: A literature review to assess implications and future perspectives. Sustainability 11(12):3303
Carbone F (2017) International tourism and cultural diplomacy: a new conceptual approach towards global mutual understanding and peace through tourism. Tourism 65(1):61–74
Cavalcante WQ, de F, Coelho A, Bairrada CM (2021) Sustainability and tourism marketing: a bibliometric analysis of publications between 1997 and 2020 using VOSviewer software. Sustainability 13(9):4987
Chang W-J, Katrichis JM (2016) A literature review of tourism management (1990–2013): a content analysis perspective. Current Issues Tour 19(8):791–823
Chaudhary S, Kumar A, Pramanik M, Negi M (n.d.) Land evaluation and sustainable development of ecotourism in the Garhwal Himalayan region using geospatial technology and analytical hierarchy process. Environ Dev Sustain https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01528-4
Cocchia A (2014) Smart and digital city: a systematic literature review. Smart City p 13–43
Colicchia C, Strozzi F (2012) Supply chain risk management: a new methodology for a systematic literature review. Supply Chain Manag 17(4), 403–418
Comerio N, Strozzi F (2019) Tourism and its economic impact: a literature review using bibliometric tools. Tour Econ 25(1):109–131
Cranmer E, Urquhart C, Dieck M, Jung T (2021) Developing augmented reality business models for SMEs in tourism. Inf Manag 58(8). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2021.103551
Croitoru A, Manoliu A (2016) BIG DATA—a new tool shaping the future of the tourism industry. In: Pamfilie R, Dinu V, Tachiciu L, Plesea D, Vasiliu C (eds) Basiq international conference: new trends in sustainable business and consumption, pp. 69–74
Cuesta-Valiño P, Bolifa F, Núñez-Barriopedro E (2020) Sustainable, smart and muslim-friendly tourist destinations. Sustainability 12(5):1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051778
da Silva A (2021) In quest of a new AR technology application to enhance the sustainability of cultural tourism: the Olive Heritage in Madeira through the looking glass of a “Sandbox” approach. Eur J Tour Hosp Recreation 11(1):66–76. https://doi.org/10.2478/ejthr-2021-0007
De Lucia C, Pazienza P, Balena P (2021) How does ICT influence residents’ attitudes towards tourism as a driver of development? A generalised ordered logistic regression analysis: ICT for tourism as driver of development in lagging behind regions. Int J Tour Res jtr.2473. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.2473
del Vecchio P, Malandugno C, Passiante G, Sakka G (n.d.) Circular economy business model for smart tourism: the case of Ecobnb. Euromed J Bus. https://doi.org/10.1108/EMJB-09-2020-0098
Del Vecchio P, Mele G, Ndou V, Secundo G (2018) Open innovation and social big data for sustainability: evidence from the tourism industry. Sustainability 10(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093215
Dionisio M, Silva C, Nisi V (2019) Fostering interaction between locals and visitors by designing a community-based tourism platform on a touristic island. In: Lamas D, Loizides F, Nacke L, Petrie H, Winckler M, Zaphiris P (eds) Human-Computer Interaction–INTERACT 2019: 17th IFIP TC 13 International Conference, Paphos, Cyprus, September 2–6, 2019, Proceedings, Part II 17, Springer International Publishing. vol 11747, pp. 768–787
Doborjeh Z, Hemmington N, Doborjeh M, Kasabov N (2022) Artificial intelligence: a systematic review of methods and applications in hospitality and tourism. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 34(3):1154–1176
Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM (2021) How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 133:285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Duy N, Mondal S, Van N, Dzung P, Minh D, Das S (2020) A study on the role of web 4.0 and 5.0 in the sustainable tourism ecosystem of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Sustainability 12(17). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177140
Dwivedi YK, Kshetri N, Hughes L, Slade EL, Jeyaraj A, Kar AK, Baabdullah AM, Koohang A, Raghavan V, Ahuja M (2023) “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy. Int J Inf Manag 71:102642
Elkhwesky Z, El Manzani Y, Elbayoumi Salem I (2022) Driving hospitality and tourism to foster sustainable innovation: a systematic review of COVID-19-related studies and practical implications in the digital era. Tour Hosp Res 0(0). https://doi.org/10.1177/14673584221126792
Encalada L, Boavida-Portugal I, Ferreira C, Rocha J (2017) Identifying tourist places of interest based on digital imprints: towards a sustainable smart city. Sustainability 9(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122317
Ferguson L (2011) Promoting gender equality and empowering women? Tourism and the third Millennium Development Goal. Current Issues Tour 14(3):235–249
Fernandez-Lores S, Crespo-Tejero N, Fernández-Hernández R (2022) Driving traffic to the museum: the role of the digital communication tools. Technol Forecast Soc Change Scopus 174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121273
Feroz AK, Zo H, Chiravuri A (2021) Digital transformation and environmental sustainability: a review and research agenda. Sustainability 13(3):1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031530
Filipiak BZ, Dylewski M, Kalinowski M (2020) Economic development trends in the EU tourism industry. Towards the digitalization process and sustainability. Qual Quant Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-020-01056-9
Franco M, Mota L (2021) Reopening for business post-COVID-19: augmented reality as a strategy for attracting visitors to a tourist destination. Eur J Tour Hosp Recreation 11(1):54–65. https://doi.org/10.2478/ejthr-2021-0006
Gajdosik T (2019) Big data analytics in smart tourism destinations. a new tool for destination management organizations ? In: Katsoni V, SegarraOna M (eds) Smart Tourism as a Driver for Culture and Sustainability: Fifth International Conference IACuDiT, Athens 2018, Springer International Publishing, pp. 15–33
Garrigos-Simon FJ, Narangajavana-Kaosiri Y, Lengua-Lengua I (2018) Tourism and sustainability: a bibliometric and visualization analysis. Sustainability 10(6):1976
Garzon J, Acevedo J, Pavon J, Baldiris S (2018) ARtour: Augmented Reality-based game to promote agritourism. In: DePaolis L, Bourdot P (eds) Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Computer Graphics: 5th International Conference, AVR 2018, Otranto, Italy, June 24–27, 2018, Proceedings, Part I 5, Springer International Publishing, vol 10850, pp. 413–422
Giaccone SC, Bonacini E (2019) New technologies in smart tourism development: The #iziTRAVELSicilia experience. Tour Anal 24(3):341–354. https://doi.org/10.3727/108354219X15511864843867
Go H, Kang M (2023) Metaverse tourism for sustainable tourism development: tourism agenda 2030. Tour Rev 78(2):381–394
Goh E, King B (2020) Four decades (1980–2020) of hospitality and tourism higher education in Australia: developments and future prospects. J Hosp Tour Educ 32(4):266–272
Gomez-Oliva A, Alvarado-Uribe J, Parra-Merono M, Jara A (2019) Transforming communication channels to the co-creation and diffusion of intangible heritage in smart tourism destination: creation and testing in Ceuti (Spain). Sustainability 11(14). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11143848
Goralski MA, Tan TK (2020) Artificial intelligence and sustainable development. Int J Manag Educ 18(1):100330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.100330
Gössling S (2017) Tourism, information technologies and sustainability: an exploratory review. J Sustain Tour 25(7):1024–1041
Gössling S, Hall CM (eds) (2006) An introduction to tourism and global environmental change. In: Tourism and global environmental change. Routledge, pp. 1–33
Graziano T, Privitera D (2020) Cultural heritage, tourist attractiveness and augmented reality: Insights from Italy. J Herit Tour 15(6):666–679. https://doi.org/10.1080/1743873X.2020.1719116
Hammady R, Ma M, AL-Kalha Z, Strathearn C (2021) A framework for constructing and evaluating the role of MR as a holographic virtual guide in museums. Virtual Real 25(4):895–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-020-00497-9
Han H, Eom T, Al-Ansi A, Ryu HB, Kim W (2019) Community-based tourism as a sustainable direction in destination development: an empirical examination of visitor behaviors. Sustainability 11(10):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102864
Handayani B, Korstanje ME (2017) Place brand authenticity in social media interaction: a postmodern perspective. Études Caribéennes 37–38, Article 37–38. https://doi.org/10.4000/etudescaribeennes.11182
Haque E, Sungsuwan T, Sanglimsuwan S (2021) Can social media be a tool for increasing tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior? Geoj Tour Geosites 38(4):1211–1222. https://doi.org/10.30892/gtg.38428-762
Hart C (2018) Doing a literature review: releasing the research imagination. Doing a Literature Review, p 1–352
Higgins-Desbiolles F, Carnicelli S, Krolikowski C, Wijesinghe G, Boluk K (2019) Degrowing tourism: rethinking tourism. J Sustain Tour 27(12):1926–1944. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2019.1601732
Huang T, Liu B (2021) Augmented reality is human-like: how the humanizing experience inspires destination brand love. Technol Forecast Soc Change 170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120853
Ivanov S, Gretzel U, Berezina K, Sigala M, Webster C (2019) Progress on robotics in hospitality and tourism: a review of the literature. J Hosp Tour Technol 10(4):489–521
Jamshidi D, Rousta A, Shafei R (2021). Social media destination information features and destination loyalty: does perceived coolness and memorable tourism experiences matter? Curr Issues Tour Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.2019204
Jingen Liang L, Elliot S (2021) A systematic review of augmented reality tourism research: what is now and what is next? Tour Hosp Res 21(1):15–30
Kabassi K (2017) Evaluating websites of museums: state of the art. J Cult Herit 24:184–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2016.10.016
Kang H (2020) Impact of VR on impulsive desire for a destination. J Hosp Tour Manag 42:244–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2020.02.003
Kaźmierczak R, Szczepańska A, Kowalczyk C, Grunwald G, Janowski A (2021) Using AR technology in tourism based on the example of maritime educational trips—a conceptual model. Sustainability (Switzerland) Scopus 13(13). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137172
Kim D, Kim S (2017) The role of mobile technology in tourism: patents, articles, news, and mobile tour app reviews. Sustainability 9(11):2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112082
Kim H, Chang B (2020) A study on the effects of crowdfunding values on the intention to visit local festivals: focusing on mediating effects of perceived risk and e-WOM. Sustainability 12(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083264
Kim K-H, Park D-B (2017) Relationships among perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty: community-based ecotourism in Korea. J Travel Tour Mark 34(2):171–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2016.1156609
Kim S, Kang Y (2020) Why do residents in an overtourism destination develop anti-tourist attitudes? An exploration of residents’ experience through the lens of the community-based tourism. Asia Pac J Tour Res 25(8):858–876
Ko Y, Song B (2021) Complementary cooperation of CCTV and UAV systems for tourism security and sustainability. Sustainability 13(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910693
Koohang A, Nord JH, Ooi K-B, Tan GW-H, Al-Emran M, Aw EC-X, Baabdullah AM, Buhalis D, Cham T-H, Dennis C (2023) Shaping the metaverse into reality: a holistic multidisciplinary understanding of opportunities, challenges, and avenues for future investigation. J Comput Inf Syst 63(3):735–765
Korstanje ME, George BP (2020) Education as a strategy to tackle over tourism for overtourism and inclusive sustainability in the twenty-first century. In: Séraphin H, Gladkikh T, Thanh TV (eds) Overtourism: causes, implications and solutions. Springer International Publishing, pp. 341–359
Korstanje ME, Seraphin H, Maingi SW (eds) (2022) Tourism through troubled times: emerging issues and new pathways for the 21st century tourism. In: Tourism through troubled times. Emerald Publishing Limited, pp. 1–5
Kotsopoulos KI, Chourdaki P, Tsolis D, Antoniadis R, Pavlidis G, Assimakopoulos N (2019) An authoring platform for developing smart apps which elevate cultural heritage experiences: a system dynamics approach in gamification. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01505-w
Koukopoulos Z, Koukopoulos D (2018) Intelligent management of outdoor cultural events promoting exploitation in smart city environments. In: Katsoni V, Velander K (eds) Innovative Approaches to Tourism and Leisure: Fourth International Conference IACuDiT, Athens 2017, Springer International Publishing, pp. 303–319
Koukopoulos Z, Koukopoulos D (2019) Evaluating the usability and the personal and social acceptance of a participatory digital platform for cultural heritage. Heritage 2(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage2010001
Kreishan FM (2010) Tourism and economic growth: the case of Jordan. Eur J Soc Sci 15(2):63–68
Kumar N, Kumar RR (2020) Relationship between ICT and international tourism demand: a study of major tourist destinations. Tour Econ 26(6):908–925
Law R, Buhalis D, Cobanoglu C (2014) Progress on information and communication technologies in hospitality and tourism. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 26(5):727–750
Lee W, Kim Y (2021) Does VR tourism enhance users’ experience? Sustainability 13(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020806
Lemmi E, Deri M (2020) A new model for the “tourism renaissance”: the case study of the Tuscan Village of San Pellegrino in Alpe. Almatourism—J Tour Cult Territ Dev 11(22):19–43. https://doi.org/10.6092/issn.2036-5195/12345
León-Gómez A, Ruiz-Palomo D, Fernández-Gámez MA, García-Revilla MR (2021) Sustainable tourism development and economic growth: bibliometric review and analysis. Sustainability 13(4):2270
Li J, Xu L, Tang L, Wang S, Li L (2018) Big data in tourism research: a literature review. Tour Manag 68:301–323
Li W (2006) Community decisionmaking participation in development. Ann Tour Res 33(1):132–143
Lim C, Mostafa N, Park J (2017) Digital Omotenashi: toward a smart tourism design systems. Sustainability 9(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122175
Lin M, Li F, Zhou H (2020a) A research on the combination of oblique photography and mobile applications based on the sustainable development of tourism. Sustainability 12(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093501
Lin S, Juan P, Lin S (2020b) A TAM framework to evaluate the effect of smartphone application on tourism information search behavior of foreign independent travelers. Sustainability 12(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12229366
Liu Z, Lan J, Chien F, Sadiq M, Nawaz MA (2022) Role of tourism development in environmental degradation: a step towards emission reduction. J Environ Manag 303:114078
CAS Google Scholar
Lopes R, Malik O, Kumpoh A, Keasberry C, Hong O, Lee S, Liu Y & IEEE (2019) Exploring digital architectural heritage in Brunei Darussalam: towards heritage safeguarding, smart tourism, and interactive education. 2019 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM) At: Singapore Proceedings. p 383–390. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigMM.2019.00067
Lou L, Tian Z, Koh J (2017) Tourist satisfaction enhancement using mobile QR code payment: an empirical investigation. Sustainability 9(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071186
Loureiro SMC, Nascimento J (2021) Shaping a view on the influence of technologies on sustainable tourism. Sustainability 13(22):12691. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212691
Lu J, Xiao X, Xu Z, Wang C, Zhang M, Zhou Y (2022) The potential of virtual tourism in the recovery of tourism industry during the COVID-19 pandemic. Current Issues Tour 25(3):441–457. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.1959526
Ma D, Hu J, Yao F (2021) Big data empowering low-carbon smart tourism study on low-carbon tourism O2O supply chain considering consumer behaviors and corporate altruistic preferences. Comput Ind Eng 153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.107061
Maiorescu I, Negrea M, Popescu D, Sabou G (2016) Best practices regarding the use of electronic environment for Romanian tourism development. Amfiteatru Econ 18(42):474–486
Manglis A, Fourkiotou A, Papadopoulou D (2021) A roadmap for the sustainable valorization of accessible underwater cultural heritage sites. Heritage 4(4):4700–4715. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040259
Manoharan A, Singal M (2017) A systematic literature review of research on diversity and diversity management in the hospitality literature. Int J Hosp Manag 66:77–91
Martinez-Grana A, Goy J, Gonzalez-Delgado J, Cruz R, Sanz J, Cimarra C, de Bustamante I (2019) 3D Virtual itinerary in the geological heritage from natural areas in Salamanca-Avila-Caceres, Spain. Sustainability 11(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11010144
Martins J, Gonçalves R, Branco F, Barbosa L, Melo M, Bessa M (2017) A multisensory virtual experience model for thematic tourism: a Port wine tourism application proposal. J Destin Mark Manag 6(2):103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2017.02.002 . Scopus
Mehraliyev F, Chan ICC, Choi Y, Koseoglu MA, Law R (2020) A state-of-the-art review of smart tourism research. J Travel Tour Mark 37(1):78–91
Miceli A, Hagen B, Riccardi M, Sotti F, Settembre-Blundo D (2021) Thriving, not just surviving in changing times: how sustainability, agility and digitalization intertwine with organizational resilience. Sustainability 13(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042052
Mirzaalian F, Halpenny E (2019) Social media analytics in hospitality and tourism: a systematic literature review and future trends. J Hosp Tour Technol 10(4):764–790
Mohd NS, Ismail HN, Jaafar SMRS, Isa N (2020) Experience co-creation of city visitors from the perspective of technological engagement. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci Scopus 447(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/447/1/012002
Monterroso-Checa A, Redondo-Villa A, Gasparini M, Hornero A, Iraci B, Martin-Talaverano R, Moreno-Escribano J, Munoz-Cadiz J, Murillo-Fragero J, Obregon-Romero R, Vargas N, Young S, Yuste R, Zarco-Tejada P (2020) A heritage science workflow to preserve and narrate a rural archeological landscape using virtual reality: the Cerro del Castillo of Belmez and its surrounding environment (Cordoba, Spain). Appl Sci-Basel 10(23). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238659
Moya‐Anegón SGFde, Vargas‐Quesada B, Chinchilla‐Rodríguez Z, Corera‐Álvarez E, Munoz‐Fernández FJ, Herrero‐Solana V (2007) Visualizing the marrow of science. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 58(14):2167–2179
Mulet-Forteza C, Martorell-Cunill O, Merigó JM, Genovart-Balaguer J, Mauleon-Mendez E (2018) Twenty five years of the Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing: a bibliometric ranking. J Travel Tour Mark 35(9):1201–1221
Muñoz-Leiva F, Hernández-Méndez J, Gómez-Carmona D (2019) Measuring advertising effectiveness in Travel 2.0 websites through eye-tracking technology. Physiol Behav 200:83–95
Muthuraman S, Al Haziazi M & IEEE (2019) Smart tourism destination—new exploration towards sustainable development in Sultanate of Oman. In 2019 5th International Conference on Information Management (ICIM). p 332–335
Mwinuka OH (2017) Reviewing the role of tourism marketing in successful sustainable tourist destinations. Afr J Hosp Tour Leis 6(2):1–11
Nascimento J, Loureiro SMC (2022) The impact of augmented and virtual reality for sustainable tourism. In: Jung T, Dieck MCT, Loureiro SMC (eds) International XR conference. Springer, pp. 148–156
Navarro-Drazich D, Lorenzo C (2021) Sensitivity and vulnerability of international tourism by covid crisis: South America in context. Res Glob 3:100042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resglo.2021.100042
Obonyo G, Okeyo D, Kambona O (2018) Effect of management practices on actual ICT application in Kenyan hotels: a PLS-SEM approach. Int J Hosp Tour Adm 19(2):142–166. https://doi.org/10.1080/15256480.2017.1305311
Palumbo R (2021) Enhancing museums’ attractiveness through digitization: an investigation of Italian medium and large-sized museums and cultural institutions. Int J Tour Res Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.2494
Pavlidis G, Solomou A, Stamouli S, Papavassiliou V, Kritsis K, Kiourt C, Sevetlidis V, Karetsos G, Trigas P, Kougioumoutzis K, Goula K, Proutsos N, Pistikos G, Theodoridis Y, Galanopoulos E, Paraskevas N, Foskolou U, Papadopoulos M (2022) Sustainable ecotourism through cutting-edge technologies. Sustainability 14(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14020800
Pehlivanides G, Monastiridis K, Tourtas A, Karyati E, Ioannidis G, Bejelou K, Antoniou V, Nomikou P (2020) The virtualdiver project. Making Greece’s underwater cultural heritage accessible to the public. Appl Sci (Switzerland) 10(22):1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228172
Article CAS Google Scholar
Permatasari P, Qohar A, Rachman A (2020) From web 1.0 to web 4.0: the digital heritage platforms for UNESCO’s heritage properties in Indonesia. Virtual Archaeol Rev 11(23):75–93. https://doi.org/10.4995/var.2020.13121
Phoong SW, Phoong SY, Ho ST (2022) Technology, organisation and environment factor on mobile payment implementation: focus on SMEs in Malaysia. Int J Mob Commun 20(5):519–540. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMC.2022.125420
Phoong SW, Phoong SY, Khek SL (2022). Systematic Literature Review With Bibliometric Analysis on Markov Switching Model: Methods and Applications, Sage Open 12(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221093062
Pica A, Reynard E, Grangier L, Kaiser C, Ghiraldi L, Perotti L, Del Monte M (2018) GeoGuides, urban geotourism offer powered by mobile application technology. Geoheritage 10(2):311–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-017-0237-0
Pilkington A, Meredith J (2009) The evolution of the intellectual structure of operations management—1980–2006: a citation/co-citation analysis. J Oper Manag 27(3):185–202
Pitoska E (2013) E-tourism: the use of internet and information and communication technologies in tourism: the case of hotel units in peripheral areas. In: Jankovic S, Jurdana D (eds) Tourism in Southern and Eastern Europe. vol 2. WOS:000323235000025, pp. 335–344
Pizam A, Ozturk AB, Balderas-Cejudo A, Buhalis D, Fuchs G, Hara T, Meira J, Revilla MRG, Sethi D, Shen Y (2022) Factors affecting hotel managers’ intentions to adopt robotic technologies: a global study. Int J Hosp Manag 102:103139
Rahmadian E, Feitosa D, Zwitter A (2022) A systematic literature review on the use of big data for sustainable tourism. Current Issues Tour 25(11):1711–1730
Ramos-Soler I, Martinez-Sala A, Campillo-Alhama C (2019) ICT and the sustainability of world heritage sites. Analysis of senior citizens’ use of tourism apps. Sustainability 11(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113203
Ruhanen L, Moyle C, Moyle B (2018) New directions in sustainable tourism research. Tour Rev 74(2):138–149. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-12-2017-0196
Saarinen J, Rogerson CM (2014) Tourism and the millennium development goals: perspectives beyond 2015. Tour Geogr 16(1):23–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2013.851269
Saarinen J, Rogerson C, Manwa H (2011) Tourism and millennium development goals: tourism for global development? Current Issues Tour 14(3):201–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2011.555180
Scott N, Zhang R, Le D, Moyle B (2019) A review of eye-tracking research in tourism. Current Issues Tour 22(10):1244–1261
Shafiee M, Shafiee M, Shams H, Yahai M, Golchin H & IEEE (2013) ICT capacities in creating sustainable urban tourism and its effects on resident quality of life (WOS:000326046500028). In: Shafiee MM, Shafiee MM, Shams H, Yahai MR, Golchin H (eds) 2013 7th international conference on E-commerce in developing countries: with focus on E-Security (ECDC), IEEE
Sharmin F, Sultan M, Badulescu D, Badulescu A, Borma A, Li B (2021) Sustainable destination marketing ecosystem through smartphone-based social media: the consumers’ acceptance perspective. Sustainability 13(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042308
Shehzad K, Liu X, Rauf A, Arif M, Mazhar S, Sohail N, Amin W (2019) Revolutionising tourism development in China: an effective role of ICT and Western Silk Road project. Asia Pac J Tour Res 24(9):965–977
Singh S (2017) Mobile money for promoting conservation and community-based tourism and ecotourism in underdeveloped regions. Tour Recreation Res 42(1):108–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508281.2016.1251011
Streimikiene D, Svagzdiene B, Jasinskas E, Simanavicius A (2021) Sustainable tourism development and competitiveness: the systematic literature review. Sustain Dev 29(1):259–271
Stylos N, Zwiegelaar J, Buhalis D (2021) Big data empowered agility for dynamic, volatile, and time-sensitive service industries: the case of tourism sector. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 33(3):1015–1036
Talafubieke M, Mai S, Xialifuhan N (2021) Evaluation of the virtual economic effect of tourism product emotional marketing based on virtual reality. Front Psychol 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.759268
Tan W, Shrestha D, Jeong S (2019) Digital tourism development and sustainability model for Nepal. In: Shen W, Paredes H, Luo J, Barthes J (eds) 2019 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD). IEEE, pp. 182–187
Taylor JP (2001) Authenticity and sincerity in tourism. Ann Tour Res 28(1):7–26
ADS Google Scholar
Telfer DJ, Sharpley R (2015) Tourism and development in the developing world. Routledge
Theocharidis A, Argyropoulou M, Karavasilis G, Vrana V, Kehris E (2020) An approach towards investigating factors affecting intention to book a hotel room through social media. Sustainability 12(21). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218973
tom Dieck MC, Jung T, Han D-I (2016) Mapping requirements for the wearable smart glasses augmented reality museum application. J Hosp Tour Technol 7(3):230–253. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHTT-09-2015-0036 . Scopus
Tsai T-H, Chang H-T, Lin Y-W, Yu M-C, Lien P-J, Yan W-C, Ho W-L (2018) Emerging social media and social networks analysis transforms the tourism industry: living green smart tourism ecosystem. In: Antona M, Stephanidis C (eds) Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction. Virtual, Augmented, and Intelligent Environments, Springer International Publishing, vol. 10908, pp. 583–590
Tscheu F, Buhalis D (eds) (2016) Augmented reality at cultural heritage sites. In: Proceedings of the international conference on information and communication technologies in tourism, Bilbao, Spain, Springer, Cham, February 2–5. pp. 607–619
Tussyadiah IP, Wang D, Jung TH, Tom Dieck MC (2018) Virtual reality, presence, and attitude change: empirical evidence from tourism. Tour Manag 66:140–154
Ülker P, Ülker M, Karamustafa K (2023) Bibliometric analysis of bibliometric studies in the field of tourism and hospitality. J Hosp Tour Insights 6(2):797–818
Um T, Jia J, Xiaorui T, Chung N (2021) Technology readiness as moderator for satisfaction and destination loyalty in augmented reality environments. Asia Pac J Inf Syst 31(2):220–235. https://doi.org/10.14329/apjis.2021.31.2.220
United Nations Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda
Van NTT, Vrana V, Duy NT, Minh DXH, Dzung PT, Mondal SR, Das S (2020) The role of human–machine interactive devices for post-COVID-19 innovative sustainable tourism in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Sustainability 12(22):9523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12229523
Vitezic V, Car T, Simunic M (2015) Managing innovative technology in the hotel industry—response to growing consumer preferences. In: Jankovic S, Jurdana D (eds) Tourism in Southern and Eastern Europe, vol 3, pp. 467–478
Wang F, Liu Z, Shang S, Qin Y, Wu B (2019) Vitality continuation or over-commercialization? Spatial structure characteristics of commercial services and population agglomeration in historic and cultural areas. Tour Econ 25(8):1302–1326
Wang G, Wang H, Wang L (2023) Research trends in tourism and hospitality from 1991 to 2020: an integrated approach of corpus linguistics and bibliometrics. J Hosp Tour Insights 6(2):509–529
Wang Y, Lin Y-J, Lin B-S (2020) The factors that affect usage intentions and travel intentions of travel-related WeChat official accounts. Sustainability (Switzerland) 12(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156108
Wei W (2019) Research progress on virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in tourism and hospitality: a critical review of publications from 2000 to 2018. J Hosp Tour Technol 10(4):539–570
Winter PL, Selin S, Cerveny L, Bricker K (2020) Outdoor recreation, nature-based tourism, and sustainability. Sustainability 12(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010081
Xie X, Zhang W (2021) Regulation mechanism of spatial capacity of tourist resources in scenic spots based on Internet of things technology. Complexity https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3934894
Yalina N, Rozas IS (2020) Digital workplace: digital transformation for environmental sustainability. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 456(1):012022. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/456/1/012022
Yang J, Yang R, Chen M-H, Su C-HJ, Zhi Y, Xi J (2021) Effects of rural revitalization on rural tourism. J Hosp Tour Manag 47:35–45
Yin C, Jung T, Dieck M, Lee M (2021) Mobile augmented reality heritage applications: meeting the needs of heritage tourists. Sustainability 13(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052523
Yovcheva Z, Buhalis D, Gatzidis C (2012) Smartphone augmented reality applications for tourism. E-Rev Tour Res 10(2):63–66
Yuce A, Arasli H, Ozturen A, Daskin M (2020) Feeling the service product closer: triggering visit intention via virtual reality. Sustainability 12(16). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166632
Zhang C, Fyall A, Zheng Y (2015) Heritage and tourism conflict within world heritage sites in China: a longitudinal study. Current Issues Tour 18(2):110–136
Zhao J, Li S-M (2018) The impact of tourism development on the environment in China. Acta Sci Malays 2(1):1–4
MathSciNet ADS Google Scholar
Zhong L, Sun S, Law R, Li X (2021) Tourism crisis management: evidence from COVID-19. Current Issues Tour 24(19):2671–2682. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.1901866
Zhou C, Sotiriadis M (2021) Exploring and evaluating the Impact of ICTs on culture and tourism industries’ convergence: evidence from China. Sustainability 13(21). https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111769
Zubiaga M, Izkara J, Gandini A, Alonso I, Saralegui U (2019) Towards smarter management of overtourism in historic centres through visitor-flow monitoring. Sustainability 11(24). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247254
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the Universiti Malaya International Collaboration Grant, grant number ST013-2022.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Decision Science, Universiti Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Chunyu Jiang & Seuk Wai Phoong
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Seuk Wai Phoong .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jiang, C., Phoong, S.W. A ten-year review analysis of the impact of digitization on tourism development (2012–2022). Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-02150-7
Download citation
Received : 25 April 2023
Accepted : 11 September 2023
Published : 07 October 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-02150-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

National Congress of Commodity Science
AISME 2022: Innovation, Quality and Sustainability for a Resilient Circular Economy pp 479–486 Cite as
Innovative Approaches for the Digitalization of Tourism Businesses
- Carlo Amendola 12 &
- Marco Savastano 12
- Conference paper
- First Online: 24 February 2024
50 Accesses
Part of the book series: Circular Economy and Sustainability ((CES))
Over the last few decades, tourism has changed profoundly, and at the same time, both the types of travel and the profiles of travelers have changed. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, tourism was one of the sectors that paid the highest price in economic terms, not only in the lockdown period but also in the following months in which, in correspondence with the first reopening, consumers associated a high perception of risk to travel, many giving up planning their own departures. The entire supply chain of the tourism industry has been affected, from the hoteliers of the largest and most renowned structures to small Bed & Breakfasts, from guest houses to hostels, from restaurateurs to suppliers, and from operators to tour guides and museums. This work aims to investigate new dimensions of post-COVID-19 tourism by including some innovation factors, such as the alternatives offered by smart working to tourists and to the citizens of large cities in which many hotels are placed. The research work highlights how the digitalization of tourism services has thus far changed the information-decision-making process that leads to the choice of travel, its experiential and post-experiential phases, and how in the new post-pandemic normal, it can change the way of living the vacation, traveling, and ancillary services connected to them.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Amendola C, Casalino N, La Bella S et al (2022) Innovazione dei processi lavorativi e ruolo degli artefatti nei modelli di cultura organizzativa: un’indagine empirica sulla trasformazione digitale della Pubblica Amministrazione. Prospettive in Organizzazione, La rivista di organizzazione aziendale
Google Scholar
Benevolo C, Grasso M (2018) L’impresa alberghiera. Produzione, strategie e politiche di marketing. Franco Angeli, Milano
Corigliano M, Baggio R (2017) Internet e Turismo 2.0, Egea, Milano
Dall’Ara G (2017) Le nuove frontiere del marketing applicato al turismo. Franco Angeli, Milano
Gabetti Property Solutions (2020) L’hospitality del futuro. Tendenze, prospettive e opportunità del settore alberghiero in Italia. Gabetti Property Solutions, Ufficio Studi, Milano
Hepburn C, O’Callaghan B, Stern N et al (2020) Will COVID-19 fiscal recovery packages accelerate or retard progress on climate change? Oxford rev econ. Policy 36:S359–S381
Ronchi M, Ciancia M (2019) Digital transformation. Metodi e strumenti per guidare l’evoluzione digitale delle imprese attraverso design, marketing e comunicazione. Franco Angeli, Milano
Rossi C (2018) In viaggio…verso il digitale. Le imprese della distribuzione turistica di fronte alla sfida del web. In: Congresso Internazionale “Le Tendenze del Marketing”, Egea, Milano
Ruggieri R, Savastano M, Scalingi A et al (2018) The impact of digital platforms on business models: an empirical investigation on innovative start-ups. Manag Mark 13:1210–1225
Stentoft J, Adsbøll Wickstrøm K, Philipsen K et al (2021) Drivers and barriers for industry 4.0 readiness and practice: empirical evidence from small and medium-sized manufacturers. Prod Plan Control 32:811–828
Article Google Scholar
Tortorella G, Miorando R, Caiado R et al (2021) The mediating effect of employees’ involvement on the relationship between industry 4.0 and operational performance improvement. Total Qual Manag Bus Excell 32:119–133
Vescovi T (2019) Il marketing e la rete. Il Sole 24 ore. Milano
Vescovi T, Gazzola P, Checchinato F (2010) I clienti invadenti: nuove relazioni di mercato tra clienti e imprese. J Market Trends 1:41–57
World Travel & Tourism Council (2021) Travel & tourism. Economic impact 2021. Global economic impact & trends 2021. World Travel & Tourism Council, London, UK www.formazioneturismo.com . Accessed 30 May 2022
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Management Department, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
Carlo Amendola & Marco Savastano
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Carlo Amendola .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, Management and Business Law, University of Bari Aldo Moro, Bari, Italy
Giovanni Lagioia
Annarita Paiano
Vera Amicarelli
Teodoro Gallucci
Carlo Ingrao
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions

Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Amendola, C., Savastano, M. (2024). Innovative Approaches for the Digitalization of Tourism Businesses. In: Lagioia, G., Paiano, A., Amicarelli, V., Gallucci, T., Ingrao, C. (eds) Innovation, Quality and Sustainability for a Resilient Circular Economy. AISME 2022. Circular Economy and Sustainability. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-28292-8_58
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-28292-8_58
Published : 24 February 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-28291-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-28292-8
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Hi, what are you looking for?
US Senate to vote to extend foreign surveillance Bill

US Federal Communications Commission’s net neutrality rules allow for telcos to operate 5G fast lanes

X banned in Pakistan, Interior Ministry confirms: Report

IT Ministry Introduces Mandatory Security Requirements for CCTV Cameras

Video: Are Indian news publishers right in demanding copyright protection against generative AI models?
- Free Newsletter
- Consultations
- Freedom Of Expression
- Artificial Intelligence
- Competition
- Facial Recognition
- Net Neutrality
- Platform Regulation
Summary: Enabling data exchange in the tourism industry under the National Digital Tourism Mission
The report follows a familiar pattern in proposing data registries, open APIs, aggregate platforms, and a separate regulatory body.
The government constituted the task force in July 2021, noting that it wants to emulate the success of UPI and the National Digital Health Mission for the tourism ecosystem.
“At a collective level, it will help to develop and customize product offerings, improve destination connectivity, generate data to track performance, and help to improve destination management.” – NDTM task force report
MediaNama’s Take: What to watch out for?
Here are two lenses to read the summary of the report that follows:
Privacy concerns
Inclusivity.
The second major concern is how inclusive will the NDTM be. The issue we’ve had with many digitisation programmes is that not all sections of society have benefitted in an equitable way, and in some cases, digitisation has negatively affected some sections of society. For example, many doctors and smaller hospitals have complained about the high compliance cost of the National Digital Health Mission. With NDTM, the question is whether smaller establishments will be left out because of the compliance costs and how this will affect them.
Why digitise the tourism ecosystem?
Currently, most of the tourism systems developed by the central government, state governments, public sector and private sector function in silos because of which the tourism ecosystem is unable to harvest the combinatorial benefits of information exchange , the report states. There are no mechanisms in place to allow the interactions of various data systems through a common language, thereby curtailing data analytics and resultant policy-making, the report adds. To overcome this hurdle, there is a need for a standardised data exchange amongst various stakeholders, the report states.
The report looks to bridge the information gap amongst different stakeholders by creating a digital highway :
What comprises the digital stack of NDTM?
The following graphic gives an overview of the four different layers of the NDTM digital stack:
Layer 1: Cross-domain generic building blocks
The first layer of the stack is the existing digital infrastructure available to use such as Aadhaar, DigiLocker, UPI/BHIM etc. “This digital infrastructure layer helps to achieve uniqueness of key data sets, economies of scale and facilitates all India portability for stakeholders of the ecosystem,” the report states.
Layer 2: Tourism domain data
The second layer consists of core domain data related to tourism such as:
- Tourism directories: Directories of tourist attractions, tourist activities, associations, routes, accommodation type, tourist transport facilities (e.g. ropeways), festival calendar, convention halls, public utilities, etc.
- Tourism registries: Registries of tour operators, travel agents, online travel aggregators, waiters, destination wedding managers, tourist guides, chefs, coach drivers, accommodation units, eateries, circus, parks, theatre, spas, events, casinos, tourist info, etc.
- Tourism records: Tourism records will include rules and permissions, location and purpose-wise activity records, travel insurance, event calendar, shopping rate range, conferences, room rate range, footfall records, etc.
The report proposes that there be a single source of truth among departments and external agencies for the above domain data thereby providing opportunities for improved efficiency and effectiveness in governance. The creation of these directories and registries shall enable digital verification of tour operators, travel agents, licensed bars, etc., and can lead to increased trust amongst the tourist and ecosystem actors, the report adds.
Layer 3: Unified Tourism Interface
The third layer of the NDTM digital stack promotes data and information exchange amongst multiple ecosystem actors through the creation of the UTI.
To build this interface layer, actors of NDTM will be encouraged to deploy their APIs and micro-services as open APIs following the specifications and standards of NDTM. These APIs shall be deployed on the NDTM eMarketplace or API exchange, the report states. Some of the APIs in the NDTM context are:
- Discovery APIs: These APIs help the tourism ecosystem actors and tourists to connect with the ecosystem in a convenient and cost-effective manner. The systems in the tourism domain would be able to share live rate cards, get tourist accommodations availability details, tourist travel availability details, the know-how of required permissions, the know-how of applicable rules, discount details, access to multi-modal search for travel and route planning, nearby public utilities, etc., the report explains.
- Booking APIs: These APIs will allow the ecosystem actors to reserve accommodations, restaurant tables, entertainment tickets, tourist coaches, tickets and cancel reservations, apply for eVisa services etc. for tourists who provide explicit consent for data sharing, the report states.
- Other Tourism APIs: These APIs include services related to rating, payment services, certification services, licensing services, permissions services, help services and other such services, the report states.
Layer 4: User systems
The fourth layer consists of core, common, and reference systems and aggregate platforms. These aggregate platforms will be built using the Unified Tourism Interface.
- Single window compliance platform: This system will provide a single-window platform to gain knowledge about rules, regulations, and compliance requirements for all actors of the tourism ecosystem. For example, tourist visitor timings, ticketing rules, special travel requirements, medical requirements, conflict zone, etc. shall be made available. For service providers, various license requirements, NOC requirements, compliance requirements, etc.
- Data analytics platform: The data analytics platform will use aggregate anonymised data for research, planning and policy-making, etc. Aggregate data sources like telecom can be used to understand the seasonality, movement patterns, trip length, etc., of tourists, the report explains.
- Common applications: This includes some common applications which can be used by both public and private players like sandbox environment, API exchange gateway, and eMarketplace. The sandbox environment, for example, will enable the various ecosystem actors to discover, understand, engage, experiment, innovate, and build on existing core data, infrastructure and exchange, the report states. The tourism eMarketplace, on the other hand, will be a national aggregate platform where customised tour packages can be made available from authorised providers for domestic and international tourists.
- Reference applications: The government may foray into building reference applications, which shall be built as open-source, and technology companies shall be encouraged to build upon these products, the report states. Examples of these applications include tour planning software for tour operators who do not have access to large aggregate digital platforms but want to provide customised deals to the client and Hospitality Facility Management ERPs as low-cost digital options for small hospitality service providers.
An autonomous body will be set up as part of NDTM
Will be modelled after other institutional set-ups: The NDTM will adopt institutional structure after study of several analogous digital infrastructures created in other sectors in India such as GSTN, NPCI, UIDAI, National Health Authority, etc, the report states. It will be composed of diverse stakeholders and will be created as an autonomous entity under the aegis of the Ministry of Tourism , the report adds.
Roles and responsibilities of the institution: The institutional structure of the NDTM will be responsible to:
- Catalyse the tourism ecosystem: The institution will be responsible for implementing the objectives of the NDTM blueprint and promoting its adoption in the ecosystem by engaging in events, hackathons, innovations, fests and other such outreach, engagement and development programs.
- Enable the development of the building blocks: The institution will also be responsible for enabling the development of the building blocks of NDTM.
- Framing standards, specifications, and policies: The institution will develop technological standards, specifications and policies for tourism, open data, and protection of data of individuals. This includes specifications of core, common, reference and other building blocks as well as setting up standards for establishment and management of registries which will be a single source of truth for tour operators, hoteliers, event managers etc.
- Encouraging innovation: The institution is expected to foster innovation and solutions by leveraging emerging technologies for the tourism ecosystem such as AI/ML, AR/VR, etc as well by creating an ecosystem sandbox.
What are the potential benefits of NDTM?
According to the report, the NDTM is envisaged to bring the following benefits to the various stakeholders of the tourism ecosystem:
What standards need to be developed for the tourism ecosystem?
- Open protocols: The report proposed setting up a committee consisting of technical representatives from different ministries, states, experts, academia, and industry to collaborate with BIS for ratification of open API specifications and protocols that pertain to microservices for standardised open data and other domain apps in the tourism ecosystem.
- Data governance policy: “In order to ensure data protection, data quality, data security, data privacy, data sharing obligations, portability and interoperability and compliances under the applicable laws, a data governance policy will be framed specifying roles and responsibilities of various ecosystem actors towards maintaining and facilitating reliable data exchange,” the report states.
- Domain standards: The report prescribed introducing domain standards for star ratings of accommodation units, classification of transport as luxury, standard or local, badges for tourist agents and tourist drivers, classification of tour operators, sustainable tourism criteria of India etc.
Ten key principles of NDTM
- Building block approach: The ecosystem will be built with minimal and reusable building blocks, categorised as Core, Common and Reference Building Blocks which are loosely coupled and combinable.
- Federated architecture: The report proposes a federated architecture model for designing the digital ecosystems, which will be built around the constructs of Single-Source-of-Truth and System-of-Records. “While a central system can speed up adoption, it should be a choice, and bringing interoperability across many federated systems through common specifications is necessary,” the report explains.
- Be open and interoperable: The digital ecosystem should be developed using open standards, licenses, databases, APIs, etc. and promote interoperability. This helps realise inter-platform efficiencies, promotes competitive behaviour and guards against potential monopolies of unfair value capture, the report states.
- Resilient: There should not be single points of failure and services must be built to withstand failures by building automated recoveries and adaptation.
- Minimal, reusable, unbundled, and shareable: The various building blocks must be minimal (both data and functional), atomic, and generalised allowing solution builders to “reuse and extend” them to build contextual and scalable solutions.
- Setting up data marketplace: The report states that data systems should be designed in a manner that creates, supports, maintains and enhances value to the ecosystem in general. To do some, the report proposes the establishment of Data Marketplace(s) that enables regulated exchange of data.
- Data sharing: The report calls for clear policies specific to the relevant domain(s), that enable and regulate the sharing of data.
- Standards: The report states that existing technology and data standards applicable to the ecosystem should be specified and methods to ensure compliance should be designed.
- Privacy-by-Design: The report advocates for designing and publishing a privacy policy that conforms to the principles of privacy-by-design.
- Secure and trust-based: The NDTM should be designed to protect the privacy of users and entities while inducing trust in every interaction.
What will be the future of data governance in India?
Do you want to keep track of data sharing frameworks in India but don’t have the time? Relying on scattered content from across the web makes it feel harder than it needs to be.
Latest Headlines
- US Senate to vote to extend foreign surveillance Bill April 20, 2024
- US Federal Communications Commission’s net neutrality rules allow for telcos to operate 5G fast lanes April 19, 2024
- X banned in Pakistan, Interior Ministry confirms: Report April 19, 2024
- IT Ministry Introduces Mandatory Security Requirements for CCTV Cameras April 19, 2024
- Video: Are Indian news publishers right in demanding copyright protection against generative AI models? April 19, 2024
The ‘Reforming Intelligence and Securing America Act’ (RISAA) is a legislation to reauthorize Section 702 of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA).

In its submission, the Interior Ministry said the decision to impose a ban was "made in the interest of upholding national security, maintaining public...

Among other things, the security requirements include data encryption and regular review and updated access permissions to reflect personnel changes.
MediaNama’s mission is to help build a digital ecosystem which is open, fair, global and competitive.

Views: Response to NPCI CEO’s comments that what is not written in regulations is a no-go for fintech entities
NPCI CEO Dilip Asbe recently said that what is not written in regulations is a no-go for fintech entities. But following this advice could...

Views: The opportunities and challenges for PhonePe’s Indus Appstore
Notably, Indus Appstore will allow app developers to use third-party billing systems for in-app billing without having to pay any commission to Indus, a...

Views: Why Rapido is moving to subscription model
The existing commission-based model, which companies like Uber and Ola have used for a long time and still stick to, has received criticism from...

Views: Why PhonePe’s Indus Appstore can challenge Google Play’s dominance in India
Factors like Indus not charging developers any commission for in-app payments and antitrust orders issued by India's competition regulator against Google could contribute to...

Views: Open Source AI—A Nebulous Concept Bearing a Heavy Weight
Is open-sourcing of AI, and the use cases that come with it, a good starting point to discuss the responsibility and liability of AI?...
Please subscribe to MediaNama. Don't share prints and PDFs.
You may also like.

Search queries for international air tickets growing at 43% – Google
Google has released a Google Travel Trends Report which states that branded budget hotel search queries grew 179% year over year (YOY) in India, in...
Advertisement: 135 Digital Job Listings at JobNama – 9th June 2010
135 job openings in over 60 companies are listed at our free Digital and Mobile Job Board: If you’re looking for a job, or...

Twitter takes down tweets from MP, MLA, editor criticising handling of pandemic upon government request
By Aroon Deep and Aditya Chunduru You’re reading it here first: Twitter has complied with government requests to censor 52 tweets that mostly criticised...

Ola, Uber drivers say they are exhausted, fear being wiped out
Rajesh Kumar* doesn’t have many enemies in life. But, Uber, for which he drives a cab everyday, is starting to look like one, he...
- Government Policies
- Modi Government
- Rules and Relguation
- TATA Merger
Latest News
- WhatsApp Launches UPI-Based Payments Feature In India
- MediaNama: Roundtable On Copyright And Digital Media
- Should Amazon, Flipkart Show Country Of Origin Of Products?
- After CEO Dick Costolo, Twitter’s M&A Head Rishi Garg Quits
- Gujarat HC Gives Livestreaming Court Proceedings A Shot

MediaNama is the premier source of information and analysis on Technology Policy in India. More about MediaNama, and contact information, here.

© 2008-2021 Mixed Bag Media Pvt. Ltd. Developed By PixelVJ
- Terms Of Use
- Privacy Policy

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Digitalisation in Daily Life Essay
Essay – digitalisation in daily life.
Digitalisation in Daily Life Essay: Digitalization refers to the use of computers and internet to facilitate various functions and actions. Digitalization started way back in the 1950s with the advent of computers. Since then, the process has continued to increase its usage diversity. In 2015, the flagship programme “Digital India” enabled the mainstreaming of digital services in India. Digitalization has enabled efficiency and lower operational costs in production. With better User Interface (UI) and seamless communication, digitalization has some very obvious advantages.

Digitalization of communication through the introduction of software applications such as WhatsApp, Telegram, Microsoft Teams, etc., drastically changed the way we communicate with each other. We can now connect with anyone at any given time without being restricted by time and space/place. Improved and fast communication due to digitalization has allowed us humans to function easily and with much less errors. Also, digitalization has aided the infotainment industry. We can watch documentaries, news, movies with a click on the screen in the comfort of our homes or from anywhere we want.
In the economic and commercial sector too, we see how digitalization has revolutionized our functions. One of the most prominent changes as can be seen has been the increased usage of UPI or Unified Payments Interface. UPI has reformed the way we conduct commercial transactions. It has provided inclusivity for small scale businesses in the economy by allowing them to set up credit-acquiring systems conveniently. The introduction of UPI has reduced the dependency on the previous card/cash-based payment systems. The new digital infrastructure has moreover encouraged entrepreneurs to open up start-ups and online businesses. Thus, we see that many Indian businesses have started emerging in the domestic and international market, boosting the country’s economy as well as providing a much-needed self-dependent employment ecosystem. Moreover, availing services like applying for Aadhaar or PAN has been digitalized too which makes the process easier and more efficient.
The Covid-19 pandemic best highlighted the digitalization of daily life. With every physical contact-based activity being suspended for a considerable period of time, digitalization of daily life was the only option. Education was made digital through online classes conducted through apps like Google meet. Use of various online software for daily activities increased. Even the healthcare sector had been digitalized. It can be insisted that a rapid digitalization of daily life was what helped us avoid stagnancy. Thus, one can easily witness their digitalized life wherever they look.
Read: Essay on Tourism in India
Very Bad Service
I like this essay
Nice essay….
GOOD KEEP IT UP THANK YOU FOR THIS
This was a great explanation, and a quick an as effeceint essay
Love it ,thanks for helping
Good one I really like it Keep it up
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Rs aggarwal class 8 math first chapter rational numbers exercise 1c solution, new learning composite mathematics class 5 s.k. gupta anubhuti gangal volume chapter 18a solution, new learning composite mathematics class 5 s.k. gupta anubhuti gangal volume chapter 18b solution, madam rides the bus extra questions and answers english first flight chapter 9.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Digitalization and Tourism Sector 5 1.5. Inter-Ministerial Task Force for National Digital Tourism Mission 6 1.6. Constitution of Working Group 6 1.7. NDTM Report 6 ... Introduction to India's Tourism Sector 17 3.2. Performance of India's Tourism Sector 18 3.3. SWOT Analysis 20 3.4. Targets set by SGOS by 2024 22 3.5. Challenges faced by Indian
The present paper on 'Digitalization: A Strategic Approach for Development of Tourism Industry in India' aims to throw a light on similar aspects. With the identification of the driving forces of digitalization in tourism industry, challenges and issues pertaining to it can easily be addressed.
From the perspective of Cuomo et al. (2020), this drives the need to deepen our knowledge about the contribution of the usage of digital technologies beyond a focus on tourism services.Furthermore, these authors stress the need to carry out scientific research able to illuminate how tourism is evolving concerning these technological advances, which open up spaces and opportunities for studies ...
The travel and tourism industry of India is no exception. Digitalization has transformed the overall experience of a traveler or tourist. The importance of digitalization is even more important in the present scenario of COVID-19, which has displayed a fragile picture of this sector and has halted almost every activity making it one of the ...
Virtual tourism, ICT, mobile technology, smart heritage tourism technology, and innovative marketing methods improve stakeholders' quality of life, increasing the tourism system and community ...
Since then, Digital India has. affected almost all aspects of our lives, ranging from. work, tra vel, communication to shopping, education. going to be digital and travel. and tourism are no ...
ArticlePDF Available. Digitalization: A Strategic Approach for Development of Tourism Industry in India. April 2020. Paradigm 24 (1):097189072091411. DOI: 10.1177/0971890720914111. Authors: Suneel ...
The technological innovations promising to have disruptive effects on the tourism market mainly concern the areas of entertainment, comfort during travel, robotics, and information (big data, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and social networks play an increasingly central role) (Rossi 2018).The COVID-19 pandemic, in addition to the significant impact on social life and economic ...
2.2. Evolution of tourism sector in India. The very first step towards sustainable tourism was through National Tourism Policy in 1982, when the then government formulated a comprehensive plan in 1988 to promote tourism. By the year 2000 major states in India declared tourism as an industry and its contribution as a part of the development ...
March 15, 2022. The National Digital Tourism Mission (NDTM) task force on March 9 submitted its report which proposes the creation of a Unified Tourism Interface (UTI) to enable the exchange of ...
Digitalization in tourism sector presents opportunities for tourism enterprises to expand their market reach, increased growth, improved operational efficiencies, and sharpen 1 A digital ecosystem is a distributed, open socio-technical system with properties of self-organisation, evolution,
"Success of Digitalization in Tourism Industry in India" by (Shigaonker, 2018) explores the concept of digitalization in travel & tourism, and how mobile, online travel portal and social media are ...
THINK INDIA JOURNAL ISSN:0971-1260 Vol-22-Issue-32-December-2019 Digital Revolution in Indian travel and tourism industry Prof. Sabir N. Mujawar Assistant Professor, Chetana College, Self Financing Section, Bandra (E). ABSTRACT Nowadays digitalization has a major impact on our day to day work and business activities, our life and the way we live.
A key concern in the post-tourism debate of the 1980s and 1990s was the gradual de-differentiation of tourism and social life. Theorists like Feifer (1985), Munt (1994) and Lash and Urry (1994; see also Urry, 1995) argued that tourism in (post)modern, post-Fordist societies was becoming less spectacular; something that was spread out across ever more time-spaces of everyday life and that a ...
According to World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) India's travel and tourism sector ranks 7th in the world in terms of its total contribution to the country's GDP, generated Rs. 14.1 trillion (USD208.9 billion) in 2016, which is world's 7th largest in terms of absolute size; the sum is equivalent to 9.6% of India's GDP.
Cashless Economy and Digitalization of Tourism & Hospitality Practices in India Available on SSRN-Elsevier 454 Introduction Demonetization is to be considered as a new era of digital economy. Digitalization has brought lots of technological transformations and innovations to ease the routine economic transactions with less cash options.
By adopting the 2030 Agenda and its Sustainable Development Goals, the Member States of the United Nations pledged to "leave no one behind" in the journey to build a better world. Moreover, the Agenda also emphasises the importance of "reaching the furthest behind first". Ever since mankind first started travelling for leisure, tourism has been a source of employment and of economic ...
in food outlets, 34% twice, 14% thrice, 10% four times and 15% of the respondents. visits more than four times a month in food outlets. 63% of the respondents. Analysing the Factors A ecting ...
Home | Ministry of Tourism | Government of India
Also, various challenges that are arising in course of digitalization in tourism industry are identified and suggestions have been made to resolve these issues. The study makes use of interpretive structural modelling (ISM) to develop a strategic framework related to digitalization in the industry.
Digitalisation in Daily Life Essay: Digitalization refers to the use of computers and internet to facilitate various functions and actions. Digitalization started way back in the 1950s with the advent of computers. Since then, the process has continued to increase its usage diversity. In 2015, the flagship programme "Digital India" enabled ...
The proportion of th e Internet economy in India's technology industry will increa se from 48% in 2022 to. 62% in 2030. By 2023, it will acco unt for 12 - 13% of India's GDP, up from 4% in 2022 ...