Voyager 2 News Updates

News updates on Voyager 2's encounter with Neptune will be available to the public during late August on special telephone numbers from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Frequently updated reports on the spacecraft mission can be heard August 19-31 by phoning (900) 590-1234. Cost for each call on this 900 number is 45 cents for the first minute, 35 cents per additional minute.
Depending on their location and the time of day, some members of the public may prefer to call regular telephone number in Pasadena, Calif., carrying the same audio reports. That number is (818) 354-4227. Normal long distance charges, if any, will apply.
In addition to mission status reports, the telephone lines will carry live audio from daily press conferences at JPL if callers dial in when one is in progress. Press conferences are scheduled at 10 a.m. PDT daily August 21-29.
Another telephone line, (818) 354-0409, will carry the mission status reports only (no press conference audio). Normal long-distance charges, if any, will apply.
A fourth telephone line available to the public, (818) 354-7292, will carry press conference audio as well as audio from hourly NASA Select television reports (no mission status reports). NASA Select television programs are scheduled approximately hourly from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. PDT August 21-29, except as preempted by the daily press conference. Normal long-distance charges, if any, will apply on this phone line.
Voyager 2 will make the first-ever flyby of the planet Neptune on August 24 (Pacific time). The Voyager Mission is managed by JPL for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications. BR>
PUBLIC INFORMATION OFFICE
JET PROPULSION LABORATORY
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
NATIONAL AERONAUTICS AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION
PASADENA, CALIF. 91109. TELEPHONE (818) 354-5011
NOTE TO EDITORS
August 15, 1989
News organizations planning coverage of Voyager 2's flyby of Neptune may wish to make note of the following telephone numbers which will be activated in late August.
Mission status reports will be carried August 19-31 on special 900 phone line and two conventional phone lines. During Voyager-Neptune newsroom operations August 21-29, two of the lines will also carry live audio from daily press conferences, scheduled to begin at 10 a.m. PDT.
In addition, another phone line will carry live audio from the press conferences as well as audio from NASA Select television programs during Voyager-Neptune newsroom operations August 21-29 (no status reports). The television programs are scheduled approximately hourly from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. PDT daily.
The phone numbers are: (900) 590-1234 Status reports and press conference audio; 45 cents for first minute, 35 cents per additional minute (818) 354-4227 Status reports and press conference audio; normal long-distance charges, if any, apply (818) 354-0409 Status reports only; normal long-distance charges, if any, apply (818) 354-7292 Press conference and NASA Select television audio; normal long-distance charges, if any, apply
News organizations may also wish to make note of the main telephone number for the Voyager-Neptune newsroom, which may be used to contact the JPL Public Information Office staff August 21-29. This number is: (818) 354-7700 .
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

After a 12.3 billion-mile 'shout,' NASA regains full contact with Voyager 2
Emily Olson
Ayana Archie

A NASA image of one of the twin Voyager space probes. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 after mistakenly pointing its antenna 2 degrees away from Earth. On Friday, contact was fully restored. NASA/Getty Images hide caption
A NASA image of one of the twin Voyager space probes. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 after mistakenly pointing its antenna 2 degrees away from Earth. On Friday, contact was fully restored.
Talk about a long-distance call.
NASA said it resumed full communications with the Voyager 2 on Friday after almost two weeks of silence from the interstellar spacecraft.
The agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory said a series of ground antennas, part of the Deep Space Network, registered a carrier signal from Voyager 2 on Tuesday. However, the signal was too faint.
A Deep Space Network facility in Australia then sent "the equivalent of an interstellar 'shout' " to the Voyager 2 telling it to turn its antenna back toward Earth. The signal was sent more than 12.3 billion miles away and it took 37 hours to get a response from the spacecraft, NASA said.
Scientists received a response at about 12:30 a.m. ET Friday. Voyager 2 is now operating normally, returning science and telemetry data, and "remains on its expected trajectory," NASA said.
NASA said Friday that it lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 after "a series of planned commands" inadvertently caused the craft to turn its antenna 2 degrees away from the direction of its home planet.

NASA is keeping Voyager 2 going until at least 2026 by tapping into backup power
What might seem like a slight error had big consequences: NASA previously said it wouldn't be able to communicate with the craft until October, when the satellite would go through one of its routine repositioning steps.
"That is a long time to wait, so we'll try sending up commands several times" before October, program manager Suzanne Dodd told The Associated Press.

These are the 4 astronauts who'll take a trip around the moon next year
Even if Voyager 2 had failed to reestablish communications until fall, the engineers expected it to stay moving on its planned trajectory on the edge of the solar system.
Voyager 2 entered interstellar space in November 2018 — more than 40 years since it launched from Cape Canaveral, Fla. To this day, Voyager 2 remains one of only two human-made objects to ever operate outside the heliosphere, which NASA defines as "the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun."
Its primary mission was to study the outer solar system, and already, Voyager 2 has proved its status as a planetary pioneer . Equipped with several imaging instruments, the spacecraft is credited with documenting the discovery of 16 new moons, six new rings and Neptune's "Great Dark Spot."

Voyager 2 Bids Adieu To The Heliosphere, Entering Interstellar Space
Voyager 2 is also carrying some precious cargo, like a message in a bottle, should it find itself as the subject of another world's discovery: a golden record containing a variety of natural sounds, greetings in 55 languages and a 90-minute selection of music.
Last month's command mix-up foreshadows the craft's inevitable end an estimated three years from now.
"Eventually, there will not be enough electricity to power even one instrument," reads a NASA page documenting the spacecraft's travels . "Then, Voyager 2 will silently continue its eternal journey among the stars."
Meanwhile, Voyager 2's sister spacecraft, Voyager 1, is still broadcasting and transmitting data just fine from a slightly farther vantage point of 15 billion miles away.
Correction Aug. 3, 2023
A previous version of this article implied that Voyager 2 flew past Uranus in 2018 when, in fact, the spacecraft concluded its encounter with the planet and started heading toward Neptune in 1986. Voyager 2 entered interstellar space in November 2018.
- Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Voyager 2: An iconic spacecraft that's still exploring 45 years on
The interstellar vagabond continues to explore the cosmos along with its twin, Voyager 1.

Voyager 2 as the backup
Jupiter and saturn flyby, uranus and neptune flyby, voyager 2's interstellar adventure, voyager 2's legacy, additional information.
Voyager 2, was the first of two twin probes NASA sent to investigate the outer planets of our solar system.
The probe was launched aboard a Titan IIIE-Centaur from Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 41 (previously Launch Complex 41) on Aug. 20, 1977, its twin spacecraft Voyager 1 was launched about two weeks later on Sept. 5. NASA planned for the Voyager spacecraft to take advantage of an alignment of the outer planets that takes place only every 176 years. The alignment would allow both probes to swing from one planet to the next, with a gravity boost to help them along the way.
While Voyager 1 focused on Jupiter and Saturn , Voyager 2 visited both those planets and also ventured to Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 2's mission to those last two planets would be humanity's only visit in the 20th century.
Related: Celebrate 45 years of Voyager with these amazing images of our solar system (gallery)
Voyager 2 is now traveling through interstellar space. As of early November 2018, NASA announced that Voyager 2 had crossed the outer edge of our solar system ( Voyager 1 crossed the boundary into interstellar space in 2012. ) Voyager 2 is now approximately 12 billion miles (19 billion kilometers) away from Earth and counting!

Although there was not enough money in Voyager 2's budget to guarantee it would still work when flying past Uranus and Neptune, its trajectory was designed to go past those planets anyway. If the spacecraft were still working after Saturn, NASA could try to take pictures of the other planets.
Voyager 2 was ready as a backup for Voyager 1. If Voyager 1 failed when taking pictures of Jupiter and Saturn, NASA was prepared to alter Voyager 2's path to follow Voyager 1's trajectory. It would cut off the Uranus and Neptune option, but still, preserve the possibility of capturing images.
The backup plan was never executed, though, because Voyager 1 went on to make many discoveries at Jupiter and Saturn, working well enough for NASA to carry out its original plans for Voyager 2.

Voyager 2 reached Jupiter in 1979, two years after launching from Cape Canaveral. Since Voyager 1 had just gone through the system four months earlier, Voyager 2's arrival allowed NASA to take valuable comparison shots of Jupiter and its moons. It captured changes in the Great Red Spot and also resolved some of the moon's surfaces in greater detail.
Voyager 2 took pictures of many of Jupiter's satellites. Among its most spectacular findings were pictures from the icy moon Europa . Voyager 2 snapped detailed photos of the icy moon's cracks from 128,000 miles (205,996 km) away and revealed no change in elevation anywhere on the moon's surface.
Proving that moons are abundant around the outer planets, Voyager 2 happened to image Adrastea, a small moon of Jupiter, only months after Voyager 1 found two other Jupiter moons, Thebe and Metis. Adrastea is exceptionally small, only about 19 miles (30.5 kilometers) in diameter at the smallest estimate.

Next in line was Saturn. Voyager 2 became the third spacecraft to visit Saturn when it arrived at its closest point to the ringed planet on Aug. 26, 1981, and took hundreds of pictures of the planet, its moons and its rings . Suspecting that Saturn might be circled by many ringlets, scientists conducted an experiment. They watched the star Delta Scorpii for nearly two and a half hours as it passed through the plane of the rings. As expected, the star's flickering light revealed ringlets as small as 330 feet (100 meters) in diameter.

Voyager 2's made its closest approach to Uranus on Jan. 24, 1986, becoming the first spacecraft to visit the ice giant. The probe made several observations of the planet, noting that the south pole was facing the sun and that its atmosphere is about 85% hydrogen and 15% helium.
Additionally, Voyager 2 discovered rings around Uranus, 10 new moons and a magnetic field that, oddly, was 55 degrees off the planet's axis. Astronomers are still puzzling over Uranus' orientation today.
Voyager 2's pictures of the moon Miranda revealed it to be perhaps the strangest moon in the solar system. Its jumbled-up surface appears as though it was pushed together and broken apart several times.
The spacecraft then made it to Neptune , reaching the closest point on Aug. 25, 1989. It skimmed about 3,000 miles from the top of the planet's atmosphere and spotted five new moons as well as four rings around the planet. Remarkably, Voyager 2 is currently the only human-made object to have flown by the intriguing ice giant, according to NASA .
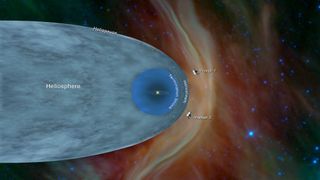
On November 5, 2018, Voyager 2 crossed the heliopause — the boundary between the heliosphere and interstellar space. At this stage, the probe was 119 astronomical units from the sun. (One AU is the average Earth-sun distance, which is about 93 million miles, or 150 million kilometers.) Voyager 1 made the crossing at nearly the same distance, 121.6 AU.
According to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) , Voyager 2 has enough fuel to keep its instruments running until at least 2025. By then, the spacecraft will be approximately 11.4 billion miles (18.4 billion kilometers) away from the sun.
But Voyager 2 is destined to roam the Milky Way long after its instruments have stopped working.
In about 40,000 years Voyager 2 will pass 1.7 light-years (9.7 trillion miles) from the star Ross 248, according to NASA JPL. The cosmic vagabond will continue its journey through interstellar space and pass 4.3 light-years, (25 trillion miles) from Sirius in about 296,000 years.
Voyager 2's observations paved the way for later missions. The Cassini spacecraft, which was at Saturn between 2004 and 2017, tracked down evidence of liquid water at the planet's icy moons several decades after the Voyagers initially revealed the possible presence of water. Cassini also mapped the moon, Titan , after the Voyagers took pictures of its thick atmosphere.
Voyager 2's images of Uranus and Neptune also serve as a baseline for current observations of those giant planets. In 2014, astronomers were surprised to see giant storms on Uranus — a big change from when Voyager 2 flew by the planet in 1986.
To see where Voyager 2 is now you can check out the mission status with resources from NASA . Learn more about the iconic spacecraft with the National Air and Space Museum .
Bibliography
NASA. In depth: Voyager 2. NASA. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from www.solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/voyager-2/in-depth/
NASA. Voyager - mission status. NASA. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from www.voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/status/
NASA. Voyager - the interstellar mission. NASA. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from www. voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/interstellar-mission
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, " Why Am I Taller ?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
- Daisy Dobrijevic Reference Editor
A billionaire hopes to upgrade the Hubble Telescope on a private SpaceX mission, but could it really happen?
'It's so complicated:' Boeing Starliner teams diagnosing helium leak ahead of June 1 astronaut launch
Will a 'rare' lineup of planets be visible to the naked eye in the night sky on June 3?
Most Popular
- 2 'Alien' heard us all scream 45 years ago today. Here's what it was like on opening day
- 3 This Week In Space podcast: Episode 112 — Mars on Pause?
- 4 Towel Day 2024: What's the deal with towels in 'The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy?'
- 5 A billionaire hopes to upgrade the Hubble Telescope on a private SpaceX mission, but could it really happen?
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
NASA Reaches Voyager 2 With a Last-Ditch ‘Shout’ Across the Void
After an erroneous command sent the spacecraft’s antenna askew, mission specialists hatched a plan to point it back toward Earth.

By Katrina Miller
It took an interstellar “shout” across the solar system. But NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory said on Friday that it re-established full communications with Voyager 2, an aging probe exploring the outer edges of the solar system.
“After two weeks of not hearing anything, we’re back to getting unique data from the interstellar medium,” said Linda Spilker, a planetary scientist at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the lead mission scientist for Voyager 2.
The space agency lost contact with Voyager 2 on July 21 when the mission team accidentally sent a command that pushed the spacecraft’s antenna two degrees away from Earth. On Tuesday morning, officials from the Deep Space Network, a worldwide system of radio dishes NASA uses to communicate with various space probes, detected a carrier signal known as a heartbeat from Voyager 2. It was too faint to extract any data, but enough to confirm that the mission was still operating.
Nonetheless, being able to pick up only the heartbeat “was upsetting and worrisome,” said Suzanne Dodd, the project manager for Voyager 2.
The mission team hatched a plan to send a command on Wednesday reorienting Voyager 2’s antenna back to Earth, using a Deep Space Network radio dish in Canberra, Australia.
The chances of success were slim, according to a spokeswoman at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. It took 37 hours to know whether the attempt was successful — 18.5 hours for the signal to make it to Voyager 2, and another 18.5 for the data to return.
Ms. Dodd said the waiting period “was pretty nervewracking. You don’t sleep well.”
Scientists, engineers and the flight team were “waiting on pins and needles to hear back from Voyager 2, to see if the command was successful,” Dr. Spilker said. “It was all hands on deck.”
But it worked: On Friday at 12:29 a.m. Eastern time, Voyager 2 began transmitting science data once again. Scientists also confirmed that the probe remained on its original path.
According to Dr. Spilker, mission control in California reacted to the good news with a lot of high fives, tears and sighs of relief.
Voyager 2 launched to space on Aug. 20, 1977, to fly by the solar system’s outer planets and then explore the interstellar space that lies beyond it. The nearly 46-year-old probe is currently more than 12.5 billion miles away from Earth and is collecting data on the distant region of space for scientists to study. Its twin, Voyager 1, was launched weeks after Voyager 2 and became the first to cross the solar system’s boundary.
Had it not established contact, the mission team would have had to wait until Oct. 15, when Voyager 2 is programmed to do an automatic reset of the direction of its antenna.
But it no longer needs to wait, and the mission has resumed data transmissions from beyond the solar system’s heliosphere.
“We did an assessment and the spacecraft looks very healthy, very normal,” Ms. Dodd said. The mission team will continue to run tests to fully understand the status of the spacecraft before resuming regular activity.
Ms. Dodd looks forward to celebrating the probe’s launch anniversary later this month. “Both of these spacecraft are truly remarkable in their longevity,” she said, referring to Voyager 2 and Voyager 1. “They’re like the spacecraft with nine lives.”
Katrina Miller is a science reporting fellow for The Times. She recently earned her Ph.D. in particle physics from the University of Chicago. More about Katrina Miller
What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
A dramatic blast from the sun set off the highest-level geomagnetic storm in Earth’s atmosphere, making the northern lights visible around the world .
With the help of Google Cloud, scientists who hunt killer asteroids churned through hundreds of thousands of images of the night sky to reveal 27,500 overlooked space rocks in the solar system .
A celestial image, an Impressionistic swirl of color in the center of the Milky Way, represents a first step toward understanding the role of magnetic fields in the cycle of stellar death and rebirth.
Scientists may have discovered a major flaw in their understanding of dark energy, a mysterious cosmic force . That could be good news for the fate of the universe.
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .

Voyager 1 and 2: The Interstellar Mission

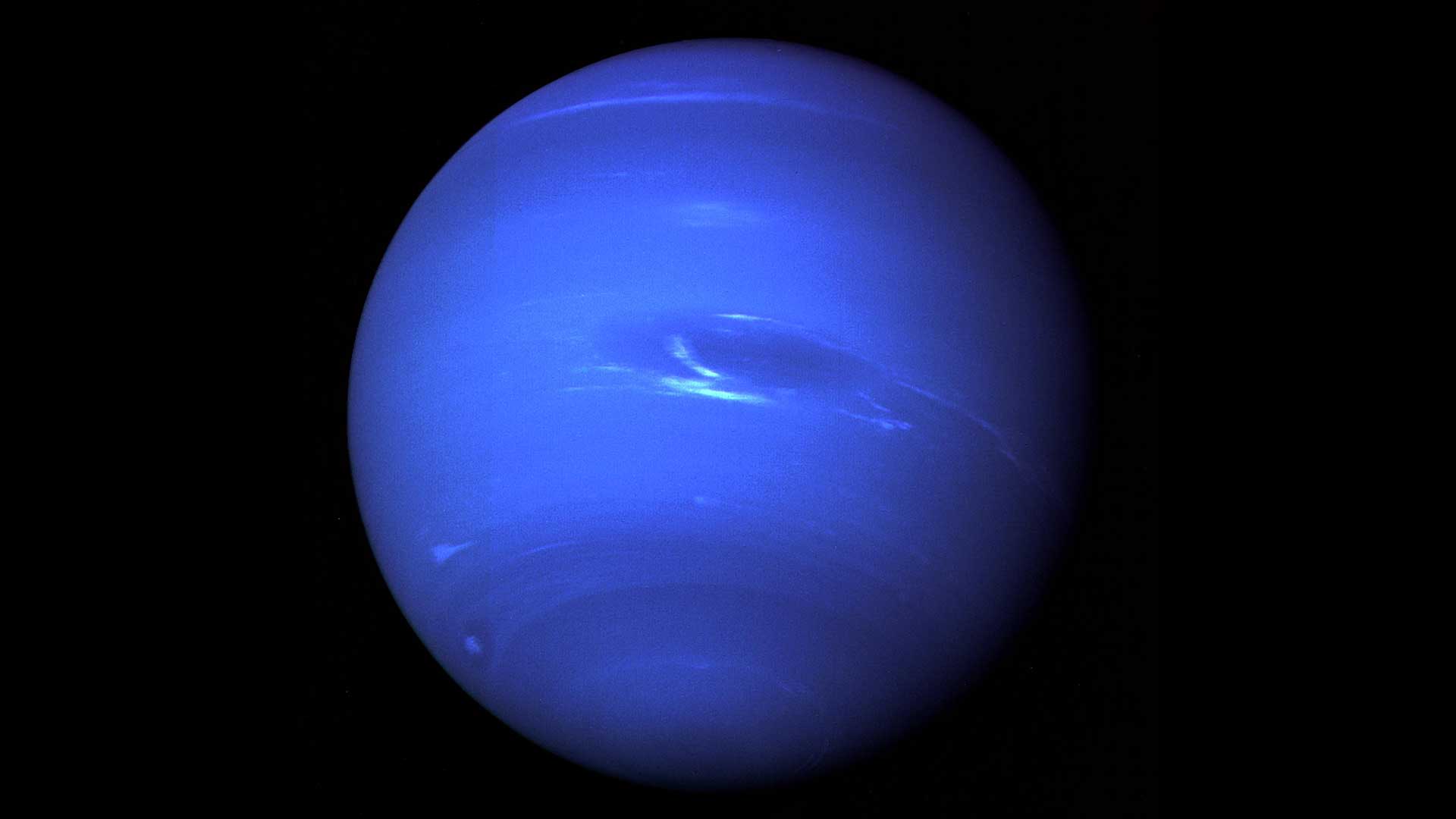
An image of Neptune taken by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
NASA has beautiful photos of every planet in our solar system. We even have images of faraway Neptune , as you can see in the photo above.
Neptune is much too distant for an astronaut to travel there with a camera. So, how do we have pictures from distant locations in our solar system? Our photographers were two spacecraft, called Voyager 1 and Voyager 2!

An artist’s rendering of one of the Voyager spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. Their mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn —and beyond to the outer planets of our solar system. This was a big task. No human-made object had ever attempted a journey like that before.
The two spacecraft took tens of thousands of pictures of Jupiter and Saturn and their moons. The pictures from Voyager 1 and 2 allowed us to see lots of things for the first time. For example, they captured detailed photos of Jupiter's clouds and storms, and the structure of Saturn's rings .

Image of storms on Jupiter taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft. Image credit: NASA
Voyager 1 and 2 also discovered active volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io , and much more. Voyager 2 also took pictures of Uranus and Neptune. Together, the Voyager missions discovered 22 moons.
Since then, these spacecraft have continued to travel farther away from us. Voyager 1 and 2 are now so far away that they are in interstellar space —the region between the stars. No other spacecraft have ever flown this far away.
Where will Voyager go next?
Watch this video to find out what's beyond our solar system!
Both spacecraft are still sending information back to Earth. This data will help us learn about conditions in the distant solar system and interstellar space.
The Voyagers have enough fuel and power to operate until 2025 and beyond. Sometime after this they will not be able to communicate with Earth anymore. Unless something stops them, they will continue to travel on and on, passing other stars after many thousands of years.
Each Voyager spacecraft also carries a message. Both spacecraft carry a golden record with scenes and sounds from Earth. The records also contain music and greetings in different languages. So, if intelligent life ever find these spacecraft, they may learn something about Earth and us as well!

A photo of the golden record that was sent into space on both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
More about our universe!

Where does interstellar space begin?

Searching for other planets like ours

Play Galactic Explorer!
If you liked this, you may like:
- Become A Member
- Gift Membership
- Kids Membership
- Other Ways to Give
- Explore Worlds
- Defend Earth
How We Work
- Education & Public Outreach
- Space Policy & Advocacy
- Science & Technology
- Global Collaboration

Our Results
Learn how our members and community are changing the worlds.
Our citizen-funded spacecraft successfully demonstrated solar sailing for CubeSats.
Space Topics
- Planets & Other Worlds
- Space Missions
- Space Policy
- Planetary Radio
- Space Images
The Planetary Report
The eclipse issue.
Science and splendor under the shadow.
Get Involved
Membership programs for explorers of all ages.
Get updates and weekly tools to learn, share, and advocate for space exploration.
Volunteer as a space advocate.
Support Our Mission
- Renew Membership
- Society Projects
The Planetary Fund
Accelerate progress in our three core enterprises — Explore Worlds, Find Life, and Defend Earth. You can support the entire fund, or designate a core enterprise of your choice.
- Strategic Framework
- News & Press
The Planetary Society
Know the cosmos and our place within it.
Our Mission
Empowering the world's citizens to advance space science and exploration.
- Explore Space
- Take Action
- Member Community
- Account Center
- “Exploration is in our nature.” - Carl Sagan
The Voyager missions
Highlights Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 launched in 1977 and made a grand tour of the solar system's outer planets. They are the only functioning spacecraft in interstellar space, and they are still sending back measurements of the interstellar medium. Each spacecraft carries a copy of the golden record, a missive from Earth to any alien lifeforms that may find the probes in the future.
What are the Voyager missions?
The Voyager program consists of two spacecraft: Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Voyager 2 was actually launched first, in August 1977, but Voyager 1 was sent on a faster trajectory when it launched about two weeks later. They are the only two functioning spacecraft currently in interstellar space, beyond the environment controlled by the sun.
Voyager 2’s path took it past Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1985, and Neptune in 1989. It is the only spacecraft to have visited Uranus or Neptune, and has provided much of the information that we use to characterize them now.
Because of its higher speed and more direct trajectory, Voyager 1 overtook Voyager 2 just a few months after they launched. It visited Jupiter in 1979 and Saturn in 1980. It overtook Pioneer 10 — the only other spacecraft in interstellar space thus far — in 1998 and is now the most distant artificial object from Earth.
How the Voyagers work
The two spacecraft are identical, each with a radio dish 3.7 meters (12 feet) across to transmit data back to Earth and a set of 16 thrusters to control their orientations and point their dishes toward Earth. The thrusters run on hydrazine fuel, but the electronic components of each spacecraft are powered by thermoelectric generators that run on plutonium. Each carries 11 scientific instruments, about half of which were designed just for observing planets and have now been shut off. The instruments that are now off include several cameras and spectrometers to examine the planets, as well as two radio-based experiments. Voyager 2 now has five functioning instruments: a magnetometer, a spectrometer designed to investigate plasmas, an instrument to measure low-energy charged particles and one for cosmic rays, and one that measures plasma waves. Voyager 1 only has four of those, as its plasma spectrometer is broken.
Jupiter findings
Over the course of their grand tours of the solar system, the Voyagers took tens of thousands of images and measurements that significantly changed our understanding of the outer planets.
At Jupiter, they gave us our first detailed ideas of how the planet’s atmosphere moves and evolves, showing that the Great Red Spot was a counter-clockwise rotating storm that interacted with other, smaller storms. They were also the first missions to spot a faint, dusty ring around Jupiter. Finally, they observed some of Jupiter’s moons, discovering Io’s volcanism, finding the linear features on Europa that were among the first hints that it might have an ocean beneath its surface, and granting Ganymede the title of largest moon in the solar system, a superlative that was previously thought to belong to Saturn’s moon Titan.
Saturn findings
Next, each spacecraft flew past Saturn, where they measured the composition and structure of Saturn’s atmosphere , and Voyager 1 also peered into Titan’s thick haze. Its observations led to the idea that Titan might have liquid hydrocarbons on its surface, a hypothesis that has since been verified by other missions. When the two missions observed Saturn’s rings, they found the gaps and waves that are well-known today. Voyager 1 also spotted three previously-unknown moons orbiting Saturn: Atlas, Prometheus, and Pandora.
Uranus and Neptune findings
After this, Voyager 1 headed out of the solar system, while Voyager 2 headed toward Uranus . There, it found 11 previously-unknown moons and two previously-unknown rings. Many of the phenomena it observed on Uranus remained unexplained, such as its unusual magnetic field and an unexpected lack of major temperature changes at different latitudes.
Voyager 2’s final stop, 12 years after it left Earth, was Neptune. When it arrived , it continued its streak of finding new moons with another haul of 6 small satellites, as well as finding rings around Neptune. As it did at Uranus, it observed the planet’s composition and magnetic field. It also found volcanic vents on Neptune’s huge moon Triton before it joined Voyager 1 on the way to interstellar space.
Interstellar space
Interstellar space begins at the heliopause, where the solar wind – a flow of charged particles released by the sun – is too weak to continue pushing against the interstellar medium, and the pressure from the two balances out. Voyager 1 officially entered interstellar space in August 2012, and Voyager 2 joined it in November 2018.
These exits were instrumental in enabling astronomers to determine where exactly the edge of interstellar space is, something that’s difficult to measure from within the solar system. They showed that interstellar space begins just over 18 billion kilometers (about 11 billion miles) from the sun. The spacecraft continue to send back data on the structure of the interstellar medium.
After its planetary encounters, Voyager 1 took the iconic “Pale Blue Dot” image , showing Earth from about 6 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles) away. As of 2021 , Voyager 1 is about 155 astronomical units (14.4 billion miles) from Earth, and Voyager 2 is nearly 129 astronomical units (12 billion miles) away.
The golden records
Each Voyager spacecraft has a golden phonograph record affixed to its side, intended as time capsules from Earth to any extraterrestrial life that might find the probes sometime in the distant future. They are inscribed with a message from Jimmy Carter, the U.S. President at the time of launch, which reads: “This is a present from a small, distant world, a token of our sounds, our science, our images, our music, our thoughts and our feelings. We are attempting to survive our time so we may live into yours.”
The covers of the records have several images inscribed, including visual instructions on how to play them, a map of our solar system’s location with respect to a set of 14 pulsars, and a drawing of a hydrogen atom. They are plated with uranium – its rate of decay will allow any future discoverers of either of the records to calculate when they were created.
The records’ contents were selected by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan. Each contains 115 images, including scientific diagrams of the solar system and its planets, the flora and fauna of Earth, and examples of human culture. There are natural sounds, including breaking surf and birdsong, spoken greetings in 55 languages, an hour of brainwave recordings, and an eclectic selection of music ranging from Beethoven to Chuck Berry to a variety of folk music.
Learn more Voyager Mission Status Bulletin Archives Experience A Message From Earth - Inspired by the Voyager Golden Record Neptune, planet of wind and ice
Support missions like Voyager 1 and 2
Whether it's advocating, teaching, inspiring, or learning, you can do something for space, right now. Let's get to work.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Here are instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .

Voyager 2 Enters Final Planetary Encounter

NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft today entered the observatory phase of its flyby of Neptune, signaling the beginning of its final planetary encounter after nearly 12 years of exploring the outer solar system.
Voyager mission controllers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., will now be tracking the spacecraft around the clock as Voyager begins taking systematic images of Neptune and sending back about 50 pictures day.
"Now that we've entered the observatory phase we'll be taking about six images every three hours to study changes in the atmosphere from rotation to rotation," said Dr. Ellis Miner, Voyager deputy project scientist.
Signals from Voyager 2 marking the beginning of the observatory phase were received at 3:40 a.m. Pacific Daylight Time. This official start of the Neptune encounter places Voyager at the top of the priority list of spacecraft being tracked by the NASA/JPL Deep Space Network. Before today, Voyager had to compete with other projects for DSN coverage. During the observatory phase, the spacecraft will be monitored at regular intervals by more than one antenna at each of the DSN sites in California, Spain and Australia.
In addition to taking images of the planet, Voyager 2 will also be making systematic ultraviolet observations of Neptune looking for any auroral activity and escaping gases. Calibrations of the spacecraft's instruments will also be done in preparation for critical near-encounter observations.
In observations of Neptune made by Voyager 2 in late 1988 and January of 1989, scientists saw bright spot in the southern hemisphere of the planet. Since January, that spot has dimmed and larger dark area has been seen in the images. Recently, the bright spot has begun to brighten again and other spots are becoming apparent. Neptune's atmosphere has also revealed regions of dark banding near its southern pole and similar banding has been seen north of the planet's equator.
Voyager's observatory phase ends and its far encounter phase starts on Aug. 6, 1989.
The near-encounter phase of the mission includes Voyager's closest approach to Neptune at 9 p.m. Pacific Daylight Time on Aug. 24, 1989, when the spacecraft passes just 4,850 kilometers (3,000 miles) from the planet's cloud tops. Five hours later, the spacecraft will fly about 39,000 kilometers (24,000 miles) from the planet's major moon Triton.
Voyager 2 is now 117 million kilometers (73 million miles) from Neptune. The Neptune flyby will be Voyager 2's fourth and final planetary encounter before the spacecraft heads out of the solar system to explore interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 2 and its twin Voyager 1 have encountered Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 went on to fly by Uranus in January 1986 while Voyager 1 continues its trek out of the solar system.
Now 4.271 billion kilometers (2.654 billion miles) from Earth, Voyager 2 is so far away that data radioed at the speed of light (186,000 miles per second) take nearly four hours to reach Earth. Voyager's images are being recorded on the spacecraft's tape recorders and will be played back to Earth beginning Tuesday morning.
The Voyager project is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. Distance and velocities are updated in real-time. For a full 3D, immersive experience click on View Voyagers link below to launch the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app. View Voyager.
NASA's Voyager 2 is the second spacecraft to enter interstellar space. On Dec. 10, 2018, the spacecraft joined its twin - Voyager 1 - as the only human-made objects to enter the space between the stars. Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to study all four of the solar system's giant planets at close range. Voyager 2 discovered a 14th moon at ...
Voyager 2 is exploring interstellar space, the region between stars, since 2018. It visited Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, and is still sending scientific data through the Deep Space Network.
The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-45-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the Sun than Pluto. ... Status. Learn about Voyagers' mission status: where they are in the space, the time required to communicate ...
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech. UPDATE, Aug. 4, 2023: NASA has reestablished full communications with Voyager 2. The agency's Deep Space Network facility in Canberra, Australia, sent the equivalent of an interstellar "shout" more than 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) to Voyager 2, instructing the spacecraft to reorient itself and ...
News updates on Voyager 2's encounter with Neptune will be available to the public during late August on special telephone numbers from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Frequently updated reports on the spacecraft mission can be heard August 19-31 by phoning (900) 590-1234. Cost for each call on this 900 number is 45 cents for the first minute ...
The mission team expects Voyager 2 to remain on its planned trajectory during the quiet period. Voyager 1, which is almost 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, continues to operate normally. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and operates the Voyager spacecraft. The Voyager missions are a ...
Its primary mission was to study the outer solar system, and already, Voyager 2 has proved its status as a planetary pioneer. Equipped with several imaging instruments, the spacecraft is credited ...
Voyager 2. Heliocentric positions of the five interstellar probes (squares) and other bodies (circles) until 2020, with launch and flyby dates. Markers denote positions on 1 January of each year, with every fifth year labelled. Plot 1 is viewed from the north ecliptic pole, to scale. Plots 2 to 4 are third-angle projections at 20% scale.
NASA extended the mission so that Voyager 2 could visit Neptune and Uranus; it is still the only spacecraft ever to have encountered the ice giants. In 1990, NASA extended the mission again, this time with the goal of sending the probes outside the heliosphere. Voyager 1 reached the boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a ...
In about 40,000 years Voyager 2 will pass 1.7 light-years (9.7 trillion miles) from the star Ross 248, according to NASA JPL. The cosmic vagabond will continue its journey through interstellar ...
The mission team hatched a plan to send a command on Wednesday reorienting Voyager 2's antenna back to Earth, using a Deep Space Network radio dish in Canberra, Australia.. The chances of ...
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018. Mission Type.
Article. Forty-five years ago, the Voyager 2 spacecraft left Earth to begin an epic journey that continues to this day. The first of a pair of spacecraft, Voyager 2 lifted off on Aug. 20, 1977. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, manages the spacecraft on their missions to explore the outer planets and beyond.
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. Their mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn —and beyond to the outer planets of our solar system. This was a big task. No human-made object had ever attempted a journey like that before. The two spacecraft took tens of thousands of pictures of Jupiter and Saturn and their moons.
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
What are the Voyager missions? The Voyager program consists of two spacecraft: Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Voyager 2 was actually launched first, in August 1977, but Voyager 1 was sent on a faster trajectory when it launched about two weeks later. They are the only two functioning spacecraft currently in interstellar space, beyond the environment ...
NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft today entered the observatory phase of its flyby of Neptune, signaling the beginning of its final planetary encounter after nearly 12 years of exploring the outer solar system. Voyager mission controllers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., will now be tracking the spacecraft around the clock as ...
Mission operators report that Voyager 2 continues to be stable and that communications between Earth and the spacecraft are good. The spacecraft has resumed taking science data, and the science teams are now evaluating the health of the instruments following their brief shutoff. ... The team is now reviewing the status of the rest of the ...
Voyager 2 is also escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.3 AU per year, 48 degrees out of the ecliptic plane to the south. To check Voyager 1 and 2's current distance from the sun, visit the mission status page. Passage through the termination shock ended the termination shock phase and began the heliosheath exploration phase.
Their mission complete, the probes continued toward the edge of the heliosphere—a bubble of plasma, inflated by the Sun, that surrounds the Solar System. Voyager 1 exited the heliosphere in 2012, the first earthly object to reach interstellar space. Voyager 2 followed in 2018.
NASA/JPL-Caltech. Not bad for a 46-year-old spacecraft. NASA's Voyager 1 is back in business after a serious glitch in November put a stop to its science work for months. The probe is humanity ...
LEGEND: = R/T Command (Last chance or Contingency) = R/T Command (Scheduled) * = Result of R/T Command n = (where n = 1,2,3 ..) Special Note, see bottom of page. = Arrayed station. = BLF. D = Downlink only pass. H = High Power Transmitter. R = Array Reference Antenna.