FAC Number: 2024-03 Effective Date: 02/23/2024

31.205-46 Travel costs.
(a) Costs for transportation, lodging, meals, and incidental expenses.
(1) Costs incurred by contractor personnel on official company business are allowable, subject to the limitations contained in this subsection. Costs for transportation may be based on mileage rates, actual costs incurred, or on a combination thereof, provided the method used results in a reasonable charge. Costs for lodging, meals, and incidental expenses may be based on per diem, actual expenses, or a combination thereof, provided the method used results in a reasonable charge.
(2) Except as provided in paragraph (a)(3) of this subsection, costs incurred for lodging, meals, and incidental expenses (as defined in the regulations cited in (a)(2)(i) through (iii) of this section) shall be considered to be reasonable and allowable only to the extent that they do not exceed on a daily basis the maximum per diem rates in effect at the time of travel as set forth in the-
(i) Federal Travel Regulations, prescribed by the General Services Administration, for travel in the contiguous United States , available on a subscription basis from the-
Superintendent of Documents
U.S. Government Publishing Office
Washington DC 20402
Stock No.922-002-00000-2;
(ii) Joint Travel Regulation, Volume2, DoD Civilian Personnel, AppendixA, prescribed by the Department of Defense, for travel in Alaska, Hawaii, and outlying areas of the United States , available on a subscription basis from the-
Stock No.908-010-00000-1; or
(iii) Standardized Regulations (Government Civilians, Foreign Areas), Section 925, "Maximum Travel Per Diem Allowances for Foreign Areas," prescribed by the Department of State, for travel in areas not covered in (a)(2)(i) and (ii) of this paragraph, available on a subscription basis from the-
Washington, DC 20402
Stock No.744-008-00000-0.
(3) In special or unusual situations, actual costs in excess of the above-referenced maximum per diem rates are allowable provided that such amounts do not exceed the higher amounts authorized for Federal civilian employees as permitted in the regulations referenced in (a)(2)(i), (ii), or (iii) of this section. For such higher amounts to be allowable, all of the following conditions must be met:
(i) One of the conditions warranting approval of the actual expense method, as set forth in the regulations referenced in paragraphs (a)(2)(i), (ii), or (iii) of this section, must exist.
(ii) A written justification for use of the higher amounts must be approved by an officer of the contractor’s organization or designee to ensure that the authority is properly administered and controlled to prevent abuse.
(iii) If it becomes necessary to exercise the authority to use the higher actual expense method repetitively or on a continuing basis in a particular area, the contractor must obtain advance approval from the contracting officer .
(iv) Documentation to support actual costs incurred shall be in accordance with the contractor’s established practices, subject to paragraph (a)(7) of this section, and provided that a receipt is required for each expenditure of $75.00 or more. The approved justification required by paragraph (a)(3)(ii) of this section and, if applicable, paragraph (a)(3)(iii) of this section must be retained.
(4) Paragraphs (a)(2) and (3) of this section do not incorporate the regulations cited in paragraphs (a)(2)(i), (ii), and (iii) of this section in their entirety. Only the maximum per diem rates, the definitions of lodging, meals, and incidental expenses, and the regulatory coverage dealing with special or unusual situations are incorporated herein.
(5) An advance agreement (see 31.109 ) with respect to compliance with paragraphs (a)(2) and (3) of this subsection may be useful and desirable.
(6) The maximum per diem rates referenced in paragraph (a)(2) of this subsection generally would not constitute a reasonable daily charge-
(i) When no lodging costs are incurred; and/or
(ii) On partial travel days ( e.g., day of departure and return).
Appropriate downward adjustments from the maximum per diem rates would normally be required under these circumstances. While these adjustments need not be calculated in accordance with the Federal Travel Regulation or Joint Travel Regulations, they must result in a reasonable charge.
(7) Costs shall be allowable only if the following information is documented-
(i) Date and place (city, town, or other similar designation) of the expenses;
(ii) Purpose of the trip; and
(iii) Name of person on trip and that person’s title or relationship to the contractor.
(b) Airfare costs in excess of the lowest priced airfare available to the contractor during normal business hours are unallowable except when such accommodations require circuitous routing, require travel during unreasonable hours, excessively prolong travel, result in increased cost that would offset transportation savings, are not reasonably adequate for the physical or medical needs of the traveler, or are not reasonably available to meet mission requirements. However, in order for airfare costs in excess of the above airfare to be allowable, the applicable condition(s) set forth above must be documented and justified.
(1) "Cost of travel by contractor-owned, -leased, or -chartered aircraft," as used in this paragraph, includes the cost of lease, charter, operation (including personnel), maintenance, depreciation , insurance , and other related costs .
(2) The costs of travel by contractor-owned, -leased, or -chartered aircraft are limited to the allowable airfare described in paragraph (b) of this section for the flight destination unless travel by such aircraft is specifically required by contract specification, term, or condition, or a higher amount is approved by the contracting officer . A higher amount may be agreed to when one or more of the circumstances for justifying higher than allowable airfare listed in paragraph (b) of this section are applicable, or when an advance agreement under paragraph (c)(3) of this section has been executed. In all cases, travel by contractor-owned, -leased, or -chartered aircraft must be fully documented and justified. For each contractor-owned, -leased, or -chartered aircraft used for any business purpose which is charged or allocated, directly or indirectly, to a Government contract, the contractor must maintain and make available manifest/logs for all flights on such company aircraft. As a minimum, the manifest/log shall indicate-
(i) Date, time, and points of departure;
(ii) Destination, date, and time of arrival;
(iii) Name of each passenger and relationship to the contractor;
(iv) Authorization for trip; and
(v) Purpose of trip.
(3) Where an advance agreement is proposed (see 31.109 ), consideration may be given to the following:
(i) Whether scheduled commercial airlines or other suitable, less costly, travel facilities are available at reasonable times, with reasonable frequency, and serve the required destinations conveniently.
(ii) Whether increased flexibility in scheduling results in time savings and more effective use of personnel that would outweigh additional travel costs .
(d) Costs of contractor-owned or -leased automobiles, as used in this paragraph, include the costs of lease, operation (including personnel), maintenance, depreciation , insurance , etc. These costs are allowable, if reasonable, to the extent that the automobiles are used for company business. That portion of the cost of company -furnished automobiles that relates to personal use by employees (including transportation to and from work) is compensation for personal services and is unallowable as stated in 31.205-6 (m)(2).
Definitions
FAC Changes
Style Formatter
- Data Initiatives
- Regulations
- Smart Matrix
- Regulations Search
- Acquisition Regulation Comparator (ARC)
- Large Agencies
- Small Agencies
- CAOC History
- CAOC Charter
- Civilian Agency Acquisition Council (CAAC)
- Federal Acquisition Regulatory Council
- Interagency Suspension and Debarment Committee (ISDC)

ACQUISITION.GOV
An official website of the General Services Administration
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Explore sell to government
- Ways you can sell to government
- How to access contract opportunities
- Conduct market research
- Register your business
- Certify as a small business
- Become a schedule holder
- Market your business
- Research active solicitations
- Respond to a solicitation
- What to expect during the award process
- Comply with contractual requirements
- Handle contract modifications
- Monitor past performance evaluations
- Explore real estate
- 3D-4D building information modeling
- Art in architecture | Fine arts
- Computer-aided design standards
- Commissioning
- Design excellence
- Engineering
- Project management information system
- Spatial data management
- Facilities operations
- Smart buildings
- Tenant services
- Utility services
- Water quality management
- Explore historic buildings
- Heritage tourism
- Historic preservation policy, tools and resources
- Historic building stewardship
- Videos, pictures, posters and more
- NEPA implementation
- Courthouse program
- Land ports of entry
- Prospectus library
- Regional buildings
- Renting property
- Visiting public buildings
- Real property disposal
- Reimbursable services (RWA)
- Rental policy and procedures
- Site selection and relocation
- For businesses seeking opportunities
- For federal customers
- For workers in federal buildings
- Explore policy and regulations
- Acquisition management policy
- Aviation management policy
- Information technology policy
- Real property management policy
- Relocation management policy
- Travel management policy
- Vehicle management policy
- Federal acquisition regulations
- Federal management regulations
- Federal travel regulations
- GSA acquisition manual
- Managing the federal rulemaking process
- Explore small business
- Explore business models
- Research the federal market
- Forecast of contracting opportunities
- Events and contacts
- Explore travel
- Per diem rates
- Transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.)
- State tax exemption
- Travel charge card
- Conferences and meetings
- E-gov travel service (ETS)
- Travel category schedule
- Federal travel regulation
Travel policy
- Explore technology
- Cloud computing services
- Cybersecurity products and services
- Data center services
- Hardware products and services
- Professional IT services
- Software products and services
- Telecommunications and network services
- Work with small businesses
- Governmentwide acquisition contracts
- MAS information technology
- Software purchase agreements
- Cybersecurity
- Digital strategy
- Emerging citizen technology
- Federal identity, credentials, and access management
- Mobile government
- Technology modernization fund
- Explore about us
- Annual reports
- Mission and strategic goals
- Role in presidential transitions
- Get an internship
- Launch your career
- Elevate your professional career
- Discover special hiring paths
- Events and training
- Agency blog
- Congressional testimony
- GSA does that podcast
- News releases
- Leadership directory
- Staff directory
- Office of the administrator
- Federal Acquisition Service
- Public Buildings Service
- Staff offices
- Board of Contract Appeals
- Office of Inspector General
- Region 1 | New England
- Region 2 | Northeast and Caribbean
- Region 3 | Mid-Atlantic
- Region 4 | Southeast Sunbelt
- Region 5 | Great Lakes
- Region 6 | Heartland
- Region 7 | Greater Southwest
- Region 8 | Rocky Mountain
- Region 9 | Pacific Rim
- Region 10 | Northwest/Arctic
- Region 11 | National Capital Region
- Per Diem Lookup
Travel resources
Per diem look-up, 1 choose a location.
Error, The Per Diem API is not responding. Please try again later.
No results could be found for the location you've entered.
Rates for Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. Territories and Possessions are set by the Department of Defense .
Rates for foreign countries are set by the State Department .
2 Choose a date
Rates are available between 10/1/2021 and 09/30/2024.
The End Date of your trip can not occur before the Start Date.
Traveler reimbursement is based on the location of the work activities and not the accommodations, unless lodging is not available at the work activity, then the agency may authorize the rate where lodging is obtained.
Unless otherwise specified, the per diem locality is defined as "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city, including independent entities located within those boundaries."
Per diem localities with county definitions shall include "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city as well as the boundaries of the listed counties, including independent entities located within the boundaries of the key city and the listed counties (unless otherwise listed separately)."
When a military installation or Government - related facility(whether or not specifically named) is located partially within more than one city or county boundary, the applicable per diem rate for the entire installation or facility is the higher of the rates which apply to the cities and / or counties, even though part(s) of such activities may be located outside the defined per diem locality.
City Pair airfares
Visit City Pair Program to learn about its competitive, federally-negotiated airline rates for 7,500+ domestic and international cities, equating to over 13,000 city pairs.
- Search for contract fares
Note: All fares are listed one-way and are valid in either direction. Disclaimer - taxes and fees may apply to the final price
Taxes and fees may apply to the final price
Your agency’s authorized travel management system will show the final price, excluding baggage fees. Commercial baggage fees can be found on the Airline information page.
Domestic fares include all existing Federal, State, and local taxes, as well as airport maintenance fees and other administrative fees. Domestic fares do not include fees such as passenger facility charges, segment fees, and passenger security service fees.
International
International fares do not include taxes and fees, but include fuel surcharge fees.
Note for international fares: City codes, such as Washington (WAS), are used for international routes.
Federal travelers should use their authorized travel management system when booking airfare.
- E-Gov Travel Service for civilian agencies.
- Defense Travel System for the Department of Defense.
If these services are not fully implemented, travelers should use these links:
- Travel Management Center for civilian agencies.
- Defense Travel Management Office for the Department of Defense.
GSA lodging programs
Shop for lodging at competitive, often below-market hotel rates negotiated by the federal government.
FedRooms provides federal travelers on official business with FTR compliant hotel rooms for transient and extended stays (up to 29 days). The program uses FEMA and ADA-compliant rooms with flexible booking terms at or below per diem rates. Federal employees should make reservations, including FedRooms reservations, via their travel management service.
Visit GSALodging for more details on FedRooms and for additional programs offering meeting space, long term lodging, and emergency lodging.
Privately owned vehicle (POV) mileage reimbursement rates
GSA has adjusted all POV mileage reimbursement rates effective January 1, 2024.
* Airplane nautical miles (NMs) should be converted into statute miles (SMs) or regular miles when submitting a voucher using the formula (1 NM equals 1.15077945 SMs).
For calculating the mileage difference between airports, please visit the U.S. Department of Transportation's Inter-Airport Distance website.

Plan a trip
Research and prepare for government travel.
Per diem, meals & incidental expenses (M&IE) Passenger transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.) Lodging Conferences/meetings Travel charge card State tax exemption

Services for government agencies
Programs providing commercial travel services.
Travel Category Schedule (Schedule L) E-Gov Travel Service (ETS) Emergency Lodging Services (ELS) Employee relocation

Travel reporting
Federal Travel Regulation Table of contents Chapter 300—General Chapter 301—Temporary Duty (TDY) Travel allowances Chapter 302 - Relocation allowances
Cherry Picked!
Hand-selected articles, guides, and more from the makers of Check Cherry, designed to help your business grow and flourish.
Charging Your Clients Travel Fees [Beginners Guide]

If you travel to provide services to your clients, there is a good chance you've considered implementing travel fees. In this article, we'll cover everything you need to know about travel fees and provide some actionable advice to ensure you're doing it right.
What is a travel fee?
A travel fee is an additional fee added to your standard pricing. Often, travel fees vary based on the distance one travels. The further one travels, the higher the travel fee.
👉 Use a quality online booking system with travel fees built-in, like Check Cherry, so you can automatically calculate and charge clients travel fees. It saves a lot of time and ensures accurate billing.
Why do people charge travel fees?
If you package your services, there is a good chance you've factored some travel into your pricing. However, if a client needs you to drive 62 miles, your standard pricing may no longer be profitable. Travel fees allow you to service a larger geographic area by offering clients the option to compensate you for travel.
Should I charge travel fees?
If you're open to traveling further distances to work and leveraging packages to sell your services, you should charge travel fees because they will ensure you are operating profitably.
If you are unwilling to travel outside a smaller area or send proposals with custom pricing to each client, you might want to lump all costs into one price to ensure each booking is profitable.
👉 Travel fees give more people the opportunity to hire you because it expands the geographic area you are willing to serve.
Distance-Based Travel Fees
We often see our customers include a free travel range with all packages. For example, the first 30 miles are free, and if they must drive more than 30 miles, it's $2.00 per mile. Distance-based travel fees are outstanding because they are granular and account for time and fuel costs best.
Flat Rate Travel Fees Tiers
Some people like to charge a flat fee for travel. For example, one's travel fee structure might look like this:
0-25 miles - FREE
25-50 miles - $35 Flat Fee
50-100 miles - $125 Flat Fee
This option is much less popular. One positive aspect is you can make one tier meaningfully more expensive than another.
Round-trip or one-way?
The majority of Check Cherry customers charge one-way travel fees. If a wedding venue is 55 miles away, they charge a travel fee based on 55 miles (single trip). Another option is calculating based on the length of getting to and from the service address (round trip).
One-way calculations make it easier for the client to understand your fee structure because most clients will not think to double the distance. If you opt to charge on a one-way basis, consider increasing your per-mile fee to account for the trip back home.
On the other hand, the round trip calculation will make the per-mile fee appear lower than a single trip fee. This may be helpful during the initial sales process. Round-trip is also a more accurate representation of actual costs associated with you traveling on behalf of a client.
Should I just use the rates provided by the IRS?
Each year, the IRS releases Standard Mileage Rates . In 2022, the amount was 58.5 cents per mile. Check with the IRS or your tax professional each year and track mileage for any business purposes. Regardless if you charge travel fees or not, you can deduct the cost per mile that you travel for business. Talk to your accountant about how to do it right.
Remember that the number provided by the IRS each year is based on an annual study of the fixed and variable costs of operating an automobile. It's probably a mistake to charge clients based on rates set by the IRS.
How much should I charge my clients for mileage?
This answer will vary by market, service type, and ideal customer profile. Here are three factors to consider when calculating a travel fee:
Travel time
One of the more significant expenses is your time, and travel will effectively increase the time you need to dedicate to complete your service. If you have staff, you probably want to pay them for travel time to ensure they want to work a booking or event.
Gas prices are outrageous. Do a rough calculation to see what it goes to drive 15, 25, or 50 miles based on your fully-loaded vehicle.
Vehicle wear and tear
The more you drive a vehicle, the more it costs to own due to depreciation, interest on your loan, insurance premiums, maintenance, and repairs. Estimates can be as low as $0.21 per mile and more than $0.62 per mile. You can use this handy calculator to get an estimate for your vehicle.
Example Travel Fee Calculation
Here is an example of how one might estimate the true costs of travel.
Fuel - $0.206 per mile
Cost per gallon of fuel: $4.33
Miles per gallon of fuel: 21
Fuel cost per mile = $0.206 cents per mile ($4.33 / 21)
Wear & Tear - $0.66 per mile
5 Year Vehicle Wear and Tear = $49,515
Vehicle Wear and Tear Per Year = $ 9903 ($49,515/ 5)
Per Mile Wear and Tear = $0.66 ($9903 / 15,000 miles)

Staff Costs - $0.517 per mile
Distance to Venue: 38.7 Miles
Travel Time: 1 Hour
Hourly Rate: $20
Cost per mile = $0.517 ($20 / 38.7 miles)

Estimated Travel Fee
$1.38 per mile ($0.206 + $0.66 + $0.517)
Automatic Travel Fee Calculations
Watch how Check Cherry makes it easy to calculate and charge travel fees . You can create multiple travel zones, limit bookings outside your service area, and more.
People will ❤️ how easy it is to book you online.
Try Check Cherry free for 14 days, no credit card required.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ "I love it!"
"I found Check Cherry when doing a search for something to schedule mini sessions for my photography business. It's the perfect end to end online booking and payment solution. I has made my work so much easier, and its convenient for my clients to click to select their session, sign the contract, and pay. I love it! Not to mention, their customer service is on point. Quick response time and open to suggestions. Fantastic!"

- You are here:
- Home »
- Blog »
- Starting A Computer Repair Business »
How to Effectively Charge Customers for Travel Time

Tackling any topic related to rates is likely one of the most debatable areas to touch with a ten foot pole. Technicians are stoutly protective of their pricing structures when the discussion comes up. However, I’m admittedly adventurous in this realm and believe that the more open we are with effective ways to address travel costs, the better we can serve our customers in settings fees that are appropriate for both sides. I took a chance to address proper self-worth valuation when it comes to pricing a little while back, but let’s see if we can tackle travel costs this time around. My goal here is not to say that my methodology is necessarily better; it works for my computer repair company FireLogic and I’m open to sharing it fully with fellow techs. The overarching goal with this article is to merely establish a friendly debate on all of the available methods for charging on travel, and weighing the pros/cons of each. There is no single method or rate that fits all technicians. We’re all disparate in our own ways: serving different communities, working with different customers, and operating within distinct socioeconomic regions.
The Technibble forums are generally host to some interesting discussion on travel fees and how to determine them. A few particular threads hosted some great insight like this one, a thread related to call out charges, and this discussion on how to charge for visits that are out of area. I’m going to admittedly pull a mixture of ideas from various forum postings below to give people an idea of what various techs have concocted to meet this growing need. Let’s take a look at the different ways you can charge your own customers for travel time.
The flat hourly rate
I’ll cover this one first since this is how FireLogic handles travel costs. I like this model because it’s simple for a customer to understand and doesn’t require any extensive tracking/recording besides time. My view is that if someone is willing to pay for us to travel out to visit them, a flat hourly travel rate properly compensates the tech that needs to make the trip and covers gas expenses. Our travel rate is currently $20USD/hr (about 1/4 of what our hourly onsite rate is) and has proven to be a happy medium for our customers and techs. We do not charge for return travel, as the notion goes that the next customer being visited will pick up the subsequent trip as their visit charge. Some forum goers admit to charging their full hourly rate for travel, which is understandable depending on your situation. Do your research before establishing anything, but for the Park Ridge and suburban Chicago area (USA) this system has been very successful for us with little customer pushback.
Enforcing minimum onsite service fees
This is an roundabout to charging outright travel fees or an hourly trip rate. In this method, you notify your customer that they will be paying, for example, a one hour minimum of service for the visit. More than a few techs on the forums prefer this approach as it keeps travel fees out of the customer’s sight, and also cuts back on excessive abuse of onsite labor for small tasks. From the consensus I could gather, it seems that rural techs tend to like this method as travel fees are frowned upon in such locales but customers take positively to this approach. I don’t think it would be a bad idea to use a hybrid approach of a travel rate with an onsite minimum. Again, your circumstances and competition’s methods will have a big bearing on your own attitude towards this model.
Staggered travel flat-rate fee
Yet another way to charge for travel is to create a graduated, or staggered, trip charge schedule that is based upon the number of miles from your home base to the customer location. The benefit of this model is that it directly segregates shorter trips from longer ones, and gives the customer an easy way to estimate their final total. However, the downside is that if traffic catches a technician, even a short 4 mile trip in an urban area could turn out to take just as much, if not more time, than a 10 mile journey in the countryside. I personally frown upon this model since I service the suburban Park Ridge region of Chicago, and traffic can be dicey depending on time of day and the direction of a customer location. For rural techs, this may be more appealing.
Charging “by the mile” based on a standard rate
A similar method as the staggered model above, but this one ties exact mileage or distance traveled to a standardized rate “per mile” or “per kilometer.” For the United States, I have heard of many techs tie their rate to correlate directly with the mileage rate used by the federal government. As with the staggered method, I don’t believe it fully takes into account the time spent traveling to a customer in busy, traffic-drenched areas. But for techs that want a simpler, streamlined way to present their travel rates to customers, this is about as clean cut as it gets. Tying your travel rate to the same as the government uses cuts down on arguments from clients because you can merely point them to the higher authority for why you charge what you do.
Utilizing different onsite vs offsite service rates
My company uses this notion for how our prices are set. For our case, it’s not directly to take into account travel costs. We differentiate hourly rates moreso because of the simple fact that when I am onsite, I am dedicated solely to that single customer. I cannot multi-task in any way like one can do in-shop or from their home office. For this reason, a different price is justified. But some techs claim that merely forgoing a separate travel fee and charging an inflated 20-30% of their regular rate is effective. The benefit is that you can mask your travel costs to the customer. The downside is that such a massive difference in rate may sway more customers than you wish to use your services at the “discounted” rate and stick to remote support or the like. Good or bad, it’s up to you to decide how this may work out.
Whichever method you ultimately decide to use, remember that doing some competitive analysis is always key to a rate structure that customers will be open to. You don’t want to blindly change your travel fee methodology without sniffing around to see what your local techs are charging, and how they are structuring their fees. Systems that may work well for rural areas are not always suitable for urban areas as I described above. Do your homework, reach out to some customers for their feelings, and make an informed decision. How you publicly account for travel expenses using any of the methods above may be just as important as what amount you charge a customer.
Feel free to post your own ideas or comments on what you think is the best way to charge for travel. What works? What doesn’t? Let us know!
Related Posts
Personal Security When You’re an On-Site Technician
My 7 Point Approach to Every Support Call
Become A Computer Technician: Starting Out On Your Own
This was a sticking point for me for a while. Because there is a major interstate that runs right past me, 20 miles north or south can take only 20 minutes to drive, while 20 miles east or west can take 45 minutes or more.
For that reason, the easiest way for me to do this was to charge a flat “travel fee” for any work done outside of my county. This is flexible, and depends on the work being done as well. If it’s a long-time client that I get a lot of work from, I may waive the fee. But I usually charge first time customers the travel fee just to make sure they’re serious about the job.
This is a very situational issue, and you seem to have covered most of the scenarios. Great read!
Matt http://www.yfncg.com
Thanks Derrick, good article.
One idea I thought was not directly stated in your article about the difference between bench rate and outside or the on-site consulting call is that they often require different levels of training thus have different levels of service in addition to the convince to the customer and different levels of cost to the provider. I can often schedule our bench with a brand new, out of tech school tech with minimal additional training and experience which we call a Jr. Tech who also BTW, makes minimal wages. I would never send this person to someone’s business or home not knowing exactly what he was walking into. On the other end I cannot send a senior tech to Cisco routing or Windows Server active directory/permissions issues. So there are at least three levels of training and experience required for these three types of service. We also have a fourth level tech which I pay on contract when things get above my head and I bill him out at $200 per hour.
At Computer Fix-It we have four levels of tech. Jr bench tech, senior tech that can do all sorts of calls everything short of heavy networking/server permissions and a Consultant who does the network design and maintenance. We get three rates. $59.99 bench rate, also that is our most profitable as you stated we can work on three or more computers at the same time. This level is supervised by a manager or Senior tech or senior consultant. Our senior tech bills out at $99.99 per hour on site to your home or small office. We also charge one way travel within the county (about 20 mile radius). Then we have a Consultant who can do minor routing, server permissions or active Directory type issues at $120 per hour also one way travel. If travel is outside our county we have a one way travel added and a 2 hr minimum billing. Finally, we have a 25 year Novell CNE and senior consultant who we bill out at $200 per hour when we need him. He is a contract employee as most of my clients do not require his level of skills.
With regards to travel, I inquired with one friend who owns a business in NYC “how you handle peak traffic and get across town which could be 1 hr or more travel?” He said that they schedule first of the day appointments which is during rush hour and they just show up at the clients site same as they would show up at their office so there was no additional travel and by the time they finished the first job it was no longer peak traffic so they go to the next appointment. Likewise for evening peak traffic they would schedule a job no later than 3pm so that they would be onsite working when peak travel began in the afternoons and then would just travel home same as if they left their office at 4 or 5pm. One thing they do is bill 2 hr minimum call no matter what time of work day which helps offset some of the additional travel expenses and they charge parking which is easily $25 per call.
Derrick, I hope to see an article on how to set adjust your prices. I believe most members could benefit from that. When initially setting your prices, one should be careful and not give too much attention to the lowest priced competition. At least not pay attention to the small or new competition which have not taken care to professionally setup their operations. It seems every tech how has the idea to start his own company thinks he is going to undercut the market and steal always all the customers. I have seen many small startups price themselves out of business. I mean they are too cheap and even if they get the requisite business, cannot get enough revenues to sustain their company. Then new companies come in and also practice the art of followership thus set their prices at what they perceive is the going cheap rate and they all go off a cliff together like a stampeding herd of buffaloes.
I live in a semi-rural area – in the city I can be anywhere within 1/2 hour, even during our “rush hour”. I have several rural clients, which, as I live near the edge of town, I can get to just as quickly as I can to clients living cross-town. I charge a flat hourly rate, minimum 1 hour and charge in 1/2 hour increments, and include travel time (which is usually not a factor). For example, if I spend 15 minutes traveling and 1 hour on site, then I charge 1.5 hours; if I spend 15 minutes travel and 1/2 hour on site, I charge for an hour. However, if I spend 10 minutes travelling and 55 minutes on site, I only charge for one hour (one does need to use some discretion). In the end, it all evens out – I don’t even mention travel charges unless the time will be 1/2 hour or more.
I add half hour at my hourly rate as long as the drive doesn’t last longer than 1 hour for the two way trip.
Interesting to hear about the different ways you all handle travel. I could never have covered every possible method, so good to see people chiming in with their own personalized styles!
I think customers prefer to see a price breakdown for every cent charged. I like using the gas price to mileage formula. I feel that charging for traffic is unnecessary and traffic should be calculated and dealt with personally. Our customers should not have to pay for traffic. Calculate your routes according to traffic and time a day.
I charge a minimum 1 hour fee per visit. All my traveling across the city (Toronto) is by bicycle. Any job that it takes me less than 30 minutes to get to from my home I don’t charge a travel fee. Over than and I charge roughly half my hourly rate for the whole travel time (including return trip). All my customers are totally fine with this.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
7 hidden fees you may encounter when traveling — and how to avoid them

"Easy Travel” is a ten-part series focusing on how to reduce bumps during vacations, anticipate roadblocks and be ready when things aren’t going your way. If you'd like to contribute to our future reporting and share your experience as a source, you can click here to fill out this quick form .
Budgeting for a vacation requires crunching numbers and seeing how much wiggle room your expenses have. But when it’s time to hit checkout on that flight or hotel reservation, you may be surprised when the final total is way higher than when you were booking.
Hold up, what?
Enter junk fees, also known as hidden fees.
Hidden fees can come in the form of paying extra to pick your seat on a flight or for on-site parking at a resort. They can even be so hidden that you think you’re getting a complimentary service–at least it’s marketed as so–when it’s not, or it’s an amenity you aren’t planning on using.
Learn more: Best travel insurance
At the Thompson Central Park New York hotel, the “destination fee” of $34.86 plus tax covers access to the fitness center and internet plus an hour of free bike rentals, but only if you pay for an hour already.
“These fees can sometimes catch travelers off guard and add unexpected expenses to their trip. While some fees may be legitimate charges for specific services, others can feel misleading or unfair if not properly communicated during the booking process,” said April Cheng, founder of Honolulu-based travel agency TravelChic World .
About half of U.S. adults said they ended up spending more than they budgeted for when it came to their hotel, air travel and car rental bills, according to a 2018 Consumer Reports survey .
These additional costs are coming under fire lately. Last year, President Joe Biden announced that he was going to crack down on these junk fees for being unfair to consumers, especially the most marginalized Americans.
Typically, going through a travel agent can help bring some clarity and transparency to any additional costs, Cheng said. Still, it’s essential to read all terms and conditions before offering up your credit card.
In the meantime, here are some common hidden fees you may encounter when booking travel plans and what you can do about them, according to travel exports.
1. Resort fees
According to a January 2023 NerdWallet analysis of 100 U.S. hotels, the average resort fee was $42.41 – or about 11% of one night’s stay. If your vacation is a week long, this is an additional nearly $300 you’re on your hotel bill.
However, about 7% of U.S. hotels charge a hidden resort fee, according to the American Hotel and Lodging Association (AHLA).
“They can sometimes be buried in the fine print or only disclosed at check-in, leading to frustration among travelers,” Cheng said.
According to NerdWallet, Wyndham and Hyatt properties have the highest average resort fees compared to their room rates. The hospitality brand with the lowest resort fees was Marriott (who implemented a policy to be upfront about mandatory fees in 2021 after being sued in 2019).
➤ How to avoid resort fees: You can try to avoid these fees by doing your research when booking your hotel on the hotel website or a website called Resort Fee Checker – or at least to see what you’d be paying for and if you find these amenities worth it. Some hotel brands like Hilton Honors don’t charge resort fees if you book with points.
2. Airline class fees
When booking your airfare, you’re likely using a third-party platform like Google Flights. But that low price is typically not what you’re going to end up paying, especially if you don’t want to be the last to board, earn no miles and sit wherever the airline allows you (at least according to Delta Air Lines’ Basic Economy).
Typically, the fares you see are for the lowest economy class, which has little to no benefits – and is usually non-refundable – so you’re encouraged to pay extra money to go a class up if you want to select your seat or cancel for full credit.
➤ How to avoid airline class fees: One way to reduce the surprise fees with airlines is to do your research with each airline’s policy when it comes to their basic economy policies. For example, Alaska Airlines’ lowest Saver fares still let passengers bring a carry-on for free and can cancel for a full refund within 24 hours of booking. However, JetBlue doesn’t allow its Blue Basic passengers to bring carry-on bags for domestic flights.
In the long term, consider using an airline credit card, which often comes with benefits like free checked bags. Enrolling in the airlines’ loyalty programs can help rack up miles to get benefits such as priority boarding and upgrades.
Story continues below.
3. Booking fees
“Booking platforms may add service fees or booking fees to the final price of your reservation,” Cheng said. “These fees are often not immediately visible during the search process and may only be revealed during the checkout.”
According to a 2017 AHLA survey , 23% of travelers said they were misled when using a third-party booking site, including being charged extra fees.
For example, Reservations.com charges people a non-refundable $35.85 service fee for using the platform.
➤ How to avoid booking fees: If you book directly through the hotel website, you’ll probably avoid the extra cost.
4. Hotel parking
Just because you’re a guest at a hotel doesn’t mean you can park on-property for free, said Bruce Fisher from Hawaii Aloha Travel . This is especially true for crowded touristy locations and urban areas like Honolulu’s Waikiki. Since 2021 at the Park Shore Waikiki , guests have to pay $48 per day for overnight parking–not including tip for the valet.
➤ How to avoid hotel parking fees: If you need to park a car at your hotel, be sure to find out if there are any parking fees. Cheng suggested looking into hotel reviews to see what previous guests had to say about other potential parking lots or what the parking situation is like.
5. Early check-in or late check-out
It’s not uncommon for your travel plans to have you arriving at your destination before afternoon check-in times or departing way after check-out time.
At the Hilton Hawaiian Village Waikiki Beach Resort , check-in is typically at 4 p.m., but if your room is ready before then, you could check in for a fee of $75. Standard check-out is at 11 a.m., but if you want to depart early, it costs $100 and checking out later in the afternoon is an extra $175.
➤ How to avoid early check-in or late check-out fees: Be sure to find out your hotel’s policy before you arrive because some properties charge a fee for early check-in or late check-out, Cheng said.
6. Family hotel rooms
Karen Morales, a travel advisor for Fora Travel who specializes in accessible travel, said to look out for extra charges if you’re hoping to use a rollaway bed or add an extra person to a room.
“I recently did a reward stay in Barcelona, praising myself for maximizing my points redemption,” she said. “It wasn’t until checkout that I saw the fine print, the rollaway bed charge was $50 a day! Be careful with adding children to rooms. You should check to see if there is a charge for bedding, even on a free stay.”
➤ How to avoid family room fees: When booking a hotel with children, call ahead to check for these extra charges.
7. Rental cars
Fisher said many consumers overlook rental car fees and taxes , but they can drastically change the total price. For a two-day medium SUV car rental from Hertz from Aug. 30 to Sept. 1, a renter would be charged almost $50 in additional fees, bringing the total from about $180 to almost $225.
The hidden fees include about a $40 charge just because I’m picking up at the airport and $4.10 to cover “the cost Hertz pays for registration, licensing and other related fees for applicable car materials,” according to the Hertz website .
➤ How to avoid rental car fees: “I tell customers that the rental car companies are not in the rental car business. They’re in the insurance business that’s why they try so hard to get people to sign up for services they don’t need,” Fisher said, advising people to always read the fine print. He also said to check with your credit card company since some cards will cover car rental insurance.
What are some hidden fees you've encountered?
Kathleen Wong is a travel reporter for USA TODAY based in Hawaii. You can reach her at [email protected]
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Sweepstakes
The Fee for Global Entry Is Increasing — Here's How Much It'll Cost
Application costs for the NEXUS and SENTRI programs are also increasing.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/alison-fox-author-pic-15f25761041b477aaf424ceca6618580.jpg)
Jerry Holt/Star Tribune via Getty Images
The federal government will raise the cost of the popular Global Entry program this fall for the first time in more than 15 years.
Starting Oct. 1, the application fee for Global Entry will increase to $120, according to the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). Currently the cost is $100.
“As these programs have matured and expanded, updating the fee structures is critical to the continuation and management of the programs,” CBP wrote in a statement.
While the fee may be going up, CBP said when it does, applicants under 18 will be exempt from an application fee if a parent or legal guardian is already a member of the program or applying themselves.
Global Entry is part of the Department of Homeland Security’s Trusted Traveler programs and allows travelers who are re-entering the United States from an international trip to expedite the customs process. To apply, travelers must undergo a background check and complete an in-person interview, which can be done when they return to the U.S. through the Enrollment on Arrival program or even when they leave through the new Enrollment on Departure program at Washington Dulles International Airport.
Travelers who obtain a Global Entry membership also receive the benefits of TSA PreCheck.
Several credit cards will reimburse card holders for the application fee, including those from American Express , Capital One , Bank of America , and Chase .
In addition to increasing the application cost for Global Entry, application fees for the NEXUS and SENTRI programs, which allow expedited security when entering the U.S. from Canada and Mexico’s land borders, respectively, are also changing.
The fee for NEXUS will increase from $50 to $120, while the fee for SENTRI will change from an “a la carte” fee structure to a uniform fee of $120.
Complete guide to taxes and fees on airline tickets

Editor's Note
If you've ever looked at the price breakdown of a plane ticket, you may have noticed taxes and fees tacked on to the final fare price.
Some of these are required by the government of the country from which you are departing, such as the 7.5% excise tax for domestic flights and a segment fee that the U.S. government charges.
The second category of fees is surcharges imposed by the airlines.
You'll see these taxes and fees whether you use cash or redeem an award ticket; fees placed on award bookings can be especially high since airlines want to recover more than just the value of the redemption itself due to high fuel costs.
This guide examines these different ancillary costs of airline bookings so you're not caught off-guard the next time you book a flight.
For more TPG news delivered each morning to your inbox, sign up for our daily newsletter .
Government-imposed taxes and fees

When you book a flight with cash or miles, expect to pay various taxes and fees. These fees may be imposed by the country in which your trip starts, the country in which your trip ends or both.
The amount of these fees can vary significantly. For example, you've likely noticed a $5.60 fee for flights in the U.S.
The U.S. Transportation Security Administration instituted this fee, known as the Passenger Fee or the September 11 Security Fee, in response to the 9/11 attacks to help offset the costs of additional security. You'll see the fare tacked on to all flights from the U.S., regardless of carrier.
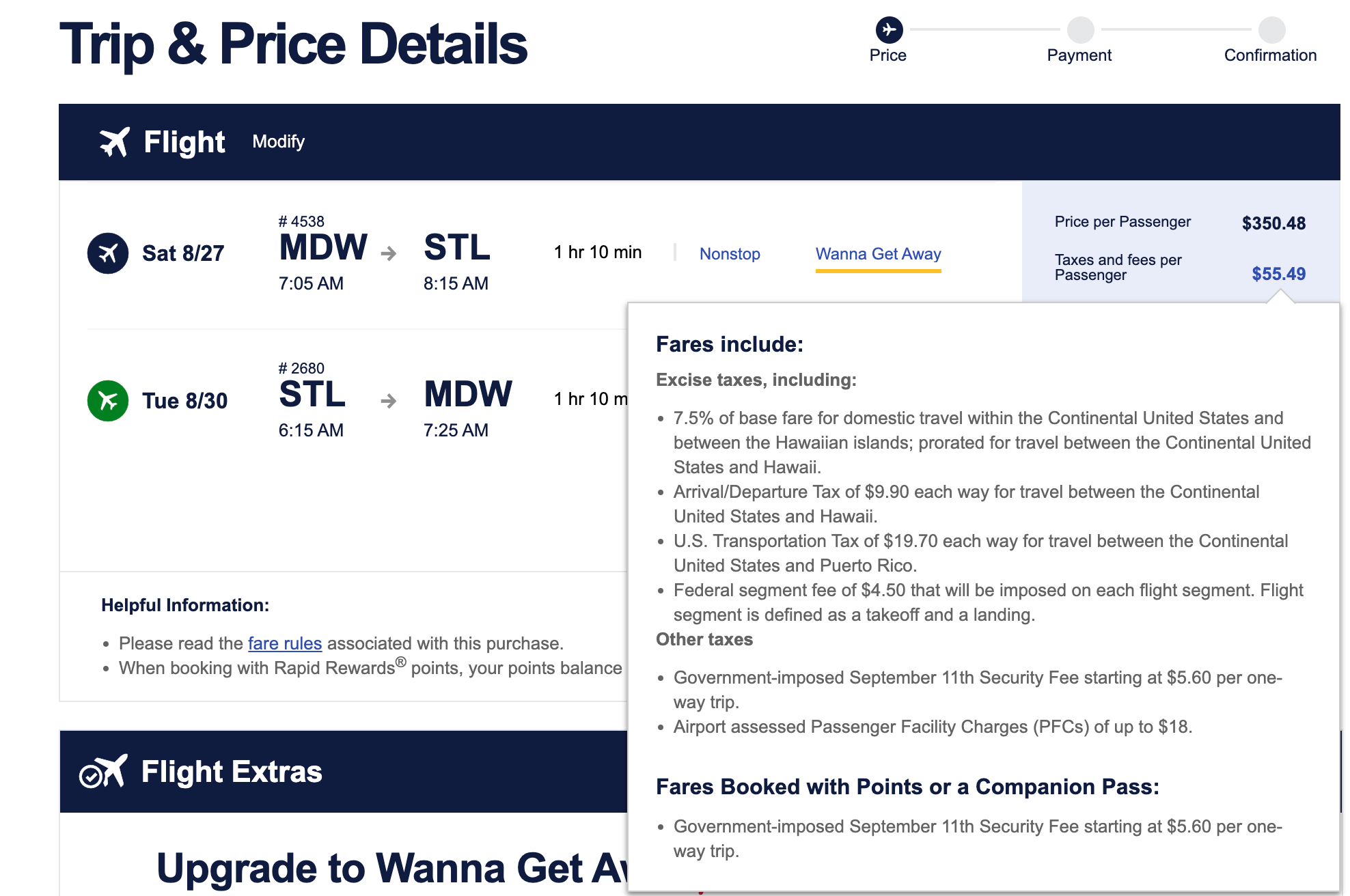
"The fee is collected by air carriers from passengers at the time air transportation is purchased," according to TSA. "Air carriers then remit the fees to TSA."
TSA raised the fee to its current price in 2014, but the round-trip fee cannot exceed $11.20. Most countries have similar charges for flights, often referred to as a passenger service charge.
For example, the United Kingdom applies an Air Passenger Duty on all international flights departing from the U.K. based on the distance traveled and the fare type. As a result, these fees for flights from the U.K. can range anywhere from $16.50 to $218, depending on the route and ticket type.
In addition to passenger service charges, virtually all countries impose an air transport tax. In the U.S., there's also a federal segment fee and a passenger facility charge of up to $18, determined by the U.S. airport(s) from which you are departing.
Other charges you might come across on U.S. flights are only applicable to certain routes. For example, there is a 7.5% base fare for domestic travel from the continental U.S. to Hawaii.
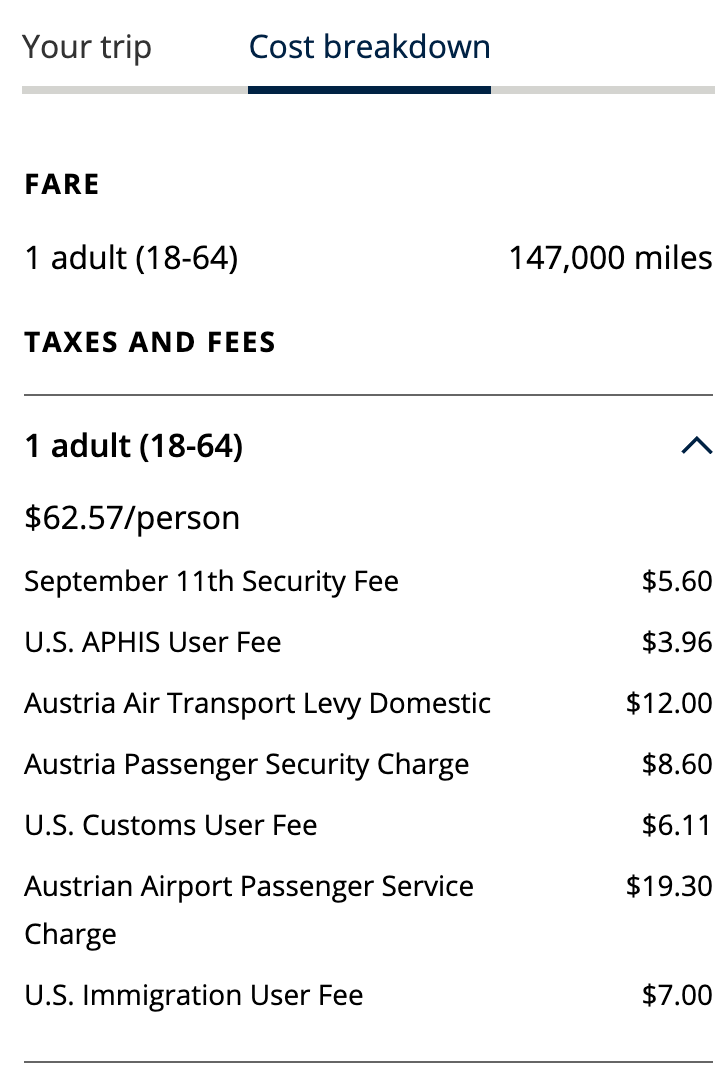
If you're flying internationally from the U.S. with a layover, know that you'll be on the hook for the taxes and fees of each country you take a flight from. For example, take a look at the below round-trip flight on American Airlines, from Chicago's O'Hare International Airport (ORD) to Berlin Brandenburg Airport (BER), with a layover each way at Heathrow Airport (LHR).
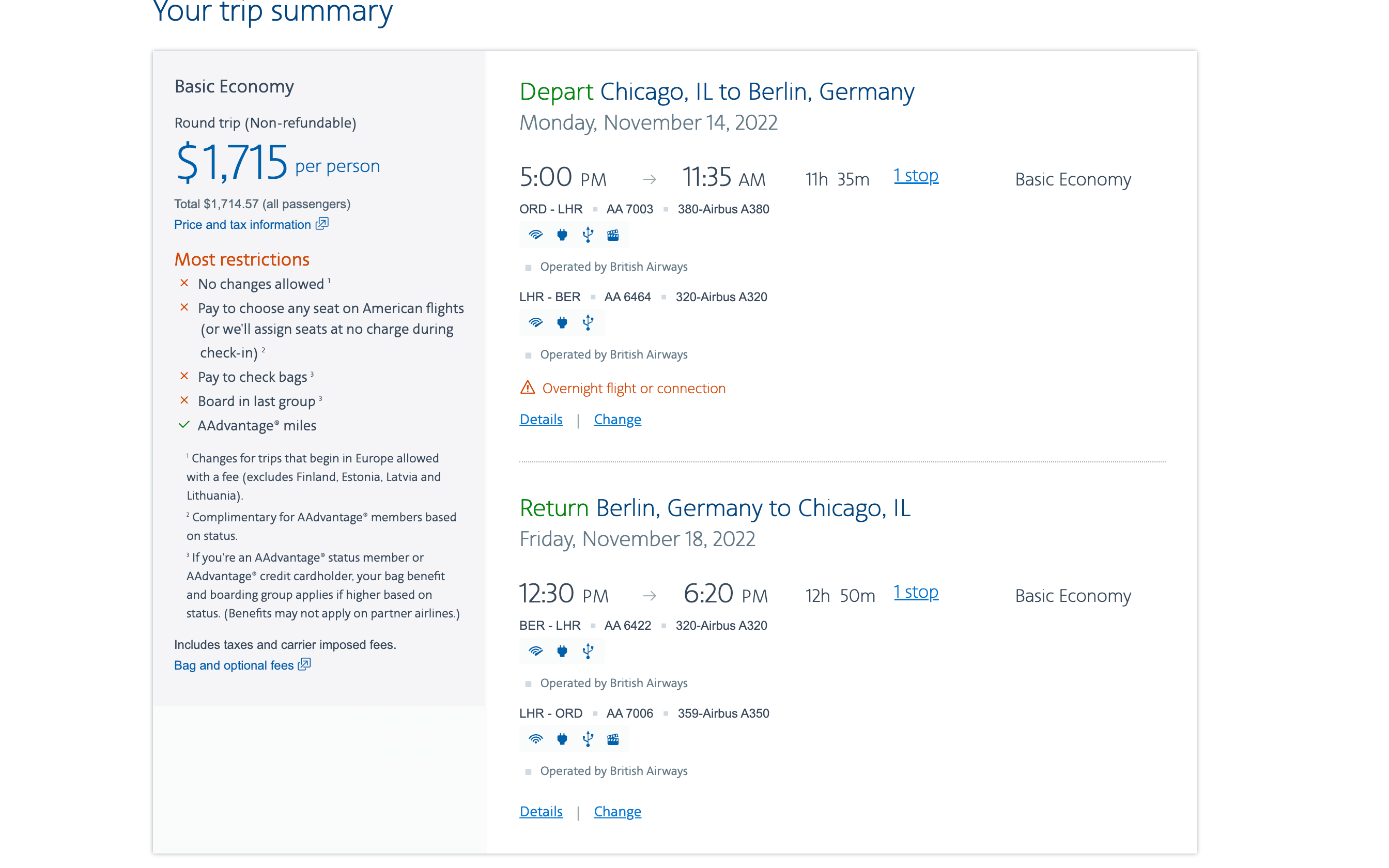
Although the base fare is only $1,100, the overall price includes more than $600 in taxes and fees; it includes a $5.60 U.S. security fee, $78 in German taxes and a $70 passenger service charge from the U.K.
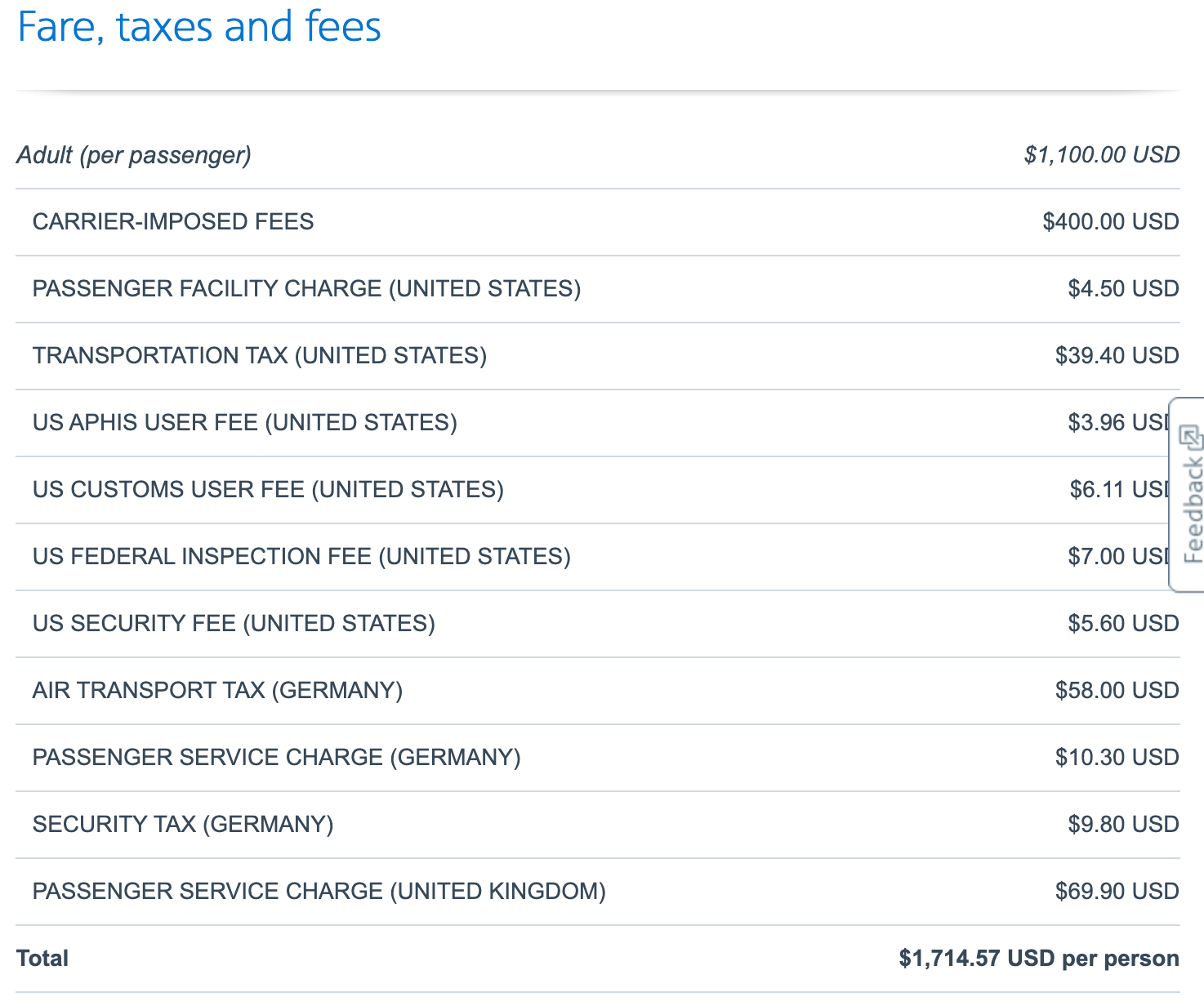
Each carrier should provide a breakdown detailing the taxes and fees applied to your ticket. There's also $400 in carrier-imposed fees, which we will get to next.
Related: Everything you need to know about American Airlines AAdvantage
Carrier-imposed charges

In addition to government-imposed taxes and fees, you'll also see carrier-imposed fees.
In the case of award tickets, these fees come from the operating carrier, not the program you use to book your award ticket. However, you may or may not be liable for actually paying them depending on the loyalty program you use to book your award ticket.
This is where my warning comes in about these carrier charges being extremely expensive. I recently discovered this when attempting to book award travel through ANA Mileage Club .
As we've previously covered , one of ANA's best sweet spots available for award travel is its 88,000-mile round-trip business-class award availability to Europe . This makes it a great option for booking tickets on other Star Alliance partners, such as Air Canada, United and Lufthansa.
The typical business-class award ticket to Europe through other programs — such as American AAdvantage and United MileagePlus — usually costs 115,000 to 154,000 miles round-trip. So, transferring points and booking through ANA is a seemingly fantastic deal.
In conducting a test for this story, I searched for award availability on ANA for a round-trip ticket from John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK) to Vienna International Airport (VIE).
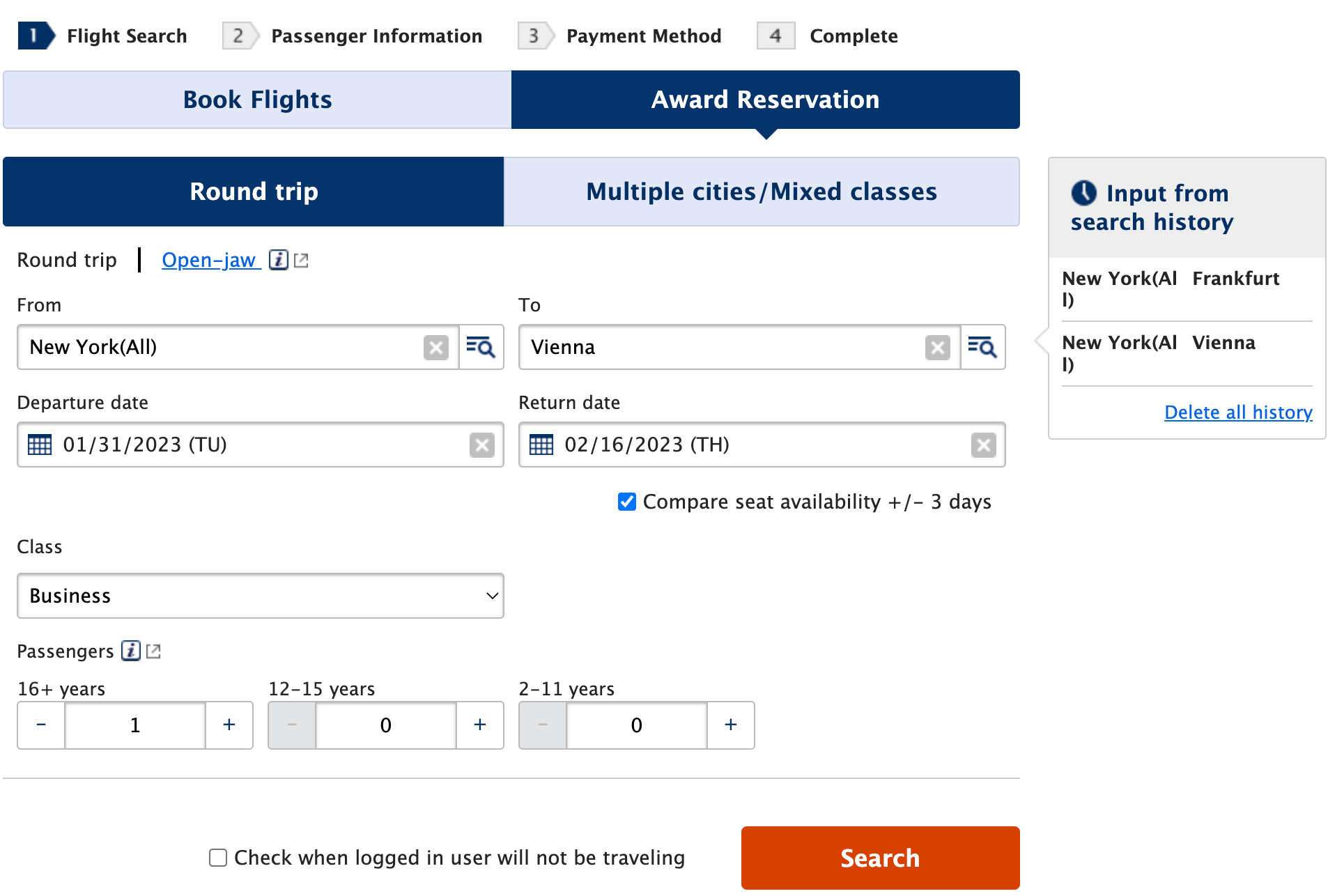
You'll likely have to play around with your dates to find a round-trip flight with business-class fares on each segment. I eventually found a round-trip business-class ticket at the 88,000-mileage price tag for early 2023.
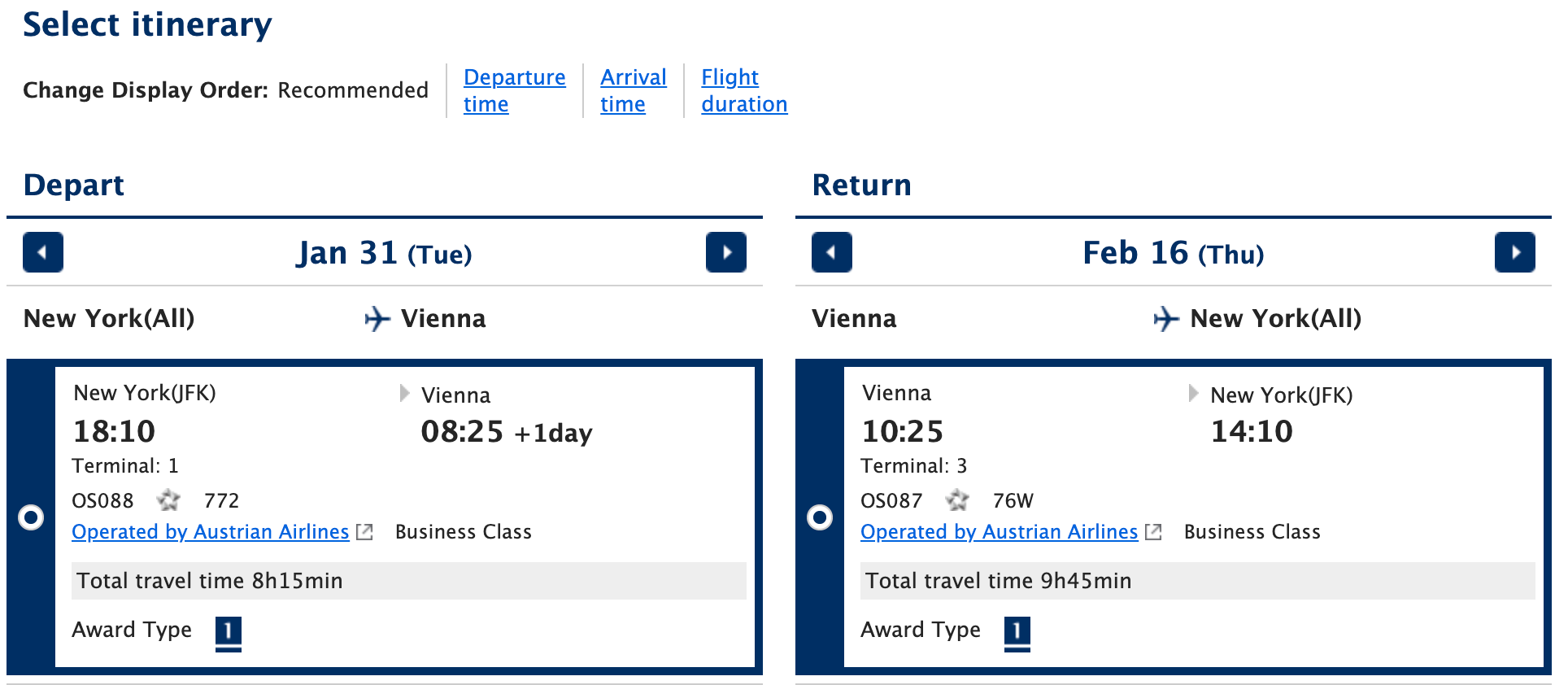
Although I was thrilled to find this, I was startled to see nearly $2,000 in taxes and fees tacked on to the base mileage fare; the fees were composed almost entirely of carrier-imposed surcharges.
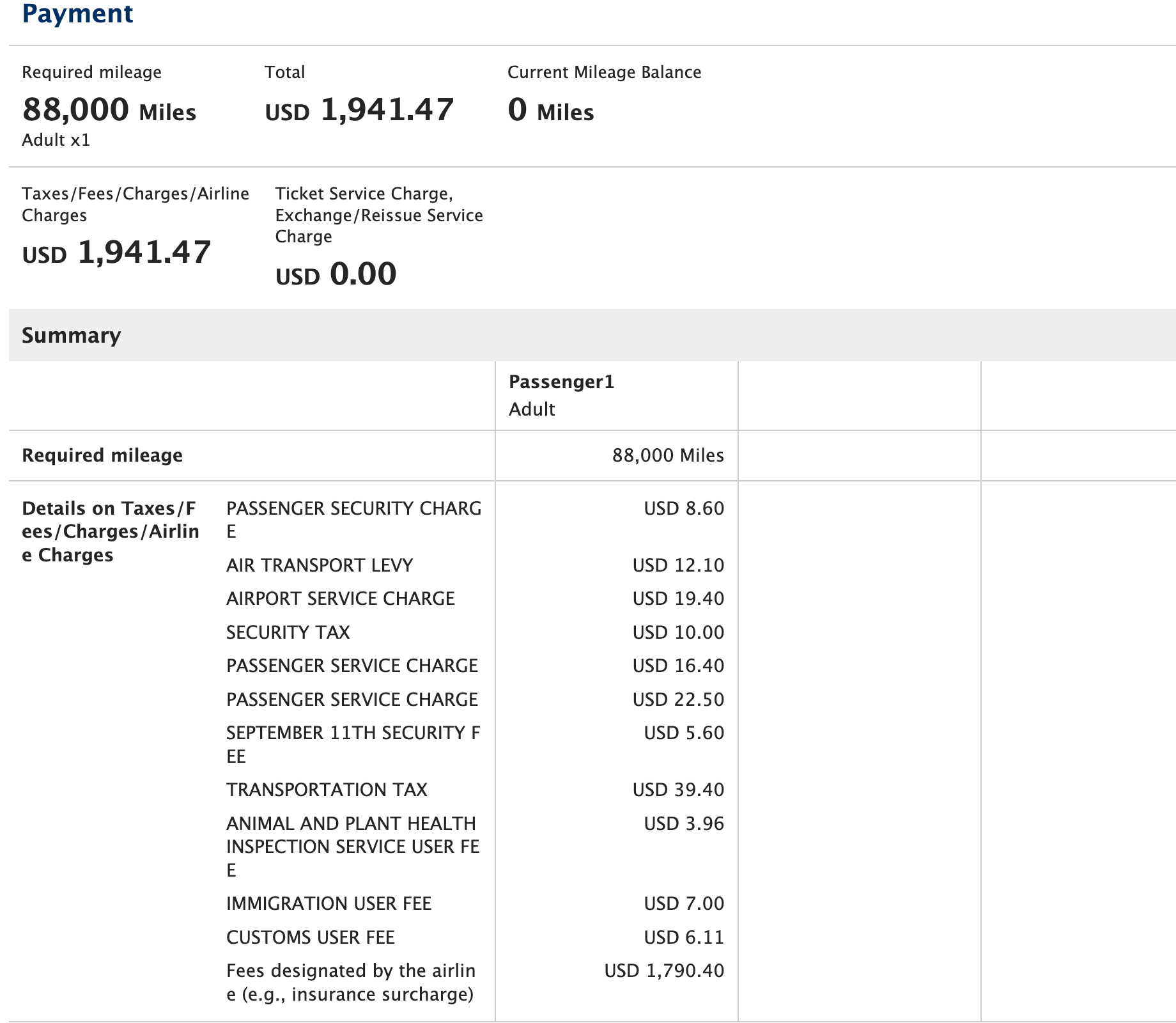
For context, booking the same flight through United would cost 147,000 MileagePlus miles plus just more than $62 in taxes and fees.
So what's the reason for this discrepancy? Austrian Airlines adds fuel surcharges — one of the most common carrier-imposed surcharges — to its award tickets. ANA Mileage Club passes these carrier-imposed surcharges on to the consumer while United MileagePlus doesn't charge them.
This example is precisely why it's important to know which frequent flyer programs pass on fuel surcharges to their customers . Regarding Star Alliance award tickets, other programs that don't pass these on include Air Canada Aeroplan and Avianca LifeMiles.
However, that doesn't mean all ANA Mileage Club award tickets will have high fees.
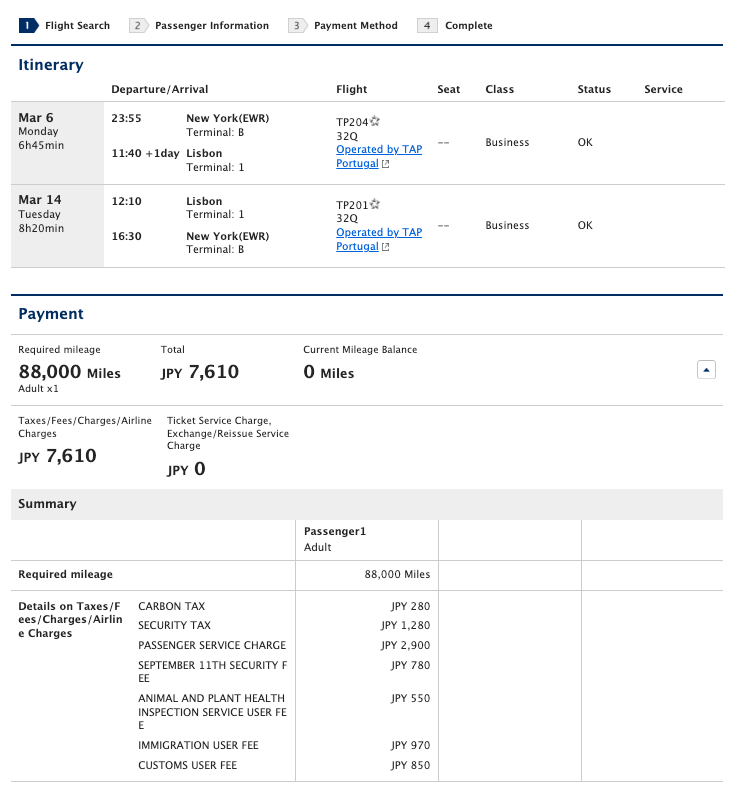
Thankfully, many airlines do not add fuel surcharges to award tickets. Some of these airlines are TAP Air Portugal, SAS and United, among others. No matter how you book an award ticket with one of these carriers — whether through United MileagePlus, ANA Mileage Club or another Star Alliance program — you'll only pay the government-imposed taxes and fees.
For example, this business-class award ticket from Newark Liberty International Airport (EWR) to Lisbon Airport (LIS) costs 88,000 miles and $56.67 in taxes and fees after currency conversion.
It's also important to note that these surcharges depend on the route you're flying and the class of service you're booking.
Related: How to fly business class to Europe with no fuel surcharges
Additional award-booking fees

Finally, it's also important to note the fees associated with the ticket itself; some airlines charge additional costs for award travel depending on how you book, including close-in fees and service fees for booking via phone.
Although most airlines have eliminated close-in booking fees for travel booked within a certain time frame of departure, some airlines still charge an extra fee for this.
Airlines may charge you extra to book via phone. For instance, United charges $25 for most United MileagePlus members (excluding Premier Platinum and Premier 1K elite members) and Alaska Airlines charges a $15 call center service charge plus a $12.50 booking fee each way for all of its partner bookings.
Additionally, some loyalty programs charge a fee for booking partner award tickets. Air Canada Aeroplan charges roughly $30 for all tickets booked with a partner airline. Likewise, Alaska Airlines Mileage Plan charges $12.50 per partner award ticket booked.
Finally, some frequent flyer programs will impose change or cancellation fees to modify or cancel an award ticket. Thankfully, most U.S. airlines ended this practice during the coronavirus pandemic.
Related: Everything you need to know about points, miles, airlines and credit cards
Bottom line
Award fees for airline bookings vary from frequent flyer program to frequent flyer program. Some pass on carrier-imposed surcharges while others don't. Likewise, some airlines add fuel surcharges, while others do not.
Before you make an award booking, browse through different airline booking portals to find a flight with the right combination of minimal miles and minimal surcharges.
For even more information on how to best avoid extra surcharges on bookings, read:
- How to avoid fuel surcharges on award travel
- British Airways increases fuel surcharges — here's how to avoid them
- Here's why you need a healthy stash of Avianca LifeMiles
- Sweet Spot Sunday: How to fly round-trip to Europe in business class for 88,000 miles
Additional reporting by Ethan Steinberg, Kyle Olsen and Andrew Kunesh.
Understanding travel agency fees: the essential guide

Whether you're planning a business or leisure trip, you might want to save time by using a travel agency. The concept of a tour operator is simple: buy holidays in bulk and for less. This solution often saves you a lot of money, but it's essential to take travel agency fees into account. Here's what they include!

What are the travel agency fees?
Travel agency fees cover part of the administrative costs involved in booking and managing your trip. These may include flight searches, accommodation reservations, train or plane tickets, transfer coordination, etc.
Not all travel agencies charge handling fees, but the vast majority do. When you're planning a trip with a travel agency, we advise you to find out about any fees beforehand. This should be done right from the start of the process, so that you clearly understand the costs associated with their services, and avoid unpleasant surprises at the final settlement!
To give you an idea, here's an overview of what a travel agency's handling fee includes.

Consulting fees
First of all, travel agencies may charge a consulting fee for the time spent talking with you, understanding your needs, your preferences in terms of destinations, airlines and type of accommodation, and developing a customized itinerary. Consulting fees also include planning fees, covering the time and effort invested by the agency in designing a trip tailored to your specific needs.
Service, management and transaction fees
Service fees refer to reservations for airfare, accommodations, car rentals, as well as certain travel-related activities. Travel agents coordinate the various elements of the trip to ensure that everything is synchronized, such as flight schedules and hotel reservations. Typically, transaction fees are charged as a percentage of each reservation, modification or cancellation on your behalf.
Service and management fees can also include administrative costs, linked to the agency's general administrative costs, such as the maintenance of reservation systems, personnel, office expenses, etc.
Assistance costs
The advantage of using a travel agency is that they often offer 24/7 assistance throughout the planning stage, as well as ongoing assistance during the trip in case of problems or unforeseen situations.
Insurance costs
Going through a travel agency sometimes involves extra charges for travel insurance, either included or optional. This offers protection to travelers in the event of unforeseen circumstances. Travel insurance costs cover various aspects:
- trip cancellation due to unforeseen circumstances such as illness, accident or death of a family member;
- trip interruption for medical emergencies or unexpected events ;
- medical insurance to cover emergency medical expenses abroad, including hospitalization;
- baggage insurance guaranteeing reimbursement in the event of loss, theft or damage to baggage during the trip;
- third-party liability covering damage caused to third parties during the trip.
Insurance costs in France may vary according to the coverage chosen by the agency and the duration of the trip. Find out which travel insurances are best for you , and contact your bank. You may already have adequate travel insurance with your bank card!
Booking through a travel agency: is it more expensive?
If you're thinking of entrusting your travel project to an agency, you're probably wondering: will I pay more? Because if the travel agency is working on my trip, there are bound to be costs!
The answer is no, it won't cost you more. On the contrary, it often saves you money! Whether it's for low-cost or first-class air tickets, accommodation, activities or tours, the travel agency negotiates contracts with various brands and companies at the best price, and obtains exclusive promotions.
So, if you use a travel agency, the chances are that the price of your holiday will be lower than if you booked directly with each service provider. In many cases, travel agencies can help you save money. The only thing to bear in mind is the booking fee, which varies from one agency to another, depending on the services offered.
What percentage does a travel agency take?
Most travel agencies take between 9% and 15% commission for anything to do with services, stays or tours. For a single airline ticket sold, a travel agency might take 8% of the public price.
However, this percentage varies from one travel agency to another, depending on the services they offer. Some travel agencies may charge between 15% and 20% commission. Make sure you find out what the fees are before embarking on your adventure with a travel agency, and above all, use an agency that is transparent about them!
Why use a travel agency?
The first advantage of using a travel agency is that it saves you time . Travel agents can take care of your trip from A to Z. If you've ever planned a trip, you know how complex and time-consuming it can be. Travel agents take care of planning, hotel reservations, flights, transfers and other details that save you time and energy.
Travel agents are experts in their field and can provide you with useful advice on destinations, the best times to go there, activities to do, and so on. Their in-depth knowledge can help you plan a trip perfectly suited to your needs and preferences.
Then, the second big advantage is that they give you access to preferential rates and exclusive offers, having negotiated with their partners. This means you'll get better deals than if you booked with each provider yourself.
Finally, when you use a travel agency, you often benefit from assistance in the event of a problem (flight delays, cancellations or accommodation problems, etc.). This takes the stress out of your trip, and allows you to quickly resolve any unforeseen situations with a single point of contact!
What's the difference between a travel agent and a travel agency?
A travel agent is someone who works for a travel agency, or who works independently. They help you plan your trip, book flights and hotels, and advise you on visas, travel insurance and tourist activities.
A travel agency is a commercial enterprise that composes and sells a range of travel-related services. It is made up of one or more travel agents.
There is no better option between the two, it all depends on the quality of the services provided by the agency and the independent travel agent, and of course, the prices of the trips offered and the handling fees!
Travel agencies are required to provide a financial guarantee to ensure that travelers are reimbursed in certain situations, such as trip cancellation, non-performance of scheduled services or even bankruptcy of the agency itself. The aim is that, should something go wrong, you're protected from A to Z.
Today, the majority of companies work with a travel agency to plan their business trips, and find it a real added value in terms of travel management.
To help office managers, we've developed Fairfees , which compares your travel costs across different agencies. This easy-to-use simulator will help you choose the travel agency best suited to your needs.

Which hotel to choose for a seminar in Cannes?
Discover the best hotels in Cannes to organize a seminar. Enjoy unique settings for your business events.

Transavia cancellation insurance: all you need to know
Protect your trip with Transavia cancellation insurance. Information on coverage, exclusions, prices, ...

The best sites for calculating the carbon footprint of a journey
Discover the best online sites and tools for calculating the carbon footprint of a journey and its impact on the environment.
.png)
Top 15 hotels for a seminar in Paris with accommodation and meetings
To organize your company seminar properly, you'll need to find a hotel suited to your meeting and accommodation needs.
See Fairjungle in action.
Take back control of your business travel! Discover the new-generation corporate travel agency.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
Dynamic Pricing Is Coming for Everything in Travel

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
First it was Ubers. Then it was Wendy’s hamburgers (except the fast food chain clarified it was technically dynamic pricing, not surge pricing). But now, the real deal — surge pricing — is targeting your checked bags.
JetBlue quietly (sneakily?) introduced “peak” and “off-peak” pricing to its checked bag fees on March 22, a fact the world was alerted to because my editor happened to check the JetBlue website. That means you have to pay $5 to $10 more each way for checked bags on JetBlue when flying during busy travel times, such as the summer, much of the winter and some random weeks in the spring.
It's a classic example of surge pricing — a type of dynamic pricing where companies only increase prices during times of high demand, but don't lower pricing during times of low demand.
Technically, these new dynamic baggage fees won’t affect all customers like the blanket increases some other airlines, such as Alaska and Delta , recently added. Yet they also mean more complication and confusion for customers who are trying to figure out which airline offers the lowest total price for a given route.
Dynamic prices are nothing new in the travel industry. In fact, prices that rise and fall based on the balance of supply and demand are taken for granted in everything from airfare to hotel rooms and rental cars.
What’s new is how these companies are fluctuating the price of the add-on fees many travelers are growing to deplore .
And airlines are increasingly relying on these add-on fees for revenue. In 2023, airlines made a record $117.9 billion worldwide in ancillary fees, according to airline consulting firm IdeaWorksCompany and car rental technology platform CarTrawler. About $33.3 billion of that was baggage fees.
Some industry experts say the move to more fluid fee prices has been a long time coming.
“Airlines have had capabilities for years to price fares based on demand. Why not other fees as well?” says Jay Sorensen, president of IdeaWorksCompany.
Sorenson notes that many airlines have been dynamically adjusting the price of seat assignment fees for years. The cost of choosing a window seat near the front of the plane for a particular flight might cost more in December than in February because of increased demand.
Yet, it seems like airlines have been so preoccupied with whether they can make more money from increasingly complex fee structures that they haven’t stopped to think about whether they should.
What makes a fare fair?
It all comes down to how we think travel companies should price their products. Sorenson thinks we are holding airlines to a standard to which we don’t hold other retailers.
“Shopping for an airline seat is like shopping at a grocery store,” he says. "If the grocery store was required to tell you beforehand how much you were going to spend, it would be ludicrous.”
The base fare is more like the shopping cart into which we toss other add-ons, such as seat assignments, premium seating upgrades and baggage. It’s up to the consumer to compare prices at different airlines, just as it’s on them to compare prices at different grocery stores.
If JetBlue wants to charge more for eggs (baggage) near the holidays, we can decide whether we want to pay the premium or shop with an airline that doesn’t, according to Sorenson.
But I would counter by saying that charging extra for checked baggage on peak dates is more akin to charging extra for the carton that carries your eggs. It feels like a tacked-on “gotcha” fee meant to sneak under most consumers' radar rather than a meaningful price for a meaningful good.
Whatever you think about dynamic travel fees, it’s clear that they’ll become more common than less in the coming years. What can you do?
Tips for navigating dynamic fees
It’s not reasonable to keep track of which travel providers are charging which fees at which times. I can barely do it, and it’s my entire job.
Instead, it’s worth getting a sense of which airlines tend to charge higher fees overall, and, frankly, avoiding those brands if you want any add-ons at all.
For example, Frontier Airlines charges $157 each way in basic add-on fees while Southwest Airlines charges $0, according to the latest NerdWallet analysis .
So the simplest tip is to fly on Southwest Airlines. It doesn't have dynamic prices for fees because it has so few fees, period. Two checked bags per person are free.
If that’s not feasible, you might consider getting a co-branded airline credit card, many of which offer free checked bags . Because baggage fees are becoming increasingly complex, this type of credit card lets you avoid the headache of dealing with them altogether, just as paying for Spotify Premium lets you avoid those terrible ads.
Finally, skip seat selection fees if you possibly can. These fees are sneaky and difficult to compare between airlines, but they’re almost always optional. And, as Sorensen points out, they are essentially charging for something that costs the airlines nothing.
“When something is pure margin, my advice to airlines is ‘don’t be so greedy,’" he says.
How to maximize your rewards
You want a travel credit card that prioritizes what’s important to you. Here are our picks for the best travel credit cards of 2024 , including those best for:
Flexibility, point transfers and a large bonus: Chase Sapphire Preferred® Card
No annual fee: Bank of America® Travel Rewards credit card
Flat-rate travel rewards: Capital One Venture Rewards Credit Card
Bonus travel rewards and high-end perks: Chase Sapphire Reserve®
Luxury perks: The Platinum Card® from American Express
Business travelers: Ink Business Preferred® Credit Card

on Chase's website
1x-5x 5x on travel purchased through Chase Travel℠, 3x on dining, select streaming services and online groceries, 2x on all other travel purchases, 1x on all other purchases.
60,000 Earn 60,000 bonus points after you spend $4,000 on purchases in the first 3 months from account opening. That's $750 when you redeem through Chase Travel℠.

1.5%-6.5% Enjoy 6.5% cash back on travel purchased through Chase Travel; 4.5% cash back on drugstore purchases and dining at restaurants, including takeout and eligible delivery service, and 3% on all other purchases (on up to $20,000 spent in the first year). After your first year or $20,000 spent, enjoy 5% cash back on travel purchased through Chase Travel, 3% cash back on drugstore purchases and dining at restaurants, including takeout and eligible delivery service, and unlimited 1.5% cash back on all other purchases.
$300 Earn an additional 1.5% cash back on everything you buy (on up to $20,000 spent in the first year) - worth up to $300 cash back!

on Capital One's website
2x-5x Earn unlimited 2X miles on every purchase, every day. Earn 5X miles on hotels and rental cars booked through Capital One Travel, where you'll get Capital One's best prices on thousands of trip options.
75,000 Enjoy a one-time bonus of 75,000 miles once you spend $4,000 on purchases within 3 months from account opening, equal to $750 in travel.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know

Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- National Media Release
CBP Announces Trusted Traveler Programs Fee Changes
WASHINGTON – U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) announced today an upcoming fee change for some of its most popular Trusted Traveler Programs (TTP).
On April 2, a final rule was published in the Federal Register , harmonizing the fees for the NEXUS , Global Entry, and SENTRI programs, better reflecting the program costs. The new fees, which have not been updated in over 15 years, will go into effect October 1, 2024. As these programs have matured and expanded, updating the fee structures is critical to the continuation and management of the programs.
Once the rule goes into effect, applicants under the age of 18 will be exempt from the application fee when a parent or legal guardian is already a member of, or concurrently applying for NEXUS, SENTRI, or Global Entry. SENTRI, which allows expedited clearance for pre-approved, low-risk travelers entering the United States using dedicated primary lanes at Southern land border ports, will move from an “a la carte” fee structure to a uniform fee of $120, which will be collected in full when each application is submitted. The fees for NEXUS, a joint program managed by CBP and Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) that allows dedicated processing between the U.S. and Canada, will increase from $50 to $120, and Global Entry fees will increase from $100 to $120.
TTP supports CBP’s mission of securing U.S. borders while facilitating lawful travel and trade. Travelers must be pre-approved for TTP. All applicants undergo rigorous and recurring background checks and an in-person interview before enrollment. While a key goal of the programs is to expedite travelers through the process, members may still be selected for further examination when entering the United States. To maintain a strict standard in establishing TTP members as low-risk travelers, any violation of a program’s terms and conditions will result in the appropriate enforcement action and termination of the traveler’s membership privileges.
For more information on TTP, follow @CBP or visit ttp.dhs.gov .
U.S. Customs and Border Protection is the unified border agency within the Department of Homeland Security charged with the comprehensive management, control, and protection of our nation’s borders, combining customs, immigration, border security, and agricultural protection at and between official ports of entry.
UNCLASSIFIED (U)
allowable travel and miscellaneous expenses
(CT:LOG-392; 03-20-2024) (Office of Origin: A/LM)
14 FAM 561 POLICY AND AUTHORITIES
14 FAM 561.1 Policy
(CT:LOG-381; 09-26-2023)
It is the general policy of the U.S. Government that less-than-premium-class accommodations must be used for all modes of passenger transportation. The policies in 14 FAM 567 govern the use of common carrier accommodations and apply to travel while on official U.S. Government business.
14 FAM 561.2 Exercising Care in Incurring Expenses
An employee traveling on official business is expected to exercise the same care in incurring expenses that a prudent person would exercise if traveling on personal business and expending personal funds. Excess costs, circuitous routes, delays, or luxury accommodations and services unnecessary or unjustified in the performance of official business are not acceptable under this standard. Employees will be responsible for excess costs and any additional expenses incurred for personal preference or convenience.
14 FAM 561.3 Authorities
In addition to the authorities listed in 14 FAM 511.4 , the following authorities apply:
(1) State Department Delegation of Authority No. 462, dated January 9, 2019, delegates the Secretary of State's travel authority to the Under Secretary and Deputy Under Secretary of State for Management;
(2) 22 U.S.C. 4081 is the travel payment authorization provision of the Foreign Service Act that provides for a domestic relocation allowance;
(3) The Federal Travel Regulation (FTR) 41 CFR 301.10-124 addresses coach-class seating upgrade programs;
(4) FTR 41 CFR Part 301-13 addresses travel of employees with special needs, and
(5) The General Services Agency's (GSA) FTR Bulletin FTR 09-02, dated 31 Dec. 2008, clarifies the seat choice options and other miscellaneous fees Federal agencies may reimburse their employees while on official travel.
14 FAM 562 EXPENSES ALLOWABLE
14 FAM 562.1 Miscellaneous Expenses not Covered by Per Diem
(CT:LOG-392; 03-20-2024)
a. The following travel expenses, when actually incurred and necessary, can be itemized and reimbursed over and above the per diem allowance for lodging and meals and incidental expenses (M&IE):
(1) Official telephone calls and faxes in connection with official business; internet access fees while performing official business. Reimbursement for expenses must be authorized in advance of travel on the travel authorization;
(2) Commissions for conversion of currency; fees to obtain travelers checks, money orders and certified checks; transaction fees for use of ATMs and other vendors such as hotels when using a U.S. Government contractor-issued charge card. For locally employed (LE) staff who use their personal charge cards and for other travelers who the Department has determined may not be issued a U.S. Government charge card or who have been authorized to use their personal charge cards for official travel, transaction fees for the use of ATMs and other vendors such as hotels may be allowed, if stated on the travel authorization in advance of travel;
(3) Lodging taxes in domestic and nonforeign areas (see FTR, 41 CFR 301-11.27); energy surcharge and lodging resort fees when such fees are not optional;
NOTE : Lodging taxes and mandatory fees in foreign areas are incorporated into the per diem rate for lodging for those areas. In order to be fully reimbursed, the sum total cost of lodging plus mandatory taxes and fees in foreign areas must be within the prescribed lodging component of per diem for that area;
(4) Fees in connection with the issuance of passports and visas and other legally required costs; photographs for passports and visas; certificates of birth, health and identity, and affidavits attesting thereto; foreign country entrance and exit fees;
(5) Inoculations that cannot be obtained for free through a Federal dispensary (reimbursement must be authorized on the travel authorization before travel begins). For yellow fever inoculations, there is no requirement for prior authorization for reimbursement; and
(6) Expenses associated with the transport of human milk expressed by an employee or Eligible Family Member (EFM) while on TDY, approved medical travel, or on PCS travel (including for the authorized PCS travel to post for new infants following a parent's authorized obstetrical medevac) in accordance with the FTR, 41 CFR 301-13.2, up to a maximum of $1000. Reimbursement for expenses must be authorized in advance on the travel authorization and the traveler must submit all receipts, regardless of amount, with the travel voucher. Expenses may include commercial shipping fees, excess baggage, disposable storage bags, cold shipping packages, refrigeration, transport, and non-durable containers. Durable containers that are not reimbursable include canvas, polypropylene, and soft- or hard-sided containers . For special cases of TDY travel where expenses exceed $1000, the traveler may receive reimbursement above $1000 only when authorized in writing by the EX Director (or agency equivalent) of the funding bureau in advance of travel. Such authorization must also accompany the travel authorization and the travel voucher. Travelers are ultimately responsible for arranging all transport of human milk and for handling all related logistics. See 3 FAM 3860 for more information on the Department’s lactation policy.
b. For Agriculture only : Foreign Agricultural Service allows for reimbursement of authorized telephone calls of a personal nature during official travel. For foreign travel, the maximum reimbursement is $15.00 per day. For domestic travel, the maximum reimbursement is $5.00 per day. The maximum aggregate amount that may be approved for each travel period (i.e., consecutive days of official travel) cannot exceed the amount equal to the daily reimbursement rate multiplied by the number of lodging nights. This reimbursement is not an automatic claim and should only be reflected on a voucher if actual expenses were incurred while in a TDY travel status.
c. For USAID only : ADS 633.3.6.1 Financial Management Aspects of TDY, and ADS 549, Telecommunications Management, defines some telephone calls to family as “Official” and allows for reimbursement of those telephone calls when an employee is traveling on government business. See those ADS chapters for further details.
14 FAM 562.2 Transportation Expenses
a. The following transportation expenses, when actually incurred and necessary, can be itemized and reimbursed if not paid directly by the U.S. Government:
(1) Travel on railroads, aircraft, sailing vessels, buses, streetcars, and other usual means of common carrier conveyance;
(2) Transfer, storage, and checking of baggage necessary for the purpose of the official travel;
(3) Charges for transfer, storage, checking, and porters' fees and tips for handling U.S. Government property carried by the traveler;
(4) Transportation charges for authorized excess official baggage;
(5) Shipments by express or freight of U.S. Government property not classed as baggage and not admissible to the mail (normally made on U.S. Government bills-of-lading (GBLs) where feasible);
(6) Packing and necessary preparation for shipment, cost of unboxing at destination, and necessary cartage of unaccompanied baggage or personal effects, or baggage accompanying traveler;
(7) Hire of a boat, automobile, taxicab, aircraft, or other conveyance when authorized or approved as advantageous to the U.S. Government and when employee is engaged in official business within or outside employee's post of duty;
(8) Daily travel to procure meals or lodging at the nearest available place when such cannot be procured at a temporary duty station; and
(9) Transportation by bus, subway, streetcar, taxicab, transportation network company (TNC), or innovative mobility technology company (IMTC) (see 14 FAM 511.3 for definitions):
(a) Between places of business;
(b) Between place of lodging and place of business at a temporary duty station;
(c) Between place of lodging or employee’s home and common carrier transportation terminal in connection with official travel;
(d) From employee's office to a common carrier transportation terminal on the day of departure from the office on an official trip requiring at least one night's lodging.
b. Use of taxicabs, TNCs, or IMTCs (see 14 FAM 511.3 for definitions):
(1) When suitable common carrier transportation is available for travel between points other than those listed above, but the traveler elects to use a taxicab or TNC, or IMTC, detailed remarks noting the circumstances must be furnished on the travel voucher;
(2) Taxicab, TNC, or IMTC reimbursement in excess of $75.00 plus tip must be supported by a receipt along with a statement justifying the use of such conveyance;
(3) The maximum tip allowable under this section is 20 percent of the reimbursable fare;
(4) In lieu of the use of a taxicab, TNC, or IMTC as provided in this section, payment on a mileage basis at the approved rate, as described in 14 FAM 566.2-2 , is allowed for the mileage of a privately owned automobile used for a purpose detailed above, provided that the amount of reimbursement for mileage does not exceed the estimated taxicab, TNC, or IMTC cost, including allowable tip, for transportation between the applicable points;
(5) Membership or application fees, tickets, fines, cancellation fees or fees charged for waiting for the traveler, or other such expenses associated with TNCs or IMTCs are not reimbursable. Only actual usage charges, booking charges, and reservation charges made directly with the TNC or ITMC (not a third-party company) are eligible for reimbursement; and
(6) Travelers may not know prior to beginning a trip what ground transportation options will be available at a particular location. Thus, travel authorizations that contain advance authorization for a taxi, a TNC, or an IMTC are considered to confer authority to use any or all of those ground transportation options. When completing a travel voucher, however, it is necessary to specify whether a taxi, TNC, or IMTC was actually utilized for each instance of ground transportation in order to facilitate preparation of certain congressionally mandated reports.
14 FAM 562.3 Unaccompanied Minor Charges
Most airlines provide a service for children traveling unaccompanied on their airline without the presence of a legal guardian, but fees for this service differ by airplane. This charge is reimbursable when:
(1) The EFM child (16 years of age or younger) is the only individual entitled to travel at U.S. Government expense for the type of official travel authorized (e.g., travel of children of separated families, educational travel, educational allowance, or on authorized or ordered departure); and
(2) The child is engaged in direct travel with no deviation from the authorized itinerary; and
(3) The fee is authorized on the travel authorization in advance of travel.
14 FAM 563 EXPENSES NOT ALLOWABLE
14 FAM 563.1 Items Included in Per Diem
The following items are included within the lodging and/or meals and incidentals (M&IE) portions of the per diem allowance (see definition in 14 FAM 511.3 ) and may not be paid, itemized, or reimbursed separately:
(1) Charges for lodging, including:
(a) Overnight sleeping facilities;
(b) Personal use of room and bath during daytime;
(c) Telephone access fee; and
(d) Service charges for fans, televisions, air conditioning, heaters, microwaves, and refrigerators in rooms;
(2) Charges for meals, including:
(a) Expenses for breakfast, lunch, and dinner; and
(b) Related tips and taxes;
(3) Incidental expenses, including:
(a) Fees and tips given to waiters, porters, baggage handlers, bellhops, hotel personnel, restaurant staff, and similar employees;
(b) Transportation between place of lodging or business and places where meals are taken, except as specified in 14 FAM 562.2 , subparagraph a(8); and
(c) Bottled water;
(4) Complimentary meals provided by common carriers or hotels (e.g., complimentary breakfast meals on airplanes, etc.) have no impact on per diem rates paid per FTR, 41 CFR 301-11.17.
14 FAM 563.2 Personal and Other Expenses
Costs of a personal nature are not reimbursable, such as:
(1) Personal telephone calls or faxes, including messages, requesting leave, inquiring as to status of salary, expense vouchers, advance of funds, and reply thereto, or any other matter of personal nature. This section does not apply to Agriculture or USAID employees (see exceptions for Agriculture employees in 14 FAM 562.1 , paragraph b, and for USAID employees in 14 FAM 562.1 , paragraph c);
(2) Internet access fees for conducting personal business; internet service provider (ISP) fees (e.g., monthly charges for satellite, fiber, cable, or DSL internet access);
(3) Transaction fees for use of ATMs and other vendors, such as hotels, with a personal charge card except when authorized in accordance with 14 FAM 562.1 , subparagraph a(2);
(4) Laundry, dry cleaning, and pressing when traveling OCONUS or when traveling in CONUS for less than four consecutive nights;
(5) Alcoholic beverages;
(6) Entertainment expenses;
(7) Any expenses incurred for other persons; and
(8) Miscellaneous service fees (i.e., administrative, booking, and third-party fees) resulting from booking transportation or lodging outside a government-contracted travel management center or government lodging program (e.g., FedRooms).
14 FAM 564 Fare types
14 FAM 564.1 Unrestricted Fare Policy
(CT:LOG-381; 09-26-2023) (State and USAID)
a. In general and when possible, the Department utilizes the lowest-cost unrestricted fares available for travel between authorized origin and destination, respecting the terms of the General Services Administration (GSA) city-pair program, for all official travel.
b. An individual may request the purchase of a restricted or penalty fare for official travel based on personal convenience (e.g., taking an indirect route for personal reasons or wishing to travel in a class of service other than the one authorized), but the individual is responsible for any and all additional costs and/or penalties incurred in connection with such fares regardless of whether those costs are due to official or personal reasons. See 14 FAM 561 for an employee's responsibility to exercise due care.
c. When an individual is authorized an unrestricted fare but engages in indirect (cost-constructed) travel and elects to use a restricted fare, the cost of that restricted fare, in the class of service and the route used by the traveler, must be compared to the cost of an unrestricted fare along the authorized route in the authorized class of service in order to determine whether the individual’s deviation results in an additional cost to the U.S. Government:
(1) If an additional cost would be incurred because of the individual’s decision to engage in indirect travel and/or travel in a class of service other than the one authorized, the individual must pay, to the TMC or air carrier issuing the ticket, the difference in fare between the restricted fare elected by the traveler and the unrestricted fare that would have been purchased by the U.S. Government; and
(2) If no additional cost would be incurred, the U.S. Government may purchase the restricted fare along the indirect route and/or in the class of service other than the one authorized. Any cost saving associated with the purchase of a restricted fare in this case is not transferrable to the traveler, and a fare saving may not be used to offset change or cancellation fees incurred as a result of the individual’s decision to use a restricted fare.
d. Whenever a cost comparison is made, documentation of the specific flight itineraries and their respective costs must be retained and included in the travel authorization for future reference and to meet auditing requirements.
14 FAM 564.2 Restricted Fare Policy
a. Restricted penalty fares should be authorized for official travel only when their use is practical and economical to the U.S. Government. Round-trip tickets with such fares should be authorized only when, based on the journey as planned, the traveler knows or reasonably anticipates that such tickets will be utilized in accordance with their restrictions (see 14 FAM 542 for details of contract city-pair fares). The use of prohibited ticketing practices, such as “throw-away,” “hidden city,” or “back-to-back” ticketing, is not permitted for any part of either authorized or cost constructed travel itineraries because those tactics violate air carrier contracts of carriage.
b. A mission or bureau has the option of developing a policy requiring the use of restricted, penalty fares subject to the conditions set out in paragraph a of this section. The authorizing mission or bureau will assume financial responsibility for any penalties associated with these fares, should changes or cancellations be required by the U.S. Government. The employee will be responsible for any penalties incurred for personal convenience.
c. If a mission or bureau chooses to use restricted, penalty fares, the mission or bureau must provide the travel management center with a written policy for the use of these fares and the appropriate fare type (restricted or unrestricted) must be indicated in the remarks of each travel authorization. At posts where a travel management center does not exist, the written policy must be provided to the travel section in the general services office.
d. When an employee is authorized a restricted fare under 14 FAM 564.2 , paragraph b, and engages in indirect (cost-constructed) travel also using a restricted fare, penalties incurred due to changes or cancellations required by the U.S. Government are reimbursable up to the cost that would have been incurred for similar modifications to the authorized routing. The employee will be responsible for any penalties incurred for personal reasons.
14 FAM 564.3 Disposition of Airline Promotional Items
a. All Department employees, their dependents, and others whose travel is funded by the Department may retain for personal use promotional items (i.e., frequent flyer miles, upgrades, access to carrier lounges) earned from official travel under terms available to the general public and at no extra cost to the U.S. Government.
b. Travelers may accept free upgrades of services to business-class or first-class accommodations if they are obtained under terms available to the general public and at no extra cost to the U.S. Government.
c. Travelers may redeem frequent flier miles (or use personal funds) to upgrade to business or first-class accommodations when performing official travel.
d. It is the responsibility of each traveler to communicate directly with a service provider to establish his or her frequent travel promotional benefits account. Costs associated with establishing this account are to be paid by the traveler and are not a reimbursable expense.
e. Travelers need not report as taxable income promotional items obtained from official travel.
14 FAM 564.4 Compensation Received from Airlines for Denied Boarding
a. Voluntary : A traveler may keep payments from a carrier for voluntarily vacating a transportation seat. However, no additional expenses (per diem or miscellaneous reimbursable) may be paid because of the traveler’s delay. Additional travel expenses incurred because of voluntarily giving up a seat are the traveler’s financial responsibility.
b. Involuntary : If a traveler is involuntarily denied a transportation seat, the traveler enters an onward travel status for per diem and miscellaneous travel expense reimbursement. Any monetary compensation (including meal and/or lodging vouchers) for the denied seat belongs to the U.S. Government.
14 FAM 565 CANCELED RESERVATIONS
14 FAM 565.1 Service/Cancellation Expenses
When a train, sailing vessel, or hotel reservation is canceled because of unavoidable, nonpersonal delay or because of official necessity, the cost of a service fee or cancellation expense charged by the service provider is allowed. Fees paid for cancellations of reservations for personal reasons or avoidable delays in notifying the service provider are not reimbursable.
14 FAM 565.2 Liquidated Damage Payments to Traveler
a. When carrier tariffs require liquidated damage payments to travelers for the carrier's failure to provide confirmed reserved space, such payments by the liable carrier are to be by check, made payable to the "Treasurer of the United States." In no case is the traveler permitted to accept from the carrier a check showing the traveler as payee.
b. The traveler is to acknowledge receipt of the check and submit a copy of the acknowledgment and the check with travel voucher. Payment of denied boarding compensation to the Treasurer of the United States is a U.S. Government requirement and is no reflection on the carrier (see 4 FAM 470 ).
14 FAM 566 TRAVEL BY PRIVATELY OWNED VEHICLE OR PRIVATELY OWNED CONVEYANCE
14 FAM 566.1 Policy
a. Travel by common carrier is generally considered the most advantageous method to perform official travel. Other methods of transportation may be authorized if they are determined to be more advantageous to the U.S. Government. A determination that another method of transportation is more advantageous to the U.S. Government than common carrier transportation will not be made based on personal preference or inconvenience to the traveler.
b. In determining whether the use of a privately owned vehicle is advantageous to the U.S. Government, consider:
(1) The feasibility of using common carrier transportation or U.S. Government-owned conveyances based on availability, suitability of schedules, and other applicable requirements;
(2) The total cost to the government, including per diem, overtime, lost work time, actual transportation costs, total distance of travel, number of points visited on official travel, the number of travelers, and energy conservation;
(3) The advantages resulting from the more expeditious transactions of the public business, economy, and employee performance effectiveness; and
(4) Any other advantages and/or disadvantages to the U.S. Government in the particular case.
c. The authority to travel by privately owned vehicle (POV) contained in this section is applicable to the employee and/or other family member(s) authorized to travel. The vehicle to be used must be the property of the employee or family member prior to the initiation of travel and must be driven or shipped to the ultimate destination stipulated in the travel orders. Only such vehicles as are eligible for shipment at U.S. Government expense are authorized to be driven on a mileage per diem basis under this provision.
d. Any reimbursement for travel by POV, under the mileage (see 14 FAM 566.2-1 ) per diem basis authorized by this section is limited to the actual mileage between authorized points on a direct route plus related per diem, not to exceed 10 days to each authorized destination.
14 FAM 566.2 Use Advantageous to the U.S. Government
14 FAM 566.2-1 General
(CT:LOG-388; 01-19-2024)
a. When the authorized travel from origin to destination (combined with TDY, consultation and/or home leave, as applicable) can be performed entirely using a privately owned vehicle (POV), such use may be authorized.
b. Travel by POV to separation address in the United States, when not otherwise covered under 14 FAM 566.1 , is hereby authorized from the port of discharge of the vehicle to the separation address via consultation point (as applicable). In accordance with 14 FAM 618.4 , however, this authorization does not apply to vehicles acquired en route to a separation point.
c. When an employee's vehicle is authorized emergency storage in accordance with 14 FAM 626 , an authorizing officer may determine that it is advantageous for the vehicle to be driven all or part of the distance to the designated storage point.
d. An employee who acquires a vehicle at a point on a direct route to the post of assignment abroad, and who has not previously shipped a vehicle under the provisions of the authorizing travel orders, may drive the POV to the destination. The point of acquisition is considered the point of origin. In no case may the cost of driving the vehicle from where it is acquired exceed the cost to the U.S. Government had the vehicle been shipped from the point of origin specified in the travel authorization to the authorized destination.
e. Travel by a POV is considered advantageous to the U.S. Government when the authorized or actual point of origin and the final destination are:
(1) Connected by a hard-surface, all-weather highway or by vehicular ferry, or both (see 14 FAM 615.1 ); and
(2) Within the continental United States or Canada or one of the following Mexican border posts:
(a) Ciudad Juárez;
(b) Matamoros;
(c) Nuevo Laredo;
(d) Tijuana; or
(e) Nogales.
f. When use of a rental vehicle in the United States is authorized, reimbursement for rental fees and actual expenses for fuel (gas, diesel, electricity, etc.) and tolls is authorized. U.S. Government-contracted rental vehicle services should be used whenever possible. Collision damage waiver (CDW) is included in the contract amount and should not be accepted at extra cost. When renting from companies not on the U.S. Government contracting list, travelers will not be reimbursed for CDW. However, payments for damages to a rental car company or reimbursement to the employee, up to the deductible amount contained in the rental contract, are authorized, providing the employee was acting within the scope of his or her employment at the time of the incident.
g. When use of a rental vehicle abroad is authorized, reimbursement may include rental fees, including value added tax (VAT), and actual expenses for fuel and tolls. U.S. Government-contracted rental vehicle services should be used whenever possible. The contract rate includes CDW, VAT, and unlimited mileage. When renting from companies not on the U.S. Government contracting list, CDW, VAT, and unlimited mileage will not usually be included. CDW is a reimbursable expense abroad. In addition, payments for damages to a rental car company or reimbursement to the employee are authorized up to the deductible amount contained in the rental contract, providing the employee was acting within the scope of his or her employment at the time of the incident.
h. When use of a rental vehicle is authorized for official travel, the least expensive “compact” car available must be used unless one of the following exceptions for another class of vehicle applies and is indicated on the travel authorization:
(1) When use of other than a compact car is necessary to accommodate a medical disability or other special need, and all applicable requirements set forth in 41 CFR 301-10.450(c)(1) have been met;
(2) When additional room is required to accommodate multiple employees authorized to travel together in the same rental vehicle;
(3) When security circumstances (as defined in writing by DS or the RSO) require a larger vehicle;
(4) When necessary for other safety reasons, such as during severe weather or having to travel on rough or difficult terrain;
(5) When travelers must carry a large amount of U.S. Government material incident to their official business, and a compact rental vehicle does not contain sufficient space; or
(6) When the cost of other than a compact car is less than or equal to the cost of the least expensive compact car.
i. For non-electric rental vehicles, t ravelers may not be reimbursed for purchasing prepaid refueling options. Therefore, travelers must refuel prior to returning the rental vehicle to the drop-off location. NOTE : If it is not possible to refuel completely prior to returning the vehicle because of safety issues or due to the location of closest fueling station, travelers will be reimbursed for vendor refueling charges. For electric rental vehicles, travelers may be reimbursed for pre-paid charging costs and/or necessary costs paid via credit card or billed back to the rental vehicle company to recharge the vehicle before return.
j. Travelers will not be reimbursed for fees associated with rental car loyalty points or the transfer of points charged by car companies.
14 FAM 566.2-2 Mileage Reimbursement
Mileage reimbursement rates for automobiles (including trucks, vans, etc.), airplanes, motorcycles, and motor scooters are set by GSA. The current rates may be found on the GSA website.
14 FAM 566.3 Privately Owned Vehicle (POV) Use for Personal Convenience
14 FAM 566.3-1 General
When no determination of advantage to the U.S. Government is made (see 14 FAM 566.2 ), the employee may elect to use a privately owned vehicle for personal convenience. Any reimbursement for expenses for travel will be the lesser of:
(1) Mileage for the authorized mode of travel at the rates provided in 14 FAM 566.2-2 , plus related per diem; or
(2) For the portion of the route connected by air service, reimbursement may not exceed the constructive cost of the authorized U.S. Government fare for the authorized mode of travel on a direct route, plus related per diem and other expenses. For any portion of the route not connected by air service, reimbursement may not exceed the constructive cost of commercial fares on a surface common carrier.
14 FAM 566.3-2 Use of Rental Vehicle
When the employee elects to use a rented vehicle for personal convenience, and use of the rental vehicle has not been specifically authorized, per 14 FAM 566.2-1 , paragraphs f and g, reimbursement for travel expenses will be the lesser of:
(1) Mileage, plus per diem and other expenses allowable on the authorized mode of transportation stated in the travel authorization; or
(2) The constructive cost of the U.S. Government airfare on a direct route, plus per diem and other expenses. For any portion of the journey not connected by air service, reimbursement may not exceed the constructive cost of less than premium-class accommodations on a surface common carrier.
14 FAM 566.4 Computing Expenses
14 FAM 566.4-1 Distances
When travel is performed by a privately owned motor vehicle, distances are to be determined by use of standard highway mileage guides. Travelers must explain any substantial deviation from distances shown in the standard highway mileage. When travel is performed by privately owned airplanes, distances are to be determined from airways charts issued by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce. If a detour is necessary on account of adverse weather, mechanical difficulty, or other unusual conditions, the additional highway or charted air mileage may be included but must be explained.
14 FAM 566.4-2 Allowable Travel Time
Allowable time for travel by privately owned conveyance is limited to that which is reasonably required. Variations in driving conditions do not permit the establishment of daily mileage requirements. In the United States, however, 360 miles per day is considered the average normal driving distance. Where road, climate, and other factors beyond the control of the traveler cause interruptions and deviations resulting in longer than normal travel time, the traveler will include a full explanation on the travel voucher. The traveler must also explain any unusual circumstances that influence the elapsed time for travel by privately owned aircraft.
14 FAM 566.4-3 Shared Expenses
When two or more authorized travelers share the same privately owned conveyance, payment of mileage expenses is made to only one of them.
14 FAM 567 ACCOMMODATIONS
14 FAM 567.1 Accommodations on Trains and Vessels
a. U.S. Government employees who travel by train or sailing vessel (ship/ferry) are authorized the lowest class of accommodation on the train or sailing vessel. For overnight train travel, employees must use slumber coach sleeping accommodations or the lowest level of economy sleeping accommodations available. For overnight travel on a sailing vessel, employees must use the lowest-cost stateroom. First-class train or steamer accommodations may be used only as permitted in 14 FAM 567.1-2 .
b. In some countries, the lowest class of train or sailing vessel service available locally may be considered by posts to be unacceptable by U.S. standards and not comparable to what would be considered as a reasonable basic class of accommodation as defined in 14 FAM 511.3 . For example, train service described as first class at some posts may only equate to the coach-class definition in the United States. Accordingly, posts may establish a policy re-defining the acceptable level of local train accommodations that would meet each definition and document this in a written policy for travelers, inspectors, and U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) auditors.
c. If a train has only two classes of accommodation available (i.e., first and business), then the business class accommodation is deemed to be classified as coach class for the purposes of official travel since it is the lowest class offered. In such cases, the travel authorization should reflect that use of the lowest class of service available is authorized. While such travel may take place in the train’s business class compartment, is not reportable to GSA as premium class travel and no Form DS-4087 is required.
14 FAM 567.1-1 Authorization and Approval for the Use of Business- or First-Class Train or Sailing Vessel Accommodations
a. First class : Heads of agencies, or their designees as listed in 14 FAM 567.2-3 , may authorize or approve the use of first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations under criteria specified in 14 FAM 567.1-2 .
b. Business class : Officials listed in 14 FAM 567.2-4 may authorize or approve the use of business-class train or sailing vessel accommodations under criteria specified in 14 FAM 567.1-2 .
14 FAM 567.1-2 Use of Business- or First-Class Train or Sailing Vessel Accommodations
The use of business- or first-class accommodation may not be authorized strictly based on position or rank. When business- or first-class accommodations are authorized under the following circumstances, only the next higher available accommodations satisfying the needs may be used; for example, business-class accommodations should be utilized before going to first-class accommodations. Circumstances justifying the use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations are limited to those listed below ( NOTE : 14 FAM 567.1-2 , subparagraph (4), applies only to trains):
(1) No reasonably available coach-class train accommodations or lowest class sailing vessel accommodations :
(a) Trains : The use of business-class train accommodations may be authorized when no coach-class train accommodations are reasonably available. For this paragraph, "reasonably available" means coach-class train accommodations that are scheduled to leave within 24 hours of the employee's proposed departure time or scheduled to arrive within 24 hours of the employee's proposed arrival time. In the case of a direct route that requires overnight travel, "reasonably available” must be based on the availability of slumber coach, or lowest economy, sleeping accommodations. "Reasonably available" does not include any accommodation with a scheduled arrival time that is later than the employee's required reporting time at the duty site, or with a scheduled departure time that is earlier than the time the employee is scheduled to complete duty;
(b) When the traveler determines that coach seats are unavailable for reservation for the day he or she must travel to arrive at a destination in time to conduct official business, the traveler may proceed to obtain a reserved seat in the next higher class where a reserved seat is available. This is only permissible when the traveler has made a good-faith effort to obtain a reservation in coach class at the earliest practicable time, i.e., the employee cannot unreasonably delay or postpone making reservations and travel plans to justify premium class travel; and
(c) Sailing vessels : The use of the next higher-class accommodations may be authorized or approved only when lowest-class accommodations are not available on the vessel;
(2) Travel on trains or sailing vessels by an employee with a disability : The use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations may be authorized or approved when necessary to accommodate an employee's disability or other physical impairment, and the employee's condition and need for business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations are substantiated in writing by MED or the regional medical officer or other competent medical authority. The use of business- or first-class accommodations may also be authorized for an attendant, when the employee is authorized use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations and MED, or the regional medical officer or other competent medical authority certifies that the employee's disability or other physical impairment requires the services of an attendant en route;
(3) Security reasons aboard trains or sailing vessels : The use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel accommodations may be authorized or approved when exceptional security circumstances require such travel. Exceptional security circumstances include but are not limited to:
(a) Travel by an employee whose use of coach train or lowest-class sailing vessel accommodations would endanger the employee's life or U.S. Government property;
(b) Travel by agents in charge of protective details and accompanying individuals authorized business- or first-class accommodations; or
(c) Travel by couriers or control officers accompanying controlled pouches or packages and the lowest-class accommodations cannot fulfill the mission; and
(4) Inadequate foreign coach-class train accommodations (foreign trains only) : The use of business- or first-class train accommodations may be authorized or approved when coach-class accommodations on a foreign rail carrier lack adequate sanitation or health standards.
14 FAM 567.1-3 Reporting Requirements for Business- or First-Class Travel on a Train or Sailing Vessel
a. Refer to 14 FAM 567.2-5 for instructions on reporting the use of business- or first-class train or sailing vessel travel to GSA.
b. Extra-fare train service does not need to be reported to GSA if the traveler was ticketed in the lowest class of service offered, even if that class of service was business class.
c. Travel that has been authorized under 14 FAM 567.1-2 , subparagraph (4) for inadequate sanitation or health standards does not need to be reported to GSA.
14 FAM 567.1-4 Extra-Fare Train Service (Express Trains)
a. Extra-fare train service is enhanced performance (i.e., faster speed or fewer stops) relative to other trains available between the same origin and destination.
b. Use of extra-fare trains is not authorized unless determined more advantageous to the U.S. Government or required for security reasons.
c. To justify time savings as an advantage to the U.S. Government, the extra-fare train must reduce overall journey time by one hour or more. Authorizing officials are reminded that air travel may be less expensive than extra-fare trains and, if so, should be the authorized mode of transportation.
d. To justify cost savings as an advantage to the U.S. Government, a ticket for the lowest class of service available on an extra-fare train must, relative to a ticket for the lowest class of service available on a standard train:
(1) Have the same restrictions;
(2) Be less expensive; and/or
(3) Depart within 3 hours of the standard train that would otherwise be booked.
e. Authorizing officials listed in 14 FAM 567.1-1 must approve this and the requirements of 14 FAM 567.1-2 must be met to authorize business class (when it is other than the lowest class of service offered on the train) or first class on an extra-fare train.
14 FAM 567.2 Airplanes
a. See 14 FAM 583 .
b. U.S. Government employees who use commercial air carriers for domestic and international travel on official business must be authorized coach-class airline accommodations. When available, the use of contract-air carriers offering discount (city-pair) fare is mandatory (see 14 FAM 542 , paragraph b). First-class air accommodations may be authorized only as permitted in 14 FAM 567.2-3 . Business-class air accommodations may be authorized only as permitted in 14 FAM 567.2-4 .
14 FAM 567.2-1 Seat Selection and Assignment
a. Each traveler, regardless of age, is entitled to occupy a seat on an airplane.
b. The policies and business practices of the airline(s) operating and/or marketing a particular flight determine whether a seat selection is available and, if they are available, whether a fee must be paid to obtain a seat.
c. Inability to obtain a seat selection or assignment, either for "free" or upon payment of a fee, does not confer an exception to the mandatory use of contract carriers ( 14 FAM 543 ), the provisions of the Fly America Act ( 14 FAM 583 ), or the requirement to authorize travel on the carrier offering the lowest fare that is consistent with all travel regulations.
d. Except as specified in subparagraphs d(1) through d(3) of this section, travelers are eligible for reimbursement of charges to obtain an economy class seat selection in an amount not to exceed $300 (each way) between any two authorized duty locations (i.e., origin and destination pairs), as indicated on a travel authorization. When a traveler qualifies for and is authorized a rest stop, the rest stop location is not considered a separate duty location for the purposes of this provision:
(1) If a bureau/post has a written policy stating that it wishes to limit this benefit, a traveler’s authorizing official may cap reimbursement at a lower amount for a particular instance of travel. In such cases, the authorizing official must specify, in advance of travel, the amount authorized for reimbursement between each duty location and should offer the traveler an explanation for the reduction;
(2) Seat selection fees are not reimbursable for any segment(s) of travel:
(a) Conducted in an indirect manner; or
(b) For which a traveler has cost-constructed to use accommodation in business or first class; or
(c) For which a traveler has been authorized business class or first-class accommodations; and
(3) The "value" of a seat selection fee cannot be applied towards the cost of obtaining a ticket in an other-than-coach class of service or be considered as part of any cost-construct calculation.
e. Payment of a seat selection fee must be made directly to the airline by the traveler. TMCs are not authorized to pay for seat selection fees, either by charging them directly to the U.S. Government or by facilitating payment on behalf of the traveler.
f. Reimbursement for a seat selection fee must be approved on the travel authorization prior to commencing travel and can only be approved for authorized direct travel (see 14 FAM 511.3 ).
g. Receipts are required for reimbursement of seat selection fees, regardless of amount.
h. For the purposes of determining eligibility for reimbursement, a seat selection in any cabin except business class or first class will be considered an economy class seat selection. Travelers may purchase any seating product, including those that offer increased seat width, additional legroom (formerly referred to as “extended economy seating”), or which are bundled/packaged with enhanced onboard or on-ground service, if the seating product is not business class or first class. For example, whether an airline calls a seating product Economy Plus, Premium Economy, or Preferred Seats has no bearing on eligibility for reimbursement as long as the seats are not business or first-class seats.
i. Travelers, not the TMC or airline, are responsible for making accurate determinations regarding whether a particular airline product is eligible for reimbursement as an economy-class seat assignment. Because some airlines have developed branded names that do not give direct indication of their product’s status as business or first class (e.g., United Polaris, Delta One, Copa Dreams Class), travelers who are uncertain whether a product qualifies for reimbursement as an economy class seat selection fee may request a determination of eligibility, before travel commences, by contacting [email protected].
14 FAM 567.2-2 Requirements
14 FAM 567.2-2(A) Authorization
a. Authorization for first-class or business-class air accommodations must be made in advance of the actual travel and must be documented in accordance with 14 FAM 567.2-2(B) . The designated approving official must not be subordinate to the traveler except that the Executive Secretary may approve first-class or business-class air accommodations for the Secretary and the Deputy Secretaries.
b. If the documents required under 14 FAM 567.2-2(B) cannot be completed in advance of travel due to an emergency, the employee must obtain advance approval from an agency official not subordinate to the traveler or from the chief of the agency’s transportation and travel management division or other designated office and must submit the required documents with the appropriate signatures at the earliest possible time.
c. If the employee does not obtain written authorization in accordance with this section, the employee is responsible for the difference between the first-class or business-class air accommodations used and the authorized coach-class or equivalent accommodations.
14 FAM 567.2-2(B) Documentation
a. Authorization : All requests for authorization must contain the name, grade, and position of the travelers; points between which first-class or business-class air accommodations are authorized; additional cost to the U.S. Government resulting from the difference between first-class or business-class and coach-class air accommodations; beginning date of travel; and an explanation of circumstances justifying the use of first-class or business-class air accommodations:
(1) Authorization for first-class air accommodations must be reflected in the travel authorization and accompanied by a memo from the appropriate agency head or designee (see 14 FAM 567.2-3 );
(2) Authorization for business-class air accommodations must be reflected in the travel authorization and accompanied by the appropriate form signed by the designated approving official (see 14 FAM 567.2-4 ):
(a) State : Form DS-4087, Authorization Request for Business-Class Air Travel; or Form DS-4086, Special Seating Request Form for Air Travel, if the justification for use of premium-class accommodations is authorized for disability or special need under 14 FAM 567.2-4 , subparagraph (b)(3);
(b) USAID : Form AID-522-2, Business Class Memorandum to M/MS/TTD;
(c) Commerce : Form CD-334, Request for Approval of Other Than Coach-Class Accommodations;
(d) USDA/FAS : Memo requesting premium-class travel;
(e) APHIS : Memo to approving official; and
(f) USAGM : Memo to approving official.
b. Ticketing : The travel management center (where applicable) will not ticket first-class or business-class accommodations without the appropriate documentation. Posts that do not have a travel management center must retain the required documentation for the record.
c. Blanket orders : The use of blanket travel authorizations for first-class or business-class accommodations is prohibited (State Department personnel). Each trip involving first- or business-class travel accommodations must be separately authorized.
d. Couriers : A courier who flies first class when business-class air accommodations are not available, must complete and sign Form DS-3031, Certification for Use of First-Class Air Accommodations. A copy of the certification must be retained by the courier and the original is to be maintained in the courier's regional office.
14 FAM 567.2-3 First-Class Travel
a. Authorization or approval : Authority to approve the use of first-class air accommodations is limited to the respective agency heads (the Secretary of State, the Administrator of USAID, the Secretary of Commerce, the Director of the U.S. International Broadcasting Bureau of the Broadcasting Board of Governors (USAGM/IBB), and the Secretary of Agriculture) or their designees. Designees are as follows:
(1) State : The Under Secretary for Management (M) per State Department Delegation of Authority No. 198, dated September 16, 1992, except that the Executive Secretary may approve the use of first-class air accommodations for the Secretary and the Deputy Secretary;
(2) USAID : The Deputy Administrator;
(3) Commerce : The Chief Financial Officer and the Assistant Secretary for Administration except in cases of medical necessity or emergency evacuation when the Deputy Assistant Secretary for International Operations is delegated authority to approve. First-class travel will only be authorized if no other commercial service is reasonably available or such travel is necessary for reasons of disability or medical condition (for details on Commerce’s policy on use of business-class accommodations, contact the Office of Foreign Service Human Capital);
(4) USDA/FAS : The Administrator, Foreign Agricultural Service;
(5) APHIS : The Under Secretary for Marketing and Regulatory Programs; and
(6) USAGM : The Director of the International Broadcasting Bureau or as specified in the Manual of Administration.
b. Use of first-class accommodations : Circumstances justifying the use of first-class air accommodations are limited to those listed below:
(1) No other reasonably available accommodations : The use of first-class air accommodations may be authorized or approved when coach-class air accommodations or business-class air accommodations are not reasonably available. "Not reasonably available" means no other class of accommodations other than first-class accommodations is available on any scheduled flight in time to accomplish the purpose of the official travel;
(2) Travel by an employee with a disability : The use of first-class air accommodations may be authorized or approved when necessary to accommodate an employee's disability or other physical impairment, and the employee's condition and need for first-class air accommodations are substantiated in writing by MED or the regional medical officer or other competent medical authority. The use of first-class air accommodations also may be authorized for an attendant(s) who is authorized to accompany the employee, when the employee is authorized first-class air accommodations and MED or the regional medical officer or other competent medical authority or the Disability/Reasonable Accommodation Division (GTM/ER/DRAD) certifies in writing that the employee's disability or other physical impairment requires the services of the attendant(s) en route;
(3) Security reasons : The use of first-class air accommodations may be authorized or approved when exceptional security circumstances require such travel. Exceptional security circumstances include but are not limited to:
(a) Travel by couriers or control officers accompanying controlled pouches or packages when business-class air accommodations are not available (see 14 FAM 567.1-2 , subparagraph (3)(c)); or
(b) Travel by agents in charge of protective details accompanying first-class travelers; and
(c) When required because of agency mission.
14 FAM 567.2-4 Business-Class Travel
a. Authorization or approval :
(1) State : For PCS travel, the designated approving official is the Executive Director, Bureau of Global Talent Management (GTM/EX). Except where otherwise indicated, business-class air accommodations may be authorized only with approval from the officials below (or their designated representative(s)) as provided to TMP. For travelers not mentioned below, the designated approving official must not be subordinate to the traveler:
(2) USAID : The Chief of the Travel and Transportation Division (M/MS/TTD), the director of the funding bureau, office, or mission or designee;
(3) Commerce : The Chief Financial Officer and the Assistant Secretary for Administration except in cases of medical necessity or emergency evacuation when the Deputy Assistant Secretary for International Operations is delegated authority to approve. Business-class travel will only be authorized if no other commercial service is reasonably available or such travel is necessary for reasons of disability or medical condition (for details on Commerce's policy on the use of business-class accommodations, contact the Office of Foreign Service Human Capital);
(4) USDA/FAS : The Under Secretary for Farm and Foreign Agricultural Services and the USDA Chief Financial Officer;
(5) APHIS : The Under Secretary for Marketing and Regulatory Programs and the USDA Chief Financial Officer; and
b. Justification : Travelers may use business-class air accommodations when an approving/authorizing official specifically approves or authorizes the travel in accordance with one or more of the following reasons:
(1) Coach-class air accommodations not available : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when regularly scheduled flights between the authorized origin and destination points (including connection points) provide only business-class air accommodations;
(2) No space available in coach-class air accommodations : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when space is not available in coach-class accommodations on any scheduled flight in time to accomplish the purpose of the official travel;
(3) Travel by an individual with a disability or special need : Upon the recommendation of the Bureau of Medical Services (MED), other competent medical authority in exigent circumstances, or the Disability/Reasonable Accommodation Division (GTM/ER/DRAD), business-class air accommodations may be authorized when necessary to accommodate an employee's disability or special need. Other competent medical authority must certify in writing (to include the supporting clinical findings) the traveler’s condition and need for business-class air accommodations. Upon the recommendation of MED or, in exigent circumstances, other competent medical authority, business-class air accommodations may also be authorized for an attendant authorized to accompany the traveler when the traveler is authorized use of business-class air accommodations. Authorization for an attendant to accompany the traveler, by other competent medical authority, must include written certification that the traveler’s disability or other special need requires the services of the attendant en route;
(4) Security or exceptional circumstances : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when such accommodations are required for security purposes or because exceptional circumstances, as determined by the agency head, or his or her designee, make their use essential to the successful performance of the agency's mission. NOTE : Exceptional circumstances may include, but are not limited to, a chief of mission (COM) and their eligible family member spouse (whether traveling together or at different times) going to post for the first time or leaving post the last time, in accordance with protocol and diplomatic practice for a COM. The tandem spouse of a COM assigned to the same post may also be authorized business class on this basis. Other eligible family members who accompany either the COM or spouse may be authorized business class. If consultations are authorized en route to and from post, business-class accommodations may be authorized to and from the consultation location(s);
(5) Overall cost savings : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when such accommodations would result in an overall savings to the U.S. Government, including by avoiding additional subsistence costs, overtime, or lost productive time while awaiting coach class accommodations. Whenever a cost comparison is made, documentation of the specific flight itineraries and their respective costs must be retained and included in the travel authorization for future reference and to meet auditing requirements:
(a) If a traveler is otherwise authorized an unrestricted economy fare and seeks to be authorized a business-class fare under this provision, the unrestricted economy fare must be compared to the cost of an unrestricted business-class fare;
(b) If a traveler is otherwise authorized a restricted economy fare and seeks to be authorized a business-class fare under this provision, the restricted economy fare must be compared to the cost of a restricted business-class fare;
(6) Agency mission : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when required due to agency mission. State only : Business-class travel of 14 hours or less based on this criteria must be approved by the traveler's under secretary or equivalent in their supervisory chain. Deputy secretary and under secretary business-class travel is approved by the Executive Secretary;
(7) Acceptance of payment from non-Federal source : Business-class air accommodations may be authorized when the employee's transportation is paid in full through agency acceptance of payment from a non-Federal source in accordance with 2 FAM 962.12 (g) and 41 CFR 304-5.5; and
(8) Travel in excess of 14 hours for temporary duty (TDY) travel, or medical evacuation travel (exception : USAGM; for further USAGM guidance on when business-class accommodations can be authorized, refer to USAGM’s Manual of Operations and Administration (MOA) directive PART IV Section 636.3, Business-Class Travel Exceptions):
(a) TDY travel to receive training: Business-class air accommodations are not authorized for TDY travel over 14 hours where the primary purpose of the travel, as determined by the funding bureau or post approving/authorizing officer, is for the traveler to receive training or instruction;
(b) TDY travel not related to training: For TDY travel over 14 hours, travelers are authorized economy-class accommodations with a rest stop or a paid day pass to a business-class lounge at an intermediate point on the traveler’s authorized itinerary. However, the funding bureau's executive director or authorizing official at post may determine that circumstances warrant issuance of a business-class ticket provided the following criteria are met:
(i) The origin and/or destination is outside the continental United States;
(ii) The scheduled flight time (including stopovers, but not including rest stops) on the usually traveled route is in excess of 14 hours;
(iii) The purpose of the trip is urgent and cannot be postponed. The traveler must physically report to the duty location immediately upon arrival or the following day, and work until the urgent requirements are fulfilled; and
(iv) Travelers taking leave during or near the dates of their travel indicate that there are no urgent duties requiring the traveler’s immediate departure or return. Travelers who do not report for duty immediately upon arrival or no later than the next day, or take leave within days of their TDY travel should not be authorized business class travel. The traveler may be held liable for excess business class accommodations;
(c) Travelers in U.S. Government-funded business class are not entitled to a U.S. Government-funded rest stop en route to or upon arrival at the duty site. They are not eligible for a U.S. Government-funded business-class lounge day pass, (see 14 FAM 584 ). For definition of travel in excess of 14 hours and rest stop en route, see 14 FAM 567.2-4 , subparagraph b(10)(d);
(d) Medical evacuation travel: Premium-class travel is not authorized for medical evacuation unless MED, in consultation with the Foreign Service medical provider, or in an exigent situation, authorizes business-class accommodations for medical reasons. Travelers authorized by MED to use premium accommodations may not be authorized a rest stop en route or a rest period upon arrival at destination, unless specifically authorized by MED. Travel over 14 hours in duration that is not deemed medically necessary for premium class by MED, will be authorized economy class with a rest stop or a U.S. Government-funded day pass to a business-class lounge at the intermediate point;
(e) Other official travel: Business-class air accommodations may not be authorized or approved for other types of official travel more than 14 hours (such as R&R, PCS, home leave/return to post, educational travel, EVT, etc.) unless justified under one of the other provisions (see 14 FAM 567.2-4 ); and
(f) Calculation of 14-hour travel period:
(i) The “14-hour travel time" is defined as the scheduled flight time on the most expeditious available routing from your point of origin to scheduled arrival at point of destination (wheels up at origin to wheels down at destination). It does not include rest stops or travel from residence/hotel to the airport. Travel in excess of 14 hours includes a leg of travel (a travel segment) in excess of 14 hour or continuous legs of travel (continuous travel segments) without a U.S. Government-funded rest stop in excess of 14 hours on the most direct route;
(ii) The time zone dislocation provision for a rest period upon arrival ( 14 FAM 584.5 ) does not apply to business-class travel. However, business-class travelers may arrive the night before a meeting and be provided per diem for the night if such arrival is necessary to ensure attendance at the meeting. This is not considered a rest period upon arrival; and
(iii) The traveler will not be penalized and deprived of business-class accommodations if travel is delayed or accelerated due to airline schedules rather than to accommodate a traveler’s personal convenience. This is not a rest period or rest stop.
c. Use of the lowest upgradeable fare : In cases where business-class travel is authorized in accordance with the justifications above, but not funded by the bureau or post, the bureau or post may approve the lowest-cost upgradable fare if the traveler commits to upgrading to a business-class fare at their own expense:
(1) Travelers are responsible for obtaining approval for the lowest-cost upgradable fare from the authorizing official by completing a Form DS-4087 prior to travel;
(2) The cost of the upgradable fare may not exceed the cost of the business-class fare for which the traveler is eligible;
(3) When available and approved by the authorizing official, the discounted GSA city-pair YCA fare may qualify as the lowest upgradable fare in lieu of the CA fare;
(4) When a GSA city-pair fare is not available, the authorizing official may approve a fare up to and including the full "Y" fare as the lowest upgradable fare;
(5) A traveler may be authorized the upgradable fare only when the cost of the upgrade is borne by the traveler; and
(6) Rest stops or day passes to a business-class lounge are not authorized when a traveler elects this option.
d. Business-class travel within the United States : U.S. domestic flights do not usually offer separate and distinct business-class seats. The U.S. Government, however, cannot directly book employees eligible for business-class into first-class accommodations. When business-class accommodations are authorized and the airline places the individual in first-class seating at no additional cost for the part of the routing within the United States via a connection, such seating would be considered business-class accommodations for the purpose of this rule.
e. Traveler-paid or airline-provided business class : When a traveler is authorized economy class but actually travels in business class, such as by redeeming airline miles or points, completion of a Form DS-4087 is not necessary. Such instances are also not included in the annual premium-class travel report since they do not change the authorized class of accommodation or expend more U.S. Government funds than would have been spent on the authorized class of service.
f. Exceptions : The Under Secretary for Management or designee may make exceptions to this section to the extent consistent with the law.
14 FAM 567.3 Premium-Class Travel Reporting
a. Each post and domestic office that issues travel tickets must submit a premium-class (first-class and business-class) travel report identifying all premium-class commercial travel (i.e., airplanes, trains, vessels) ticketed and utilized during the fiscal year. The only exception for reporting premium-class travel is outlined in 14 FAM 567.1-3 . A negative report is required if no premium-class travel was utilized. The Department is required to report to the General Services Administration (GSA) no later than October 31 each year. Travel on U.S. Government aircraft is reported separately and is covered in 14 FAM 558 .
b. When the traveler was ticketed in the lowest class of service offered, or use is authorized under 14 FAM 567.1-2 , subparagraph (4), travel on an extra-fare train does not need to be reported to GSA.
c. State only : The Department ‘s Travel Management and Policy Division (A/LM/OPS/TMP) will compile the premium-class travel report from each post with a report from the domestic TMC including domestically issued tickets and submit a consolidated report to GSA in accordance with the guidelines in 41 CFR 300-70.100-103 of the Federal Travel Regulations.
14 FAM 568 AIRLINE LUGGAGE ALLOWANCE
14 FAM 568.1 Authorized Luggage
a. Each traveler is authorized to check, at U.S. Government expense, two pieces of luggage which do not exceed the airline's size limitations or are not considered "oversized" by the operating air carrier, and which weigh up to 50 pounds (23 kilograms) per piece. This allowance constitutes "authorized luggage." It applies to all types of travel and to/from all locations.
b. If a traveler checks items that exceed this authorized weight, size, and/or quantity limitation, reimbursement from the U.S. Government is limited to the cost that would have been incurred to transport “authorized luggage.”
c. Up to two additional pieces of luggage (a maximum of four), which do not exceed the airline's size limitations and which weigh up to 50 pounds per piece, per authorized traveler, may be approved in lieu of an allowable unaccompanied baggage (UAB) entitlement for direct travel if approved in the travel authorization prior to commencing travel.
d. If, for a particular segment of a journey, an air carrier makes a more generous (weight, quantity, or size) checked luggage allowance available to a traveler at no, or no additional, cost to the U.S. Government, the traveler is welcome to utilize the more generous allowance for that segment. This privilege does not , however, increase the “authorized luggage” allowance for subsequent segments.
e. Authorized luggage for indirect (cost-constructed) travel : When a traveler elects to engage in indirect (cost-constructed) travel, the total amount that may be reimbursed by the U.S. Government for checked luggage fees is limited to the sum of expenses that would have been incurred to transport authorized luggage along all segments of the direct route.
14 FAM 568.2 Excess Luggage
a. Luggage exceeding the weight, size, or quantity limit for “authorized luggage” is considered “excess luggage.” To be transported at U.S. Government expense, excess luggage must be required for an official purpose and be specifically authorized in advance of travel. Travel orders that include authorization for the transport of excess luggage must include a justification detailing the specific official purpose necessitating the transport and an estimated cost of such transport.
b. Travel orders for an individual required to transport a checked luggage piece or pieces entirely comprised of U.S. Government materials should include authorization for the transport of those pieces as excess luggage to ensure that the traveler’s personal authorized luggage allowance is not diminished.
c. Excess luggage is not authorized at U.S. Government expense for permanent change-of-station, rest-and-recuperation, family-visitation, and/or emergency-visitation travel. For medical travel, please refer to 16 FAM 310 .
14 FAM 568.3 Receipts
Receipts are required for reimbursement of checked luggage fees in any amount, including fees assessed by an air carrier to transport “authorized luggage.”
14 FAM 569 UNASSIGNED
U.S. Customs to Hike Global Entry Program Fees by 20%
Elizabeth Casolo , Skift
April 2nd, 2024 at 6:07 PM EDT
While Global Entry fees will increase to account for "continuation and management of the programs," U.S. Customs and Border Protection will eliminate application fees for minors.
Elizabeth Casolo
U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) will increase fees for some Trusted Traveler Programs, including Global Entry , on October 1, 2024.
The Global Entry application fee will be $120, a 20% increase from its current $100 cost, CBP said Tuesday . Global Entry allows pre-approved travelers expedited entry into the United States. Programs designed to ease crossings at the Mexican and Canadian borders — SENTRI and NEXUS — will have the same price tag. The fee for NEXUS will see a steep 140% increase from its original $50 cost.
“As these programs have matured and expanded, updating the fee structures is critical to the continuation and management of the programs,” the statement said. The fees “have not been updated in over 15 years.”
TSA PreCheck will not be affected by this price hike.
Some premium credit cards — such as those offered by American Express , Chase , Capital One , and U.S. Bank — dedicate credits to cover the current $100 Global Entry application fee. While some credit cards provide travel credits that would cover the higher fee, other companies must determine whether they will continue covering the full expense.
A spokesperson for Chase Bank said it does not have any updates at this time. Skift contacted several other credit card companies but did not get an immediate response.
There is one bright spot: Minors will no longer pay an application fee for these programs, as long as their parent or legal guardian is already enrolled or actively applying. Members under 18 currently pay the full $100 fee .
As of August 2023, Global Entry had over 12 million members . Members must renew every five years , paying a fee each time.
The Daily Newsletter
Our daily coverage of the global travel industry. Written by editors and analysts from across Skift’s brands.
Have a confidential tip for Skift? Get in touch
Tags: airport , airport security , airport technology , amex , borders , canada , chase , customs , global entry , mexico , nexus , sentri , travel credit card , u.s. customs and border protection , united states
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Create Account
I-131, Application for Travel Document
ALERT: On Jan. 31, 2024, we published a final rule in the Federal Register, that adjusts the fees required for most immigration applications and petitions. The new fees will be effective April 1, 2024.
Applications and petitions postmarked on or after April 1, 2024, must include the new fees or we will not accept them.
What to Know About Sending Us Your Form
The new filing fee is effective for filings postmarked April 1, 2024, and later. If you are filing an acceptable prior form edition on or after April 1, 2024, you must include the new filing fee.
Alert: Beginning July 1, 2022, we will issue a new travel authorization document to Temporary Protected Status (TPS) beneficiaries: Form I-512T, Authorization for Travel by a Noncitizen to the United States, at our discretion if we find the beneficiary merits this authorization. We will no longer issue advance parole documents as evidence of our prior authorization for a TPS beneficiary to be permitted to reenter the United States if the beneficiary travels outside the United States.
Beginning July 1, 2022, we will issue a new travel authorization document to Temporary Protected Status (TPS) beneficiaries: Form I-512T, Authorization for Travel by a Noncitizen to the United States, at our discretion if we find the beneficiary merits this authorization. We will no longer issue advance parole documents as evidence of our prior authorization for a TPS beneficiary to be permitted to reenter the United States if the beneficiary travels outside the United States.
If you are a TPS beneficiary with an existing, unexpired advance parole document, you may continue to travel and seek reentry to the United States after a trip outside the United States through the period of validity printed on your advance parole document.
If you are a TPS beneficiary applying for a new travel authorization document, you should continue to use Form I-131, Application for Travel Document. If you have a pending Form I-131, you do not need to file a new application.
We will continue to issue advance parole documents to noncitizens with pending initial applications for TPS (Form I-821).
TPS beneficiaries and individuals with pending initial TPS applications should carefully read the Form I-131 Instructions which contain warnings about certain risks an individual may face if they are outside of the United States while USCIS is considering their TPS reregistration or initial application, such as missing important request for evidence or other notices or being denied TPS while outside the United States.
ALERT: Court decisions regarding DACA.
On Sept. 13, 2023, the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Texas issued a decision finding the DACA Final Rule unlawful and expanding the original July 16, 2021, injunction and order of vacatur to cover the Final Rule. However, the court maintained a partial stay of the order for “all DACA recipients who received their initial DACA status prior to July 16, 2021.” See the Memorandum and Order (PDF, 1.35 MB) and Supplemental Order of Injunction (PDF, 72.53 KB) .
Accordingly, current grants of DACA and related Employment Authorization Documents (EADs) remain valid until they expire, unless individually terminated. In accordance with this decision, USCIS will continue to accept and process DACA renewal requests and accompanying applications for employment authorization under the DACA regulations at 8 CFR 236.22 and 236.23, as it has since October 31, 2022. We will also continue to accept initial DACA requests, but in accordance with the District Court’s order, we will not process initial DACA requests.
Current valid grants of DACA and related EADs will continue to be recognized as valid under the Final Rule. This means that individuals with DACA and related EADs do not have to submit a request for DACA or employment authorization until the appropriate time to seek renewal.
Please see the DACA Litigation Information Page for important updates and information related to court rulings on the DACA policy.
Use this form to apply for a reentry permit, refugee travel document, TPS travel authorization document, advance parole document (including parole into the United States for urgent humanitarian reasons or significant public benefit), or advance permission to travel for Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI) long-term residents.
For information on travel documents, including potential immigration-related consequences of traveling outside the United States, see our Travel Documents page. If you are in the United States and you have an urgent need to travel outside the United States, see our Expedite Requests page and Emergency Travel page.
If you file this form to request an Advance Parole Document authorizing you to seek parole in the United States when you return to the United States after temporary travel abroad, and you depart the United States before we issue your Advance Parole Document, we will consider your Form I-131 abandoned unless you were previously issued an Advance Parole Document that remains valid for the entire time you are outside the United States.
If you file this form to request an advance permission to travel for CNMI long-term residents document, and you leave the CNMI without having an advance permission to travel document, your status will automatically terminate.
File Online
Form Details
Form I-131 (PDF, 451.87 KB)
Instructions for Form I-131 (PDF, 285.07 KB)
04/01/24 . Starting June 3, 2024, we will accept only the 04/01/24 edition. Until then, you can also use the 06/06/23 E edition. You can find the edition date at the bottom of the page on the form and instructions.
Dates are listed in mm/dd/yy format.
If you complete and print this form to mail it, make sure that the form edition date and page numbers are visible at the bottom of all pages and that all pages are from the same form edition. If any of the form’s pages are missing or are from a different form edition, we may reject your form.
If you need help downloading and printing forms, read our instructions .
Please check our Filing Addresses for Form I-131 page for information on where to mail your application. Applications that are not submitted to the appropriate direct filing address may experience processing delays.
You can find the filing fee for Form I-131 by visiting our Fee Schedule page.
The fee is effective for filings postmarked April 1, 2024, and later.
You can pay the fee with a money order, personal check, or cashier’s check, or pay by credit card or debit card using Form G-1450, Authorization for Credit Card Transactions . If you pay by check, you must make your check payable to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
When you send a payment, you agree to pay for a government service. Filing fees are final and non-refundable, regardless of any action we take on your application, petition, or request, or if you withdraw your request. If you pay by credit card or debit card, you cannot later dispute the payment. Use our Fee Calculator to help determine your fee.
If you are submitting multiple forms, pay each filing fee separately. We are transitioning to electronically processing immigration benefit requests, which requires us to use multiple systems to process your package. We may reject your entire package if you submit a single, combined payment for multiple forms.
Payment if you file at a field office: You cannot pay fees with a money order or cashier’s check when filing at a field office. You can only pay with a personal check, debit card, credit card, or reloadable prepaid credit or debit card.
You do not need to pay an additional fee for Form I-131 if:
- You are filing Form I-131 Application Type B or D;
- You filed a Form I-485 with a fee on or after July 30, 2007, and before April 1, 2024; and
- Your Form I-485 is still pending.
For refugee travel document applications filed from outside of the United States, you must pay the applicable fee(s) to the cashier at the USCIS overseas office or U.S. embassy or consulate with jurisdiction over your location. Please see the website of the appropriate embassy or consulate to confirm acceptable forms of payment. Include the fee receipt from the U.S. embassy or consulate when you file your application package.
Please do not mail cash, personal checks or traveler’s checks. If you do not include a fee receipt with your filing, we will reject your application.
Please do not submit this checklist with your Form I-131. The checklist is an optional tool to use as you prepare your form, but does not replace statutory, regulatory, and form instruction requirements. We recommend that you review these requirements before completing and submitting your form. Do not send original documents unless specifically requested in the form instructions or applicable regulations.
If you submit any documents (copies or original documents, if requested) in a foreign language, you must include a full English translation along with a certification from the translator verifying that the translation is complete and accurate, and that they are competent to translate from the foreign language into English.
Read more information about the types of evidence that may be relevant to specific parole requests on our Humanitarian Parole page.
Complete all sections of the form. We will reject the form if these fields are missing:
- Family Name
- Physical Address
- Date of Birth
- 1.a. – 1.f.
- Family Name (If 1.f. selected)
- Physical Address (If 1.f. selected)
Filing Tips: Review our Tips for Filing Forms by Mail page for information on how to ensure we will accept your form.
Don’t forget to sign your form. We will reject any unsigned form.
E-Notification: If you want to receive an e-mail and/or text message that we have accepted your form at a USCIS lockbox, complete Form G-1145, E-Notification of Application/Petition Acceptance , and clip it to the first page of your form.
- Re-Parole Process for Certain Ukrainian Citizens and Their Immediate Family Members
- Re-Parole Process for Certain Afghans
- Card Delivery Tracking
- Department of State: Photo Specifications
- Travel Documents

Travel Cost Calculator
Quick links, trip pricing calculator.
Travelmath provides an online cost calculator to help you determine the cost of driving between cities. You can use this data to figure out a budget for a road trip. The driving calculation is based on the average fuel efficiency of your vehicle, and you can change the gas mileage in mpg or L/100 km to match your exact make and model. Gas prices are automatically estimated based on current fluctuations, and again you can adjust these to fit your local gas station prices. Both U.S. and international units are available to make the calculations easier to use, and the output is given for both one-way and round trip travel routes.
Check the driving distance for your planned route, and see if the total driving time requires an overnight stay. If it's a long trip, you may want to research some hotels along the way . Or compare whether it's better to fly or drive to your destination.
Home · About · Terms · Privacy

More From Forbes
Expert: here’s what you should do about airline luggage fee increases.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Sasha Gainullin, CEO of the travel insurance company battleface.
Since the beginning of the year, most of the major U.S. airlines have raised their baggage fees. It now costs an average of $35 to check your bag on a domestic flight.
In the travel industry, charging separately for luggage is called unbundling. And it turns out there are experts who specialize in unbundling and have a deep knowledge of what's happening behind the scenes.
Sasha Gainullin, CEO of the travel insurance company battleface , is one of the world's leading authorities on unbundling. I asked him for his thoughts on the latest airline baggage fee increases — and what passengers should do about it.
Here's our interview.
What do you think of the way airlines have unbundled their product, and specifically luggage fees?
I think unbundling is necessary for any customer-driven industry. But as an airline customer, making things more expensive without transparency is something I generally disagree with. While unbundling allows airlines to become more profitable, they should also be more transparent with customers.
How would you make it more transparent?
In general, airfares are being promoted across multiple comparison sites, and travelers aren't loyal to one specific airline. They will more than likely choose a ticket based on the actual flight cost without factoring in the additional costs that will be presented to them in an online purchase experience.
Best Travel Insurance Companies
Best covid travel insurance plans.
Unbundling ancillary additions like bags, seats and meals potentially lowers the base price for an airline ticket, so there’s an opportunity to present negatively viewed fees into something positive.
Unbundling allows choice and the ability to pay for what you want, which is a positive for the customer. I think they’ve done a good job rolling out “basic economy” seats. There’s definitely a market out there for people who just want cheap airfare without the bells and whistles.
So how would you handle it?
There is so much about airfare costs that the general public doesn’t understand. Why is the J fare more expensive than the L fare? Why does seat 10D cost $85, but seat 11D costs $40?
I'd invest heavily in teams that have a full understanding of the products being offered, including product, data and marketing. Then, through extensive testing, I'd focus on optimizing the e-commerce information architecture to improve customer experience, which in turn leads to loyalty and repeat customers.
Finally, I'd look to using the data obtained to build out AI models to help guide customers by giving them recommendations based on their profile, leading to an exceptional experience, because choice can also be overwhelming when trying to make decisions.
What's your advice to air travelers on dealing with these new fees?
My advice would be to choose what you — and your wallet — feel comfortable with in the most direct route possible.
With travel back to or at times exceeding pre-COVID levels, extra fees don’t seem to be a deal-breaker for customers. The hard reality is that most low-cost airlines have multiple unbundled charges, except for Southwest, which still offers the first two checked bags for free and does not charge any change fees.
Many airlines are also starting to add value items back into the fare. JetBlue is unique in that it does not charge for Wi-Fi, and Delta has recently moved in that direction for domestic flights if you are a member of SkyMiles rewards, which is free to join.
So fly the right airline. Beyond that, what would you do with these fees?
Buy what you need and read each step of the buying process thoroughly. Also, packing light to fit everything into a carry-on and a personal item is important, too. This, of course, will not save you money when flying on an airline like Frontier, which probably has the most unbundled add-ons in the airline industry. This includes paying for a carry-on, or, if you don’t, you’re subjected to boarding the plane last, with limited to no room for overhead storage.
I wanted to ask you about hotels, since they've had some interesting fees, too. You get charged extra for a lot of things now, but perhaps most notably, you often have to pay a mandatory resort fee that covers items like pool towels and free Wi-Fi. Any thoughts on hotel fees?
I don't think mandatory resort fees are a choice. Therefore, they can't be considered unbundling. Although it seems transparent now, it is still an imposed fee and should remain in that category, like taxes.
You've been one of the innovators in unbundling travel insurance. How does the way you've unbundled insurance compare to the way airlines have unbundled their products?
Very similar. Giving choice back to the customer and making it specific to their actual needs and travel type.
The more items you add to your cart, the more expensive your airfare or travel insurance is going to be. I think customers get this by now and are willing to pay for it if it makes sense to them based on what they are looking for.
But you're doing more than just unbundling here — you're doing demand-based pricing, just like the airlines, right?
When you think about the process of buying a seat on a flight, the rates will vary depending on a myriad of factors like day of travel, destination, departure time, plane capacity, or where the seat is on the plane. A short flight may not be worth $80 to sit in a seat with extra legroom. But a six-hour flight may be worth premium economy or business class.
These rating factors are different with travel insurance, but they are similar in that the pricing can vary based on other factors. Our rates are dependent on multiple risk factors, including age of travelers, trip length, benefits selected, and trip cost.
Customization of your travel insurance policy should be based on your destination and the type of trip you’re on. For example, when traveling domestically, many do not need travel medical insurance, so why include that in your policy?
How do you sell travel insurance? How is it different from traditional travel insurance?
The travel insurance industry is extremely fragmented, with several independent parties responsible for technology, underwriting, product creation, customer service, claims, and emergency assistance. Often, none of them speak or connect to each other. Our vision for battleface is to change that and to support the travel insurance industry globally.
We have diversified our distribution channels in a big way since 2022. When we first launched in the U.S., we leaned into a direct-to-customer approach, selling travel insurance to build our brand.
An unbundled approach gave us an opportunity to be transparent about what each benefit costs, allowing customers to weigh the importance of each benefit to purchase — a self-assessment, in a way, while also allowing us to test our theory that unbundling increases the likelihood that customers will buy more travel insurance when presented with choice. Now we’ve taken the same model to our partners, who create their own products that are relevant and make the most sense to their customers.
You have a highly regarded business-to-business product called Robin Assist that provides claims handling and assistance services. So I wanted to ask you about the role of technology in unbundling. Is there a way that technology can make this process better — in other words, to give travelers what they want without making them overpay?
The unbundled philosophy is firmly ingrained in everything we do on the platform, from our travel insurance offerings to our assistance and claims services. Without tech, none of this would be possible.
We’re fortunate to have highly skilled product and engineering teams that helped us build the platform and continually update it for faster and faster feature development releases. This rapid release cycle has allowed us to move into an unbundled platform powering API-led distribution, product creation, policy administration, travel assistance services, and claims automation.
Which extras do you buy when you travel? And how has that changed since the beginning of the year?
It all depends on where I’m traveling and how long my flight is. For longer flights, I would buy Wi-Fi. When selecting my preferred seat, I’d pay extra. In addition, I’ve started to opt for more flexible fares in case of changes and cancellations. I also continue to travel with the same airline as much as possible to take advantage of the extra perks.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Frugal Traveler
Credit Card Swipe Fees Are Going Down. Are Points Going With Them?
A new agreement by Visa and Mastercard to reduce fees charged to merchants may drain the lucrative rewards that grant free travel to many credit card users.

By Elaine Glusac
Elaine Glusac is the Frugal Traveler columnist, focusing on budget-friendly tips and journeys.
On Tuesday, the largest credit card companies in the United States reached an agreement with merchants to reduce the so-called swipe fees retailers pay for accepting credit card payments, potentially saving the retailers $30 billion.
These fees also help fund the credit card rewards programs that many travelers redeem for things like free flights and hotel stays, leading points hawks to wonder: Are loyalty programs at risk?
Here’s what we know so far about the changes.
What are the terms of the deal?
Last year, credit card payments generated an estimated $72 billion in fees paid by merchants, which are generally passed along to customers in the form of higher prices. For nearly 20 years, merchants have been seeking reductions in the fees they pay Visa and Mastercard for handling transactions where the cards are used.
The proposed settlement , awaiting approval in a federal court, reduces and caps those fees for five years. It would also allow merchants to potentially charge consumers more based on the card they pay with. For example, a person paying with a premium card like the Chase Sapphire Reserve, which costs $550 a year, could be charged more than someone paying with the more basic Chase Sapphire Preferred card, with an annual fee of $95.
Why does it matter?
The majority of the fees collected go back to the banks that issue the credit cards. Those banks have used the funds to push premium credit cards that offer loyalty points, which can be redeemed for free travel and other perks. The cards with the biggest benefits tend to be those that charge higher swipe fees.
While the reduction in the fees collected sounds small — averaging at least .07 percent — they represent an estimated $30 billion over the five-year term of the deal, which banks could try to make up by reducing points perks.
“It’s reasonable to think that,” said Brian Kelly, the founder of the Points Guy , a news site devoted to maximizing credit card points.
While he speculated that banks will be able to “find other ways to make up the difference,” he acknowledged that a points squeeze could emerge.
“Opportunities to earn probably aren’t going to flourish,” he said.
The idea that merchants could charge more to the holders of premium, perks-rich cards, which are expensive, might also deter consumers from using them. Some experts question the viability of the practice given the potential for consumer backlash.
Is the new agreement related to the Credit Card Competition Act?
The legal actions that led to the new credit card agreement date back to 2005. But the newer Credit Card Competition Act , proposed in 2023, aims to introduce more competition in the credit card payment system. By creating a cheaper alternative pipeline for processing payments, the proposed legislation is seen as a greater threat to rewards programs.
Responding to the just-announced agreement between the credit card companies and retailers, Senator Dick Durbin, Democrat of Illinois, and the lead sponsor of the Credit Card Competition Act, released a statement urging the act’s passage.
“I fear that this deal only provides temporary concessions negotiated by a few lawyers behind closed doors,” he said in the statement.
Other experts said the agreement may ease the pressure on Congress to pass the act.
“I think it’s a way for Visa and Mastercard to show that they are making a good-faith effort to help out merchants by lowering the fees they’ve been complaining about for 20 years, and hopefully enough to let senators know they’re doing their part,” said Chris Hassan, the social media and brand manager for Upgraded Points , a website that tracks credit card benefits.
Separately, the proposed merger between Capital One and Discover, which is pending federal approval, could introduce more competition among credit cards and potentially improve rewards for holders of those cards.
What should I do now?
The points and payments systems won’t change until the agreement is approved, which is expected in late 2024 or early 2025, according to a news release from Mastercard.
But the topic should remind travelers of the reality of playing with points: The rules always change. Values tend to fall as redemption levels rise, which companies issuing these currencies are free to adjust at will.
If you have points, spend them, say experts like Sara Rathner, a travel and credit card specialist at the financial website NerdWallet . “They’re not a trophy to dust and admire.”
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram and sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to get expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places to Go in 2024 .
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
Mumbai: Spend 36 hours in this fast-changing Indian city by exploring ancient caves, catching a concert in a former textile mill and feasting on mangoes.
Kyoto: The Japanese city’s dry gardens offer spots for quiet contemplation in an increasingly overtouristed destination.
Iceland: The country markets itself as a destination to see the northern lights. But they can be elusive, as one writer recently found .
Texas: Canoeing the Rio Grande near Big Bend National Park can be magical. But as the river dries, it’s getting harder to find where a boat will actually float .
Situation in Haiti March 29, 2024
U.s. citizens in haiti, update january 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Tourism & Visit
Study & Exchange
Other Visa Categories
U.S. Visa: Reciprocity and Civil Documents by Country
Visa Information & Resources
Share this page:
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Japanese
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Turkish
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Hebrew
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Albanian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Tagalog
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Russian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Polish
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Ukranian
Visa Wizard
Visa Denials
Fraud Warning
What the Visa Expiration Date Means
Automatic Revalidation
Lost and Stolen Passports, Visas, and Arrival/Departure Records (Form I-94)
Directory of Visa Categories
Straight Facts on U.S. Visas
Customer Service Statement
Photo Requirements
Photo Examples
Digital Image Requirements
Photo Frequently Asked Questions
Photo Composition Template
Online Immigrant Visa Forms
DS-260 Immigrant Visa Electronic Application - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
DS-160: Online Nonimmigrant Visa Application
DS-160: Frequently Asked Questions
Administrative Processing Information
Visa Appointment Wait Times
Nonimmigrants in the United States–Applying for Visas in Canada or Mexico
Frequently Asked Questions
Visa Applicants - State Sponsors of Terrorism Countries
What is a U.S. Visa?
About Visas - The Basics
Rights and Protections for Foreign-Citizen Fiancé(e)s and Spouses of U.S. Citizens and Spouses of Lawful Permanent Residents
Your Rights and Protections
Ineligibilities and Waivers: Laws
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers
Advisory Opinions
Fees for Visa Services
Treaty Countries
Fees and Reciprocity Tables
Temporary Reciprocity Schedule
Country Acronyms
Reciprocity: What's New? 2019 Archive
Reciprocity: What's New? 2022 Archive
Reciprocity: What's New? 2020 Archive
Reciprocity: What's New? 2021 Archive
Reciprocity: What's New?
Reciprocity: What's New? 2023 Archive
Safety & Security of U.S. Borders: Biometrics
National Visa Center Customer Service Pledge
Americans Traveling Abroad
The United States and China Agree to Extending Visas for Short-term Business Travelers, Tourists, and Students
Special Visa Processing Procedures Pursuant to Section 306
Capitalizing on Visa Demand to Spur Economic Growth in the United States
Congressional Testimony
Cuban Family Reunification Parole (CRFP) Program Appointments
List of U.S. Embassies and Consulates - K1-K3 Visas
U.S. Government Fact Sheet on Female Genital Mutilation or Cutting (FGM/C)
Skill List by Country
Presidential Proclamation 9645 and the January 2020 Presidential Proclamation
Public Inquiry Form
List of U.S. Embassies and Consulates
Affidavit of Support Fee Refund
Immigrant Visa Prioritization
USCIS Extends Suspension of Premium Processing Service for Religious Workers (R-1) Nonimmigrant Visa Classification
Record Numbers of U.S. Students Are Studying Abroad
U.S. Student Visas Reach Record Numbers in 2007
U.S. security officials will begin scanning all 10 fingerprints of most non-Americans traveling to the United States
Electronic Submission of Diversity Visa Lottery Applications
USCIS Centralizes Filing for H-2A Petitions
USCIS Field Office Adopts Teletech Call Appointment System For Filing Waiver of Inadmissibility Applications
Application Fees for Non-Immigrant Visas to Increase on January 1, 2008
Senior Advisors to Brief Press on the Latest Developments in Iraqi Refugee and Special Immigrant Visa Issues
Briefing on Developments in the Iraqi Refugee and Special Immigrant Visa (SIV) Admissions Programs
DHS Proposes Changes to Improve H-2A Temporary Agricultural Worker Program
Testimony of Stephen A. “Tony” Edson on U.S. House of Representatives, Committee on Science and Technology Subcommittee on Research and Science Education, House Committee on Science and Technology
Update: Biometric Changes for Re-entry Permits and Refugee Travel Documents
With All the Talk about Illegal Immigration, a Look at the Legal Kind
Latvia, Estonia Sign Deals with US on Visa-Free Travel
Fact Sheet: Changes to the FY2009 H-1B Program
USCIS Announces Interim Rule on H-1B Visas
USCIS Releases Preliminary Number of FY 2009 H-1B Cap Filings
USCIS Extends Comment Period for Proposed Change to H-2A Program
USCIS Runs Random Selection Process for H-1B Petitions
17-Month Extension of Optional Practical Training for Certain Highly Skilled Foreign Students
DHS Begins Collecting 10 Fingerprints from International Visitors at Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport
Hague Convention on Intercountry Adoption Enters into Force
USCIS to Accept H-1B Petitions Sent to California or Vermont Service Centers Temporary Accommodation Made for FY 09 Cap-Subject H-1B Petitions
USCIS Revises Filing Instructions for Petition for Alien Relative
USCIS Announces Update for Processing Petitions for Nonimmigrant Victims of Criminal Activity
USCIS to Allow F-1 Students Opportunity to Request Change of Status
Immigration Tops Agenda at North American Summit
USCIS Issues Guidance for Approved Violence against Women Act (VAWA) Self-Petitioners
USCIS Modifies Application for Employment Authorization Previous Versions of Form I-765 Accepted until July 8, 2008
Overseas Education More Attainable for Chinese Students
New York Business Group Seeks Fewer Restrictions on Foreign Worker Visas
Coming to the United States Temporarily - Nonimmigrant Visa Services Coming to the United States Permanently - Immigrant Services Special Visa Services
This webpage lists visa application fees and other visa related fees collected by Department of State. Note that many immigration-related forms are submitted to the Department of Homeland Security’s United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), and not to the Department of State. If the type of information or form you are seeking is not shown here, select USCIS Forms and Fees to go to the USCIS Website to review more.
Coming to the United States Temporarily - Nonimmigrant Visa Services
Nonimmigrant visa application processing fees are tiered, as shown below, based on the visa category for which you are applying.
Notice: Every visa applicant must pay the visa application processing fee for the visa category being applied for, unless the application fee is not required, as listed below .
Description of Service and Fee Amount (All fees = $ in US currency)
Nonimmigrant visa application processing fee (non-refundable) for all categories below
- Non-petition-based nonimmigrant visa (except E): $185.00
Includes (but not limited to), the following visa categories:
*Though petition-based nonimmigrant visas, the processing fee for these visas is $185.00
- Petition based visa categories: $205.00
Includes these visa categories:
- E - Treaty Trader/Investor, Australian Professional Specialty category visa: $315.00
- K – Fiancé(e) or Spouse of U.S. citizen category visa: $265.00
Border crossing card fees
- Border crossing card - age 15 and over (Valid 10 years): $185.00
- Border crossing card - under age 15; for Mexican citizens if parent or guardian has or is applying for a border crossing card (valid 10 years or until the applicant reaches age 15, whichever is sooner): $15.00
- L visa fraud prevention and detection fee - for visa applicant included in L blanket petition (principal applicant only): $500.00
- The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2016 (Public Law 114-113) increases fees for certain H-1B and L-1 petitioners. Consular sections collect this fee for blanket L-1 visa applications (principal applicant only) filed by petitioners who employ 50 or more individuals in the United States if more than 50 percent of those individuals are in H-1B or L-1 nonimmigrant status: $4,500.00
When the nonimmigrant visa application processing fee is not required:
- Applicants for A, G, C-2, C-3, NATO, and diplomatic visas (defined in 22 CFR 41.26): No Fee
- Applicants for J visas participating in official U.S. Government-sponsored educational and cultural exchanges: No Fee (See Exchange Visitor Visas for further detailed fee information.)
- Replacement of machine-readable visa when the original visa was not properly affixed or needs to be reissued through no fault of the applicant: No Fee
- Applicants exempted by international agreement as determined by Visa Services, including members and staff of an observer mission to United Nations Headquarters recognized by the UN General Assembly, and their immediate families: No Fee
- Applicants travelling to provide charitable services as determined by Visa Services: No Fee
- U.S. government employees travelling on official business: No Fee
- A parent, sibling, spouse or child of a U.S. government employee killed in the line of duty who is traveling to attend the employee’s funeral and/or burial; or a parent, sibling, spouse, son or daughter of a U.S. government employee critically injured in the line of duty for visitation during emergency treatment and convalescence: No Fee
Nonimmigrant visa issuance fee, including border-crossing cards.
- See the Visa Reciprocity Tables to find out the visa issuance fee amount, if applicable: Fee varies (Reciprocal)
When the nonimmigrant visa issuance fee is not required:
- An official representative of a foreign government or an international or regional organization of which the United States is a member; members and staff of an observer mission to United Nations Headquarters recognized by the UN General Assembly; and applicants for diplomatic visas as defined under item 22(a); and their immediate families: No Fee
- An applicant transiting to and from the United Nations Headquarters: No Fee
- An applicant participating in a U.S. government sponsored program which may include applicant’s dependent spouse and children: No Fee
- An applicant travelling to provide charitable services as determined by Visa Services: No Fee
Other - When a Visa is Not Required - Visa Waiver Program
- Citizens of Visa Waiver Program participating countries, and meeting requirements pay a small fee. Select USCIS fees to learn more.
Coming to the United States Permanently - Immigrant Services
Immigrant visa application processing fees are tiered, as shown below, based on the visa category you apply for.
Notice: Every visa applicant must pay the visa application processing fee for the visa category being applied for.
Filing an Immigrant Visa Petition (When collected by U.S. Embassies and Consulates for USCIS. Fees subject to change.)
Immigrant Visa Application Processing Fees (non-refundable, per person)
Note: Forms and fee amounts are listed for immigration petitions which are submitted to Department of State, either accepted at a U.S. Embassy or Consulate abroad, or within the United States to the National Visa Center or Kentucky Consular Center. Other immigration related forms can only be approved by the Department of Homeland Security's United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). For other fees (relating to forms starting with an "I" select USCIS Forms and Fees for additional information.
Special Visa Services
Note: These fee charts are based on the Code of Federal Regulations - Title 22, Part 22, Sections 22.1 through 22.7.)
More Information
A-Z Index Latest News What is a U.S. Visa? Diversity Visa Program Visa Waiver Program Fraud Warning Find a U.S. Embassy or Consulate Straight Facts on U.S. Visas
Immigrant Visa Interview-Ready Backlog Report
Global Visa Wait Times
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - English
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - French
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Spanish
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Portuguese
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Mandarin
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Arabic
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Italian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - German
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Vietnamese
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Romanian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Korean
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Armenian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Bulgarian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Czech
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Hungarian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Indonesian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Lithuanian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Serbian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Thai
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Mongolian
Rights and Protections for Temporary Workers - Kurdish
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
How air travel has changed since the pandemic
Travel troubleshooter.
If you haven’t flown in a while, fasten your seat belts. I’ve got good news — and bad news.
You’ve probably already heard the bad news because it travels faster than the speed of sound. Airfares are up. So are luggage fees. And we seem to have a problem with in-flight violence again.
But there’s more to the story, and if you’re an occasional air traveler, you’ll want to get the big picture. You might be surprised by what you find.
First, the bad news about air travel in 2024
Some of the changes have not been for the better. For example:
- Airfares are climbing. Cheap pandemic airfares are history. Average domestic round-trip fares fell to a low of $186 in May 2020 . But they were back up to $261 by the beginning of this year — and they continue to climb.
- Checked baggage fees are soaring. All of the major airlines have recently raised their baggage fees. On domestic flights, a checked bag may cost as much as $35 (more if you wait until the last minute or your bag is overweight).
- Air rage is back. In-flight air rage hit record highs in 2021, mostly because of masking requirements. But the number of violent in-flight incidents remains high — this time, a combination of fuller flights and a continuing decline of civility. We’re on track to exceed 2020’s unruly passenger incidents.
But don’t despair. The air travel experience is changing in small ways — and, potentially, in big ways.
What’s it like to fly now?
Let’s start with the air travel experience itself. Flights are fuller and space is tighter than ever. In fact, if you’re flying somewhere this spring or summer, you should congratulate yourself. You’re probably part of the busiest year in the history of air travel.
“Air travel has rebounded,” says Jason Block, CEO of WorldVia Travel Group . That puts a squeeze on regular passengers. If you’ve booked a no-frills economy ticket, you may face a higher risk of being bumped from your flight. So if you have a little extra money, Block suggests buying a more flexible ticket. You’re still not bump-proof, but at least you’ll move up the list.
Smile for the TSA
The passenger screening experience is different but not necessarily better. The Transportation Security Administration has new scanners that take your picture to verify your identity. New technology might allow you to keep all your belongings in your bag and speed up screening — “might” being the operative word.
“The process is more inconsistent than ever,” says Andy Abramson, a frequent traveler and a communications consultant from Las Vegas. “Procedures change from airport to airport. In some cases, all you need is your boarding pass. In others, you need your ID, and in others, nothing but your facial scan.”
Speaking of technology, many air travelers have raved about new onboard Wi-Fi capabilities. Airlines like Air New Zealand, Emirates and JetBlue include the price of Wi-Fi in their tickets, and the connections have just gotten better since the pandemic.
Your face is your boarding pass
The TSA isn’t the only one using facial scans. Some U.S. airlines have started using facial scans instead of boarding passes. It’s a little bit of an adjustment for passengers.
“I stood awkwardly in front of a camera, feeling like a contestant in a dystopian game show,” says Chris McGuire, a real estate broker from Birmingham, Ala.
A few months ago, Frankfurt became the first airport in Europe to fully adopt facial recognition . Other airports, including Tokyo and Dubai, also have face-scanning technology. If you haven’t flown in a while, you may not have to fumble for your boarding pass before you get on the plane.
I’ve used face-scanning technology on many occasions and it usually works, but it can be slow. Getting through customs in Santiago, Chile, took a while and the agent kept apologizing for the technology. So don’t forget to pack your patience.
No more ticket change fees
Airline ticket change fees disappeared during the pandemic on U.S. airlines. So if you have to change your flight, you won’t have to pay a $250 fee on top of any fare difference.
“That’s one of the most significant changes,” says frequent air traveler Bob Bacheler, who is the managing director of Flying Angels , a medical transport service. “Airlines introduced more flexible booking and cancellation policies, allowing passengers to change or cancel flights without heavy penalties”
Bacheler thinks the fees will return eventually, and he’s right. If they do, airlines will call them something else — maybe a “convenience” fee?
You may board your flight differently
“Some airlines are implementing new boarding procedures,” says Andy Palacios, vice president of growth and strategic partnerships for App in the Air . The most significant is United Airlines, which last fall began boarding economy passengers with window seats before those with middle and aisle seats.
Palacios recommends avoiding the general boarding mayhem by getting a credit card or earning elite status. Anything that gets you into the first boarding group can save you from having to gate-check your carry-on or just getting stuck in a crowd.
You have new rights, too
If something goes wrong on your flight, you may find that your airline will do more for you. That’s because the Department of Transportation, which regulates airlines, has been applying steady pressure on domestic airlines to improve customer service. (After all, taxpayers bailed out the airlines during the pandemic.)
Airlines now offer guaranteed meals, accommodations and ground transportation to and from a hotel when they’re at fault for a cancellation. (You can find out about all your rights on the DOT’s Fly Rights website.)
Most Read Life Stories
- 4 great restaurants for your Skagit Valley Tulip Festival road trip
- 6 WA chefs and restaurants named finalists for James Beard Awards
- Direct flights from Sea-Tac airport to Philippines start this fall
- Clark County woman is first WA musher to finish Iditarod since 2012
- Multivitamin leads to painful constipation
The government is working on carving out more rights for air travelers, dealing with everything from more straightforward and honest pricing to minimum seat size. But it’s a work in progress.
Flying “feels different” now
Passengers say it feels like something has shifted when it comes to air travel.
“Flying feels different,” says Robert Khachatryan, a frequent flyer and founder of a freight forwarding service in La Crescenta, Calif.
He’s correct. It’s not just that customers have a few new rights or that the technology is getting an upgrade — or even that boarding is a little different.
There’s a sense that something big lies just ahead. With people like Elon Musk teasing a Tesla that can fly and personal flying vehicles making headlines almost every day, there’s a feeling that flying is about to evolve in a significant way.
Air travelers have become disenchanted with commercial air travel, with its high fares, fees, long lines and terrible customer service. And the relief may not come from new rules to protect the rights of air travelers but from a fundamental change in the way we fly.
So if flying feels different to you now, just wait. You ain’t seen nothing yet.
This is the first of a two-part series on the future of air travel. Next week: Flying cars. Yeah, we’re going to go there.
The opinions expressed in reader comments are those of the author only and do not reflect the opinions of The Seattle Times.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Passport Fees. Find your passport fee in one of three ways: Use the fee calculator. Download the fee chart PDF, or. Expand the boxes on this page. Our fees on this page are for customers applying in the United States and renewing by mail from Canada. If you need to apply for or renew your U.S. passport in another country, visit the webpage of ...
A passport card is valid only for travel by land and by sea to the following locations: Canada, Mexico, Bermuda, and the Caribbean. DS-11 $15 $35 Minor Passport Book & Card DS-11 $115 $35 OPTIONAL FEES (Paid to the U.S. Department of State) Expedite Fee Paid per application, in addition to required fees. Provides faster processing than routine ...
Routine: 6-8 weeks* Expedited: 2-3 weeks and an extra $60* *Consider the total time it will take to get a passport when you are booking travel. Processing times only include the time your application is at a passport agency or center.. It may take up to 2 weeks for applications to arrive at a passport agency or center. It may take up to 2 weeks for you to receive a completed passport after we ...
31.205-46. Travel costs. (a) Costs for transportation, lodging, meals, and incidental expenses. (1) Costs incurred by contractor personnel on official company business are allowable, subject to the limitations contained in this subsection. Costs for transportation may be based on mileage rates, actual costs incurred, or on a combination thereof ...
Your agency's authorized travel management system will show the final price, excluding baggage fees. Commercial baggage fees can be found on the Airline information page. Domestic Domestic fares include all existing Federal, State, and local taxes, as well as airport maintenance fees and other administrative fees.
Here are our picks for the best travel credit cards of 2023, including those best for: Flexibility, point transfers and a large bonus: Chase Sapphire Preferred® Card. No annual fee: Bank of ...
April 2 (UPI) --U.S. Customs and Border Protection said Tuesday it will increase the fees for some of the most well-known Trusted Travel Programs.As of Oct. 1, the fee for NEXUS, a joint program ...
What is a travel fee? A travel fee is an additional fee added to your standard pricing. Often, travel fees vary based on the distance one travels. The further one travels, the higher the travel fee. 👉 Use a quality online booking system with travel fees built-in, like Check Cherry, so you can automatically calculate and charge clients travel ...
Enforcing minimum onsite service fees. This is an roundabout to charging outright travel fees or an hourly trip rate. In this method, you notify your customer that they will be paying, for example, a one hour minimum of service for the visit. More than a few techs on the forums prefer this approach as it keeps travel fees out of the customer ...
1. Resort fees. According to a January 2023 NerdWallet analysis of 100 U.S. hotels, the average resort fee was $42.41 - or about 11% of one night's stay. If your vacation is a week long, this ...
The federal government will raise the cost of the popular Global Entry program this fall for the first time in more than 15 years. Starting Oct. 1, the application fee for Global Entry will ...
Please call 1 (888) 407-4747 (U.S. and Canada) or 1 (202) 501-4444 (overseas) or contact the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate. As a first step in planning any trip abroad, check the Travel Advisories for your intended destination. Our highest priority is to protect the lives and interests of U.S. citizens overseas.
Although the base fare is only $1,100, the overall price includes more than $600 in taxes and fees; it includes a $5.60 U.S. security fee, $78 in German taxes and a $70 passenger service charge from the U.K. Each carrier should provide a breakdown detailing the taxes and fees applied to your ticket.
Most travel agencies take between 9% and 15% commission for anything to do with services, stays or tours. For a single airline ticket sold, a travel agency might take 8% of the public price. However, this percentage varies from one travel agency to another, depending on the services they offer. Some travel agencies may charge between 15% and 20 ...
In 2023, airlines made a record $117.9 billion worldwide in ancillary fees, according to airline consulting firm IdeaWorksCompany and car rental technology platform CarTrawler. About $33.3 billion ...
In Arizona and Nebraska, travel fees are based on state mileage rates.For the latest authorized mileage rate in Arizona, check the fee schedule online.The Nebraska mileage rate, which applies only to serving notices of protest and not to other notarial acts, is set by the State Department of Administrative Services (433 NAC 6.008.04[F]), which according to state Notary officials is currently ...
Tue, 04/02/2024. WASHINGTON - U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) announced today an upcoming fee change for some of its most popular Trusted Traveler Programs (TTP). On April 2, a final rule was published in the Federal Register, harmonizing the fees for the NEXUS, Global Entry, and SENTRI programs, better reflecting the program costs.
To calculate the total cost of your new passport, select the passport type (s) and the method of processing you would like to use. Please note, the application cost is non-refundable and is retained by the Department of State whether or not the passport is issued. We accept different forms of payment depending on where you apply.
Reimbursement for a seat selection fee must be approved on the travel authorization prior to commencing travel and can only be approved for authorized direct travel (see 14 FAM 511.3). g. Receipts are required for reimbursement of seat selection fees, regardless of amount. h. For the purposes of determining eligibility for reimbursement, a seat ...
U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) will increase fees for some Trusted Traveler Programs, including Global Entry, on October 1, 2024. The Global Entry application fee will be $120, a 20% ...
I-131, Application for Travel Document. ALERT: On Jan. 31, 2024, we published a final rule in the Federal Register, that adjusts the fees required for most immigration applications and petitions. The new fees will be effective April 1, 2024. Applications and petitions postmarked on or after April 1, 2024, must include the new fees or we will ...
Citi customer service provides 24/7 assistance to cardholders at 1-800-200-7056 and 1-757-852-9076 (toll-free). These numbers are designated for DoD customers only. Remember, your APC is your first point of contact for travel card-related questions or issues. Call Citi Customer Service, or log on to CitiManager, to quickly obtain balance and ...
Trip pricing calculator. Travelmath provides an online cost calculator to help you determine the cost of driving between cities. You can use this data to figure out a budget for a road trip. The driving calculation is based on the average fuel efficiency of your vehicle, and you can change the gas mileage in mpg or L/100 km to match your exact ...
battleface. Since the beginning of the year, most of the major U.S. airlines have raised their baggage fees. It now costs an average of $35 to check your bag on a domestic flight. In the travel ...
The price of a first checked bag now ranges from $35 to $50 under a recently revealed fee structure that depends on a number of factors, including dates JetBlue determines to be peak or off-peak ...
A new agreement by Visa and Mastercard to reduce fees charged to merchants may drain the lucrative rewards that grant free travel to many credit card users. By Elaine Glusac Elaine Glusac is the ...
The phenomenon was named Havana Syndrome after US Embassy staff in Cuba began complaining about suspicious symptoms in 2016. Victims suffered from a range of mysterious health problems, including hearing loss, insomnia, memory loss, balance disturbances and an inability to concentrate. Symptoms lasting for months were accompanied by victims ...
Description of Service and Fee Amount (All fees = $ in US currency) Filing an Immigrant Visa Petition (When collected by U.S. Embassies and Consulates for USCIS. Fees subject to change.) Immigrant petition for relative (I-130) $535.00. Orphan (intercountry adoption) immediate relative petition (I-600, I-800) $775.00.
Apply for a U.S. Visa. At this website, you can learn about obtaining a visa, as well as applying for your visa. How to apply for your nonimmigrant visa for travel to the United States. What documents, photos and information you need to apply for your visa. How to access visa application forms and instructions.
Cheap pandemic airfares are history. Average domestic round-trip fares fell to a low of $186 in May 2020. But they were back up to $261 by the beginning of this year — and they continue to climb ...