

Everything You Need to Know About the Business Travel Tax Deduction
.jpeg)
Justin is an IRS Enrolled Agent, allowing him to represent taxpayers before the IRS. He loves helping freelancers and small business owners save on taxes. He is also an attorney and works part-time with the Keeper Tax team.
You don’t have to fly first class and stay at a fancy hotel to claim travel expense tax deductions. Conferences, worksite visits, and even a change of scenery can (sometimes) qualify as business travel.
What counts as business travel?
The IRS does have a few simple guidelines for determining what counts as business travel. Your trip has to be:
- Mostly business
- An “ordinary and necessary” expense
- Someplace far away from your “tax home”
What counts as "mostly business"?
The IRS will measure your time away in days. If you spend more days doing business activities than not, your trip is considered "mostly business". Your travel days are counted as work days.
Special rules for traveling abroad
If you are traveling abroad for business purposes, you trip counts as " entirely for business " as long as you spend less than 25% of your time on personal activities (like vacationing). Your travel days count as work days.
So say you you head off to Zurich for nine days. You've got a seven-day run of conference talks, client meetings, and the travel it takes to get you there. You then tack on two days skiing on the nearby slopes.
Good news: Your trip still counts as "entirely for business." That's because two out of nine days is less than 25%.
What is an “ordinary and necessary” expense?
“Ordinary and necessary” means that the trip:
- Makes sense given your industry, and
- Was taken for the purpose of carrying out business activities
If you have a choice between two conferences — one in your hometown, and one in London — the British one wouldn’t be an ordinary and necessary expense.
What is your tax home?
A taxpayer can deduct travel expenses anytime you are traveling away from home but depending on where you work the IRS definition of “home” can get complicated.
Your tax home is often — but not always — where you live with your family (what the IRS calls your "family home"). When it comes to defining it, there are two factors to consider:
- What's your main place of business, and
- How large is your tax home
What's your main place of business?
If your main place of business is somewhere other than your family home, your tax home will be the former — where you work, not where your family lives.
For example, say you:
- Live with your family in Chicago, but
- Work in Milwaukee during the week (where you stay in hotels and eat in restaurants)
Then your tax home is Milwaukee. That's your main place of business, even if you travel back to your family home every weekend.
How large is your tax home?
In most cases, your tax home is the entire city or general area where your main place of business is located.
The “entire city” is easy to define but “general area” gets a bit tricker. For example, if you live in a rural area, then your general area may span several counties during a regular work week.
Rules for business travel
Want to check if your trip is tax-deductible? Make sure it follows these rules set by the IRS.
1. Your trip should take you away from your home base
A good rule of thumb is 100 miles. That’s about a two hour drive, or any kind of plane ride. To be able to claim all the possible travel deductions, your trip should require you to sleep somewhere that isn’t your home.
2. You should be working regular hours
In general, that means eight hours a day of work-related activity.
It’s fine to take personal time in the evenings, and you can still take weekends off. But you can’t take a half-hour call from Disneyland and call it a business trip.
Here's an example. Let’s say you’re a real estate agent living in Chicago. You travel to an industry conference in Las Vegas. You go to the conference during the day, go out in the evenings, and then stay the weekend. That’s a business trip!
3. The trip should last less than a year
Once you’ve been somewhere for over a year, you’re essentially living there. However, traveling for six months at a time is fine!
For example, say you’re a freelancer on Upwork, living in Seattle. You go down to stay with your sister in San Diego for the winter to expand your client network, and you work regular hours while you’re there. That counts as business travel.
What about digital nomads?
With the rise of remote-first workplaces, many freelancers choose to take their work with them as they travel the globe. There are a couple of requirements these expats have to meet if they want to write off travel costs.
Requirement #1: A tax home
Digital nomads have to be able to claim a particular foreign city as a tax home if they want to write off any travel expenses. You don't have to be there all the time — but it should be your professional home base when you're abroad.
For example, say you've rent a room or a studio apartment in Prague for the year. You regularly call clients and finish projects from there. You still travel a lot, for both work and play. But Prague is your tax home, so you can write off travel expenses.
Requirement #2: Some work-related reason for traveling
As long as you've got a tax home and some work-related reason for traveling, these excursion count as business trips. Plausible reasons include meeting with local clients, or attending a local conference and then extending your stay.
However, if you’re a freelance software developer working from Thailand because you like the weather, that unfortunately doesn't count as business travel.
The travel expenses you can write off
As a rule of thumb, all travel-related expenses on a business trip are tax-deductible. You can also claim meals while traveling, but be careful with entertainment expenses (like going out for drinks!).
Here are some common travel-related write-offs you can take.
🛫 All transportation
Any transportation costs are a travel tax deduction. This includes traveling by airplane, train, bus, or car. Baggage fees are deductible, and so are Uber rides to and from the airport.
Just remember: if a client is comping your airfare, or if you booked your ticket with frequent flier miles, then it isn't deductible since your cost was $0.
If you rent a car to go on a business trip, that rental is tax-deductible. If you drive your own vehicle, you can either take actual costs or use the standard mileage deduction. There's more info on that in our guide to deducting car expenses .
Hotels, motels, Airbnb stays, sublets on Craigslist, even reimbursing a friend for crashing on their couch: all of these are tax-deductible lodging expenses.
🥡 Meals while traveling
If your trip has you staying overnight — or even crashing somewhere for a few hours before you can head back — you can write off food expenses. Grabbing a burger alone or a coffee at your airport terminal counts! Even groceries and takeout are tax-deductible.
One important thing to keep in mind: You can usually deduct 50% of your meal costs. For 2021 and 2022, meals you get at restaurants are 100% tax-deductible. Go to the grocery store, though, and you’re limited to the usual 50%.
{upsell_block}
🌐 Wi-Fi and communications
Wi-Fi — on a plane or at your hotel — is completely deductible when you’re traveling for work. This also goes for other communication expenses, like hotspots and international calls.
If you need to ship things as part of your trip — think conference booth materials or extra clothes — those expenses are also tax-deductible.
👔 Dry cleaning
Need to look your best on the trip? You can write off related expenses, like laundry charges.
{write_off_block}
Travel expenses you can't deduct
Some travel costs may seem like no-brainers, but they're not actually tax-deductible. Here are a couple of common ones to watch our for.
The cost of bringing your child or spouse
If you bring your child or spouse on a business trip, your travel expense deductions get a little trickier. In general, the cost of bring other people on a business trip is considered personal expense — which means it's not deductible.
You can only deduct travel expenses if your child or spouse:
- Is an employee,
- Has a bona fide business purpose for traveling with you, and
- Would otherwise be allowed to deduct the travel expense on their own
Some hotel bill charges
Staying in a hotel may be required for travel purposes. That's why the room charge and taxes are deductible.
Some additional charges, though, won't qualify. Here are some examples of fees that aren't tax-deductible:
- Gym or fitness center fees
- Movie rental fees
- Game rental fees
{email_capture}
Where to claim travel expenses when filing your taxes
If you are self-employed, you will claim all your income tax deduction on the Schedule C. This is part of the Form 1040 that self-employed people complete ever year.
What happens if your business deductions are disallowed?
If the IRS challenges your business deduction and they are disallowed, there are potential penalties. This can happen if:
- The deduction was not legitimate and shouldn't have been claimed in the first place, or
- The deduction was legitimate, but you don't have the documentation to support it
When does the penalty come into play?
The 20% penalty is not automatic. It only applies if it allowed you to pay substantially less taxes than you normally would. In most cases, the IRS considers “substantially less” to mean you paid at least 10% less.
In practice, you would only reach this 10% threshold if the IRS disqualified a significant number of your travel deductions.
How much is the penalty?
The penalty is normally 20% of the difference between what you should have paid and what you actually paid. You also have to make up the original difference.
In total, this means you will be paying 120% of your original tax obligation: your original obligation, plus 20% penalty.
.jpeg)
Justin W. Jones, EA, JD

Over 1M freelancers trust Keeper with their taxes
Keeper is the top-rated all-in-one business expense tracker, tax filing service, and personal accountant.

Sign up for Tax University
Get the tax info they should have taught us in school
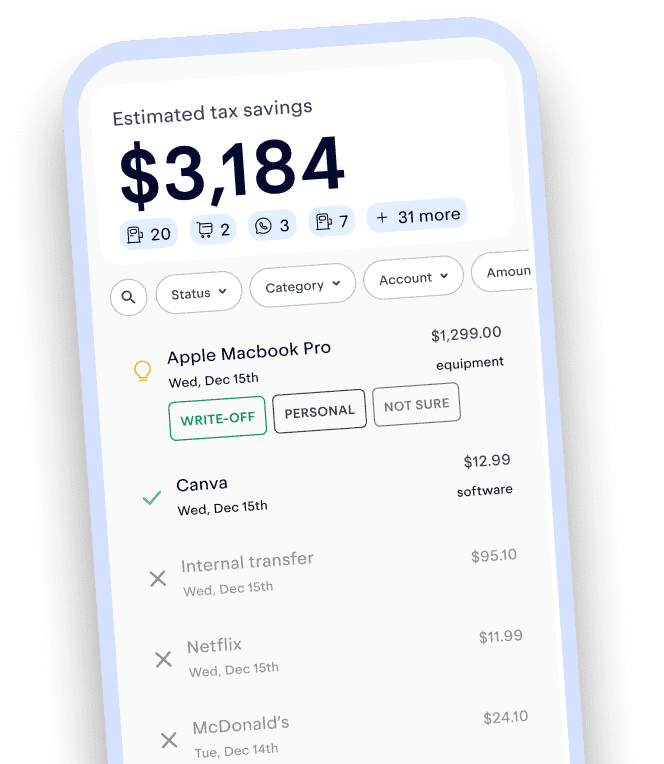
Expense tracking has never been easier
What tax write-offs can I claim?
At Keeper, we’re on a mission to help people overcome the complexity of taxes. We’ve provided this information for educational purposes, and it does not constitute tax, legal, or accounting advice. If you would like a tax expert to clarify it for you, feel free to sign up for Keeper. You may also email [email protected] with your questions.
Voted best tax app for freelancers
More Articles to Read
Free Tax Tools
1099 Tax Calculator
- Quarterly Tax Calculator
How Much Should I Set Aside for 1099 Taxes?
Keeper users have found write-offs worth
- Affiliate program
- Partnership program
- Tax bill calculator
- Tax rate calculator
- Tax deduction finder
- Quarterly tax calculator
- Ask an accountant
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Affiliate Program
- Partnership Program
- Tax Bill Calculator
- Tax Rate Calculator
- Tax Deduction Finder
- Ask an Accountant

How to Deduct Travel Expenses (with Examples)
Reviewed by
November 3, 2022
This article is Tax Professional approved
Good news: most of the regular costs of business travel are tax deductible.
Even better news: as long as the trip is primarily for business, you can tack on a few vacation days and still deduct the trip from your taxes (in good conscience).
I am the text that will be copied.
Even though we advise against exploiting this deduction, we do want you to understand how to leverage the process to save on your taxes, and get some R&R while you’re at it.
Follow the steps in this guide to exactly what qualifies as a travel expense, and how to not cross the line.
The travel needs to qualify as a “business trip”
Unfortunately, you can’t just jump on the next plane to the Bahamas and write the trip off as one giant business expense. To write off travel expenses, the IRS requires that the primary purpose of the trip needs to be for business purposes.
Here’s how to make sure your travel qualifies as a business trip.
1. You need to leave your tax home
Your tax home is the locale where your business is based. Traveling for work isn’t technically a “business trip” until you leave your tax home for longer than a normal work day, with the intention of doing business in another location.
2. Your trip must consist “mostly” of business
The IRS measures your time away in days. For a getaway to qualify as a business trip, you need to spend the majority of your trip doing business.
For example, say you go away for a week (seven days). You spend five days meeting with clients, and a couple of days lounging on the beach. That qualifies as business trip.
But if you spend three days meeting with clients, and four days on the beach? That’s a vacation. Luckily, the days that you travel to and from your location are counted as work days.
3. The trip needs to be an “ordinary and necessary” expense
“Ordinary and necessary ” is a term used by the IRS to designate expenses that are “ordinary” for a business, given the industry it’s in, and “necessary” for the sake of carrying out business activities.
If there are two virtually identical conferences taking place—one in Honolulu, the other in your hometown—you can’t write off an all-expense-paid trip to Hawaii.
Likewise, if you need to rent a car to get around, you’ll have trouble writing off the cost of a Range Rover if a Toyota Camry will get you there just as fast.
What qualifies as “ordinary and necessary” can seem like a gray area at times, and you may be tempted to fudge it. Our advice: err on the side of caution. if the IRS chooses to investigate and discovers you’ve claimed an expense that wasn’t necessary for conducting business, you could face serious penalties .
4. You need to plan the trip in advance
You can’t show up at Universal Studios , hand out business cards to everyone you meet in line for the roller coaster, call it “networking,” and deduct the cost of the trip from your taxes. A business trip needs to be planned in advance.
Before your trip, plan where you’ll be each day, when, and outline who you’ll spend it with. Document your plans in writing before you leave. If possible, email a copy to someone so it gets a timestamp. This helps prove that there was professional intent behind your trip.
The rules are different when you travel outside the United States
Business travel rules are slightly relaxed when you travel abroad.
If you travel outside the USA for more than a week (seven consecutive days, not counting the day you depart the United States):
You must spend at least 75% of your time outside of the country conducting business for the entire getaway to qualify as a business trip.
If you travel outside the USA for more than a week, but spend less than 75% of your time doing business, you can still deduct travel costs proportional to how much time you do spend working during the trip.
For example, say you go on an eight-day international trip. If you spend at least six days conducting business, you can deduct the entire cost of the trip as a business expense—because 6 is equivalent to 75% of your time away, which, remember, is the minimum you must spend on business in order for the entire trip to qualify as a deductible business expense.
But if you only spend four days out of the eight-day trip conducting business—or just 50% of your time away—you would only be able to deduct 50% of the cost of your travel expenses, because the trip no longer qualifies as entirely for business.
List of travel expenses
Here are some examples of business travel deductions you can claim:
- Plane, train, and bus tickets between your home and your business destination
- Baggage fees
- Laundry and dry cleaning during your trip
- Rental car costs
- Hotel and Airbnb costs
- 50% of eligible business meals
- 50% of meals while traveling to and from your destination
On a business trip, you can deduct 100% of the cost of travel to your destination, whether that’s a plane, train, or bus ticket. If you rent a car to get there, and to get around, that cost is deductible, too.
The cost of your lodging is tax deductible. You can also potentially deduct the cost of lodging on the days when you’re not conducting business, but it depends on how you schedule your trip. The trick is to wedge “vacation days” in between work days.
Here’s a sample itinerary to explain how this works:
Thursday: Fly to Durham, NC. Friday: Meet with clients. Saturday: Intermediate line dancing lessons. Sunday: Advanced line dancing lessons. Monday: Meet with clients. Tuesday: Fly home.
Thursday and Tuesday are travel days (remember: travel days on business trips count as work days). And Friday and Monday, you’ll be conducting business.
It wouldn’t make sense to fly home for the weekend (your non-work days), only to fly back into Durham for your business meetings on Monday morning.
So, since you’re technically staying in Durham on Saturday and Sunday, between the days when you’ll be conducting business, the total cost of your lodging on the trip is tax deductible, even if you aren’t actually doing any work on the weekend.
It’s not your fault that your client meetings are happening in Durham—the unofficial line dancing capital of America .
Meals and entertainment during your stay
Even on a business trip, you can only deduct a portion of the meal and entertainment expenses that specifically facilitate business. So, if you’re in Louisiana closing a deal over some alligator nuggets, you can write off 50% of the bill.
Just make sure you make a note on the receipt, or in your expense-tracking app , about the nature of the meeting you conducted—who you met with, when, and what you discussed.
On the other hand, if you’re sampling the local cuisine and there’s no clear business justification for doing so, you’ll have to pay for the meal out of your own pocket.
Meals and entertainment while you travel
While you are traveling to the destination where you’re doing business, the meals you eat along the way can be deducted by 50% as business expenses.
This could be your chance to sample local delicacies and write them off on your tax return. Just make sure your tastes aren’t too extravagant. Just like any deductible business expense, the meals must remain “ordinary and necessary” for conducting business.
How Bench can help
Surprised at the kinds of expenses that are tax-deductible? Travel expenses are just one of many unexpected deductible costs that can reduce your tax bill. But with messy or incomplete financials, you can miss these tax saving expenses and end up with a bigger bill than necessary.
Enter Bench, America’s largest bookkeeping service. With a Bench subscription, your team of bookkeepers imports every transaction from your bank, credit cards, and merchant processors, accurately categorizing each and reviewing for hidden tax deductions. We provide you with complete and up-to-date bookkeeping, guaranteeing that you won’t miss a single opportunity to save.
Want to talk taxes with a professional? With a premium subscription, you get access to unlimited, on-demand consultations with our tax professionals. They can help you identify deductions, find unexpected opportunities for savings, and ensure you’re paying the smallest possible tax bill. Learn more .
Bringing friends & family on a business trip
Don’t feel like spending the vacation portion of your business trip all alone? While you can’t directly deduct the expense of bringing friends and family on business trips, some costs can be offset indirectly.
Driving to your destination
Have three or four empty seats in your car? Feel free to fill them. As long as you’re traveling for business, and renting a vehicle is a “necessary and ordinary” expense, you can still deduct your business mileage or car rental costs even when others join you for the ride.
One exception: If you incur extra mileage or “unnecessary” rental costs because you bring your family along for the ride, the expense is no longer deductible because it isn’t “necessary or ordinary.”
For example, let’s say you had to rent an extra large van to bring your children on a business trip. If you wouldn’t have needed to rent the same vehicle to travel alone, the expense of the extra large van no longer qualifies as a business deduction.
Renting a place to stay
Similar to the driving expense, you can only deduct lodging equivalent to what you would use if you were travelling alone.
However, there is some flexibility. If you pay for lodging to accommodate you and your family, you can deduct the portion of lodging costs that is equivalent to what you would pay only for yourself .
For example, let’s say a hotel room for one person costs $100, but a hotel room that can accommodate your family costs $150. You can rent the $150 option and deduct $100 of the cost as a business expense—because $100 is how much you’d be paying if you were staying there alone.
This deduction has the potential to save you a lot of money on accommodation for your family. Just make sure you hold on to receipts and records that state the prices of different rooms, in case you need to justify the expense to the IRS
Heads up. When it comes to AirBnB, the lines get blurry. It’s easy to compare the cost of a hotel room with one bed to a hotel room with two beds. But when you’re comparing significantly different lodgings, with different owners—a pool house versus a condo, for example—it becomes hard to justify deductions. Sticking to “traditional” lodging like hotels and motels may help you avoid scrutiny during an audit. And when in doubt: ask your tax advisor.
So your trip is technically a vacation? You can still claim any business-related expenses
The moment your getaway crosses the line from “business trip” to “vacation” (e.g. you spend more days toasting your buns than closing deals) you can no longer deduct business travel expenses.
Generally, a “vacation” is:
- A trip where you don’t spend the majority of your days doing business
- A business trip you can’t back up with correct documentation
However, you can still deduct regular business-related expenses if you happen to conduct business while you’re on vacay.
For example, say you visit Portland for fun, and one of your clients also lives in that city. You have a lunch meeting with your client while you’re in town. Because the lunch is business related, you can write off 50% of the cost of the meal, the same way you would any other business meal and entertainment expense . Just make sure you keep the receipt.
Meanwhile, the other “vacation” related expenses that made it possible to meet with this client in person—plane tickets to Portland, vehicle rental so you could drive around the city—cannot be deducted; the trip is still a vacation.
If your business travel is with your own vehicle
There are two ways to deduct business travel expenses when you’re using your own vehicle.
- Actual expenses method
- Standard mileage rate method
Actual expenses is where you total up the actual cost associated with using your vehicle (gas, insurance, new tires, parking fees, parking tickets while visiting a client etc.) and multiply it by the percentage of time you used it for business. If it was 50% for business during the tax year, you’d multiply your total car costs by 50%, and that’d be the amount you deduct.
Standard mileage is where you keep track of the business miles you drove during the tax year, and then you claim the standard mileage rate .
The cost of breaking the rules
Don’t bother trying to claim a business trip unless you have the paperwork to back it up. Use an app like Expensify to track business expenditure (especially when you travel for work) and master the art of small business recordkeeping .
If you claim eligible write offs and maintain proper documentation, you should have all of the records you need to justify your deductions during a tax audit.
Speaking of which, if your business is flagged to be audited, the IRS will make it a goal to notify you by mail as soon as possible after your filing. Usually, this is within two years of the date for which you’ve filed. However, the IRS reserves the right to go as far back as six years.
Tax penalties for disallowed business expense deductions
If you’re caught claiming a deduction you don’t qualify for, which helped you pay substantially less income tax than you should have, you’ll be penalized. In this case, “substantially less” means the equivalent of a difference of 10% of what you should have paid, or $5,000—whichever amount is higher.
The penalty is typically 20% of the difference between what you should have paid and what you actually paid in income tax. This is on top of making up the difference.
Ultimately, you’re paying back 120% of what you cheated off the IRS.
If you’re slightly confused at this point, don’t stress. Here’s an example to show you how this works:
Suppose you would normally pay $30,000 income tax. But because of a deduction you claimed, you only pay $29,000 income tax.
If the IRS determines that the deduction you claimed is illegitimate, you’ll have to pay the IRS $1200. That’s $1000 to make up the difference, and $200 for the penalty.
Form 8275 can help you avoid tax penalties
If you think a tax deduction may be challenged by the IRS, there’s a way you can file it while avoiding any chance of being penalized.
File Form 8275 along with your tax return. This form gives you the chance to highlight and explain the deduction in detail.
In the event you’re audited and the deduction you’ve listed on Form 8275 turns out to be illegitimate, you’ll still have to pay the difference to make up for what you should have paid in income tax—but you’ll be saved the 20% penalty.
Unfortunately, filing Form 8275 doesn’t reduce your chances of being audited.
Where to claim travel expenses
If you’re self-employed, you’ll claim travel expenses on Schedule C , which is part of Form 1040.
When it comes to taking advantage of the tax write-offs we’ve discussed in this article—or any tax write-offs, for that matter—the support of a professional bookkeeping team and a trusted CPA is essential.
Accurate financial statements will help you understand cash flow and track deductible expenses. And beyond filing your taxes, a CPA can spot deductions you may have overlooked, and represent you during a tax audit.
Learn more about how to find, hire, and work with an accountant . And when you’re ready to outsource your bookkeeping, try Bench .
Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
Get a regular dose of educational guides and resources curated from the experts at Bench to help you confidently make the right decisions to grow your business. No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

Small Business Trends
10 tax deductions for travel expenses (2023 tax year).

Tax season can be stressful, especially if you’re unaware of the tax deductions available to you. If you’ve traveled for work throughout the year, there are a number of deductions for travel expenses that can help reduce your taxable income in 2024 and save you money.
Read on for 10 tax deductions for travel expenses in the 2023 tax year.
Are business travel expenses tax deductible?
Business travel expenses incurred while away from your home and principal place of business are tax deductible. These expenses may include transportation costs, baggage fees, car rentals, taxis, shuttles, lodging, tips, and fees.
It is important to keep receipts and records of the actual expenses for tax purposes and deduct the actual cost.
What kinds of travel expenses are tax deductible?
To deduct business travel expenses, they must meet certain criteria set by the IRS.
The following are the primary requirements that a travel expense must meet in order to be eligible for a tax deduction:
- Ordinary and necessary expenses: The expense must be common and accepted in the trade or business and be helpful and appropriate for the business.
- Directly related to trade or business: The expense must be directly related to the trade or business and not of a personal nature.
- Away from home overnight: The expense must have been incurred while away from both the taxpayer’s home and the location of their main place of business (tax home) overnight.
- Proper documentation: The taxpayer must keep proper documentation, such as receipts and records, of the expenses incurred.
Eligible Business Travel Tax Deductions
Business travel expenses can quickly add up. Fortunately, many of these expenses are tax deductible for businesses and business owners.
Here is an overview of the types of business travel expenses that are eligible for tax deductions in the United States:
Accommodation Expenses
Accommodation expenses can be claimed as tax deductions on business trips. This includes lodging at hotels, rental costs of vacation homes, and other lodgings while traveling.
Meal Expenses
Food and beverage expenses incurred on a business trip may be deducted from taxes. This includes meals while traveling and meals during meetings with clients or contractors.
Transportation Expenses
Deducting business travel expenses incurred while on a business trip may also be claimed.
This includes flights, train tickets, car rentals, gas for personal vehicles used for the business trip, toll fees, parking fees, taxi rides to and from the airport or train station, and more.
Expenses of operating and maintaining a car
Expenses of operating and maintaining a car used for business travel may also be claimed as tax deductions.
This includes fuel, insurance, registration costs, actual costs of repairs, and maintenance fees. Fees paid to hire a chauffeur or driver may also be deducted.
Operating and maintaining house-trailers
Operating and maintaining house trailers for business travel may be eligible for tax deductions, provided that the use of such trailers is considered “ordinary” and “necessary” for your business.
This includes any costs associated with renting or owning a trailer, such as fuel costs, repair and maintenance fees, insurance, and registration charges.
Internet and phone expenses
Internet and phone expenses associated with business travel can also be claimed as tax deductions. This includes the cost of any internet service, such as Wi-Fi or data plans, and phone services, such as roaming charges or international calls.
Any communication devices purchased for business use, such as smartphones and laptops, may also be eligible for tax deductions.
Computer rental fees
Rental fees for computers and other computing devices used during business travel may also be deducted from taxes. This includes any applicable charges for purchasing, leasing, or renting a computer, as well as the related costs of connecting to the Internet and other digital services.
All such expenses must be necessary for the success of the business trip in order to qualify for a tax deduction.
Travel supplies
Travel supplies, such as suitcases and other bags, are also eligible for tax deductions when used for business travel. Any costs associated with keeping the items protected, such as locks and tracking devices, can also be claimed as tax deductions.
Other necessary supplies, such as office equipment or reference materials, may also be eligible for deductions.
Conference fees and events
Conference fees and events related to business travel may also be eligible for tax deductions. This includes fees associated with attending a conference, such as registration, accommodation, and meals.
Any costs related to the organization of business events, such as venue hire and catering, may also be claimed as tax deductions.
Cleaning and laundry expenses
Business travel expenses associated with cleaning and laundry may also be claimed as tax deductions. This includes a portion of the cost of hotel and motel services, such as cleaning fees charged for laundering clothing, as well as any other reasonable expenses related to keeping clean clothes while traveling away from home.
Ineligible Travel Expenses Deductions
When it comes to business expenses and taxes, not all travel expenses are created equal. Some expenses are considered “Ineligible Travel Expenses Deductions” and cannot be claimed as deductions on your income taxes.
Here is a list of common travel expenses that cannot be deducted, with a brief explanation of each:
- Personal Vacations: Expenses incurred during a personal vacation are not deductible, even if you conduct some business while on the trip. In addition, expenses related to personal pleasure or recreation activities are also not eligible for deductions.
- Gifts: Gifts purchased for business reasons during travel are not deductible, even if the gifts are intended to benefit the business in some way.
- Commuting: The cost of commuting between your home and regular place of business is not considered a deductible expense.
- Meals: Meals consumed while traveling on business can only be partially deducted, with certain limits on the amount.
- Lodging: The cost of lodging is a deductible expense, but only if it is deemed reasonable and necessary for the business trip.
- Entertainment: Entertainment expenses, such as tickets to a show or sporting event, are not deductible, even if they are associated with a business trip.
How to Deduct Travel Expenses
To deduct travel expenses from income taxes, the expenses must be considered ordinary and necessary for the operation of the business. This means the expenses must be common and accepted business activities in your industry, and they must be helpful, appropriate, and for business purposes.
In order to claim travel expenses as a deduction, they must be itemized on Form 2106 for employees or Schedule C for self-employed individuals.
How much can you deduct for travel expenses?
While on a business trip, the full cost of transportation to your destination, whether it’s by plane, train, or bus, is eligible for deduction.
Similarly, if you rent a car for transportation to and around your destination, the cost of the rental is also deductible. For food expenses incurred during a business trip, only 50% of the cost is eligible for a write-off.
How do you prove your tax deductions for travel expenses?
To prove your tax deductions for travel expenses, you should maintain accurate records such as receipts, invoices, and any other supporting documentation that shows the amount and purpose of the expenses.
Some of the documentation you may need to provide include receipts for transportation, lodging, and meals, a detailed itinerary or schedule of the trip, an explanation of the bona fide business purpose of the trip, or proof of payment for all expenses.
What are the penalties for deducting a disallowed business expense?
Deducting a disallowed business expense can result in accuracy-related penalties of 20% of the underpayment, interest charges, re-assessment of the tax return, and in severe cases, fines and imprisonment for tax fraud. To avoid these penalties, it’s important to understand expense deduction rules and keep accurate records.
Can you deduct travel expenses when you bring family or friends on a business trip?
It is not usually possible to deduct the expenses of taking family or friends on a business trip. However, if these individuals provided value to the company, it may be possible. It’s advisable to speak with an accountant or financial expert before claiming any deductions related to bringing family and friends on a business trip.
Can you deduct business-related expenses incurred while on vacation?
Expenses incurred while on a personal vacation are not deductible, even if some business is conducted during the trip. To be eligible for a deduction, the primary purpose of the trip must be for business and the expenses must be directly related to conducting that business.
Can you claim a travel expenses tax deduction for employees?
Employers can deduct employee travel expenses if they are ordinary, necessary, and adequately documented. The expenses must also be reported as taxable income on the employee’s W-2.
What are the limits on deducting the cost of meals during business travel?
The IRS permits a 50% deduction of meal and hotel expenses for business travelers that are reasonable and not lavish. If no meal expenses are incurred, $5.00 daily can be deducted for incidental expenses. The federal meals and incidental expense per diem rate is what determines the standard meal allowance.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE:
- nondeductible expenses
- standard deduction amounts
- Hipmunk small business
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
- Credits and deductions
- Business expenses
Can I deduct travel expenses?
If you’re self-employed or own a business , you can deduct work-related travel expenses, including vehicles, airfare, lodging, and meals. The expenses must be ordinary and necessary.
For vehicle expenses, you can choose between the standard mileage rate or the actual cost method where you track what you paid for gas and maintenance.
You can generally only claim 50% of the cost of your meals while on business-related travel away from your tax home, provided your trip requires an overnight stay. You can also deduct 50% of the cost of meals for entertaining clients (regardless of location), but due to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (TCJA), you can no longer deduct entertainment expenses in tax years 2018 through 2025. In 2021 and 2022, the law allows a deduction for 100% of your cost of food and beverages that are provided by a restaurant, instead of the usual 50% deduction.
On the other hand, employees can no longer deduct out-of-pocket travel costs in tax years 2018 through 2025 per the TCJA (this does not apply to Armed Forces reservists, qualified performing artists, fee-basis state or local government officials, and employees with impairment-related work expenses). Prior to the tax rule change, employees could claim 50% of the cost of unreimbursed meals while on business-related travel away from their tax home if the trip required an overnight stay, as well as other unreimbursed job-related travel costs. These expenses were handled as a 2% miscellaneous itemized deduction.
Related Information:
- Can I deduct medical mileage and travel?
- Can I deduct my moving expenses?
- Can I deduct rent?
- Can I deduct mileage?
- Can employees deduct commuting expenses like gas, mileage, fares, and tolls?
Was this helpful?
Found what you need?
Already have an account? Sign In

How to find deductions for travel expenses
With more consultants and business travelers hitting the road for business travel, it's time for a brush-up on what expenses are eligible for tax deduction while they're away. If you're unsure about what qualifies, read on.
Find out more about Business Taxes

by Grace L. Williams
Grace L. Williams is a journalist. Her areas of expertise include small business, career, personal finance, and inve...
Read more...
Updated on: October 27, 2023 · 15min read
Key takeaways
What is business travel or a business trip, what is a business-related travel expense, what business travel expenses are tax deductible, are there other tax deductions for travel expenses, tracking expenses on your business trip, importance of documentation, combining business and personal travel, special considerations for self-employed individuals, getting help with tax deductions for travel expenses, frequently asked questions.
Business travel is back after the pandemic, and with that increase comes the age-old question every business traveler must ask at least once: "What can I deduct as a business expense while I'm on the road?"
You've likely heard the term "write-off" somewhere and may have used it somewhere within your business circles. But what exactly is it? You might wonder if you can book first-class travel or five-star lodging and eat in fancy dining establishments and then submit them as business write-offs. The short, overarching rule for those specifics is no, you probably cannot, but there is more to eligible business travel expenses than that.

So before you book travel arrangements on your credit card (hopefully a designated business credit card), read on for more information about making expensing your business travel less stressful.
- Understand IRS guidelines for deductible travel expenses to maximize tax savings.
- Proper documentation is essential for claiming deductions, including meals and entertainment, with a clear business justification.
- Utilize tax professionals and leverage technology to ensure accurate deductions, compliance with laws, and maximum savings on travel expense deductions.

Simply put, business travel or a business trip is defined as any travel conducted that is business-related. To be considered eligible as a business trip, the travel itself must meet the following criteria:
- The trip must be conducted for legitimate business purposes, not as leisure time, vacation, or personal purposes.
- The trip must occur outside the bounds of a regular commute to and from work (or the main place of business) and home.
If the trip meets these criteria, it falls under the category of a business trip. It also means that you can deduct travel expenses whether you are a business owner sending an employee on your behalf or a self-employed individual.
To better understand business-related travel expenses, it's a good idea to look at overall business expenses. A business expense is incurred as part of the regular day-to-day operations of your employer (or for you if you are a self-employed individual) to conduct the business. Under current Internal Revenue Service (IRS) laws, special rules allow portions of business expenses to be deducted from the overall business income. These expenses are considered tax deductible, which means they are applied before any taxes are. The umbrella term "write-off" comes from this business tax deduction category.
In business, eligible tax deductions can have a significant impact. Being able to deduct expenses can often reduce the total overall taxable income . Cumulatively, tax-deductible expenses will likely reduce the total bill when it is time to file your tax return.
A deductible business travel expense is one that you or an employee incur during travel directly related to conducting business. In both instances (a business expense or a business travel expense), it is essential to ensure the expense falls under the category of being for bona fide business purposes. This means that deducting the travel expenses must be something genuinely related to conducting or doing a bona fide business purpose. If it is, its cost can be written off as part of business or business travel-related expenses. It applies to self-employed individuals or employees traveling for an employer or business owner.
So what exactly can you expense?
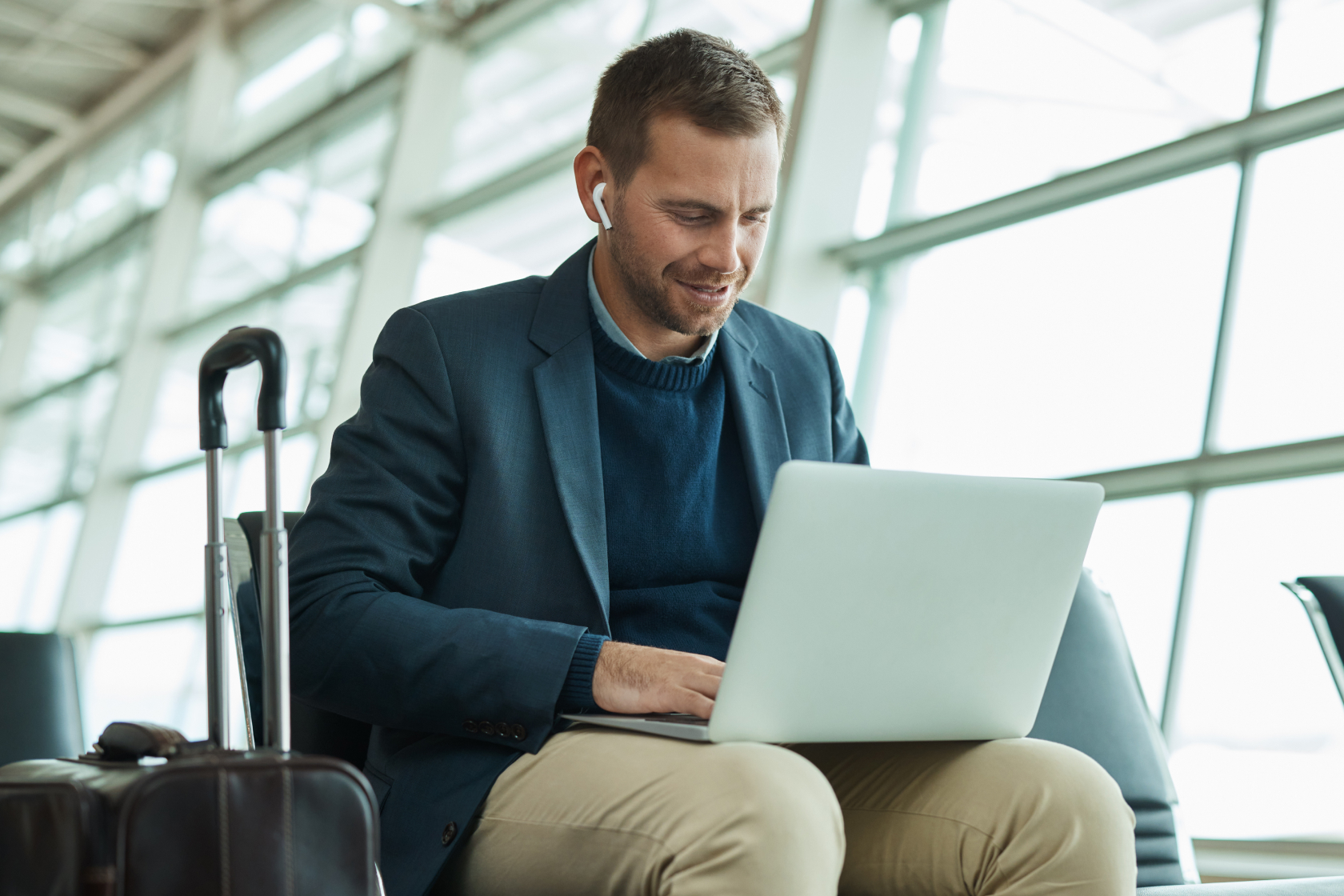

First and foremost, consider the basics, or the "Big 3" in business travel. Essentials here include these three actual expenses: costs related to how you will get to your destination (travel), where you will stay (lodging), and what you will eat and drink when you are there and in transit. Each category within the Big Three can be an eligible travel expense and, therefore, a tax write-off, but they come with some criteria worth exploring.
Transportation expenses: If you plan to travel by car, and you will either use a vehicle you lease long-term or your car, there are two choices related to how this mode of transportation might be expensed. One choice is known as the “ standard mileage rate ." Under current IRS allowances, the standard mileage rate deduction for self-employed individuals and employees is 65.5 cents per mile for business-related travel. The rate per mile would apply to any driving conducted to or from the business destination. It would also apply to any driving conducted while you are at the destination if it is business-related. For instance, once at the destination, if driving must be done to run errands, those miles can be added to the total mileage count.
The other vehicle expense option for a business trip is to itemize the individual expenses. Eligible business costs, in this instance, include the lease, insurance, fuel, costs related to the upkeep and maintenance of the vehicle, such as oil changes or tune-ups, and any major repairs on the vehicle, such as fixing a flat tire.
If you are renting a car as part of your transportation expenses and it falls under the ordinary and necessary business travel expense category, the cost to rent a car would qualify as an eligible business expense. Other vehicle-related expenses that qualify for travel deductions include tolls and parking fees.
Actual expenses method
The actual expenses method involves calculating the total cost of vehicle use and multiplying it by the percentage used for business purposes. This includes:
- Depreciation
- Garage rent
- Vehicle registration fees
- Lease payments
To calculate the percentage of business use, divide the total business miles driven by the total miles driven in the year. While this method can lead to larger deductions, it requires detailed record-keeping and more complex calculations than the standard mileage method.
Standard mileage rate
The standard mileage rate allows you to claim a fixed rate per mile driven for business purposes, plus parking fees and tolls. The standard mileage rate for business in the United States is 65.5 cents per mile. The IRS determines This rate annually based on a study of the fixed and variable costs of operating a vehicle for business reasons, such as gas, maintenance, and depreciation.
This method can be used for self-employment, business-related travel, or when using a vehicle for work as an independent contractor. However, personal use of the vehicle is not eligible for this deduction.
Ticketed travel: For ticketed travel, like flights or trips by train, the cost of your ticket can be expensed as a travel deduction if your class fare qualifies as an eligible and reasonable expense. This means that while you likely won't be able to deduct first-class fare, you can deduct what is known as the ordinary and necessary expense related to the fare, which covers classes such as economy. You can also expense costs incurred while en route, such as baggage fees. And, if you are waiting at an airport or train station, any meal costs, snacks, or drinks would also qualify as business-related expenses.
Meal expenses and entertainment: Business meals cut eligible business expenses but with some stipulations, including the standard meal allowance. While current IRS laws permit for up to 50% of a business meal to be deducted, like ticketed travel, rental cars, and other business-travel-related costs, the meal must fall under an ordinary and necessary expense to be eligible as a tax-deductible business expense. If you are tempted to go all out and splurge on your dining, you might find that it is not an eligible business travel expense.
But changes have been made to the entertainment category. While entertainment used to be an allowed business expense, it is sometimes no longer eligible to claim tax deductions. This means that if you expect to take clients out as part of client meetings or conduct business, be sure to read the fine print since you might discover you cannot claim entertainment as a legitimate business expense.
Lodging expenses: Business travelers must consider where they will sleep while away. To be considered eligible as a business expense, the location of your stay must be outside of the main place of business and require overnight accommodation. Notably, in this expense category, IRS rules stipulate that for it to be an eligible business expense, the lodging cannot fall into the extravagant or considered recreational category.
Remember: With each of the "Big 3" and all other related business expenses to be deducted, the expenses must be ordinary and fall under the category of reasonable business expenses. If you opt for pricey vehicles, tickets, meals, and rooms instead of the available moderately-priced alternatives, you risk losing eligibility as legitimate business expenses.
There are some other expenses anyone traveling for business should consider submitting as tax-deductible expenses.
Event fees: These could come into play if you travel to an event such as a conference, convention, or trade show. In addition to the Big 3, certain expenses related to attending these events would qualify as eligible business travel expenses. The expenses are deductible if the event has an entry or booth fee. While you are there, if you attend workshops, lectures, or courses that require materials such as a workbook or registration, these would also be eligible as tax-deductible travel expenses. And, if you are running a booth or table at an event and need materials or supplies, the cost to purchase them would also qualify as legitimate business expenses.
Incidental expenses: Any reasonable additional expenses you incur while traveling for a business activity can be considered incidental expenses. For instance, if you incur expenses on ground transportation, a rideshare fee, taxi fare, or a subway ticket qualify as business expenses. Laundry and dry cleaning services are also eligible business activities. In addition, indirect expenses like office supplies can be eligible business expenses.
Organization before, during, and after the business trip will help you avoid potential pitfalls or headaches when filing expenses or taxes. From the outset, one great way to separate your business trips and expenses from personal expenses is to have a single credit or debit card that you designate for business use only. This de facto "corporate" card will come in handy and be a best friend on the road since it automatically creates a tally of itemized expenses courtesy of the real-time accounting and monthly statements that come with it.
Beyond the lone card designated for business expenses, your meticulous record-keeping will greatly help you when it's time to account for everything. If you don't want to use a third-party software program or expense-tracking app to track your expenses, a simple solution is to use a basic spreadsheet that tracks the date, the reason for the expense, and the cost. To set this up, once you have incurred an expense, note it down using the aforementioned basic information.
While on the trip, another simple organizational tool is keeping all receipts and other applicable hard-copy records and materials in one designated place. A pouch or envelope will work fine as the place to keep these items. Make sure you read the receipt or record, and if it does not have information such as the name and address of the business, write it on the back before you stash it away. Finally, if a receipt is for something like a business lunch, ensure the date and information about the place of business are on the receipt. Then, write the name of the person you shared your time with and the reason for meeting up somewhere on the receipt.
Claiming travel expense deductions requires proper documentation. This includes retaining receipts and records for all expenses incurred during your business trip. For meals and entertainment expenses, you'll need to note the nature of the meeting, including who you met with, when, and the topics discussed.
It's worth noting that lodging expenses on non-business days may still be eligible for deductions if specific strategies are employed, such as incorporating “vacation days" between workdays. In such cases, the total cost of lodging for the trip can still be tax deductible even when no work is taking place on the weekend. However, meals and entertainment expenses without a clear business justification won't be deductible and must be paid personally.

Allocating expenses between business and personal activities is essential to ensure accurate deduction claims. Expenses must be allocated based on actual usage, so the non-business portion of the expenses may be viewed as taxable income if paid by the individual or company.
To accurately allocate expenses between business and personal activities for tax deductions, follow these steps:
- Track usage for a period of time.
- Determine the allocation by proportionally dividing the expenses based on the amount of business and personal use.
- Maintain proper records to support the allocation.
When combining business and personal travel, careful allocation of expenses and adherence to specific rules is important. Expenses related to the personal nature of the trip cannot be deducted; only those incurred for business purposes can be.
If traveling abroad, you must spend a minimum of 25% of your time conducting business to qualify as a business trip and claim travel expense deductions. If you conduct business for less than 25% of the time while on a trip, you can still deduct travel costs. This deduction must be proportional to the amount of time spent on business.
Rules for international travel
International travel has additional rules to consider when claiming travel expense deductions. As mentioned, you must spend at least 25% of your time abroad conducting business to claim travel-expense deductions.
If you use 25% or less of your trip for business purposes, you can deduct related travel costs in proportion to the time spent on work. This can help to make international business trips more affordable. For example, if 40% of your time is spent on business activities, you can claim the entire cost of airfare as a business expense.
Self-employed individuals should be aware of special considerations when deducting travel expenses, such as home office deductions and computer rental fees. Understanding these unique aspects can help self-employed individuals maximize their tax savings and ensure compliance with tax laws, especially regarding their tax home.
Home office considerations
Home office deductions can be claimed if the office is the primary place of business and is regularly used for business purposes. The IRS has specific guidelines for the regular use of a home office for business purposes, such as the office being used exclusively and regularly for business purposes.
To claim a home office deduction, you can use the simplified method the IRS provides. Here's how it works:
- Multiply the allowable square footage of your home office by the prescribed rate of $5 per square foot.
- The maximum allowable square footage is 300 square feet, so the maximum deduction you can claim using this method is $1,500 annually.
- The simplified option allows for a standard deduction without the need for detailed record-keeping.
Deducting computer rental fees
Computer rental fees can be deducted if the equipment is used for business during the trip. The full cost of the computer rental may be deducted as a business expense.
To claim a deduction for computer rental fees from business travel expenses, you must provide relevant documentation demonstrating the rental fees paid, such as receipts or invoices. Proper record-keeping is essential to support your deduction and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Leveraging technology
Technology, such as expense tracking apps and online bookkeeping services, can simplify record-keeping and documentation for travel expense deductions. These tools can help you track and categorize expenses, making it easier to identify and compute deductible expenses for tax purposes.
Expense tracking applications can:
- Generate reports and summaries of travel expenses
- Be beneficial for tax filing and auditing purposes
- Save time and effort in tracking and documenting your travel expenses
- Ensure accurate deductions and compliance with tax laws
Leveraging technology in expense tracking can be a valuable tool for managing your finances.
Sometimes, you might need more help. This guide provides basic questions about business travel deductions and expenses. Still, you are not alone if you have other questions about what might qualify as a tax-deductible business expense. There are experts at LegalZoom who can answer specific questions and better advise you about both business expenses and business travel-related expenses.
You might have questions about whether specific costs related to your business qualify as ordinary and necessary expenses or wonder if percentages of a certain expense or the entire cost can be completely deductible. Additionally, professionals in the know about things like a specific tax home can help you sort out concerns related to your business so that you can always claim the proper travel expenses. For any consultant looking to get back into the swing of travel, help and practical tips are just a click away.
Understanding and maximizing travel expense deductions can save you significant money on your tax return. By familiarizing yourself with the requirements, maintaining proper documentation, and leveraging the expertise of tax professionals and technology, you can ensure accurate deductions, compliance with tax laws, and, ultimately, keep more money in your pocket.
What kind of travel expenses are tax deductible?
Tax deductible travel expenses include airfare, train/bus fares, taxi rides between an airport or station and a hotel, or from the hotel to a work location.
What are the three requirements for a traveling expense deduction?
To qualify for a traveling expense deduction, you must have a “business trip," leave your tax home, have most of the trip business-related, and plan the trip in advance.
How do I prove travel expenses for taxes?
To prove business travel expenses for taxes, use credit card slips with notes on the business purpose made at the time of incurring the expense.
Are daily travel expenses tax deductible?
Daily travel expenses from your home to a regular place of business are not tax deductible. However, you can deduct transport expenses when traveling between your home and a temporary work location outside the metropolitan area where you live and normally work. Additionally, ordinary and necessary travel expenses incurred while away from your home and your main place of business can be deducted.
How do I allocate expenses between business and personal activities during a combined trip?
Allocate expenses proportionally based on the amount of business and personal use for a period of time, and maintain proper records to support deductions.
You may also like

What does 'inc.' mean in a company name?
'Inc.' in a company name means the business is incorporated, but what does that entail, exactly? Here's everything you need to know about incorporating your business.
October 9, 2023 · 10min read

How to get an LLC and start a limited liability company
Considering an LLC for your business? The application process isn't complicated, but to apply for an LLC, you'll have to do some homework first.
March 21, 2024 · 11min read

What is a power of attorney (POA)? A comprehensive guide
Setting up a power of attorney to make your decisions when you can't is a smart thing to do because you never know when you'll need help from someone you trust.
February 8, 2024 · 15min read
Here Are the Work Expenses You Can Deduct on Your Tax Return This Year
Take advantage of these deductions to pay fewer taxes and score a bigger refund when you file your tax return.

The biggest deductions for work expenses are restricted to self-employed people and small business owners, but some full-time employees can get a few tax breaks, too.
You have one day left (though some states get deadline extensions due to severe weather) to file your tax returns . If you're just beginning the filing process, you might be wondering which work expenses are deductible. The simplest answer is it depends on the sort of work you do. The biggest deductions for work expenses are restricted to self-employed people and small business owners, but some full-time employees can get a few tax breaks too.

If you're one of the many taxpayers who pivoted to remote work or started working for yourself, you can take advantage of a few deductions this tax season from the work expenses you incurred during 2022.
Learn which expenses you can deduct from your taxable income if you're an employee or self-employed and how to claim them when you file your tax return this year.
For more, here are the best free tax filing options for 2023 , why you should create an online IRS account before you file your taxes and how to track your tax refund .
Which work expenses can W-2 employees deduct from their taxes?
Unfortunately for W-2 employees, the Tax Cut and Jobs Act of 2017 eliminated almost all tax deductions for unreimbursed employee expenses.
Only a few specific types of W-2 employees can still claim work expenses:
- Reservists in the armed forces
- Qualified performing artists
- Fee-basis state or local government officials
- Employees with work expenses related to an impairment
Those eligible taxpayers can report and claim their unreimbursed work expenses using Form 2106 , "Employee Business Expenses." These expenses can include vehicle costs, travel costs, work clothes and meals, but the IRS has stringent rules for documentation -- taxpayers must "prove the time, place, business purpose, business relationship (for gifts), and amounts of these expenses," the instructions to the form explain . Receipts must be provided for all lodging expenses or for any work expense of $75 or greater.
Eligible educators working in kindergarten through 12th grade can also deduct some of their work expenses, including professional development and classroom supplies. Each eligible teacher can deduct up to $300 of unreimbursed expenses on line 11 of Form 1040 Schedule 1 .
Eligible W-2 employees need to itemize to deduct work expenses
If you are an eligible W-2 employee, you can only deduct work expenses on your taxes if you decide to itemize your deductions. Your decision will depend on whether the total of your itemized deductions is greater than the standard deduction -- $12,950 for single filers, $19,400 for head-of-household filers and $25,900 for married people filing a joint return.
Along with eligible work expenses, personal itemized deductions can include mortgage interest, retirement contributions, property taxes, charitable donations, medical expenses and student loan interest.
Most Americans choose the standard deduction when filing their taxes. It is a simpler route than itemizing your deductions, which requires further proof of expenses and receipts.
The IRS encourages taxpayers to itemize when your "allowable itemized deductions are greater than the standard deduction or you can't use the standard deduction."
Self-employed and business owners can deduct work expenses even if they take the standard deduction
If you're self-employed or own a business, you can deduct business expenses on your taxes regardless of whether you take the standard deduction or itemize.
"Business expenses are known as above the line deductions which are available regardless of the choice to itemize. Consequently, a taxpayer could have substantial business expenses and still claim the standard deduction," Eric Bronnenkant , CPA/CFP and Head of Tax at online financial advisor Betterment , told CNET in an email.
On Schedule C , freelancers and business owners will report their business income and work expenses. Bronnenkant said taxpayers should familiarize themselves with the form prior to filing.
"The IRS allows businesses to deduct ordinary and necessary business expenses. The key question: Was this an ordinary and necessary expense for the business activity? Notably, this excludes any personal expenses," Bronnenkant said.
What is the home-office tax deduction and who can claim it?
The home office deduction is a major work expense deduction that self-employed people can claim. If you use your home office space for work purposes -- and work purposes only -- you may be eligible for the home office deduction.
The home office deduction has strict requirements you must follow to be eligible. First, you will need to be self-employed to take advantage of this deduction, meaning that you receive a 1099 form for self-employed workers and not a W-2 form for employees. Taxpayers must "exclusively and regularly" use a part of their home for work purposes, the IRS says. So your desk inside your bedroom doesn't count, and remote employees working from home do not qualify.
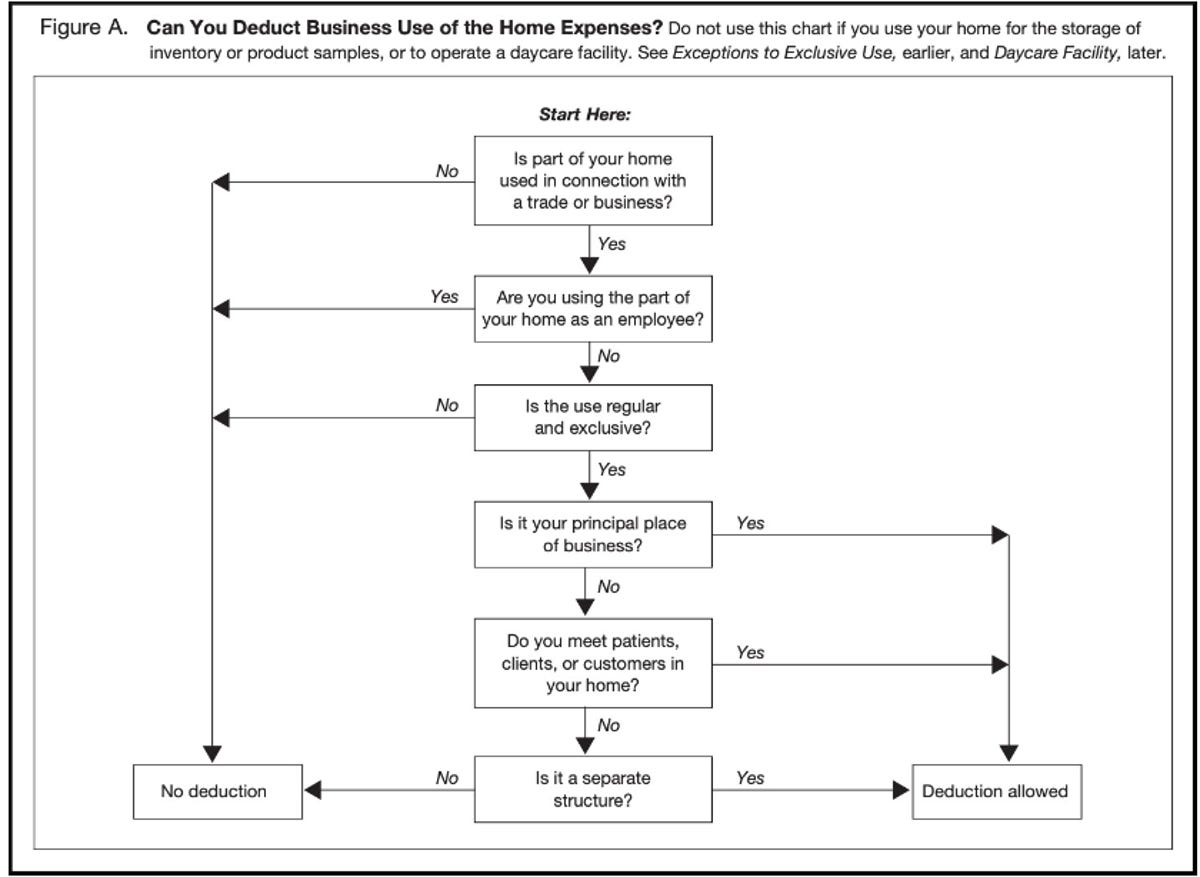
Use this chart to figure out whether your home expenses qualify for a deduction.
If you are eligible for the home-office deduction, there are two ways to calculate it. A simplified option introduced in 2013 lets taxpayers claim $5 per square foot of space used to a maximum of 300 square feet. The traditional "regular" method for claiming the deduction requires detailed records of all expenses.
To use the simplified method, you'll complete the worksheet in Form 1040 Schedule C . For the regular method, you'll need to complete and file Form 8829 , "Expenses for Business Use of Your Home."
How do I deduct the self-employment tax?
Self-employed workers may get substantial tax breaks like the home office deduction, but they also pay a hefty federal tax of 15.3% on their income. This self-employment tax is comparable to the Social Security and Medicare taxes that companies pay for employees.
Even if you are an employee of a company, if you earn more than $400 on freelance work you must pay self-employment tax on that income. The self-employment tax generally applies to 92.35% of your net income as determined on Schedule C .
The good news for self-employed taxpayers is that half of the self-employment tax is deductible. After you calculate the self-employment taxes that you owe using Schedule SE , you'll take 50% of it and enter the deduction on line 15 of Form 1040 .
Can I deduct health care premiums if I'm self-employed?
Yes, you can. If you work for yourself and weren't eligible for an employer-provided health care plan in 2022, you can likely claim the cost of your health insurance premiums as an above-the-line deduction . That means you don't need to itemize personal deductions to claim it.
These premiums can include medical, dental and qualifying long-term care insurance. You can claim them for yourself, a spouse or any dependents.
You can only claim insurance premiums up to the amount of business income that you earned in 2022. If your business didn't make any money, you can't claim any deduction.
Your deductions for long-term care insurance are limited by your age. Here are the deduction limits for 2022:
2022 Deduction Limits
To take the self-employed health insurance premium deduction, you'll enter the total amount you are claiming as an adjustment to income in Part II of Form 1040 Schedule 1.
What is the qualified business income deduction?
In addition to deducting business expenses, many freelancers, business owners and business partners can take advantage of the qualified business income deduction , Bronnenkant said. It allows business owners to deduct up to 20% of qualified business income plus 20% of qualified real estate investment trust dividends and qualified publicly traded partnership income.
To be eligible for the QBI deduction, you must either be a sole proprietor (including freelancers) or receive "pass-through" income from an S corporation, partnership or limited liability corporation (LLC). You can take the full QBI deduction if your income is less than $170,050 for single filers or $340,100 for joint filers. Higher incomes can claim a partial deduction using a complicated system that takes into account the type of business involved, property owned by the business and total wages paid to employees.
- Toronto Tax Lawyer
- Articling Program
- Canadian Tax Lawyers
- Case Results
- Case Studies
- Certified Specialists in Taxation
- Company Profile
- Leadership Team
- Articles & tips
- Canadian Accountant Articles
- Definitions
- Media Appearances
- News Releases
- Related Links
- CRA Tax Audits
- Unfiled Taxes
- Net Worth Audits
- Taxes Owing & Liens
- Tax Minimization
- CRA & Bitcoin Taxation
- Unreported Offshore Assets
- Unreported Offshore Income
- Unreported Foreign Pension
- Unreported Internet Income
- Unfiled GST/HST returns
- Individual & Family Income Tax Planning
- Succession Will, Estate and Tax Planning Ontario
- Tax Problems & Representation
- Tax Shelters
- Corporate Reorganizations
- Butterfly Transactions
- Incorporations
- Business Agreements
- Business Startup Planning
- Tax Consulting & Planning
- CEWS Tax Audit Services
- CERB Tax Audit Services
- CEBA Tax Audit Services
- Contact a Tax Lawyer
Employee Tax Deduction of Travel Expenses for Commuting
Published: March 10, 2020
Last Updated: October 21, 2022
As a general rule, you may not deduct expenses from employment income except for certain employment – related expenses that are specifically allowed. One example of such an allowable deduction is the motor vehicle travel expense in a limited number of situations. An employee who is ordinarily required to perform their work away from the employer’s place of business or who is “on the road” for work at all times and is required to use a vehicle can use the travel expenses incurred as a deduction against employment income. The employer must complete Form T2200 “Declaration of Conditions of Employment” in order for the employee to be able to deduct employment expenses from his/her income.
In general, motor vehicle expenses can only be claimed as expenses related to “on the job” travel. If you drive from your home to your place of employment and then back home, you may not claim the travel costs associated with that commute. This is because Canada Revenue Agency (“CRA”) regards this use as a personal use of your motor vehicle. However, if you are required by your employer to take your motor vehicle to work and would have taken a less expensive means of transport to work had it not been for your employer’s requirement, you may be eligible to claim the costs associated with your commute to work as a deduction on your income tax return.
In the Tax Court of Canada decision of Tolson v. HMQ [2007TCC661], the taxpayer was required to travel for employment related purposes and his employer gave him two vehicle allowances – a per kilometre allowance and a fixed allowance. When claiming motor vehicle expenses, the taxpayer included the expenses associated with his daily 30-kilometre drive between his residence and his office. The taxpayer justified this by stating that the only reason he took his motor vehicle to work was because his employer required him to do so. If it had not been for his employer’s requirement, he would have carpooled or taken public transportation. The Minister denied the deduction on the basis that traveling to and from work was personal use of a motor vehicle. In addition, although the taxpayer was entitled to claim a per kilometre allowance, he did not do so. Therefore the Minister presumed that the taxpayer did not use the vehicle for employment-related purposes and denied all motor vehicle expenses.
Justice Sheridan found that the taxpayer was required to have his motor vehicle available at the office and that the only way that requirement could be satisfied was to drive it to work each day. Although counsel for the Crown suggested that the taxpayer should have left his vehicle permanently parked at the office, the judge stated that this would have deprived the taxpayer of all personal use of his vehicle and that such deprivation would be unreasonable. Therefore, the taxpayer was allowed to claim the deduction for the travel expenses associated with his commute to and from work. The taxpayer was also permitted to claim his “on the job” travel expenses despite the fact that he did not claim the per kilometre travel allowance.
Related Post
Disclaimer:.
"This article provides information of a general nature only. It is only current at the posting date. It is not updated and it may no longer be current. It does not provide legal advice nor can it or should it be relied upon. All tax situations are specific to their facts and will differ from the situations in the articles. If you have specific legal questions you should consult a lawyer."
About the Author
David j. rotfleisch.
David J. Rotfleisch, a leading Canadian tax lawyer, is not only a certified specialist in taxation but also a chartered professional accountant. Most recently, David is a pioneer in Canadian crypto taxation.
As of April 2020, he was one of 12 Ontario Certified Specialists In Taxation™.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much can i claim for travel expenses without receipts.
You cannot claim any expenses without receipts. If you have receipts then you can claim business-related travel expenses except for regular commuting to and from your place of employment. You can also potentially claim for 50% of the cost of some of the meals you eat while travelling for business. Your tax lawyer or accountant will explain which ones you can claim for.
What if I get audited and don't have receipts?
If you get audited by the CRA and don’t have receipts, you will lose your deductions. There are no exceptions to this. No receipt means no deduction. Unfortunately, credit card and bank statements are not accepted as proof of expenditure. However, certain taxpayers may be able to claim some of their vehicle and meal expenses by using the simplified method.
What is the maximum I can claim on tax without receipts?
The maximum you can claim on tax without receipts is zero. The CRA only accepts deductions if you produce the original receipts or invoices. If you have lost some, you could try contacting the seller and asking for a duplicate. You need to hang onto your receipts for a minimum of 6 years because you could be audited at any time during that period.
One exception to this is work-from-home expenses during the 2020, 2021, and 2022 tax years which can be claimed using a temporary flat-rate. The flat rate is $2 for each day you worked at home due to COVID-19 to a maximum of $500 or 250 working days.

Subscribe to our Newsletter
Looking for tax assistance.
Fill the form and we’ll get back to you.
Additional Areas Served
- Brampton Tax Lawyer
- Hamilton Tax Lawyer
- London Tax Lawyer
- Mississauga Tax Lawyer
- Montreal Tax Lawyer
- Ottawa Tax Lawyer
- Tax Lawyer Calgary
- Vancouver Tax Lawyer
- Winnipeg Tax Lawyer
- Edmonton Tax Lawyer
We are a Toronto tax law firm with a Canada wide full service income tax law practice.
Tax Solutions
- Tax Appeals
- Taxes Owning & Liens
Voluntary Disclosure
- Offshore Assets
- Offshore Income
- Offshore Pension
- Internet Income
Corporate Planning
- Tax Reorganizations
Get your CRA tax issue solved
Address: Rotfleisch & Samulovitch P.C. 2822 Danforth Avenue Toronto, Ontario M4C 1M1
416-367-4222 OR SCHEDULE ASSESSMENT
Copyright © 2024 Rotfleisch & Samulovitch Professional Corporation, Taxpage
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Tax Planning
What Are Travel Expenses for Tax Purposes?
How travel expenses work, how to calculate and file travel expenses, what tax-deductible travel costs mean for individuals, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Marko Geber / Getty Images
Travel expenses are certain travel-related business costs that you can deduct for tax purposes.
Key Takeaways
- Travel expenses are tax-deductible costs associated with traveling for business, away from your main workplace.
- Travel expenses eligible for tax deduction need to be “ordinary and necessary” and have a business purpose
- You generally can’t deduct costs such as those incurred for a personal vacation.
- Only businesses, including self-employed individuals, can typically deduct travel expenses.
When filing taxes, your travel expenses are the costs associated with travel that a business can generally deduct. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) defines these costs as “ordinary and necessary expenses of traveling away from home for your business, profession, or job.”
For example, a business owner might drive to a client’s office a few hours away and stay at a hotel overnight before driving home the next day. In that case, the business owner can often deduct travel expenses such as gas (or they might use the standard mileage rate rather than adding up actual car expenses ) and lodging.
However, not all travel costs are tax-deductible travel expenses. For one, traveling to and from your home to your main office wouldn’t count as travel, because that would just be commuting, which isn’t deductible. Also, tax-deductible travel expenses can’t be “lavish or extravagant,” per the IRS.
While these terms can be somewhat subjective, it helps to refer back to the “ordinary and necessary” guidelines. If your business is centered around blogging about luxury resorts, then perhaps staying at some higher-end hotels could be considered an ordinary part of doing your job. Yet, if you’re a self-employed graphic designer and you travel to another city to see a client, it might not be considered ordinary to stay at a $1,000-per-night hotel when plenty of other reasonable options exist at around a $200 price point.
In addition to being ordinary and necessary, travel expenses also need to be for business use to be deductible, rather than personal use. So you generally can’t deduct the cost of a family vacation as travel expenses just because you’re a business owner.
Travel expenses are reported by businesses on relevant forms when filing taxes, which can reduce taxable income. For example, a self-employed individual often uses Schedule C to report their business income and business expenses , with travel being a line item within the “Expenses” section.
Adding up travel costs can differ a bit based on the taxpayer’s preferences. For example, when it comes to accounting for travel expenses related to driving, you can use either the standard mileage rate (58.5 cents per mile for tax year 2022) or add up actual costs, such as gas, depreciation, insurance, etc. Also keep in mind that someone who has a vehicle that they drive for both business and personal use can only deduct the portion used for business.
Other nuances include the cost of meals while traveling. Generally, only 50% of business meals can be deducted, although certain exceptions apply. However, business owners might decide instead to take the standard meal allowance , which is a daily amount that covers food and incidental expenses, with the exact amount depending on where the travel takes place.
By taking generalized deductions such as the standard meal allowance when counting up travel expenses, a business owner doesn’t necessarily need to save receipts from every food purchase while on the road.
You still need to keep records to prove the business travel took place. Otherwise, if your business gets audited and has insufficient records to justify travel expenses, you could potentially face penalties.
Understanding travel expenses can be helpful for individuals who have their own businesses, including those who freelance or do gig work, thus filling out tax forms such as Schedule C . By accounting for these costs, you can reduce your taxable income, meaning you pay less in taxes than you would if you didn’t deduct these expenses. Consulting with a tax professional or other relevant expert could help you fully and accurately take advantage of these tax-saving opportunities.
However, individuals who do not have business income, such as those who are W-2 employees, generally can’t take any travel expenses on their personal returns. So, even if your employer doesn’t pay you back for business travel, you typically can’t deduct these expenses.
Which business travel expenses are tax deductible?
Expenses incurred when you travel away from your home for your job may be tax deductible. These expenses include costs of travel by airplane, train, bus or car. Transportation fare between hotel and work on the trip and cost of baggage. Eligible expenses may also include lodging, meals, drying cleaning, laundry, cost of business communication and any tips paid out while on the business trip.
What percentage of business travel expenses are tax deductible?
You can deduct 100% of your business travel expenses if they meet certain criteria. The expenses should be "ordinary and necessary" expenses incurred while traveling away form home for your job and must not be "lavish or extravagant." You cannot deduct expenses incurred in your commute to work as travel expenses. If you drive a car for both personal and business trips, only the business part of the usage is deductible. You may also be able to deduct up to 50% of your meals while traveling as business expense.
IRS. " Topic No. 511 Business Travel Expenses ."
IRS. " Schedule C (Form 1040) Profit or Loss From Business ."
IRS. " IRS Issues Standard Mileage Rates for 2022 ."
IRS. " Here’s what taxpayers need to know about business related travel deductions ."
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Are Travel Expenses?
Understanding travel expenses, the bottom line.
- Deductions & Credits
- Tax Deductions
Travel Expenses Definition and Tax Deductible Categories
Michelle P. Scott is a New York attorney with extensive experience in tax, corporate, financial, and nonprofit law, and public policy. As General Counsel, private practitioner, and Congressional counsel, she has advised financial institutions, businesses, charities, individuals, and public officials, and written and lectured extensively.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/MichellePScott-9-30-2020.resized-ef960b87116444b7b3cdf25267a4b230.jpg)
For tax purposes, travel expenses are costs associated with traveling to conduct business-related activities. Reasonable travel expenses can generally be deducted from taxable income by a company when its employees incur costs while traveling away from home specifically for business. That business can include conferences or meetings.
Key Takeaways
- Travel expenses are tax-deductible only if they were incurred to conduct business-related activities.
- Only ordinary and necessary travel expenses are deductible; expenses that are deemed unreasonable, lavish, or extravagant are not deductible.
- The IRS considers employees to be traveling if their business obligations require them to be away from their "tax home” substantially longer than an ordinary day's work.
- Examples of deductible travel expenses include airfare, lodging, transportation services, meals and tips, and the use of communications devices.
Travel expenses incurred while on an indefinite work assignment that lasts more than one year are not deductible for tax purposes.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers employees to be traveling if their business obligations require them to be away from their "tax home" (the area where their main place of business is located) for substantially longer than an ordinary workday, and they need to get sleep or rest to meet the demands of their work while away.
Well-organized records—such as receipts, canceled checks, and other documents that support a deduction—can help you get reimbursed by your employer and can help your employer prepare tax returns. Examples of travel expenses can include:
- Airfare and lodging for the express purpose of conducting business away from home
- Transportation services such as taxis, buses, or trains to the airport or to and around the travel destination
- The cost of meals and tips, dry cleaning service for clothes, and the cost of business calls during business travel
- The cost of computer rental and other communications devices while on the business trip
Travel expenses do not include regular commuting costs.
Individual wage earners can no longer deduct unreimbursed business expenses. That deduction was one of many eliminated by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017.
While many travel expenses can be deducted by businesses, those that are deemed unreasonable, lavish, or extravagant, or expenditures for personal purposes, may be excluded.
Types of Travel Expenses
Types of travel expenses can include:
- Personal vehicle expenses
- Taxi or rideshare expenses
- Airfare, train fare, or ferry fees
- Laundry and dry cleaning
- Business meals
- Business calls
- Shipment costs for work-related materials
- Some equipment rentals, such as computers or trailers
The use of a personal vehicle in conjunction with a business trip, including actual mileage, tolls, and parking fees, can be included as a travel expense. The cost of using rental vehicles can also be counted as a travel expense, though only for the business-use portion of the trip. For instance, if in the course of a business trip, you visited a family member or acquaintance, the cost of driving from the hotel to visit them would not qualify for travel expense deductions .
The IRS allows other types of ordinary and necessary expenses to be treated as related to business travel for deduction purposes. Such expenses can include transport to and from a business meal, the hiring of a public stenographer, payment for computer rental fees related to the trip, and the shipment of luggage and display materials used for business presentations.
Travel expenses can also include operating and maintaining a house trailer as part of the business trip.
Can I Deduct My Business Travel Expenses?
Business travel expenses can no longer be deducted by individuals.
If you are self-employed or operate your own business, you can deduct those "ordinary and necessary" business expenses from your return.
If you work for a company and are reimbursed for the costs of your business travel , your employer will deduct those costs at tax time.
Do I Need Receipts for Travel Expenses?
Yes. Whether you're an employee claiming reimbursement from an employer or a business owner claiming a tax deduction, you need to prepare to prove your expenditures. Keep a running log of your expenses and file away the receipts as backup.
What Are Reasonable Travel Expenses?
Reasonable travel expenses, from the viewpoint of an employer or the IRS, would include transportation to and from the business destination, accommodation costs, and meal costs. Certainly, business supplies and equipment necessary to do the job away from home are reasonable. Taxis or Ubers taken during the business trip are reasonable.
Unreasonable is a judgment call. The boss or the IRS might well frown upon a bill for a hotel suite instead of a room, or a sports car rental instead of a sedan.
Individual taxpayers need no longer fret over recordkeeping for unreimbursed travel expenses. They're no longer tax deductible by individuals, at least until 2025 when the provisions in the latest tax reform package are due to expire or be extended.
If you are self-employed or own your own business, you should keep records of your business travel expenses so that you can deduct them properly.
Internal Revenue Service. " Topic No. 511, Business Travel Expenses ."
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 463, Travel, Gift, and Car Expenses ," Page 13.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 5307, Tax Reform Basics for Individuals and Families ," Page 7.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 463, Travel, Gift, and Car Expenses ," Pages 6-7, 13-14.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 463, Travel, Gift, and Car Expenses ," Page 4.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 5307, Tax Reform Basics for Individuals and Families ," Pages 5, 7.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TaxHome-3b9f1ac36f6c4e28889c34943d991fc9.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Claim Travel Expenses
Last Updated: May 3, 2021 References
This article was co-authored by Kathy Duong and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Kathy Duong is a certified accountant who has been working as an accountant for over 25 years. She received her BS in Finance and Accounting from California State University, Los Angeles in 1992. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 9,033 times.
If you have to travel for work, you may be able to claim at least a portion of your travel expenses as a deduction on your taxes. If you earn an hourly wage or salary, these expenses are miscellaneous itemized deductions. Miscellaneous deductions are subject to the 2 percent rule, meaning you can't deduct them unless they are at least 2 percent of your adjusted gross income (AGI). If you're self-employed, you can claim work-related travel expenses on your Schedule C.
Categorizing Deductible Expenses

- It's usually easier to just save receipts for everything. You can sit down later and analyze exactly which expenses are deductible.
- For example, suppose you fly from New York to Los Angeles for business. Your food in the airport would be deductible, but the magazines you bought probably wouldn't be.

- For example, the amount you were charged for your stay typically is deductible. However, if you raided the mini bar in your room and ordered a movie, those expenses can't be deducted.
- If your employer picked up the tab for your lodging, you cannot deduct those expenses since it didn't actually cost you anything. You can only deduct expenses that you paid for out of your own pocket. Likewise, you can't deduct expenses that your employer reimbursed you for later.

- If you travel extensively, your deduction may end up being larger if you use your actual expenses. This is especially true if you have an older vehicle that needs frequent repairs.
- You can still deduct your travel even if you failed to keep meticulous mileage records. Estimate the mileage using an online map service such as Google Maps. Measure the distance from your workplace, not from your home. [4] X Research source

- You can also document these expenses by taking a picture of meters or payment kiosks with your smart phone.
- As long as these expenses seem reasonable, it isn't going to matter that you don't have receipts to prove them.

- For example, suppose you went to Denver, Colorado on a business trip. While there, you decided to spend an afternoon skiing. Your ski expenses would not be deductible on your taxes, even though you were there on business, because your skiing was not work-related.

- The standard meal allowance is the federal per diem rate. It varies depending on where you are, but for most smaller places it's around $50 a day.
- Find the per diem rate to use by going to https://www.gsa.gov/travel/plan-book/per-diem-rates and entering the ZIP code of the place where you traveled for work.
- If you use the standard meal allowance, you only have to keep records that prove the time, place, and business purpose of your travel.
Using Form 2016 and Schedule A

- You can download these forms from the IRS website if you're doing your taxes manually. If you're using a tax preparation service, simply indicate when asked that you have unreimbursed work-related expenses, and follow the prompts.

- When you use the standard meal allowance, you still only have the ability to deduct a portion of that expense. The main benefit of using the standard meal allowance is that you don't have to keep track of all of those receipts.
- If you're using the standard meal allowance, you must prorate it for your departure and return dates. You can do so by taking 75 percent of the meal allowance on those days, or you can reduce it by the actual hours you were away from home. Whichever method you use, apply it consistently to every business trip.

- If you flew and then rented a car at your destination, you can include the miles you drove while at your destination as well, provided you were driving for a work-related reason. For example, if you drove from your hotel to an office, the mileage to and from would be tax-deductible. However, if you decided to go to a concert one evening, that mileage would not be tax-deductible.
- If you drive your personal car frequently for work, you may want to use actual expenses rather than the standard mileage deduction. However, if you go this route you must maintain receipts for those expenses. You'll also have to figure the percentage of time you use your vehicle for work and discount your actual expenses by that amount.

- This section includes other miscellaneous deductions, such as tax preparation expenses, that are subject to the 2-percent rule.
- If you have any other itemized deductions, you'll add them in the appropriate place on Schedule A as well.

- For example, if your AGI is $32,000, you must have at least $640 in travel expenses to deduct anything at all. If you had $900 in deductible travel expenses, you would be able to deduct $260 of those expenses on your taxes.

- You may want to take your itemized deductions instead of the standard deduction even though it's less than the standard. If you decide you want to do this, check the appropriate box on Schedule A indicating your preference and enter your total itemized deductions on your return.
Deducting Travel Expenses on Schedule C

- If you're doing your taxes manually, all of your business-related travel expenses, such as air fare, rental cars, or hotel fees, go on line 24a.
- If you're using tax preparation software, you don't necessarily have to keep track of the specific lines where expenses are deducted. Simply indicate that you have travel expenses and enter your total expenses for the year when prompted.

- If you're away from home on business, you can deduct 80 percent of your meals. Your "tax home" doesn't necessarily mean your residence. It generally means the town or region where you work or where your business operates. If you have more than one business location, consult a professional tax advisor regarding which expenses you can deduct.
- For example, if you work from home and live in New York City, you can only deduct 50 percent of any business-related meals and entertainment you consume in New York City. However, if you traveled to Hartford, Connecticut for business and stayed overnight, you would be able to deduct 80 percent of the meals you consumed in Hartford.

- For example, if you drive for a ride-share service, your mileage while you have a fare, or are driving to a fare, is a deductible business expense.
- Generally you'll want to use the standard mileage deduction of 54 cents a mile rather than actual costs. However, if you use your car more for business than for personal use, you may find that using your actual costs gives you a larger deduction.

- Make sure you keep detailed records about every expense you include as a deduction. You may want to use bookkeeping software, such as QuickBooks, to more easily organize your receipts and keep up with your business expenses so you don't miss any important deductions.

- What you have left after you subtract your expenses from your gross profit is your net profit . This is the amount of money you'll owe federal taxes on. If you received a salary or hourly wages from another employer, you would add this amount to your other income to determine the total amount of taxes you owe.
Expert Q&A
- You typically can't deduct commuting expenses, even if you live far away from your workplace. However, you may be able to deduct some commuting expenses if you have to travel to a temporary work location, such as to help train employees at a new store. [19] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- After you claim travel expenses, keep your receipts for your expenses in a digital or paper file along with your tax return. You want to have everything together in case you get audited. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Miscellaneous deductions in general, and travel expenses specifically, are red flags that can increase your audit risk, especially if they seem high in comparison to your income. If you have significant travel expenses, keep meticulous records and hire a tax professional to do your taxes for you. [20] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://turbotax.intuit.com/tax-tips/jobs-and-career/employees-can-deduct-workplace-expenses/L58LFjAPa
- ↑ https://quickbooks.intuit.com/r/taxes/what-you-can-and-cant-write-off-with-business-travel/
- ↑ https://themilitarywallet.com/national-guard-reserves-travel-deductions/
- ↑ https://www.irs.gov/publications/p463#en_US_2016_publink100033785
- ↑ https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/f2106.pdf
- ↑ https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/f1040sa.pdf
- ↑ https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/f1040sc.pdf
- ↑ https://ttlc.intuit.com/questions/1899669-can-i-deduct-commuting-expenses-like-gas-mileage-or-toll-fees
- ↑ https://quickbooks.intuit.com/r/taxes/10-red-flags-can-cause-tax-audit/
About this article
Did this article help you.

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info

Can You Deduct Your Vacation From Your Taxes? Experts Weigh In
Know what’s deductible and what’s not when it comes to submitting travel expenses on your taxes..
- Copy Link copied

If there’s a certain amount of work involved, you may be able to claim travel costs on your taxes.
Photo by GaudiLab/Shutterstock
People are traveling like crazy these days. The Sunday after Thanksgiving 2023 was the biggest single travel day in U.S. aviation history, with TSA screening more than 2.9 million passengers on November 26.
If you’re one of those travelers racking up frequent flier miles as quickly as you can fasten your seat belt, you may be looking for ways to recoup some of the cost. Can you legally write off your trip? If you’re self-employed (for example, if you’re an entrepreneur, freelancer, or consultant, or have an online business) and you did some work while on the road, there’s a good chance you can.
Here’s what it takes to get two thumbs up from the IRS.
Pass these four tests
For starters, your trip must have a business purpose, meaning it must include activities such as client meetings, attending a conference, being a guest speaker at a conference, doing research and development for the business, or holding a board meeting or annual shareholders’ meeting. The activity should have the potential to generate revenue.
“Don’t think you can take a personal trip, talk business for an hour and then try and deduct the whole amount of your trip. The intent of the trip needs to be business,” says Caitlynn Eldridge, founder and CEO of Eldridge CPA .
The second and third requirements deem that the trip must be both “ordinary and necessary,” according to IRS guidelines on business travel expenses . “An ordinary expense means it’s typical in your business, both [in terms of] amount [as well as in] frequency and purpose. Necessary means it actually helps you increase your profits or expand your business,” explains Tom Wheelwright, a certified public accountant and author of the book Tax-Free Wealth (BZK Press, 2018).
Lastly, every expense must be properly documented. To get a deduction for travel, Wheelwright said that you must spend more than half your time during the business day doing business and have everything documented. “So, if you spend four and a half hours a day doing business, it becomes deductible. You also must have documentation, which includes receipts, of what you did, and a log of your expenses,” says Wheelwright.
On receipts, write the name of the client who you had the meal with for further proof. “Save the emailed confirmation and receipt from the hotel reservation or conference ticket payment that show the dates, times, and name of the events as well as the receipts from the travel it took to get there and back [such as for gas or flights],” says Ben Watson, founder of Fiscal Fluency , a personal finance and business coaching company.
Note that for 2024, the IRS mileage reimbursement rate is 67 cents for employees or a self-employed individual traveling for work, up from 65.5 cents in 2023.
Know, too, that you must be away from home overnight—the IRS requires an overnight stay for the trip to qualify as business travel, Wheelwright says.
Domestic travel versus travel abroad
There’s a big difference between how you calculate deductions if the work trip was taken in the United States versus abroad. According to Wheelwright, “It’s an all-or-nothing test in the U.S., so either you spent more than 50 percent of your time on business, and it’s all deductible, or you spent 50 percent or less and none of it’s deductible.”
For international business travel, the deductions work differently. He explained that when you travel to another country, the deduction is proportionate. “For example, if you spent 40 percent of your time doing business in Italy, then 40 percent is deductible,” says Wheelwright.
Stick to the rules

If you normally stay in more modest hotels, trying to deduct a luxe property stay could raise red flags.
Photo by Yokwar/Shutterstock
It has to be a legitimate business trip. “You can’t simply do some work while on the beach and call it a business trip,” says Watson. But if you make it a “bleisure trip” by adding a couple days at the beach onto your preplanned business trip to the coast, you could still write off at least some of your lodging fees, he explained. If you do extend your trip for vacation, you can only deduct the expenses that were directly related to work and took place on the days that you conducted business. If you are traveling to multiple cities, keep in mind that each must have a business purpose.
You do have to work. If you are at a conference, make sure you fully participate, which means not just attending one or two sessions. If you only attend a small number of the business-related events, the entire purpose of the trip would be considered a personal trip with “incidental” business activities, Watson points out. Remember you need a log of what you did, and if it’s thin on details, it could prove problematic. “You don’t want to lose the ability to deduct transportation, lodging, meals, and other expenses,” says Watson.
If it’s a business trip of your own making, be sure it includes meetings with clients or participating in some work-related activity. “To demonstrate evidence of these events, it’s wise to put calendar appointments down in your phone in advance and hold onto receipts when the time comes to file your tax return and claim your deductions. Remember, the primary purpose of this trip is [supposed to be] for work,” says Riley Adams, a CPA and CEO and founder of WealthUp , a financial literacy website.
Don’t try to bend what “ordinary and necessary” means. “If you have the ability to accomplish the same business tasks while staying at a modest hotel as you would at the Four Seasons, you’ll have a hard time justifying the extra cost if you’re ever audited,” Watson cautions.
Stay at a place that is similar to places you normally stay on a business trip, so your expenses are considered “ordinary.” Wheelwright explains that if you usually stay at five-star hotels for your business trips, then the Four Seasons would fall into the same category. However, if you usually stay at hotels like the Comfort Inn, and suddenly switch to a luxury hotel, the high-end venue could raise red flags with the IRS. He says that it doesn’t matter whether you stay at a hotel or a vacation rental, the quality level and price tag should be similar to what is typical for your business trips.
When traveling with non–business companions, such as a spouse or family members, you may only deduct the cost of the lodging you would have paid if you were traveling alone—for example, if a single room costs $150 per night, and you paid $200 for a double room, you could only deduct at the $150 rate.
What can you deduct?

You can deduct 50 percent of the cost of business meals.
Photo by Rawpixel.com/Shutterstock
Personal meals are not deductible, but half the cost of food expenses related to business can be deducted. Expenses for your family’s meals and entertainment cannot be deducted unless they are actively engaged in the business and you can show that their expense is both ordinary and necessary.
Travel expenses are only deductible on the days in which the work-related event occurs. “For example, a taxi ride to the meeting, train to a conference, or plane ride to the event [are deductible],” says Adams. “Lodging, much like travel expenses, is deductible on the days in which business is set to occur.”
Understand too, that if you’re provided with a plane ticket paid for by your company, or you’re riding free because you’re redeeming frequent flier miles, your cost is zero, so you can’t deduct it.
But there are a couple of things you may not be aware of. For example, if you have to ship your baggage, you can deduct that cost; you also can deduct for tips for services, such as a tip to the waiter during a meal with a client.
Be strategic
It’s best to put your “vacation” days in the middle of the business days, advises CPA Greg O’Brien. “For example, if [a] business owner took a seven-day trip to Florida and spent five days meeting with clients or prospects and two days relaxing on the beach, this would still qualify as a deductible business trip. The trick is to stick the ‘vacation’ days in the middle of the business days,” he says.
By placing the vacation days in the middle, the travel days to and from are still considered business related, rather than personal.
Watson offers another tip: “Laundry, dry-cleaning and shoe-shine expenses are perfectly acceptable expenses if incurred shortly after returning home.”

Save up to 500 Hours on Paperwork 🙌 50% Off for 3 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
50% Off for 3 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
- Online Accountants
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Self-Employed
- Freelancers
- Marketing & Agencies
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- A Beginner’s Guide to MTD
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs Quickbooks
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Markup Calculator
- VAT Calculator
Call Sales: +44 (800) 047 8164
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Making Tax Digital
Resources for Your Growing Business
How employees can claim travel expenses.

Claiming travel expenses can be quite a tricky area, but it’s one that affects a large portion of the working population.
Thousands of workers across the UK have to travel in some form or another for work. There are a number of reasons to travel. Whether they’re travelling to visit a client, heading to a conference or simply running errands for the business.
HMRC offers a tax relief for any costs incurred whilst you are on the road for work-related reasons. These are known as travel expenses.
For one reason or another, lots of taxpayers aren’t making full use of this tax relief. Thousands of workers aren’t claiming back the travel expenses that they are entitled to.
So, what exactly are travel expenses? And how do you claim this rebate?
We’ll take a closer look at everything you need to know about how employees can claim travel expenses.
Here’s What We’ll Cover:
What Are Travel Expenses?
What counts as a travel expense, what counts as business travel, what counts as a workplace, can i claim travel expenses if i work from home, how can i claim for travel expenses, how much can i claim, key takeaways.
As the name suggests, travel expenses are expenses incurred whilst travelling. In this case, they are expenses incurred whilst travelling for business purposes. These expenses include transport costs, meals and vehicle mileage among a number of others.
As with all legitimate business expenses, companies and employees are able to claim tax relief on these costs. This is because if the expenses tick all of the required boxes, business travel is free from tax.
This is why it makes financial sense for both companies and individual employees to keep track and claim tax relief on business trips.

HMRC may provide tax relief on business-related travel expenses, also known as HMRC travel expenses , if the costs fall into the following categories:
- Public transport costs
- Hotel accommodation if you have to stay overnight
- Food and drink
- Parking fees
- Congestion charges and tolls
- Business phone calls
- Printing costs
Essentially, as long as any of the above occurs during business travel then the company should be able to claim relief.
According to HMRC, to be eligible to claim for relief if you have to be travelling for a ‘business purpose’.
Simply put, you can claim for any trip that’s outside your everyday commute to and from work. The journey you take to and from work is classed as regular commuting and is not seen as counting as a business trip by HMRC.
You can, however, claim for journeys that fall under a business category. They also require you to travel to a location that isn’t your place of work or your home.
For example, this may mean you driving to:
- An office location that isn’t your usual base of operations.
- An event, such as a work-related conference or seminar.
- A customer’s workplace for a business meeting.
- A training centre for a required training course.
- A temporary separate office if your usual office is out of action.
There are two types of workplaces that are recognised by HMRC. Those are:
Permanent Workplaces
This is judged by HMRC looking at how much of an employee’s time is spent at a particular workplace and if they are regularly there or not.
There isn’t a particularly large requirement for a place being a permanent workplace. For example, if an employee goes somewhere just once a week this is almost always counted as a permanent workplace.
HMRC defines it as:
“If the task is going to last more than 24 months and the employee is going to spend more than 40% of their time on-site, the workplace where the task is carried out becomes permanent.”
Temporary Workplaces
A workplace is defined as temporary if an employee only goes there for a short-term task. Travel to and from a temporary workplace can be counted as business travel, not normal commuting.
This means that you can claim expenses for business travel if you are travelling between both permanent and temporary workplaces.
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, we have seen a huge increase in employees working from home.
According to HMRC, if an employee works from home for no other reason than convenience, then any home-to-work journeys count as normal commuting.
However, if an employee works from home because their job requires them to, then that changes. Let’s say that their employer doesn’t provide the facilities on-site, then your home becomes a workplace. This means that travel from your home to other workplaces becomes business travel.
To claim for travel expenses as a form of relief, you will need to have detailed records to back up your claim. These could include:
- Details of Your Journeys: This may be a diary of locations visited and the dates that you made the trip.
- Pay Slips: If your payslips show your business mileage or lodging costs paid by your employer then they can be used as evidence.
- Receipts for Accommodation: You will need to provide the receipts for travel expenses and/or sustenance expenses.
To claim your travel expenses as an actual expense you have to file a claim with HMRC. You have up to four years from the end of the tax year to claim it.
To make a claim, you must:
- Keep a record of your business-related mileage expenses.
- Multiply your yearly mileage by the current AMAP mileage rate and deduct your employer’s mileage allowance, if any.
- If it is under £2,500, you can file your claim on your self-assessment tax return.
- If your claim is over £2,500 then you must file a self-assessment tax return.

In terms of how much you can claim, it depends on a number of factors:
- How much you have spent.
- How much tax you have paid.
- If your employer has reimbursed you.
There may be a scenario where an employer has paid their employee some percentage of their travelling expenses. If that is the case then they may still be eligible to claim for travel expenses if:
- The allowance doesn’t cover the full cost of your expenses.
- The allowance paid by the employer is then taxed.
- The employee uses their own car and the mileage allowance is less than the government-approved rates.
It’s important for both business owners and employees to know how much they can claim and what they can claim for.
The amount of tax relief you can claim can really add up and make a difference to your overall bottom line. It is a form of relief that any business is entitled to so it should be utilised.
To keep track of your business expenses and business miles, try using expense tracking software such as FreshBooks.
Are you looking for more business advice on everything from starting a new business to new business practices?
Then check out the FreshBooks Resource Hub .
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Money and tax
Claim tax relief for your job expenses
Travel and overnight expenses.
If you have to travel for your work you may be able to claim tax relief on the cost or money you’ve spent on food or overnight expenses.
You cannot claim for travelling to and from work, unless you’re travelling to a temporary place of work.
You can claim tax relief for money you’ve spent on things like:
- public transport costs
- hotel accommodation if you have to stay overnight
- food and drink
- congestion charges and tolls
- parking fees
- business phone calls and printing costs
For hotel and meal expenses, you’ll need to send receipts that include the date of your stay or of the meal and the name of the hotel or restaurant.
You may also be able to claim tax relief on business mileage.
You can claim for this tax year and the 4 previous tax years.
How to claim
Use this service to:
- check if you can claim
- make a claim if you’re eligible
If you complete a Self Assessment tax return , you must claim through your tax return instead.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
- ATO Community
- Legal Database
- What's New
Log in to ATO online services
Access secure services, view your details and lodge online.
myTax 2022 Work-related travel expenses
How to complete myTax if you have work-related expenses.
Last updated 31 May 2022
Complete this section if you incurred travel expenses in performing your work as an employee.
Things to know
To claim a deduction for a work-related expense:
- you must have spent the money yourself and weren't reimbursed
- it must be directly related to earning your income
- you must have a record to prove it (usually a receipt).
If the expense was for both work and private purposes, you can only claim a deduction for the work-related portion.
If your total claim for work-related expenses is more than $300, you must have written evidence to prove your claims.
Work-related travel expenses include:
- public transport, air travel and taxi fares
- short-term car hire
- meal, accommodation and incidental expenses you incur while away overnight for work
- actual expenses such as petrol, repair and maintenance costs, that you incur to travel in a car that is owned or leased by someone else
- cars (don't claim these at 'Work-related car expenses')
- motorcycles and vehicles with a carrying capacity of one tonne or more, or nine or more passengers
- expenses for motorcycles and vehicles with a carrying capacity of one tonne or more, or nine or more passengers, such as utility trucks and panel vans.
You can claim
You can claim the cost of trips you undertake while performing your work duties. This may also include trips between your home and your workplace if:
- you used the vehicle because you had to carry bulky tools or equipment that are essential to perform your employment duties and could not leave at your workplace (for example, an extension ladder or cello)
- your home was a base of employment (that is, you were required to start your work at home and travel to a workplace to continue your work for the same employer)
- you had shifting places of employment (that is, you regularly worked at more than one site each day before returning home).
Work-related travel expenses also include the cost of trips:
- between two separate places of employment when you have a second job, providing one of those places is not your home
- from your normal workplace or your home to an alternative workplace that is not a regular workplace (for example, a client’s premises) while you are on duty
- from an alternative workplace that is not a regular workplace back to your normal workplace or directly home.
If the travel was partly private, you can claim only the work-related part.
Claim at this section any work-related travel expenses incurred in earning assessable foreign employment income shown on an income statement or PAYG payment summary – foreign employment .
If you received an award transport payment from your employer, you can claim a deduction for work-related transport expenses these payments cover.
To claim meal, accommodation and incidental expenses incurred when you travelled away overnight for work you must:
- have been required to travel as part of performing your work duties
- only be working away from home for a relatively short period or periods of time (not living away from home)
- not have incurred the expenses because of a choice you made about where to live
- have a permanent home at a location away from the work location to which you are travelling
- have paid the expenses yourself and not been reimbursed for them.
Travel expenses includes information about:
- evidence you need if you wish to claim meal, accommodation and incidental expenses you incurred when you travelled away overnight for work
- if you received a travel allowance to cover accommodation, food, drink or incidental expenses.
If your employer provided a car for you or your relatives’ exclusive use (including under a salary sacrifice arrangement) and you or your relatives were entitled to use it for non-work purposes:
- other maintenance
- bridge and road tolls.
Parking at or travelling to a regular workplace is not ordinarily considered to be a work-related use of the car.
If you no longer own or use an item costing over $300 (such as a ute or van with a carrying capacity of a tonne or more) and you previously claimed a deduction for its decline in value, you may need to make a balancing adjustment.
For information on:
- Taxation Ruling TR 2021/1 Income tax: when are deductions allowed for employees' transport expenses?
- Taxation Ruling TR 2021/4 Income tax and fringe benefits tax: employees: accommodation and food and drink expenses, travel allowances, and living-away-from-home allowances
- shifting places of employment, see Taxation Ruling TR 95/34 Income tax: employees carrying out itinerant work – deductions, allowances and reimbursements for transport expenses .
- reasonable allowance amounts, see Taxation Determination TD 2021/6 Income tax: what are the reasonable travel and overtime meal allowance expense amounts for the 2021–22 income year? together with Taxation Ruling TR 2004/6 Income tax: substantiation exception for reasonable travel and overtime meal allowance expenses.
Related page
Claiming deductions You may be able to claim deductions for work-related expenses you incurred while performing your job as an employee.
You can't claim
You can't claim normal trips between your home and your workplace, even if:
- you did minor work-related tasks at home or between home and your workplace
- you travelled between your home and workplace more than once a day
- you were on call
- there was no public transport near work
- you worked outside normal business hours
- your home was a place where you ran your own business and you travelled directly to a place of employment where you worked for somebody else.
Do not show at this section
Don't show the following at this section:
- Expenses (apart from bridge and road tolls, and parking fees) relating to a car you owned, leased or hired under a hire purchase agreement where the expense is not related to motorcycles and vehicles with a carrying capacity of one tonne or more, or nine or more passengers, such as utility trucks and panel vans, go to Work-related car expenses
- Expenses you incurred in earning assessable foreign employment income not shown on an income statement or PAYG payment summary – foreign employment , go to Foreign employment
- losses at Other work-related expenses
- profits at Other income
Any balancing adjustment amounts calculated in the Depreciation and capital allowance tool will show automatically.
Completing this section
You must have written evidence for the whole of your claim.
We pre-fill your tax return with work-related travel expense information you uploaded from myDeductions. Check them and add any work-related travel expenses that have not pre-filled.
To claim work-related travel expenses, you must first show income from salary and wages or foreign employment income in the Income statements and payment summaries section.
To personalise your return to show work-related travel expenses, at Personalise return select:
- You had deductions you want to claim.
- Work-related expenses.
To claim your work-related travel expenses, at Prepare return select 'Add/Edit' at the Deductions banner.
At the Work-related travel expenses banner:
- enter Your description . To assist in record keeping, add a short description of your expense.
- enter the Amount . The Depreciation and capital allowances tool can help you to work out any decline in value deduction. It can also work out any deductible balancing adjustment when you stop holding a depreciating asset. Access this tool in the Deductions section. Fields from this tool can't be adjusted in myTax. To make any adjustments, or to add new assets to the tool, select the 'Use the depreciation and capital allowances tool' link.
- Select Save .
- Select Save and continue when you have completed the Deductions section.
You need to keep records for five years (in most cases) from the date you lodge your tax return.
Our myDeductions tool is free to use and is available through the ATO app. The tool makes it easier and more convenient to keep records of your expenses and income in one place, including photos of your receipts and invoices.
Tax deadline is April 15 - Our experts can help with your taxes, or do them for you as soon as today. Get started
Employees Can Deduct Workplace Expenses For Tax Years Prior to 2018
Deducting business expenses isn't just for the self-employed. Taxpayers classified as employees can also deduct some of their unreimbursed business expenses.
The importance of the 2% floor
Auto and travel expenses, other common deductions.

Paying taxes is inevitable—but finding extra tax deductions is enviable. If you’re a salaried employee, you may be surprised to learn that your deductions include certain job-related expenses.
To deduct workplace expenses, your total itemized deductions must exceed the standard deduction. You must also meet what’s called "the 2% floor." That is, the total of the expenses you deduct must be greater than 2% of your adjusted gross income, and you can deduct only the expenses over that amount.
Once you are sure you qualify to deduct work-related expenses as an employee, you’ll have to be sure your deductions qualify. All expenses must be incurred during the tax year, must be trade- or business-related, and must be “ordinary and necessary.” The expenses don’t have to be required, however: In IRS-speak, a necessary expense is simply one that is helpful and appropriate for your business. And, of course, the costs can’t be reimbursed by your employer.
Here are some of the more common workplace deductions. As with all deductions, it’s important to keep detailed records and/or receipts.
Business travel expenses are some of the most frequent work-related deductions.
Deductible auto costs include expenses for traveling between one workplace and another (not including a home office), visiting clients, going to a business meeting away from your regular workplace or getting to a temporary workplace. If you work in two places in one day, whether or not for the same employer, you can deduct the cost of going between them.
If you have no permanent office and work regularly within your metropolitan area, you can deduct the cost of travel outside that metropolitan area. You cannot, however, deduct typical commuting costs within your metropolitan area.
For commuters, the costs of traveling to and from work, whether by train, car, cab or bus, are considered personal expenses—even if you do work on the trip. The cost of parking at your permanent place of work is not deductible, but parking to attend a business meeting is. Similarly, tolls and gas are not deductible for regular transportation to work, but are deductible for work-related trips.
If you use your car for business purposes you can deduct either the standard mileage rate (53.5¢ per mile in 2017) or actual car expenses for the year. For leased cars, whichever method you choose in the first year is the one you will be required to use for the remaining years of the lease.
Work-related travel expenses are deductible, as long as you incurred the costs for a taxi, plane, train or car while working away from home on an assignment that lasts one year or less. You can also deduct the cost of laundry, meals, baggage, telephone expenses and tips while you are on business in a temporary setting.
You have a choice about how to deduct the cost of meals that are business-related, or eaten while on an unreimbursed travel excursion. You can deduct 50% of the actual meal cost, or take 50% of the per diem rate for the location of your travel. A list of these cities is available on the IRS web site at www.IRS.gov .
Here are some other business expenses employees can deduct on their tax return:
- Dues to professional societies, excluding lobbying and political organizations.
- Home office costs. The office must be your principal place of business and be for the convenience of your employer—not just helpful in conducting your job.
- Job search expenses in your current occupation, even if you don’t land a new job. This includes everything from the cost of producing and copying your resume to travel expenses you incur while interviewing or searching for a job.
- Legal fees related to doing or keeping your job.
- The cost of a passport for a business trip.
- Union dues and expenses. However, you cannot deduct the portion of the fees that pays for sick, accident or death benefits or for a pension fund, even if the fees are required dues.
- Work clothes and uniforms that are not suitable for everyday use and are a condition of your employment.
Not sure if your business expenses are deductible? TurboTax will ask you simple questions about your expenses and tell you which ones you can deduct, or if you are better off taking the standard deduction.
With TurboTax Live Full Service , a local expert matched to your unique situation will do your taxes for you start to finish. Or, get unlimited help and advice from tax experts while you do your taxes with TurboTax Live Assisted . And if you want to file your own taxes, you can still feel confident you'll do them right with TurboTax as we guide you step by step. No matter which way you file, we guarantee 100% accuracy and your maximum refund.
Get unlimited advice, an expert final review and your maximum refund, guaranteed .
~37% of taxpayers qualify. Form 1040 + limited credits only .
Looking for more information?
Related articles, more in jobs and career.
The above article is intended to provide generalized financial information designed to educate a broad segment of the public; it does not give personalized tax, investment, legal, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any action, you should always seek the assistance of a professional who knows your particular situation for advice on taxes, your investments, the law, or any other business and professional matters that affect you and/or your business.
TaxCaster Tax Calculator
Estimate your tax refund and where you stand
I’m a TurboTax customer
I’m a new user
Tax Bracket Calculator
Easily calculate your tax rate to make smart financial decisions
Get started
W-4 Withholding Calculator
Know how much to withhold from your paycheck to get a bigger refund
Self-Employed Tax Calculator
Estimate your self-employment tax and eliminate any surprises
Crypto Calculator
Estimate capital gains, losses, and taxes for cryptocurrency sales
Self-Employed Tax Deductions Calculator
Find deductions as a 1099 contractor, freelancer, creator, or if you have a side gig
ItsDeductible™
See how much your charitable donations are worth
Read why our customers love Intuit TurboTax
Rated 4.5 out of 5 stars by our customers.
(125630 reviews of TurboTax Online)
Star ratings are from 2023
Your security. Built into everything we do.
File faster and easier with the free turbotax app.

TurboTax Online: Important Details about Filing Form 1040 Returns with Limited Credits
A Form 1040 return with limited credits is one that's filed using IRS Form 1040 only (with the exception of the specific covered situations described below). Roughly 37% of taxpayers are eligible. If you have a Form 1040 return and are claiming limited credits only, you can file for free yourself with TurboTax Free Edition, or you can file with TurboTax Live Assisted Basic or TurboTax Full Service at the listed price.
Situations covered (assuming no added tax complexity):
- Interest or dividends (1099-INT/1099-DIV) that don’t require filing a Schedule B
- IRS standard deduction
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit (CTC)
- Student loan interest deduction
Situations not covered:
- Itemized deductions claimed on Schedule A
- Unemployment income reported on a 1099-G
- Business or 1099-NEC income
- Stock sales (including crypto investments)
- Rental property income
- Credits, deductions and income reported on other forms or schedules
* More important offer details and disclosures
Turbotax online guarantees.
TurboTax Individual Returns:
- 100% Accurate Calculations Guarantee – Individual Returns: If you pay an IRS or state penalty or interest because of a TurboTax calculation error, we'll pay you the penalty and interest. Excludes payment plans. This guarantee is good for the lifetime of your personal, individual tax return, which Intuit defines as seven years from the date you filed it with TurboTax. Excludes TurboTax Business returns. Additional terms and limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
- Maximum Refund Guarantee / Maximum Tax Savings Guarantee - or Your Money Back – Individual Returns: If you get a larger refund or smaller tax due from another tax preparation method by filing an amended return, we'll refund the applicable TurboTax federal and/or state purchase price paid. (TurboTax Free Edition customers are entitled to payment of $30.) This guarantee is good for the lifetime of your personal, individual tax return, which Intuit defines as seven years from the date you filed it with TurboTax. Excludes TurboTax Business returns. Additional terms and limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
- Audit Support Guarantee – Individual Returns: If you receive an audit letter from the IRS or State Department of Revenue based on your 2023 TurboTax individual tax return, we will provide one-on-one question-and-answer support with a tax professional, if requested through our Audit Report Center , for audited individual returns filed with TurboTax for the current 2023 tax year and for individual, non-business returns for the past two tax years (2022, 2021). Audit support is informational only. We will not represent you before the IRS or state tax authority or provide legal advice. If we are not able to connect you to one of our tax professionals, we will refund the applicable TurboTax federal and/or state purchase price paid. (TurboTax Free Edition customers are entitled to payment of $30.) This guarantee is good for the lifetime of your personal, individual tax return, which Intuit defines as seven years from the date you filed it with TurboTax. Excludes TurboTax Business returns. Additional terms and limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
- Satisfaction Guaranteed: You may use TurboTax Online without charge up to the point you decide to print or electronically file your tax return. Printing or electronically filing your return reflects your satisfaction with TurboTax Online, at which time you will be required to pay or register for the product.
- Our TurboTax Live Full Service Guarantee means your tax expert will find every dollar you deserve. Your expert will only sign and file your return if they believe it's 100% correct and you are getting your best outcome possible. If you get a larger refund or smaller tax due from another tax preparer, we'll refund the applicable TurboTax Live Full Service federal and/or state purchase price paid. If you pay an IRS or state penalty (or interest) because of an error that a TurboTax tax expert or CPA made while acting as a signed preparer for your return, we'll pay you the penalty and interest. Limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
- 100% Accurate Expert-Approved Guarantee: If you pay an IRS or state penalty (or interest) because of an error that a TurboTax tax expert or CPA made while providing topic-specific tax advice, a section review, or acting as a signed preparer for your return, we'll pay you the penalty and interest. Limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
TurboTax Business Returns:
- 100% Accurate Calculations Guarantee – Business Returns. If you pay an IRS or state penalty or interest because of a TurboTax calculation error, we'll pay you the penalty and interest. Excludes payment plans. You are responsible for paying any additional tax liability you may owe. Additional terms and limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
- TurboTax Audit Support Guarantee – Business Returns. If you receive an audit letter from the IRS or State Department of Revenue on your 2023 TurboTax business return, we will provide one-on-one question-and-answer support with a tax professional, if requested through our Audit Report Center , for audited business returns filed with TurboTax for the current 2023 tax year. Audit support is informational only. We will not represent you before the IRS or state tax authority or provide legal advice. If we are not able to connect you to one of our tax professionals for this question-and-answer support, we will refund the applicable TurboTax Live Business or TurboTax Live Full Service Business federal and/or state purchase price paid. Additional terms and limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
TURBOTAX ONLINE/MOBILE PRICING:
- Start for Free/Pay When You File: TurboTax online and mobile pricing is based on your tax situation and varies by product. For most paid TurboTax online and mobile offerings, you may start using the tax preparation features without paying upfront, and pay only when you are ready to file or purchase add-on products or services. Actual prices for paid versions are determined based on the version you use and the time of print or e-file and are subject to change without notice. Special discount offers may not be valid for mobile in-app purchases. Strikethrough prices reflect anticipated final prices for tax year 2023.
- TurboTax Free Edition: TurboTax Free Edition ($0 Federal + $0 State + $0 To File) is available for those filing Form 1040 and limited credits only, as detailed in the TurboTax Free Edition disclosures. Roughly 37% of taxpayers qualify. Offer may change or end at any time without notice.
- TurboTax Live Assisted Basic Offer: Offer only available with TurboTax Live Assisted Basic and for those filing Form 1040 and limited credits only. Roughly 37% of taxpayers qualify. Must file between November 29, 2023 and March 31, 2024 to be eligible for the offer. Includes state(s) and one (1) federal tax filing. Intuit reserves the right to modify or terminate this TurboTax Live Assisted Basic Offer at any time for any reason in its sole and absolute discretion. If you add services, your service fees will be adjusted accordingly. If you file after 11:59pm EST, March 31, 2024, you will be charged the then-current list price for TurboTax Live Assisted Basic and state tax filing is an additional fee. See current prices here.
- Full Service $100 Back Offer: Credit applies only to federal filing fees for TurboTax Full Service and not returns filed using other TurboTax products or returns filed by Intuit TurboTax Verified Pros. Excludes TurboTax Live Full Service Business and TurboTax Canada products . Credit does not apply to state tax filing fees or other additional services. If federal filing fees are less than $100, the remaining credit will be provided via electronic gift card. Intuit reserves the right to modify or terminate this offer at any time for any reason in its sole discretion. Must file by April 15, 2024 11:59 PM ET.
- TurboTax Full Service - Forms-Based Pricing: “Starting at” pricing represents the base price for one federal return (includes one W-2 and one Form 1040). Final price may vary based on your actual tax situation and forms used or included with your return. Price estimates are provided prior to a tax expert starting work on your taxes. Estimates are based on initial information you provide about your tax situation, including forms you upload to assist your expert in preparing your tax return and forms or schedules we think you’ll need to file based on what you tell us about your tax situation. Final price is determined at the time of print or electronic filing and may vary based on your actual tax situation, forms used to prepare your return, and forms or schedules included in your individual return. Prices are subject to change without notice and may impact your final price. If you decide to leave Full Service and work with an independent Intuit TurboTax Verified Pro, your Pro will provide information about their individual pricing and a separate estimate when you connect with them.
- Pays for itself (TurboTax Premium, formerly Self-Employed): Estimates based on deductible business expenses calculated at the self-employment tax income rate (15.3%) for tax year 2022. Actual results will vary based on your tax situation.
TURBOTAX ONLINE/MOBILE:
- Anytime, anywhere: Internet access required; standard data rates apply to download and use mobile app.
- Fastest refund possible: Fastest tax refund with e-file and direct deposit; tax refund time frames will vary. The IRS issues more than 9 out of 10 refunds in less than 21 days.
- Get your tax refund up to 5 days early: Individual taxes only. When it’s time to file, have your tax refund direct deposited with Credit Karma Money™, and you could receive your funds up to 5 days early. If you choose to pay your tax preparation fee with TurboTax using your federal tax refund or if you choose to take the Refund Advance loan, you will not be eligible to receive your refund up to 5 days early. 5-day early program may change or discontinue at any time. Up to 5 days early access to your federal tax refund is compared to standard tax refund electronic deposit and is dependent on and subject to IRS submitting refund information to the bank before release date. IRS may not submit refund information early.
- For Credit Karma Money (checking account): Banking services provided by MVB Bank, Inc., Member FDIC. Maximum balance and transfer limits apply per account.
- Fees: Third-party fees may apply. Please see Credit Karma Money Account Terms & Disclosures for more information.
- Pay for TurboTax out of your federal refund or state refund (if applicable): Individual taxes only. Subject to eligibility requirements. Additional terms apply. A $40 Refund Processing Service fee may apply to this payment method. Prices are subject to change without notice.
- TurboTax Help and Support: Access to a TurboTax product specialist is included with TurboTax Deluxe, Premium, TurboTax Live Assisted and TurboTax Live Full Service; not included with Free Edition (but is available as an upgrade). TurboTax specialists are available to provide general customer help and support using the TurboTax product. Services, areas of expertise, experience levels, wait times, hours of operation and availability vary, and are subject to restriction and change without notice. Limitations apply See Terms of Service for details.
- Tax Advice, Expert Review and TurboTax Live: Access to tax advice and Expert Review (the ability to have a Tax Expert review and/or sign your tax return) is included with TurboTax Live Assisted or as an upgrade from another version, and available through December 31, 2024. Intuit will assign you a tax expert based on availability. Tax expert and CPA availability may be limited. Some tax topics or situations may not be included as part of this service, which shall be determined in the tax expert’s sole discretion. For the TurboTax Live Assisted product, if your return requires a significant level of tax advice or actual preparation, the tax expert may be required to sign as the preparer at which point they will assume primary responsibility for the preparation of your return. For the TurboTax Live Full Service product: Handoff tax preparation by uploading your tax documents, getting matched with an expert, and meeting with an expert in real time. The tax expert will sign your return as a preparer. The ability to retain the same expert preparer in subsequent years will be based on an expert’s choice to continue employment with Intuit. Administrative services may be provided by assistants to the tax expert. On-screen help is available on a desktop, laptop or the TurboTax mobile app. Unlimited access to TurboTax Live tax experts refers to an unlimited quantity of contacts available to each customer, but does not refer to hours of operation or service coverage. Service, area of expertise, experience levels, wait times, hours of operation and availability vary, and are subject to restriction and change without notice.
- TurboTax Live Full Service – Qualification for Offer: Depending on your tax situation, you may be asked to answer additional questions to determine your qualification for the Full Service offer. Certain complicated tax situations will require an additional fee, and some will not qualify for the Full Service offering. These situations may include but are not limited to multiple sources of business income, large amounts of cryptocurrency transactions, taxable foreign assets and/or significant foreign investment income. Offer details subject to change at any time without notice. Intuit, in its sole discretion and at any time, may determine that certain tax topics, forms and/or situations are not included as part of TurboTax Live Full Service. Intuit reserves the right to refuse to prepare a tax return for any reason in its sole discretion. Additional limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
- TurboTax Live Full Service - File your taxes as soon as today: TurboTax Full Service Experts are available to prepare 2023 tax returns starting January 8, 2024. Based on completion time for the majority of customers and may vary based on expert availability. The tax preparation assistant will validate the customer’s tax situation during the welcome call and review uploaded documents to assess readiness. All tax forms and documents must be ready and uploaded by the customer for the tax preparation assistant to refer the customer to an available expert for live tax preparation.
- TurboTax Live Full Service -- Verified Pro -- “Local” and “In-Person”: Not all feature combinations are available for all locations. "Local" experts are defined as being located within the same state as the consumer’s zip code for virtual meetings. "Local" Pros for the purpose of in-person meetings are defined as being located within 50 miles of the consumer's zip code. In-person meetings with local Pros are available on a limited basis in some locations, but not available in all States or locations. Not all pros provide in-person services.
- Smart Insights: Individual taxes only. Included with TurboTax Deluxe, Premium, TurboTax Live, TurboTax Live Full Service, or with PLUS benefits, and is available through 11/1/2024. Terms and conditions may vary and are subject to change without notice.
- My Docs features: Included with TurboTax Deluxe, Premium TurboTax Live, TurboTax Live Full Service, or with PLUS benefits and is available through 12/31/2024. Terms and conditions may vary and are subject to change without notice.
- Tax Return Access: Included with all TurboTax Free Edition, Deluxe, Premium, TurboTax Live, TurboTax Live Full Service customers and access to up to the prior seven years of tax returns we have on file for you is available through 12/31/2024. Terms and conditions may vary and are subject to change without notice.
- Easy Online Amend: Individual taxes only. Included with TurboTax Deluxe, Premium, TurboTax Live, TurboTax Live Full Service, or with PLUS benefits. Make changes to your 2023 tax return online for up to 3 years after it has been filed and accepted by the IRS through 10/31/2026. Terms and conditions may vary and are subject to change without notice. For TurboTax Live Full Service, your tax expert will amend your 2023 tax return for you through 11/15/2024. After 11/15/2024, TurboTax Live Full Service customers will be able to amend their 2023 tax return themselves using the Easy Online Amend process described above.
- #1 best-selling tax software: Based on aggregated sales data for all tax year 2022 TurboTax products.
- #1 online tax filing solution for self-employed: Based upon IRS Sole Proprietor data as of 2023, tax year 2022. Self-Employed defined as a return with a Schedule C tax form. Online competitor data is extrapolated from press releases and SEC filings. “Online” is defined as an individual income tax DIY return (non-preparer signed) that was prepared online & either e-filed or printed, not including returns prepared through desktop software or FFA prepared returns, 2022.
- CompleteCheck: Covered under the TurboTax accurate calculations and maximum refund guarantees . Limitations apply. See Terms of Service for details.
- TurboTax Premium Pricing Comparison: Cost savings based on a comparison of TurboTax product prices to average prices set forth in the 2020-2021 NSA Fees-Acct-Tax Practices Survey Report.
- 1099-K Snap and Autofill: Available in mobile app and mobile web only.
- 1099-NEC Snap and Autofill: Available in TurboTax Premium (formerly Self-Employed) and TurboTax Live Assisted Premium (formerly Self-Employed). Available in mobile app only. Feature available within Schedule C tax form for TurboTax filers with 1099-NEC income.
- Year-Round Tax Estimator: Available in TurboTax Premium (formerly Self-Employed) and TurboTax Live Assisted Premium (formerly Self-Employed). This product feature is only available after you finish and file in a self-employed TurboTax product.
- **Refer a Friend: Rewards good for up to 20 friends, or $500 - see official terms and conditions for more details.
- Refer your Expert (Intuit’s own experts): Rewards good for up to 20 referrals, or $500 - see official terms and conditions for more details.
- Refer your Expert (TurboTax Verified Independent Pro): Rewards good for up to 20 referrals, or $500 - see official terms and conditions for more details
- Average Refund Amount: Sum of $3140 is the average refund American taxpayers received based upon IRS data date ending 2/17/23 and may not reflect actual refund amount received.
- Average Deduction Amount: Based on the average amount of deductions/expenses found by TurboTax Self Employed customers who filed expenses on Schedule C in Tax Year 2022 and may not reflect actual deductions found.
- More self-employed deductions based on the median amount of expenses found by TurboTax Premium (formerly Self Employed) customers who synced accounts, imported and categorized transactions compared to manual entry. Individual results may vary.
- TurboTax Online Business Products: For TurboTax Live Assisted Business and TurboTax Full Service Business, we currently don’t support the following tax situations: C-Corps (Form 1120-C), Trust/Estates (Form 1041), Multiple state filings, Tax Exempt Entities/Non-Profits, Entities electing to be treated as a C-Corp, Schedule C Sole proprietorship, Payroll, Sales tax, Quarterly filings, and Foreign Income. TurboTax Live Assisted Business is currently available only in AK, AZ, CA, CO, FL, GA, IL, MI, MO, NC, NV, NY, OH, PA, SD, TX, UT, VA, WA, and WY.
- Audit Defense: Audit Defense is a third-party add-on service provided, for a fee, by TaxResources, Inc., dba Tax Audit. See Membership Agreements at https://turbotax.intuit.com/corp/softwarelicense/ for service terms and conditions.
TURBOTAX DESKTOP GUARANTEES
TurboTax Desktop Individual Returns:
- 100% Accurate Calculations Guarantee – Individual Returns: If you pay an IRS or state penalty or interest because of a TurboTax calculation error, we’ll pay you the penalty and interest. Excludes payment plans. This guarantee is good for the lifetime of your personal, individual tax return, which Intuit defines as seven years from the date you filed it with TurboTax Desktop. Excludes TurboTax Desktop Business returns. Additional terms and limitations apply. See License Agreement for details.
- Maximum Refund Guarantee / Maximum Tax Savings Guarantee - or Your Money Back – Individual Returns: If you get a larger refund or smaller tax due from another tax preparation method by filing an amended return, we'll refund the applicable TurboTax federal and/or state software license purchase price you paid. This guarantee is good for the lifetime of your personal, individual tax return, which Intuit defines as seven years from the date you filed it with TurboTax Desktop. Excludes TurboTax Desktop Business returns. Additional terms and limitations apply. See License Agreement for details.
- Audit Support Guarantee – Individual Returns: If you receive an audit letter from the IRS or State Department of Revenue based on your 2023 TurboTax individual tax return, we will provide one-on-one question-and-answer support with a tax professional, if requested through our Audit Report Center , for audited individual returns filed with TurboTax Desktop for the current 2023 tax year and, for individual, non-business returns, for the past two tax years (2021, 2022). Audit support is informational only. We will not represent you before the IRS or state tax authority or provide legal advice. If we are not able to connect you to one of our tax professionals, we will refund the applicable TurboTax federal and/or state license purchase price you paid. This guarantee is good for the lifetime of your personal, individual tax return, which Intuit defines as seven years from the date you filed it with TurboTax Desktop. Excludes TurboTax Desktop Business returns. Additional terms and limitations apply. See License Agreement for details.
- Satisfaction Guarantee/ 60-Day Money Back Guarantee: If you're not completely satisfied with TurboTax Desktop, go to refundrequest.intuit.com within 60 days of purchase and follow the process listed to submit a refund request. You must return this product using your license code or order number and dated receipt.
TurboTax Desktop Business Returns:
- 100% Accurate Calculations Guarantee – Business Returns: If you pay an IRS or state penalty or interest because of a TurboTax calculation error, we’ll pay you the penalty and interest. Excludes payment plans. You are responsible for paying any additional tax liability you may owe. Additional terms and limitations apply. See License Agreement for details.
- Maximum Tax Savings Guarantee – Business Returns: If you get a smaller tax due (or larger business tax refund) from another tax preparation method using the same data, TurboTax will refund the applicable TurboTax Business Desktop license purchase price you paid. Additional terms and limitations apply. See License Agreement for details.
TURBOTAX DESKTOP
- Installation Requirements: Product download, installation and activation requires an Intuit Account and internet connection. Product limited to one account per license code. You must accept the TurboTax License Agreement to use this product. Not for use by paid preparers.
- TurboTax Desktop Products: Price includes tax preparation and printing of federal tax returns and free federal e-file of up to 5 federal tax returns. Additional fees may apply for e-filing state returns. E-file fees may not apply in certain states, check here for details . Savings and price comparison based on anticipated price increase. Software updates and optional online features require internet connectivity.
- Fastest Refund Possible: Fastest federal tax refund with e-file and direct deposit; tax refund time frames will vary. The IRS issues more than 9 out of 10 refunds in less than 21 days.
- Average Refund Amount: Sum of $3140 is the average refund American taxpayers received based upon IRS data date ending 02/17/23 and may not reflect actual refund amount received.
- TurboTax Product Support: Customer service and product support hours and options vary by time of year.
- #1 Best Selling Tax Software: Based on aggregated sales data for all tax year 2022 TurboTax products.
- Deduct From Your Federal or State Refund (if applicable): A $40 Refund Processing Service fee may apply to this payment method. Prices are subject to change without notice.
- Data Import: Imports financial data from participating companies; Requires Intuit Account. Quicken and QuickBooks import not available with TurboTax installed on a Mac. Imports from Quicken (2021 and higher) and QuickBooks Desktop (2021 and higher); both Windows only. Quicken import not available for TurboTax Desktop Business. Quicken products provided by Quicken Inc., Quicken import subject to change.
- Audit Defense: Audit Defense is a third-party add-on service provided, for a fee, by TaxResources, Inc., dba Tax Audit. See Membership Agreements at https://turbotax.intuit.com/corp/softwarelicense/ for service terms and conditions.
All features, services, support, prices, offers, terms and conditions are subject to change without notice.
Compare TurboTax products
All online tax preparation software
TurboTax online guarantees
TurboTax security and fraud protection
Tax forms included with TurboTax
TurboTax en español
TurboTax Live en español
Self-employed tax center
Tax law and stimulus updates
Tax Refund Advance
Unemployment benefits and taxes
File your own taxes
TurboTax crypto taxes
Credit Karma Money
Investment tax tips
Online software products
TurboTax login
Free Edition tax filing
Deluxe to maximize tax deductions
TurboTax self-employed & investor taxes
Free military tax filing discount
TurboTax Live tax expert products
TurboTax Live Premium
TurboTax Live Full Service Pricing
TurboTax Live Full Service Business Taxes
TurboTax Live Assisted Business Taxes
TurboTax Business Tax Online
Desktop products
TurboTax Desktop login
All Desktop products
Install TurboTax Desktop
Check order status
TurboTax Advantage
TurboTax Desktop Business for corps
Products for previous tax years
Tax tips and video homepage
Browse all tax tips
Married filing jointly vs separately
Guide to head of household
Rules for claiming dependents
File taxes with no income
About form 1099-NEC
Crypto taxes
About form 1099-K
Small business taxes
Amended tax return
Capital gains tax rate
File back taxes
Find your AGI
Help and support
TurboTax support
Where's my refund
File an IRS tax extension
Tax calculators and tools
TaxCaster tax calculator
Tax bracket calculator
Check e-file status refund tracker
W-4 tax withholding calculator
ItsDeductible donation tracker
Self-employed tax calculator
Crypto tax calculator
Capital gains tax calculator
Bonus tax calculator
Tax documents checklist
Social and customer reviews
TurboTax customer reviews
TurboTax blog
TurboTax Super Bowl commercial
TurboTax vs H&R Block reviews
TurboTax vs TaxSlayer reviews
TurboTax vs TaxAct reviews
TurboTax vs Jackson Hewitt reviews
More products from Intuit
TurboTax Canada
Accounting software
QuickBooks Payments
Professional tax software
Professional accounting software
Credit Karma credit score
More from Intuit
©1997-2024 Intuit, Inc. All rights reserved. Intuit, QuickBooks, QB, TurboTax, ProConnect, and Mint are registered trademarks of Intuit Inc. Terms and conditions, features, support, pricing, and service options subject to change without notice.
Security Certification of the TurboTax Online application has been performed by C-Level Security.
By accessing and using this page you agree to the Terms of Use .
Key benefits of travel medical insurance
- Travel medical insurance coverage
- Who needs medical travel insurance?
Choosing the right travel medical insurance
How to use travel medical insurance, is travel medical insurance right for your next trip, travel medical insurance: essential coverage for health and safety abroad.
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate insurance products to write unbiased product reviews.
- Travel medical insurance covers unexpected emergency medical expenses while traveling.
- Travelers off to foreign countries or remote areas should strongly consider travel medical insurance.
- If you have to use your travel medical insurance, keep all documents related to your treatment.
Of all the delights associated with travel to far-flung locales, getting sick or injured while away from home is low on the savvy traveler's list. Beyond gut-wrenching anxiety, seeking medical treatment in a foreign country can be exceedingly inconvenient and expensive.
The peace of mind that comes with travel insurance for the many things that could ail you while abroad is priceless. As options for travel-related insurance abound, it's essential to research, read the fine print, and act according to the specifics of your itinerary, pocketbook, and other needs.
Travel insurance reimburses you for any unexpected medical expenses incurred while traveling. On domestic trips, travel medical insurance usually take a backseat to your health insurance. However, when traveling to a foreign country, where your primary health insurance can't cover you, travel medical insurance takes the wheel. This can be especially helpful in countries with high medical care costs, such as Scandinavian countries.
Emergency medical evacuation insurance
Another benefit that often comes with travel medical insurance, emergency medical evacuation insurance covers you for any costs to transport you to an adequately equipped medical center. Emergency medical evacuation insurance is often paired with repatriation insurance, which covers costs associated with returning your remains to your home country if the worst happens.
These benefits are for worst-case scenarios, but they might be more necessary depending on the type of trips you take. Emergency medical evacuation insurance is helpful if you're planning on traveling to a remote location or if you're traveling on a cruise as sea to land evacuations can be costly. Some of the best travel insurance companies also offer non-medical evacuations as part of an adventure sports insurance package.
It's also worth mentioning that emergency medical evacuation insurance is required for international students studying in the US on a J Visa.
Types of coverage offered by travel medical insurance
The exact terms of your coverage will vary depending on your insurer, but you can expect most travel medical insurance policies to offer the following coverages.
- Hospital room and board
- Inpatient/outpatient hospital services
- Prescription Drugs
- COVID-19 treatment
- Emergency room services
- Urgent care visits
- Local ambulance
- Acute onset of pre-existing conditions
- Dental coverage (accident/sudden relief of pain)
- Medical care due to terrorist attack
- Emergency medical evacuation
- Repatriation of mortal remains
- Accidental death and dismemberment
Travel medical insurance and pre-existing conditions
Many travel insurance providers will cover pre-existing conditions as long as certain conditions are met. For one, travelers need to purchase their travel insurance within a certain time frame from when they placed a deposit on their trip, usually two to three weeks.
Additionally, travel insurance companies usually only cover stable medical conditions, which are conditions that don't need additional medical treatment, diagnosis, or medications.
Who needs travel medical insurance?
Even the best-laid travel plans can go awry. As such, it pays to consider your potential healthcare needs before taking off, even if you are generally healthy. Even if well-managed, preexisting conditions like diabetes or asthma can make a medical backup plan even more vital.
Having what you need to refill prescriptions or get other care if you get stuck somewhere other than home could be essential to your health and well-being. That's without counting all the accidents and illnesses that can hit us when away from home.
Individuals traveling for extended periods (more than six months) or engaging in high-risk activities (think scuba diving or parasailing) should also consider a solid medical travel plan. Both scenarios increase the likelihood that medical attention, whether routine or emergency, could be needed.
In the case of travel via the friendly seas, it's also worth considering cruise trip medical travel insurance . Routine care will be available onboard. But anything beyond that will require transportation to the nearest land mass (and could quickly become extremely expensive, especially if you're in another country).
Like other types of insurance, medical travel insurance rates are calculated based on various factors. Failing to disclose a preexisting health condition could result in a lapse of coverage right when you need it, as insurers can cancel your policy if you withhold material information. So honesty is always the best policy.
Even the best-laid travel plans can go awry. As such, it pays to consider your potential healthcare needs before taking off, even if you are generally healthy. Making the right choice when shopping for travel medical insurance can mean the difference between a minor hiccup in your travels and a financial nightmare.
When a travel insurance company comes up with a quote for your policy, they take a few factors into consideration, such as your age, your destination, and the duration of your trip. You should do the same when assessing a travel insurance company.
For example, older travelers who are more susceptible to injury may benefit from travel medical insurance (though your premiums will be higher). If you're traveling for extended periods throughout one calendar year, you should look into an annual travel medical insurance plan . If you're engaging in high-risk activities (think scuba diving or parasailing), you should seek a plan that includes coverage for injuries sustained in adventure sports.
Travel medical insurance isn't just for peace of mind. If you travel often enough, there's a good chance you'll eventually experience an incident where medical treatment is necessary.
Before you submit your claim, you should take some time to understand your policy. Your travel medical insurance is either primary (you can submit claims directly to your travel medical insurance provider) or secondary (you must first submit claims to your primary insurance provider). In the case of secondary travel medical insurance, a refusal notice from your primary insurance provider, even if it does not cover medical claims outside the US, is often required as evidence of protocol.
On that note, you should be sure to document every step of your medical treatment. You should keep any receipts for filled prescriptions, hospital bills, and anything else documenting your medical emergency.
As many people have found out the hard way, reading the fine print is vital. Most travel insurance policies will reimburse your prepaid, nonrefundable expenses if you fall ill with a severe condition, including illnesses like COVID-19.
Still on the fence about whether or not medical travel insurance is worth it ? It's worth noting that many travel insurance plans also include medical protections, so you can also protect against trip cancellations and other unexpected developments while obtaining travel medical insurance.
While short, domestic trips may not warrant travel medical insurance, it may be a good idea to insure longer, international trips. You should also consider travel medical insurance for trips to remote areas, where a medical evacuation may be expensive, and more physically tasking trips.
While shopping for travel medical insurance may not be fun, a little advance leg work can let you relax on your trip and give you peace of mind. After all, that is the point of a vacation.
Medical travel insurance frequently asked questions
Trip insurance covers any unexpected financial losses while traveling, such as the cost of replacing lost luggage, trip interruptions, and unexpected medical expenses. Travel medical insurance just covers those medical expenses without the trip interruption or cancellation insurance.
Travel insurance companies usually offer adventure sports as add-on coverage or a separate plan entirely. You'll likely pay more for a policy with adventure sports coverage.
Many travel medical insurance policies now include coverage for COVID-19 related medical expenses and treat it like any other illness. However, you should double-check your policy to ensure that is the case.
Editorial Note: Any opinions, analyses, reviews, or recommendations expressed in this article are the author’s alone, and have not been reviewed, approved, or otherwise endorsed by any card issuer. Read our editorial standards .
Please note: While the offers mentioned above are accurate at the time of publication, they're subject to change at any time and may have changed, or may no longer be available.
**Enrollment required.

- Main content

What you need to know about work-related travel expenses in Australia
I f you are required to travel as part of your job, then you likely incur various costs. Whether making a short trip to attend a meeting or taking an overseas trip for an extended period, you can deduct your travel expenses. However, the laws surrounding travel expenses are complicated, and the Australia Taxation Office (ATO) keeps close tabs on travel expenses . So, it's vital to pay close attention to what you claim to avoid mistakes.
What is work-related travel expenses
Work-related travel expenses are expenses incurred while travelling for work. If you incur any expenses related to work-related travel, such as accommodation or meals, you may be able to claim them as travel expenses on your tax return.
Using your car for work
If your job requires you to use a personal vehicle, you are entitled to deduct the motoring costs you incur while completing your job. This does not generally include the commute you make from your home to your place of work.
Eligibility
However, there are limited circumstances that may allow it. For example,
- An employee travelling between work sites throughout the day can claim their commute.
- If you travel directly from one job to a second job, as long as you do not return home in between.
- If you are travelling to a course or meeting for work, you can deduct expenses.
Methods to calculate work-related travel expenses
There are two options when it comes to vehicle travel for work tax deductions.
- As of April 2023, there is a flat rate of 78 cents per kilometre, and you can claim up to 5,000 km . You will need to keep a log of your travel to determine how far you travel for work purposes.
- Use a logbook if you travel and detail your running expenses, from mileage to fuel, servicing, repairs, insurance, and depreciation. If you use the logbook method, your logbook needs to show your work-related trips for a minimum continuous period of 12 weeks
Alternatively, you can use a r eputable tax software that will provide you with mileage auto-tracking and a simple snap and store for all of the receipts related to your business expenses.
Ensure you maintain your logbook for a minimum of 12 weeks before relying on it for your income tax return. The log should include odometer readings to determine the proportion of time you use it for work purposes. Store all receipts and invoices noting your spending on your vehicle so that you can claim the correct percentage of vehicle expenses.
Travel to and from work is considered a private expenditure unless your employer requires you to transport bulky equipment and vehicles. That being said, the ATO pays close attention to these types of claims and may disallow them.
Other work-related transport expenses in Australia
There are other expenses that can also be claimed for work-related travel if they are for:
- Heavy vehicles and utes if they have a carrying capacity of more than one tonne
- Vans with a carrying capacity of 9 or more passengers
- Fees for hiring or renting a car
- Costs incurred while driving someone else's vehicle for work purposes, such as fuel expenses
- Public transportation fares, including air, bus, train, tram, ferry, taxi, ride-share or ride-sourcing fares
- Expenses associated with work-related transport expenses such as bridge tolls, road tolls, and car parking fees
Other travel expenses
You can claim additional work-related travel expenses for costs you incur that your employer doesn't reimburse. These travel expenses must be work-related rather than your daily commute to and from work.
- Airfare and taxi fares
- Tunnel or bridge tolls
- Car parking
- The cost of public transport
If you are fined for a motoring offence, whether it is for parking, speeding or otherwise, you cannot claim these.
Overnight meals & accommodation
If you are travelling away from home, you can claim accommodation, meals and entertainment. You cannot claim meal expenses if your employer reimburses you or provides you with a full allowance for these expenses. A number of businesses will provide an allowance, expenses included, so the employee doesn't need to cover the costs. You may be taxed for those allowances, in which case a deduction is possible for costs incurred.
The ATO provides a lengthy list of what is viewed as a reasonable spend on accommodation, meals, and incidental expenses. You won't need to produce detailed records with receipts or invoices if you claim below the specified ATO allowance. If you exceed the reasonable amounts as laid out by the ATO, or you don't receive an allowance, then you need to keep detailed records to show your spending wasn't extravagant.
The ATO established a reasonable amount to highlight when detailed records must be kept. Many people would assume that they can claim this maximum amount, but we don't recommend you do this. You must only claim the amount of money you spent.
Even if you claim below the reasonable amount, you should be able to prove the expenses you incurred. A bank or credit card statement is viewed as sufficient evidence should the need arise. It will help support your claim that you were in the particular area at the time you claimed.
As long as your travel includes an overnight stay, you can claim business meals, food and beverages. You can't claim meals when you work from home. You could claim tax travel expenses if you always work from home and need to travel to an office.
What you can’t claim
Travel for personal reasons or between your home and your workplace can’t be claimed Examples include:
- Travel between your home and regular place of work or vice versa
- Travel for personal reasons, like running errands on the way to or from work
- Travel for overtime or out-of-hours work
- Travel from your home (which is also your place of work for one job) to another location where you work for someone else
Read our guide to tax deductions to learn about other tax deductions.
Other situations that allow you to claim travel deductions
You may be able to claim work-related travel expenses tax if you attend a work conference or course. If it is local, you can claim transport or mileage. If it's interstate or overseas, you can claim accommodation, airfares and meals.
In all cases, your best bet is to visit a tax agent to ensure your travel deductions are above board.
This article originally appeared on QuickBooks and was syndicated by MediaFeed.org .
43 incredible facts about Australia you may not believe are true

That home office tax deduction may not apply to you. Here's who qualifies

If you took advantage of your company's flexible work from home policy last year, don't be surprised if all those receipts you diligently kept all through the year for tax deductions end up in the bin.
That's because wage employees who choose to work from home take on the full weight of their related expenses, tax experts say. And some of those expenses can add up. A survey by credit card comparison site creditcards.com in 2020 said people working from home spent an average of $108 more per month , led by higher expenses for food and utilities.
The 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act eliminated unreimbursed itemized deductions for employees, and Congress never brought them back despite a surge in people working from home. The rule runs through 2025, said Eric Scaringe, principal at certified public accounting firm UHY.
Need to know: When is Tax Day 2024? Deadlines for filing tax returns, extensions and what you need to know
Among those who have a workplace outside of their home, 35% said they never enter their offices, down from 43% in January 2022 and 55% in October 2020 but up from only 7% before the pandemic, according to Pew Research Center . Forty-one percent split their time between home and office, up from 35% in January 2022, it said. Despite all that work at home, most of them likely aren't eligible for any home office deductions.
Home office deductions only apply to small business owners who are self-employed. If you do freelance work unrelated to your regular job at home, you might qualify. The rules are strict, though, and calculating your deductions can be complicated.
Here’s a step-by-step guide for figuring out if you qualify for deductions and if so, what to consider in your calculations :
Who qualifies for home office deductions?
Generally, if you receive a W-2 wages tax document, you’re not eligible unless you also have a side gig that you do from home - at least on the federal level.
"Some states might allow you to take some deductions," said Mark Jaeger, vice president of tax operations at preparer TaxAct.]
Pennsylvania and New York, for example, allow employees to deduct some unreimbursed expenses. Check your state's rules.
Self-employed: If you're self-employed and use your home office exclusively and regularly for that work, you may be able to deduct from your federal taxes a portion of home-related expenses, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, homeowners' insurance, and utilities.
But be mindful of details, experts say.
“If you work on your dining table, you can't deduct that because it’s not used exclusively for work,” said Therese Tippie, EP Wealth Advisors’ tax manager and financial planner. “But you could purchase a desk and have it in a corner of your house and if that’s used exclusively and regularly for work, you can deduct that space.”
There are two ways to take a deduction for your home office space: simplified or regular.
Simplified home office deduction
You can deduct $5 per square foot, up to $1,500 or 300 square feet, a year for your exclusive home office space -- if it's used for the full year. If you only use that space part of the time, then you prorate that amount, Tippie said.
Regular direct home office deduction
This could result in a larger deduction. However, it requires you to track all your home office expenses, including any costs for repairing and maintaining the space.
“If you have a spare bedroom and made repairs to turn it into an office -- added built-in shelving, painted it to get it ready for Zoom meetings ... all that can be counted toward home office expenses,” Tippie said.
You can also claim deductions for a portion of other expenses such as rent or property taxes, home depreciation, and utilities -- based on the proportion of the space to the rest of your house.
For example, if your office is 250 square feet and your home is 1,000 square feet, you'd deduct 25% of your allowable expenses (250/1,000 = 0.25). If you had $10,000 in eligible home-related expenses, you could claim up to $2,500 in deductions. There isn’t a limit on how much you can deduct.
Expensive utilities: Even with a mild winter, more Americans struggle to pay their energy bills
Fairness: A 30% national sales tax? Abolishing the IRS? What the FairTax Act of 2023 would do.
Can I deduct supplies?
Yes, if they are both common to your industry and necessary to help your business -- and you have receipts.
Items you might deduct include cell phones, laptops, printers, and other office supplies.
“Given the value of these items, you can just write off the entire amount and expense it,” Tippie said. “You don't need to capitalize it. It would go on Schedule C as office or supplies expense in the other expense section.”
Remember, though, if you also use any of these items for personal things, only the proportion used for work should be deducted. For example, if you buy a $2,500 laptop but use it 40% of the time for work, you can write off $1,000.
Who files returns: Who has to file a tax return: It's not necessary for everyone. Here are the rules.
Side gigs: Higher inflation means more work. More Americans take on multiple jobs to make ends meet
Business lunch tax deduction reverts to half
As of Jan. 1, 2023, companies had to go Dutch. The business lunch deduction reverted to the pre-pandemic 50% in 2023. The Taxpayer Certainty and Disaster Relief Act of 2020 temporarily boosted the business deduction for food and beverages to 100%, including tax and tip, for 2021 and 2022.
Note, entertainment expenses are not deductible and haven’t been since the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act in 2017, the IRS said. If you take someone to an establishment that offers entertainment and food, you must separate the food from the entertainment cost and only deduct that portion.
Working cars: Tax season 2023: What exactly is the mileage rate? There's more than one.
Get out of my business: Who needs to know? Small businesses object as feds infringe on Americans' privacy.
Is there any way for W-2 wage workers to get some money back for business expenses?
Not through your taxes, but you might be able to ask your employer.
"You can try to get your company to pay for it if they require you to work from home,” Tippie said. "They can reimburse you and deduct it, but then, some might just require employees to come to the office.”
More of your 2024 tax season questions answered:
IRS announces new tax brackets for 2024. What does that mean for you?
Flush with new funding, the IRS zeroes in on the taxes of uber-wealthy Americans
Need a new tax strategy? These money-saving tips taken by Dec 31 may help pad your pockets
Your single largest payday may be a 2023 tax filing away. File early to get a refund sooner
Is it better to pay someone to do your taxes or do them yourself? We'll help you decide.
New IRS tax brackets and standard deductions for 2024: See how much they were raised
IRS delays 1099-K rules for ticket sales, announces new $5,000 threshold for 2024
IRS to offer pandemic-related relief on some penalties to nearly 5 million taxpayers
Driving for work will pay more next year after IRS boosts 2024 mileage rate
What is OASDI tax on my paycheck? Here's why you and your employer pay this federal tax.
A 30% national sales tax? Abolishing the IRS? Here's what the FairTax Act of 2023 would do
These 8 states don’t have an income tax. Does yours make the list?
What is net pay? How it works, how to calculate it and its difference from gross pay
Medora Lee is a money, markets, and personal finance reporter at USA TODAY. You can reach her at [email protected] and subscribe to our free Daily Money newsletter for personal finance tips and business news every Monday through Friday.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tax Tip 2023-15, February 7, 2023 — Whether someone travels for work once a year or once a month, figuring out travel expense tax write-offs might seem confusing. The IRS has information to help all business travelers properly claim these valuable deductions.
Travel expenses are the ordinary and necessary expenses of traveling away from home for your business, profession, or job. ... you may not deduct travel expenses at a work location if you realistically expect that you'll work there for more than one year, whether or not you actually work there that long. ... plus any parking fees, ferry fees ...
To find the percentage, compare the size of space you use for business to that of your entire home, and then apply the percentage to the specific expenses. For instance, if your home is 1,800 ...
To be able to claim all the possible travel deductions, your trip should require you to sleep somewhere that isn't your home. 2. You should be working regular hours. In general, that means eight hours a day of work-related activity. It's fine to take personal time in the evenings, and you can still take weekends off.
You figure the deductible part of your air travel expenses by subtracting 7 / 18 of the round-trip airfare and other expenses you would have had in traveling directly between New York and Dublin ($1,250 × 7 / 18 = $486) from your total expenses in traveling from New York to Paris to Dublin and back to New York ($750 + $400 + $700 = $1,850).
You can also potentially deduct the cost of lodging on the days when you're not conducting business, but it depends on how you schedule your trip. The trick is to wedge "vacation days" in between work days. Here's a sample itinerary to explain how this works: Thursday: Fly to Durham, NC. Friday: Meet with clients.
You can deduct business travel expenses when you are away from both your home and the location of your main place of business (tax home). Deductible expenses include transportation, baggage fees, car rentals, taxis and shuttles, lodging, tips, and fees. You can also deduct 50% of either the actual cost of meals or the standard meal allowance ...
Standard business travel expenses include lodging, food, transportation costs, shipping of baggage and/or work items, laundry and dry cleaning, communication costs, and tips. But numerous rules apply so check with a tax professional before you claim them.
If you regularly travel as part of your work, here are the top deductions for travel expenses you can use as well as some you can't deduct. ... In order to claim travel expenses as a deduction, they must be itemized on Form 2106 for employees or Schedule C for self-employed individuals. FAQ
If you're self-employed or own a business, you can deduct work-related travel expenses, including vehicles, airfare, lodging, and meals.The expenses must be ordinary and necessary. For vehicle expenses, you can choose between the standard mileage rate or the actual cost method where you track what you paid for gas and maintenance.. You can generally only claim 50% of the cost of your meals ...
International travel has additional rules to consider when claiming travel expense deductions. As mentioned, you must spend at least 25% of your time abroad conducting business to claim travel-expense deductions. If you use 25% or less of your trip for business purposes, you can deduct related travel costs in proportion to the time spent on work.
Here's a list of common self-employed business travel expenses you can deduct as a taxpayer: Meal expenses (50% deductible) Lodging. Transportation costs (can include gas, airfare, car rental fees, taxis, baggage fees and other travel-related expenses) The cost of transporting supplies, such as display materials.
Eligible W-2 employees need to itemize to deduct work expenses. If you are an eligible W-2 employee, you can only deduct work expenses on your taxes if you decide to itemize your deductions. Your ...
If you have receipts then you can claim business-related travel expenses except for regular commuting to and from your place of employment. You can also potentially claim for 50% of the cost of some of the meals you eat while travelling for business. ... One exception to this is work-from-home expenses during the 2020, 2021, and 2022 tax years ...
What Tax-Deductible Travel Costs Mean for Individuals . Understanding travel expenses can be helpful for individuals who have their own businesses, including those who freelance or do gig work, thus filling out tax forms such as Schedule C.By accounting for these costs, you can reduce your taxable income, meaning you pay less in taxes than you would if you didn't deduct these expenses.
Travel expenses are costs associated with traveling for the purpose of conducting business-related activities. Travel expenses can generally be deducted by employees as non-reimbursed travel ...
For self-employed travel expenses, you will list travel write-offs on Schedule C Form 1040. Businesses must claim travel expenses on Form 2106 and report them on Form 1040 or Form 1040-SR as an adjustment to their total income. While there's no annual travel deduction limit, the IRS scrutinizes higher write-offs.
Business travel deductions are available when employees must travel away from their tax home or main place of work for business reasons. The travel period must be substantially longer than an ordinary day's work and a need for sleep or rest to meet the demands the work while away. Travel expenses must be ordinary and necessary. They can't be ...
Using Form 2016 and Schedule A. 1. Total your transportation and lodging expenses. To claim your travel expenses as a deduction on your taxes, start with Form 2016 or Form 2016-EZ. The first lines of these forms ask for your total transportation and lodging expenses for the year.
Travel expenses are only deductible on the days in which the work-related event occurs. "For example, a taxi ride to the meeting, train to a conference, or plane ride to the event [are deductible]," says Adams. "Lodging, much like travel expenses, is deductible on the days in which business is set to occur."
Keep a record of your business-related mileage expenses. Multiply your yearly mileage by the current AMAP mileage rate and deduct your employer's mileage allowance, if any. If it is under £2,500, you can file your claim on your self-assessment tax return. If your claim is over £2,500 then you must file a self-assessment tax return.
If you have to travel for your work you may be able to claim tax relief on the cost or money you've spent on food or overnight expenses. You cannot claim for travelling to and from work, unless ...
If the expense was for both work and private purposes, you can only claim a deduction for the work-related portion. If your total claim for work-related expenses is more than $300, you must have written evidence to prove your claims. Work-related travel expenses include: public transport, air travel and taxi fares. short-term car hire.
Auto and travel expenses. Business travel expenses are some of the most frequent work-related deductions. Deductible auto costs include expenses for traveling between one workplace and another (not including a home office), visiting clients, going to a business meeting away from your regular workplace or getting to a temporary workplace. If you ...
File a claim for general health care travel reimbursement online. General health care travel reimbursement covers these expenses for eligible Veterans and caregivers: Regular transportation, such as by car, plane, train, bus, taxi, or light rail. Approved meals and lodging expenses. You can file a claim online through the Beneficiary Travel ...
Travel insurance reimburses you for any unexpected medical expenses incurred while traveling. On domestic trips, travel medical insurance usually take a backseat to your health insurance.
travel agency) is encouraged and in some cases mandatory. Use of purchasing cards or central billing is highly encouraged. Employees in travel status are expected to use good judgment when incurring travel costs. Only expenses incurred while conducting official State business will be reimbursed.
Work-related travel expenses are expenses incurred while travelling for work. If you incur any expenses related to work-related travel, such as accommodation or meals, you may be able to claim ...
You may be eligible for travel reimbursement if you pay expenses to and from your appointment. Learn if you're eligible and how to file a claim. ...
Pennsylvania and New York, for example, allow employees to deduct some unreimbursed expenses. Check your state's rules. Self-employed: If you're self-employed and use your home office exclusively ...