Language selection
- Français fr

How can I come to Canada as a visitor, worker or student?
We have created an online tool called Come to Canada . It will help you figure out whether you can come to Canada as an immigrant , visitor , worker or student .
This tool guides you through some questions and based on your responses and your situation, it then gives you:
- a list of options and
- step-by-step instructions on how to apply.
This tool will help you understand the requirements for immigrating to, visiting, studying in or working in Canada. If you are eligible as a visitor, worker or student you can apply online through this tool. You will also have the option to complete a paper application .
Did you find what you were looking for?
If not, tell us why:
You will not receive a reply. Telephone numbers and email addresses will be removed. Maximum 300 characters
Thank you for your feedback
Answers others found useful
- If you return my application, will I get a refund?
- How do I fill out and validate IRCC application forms with 2D barcodes?
- Why won’t my application form let me save my information or digitally sign it?
- How can I check if my application has been received?
- What happens after I send in my application?
- What is a UCI?
- What is an application number?
- How can I find a doctor to provide my medical exam?
- How can I get my citizenship application processed urgently?
- How can I get help with my application?

How to video

Form and guide
- Form Quick Find
Glossary term
- Admissibility
- Application package
- Meet our partners
- Advertise with us
10 frequently asked questions by visitors to Canada

Recent changes to visitor visa requirements for some Mexican nationals may leave some foreign nationals looking to visit Canada with questions about their own situation.
To assist, CIC News has compiled a list of frequently asked questions that may be helpful to review before expending the time, energy and money necessary to come to Canada.
How long can I stay in Canada as a visitor?
In most cases, visitors to Canada can remain in the country for six months from the day they enter Canada (or until their passport expires, whichever comes first). The date by which a visitor must leave Canada will be indicated by a stamp in their passport and/or a document provided to them by a Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) officer.
Discover if You Are Eligible for Canadian Immigration
Visitors who would like to remain in Canada beyond their initially authorized stay can apply for an extension (more on this later).
What is the difference between a single and a multiple-entry visa?
As indicated by the name of the visa, single-entry visas permit the holder to enter Canada one time only, while a multiple-entry visa allows repeated entry to Canada so long as the visa remains valid.
Note: All visitor visa applicants are automatically considered for a multiple-entry visa but Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) reviews each application separately and issues every visitor a visa accordingly.
IRCC clarifies that single-entry visa recipients will require a new visa to enter Canada once they have left, unless they are travelling directly to either the United States or St. Pierre and Miquelon.
Meanwhile, multiple-entry visas are valid for the shorter of the following two periods: 10 years or one month before the expiration of the visa holder’s passport. Every entry to Canada using a multiple-entry visa allows the visa holder to remain in Canada for up to six months at a time.
Can I fill out one visa application for my whole family if we are travelling together?
No. While all visitor visa applications for one group of family members may be submitted in the same envelope (alongside one payment receipt accounting for the total fee of all applications), everyone must complete and sign their own visitor visa application.
This rule also applies to any other required forms, excluding the Family Information form, which must only be completed by applicants 18 years or older.
Note: Parents and guardians can help their children fill out their form(s), and every visitor visa applicant under the age of 18 must have their document(s) signed by a parent/guardian.
Is there any way I can help a friend or family member visit Canada?
Although your friends and family members must complete their own visa applications, a letter of invitation is a document you can submit to help a loved one come to Canada.
It should be noted that this document, which details how you may help the visa applicant (ex. offering to pay for accommodation), can help but does not guarantee the applicant will be approved for their visitor visa.
Do I need a medical exam to get a visitor visa?
This depends on the visitor’s length of stay in Canada.
In most cases, visitors in Canada for six months or less do not require a medical exam unless they will be working in a job where the “protection of public health is essential.” The list of jobs under this requirement is available here .
The above public health protection condition also applies to visitors who will be in Canada for longer than six months. In addition, visitors in Canada for six months or longer will need a medical exam if they meet either of the following two requirements:
- The applicant has been, for six or more consecutive months, living or residing in a designated country or territory *
- The applicant is applying for a Parent and Grandparent Super Visa
*This applies to all visitors, even those who are citizens of visa-exempt countries, who have been in any of the eligible countries “in the one year immediately preceding the date [the visitor] sought entry into Canada.”
Is a visitor visa the same thing as a visitor record?
No. A visitor visa is required by foreign nationals looking to travel and enter Canada as a visitor (in most cases, for up to six months).
Conversely, a visitor record is provided by CBSA officers to either extend or restrict the recipient’s stay in Canada. This type of document may also be given to foreign nationals, by either CBSA or IRCC, after their application to extend their stay or restore their status in Canada is approved.
Click here for additional details regarding the difference between a visitor visa and a visitor record.
I got a new passport but I have a valid visa in my old one. Can I use the visa in my old passport?
IRCC notes that it is possible to travel to Canada using a valid visitor visa placed in an old passport. However, travellers in this situation must bring both of the following documents with them to Canada:
- The old passport with the valid visa*
- The new valid passport or travel document
*Travellers may need to explain to CBSA officers why their old passport is no longer valid
Note: To avoid processing delays at the Canadian border, IRCC recommends that all visitors to Canada obtain a new visitor visa in their new, valid passport.
How can I extend my stay as a visitor?
Extending your stay in Canada requires that you submit biometrics (fingerprints and a photograph) and apply for a visitor record. This document allows visitors to Canada three options to extend their stay in the country:
- As a visitor
- As a worker authorized to work in Canada without a work permit
- As a student authorized to study in Canada without a study permit
The steps to applying for a visitor record online can be found on this IRCC webpage .
Can I file an appeal if my visitor visa is denied?
There is no appeal process for a visitor visa application from IRCC.
When an applicant is denied a visitor visa to enter Canada, they may re-apply, but IRCC recommends that they only do so if their situation has changed, or they have new information to submit that may alter the outcome of their application.
Do I need a visa if I’m just travelling through Canada on my way to another country?
Documentation for those transiting through Canada depends on an indvidual’s unique situation.
Generally, travellers can be broken down into two categories: visa-required travellers (from a visa-required country ) and visa-exempt travellers (from a country that requires an electronic Travel Authorization , eTA).
Some visa-required travellers need a visitor visa. This applies to travellers who are:
- Visiting Canada (even if travelling by air and the traveller is in Canada for less than 48 hours)
- Staying in Canada for more than 48 hours while transiting through the country to another destination
- Crossing the Canadian border via any of the following five modes of transportation: bus, car, train, boat or cruise ship
Other visa-required travellers may only require a transit visa. This applies to travellers who:
- Have an international flight that stops at a Canadian airport on the way to another country
- Will be connecting between two international flights at a Canadian airport
- Will be transiting through Canada in 48 hours or less
- Do not have a valid visitor visa
Visa-exempt travellers need an eTA to transit through Canada by air. Travellers transiting through Canada by train, bus, boat or cruise ship are not required to obtain an eTA, but must still bring with them the correct travel documents .
- Canada Border Service Agency
- Canada News
- visitor visa
- Do you need Canadian immigration assistance? Contact the Contact Cohen Immigration Law firm by completing our form
- Send us your feedback or your non-legal assistance questions by emailing us at [email protected]

- Life in Canada

- Express Entry
- Family Sponsorship
- Citizenship

Language selection
- Français fr
Crossing the border into Canada
October 1, 2022 : covid-19 emergency border measures ended.
Refer to COVID-19: Travel, testing and borders for details.
Everyone wants their border crossing to go smoothly with few delays. The best way to make sure this happens is to know what to expect and be prepared.
Whether you're returning home or visiting, Canada Border Services Agency ( CBSA ) wants to help you plan your trip across the border with some useful tools.
Most requested
- Border wait times
- Travel documents and identification requirements
- Estimate duty and taxes on imported goods
- Restricted and prohibited goods
- Penalties for cannabis-related offences
- Border reminder checklist
- Secondary services and inspections
Contributors
- Canada Border Services Agency
- Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada
Services and information
Covid-19: travel, testing and borders.
End of COVID-19 requirements for travelling to and within Canada.
Advance Declaration: Save time at the border
Use Advance Declaration in ArriveCAN to submit your customs and immigration declaration before flying into Canada.
Programs for trusted travellers
Learn about programs to make border crossings faster and easier for travellers and private or commercial operators.
Plan your trip across the border
Border wait times, reporting requirement, tips to improve your experience crossing the border.
Paying duty and taxes
Limits on goods purchased while abroad, personal exemptions.
Visitors to Canada
Who can enter, visas, what you can bring in, travelling with gifts, currency limits.
Airport arrival kiosks and eGates
Verify your identity and make an on-screen declaration at Canada's major international airports.
Examining digital devices at the Canadian border
When CBSA officers decide to examine your device at the border. Know your rights.
Travel tips
Border services and requirements for visitors, legal guardians, travellers with a disability, pet owners.
Refugees and asylum
Claim refugee protection, sponsor a refugee, find services for refugees in Canada and appeal a refugee claim.
Bring goods across the border
Types of goods you can bring to Canada and personal exemptions.
Moving or returning to Canada
For people settling in Canada or former residents moving back.
Renewing work and study permits and confirming permanent residence
Select ports of entry may process these requests if you meet the criteria.
How the CBSA collects, uses and protects your information
Find out what happens to your personal information when your cross the border.
Canadians, Indigenous people, and permanent residents
Travel restrictions, COVID-19 measures, returning to Canada.
General information for non-residents about crossing the border, travelling to Canada, doing business in Canada and more.
COVID-19 : Travel, testing and borders
Who can come to Canada, testing and quarantine requirements, transiting and more.
What to expect at the border
Processes to expect when you cross the border based on the type of transportation you use.
Related links
- Smart and secure border tools for travel and trade
- Finding our missing children
- Importing goods for personal use
- Travel health measures
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Forgot Password?
You can reset your password here.

Email was Sent
Please check Your email
Come to Canada
Get a free e-book to get you started on your journey!
We take the security of your personal information very seriously. All data and information disclosed on this site are highly confidential. Once you personal data is stored, we employ highly secure servers that restrict access to potential third parties.
Sign Up To Our Newsletter Today & Get a Free e-Book

Canadianvisa.org
We Make Immigration Simple
2021-02-20T01:00:00
What does Canada’s immigration application process actually entail? Here are 7 steps to follow to apply to move to Canada!
- Immigration
A Step By Step Guide to Canada's Immigration Application Process
What does Canada’s immigration application process actually entail? How long does the process take? What do I need to qualify? If you’re interested in moving to Canada then these are the questions you might want to ask to prepare for an incredible journey that could result in a new life in the Great North.
Canada receives thousands of immigration applications each year and has become one of the most sought-after immigration destinations. Ranked as the second-best country in the world for qualities such as job opportunities, high quality of life, and multiculturalism, newcomers are flourishing in Canada. By 2023, the Canadian government hopes to admit 1.23 million immigrants to the country. Find out what it takes to be one of them below!
7 Important Steps to Immigrating to Canada
If you apply to immigrate to Canada and your application is successful you will be issued with a permanent resident (PR) visa. This allows you to live and work in the country permanently. If you travel outside Canada, you will need to show your PR card and your passport when you return. As a permanent resident, you will enjoy most social benefits, including public healthcare coverage, and be protected under Canadian law. You can apply for citizenship after you have lived in Canada for five years, and receive a Canadian passport.

Step 1. Check if you are not inadmissible to Canada
The first step in Canada’s immigration application process is to check if you are not inadmissible to Canada. If found inadmissible, you won’t be allowed to come to Canada under Canada’s immigration law. The reasons why you may be inadmissible include security, criminal and medical reasons, among others.
Step 2. Find a Canadian immigration program that you qualify for

This may be the most challenging step in the immigration application process purely because Canada has over 100 immigration and visa programs available. Each program comes with different eligibility criteria, application methods, processing times as well as specific documents that are required.
1. Eligibility assessments
The majority of successful applicants use the professional services of certified immigration consultants to help them find the right path to Canada. Immigration consultants use an in-depth eligibility assessment to strategize an immigration plan according to your goals.
It’s good to keep in mind that even if you don’t qualify for a direct immigration program to Canada, your immigration consultant can find other alternatives for you. For example, if you need to gain Canadian work experience or education to be eligible for an immigration program then a consultant may guide you to apply for a Canadian work or study permit instead.
2. Canadian immigration programs, annual targets, and processing times
How do Canada select immigrants? Well, the majority of newcomers to Canada are economic immigrants who can fill skills and labor shortages in the country as well as start businesses and create employment opportunities for Canadians and permanent residents, alike. In 2021, Canada aims to admit 401,000 immigrants through the economic categories in the table below.
Each immigration category has a number of immigration programs associated with it, for example, the Provincial Nominee Program is managed by 11 provinces and territories in Canada and has more than 80 immigration programs. Find out more below.
Step 3. Collect your immigration documents

What are immigration documents? They are forms, certificates, and records that are used to support your claims during Canada’s immigration application process. For example, if you state that you are in good health then you need to include a medical examination certificate with your application.
The following documents will always be required for immigration purposes:
Find out more information about these mandatory documents here.
Depending on the immigration program you qualify for and the number of immediate family members you have, even if they don’t move to Canada with you, you may have to submit additional documentation as specified in the program requirements. These documents can include any of the following:
- Proof of work experience (resume with contactable references);
- Provincial nomination certificate;
- Valid job offer letter;
- Marriage or divorce certificate;
- Dependant children’s birth certificates or adoption papers; and
- Evidence of family members living in Canada
Step 4. Give your biometrics at a center near you

You need to give your biometrics (fingerprints and photos) during Canada’s immigration application process. If you have previously given your biometrics you can check if they are still valid . The first step is to pay an $85 biometrics fee when you submit your application. Then, you’ll get a letter confirming that you need to give your biometrics and telling you where you can go. Remember to make an appointment beforehand. There are biometrics location centers in every country, use this tool to find a location near you.
Step 5. Fill in government forms

Unfortunately, there is no escaping tedious admin when you’re applying for permanent residency in Canada. You need to complete quite a few pages of government forms that are associated with your immigration program. It’s also very important that you complete the forms accurately because something as small as a typo or accidentally skipping information can result in your application being returned. No one can escape the strict rules as set forward by the Canadian government.
Then there is a matter of where to find the forms. They are available on the Canadian federal government website or on the provincial government websites. Fair warning, it may feel like you’re on a wild goose chase. Government websites aren’t known to be extremely user-friendly with clear indications of where to find the forms you need or even what your form numbers are called. For example, the form to apply for permanent resident cards is called IMM 5444.
Is there an easier way to do it?
Yes, there is. You can use the services of a licensed immigration consultant to take care of the paperwork on your behalf. Regulated Canadian Immigration Consultants (RCICs) and immigration lawyers are authorized by the Canadian government to do just that. You can also rest assured that your forms will be filled in accurately without the possibility of rejection.

Step 6. Submit your application to the correct department

Finally, you get to submit your application! Where you need to send your application depends on which permanent resident program you want to apply for. The majority of immigration applications are processed at case centers in Nova Scotia, Canada. The only immigration program that is online-based is the Express Entry system, otherwise, you’ll have to mail or courier your application to one of the addresses below:
Step 7. Wait for your results

The wait may be long but it’ll surely be worth it, especially if you get to pack your bags for Canada! It typically takes a few months to process certain immigration applications. (See step two.) There has been a slight delay in Canada’s immigration application process due to the COVID-19 pandemic and processing times may take a little longer than usual. For this reason, it’s a good idea to start your journey as soon as possible to beat the rush of applicants.
Read more: Latest COVID-19 Immigration News
Are You Ready to Start Your Immigration Application Process?
If you want professional guidance and advice, discuss your immigration options with our certified visa professionals. Simply, click on the link below to get started.
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Recent posts
Find a job this spring in canada.
You'll find valuable tips and resources to kickstart your job search this spring in Canada, from updating your resume to exploring job opportunities
The Newcomer's Guide to Renting a House in Canada
Worried about where you’ll live once you settle in the Great White North? Here’s everything you need to know about renting a house in Canada
Are You Covered? How Does Healthcare in Canada Work?
Uncover the ins and outs of Canada's healthcare system, from coverage to registration, ensuring newcomers are equipped with the knowledge to access th
10 Things Every Newcomer to Canada Should Prioritize
Learn how to prepare for life in Canada as a newcomer, ensuring your smooth transition and successful integration into Canadian society.
Get your free e-book today!
Want to learn more about Canada? Subscribe to our newsletter and get an e-book on Canadian immigration filled with mesmerizing sights of Canada!
CanadianVisa.org is a private recognized immigration agent and is not affiliated with the Canadian Government. Privacy policy
Back To Top
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 17, 2023
Canada - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise normal precautions in Canada.
Read the Country Information page for additional information on travel to Canada.
If you decide to travel to Canada:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Canada.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel. Exercise normal precautions in Canada.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Valid at time of entry
One page required.
Not required for stays under 180 days
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Ottawa
490 Sussex Drive Ottawa, Ontario K1N 1G8 Canada Telephone: +1 (613) 688-5335 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +1 (613) 238-5335 Fax: +1 (613) 688-3082 Email: [email protected]
The Ottawa consular district includes the counties of Kingston, Lanark, Leeds, Prescott, Refrew, Russell, and Stormont in Eastern Ontario, and those parts of the Québec regions of Outaouais and Abitibi-Témiscamingue near Ottawa.
U.S. Consulate General Montreal
1134 Rue Ste- Catherine West Montréal, Quebec H3B 1H4 Canada Telephone: +1 (514) 398-9695 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +1 (416) 645-9124 Fax: +1 (514) 398-9748 Email: [email protected]
The Montreal consular district includes Greater Montreal and the regions of Southern Quebec Province (Laurentides, Lanaudiere, Laval, Montreal, Montregie, Estrie, and the southern parts of Centre-du-Quebec), including Joliete, Drummondville, and Sherbrooke.
U.S. Consulate General Toronto
360 University Ave Toronto, Ontario M5G 1S4 Canada Telephone: +1 (416) 595-1700 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +1 (416) 201-4056 Fax: +1 (416) 595-5466 Email: [email protected]
The consular district includes the province of Ontario except for the counties of Kingston, Lanark, Leeds, Prescott, Refrew, Russell, and Stormont, which are served by the U.S. Embassy in Ottawa.
U.S. Consulate General Vancouver
1075 West Pender Street Vancouver, British Columbia V6E 2M6 Canada Telephone: +1 (604) 685-4311 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +1 (604) 685-4311 Fax: +1 (604) 685-7175 Email: [email protected]
The consular district includes British Columbia and the Yukon Territory.
U.S. Consulate General Halifax
Purdy's Wharf Tower II 1969 Upper Water Street, Suite 904 Halifax, Nova Scotia B3J 3R7 Canada Telephone: +1 (902) 429-2480 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +1 (902) 429-2480, Press 1 Email: [email protected]
The Halifax consular district includes New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and the French islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon.
U.S. Consulate Winnipeg
201 Portage Avenue, Suite 860 Winnipeg, Manitoba R3B 3K6 Canada Telephone: +1 (204) 940-1800 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +1 (403) 266-8962 and press "0" for assistance (Consulate General Calgary) Fax: +1 (204) 940-1809
The Consulate in Winnipeg provides only emergency services for U.S. citizens. Routine services such as visas, passports and notarials are handled at other U.S. Consulates General, primarily Calgary.
U.S. Consulate General Quebec 2, rue de la Terrasse Dufferin (Vieux Quebec, behind Chateau Frontenac) Quebec, Quebec G1R 4T9 Canada Telephone: +1 (418) 692-2095 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +1 (418) 692-2096 Fax: +1 (418) 692-4640 Email: [email protected]
The consular district includes Quebec City and those regions of Quebec Province to the North and East of the Montreal and Ottawa Districts (indicated above) – to include the area around Saguenay/Lac Saint-Jean, Rimouski and the Gaspé Peninsula – as well as the Territory of Nunavut.
U.S. Consulate General Calgary 615 Macleod Trail S.E., 10th Floor Calgary, Alberta T2G 4T8 Canada Telephone: +1 (403) 266-8962 Fax: +1 (403) 264-6630 Email: [email protected] The consular district includes Alberta, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and the Northwest Territories, excluding Nunavut.
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
For tourist visits to Canada of less than 180 days, U.S. citizens do not need visas. Other types of travel generally require visas. Visit the Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) website for current information.
If you have a criminal record, you may be unable to enter Canada. To determine whether you are criminally inadmissible and get information about how to overcome this finding, refer to the IRCC website . Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) officials determine if you can enter Canada in accordance with Canadian law.
Travel Programs: Both the U.S. and Canadian governments urge frequent travelers to join the NEXUS trusted traveler program .
Entry into Canada: Canadian law requires that all persons entering Canada carry proof of citizenship and identity. A valid U.S. passport, passport card, or NEXUS card satisfies these requirements for U.S. citizens.
Children under 16 only need proof of U.S. citizenship.
Entry into the United States: When traveling by air from Canada, U.S. citizens must present a U.S. passport book or other approved identification document. The U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) website provides a full list of allowable documents.
Travel with Minors: If you plan to travel to Canada with a minor for whom you do not have full legal custody, CBSA may require a letter of authorization from the minor’s parents or legal guardian(s). Please refer to the CBSA website for more details.
Private Boaters Entering Canada: Canadian law requires all foreign private boaters, including recreational vessels, to present themselves upon their arrival in Canada to the CBSA. See the CBSA website for relevant reporting requirements.
Private Boaters Exiting Canada: Boaters may report their arrival to the United States or apply for a registered boater program using the CBP Reporting Offsite Arrival – Mobile (CBP ROAM) app. Please visit the CBP ROAM webpage for more information.
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to Canada. For information on restrictions for HIV positive foreign residents of Canada visit the IRCC website .
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
911 is the emergency telephone number in Canada.
Crime: Although Canada generally has a lower crime rate than the United States, violent crimes occur throughout the country, especially in urban areas. Criminals may target parked cars, especially in large cities and popular tourist destination, for opportunistic smash-and-grab thefts. Do not leave unattended possessions in a vehicle, even in the trunk. Some jurisdictions such as Montreal, Toronto, and Vancouver may fine you for leaving your car doors unlocked or for leaving valuables in view. Pickpockets may target you, especially in popular tourist areas. Exercise caution. Safeguard yourself and your property.
Demonstrations occur frequently. They may take place in response to political or economic issues, on politically significant holidays, and during international events.
- Demonstrations can be unpredictable, avoid areas around protests and demonstrations.
- Check local media for updates and traffic advisories.
While there is a very small likelihood of violence at a political gathering in Canada, we strongly encourage U.S. citizens to avoid all protests and demonstrations and maintain a high level of vigilance and practice good situational awareness when traveling abroad.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Victims of Crime: U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy for assistance. Report crimes to the local police at 911 and contact the U.S. Embassy at +1(613) 688-5335. Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crime.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
• Help you find appropriate medical care
• Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
• Contact relatives or friends with your written consent
• Provide general information regarding the victim’s role during the local investigation and following its conclusion
• Provide a list of local attorneys
• Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
• Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution
• Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
• Replace a stolen or lost passport
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulates for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism industry is generally regulated and rules with regard to best practices and safety inspections are regularly enforced. Hazardous areas/activities are identified with appropriate signage and professional staff is typically on hand in support of organized activities. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is widely available throughout the country.
Outside of a major metropolitan center, it may take more time for first responders and medical professionals to stabilize a patient and provide life-saving assistance. If you are considering travel outside of populated areas, particularly in the northern Arctic territories, you need to know that search and rescue capabilities are limited because of extreme isolation and the harsh climate. You must be prepared for significant delays in receiving emergency assistance in these areas and plan accordingly.
U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Controlled Substances: Canadian law prohibits possession and trafficking of controlled substances and narcotics, including some substances that may be legal to possess under the law of certain U.S. states. Canada has legalized the personal consumption of recreational cannabis, but Canadian law prohibits taking cannabis across Canada’s national borders . Drug smugglers risk substantial fines, a permanent bar from Canada, and imprisonment.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
Firearms : Canada controls firearms more strictly than the United States. Violation of firearms restrictions may result in prosecution and imprisonment.
Visitors bringing any firearms or ammunition into Canada must declare the firearms in writing using a Non-Resident Firearm Declaration form. If you plan to borrow and use a firearm in Canada, you must obtain a Temporary Firearms Borrowing License in advance. You must present these forms in triplicate and sign them in front of a CBSA officer at the border. (It is not possible to make photocopies at the border). Full details and downloadable forms are available at the Canadian Firearms Program website .
Canadian law requires officials to confiscate firearms, ammunition, and other weapons from persons crossing the border who do not declare having the items in their possession. Officials will not return confiscated firearms, ammunition, and weapons and possession of any of these items may result in your arrest and imprisonment. You should inspect all belongings thoroughly before traveling to Canada to avoid the accidentally importing firearms, ammunition, or other weapons.
LGBTQI+ Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTQI+ events in Canada. See our LGBTQI+ Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Pornography: Canada has strict laws concerning child pornography, and in recent years there has been an increase in random checks of electronic media of travelers entering Canada.
Canadian officials may search your computers, cell phones, and other electronic devices without a warrant at the border and illegal content can result in the seizure of the device as well as detention, arrest, and prosecution of the bearer.
Tax Issues: For information on U.S. Federal tax issues, please refer to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website for international taxpayers .
- Refer to this link for reporting requirements regarding Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR) .
- Refer to this link for information on the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) .
- Refer to this link for information about the Voluntary Disclosure Practice .
Travelers with Disabilities: The law in Canada prohibitsdiscrimination against persons with physical or mental disabilities and the law is enforced. Social acceptance of persons with disabilities in public is as prevalent as in the United States. For more information, visit the Accessibility Standards Canada website .
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
For emergency services in Canada, dial 911 . Ambulance services are widely available.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription. Check with Health Canada to ensure the medication is legal in Canada.
Healthcare in Canada : The level of public health and sanitation in Canada is high. Adequate health facilities are available throughout Canada. Canada’s medical care is of a high standard but is government controlled. Access to ongoing medical care is difficult for temporary visitors who are not members of a Canadian province’s government-run health care plan. Many physicians will not take new patients. Specialist care is only by referral and may take months to obtain. Although trauma-care is on par with that in the United States, emergency room waits for non-life threatening problems can be very long. Some health care professionals in the Quebec may only speak French.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of doctors and hospitals . We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all CDC-recommended vaccinations .
Further health information:
World Health Organization U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery: We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation in the event of unforeseen medical complications.
Pharmaceuticals: U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration are responsible for rules governing the transport of medication back to the United States. Medication purchased abroad must meet their requirements to be legally brought back into the United States. Medication should be for personal use and must be approved for usage in the United States. Please visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration websites for more information.
Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy: If you are considering traveling to Canada to have a child through use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) or surrogacy, please see our ART and Surrogacy Abroad page .
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: As in the United States, all emergency assistance in Canada can be reached by dialing 911.
For detailed information on road conditions throughout Canada, as well as links to provincial government websites, please see the Transport Canada website or the Canadian Automobile Association (CAA) website. The CAA honors American Automobile Association memberships. Automobile warranties of vehicles purchased in the United States may not be valid in Canada.
Winter travel can be dangerous due to heavy snowfalls and hazardous icy conditions. Some provinces require snow tires. CAA has tips for winter driving . Both winter conditions and wildfires may prompt the sudden closure of highways. Provincial ministries of transport typically post closures and other alerts about road conditions on their websites.
Traffic Laws: Driving in Canada is similar to driving in many parts of the United States. Distances and speeds, however, are posted in kilometers per hour and some signs, particularly in Québec, may only be in French. U.S. driver’s licenses are valid for visitors in Canada. Proof of auto insurance is required. U.S. auto insurance is accepted for tourists in Canada. For specific information concerning Canadian driving permits, mandatory insurance, and entry regulations, please contact the Canadian National Tourist Organization .
Some provinces require drivers to keep their vehicles’ headlights on during the day and some have banned driving while using a hand-held cell phone. Motorcycles cannot share a lane, and safety helmets for motorcycle riders and passengers are mandatory.
It is illegal to take automobile radar detectors into Québec, Ontario, Manitoba, the Yukon, or the Northwest Territories, regardless of whether they are used. Police may confiscate radar detectors and impose substantial fines.
Drivers approaching border crossings into the United States may encounter traffic backups. Drivers should be alert, as lane restrictions at border approaches exist for drivers in NEXUS and FAST expedited inspection programs.
Public Transportation: Public transportation options vary across Canada, but all cities and most major towns have a public transit system .
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Canada’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Canada’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Canada should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Canada . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Check passport expiration dates carefully for all travelers! Children’s passports are issued for 5 years, adult passports for 10 years.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
Travel advice and advisories by destination
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
The Government of Canada’s official source of travel information and advice, the Travel Advice and Advisories help you to make informed decisions and travel safely while you are outside Canada. Check the page for your destination often, because safety and security conditions may change. See Travel Advice and Advisories – FAQ for more information.
Where are you going?
Take normal security precautions
Exercise a high degree of caution
Avoid non-essential travel
Avoid all travel
Travel advice from other countries
Travel advice is also provided by the governments of Australia , New Zealand , the United Kingdom and the United States .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Language selection
- Français fr
Travel tips for snowbirds returning to Canada
From: Canada Border Services Agency
News release
April 12, 2024 Ottawa, Ontario
The Canada Border Services Agency and the Canadian Snowbird Association are encouraging Canadians who have spent the winter abroad to plan ahead for a smooth return to Canada this spring.
These are the top travel tips to know before arriving at the border:
Have your travel documents handy. Whether travelling by land, air or water, you can help speed up processing times by coming prepared with your travel documents.
Driving home? Plan ahead and check border wait times . You can avoid waiting in line by planning your drive to cross the border during non-peak hours such as early morning.
Flying home? Save time with Advance Declaration . Download the application on your smart phone to make your customs declaration up to 72 hours in advance of your arrival into Canada at the Toronto, Vancouver, Montréal, Winnipeg, Halifax, Québec City, Ottawa, Billy Bishop, Calgary and Edmonton international airports. Data shows that using this tool can reduce time at a kiosk or eGate by up to 50%.
Be prepared to declare your goods upon entry into Canada. Gather your receipts for goods purchased or received while away before you travel and keep them readily available. Visit I Declare: A guide for residents returning to Canada and use the CBSA duty and taxes estimator to help calculate your monies owed. You should be aware of everything that is inside your vehicle as you are responsible for its contents.
Know your exemptions from duties and taxes . If you have been outside of Canada seven days or more, you can import goods worth up to CAN$800, duty-and tax-free. Within this personal exemption, you are allowed to bring back duty and tax free:
- Two bottles of wine (1.5 litres total), or one large standard bottle of liquor (1.14 litres), or approximately 24 cans or bottles (355 ml each) of beer (8.5 litres total); and,
- 200 cigarettes, and 50 cigars, and 200 grams manufactured tobacco, and 200 tobacco sticks. The packages must be stamped “duty paid,” as you would find them at a duty-free store.
Travelling with medication? If you have a prescription for a narcotic or controlled drug, you must declare it and ensure its in properly labelled container. Learn more about your responsibilities .
Travelling with firearms? If you are travelling with a firearm be sure to check the rules on importing firearms and other restricted and prohibited goods before your departure. Better yet, consider leaving the firearm at home.
Importing a vehicle ? If you are a resident of Canada you can temporarily import a vehicle that is licensed and registered in the United States, however, the duty and tax implications, the length of time the vehicle can remain in Canada, and how the vehicle can be used in Canada may differ. If you are permanently importing a vehicle from the U.S. or Mexico, visit Canada’s Registrar of Imported Vehicles website prior to arriving at the border for details about vehicle eligibility and the overall process, including the necessary duties and taxes.
Bringing poultry across the border? Any poultry products you wish to bring into Canada must be for human consumption, retail packaged and labelled as a "Product of the USA." Homemade food or leftovers containing poultry cannot be brought into Canada. Check the latest Information for travellers: Restrictions on poultry and birds from the United States before bringing these products across the border.
Travelling with a pet or importing an animal into Canada? You will need the right paperwork at the border to meet Canada's import requirements.
Not sure? Ask a border officer. The best thing you can do to save time is to be open and honest with the CBSA officer. Be sure to follow all instructions they provide to you. If you are not sure about what to declare, don't hesitate to ask. Our officers are here to help!
Quick facts
The Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) supports national security and public safety priorities by facilitating the free flow of persons and goods, including animals and plants.
The Canadian Snowbird Association is a not-for-profit advocacy organization for travelling Canadians, representing more than 115,000 members.
Associated links
- Plan your trip across the border
- Duties and taxes estimator
- I Declare: A guide for residents returning to Canada
- Border reminder checklist
- Advance Declaration video
- The CBSA and U.S. CBP provide an update on the NEXUS program
For more information about CBSA programs, services and initiatives, please visit the CBSA website or contact:
Border Information Services Canada Border Services Agency 1-800-461-9999 Contact us online Live agents are available Monday to Friday from 8 am to 4 pm local time
For more information or to schedule a media interview, please contact:
Media Relations Canada Border Services Agency [email protected] 1-877-761-5945
Communications Canadian Snowbird Association [email protected]
For more travel tips for Canadian snowbirds, join the Canada Border Services Agency on Facebook and YouTube and visit the Canadian Snowbird Association website .
Page details
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What we know about unauthorized immigrants living in the U.S.
The unauthorized immigrant population in the United States reached 10.5 million in 2021, according to new Pew Research Center estimates. That was a modest increase over 2019 but nearly identical to 2017.
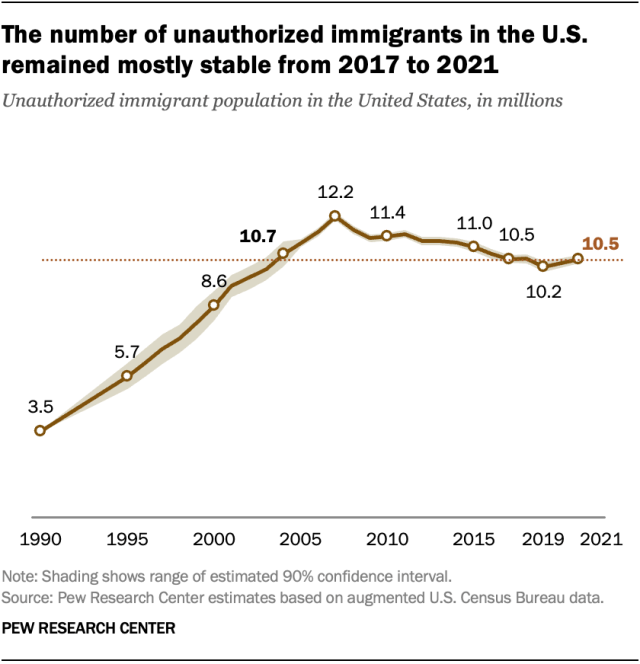
The number of unauthorized immigrants living in the U.S. in 2021 remained below its peak of 12.2 million in 2007. It was about the same size as in 2004 and lower than every year from 2005 to 2015.
The new estimates do not reflect changes that have occurred since apprehensions and expulsions of migrants along the U.S.-Mexico border started increasing in March 2021 . Migrant encounters at the border have since reached historic highs .
Pew Research Center undertook this research to understand ongoing changes in the size and characteristics of the unauthorized immigrant population in the United States. The Center has published estimates of the U.S. unauthorized immigrant population for more than two decades. The estimates presented in this research are the Center’s latest, adding new and updated annual estimates for 2017 through 2021.
Center estimates of the unauthorized immigrant population use a “residual method.” It is similar to methods used by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Office of Immigration Statistics and nongovernmental organizations, including the Center for Migration Studies and the Migration Policy Institute . Those organizations’ estimates are generally consistent with ours. Our estimates also align with official U.S. data sources, including birth records, school enrollment figures and tax data, as well as Mexican censuses and surveys.
Our “residual” method for estimating the nation’s unauthorized immigrant population includes these steps:
- Estimate the total number of immigrants living in the country in a particular year using data from U.S. censuses and government surveys such as the American Community Survey and the Current Population Survey.
- Estimate the number of immigrants living in the U.S. legally using official counts of immigrant and refugee admissions together with other demographic data (for example, death and out-migration rates).
- Subtract our estimate of lawful immigrants from our estimate of the total immigrant population . This provides an initial estimate of the unauthorized immigrant population .
Our final estimate of the U.S. unauthorized immigrant population, as well as estimates for lawful immigrants, includes an upward adjustment. We do this because censuses and surveys tend to miss some people . Undercounts for immigrants, especially unauthorized immigrants, tend to be higher than for other groups. (Our 1990 estimate comes from work by Robert Warren and John Robert Warren; details can be found here .)
The term “unauthorized immigrant” reflects standard and customary usage by many academic researchers and policy analysts. The U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Office of Immigration Statistics also generally uses it. The term means the same thing as undocumented immigrants, illegal immigrants and illegal aliens.
For more details on how we produced our estimates, read the Methodology section of our November 2018 report on unauthorized immigrants.
The unauthorized immigrant population includes any immigrants not in the following groups:
- Immigrants admitted for lawful residence (i.e., green card admissions)
- People admitted formally as refugees
- People granted asylum
- Former unauthorized immigrants granted legal residence under the 1985 Immigration Reform and Control Act
- Immigrants admitted under any of categories 1-4 who have become naturalized U.S. citizens
- Individuals admitted as lawful temporary residents under specific visa categories
Read the Methodology section of our November 2018 report on unauthorized immigrants for more details.
Pew Research Center’s estimate of unauthorized immigrants includes more than 2 million immigrants who have temporary permission to be in the United States. (Some also have permission to work in the country.) These immigrants account for about 20% of our national estimate of 10.5 million unauthorized immigrants for 2021.
Although these immigrants have permission to be in the country, they could be subject to deportation if government policy changes. Other organizations and the federal government also include these immigrants in their estimates of the U.S. unauthorized immigrant population.
Immigrants can receive temporary permission to be in the U.S. through the following ways:
Temporary Protected Status (TPS)
In 2021, there were about 500,000 unauthorized immigrants with Temporary Protected Status . This status provides protection from removal or deportation to individuals who cannot safely return to their country because of civil unrest, violence or natural disaster.
Deferred Enforced Departure (DED) is a similar program that grants protection from removal. The number of immigrants with DED is much smaller than the number with TPS.
Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA)
Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals is a program that offers protection from deportation to individuals who were brought to the U.S. as children before June 15, 2007. As of the end of 2021, there were slightly more than 600,000 DACA beneficiaries , largely immigrants from Mexico.
Asylum applicants
Individuals who have applied for asylum but are awaiting a ruling are not legal residents yet but cannot be deported. There are two types of asylum claims, defensive and affirmative .
Defensive asylum applications are generally filed by individuals facing deportation or removal from the U.S. These are processed by the Department of Justice’s Executive Office for Immigration Review. At the end of 2021, there were almost 600,000 applications pending.
Affirmative asylum claims are made by individuals already in the U.S. who are not in the process of being deported or removed. These claims are handled by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). At the end of 2021, more than 400,000 applications for affirmative asylum were pending, some covering more than one applicant.
Here are key findings about how the U.S. unauthorized immigrant population changed from 2017 to 2021:
- The most common country of birth for unauthorized immigrants is Mexico. However, the population of unauthorized immigrants from Mexico dropped by 900,000 from 2017 to 2021 , to 4.1 million.
- There were increases in unauthorized immigrants from nearly every other region of the world – Central America, the Caribbean, South America, Asia, Europe and sub-Saharan Africa.
- Among U.S. states, only Florida and Washington saw increases to their unauthorized immigrant populations , while California and Nevada saw decreases. In all other states, unauthorized immigrant populations were unchanged.
- 4.6% of U.S. workers in 2021 were unauthorized immigrants , virtually identical to the share in 2017.
Trends in the U.S. immigrant population
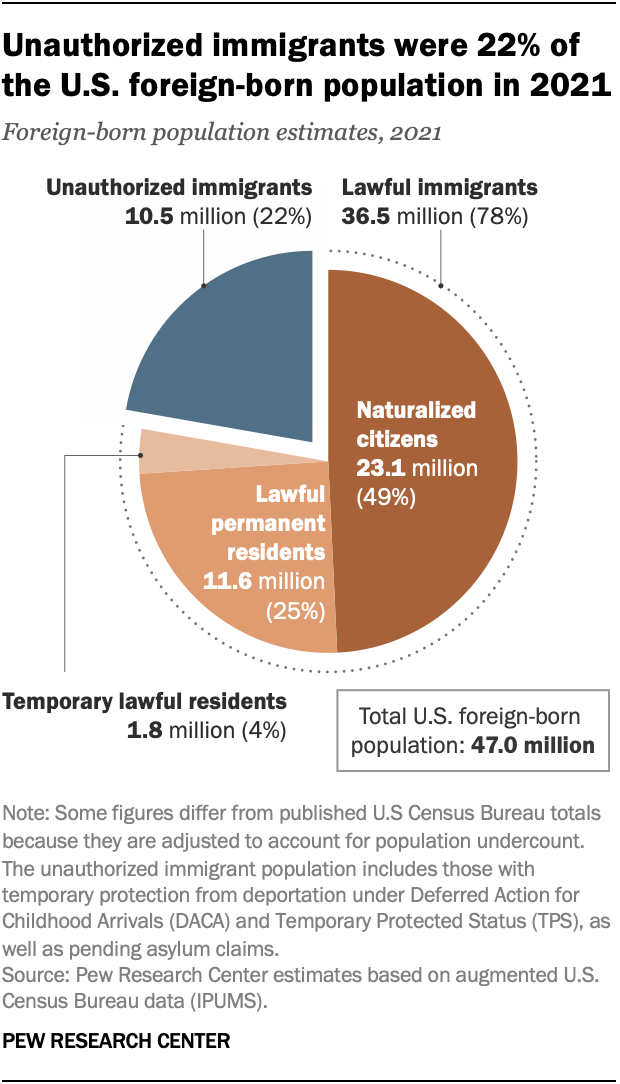
The U.S. foreign-born population was 14.1% of the nation’s population in 2021. That was very slightly higher than in the last five years but below the record high of 14.8% in 1890.
As of 2021, the nation’s 10.5 million unauthorized immigrants represented about 3% of the total U.S. population and 22% of the foreign-born population. These shares were among the lowest since the 1990s.
Between 2007 and 2021, the unauthorized immigrant population decreased by 1.75 million, or 14%.
Meanwhile, the lawful immigrant population grew by more than 8 million, a 29% increase, and the number of naturalized U.S. citizens grew by 49%. In 2021, naturalized citizens accounted for about half (49%) of all immigrants in the country.
Where unauthorized immigrants come from
Unauthorized immigrants living in the U.S. come from many parts of the world, with Mexico being the most common origin country.
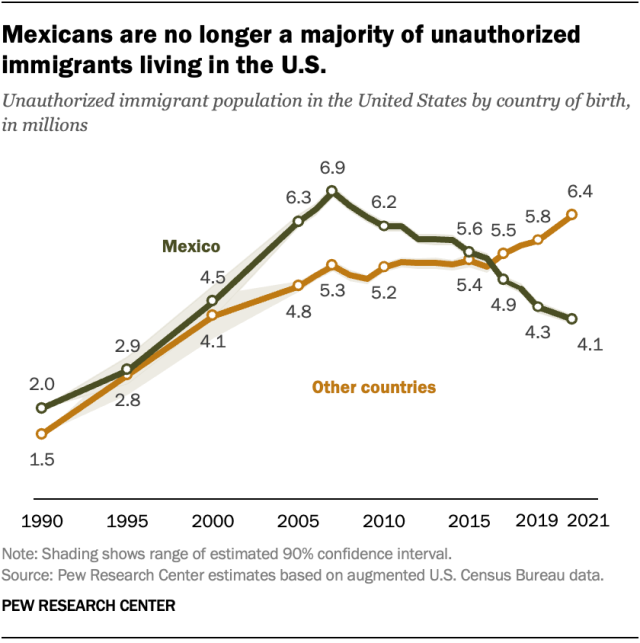
The origin countries for unauthorized immigrants have changed since the population peaked in 2007, before the Great Recession slowed immigration. Here are some highlights of those changes:
The number of unauthorized immigrants from Mexico living in the U.S. (4.1 million in 2021) was the lowest since the 1990s. Mexico accounted for 39% of the nation’s unauthorized immigrants in 2021, by far the smallest share on record .
The decrease in unauthorized immigrants from Mexico reflects several factors:
- A broader decline in migration from Mexico to the U.S.
- Mexican immigrants to the U.S. continuing to return to Mexico
- Expanded opportunities for lawful immigration from Mexico and other countries, especially for temporary agricultural workers.
The rest of the world
The total number of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. from countries other than Mexico has grown rapidly. In 2021, this population was 6.4 million, up by 900,000 from 2017.
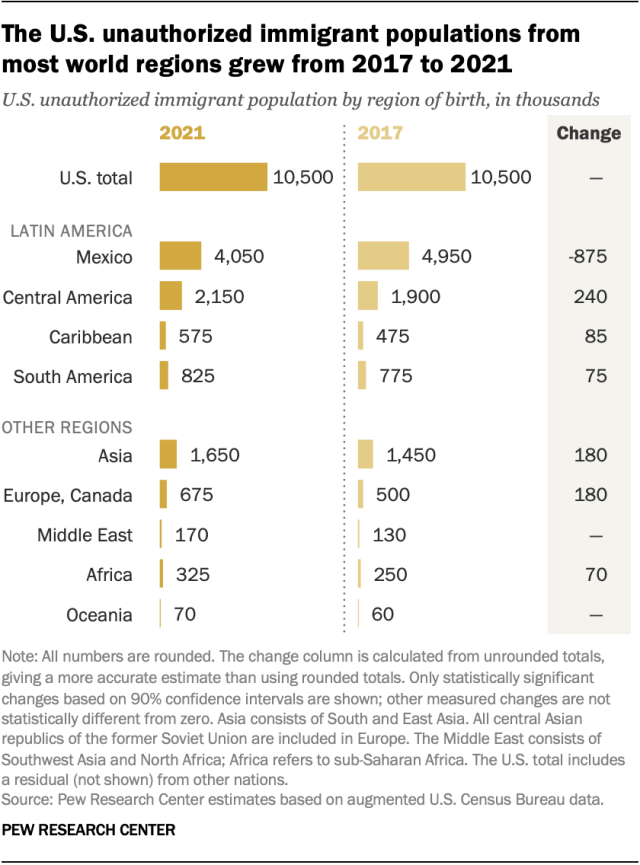
Almost every region in the world had a notable increase in the number of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. from 2007 to 2021. The largest increases were from Central America (240,000) and South and East Asia (180,000).
After Mexico, the countries of origin with the largest unauthorized immigrant populations in the U.S. in 2021 were:
- El Salvador (800,000)
- India (725,000)
- Guatemala (700,000)
- Honduras (525,000)
India, Guatemala and Honduras all saw increases from 2017.
The Northern Triangle
Three Central American countries – El Salvador, Honduras and Guatemala – together represented 2.0 million unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. in 2021, or almost 20% of the total. The unauthorized immigrant population from the Northern Triangle grew by about 250,000 from 2017 and about 700,000 from 2007.
Other origin countries
Venezuela was the country of birth for 190,000 U.S. unauthorized immigrants in 2021. This population saw particularly fast growth, from 130,000 in 2017 and 55,000 in 2007.
Among countries with the largest numbers of U.S. unauthorized immigrants, India, Brazil, Canada and former Soviet Union countries all experienced growth from 2017 to 2021.
Some origin countries with significant unauthorized immigrant populations showed no change, notably China (375,000) and the Dominican Republic (230,000).
Detailed table: Unauthorized immigrant population by region and selected country of birth (and margins of error), 1990-2021 (Excel)
U.S. states of residence of unauthorized immigrants
The unauthorized immigrant population in most U.S. states stayed steady from 2017 to 2021. However, four states saw significant changes:
- Florida (+80,000)
- Washington (+60,000)
- California (-150,000)
- Nevada (-25,000)
States with the most unauthorized immigrants
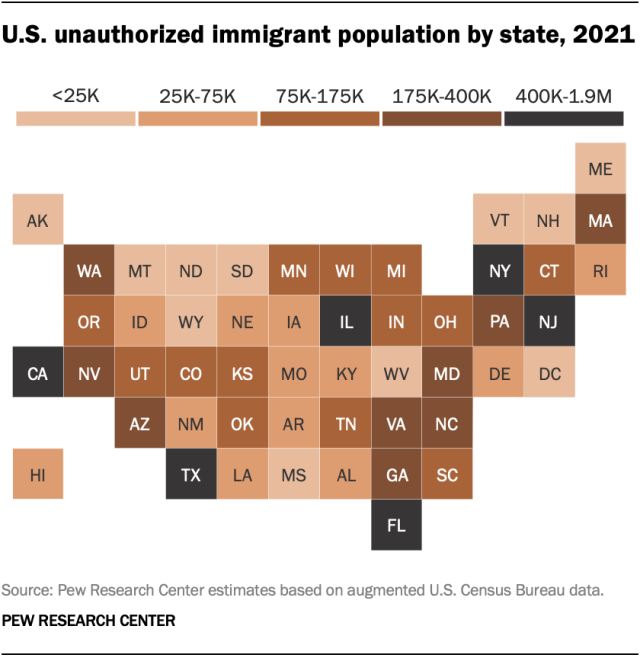
The six states with the largest unauthorized immigrant populations in 2021 were:
- California (1.9 million)
- Texas (1.6 million)
- Florida (900,000)
- New York (600,000)
- New Jersey (450,000)
- Illinois (400,000)
These states have consistently had the most unauthorized immigrants since 1990 and earlier .
At the same time, the unauthorized immigrant population has become less geographically concentrated. In 2021, these six states were home to 56% of the nation’s unauthorized immigrants, down from 80% in 1990.
Detailed table: Unauthorized immigrant population for states (and margins of error), 1990-2021 (Excel)
Detailed table: Unauthorized immigrants and characteristics for states, 2021 (Excel)
Unauthorized immigrants in the labor force
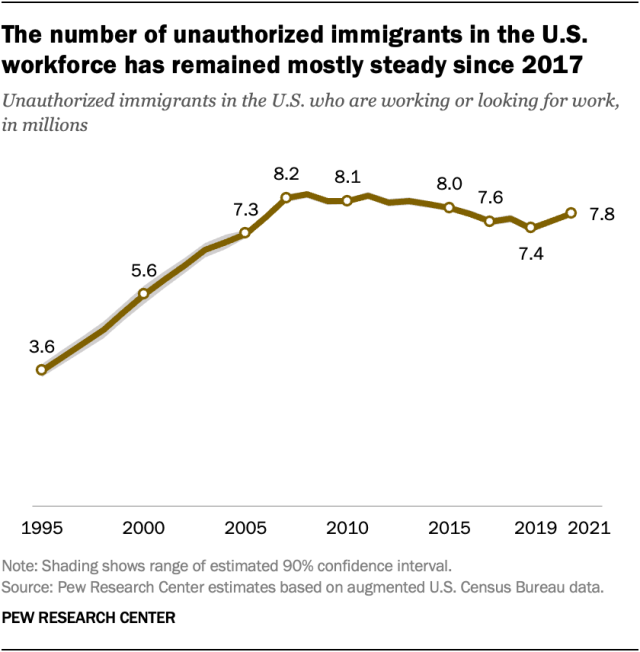
The share of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. workforce was slightly less than 5% in 2021, compared with 3% of the total U.S. population.
Demographics help explain the difference: The unauthorized immigrant population includes relatively few children or elderly adults, groups that tend not to be in the labor force.
Overall, about 7.8 million unauthorized immigrants were in the U.S. labor force in 2021. That was up slightly from 2019 but smaller than every year from 2007 through 2015.
Detailed table: Unauthorized immigrants in the labor force for states, 2021 (Excel)
Here are some additional findings about unauthorized immigrants as a share of the workforce nationwide and in certain states:
- Since 2003, unauthorized immigrants have made up 4.4% to 5.4% of all U.S. workers, a relatively narrow range.
- Fewer than 1% of workers in Maine, Montana, Vermont and West Virginia in 2021 were unauthorized immigrants.
- Nevada (9%) and Texas (8%) had the highest shares of unauthorized immigrants in the workforce.
- Immigrant Populations
- Immigration Issues
- Unauthorized Immigration

Key facts about Asian Americans living in poverty
Latinos’ views on the migrant situation at the u.s.-mexico border, key facts about the nation’s 47.9 million black americans, key facts about the wealth of immigrant households during the covid-19 pandemic, 8 facts about recent latino immigrants to the u.s., most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Visit Canada. Find out what document you need to travel, visit family and friends, do business, or transit through Canada, and how to extend your stay. Special measures for. For people affected by. Iranian temporary residents in Canada. The situation in Lebanon.
To apply for a visitor visa to visit Canada on business, you need to qualify as a business visitor. To qualify, you must show that: you plan to stay for less than 6 months. you don't plan to enter the Canadian labour market. your main place of business and source of income and profits is outside Canada.
Immigration and citizenship. Apply to travel, study, work or immigrate to Canada, apply for citizenship, a permanent resident card or refugee protection, check the status of your application or find a form. ... Know why you may not be allowed in Canada, and learn about immigration violations, the detention review process and immigration ...
Step 1. Pre-arrival: Use Advance Declaration or complete a Declaration Card. If you're arriving by air at one of Canada's participating international airports, you can save time at the border. Submit your customs and immigration declaration online using Advance Declaration up to 72 hours before you arrive in Canada.
5. You travel to Canada (if you're approved) Make sure you travel with the documents we gave you. This includes travel documents like a visitor visa, study or work permits or an eTA (electronically linked to your passport). Airline staff and border service officers at ports of entry will ask to see your travel documents.
Use Advance Declaration in ArriveCAN to submit your customs and immigration declaration before flying into Canada. Government of Canada's official one-stop-shop for comprehensive international travel information.
Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada. Building a stronger Canada through immigration programs, citizenship services, refugee protection, and issuing Canadian travel documents. Information on the situation in.
Travel outside Canada. Travel documents, travel health and safety, border wait times and more. Air travel. Prepare for a flight, airport security, health concerns and more. ... Information on travelling to Canada, border wait times, customs and immigration. Canadian attractions, events and experiences. Discover Canada's museums, national parks ...
Immigration and citizenship. Apply to travel, study, work or immigrate to Canada, apply for citizenship, a permanent resident card or refugee protection, check the status of your application or find a form. Follow:
It was created to assist you as you decide what travel document you may need to travel to Canada. This tool may not provide information on all travel documents or your particular situation. If you choose to apply, we will assess your application in accordance with the Immigration and Refugee Protection Act and its related Regulations.
Temporary resident to permanent resident pathway. The temporary resident to permanent resident pathway is a limited-time pathway to permanent residence. It is for certain temporary residents who are currently working in Canada and their families.
What you can bring back to Canada. General guidelines on what you can and cannot bring into Canada when you return from abroad. Date modified: 2023-02-06. Government of Canada's official one-stop-shop for comprehensive international travel information.
If you are an American citizen who wants to enter Canada, you need to know the requirements and procedures for crossing the border. This webpage provides you with the information on what documents you need, how to apply for an eTA or a visa, and what to expect upon arrival. You can also find links to other useful resources on health, taxes, and benefits in Canada.
We have created an online tool called Come to Canada. It will help you figure out whether you can come to Canada as an immigrant, visitor, worker or student. This tool guides you through some questions and based on your responses and your situation, it then gives you: a list of options and. step-by-step instructions on how to apply. This tool ...
If you do not have a passport, and are returning to Canada, the following documents can denote identity and citizenship: NEXUS card, held by a Canadian citizen, when entering Canada by air (when coming from the U.S.), land, or marine modes. FAST card (Free and Secure Trade), issued to a Canadian citizen (when arriving by land or marine modes ...
Proof of COVID-19 vaccination is not required. Pre-board testing is not required. COVID-19 pre-entry and arrival tests are not required. Quarantine after you enter Canada is not required. Using ArriveCAN is not required, but. to save time at the border, you can use Advance Declaration in ArriveCAN to submit your customs and immigration ...
This applies to travellers who: Have an international flight that stops at a Canadian airport on the way to another country. Will be connecting between two international flights at a Canadian airport. Will be transiting through Canada in 48 hours or less. Do not have a valid visitor visa.
Everyone wants their border crossing to go smoothly with few delays. The best way to make sure this happens is to know what to expect and be prepared. Whether you're returning home or visiting, Canada Border Services Agency ( CBSA) wants to help you plan your trip across the border with some useful tools.
Step 10: Travel to Canada. Board your flight to Canada. When you arrive, the airline staff will verify your eTA before you can board. Does Canada have any COVID-19 Travel Restrictions? As of October 1, 2022, the border measures related to COVID-19 have ceased for all individuals arriving or coming back to Canada via air, land, or sea.
Step 2. Find a Canadian immigration program that you qualify for. This may be the most challenging step in the immigration application process purely because Canada has over 100 immigration and visa programs available. Each program comes with different eligibility criteria, application methods, processing times as well as specific documents that are required.
Find helpful information on health and safety, travel documents, baggage, airport security, country advice and more. Information on a recommended consent letter for Canadian children travelling abroad. You need a valid Canadian passport to board a flight to Canada. Government of Canada's official one-stop-shop for comprehensive international ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
The Government of Canada's official source of travel information and advice, the Travel Advice and Advisories help you to make informed decisions and travel safely while you are outside Canada. Check the page for your destination often, because safety and security conditions may change. See Travel Advice and Advisories - FAQ for more ...
Visit Canada (includes visas and electronic travel authorizations) Immigrate to Canada (includes family sponsorship, Express entry and other economic immigration programs) ... not see the status of your results updated in your account until we finish processing your immigration application. We need time to. process your application ...
News release. The Canada Border Services Agency and the Canadian Snowbird Association are encouraging Canadians who have spent the winter abroad to plan ahead for a smooth return to Canada this spring. These are the top travel tips to know before arriving at the border: Have your travel documents handy. Whether travelling by land, air or water ...
As of 2021, the nation's 10.5 million unauthorized immigrants represented about 3% of the total U.S. population and 22% of the foreign-born population. These shares were among the lowest since the 1990s. Between 2007 and 2021, the unauthorized immigrant population decreased by 1.75 million, or 14%. Meanwhile, the lawful immigrant population ...