Can we store analytics cookies on your device?
Analytics cookies help us understand how our website is being used. They are not used to identify you personally.
You’ve accepted all cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Ethnicity facts and figures homepage Home

Gypsy, Roma and Irish Traveller ethnicity summary
Updated 29 March 2022
1. About this page
2. the gypsy, roma and traveller group, 3. classifications, 4. improving data availability and quality, 5. population data, 6. education data, 7. economic activity and employment data.
- 8. Home ownership data data
- 9. Health data
This is a summary of statistics about people from the Gypsy, Roma and Traveller ethnic groups living in England and Wales.
It is part of a series of summaries about different ethnic groups .
Gypsy, Roma and Traveller (GRT) is a term used to describe people from a range of ethnicities who are believed to face similar challenges. These groups are distinct, but are often reported together.
This page includes:
- information about GRT data and its reliability
- some statistics from the 2011 Census
- other statistics on the experiences of people from the GRT groups in topics including education, housing and health
This is an overview based on a selection of data published on Ethnicity facts and figures or analyses of other sources. Some published data (for example, on higher education) is only available for the aggregated White ethnic group, and is not included here.
Through this report, we sometimes make comparisons with national averages. While in other reports we might compare with another ethnic group (usually White British), we have made this decision here because of the relatively small impact the GRT group has on the overall national average.
The term Gypsy, Roma and Traveller has been used to describe a range of ethnic groups or people with nomadic ways of life who are not from a specific ethnicity.
In the UK, it is common in data collections to differentiate between:
- Gypsies (including English Gypsies, Scottish Gypsies or Travellers, Welsh Gypsies and other Romany people)
- Irish Travellers (who have specific Irish roots)
- Roma, understood to be more recent migrants from Central and Eastern Europe
The term Traveller can also encompass groups that travel. This includes, but is not limited to, New Travellers, Boaters, Bargees and Showpeople. (See the House of Commons Committee report on Tackling inequalities faced by Gypsy, Roma and Traveller communities .)
For the first time, the 2011 Census ethnic group question included a tick box for the ethnic group ‘Gypsy or Irish Traveller’. This was not intended for people who identify as Roma because they are a distinct group with different needs to Gypsy or Irish Travellers.
The 2021 Census had a ‘Gypsy or Irish Traveller’ category, and a new ‘Roma’ category.
A 2018 YouGov poll found that 66% of people in the UK wrongly viewed GRT not to be an ethnic group, with many mistaking them as a single group (PDF). It is therefore important that GRT communities are categorised correctly on data forms, using separate tick boxes when possible to reflect this.
The 2011 Census figures used in this report and on Ethnicity facts and figures are based on respondents who chose to identify with the Gypsy or Irish Traveller ethnic group. People who chose to write in Roma as their ethnicity were allocated to the White Other group, and data for them is not included here. Other data, such as that from the Department for Education, includes Roma as a category combined with Gypsy, with Irish Traveller shown separately.
The commentary in this report uses the specific classifications in each dataset. Users should exercise caution when comparing different datasets, for example between education data (which uses Gypsy/Roma, and Irish Traveller in 2 separate categories) and the Census (which uses Gypsy and Irish Traveller together, but excludes data for people who identify as Roma).
Finally, it should be noted that there is also a distinction that the government makes, for the purposes of planning policy, between those who travel and the Gypsy, Roma and Traveller ethnicities. The Department for Communities and Local Government (at the time, now the Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities) planning policy for traveller sites (PDF) defines "gypsies and travellers" as:
"Persons of nomadic habit of life whatever their race or origin, including such persons who on grounds only of their own or their family’s or dependants’ educational or health needs or old age have ceased to travel temporarily, but excluding members of an organised group of travelling showpeople or circus people travelling together as such."
This definition for planning purposes includes any person with a nomadic habit, whether or not they might have identified as Gypsy, Roma or Traveller in a data collection.
The April 2019 House of Commons Women and Equalities Select Committee report on inequalities faced by Gypsy, Roma and Traveller communities noted that there was a lack of data on these groups.
The next section highlights some of the problems associated with collecting data on these groups, and what is available. Some of the points made about surveys, sample sizes and administrative data are generally applicable to any group with a small population.
Improving data for the Gypsy, Roma and Traveller populations, as well as other under-represented groups in the population is part of the recommendations in the Inclusive Data Taskforce report and the key activities described in the ONS response to them. For example, in response to recommendation 3 of the report, ONS, RDU and others will "build on existing work and develop new collaborative initiatives and action plans to improve inclusion of under-represented population groups in UK data in partnership with others across government and more widely".
Also, the ONS response to recommendation 4 notes the development of a range of strategies to improve the UK data infrastructure and fill data gaps to provide more granular data through new or boosted surveys and data linkage. Recommendation 6 notes that research will be undertaken using innovative methods best suited to the research question and prospective participants, to understand more about the lived experiences of several groups under-represented in UK data and evidence, such as people from Gypsy, Roma and Traveller groups.
4.1 Classifications
In some data collections, the option for people to identify as Gypsy, Roma or Traveller is not available. Any data grouped to the 5 aggregated ethnic groups does not show the groups separately. Data based on the 2001 Census does not show them separately as there was no category for people identifying as Gypsy, Roma or Traveller. As part of our Quality Improvement Plan, the Race Disparity Unit (RDU) has committed to working with government departments to maintain a harmonised approach to collecting data about Gypsy, Roma and Traveller people using the GSS harmonised classification. The harmonised classification is currently based on the 2011 Census, and an update is currently being considered by the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
In particular, RDU has identified working with DHSC and NHS Digital colleagues as a priority – the NHS classification is based on 2001 Census classifications and does not capture information on any of the GRT groups separately (they were categorised as White Other in the 2001 Census). Some of these issues have been outlined in the quarterly reports on progress to address COVID-19 health inequalities .
Research into how similar or different the aggregate ethnic groups are shows how many datasets are available for the GRT group.
Further information on the importance of harmonisation is also available.
4.2 Census data
A main source of data on the Gypsy and Irish Traveller groups is the 2011 Census. This will be replaced by the 2021 Census when results are published by the ONS. The statistics in this summary use information from Ethnicity facts and figures and the Census section of ONS’s NOMIS website.
4.3 Survey data
It is often difficult to conclude at any one point in time whether a disparity is significant for the GRT population, as the population is so small in comparison to other ethnic groups.
Even a large sample survey like the Annual Population Survey (APS) has a small number of responses from the Gypsy and Irish Traveller ethnic group each year. Analysis of 3 years of combined data for 2016, 2017 and 2018 showed there were 62 people in the sample (out of around 500,000 sampled cases in total over those 3 years) in England and Wales. Another large survey, the Department for Transport’s National Travel Survey, recorded 58 people identifying as Gypsy or Traveller out of 157,000 people surveyed between 2011 and 2019.
Small sample sizes need not be a barrier to presenting data if confidence intervals are provided to help the user. But smaller sample sizes will mean wider confidence intervals, and these will provide limited analytical value. For the 2016 to 2018 APS dataset – and using the standard error approximation method given in the LFS User Guide volume 6 with a fixed design factor of 1.6 (the formula is 1.6 * √p(1 − p)/n where p is the proportion in employment and n is the sample size.) – the employment rate of 35% for working age people in the Gypsy and Traveller group in England and Wales would be between 16% and 54% (based on a 95% confidence interval). This uses the same methodology as the ONS’s Sampling variability estimates for labour market status by ethnicity .
A further reason for smaller sample sizes might be lower response rates. The Women and Select Committee report on the inequalities faced by Gypsy, Roma and Traveller communities noted that people in these groups may be reluctant to self-identify, even where the option is available to them. This is because Gypsy, Roma and Traveller people might mistrust the intent behind data collection.
The RDU recently published a method and quality report on working out significant differences between estimates for small groups using different analytical techniques.
4.4 Administrative data
While administrative data does not suffer from the same issues of sampling variability, small numbers of respondents can mean that data is either disclosive and needs to be suppressed to protect the identity of individuals, or results can fluctuate over time.
An example of this is the measure of students getting 3 A grades or better at A level . In 2019 to 2020, no Irish Traveller students achieved this (there were 6 students in the cohort). In 2017 to 2018, 2 out of 7 Irish Traveller students achieved 3 A grades, or 28.6% – the highest percentage of all ethnic groups.
Aggregating time periods might help with this, although data collected in administrative datasets can change over time to reflect the information that needs to be collected for the administrative process. The data collected would not necessarily be governed by trying to maintain a consistent time series in the same way that data collected through surveys sometimes are.
4.5 Data linkage
Linking datasets together provides a way of producing more robust data for the GRT groups, or in fact, any ethnic group. This might improve the quality of the ethnicity coding in the dataset being analysed if an ethnicity classification that is known to be more reliable is linked from another dataset.
Data linkage does not always increase the sample size or the number of records available in the dataset to be analysed, but it might do if records that have missing ethnicity are replaced by a known ethnicity classification from a linked dataset.
An example is the linking of the Census data to Hospital Episode Statistics (HES) data and death registrations by the ONS. The ethnicity classifications for GRT groups are not included in the HES data, and are not collected in the death registrations process at the moment. So this data linking gives a way to provide some information for Gypsy and Irish Travellers and other smaller groups. The report with data up to 15 May 2020 noted 16 Gypsy or Irish Traveller deaths from COVID-19.
RDU will be working with ONS and others to explore the potential for using data linking to get more information for the GRT groups.
4.6 Bespoke surveys and sample boosts
A country-wide, or even local authority, boost of a sample survey is unlikely to make estimates for the GRT groups substantially more robust. This is because of the relatively small number in the groups to begin with.
Bespoke surveys can be used to get specific information about these groups. The Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities list of traveller sites available through their Traveller caravan count statistics can help target sampling for surveys, for example. Bespoke surveys might be limited in geographical coverage, and more suitable for understanding GRT views in a local area and then developing local policy responses. An example of a bespoke survey is the Roma and Travellers in 6 countries survey .
Another method that could be useful is snowball sampling. Snowball sampling (or chain-referral sampling) is a sampling technique in which the respondents have traits that are rare to find. In snowball sampling, existing survey respondents provide referrals to recruit further people for the survey, which helps the survey grow larger.
There are advantages to snowball sampling. It can target hidden or difficult to reach populations. It can be a good way to sample hesitant respondents, as a person might be more likely to participate in a survey if they have been referred by a friend or family member. It can also be quick and cost effective. Snowball sampling may also be facilitated with a GRT community lead or cultural mediator. This would help bridge the gap between the GRT communities and the commissioning department to encourage respondent participation.
However, one statistical disadvantage is that the sampling is non-random. This reduces the knowledge of whether the sample is representative, and can invalidate some of the usual statistical tests for statistical significance, for example.
All data in this section comes from the 2011 Census of England and Wales, unless stated otherwise.
In 2011, there were 57,680 people from the Gypsy or Irish Traveller ethnic group in England and Wales, making up 0.1% of the total population. In terms of population, it is the smallest of the 18 groups used in the 2011 Census.
Further ONS analysis of write-in responses in the Census estimated the Roma population as 730, and 1,712 people as Gypsy/Romany.
Table A: Gypsy, Roma and Traveller write-in ethnicity responses on the 2011 Census
Source: Census - Ethnic group (write-in response) Gypsy, Traveller, Roma, GypsyRomany - national to county (ONS). The figures do not add to the 57,680 classified as White: Gypsy/Traveller because Roma is included as White Other, and some people in the other categories shown will have classified themselves in an ethnic group other than White.
An ONS report in 2014 noted that variations in the definitions used for this ethnic group has made comparisons between estimates difficult. For example, some previous estimates for Gypsy or Irish Travellers have included Roma or have been derived from counts of caravans rather than people's own self-identity. It noted that other sources of data estimate the UK’s Gypsy, Roma and Traveller population to be in the region of 150,000 to 300,000 , or as high as 500,000 (PDF).
5.1 Where Gypsy and Irish Traveller people live
There were 348 local authorities in England and Wales in 2011. The Gypsy or Irish Traveller population was evenly spread throughout them. The 10 local authorities with the largest Gypsy or Irish Traveller populations constituted 11.9% of the total population.
Figure 1: Percentage of the Gypsy or Irish Traveller population of England and Wales living in each local authority area (top 10 areas labelled)
Basildon was home to the largest Gypsy or Irish Traveller population, with 1.5% of all Gypsy or Irish Traveller people living there, followed by Maidstone (also 1.5%, although it had a smaller population).
Table 1: Percentage of the Gypsy or Irish Traveller population of England and Wales living in each local authority area (top 10)
28 local authorities had fewer than 20 Gypsy or Irish Traveller residents each. This is around 1 in 12 of all local authorities.
11.7% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller people lived in the most deprived 10% of neighbourhoods , higher than the national average of 9.9% (England, 2019 Indices of Multiple Deprivation).
81.6% of people from the Gypsy or Irish Traveller ethnic group were born in England, and 6.1% in the other countries of the UK. 3.0% were born in Ireland and 8.3% were born somewhere else in Europe (other than the UK and Ireland). Less than 1.0% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller people were born outside of Europe.
5.2 Age profile
The Gypsy or Irish Traveller ethnic group had a younger age profile than the national average in England and Wales in 2011.
People aged under 18 made up over a third (36%) of the Gypsy or Irish Traveller population, higher than the national average of 21%.
18.0% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller people were aged 50 and above , lower than the national average of 35.0%.
Figure 2: Age profile of Gypsy or Irish Traveller and the England and Wales average
Table 2: age profile of gypsy or irish traveller and the england and wales average, 5.3 families and households.
20.4% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller households were made up of lone parents with dependent children , compared with 7.2% on average for England and Wales.
Across all household types, 44.9% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller households had dependent children, compared with an average of 29.1%.
8.4% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller households were made up of pensioners (either couples, single pensioners, or other households where everyone was aged 65 and over), compared with 20.9% on average.
All data in this section covers pupil performance in state-funded mainstream schools in England.
At all key stages, Gypsy, Roma and Irish Traveller pupils’ attainment was below the national average.
Figure 3: Educational attainment among Gypsy, Roma, Irish Traveller and pupils from all ethnic groups
Table 3: educational attainment among gypsy, roma, irish traveller and pupils from all ethnic groups.
Source: England, Key Stage 2 Statistics, 2018/19; Key Stage 4 Statistics, 2019/20; and A Level and other 16 to 18 results, 2020/21. Ethnicity facts and figures and Department for Education (DfE). Figures for Key Stage 2 are rounded to whole numbers by DfE.
6.1 Primary education
In the 2018 to 2019 school year, 19% of White Gypsy or Roma pupils, and 26% of Irish Traveller pupils met the expected standard in key stage 2 reading, writing and maths . These were the 2 lowest percentages out of all ethnic groups.
6.2 Secondary education
In the 2019 to 2020 school year, 8.1% of White Gypsy or Roma pupils in state-funded schools in England got a grade 5 or above in GCSE English and maths, the lowest percentage of all ethnic groups.
Gypsy or Roma (58%) and Irish Traveller (59%) pupils were the least likely to stay in education after GCSEs (and equivalent qualifications). They were the most likely to go into employment (8% and 9% respectively) – however, it is not possible to draw firm conclusions about these groups due to the small number of pupils in key stage 4.
6.3 Further education
Gypsy or Roma students were least likely to get at least 3 A grades at A level, with 10.8% of students doing so in the 2020 to 2021 school year. 20.0% of Irish Traveller students achieved at least 3 A grades, compared to the national average of 28.9%. The figures for Gypsy or Roma (61) and Irish Traveller (19) students are based on small numbers, so any generalisations are unreliable.
Due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the summer exam series was cancelled in 2021, and alternative processes were set up to award grades. In 2020/21 attainment is higher than would be expected in a typical year. This likely reflects the changes to the way A/AS level grades were awarded rather than improvements in student performance.
6.4 School exclusions
In the 2019 to 2020 school year, the suspension rates were 15.28% for Gypsy or Roma pupils, and 10.12% for Irish Traveller pupils – the highest rates out of all ethnic groups.
Also, the highest permanent exclusion rates were among Gypsy or Roma pupils (0.23%, or 23 exclusions for every 10,000 pupils). Irish Traveller pupils were permanently excluded at a rate of 0.14%, or 14 exclusions for every 10,000 pupils.
6.5 School absence
In the autumn term of the 2020 to 2021 school year, 52.6% of Gypsy or Roma pupils, and 56.7% of Irish Traveller pupils were persistently absent from school . Pupils from these ethnic groups had the highest rates of overall absence and persistent absence.
For the 2020 to 2021 school year, not attending in circumstances related to coronavirus (COVID-19) was not counted toward the overall absence rate and persistent absence rates.
Data in this section is from the 2011 Census for England and Wales, and for people aged 16 and over. Economic activity and employment rates might vary from other published figures that are based on people of working age.
47% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller people aged 16 and over were economically active, compared to an average of 63% in England and Wales.
Of economically active people, 51% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller people were employees, and 26% were self-employed. 20% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller people were unemployed, compared to an average for all ethnic groups of 7%.
7.1 Socio-economic group
Figure 4: socio-economic group of gypsy or irish traveller and average for all ethnic groups for people aged 16 and over, table 4: socio-economic group of gypsy or irish traveller and average for all ethnic groups for people aged 16 and over.
Source: 2011 Census
31.2% of people in the Gypsy or Irish Traveller group were in the socio-economic group of ‘never worked or long-term unemployed’. This was the highest percentage of all ethnic groups.
The Gypsy or Irish Traveller group had the smallest percentage of people in the highest socio-economic groups. 2.5% were in the ‘higher, managerial, administrative, professional’ group.
15.1% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller people were small employers and own account workers. These are people who are generally self-employed and have responsibility for a small number of workers.
For Gypsy or Irish Travellers, who were 16 and over and in employment, the largest group worked in elementary occupations (22%). This can include occupations such as farm workers, process plant workers, cleaners, or service staff (for example, bar or cleaning staff).
The second highest occupation group was skilled trades (19%), which can include farmers, electrical and building trades. The Gypsy or Irish Traveller group had the highest percentage of elementary and skilled trade workers out of all ethnic groups.
7.2 Employment gender gap
The gender gap in employment rates for the Gypsy or Irish Traveller group aged 16 and over was nearly twice as large as for all ethnic groups combined. In the Gypsy or Irish Traveller ethnic group, 46% of men and 29% of women were employed, a gap of 17%. For all ethnic groups combined, 64% of men and 54% of women were employed, a gap of 10%.
This is likely to be due to the fact that Gypsy or Irish Traveller women (63%) were about 1.5 times as likely as Gypsy or Irish Traveller men (43%) to be economically inactive, which means they were out of work and not looking for work.
7.3 Economic inactivity
There are a range of reasons why people can be economically inactive. The most common reason for Gypsy or Irish Travellers being economically inactive was looking after the home or family (27%). This is higher than the average for England and Wales (11%). The second most common reason was being long term sick or disabled (26%) – the highest percentage out of all ethnic groups.
8. Home ownership data
Figure 5: home ownership and renting among gypsy or irish traveller households and all households, table 5: home ownership and renting among gypsy or irish traveller households and all households.
Source: England, 2011 Census
In 2011, 34% of Gypsy or Irish Traveller households owned their own home, compared with a national average of 64%. 42% lived in social rented accommodation, compared with a national average of 18%.
In 2016 to 2017, 0.1% of new social housing lettings went to people from Gypsy or Irish Traveller backgrounds (429 lettings).
In 2011, a whole house or bungalow was the most common type of accommodation for Gypsy or Irish Traveller households (61%). This was lower than for all usual residents in England and Wales (84%).
Caravans or other mobile or temporary homes accounted for 24% of Gypsy or Irish Travellers accommodation, a far higher percentage than for the whole of England and Wales (0.3%).
The percentage of people living in a flat, maisonette or apartment was 15% for both Gypsy or Irish Travellers and all usual residents in England and Wales.
In 2011, 14.1% of Gypsy and Irish Traveller people in England and Wales rated their health as bad or very bad, compared with 5.6% on average for all ethnic groups.
In 2016 to 2017, Gypsy or Irish Traveller people aged 65 and over had the lowest health-related quality of life of all ethnic groups (average score of 0.509 out of 1). The quality of life scores for the White Gypsy or Irish Traveller ethnic group are based on a small number of responses (around 35 each year) and are less reliable as a result.
Ethnicity facts and figures has information on satisfaction of different health services for different ethnic groups. For the results presented below, the Gypsy or Irish Traveller figures are based on a relatively small number of respondents, and are less reliable than figures for other ethnic groups.
In 2014 to 2015 (the most recent data available), these groups were the most satisfied with their experience of GP-out-of-hours service , with 75.2% reporting a positive experience.
In 2018 to 2019, they were less satisfied with their experience of GP services than most ethnic groups – 73.0% reported a positive experience.
They were also among the groups that had least success when booking an NHS dentist appointment – 89.0% reported successfully booking an appointment in 2018 to 2019.
The Gypsy or Irish Traveller group were also less satisfied with their access to GP services in 2018 to 2019 – 56.9% reported a positive experience of making a GP appointment, compared to an average of 67.4% for all respondents.
Publication release date: 31 January 2022
Updated: 29 March 2022
29 March 2022: Corrected A-level data in Table 3, and All ethnic groups data in Table 4. Corrected the legend in Figure 1 (map).
31 January 2022: Initial publication.

Subscription Offers
Give a Gift

Britain's Gypsy Travellers: A People on the Outside
Despite the popularity of shows like My Big Fat Gypsy Wedding , Britain’s Gypsy Travellers still face longstanding prejudice, warns Becky Taylor.
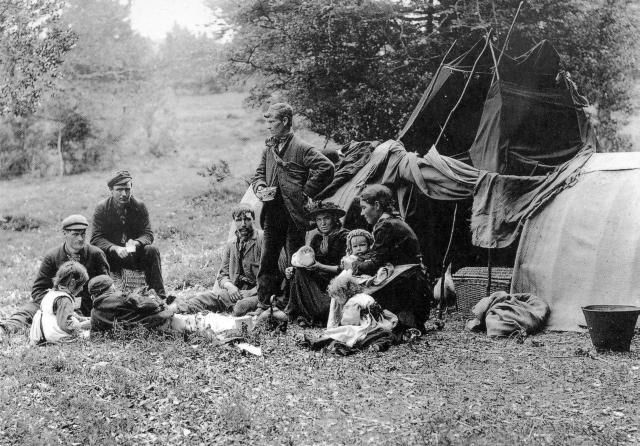

Two months later and Channel 4’s My Big Fat Gypsy Wedding is generating waves on television. While sympathetic and giving a voice to Gypsy Travellers, it nevertheless presents an exoticised image of their lives: the horse-drawn wagons, extravagant dresses and flamboyant wedding arrangements seem to encapsulate how they remain the ‘other’ of British society. As the opening voiceover put it: ‘For hundreds of years the Gypsy way of life was one of ancient traditions and simple tastes. Then their world collided with the 21st century. With unprecedented access to the UK’s most secretive community … this series will take you to the very heart of Gypsy life.’ If contemporary images of Gypsy Travellers seem to be polarised between vilification and the exotic, can the same be said for historical depictions of one of Britain’s oldest minority groups?
While the details remain contested, it is now broadly agreed that Europe’s Roma and Gypsy populations can trace their origins back to an Indian diaspora in the tenth century, with ‘Egyptians’ arriving in Britain by the early 16th century. Despite persecution, Gypsies established themselves, finding niches in both town and countryside, sometimes being protected by landowners who found them useful as a supply of casual labour, for entertainment and sometimes simply by the inconsistent application of the law. Their treatment reflected majority society’s deep ambivalence about the presence of Gypsies and a nomadic way of life. On the one hand it symbolised freedom from the responsibilities and duties associated with settled lifestyles – typified in folk songs such as ‘The Raggle-taggle Gypsy’; on the other it provoked an almost visceral hatred, a suspicion that Gypsies could evade the law and the codes of behaviour that bound settled society to a place and a parish.
Rather than being polar opposites, however, we might understand these stereotypes as two sides of a coin – as the product of a tendency to view Gypsy lives through the lens of the preoccupations and assumptions of mainstream society – rather than being grounded in reality. Whether articulated positively or negatively these stereotypes stem from the assumption that Gypsies were irredeemably separate from the rest of the population.
Yet, contrary to these stereotypes, Gypsies and Travellers traded with, worked and lived alongside the rest of the population: an analysis of the traditional songs sung by Gypsies and Travellers, for example, shows significant overlap with those current in wider society, suggesting a high degree of interaction between the communities, particularly in casual agricultural and seasonal labour. Arthur Harding’s classic account of the East End underworld at the beginning of the 20th century, compiled by the historian Raphael Samuel, revealed in passing how Gypsy Travellers were part of the everyday fabric of poor urban life. David Mayall’s work on the 19th century, my own on the 20th and that of the Dutch scholars Lucassen, Willems and Cottars for the European context all confirm the ways in which the lives of Gypsy Travellers and settled populations were intimately interconnected and often how the lines between them were in fact blurred. Gypsies lived in peri-urban encampments or even cheap lodging in cities over winter alongside working-class populations, making and selling goods, moving in regular circuits across the countryside in the spring and summer, picking up seasonal work, hawking and attending fairs. Far from being ‘a separate people’, their economic survival in fact depended on close engagement with the wider population.
The stereotypes became increasingly entrenched over the course of the 19th century as Britain’s population became increasingly urbanised and the countryside became the repository for the working out of anxieties related to the rapidly changing social and physical landscape. Alongside phenomena like the folk song revival, the cult of the ‘outdoors’ and the early caravanning movements there emerged a movement of amateur ‘gentlemen scholars’, self-styled ‘gypsiologists’, who developed an interest in recording the origins, language and customs of Britain’s Gypsy Travellers. Focused around the activities of the Gypsy Lore Society (GLS), established in 1889, they became preoccupied with the foreign ancestry of British Gypsies and with developing theories about their ‘pure bred’ nature, which often tied blood lines to Romany language use and ‘proper’ nomadic living. The Gypsy caravan, which had only made its appearance in the 1830s as a result of the improving road system, became central to settled society’s image of ‘the Gypsy’, in part through paintings, such as those of the prominent GLS member Augustus John. Fed by an outpouring of writings on the subject from the 1880s, popular imagination saw Gypsies as a people who turned up out of the blue, camped on commons or byways in their bow-topped caravan, grazed horses, sold pegs, perhaps ‘tinkering’, ‘here today and gone tomorrow’. Just as the producers of My Big Fat Gypsy Wedding promised ‘unprecedented access’, so too did numerous gypsiologists spend a summer living with a group of Gypsy Travellers gaining an insight into ‘the secret people’ before writing a book about their experiences. Crucially, such Gypsies were always portrayed as ‘pure blooded’ or ‘true’ Romanies, largely untouched by modern, industrialised Britain. As one gypsiologist, Arthur Symons, wrote in the early 20th century:
Why ... are we setting ourselves the impossible task of spoiling the Gypsies? ... they stand for the will of freedom, for friendship with nature, for the open air, for change and the sight of many lands; for all of us that are in protest against progress ... The Gypsies represent nature before civilisation ... the last romance left in the world.
Crucially, for these stereotypes to find resonance in modern Britain, gypsiologists constructed a theory around the decline in the racial purity of Gypsies as they increasingly mixed and married with ‘degenerate’ members of the settled population. They developed a racial hierarchy which placed ‘pure-blooded’ Gypsies, who were believed to speak the best Romany, at the top; followed by ‘didikais’, half-breeds, or ‘pikies’ – groups with varying proportions of Gypsy blood depending on which source one reads; and ‘mumpers’, who were vagrants with no Romany ancestry, at the bottom. As David Mayall observed:
To confuse the ‘true’ Gypsy with those of diluted blood was presented as a grave error that led to much injustice being directed towards the clean-living Romany. The latter, declining in numbers as the century progressed, were superior in manners, morals and occupations to their degenerate and impoverished ‘mumply-brothers’. These half-breeds were said to have inherited all the vices of the Romany and the Gaujo [non-Gypsy] but none of their virtues.
For gypsiologists anxious to discover a Golden Age and a pure Gypsy culture this outlook allowed them to pursue their pet theories, with any contradictory findings dismissed as the result of cultural pollution and miscegenation. This enabled gypsiologists to distance themselves from the squalid, urban Traveller encampments that existed around all Britain’s major cities and any other elements that impinged on romantic notions of a rural Gypsy idyll.
Just as the impetus to romanticise Gypsies gained ground in the later 19th century, so too did negative stereotypes, as a growing body of opinion saw Travellers as being out of step with modern society. Along with longstanding beliefs about the lazy and lawless nature of Gypsies came newer concerns about their unsanitary habits, which were seen as anachronistic in a nation that increasingly set store by its housing and sanitary legislation. Added to this were commonly expressed sentiments that they were escaping from paying taxes and consequently evaded the responsibilities that came with modern living. Such views gained ground particularly in times of social difficulty. During the Second World War Gypsies were a common scapegoat for the press, which depicted them as shirkers and deserters, able to escape conscription through their nomadism and evading rationing through poaching and foraging. As the South Wales Evening Post put it: ‘Many people wonder how Gypsies get off with food rationing. It is understood, however, that hedgehogs are not rationed.’
Lacking a political voice or a representative body Gypsy Travellers responded to this entrenchment of stereotypes not by challenging them but by working within their parameters. Thomas Acton first pointed to the practice of claiming to have ‘pure Gypsy blood’ as a means of asserting an individual’s right to travel, while scapegoating other travelling communities: ‘I’m a real Gypsy/Traveller/Romani, and we don’t do that, only the (ethnic category name with pejorative overtones)’. He observed that the effect of this ‘transference of blame’ was to divert the hostility of the accuser away from that particular individual to an absent outsider group which both parties could agree was fundamentally incapable of maintaining a nomadic lifestyle. While in the short run this was ‘an attractive strategy for the individual Traveller’, it was not without its shortcomings, as it served to confirm racialised definitions of
Travellers, equating a right to travel with spurious definitions of blood purity. It was not until the 1960s and the formation of the Gypsy Council that Gypsy Travellers as a community found a collective voice, one which tried to assert that all had a right to travel and that nomadism did have a place in modern Britain. While it scored some early successes, notably in the 1968 Caravan Sites Act, its influence both within and outside the travelling community has declined over recent years and has failed to dislodge the enduring stereotypes surrounding Gypsies.
Travellers have modernised alongside the rest of society and are not a ‘secret people’ living in the manner of their great grandparents. Crucially this change in their lifestyle has removed what settled society understands as the markers of ‘true’ Gypsies: bow-topped caravans, horses and so on. These images of Gypsies have become the rod with which their back is consistently beaten: failing to conform to romantic expectations, the stereotypes most often deployed in the popular press and by politicians are the negative ones relating to anti-social behaviour and an inability to adapt to the standards of ‘normal’ society.
This leads us back to the people of Dale Farm and the stars of My Big Fat Gypsy Wedding . We may wonder at the dresses and tut over wedding venues cancelling bookings when they find they are to host a Traveller wedding, but this translates into neither an understanding of the place of Gypsy Travellers in British society nor positive political action. Living in an ex-scrapyard by the side of a busy dual carriageway, the Dale Farm homes are immaculate trailers from which furniture-selling businesses are run. Vulnerable through their lack of romantic visual appeal and unable to attract political representation, Travellers are facing the active prejudice not just of Basildon Council but of councils across the country, which decide not only that Travellers may not stay on their own land, but are also determined that there is no place for a Traveller community within its district. It is surely time for us to move beyond the stereotypes which have served Gypsy Travellers, settled society and historical analysis so ill for centuries and instead have the strength to embrace the diversity and richness represented by Britain’s nomadic communities. Seeing 80 families being put onto the highway will be Britain’s shame as much as Sarkozy’s expulsion of Roma from France.
Becky Taylor is author of A Minority and the State: Travellers in Britain in the 20th Century (Manchester University Press, 2008).
Popular articles
‘Bluestockings’ by Susannah Gibson review

Why Were the Jews Persecuted?
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

The big fat truth about Gypsy life
M y Big Fat Gypsy Wedding, the television series that ended last week and attracted nine million viewers, was designed to "throw an overdue light on a secretive, marginalised and little-understood segment of our society", according to the blurb from Channel 4. But the show largely avoided the myriad of problems, such as discrimination, poor health and poverty faced by Travellers, except for what felt like a tokenistic final episode, and instead focused on over-the-top wedding dresses and other excesses.
MBFGW was about Gypsies and Travellers, but there was criticism from both communities that C4 failed to properly distinguish between the two. There are around 300,000 Gypsy Roma and Irish Travellers in the UK – Roma Gypsies are originally from northern India, whereas Travellers are of Irish origin – and both groups are nomadic. Since 2002, Travellers have been recognised as an ethnic group and are protected under the Race Relations Act. Last week C4 was accused by the Irish Traveller Movement in Britain of fuelling "hatred and suspicion" of their way of life and have demanded a right of reply.
Kathleen, who lives with her six children in a three-bedroom trailer, is fairly typical of an Irish Traveller woman, except that she is separated from her husband. Along with many other Gypsy and Traveller women in the UK, Kathleen was a victim of domestic violence. Although there is no conclusive evidence about the prevalence of this abuse, a study in Wrexham, cited in a paper by the Equality and Human Rights Commission, 2007, found that 61% of married English Gypsy women and 81% of Irish Travellers had experienced domestic abuse. And a significant number of those women who had reported the abuse appeared to have suffered more severe and sustained violence than those within mainstream communities.
"I left him and went back to my mammy but he kept finding me, taking me home and getting me pregnant," Kathleen says. She now feels safe because she has male family members living on the same site. "With my brother close by, he wouldn't dare come here."
It is rare for women to call the police for help. "You would be seen as a grass and disowned by the whole community," says Bernie O'Roarke, outreach and resettlement worker for domestic violence charity Solas Anois (Gaelic for Comfort Now), which is based in London. The situation probably isn't helped by the fact that there is only one, 10-room refuge dedicated to Traveller women in the UK, also in London. But domestic violence is just one of the issues tackled by O'Roarke during her visits. The welfare needs, particularly those of the women and girls, of this community are vast. The women are three times more likely to miscarry or have a still-born child compared to the rest of the population, mainly, it is thought, as a result of reluctance to undergo routine gynaecological care, and infections linked to poor sanitation and lack of clean water. The rate of suicides among Traveller women is significantly higher than in the general population, and life expectancy is low for women and men, with one third of Travellers dying before the age of 59. And as many Traveller girls are taken out of education prior to secondary school to prevent them mixing with boys from other cultures, illiteracy rates are high.
O'Roarke is a familiar face on the sites around London, offering women and their children help with health care, education and finance. The men leave the women alone to deal with these issues, so if the women do want to talk about violence and abuse, they can do so without fear of the men overhearing.
I visit some trailers with O'Roarke at a site in London and am struck by how the women seem to manage, usually with large families, to keep everything so clean and tidy. There are colourful displays of Royal Crown Derby crockery, handed down from mother to daughter on her wedding day. There is certainly no sign of wealth or excessive spending. Many tell me they struggle to feed their children, and have no savings or bank account.
Things seem set to get worse for Traveller women. Only 19 days after the general election last year, £50m that had been allocated to building new sites across London was scrapped from the budget. O'Roarke is expecting to be the only Traveller liaison worker in the capital before long – her funding comes from the Irish government.
"Most of the women can't read or write. Who is supposed to help them if they get rid of the bit of support they have now?" asks O'Roarke. "We will be seeing Traveller women and their children on the streets because of these cuts. If they get a letter saying they are in danger of eviction but they can't read it, what are they supposed to do?"
Conditions on the site are as grim as the homes are spotless. The trailers are not connected to water pipes, and the toilets, bathrooms and cooking facilities are in a small, unheated shed across the yard. "In the snow and rain, the little ones are always getting colds," says Brigid, who lives in the next trailer to Kathleen. "And there are so many pot holes that the council haven't filled, you can go flying in the dark."
But living on a site is about being part of the community. When Traveller girls are growing up, they are only allowed to go out with other family members, and once married, her husband rules the roost. "The men would never allow a woman out with her friends," says Kathleen. "That's why we want to live on a site, for company." Kathleen, after spending time in a refuge after finally managing to escape her husband, was initially allocated a house, as opposed to a plot on a site. Almost immediately her children became depressed. "It's like putting a horse in a box. He would buck to get out," says Kathleen. "We can't live in houses; we need freedom and fresh air. I was on anti-depressives. The children couldn't go out because the neighbours would complain about the noise."
Since moving to their site two years ago, Kathleen and her children have been far happier. Until MBFGW was screened, that is. "Now every week I go to the school and the parents are talking about that programme. They won't let our kids mix with theirs because they say we stink and don't talk properly. Settled kids won't even play sports with ours in case they touch them."
Mary, Kathleen's 15-year-old daughter, is upset by the series too, and says that she has faced further prejudice since it hit the screens. "That programme didn't show the real way we go on. All my friends are asking if it's true what they show on telly, and I think they've gone different [towards me] since it was shown."
In one episode the viewer was informed that young Traveller men at weddings and other social occasions use something known as "grabbing" to force a reluctant girl to kiss them. One newspaper report called it a "secret courting ritual".
"Grabbing has never happened to me or any of my friends and the first time I ever saw it was on the telly," says Mary. "I wouldn't put up with it, and I don't know why they made out we all do it. It's just one nasty boy they showed."
Brigid adds: "Grabbing has never happened to my kids. I have honestly never heard of it. It's all make-believe."
Helen, a Traveller in her 20s on the same site, is also furious about the portrayal of women in MBFGW. "The way us women come across in the programme is a disgrace," she said. "It shows us as nothing but slaves to the men, only good for cooking and cleaning, and always being available to open our legs to them. We don't want that for our daughters."
Helen is also worried that Traveller women are being portrayed as rich and spoilt when, in fact, life is a struggle for the majority. "I don't know anyone so rich that they can afford to splash out on wedding dresses like that. Mine was secondhand. They'll now be saying we are all criminals, or sponging off the state." I ask a number of Traveller women how representative of the Traveller and Gypsy communities those featured in MBFGW are, and they all come back with a similar answer: the programme focused on a small number of individuals from five sites (out of an estimated 300-plus across the UK), and in any community, there are a minority who have access to large amounts of cash.
I ask O'Roarke what she thinks the future holds for Travellers. She is worried. "That TV programme has put our work back 100 years. And if these women lose the little support they have, they literally will be left to rot."
She is concerned that problems affecting Traveller women and girls, such as lack of education, forced and early marriage, and abuse within the home, are not being taken seriously.
"These issues do not just affect certain Asian communities," says O'Roarke. "We have had Traveller women in the refuge who have been forced to marry someone who they have never met, and marrying cousins is not uncommon."
But some say that things are slowly improving. "I think it's changing an awful lot for the young ones," says Kathleen. "We don't want them to have no education and get married at 16, and have loads of kids and the same life as we did."
Would Kathleen ever marry again? It is out of the question, she tells me. These things are just not done. "You marry for life," she says. "If I was to have another man, my daughters would never be married because I would have brought shame on them."
O'Roarke would like to see changes that include: "Better support for the women to keep their daughters in education, and a serious commitment from the government to challenge the prejudice thrown at these people."
While people are being entertained by watching Katie Price-replica weddings on TV, and girls dressed in Beyoncé-style outfits dirty dancing, women such as Kathleen, Brigid and Helen are living in substandard conditions and facing daily prejudice while trying to give their children the best start in life. The reality is a far cry from the C4 depiction and is rarely aired. O'Roarke tells me that Traveller women are usually reluctant to allow outsiders into their homes, despite the impression given by MBFGW. "But we just want our side of the story put across," says Brigid, "so settled people know we are not like that."
- Roma, Gypsies and Travellers
- Television (Television & radio)
- Documentary
- The news on TV
- Television (Technology)
Most viewed

Welcome to the Traveller Movement
Events & activities.
Traveller Movement Safe Space for Women Microsite

Traveller Movement Education Microsite
Traveller Movement Annual Conference: FUTURE VOICES
Thank you to everyone who attended the Traveller Movement Annual Conference 2023: Future Voices. Please find the 2023 Annual Conference Report here

Charity Excellence Framework Quality Mark
The Charity Excellence Framework quality mark achieved by the Traveller Movement, provides demonstrable evidence to stakeholders and funders, of the Traveller Movement commitment to excellence, reassurance our trustees that our charity is well run and recognition for TM staff and volunteers for what they are achieving.

Recipe Book
This recipe book has both tradition and modern, sweet and savoury Traveller and Gypsy recipes from our Facebook group ‘Traveller and Gypsy Recipes and Tips’!


The Way We Work
Community Corner
Read all about the events, news updates and upcoming talent happening in your area!
Information and Support
We have a variety of helpful guides and useful information that will provide you with the support you need
Training and Consultation
We offer professional training and resources to Romani (Gypsy), Roma and Irish Traveller service providers
We address inequalities and discrimination that Romani (Gypsy), Roma and Irish Traveller people experience through our campaigns
- 25,000+ Overall social media followers
- 79,162 Website page views
- 1,017 Event participants this year
Testimonials
For a small organisation they punch well above their weight
Promoting a diverse range of futures for GRT members is vital in gaining greater visibility and wider societal change. The tutoring programme sounds like a great step in that direction!
Thanks so much to all involved; it was excellent training. It was eye-opening and I learned so much. The film was so powerful; I can see how much effort has gone into the film and the training.
Upcoming events
Know your rights session with southwark law centre external link icon.
Join The Traveller Movement and Southwark Law Centre on Tuesday 7th May 2024 between 2-3:30 PM. …
Know Your Rights Session with Howe & Co External Link Icon
Join The Traveller Movement and Southwark Law Centre on Thursday 23rd May 2024 between 2-3:30 PM. …
Know Your Rights Session with Simpson Millar External Link Icon
Join The Traveller Movement and Simpson Millar on Monday 29th April 2024 between 11-12:30 PM. …
Latest blogs

We are hiring!

A TOOLKIT BY THE COMMUNITIES FOR THE COMMUNITIES

2023 Annual Conference Report released
Current campaigns.

The Traveller Movement launched #OperationTravellerVote to ensure Gypsies, Roma and Travellers are registered to vote and most importantly, have their voices heard during elections.

Stop Shaming
We challenge ‘shaming’ as the rise of social media channels allow public humiliation to persist which has been particularly harmful to young women
Subscribe to our newsletter
- Economy & Markets
- Digital Life

Who are the Travellers, and Why are They so Hated?
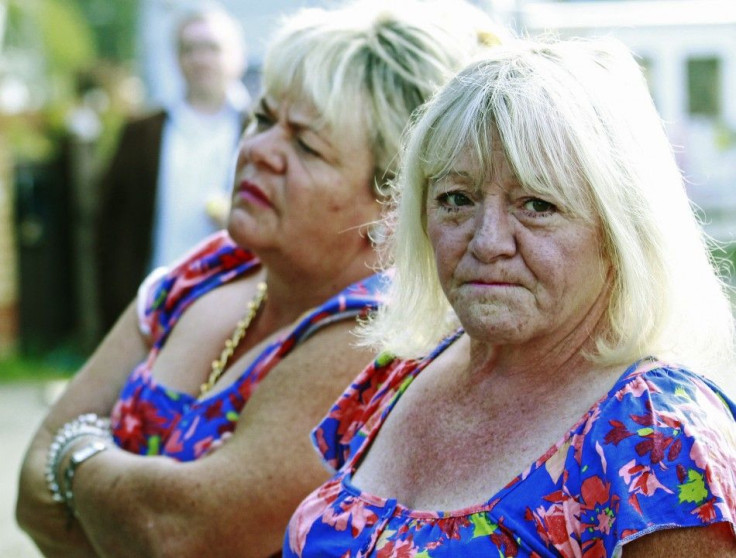

Essex Police successfully evicted the Irish Traveller residents of Dale Farm on Wednesday.
The controversial land seizure escalated into a war zone, according to a number of English news outlets, with residents and activists defending the fortified community from an invading police force. Burning mobile homes blocked paths as officers attempted to remove people from the area.
Twenty-three people were arrested, two stunned by Taser guns and at least six people were injured.
Dale Farm was just the latest eviction in England, where traveller communities have been persecuted for centuries.
So who are the travellers and why are they so hated?
The Irish Travellers, sometimes called Pavees, are an ethnically Irish nomadic community. In England, they live in small, tight-knit groups and are characterized as living on Caravan sites -- an English equivalent to a trailer park. Because of the nomadic and informal nature of traveller communities, they frequently settle in unauthorized plots and common fields.
Long subject to discrimination, hatred and eviction, England has passed a number of laws to protect traveller communities, and authorities are required to provide new caravan sites when clearing an area like Dale Farm. Nonetheless, there have been a number of forced evictions in recent years.
Along with Romani Gypsies, Irish Travellers remain an object of widespread prejudice in British society. What we're seeing take place at Dale Farm today is the culmination of years of intolerance, author Owen Jones wrote in The Telegraph.
There's a lot of talk about the travellers breaking the law -- but, in reality, it's a position they've been forced into. Rather than spending millions of pounds to forcibly throw families out of their homes, we should be looking at how build a society that's far more accepting of minority groups. As things stand, riot police charging protesters has become one of the defining images of Cameron's Britain.
The unofficial status of many of the traveller communities allows the government to ignore them.
I was aware that they had to bring in water in stainless steel milk cans for their everyday use, and I wondered what they did with their disposable nappies [diapers] and other human waste, Dale Farm resident Germaine Greer said in a Telegraph editorial, referring to a visit the traveller encampment at Stump Cross Roundabout in Essex.
I rang the local council and asked whether, as the travellers were only yards from the sewage treatment plant, they mightn't have sewerage, given there were so many children on the site. I was told the pitch was illegal and the travellers were there on sufferance.
But where does the prejudice come from?
The lawbreaking that Jones speaks of is one part of it. Traveller communities are often built without legal permission, sometimes on public greens and sometimes on privately-owned land. When the travellers first moved to Dale Farm in the 1960s, much of it was already designated as a scrap yard.
As the community grew over the decades, more homes were built on land that was part of the green belt, a ring of land around London protected from urbanization and city sprawl.
Officially, this is why the Dale Farm community was cleared. After nearly a decade of legal battles, the Basildon city council will be able to restore Dale Farm to green belt specifications over the next few months.
The Traveller community is being criminalized- it has been made illegal for them to travel, but they are not being allowed to settle, Natalie Fox, a spokesperson for Dale Farm Solidarity, told the Dale Farm Supporters blog. If Traveller families are not allowed to make their home on a former scrapyard, then where will they be allowed to live?
Not all the residents of Dale Farm are Irish Travellers. Some are Romani, a similar nomadic group that has spread across continental Europe. Traditionally a traveling community with roots tracing back to India, the Romani peoples are also oft subject to extreme, institutionalized persecution.
Facing de facto discrimination in most European countries, the Romani, or Gypsy, community is economically troubled and many Romani live in slums, shanty-towns or in substandard housing. Like the travellers, these communities have been subject to forced eviction and displacement in the past.
Land disputes aside, the travellers are an ostracized group, and an Irish researcher found in May that they were nearly as despised as drug addicts and alcohols. As discovered by many Americans and Britons on the BBC show My Big Fat Gypsy Wedding, travellers still face discrimination in the workplace, forcing many of them to lie in order to be employed.
While there is no definitive logic for these prejudices, the travellers' inclusiveness doesn't help the situation. They are a tight-knit, insular community steeped with unwavering tradition. While they fight for rights, they also sometimes fight against assimilation into normative society.
Irish Travelers are said to be 'endogamous,' that is, they marry within their own group and marriage outside the group is frowned upon. Traditionally, children are home-schooled, Southern Cross newspaper said in 2008.
Like the Romani, they are also widely considered to be violent, unkempt grafters - general menaces to society. Both men and women are thought of as drunks who like to brawl and gamble. In 2007 the Governor's Office of Consumer Affairs of Georgia published a letter titled Irish Travelers Perpetuate a Tradition of Fraud.
These descendants of Irish immigrants live in nomadic clans and make their living by perpetuating home improvement fraud and selling substandard machinery at huge mark-ups, the statement, which has been removed from the Georgia state Wed site, read.
Additionally, many Irish citizens were shocked when a family feud at a traveller camp in 2008 turned into an all-out riot.
Petrol bombs, stones, chainsaws, golf clubs, a samurai sword and other dangerous missiles were used in the clashes. The row has been described by an eyewitness as 'like a scene from 1980s' Belfast.' The Independent reported at the time.
Nonetheless, travellers are protected under the Caravan Sites Act of 1968, which restricts the eviction of caravan sites. The same local authorities that evict travellers are required to secure the establishment of such sites by local authorities for the use of gipsies [sic] and other persons of nomadic habit, and control in certain areas the unauthorized [sic] occupation of land by such persons.
So far, the Dale Farm travellers have not been shown where they will be relocated, despite a promise that land has been set aside. So Wednesday night, with many caravans burned or broken, about 82 families are left to fend for themselves.
The memory of Dale Farm will weigh heavily on Britain for generations- we are being dragged out of the only homes we have in this world, Dale Farm resident Kathleen McCarthy stated . Our entire community is being ripped apart by Basildon Council and the politicians in government.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.
Microsoft Expands Its AI Empire Abroad

Oil: 'Mother Of Corruption' In Venezuela

'Extreme' Climate Blamed For World's Worst Wine Harvest In 62 Years

Macron Warns 'Mortal' Europe Needs Credible Defence

Bitcoin And Crypto Price Review - Another Myth Gets Busted?

Mass Cancellations Loom Despite French Air Union Cancelling Strike

Mired In Crisis, Boeing Reports Another Loss

Recycled 'Zombie' Misinformation Targets US Voters

Hackers Leak Part Of Source Code Of El Salvador's Bitcoin Wallet

Azerbaijan Says 'Closer Than Ever' To Armenia Peace Deal Amid Border Talks
Earth Day: 6 eco homes for sale in the UK
Including a characterful cottage and an impressive lake house

According to new data from the property portal, there has been a steady increase in listings mentioning higher EPC ratings, with the proportion of properties for sale including them more than doubling (+104%) compared to pre-pandemic 2019.
"It's promising that an increasing proportion of agents are using higher EPC ratings as a key selling point in their listings, as awareness continues to grow over the importance of going greener in all areas of society," says Tim Bannister, Rightmove's Director of Property Science.
"However, there is still work to be done to improve the availability of more energy-efficient homes and help inform movers of the benefits of eco-friendly home features."
On that note, take a look at the top eco homes for sale around the UK...
Characterful cottage, West Sussex
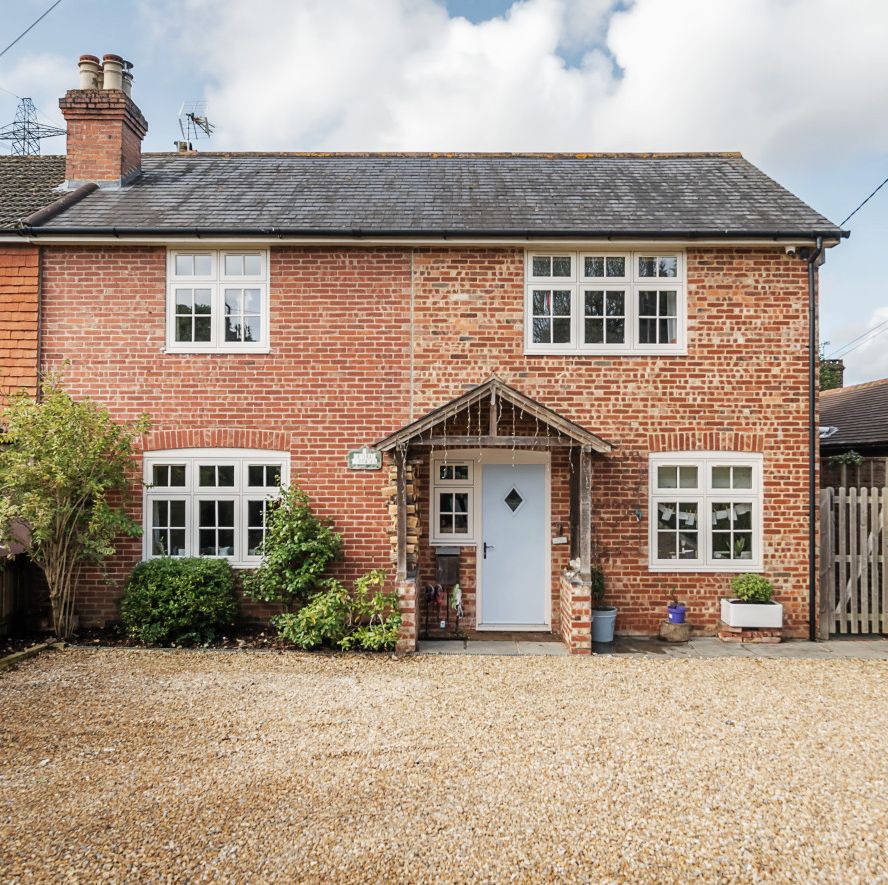

Nestled in the picturesque village of Wisborough Green, this characterful cottage for sale features many eco features including solar panels, an air source heat pump, and a smart home system that controls all heating, lighting , and AV equipment. The property also has four double bedrooms, a beautiful tiled entryway, and a spacious sitting room with a feature fireplace.
This property is on the market for £750,000 with Alex Harvey via Rightmove .
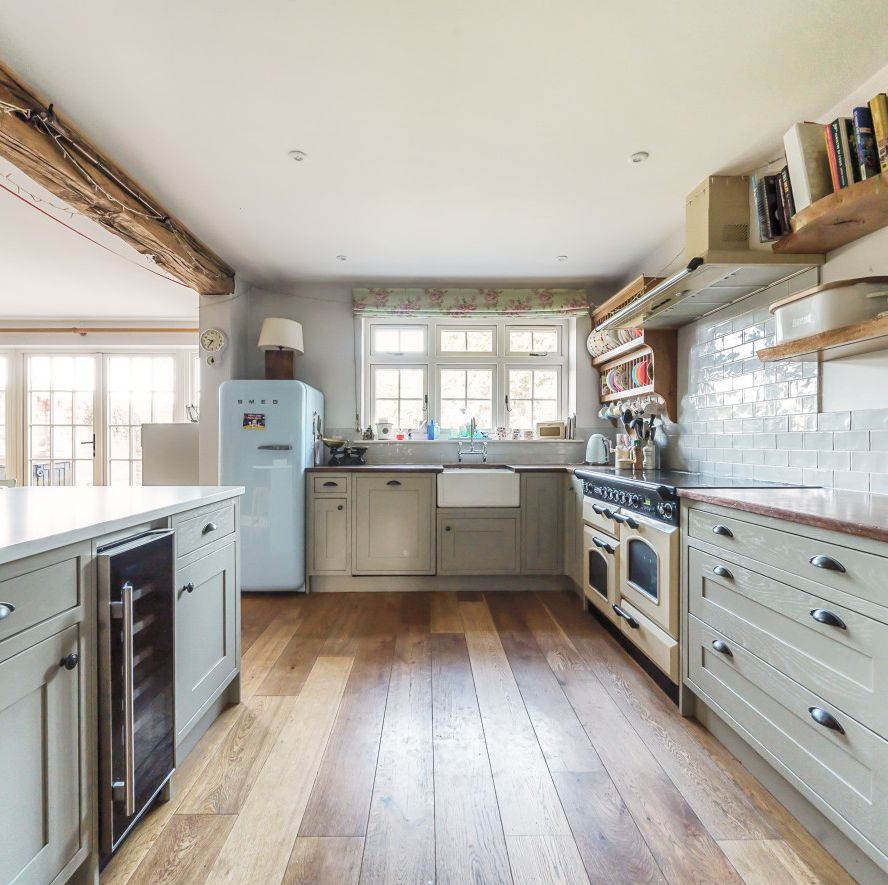

We love the rustic kitchen, complete with Smeg appliances and a butler's sink.
Rural home, Witnesham, Suffolk
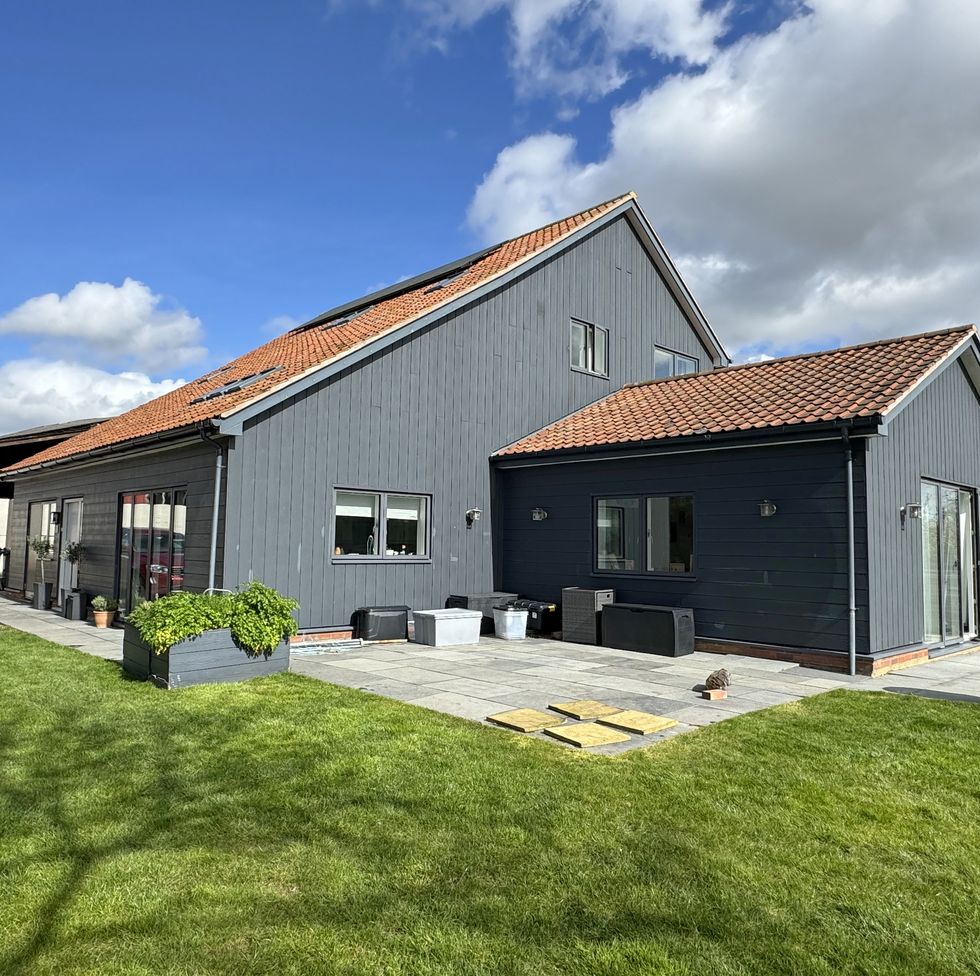

Inspired by the Passivhaus ultra-low energy building guidelines, the design of this property in Witnesham uses a Fleming Homes frame. It includes triple-glazed aluminium and wood windows, solar panels for electricity, and air source heat pumps for hot water and underfloor heating. With a rural farm setting, it's the perfect home for those looking to escape to the country. Take a peek inside...
This property is on the market for £800,000 with Fine & Country via Rightmove .
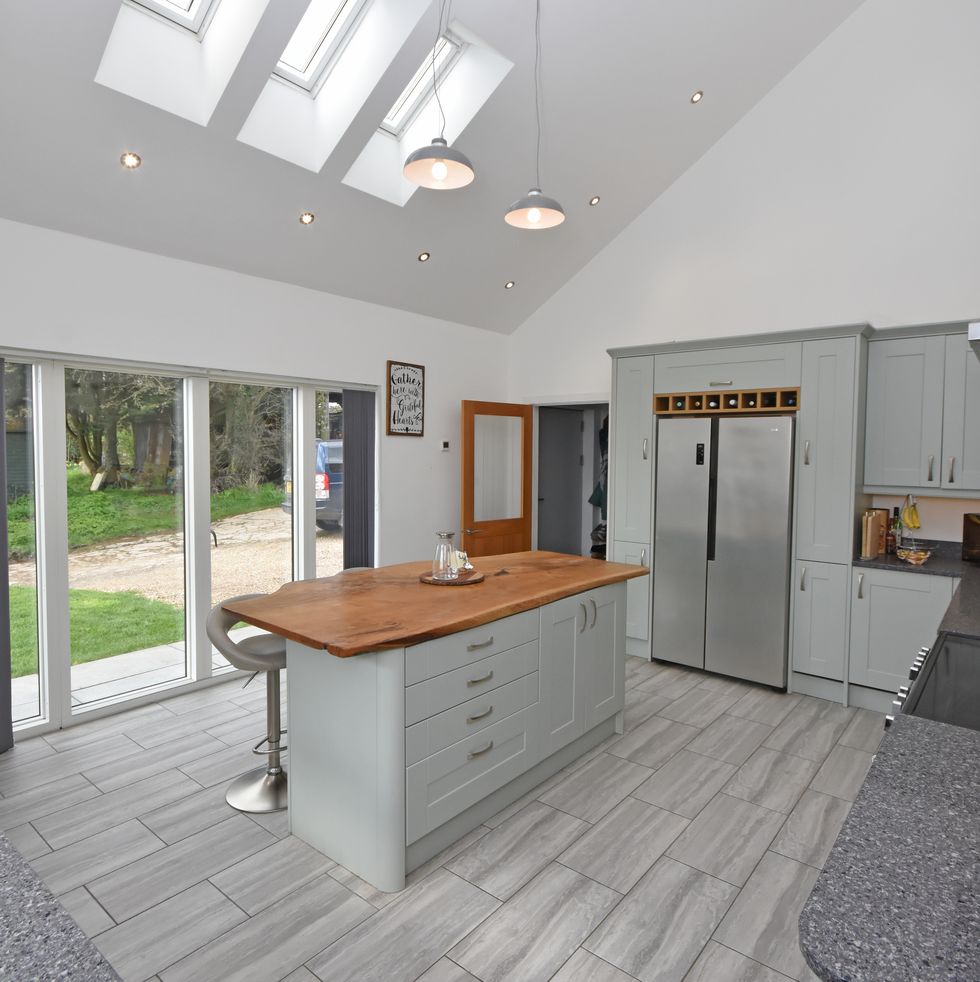

Sleek and modern interiors give this home a contemporary feel.
Smart home, Horsham, West Sussex
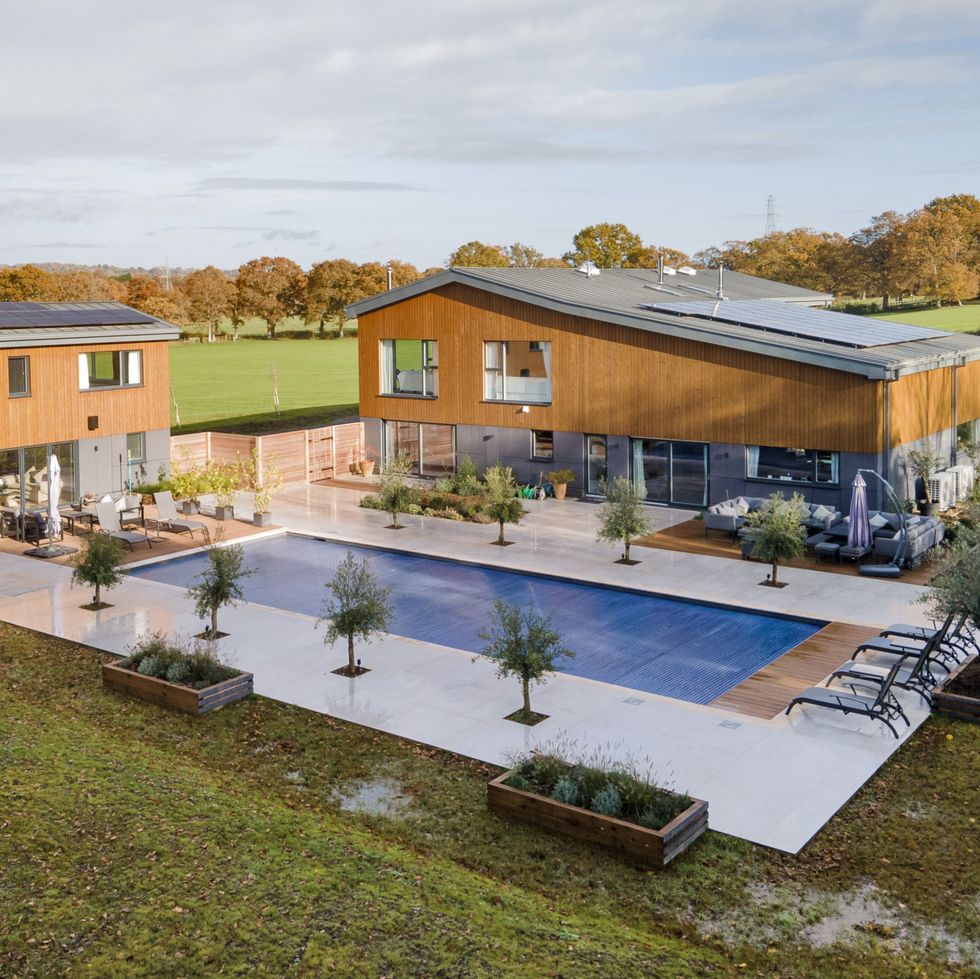

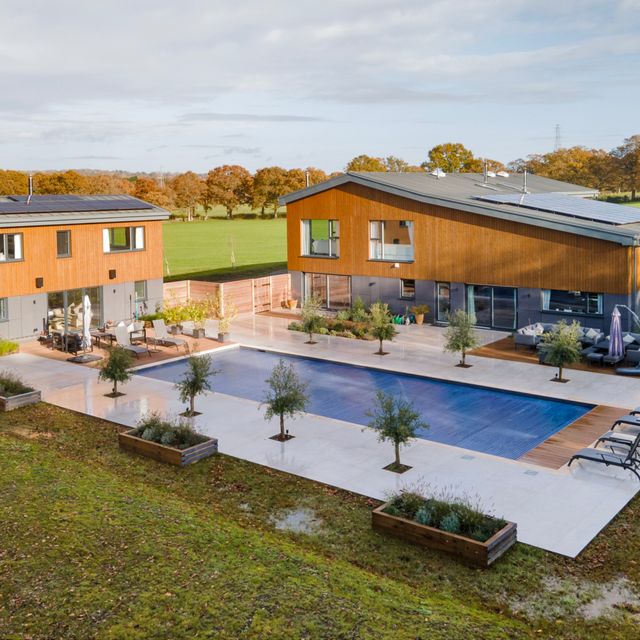
Over in Horsham, this eco-friendly home runs on solar power, with PV panels providing energy during the day. Other highlights include a heated outdoor swimming pool, Porcelanosa bathrooms , RAKO smart lighting, CCTV security, SONOS sound system on the ground floor, and a generous reception hall featuring a striking walnut bespoke floating staircase. When can we move in?
This property is on the market for £3,975,000 with Strutt & Parker via Rightmove .
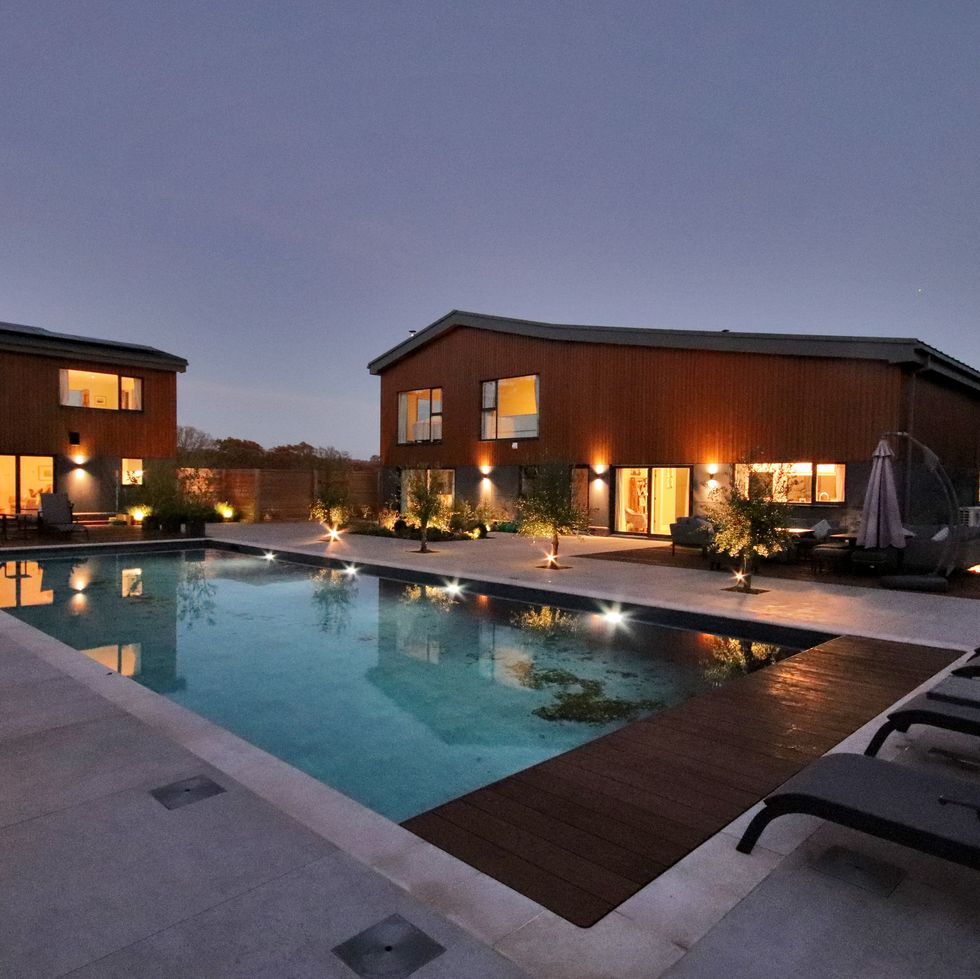

It looks even more magical in the evening!
Converted barn, Carlisle
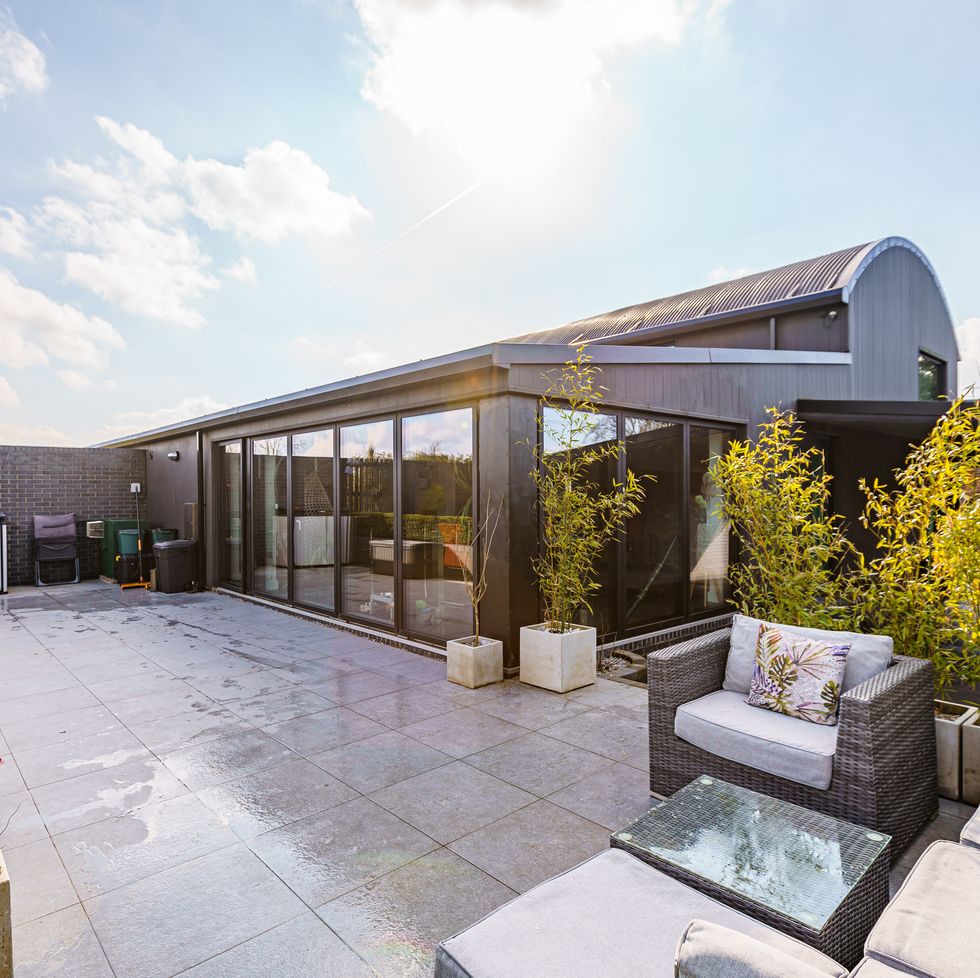

"Raven House is a superbly designed semi-detached home that has been finished to a high specification and is both tasteful and modern throughout," says the team at Rightmove.
"The property boasts impressive levels of construction and including insulation resulting in an impressive A-rated Energy performance certificate, VELFAC triple glazing, and the latest generation of solar panels with intelligent controls."
This property is on the market for £600,000 with Fine & Country via Rightmove .
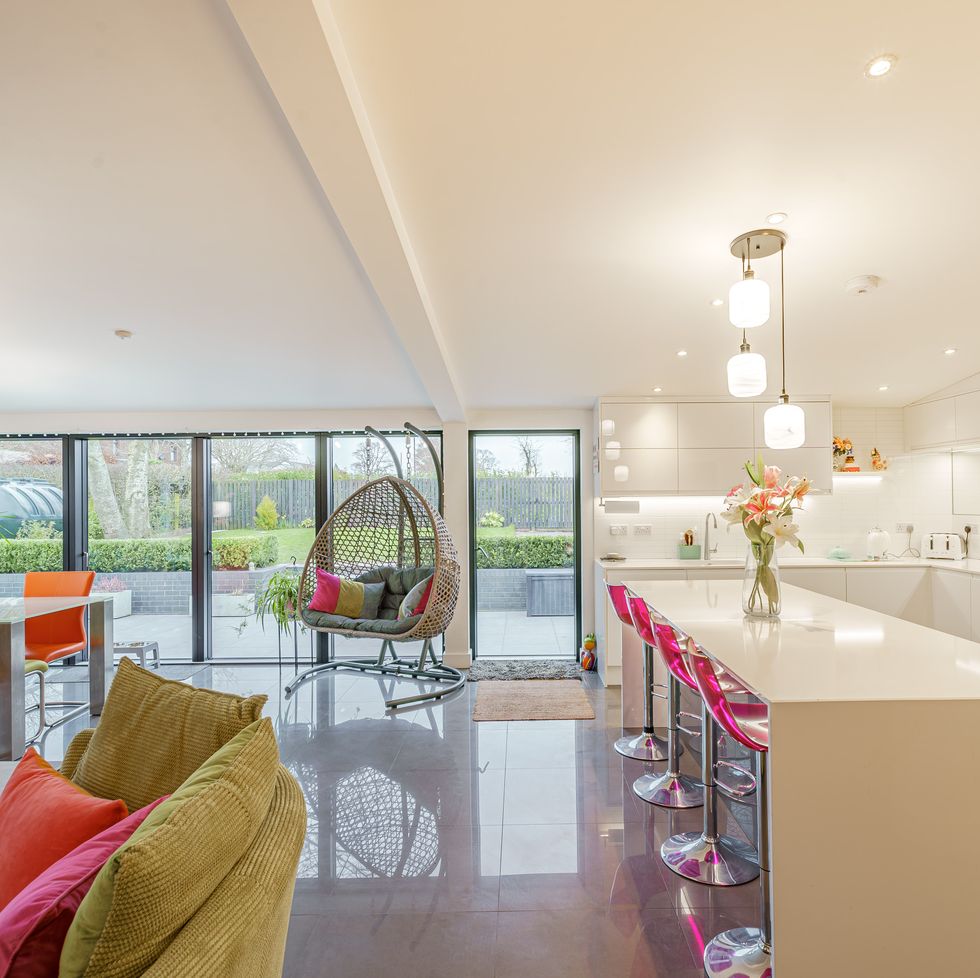

Completed over two years ago, this impressive former Dutch barn has been stylishly redesigned. Highlights include a modern kitchen (pictured), bespoke glazed doors throughout, and three generous double bedrooms.
Lake house, Southampton
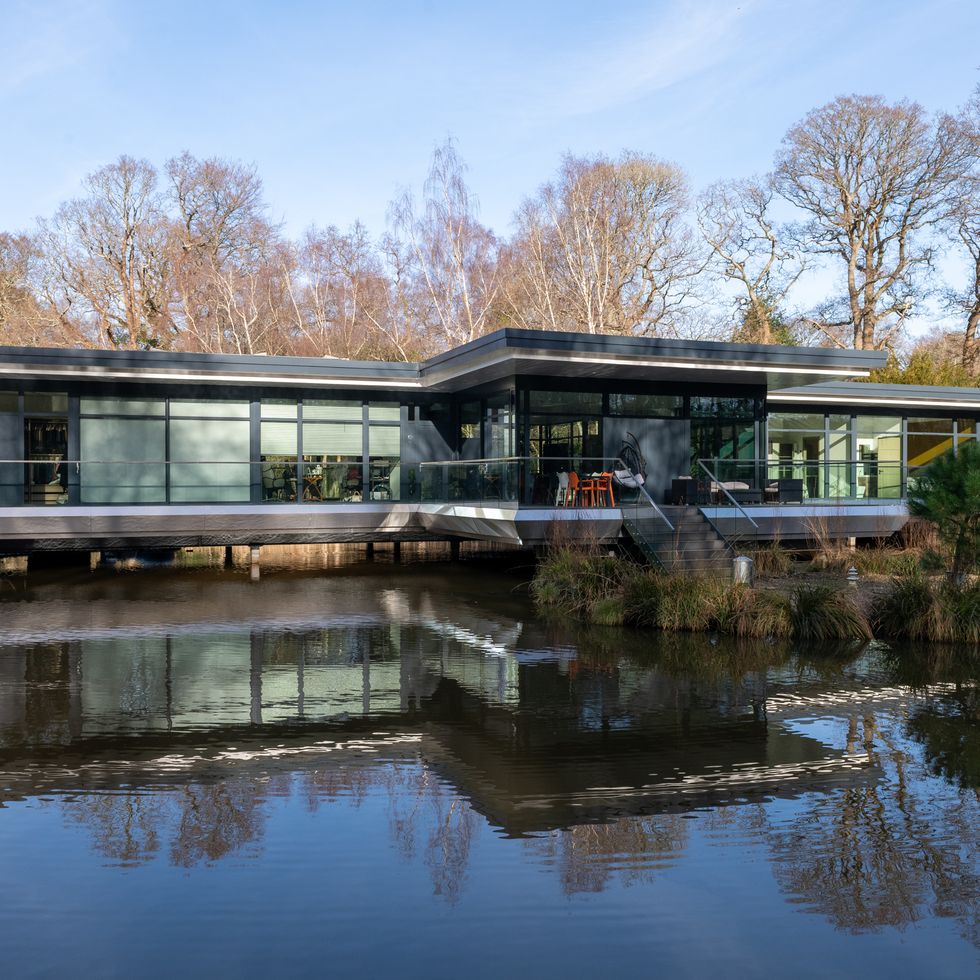

This incredible lake house in Southampton is a real head-turner. Designed by Huf Haus, it has been built like a bridge over water and is surrounded by nature. Inside, you'll find an air source heat pump, triple-glazed windows, an electric charging point, and contemporary open-plan spaces. Set on eight acres of land, the sale also includes its own slipway to the River Hamble and a large lake with two islands.
This property is on the market for £4,950,000 with Toby Gullick Independent via Rightmove .
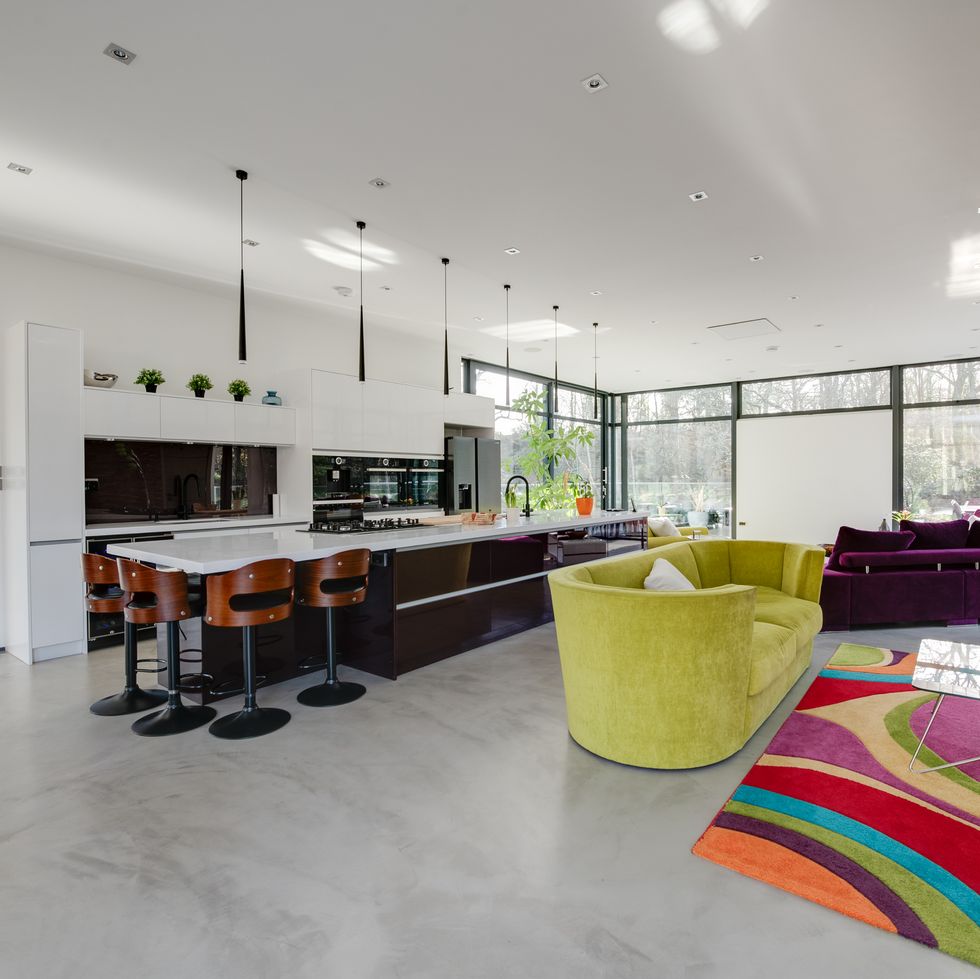

"The Lake House is a rare and exceptional home that awakens the senses with extensive open space, a stylish interior and natural light," adds the team at Rightmove.
"The light-filled living space creates a sense of openness, freedom and a seamless connection between the interior and the natural world."
Modern penthouse, London
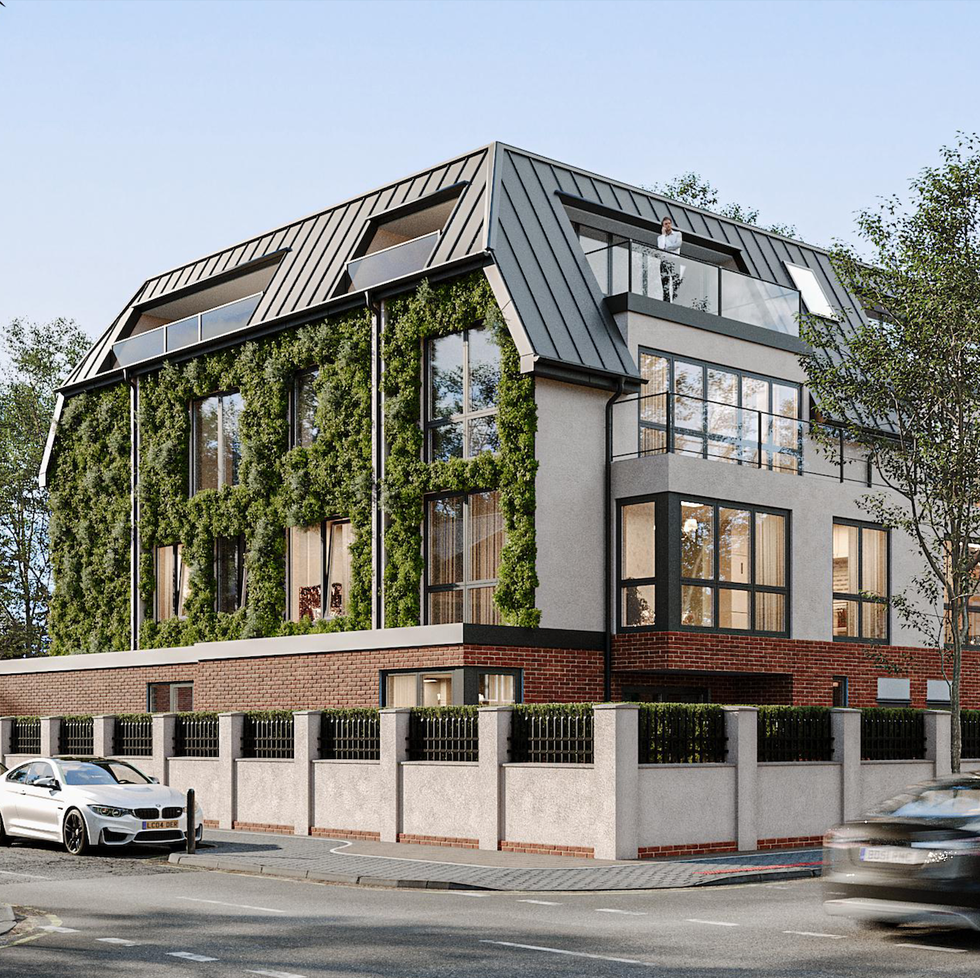

London is home to some of the most gorgeously-designed penthouses — and this beautiful modern home provides plenty of design inspiration.
Set over the entire third floor with direct lift access, it features three bedrooms and bathrooms, five terraces for outdoor entertaining, solar panels, and a 65-metre green living wall .
This property is on the market for £2,995,000 with Glentree Estates Ltd via Rightmove .
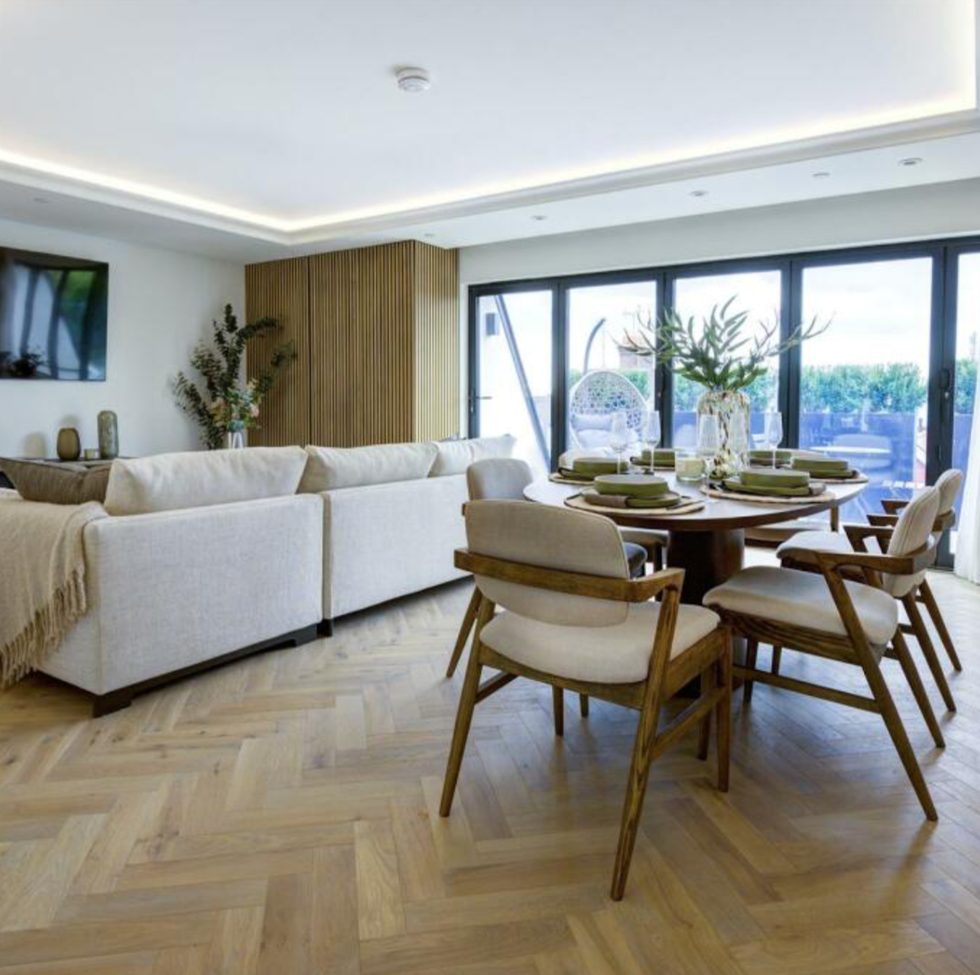

The penthouse apartment also comprises a beautifully appointed master bedroom suite, a spacious living/dining room, a utility room , and off-street parking.

.css-1shyvki:before{background-repeat:no-repeat;-webkit-background-size:contain;background-size:contain;content:'';height:0.819rem;margin-bottom:0;margin-right:-0.9375rem;width:3.125rem;}.loaded .css-1shyvki:before{background-image:url('/_assets/design-tokens/countryliving/static/images/arrow.svg');}@media(max-width: 48rem){.css-1shyvki:before{display:none;}}@media(min-width: 40.625rem){.css-1shyvki:before{display:inline-block;}} Sustainable Living .css-c08pe1:before{background-repeat:no-repeat;-webkit-background-size:contain;background-size:contain;content:'';height:0.819rem;width:3.125rem;}.loaded .css-c08pe1:before{background-image:url('/_assets/design-tokens/countryliving/static/images/arrow.svg');}@media(max-width: 48rem){.css-c08pe1:before{margin:0.7rem auto 0.9375rem;display:block;}}@media(min-width: 40.625rem){.css-c08pe1:before{margin:0 -0.9375rem 0 0;display:inline-block;-webkit-transform:scaleX(-1);-moz-transform:scaleX(-1);-ms-transform:scaleX(-1);transform:scaleX(-1);-webkit-background-position:75% 0;background-position:75% 0;}}

Everything to know about Earth Day 2024

Top cities making the world a better place

Best Eurostar destinations to visit in 2024

7 principles of slow fashion and brands to know

The best plastic-free Easter eggs for 2024

The best eco-friendly linen bedding sets

How to embrace slow gardening in 2024

RSPB Big Garden Birdwatch 2024: How to take part

25 ways to have a green, eco-friendly Christmas

12 best eco-friendly Christmas crackers

8 brands championing Green Friday 2023
Ukraine-Russia war latest: 'Putin did not order Navalny death,' - US report; Russian oil refinery suspends operations after 'Ukrainian drone attack'
US intelligence agencies have suggested Vladimir Putin most likely did not order Alexei Navalny to be killed, according to the Wall Street Journal. Meanwhile, a large fire broke out at an oil refinery it was hit with 10 Ukrainian drones, according to the Russian news agency.
Saturday 27 April 2024 11:33, UK
- 'Putin did not order Navalny death,' US report
- Russian oil refinery suspends operations after Ukrainian drone attack
- Forbes journalist placed under house arrest by Russian court
- How will Ukraine use US military aid?
- Explained : Why has Ukraine aid bill passed now, after months of delay?
- Your questions answered: Will Ukraine launch another spring offensive?
- Listen to the Sky News Daily above and tap here to follow wherever you get your podcasts
- Live reporting by Lauren Russell
One person has died and 14 have been injured after attacks on several regions in Ukraine, local authorities have said.
The areas of Kherson, Donetsk, Kharkiv, and Dnipropetrovsk were all targeted overnight.
In the Kherson region, one person died and eight others were injured, according to governor Oleksandr Prokudin.
While in Kharkiv, Russian forces hit a psychiatric hospital, injuring a 53-year-old patient.
Governor Oleh Syniehubov said 60 patients and five employees were in the hospital at the time.
Russian troops launched a total of 16 attacks against settlements in the Donetsk region, destroying or damaging 12 houses and five other unnamed buildings, Vadym Filashkin, the regional governor, said.
Three people were injured.
Dnipropetrovsk
An 82-year-old woman was injured during several strikes in the Dnipropetrovsk area.
Governor Serhii Lysak said seven blocks of flats, a market and a beauty salon were amongst the buildings damaged.
Following on from our last post, the Kremlin has said China and Russia will continue to develop ties after efforts by the US to curb relations between the two nations.
It follows US Secretary of State Antony Blinken, saying he had reiterated to China's top diplomat Wang Yi the serious concerns the US has about the country providing dual-use goods that are "powering Russia's brutal war of aggression against Ukraine".
Those weapons are being used to "demolish a power grid and other civilian infrastructure and to kill innocent children, women and men", Mr Blinken said.
When asked about Mr Blinken's comments, Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov said China is an "absolutely sovereign state".
He added: "At the same time, it [China] is our close partner. We will further develop our co-operation."
China maintains that it has not provided weaponry to any party and is "not a producer of or party involved in the Ukraine crisis".
The Kremlin has said there are currently no grounds for peace talks with Ukraine.
Dmitry Peskov, Kremlin spokesperson, said the two nations would not discuss an end to the conflict after Kyiv put in place a formal refusal to negotiate.
The comments refer to a 2022 decree signed by President Volodymyr Zelenskyy which declared the prospect of any talks with Russian leader Vladimir Putin "impossible".
The decree states that the possibility for a discussion is still open to what Mr Zelenskyy called "another president of Russia".
Russia launched a barrage of missiles against Ukraine overnight, appearing to target the country's energy infrastructure.
Ukraine's air force said that it had intercepted 21 out of 34 drones launched across the country.
Energy minister Herman Halushchenko said energy facilities in Dnipropetrovsk in the south of the country and Ivano-Frankivsk and Lviv in the west had been attacked.
An engineer was reportedly injured, Mr Halushchenko said.
Private energy operator DTEK said four of its thermal power plants were damaged and that there were "casualties" but did not provide any further detail.
It comes after the security service of Ukraine confirmed that it had launched drones at the Slavyansk and Ilsky oil refineries in Russia's Krasnoyarsk region.
The source said drones also targeted Russia's Kushchevsk military airfield in the same region.
Intelligence agencies in the US have determined that Russian President Vladimir Putin most likely did not order opposition leader Alexei Navalny to be killed, according to the Wall Street Journal (WSJ).
Mr Navalny, one of Mr Putin's fiercest critics, died at an Arctic prison camp in February at the age of 47.
His allies, including his wife, accused the Russian leader of having him murdered - an accusation the Kremlin has always denied.
But after a recent assessment based on a range of information - including some classified intelligence and an analysis of public facts - US intelligence agencies do not believe Mr Putin ordered the death of his opponent.
The assessment also took into account the timing of the death and how it overshadowed Mr Putin's presidential re-election in March, the WSJ cited some of its sources as saying.
The paper quoted sources as saying the finding had been "broadly accepted within the intelligence community and shared by several agencies, including the Central Intelligence Agency, the Office of the Director of National Intelligence and the State Department's intelligence unit".
Responding to the report, Leonid Volkov, a senior Navalny aide, called the findings naive and ridiculous, the WSJ reported.
A Russian oil refinery has partially suspended operations after being damaged in a suspected Ukrainian drone attack, the Russian TASS news agency says.
A large fire broke out at the Slavyansk oil refinery in the Krasnoyarsk region after being hit with 10 Ukrainian drones, the security director at Slavyansk ECO Group, was quoted as saying.
They said some of the damage caused may be hidden so the "work of the plant has been partially suspended".
Earlier today, Roman Siniagovskyi, head of the Slavyansk administrative district said the distillation column was damaged during the alleged strike.
Russia's Defence Ministry said its air defence units had intercepted and destroyed 66 Ukrainian drones over the Krasnoyarsk region, and two more over the Crimean Peninsula.
A source from the Security Service of Ukraine confirmed that Ukrainian drones had been launched at the Slavyansk and Ilsky oil refineries and had caused fires at the facilities.
A Ukrainian court has ordered the detention of the country's farm minister in the latest high-profile corruption investigation.
The country's High Anti-Corruption Court ruled that agriculture minister Oleksandr Solskyi should be held in custody for 60 days, but he was released after paying bail of 75 million hryvnias (£1.5m), a statement said.
He is alleged to have led an organised crime group that unlawfully obtained land worth 291 million hryvnias (£5.87m) and attempted to obtain other land worth 190 million hryvnias (£3.83m) between 2017 and 2021.
Over the past two years, a number of senior Ukrainian officials have lost their jobs, causing embarrassment as they receive thousands in foreign aid.
US military aid is currently on the way to Ukraine, which may take several weeks to arrive.
The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) says due to this, it will be a little while until any of the much-needed aid makes much of an impact on the battlefield.
It says forces in Ukraine will first have to use the aid to stabilise the frontlines and try to stop ongoing Russian advances, particularly in the areas of Avdiivka and Chasiv Yar in the Donetsk region.
No matter what way Ukraine uses the new aid, the US has not claimed that it would be enough to allow the country to regain all of its territory.
The ISW also warns of a potential summer Russian offensive operation that may begin as soon as June.
"Ukraine's ability to regain all of its territory in the long term rests on numerous future decisions in the West, in the Kremlin, and in Kyiv," the ISW says.
A Russian court has placed a journalist - who works for the Russian edition of Forbes - under house arrest, Russian state-news agency RIA has reported.
Sergei Mingazov is believed to have been detained yesterday on suspicion of spreading false information about the Russian army, his magazine said at the time.
Forbes is an American business magazine.
It is currently owned by Hong Kong-based investment group Integrated Whale Media Investments.
Welcome back to our live coverage of the war in Ukraine.
Yesterday, the US announced even more aid for Ukraine in the form of a $6bn (£4.8bn) package.
The new package includes more Patriot missiles for the country's air defence systems.
It is in addition to the $61bn (£49bn) aid package that was finally passed by Congress following a long delay.
Before we resume our live coverage and regular updates, here is a recap of the other key moments from the last 24 hours.
- Ukrainian air defences shot down 21 out of 34 Russian missiles in an overnight attack, the Ukrainian air force said;
- A Russian oil refinery has been damaged in a suspected Ukrainian attack, local authorities said;
- A 20-year-old British man has been charged with conducting hostile state activity to benefit Russia, prosecutors have said.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Gypsy, Roma and Traveller (abbreviated to GRT) is an umbrella term used in the United Kingdom to represent several diverse ethnic groups which have a shared history of nomadism.The groups include Gypsies, defined as communities of travelling people who share a Romani heritage, resident in Britain since the 16th century; Ethnic Travellers, the traditional travelling people of Ireland and ...
The Irish Traveller community is categorised as an ethnic minority group under the Race Relations Act, 1976 (amended 2000); the Human Rights Act 1998; and the Equality Act 2010. ... The Traveller, Gypsy, and Roma communities are widely considered to be among the most socially excluded communities in the UK. They have a much lower life ...
In 2011, 14.1% of Gypsy and Irish Traveller people in England and Wales rated their health as bad or very bad, compared with 5.6% on average for all ethnic groups. In 2016 to 2017, Gypsy or Irish Traveller people aged 65 and over had the lowest health-related quality of life of all ethnic groups (average score of 0.509 out of 1). The quality of ...
Gypsies' and Travellers' lived experiences, homes, England and Wales: 2022. ... Similarly, "non-Traveller", and "non-Gypsy" are also used to refer to others outside Gypsy and Traveller communities as is "the settled community", although it is important to note that Gypsies and Travellers may also live in settled accommodation in the ...
The barriers which Roma, Gypsy and Traveller people face in modern Britain have been laid bare in unprecedented survey data, which reveals extremely high levels of racial assault, poor health ...
This House of Commons Library briefing paper provides an overview of the key issues and policies relating to Gypsy and Traveller communities in England. The paper examines a range of issues including: inequalities, racial discrimination, accommodation needs, illegal encampments, health and education outcomes, employment rates, welfare reform and evidence of over-representation in the criminal ...
The government requires local authorities in England to regularly assess how many sites they need in order to serve their Gypsy and Traveller communities and come up with a five-year plan on how ...
Travellers, equating a right to travel with spurious definitions of blood purity. It was not until the 1960s and the formation of the Gypsy Council that Gypsy Travellers as a community found a collective voice, one which tried to assert that all had a right to travel and that nomadism did have a place in modern Britain.
2 What we know about inequalities facing Gypsy, Roma and Traveller communities Gypsy and Traveller communities in the UK. 10. Gypsy and Traveller people have been present in England since at least the 16th Century and the first recorded mention of Gypsies in England can be found in a document from 1514. 4 It has been suggested that the term "Gypsy" was coined due to a misapprehension that ...
Table 1: Most people who identified as Gypsy or Irish Traveller were born in England Percentage of Gypsy or Irish Traveller ethnic groups and England and Wales population born in each given country or continent, Census 2021 ; Country or continent of birth Gypsy or Irish Traveller England and Wales; Europe: United Kingdom: England: 77.1% 77.3%
Roma and Traveller communities, October 2022 . Romany Gypsy, Roma and Irish Traveller communities are known to face some of the starkest inequalities in healthcare access and outcomes amongst the UK population, including when compared with other minority ethnic groups. 1. The reasons for these poor health outcomes are complex, but include the ...
Busting myths about Travellers. The reality of Travelling life, according to Davie: "We've been around for 1000 years.". "We pay tax.". "We don't all live in trailers, many ...
In this bulletin, "community members" and "participants" refers to people currently living in England and Wales, aged 16 years and over, identifying as Gypsy or Traveller, who took part in this research. Where quotes have been used from local or central government participants, this is explicitly stated.
Official figures showing the number of Gypsy and Traveller caravan sites across England have been released today. The report published by the Department for Communities and Local Government (DCLG ...
The big fat truth about Gypsy life. Over-the-top brides were the main draw in Channel 4's series on Traveller communities. But when Julie Bindel visited, she found prejudice, poor health and ...
Advocating for and working with Gypsy, Roma and Traveller people to tackle discrimination and promote equality. ... Community Corner. Read all about the events, news updates and upcoming talent happening in your area! ... Email: [email protected] Tel: 020 7607 2002.
Irish Traveller communities are located in Ireland, the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada. As of 2016, ... as part of a total estimation of over 300,000 Romani and other Traveller groups in the UK. In the 2021 Census of England and Wales, ...
English Travellers. The term English Travellers refers to itinerant groups, and may mean: Romanichals, a Romani ethnic group also known as English Travellers or English Gypsies. British showmen, commonly referred to as Funfair Travellers. New Age travellers.
This research clearly highlights that Gypsy and Traveller communities are invisible in the Cross-Government Suicide Prevention Plan, and are largely ignored within Local Suicide Prevention Plans. It is essential that urgent action is taken to address suicide inequalities in Gypsy and Traveller communities in England. 16
The engagement of similarly socially excluded and stigmatized groups in research has previously been considered. Studies with relevance to Gypsy/Traveller research have focused on indigenous populations, people with mental health and substance use problems, disabilities, and low levels of literacy, and sex workers, who are also absent from many health records (Benoit, Jansson, Millar ...
Long subject to discrimination, hatred and eviction, England has passed a number of laws to protect traveller communities, and authorities are required to provide new caravan sites when clearing ...
To celebrate Earth Day (22nd April), Rightmove has revealed a selection of eco-friendly homes for sale around the UK.. According to new data from the property portal, there has been a steady increase in listings mentioning higher EPC ratings, with the proportion of properties for sale including them more than doubling (+104%) compared to pre-pandemic 2019.
The United States is sending weapons and equipment to Ukraine "this week", Joe Biden has said. Referring to a $61bn (£49bn) programme of funding for Kyiv that has finally been passed by Congress ...