General information
- Entry/Exit system is currently not in operation.
The Entry/Exit System (EES) is an automated IT system for registering non-EU nationals travelling for a short stay, each time they cross the external borders of European countries using the system (exemptions apply, see FAQ section ). This concerns travellers who require a short-stay visa and those who do not need a visa. Refusals of entry are also recorded in the system.
The main advantage of the EES is saving time. The EES replaces passport stamping and automates border control procedures, making travelling to European countries using the EES more efficient for the traveller.
The EES also makes it easier to identify travelers who have no right to enter or who have stayed in the European countries using the EES for too long. It makes it easier to detect travelers using fake identities or passports. Finally, the EES helps to prevent, detect and investigate terrorist offences or other serious criminal offences.
The EES applies to you if you are a non-EU national travelling to a European country using the EES for a short stay of up to 90 days within any 180 day period. It is important to remember that the period of 90 days in any 180 days is calculated as a single period for all European countries using the EES.

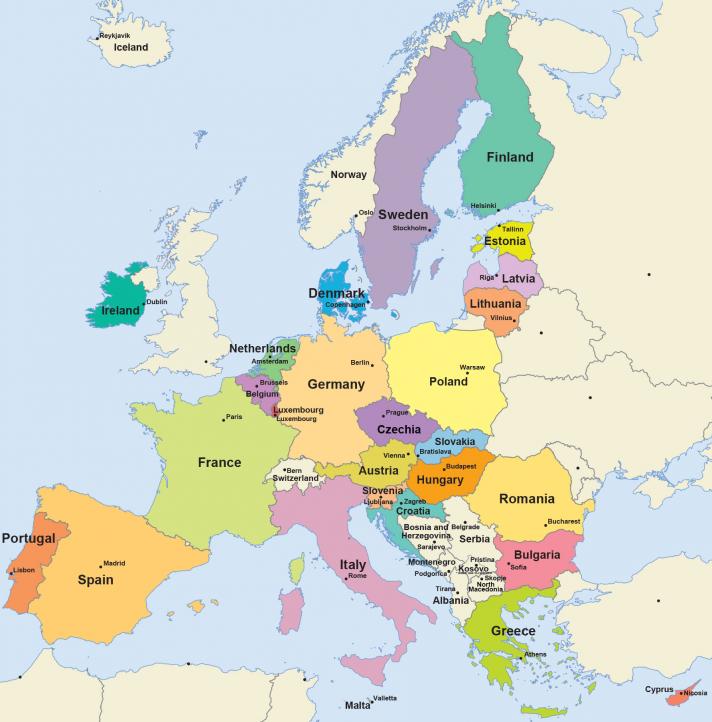
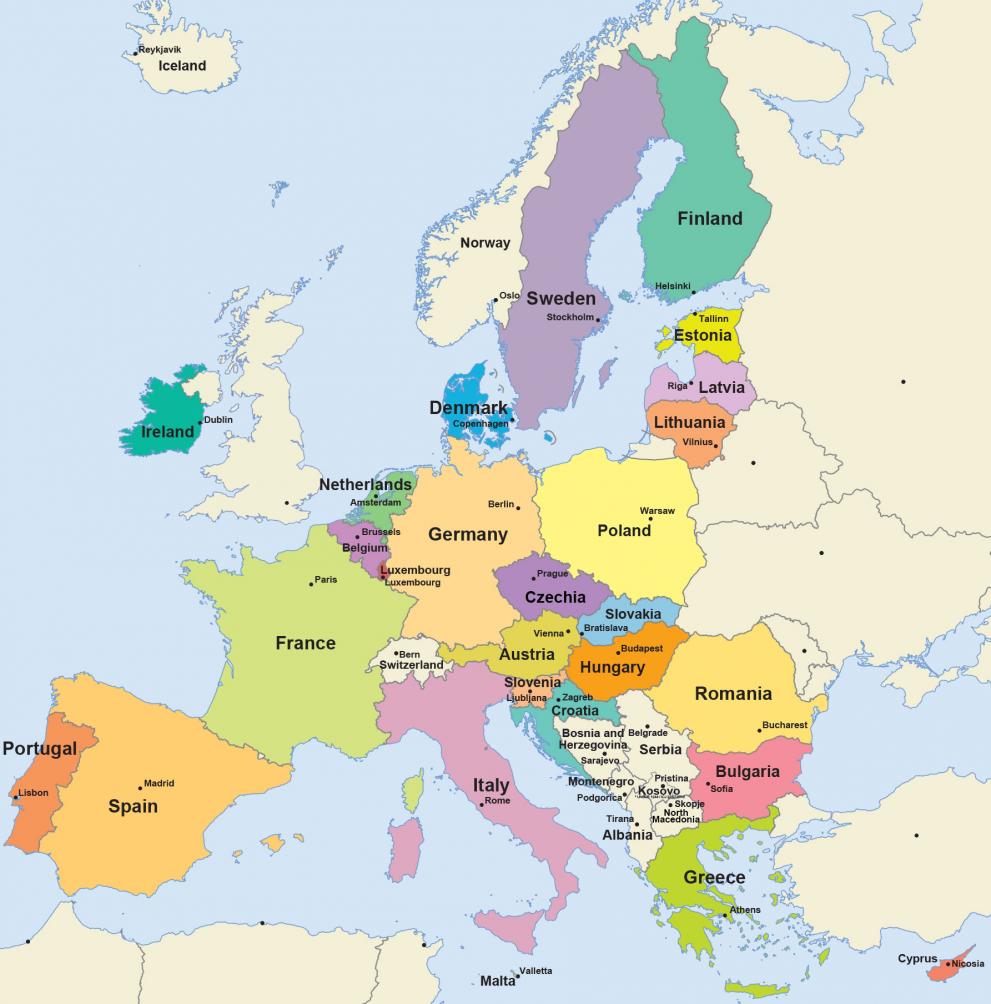
European countries using the EES

List of countries using EES
In Cyprus and Ireland, despite being countries of the European Union, passports are still stamped manually.
Why does the EES collect personal data?
The EES collects personal data provided by the traveller each time he or she reaches the borders of European countries using the EES and stores this information in the system together with the date and time of their entry or exit.
This makes border checks faster. It also makes it easier to identify travellers who have no right to enter, who have stayed in European countries using the EES for too long, or who are using fake identities or passports. The EES also collects and stores personal data to contribute to prevention, detection and investigation of terrorist offences and other serious crimes.
Conditions for collecting and storing personal data in the EES are set out in the Regulation (EU) 2017/2226 establishing the Entry/Exit System .
Information on the processing of your personal data in the Entry/Exit System
If you are a non-EU national travelling for a short stay (maximum 90 days in any 180-day period) to a European country using the EES, you will be provided with clear information in writing about the EES and your related rights at the border-crossing point.
Your data is collected and processed for the purposes of border management, preventing irregular immigration and facilitating the management of migration flows. This is required in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2017/2226 , specifically Articles 14, 16 to 19 and 23 of Chapter II and Chapter III of the Regulation.
What data will the EES collect?
The EES collects and records:
- data listed in your travel document (e.g. full name, date of birth, etc.)
- date and place of entry into and exit from a European country using the EES
- facial image and fingerprints (called ‘biometric data’)
- refusal of entry, where relevant
Please note that the fingerprint data of non-EU nationals who do not need a visa to enter the territory of European countries using the EES and holders of Facilitated Transit Documents will be stored in the EES. If you need a visa to enter the Schengen area, your fingerprints will already be stored in the Visa Information System and will not be stored again in the EES.
The system also collects your personal information, depending on your particular situation, from:
- the Visa Information System (which contains additional personal information)
- the European Travel Information and Authorisation System , in particular the status of your travel authorisation and, if applicable, your family member status
All this is done in full compliance with data protection rules and rights.
What happens if you refuse to have your fingerprints scanned or a photo of your face taken?
As a non-EU national travelling for a short stay, if you refuse to provide your biometric data, you will be denied entry into the territory of European countries using EES.
Who can access your personal data?
- Authorities in European countries using the EES such as border, visa and immigration authorities for the purpose of verifying your identity and understanding whether you should be allowed to enter or stay on the territory.
- Europol may also access your data for law enforcement purposes.
- Under strict conditions, your data may be transferred to another state (EU country or non-EU country) or international organisation (listed in Annex I of Regulation (EU) 2017/2226 ) (UN organisation, the International Organisation for Migration, or the International Committee of the Red Cross) for return ( Article 41(1) and (2) , and Article 42 and/or law enforcement purposes Article 41(6) ).
- Carriers will only be able to verify whether short-stay visa holders have already used the number of entries authorised by their visa, and will not be able to access any further personal data.
How long does the EES keep your personal data?
Your data will be stored in the system for the following durations:
- Records of entries, exits, and refusals of entry : 3 years, starting on the date on which they were recorded.
- Individual files containing personal data : 3 years and one day, starting on the date of your last exit record (or of your refusal of entry, if you were not permitted to enter).
- If no exit has been recorded : 5 years, starting on the expiry date of your authorised stay.
After each time period expires, your data is automatically erased.
As the fingerprint scans of travellers requiring Schengen visas will already be in the Visa Information System, they will not be stored again in the EES.
In the case of non-EU nationals who are family members of EU, EEA, or Swiss nationals who are travelling to a state other than the state of their nationality, or who already reside there, and who are accompanying or joining these EU, EEA, or Swiss nationals, each entry, exit, or refusal of entry record will be stored for one year following the date of the exit record or of the refusal of entry record.
How can you find out how much longer you can stay in European countries using the EES and what happens if you overstay?
You have the right to receive information from passport control officers on the maximum remaining duration of your authorised stay.
Once EES is operational, you will be able to consult an online tool available on the EES website and/or consult the equipment installed at the border crossing points (if available).
If you stay for longer than permitted, you will be identified as an ‘overstayer’ and your data will automatically be added to a list. Competent national authorities (passport control officers, immigration officers, staff issuing visas, etc.) can access this list.
If you are added to the list of overstayers, other consequences can apply depending on national legislation in place in the respective European country using EES (e.g. you may be removed from the territory; you may be subject to administrative fines or detention; you may be prevented from re-entering the EU in the future.)
If, as an overstayer, you provide credible evidence to the competent authorities, such as border authorities or immigration authorities, that you exceeded the authorised duration due to unforeseeable or mitigating circumstances (e.g. hospitalisation due to a serious injury), your data can be amended in the system and you can be removed from the list.
The calculation of the duration of the authorised stay and the generation of alerts to European countries using the EES when the authorised stay has expired do not apply to non-EU nationals who are family members of EU, EEA or Swiss nationals who travel to a state other than the state of their nationality, or already reside there, and are accompanying or joining the EU, EEA or Swiss national.
What rights do you have with respect to your personal data?
You have the right to:
- Request from the controller access to data relating to you
- Request that inaccurate or incomplete data is corrected
- Request that unlawfully processed personal data that concern you is erased and/or that the processing thereof is restricted
To exercise any of the rights listed in points (1) to (3), you must contact a data controller (e.g. the entity responsible for processing your data) or data protection officer in any of the European countries using the EES, preferably the ones to which you travelled.
You can find the relevant contact details for the European countries using the EES on this site (will be made available at a later stage) .
Where should you submit personal data-related complaints?
You can lodge a complaint with:
- The supervisory authority of the European country using the EES in charge of processing your data (e.g. if you believe that the country has recorded your data incorrectly). (The contact details will be made available at a later stage.)
- Frontex : the European Border and Coast Guard Agency hosts the central unit operating the European Travel Information and Authorisation System (ETIAS) relevant for the visa-exempt non-EU nationals
- European Union Agency for the Operational Management of Large-Scale IT Systems in the Area of Freedom, Security and Justice - eu-LISA : the European Union's Agency that through technology supports EU countries' efforts for a safer Europe
- Europol : the European Union's Law Enforcement Agency aims to achieve a safer Europe for the benefit of all the EU citizens
Lodging a complaint means that you can submit a formal request for a new assessment of your data protection rights, for instance, if your query to the data controller to access, delete or amend your data is refused.
A common approach to travel measures in the EU
Common approach to travel measures: key areas.
On 25 January 2022 the Council adopted a revised recommendation on facilitating safe and free movement in the EU during the COVID-19 pandemic. This agreement follows the Commission’s proposal of 25 November 2021 .
Under the updated recommendation, COVID-19 measures should be applied based on the individual situation of persons and no longer on the region of origin, with the exception of areas where the virus is circulating at very high levels. This means that a traveller’s COVID-19 vaccination, test or recovery status, proved by a valid EU Digital COVID Certificate , should be the key determinant. This recommendation responds to the significant increase in vaccine uptake and the rapid roll-out of the EU Digital COVID Certificate, and replaces the previously existing recommendation.
In line with the new rules, EU Member States must accept vaccination certificates for a period of 270 days (9 months) since the completion of the primary vaccination series:
- For a two-dose vaccine, this means 270 days from the second shot or, in line with the national vaccination strategy, the first and only shot after having recovered from COVID-19.
- For a single-dose vaccine, this means 270 days from the first and only shot.
EU countries should not provide for a different acceptance period for the purposes of travel within the European Union. The standard acceptance period does not apply to certificates for booster doses.
As of 1 February 2022, new rules have also been implemented regarding the encoding of booster shots in the Certificate. As already clarified in December, boosters will be recorded as:
- 3/3 for a booster dose following a primary 2-dose vaccination series
- 2/1 for a booster dose following a single-dose vaccination or a one dose of a 2-dose vaccine administered to a recovered person.
Certificates that were issued differently before that clarification need to be corrected and issued again, to make sure that boosters can be distinguished from the status of full vaccination.
This recommendation entered into force on 1 February 2022 .
On 3 February 2022, the Commission proposed to extend the EU Digital COVID Certificate system by a year, until 30 June 2023.
Read more in this factsheet
Person-based approach
Travellers in possession of a valid EU digital COVID Certificate should, in most cases, not be subject to additional restrictions to free movement.
A valid EU Digital COVID Certificate includes:
- A vaccination certificate for a vaccine approved at European level if at least 14 days and not more than 270 days have passed since the last dose of the primary vaccination series. Vaccination certificates for booster doses are valid immediately and without a maximum validity, at this stage. EU countries could also accept vaccination certificates for vaccines approved by national authorities or the WHO.
- A negative PCR test result obtained no more than 72 hours before travel or a negative rapid antigen test obtained no more than 24 hours before travel.
- A certificate of recovery indicating that no more than 180 days have passed since the date of the first positive test result.
Persons who are not in possession of an EU Digital COVID Certificate should be required to undergo a test prior to or no later than 24 hours after arrival.
Travellers with an essential function or need, cross-border commuters and children under 12 should not be required to be in the possession of a valid EU Digital COVID Certificate.
Map of EU regions
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) will continue to publish a map of Member States’ regions according to a traffic light system (green, orange, red, dark red). The map will be based on the 14-day case notification rate, vaccine uptake and testing rate.
The traffic light map serves mainly as an information tool, but also to coordinate measures for areas with particularly high circulation of the virus. Based on this map, EU countries should apply measures regarding travel to and from dark red areas , where the virus is circulating at very high levels. They should discourage non-essential travel and require persons arriving from those areas who are not in possession of a vaccination or recovery certificate to undergo a test prior to departure and to quarantine after arrival.
Certain exceptions to these measures should apply to travellers with an essential function or need, cross-border commuters and children under the age of 12.
Emergency brake
When a Member State imposes restrictions in response to the emergence of a new variant, the Council, in close cooperation with the Commission and supported by the ECDC, should review the situation. The Commission, based on the regular assessment of new evidence on variants, may also suggest a discussion within the Council. Similar measures are also possible in case the epidemiological situation in a Member State or in an area within a Member State worsens quickly.
During the discussion, the Commission could propose that the Council agree on a coordinated approach regarding travel from the areas concerned. Any situation resulting in the adoption of measures should be reviewed regularly.
Common passenger locator form and data protection
Passenger locator forms play a key role to ensure effective contact tracing of travellers. Data exchanges between Member States' contact tracing authorities can be particularly important when passengers are crossing borders in close proximity to each other, such as in airplanes or in trains. In order for Member States to exchange relevant passenger data across borders, the Commission adopted two implementing acts in May and July 2021, thus providing the necessary legal conditions for processing such personal data and establishing a passenger locator form exchange platform. To support the digitalisation and harmonisation of passenger locator forms, the EU Healthy Gateways Joint Action developed a web application for an EU Digital Passenger Locator Form . Digital passenger locator forms combined with the passenger locator form exchange platform allow for easier and more rapid data collection and exchange between Member States, making contact tracing more effective and efficient.
Share this page
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Wait, do you need a visa to go to Europe now? The new ETIAS requirements, explained
Emily Olson

St. Mark's basilica in Venice is one place U.S. passport holders may not be able to get to without approval under the new ETIAS requirements Andrea Pattaro/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
St. Mark's basilica in Venice is one place U.S. passport holders may not be able to get to without approval under the new ETIAS requirements
Already thinking about next summer's vacation plans? If Europe is on your short list, there could be one extra step to take before boarding that plane.
Starting in 2024, American passport holders traveling to 30 European countries will need authorization via the European Travel Information and Authorization System (ETIAS).
Though it may sound complicated, the ETIAS and the reasoning behind it are quite similar to existing travel requirements and reflect increasing fear of terrorism in the U.S., Europe and around the world.
Here's what you need to know.
What is ETIAS? Is it a visa?
While some media outlets are taking a cue from the European Union's travel site and calling this a visa, in truth, ETIAS is more like a travel authorization form.

Summer air travel could be expensive and chaotic. Here's how to avoid trouble
"It's definitely not a visa," said Dan Hamilton, a senior non-resident fellow for foreign policy at the Brookings Institution. "It's an electronic entry-point, an authorization for countries that are currently visa-free."
Even the European Commission has said as much (and in bold letters) , writing this is "not a visa" but rather an "automated IT system" in a press release on the discussions around it back in 2018.
Whatever you want to call it, the ETIAS form is not what you'd seek if you're trying to work or live in Europe, but rather what you'll need for short-term trips — up to 90 days within any 180-day period.
Why is it being implemented?
These new requirements have been years in the making, stemming back to a rise in terrorism fears following 9/11. It's very similar to the Electronic System for Travel Authorization — or ESTA — program that the U.S. implemented in 2008 .
At the heart of ETIAS is an electronic database system to better track who's coming and going. According to the EU's latest report on terrorism data , EU law enforcement authorities arrested about 388 suspects for terror-related offenses in 2021, more than half of whom were accused of being associated with Jihadist groups based abroad.
The European Commission says ETIAS may have the added impact of cutting down on "irregular migration" (i.e. illegal immigration), but one thing the form is definitely not aimed to do is deter tourism in general.

'Revenge travel' is surging. Here's what you need to know
Crowded cities, inflated airfare and extreme heat disasters may all be making headlines this summer, but many of these European countries are still depending on tourism revenue to help them bounce back from pandemic slumps, Hamilton said.
And the pandemic is another one of the many reasons this new requirement has been delayed by decades — there was no need for ETIAS when countries closed their borders to all travel amid fears of spreading COVID-19.
"Another part of it is simply the pace of the way this parliament and European commission works," Hamilton explained in an interview with NPR. "They're ending their term and pushing through a lot of these directives because parliamentary elections happen next June."
"And getting 30 countries to agree on anything takes a long time," he added.
When does it take effect?
The European Union's website says the new authorization will start in 2024 but hasn't clarified a specific date. A press spokesperson for the union's travel arm did not respond to NPR's request for information.
And, similarly, a spokesperson for the State Department told NPR that the U.S. government website for international travel (travel.state.gov) would be updated "once the regulation goes into effect," but didn't specify when that would be.
"Frankly, I'd be surprised if this starts on time," Hamilton said. The rollout of ETIAS has already been delayed at least once.
But it couldn't hurt to plan ahead for any 2024 travel just to be safe.
Who needs to apply for ETIAS approval?
Basically, all passport holders from 60 countries who can currently travel to most European destinations without a visa — and that includes American passport holders — will now need to get ETIAS authorization for the same trip. That's about 1.4 billion people, by the European Union's estimation.
There are 30 European countries in total on the impacted destination list , including those in the "Schengen Area" — 27 European countries, many that are part of the European Union, that agreed to ease border restrictions to facilitate the movement of people within Europe.

Planning a trip? Here's how to pack like a pro
Those Schengen countries include top vacation spots like France, Italy and Spain.
The other three countries on the list are Romania, Bulgaria and Cyprus, which are all trying to become a part of the Schengen Area soon.
You can check the full list of both impacted passport holders and affected European destinations here.
How can you apply for ETIAS approval (and does it cost money)?
The application isn't open yet, but the European Union says that when it is, all necessary forms can be filled out via a web portal or mobile phone application.
You'll be asked to share personal information such as your date of birth, parents' names and details about your current occupation and previous criminal convictions. You'll also need to share a passport that is not set to expire in less than three months.
Oh, and you'll have to pay a fee of 7 euros (about $8).
When is the right time to apply?
If you want to play it safe, apply well in advance of your trip — no later than a month out.
ETIAS says most applications "are processed within minutes" and decisions are delivered within four days. But that wait could take up to 14 days if you are requested to supply additional information and up to 30 days if you're invited to interview.

It's Been a Minute
Presenting 'life kit': making the most of travel and your time off.
Those denied an application can appeal, but that process could be even lengthier.
The European Union says ETIAS approval will stay valid for three years or until the passport you used in your application expires.
Naturally, you'll also need to follow the ETIAS rules to stay in good standing.
Those with ETIAS approval can stay in the European countries on the list for up to 90 days within any 180-day period. So you can leave and come back, but you can't stay in the confines of the countries on the list for 91 days or more non-stop.
What happens if I don't apply for this and try to travel to Europe?
Your ETIAS approval will be linked to your passport. So without it, airport security (or cruise, bus or train line staff) won't let you board.
In other words, you can kiss that dream vacation goodbye.
- European Union
- Europe travel
- European Commission
ETIAS Visa Waiver for Americans
Europe's travel authorization for u.s. citizens.
This website does not belong to, nor is it affiliated with, the EU. The official website of the European Union is europa.eu.
US passport holders will soon need ETIAS to travel to Europe. The European Travel Information and Authorisation System will be operational from 2025.
ETIAS is the new travel permit for Americans and other visa-exempt non-EU citizens visiting European destinations such as France , Italy, and Spain.
U.S. nationals can continue to go to Europe visa-free for short stays by applying for ETIAS .
Do Americans need a visa for Europe?
Americans who meet the ETIAS requirements do not need a visa for Europe. This means that US passport holders can travel to Europe without a visa:
- For up to 90 days in any 180-day period
- For tourism, business, and short-term study
Visa-free American visitors need to apply for ETIAS .
Americans must hold a visa or residence permit to stay longer than 3 months or to work in Europe.
WHAT DO AMERICANS NEED TO VISIT EUROPE?
This is what Americans need to visit Europe for up to 90 days:
- Passport valid for 3 months after exiting the Schengen Area
- ETIAS from 2025
You can find out how to apply for your ETIAS to travel from the US to Europe below.
If you’re staying for longer than 90 days, check the specific requirements for your European destination.
Do American tourists need medical insurance for Europe?
Medical insurance is not an ETIAS requirement . You do not need to provide proof of health insurance to apply.
However, all American travellers are advised to take out insurance that covers medical emergencies and other travel-related incidents.
US citizens need ETIAS for these European countries
Currently, there are 25 european countries that form part of the schengen area:.
- Czech Republic
- Netherlands
- EU Schengen
- Non-EU Schengen States
Non-Schengen EU States
Non-eu member states:.
- Liechtenstein
- Switzerland
Micro-States de facto part of Schengen Area:
- Vatican City
HOW CAN AMERICANS APPLY FOR ETIAS TO VISIT EUROPE?
As an American, you can apply for ETIAS online. Fill out the electronic form, pay the fees, and submit the application.
You’ll be asked to provide the following information on your application form:
- Name and surname
- Nationality
- Date, place, and country of birth
- Current address
- Contact phone number
- Email address
- Passport number
- Passport issue/expiry date
- Criminal records
- Travel to conflict areas
Why do Americans need ETIAS to travel to Europe?
Americans need ETIAS because they are visa-exempt non-EU citizens . The ETIAS regulation applies to third-country nationals who do not need a visa to enter the Schengen Area. Other eligible nationalities include British, Australian , and Japanese.
ETIAS pre-screens travellers before they arrive in Europe . By identifying potential threats, ETIAS improves the security of the Schengen Area.
How will my information be used by ETIAS?
The information provided on an ETIAS application form is checked against security databases. These include 3 systems managed by eu-Lisa :
- Schengen Information System (SIS) — database to identify suspected criminals, missing persons and stolen objects.
- Visa Information System (VIS) —database to share visa information
- Eurodac —database storing fingerprints of asylum seekers and irregular migrants
If there is an alert in the system, European authorities know to review the application manually. A decision can then be made on whether to grant travel authorisation.
Is my ETIAS information kept secure?
Information provided on ETIAS applications can only be accessed by authorised users. In addition, advanced technology is used to protect data and prevent any unauthorised access.
ETIAS data protection is in line with European law and the Charter of Fundamental Rights.
When do Americans need to apply for ETIAS?
Americans need to apply for ETIAS for any trips to Europe after 2025.
After the first ETIAS has been issued, US citizens need to apply in 3 years' time or when their passport expires (whichever is sooner). ETIAS is valid with the passport used to apply only.
Americans planning to visit several European countries on one trip do not need to apply for different visa waivers. ETIAS is valid across the Schengen Area.
TRAVELLING TO EUROPE FROM THE US WITH ETIAS
It is also important to note that an approved ETIAS for American citizens does not guarantee entry to Europe; it grants the holder permission to travel to Schengen countries.
The final decision for entry will be made by an immigration officer at Schengen border control. You do not need to print your ETIAS—it is linked to the passport—but you must travel with the passport you used to apply.
There are regulations and restrictions on carrying weapons, importing and exporting large quantities of tobacco, alcohol or perfume, and declaring large amounts of currency when travelling from the USA to Europe. Travellers must check the latest immigration rules.
US and Europe VISA WAIVER BILATERAL AGREEMENTS
US citizens may be able to stay in some European countries beyond the 90-day Schengen limit . The United States has bilateral visa-waiver agreements with several countries.
The Schengen Area nations that have bilateral visa-waiver reciprocal agreements with the US are listed below. The maximum stay is also shown.
- Belgium (3 months)
- Denmark (3 months)
- Italy (3 months)
- Hungary (90 days)*
- Portugal (60 days)*
- Spain (90 days)*
- France (90 days)
- Latvia (90 days in half a year)*
- The Netherlands (90 days)*
Schengen-associated country with a bilateral agreement:
- Norway (90 days)
*Only ordinary passports are permitted
US passport holders who take advantage of one of these visa waiver bilateral agreements must exit the Schengen Area from that EU nation. On departure, they must fly directly to a third country or transit in a non-Schengen airport.
In addition, travellers must remain in that particular EU Member State. It is not possible to move freely around Europe under the bilateral agreements.
Bilateral agreements between the United States and European Union Member States are subject to change.
EUROPE VISA REQUIREMENTS FOR US CITIZENS
US citizens who do not meet the ETIAS requirements need a visa for Europe. Visa applicants need to make an appointment at the embassy or consulate of their European destinations.
Documentation requirements depend on the type of visa requested but may include:
- accommodation bookings
- Round trip flight tickets , or tickets to an onward destination
- Proof of sufficient financial means to cover the stay in Europe
- Travel insurance that covers medical care in the Schengen Area
- A recent, passport-sized, photograph
Visa applications should be started several weeks before the intended travel date.

ETIAS for Americans - Related News

ETIAS Europe: the EU’s version of the US ESTA
The European Travel Information and Authorisation System (ETIAS) is being implemented by the European Union to improve safety and security within the Schengen Area. ETIAS is a visa waiver programme with…
ETIAS for Americans - FAQ
Which countries do american travellers need etias to visit.
With ETIAS, Americans can visit countries where Schengen visa policy applies . The most popular ETIAS destinations for US passport holders include France, Spain, and Italy.
There are no internal border checks in the Schengen Area—ETIAS is valid across the travel zone.

Do American children need ETIAS for Europe?
Yes , US passport holders of all ages need ETIAS for Europe, this includes children under the age of 18.
Parents or legal guardians can complete the ETIAS application on behalf of their children .
Do US citizens need ETIAS to transit through an airport in the Schengen Area?
You only need ETIAS if you will leave the international transit area of the airport. If you will stay in this area, you do not need to apply for ETIAS.
You must hold a valid travel authorisation to enter any of the countries requiring ETIAS, even if it is just for a short time between flights.
CAN AMERICANS USE AN ETIAS TO WORK IN EUROPE?
ETIAS is not a visa and is not valid to work in Europe.
US passport holders need to apply for a work permit or work visa for the European country they will work in. ETIAS is valid for short business trips, for example, to attend meetings, conferences, and other similar events.
CAN AMERICANS STUDY IN EUROPE WITH AN ETIAS?
Americans can study in Europe for up to 90 days with ETIAS. The visa waiver covers short language courses in European countries, for example.
A student visa is required for all study programmes lasting longer than 90 days.
IS ETIAS FOR US CITIZENS A VISA?
No , ETIAS is not a visa for Europe. ETIAS is an electronic travel authorisation, or visa waiver, similar to the ESTA for the United States. US tourists and business travellers do not need a visa to visit the Schengen Area short-term , provided they meet the requirements to travel visa-free. Americans will be able to register for ETIAS from 2025
How do Americans pay the ETIAS fee?
You’ll pay the ETIAS fee online at the end of the online application . All major payment methods are accepted.
The ETIAS system does not keep payment information after the transaction has been completed.
Do American tourists need confirmed travel plans to apply for ETIAS?
Your travel plans do not need to be 100% certain to apply for ETIAS. You do need to indicate which European country you’ll enter first when applying however, once you have your approved ETIAS, you can enter via any of the ETIAS countries.
New requirements for Americans traveling to Europe postponed until 2025
Visitors who now travel visa-free will need to get approval prior to departure.
Americans eyed upcoming travel to European destinations slightly differently due to news of a requirement that was set to start in 2024 for U.S. passport holders. But now, EU officials have postponed the European Travel Information and Authorisation System ( ETIAS ) launch until spring of 2025.
SchengenVisaInfo.com, a website dedicated to the world's largest visa-free zone where 27 European countries abolished their internal borders known as the Schengen Area, first reported that an EU official confirmed ETIAS won't go live until May 2025, "due to continued delays with the introduction of the related Entry-Exit System (EES), which needs to be operational before ETIAS can be implemented."
An official for the European Union did not immediately respond to ABC News' request for comment.
What to know about ETIAS for US travelers
If you previously traveled to Europe without a visa, you will now need to apply for authorization through the ETIAS , before visiting.

Today, American travelers have visa-free access to 184 global destinations, according to the Henley Passport Index . And while the U.S. passport is currently ranked eighth-most powerful passport to own, that could be set to shift when the European Union adds its new documentation requirements for U.S. visitors.
The application form, which will be available on the official ETIAS website as well as a mobile application, has a fee of 7 euros or $7.79 U.S. dollars. All communication is done by email.
Once you are approved for travel, the authorization entitles visitors to stay in European countries that require ETIAS for up to 90 days within any 180-day period and travelers must be in possession of a valid ETIAS during their entire stay.
MORE: New warning issued for rebooking air travel after delays, cancellations
According to ETIAS, most applications should be processed within minutes, but in case an application takes longer, decisions will be sent within four days or up to 14 days if the applicant is asked to provide additional documentation.
The European Union encourages travelers to apply for an ETIAS authorization "well in advance of your planned journey."
Related Stories

Tornadoes leave trail of destruction in Heartland
- Apr 28, 8:47 AM

Key moments from Trump's SCOTUS immunity hearing
- Apr 25, 3:18 PM

Man kills wife, 3 kids in mass shooting: Police
- Apr 23, 12:35 PM
Confirmation of application submission will be sent on email with a unique number that is needed for future reference.

Upon receiving ETIAS travel authorization, travelers are to ensure that their name, passport number and other information is correct because any mistake will prevent them from crossing the border.
If an application is refused, the email will include the reasons for the decision along with information about how to appeal.
ETIAS travel authorization is valid for three years, according to the EU, or until the travel document you used in your application expires, whichever comes first.
MORE: European heat wave breaking records with little relief in sight
The ETIAS authorization is linked to a person's travel document -- such as a U.S. passport -- and both documents will be needed to board a flight, bus or ship to enter any of the European countries that require ETIAS.
Similar to international border requirements with a passport, the ETIAS authorization doesn't guarantee automatic right of entry. "Border guards will verify that you meet the entry conditions" and anyone who does not meet the conditions "will be refused entry," according to the EU.
Click here to learn more about the process from the European Union.
An earlier version of this story was originally published on July 21, 2023.
Related Topics

Mom who went missing died by homicide: Autopsy
- Apr 29, 1:23 PM

Climber dead after falling 1,000 feet off mountain
- Apr 27, 6:54 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
Advertisement
Easy to read - The European Union
Easy to read version.
Easy to read is a way to make information easy for everyone to read and understand.

© European Easy-to-Read Logo: Inclusion Europe. More information at https://www.inclusion-europe.eu/easy-to-read/
The European Union
The European Union is a group of 27 countries in Europe. These countries came together to make things better, easier and safer for people. They agreed to work together and help each other.
How the European Union started

The idea to make the European Union came after two big wars happened in Europe. Countries in Europe saw that it is better to work together than fighting against each other.
In the beginning, only 6 countries in Europe started working together:
- Netherlands
Soon, more and more countries in Europe joined them and the European Union was made.
Today, 27 countries are part of the European Union. These countries are:
In June 2016 the United Kingdom decided to stop being part of the European Union. So from 31 January 2020, the United Kingdom is no longer part of the European Union.
The goals and values of the European Union
All countries that are part of the European Union work together to make sure that:

- there is peace in Europe
- people have good lives
- things are fair for all people and nobody is left out
- the languages and cultures of all people are respected
- there is a strong European economy and countries use the same coin to do business together.
The countries of the European Union share some important values. For example, they work to make sure that all people are equal and their rights are respected.
Peace in Europe

After the European Union was created, there were no more wars between the countries that are part of the European Union. Thanks to the European Union, all countries in Europe work together in peace.

In 2012, the European Union won a big award which is called ‘ the Nobel Peace Prize ’. This award was given to the European Union for its good work keeping peace in Europe.
The European Union made it easier for people to move freely from one country to another. They can live, study or work in any country of the European Union they want. For example, a person from France can choose to move to Italy and work there. Or a student from Belgium can go study in a university in Greece.

Things, services and money can also move freely from one country of the European Union to another.
The European Union in the world
The European Union plays an important role in the world in many ways. For example:
- It sells many things and services to other countries. Also, it buys things from other countries. This way it helps the world economy keep going.
- It helps millions of people who live in poorer countries outside the European Union.
- It tries to make the world a safer place where people are treated fairly and laws are respected.
Becoming part of the European Union
To become part of the European Union, a country must:

- agree with all the laws and values of the European Union.
- work to make sure these laws and values are respected.
This may take a very long time to happen.
Some countries are now working to become part of the European Union. These countries are:
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- North Macedonia
To become part of the European Union, these countries must work to make all laws and values of the European Union happen in them.
The Schengen Area
The European Union made the ‘ Schengen Area ’.
The Schengen Area is an area without borders. In this area, people can travel from country to country freely and easily. They do not have to go through checks and controls when they pass from one country to another.
Thanks to the Schengen Area, it is now easier for people to travel for work or tourism.
The Schengen Area was made in 1985. Today 25 out of the 27 countries of the European Union are part of the Schengen Area.
These countries are:
Also, 4 countries outside the European Union are part of the Schengen Area:
- Liechtenstein
- Switzerland
That means that people can travel freely and easily from one of these countries to another. This way it is easier for people to visit any of these countries for tourism or for work.
Languages of the European Union
In every country of the European Union people speak their own language. The European Union protects the right of people to communicate in their own language.

That is why the European Union makes all important information and documents in all the languages that people speak in its countries:
This way all people in the European Union can get important information in their own language and understand it.
The coin of the European Union
Most countries that are part of the European Union use the same coin.

This coin is called ‘ Euro ’. Using the same coin helps countries in the European Union to do business together. For example, people from Spain can buy things they want from Belgium easily and without extra costs. Using the same coin makes it easier for people to travel, buy things online from other countries and have more options.
Today, 20 out of 27 European Union countries use the euro.
The European flag
This is the flag of the European Union:

The flag of the European Union is blue and has a circle of gold stars on it. It is a symbol that shows that the countries of the European Union are united and stand by each other.
The European anthem
Every country has a melody that better shows its values and culture as a country. This melody is called ‘ anthem ’.
The European Union has its own anthem too. In 1985, people who make decisions in the European Union chose a melody of a very important composer to be the anthem of the European Union.
This composer is called Ludwig van Beethoven.

The melody shows how important it is that all people are free, live in peace and stand by each other. The European Union believes in these values and that is why it has chosen this melody to be its anthem.
If you want to listen to the anthem of the European Union, click here .
United in diversity
The European Union uses the phrase ‘ united in diversity ’ to show what its values are.
Being united in diversity means that:
- people in the European Union may have different cultures or languages but they stand by each other and work together in peace.
- there is nothing wrong about having different languages or cultures. On the contrary. People with different cultures can learn more things from each other and work well together.
How the European Union works
The European Union has 3 main bodies:

- the European Commission The people of the European Commission suggest laws for the European Union.

- the European Parliament The people of the European Parliament are elected by all people in Europe to stand for their rights.

- the Council of the European Union People who make decisions in every country of the European Union come together and make the Council of the European Union.
These 3 bodies are very important for the European Union. They work closely together to make things better in Europe:
- The European Commission suggests laws.
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union discuss these laws and decide if they want these laws to happen in Europe.
- If they decide that a law must happen in Europe, all countries of the European Union must work to make this law happen in them.
Other bodies that are important for the European Union are:
- The Court of Justice of the European Union that makes sure that all laws happen correctly in the European Union.
- the Court of Auditors that checks if the money of the European Union is spent in the right way.
There are also other bodies of the European Union that are doing important work. For example, there are bodies that:
- check if the European Union works in the right way and respects the rights of all people.
- publish useful information about the European Union.
- choose the people who have the skills to work for the European Union.
- stand for the rights of all people in Europe like people with disabilities, workers and others.
All these bodies work together to make sure that the European Union works in the right way for the good of its people.
More information

Click here to find more information about the European Union in your own language.
If you have questions about the European Union, you can fill this online form here .
Share this page
European Parliament updates trans-European transport network guidelines
Share this page: .
- Major transport links to finish by 2030
- Cut transport infrastructure ties with Russia and focus on Ukraine
- Create better conditions for military mobility along major EU roads and railways
On Wednesday, MEPs endorsed updated plans to complete major trans-European transport projects, such as cross-border roads, railways, bridges and tunnels, by the end of 2030.
To eliminate bottlenecks and missing transport links, MEPs backed an update of the EU’s plan to build a network of railways, roads, inland waterways and short sea shipping routes connected through ports and terminals across the EU. Current trans-European transport (TEN-T) projects include many European links, such as, Rail Baltica , connecting Helsinki and Warsaw, the Brenner Base Tunnel , linking Austria and Italy, and the Lisbon–Madrid high-speed rail line.
Major transport infrastructure projects on the core TEN-T network should be completed by the end of 2030, to secure a comprehensive network by the end of 2050. To accelerate project rollout across the network, an intermediary deadline of 2040 is introduced.
Faster trains and safer parking for truck drivers
MEPs ensured that railways in the core TEN-T network will be electrified, running at speeds of 100 km/h for freight and crossing internal EU borders in less than 25 minutes on average by the end of 2030. A minimum 160 km/h speed should become the norm on passenger trains as of the end of 2040.
Major European airports (processing more than 12 million annual passengers) will be connected to the trans-European railway network. To guarantee better rest conditions for professional truck drivers, safe and secure parking places at least each 150 km will have to be set-up along major EU roads.
End cooperation with Russia; focus on Ukraine
Under new rules, transport infrastructure projects with Russia and Belarus will be halted, reinforcing instead links with Ukraine and Moldova.
Regarding the involvement of companies from third countries in major TEN-T projects, member states will have to inform the European Commission of measures adopted to mitigate any security risk.
Military mobility
MEPs convinced EU governments to take into account military needs (weight or size of military transport) when constructing or upgrading infrastructure that overlaps with military transport networks, to ensure the seamless transfer of troops and equipment. Within one year after the entry into force of the rules, the Commission will have to conduct a study on short-notice large-scale movements across the EU, to facilitate military mobility planning.
EP rapporteur Barbara Thaler (EPP. AT) said: “The regulation will enable rail transport to compete with road transport, if it is implemented as foreseen. It is now the Commission’s responsibility to ensure that member states fulfil their duties and to put the necessary pressure on them if they don't act accordingly.”
Rapporteur Dominique Riquet (Renew, FR) added: “New rules will strengthen the performance, accessibility, security and resilience of our infrastructure, which is a key element of our sovereignty. It will also help to encourage Europeans to travel and make our economy more competitive.”
The new rules on the guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network were adopted by 565 votes in favour, 37 votes against and 29 abstentions. Once Council has approved them, they will enter into force 20 days after publication in the Official Journal.
By adopting this legislation, Parliament is responding to citizens' expectations concerning high quality, modern, green, and safe infrastructure, ensuring connectivity, including of rural and island regions, in particular through affordable public transport as expressed in proposal four of the conclusions of the Conference on the Future of Europe.
Contacts:
Gediminas vilkas .
- Phone number: (+32) 2 28 33592 (BXL)
- Mobile number: (+32) 470 89 29 21
- E-mail: [email protected]
- Twitter account: @EP_Transport
Further information
- EU draft rules on trans-European transport network
- Procedure file
- EP research service note on TEN-T revision (March 2024)
Product information
New Schengen Visa Rules for Indian Visitors: Key Questions Answered
Peden Doma Bhutia , Skift
April 23rd, 2024 at 5:39 AM EDT
Destinations value Indian travelers, but lengthy visa processing times lasting months act as significant deterrents. The adoption of these new regulations by European authorities reflects a proactive effort to tackle these concerns, aiming to boost tourism flow.
Peden Doma Bhutia
The European Commission has introduced a new visa “cascade” regime for Indian nationals applying for Schengen visas in India. This regime looks to offer longer-term, multi-entry Schengen visas, based on the applicant’s travel history.
Indian travel agents had been complaining of Schengen visa delays as a major challenge to the summer travel rush from India.
- How does one qualify for the longer duration visas?
The European Commission can issue a two-year multiple-entry visa after a traveler “has obtained and lawfully used two visas within the previous three years.” This demonstrates a positive travel history and compliance with previous visa regulations.
Subsequently, after granting the two-year visa, authorities may issue a five-year visa if the passport has has adequate validity remaining.
- What benefits do holders of these extended visas enjoy?
During the validity period of these visas, holders can enjoy travel rights equivalent to visa-free nationals within the Schengen area, allowing for short stays of up to 90 days within a 180-day period.
- Which countries are part of the Schengen area?
The Schengen area comprises 29 European countries, including 25 European Union member states: Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Germany, Estonia, Greece, Spain, France, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Hungary, Malta, Netherlands, Austria, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Slovakia, Finland, and Sweden. Additionally, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland are also part of the Schengen area.
- Are there any restrictions or conditions to these visas?
Schengen visas do not grant the right to work within the Schengen area and are for short stays only. Additionally, the visas are not purpose-bound, providing flexibility for travel within the specified period.
Industry Take
Skift also spoke to players in the Indian outbound travel industry to understand what has changed in the new Schengen visa rules.
- How is this different from the earlier visas that Schengen countries offered? Don’t they already offer multi-entry visas with longer duration to Indians?
Mahendra Vakharia, managing director of Pathfinders Holidays, said there was no standard policy of Schengen states for issuing these long-term visas earlier. Switzerland, France, Netherlands, Italy and Spain usually issued long-term visa, but it was all subjective. “With this new policy it should be a standard rule now,” Vakharia said.
- Travelers mainly complain of longer processing times, has that changed?
Here too, there is no standard processing time as it varies from country to country, according to Vakharia. “France and Spain have been processing visas within four days, and then there’s Croatia, which takes 60 days,” he said.
Processing time will not change as of now, it will take time for the visa rules to be enforced, said an industry source, while highlighting that the visa would be especially useful for corporate travelers.
What Promoted The Move?
Speaking on the possible motivations, Vakharia acknowledged various reasons, including administrative capacity constraints at embassies to cater to the huge inflow of applications.
“As there is an overwhelming demand from Indian travelers, the process of securing visa appointments has posed significant challenges , especially for travelers residing in cities lacking VFS Global centers,” he said.
The European Commission said in an statement that the decision reflects the EU-India Common Agenda on Migration and Mobility, aimed at fostering comprehensive cooperation on migration policy. Facilitating people-to-people contacts is a key aspect of this agenda, acknowledging India’s importance as an EU partner.
The decision also reflects a realization of the strong economic benefits derived through the spending power of Indian tourists. As Vakharia aptly puts it, “Why let go of the Golden Indian Goodie Bag?”
Skift India Report
The Skift India Report is your go-to newsletter for all news related to travel, tourism, airlines, and hospitality in India.
Have a confidential tip for Skift? Get in touch
Tags: asia monthly , europe , european commission , European summer travel , european union , india , india outbound , schengen , visa , visas
Photo credit: Park Guell in Spain. Unlike many Schengen countries, Spain has been processing visas within four days for Indian travelers. Mehmet Turgut Kirkgoz / Pexels
2018 Primetime Emmy & James Beard Award Winner
R&K Insider
Join our newsletter to get exclusives on where our correspondents travel, what they eat, where they stay. Free to sign up.
A History of Moscow in 13 Dishes
Featured city guides.

European Union adopts more favourable Schengen visa rules for Indians
Indian Nationals can now apply for a multiple entry Schengen visa with longer validity
On 18 April 2024, the European Commission adopted specific rules on the issuing of multiple entry visas to Indian nationals, which are more favourable than the standard rules of the Visa Code that applied to date. This new visa ‘cascade’ regime for Indian nationals residing in India who apply for Schengen (short-stay) visas in India will provide easier access to visas with multi-year validity for travellers with an established travel history, if the passport validity allows.
According to the newly adopted visa “cascade” regime for India, Indian nationals can now be issued long-term, multi-entry Schengen visas valid for two years after having obtained and lawfully used two visas within the previous three years. The two-year visa will normally be followed by a five-year visa, if the passport has sufficient validity remaining. During the validity period of these visas, holders enjoy travel rights equivalent to visa-free nationals.
This decision comes in the context of strengthened relations under the EU-India Common Agenda on Migration and Mobility, which seeks comprehensive cooperation on migration policy between the EU and India, with facilitation of people-to-people contacts being of key aspect due to the importance of India as a partner for the EU.
Schengen visas allow the holder to travel freely in the Schengen area for short stays of a maximum of 90 days in any 180-day period. The visas are not purpose-bound, but they do not grant the right to work. The Schengen area consists of 29 European countries (of which 25 are EU states): Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Germany, Estonia, Greece, Spain, France, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Hungary, Malta, Netherlands, Austria, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Slovakia, Finland and Sweden, along with Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
Ukraine-Russia war latest: At least four dead in daytime missile strike on port city - as massive building on fire
It is likely to be a "very difficult summer" for Ukrainian forces in the face of increased Russian attacks, military analyst Sean Bell says. Listen to a Daily podcast on whether the UK should send troops to Ukraine as you scroll.
Monday 29 April 2024 22:48, UK
- At least four killed in daytime missile attack on Odesa
- Watch: Massive building in flames after attack
- Ukraine in for 'difficult summer' as Russia preparing 'major offensive'
- North Korea expresses 'concern' over US sending long-range missiles to Ukraine
- Explained : Why is Chasiv Yar the next target for Russia?
- Your questions answered: Will Ukraine launch another spring offensive?
- Big picture : What you need to know as a new week begins
- Listen to the Sky News Daily above and tap here to follow wherever you get your podcasts
As we reported a short time ago, the Duchess of Edinburgh has met with Volodymyr Zelenskyy in Ukraine, in what marks the first visit to the country by a member of the Royal Family since the war begin.
Sophie met the Ukrainian president and first lady Olena Zelenska and delivered a message to them on behalf of the King, Buckingham Palace said.
You can watch footage from her trip here...
Throughout the day, we've been reporting on a Russian attack on the city of Odesa in Ukraine, which has killed at least four people.
These images show a burning educational institution building, which was struck.
Airline Finnair has said it is pausing flights to Tartu in eastern Estonia for the next month, due to GPS disturbances in the area.
"Finnair will suspend its daily flights to Tartu, Estonia, from 29 April to 31 May, so that an alternative approach solution that does not require a GPS signal can be put in place at Tartu Airport," the Finnish airline said in a statement.
Finnair last week had to divert two flights back to Helsinki after GPS interference prevented the approach to Tartu airport, although a spokesperson said the company did not now where the interference came from.
However, Tallinn seems certain as where the issues are originating.
"It is a fact that Russia affects GPS devices in our region’s airspace," Estonia's foreign minister said via a spokesperson.
Margus Tsahkna added that Estonia will raise the issue of GPS interference with its neighbours, and intends to discuss it with the EU and NATO.
GPS jamming and spoofing have grown worse in eastern Europe, the Black Sea and the Middle East, all areas close to conflict zones, according to industry group OpsGroup.
More than 30 Ukrainian conscripts have died while trying to cross the border illegally to avoid mobilisation, a Ukrainian official has said.
Andriy Demchenko, spokesman for the State Border Guard Service, told Ukrinform that some men are prepared to pay "large sums" of money to groups promising to smuggle them across the border safely.
"Then they are faced with the fact that the route runs along a mountain river," he said.
Many conscripts have lost their lives after realising they didn't have the strength to swim the river, Mr Demchenko added.
"In total, since the beginning of the full-scale invasion, about 30 people have died trying to cross the border illegally," he said.
Such attempts occur "every day", he said.
For context: Ukraine has been under martial law since the Russian invasion in February 2022.
It lets draft officers call up men of a certain age to fight on the front line.
In April, Volodymyr Zelenskyy signed off a new law lowering the age of draft-eligible men from 27 to 25, in a bid to boost troop numbers in his depleted ranks.
The Duchess of Edinburgh has met with Volodymyr Zelenskyy in Ukraine, in what marks the first visit to the country by a member of the Royal Family since the war begin.
Her visit is aimed at demonstrating "solidarity with the women, men and children impacted by the war and in a continuation of her work to champion survivors of conflict-related sexual violence", the palace said.
Three women and a man have died after a Russian attack on Odesa.
A further 28 people have been injured, including two children aged five and 16. A pregnant woman has also been hurt.
This video shows the aftermath of the attack.
Debris recovered from a missile that landed in the Ukrainian region of Kharkiv on 2 January was North Korean, the Reuters news agency is reporting.
Citing a United Nations sanctions monitor, Reuters said debris recovered was from a Hwasong-11 series ballistic missile - made in North Korea.
Three sanctions monitors travelled to Ukraine earlier this month to inspect the debris - and found no evidence that the missile was made by Russia.
They "could not independently identify from where the missile was launched, nor by whom".
"Information on the trajectory provided by Ukrainian authorities indicates it was launched within the territory of the Russian Federation," they wrote in an April 25 report to the UN Security Council's North Korea sanctions committee.
"Such a location, if the missile was under control of Russian forces, would probably indicate procurement by nationals of the Russian Federation," they said, adding that this would be a violation of the arms embargo imposed on North Korea in 2006.
International leaders have long accused North Korea of supplying Russia with weapons.
Both Moscow and Pyongyang have denied the accusations, but vowed last year to deepen military relations.
The situation in Odesa is fast-moving after the city in southern Ukraine came under Russian missile attack this afternoon.
Three women and a man have died, bringing the total number of people killed to four, according to regional governor Oleg Kiper.
He said a further 28 people have been injured, including two children aged five and 16. A pregnant woman has also been hurt.
Four people are "fighting for their lives," he said in a Telegram post .
A big building housing part of the Odessa Law Academy is ablaze after the strike...
The number of people injured in Russia's missile attack on Odesa has increased.
Regional governor Oleg Kiper said he was aware of 17 injured people, of whom at least two are in a "serious condition". Separately, Odesa mayor Gennadiy Trukhanov said at least 20 people were hurt.
Emergency services continue to work at the scene, Mr Kiper said. Earlier, he reported that at least two people had been killed in the attack (see 17.46 post).
The Odesa region has been repeatedly targeted by Russia during the war.
Last month, a Russian ballistic missile attack on a residential area killed at least 20 people and wounded more than 70.
Ukrainian troops are still defending their positions on the frontline while grappling with depleted weapons supplies and increased Russian attacks.
Western support is on full display in the pictures below, with soldiers of the Ukrainian army's 25th separate airborne brigade operating a German-made Marder infantry fighting vehicle.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Entry/Exit System (EES) is the system for registering non-EU nationals travelling for a short stay in 29 European countries (starting in the second half of 2024). ETIAS is the Travel authorisation for visa-exempt travellers to enter 30 European countries (starting in the first half of 2025).
Your rights & EU rules. As an EU national, you enjoy the right of free movement. This means you're entitled to travel, work and live in another EU country. If you're a citizen of a Schengen country - which is most EU countries - you're also free to travel to other Schengen countries without the need for border checks.
Documents you need for travel in the EU and Schengen countries. As an EU national, you have the right to travel freely in the 27 EU member countries as well as in Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland (non-EU countries but members of the Schengen area) carrying either a valid passport or a national identity card (ID card).
Passport, entry and visa requirements. If you are a national from a country outside the EU wishing to visit or travel within the EU, you will need a valid passport and possibly a visa. Your passport should be valid for at least 3 months after the date you intend to leave the EU and it must have been issued within the last 10 years.
EU air passenger rights apply: If your flight is within the EU and is operated either by an EU or a non-EU airline; If your flight arrives in the EU from outside the EU and is operated by an EU airline; If your flight departs from the EU to a non-EU country operated by an EU or a non-EU airline; If you have not already received benefits (compensation, re-routing, assistance from the airline ...
The main advantage of the EES is saving time. The EES replaces passport stamping and automates border control procedures, making travelling to European countries using the EES more efficient for the traveller. The EES also makes it easier to identify travelers who have no right to enter or who have stayed in the European countries using the EES ...
Traveling in the time of coronavirus can be complicated. Check out the latest information about border restriction, contact-tracing apps, consular support. Travelling in the EU? Find information on travel documents, passenger rights, driving abroad, roaming charges, rules on carrying animals, plants, alcohol, tobacco, and more.
In June 2020, the Council adopted a recommendation on temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU and the possible lifting of such restrictions. This recommendation was last updated on 22 February 2022. The decision on whether to introduce restrictions on free movement to protect public health remains the responsibility of the ...
EU countries should not provide for a different acceptance period for the purposes of travel within the European Union. The standard acceptance period does not apply to certificates for booster doses. As of 1 February 2022, new ruleshave also been implemented regarding the encoding of booster shots in the Certificate. As already clarified in ...
While some media outlets are taking a cue from the European Union's travel site and calling this a visa, in truth, ETIAS is more like a travel authorization form. National Summer air travel could ...
On June 18, the European Union recommended lifting the ban on nonessential travel for visitors from the United States just in time for the summer season, which is crucial to the E.U.'s economy.
US passport holders will soon need ETIAS to travel to Europe. The European Travel Information and Authorisation System will be operational from 2025. ETIAS is the new travel permit for Americans and other visa-exempt non-EU citizens visiting European destinations such as France, Italy, and Spain.. U.S. nationals can continue to go to Europe visa-free for short stays by applying for ETIAS.
Jenny Kane/AP, FILE. Americans eyed upcoming travel to European destinations slightly differently due to news of a requirement that was set to start in 2024 for U.S. passport holders. But now, EU ...
Travel restrictions are back in Europe for U.S. visitors, at least in some places. In removing the U.S. from a list of safe countries, the European Union opened the door to a new web of bans ...
A Schengen visa is a permit that allows you to enter and travel freely within the Schengen Area, which comprises 29 European countries, for short stays up to 90 days within a 180-day period, primarily for tourism or business purposes. It includes both short-stay visas for travel or transit through a Schengen state and airport transit visas.
European Union priorities 2019-2024. Discover the EU's priorities for 2019-2024: promoting a green Europe, developing the economic base, protecting citizens and their freedoms. ... to history and travel. Featured news. All featured news are available in the 24 EU official languages via machine translation. Press release; 24 April 2024;
This coin is called ' Euro '. Using the same coin helps countries. in the European Union to do business together. For example, people from Spain. can buy things they want from Belgium. easily and without extra costs. Using the same coin. makes it easier for people to travel, buy things online from other countries.
Major European airports (processing more than 12 million annual passengers) will be connected to the trans-European railway network. To guarantee better rest conditions for professional truck drivers, safe and secure parking places at least each 150 km will have to be set-up along major EU roads. End cooperation with Russia; focus on Ukraine
Indian travel agents had been complaining of Schengen visa delays as a major challenge to the summer travel rush from India. ... including 25 European Union member states: Belgium, Bulgaria ...
1: Off-kilter genius at Delicatessen: Brain pâté with kefir butter and young radishes served mezze-style, and the caviar and tartare pizza. Head for Food City. You might think that calling Food City (Фуд Сити), an agriculture depot on the outskirts of Moscow, a "city" would be some kind of hyperbole. It is not.
CGT-RATP union members announced a seven-month strike notice from 5 February to 9 September that could hit the Ile-de-France bus and metro network - including during this summer's Olympic Games.
European Union adopts more favourable Schengen visa rules for Indians. 22.04.2024 New Delhi. Press and information team of the Delegation to INDIA and BHUTAN ... Schengen visas allow the holder to travel freely in the Schengen area for short stays of a maximum of 90 days in any 180-day period. The visas are not purpose-bound, but they do not ...
Travel bans prevent listed individuals from entering or transiting through EU territory by land, air or sea. ... The European Union has prohibited all transactions with the National Central Bank of Russia related to the management of the Russian Central Bank's reserves and assets. As a result of the central bank asset freeze, the central bank ...
Walking tour around Moscow-City.Thanks for watching!MY GEAR THAT I USEMinimalist Handheld SetupiPhone 11 128GB https://amzn.to/3zfqbboMic for Street https://...
Life and travel. Travel. Documents you need for travel in Europe. Travel documents for EU nationals; Travel documents for non-EU family members; Travel documents for non-EU nationals; Travel documents for EU nationals and their non-EU family members residing in the UK; Travel documents for UK nationals and their family members residing in an EU ...
Eastern European Tours & Holidays. Eastern Europe, also known in daily talk as East Europe is considered the part of Europe from east of the "Iron Curtain" east of the old Western Germany and further south. It was then known as the Eastern Bloc. The socioeconomic and cultural level is overall lower than that for Western Europe but there is huge ...
If your pet is traveling through (transiting) a country in the European Union (EU) on the way to a third, non-EU country, you will also need a transit health certificate for your pet for the EU. The transit health certificate will be the same as if your pet's final destination was the EU country.
The big news last week was the US passing its $61bn (£48.1bn) aid package for Ukraine after months of delay. Republicans in the House of Representatives - who, spurred on by Donald Trump and his ...